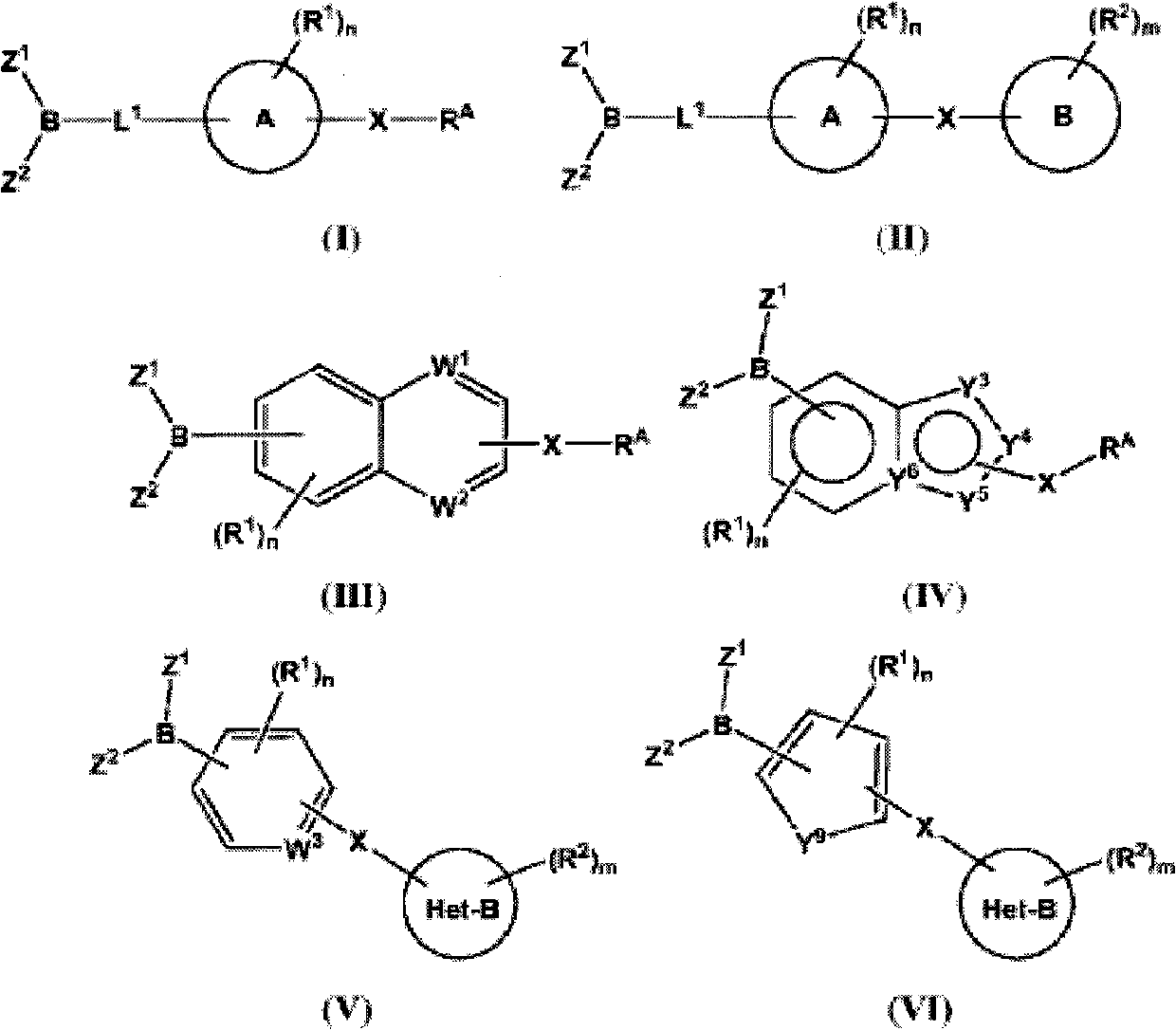
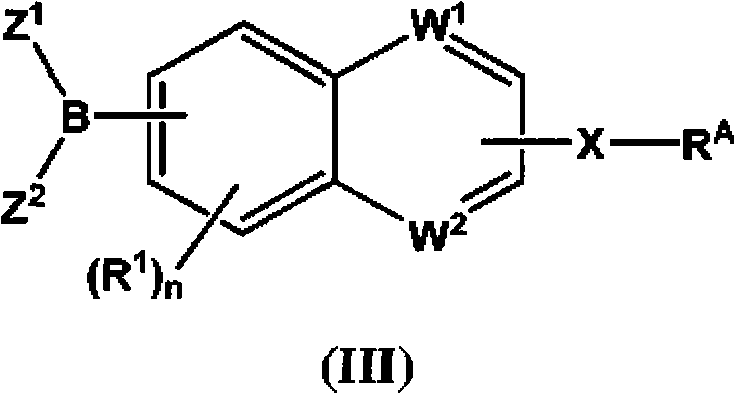
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase
A composition and compound technology, applied in the direction of anti-inflammatory agents, non-central analgesics, allergic diseases, etc., can solve the problem of unexplored therapeutic efficacy of FAAH inhibitors, lack of target selectivity, biological activity and/or bioavailability Degree and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0763] Provided formulations of the pharmaceutically acceptable compositions described herein can be prepared by any method known or hereafter developed in the art of pharmacology. In general, such methods of preparation comprise the steps of bringing into association the active ingredient with the carrier and / or one or more other auxiliary ingredients, and then, if necessary and / or desired, shaping and / or packaging the product in the desired unit. or in multiple dose units.
[0764] The pharmaceutically acceptable compositions of the invention may be prepared, packaged and / or sold in bulk, as a single unit dose and / or as a plurality of single unit doses. As used herein, a "unit dose" is a discrete quantity of a pharmaceutically acceptable composition containing a predetermined quantity of active ingredient. The amount of active ingredient is usually equal to the dose of active ingredient to be administered to the individual and / or a convenient fraction of such a dose (eg, on...
example 1
[0921]
[0922] 3-Fluoro-4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)benzoic acid (470mg, 1.77mmol) and 2-amino Acetophenone hydrochloride (318 mg, 1.89 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane. HOBt (286 mg, 2.12 mmol) and EDC (406 mg, 2.12 mmol) were added, followed by triethylamine (741 μL, 5.30 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 12 h, after which time it was transferred to a separatory funnel using excess dichloromethane and added with 0.5M citric acid (2x75 mL) and saturated NaHCO 3 (2x75 mL) wash. Then the organic layer was treated with MgSO 4 Drying, filtration and concentration afforded the desired ketoamide (680 mg) in quantitative yield as a yellow solid, which was used directly in the subsequent step to form the oxazole.
[0923] The crude ketoamide (100 mg, 0.261 mmol) was dissolved in 2 mL of concentrated H 2 SO 4 middle. The reaction solution first turned bright orange, followed by the formation of a brown solid. ...
example 2
[0925]
[0926] Oxazole 2 was prepared using the conditions described for Example 1. [M-H] - = 264.1 m / z. Activity: B
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com