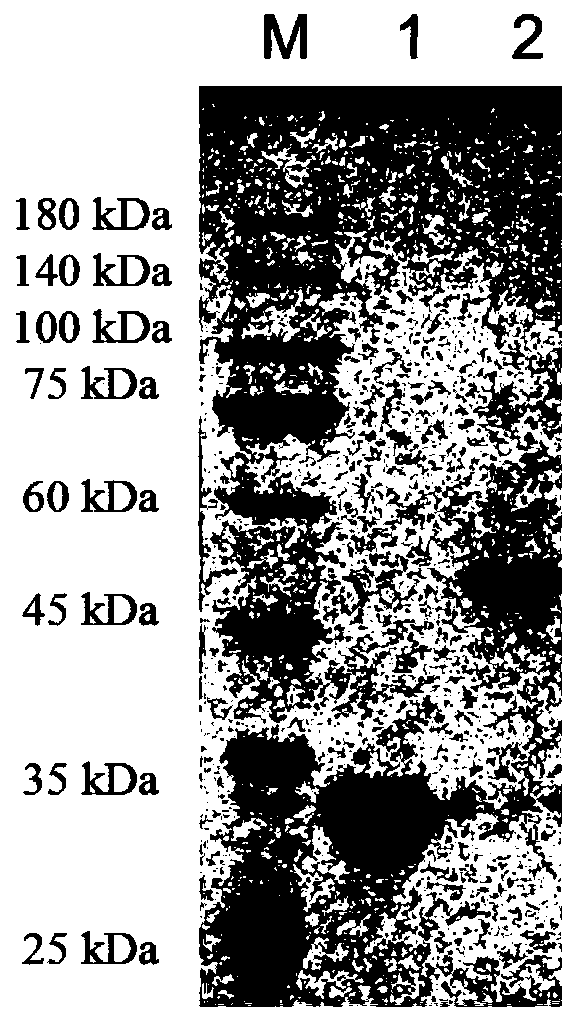
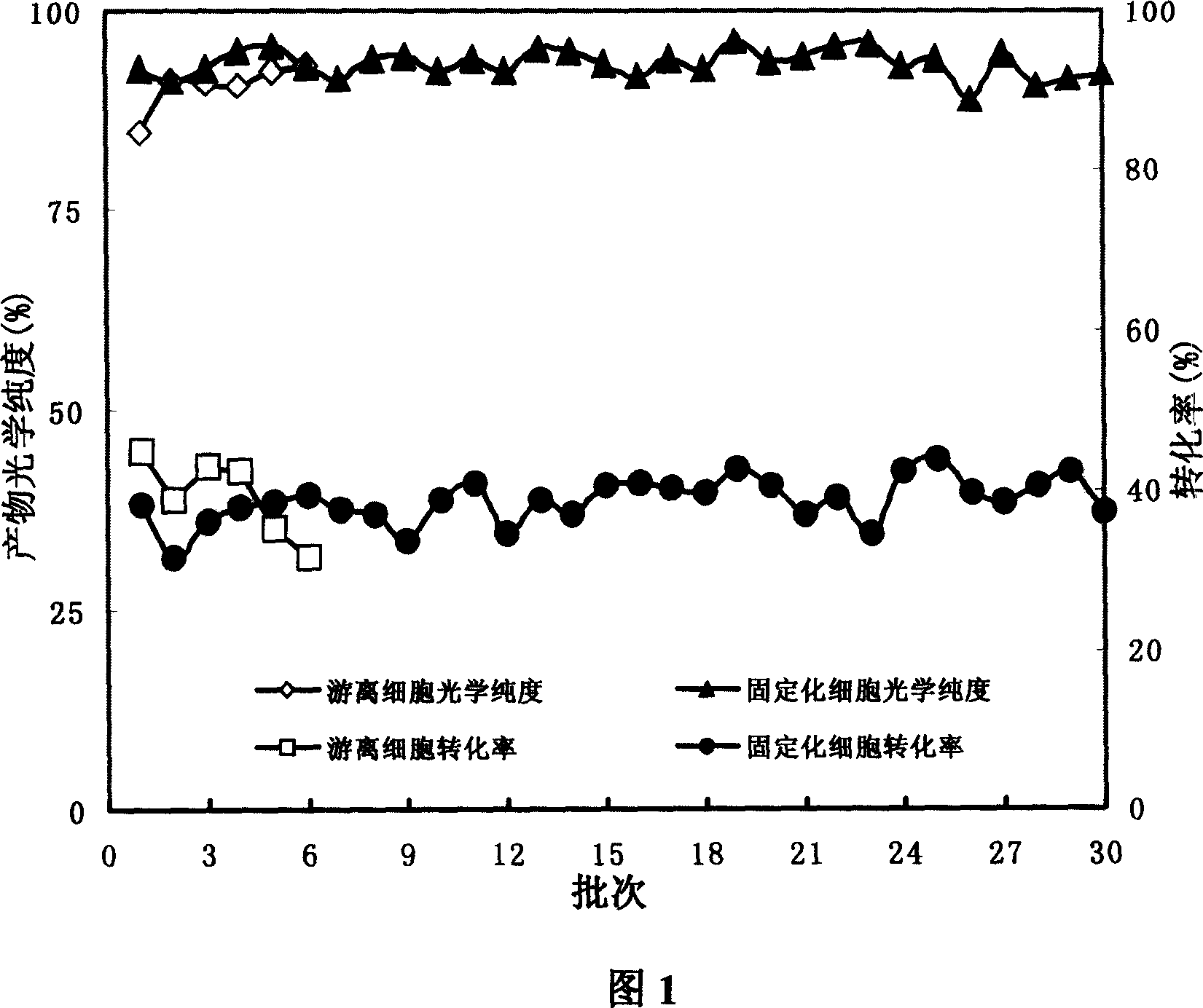
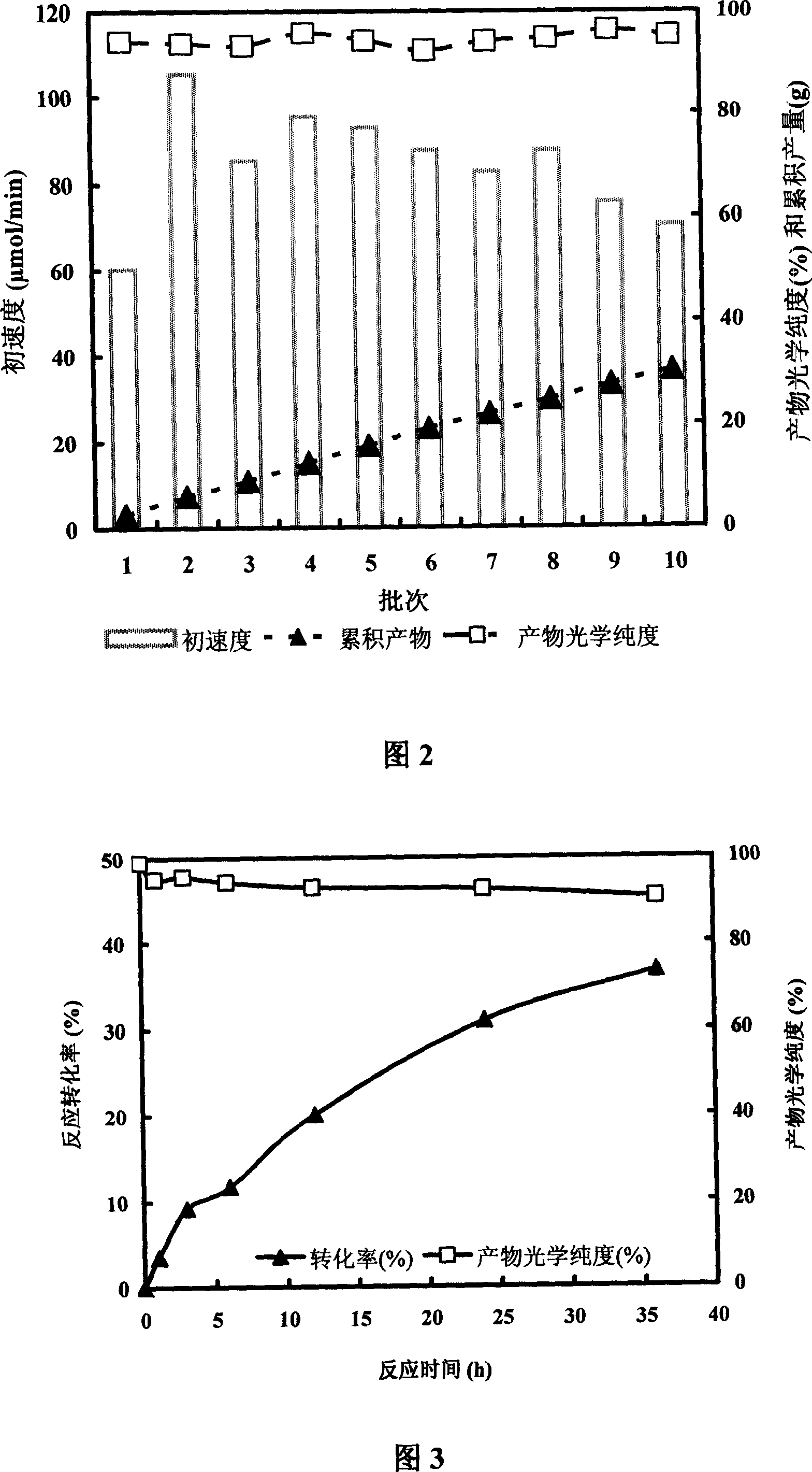
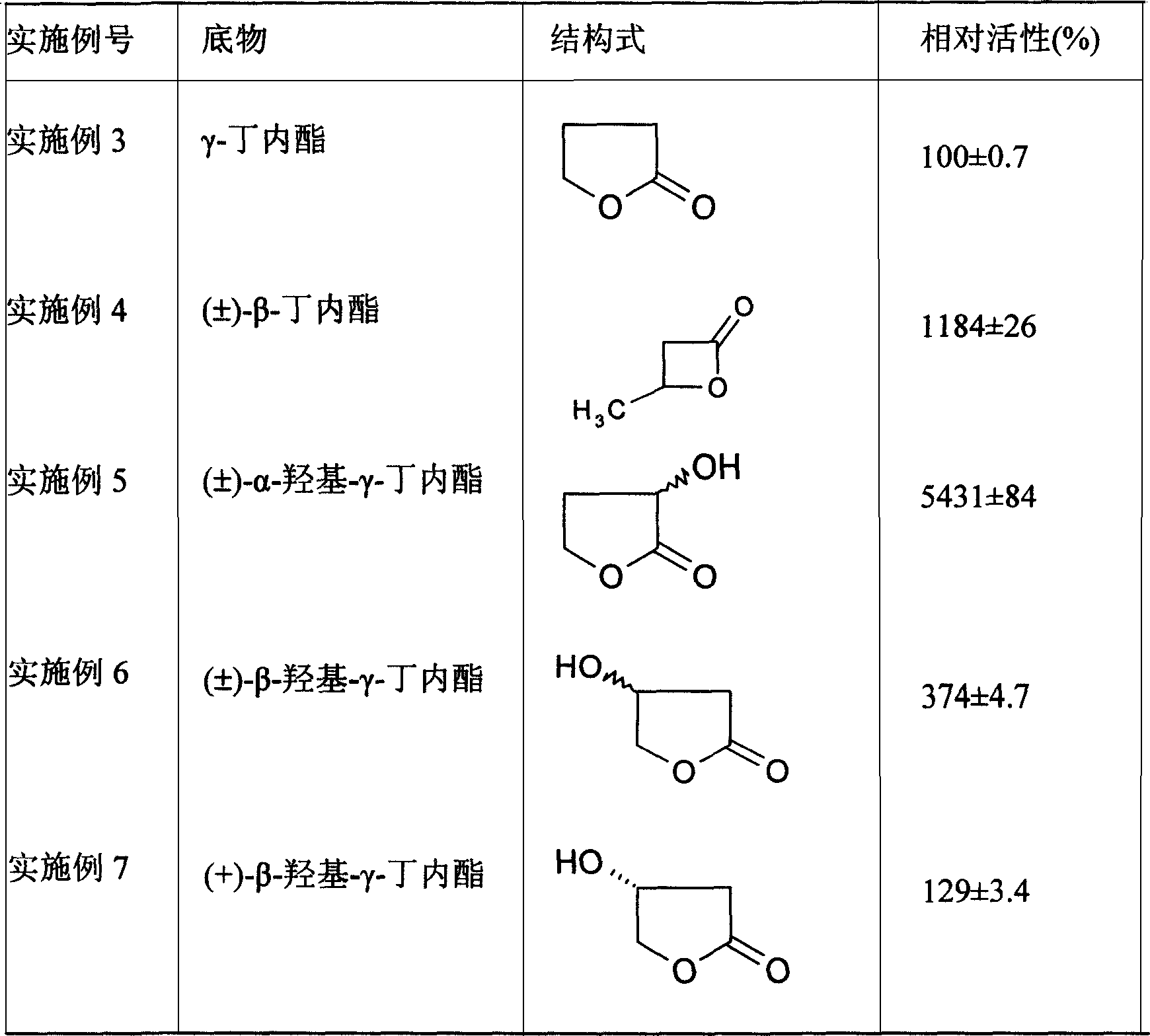
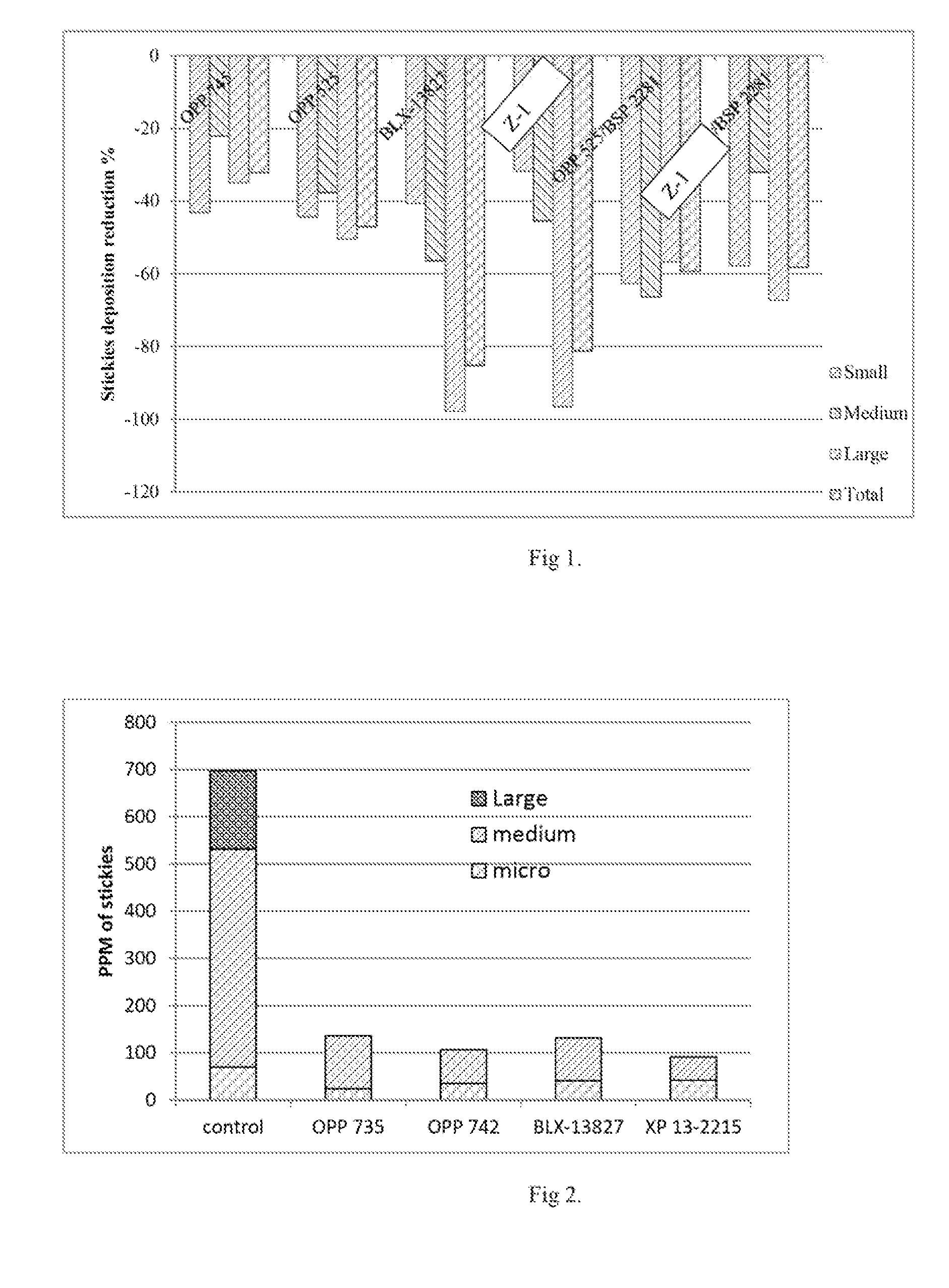
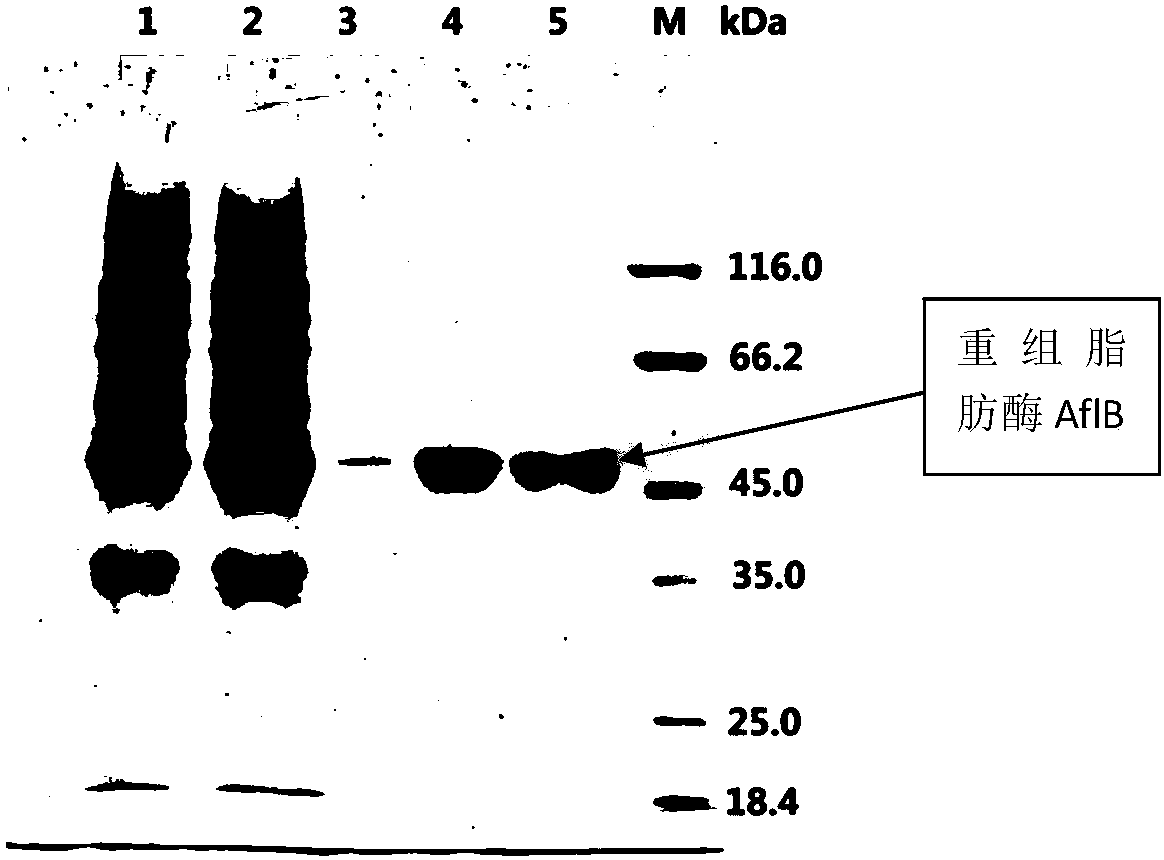
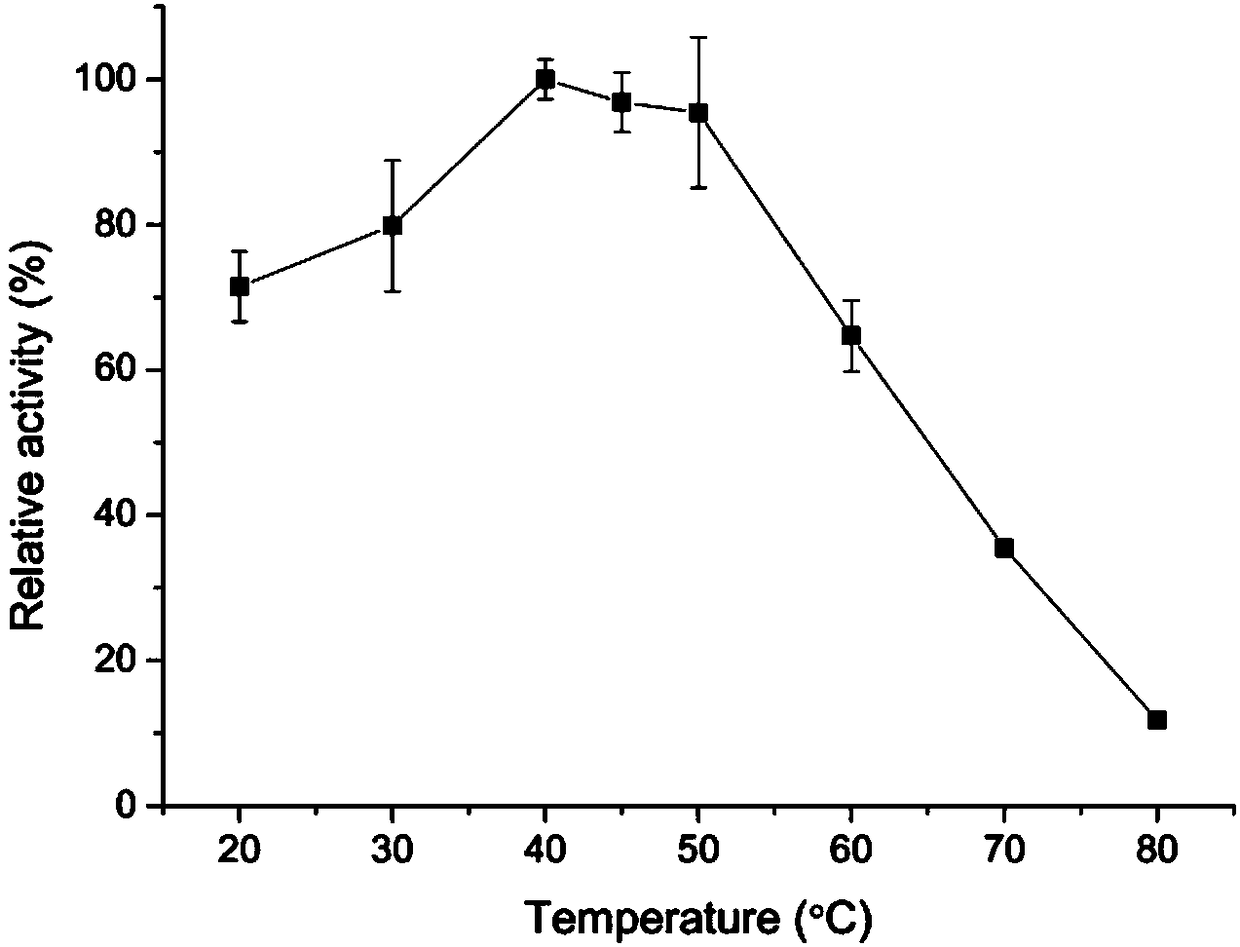
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
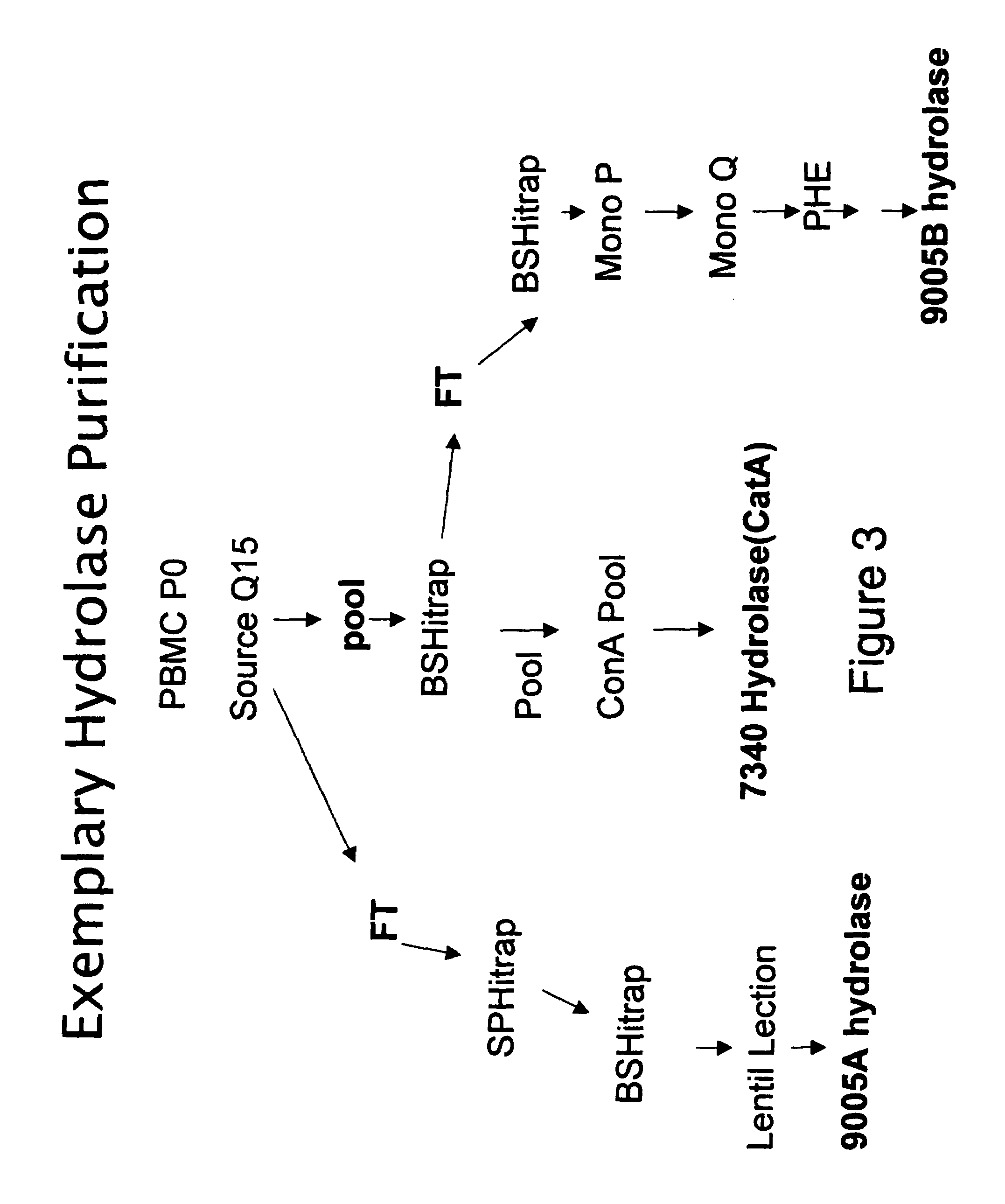
60 results about "Ester hydrolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 (NCEH) also known as arylacetamide deacetylase-like 1 (AADACL1) or KIAA1363 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NCEH1 gene. NCEH is an enzyme located in the endoplasmic reticulum. NCEH hydrolyzes 2-acetyl monoalkylglycerol ether, ...
Microorganism of producing D-pantothenic acid enternal ester hydrolase and process for preparing D-pantothenic acid thereof
The invention relates to a method used microorganism enzyme resolution DL-pantoic acid lactone to produce D-pantoic acid. It uses the D-pantoic acid lactone hydrolase strain of the fusarium, gibberella, aspergillus, penicillium, rhizopus, gliocladium, aureobasidium to ferment and culture, uses wet thallus as coarse enzyme, DL-pantoic acid lactone as substrate to produce D-pantoic acid. L- pantoic acid lactone can be reclaimed. The DL-pantoic acid lactone gained by racemization reaction can newly be used to do resolution.
Owner:重庆鑫富化工有限公司 +1
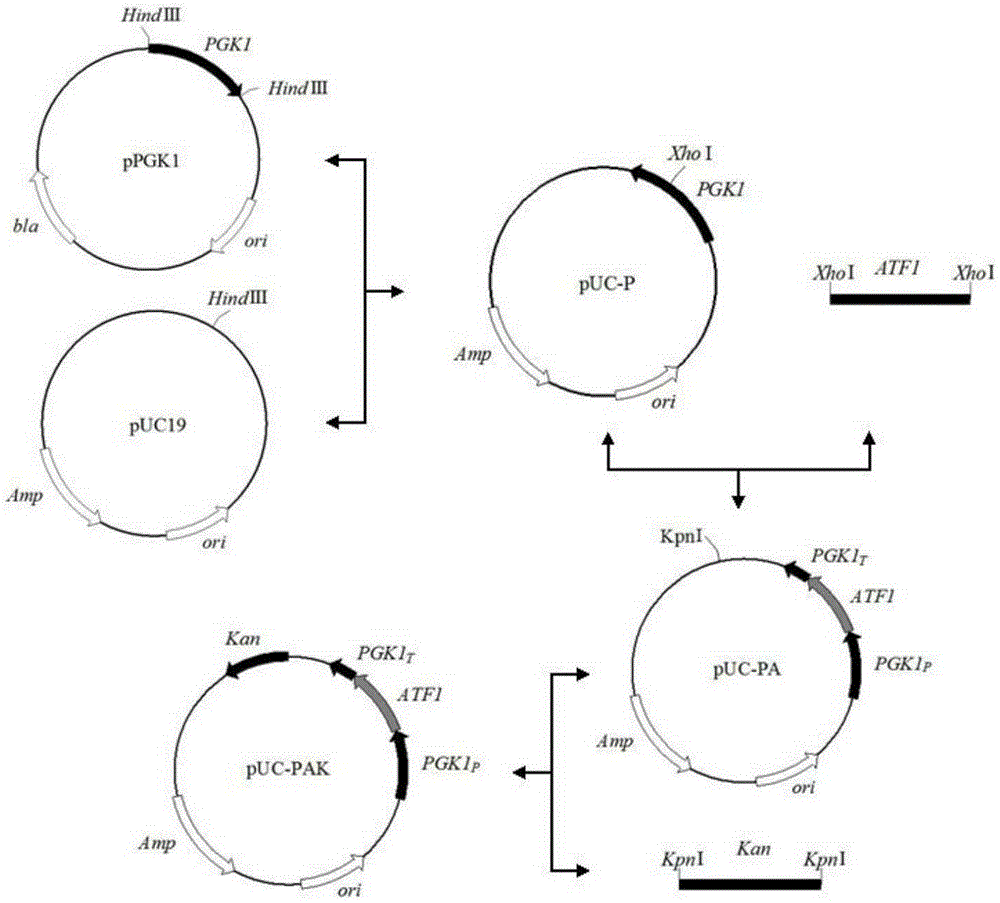
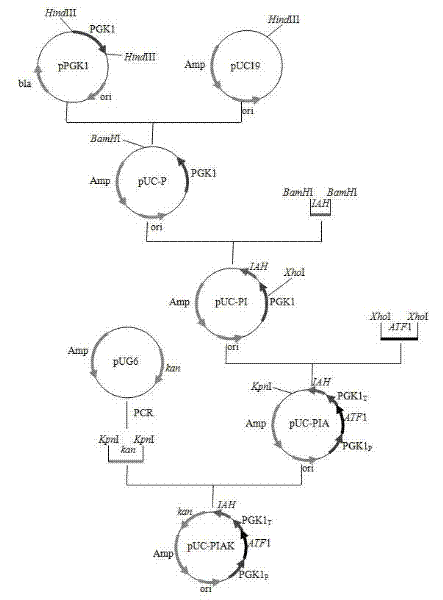
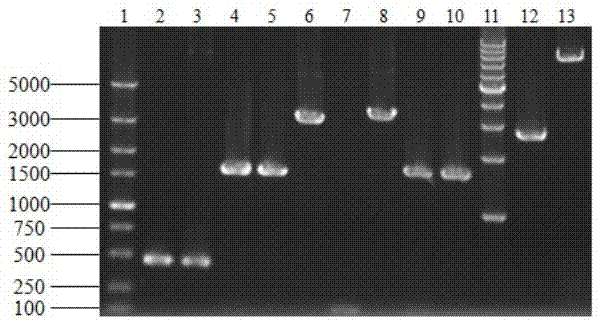
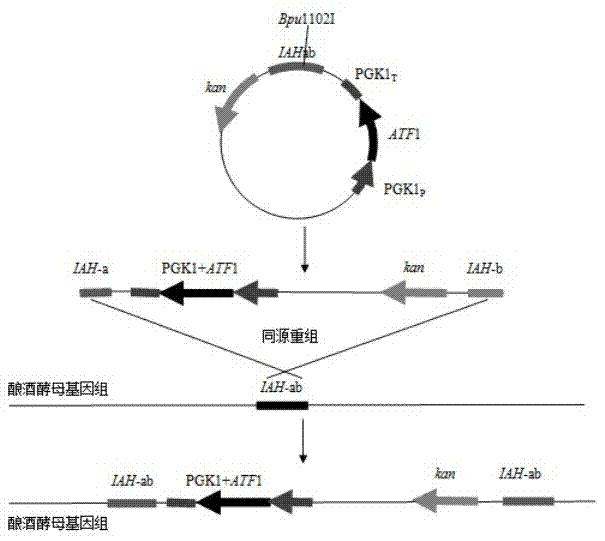
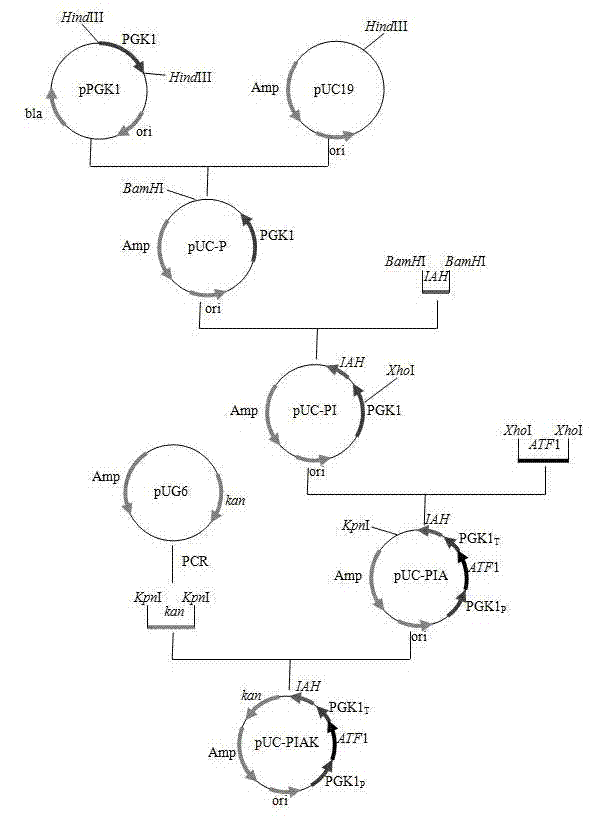
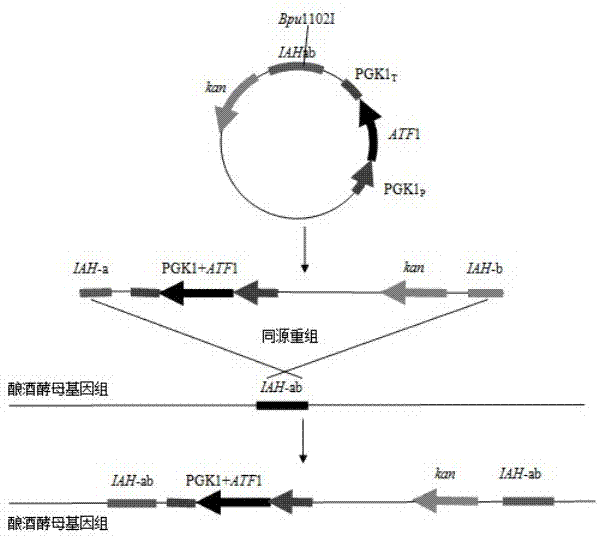
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as building and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
PendingCN105385615AReduce outputOvercome flavor incongruityFungiHydrolasesEster hydrolaseBio engineering
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as a building method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the building method provided by the invention, through completely knocking out an amino acid transaminase gene BAT2 and an ester hydrolase gene IAH1 in an original strain, and selecting a strong promoter PGK1 over-expression alcohol acetyltransferase I gene ATF1 at the same time, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol is obtained. Compared with a parent strain, other fermentation performances of built recombinant bacteria are not affected, the total quantity of acetic acid ester is obviously increased and reaches 1303.6mg / L, wherein the content of ethyl acetate is 52 times that of the original strain, isoamyl acetate is increased to 73.7mg / L, the content of main higher alcohol is 151.8mg / L and is reduced by 61.4 percent in comparison with that of the original strain. By using the saccharomyces cerevisiae, ester yield is significantly increased while the higher alcohol yield is reduced, the higher requirements of white spirit related fields on yeast are met and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102199556AReduce contentIncrease contentFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationEster hydrolaseGenetic engineering
The invention discloses Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria EY-13 were collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 17, 2010, the collection number is CGMCC NO.4350, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria are recommended to be named Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PGK1 derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is selected as a promoter; and the construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with the high esteryield comprises a step of knocking-out an IAH1 gene for encoding ester hydrolase in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome when an ATF1 gene which is derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is used for encoding alcohol acetyltransferase is overexpressed. Compared with initial recipient bacteria, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria have the advantages that: after rice wine fermentation is simulated, the content of isoamylol is about one half, the content of ethyl acetate is improved by 20 times, the content of isoamyl acetate is 100mg / L, and the content of isobutyl acetate is 5 to 7mg / L; and after liquor fermentation is simulated, the content of total esters is improved by 4 times and the content of the ethyl acetate is improved by 35 times, so an excellent strain is provided for the production of brewing industry.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
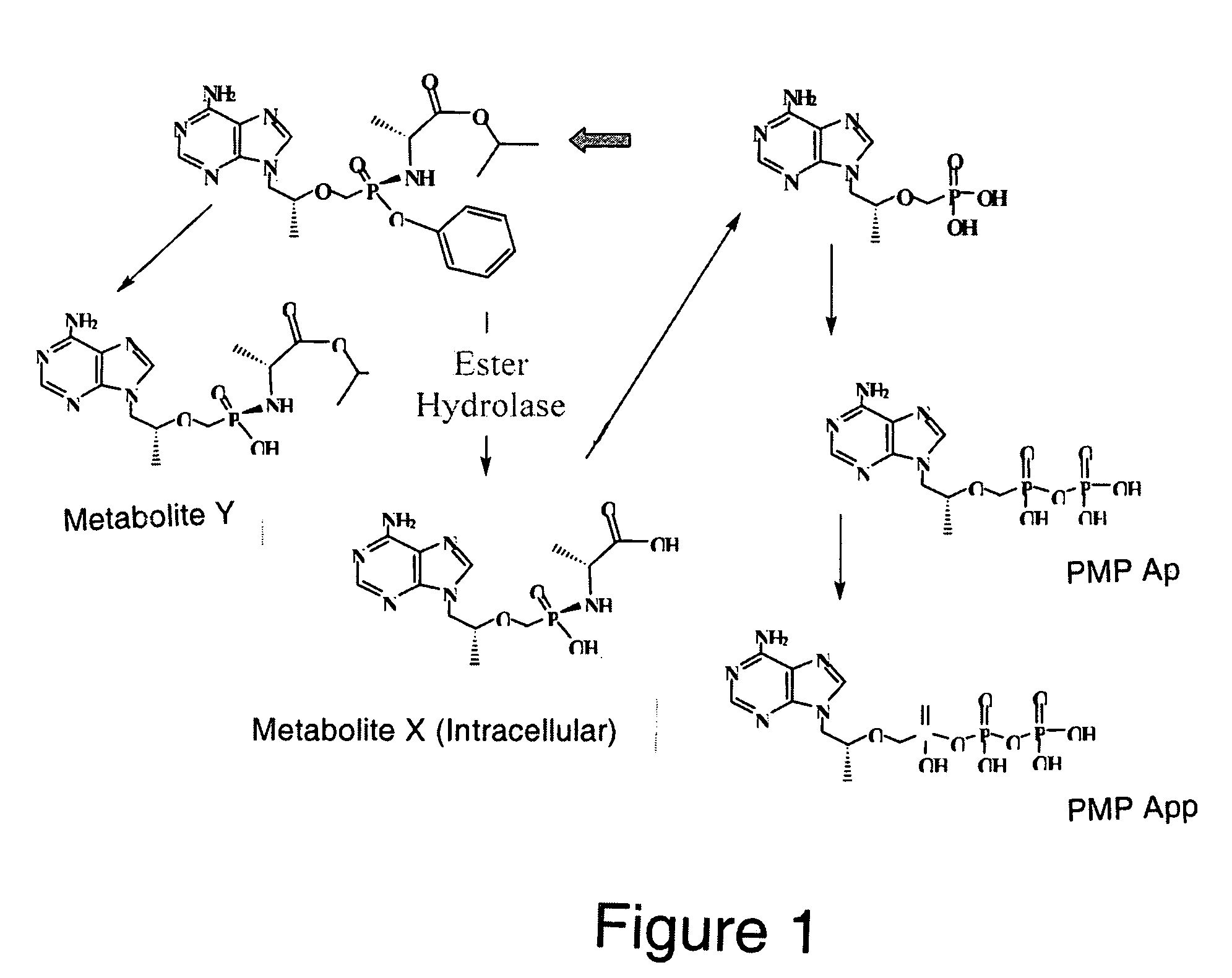
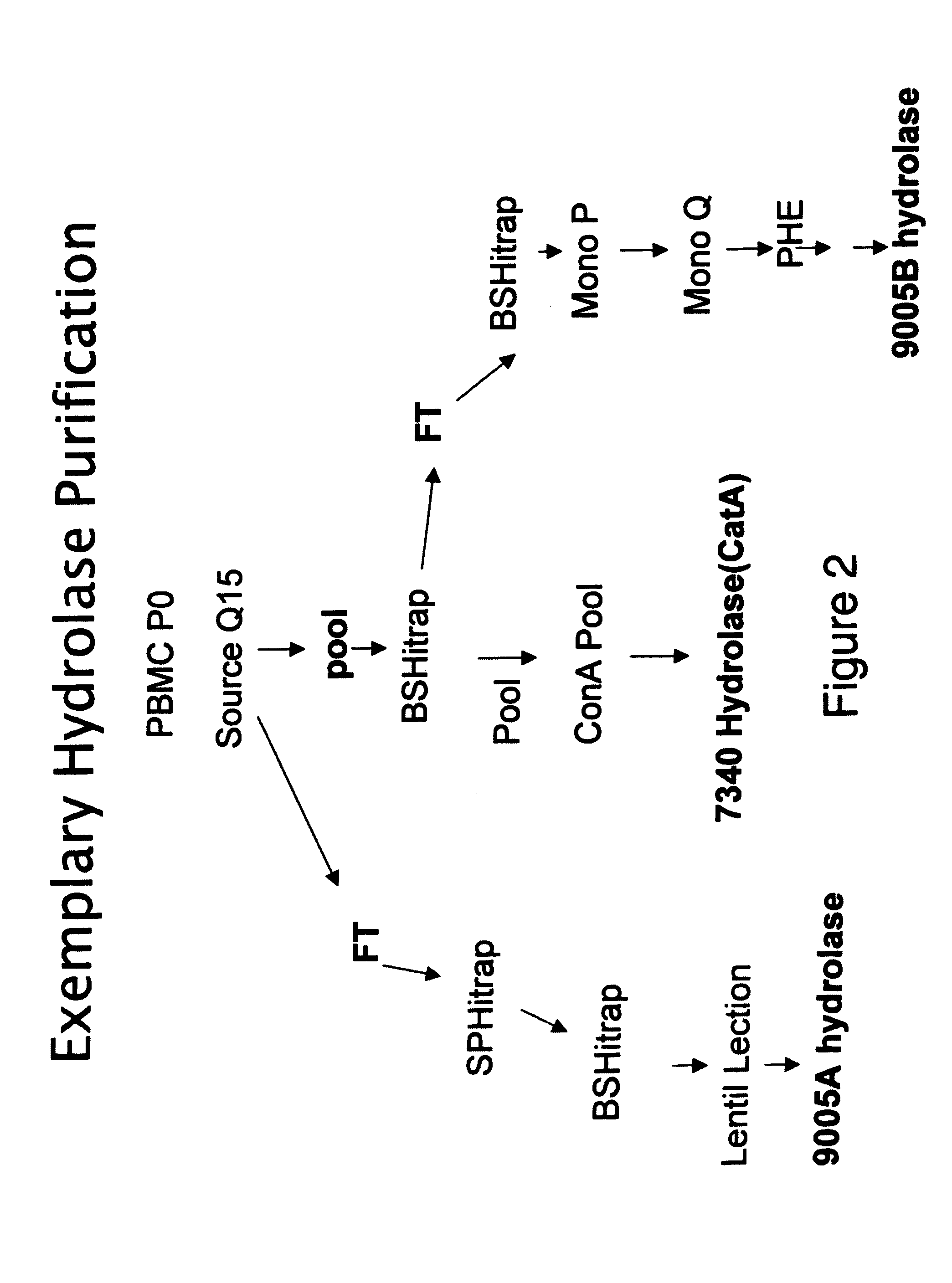
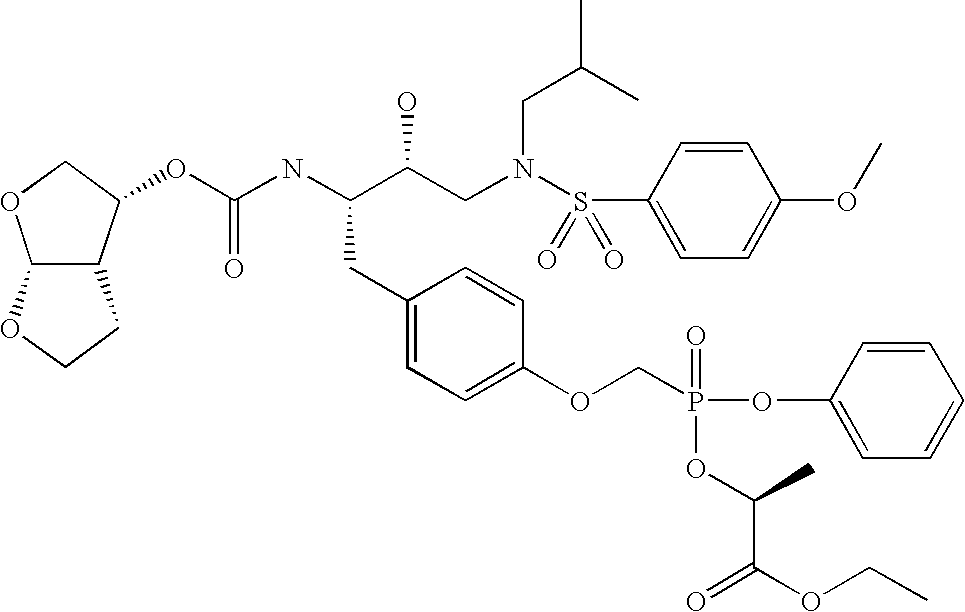
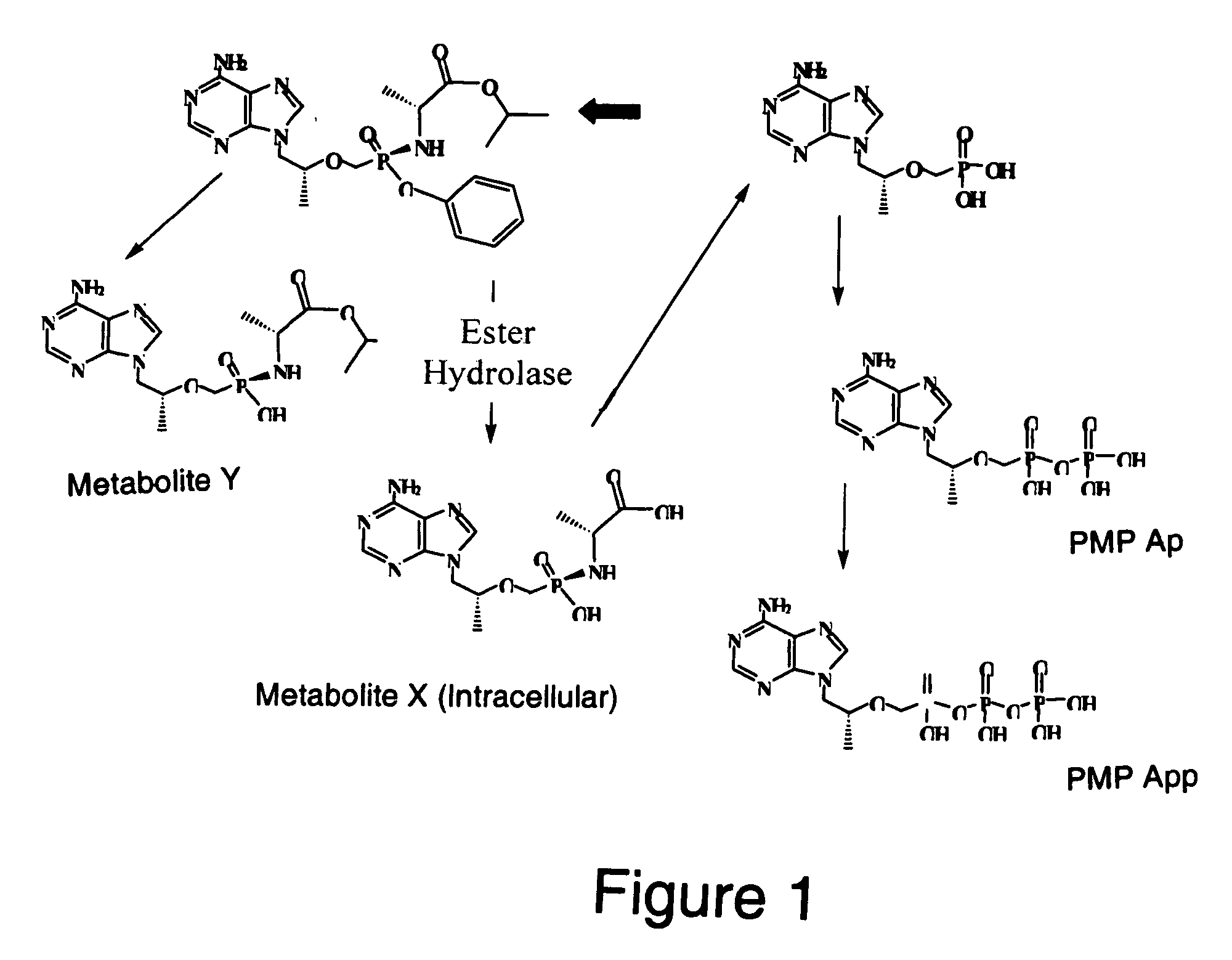
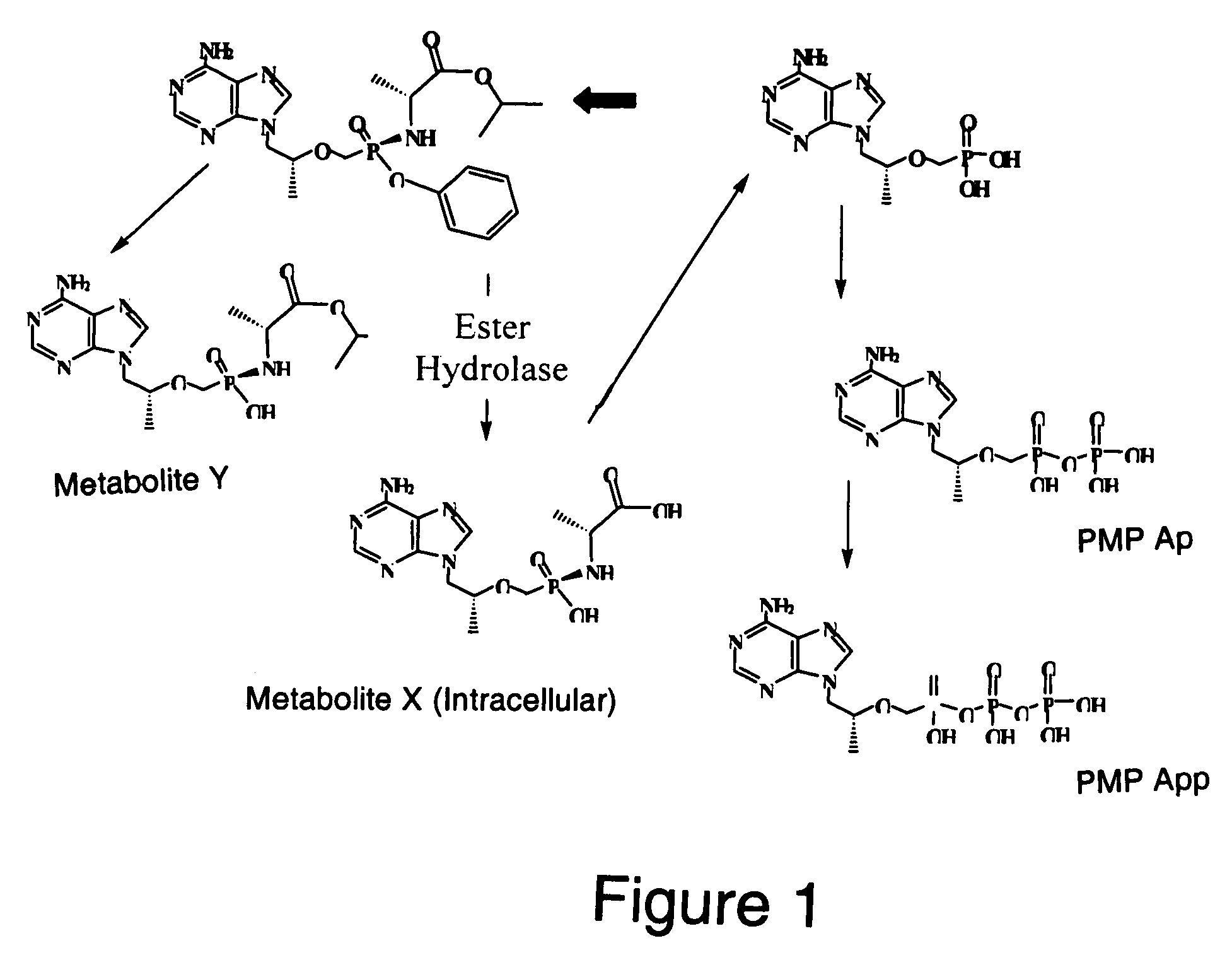
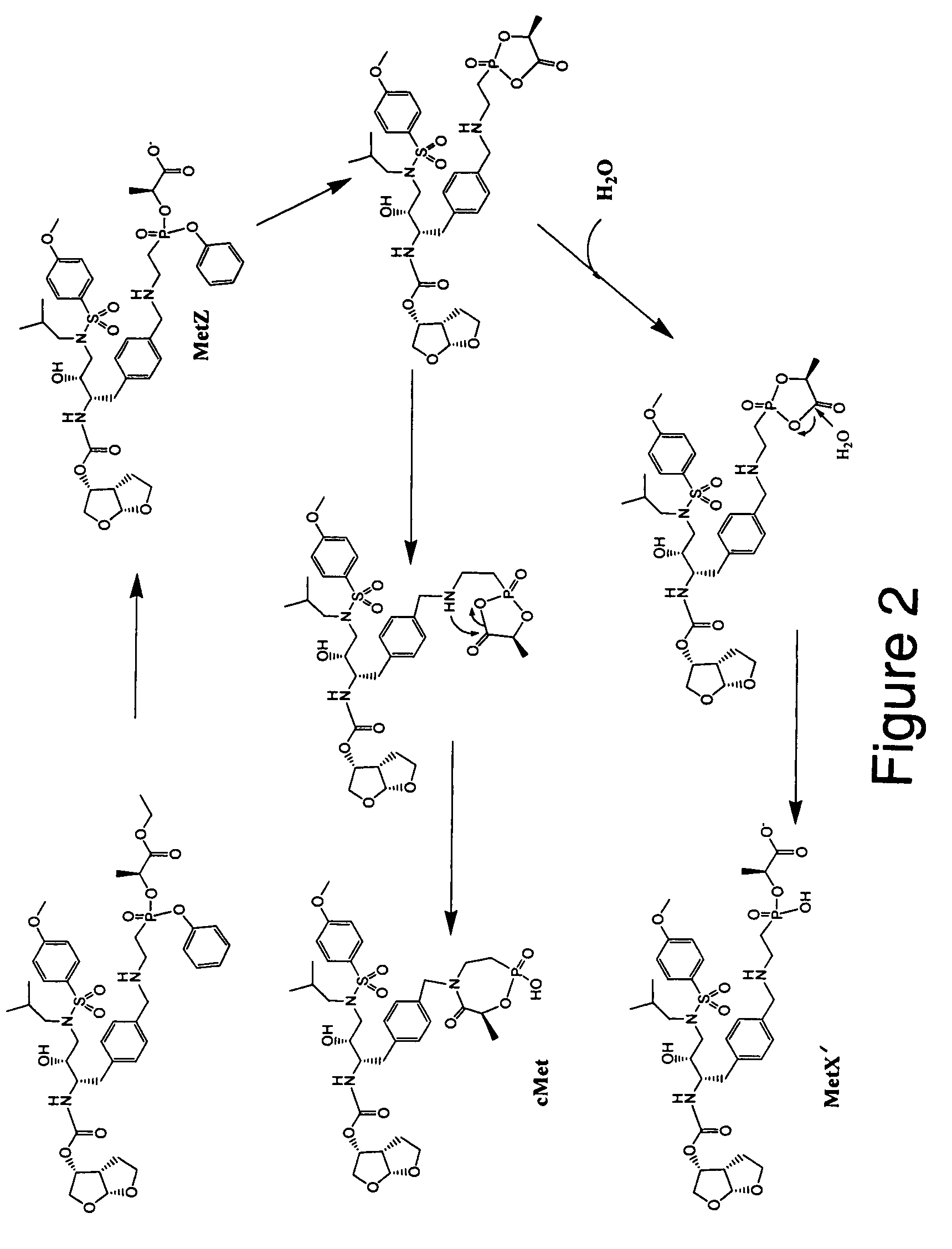
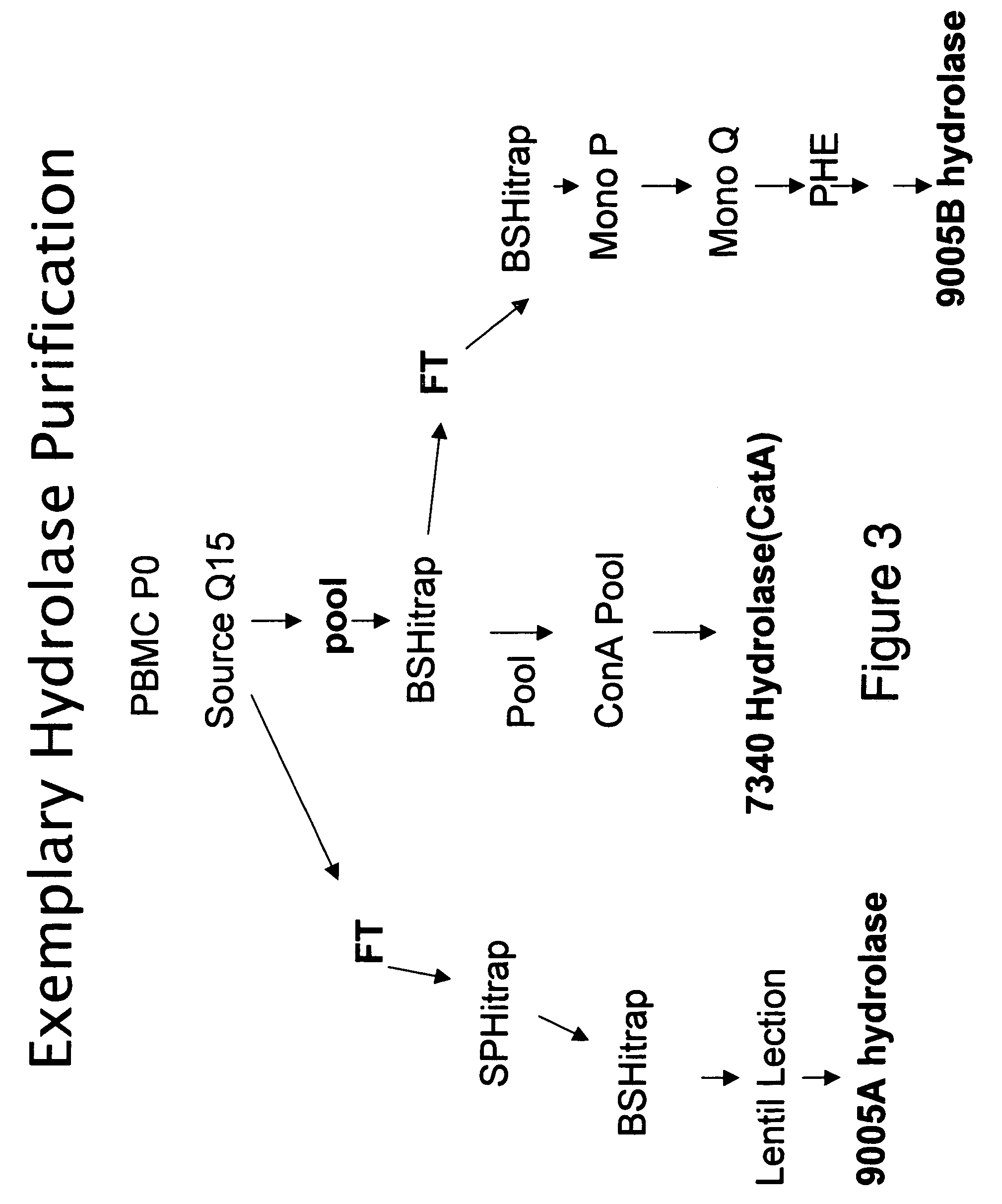
Methods and compositions for identifying therapeutic compounds with GS-7340 ester hydrolase
By the present invention, enzymes responsible for prodrug activation are identified and utilized for the identification of candidate compounds as prodrugs. The present invention includes methods for identifying a candidate compound as a suitable prodrug as well as methods of screening candidate compounds for suitability as therapeutic agents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
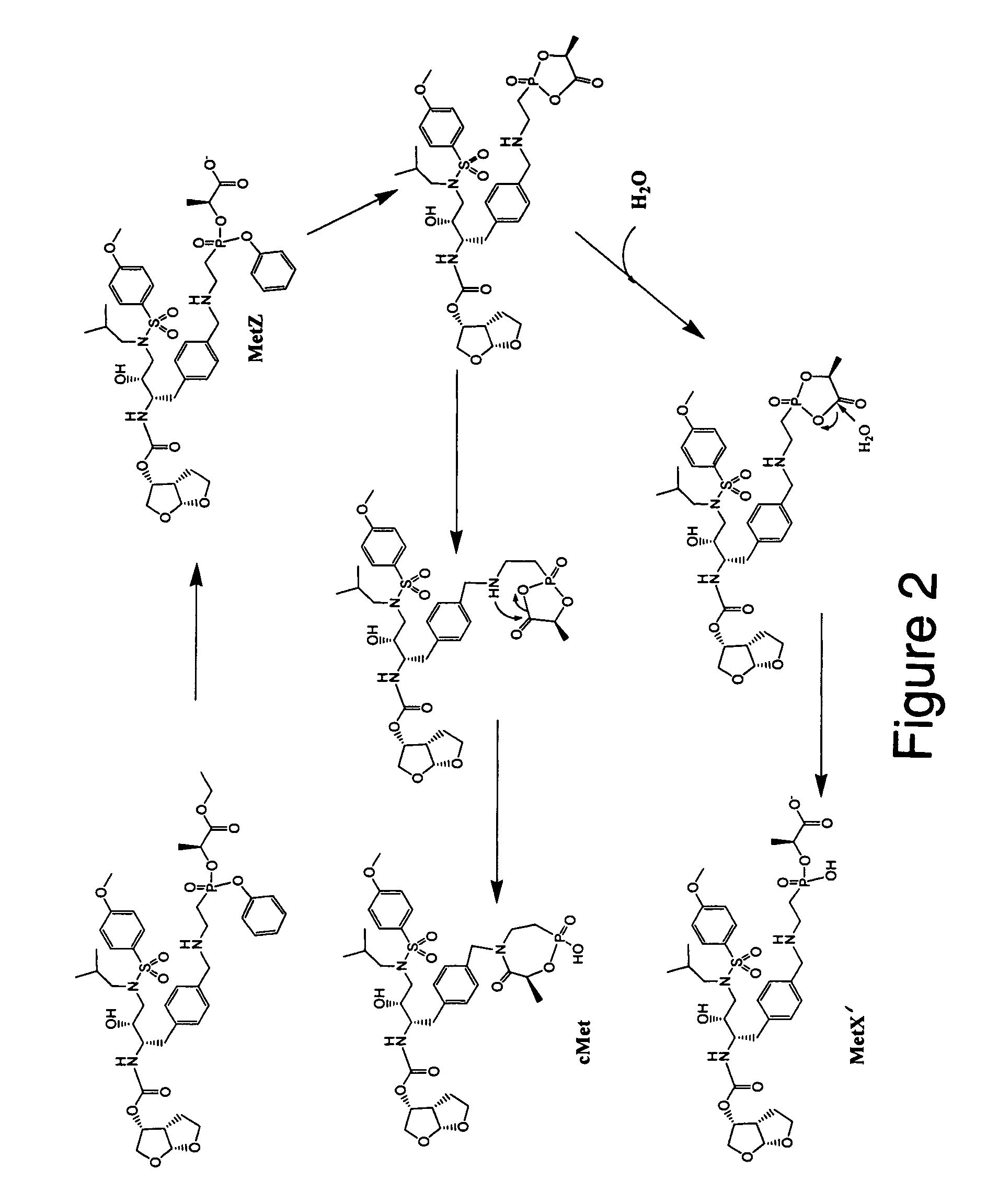
Methods and compositions for identifying therapeutic compounds with GS-9005 ester hydrolase A
By the present invention, enzymes responsible for prodrug activation are identified and utilized for the identification of candidate compounds as prodrugs. The present invention includes methods for identifying a candidate compound as a suitable prodrug as well as methods of screening candidate compounds for suitability as therapeutic agents.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
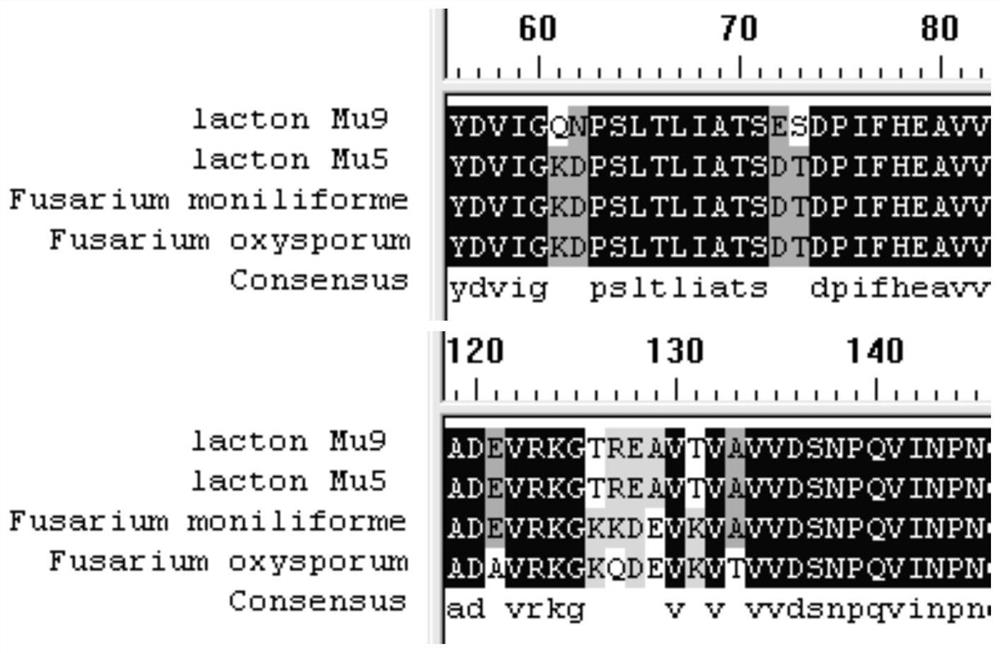
Levo lactone hydrolase producing fungus, and its method for preparing chiral hydroxy acid
InactiveCN1935977AStable enzyme productionHigh stereoselectivityImmobilised enzymesFungiEster hydrolaseEngineering industry
The invention relates to laevorotation lactone specificity hydrolytic enzyme producing strain and the method used it to make chirality oxyacid. The enzyme producing is Fusarium proliferatum Nirenberg ECU2002 with storage number CGMCC 1494. The chirality oxyacid preparing method includes the following steps: using the fungous mycelium, rough enzyme extract or their immobilization derivative as biocatalyst; processing antipode selectivity hydrolysis resolution for a series of racemic chirality lactone to gain many optically active (+)-oxyacid and (+)-lactone which can be hydrolyzed into (-)-oxyacid; (+)-alpha-hydroxyl-beta, beta-dimethyl-gamma-butyric acid which are D-(+)-pantoic acid; simple acidizing to gain chirality intermediate D-(-)-pantoic acid lactone widely used in preparing feed and daily chemical engineering industry.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods To Control Organic Contaminants In Fibers Using Zeolites
InactiveUS20150053358A1Easy to controlReduce viscosityFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulp bleachingFiberSufficient time
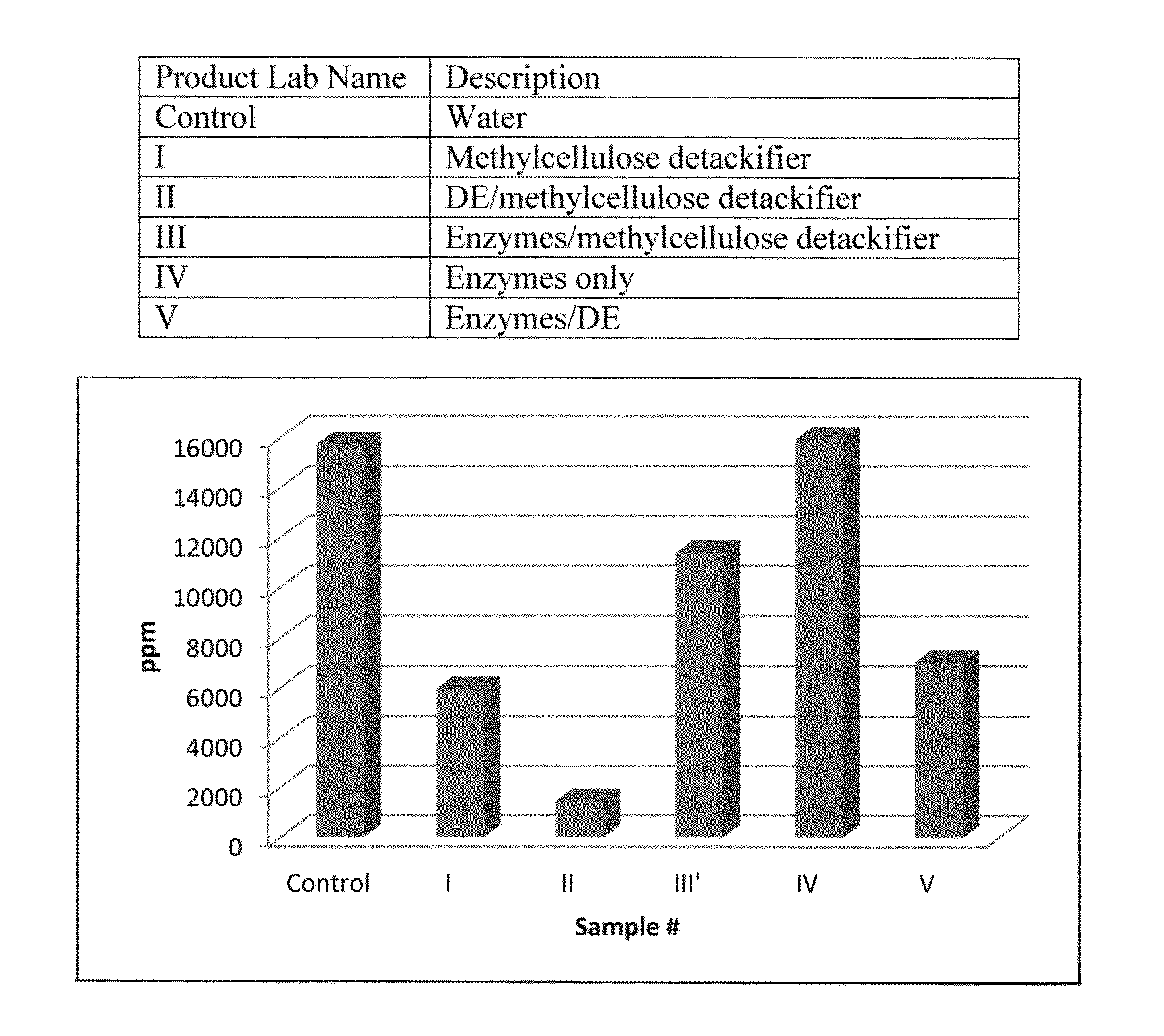
Methods to control organic contaminants in fibers are described. One method involves contacting the fibers with a) at least one zeolite and optionally b) detackifier, or an ester hydrolyzing enzyme, or both, for a sufficient time and in a sufficient amount to control the organic contaminants present in the fibers. This method is effective to reduce stickies in paper mill furnish formed with recycled fibers. A method for pitch control in paper mill furnish formed with virgin fibers is also provided. Resulting paper products formed from the processed fibers are also described as well as methods to make them.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Immobilized alpha-amino-acid ester hydrolase, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101525603AMany preparation stepsShort manufacturing cycleHydrolasesChemical industryCross-linkPenicillin
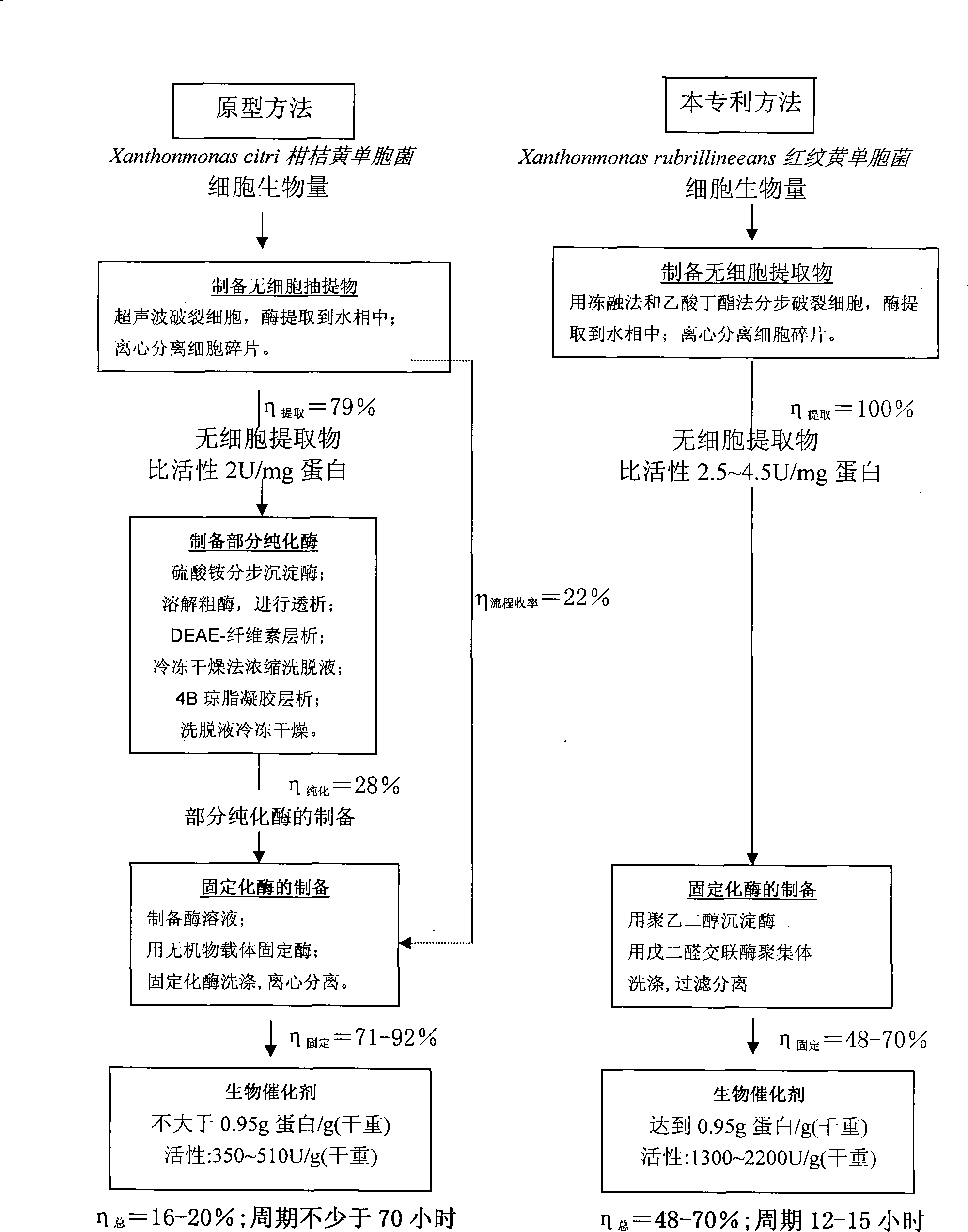
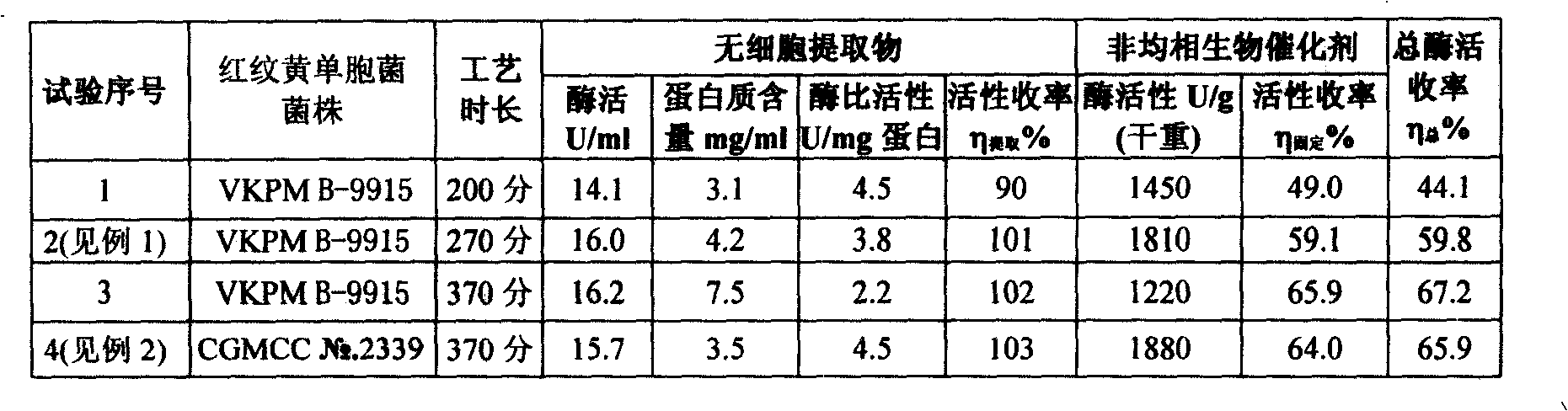
The invention discloses a heterogeneous biocatalyst taking alpha-amino-acid ester hydrolase as basis, a preparation method thereof and application in synthesizing amino beta-lactams. The activity of catalyst synthetase is 2,200 U / g by dry weight, and the content of protein is 0.95 g / g by dry weight; and xanthomonas rubrilineans cell biomass is processed in an organic solvent under a pH gradient through low temperature effect to extract enzyme, and enzyme aggregates are deposited and cross-linked to obtain the hydrolase. The alpha-amino-acid ester hydrolase as a catalyst can be synthesized into amino penicillin and amino cephalosporin drugs through acylating a beta-lactam compound by D-phenylglycine methyl ester derivatives in water or in a mixed medium of water and an organic solvent.
Owner:SICHUAN INDAL INST OF ANTIBIOTICS CHINA NAT PHARMA GROUP CORP +1
Methods To Control Organic Contaminants In Fibers
InactiveUS20130180677A1Easy to controlReduce viscosityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberSufficient time
Methods to control organic contaminants in fibers are described. One method involves contacting the fibers with a) diatomaceous earth and b) detackifier, or an ester hydrolyzing enzyme, or both, for a sufficient time and in a sufficient amount to control the organic contaminants present in the fibers. This method is effective to reduce stickies in paper mill furnish formed with recycled fibers. A method for pitch control in paper mill furnish formed with virgin fibers is also provided. Resulting paper products formed from the processed fibers are also described as well as methods to make them.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Biological resolution method for amino acid
InactiveCN101186944AAchieve the purpose of splittingReduce intermediate operationsFungiMicroorganism based processesEster hydrolaseAspergillus oryzae
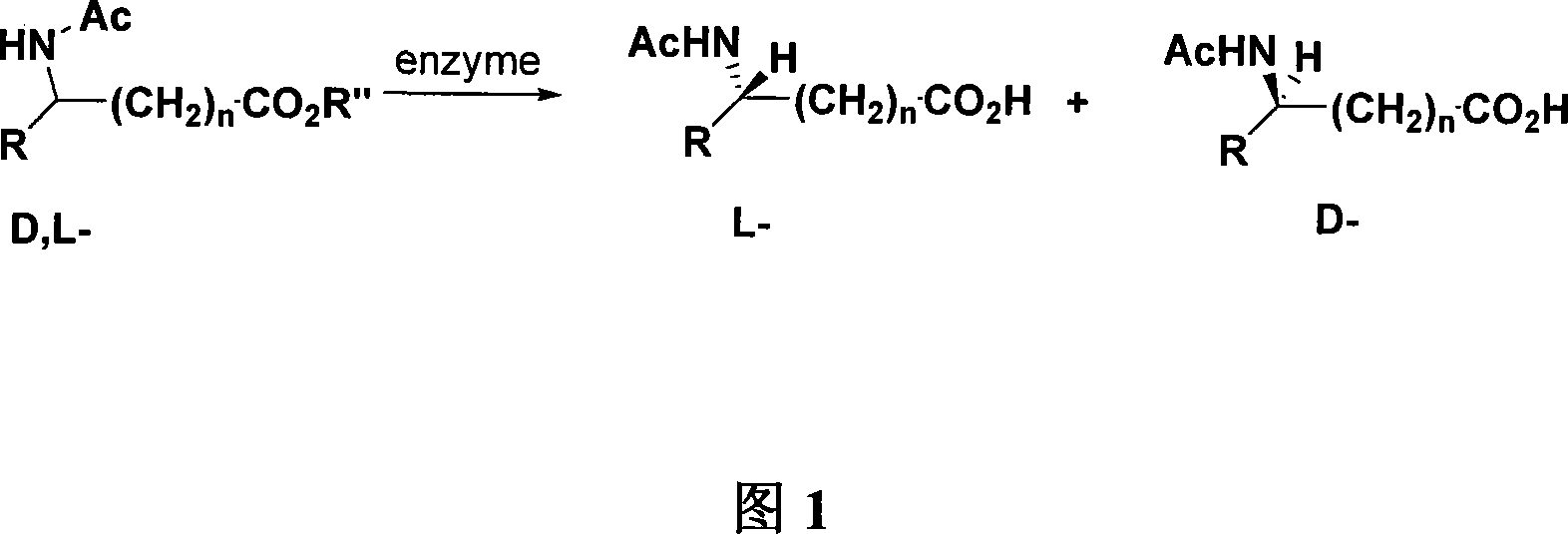
The invention relates to the field of biochemical engineering, in particular to a novel process for preparing L-amino acid and D-amino acid by direct biocatalysis and hydrolysis resolution for DL-N-acetyl amino acid esters. DL-N-acetyl amino acid esters is used as substrate, enzyme including amide hydrolase and ester hydrolase is used as catalyst, wherein the enzyme is achieved by fermenting aspergillus oryzae Lb3085, de-ionized water is utilized as solvent and added in an enzyme catalysis reactor, and L-N-acetyl amino acid esters of the substrate is hydrolyzed into L-amino acid, D-N-acetyl amino acid esters of the substrate is hydrolyzed into D-N-acetyl amino acid, thereby resolution is realized. The resolution technique of 'one bacterium two enzymes' can efficiently reduce operating intermediate process, and achieve purposes of convenience and cleaning.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methods and compositions for identifying therapeutic compounds with GS-9005 ester hydrolase B
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Esterolytic enzyme, coding gene, carrier, engineering bacterium and application of coding gene
ActiveCN103820417AHigh activityHigh stereoselectivityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyBacillus megaterium
The invention provides esterolytic enzyme from bacillus megaterium, a coding gene of the esterolytic enzyme, a carrier containing the coding gene, an engineering bacterium and application of the coding gene. The amino acid sequence of the esterolytic enzyme is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2; the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The recombined esterolytic enzyme provided by the invention can be used for synthesizing a stereoselective catalytic chiral compound and has high catalytic activity and stereoselectivity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase, encoding gene, carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN102796715AIncrease vitalityHigh resistance to organic solvents and stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesChemical industryEster hydrolase
The invention provides tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase, a gene for encoding the same, a carrier containing the encoding gene, engineering bacteria and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase is shown as SEQ ID No.2, and the amino acid sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase is high in short-carbon chain ester hydrolytic activity; and the enzymatic activity for catalyzing hydrolysis of p-nitrophenol butyrate in a Tri-HCl buffer solution with pH of 8.5 at the temperature of 50 DEG C can reach 3,010 U / mg. The esterase is high in strong organic solvent resistance stability and activity improving characteristic; and after the esterase is incubated in strong organic solvents such as normal hexane, toluene and dimethylbenzene, of which the partition coefficient Log P is greater than 3, the enzymatic activity still can be improved by 51 percent, 44 percent and 49 percent respectively. Moreover, the esterase has tertiary alcohol ester hydrolytic activity, so that the esterase can be widely used for hydrolyzing different tertiary alcohol ester substrates. The esterase, the encoding gene, the carrier, and the recombinant bacteria can be widely applied to ester catalysis of synthesis and resolution of chiral compounds related to tertiary alcohol substrates in medicine industry, food industry, chemical industry and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting G- and V-agents of chemical warfare and their degradation products
InactiveUS6897032B1Highly reliable identificationShorten the timeHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementEster hydrolaseHydrolase
Methods are described for detecting chemical warfare agents that contain organophosphorus compounds. Compositions containing either (1) a sufficient amount of phosphonate ester hydrolase with an alkali agent or (2) a sufficient amount of phosphonate ester hydrolase, a sufficient amount of organophosphorus hydrolase and a sufficient amount of a organophosphorus acid anhydrolase, may be utilized to test for organophosphorus compound-containing chemical warfare agents. These enzymes will react with such chemical warfare agents to produce degradation products, specifically phosphonate esters.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
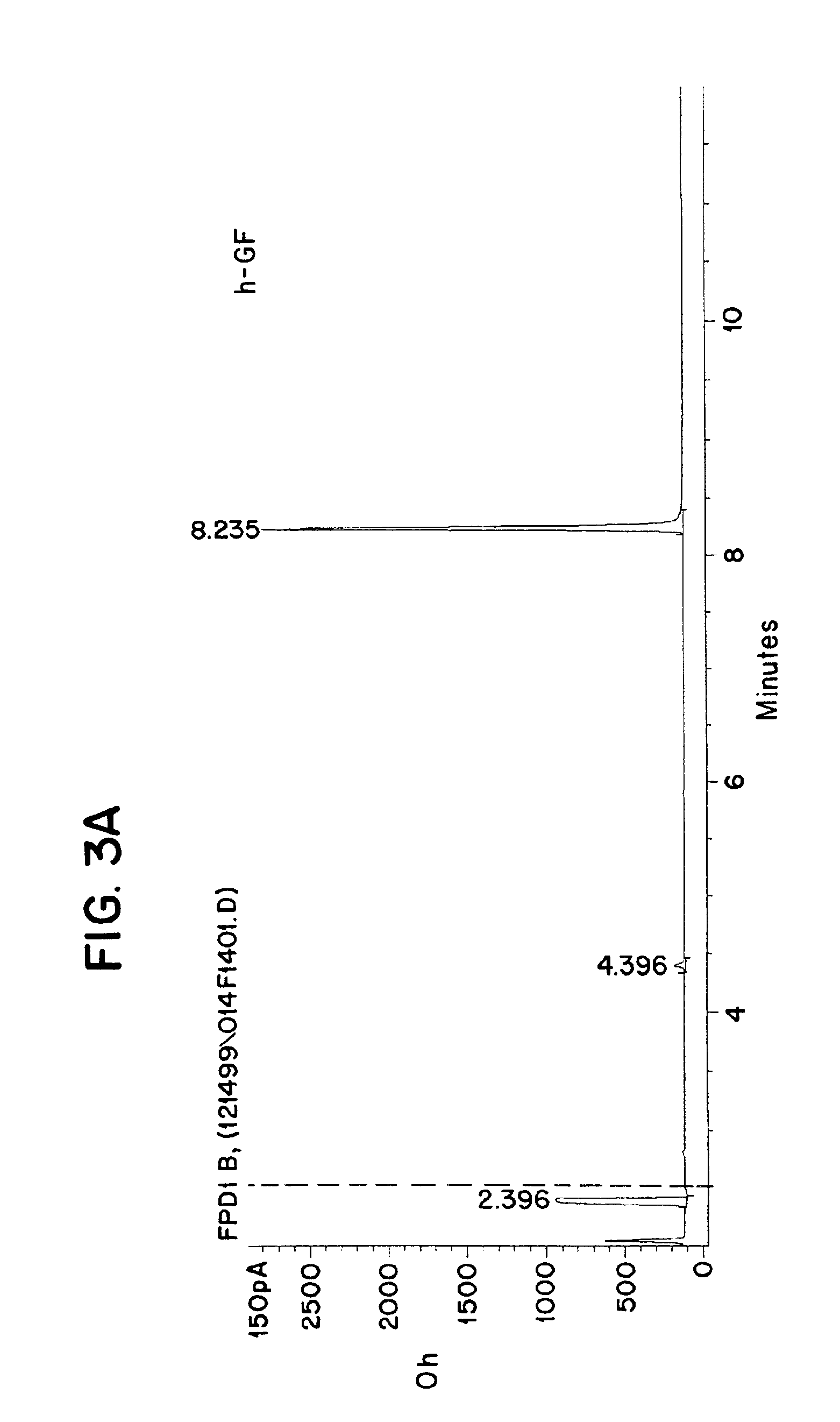
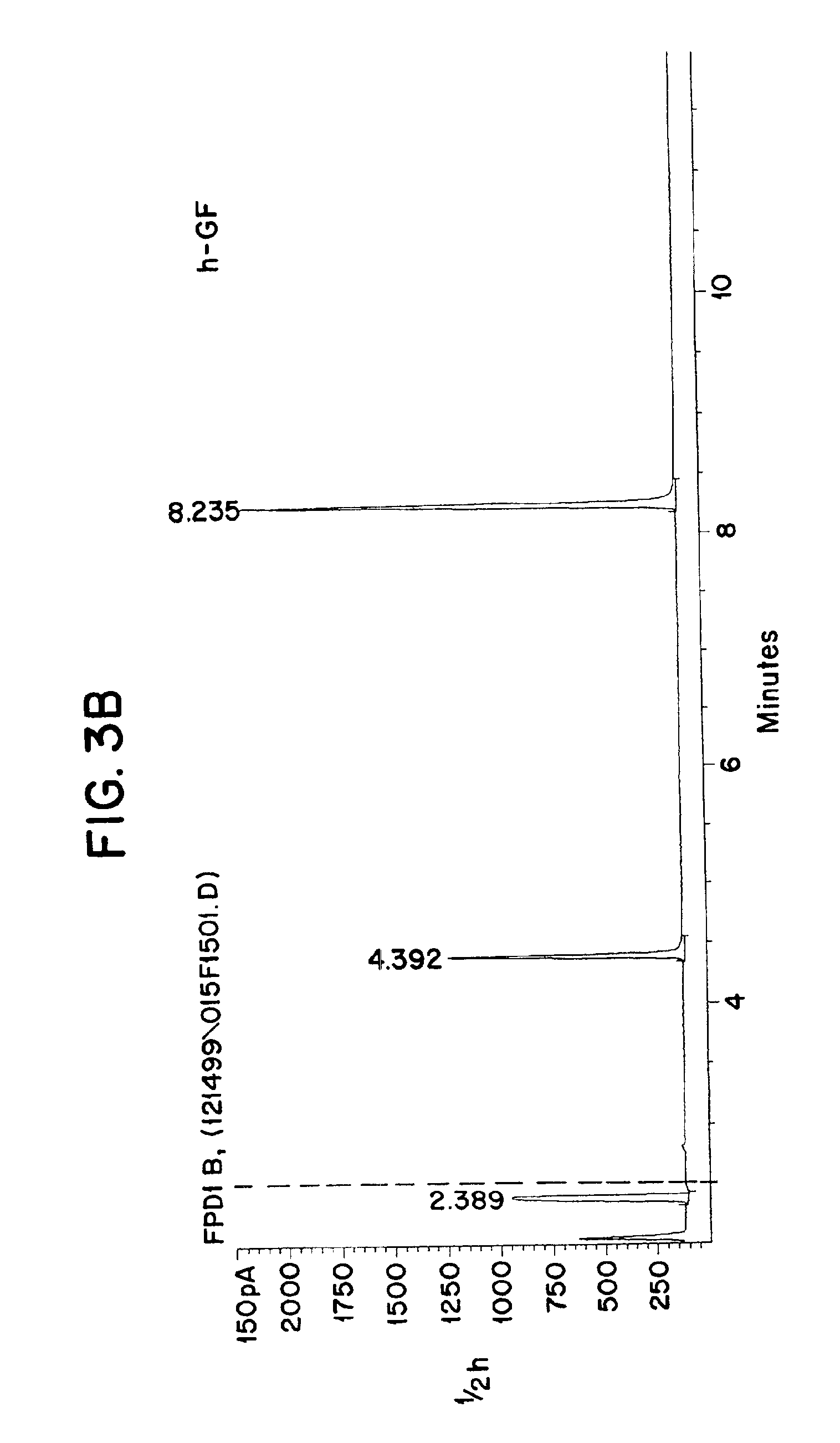
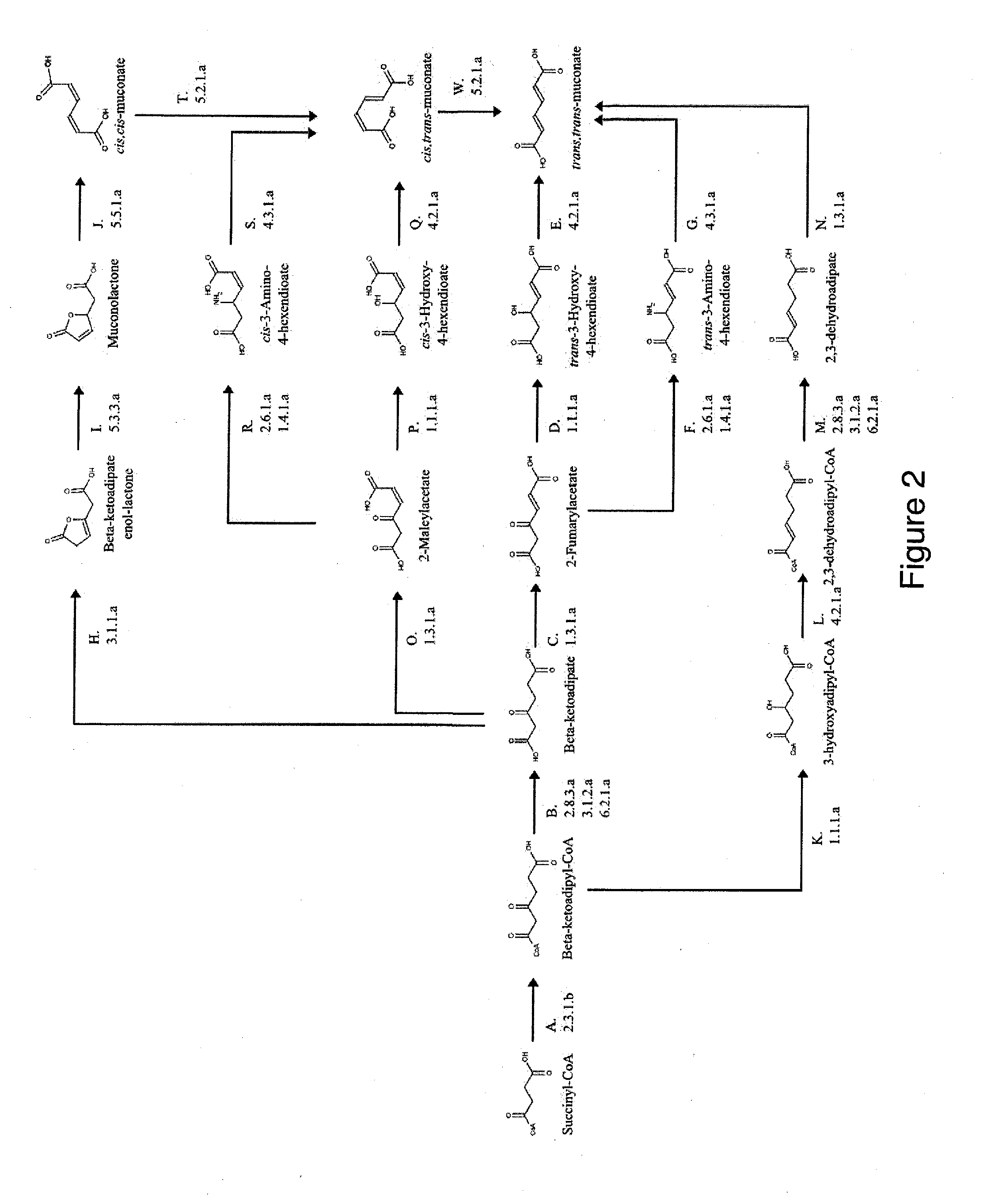
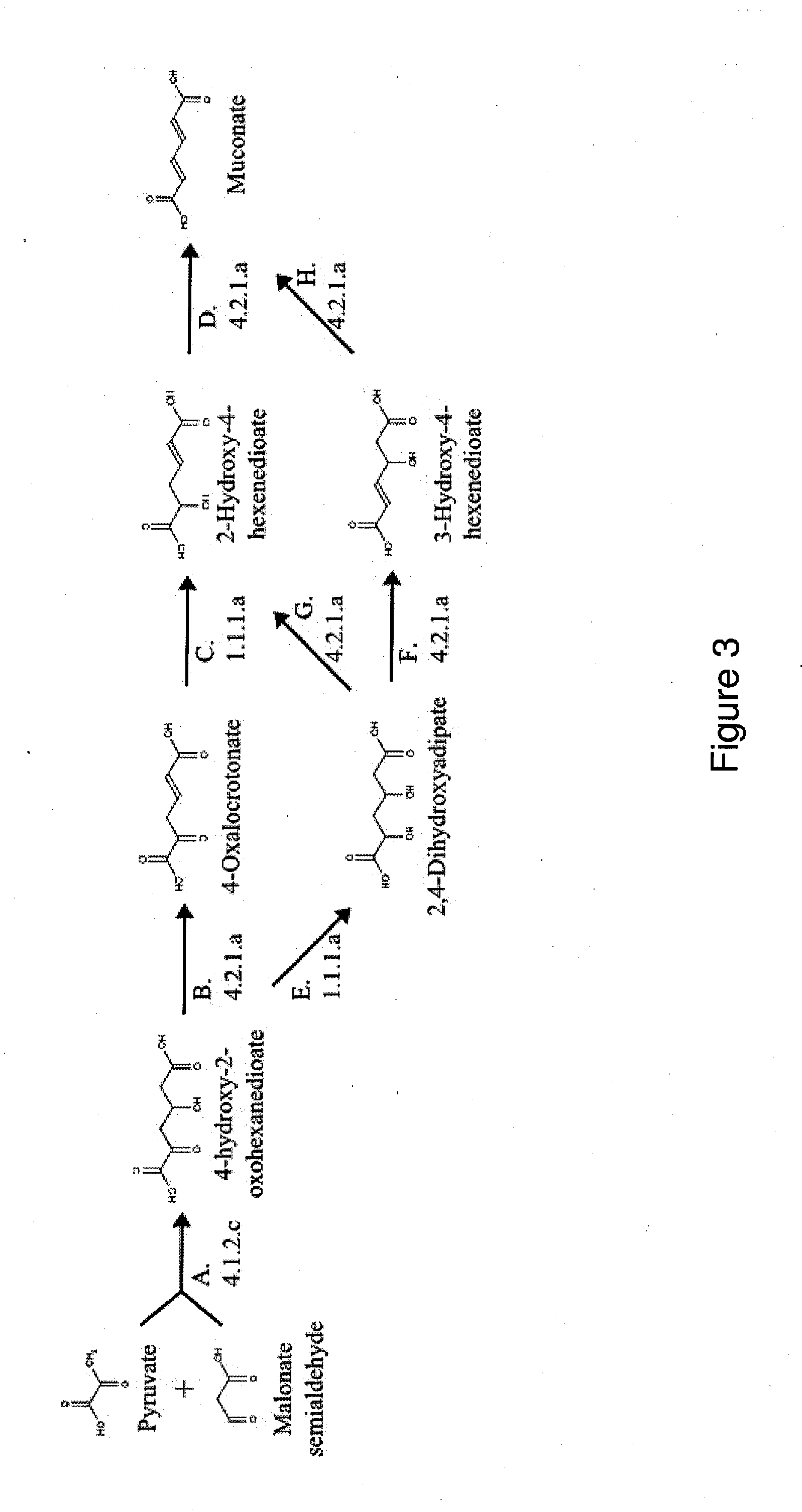
Semi-synthetic terephthalic acid via microorganisms that produce muconic acid
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a muconate pathway having at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a muconate pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce muconate. The muconate pathway including an enzyme selected from the group consisting of a beta-ketothiolase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA hydrolase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA transferase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA ligase, a 2-fumarylacetate reductase, a 2-fumarylacetate dehydrogenase, a trans-3-hydroxy-4-hexendioate dehydratase, a 2-fumarylacetate aminotransferase, a 2-fumarylacetate aminating oxidoreductase, a trans-3-amino-4-hexenoate deaminase, a beta-ketoadipate enol-lactone hydrolase, a muconolactone isomerase, a muconate cycloisomerase, a beta-ketoadipyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a 3-hydroxyadipyl-CoA dehydratase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA transferase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA hydrolase, a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA ligase, a muconate reductase, a 2-maleylacetate reductase, a 2-maleylacetate dehydrogenase, a cis-3-hydroxy-4-hexendioate dehydratase, a 2-maleylacetate aminoatransferase, a 2-maleylacetate aminating oxidoreductase, a cis-3-amino-4-hexendioate deaminase, and a muconate cis / trans isomerase. Other muconate pathway enzymes also are provided. Additionally provided are methods of producing muconate.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
High-stereoselectivity esterolytic enzyme, encoding gene and application of encoding gene
ActiveCN103820416AHigh activityHigh stereoselectivityBacteriaHydrolasesEster hydrolaseMethyl acetate
The invention provides high-R-isomer-stereoselectivity esterolytic enzyme, an encoding gene of the esterolytic enzyme, a carrier containing the encoding gene, an engineering bacterium and application of the encoding gene. An amino acid sequence of the esterolytic enzyme is shown as SEQ ID No.2, and a nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The esterolytic enzyme provided by the invention has higher catalysis activity and stereoselectivity, and can be used for preparing an optically pure chiral compound, particularly a levetiracetam intermediate, namely alpha-ethyl-2-oxygen-1-pyrrolidine methyl acetate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
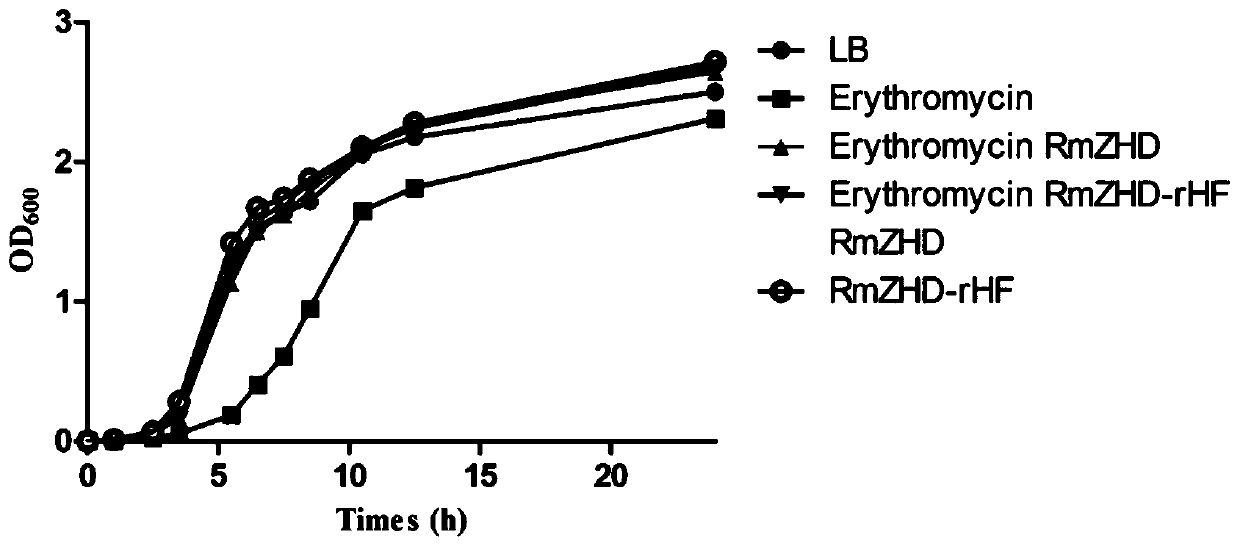
Application of zearalenone lactone hydrolase RmZHD in degradation of macrolide antibiotics
ActiveCN111202940AHigh activityHigh expressionHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEster hydrolaseMacrolide resistance
The invention discloses an application of zearalenone lactone hydrolase RmZHD in degradation of macrolide antibiotics. Research finds that the zearalenone hydrolase RmZHD can efficiently degrade macrolide antibiotics, and can be used for reducing antibiotic pollution in the environment. The invention also provides a recombinase RmZHD-rHF containing the zearalenone hydrolase RmZHD. The activity andexpression quantity of the enzyme of RmZHD can be further improved, and the application prospect is great.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
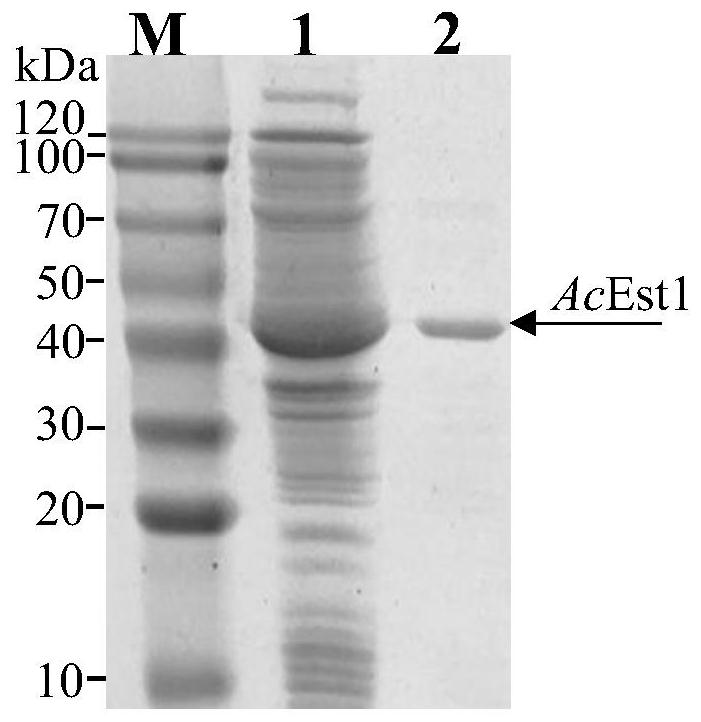
Cyclohexene formate hydrolase, and mutant, encoding gene, expression vector, recombinant bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN111778229AIncrease concentrationHigh optical purityOxygen-containing compound preparationBacteriaEster hydrolasePtru catalyst
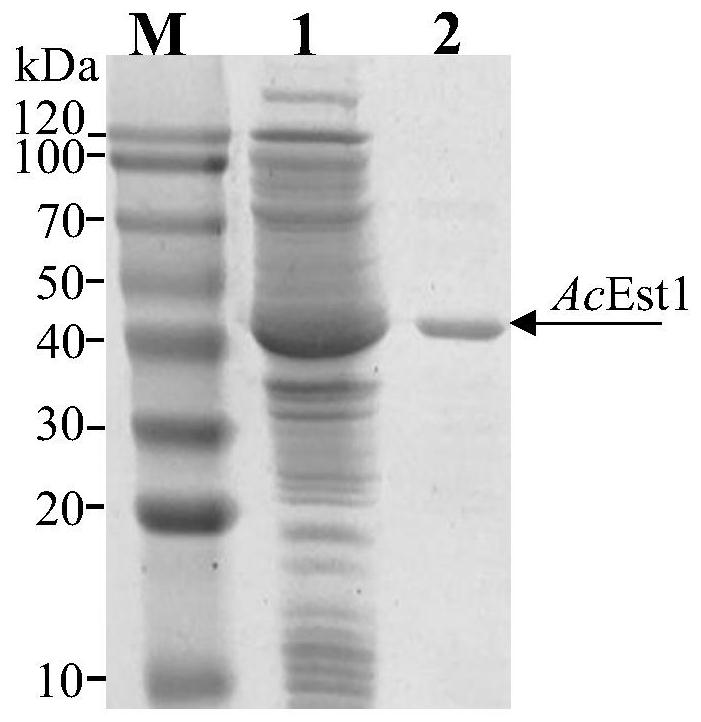
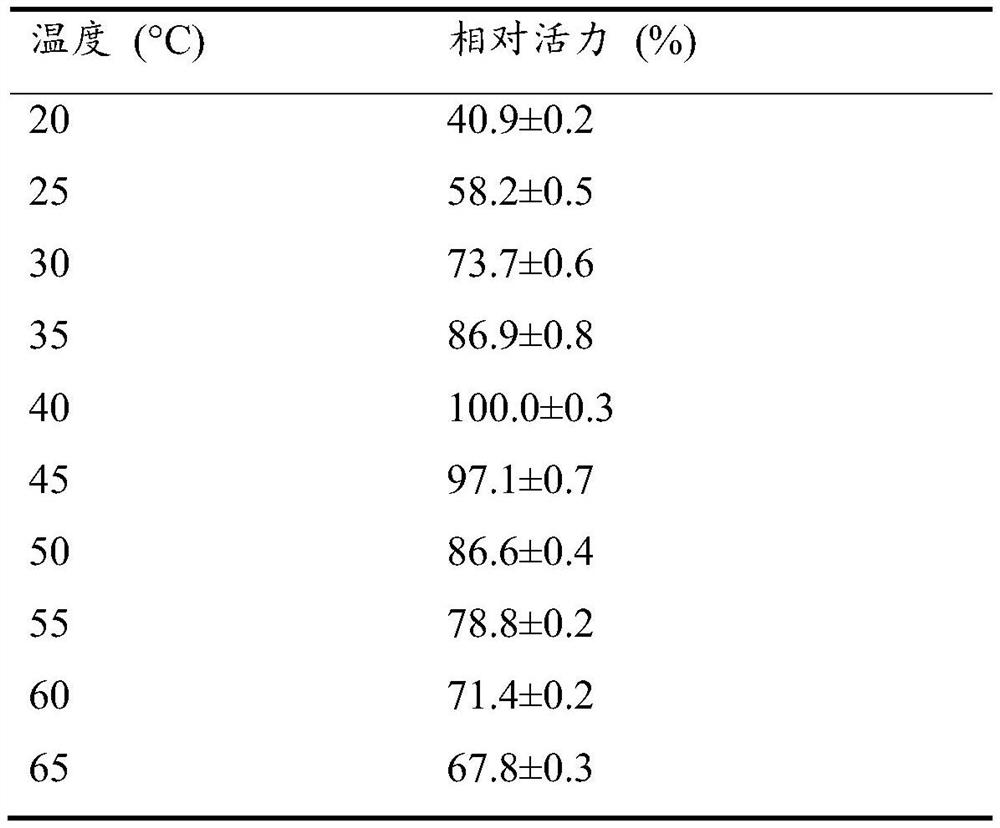
The invention discloses cyclohexene formate hydrolase, and a mutant, an encoding gene, an expression vector, recombinant bacteria and application thereof. The cyclohexene formate hydrolase AcEst1 andthe mutant thereof have the functions of efficiently splitting 3-cyclohexene-1-formate in an enantioselective mode and preparing optically active (S)-3-cyclohexene-1-formic acid. When the concentration of a substrate is up to 2000 mM (about 280 g / L), optical purity of products is higher than 99% and the substrate / catalyst is up to 3500 g / g. Compared with other preparation methods, the product prepared by the method is high in concentration, good in optical purity, high in catalyst efficiency, mild in reaction condition, environment-friendly, simple and convenient to operate and easy to industrially amplify, and thus has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
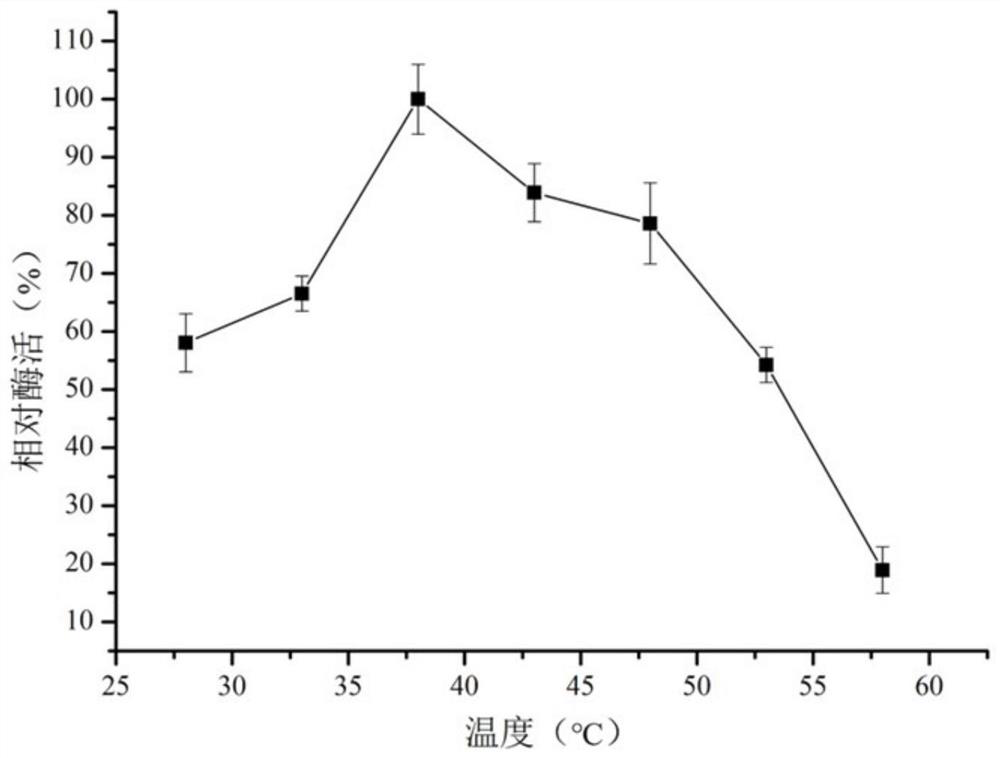
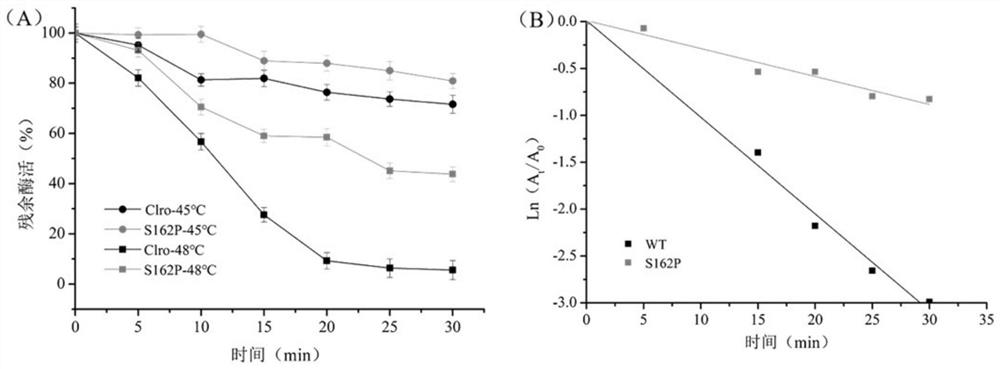
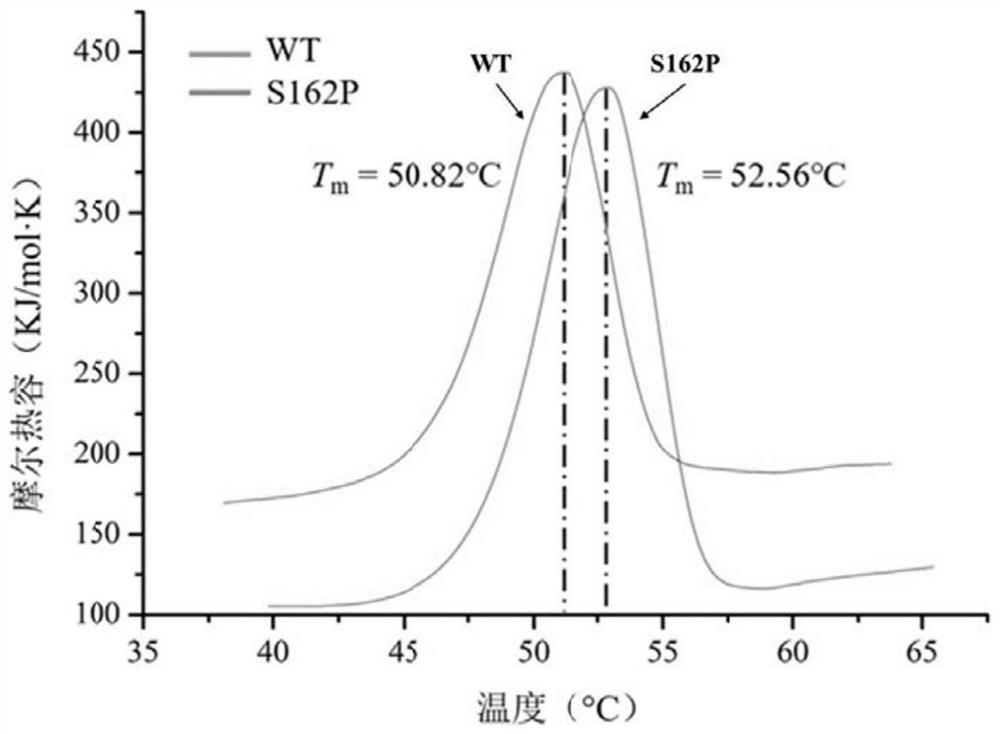
Zearalenone lactone hydrolase mutant S162P with improved thermal stability and application thereof
The invention discloses a zearalenone lactone hydrolase mutant S162P with improved thermal stability and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, zearalenone lactone hydrolase derived from a microorganism GliocladiumroseumMA918 is adopted as a parent, and a gene mutation technology is adopted to mutate serine (S) at the 162 site into proline (P) so as to obtain the single-site mutant S162P. Compared with a wild enzyme, on the basis that the original catalytic activity is not obviously changed, the thermal stability of the mutant enzyme is obviously improved: after the mutant enzyme is kept at 50 DEG C for 2 minutes, the residual enzyme activity is improved to be 1.52 times of that of the wild enzyme; and after heat preservation is conducted for 10 min and 20 min at the temperature of 48 DEG C respectively, about 80% and 58% residual enzyme activities are still remained, and the half-life period at the temperature of 48 DEG C is also increased by 3.6 times that of the wild enzyme. The invention lays a certain foundation for industrial application of the ZEN lactone hydrolase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Urine protein marker of ovarian cancer and diagnosis application thereof
InactiveCN109270276AComponent separationBiological testingEster hydrolaseRab GDP dissociation inhibitors
The invention relates to a urine protein marker of ovarian cancer and a diagnosis application thereof, in particular to a urine protein marker obtained by using in-situ injection of ovarian cancer cells in a rat ovary and mass spectrum analysis, and application in the diagnosis and disease course monitoring of human ovarian cancer. The urine protein marker is selected from cystathionine-gamma-lyase, a Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta, an ester hydrolase C11orf54 homolog, neutral and alkaline amino acid translocator rBAT, apolipoprotein A-1, OX-2 membrane glycoprotein, charged multivesicularbody protein 5, beta-amino hexosaminidase subunit beta, monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, cadherin 1, gastricsin, a serine protease inhibitor A3M, alpha-1-asialoglycoprotein and the like. Differential protein obtained from the marker provides a simpler, quicker and non-invasive choice for early diagnosis and disease course monitoring of ovarian cancer.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganism of producing D-pantothenic acid enternal ester hydrolase and process for preparing D-pantothenic acid thereof
The invention relates to a method used microorganism enzyme resolution DL-pantoic acid lactone to produce D-pantoic acid. It uses the D-pantoic acid lactone hydrolase strain of the fusarium, gibberella, aspergillus, penicillium, rhizopus, gliocladium, aureobasidium to ferment and culture, uses wet thallus as coarse enzyme, DL-pantoic acid lactone as substrate to produce D-pantoic acid. L- pantoic acid lactone can be reclaimed. The DL-pantoic acid lactone gained by racemization reaction can newly be used to do resolution.
Owner:重庆鑫富化工有限公司 +1
Cyclohexene carboxyl ester hydrolase and its mutant, coding gene, expression vector, recombinant bacteria and application
ActiveCN111778229BIncrease concentrationHigh optical purityOxygen-containing compound preparationBacteriaHigh concentrationPtru catalyst
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
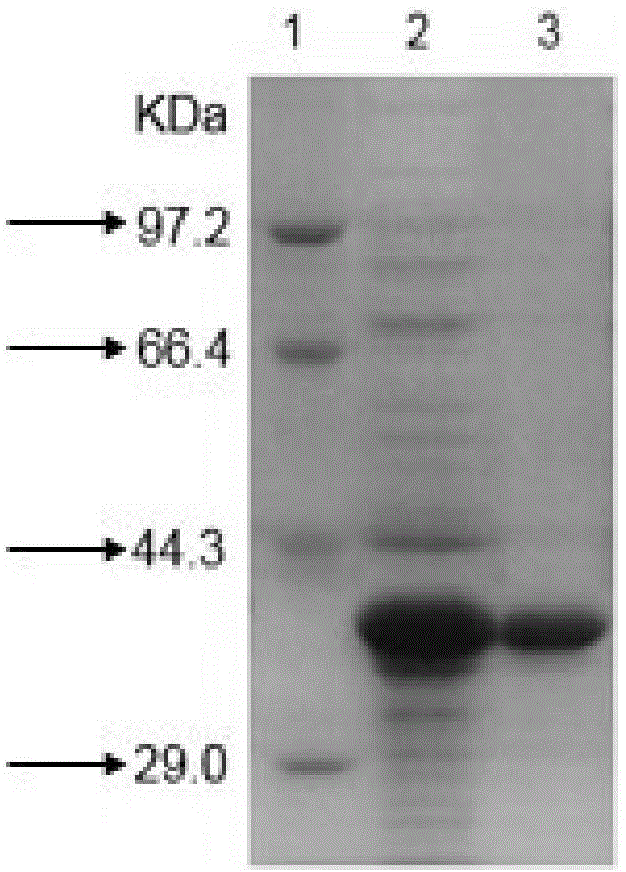
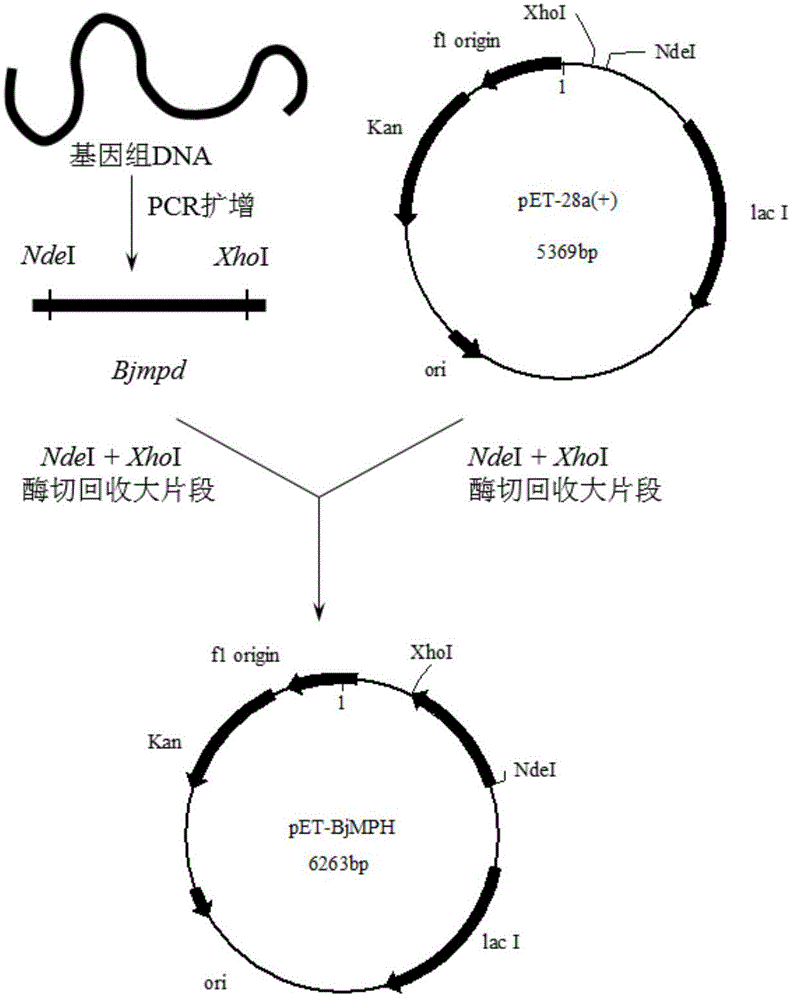
Burkholderia jiangsuensis strain, organophosphorus ester hydrolase and gene of organophosphorus ester hydrolase, and application of organophosphorus ester hydrolase in degradation of organophosphorus pesticide
The invention discloses a strain ECU1088, which is identified as burkholderia jiangsuensis. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.9028. The invention also discloses an organophosphorus ester hydrolase and the gene of the organophosphorus ester hydrolase expressed by the strain, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene of the organophosphorus ester hydrolase, a recombinant expression transformant, a recombinase of the strain and a preparation method of the recombinase, and a method for degrading an organophosphorus pesticide through the organophosphorus ester hydrolase or recombinant organophosphorus ester hydrolase. The burkholderia jiangsuensis strain and the recombinant organophosphorus ester hydrolase thereof has remarkable advantages of being good in catalyzing effect, mild in reaction conditions and environment-friendly in degrading the organophosphorus pesticide.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pantolactone hydrolase mutant strain and application thereof
The invention provides a pantolactone hydrolase mutant strain and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a mutant pantolactone hydrolase with significantly improved enzyme activity and a host cell for expressing the mutant pantolactone hydrolase. The invention further provides an enzyme preparation containing the mutant pantolactone hydrolase, D-pantolactone in a substrate DL-pantolactone can be completely hydrolyzed into D-pantoic acid, and the mutant pantolactone hydrolase is high in conversion rate, stable in property, capable of being repeatedly used and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHIFENG PHARMA CO LTD +1
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102199556BReduce contentIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesEster hydrolaseGenetic engineering
The invention discloses Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria EY-13 were collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 17, 2010, the collection number is CGMCC NO.4350, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria are recommended to be named Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PGK1 derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is selected as a promoter; and the construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with the high ester yield comprises a step of knocking-out an IAH1 gene for encoding ester hydrolase in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome when an ATF1 gene which is derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is used for encoding alcohol acetyltransferase is overexpressed. Compared with initial recipient bacteria, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria have the advantages that: after rice wine fermentation is simulated, the content of isoamylol is about one half, the content of ethyl acetate is improved by 20 times, the content of isoamyl acetate is 100mg / L, and the content of isobutyl acetate is 5 to 7mg / L; and after liquor fermentation is simulated, the content of total esters is improved by 4 times and the content of the ethyl acetate is improved by 35 times, so an excellent strain is provided for the production of brewing industry.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
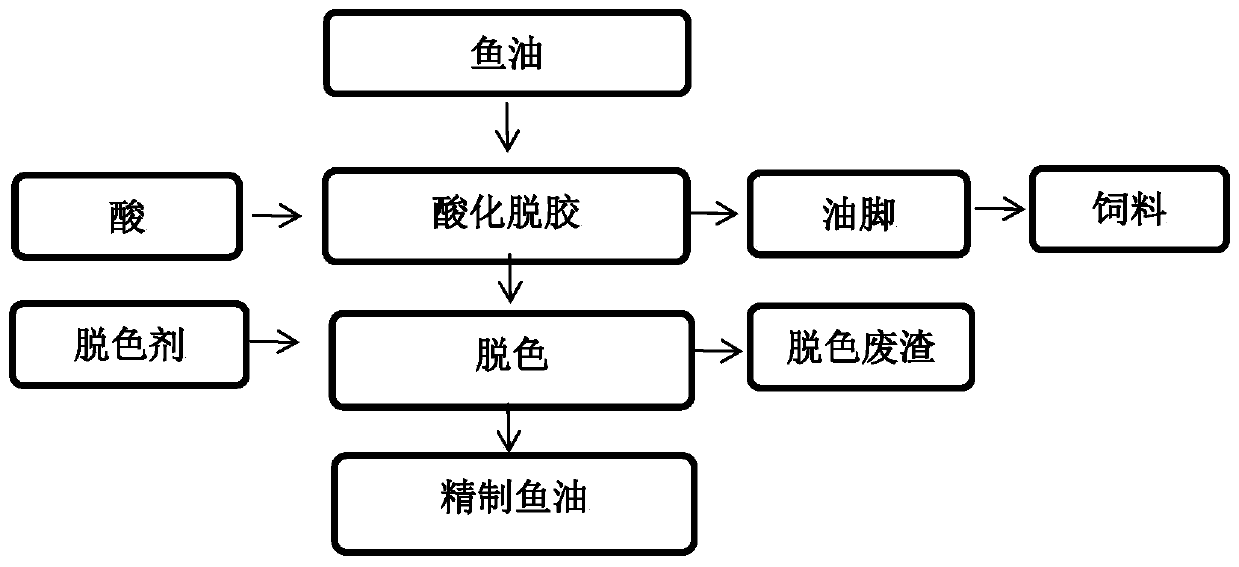
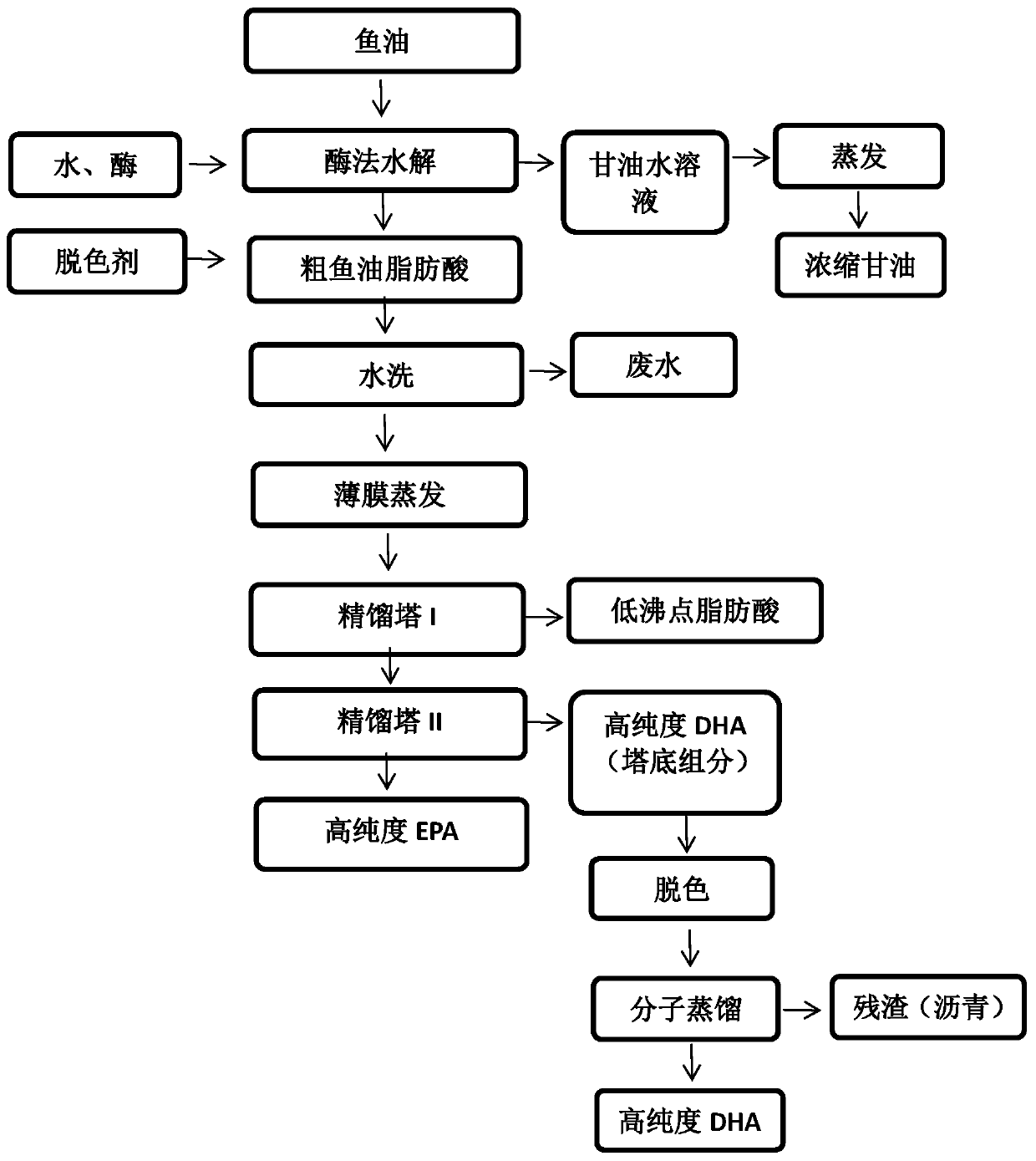
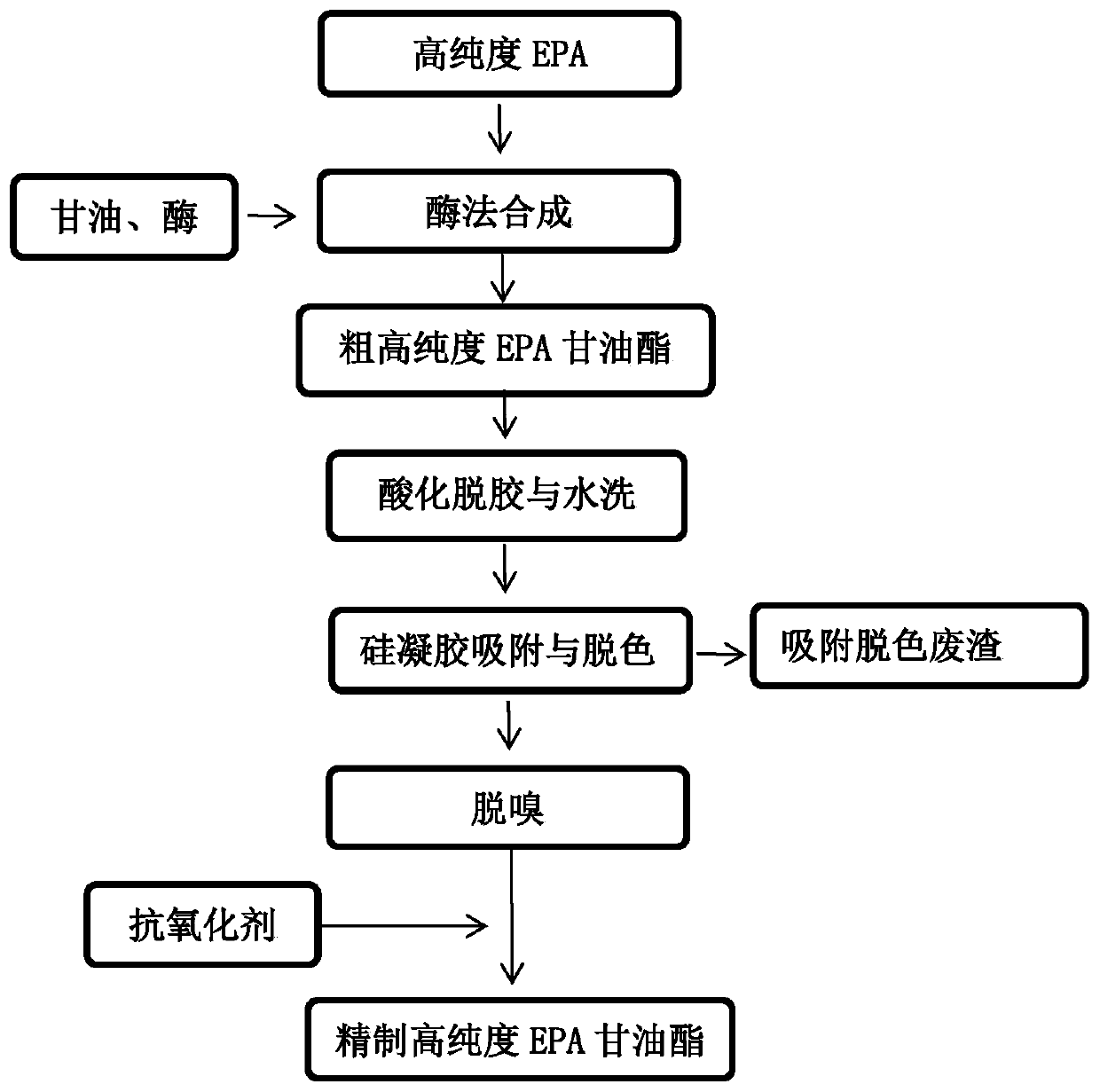
High-purity EPA glyceride and DHA glyceride preparation method
The invention discloses a high-purity EPA glyceride and DHA glyceride preparation method. The method includes steps: (1) performing fish oil enzyme catalytic hydrolysis, to be specific, adding water, fish oil and glyceryl ester hydrolase into a reactor, enabling reactants to be in an emulsified state under the condition of stirring, and adjusting pH, wherein final reaction products are fatty acid and glycerin aqueous solution; (2) separating and purifying fish oil fatty oil by a film evaporator and a rectifying tower to obtain high-purity EPA and DHA; (3) synthesizing EPA glyceride from EPA and glycerin through lipase; (4) synthesizing DHA glyceride from DHA and glycerin through lipase. The method is free of chemicals such as ethyl alcohol and urea, and a production process is simple; a multistage molecular distillation separation method which fails to realize large-scale production is substituted by a rectifying tower separation method which is easy to implement large-scale production, so that production efficiency is improved, and industrial environmental pollution is abated.
Owner:青岛和合汇途工程技术有限公司
Brewing method of nutritional and healthy blueberry wine with short brewage time
InactiveCN103146537AShorten brewing timeIncrease productivityAlcoholic beverage preparationEster hydrolaseNutrition
The invention provides a brewing method of a nutritional and healthy blueberry wine with a short brewage time, belonging to a field of wine brewage. The method comprises selecting fresh and high-quality blueberry, washing, air drying, putting into a crusher to crush into blueberry slurry, adding 15-45 ml / 480 kg of pectin methyl esters hydrolase and pectic acid enzyme into the blueberry slurry for biological enzymatic hydrolysis, with an enzymatic hydrolysis temperature being controlled between 50-60 DEG C and an enzymatic hydrolysis time being controlled between 30-90 DEG C, using an ultrahigh pressure enzyme inactivation method to inactive the enzyme under 100 Mpa, cooling the blueberry slurry to a normal temperature after the enzyme inactivation, putting in a cool and dry place for 8-20 days to form an immersing liquid with a alcohol volume content of 10-11 %, adding 3-5 % of jujube, 2-3 % of matrimony vine, 4-6 % of longan and 1-4 % of honey into the immersing liquid by weight ratio, immersing for 100-140 days to obtain a new wine, adding 0.15-0.25 % by weight ratio of a clarificant to clarify and filter the new wine, blending the new wine with a rice wine so that an alcohol concentration reaches 10-11 DEG, and then filtering to obtain the finish product. The method has advantages of short brewage time, high clarification degree and high nutrition value.
Owner:王爽
Tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase, encoding gene, carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN102796715BIncrease vitalityHigh resistance to organic solvents and stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesChemical industryEster hydrolase
The invention provides tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase, a gene for encoding the same, a carrier containing the encoding gene, engineering bacteria and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase is shown as SEQ ID No.2, and the amino acid sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The tertiary alcohol ester hydrolase is high in short-carbon chain ester hydrolytic activity; and the enzymatic activity for catalyzing hydrolysis of p-nitrophenol butyrate in a Tri-HCl buffer solution with pH of 8.5 at the temperature of 50 DEG C can reach 3,010 U / mg. The esterase is high in strong organic solvent resistance stability and activity improving characteristic; and after the esterase is incubated in strong organic solvents such as normal hexane, toluene and dimethylbenzene, of which the partition coefficient Log P is greater than 3, the enzymatic activity still can be improved by 51 percent, 44 percent and 49 percent respectively. Moreover, the esterase has tertiary alcohol ester hydrolytic activity, so that the esterase can be widely used for hydrolyzing different tertiary alcohol ester substrates. The esterase, the encoding gene, the carrier, and the recombinant bacteria can be widely applied to ester catalysis of synthesis and resolution of chiral compounds related to tertiary alcohol substrates in medicine industry, food industry, chemical industry and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ester hydrolase with R-isomer stereoselectivity, gene and recombination enzyme thereof
The invention discloses a Bacillus sp. Code with R-isomer stereoselectivity of esterase gene BSEST, which provides BSEST sequence and amino acid sequence, the expression carrier Pbsest-pet with BSEST and the gene engineering bacterial with the carrier(E. coli BL21(DE3) / pBSEST-PET CGMCC No. 1648), and also provides the recombinant method of the esterase. The recombinant esterase can apply to the synthesis of stereoselectivity catalytic chirality compounds(R shape).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Recombinant bacterium of lipase expressing R configuration selectivity and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium of lipase expressing R configuration selectivity and application thereof. A lipase gene with R configuration selectivity is inserted into a multiple cloning site of a pET28a plasmid to obtain a recombinant plasmid; the recombinant plasmid is transformed into colibacillus SHuffle T7 to obtain the recombinant bacterium; the gene sequence of the lipasegene with the R configuration selectivity is a gene sequence of the following 1) or 2), wherein 1) is a DNA sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 in a sequence table; 2) is a DNA sequence with 90% homology orabove with the DNA sequence defined in 1) and used for encoding protein with esterolysis enzymatic activity. The recombinant lipase has higher R-configuration steric selectivity and catalytic activity, more than 85% of the enzyme activity is reserved under a condition with higher temperature, and the recombinant lipase can be used for splitting racemization 2-aryl-methyl propionate substances, and obtain optical pure S-type 2-aryl-methyl propionate substances.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com