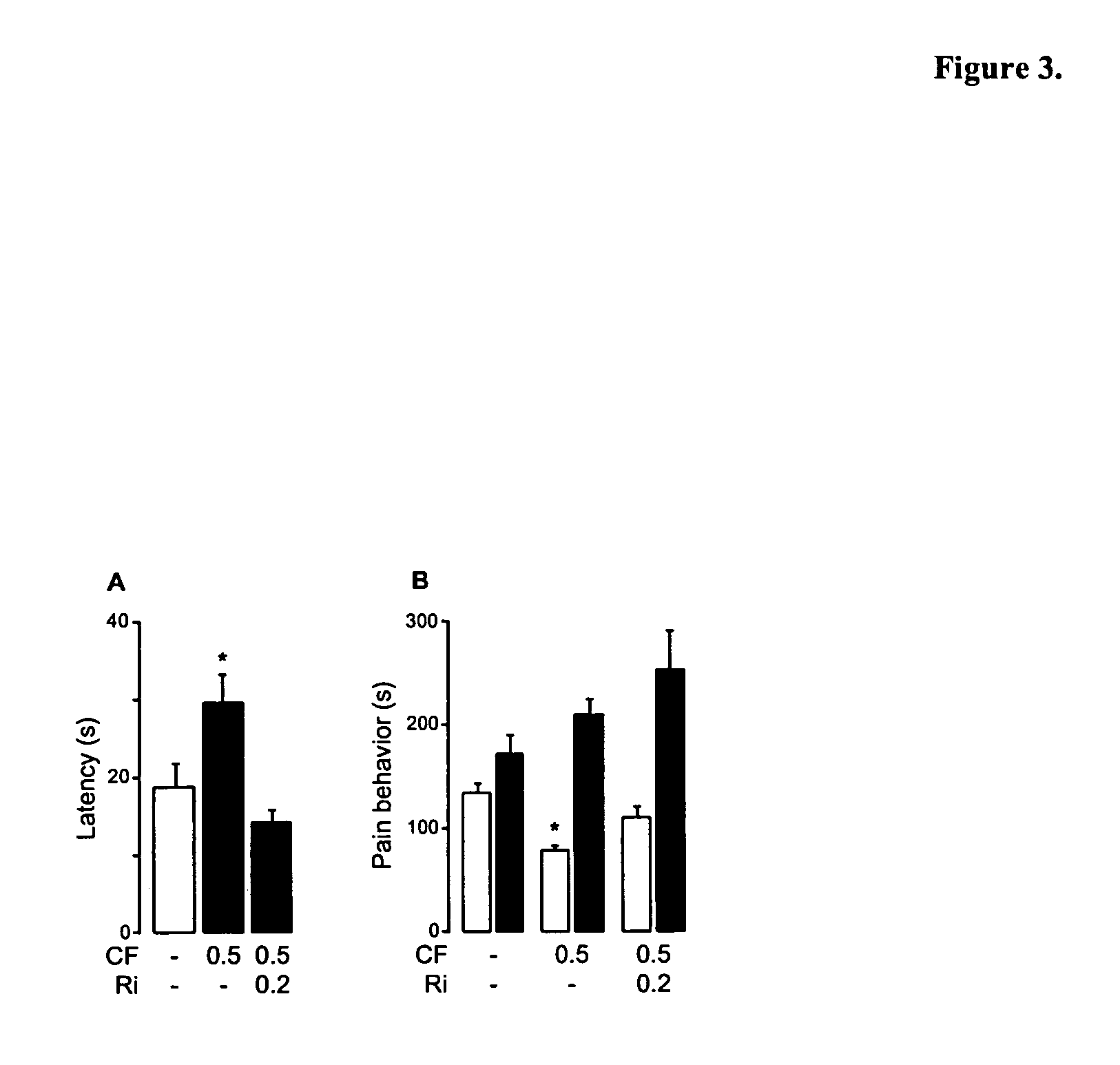
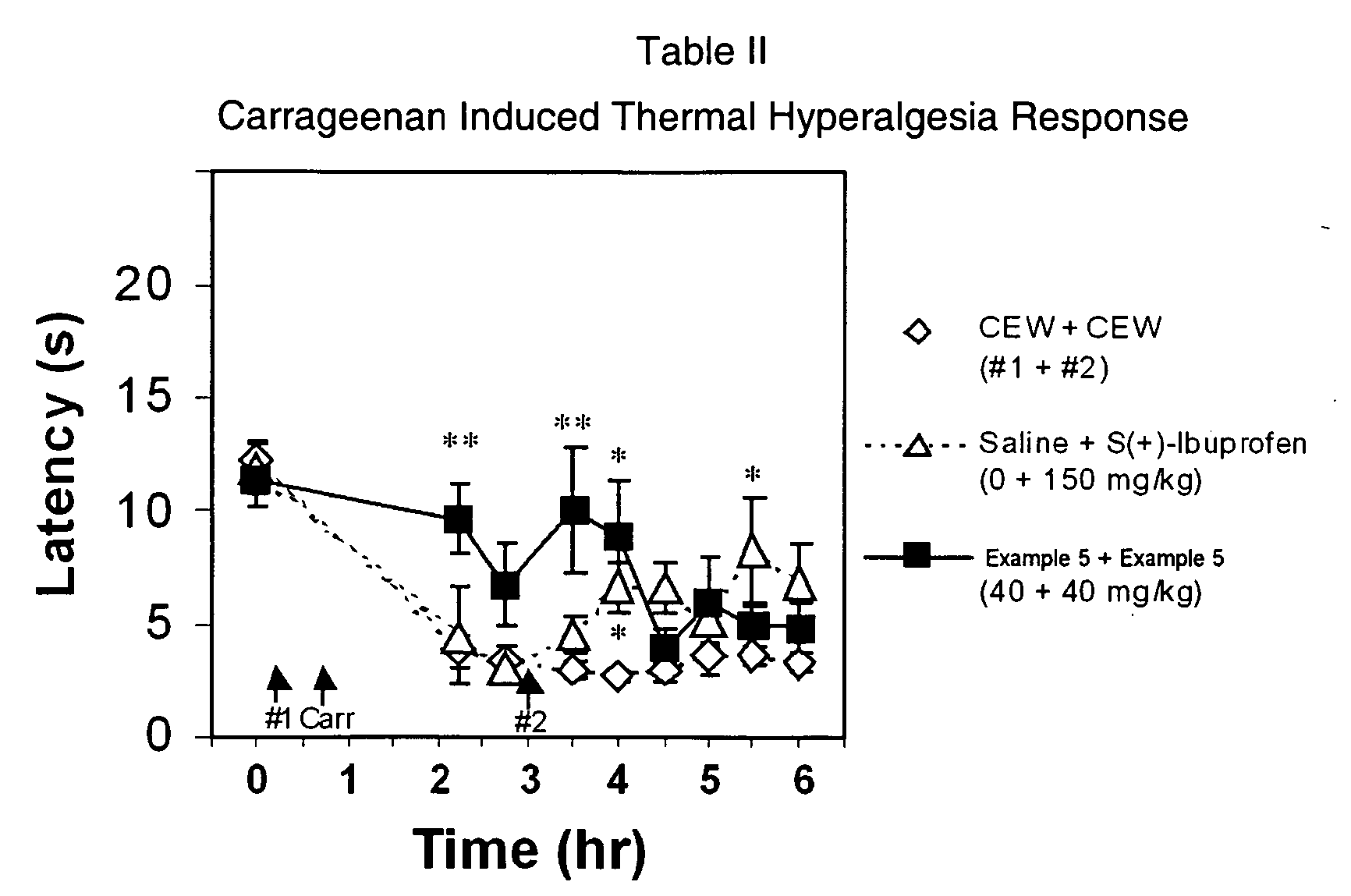
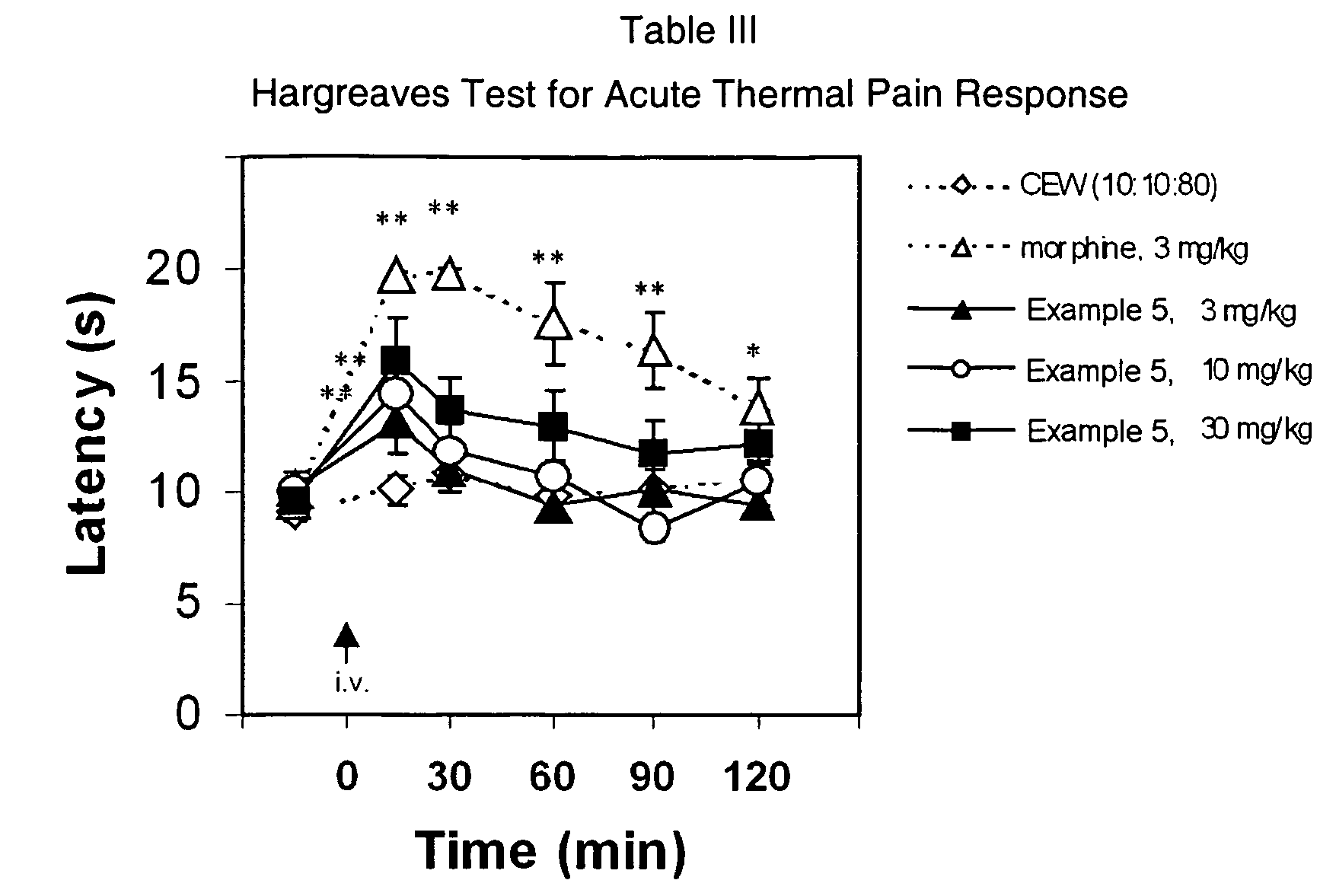
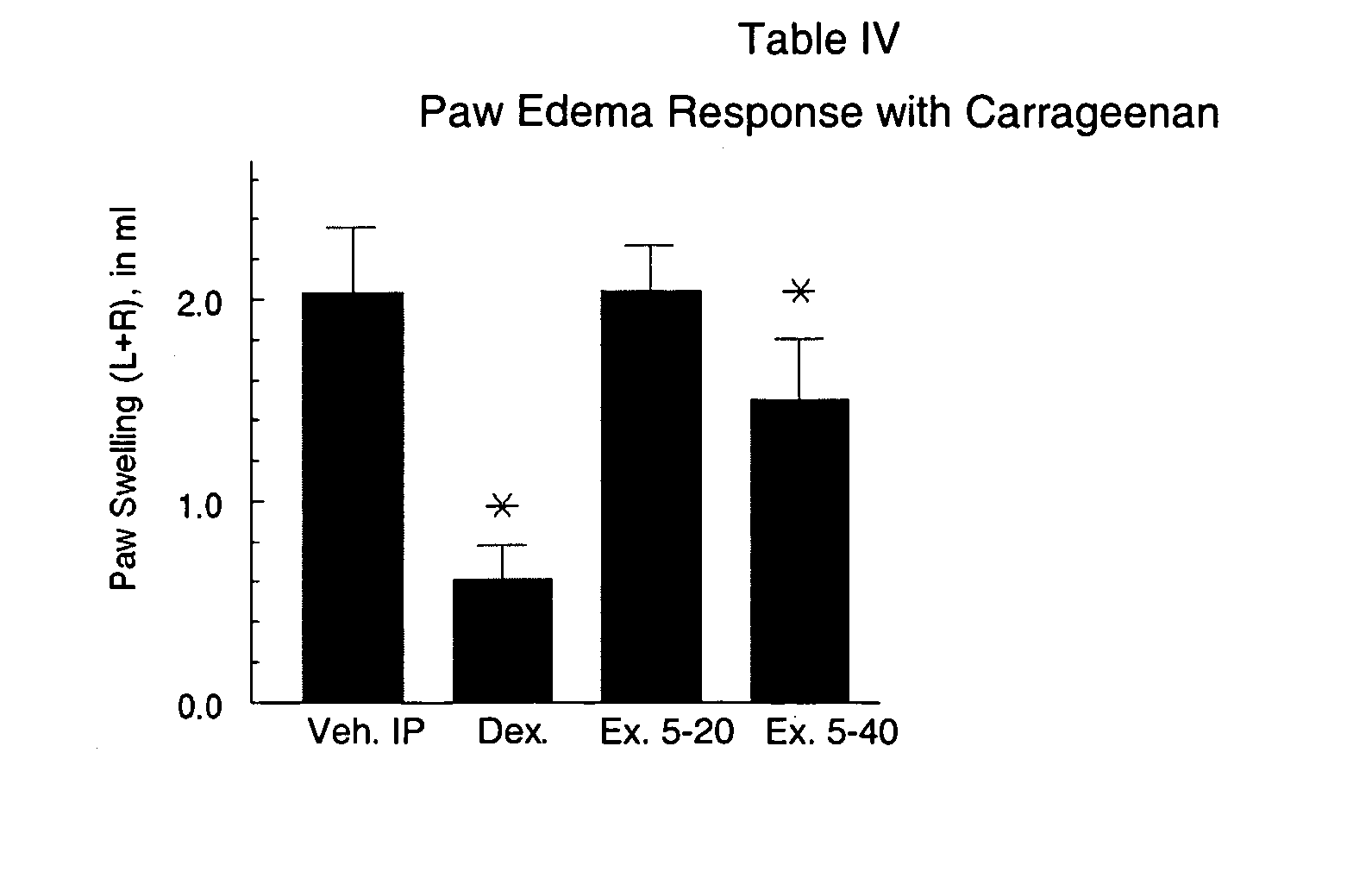
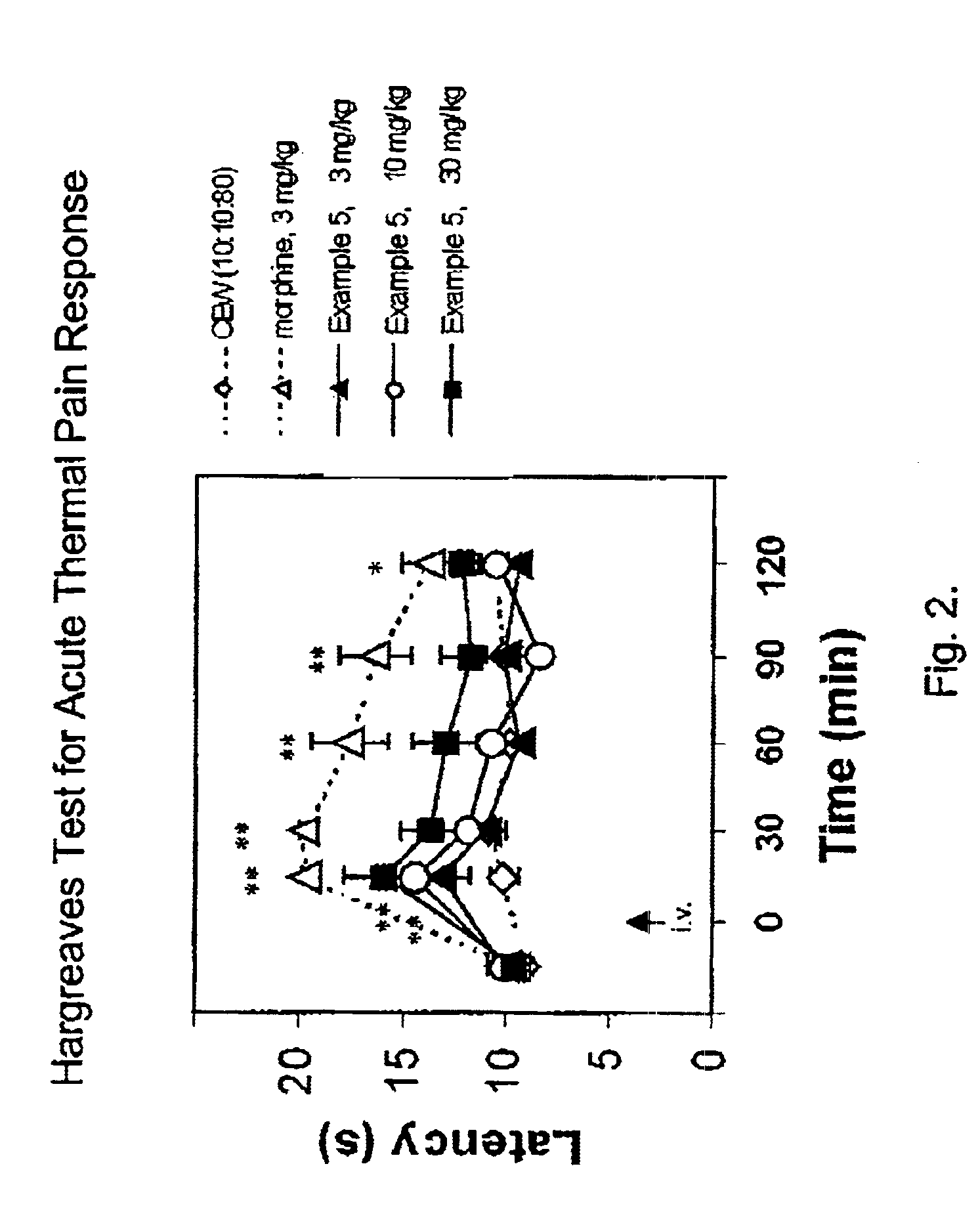
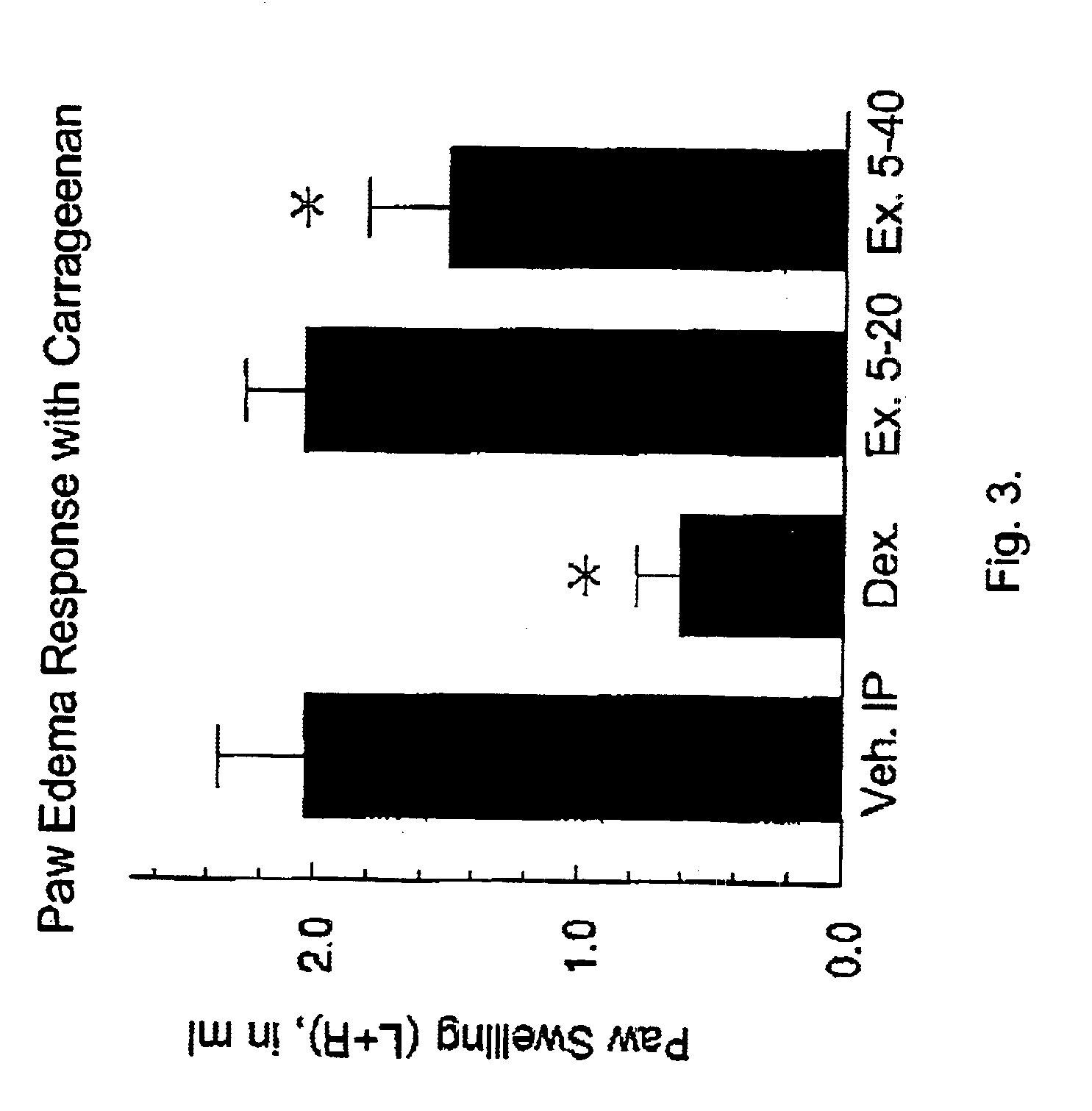
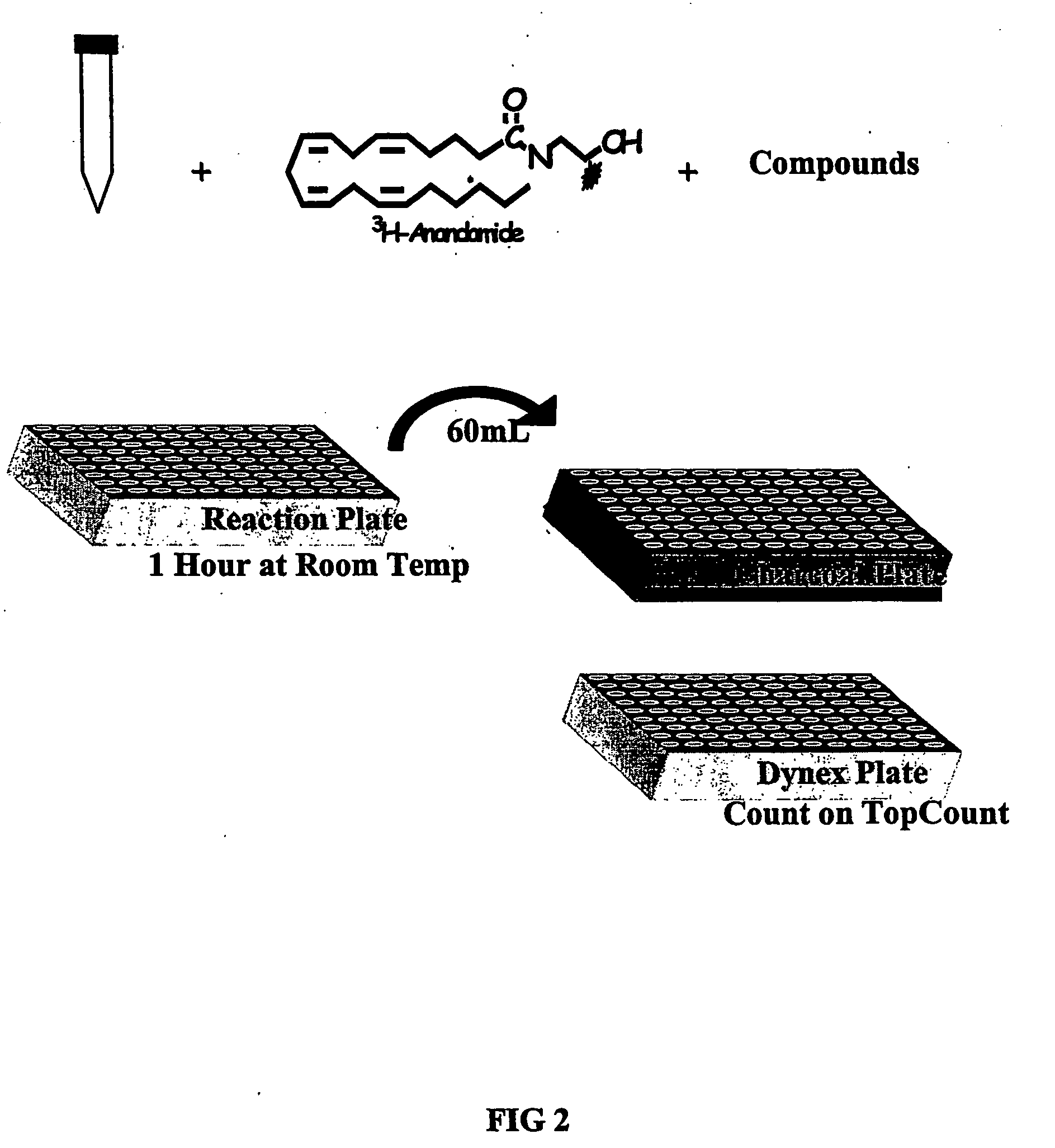
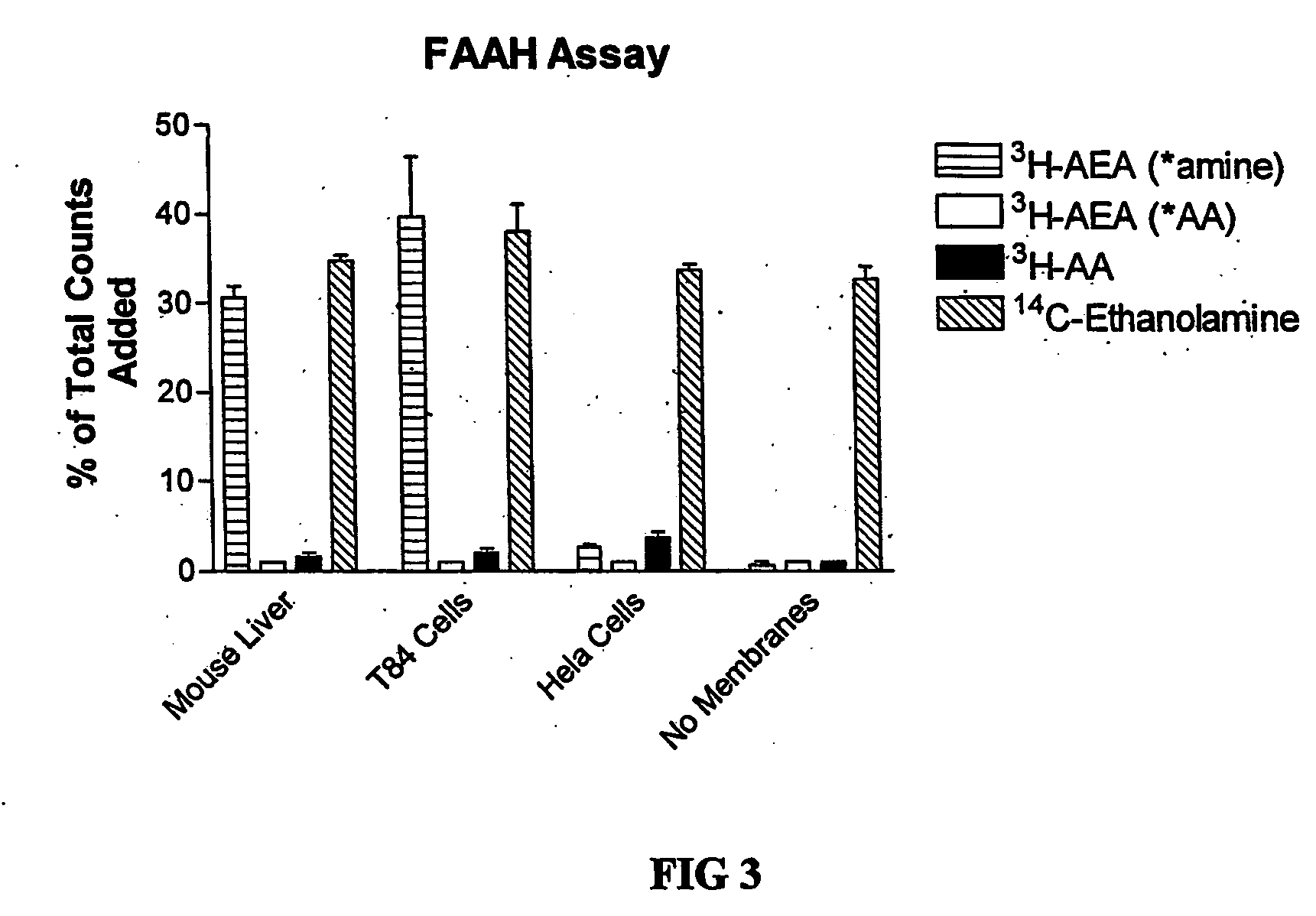
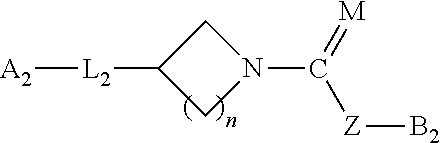
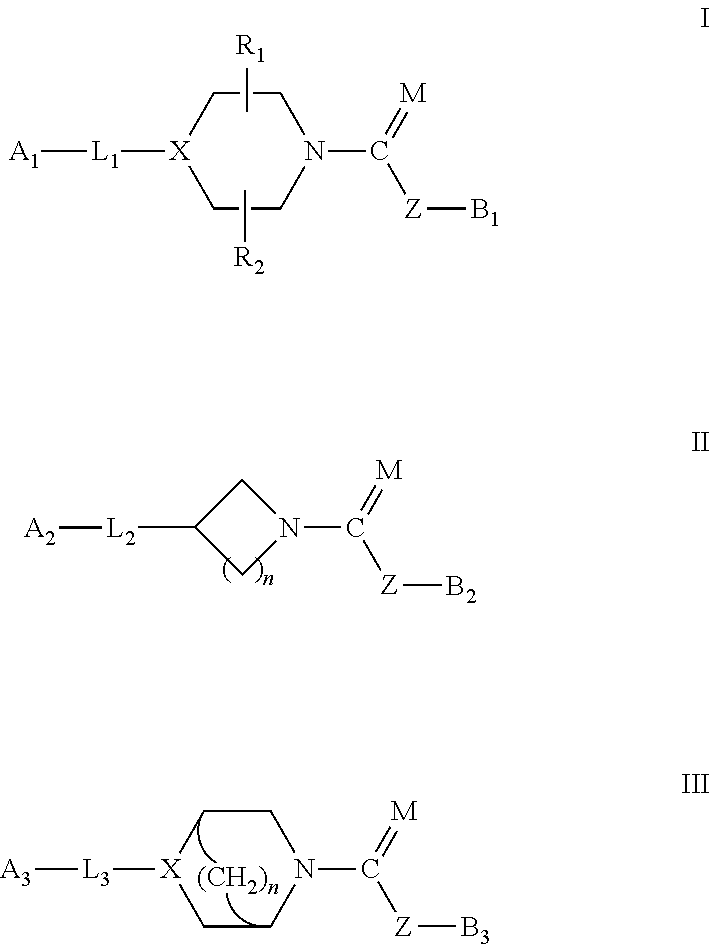
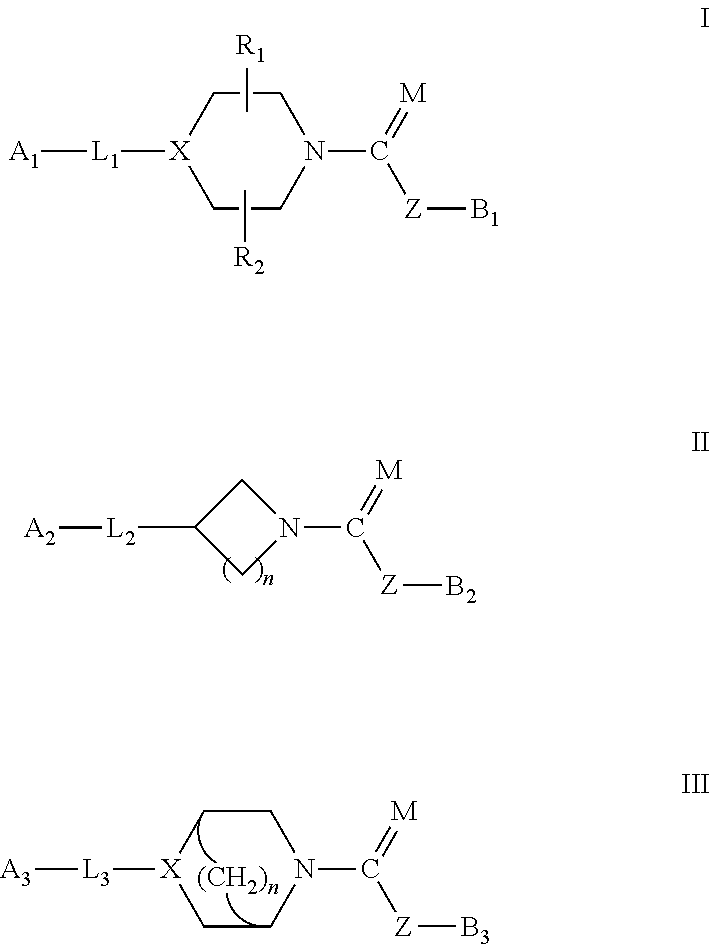
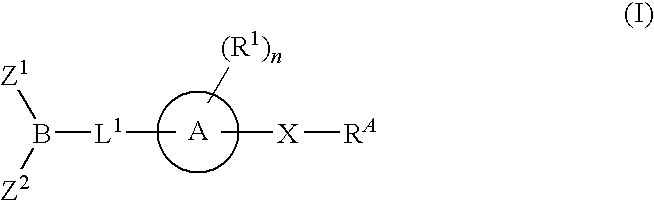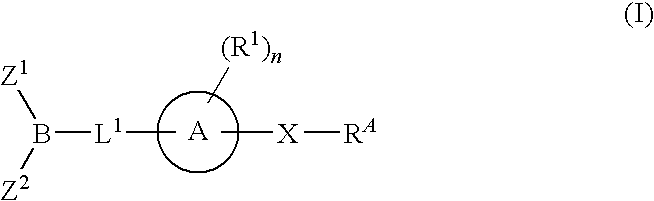Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Fatty acid amide hydrolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
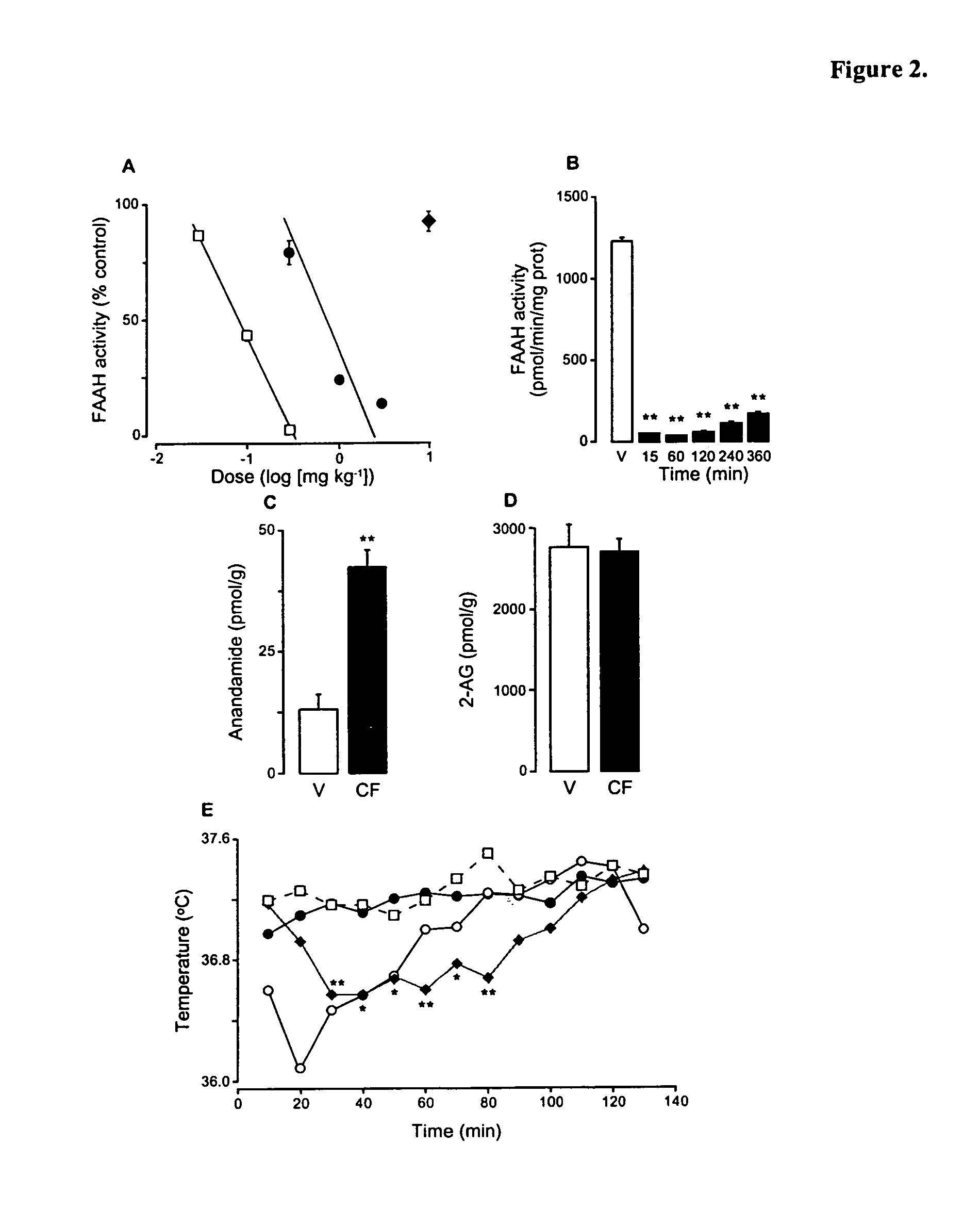
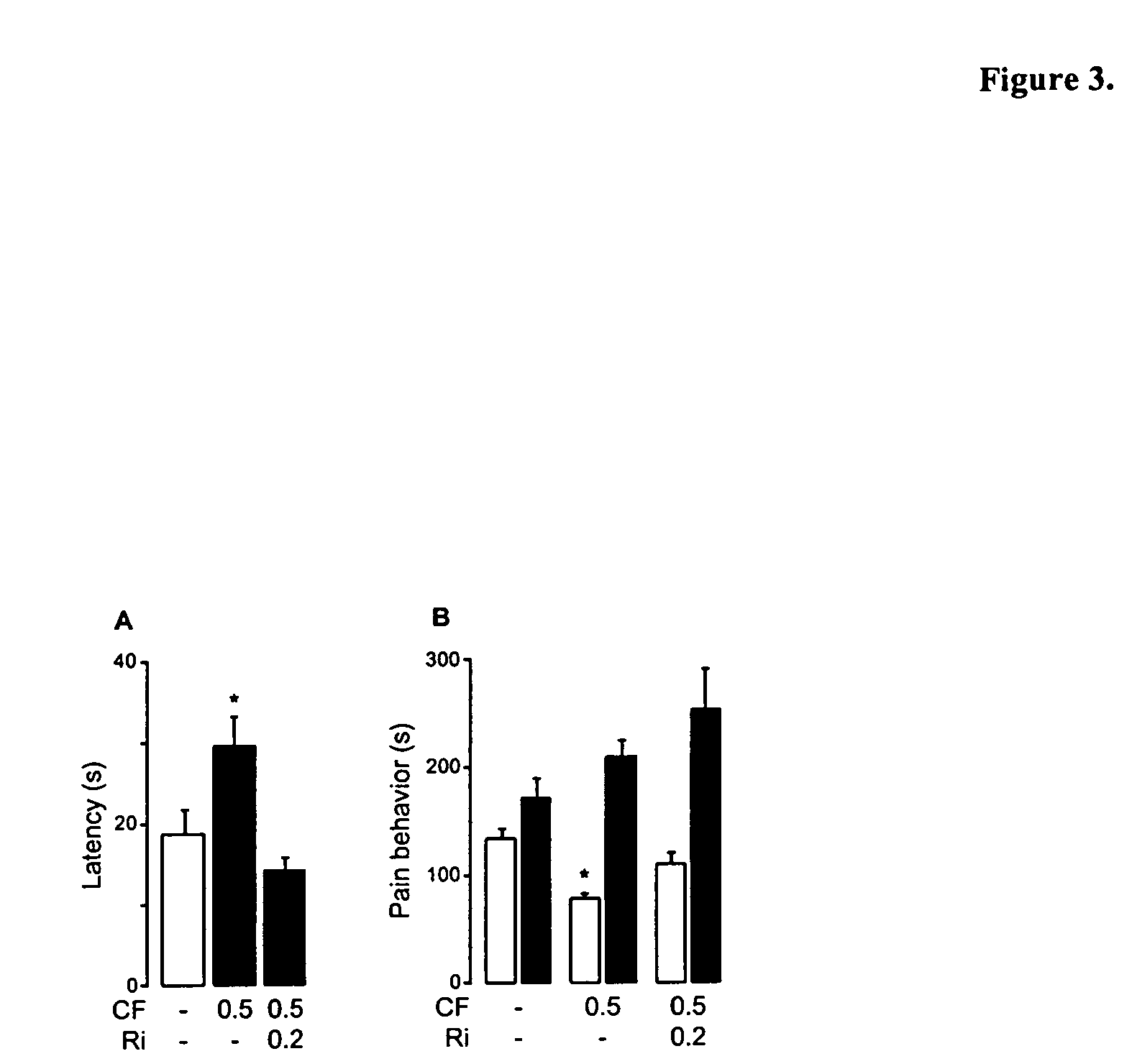
Fatty acid amide hydrolase or FAAH (EC 3.5.1.99, oleamide hydrolase, anandamide amidohydrolase) is a member of the serine hydrolase family of enzymes. It was first shown to break down anandamide in 1993. In humans, it is encoded by the gene FAAH.
Fatty-acid amide hydrolase
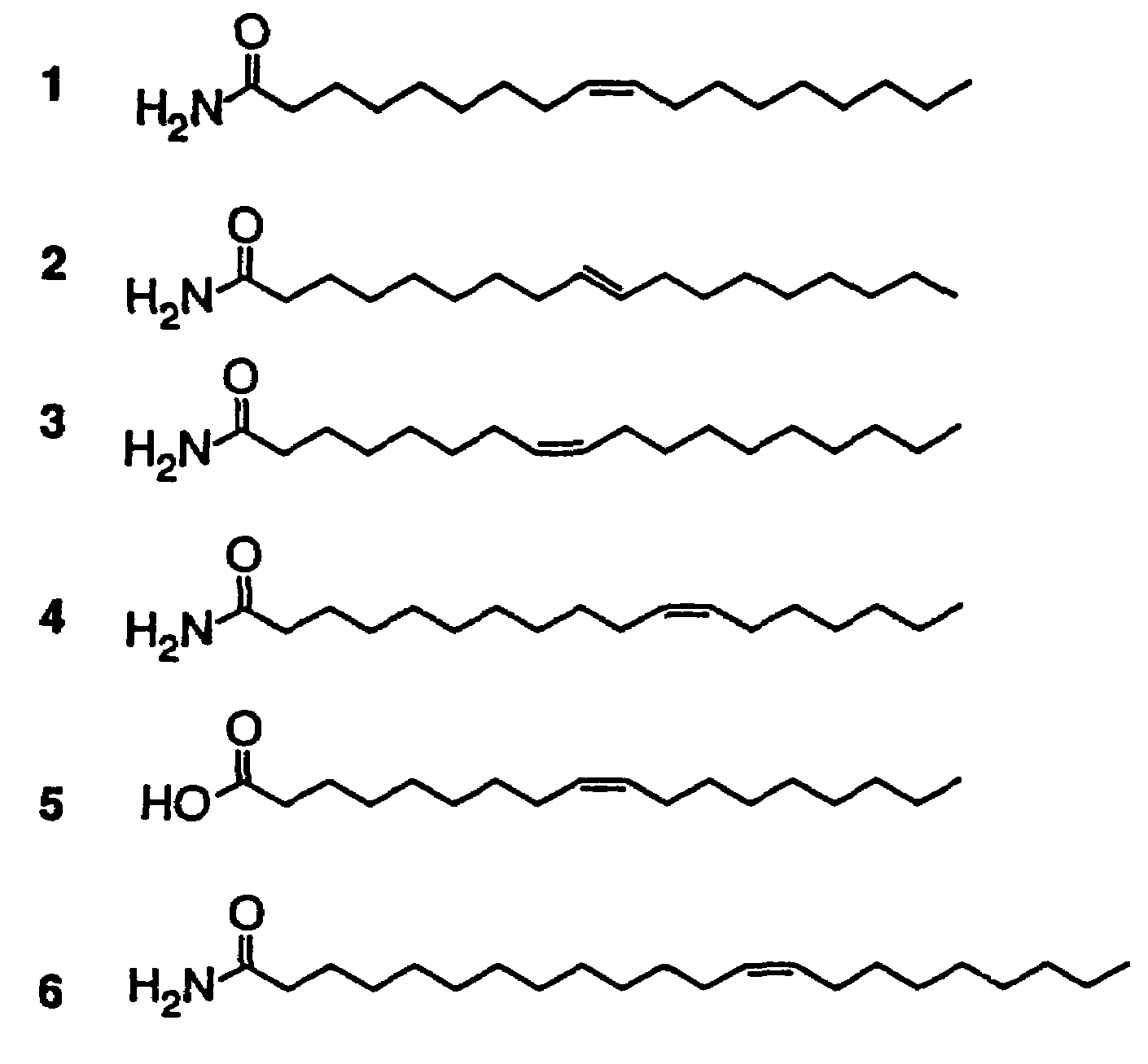
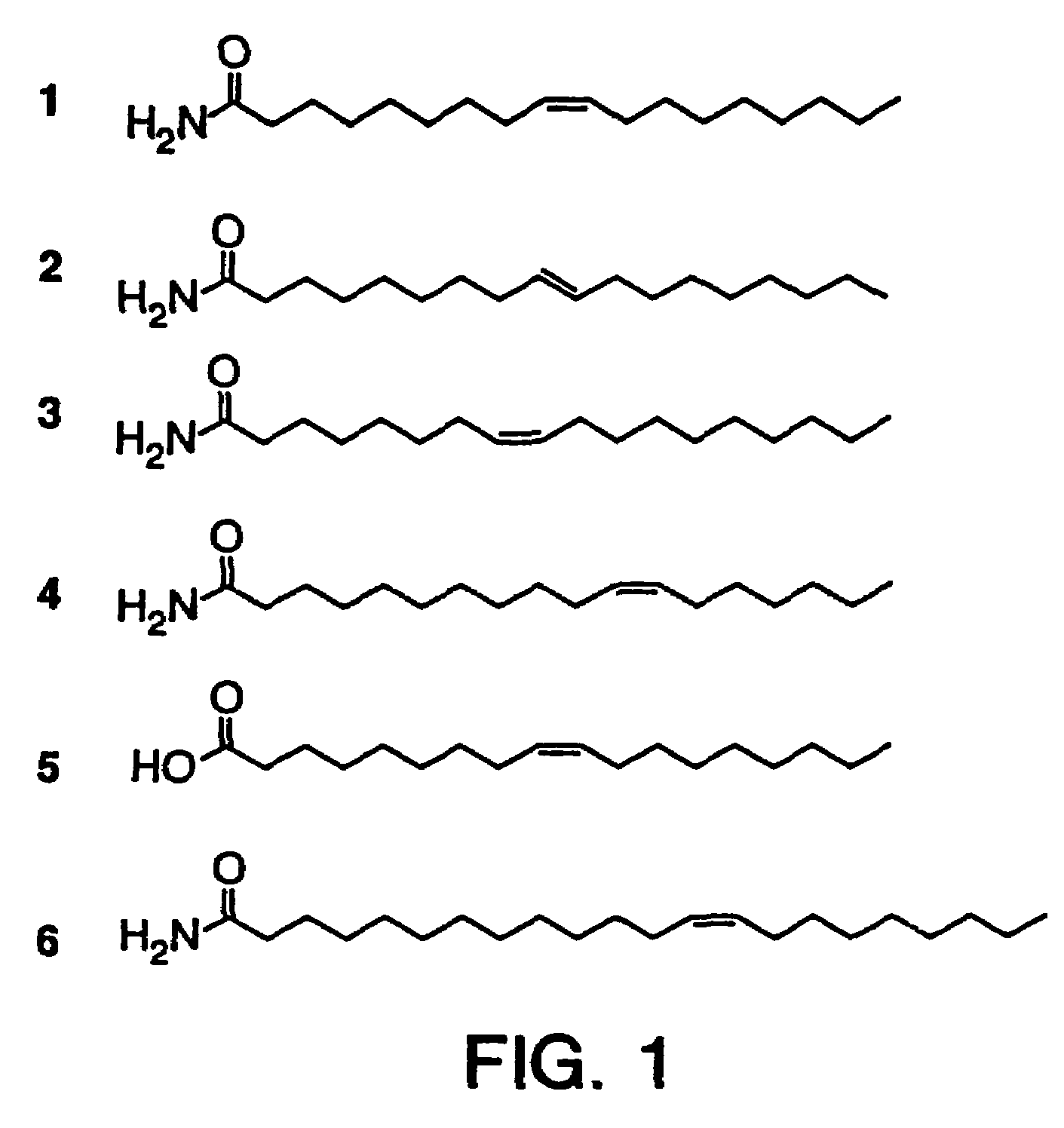
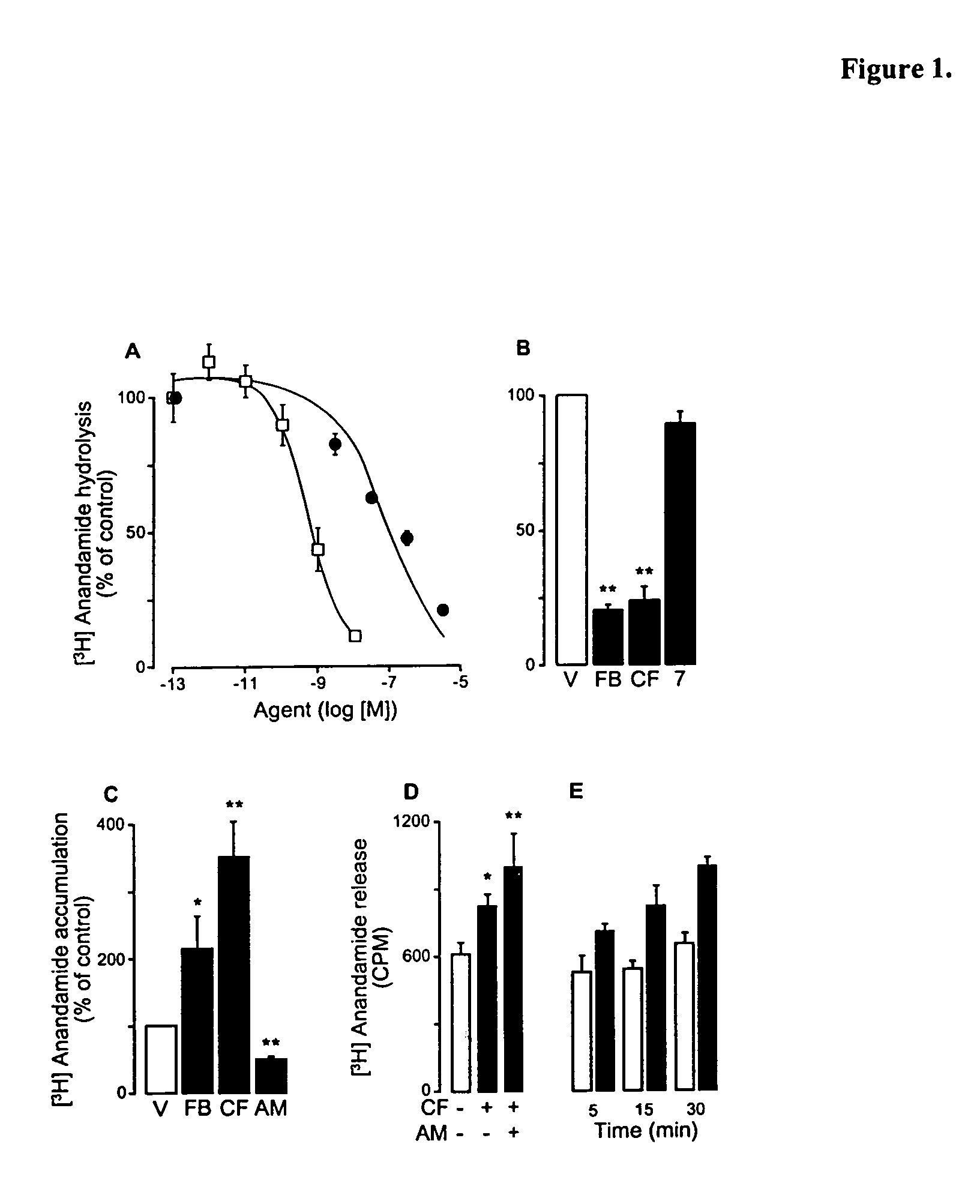
The soporific activity of cis-9,10-octadecenoamide and other soporific fatty acid primary amides is neutralized by hydrolysis in the presence of fatty-acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Hydrolysis of cis-9,10-octadecenoamide by FAAH leads to the formation of oleic acid, a compound without soporific activity. FAAH has be isolated and the gene encoding FAAH has been cloned, sequenced, and used to express recombinant FAAH. Inhibitors of FAAH are disclosed to block the hydrolase activity.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis
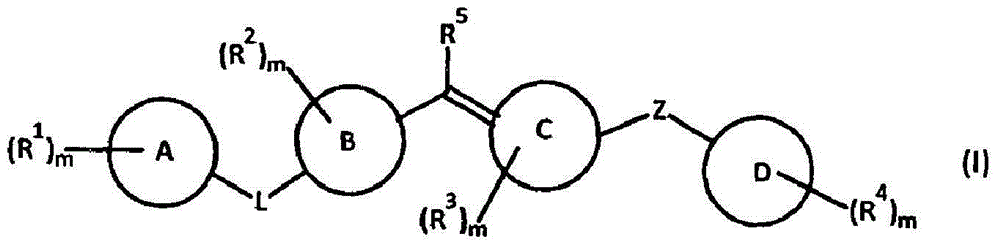
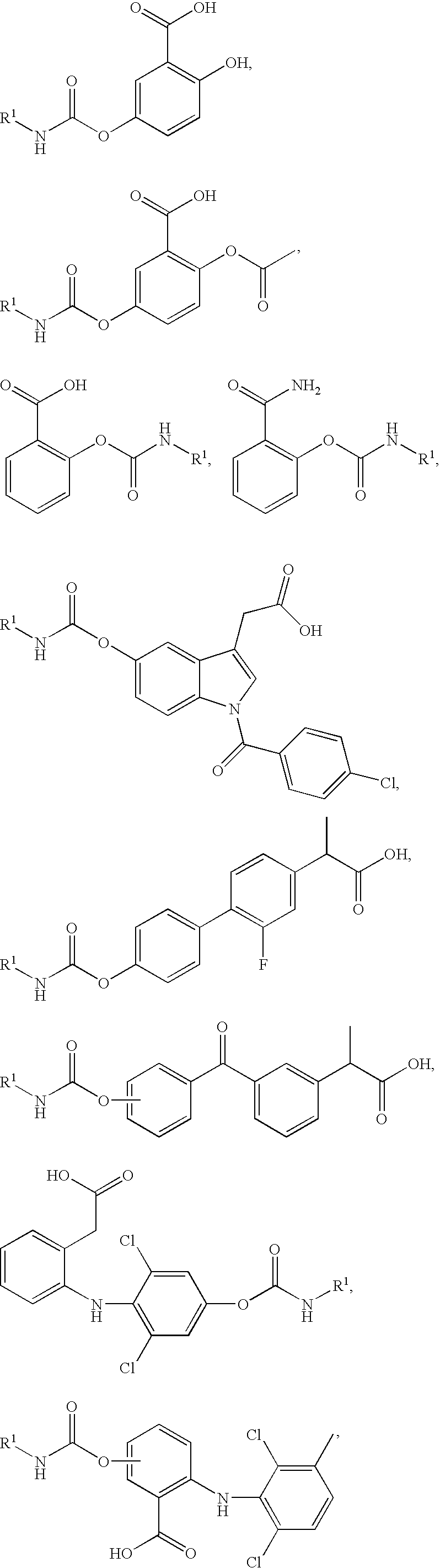
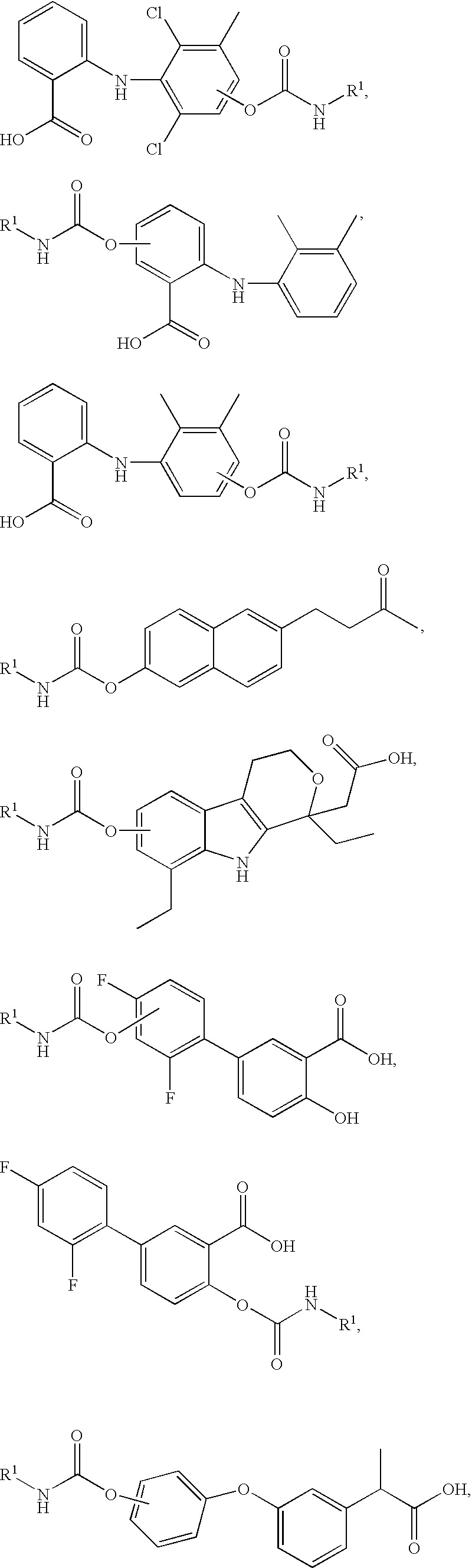
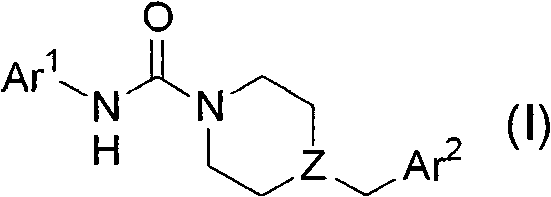
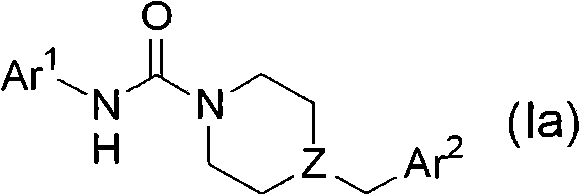
Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors of the Formula:are provided wherein X is NH, CH2, O, or S; Q is O or S; Z is O or N; R is an aromatic moiety selected from the group consisting of substituted or unsubstituted aryl; substituted or unsubstituted biphenylyl, substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl, and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl; substituted or unsubstituted terphenylyl; substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, or alkyl; and R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted heteroalkyl, and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, substituted or unsubstituted biphenylyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, and substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl; with the proviso that if Z is O, one of R1 and R2 is absent, and that if Z is N, optionally R1 and R2 may optionally be taken together to form a substituted or unsubstituted N-heterocycle or substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl with the N atom to which they are each attached. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of Formula I and methods of using them to inhibit FAAH and / or treat appetite disorders, glaucoma, pain, insomnia, and neurological and psychological disorders including anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and depression are provided.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI PARMA +1
(Oxime)carbamoyl fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors
The present invention relates to novel oxime carbamyl derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions comprising said derivatives which inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase. These pharmaceutical compositions are useful for the treatment of conditions which can be effected by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase including, but not limited to, neuropathic pain, emesis, anxiety, altering feeding behaviors, movement disorders, glaucoma, brain injury, and cardiovascular disease.
Owner:SIT SING YUEN +2
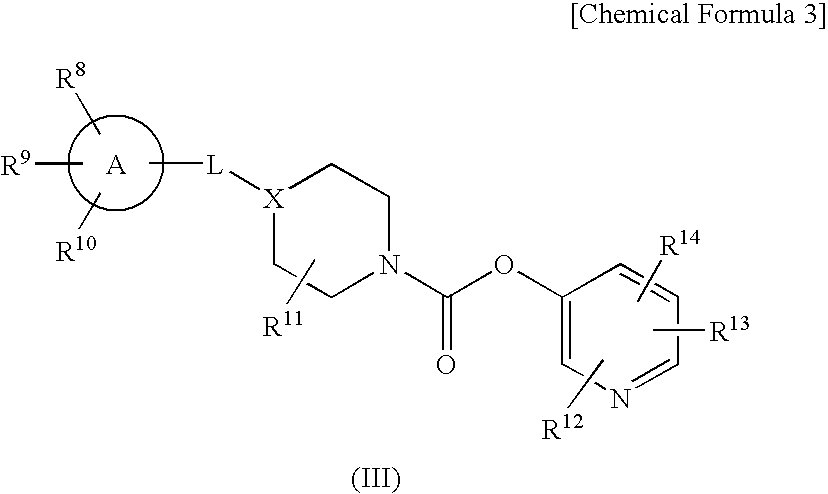
Pyridyl Non-Aromatic Nitrogen-Containing Heterocyclic-1-Carboxylate Derivative
ActiveUS20080306046A1Excellent therapeutical effectIncrease capacityBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseBladder capacity
[Problem] To provide a compound usable for treatment of diseases associated with fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), especially for treatment of urinary frequency and urinary incontinence, overactive bladder and / or pain.[Means for Solution] We have found that a novel pyridyl non-aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocyclic-1-carboxylate derivative and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt has a potent FAAH-inhibitory activity. Further, the pyridyl non-aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocyclic-1-carboxylate derivative of the present invention has an excellent effect for increasing an effective bladder capacity, an excellent effect for relieving urinary frequency and an excellent anti-allodynia effect, and is therefore usable for treatment of urinary frequency and urinary incontinence, overactive bladder and / or pain.
Owner:AUTOBAHN THERAPEUTICS INC
Heteroaryl-substituted spirocyclic diamine urea modulators of fatty acid amide hydrolase
Certain heteroaryl-substituted spirocyclic diamine urea compounds are described, which are useful as FAAH inhibitors. Such compounds may be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of disease states, disorders, and conditions mediated by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity, such as anxiety, pain, inflammation, sleep disorders, eating disorders, energy metabolism disorders, and movement disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis).
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Aryl - Hydroxyethylamino - Pyrimidines and Triazines as Modulators of Fatty Acid amide Hydrolase
Certain aryl-hydroxyethylamino-pyrimidine and triazine compounds are described, which are useful as FAAH inhibitors. Such compounds may be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of disease states, disorders, and conditions mediated by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity, such as anxiety, pain, inflammation, sleep disorders, eating disorders, energy metabolism disorders, and movement disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis). Methods of synthesizing such compounds are also disclosed.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis
ActiveUS20090048337A1Improve the level ofBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationAromatic moietyHydrolysis
Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors of the Formula:I. are provided wherein X is NH, CH2, O, or S; Q is O or S; Z is O or N; R is an aromatic moiety selected from the group consisting of substituted or unsubstituted aryl; substituted or unsubstituted biphenylyl, substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl, and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl; substituted or unsubstituted terphenylyl; substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, or alkyl; and R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted heteroalkyl, and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, substituted or unsubstituted biphenylyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, and substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl; with the proviso that if Z is O, one of R1 and R2 is absent, and that if Z is N, optionally R1 and R2 may optionally be taken together to form a substituted or unsubstituted N-heterocycle or substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl with the N atom to which they are each attached. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of Formula I and methods of using them to inhibit FAAH and / or treat appetite disorders, glaucoma, pain, insomnia, and neurological and psychological disorders including anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and depression are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
(Oxime)carbamoyl fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors
The present invention relates to novel oxime carbamyl derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions comprising said derivatives which inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase. These pharmaceutical compositions are useful for the treatment of conditions which can be effected by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase including, but not limited to, neuropathic pain, emesis, anxiety, altering feeding behaviors, movement disorders, glaucoma, brain injury, and cardiovascular disease.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase
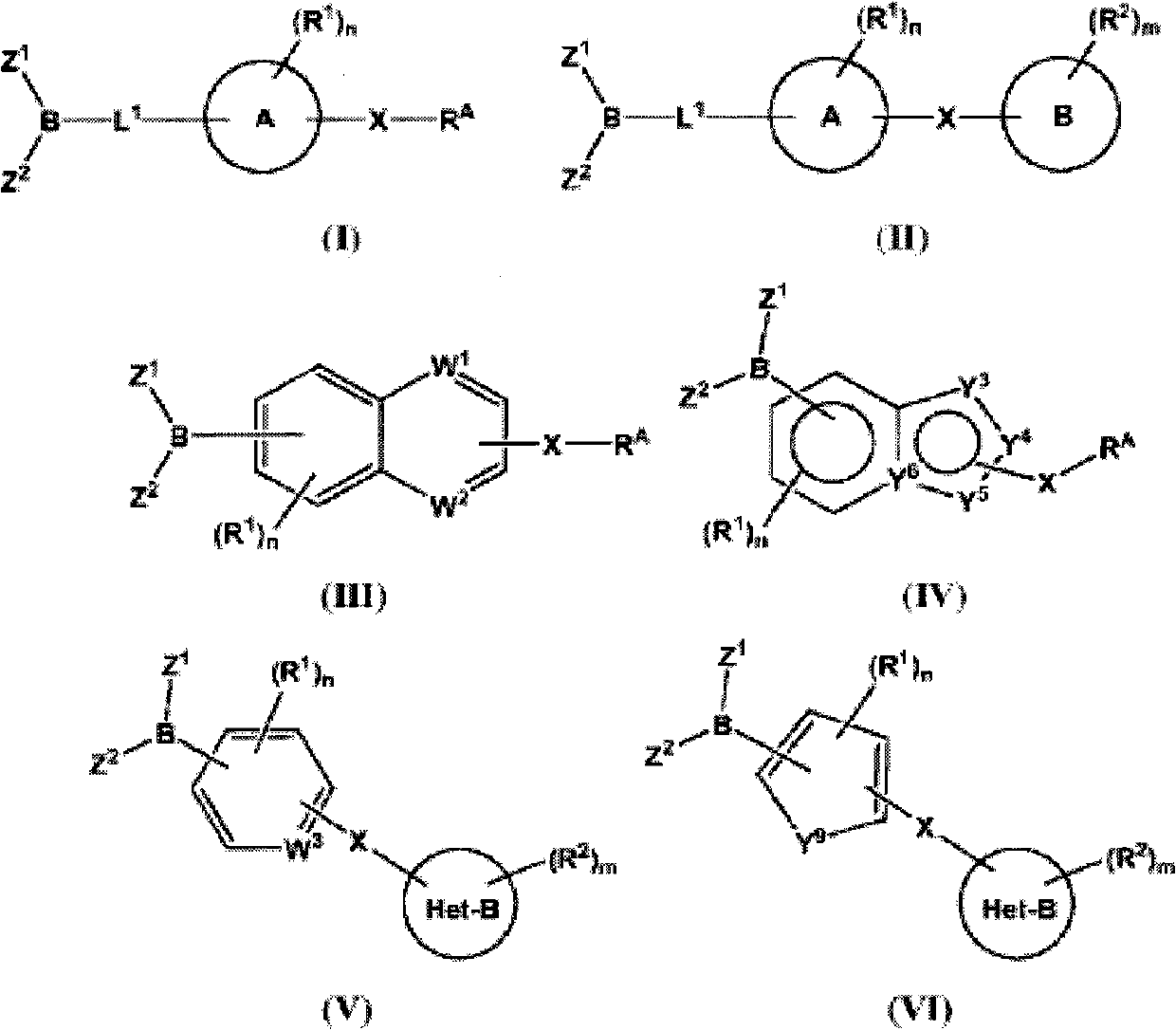
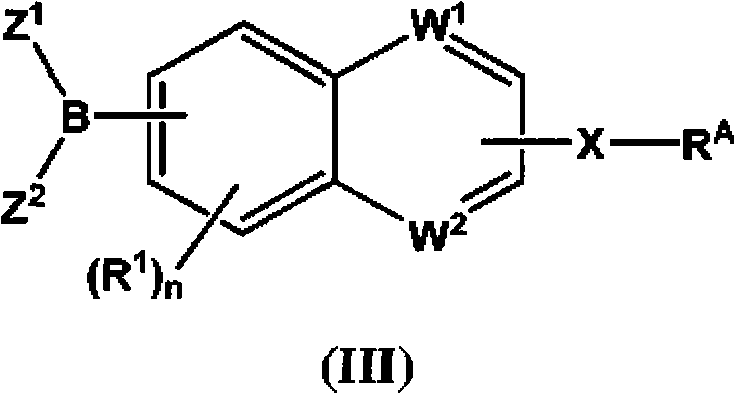
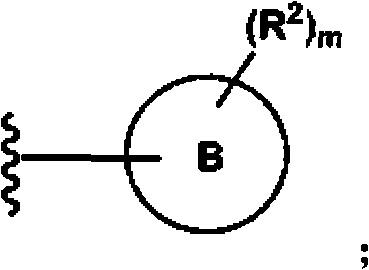
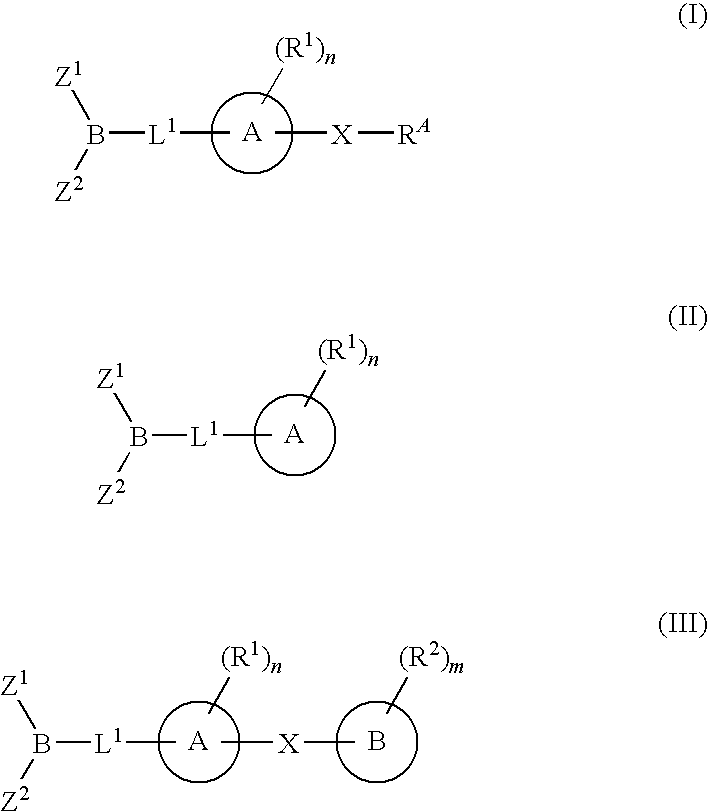
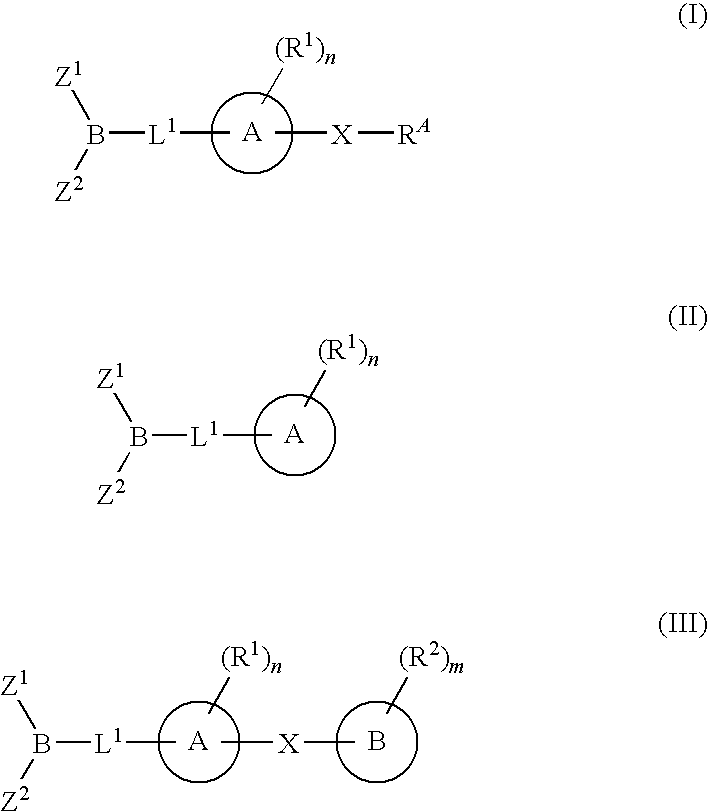
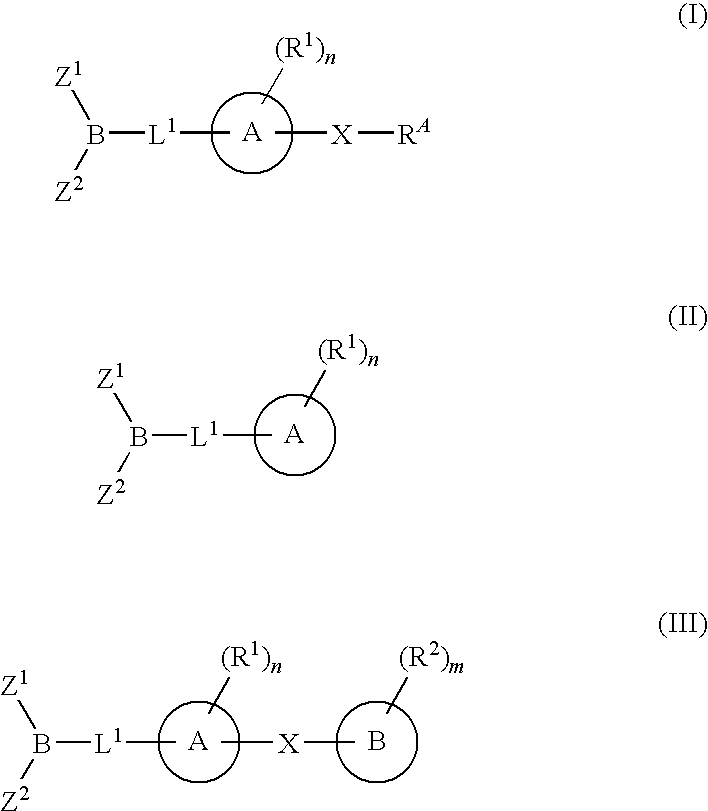
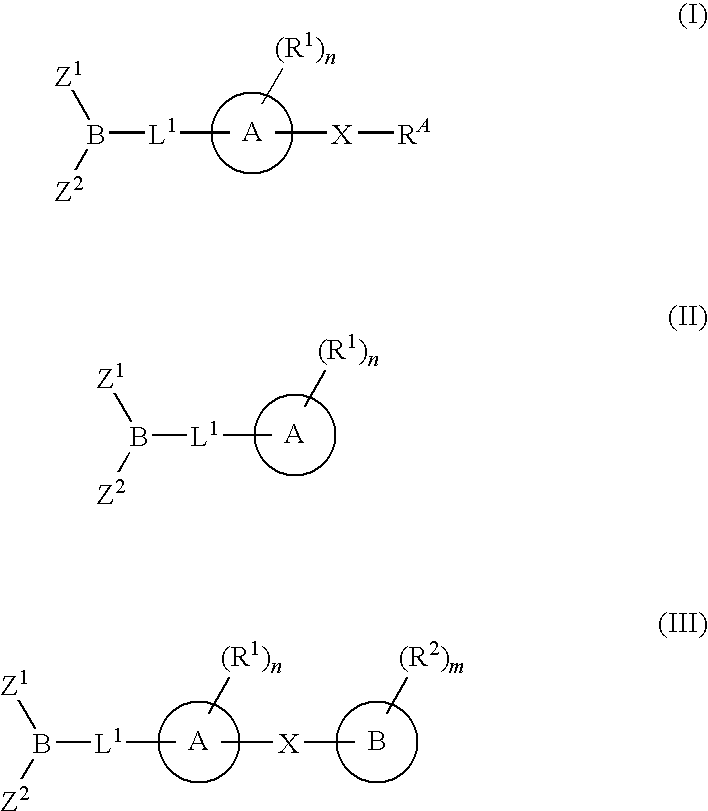
The present invention provides compounds, and pharmaceutically acceptable compositions thereof, encompassed by any of formulae (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V), or (VI), or subgenera thereof. The present invention also provides methods for treating an FAAH mediated disease, disorder or condition by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound or composition comprising a compound of any of formulae (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V), or (VI), or subgenera thereof, to a patient in need thereof. Additionally, the present invention provides methods for inhibiting FAAH by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound or composition comprising a compound of any of formulae (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V), or (VI), or subgenera thereof, to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:INFINITY PHARMA
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase
The present invention provide compounds, and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, encompassed by the formulae (I), (II) or (III).The present invention also provides methods for treating an FAAH mediated disease, disorder or condition by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a provided compound of the formulae (I), (II) or (III), or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, to a patient in need thereof. Additionally, the present invention provides methods for inhibiting FAAH in a patient by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the formulae (I), (II) or (III), or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:INFINITY PHARMA
Amide compounds, compositions and applications thereof
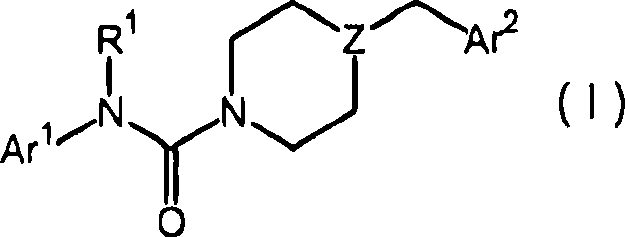
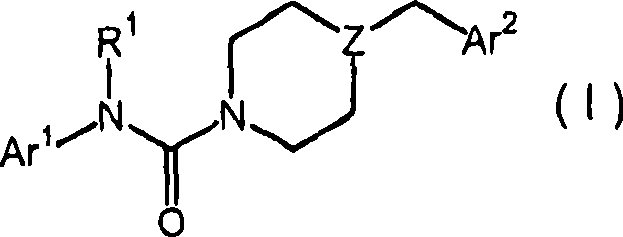
The present disclosure relates to substituted amide compounds that are inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH), their stereoisomers, tautomers, prodrugs, polymorphs, solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. These compounds are useful in the treatment, prevention, prophylaxis, management, or adjunct treatment of all medical conditions related to inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH), such as pain including acute and post operative pain, chronic pain, cancer pain, cancer chemotherapy induced pain, neuropathic pain, nociceptive pain, inflammatory pain, back pain, pain due to disease of various origin such as: diabetic neuropathy, neurotropic viral disease including human immunodeficient virus (HIV), herpes zoster such as post herpetic neuralgia; polyneuropathy, neurotoxicity, mechanical nerve injury, carpal tunnel syndrome, immunologic mechanisms like multiple sclerosis; sleep disorders, anxiety and depression disorders, inflammatory disorders, weight and eating disorders, Parkinson's disease, addiction, spasticity, hypertension or other disorders. The disclosure also relates to the process of preparation of the amide compounds. Formula (1). The present disclosure also relates to methods for the preparation of such compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
Owner:ADVINUS THERAPEUTICS PVT LTD
Animal model for fatty acid amide-related neurobehaviors
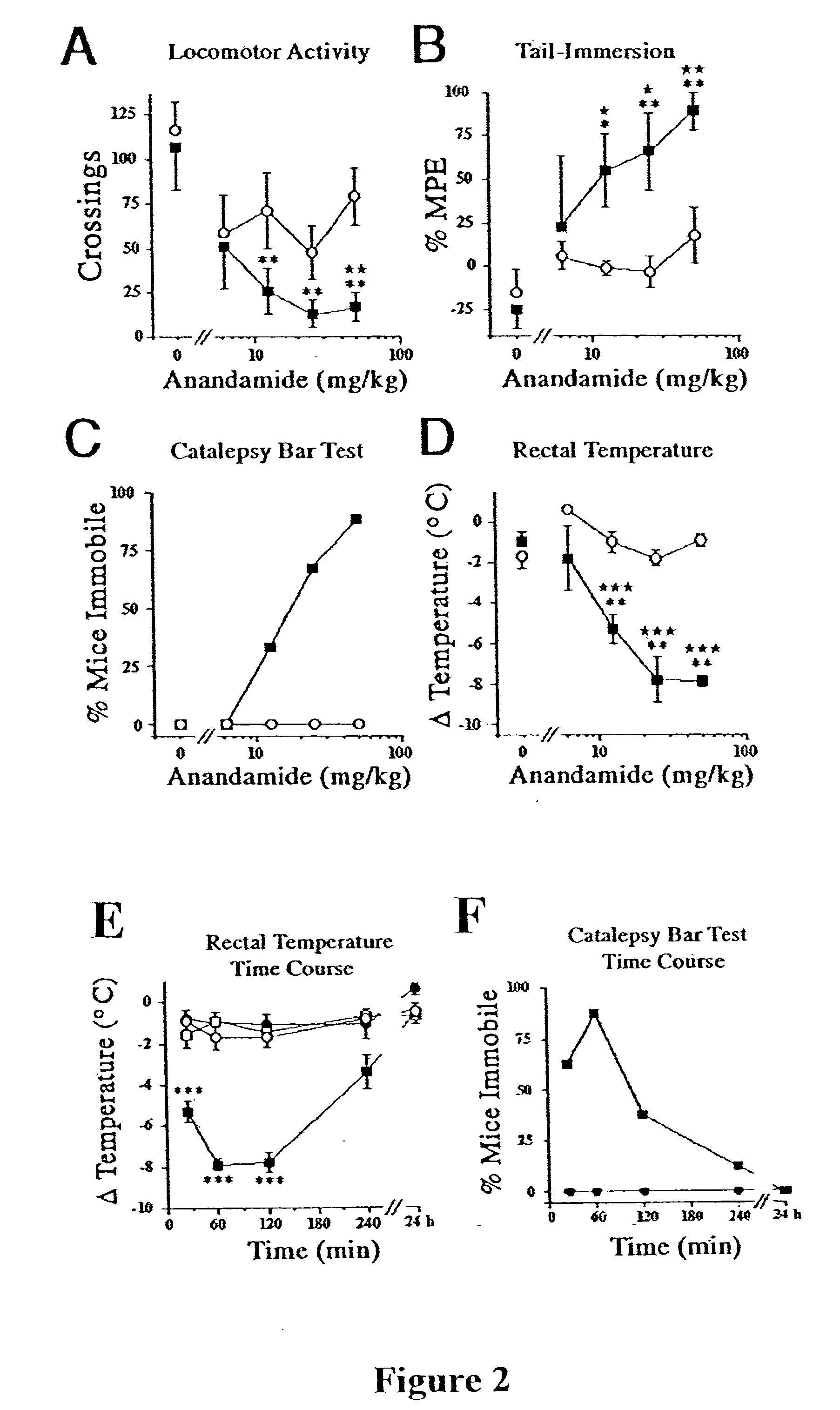
The invention relates to an animal model for studying behavior related to fatty acid amide and hydrolysis of fatty acid amide. The invention provides transgenic animals in which the protein fatty acid amide hydrolase is not expressed, and methods of using such animals.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Compounds And Methods For Treating Non-Inflammatory Pain Using Ppar Alpha Agonists
InactiveUS20080103209A1Extended half-lifeBiocideNervous disorderCannabinoid Receptor AgonistsAgonist
Compositions and methods for treating noninflammatory pain, including but not limited to, neuropathic pain by using peroxisome proliferator activated receptor a (PPARa) agonists to treat a subject having such pain are described. The agonists may be used with additional therapeutic agents such as an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase or a cannabinoid CB1 or CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Combination faah inhibitor and analgesic, Anti-inflammatory or Anti-pyretic agent
InactiveUS20080045513A1Improve the level ofBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationMedicinal chemistryAnalgesic agents
Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity leads to increased levels of fatty acid amides. Esters of alkylcarbamic acids are disclosed that are inhibitors of FAAH activity. Compounds disclosed herein inhibit FAAH activity and further provide an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, or anti-pyretic agent. Described herein is a process for the preparation of esters of alkylcarbamic acid compounds, compositions that include them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:NV ORGANON
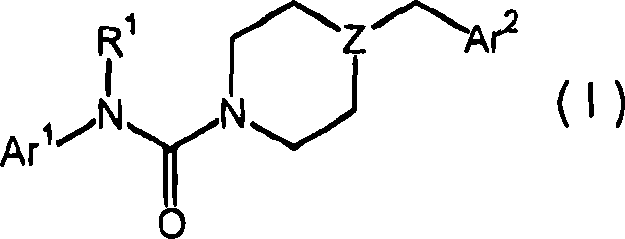
Piperazinyl and piperidinyl ureas as modulators of fatty acid amide hydrolase
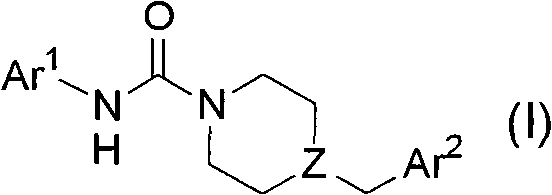
Compounds of formula (I): wherein, Z is -N-or>CH; R<1> is -H or -C1-4alkyl; Ar<1> is 2-thiazolyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, 2-pyrimidinyl, 4-primidinyl, 5-pyrimidinyl, or phenyl, each unsubstituted or substituted at a carbon ring member with one or two R moieties; where each R moiety is independently selected from the group consisting of -C1-4alkyl, -C2-4alkenyl, -OH, -OC1-4alkyl, halo, -CF3, -OCF3, -SCF3, -SH, -S(O)0-2C1-4alkyl, -OSO2C1-4alkyl, -CO2C1-4alkyl, -CO2H, -COC1-4alkyl, -N(R)R<c>, -SO2NRR<c>, -NRSO2R<c>, -C(=O)NRR<c>, -NO2, and -CN, wherein R and R<c> are each independently -H or -C1-4alkyl; and Ar<2> is defined in the claims are useful as FAAH inhibitors. Such compounds may be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of disease states, disorders, and conditions mediated by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity. Thus, the compounds may be administered to treat, e.g., anxiety, pain, inflammation, sleep disorders, eating disorders, or movement disorders (such as multiple sclerosis).
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Aza-indole derivatives useful as modulators of FAAH
The present invention is directed to certain Aza-Indole derivatives which are useful as modulators of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) and as FAAH imaging agents. The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzheimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Cannabinergic lipid ligands
ActiveUS8202893B2High affinityHigh selectivityBiocideSenses disorderReceptor subtypeEndogenous cannabinoid
One aspect of this disclosure relates generally to lipid compounds that exert diverse effects in the endocannabinoid system, such as regulating CB1 and CB2 receptor or moderating other bio-macromolecules within the endocannabinoid system. Some of the compounds showed improved receptor binding affinity, and / or improved receptor subtype selectivity, and improved bio-stability. Some of the compounds exhibit activities to regulate the enzymes that moderate the bio-disposal of endogenous cannabinoids, such as the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Some of the compounds exhibit activities to inhibit the anandamide transporter. Other aspects of the invention are pharmaceutical preparations employing these ligands and methods of administering therapeutically effective amounts of the preparations to provide a physiological effect.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Methods and compounds for treating neurologic or neuropsychiatric disorders and identifying compounds to treat the same
InactiveUS20040063726A1Improve concentrationAvoid conversionBiocideKetone active ingredientsDiseaseNeuropsychiatry
A method of treating a neurologic or neuropsychiatric disorder or disease in a mammal is provided. The method comprises administering a fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor in an amount sufficient to inhibit deamidation of a fatty acid amide. A method of identifying a fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor useful in the treatment of a neurologic or neuropsychiatric disorder is also provided. A method of identifying a fatty acid amide or fatty acid useful in the treatment of a neurologic or neuropsychiatric disorder is also provided.
Owner:NPS PHARM INC
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase
The present invention provide compounds, and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, encompassed by the formulae (I), (II) or (III).The present invention also provides methods for treating an FAAH mediated disease, disorder or condition by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a provided compound of the formulae (I), (II) or (III), or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, to a patient in need thereof. Additionally, the present invention provides methods for inhibiting FAAH in a patient by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the formulae (I), (II) or (III), or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:INFINITY PHARMA
Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase and Monoacylglycerol Lipase for Modulation of Cannabinoid Receptors
Disclosed are compounds and compositions that inhibit the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), methods of inhibiting FAAH and MGL, methods of modulating cannabinoid receptors, and methods of treating various disorders related to modulation of cannabinoid receptors.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Amide compound, composition and application thereof
The present disclosure relates to substituted amides that are inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), their stereoisomers, tautomers, prodrugs, polymorphs, solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable Salts, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. These compounds are useful in the treatment, prevention, prevention, management or adjunctive treatment of all medical conditions associated with the inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), such as pain, including acute and postoperative pain, chronic pain, Cancer pain, pain from cancer chemotherapy, neuralgia, nociceptive pain, inflammatory pain, back pain, pain from various sources such as: diabetic neuropathy, neurotropism involving human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type viral diseases, herpes zoster such as postherpetic neuralgia; polyneuropathy, neurotoxicity, mechanical nerve damage, carpal tunnel syndrome, immunological mechanisms such as multiple sclerosis; sleep disorders, anxiety and depression, inflammatory diseases, Weight and eating disorders, Parkinson's disease, addiction, cramps, high blood pressure, or other medical conditions. The present disclosure also relates to a preparation method of the amide compound. Formula 1). The disclosure also relates to processes for the preparation of such compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
Owner:ADVINUS THERAPEUTICS PVT LTD
Methods for determining effective doses of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors in vivo
InactiveUS20080089845A1Reduction and alleviationRelieve symptomsCompound screeningBiocideHydrolase inhibitorDepressant
Described herein is a method for determining an effective dose of a composition for inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase activity in vivo, by first administering to a subject a dose of a test composition, and subsequently assessing if the level of a fatty acid amide in the subject increases. Also described, is a method for optimizing therapeutic efficacy for treatment of anxiety, depression, pain, or a metabolic disorder by increasing or decreasing a dose of a fatty amide hydrolase inhibitor according to a patient's fatty acid amide levels. In addition, pharmaceutical compositions are described, which contain fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors effective for increasing a FAA level in a patient.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Metabolically-stabilized inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase
InactiveUS20080119549A1Improve the level ofElevates endogenous levelBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationMedicinal chemistryEnzyme
Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity leads to increased levels of fatty acid amides. Esters of alkylcarbamic acids are disclosed that are inhibitors of FAAH activity. Compounds disclosed herein inhibit FAAH activity. Described herein are processes for the preparation of esters of alkylcarbamic acid compounds, compositions that include them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Assay for determining the activity of fatty acid amide hydrolase
InactiveUS20070134753A1Simple methodModulate activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHydrolysisEnzyme
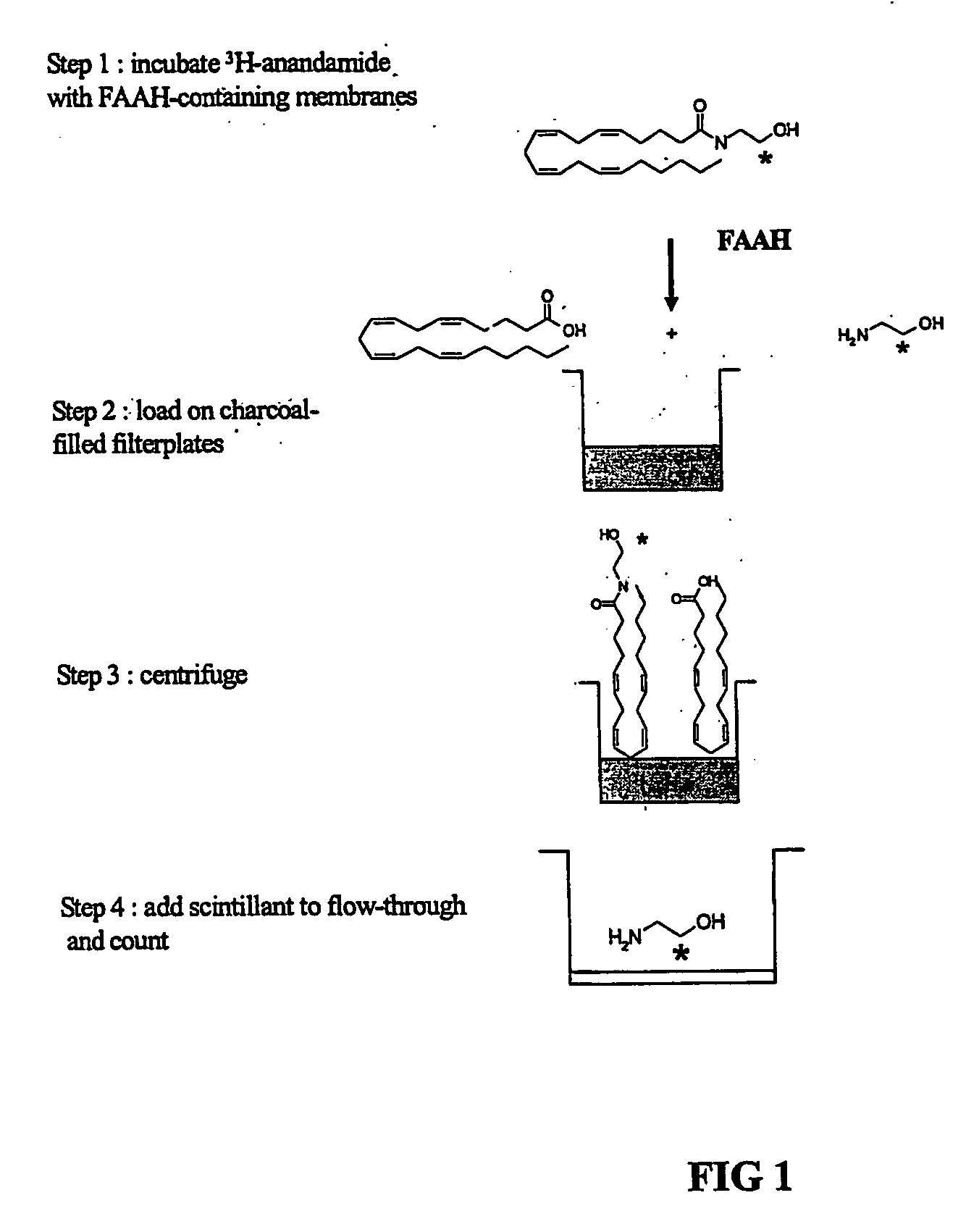
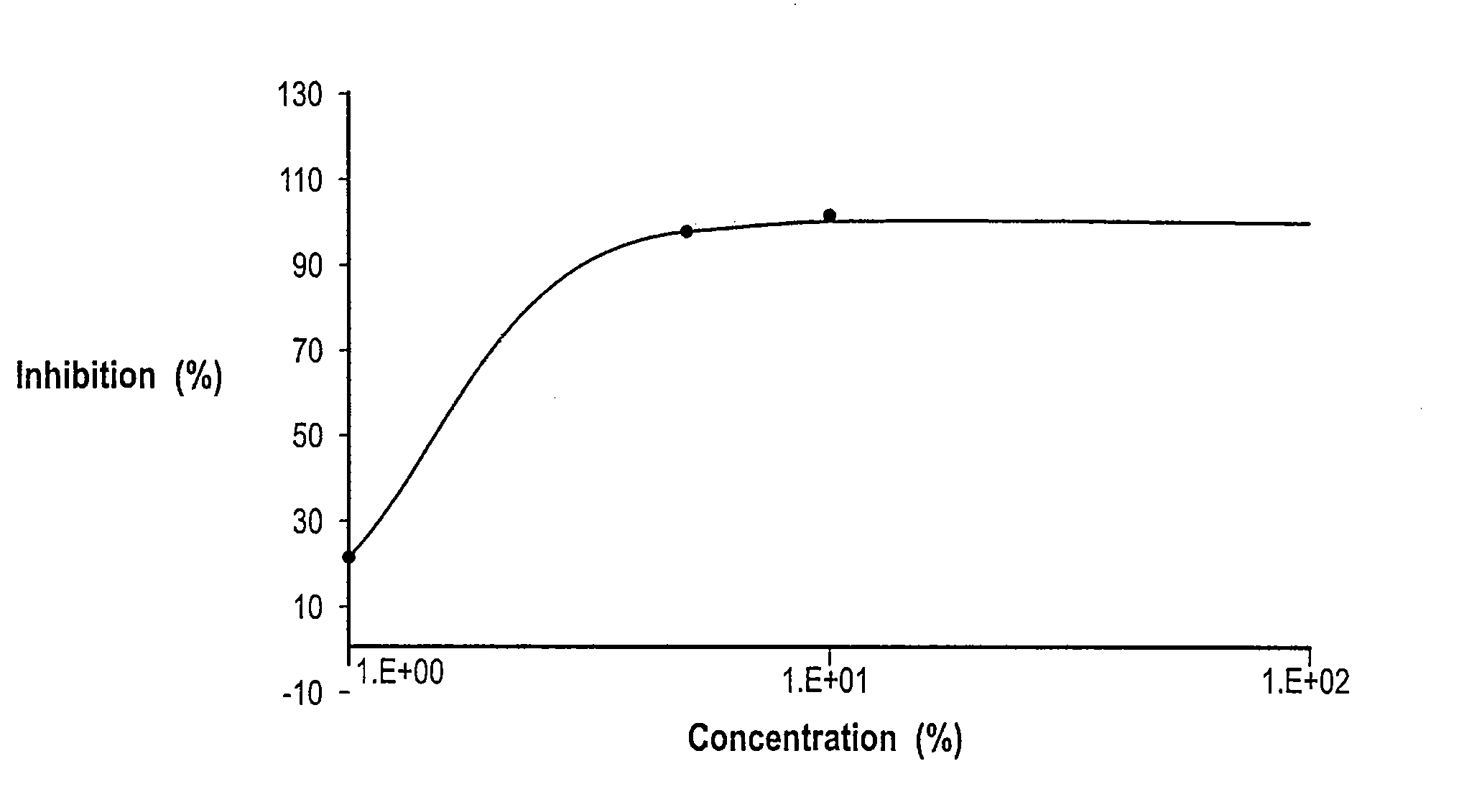
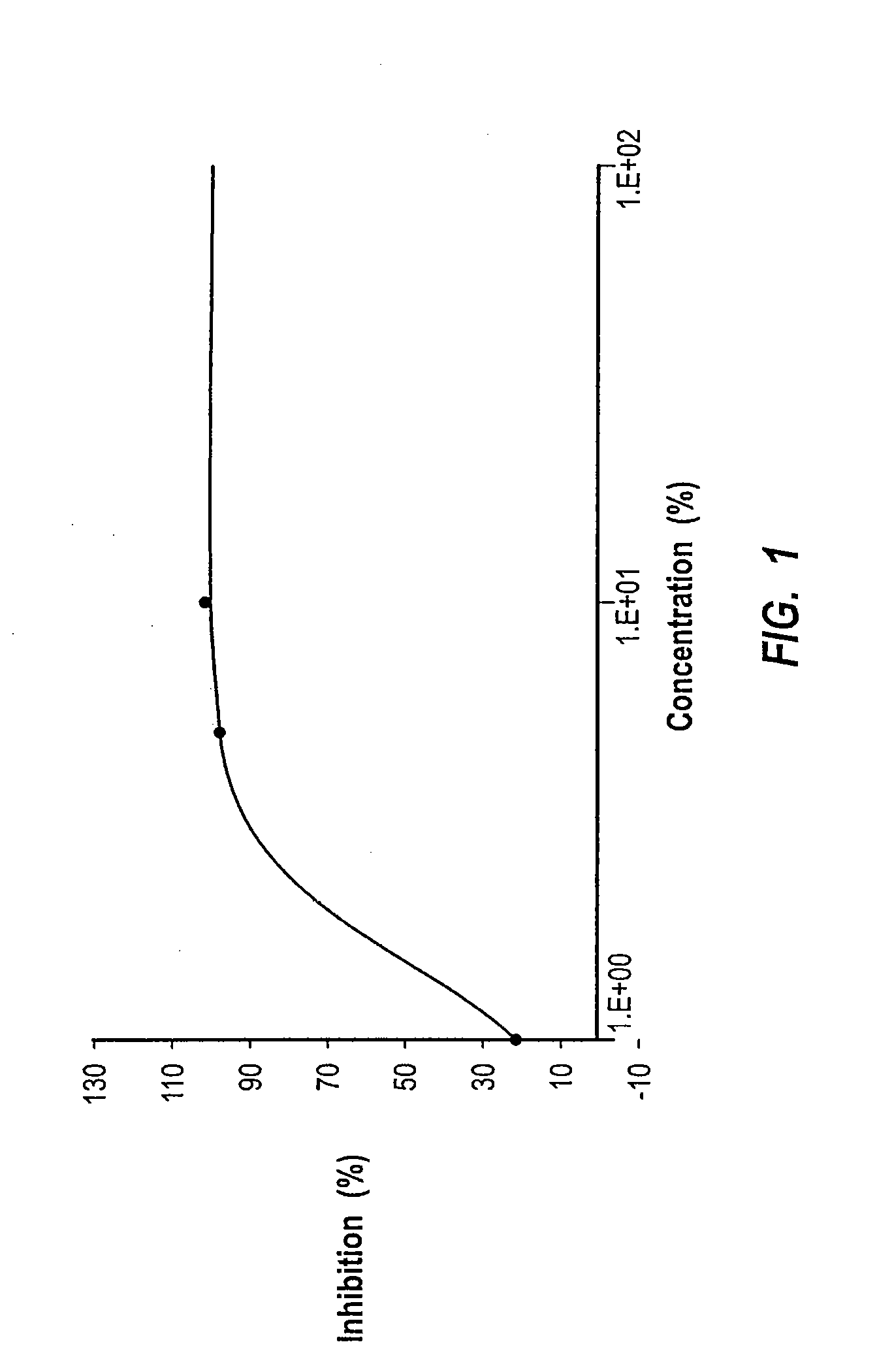
The invention provides methods of assaying fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity adaptable for high through-put screening. The methods provide for separating a labeled substrate from at least one labeled hydrolysis product, the separation facilitating the quantification. The invention also provides methods of identifying a compound to be tested as an inhibitor or an activator of FAAH activity through the addition of the compound to be tested to a reaction mixture and comparison of the enzyme activity in the presence and absence of the compounds to be tested. The methods are adaptable for use in detecting altered FAAH activity in patients, for example, those at risk for in vitro fertilization failure, or at risk for, or suffering, addictions.
Owner:BARBIER ANN JOHANNA +2
Heteroaryl-substituted urea modulators of fatty acid amide hydrolase
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
FAAH inhibitors
The present disclosure relates to compounds useful as inhibitors of the enzyme Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The disclosure also provides pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the compounds of the disclosure and methods of using the compositions in the treatment or prevention of various disorders. Compounds of the invention are described in Table 1.
Owner:硬木药品公司
Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis
Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors of the Formula:are provided wherein X is NH, CH2, O, or S; Q is O or S; Z is O or N; R is an aromatic moiety selected from the group consisting of substituted or unsubstituted aryl; substituted or unsubstituted biphenylyl, substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl, and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl; substituted or unsubstituted terphenylyl; substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, or alkyl; and R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted heteroalkyl, and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, substituted or unsubstituted biphenylyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, and substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl; with the proviso that if Z is O, one of R1 and R2 is absent, and that if Z is N, optionally R1 and R2 may optionally be taken together to form a substituted or unsubstituted N-heterocycle or substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl with the N atom to which they are each attached. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of Formula I and methods of using them to inhibit FAAH and / or treat appetite disorders, glaucoma, pain, insomnia, and neurological and psychological disorders including anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and depression are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Treatment of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy with Morinda Citrifolia Enhanced Formulations
The present invention relates to methods and formulations directed inhibiting carbonic anhydrase, fatty acid amide hydrolase and endothelin-converting enzymes comprising the administration of processed Morinda citrifolia based formulations.
Owner:TAHITIAN NONI INT INC
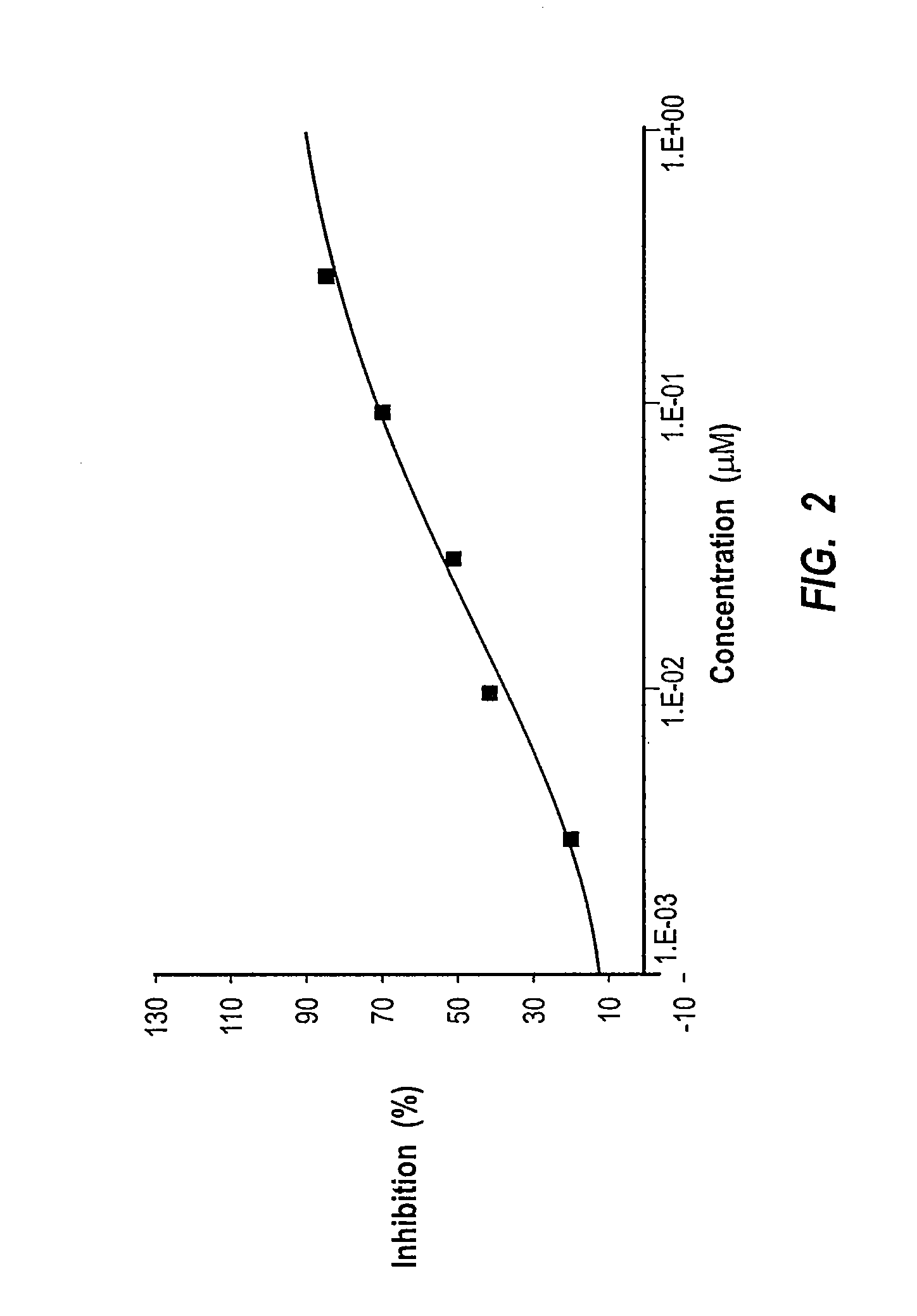
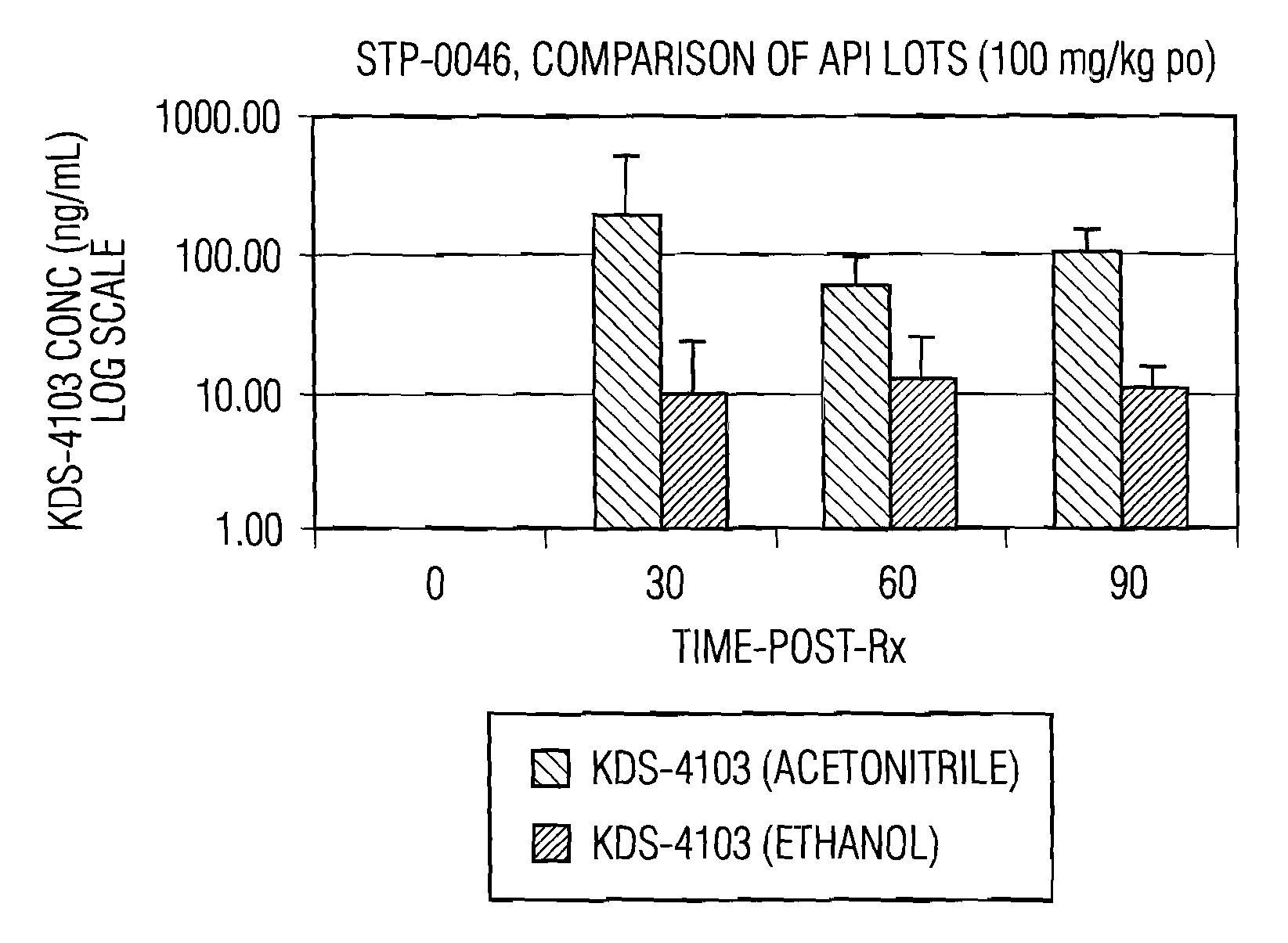
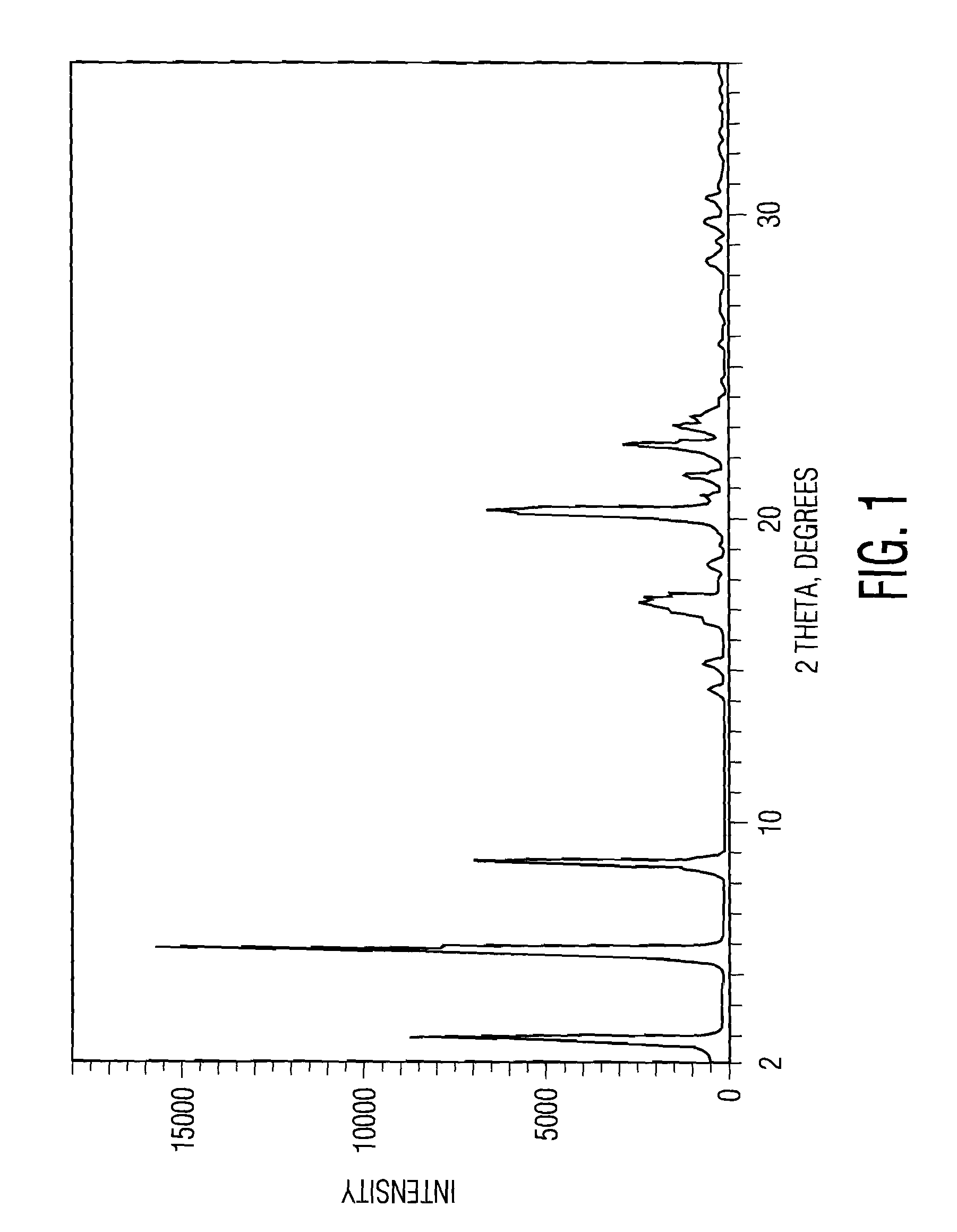
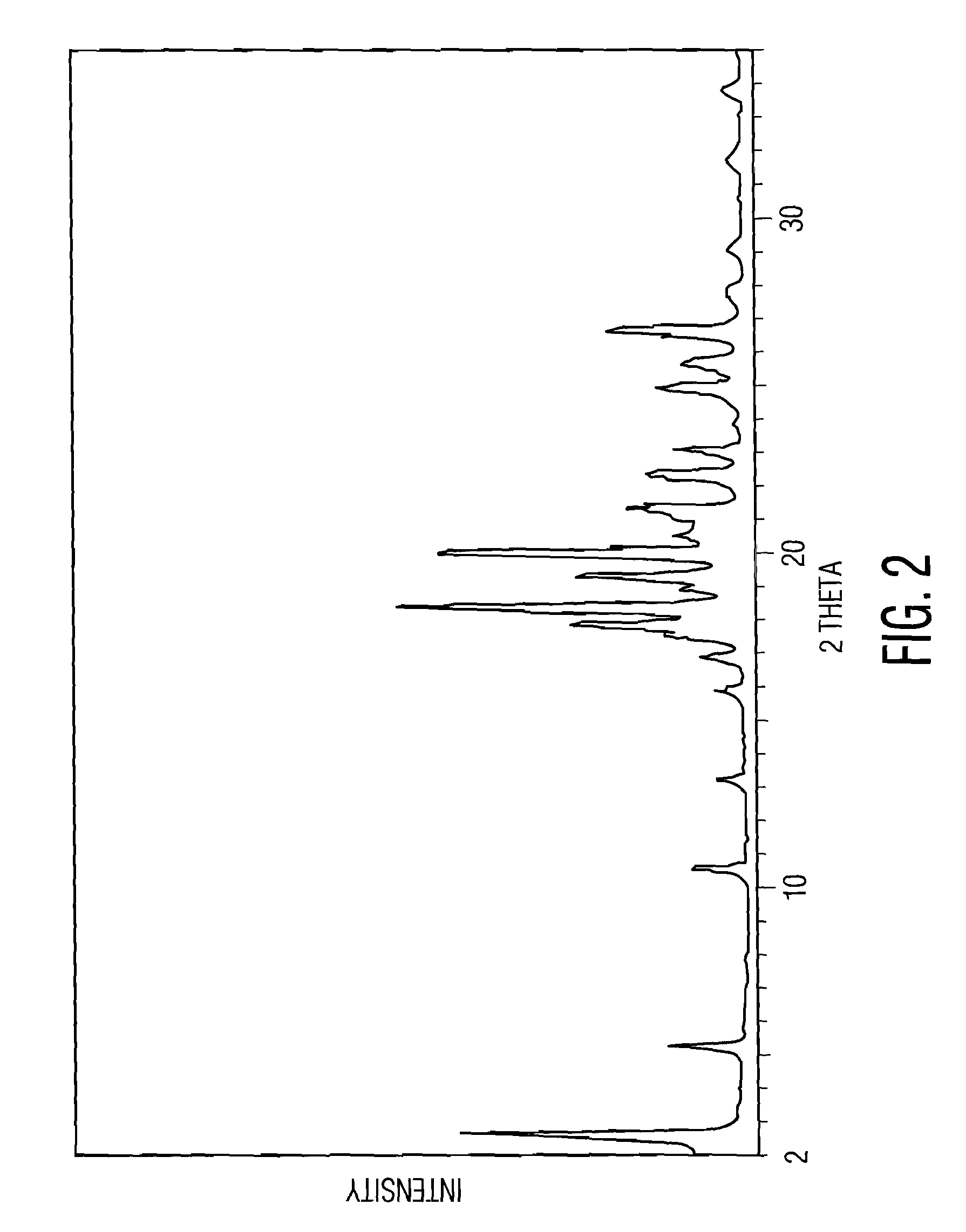
Synthesis, polymorphs, and pharmaceutical formulation of faah inhibitors
Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity leads to increased levels of fatty acid amides. The alkylcarbamic acid aryl ester of Formula (I), KDS-4103, is a FAAH inhibitor. Described herein is a process for the preparation of the compound of Formula (I), characterization of polymorphs of the FAAH inhibitor, and their uses therof.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Urea/carbamates FAAH MAGL or dual FAAH/MAGL inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS10570146B2Slow degradationReduce inactivationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCarbamateDepressant
Disclosed are compounds that may be used to inhibit the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) or dual FAAH / MAGL. More particularly, compounds of formula IIhave utility in a variety of therapeutic uses such as treatment of pain, inflammation, neuropathy, or appetite disorder.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com