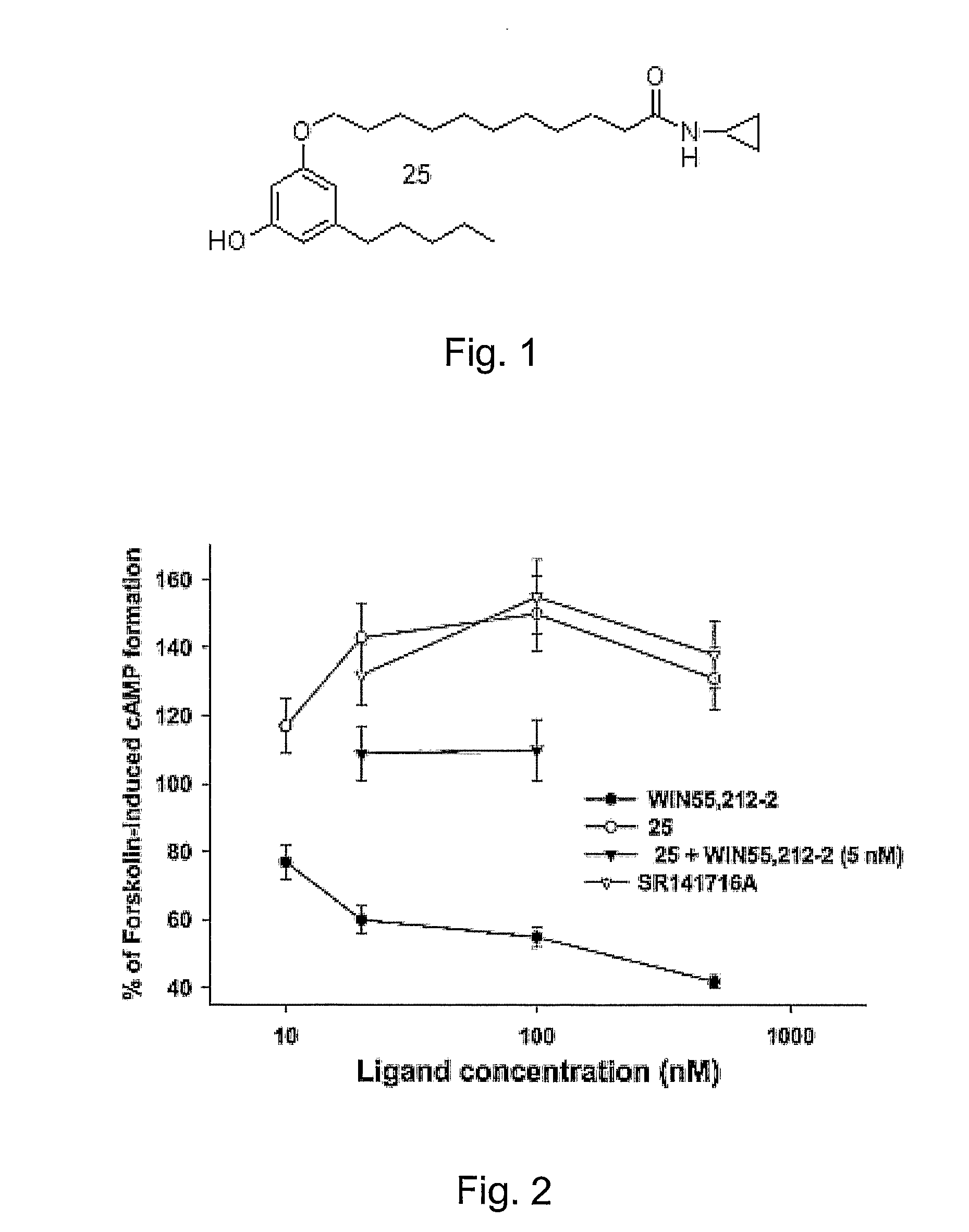
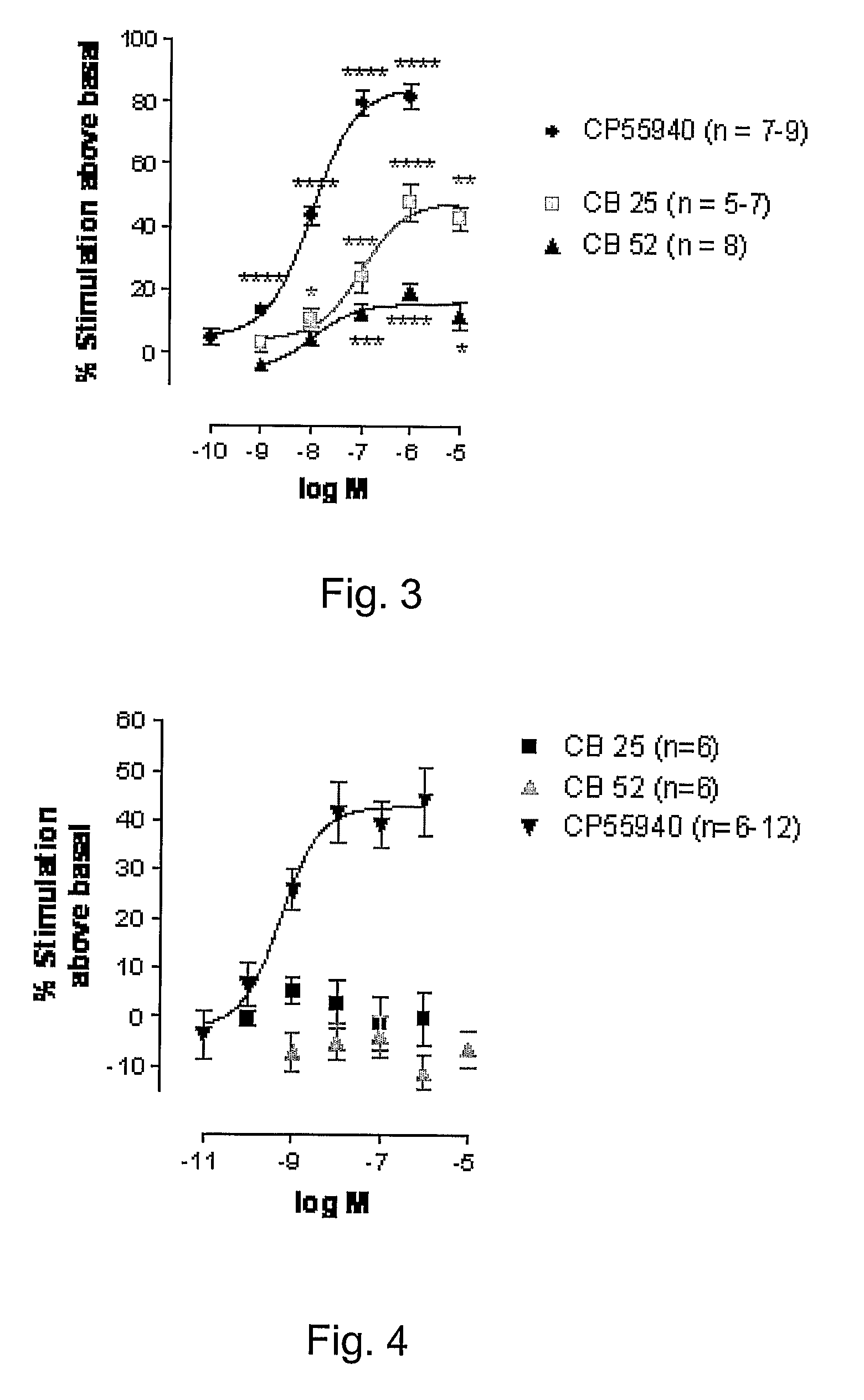
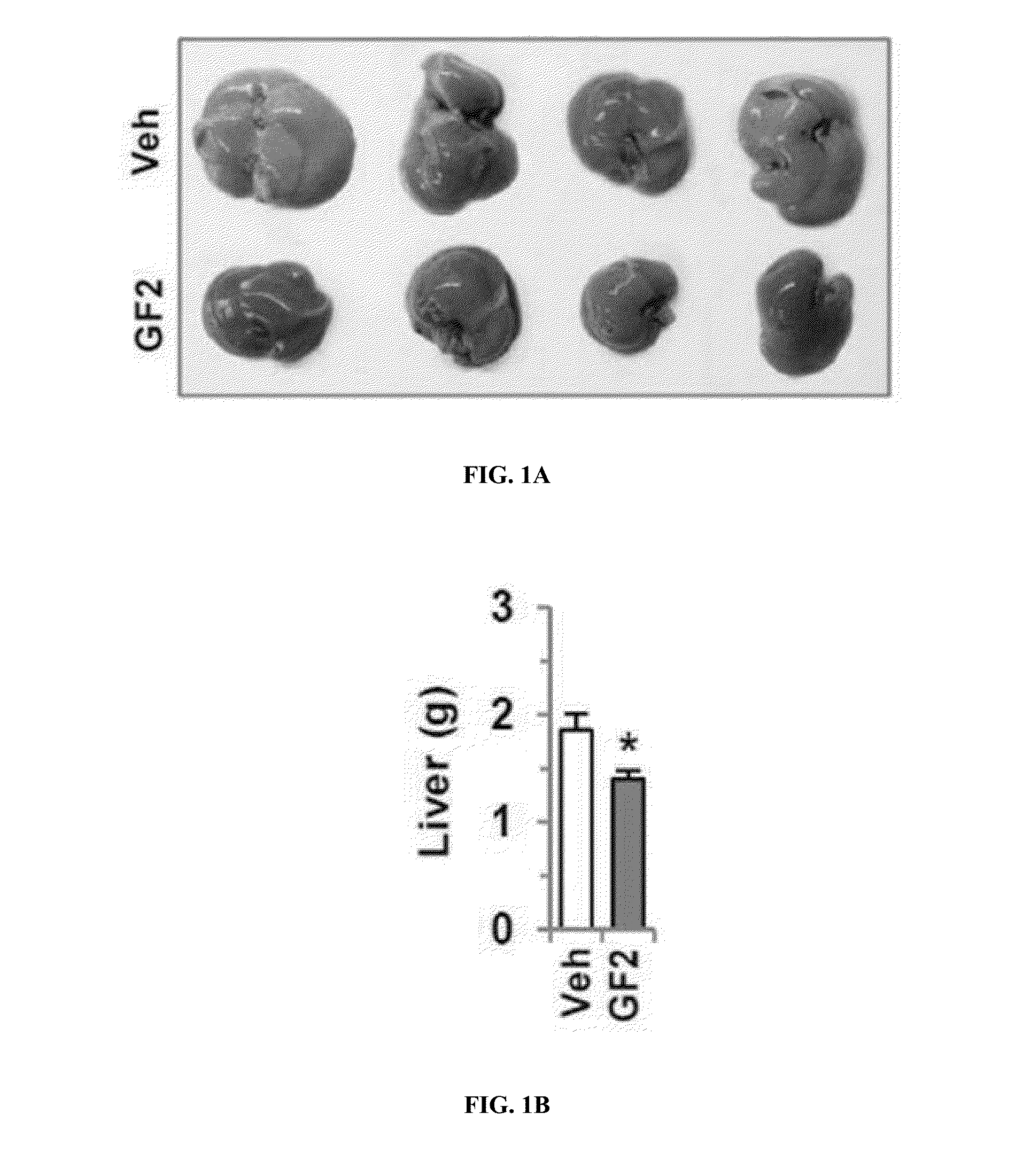
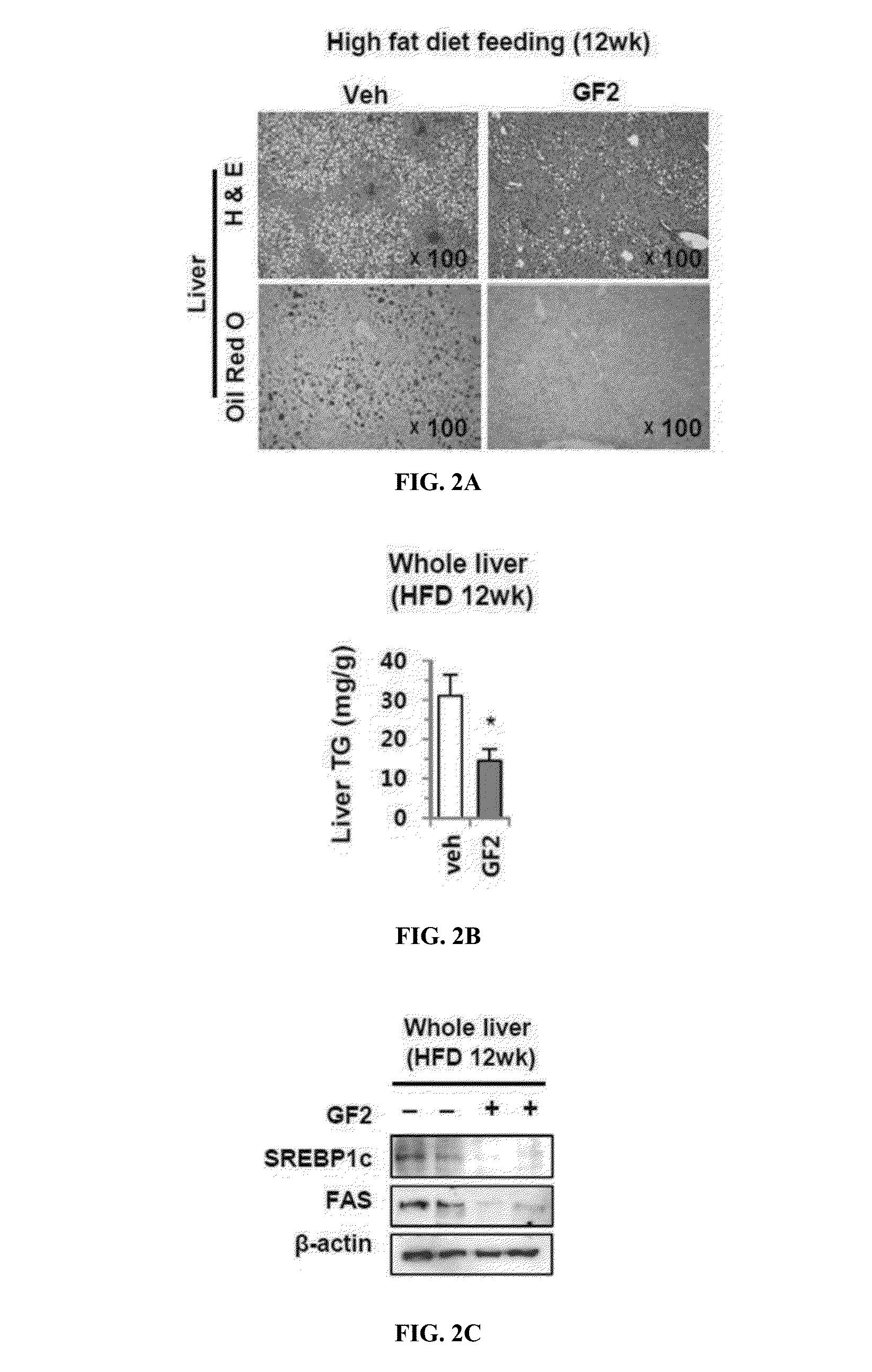
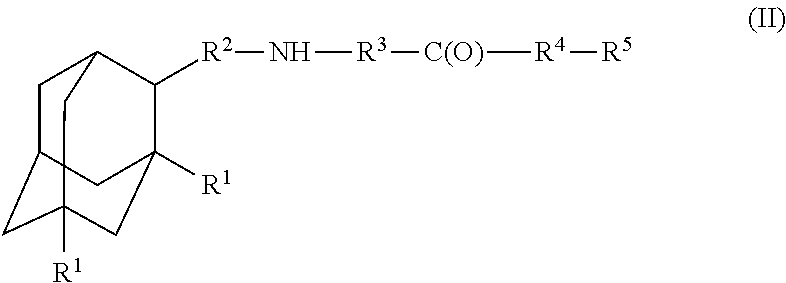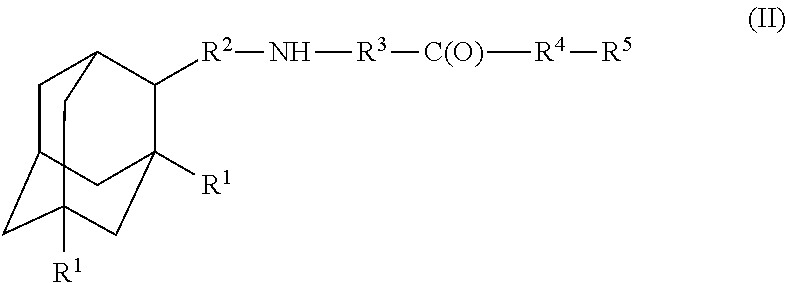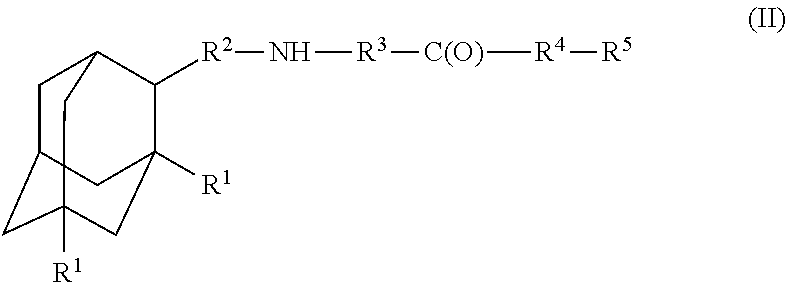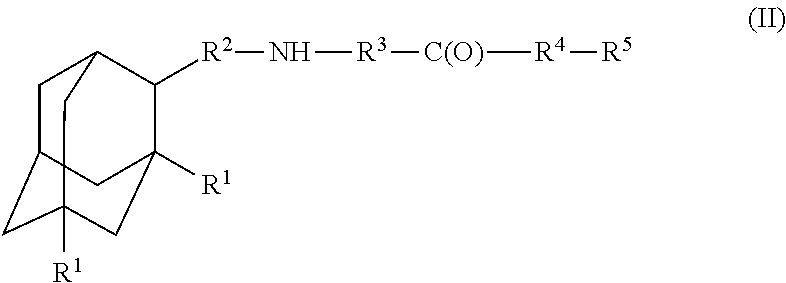Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Endogenous cannabinoid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
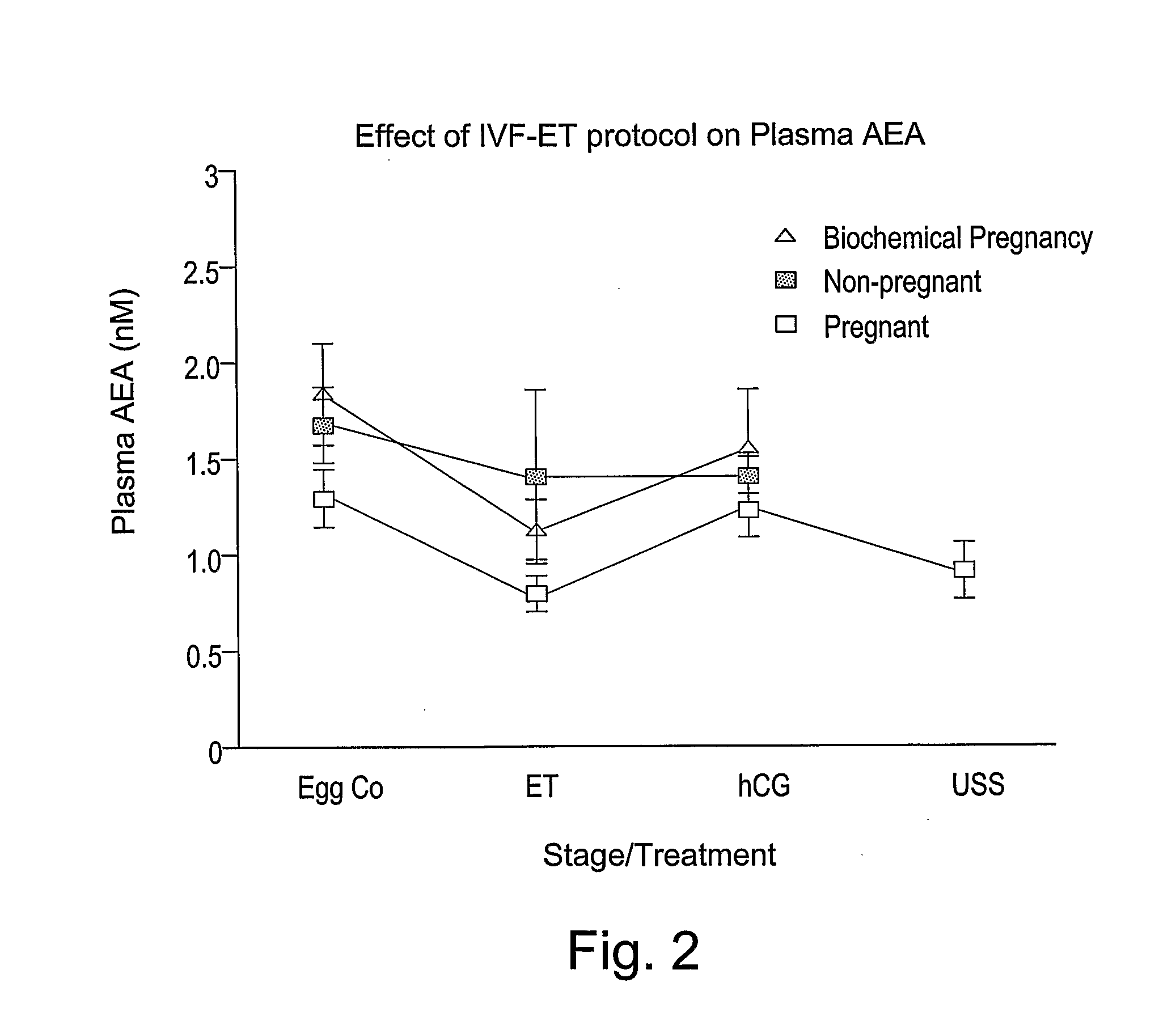
Anandamide is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to cannabinoid receptors. It has been shown that aerobic exercise causes an increase in plasma anandamide levels, where the magnitude of this increase is highest at moderate exercise intensity (i.e., exercising at ~70–80% maximum heart rate).
Methods and compositions related to targeting monoacylglycerol lipase
InactiveUS20110275650A1Strong inhibitory activityHigh selectivityBiocideSenses disorder2-ArachidonoylglycerolEndogenous cannabinoid
This invention provides compounds that selectively inhibit monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL). The invention also provides methods of using the MAGL selective inhibitors to stimulate 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) mediated endocannabinoid signaling in vivo, and to treat conditions that are associated with or linked to endocannabinoid signaling. The invention additionally provides methods of treating cancer or inhibiting tumor growth by targeting MAGL with MAGL specific inhibitors. The invention further provides methods of screening for MAGL inhibitors with improved biochemical and pharmaceutical properties.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Synthetic endogenous cannabinoids analogues and uses thereof
InactiveUS6531636B1Avoid actionPromote absorptionBiocideEther/acetal active ingredientsMigraineBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
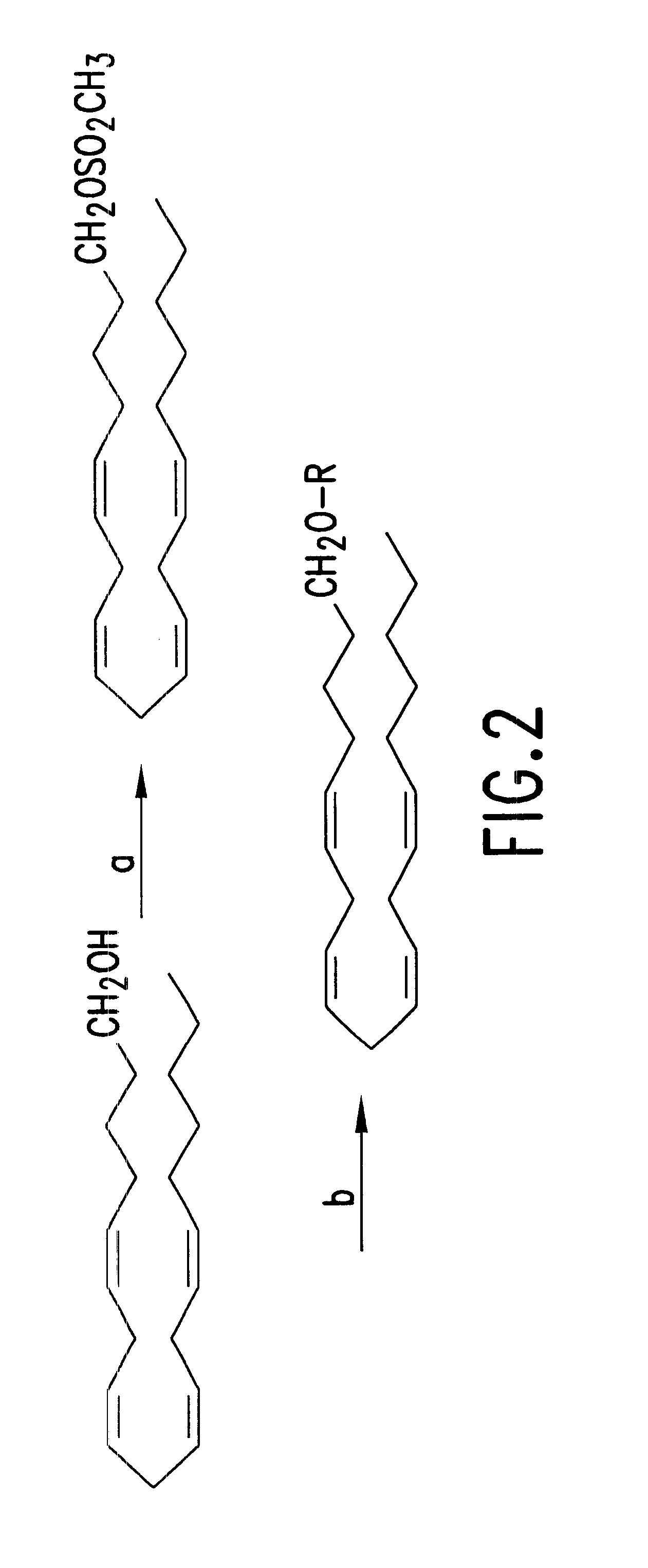
The present invention relates to a compound of the general formula (I) which is a non-hydrolysable analogue of endogenous cannabinoids, which are found to be more potent therapeutic agents as they are more stable, for example, to hydrolytic cleavage in the gastrointestinal tract. The cannabinoid analogues of the invention have a therapeutic value. Therefore, pharmaceutical compositions comprising as active ingredient a therapeutically effective amount of at least one compound of the invention may be prepared. Such compositions may be used as anti-inflammatory, anti-asthmatic, analgetic, hypotensive, antiemetic or anti-spasmodic compositions, and as compositions for treating and / or preventing glaucoma or migraine, or as compositions for relieving symptoms of multiple sclerosis and mood stimulating compositions.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Cannabinergic lipid ligands
ActiveUS8202893B2High affinityHigh selectivityBiocideSenses disorderReceptor subtypeEndogenous cannabinoid
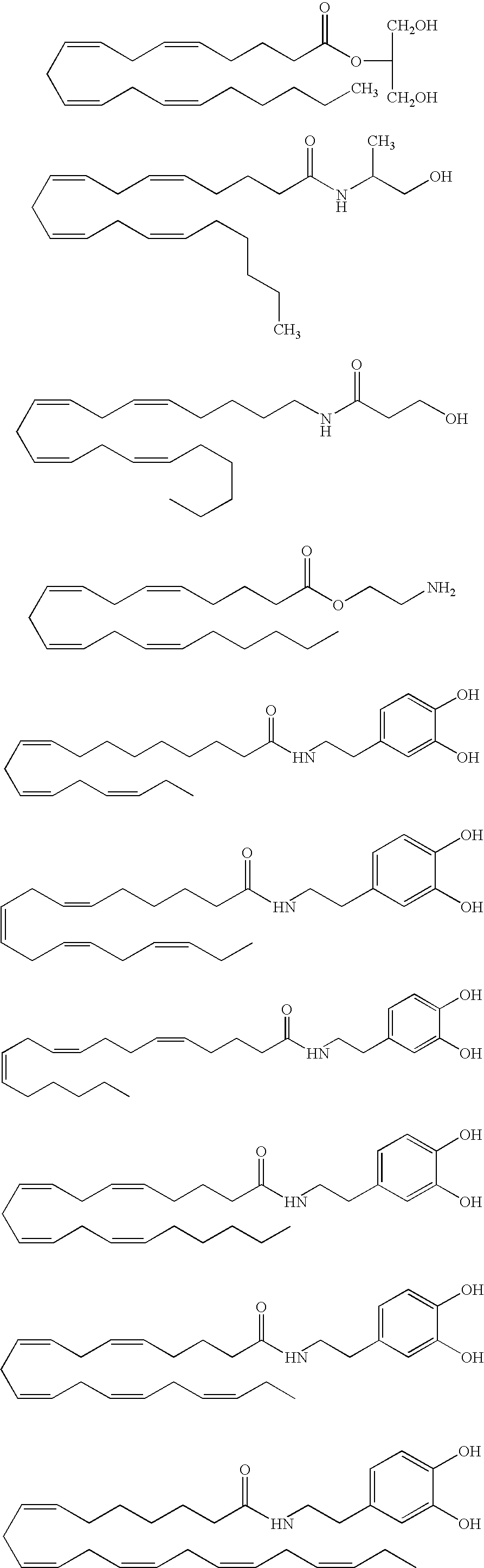
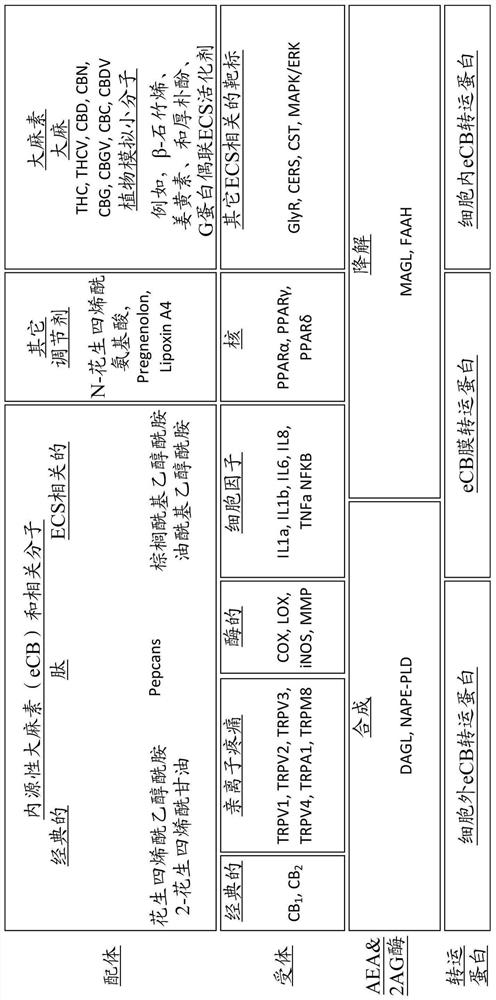
One aspect of this disclosure relates generally to lipid compounds that exert diverse effects in the endocannabinoid system, such as regulating CB1 and CB2 receptor or moderating other bio-macromolecules within the endocannabinoid system. Some of the compounds showed improved receptor binding affinity, and / or improved receptor subtype selectivity, and improved bio-stability. Some of the compounds exhibit activities to regulate the enzymes that moderate the bio-disposal of endogenous cannabinoids, such as the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Some of the compounds exhibit activities to inhibit the anandamide transporter. Other aspects of the invention are pharmaceutical preparations employing these ligands and methods of administering therapeutically effective amounts of the preparations to provide a physiological effect.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Phytosterol nano-emulsion capable of losing weight and lowering lipid and preparation method of phytosterol nano-emulsion
PendingCN109674053AAvoid side effectsPlay the role of weight loss and fat reductionFood ingredient functionsAntioxidantLipid lowering
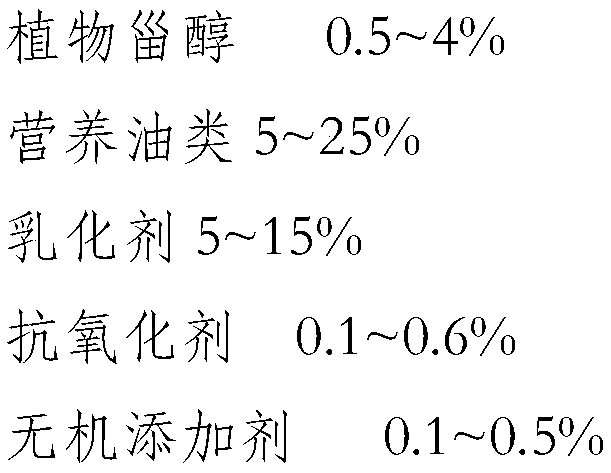
The invention discloses phytosterol nano-emulsion capable of losing weight and lowering lipid and a preparation method of the phytosterol nano-emulsion. The phytosterol nano-emulsion is prepared fromthe following raw materials in percentage by mass: 0.5 to 4 percent of phytosterol, 5 to 25 percent of nutritional oil, 5 to 15 percent of an emulsifier, 0.1 to 0.6 percent of an antioxidant, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of an inorganic additive and the balance of water which is aaded until the content is 100 percent. According to the phytosterol nano-emulsion disclosed by the invention, the ratio of threetypes of phytosterols are reasonably adjusted, and 4-demethlyate sterol and 4,4'-dimethyl sterol have a sufficient synergetic effect to alleviate the obesity; meanwhile, a cholesterol lowering effectand a mechanism of adjusting an endogenous cannabinoids system are used simultaneously to realize the effect of cooperatively lowering the lipid. The phytosterol nano-emulsion prepared by the invention can be directly applied to functional foods, medicines and the like; the dosage of lipid-lowering Western medicines is reduced and the lipid-lowering effect is remarkable; other complications can beobviously alleviated or eliminated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cannabinoid composition and products including α-tocopherol
InactiveUS10238745B2Improve production stabilityImprove biological activityHydrocarbon active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsYeastEndogenous cannabinoid
A cannabinoid composition having an excipient including α-tocopherol and at least one isolated cannabinoid having a purity of greater than 80%. The α-tocopherol inhibits oxidation, regulates viscosity of the composition, and improves bioavailability of the cannabinoid. The composition includes a carrier oil mixed with the excipient and cannabinoid. In one embodiment, the at least one cannabinoid is an isolated cannabinoid having a greater than 80% purity, and preferably greater than 90% purity. The at least one cannabinoid is selected from the group consisting of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids, and combinations thereof. The cannabinoid may be derived from plants other than cannabis sativa, or synthesized from fungi, bacteria, yeast or other synthetic method. Preferably the α-tocopherol comprises at least 10% w / w of the composition.
Owner:CONSTANCE THERAPEUTICS INC
Endocannabinoid conjugate and a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of neuronal disorders
A compound provided by the present invention includes an endocannabinoid, endocannabinoid derivative, or endocannabinoid analog moiety covalently bonded to a biologically active peptide. One example of an inventive compound described is a conjugate of an endocannabinoid, endocannabinoid derivative, or endocannabinoid analog moiety covalently coupled to an opioid peptide, such as an endorphin, enkephalin, dynorphin or endomorphin. Also detailed are processes for making the described conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions including such compounds.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
Cannabis based compositions and methods of treating hypertension
InactiveUS10105343B2Improve stabilityOrganic active ingredientsMagnoliophyta medical ingredientsCannabisPheochromocytoma
The invention relates to a Cannabis-based pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of hypertensive disorders by submucosal delivery comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable base and an effective amount of at least one cannabinoid or endocannabinoid containing extract of a cloned hybrid of the plant Cannabis sativa, subspecies sativa and Cannabis sativa, subspecies indica of the CTSX-ISS lineage; and methods of treatment of primary and secondary hypertension, the secondary hypertension resulting from pheochromocytoma, primary hyperaldosteronism, adrenal hyperplasia, pulmonary hypertension, portal hypertension, folate deficiency hypertension, arterial hypertension or familial hypertension by administration between one and eight times per day.
Owner:KUBBY PATENT & LICENSES LLC
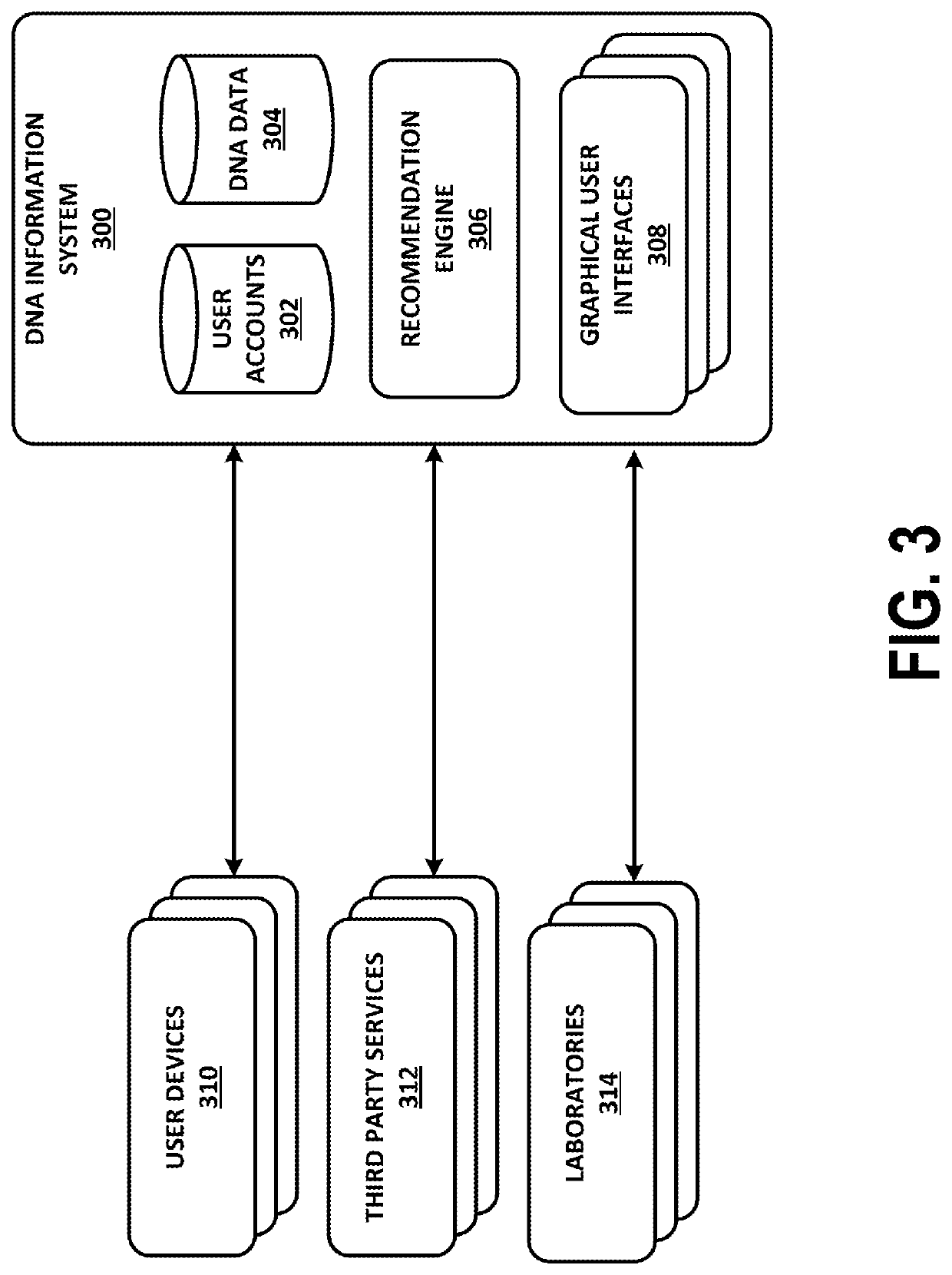
Graphical User Interfaces for Determining Personalized Endocannabinoid Genotypes and Associated Recommendations
An example embodiment may involve (i) receiving, by a server device, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) information associated with a user; (ii) parsing, by the server device, the DNA information to identify one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)—(iii) determining, by the server device and based, on the identified SNPs, an endocannabinoid genotype of the user; (iv) determining, based on the endocannabinoid genotype of the user, a recommendation of one or more cannabinoid formulations; (v) transmitting, to a client device associated with the user, a web-based representation of a first graphical user interface; and (vi) receiving, from the client device, an indication to display a detailed representation of a particular cannabinoid formulation of the one or more cannabinoid formulations.
Owner:ENDOCANNA HEALTH INC
Cannabinoid compound as well as preparation method, composition and application thereof
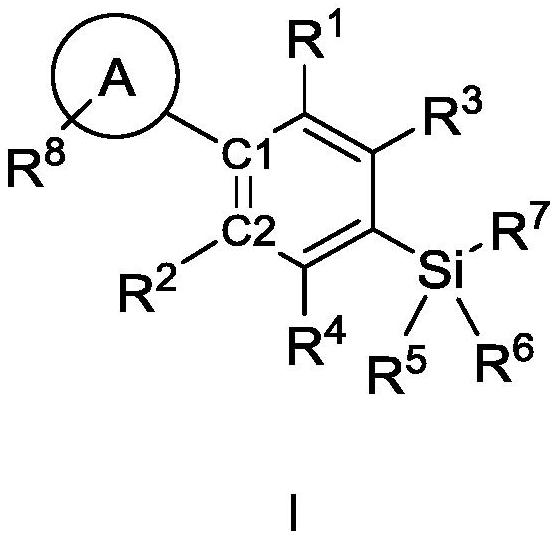
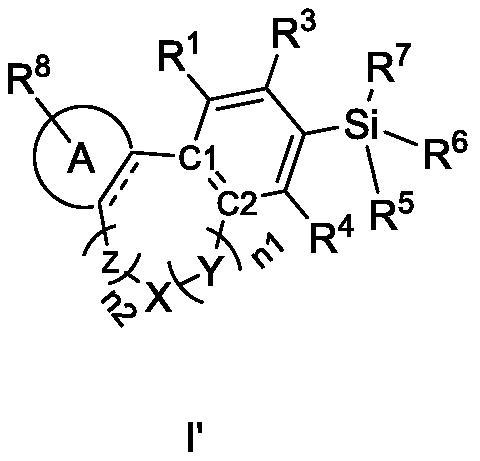
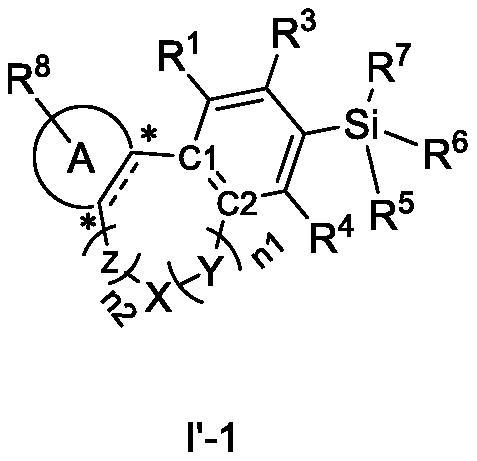
ActiveCN112047973AHigh affinitySilicon organic compoundsNervous disorderDiseasePharmaceutical medicine
The invention discloses a cannabinoid compound as well as a preparation method, a composition and application thereof. The invention discloses a compound shown as a formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compound disclosed by the invention has medium-to-strong affinity to a cannabinoid receptor 1 or a cannabinoid receptor 2, and can be used as a potential therapeutic drug fortreating diseases and symptoms related to an endogenous cannabinoid system; , including but not limited to anorexia, vomiting, pain, epilepsy, spasm, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, anxiety, depression, schizophrenia, or drug addiction.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Cannabinergic Lipid Ligands
ActiveUS20090163557A1High affinityHigh selectivityBiocideSenses disorderLipid formationReceptor subtype
One aspect of this disclosure relates generally to lipid compounds that exert diverse effects in the endocannabinoid system, such as regulating CB1 and CB2 receptor or moderating other bio-macromolecules within the endocannabinoid system. Some of the compounds showed improved receptor binding affinity, and / or improved receptor subtype selectivity, and improved bio-stability. Some of the compounds exhibit activities to regulate the enzymes that moderate the bio-disposal of endogenous cannabinoids, such as the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Some of the compounds exhibit activities to inhibit the anandamide transporter. Other aspects of the invention are pharmaceutical preparations employing these ligands and methods of administering therapeutically effective amounts of the preparations to provide a physiological effect.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
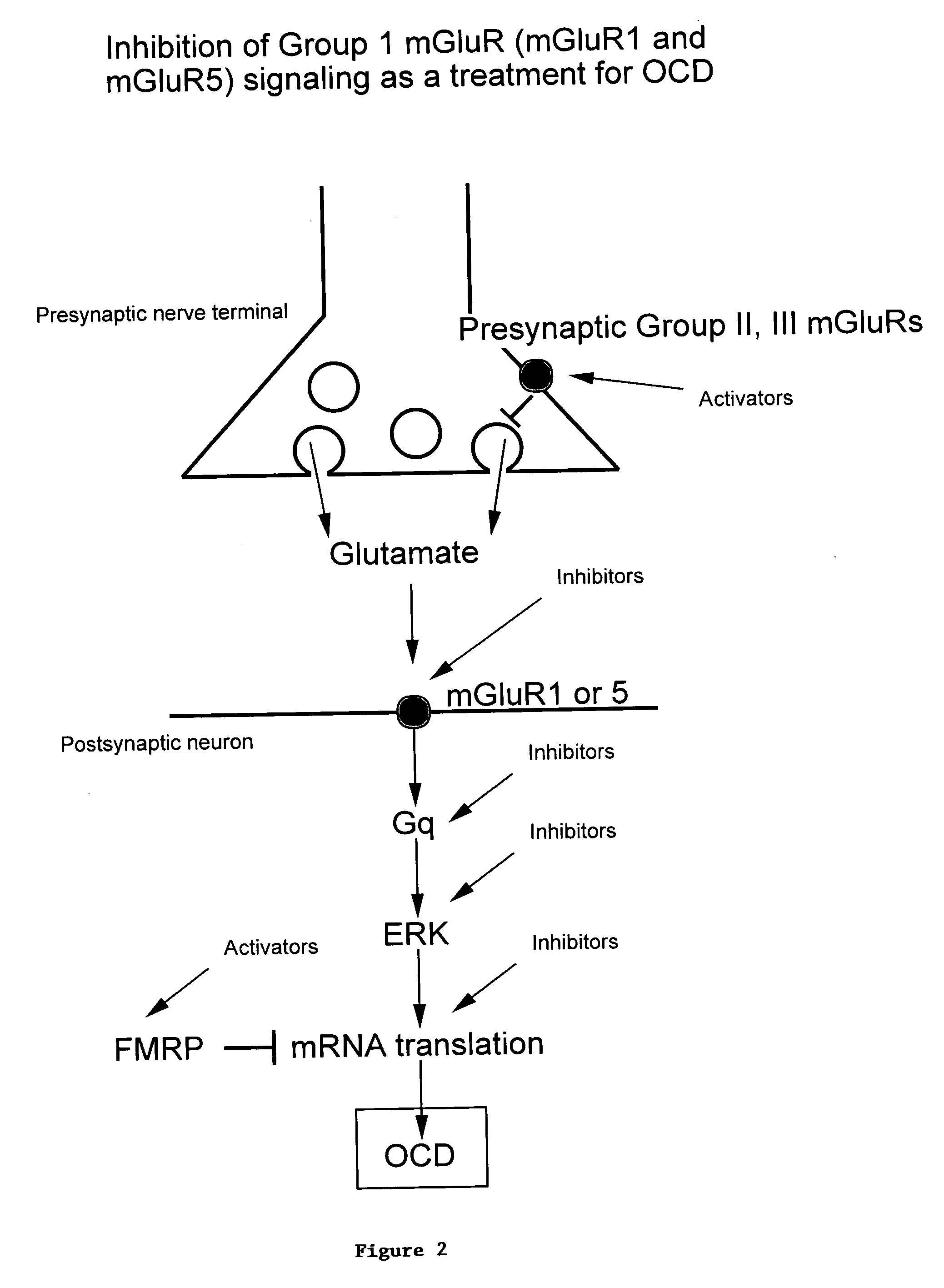
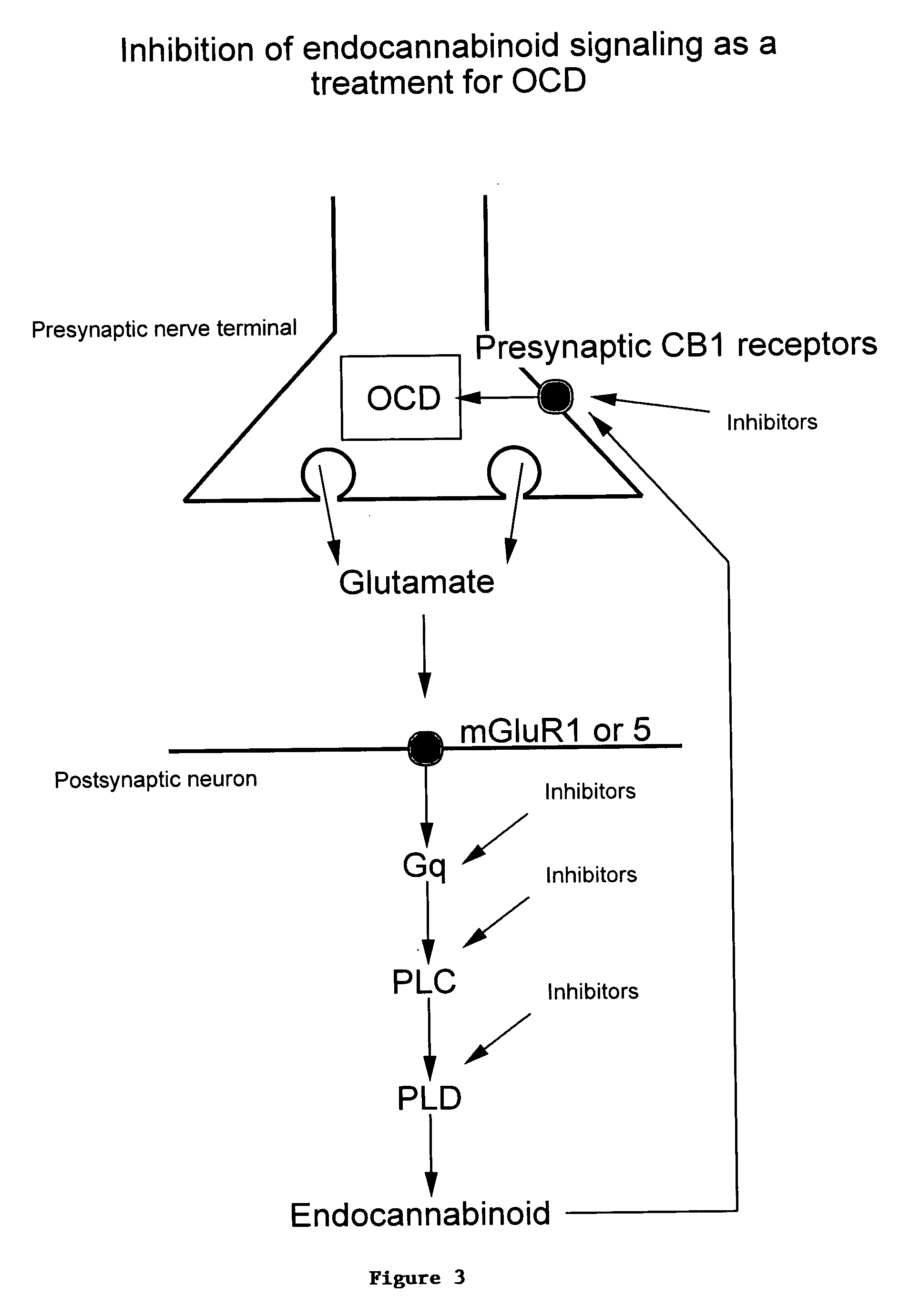
Methods of treating obsessive compulsive disorder
InactiveUS20060264381A1Easy to followEffective treatmentHormone peptidesBiocideFragile X chromosomeClinical psychology
An subjects with obsessive compulsive disorder is treated. In one embodiment, the subject is administered a compound down regulates Group I mGluR signaling. In another embodiment, the subject is administered a compound that down regulates endocannabinoid signaling. The subject that has obsessive compulsive disorder can further have at least one condition selected from the group consisting of fragile X syndrome, autism and mental retardation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
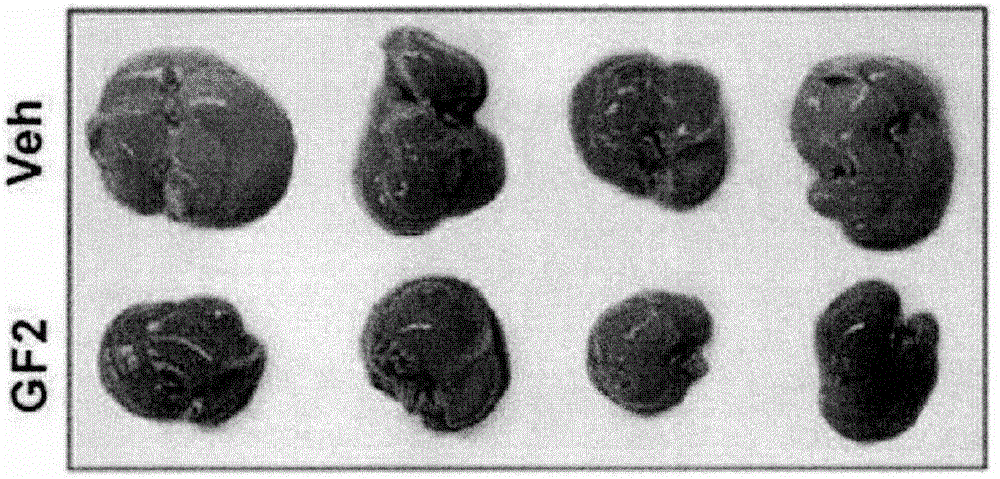
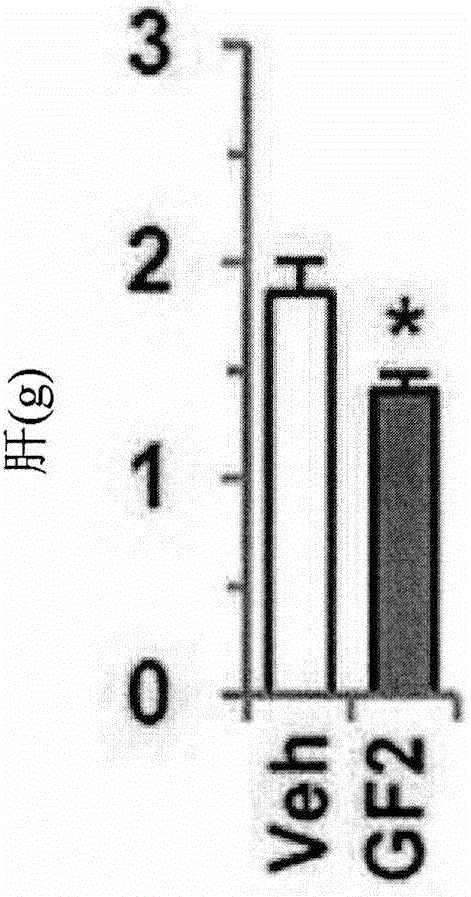
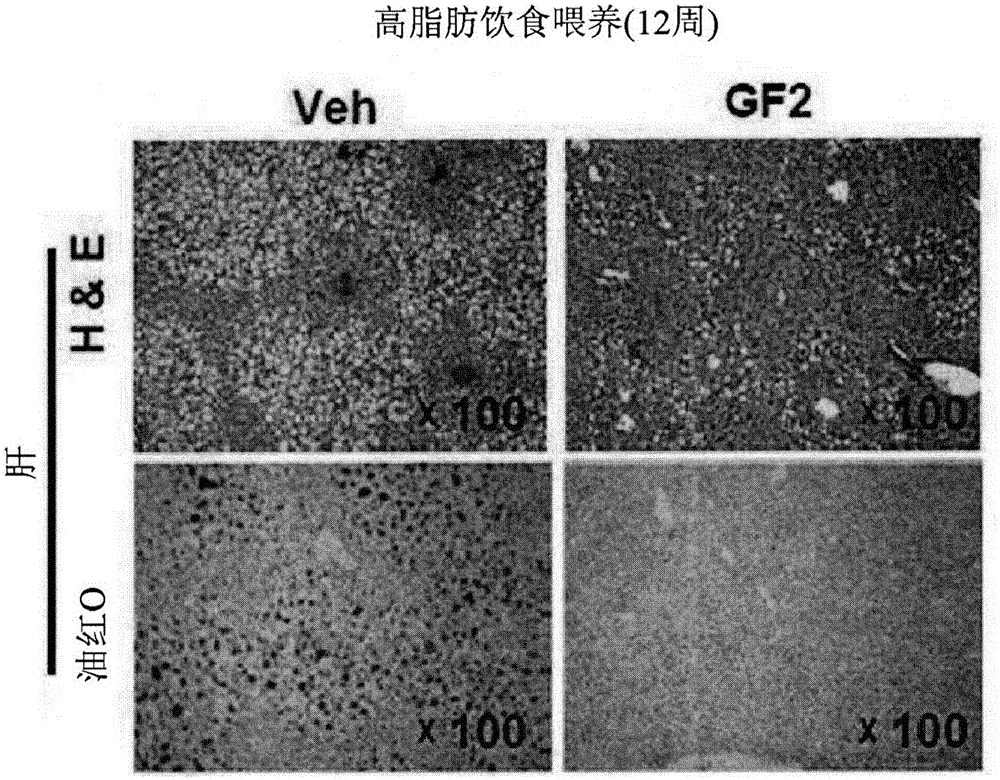
Composition for preventing or treating non-alcoholic liver disease or insulin resistance comprising ginsenoside F2
InactiveCN105935364AInhibition formationAvoid accumulationOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAdipogenesisKupffer's cell
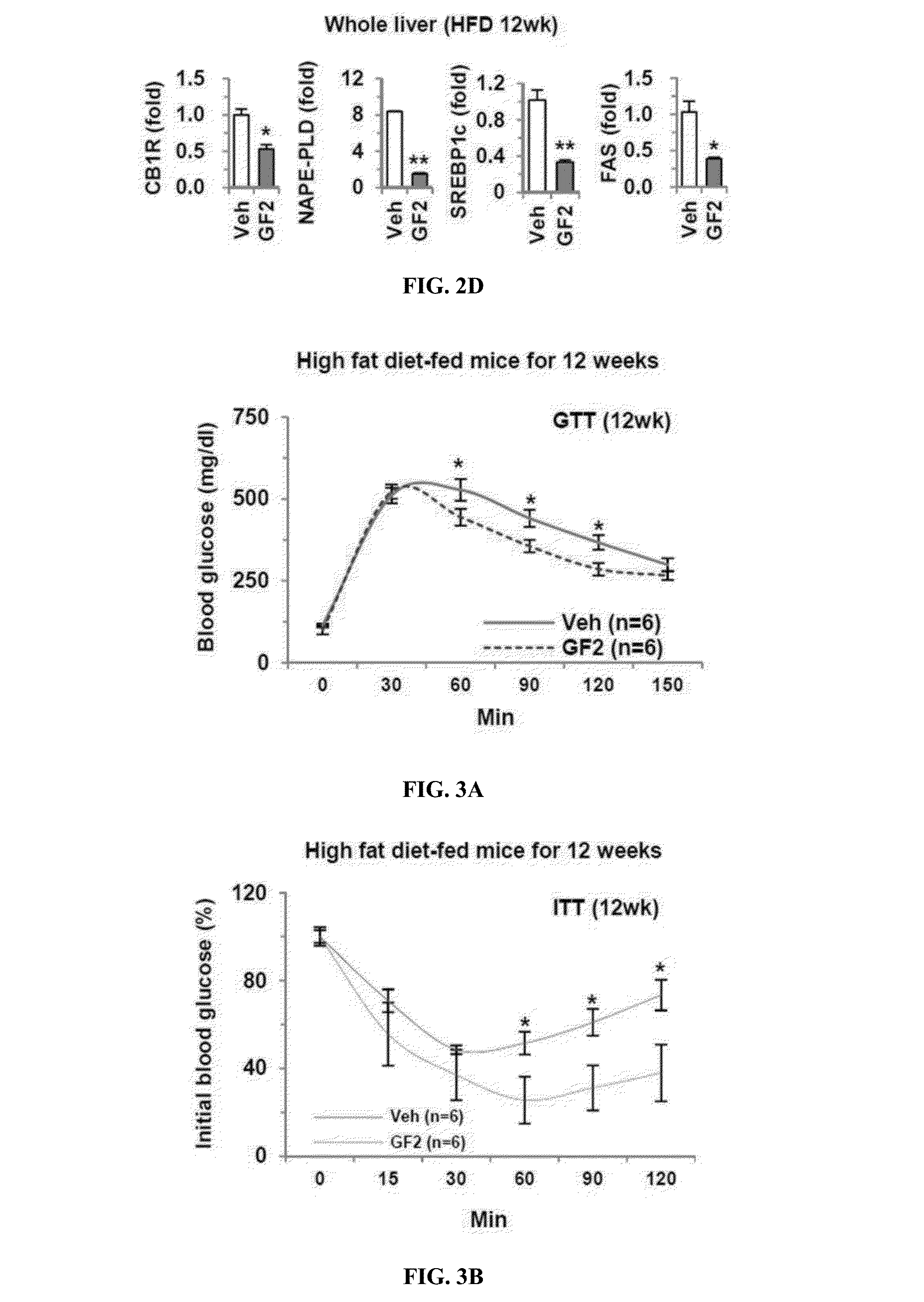
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition, a health functional food, and a feed composition for the prevention, improvement, or treatment of non-alcoholic liver disease or insulin resistance comprising ginsenoside F2. The pharmaceutical composition according to the present invention comprising ginsenoside F2 can inhibit the adipogenesis and lipid accumulation in the liver, improve insulin sensitivity, inhibit the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha, IL-beta, and IL-6 in the Kupffer cell, inhibit the expression of endocannabinoid synthase, thus capable of effectively preventing or treating non-alcoholic liver disease or insulin resistance.
Owner:INTELLIGENT SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY CENT
System and method for arresting debilitating migraine events
InactiveUS20190275270A1Work fasterAvoid delayElectrocardiographyPeptide/protein ingredientsExacerbationVisual perception
A system and method for treating acute migraine events utilizing multiple sensory / receptive channels (olfactory, audio, visual and other sensory receptors) to both treat and optimize delivery to the afflicted sites in the brain. One of the primary migraine treatment methods includes a composition delivered through the olfactory system. Absorption through the nasal membranes is rapid and avoids delays and dilution inherent in methods using the mouth and gastro-intestinal (GI) processing. Effective, but less preferred methods that avoid GI delays and dilution include delivery as eyedrops or as an intravenous infusion. The effective composition comprises a caffeinic substance to bind and antagonize adenosine receptors in the brain. This immediately blocks continued action of adenosine to dilate the afflicted vessels and inflict pain. The composition also incorporates cannabinolic substances which work simultaneously or in parallel using the body's natural endocannabinoid pathways to rebalance and control blood flow to minimize swelling and pain. Additional features may incorporate additional active components. One available feature may incorporate a recipient / patient control modulus where the patient adjusts treatment using a feedback device such as a stimulation button to increase or adjust delivery. Another additional feature comprises one or more essential oils. Although some essential oil compositions may themselves include one or more compounds that contribute to the desired cannabinolic effects, adding essential oils even those lacking an inherent cannabinolic effect can contribute to effective treatment. Fragrant inclusions in an essential oil additive may provide a calming stimulation to the olfactory system that supports reduced tension and relaxation and thereby removes a tension induced exacerbation of migraine progression.
Owner:POSTREL RICHARD
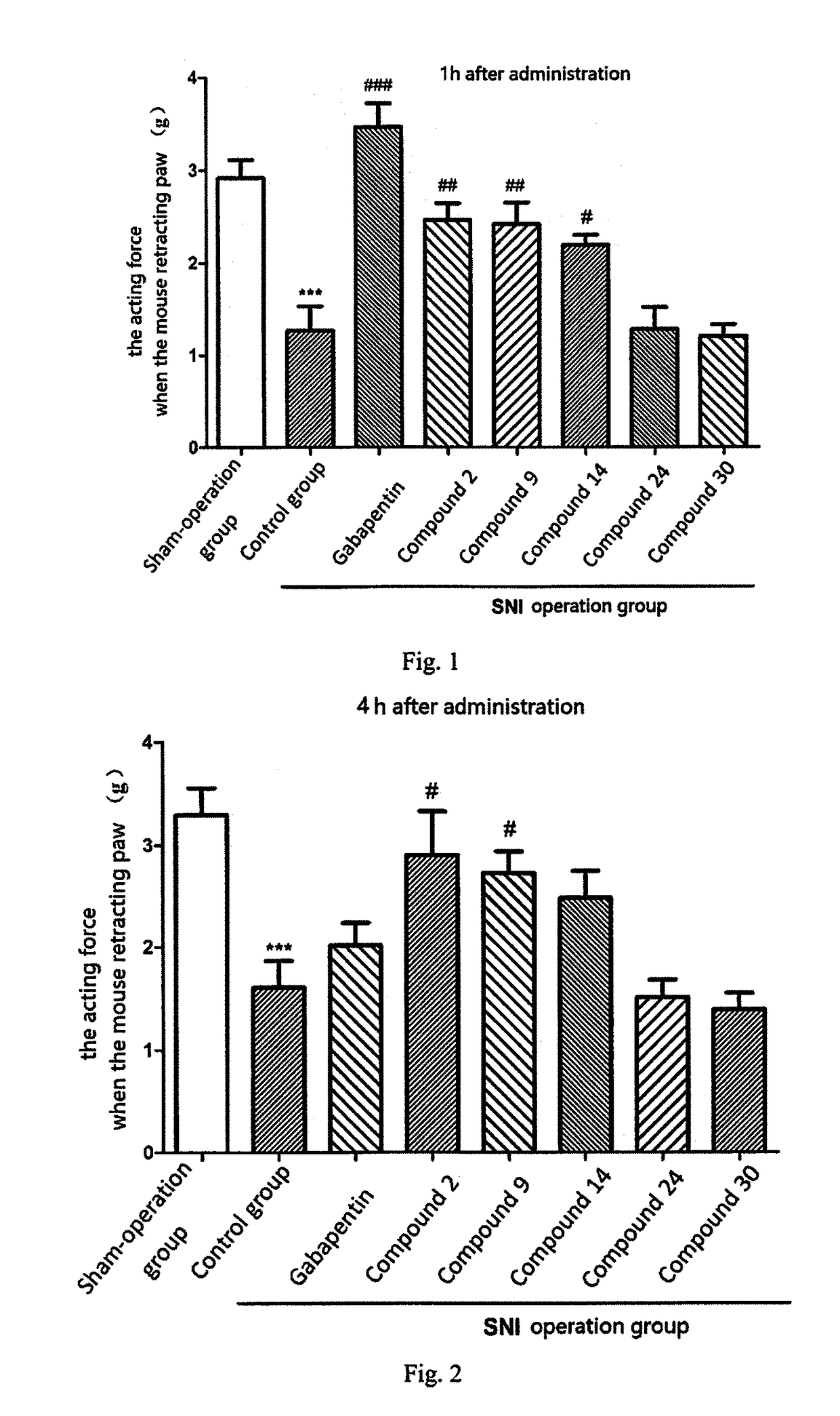
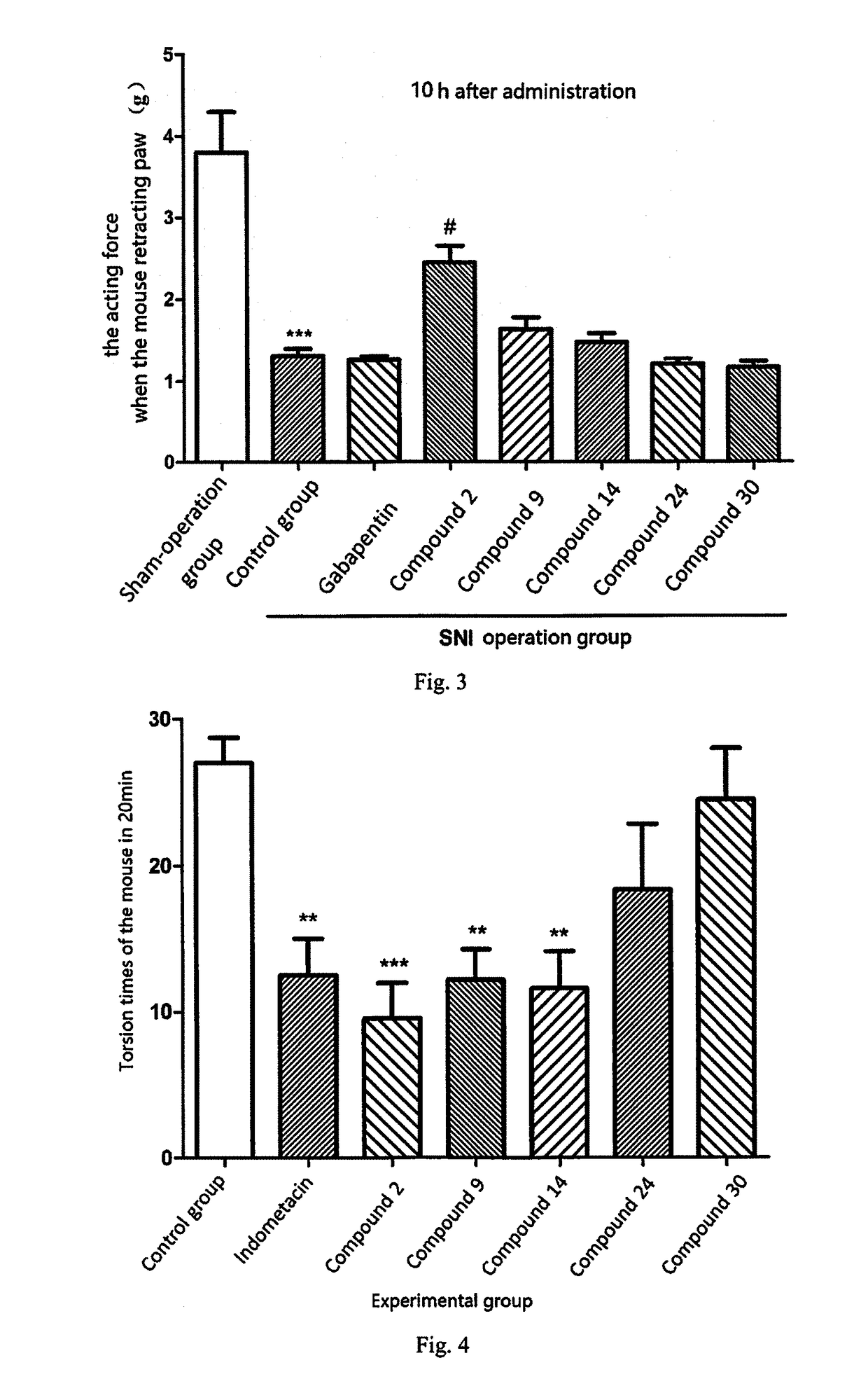
Mixed inhibitors of aminopeptidase n and of neprilysine
Mixed inhibitors of aminopeptidase N and of neprilysine are described. Pharmaceutical compositions containing at least one of these compounds, used alone or in combination with morphine and derivatives thereof, endocannabinoids and inhibitors of the metabolism thereof, GABA derivatives such as gabapentin or pregabalin, duloxetine or methadone, can be used as an analgesic, anxiolytic, antidepressant or anti-inflammatory.
Owner:智腾大中华区有限公司
Carbamyl uracil derivative and application thereof
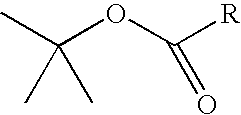
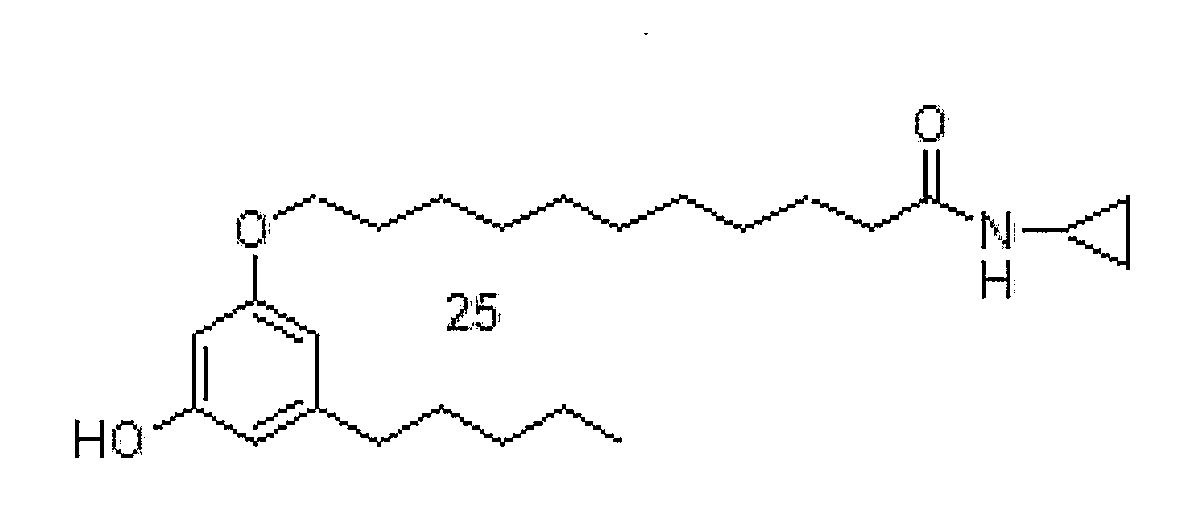
InactiveCN105503741AAvoid hydrolysisReduce foot lickingNervous disorderOrganic chemistryEndogenous cannabinoidStructural formula
The invention discloses a carbamyl uracil derivative and application thereof. The structural formula of the derivative is as shown in the description. The derivative is a novel compound with the endogenous cannabinoid hydrolase inhibiting function, and a new method is provided for inflammation and pain treatment.
Owner:XIAMEN INST OF RARE EARTH MATERIALS
Inhibitor of endocannabinoid cellular reuptake
ActiveUS10414721B1Reduce in quantityAnalgesic effect is preventedOrganic chemistryAntipyreticEndogenous cannabinoidDepressant
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN
Amantadine, memantine, and rimantadine conjugates and a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of neuronal disorders
A compound is provided that has the formula (II):where R1 in each occurrence is independently H, or C1-C4 alkyl; R2 is a nullity or CH—CH3, R3 is a nullity or C(O)—R6—NH; R6 is C2-C6 alkyl, (CH2CH2—O)n, or (CH(OH)CH2)n; n is an integer of between 1 and 4; R4 is a nullity or NH—R6—C(O); and R5 is a moiety capable of crossing the blood brain barrier and is as a free compound serotonin, dopamine, blood brain barrier (BBB) peptide, membrane translocating peptide, TAT peptides, endocannabinoids 1 & 2, bradykinin, beta-endorphin, bombesin, calcitonin, cholecystokinin, an enkephalin, dynorphin, insulin, gastrin, substance P, neurotensin, glucagon, secretin, somatostatin, motilin, vasopressin, oxytocin, prolactin, thyrotropin, an angiotensin, galanin, neuropeptide Y, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, gonadotropnin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, luteinizing hormone, vasoactive intestinal peptide transferrin, glucosyl ester, lactic acid, leucine, tryptophan, glutamic acid.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
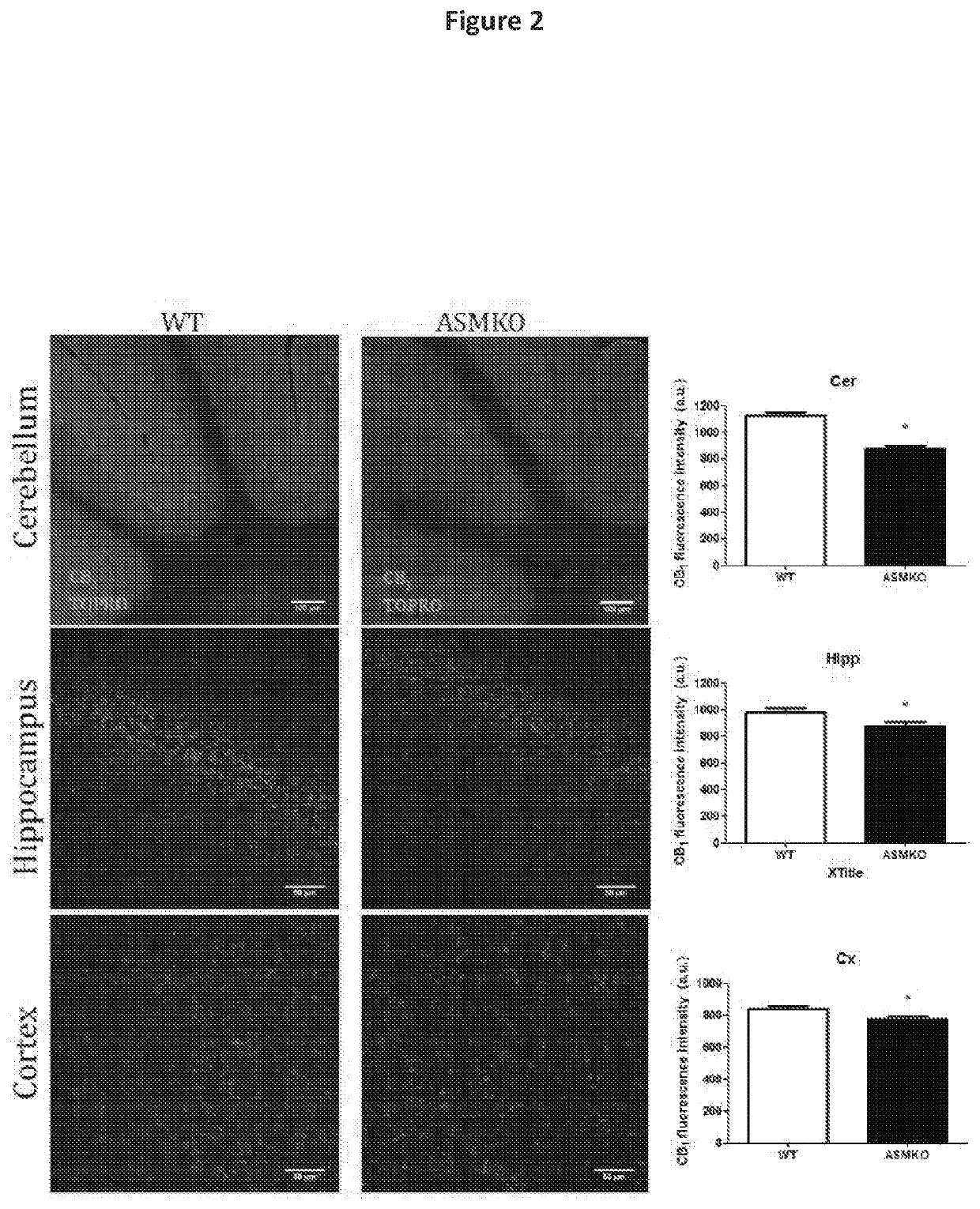
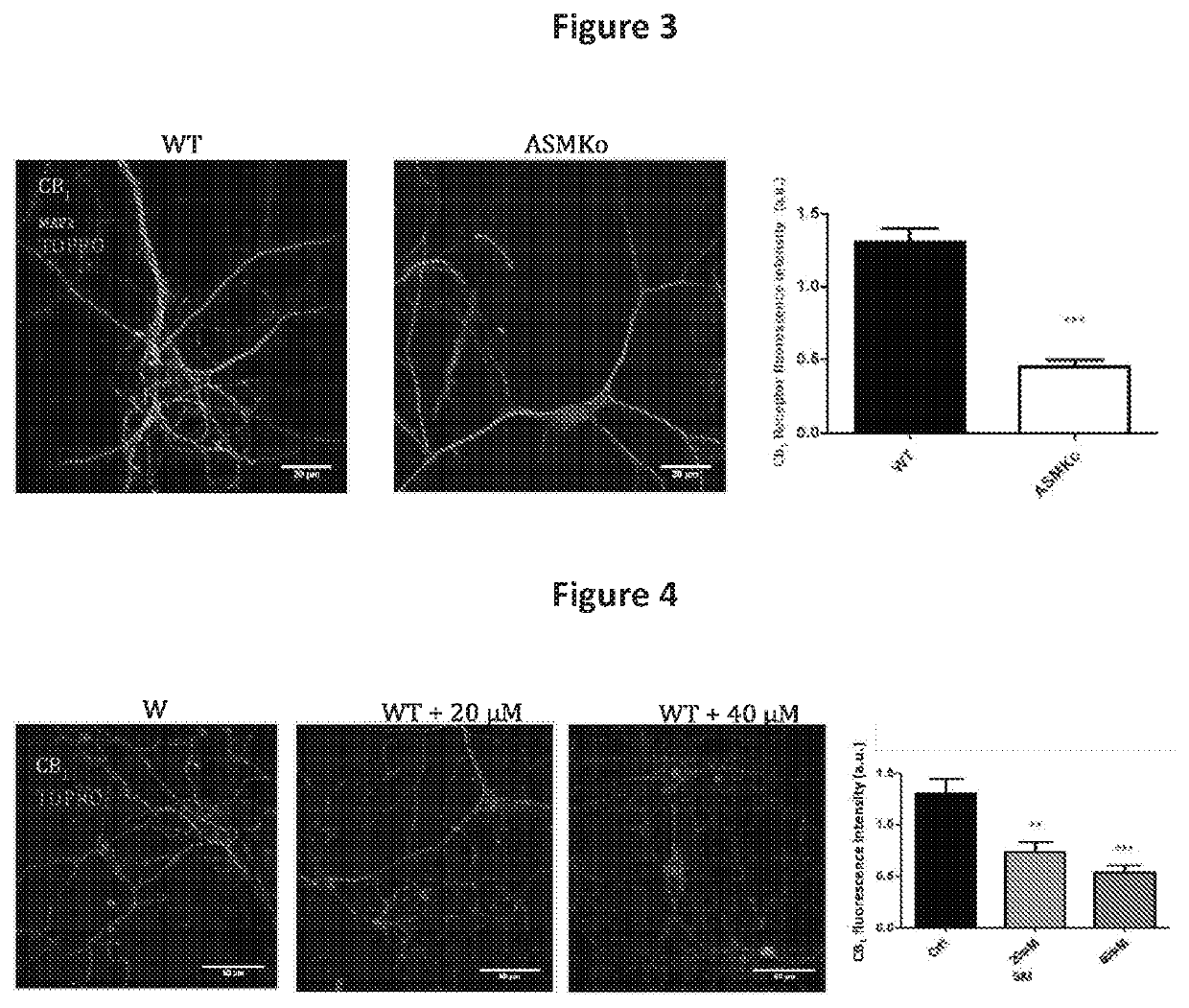
Compositions and methods for activating signaling through the cb1 cannabinoid receptor for treating and preventing diseases and disorders characterized by abnormal cellular accumulation of sphingolipids such as sphingomyelin
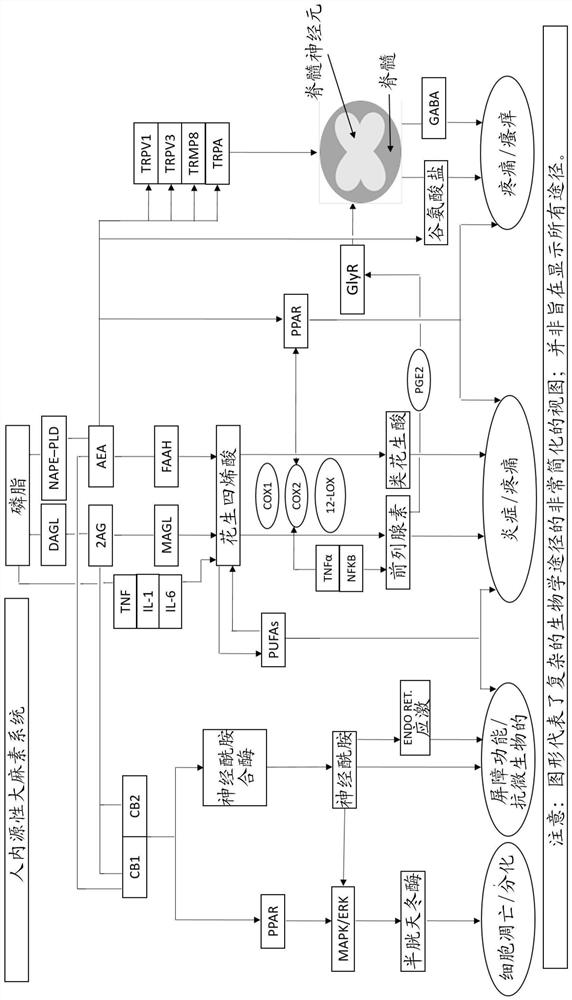
The present invention provides, inter alia, compositions and methods for using CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonists, or other compounds capable of increasing endocannabinoids or endocannabinoid signaling, for treating and preventing lysosomal storage disorders in which lipid storage occurs (including, e.g., disorders associated with sphingomyelin accumulation). In particular embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating such lysosomal storage disorders with one or more fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor alone or in combination with one or more additional agent.
Owner:WYLDER NATION FOUND
Substituted Heterocyclic Derivative, Preparation Method And Use Thereof
InactiveUS20170334896A1Inhibiting endocannabinoid hydrolase activityPain can be treatedNervous disorderOrganic chemistryEndogenous cannabinoidHydrolase
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Compositions and Methods For Delivery Of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Derivatives And Analogs
ActiveUS20180280318A1Improve bioavailabilityLong exposure timeHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntipyreticMetaboliteAntioxidant
The present invention provides a system enabling the oral delivery of therapeutics derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), their metabolites and derivatives, including, eicosanoids, prostaglandins, prostacyclins, leukotrienes, resolvins, endocannabinoids, thromboxanes, epoxyeicosa-trienoic acids (EETs), hydroxyeicostetraenoic acids (HETEs), and CMX-020. The delivery system includes a vehicle comprising a purified docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in triglyceride or ester form; a purified eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in triglyceride or ester form; a combination of DHA, EPA in either triglyceride or ester forms; or a modified DHA, EPA, or omega-3 fatty acid analog; and optionally, an antioxidant, a surfactant, a solubilizer, a stabilizer, a lubricant, or a pH / tonicity adjustment agent.
Owner:CYTOMETIX INC D B A CMXTWENTY
Embryo implantation
The present invention relates to a method for detecting an optimal time for embryo implantation in mammals, particularly humans. In particular, the invention relates to a method for determining the optimal time for implantation of an embryo in a mammalian endometrium comprising detecting the levels of an endocannabinoid in the early, mid and late stage of the menstrual cycle in a subject.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
Cannabis based compositions and methods of treating hypertension
InactiveUS20180104213A1Improve stabilityOrganic active ingredientsMagnoliophyta medical ingredientsPheochromocytomaCannabis
The invention relates to a Cannabis-based pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of hypertensive disorders by submucosal delivery comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable base and an effective amount of at least one cannabinoid or endocannabinoid containing extract of a cloned hybrid of the plant Cannabis sativa, subspecies sativa and Cannabis sativa, subspecies indica of the CTSX-ISS lineage; and methods of treatment of primary and secondary hypertension, the secondary hypertension resulting from pheochromocytoma, primary hyperaldosteronism, adrenal hyperplasia, pulmonary hypertension, portal hypertension, folate deficiency hypertension, arterial hypertension or familial hypertension by administration between one and eight times per day.
Owner:KUBBY PATENT & LICENSES LLC
Esters for treatment of ocular inflammatory conditions
InactiveCN103796635AHydrolytically stableSenses disorderElcosanoid active ingredientsMetaboliteLipoxin
The present invention relates to ophthalmic compositions and methods for the treatment of dry eye and other inflammatory ocular conditions. In particular, the present invention relates to a composition comprising an esterified anti-inflammatory lipid mediator, which is an ester of an anti-inflammatory lipid mediator that is a reaction product of the anti-inflammatory lipid mediator and a polyol wherein the majority of the anti-inflammatory lipid mediator is present in an ester form. In this way, the compositions are substantially free of an acid form of the anti-inflammatory lipid mediators. Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators can be selected from the group consisting of polyunsaturated fatty acids (e.g., omega-three and omega-six fatty acids), resolvins or a metabolically stable analog, protectins or a metabolically stable analog, lipoxins or a metabolically stable analog, prostaglandins or a metabolically stable analog, retinoic acids, endocannabinoids, metabolites thereof, and mixtures thereof. This composition can be topically delivered to the ocular surface via a preparation, solution, gel, ointment, and / or strip and / or a contact lens.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Compositions containing endocannabinoid mimetics and anti-inflammatory compounds, methods of preparation and uses thereof
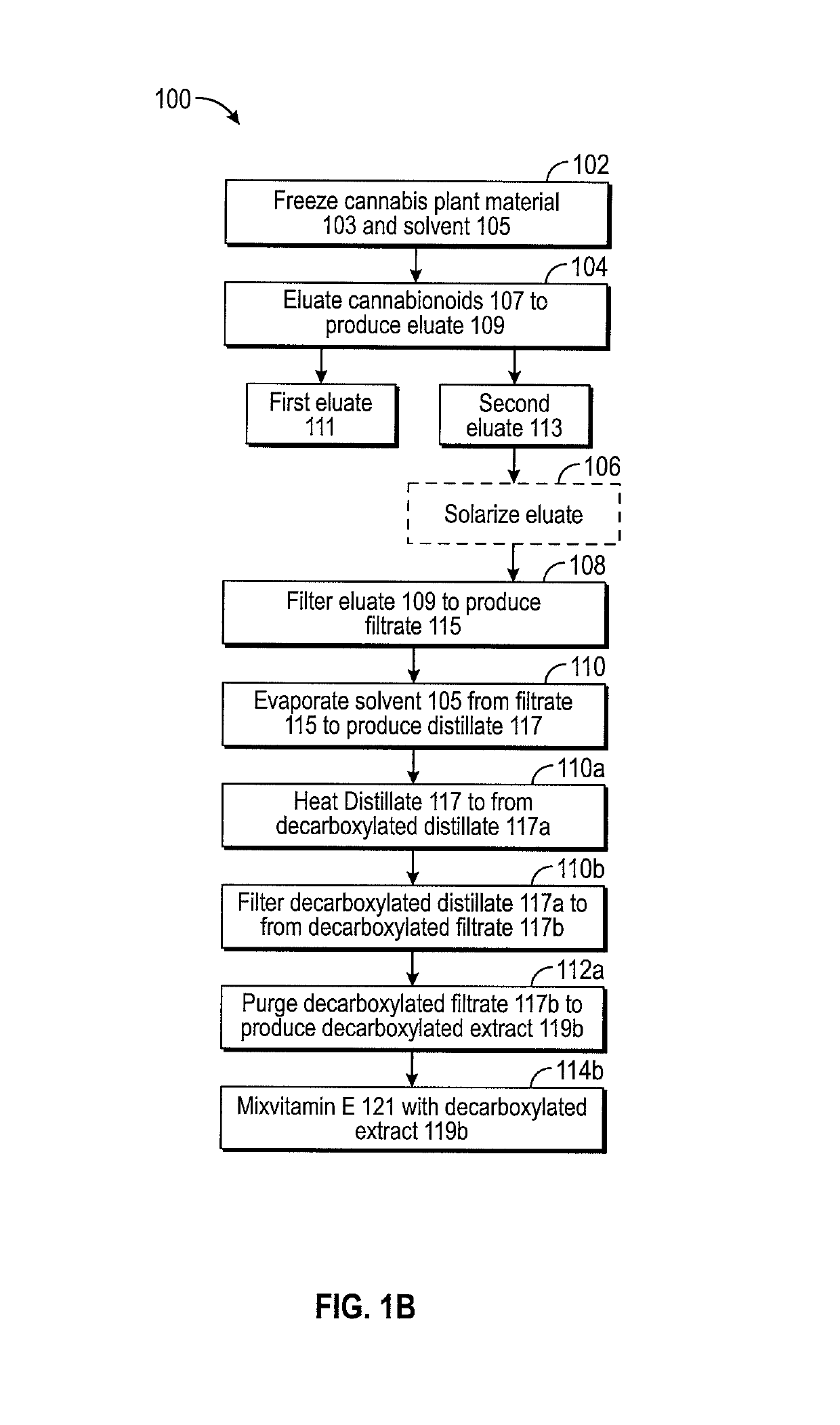
PendingCN114786725ACosmetic preparationsHydroxy compound active ingredientsEndogenous cannabinoidEndogeny
Owner:PHARMA COSMETIX RES LLC
Amantadine, memantine, and rimantadine conjugates and a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of neuronal disorders
A compound is provided that has the formula (II):where R1 in each occurrence is independently H, or C1-C4 alkyl; R2 is a nullity or CH—CH3, R3 is a nullity or C(O)—R6—NH; R6 is C2-C6 alkyl, (CH2CH2—O)n, or (CH(OH)CH2)n; n is an integer of between 1 and 4; R4 is a nullity or NH—R6—C(O); and R5 is a moiety capable of crossing the blood brain barrier and is as a free compound serotonin, dopamine, blood brain barrier (BBB) peptide, membrane translocating peptide, TAT peptides, endocannabinoids 1 & 2, bradykinin, beta-endorphin, bombesin, calcitonin, cholecystokinin, an enkephalin, dynorphin, insulin, gastrin, substance P, neurotensin, glucagon, secretin, somatostatin, motilin, vasopressin, oxytocin, prolactin, thyrotropin, an angiotensin, galanin, neuropeptide Y, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, gonadotropnin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, luteinizing hormone, vasoactive intestinal peptide transferrin, glucosyl ester, lactic acid, leucine, tryptophan, glutamic acid.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
Novel medicinal application of CB2 receptor stimulant
ActiveCN105687194AIncreased sensitivityReduce contentMetabolism disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsDiseaseEnergy balancing
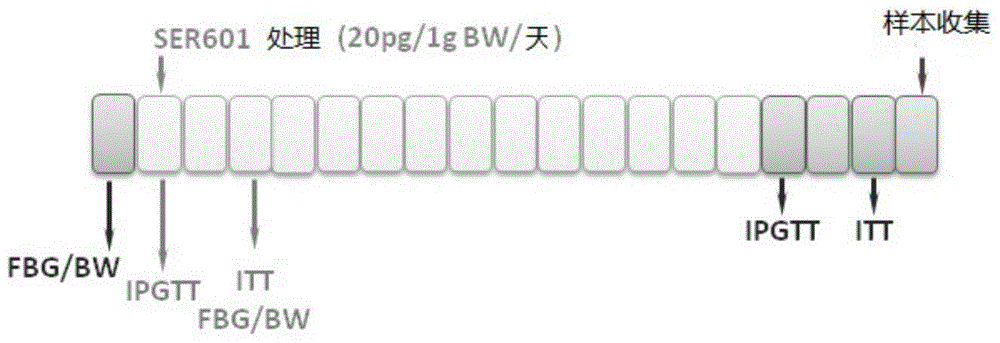
The invention relates to the technical field of novel medicinal application, and particularly relates to novel medicinal application of a CB2 receptor stimulant. An endocannabinoid signal system can be used for maintaining the energy balance and glucose homeostasis in a body; when fat and skeletal muscle cells are subjected to glucose deprivation, the messenger-ribonucleic acid (RNA) expression profile of the signal system changes, and ECS has the effects of mediating insulin resistance and regulating diabetes mellitus, obesity and other metabolic diseases. Animal tests of SER 601 in the CB2 receptor stimulant prove that the CB2 receptor stimulant has a remarkable effect for improving pancreas islet function, improving insulin sensitivity and improving accumulation of whole body fat, especially abdominal fat. The CB2 receptor stimulant can be used for reducing the content of fat in a body while improving the insulin sensitivity, preventing / treating diabetes mellitus patients, especially patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and preventing / treating obesity, lipodystrophy, weight and fat reduction and other diseases.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Treatment of brain disorders of the striatum
InactiveUS20080176963A1Reduces associated motor deficitReduces the associated motor deficitsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHydrolase inhibitor
Regulation of striatal indirect pathway endocannabinoid-mediated long-term depression (eCB-LTD) is used to improve motor deficits of striatal-based brain disorders. In such treatment, a dopamine D2 receptor agonist is administered in conjunction with an inhibitor of endocannabinoid degradation. In some embodiments, the inhibitor of endocannabinoid degradation is a fatty acid amine hydrolase inhibitor, or a monoacylglycerol lipase antagonist. The combination provides for a synergistic effect, with improved therapeutic effects. Also provided are kits and systems for practicing the subject methods, as well as methods of use of agents identified in the screening method of the invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Potent and selective ligands of cannabinoid receptors
The present invention relates to high affinity compounds, able to bind CB1 and CB2 endocannabinoid receptors. The compounds of the invention find particular application as agents for pain therapy and / or anti-inflammatory and / or anti-stress and / or anti-oxidising and / or hypotensive and / or immune suppressive therapy and / or anti-spastic activity in multiple sclerosis and / or anti-cancer.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA
Composition for preventing or treating non-alcoholic liver disease or insulin resistance comprising ginsenoside f2
InactiveUS20160256477A1Inhibit lipid accumulationEffective prevention and treatmentOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAdipogenesisEndogenous cannabinoid
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition, a health functional food, and a feed composition for the prevention, improvement, or treatment of non-alcoholic liver disease or insulin resistance comprising ginsenoside F2. The pharmaceutical composition according to the present invention comprising ginsenoside F2 can inhibit the adipogenesis and lipid accumulation in the liver, improve insulin sensitivity, inhibit the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-β, and IL-6 in the Kupffer cell, inhibit the expression of endocannabinoid synthase, thus capable of effectively preventing or treating non-alcoholic liver disease or insulin resistance.
Owner:INTELLIGENT SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY CENT
Method for predicting autism spectrum disorders by cannabinoid and cannabinoid receptor expression
InactiveUS20150374857A1Biological material analysisRadioactive preparation carriersClinical psychologyCannabinoid
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com