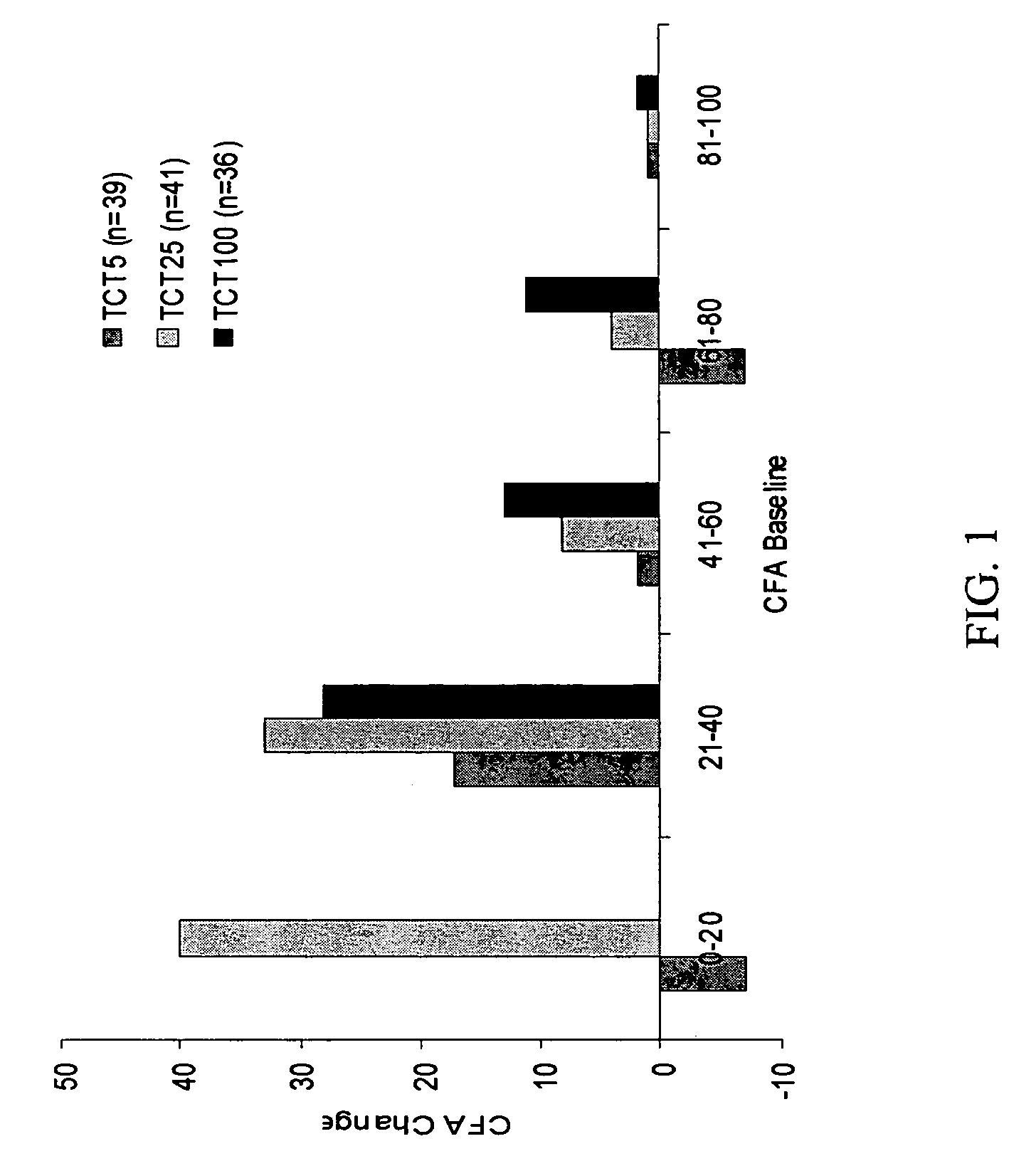
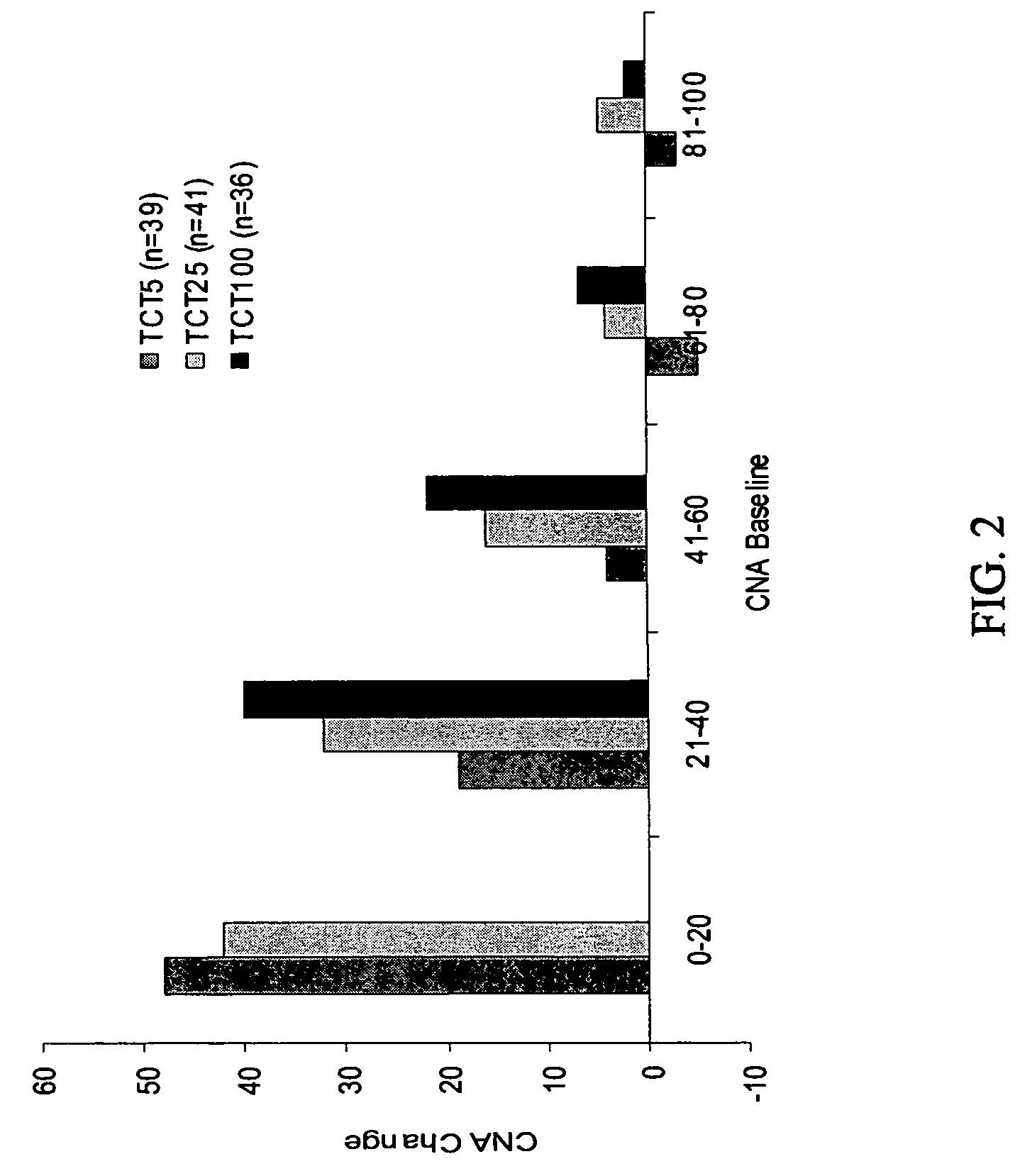
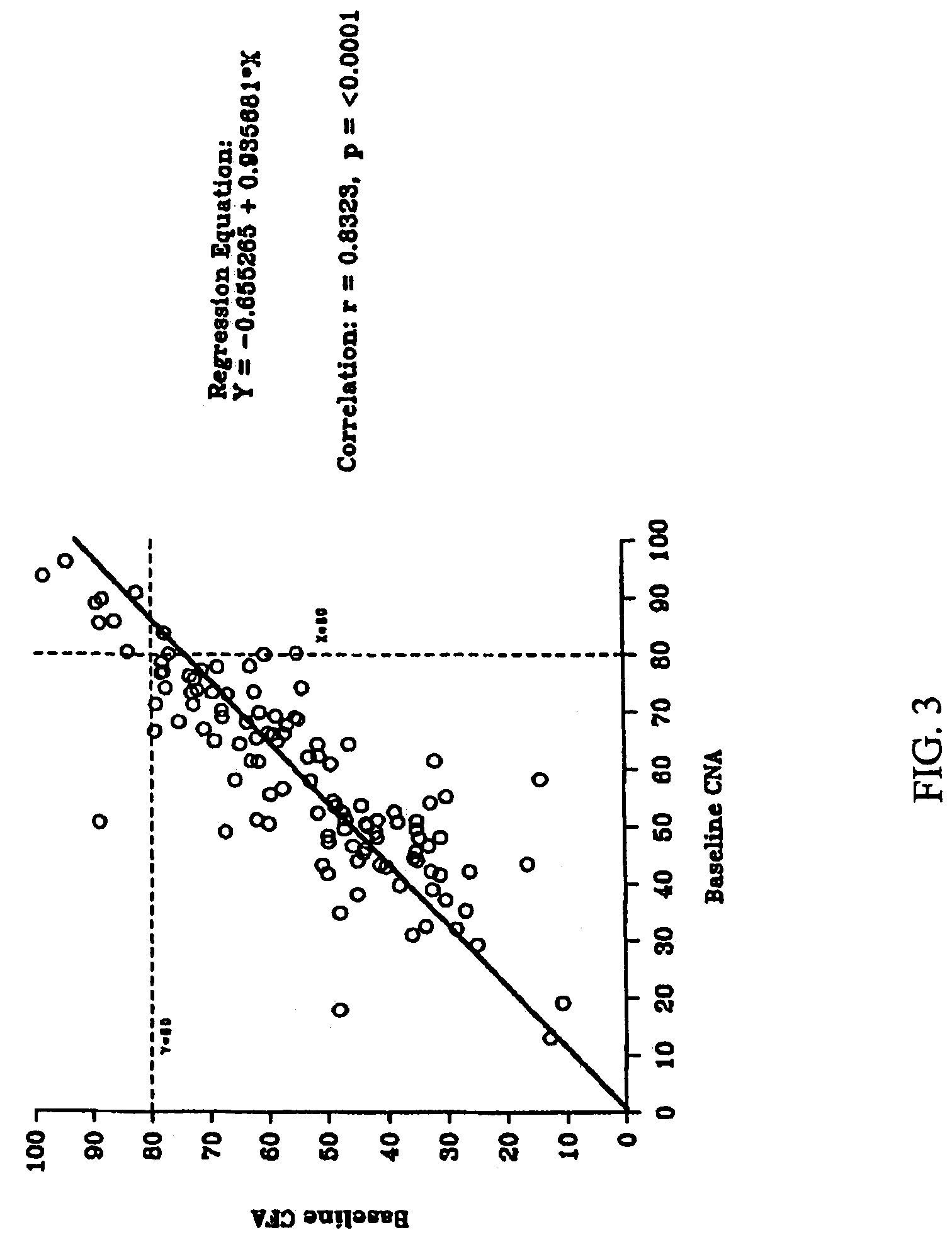
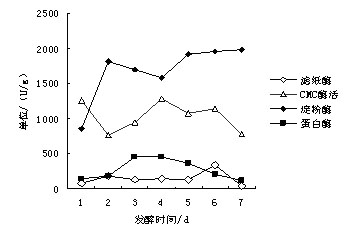
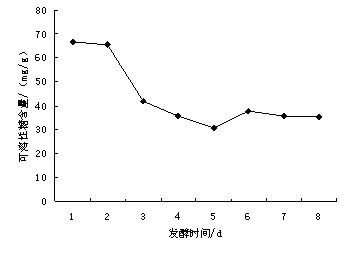
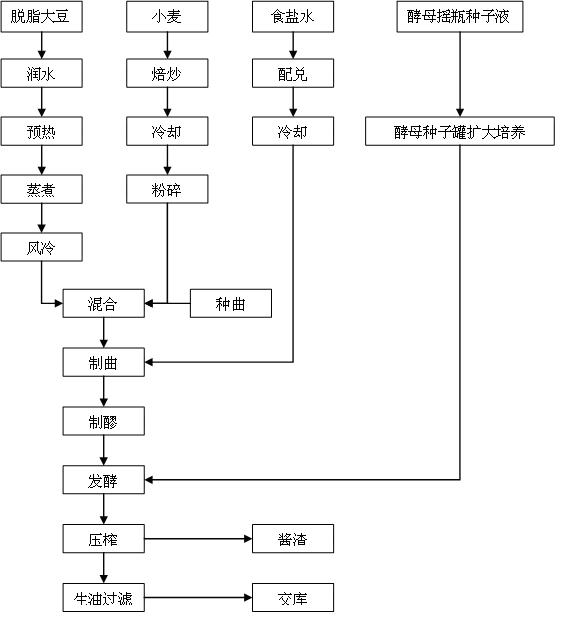
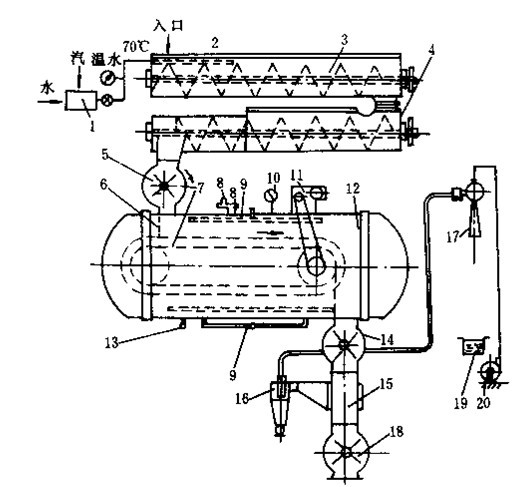
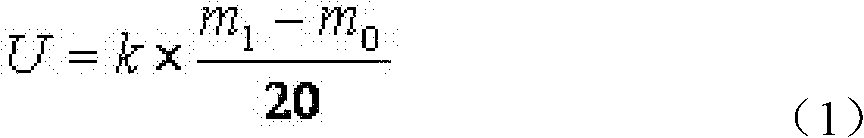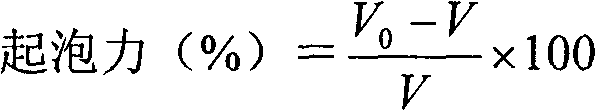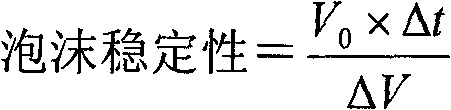Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2002 results about "Aspergillus oryzae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aspergillus oryzae, also known as kōji (Japanese: ニホンコウジカビ Hepburn: nihon kōji kabi), is a filamentous fungus (a mold) used in Japan to ferment soybeans for making soy sauce and fermented bean paste (including miso), and also to saccharify rice, other grains, and potatoes in the making of alcoholic beverages such as sake and shōchū. The domestication of Aspergillus, a supercategory of A. oryzae occurred at least 2000 years ago. A. oryzae is also used for the production of rice vinegars. Barley koji (麦麹) or rice koji (米麹) are made by fermenting the grains with aspergillus oeryzae mold.
A set of living body microorganism preparations for preparing composite microorganism fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101294141AImprove fertilityPromote growthBacteriaOrganic fertilisersDiseaseBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to a group of alive microbial preparations for preparing compound microbial fertilizer and the preparation method thereof. The alive microbial preparations include a microbial inoculant and an organic material degradation agent. The microbial inoculant includes Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus mucilaginosus, Bacillus laterosporus, Azotobocter chroococcum, etc. The organic material degradation agent includes Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus circulans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida lipolytica, Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus cereus, Streptomyces griseus, Pseudomonas alcaligenes, Pseudomonas cepacia, Streptococcus salivarius subsp. Thermophilus, Geobacillus stearothermophilus, Streptomyces Thermophilus, Geotrichum candidum and Aspergillus oryzae. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out submerged fermentation, directly mixing the bacterial liquids and stirring to obtain a liquid preparation; or mixing with an absorbent to obtain a solid preparation. The alive microbial preparations have the advantages of improving soil fertility, promoting plant growth, enhancing anti-disease, anti-insect and anti-drought capacities of plants, improving quality of agricultural products and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIJI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Process for preparing viable bacteria enzyme
InactiveCN102634490APowerfulReduce breedingMicroorganism based processesEnzymesHealth benefitsGanoderma lucidum
The invention discloses a process for preparing viable bacteria enzyme. The process comprises the following steps of: respectively adding aspergillus oryzae, ganoderma lucidum, bacillus subtilis, lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycetes into vegetables and fruits to ferment so as to obtain a vegetable ferment basic solution and a fruit ferment basic solution; vaccinating the bacillus subtilis, yeast and the lactic acid bacteria by using edible fungus to ferment so as to obtain an edible fungus ferment basic solution; vaccinating the ganoderma lucidum, the bacillus subtilis, the saccharomycetes and the lactic acid bacteria by using perennial herbs to ferment so as to obtain a herbal enzyme solution; inoculating the bacillus subtilis, the yeast and the lactic acid bacteria to ferment so as to obtain an algae ferment basic solution; and inoculating bifidobacterium, bacillus natto and bacillus aceticus to carry out secondary fermentation after combining filtrates, and then sealing for ageing for 2 months, so as to obtain the aged viable bacteria enzyme. According to the process provided by the invention, mixed fungi generation can be effectively reduced; macro-molecular substances are rapidly resolved to micro-molecular substances which can be easily absorbed by a human body; and the problem that the substances are difficult to digest and inactivate in severe environments of intestinal canals can be solved. Furthermore, the content of functional active components can be greatly improved, and various health benefits and high added value of the enzymes can be effectively improved.
Owner:桂林寻源文化有限责任公司
Process for the pre-treatment of vegetable oils for physical refining
ActiveUS20040005399A1Speed up the processFatty acids production/refiningTea extractionMicroorganismActivated carbon
The present invention relates to a simple and economically attractive process for the pretreatment of vegetable oils which involves (a) enzymatic degumming with commercially available phospholipase A1 from the sources like Aspergillus oryzae microorganism, (b) bleaching of the enzymatically degummed oil using bleaching earth and activated carbon, and (c) dewaxing (in case of rice bran oil) of degummed and bleached oil at lower temperature to obtain oil with less than 5 ppm of residual phosphorus which is amenable for physical refining.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Compositions and methods for treating pancreatic insufficiency
InactiveUS7718169B2Stable enzyme componentEffective low dose treatment regimensPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemProteinase activityExocrine pancreatic insufficiency
The present invention relates to compositions for the treatment of conditions, including pancreatic insufficiency. The compositions of the present invention comprise lipase, protease and amylase in a particular ratio that provides beneficial results in patients, such as those afflicted with pancreatic insufficiency. This invention also relates to methods using such compositions for the treatment of pancreatic insufficiency. The compositions specifically comprise crosslinked Burkholderia cepacia lipase crystals, Aspergillus melleus protease crystals and amorphous Aspergillus oryzae amylase in a ratio of about 1:1:0.15 USP units.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Matrimony vine composite health care enzyme and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104824548APromote value-addedEnsure balanceFood ingredient functionsNon-sugar sweetener food ingredientsBiotechnologyLactobacillus
The invention discloses a matrimony vine composite health care enzyme and a preparation method thereof. The matrimony vine composite health care enzyme comprises the raw materials of 1-16 parts of matrimony vine, 0-12 parts of red date, 0-1 part of licorice, 0-4 parts of black rice, 0-2 parts of white hyacinth bean, 0-5 parts of oat, 0-5 parts of tartary buckwheat, 0-3 parts of cassia seed, 0-1 part of chrysanthemum, a lot of honey, a lot of granulated sugar, a lot of high fructose corn syrup and a lot of oligosaccharide. The method comprises the following steps: beating matrimony vine and red date, extracting chrysanthemum and licorice, immersing the cereal and steaming, inoculating Aspergillus oryzae and Kluyveromyces Marxianus yeast and fermenting, and performing pulp refining, sterilizing a mixed liquor, and inoculating lactics for enclosed insulation and fermentation to obtain the matrimony vine composite health care enzyme. The matrimony vine composite health care enzyme stock solution can be prepared to a matrimony vine composite health care enzyme concentrated slurry, an enzyme paste and enzyme powder, and the enzyme powder can be prepared to a matrimony vine composite health care enzyme effervescent tablet, a particle electuary, a chewing tablet, a lozenge and a capsule.
Owner:周学义
Two-effects microbiological additives of forage specially used for ruminants
InactiveCN1559261AImproves rumen fermentationImprove payAnimal feeding stuffFood preparationBranFeed additive
A dual-effect microbial feed additive for ruminant is prepared through pulverizing corn, steaming, liquefying, saccharified, inoculating lactobacillus acidophilus and saccharomyce cerevisiae, fermenting to obtain living bacterium preparation, culturing bacillus subtilis, aspergillus oryzae and aspergillus niger in the culture medium prepared from corn, bran and soybean dregs, fermenting to obtain composite enzyme preparation, and proportionally mixing said living bacterium preparation with said composite enzyme preparation. It can promote the growth and health of ruminant and increase the utilization rate of feed.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA SILONG BIOTECH
Method for preparing health-benefiting fermented soybean meal
ActiveCN103283961AIncrease nutritionHas antibacterial effectAnimal feeding stuffAntibiotic YHealth benefits
The invention relates to a method for preparing health-benefiting fermented soybean meal enriched in small peptides, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), reducing sugar, lactobacillus plantarum and antimicrobial peptide. By utilizing strains of aspergillus oryzae, saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacillus subtilis and lactobacillus plantarum, the small peptides, free amino acids, reducing sugar, GABA and high viable count content in the lactobacillus plantarum in the health-benefiting fermented soybean meal are obtained through the two-stage solid state fermentation method, the small peptides account for 8.01-18 percent, the free amino acids has the content of 80-300mg / g, the reducing sugar reaches 20-80mg / g, the GABA reaches 0.317-0.5mg / g, the viable count content in the lactobacillus plantarum is 2-6.5*1010cfu / g, the antibacterial titer of antimicrobial peptides is 2.0*103-7.0*104 IU / g, and the yield of the health-benefiting fermented soybean meal is 82.03-90 percent. According to the process, the nutrient effect of the soybean meal can be improved, the prepared fermented soybean meal has the antibacterial effect, partial antibiotics can be replaced, the fermented soybean meal is conveniently preserved and saved, the process is simple and feasible, and the fermented soybean meal is green and environment-friendly and has application significance and wide prospect in the feed industry and breeding industry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Decomposition maturing agent for degrading straw
The invention relates to a decomposition maturing agent for degrading straw. The agent comprises active ingredients, such as candida tropicalis, aspergillus oryzae, trichoderma viride and bacillus subtilis. The decomposition maturing agent can rapidly decompose wheat straw, rice straw, grain straw, sweet potato stems, broad bean stems, rape stalks, weeds, leaves and household garbage of which the fibrous matter content is high so as to prepare an organic fertilizer. The decomposition maturing agent has the advantages of short degradation time and capability of effectively killing diseases and pests and providing nutrients for crops.
Owner:HUBEI JINDI AGRI SCI & TECH +1
Microbial fermentation antibiotic-free feed and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101828634AImprove immunityGood for healthFungiBacteriaLactobacillus acidophilusAspergillus niger
The invention discloses a microbial fermentation antibiotic-free feed, which comprises a batch and a composite fermentation material. The batch consists of the following raw materials in part by weight: 30 to 50 parts of corn, 20 to 40 parts of bean pulp, 5 to 20 parts of cotton seed meal, 2 to 5 parts of calcium hydrophosphate, 0.2 to 0.4 part of salt, 0.1 to 0.2 part of composite trace element, and 0.2 to 0.4 part of composite vitamin; and the composite fermentation material consists of the following fermentation materials in part by weight: 30 to 70 parts of lactobacillus acidophilus fermentation material, 10 to 20 parts of bacillus subtilis fermentation material, 20 to 35 parts of saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation material, 1 to 3 parts of trichoderma longbrachiatum fermentation material, 1 to 3 parts of aspergillus niger fermentation material, and 1 to 3 parts of aspergillus oryzae fermentation material, wherein the weight ratio of the batch to the composite fermentation material is 96-92:4-8.
Owner:湖南创新生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing acid organic fertilizer by orientation fermentation of organic waste
ActiveCN101935236ASimple and fast operationGuaranteed qualityBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationContinuous croppingBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides a method for preparing an acid organic fertilizer by orientation fermentation of an organic waste. The method is characterized by comprising the following specific steps of: mixing bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus pumilus, saccharomyces cerevisiae, acetobacter aceti, trichoderma, aspergillus oryzae, nocardia and geotrichum candidum to obtain a first composite microbial bacteria agent; mixing the bacillus subtilis, the bacillus licheniformis, the saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacillus coagulans, lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus plantarum, lactobacillus casei, pediococcus pentosaceus, the aspergillus oryzae, mucor racemosus and the nocardia to obtain a second composite microbial bacteria agent; adding the first composite microbial bacteria agentinto the organic waste and performing aerobic fermentation so as to form an intermediate fermentation product; and adding the second composite microbial bacteria agent into the intermediate fermentation product and performing anaerobic fermentation so as to form the organic fertilizer. The method has the advantages of capability of improving saline and alkaline lands, suitability for cultivation of acidophilous crops, effect of performing micro-ecological remediation on continuous cropping soil and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO ECOLOGICAL ENG
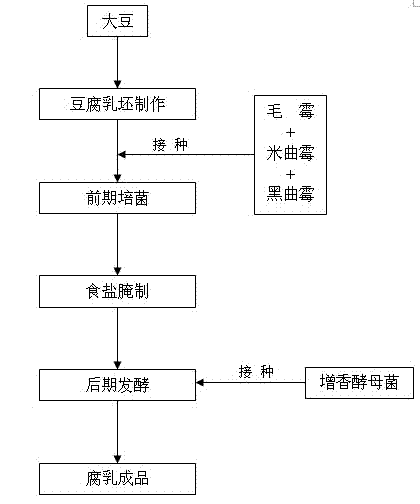
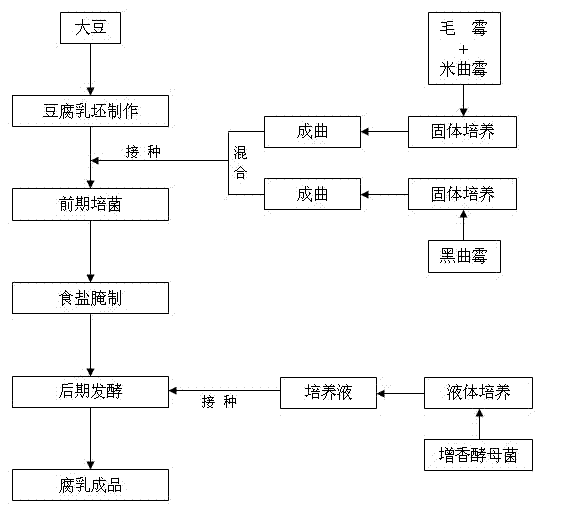
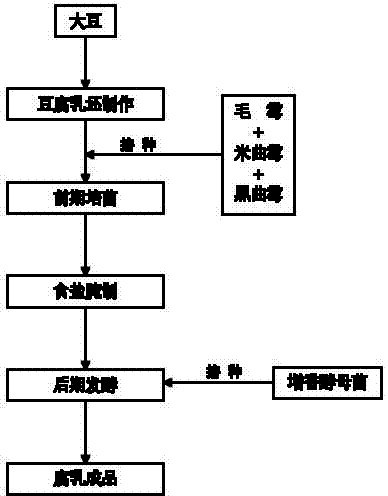
Method for producing fermented bean curd through multi-strain mixed fermentation
ActiveCN102197847APromote decompositionRich flavorCheese manufactureFood scienceYeastAspergillus oryzae
The invention discloses a method for producing fermented bean curd through multi-strain mixed fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing raw fermented bean curd, namely preparing the raw fermented bean curd from soybean; (2) culturing bacteria at the early stage, namely inoculating mixed strains comprising mucor, Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus niger into the raw fermented bean curd to culture bacteria at the early stage to obtain the fermented bean curd blanks; (3) pickling by using salt, namely placing the fermented bean curd blanks obtained in the step (2) into a rubber box, scattering salt layer by layer, and pickling with the salt to prepare salty blanks; (4) fermenting at the later stage, namely placing the pickled fermented bean curd salty blanks into a bottle, inoculating flavor-increasing yeast into wine liquid of semifinished products, and fermenting at the later stage; and (5) obtaining the fermented bean curd. By the method, the flavor of the fermented bean curd products can be enriched and the fermenting period of the fermented bean curd is shortened.
Owner:GUANGDONG CHUBANG FOOD
Method for producing glucose dehydrogenase from aspergillus oryzae
ActiveUS20080014612A1Efficient productionStable productionSugar derivativesBacteriaAspergillus oryzaeMicrobiology
The present invention effectively produces glucose dehydrogenase derived from Aspergillus oryzae, and provides more practical glucose dehydrogenase. The invention makes it possible to efficiently produce glucose dehydrogenase and to obtain glucose dehydrogenase in more practical manner by using a glucose dehydrogenase gene isolated from Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
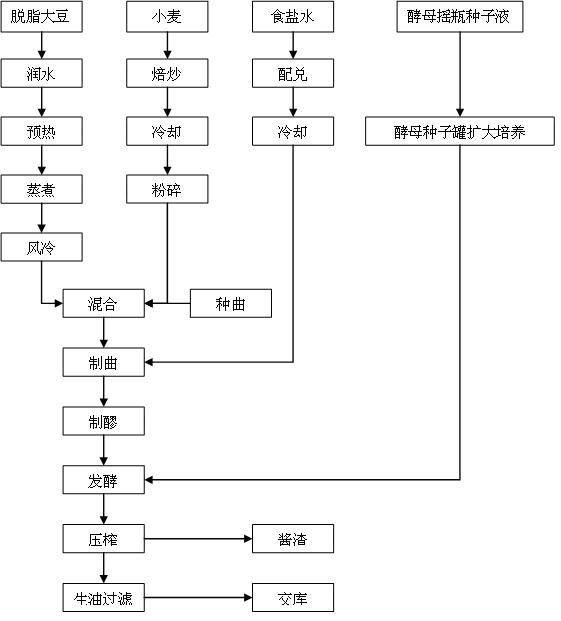
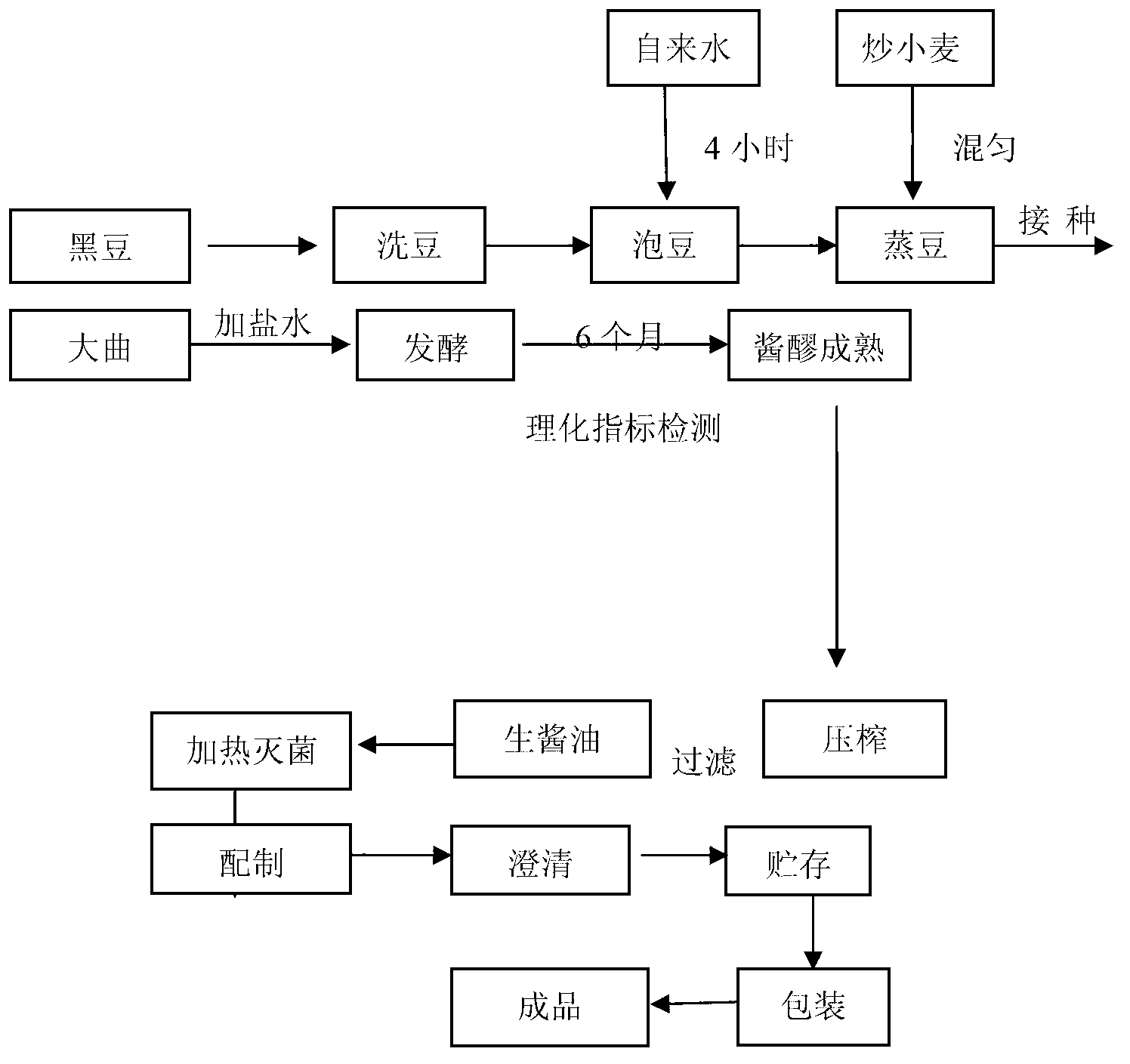
Brewing technology for soybean sauce
InactiveCN105053962AIncrease contentImprove protein utilizationFood thermal treatmentFood preparationWheat BransProtein
The invention discloses a brewing technology for soybean sauce. The brewing technology comprises the following steps: (1) soybean soaking: adding soybeans into water for soaking; (2) stewing: stewing the soybeans to obtain cooked soybeans; (3) mixing: mixing flour and roasted wheat bran to obtain a flour mixture, and mixing the cooked soybeans and the flour mixture to obtain a mixture; (4) inoculation: cooling the temperature of the mixture to be below 30 DEG C, and inoculating aspergillus oryzae; (5) distiller's yeast making: conveying the mixture into a leavening room for cultivation, wherein in the earlier stage of cultivation, the distiller's yeast temperature is 28-35 DEG C, and in the later stage of cultivation, the distiller's yeast temperature is 20-25 DEG C until the distiller's yeast is formed; and (6) fermentation: mixing the finished distiller's yeast and salty water, performing fermentation under normal temperature for more than 4 months. According to the brewing technology, the contents of reducing sugar and amino acid nitrogen in the soybean sauce can be effectively increased, the non-enzymatic browning effect in a soybean sauce brewing process is enhanced, and the flavor and the color of the soybean sauce are enhanced; and furthermore, the distiller's yeast contains rich protease, and the utilization rate of proteins in the soybean sauce brewing process is increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIWEIXIAN FLAVORING & FOOD
Method for jointly treating stalks by steam explosion and microorganism fermentation
ActiveCN102077903ACompletely degradedSolve the problem of human-animal competition for foodFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSporelingNutrient solution
The invention relates to a method for jointly treating stalks by steam explosion and microorganism fermentation, comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out steam explosion pretreatment on the stalks to obtain exploded stalks; then preparing spore seed liquid: inoculating aspergillus oryzae or trichoderma Koningi to a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium, standing and culturing for 3-5 days at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C, and preparing the spore seed liquid with the concentration of 106-108 per mL; and finally carrying out microorganism fermentation: uniformly mixing 18g of exploded stalks, 2g of bran and 30mL of mineral element nutrient solution, adjusting pH to be 7.0 with Ca(OH)2, sterilizing for 15min at the temperature of 121 DEG C and the pressure of 0.15MPa to obtain a solid fermentation medium a, inoculating the spore seed liquid according to 2-4% of inoculum size, and culturing the spore seed liquid for 5-7 days at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C. The fermentation stalks obtained by utilizing the method have low content of lignose, cellulose and hemicellulose and high activity of filter paper carbohydrase, CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) enzyme, amylase and protease.
Owner:河南德邻生物制品有限公司
Vinegar koji and biological edible vinegar, and method of producing the same
The invention relates to a vinegar melody, biological vinegar and the preparing method, which dissolve the problem that glacial acetic acid or the like in the edible vinegar has side effect for the human. The vinegar melody is made by Avena sativa, wheat, black rice, peart barley, soya bean, black soya bean, green bean, red bean, broad bean, pea, tea, traditional Chinese medicine herbal pieces prepared for decoction and vinegar melody bacterial. The preparing method of the vinegar melody comprises the following steps: 1, boiling after disintegrating high starch raw material and infiltrating with the water; 2, adding the other raw material, water and vinegar melody bacterial and fermenting. The biological vinegar is made by vinegar melody, Daqu, Shenqu, bran melody, wine yeast, aspergillus oryzae, Chinese sorghum, corn, millet, glutinous millet, peart barley, glutinous rice, black rice, citrate bacterial, yeast, acetic acid bacteria and fruit normal juice. The preparing method of the biological vinegar comprises the following steps: 1, boiling after disintegrating high starch raw material and infiltrating with the water; 2, adding the other raw material and saccharifying and acetous fermenting zymogeneous bacteria; 3, adding the salt and afterripening; 4, drenching the vinegar; ageing; sterilizing and filtering. The local flavor of the biological vinegar comes from the raw material and the metabolite of the microorganism completely without the glacial acetic acid or the like, and the biological vinegar doesn't have the side effect for the human and has the delicious taste and more than 8. 13g / 100ml high vinegar yield.
Owner:范英祝
Natural fermented cereal beverage and its production
ActiveCN101028130AEasily absorbablePromote digestionFood preparationPolygonum fagopyrumAspergillus oryzae
A fermented grain beverage is prepared from rice, wheat, oats, barley, highland barley, rye, buckwheat, sorghum, millet, corn and glutinous rice through immersing in purified water, steaming, cooling, inoculating Aspergillus oryzae, natural fermenting, mixing with non-fermented grains, hydrolyzing, saccharifying, diluting, homogenizing, sterilizing, and filling it in containers.
Owner:周大庆 +1
Making method of fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce
InactiveCN103766862AGreat tasteFood ingredient functionsFood preparationReady to eatModulation function
The invention discloses a making method of fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce, and belongs to the field of non-staple food processing. The making method of the fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce takes high-quality salty thick broad-bean sauce, bright red four-flat head chilis produced at the north slope of Tianshan mountain and chick pea meal as main raw materials. The processing method comprises the following steps: carrying out temperature control fermentation, inoculating lactic acid bacteria, adding aspergillus oryzae, inoculating for a second time, processing the finished product and the like. The prepared fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce is rich in sauce flavor, spicy in mouthfeel and slightly sweet, has flower fragrance, can be directly eaten, and is very palatable and rich in nutrition. The fermentation-type ready-to-eat red oil chili thick broad-bean sauce is rich in components such as vitamins, trace elements and amino acid. The sauce body has natural deep red color, and has very good color modulation function besides seasoning.
Owner:XINJIANG YUANYE FOOD
Method for producing inocula for livestock and poultry by multi-thalli mixed liquid
InactiveCN101386827AReduction factorReduce ammonia nitrogenFungiBacteriaDiseaseBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a method for fermentation production of a poultry bacterial agent by multi-bacteria miscible liquid, wherein aerobic bacteria, namely Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, bacillus natto, beer yeast, Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae are cultured in a shaking table according to different culture mediums, so as to culture a mother seed solution; simultaneously Lactobacillus acidophilus, bifidobacteria and enterococcus faecalis are subjected to anaerobic culture by utilization of Kille flasks, and a mother bacterial solution of photosynthetic bacteria is cultured by a Kille flask under the condition of illumination; the prior stock solution is inoculated into a seed tank for anaerobic culture and fermentation according to 4 percent of the inoculum concentration, and the fermentation time is between 48 and 60 hours; and the cultured seed liquid is inoculated into a productive tank for anaerobic culture and fermentation according to 10 percent of the inoculum concentration, the fermentation time is between 60 and 72 hours, and the fermentation end point is reached when the pH value is reduced to 4.0. The method has the advantages that the microscopic examination viable count of the bacterial agent is more than 5 billion per milliliter, so that the bacterial agent is safe and nontoxic, thereby not only improving the disease resistance of poultry but also promoting the quick growth of the poultry, reducing the feed-meat ratio and improving the quality of meat, eggs and milk.
Owner:张培举
Segmented temperature control bean paste multi-microbe co-brewing and quick fermentation method
The invention discloses a segmented temperature control bean paste multi-microbe co-brewing and quick fermentation method. The segmented bean paste multi-microbe co-brewing and quick fermentation method comprises the following steps: adding two yeasts, namely aspergillus oryzae (Huniang 3.042) and mucor rouxianus, in a yeast preparing stage, fermenting for preparing yeasts, then carrying out medium-high temperature (45-47 DEG C and 55-58 DEG C) gradient temperature control fermentation, then adding weissella cibaria and zygosaccharomyces rouxii AS2.181 while deeply turning over and stirring, so as to prepare sweet beans; adding pepper embryos into a sweet bean preparing fermentation tank until the pepper embryos account for 60-70% of the total weight, the sweet beans account for 30-40%, turning over and uniformly stirring, then controlling temperature to be 33-35 DEG C, fermenting for 30 days while a turning over and stirring machine is used for deeply turning over and uniformly stirring every 5 days, and finally Pixian bean paste is obtained after 80-90 days. The segmented bean paste multi-microbe co-brewing and quick fermentation method has the advantages of short production period, uniformity in fermentation, diversified yeasts, excellent fermentation flavour and high enzymolysis efficiency and is applicable to quick production of bean paste at present.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Soy sauce production method capable of ensuring high protein conversion rate and utilization rate
The invention discloses a soy sauce production method capable of ensuring high protein conversion rate and utilization rate, which belongs to the technical field of soy sauce seasoning production. In the method, bean pulp and wheat are taken as raw materials; a soy sauce finished product is obtained by a continuous cooking process, a process of mixing and fermenting a plurality of strains, subsequent treatment and filling; and the special raw materials treated by the continuous cooking process are mixed with screened and domesticated aspergillus oryzae strains with high proteinase activity, fermentation and starter propagation are performed on the mixture, and aroma-increasing high-salt yeast strain fermentation liquor with specific aroma-increasing flavor is added in a subsequent sauce mash fermentation stage for the soy sauce seasoning production. The soy sauce production method has the advantages of advanced equipment and treatment process, high raw material conversion rate and utilization rate, low cost, high product quality and the like.
Owner:JIAJIA FOOD GRP
Egg white powder with high foamability and preparation method thereof
The invention provides egg white powder with high foamability and a preparation method thereof and relates to reconstruction of whey protein structure and functional properties, belonging to the technical field of biological processing of foodstuffs. According to the invention, on the basis of preliminary work, enzymatic hydrolysis of lipase in advance and cooperative enzymatic hydrolysis of composite protease are utilized for treatment of egg white; total usage amount of lipase and composite protease is less than usage amount of individually used lipase or protease, and however, foamability and foam stability of egg white powder obtained by combined utilization of lipase and composite protease are higher than those of egg white powder obtained by individual utilization of lipase or composite protease; the egg white powder obtained in the invention can meet demands for high-grade products on the market, and the advantages of a simple process and high cost performance are achieved in the invention. According to the invention, the ratio of active usage amount of Aspergillus oryzae protease, papain and trypsin is determined to be 1:1:1; the usage amount and other technological parameters cooperatively allow egg white powder with high foamability to be obtained; egg white powder with high foamability provided in the invention enables the additional output value of eggs to be increased, lays a technical foundation for development and industrial production of special-purpose egg white powder products and increases economic benefits for enterprises.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
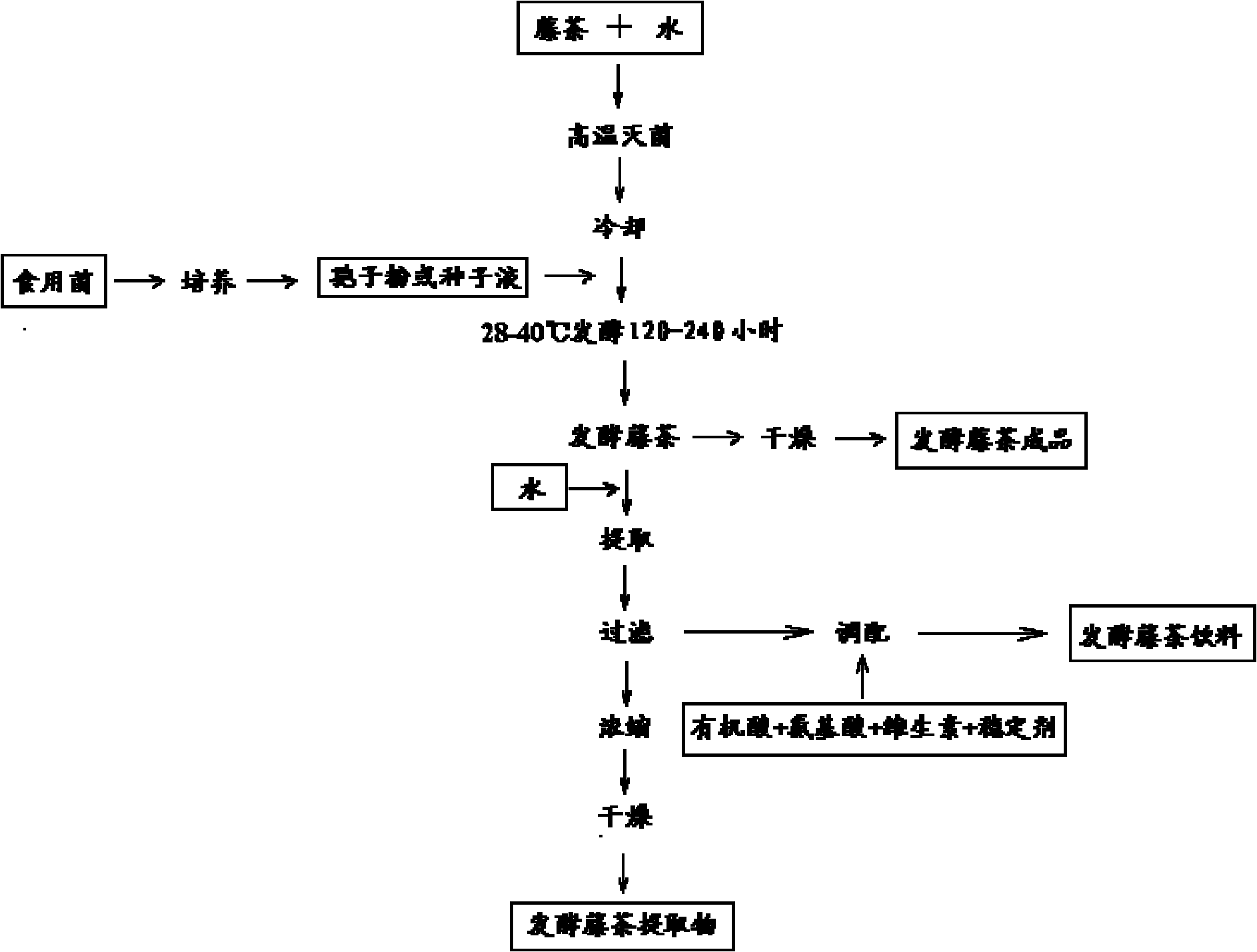
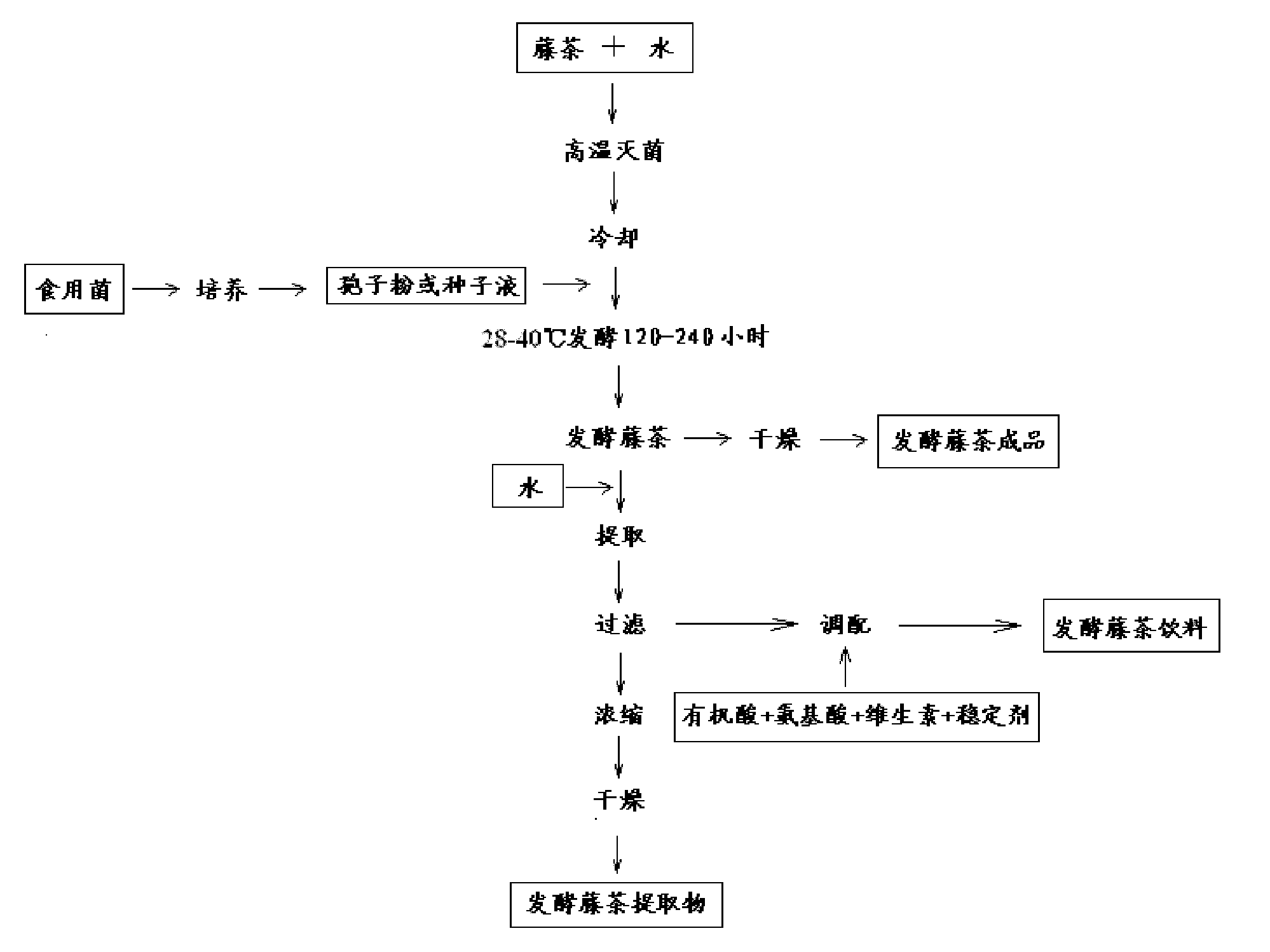
Production method of fermented vine tea, vine tea extract and vine tea drink
ActiveCN102018083ADoes not affect sleepIncrease water soluble flavonoidsTea substituesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTPolyphenol
The invention relates to a production method of fermented vine tea, vine tea extract and vine tea drink. Tender stem leaves of ampelopsis humulifolia of vitaceae are taken as raw material, fermentation technique is adopted for production, and the production method comprises the steps of preparing vine tea, wetting the vine tea by adding water and steaming; preparing a seed culture medium, autoclaving, cooling, then inoculating edible funguses, and culturing at 28-40 DEG C for 24-120 hours to obtain seeds; inoculating seeds at the ratio of 3-8% of the weight of the vine tea, fermenting at 28-40 DEG C for more than 120 hours, and drying to obtain the fermented vine tea; and extracting, concentrating and drying to obtain fermented vine tea powder. The edible funguses in the invention comprise aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae, monacus anka, saccharomycetes, lactic acid bacteria and mixed strains. In the fermentation process of the vine tea in the invention, contents of active ingredients such as soluble flavone, polyphenol, tea pigment and the like are greatly improved, thus promoting absorption and utilization of the active ingredient of the vine tea and enhancing pharmacological efficacy of the vine tea. Besides, the production process of the invention thoroughly solves the technical problem that vine tea soup is precipitated after being cooled.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
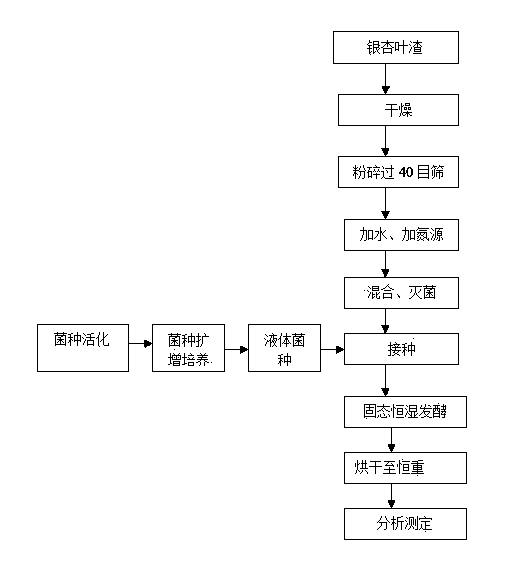
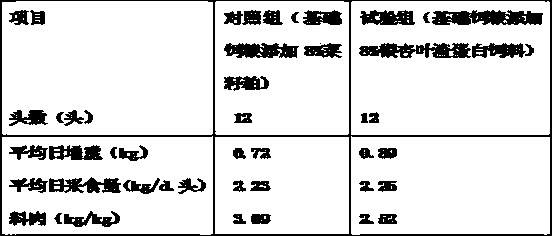
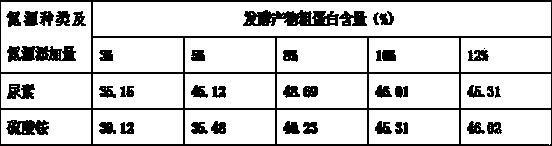
Method for producing protein feed through mixed strain solid-state fermentation of ginkgo leaf residue
ActiveCN103478413AHigh nutritional valueHigh protein contentAnimal feeding stuffFeed conversion ratioAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method for producing a protein feed by using gingko leaf residue as a raw material for mixed strain solid-state fermentation. Activation and multiplication culture are respectively performed on candida tropicalis, aspergillus oryzae, bacillus subtilis and lactobacillus plantarum, so as to obtain four liquid strains; after the gingko leaf residue is dried and smashed, a certain amount of water and a nitrogen source are added, and after mixing and sterilizing, the gingko leaf residue is taken as a solid-state fermentation culture medium; the four liquid strains are inoculated to the solid-state fermentation culture medium according to certain proportions, after sufficient mixing, fermentation for 72 to 120 hours can be performed at a nature pH value under the temperature of 28 to 30 DEG C, and after drying, a gingko leaf residue protein feed can be obtained. In the protein feed, the coarse protein content of the protein feed is high and can reach 46 percent, the nutritional ingredients are complete, the palatability is excellent, the production performance and the feed conversion rate of livestock and poultry can be effectively improved, the preparation method is simple in process, the cost is low, and the mass production can be achieved. The invention further provides a way for using the gingko leaf residue which is a waste material in forestry processing.
Owner:日照恒邦牧业科技股份有限公司
High-salt diluted-state black soybean sauce and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-salt diluted-state black soybean sauce and a preparation method thereof. Main raw materials of the black soybean sauce comprise black soybean, fried wheat, edible salt and water; and concrete steps comprise concentrating and cleaning black soybeans, soaking for 4 hours, steaming for 20 minutes at the temperature of 121 DEG C, wherein cooked material digestion rate can reach up to 85.41%, mixing and braising steamed black soybean and fried wheat for 10 minutes in mass ratio of 5:5 while the steamed black soybean and fried wheat are hot, cooling to 35 DEG C, inoculating aspergillus oryzae mould starter according to the rate of 0.3%, mixing to be uniform, preparing yeast for making hard liquor, collecting the yeast after 36 hours, then adding 20Be saline waterfor fermenting, wherein volume ratio of the saline water to the yeast is 1.1:1, then fermenting for six months, squeezing, filtering, sterilizing and packaging, thus the black soybean sauce is obtained. The black soybean sauce disclosed by the invention has excellent quality, outstanding ester fragrance and delicious taste and also has specific component of black soybean, namely anthocyanin, thusappearance and colour of the sauce and product quality can be more popular with consumers.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Complex microbial inoculant and method for preparing organic fertilizer by using same
InactiveCN103898032AImprove qualityEffective cooperationBio-organic fraction processingFungiFiberAzotobacter chroococcum
The invention discloses complex microbial inoculant which comprises the following active ingredients: bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium, trichoderma koningii, aspergillus oryzae, trichoderma viride, geotrichum candidum, aspergillus niger, rhizopus oligosporus, lactobacillus plantarum CICC20768 and azotobacter chroococcum. Correspondingly, the invention further discloses a method for preparing an organic fertilizer from the complex microbial inoculant. The method comprises the following steps: a. uniformly mixing the complex microbial inoculant with a plant fiber raw material to obtain a fermented raw material; b, composting and fermenting the fermentation raw material; c, drying the composted fermentation raw material to obtain the organic fertilizer. microbes of the complex microbial inoculant have no antagonism, and can effectively cooperate in the production process of the organic fertilizer, and the chemical components of the production raw materials can be sufficiently utilized to finally produce the high-quality organic fertilizer. The produced organic fertilizer reaches the parameter indexes of the standard (NY884-2012) of China, can improve the planting property of soil, is beneficial to optimization of soil microbial flora, and can provide comprehensive nutrients to a plant root system.
Owner:江苏联海生物科技有限公司
Multifunctional high efficient organic material decomposition agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105733975APromote growthPrevent diseaseFungiBio-organic fraction processingDiseaseRoot growth
The invention discloses a multifunctional high efficient organic material decomposition agent and a preparation method thereof. The decomposition agent of the invention comprises composite original strains consisting of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Aspergillus oryzae, Trichoderma viride, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and an organic material carrier, and an inorganic carrier. Strains of the decomposition agent can be mutualistic, and have complementary advantages. The adaptation is wide, and a plurality of organic matter clastic enzymes can be produced by metabolism. The decomposition agent has high activity and can be used for fermentation and conversion of a plurality of organic materials such as livestock and poultry excrements, crop straws, city sludge, food waste, food processing and pharmaceutical waste residues, and has fast fermentation start, fast deodorization, low temperature resistance, and low moisture resistance. The fermentation period is shorter by 5-7 days than that in the same technology. Fermented and converted organic fertilizers have the obvious rhizosphere ecological regulation and control function, promote the root growth, and improve the root vitality. A plurality of soil borne diseases are prevented by improving the flora diversity, hyperparasitism and biological antagonism.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
Aspergillus oryzae and method for preparing high purity galacto-oligosaccharides by using same
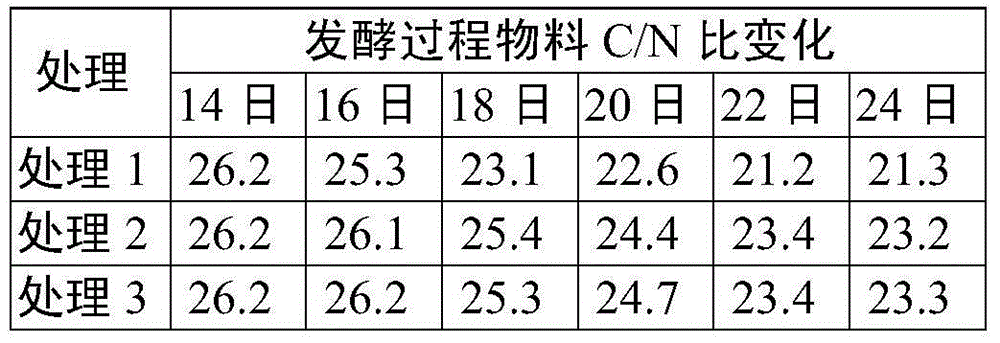
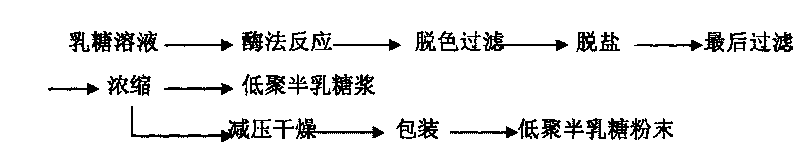
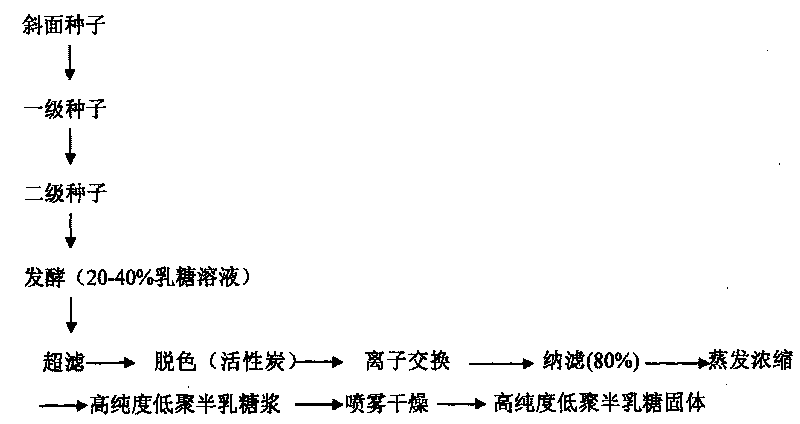
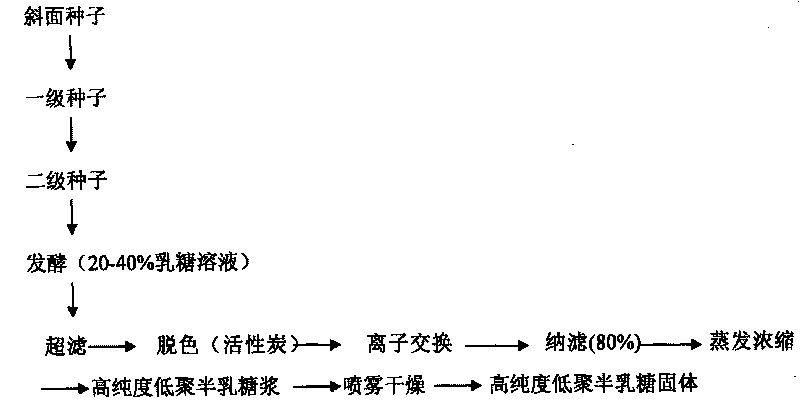
ActiveCN101691538ASimple processEase of industrial productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing high purity galacto-oligosaccharides, comprising the following product separation and purification steps: Aspergillus oryzae fermentation, ceramic membrane ultrafiltration, nanofiltration separation and the like. In the method, the Aspergillus oryzae separated from the soil is adopted as an original strain and the Aspergillus oryzae BLB-21 (with preservation number of CGMCC No.2951), a high efficiency transformed strain obtained through mutation screening in the laboratory, is directly used to ferment high concentration lactose solution, thus avoiding the steps of enzyme purification and the like in the process of preparing the galacto-oligosaccharides by an enzyme method and saving time and labor. The high purity galacto-oligosaccharides are obtained by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration separation, the process is ideal, the conditions are mild and the method has extensive industrial production prospect.
Owner:BAOLINGBAO BIOLOGY
Preparation method of compound microbial feed additive
The invention relates to a feed additive, in particular to a prepration method of a compound microbial feed additive, which is used for solving the problems that a variety of feed additives have respective different shortcomings in the actual applications. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing selenium yeast, iron yeast and zinc yeast which are rich in trace elements, taking vinegar residue, wheat bran, corn flour, compound Daqu, ammonium sulfate and other auxiliary materials as culture media, adding aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae, bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus and yeast, producing a multi-bacterial compound enzyme by the solid-state method, and mixing the functional yeast, phytase and the multi-bacterial compound enzyme for producing a biological feed micro-multi-enzyme which has a large number of live bacteria in beneficial bacterial groups, a complete enzyme system of digestive enzymes and non-digestive enzymes needed by animals and high enzyme activity, and is rich in organic trace elements, vitamins, amino acids and unknown growth-promoting factors with functional nutrition for the animals and people; furthermore, the feed additive has the advantages of advanced process, abundant nutrition, abundant bacterial groups, full enzyme spectrum, high activity, greenness, no pollution and the like.
Owner:山西金龙鱼梁汾醋业有限公司
Compound microorganism agent for treating black and odorous water body
ActiveCN108441444AImprove the problem of smelly and blackHigh transparencyFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisCandida tropicalis
The invention provides a compound microorganism agent for treating a black and odorous water body. The compound microorganism agent comprises compound bacteria and a compound enzyme preparation, wherein the compound enzyme preparation comprises candida tropicalis, candida utilis, bacillus natto, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, nitrobacter, achromobacter denitrificans, nitrosomonus, acinetobacter, lactobacillus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae and photosynthetic bacteria; the compound enzyme preparation comprises protease, amylase, lipase, sucrase, and cellulase.
Owner:POWERCHINA WATER ENVIRONMENT GOVERANCE
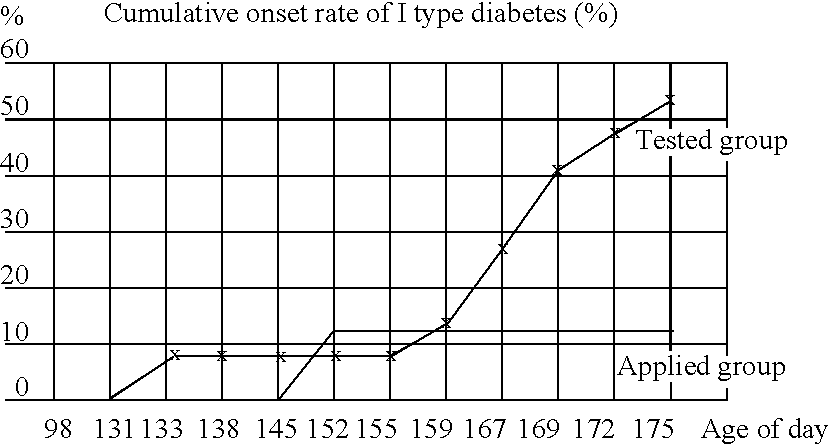
Composition containing embryo bud and seed coat from rice and fruit body of Ganoderma lucidum for treating diabetes
A composition used to treat diabetes is disclosed. The composition is made by first, mixing an isolated embryo bud and isolated seed coat from rice with a fruit body of Ganoderma lucidum to form a mixture. Next, the mixture is fermented with an Aspergillus oryzae strain to produce a resulting fermentate. Then, the resulting fermentate is dried to produce a dried fermentate. Next, the dried fermentate is crushed into a fine powder and lastly, the powder is mixed with vitamin B to form the composition.
Owner:GENMAI KOSO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com