Cyclohexene carboxyl ester hydrolase and its mutant, coding gene, expression vector, recombinant bacteria and application
A technology of cyclohexene carboxylate and coding genes, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of unsuitability for industrial production, low product concentration, and low activity of the enzyme itself, and achieve good industrial application prospects, high product concentration, and catalyst high efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
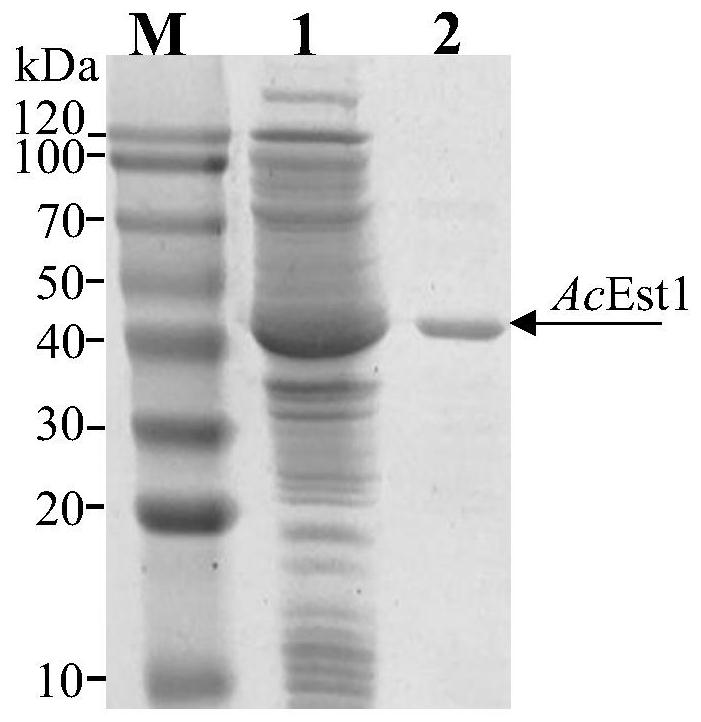
[0027] Embodiment 1: Cloning of cyclohexene carboxylate hydrolase AcEst1 gene
[0028]The strain Acinetobacter sp.JNU9335 was cultured in LB medium, and the total genomic DNA with high purity and large fragments was extracted by CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) method. Add appropriate amount of Acinetobacter sp.JNU9335 cells into liquid nitrogen to freeze, grind into powder, add appropriate amount of 2×CTAB extraction buffer (100mmol / L Tris-HCl, pH8.0, 20mmol / L EDTA, 1.4mol / L NaCl, 2% (w / v) CTAB, 40mmol / L mercaptoethanol), keep warm at 65°C for 10min, and shake intermittently. Then add an equal volume of chloroform / isoamyl alcohol, gently invert the centrifuge tube to mix, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 min at room temperature, transfer the supernatant to another centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of chloroform / isoamyl alcohol, and centrifuge upside down The tube was mixed and centrifuged at 8000rpm for 10min at room temperature. Transfer the upper aqueous phase into a...
Embodiment 2
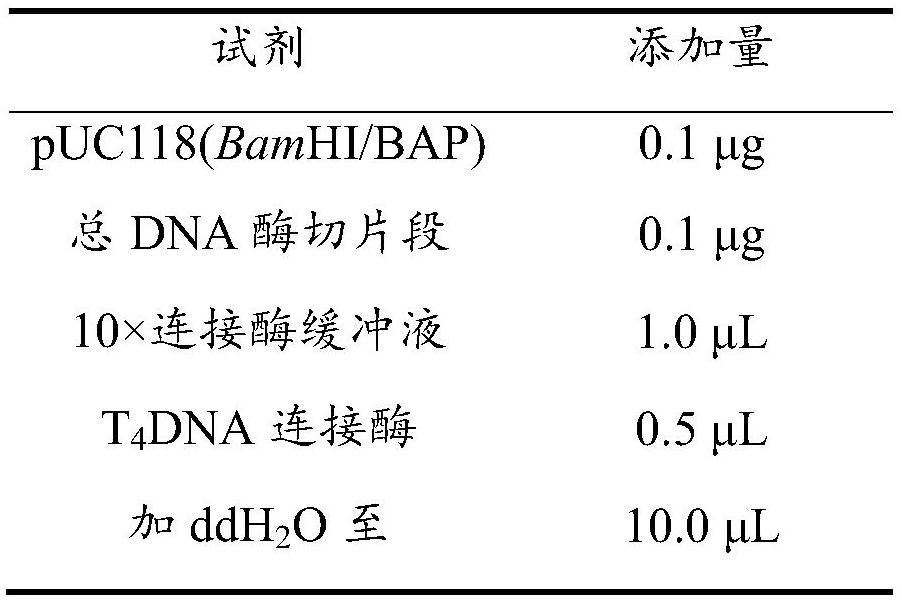
[0033] Embodiment 2: the preparation of the plasmid of recombinant AcEst1 and recombinant bacterium, recombinase
[0034] Using the polymerase chain reaction technique to obtain The nucleotide sequence of AcEst1 was amplified, and the obtained DNA fragment containing the AcEst1 sequence was double-digested with NdeI and XhoI, respectively, and then ligated with the plasmid pET-28a(+) that was also double-digested with NdeI and XhoI. The recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-AcEst1 was obtained.
[0035] The obtained recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-AcEst1 was transformed into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21, and the recombinant Escherichia coli containing cyclohexene carboxylate hydrolase AcEst1 was constructed and inoculated into the culture medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin In LB medium (peptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, pH 7.0), shake culture overnight at 37°C, and insert 600mL LB medium according to the inoculum size of 1% (v / v). Place in a 2L Erlenmeyer flask at 37°...
Embodiment 3
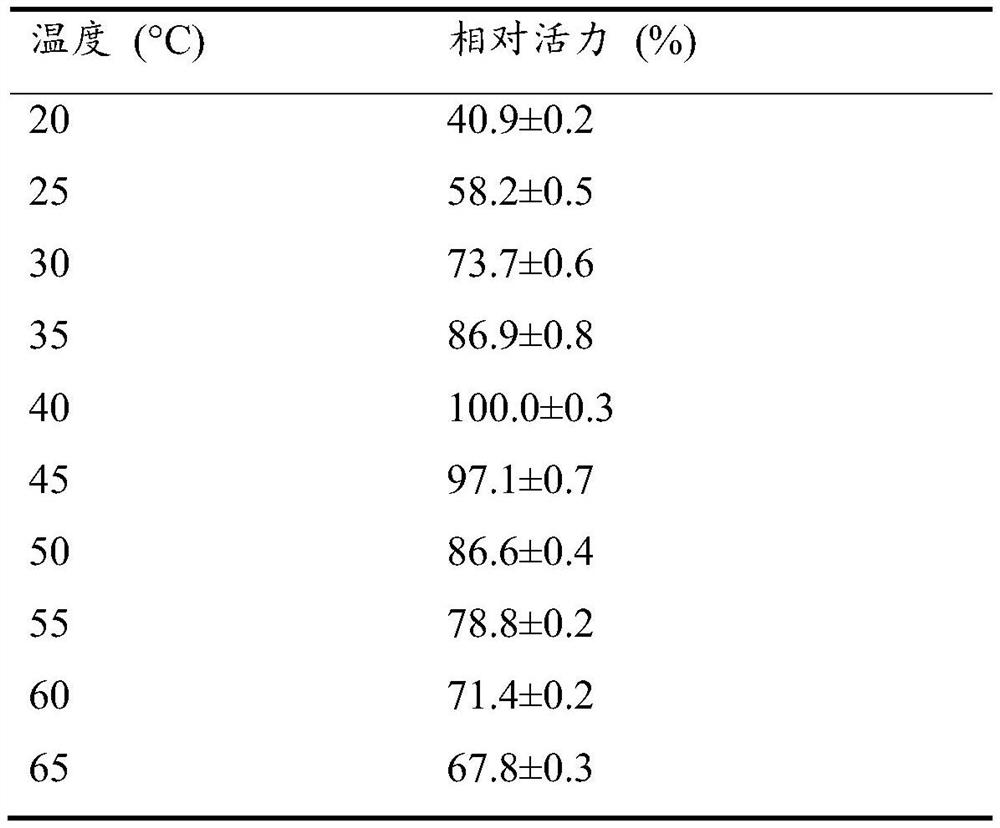
[0036] Embodiment 3: the acquisition of mutant A202K / G326A
[0037] Mutant A202K / G326A is a random mutant. The random mutant library of AcEst1 was established by error-prone PCR technology, and the color change of the indicator described in Example 1 under different pH environments was used as a means of high-throughput screening. First design primers at both ends: forward primer 5'-gtgccgcgcggcagccatatgATGGGCGTGTTGAATCAAACTT-3' (SEQ ID NO.5) reverse primer 5'-gtggtggtggtggtgctcgagTTATTTGGCATTCTTATCCCAAAA-3' (SEQ ID NO.6), PCR system (50 μL): rTaq polymerase 0.25 μL, 10×rTaq Buffer 5μL, dNTP 5μL, MgSO 4 2 μL, template plasmid about 100ng, forward primer 2 μL, reverse primer 2 μL, MnCl 2 (10mM) 0.5μL, ddH 2 O to make up to 50 μL.
[0038] PCR reaction program: (1) Denaturation at 98°C for 5min; (2) Denaturation at 98°C for 30s, (3) Annealing at 55°C for 30s, (4) Extension at 72°C for 1min, steps (2) to (4) were performed for 30 cycles in total, Finally, extend at 72°C for 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com