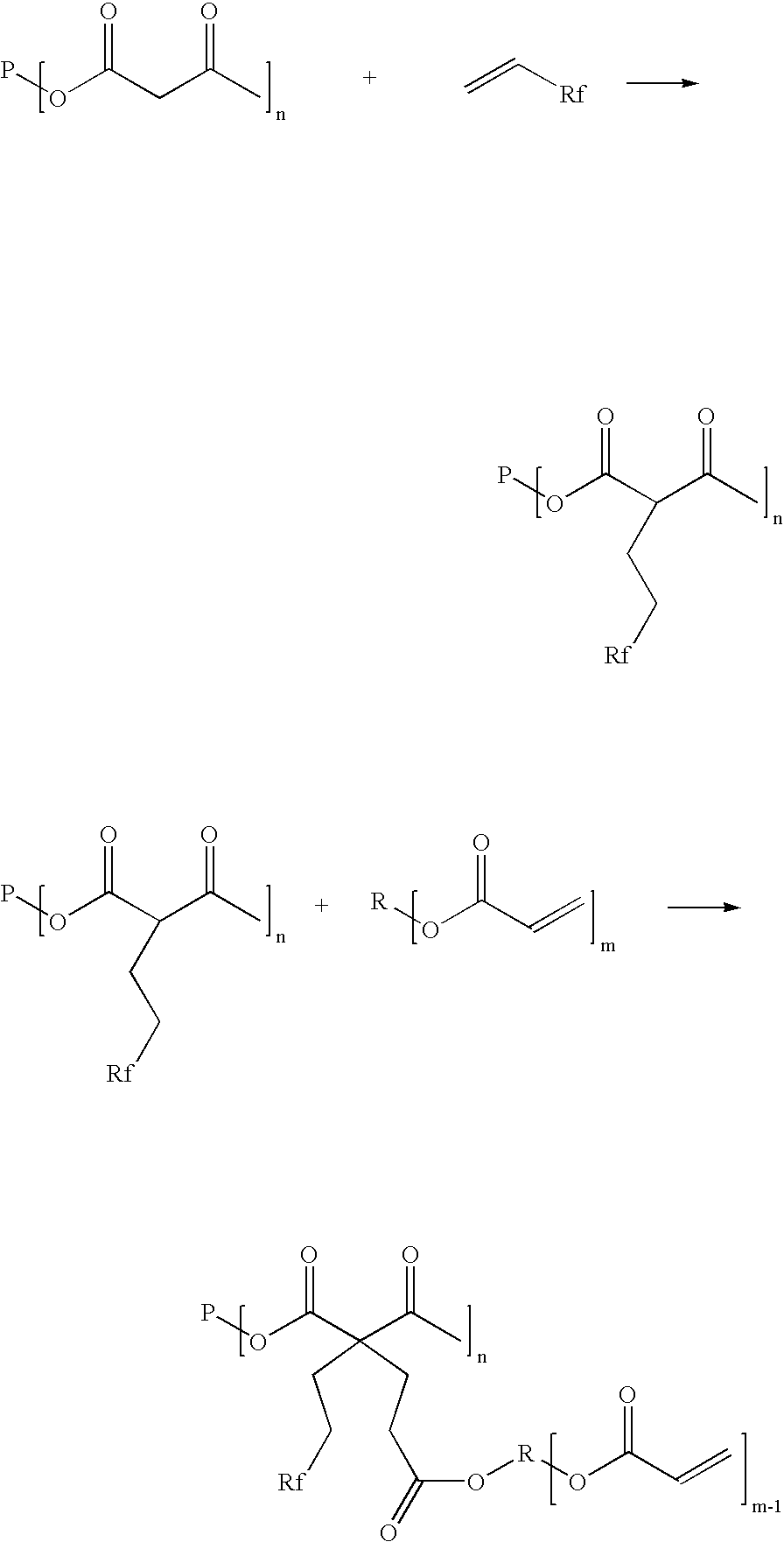
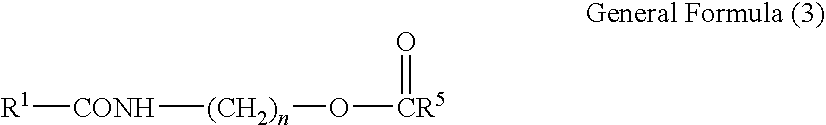Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135results about How to "Increase the molar ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amorphous silica-alumina, a carrier combination and a hydrocracking catalyst containing the same, and processes for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS6399530B1Increase surface areaLarge hole volumeMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingSilicon dioxideHigh activity
An acidic amorphous silica-amumina has a large specific surface area and a large pore volume. A carrier complex and a hydrotreating catalyst containing acidic amorphous silica-alumina, in particular a hydrocracking catalyst containing acidic amorphous silica-alumina in combination with a modified zeolite-Y, treats petroleum hydrocarbon materials to produce middle distillates. The amorphous silica-alumina has a SiO2 content of 10-50 wt. %, a specific surface area of 300-600 m2 / g, a pore volume of 0.8-1.5 ml / g and an IR acidity of 0.25-0.60 mmol / g. The catalyst shows a relatively high activity and mid-distillate selectivity and can be particularly used in hydrocracking process for producing mid-distillates with a higher yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
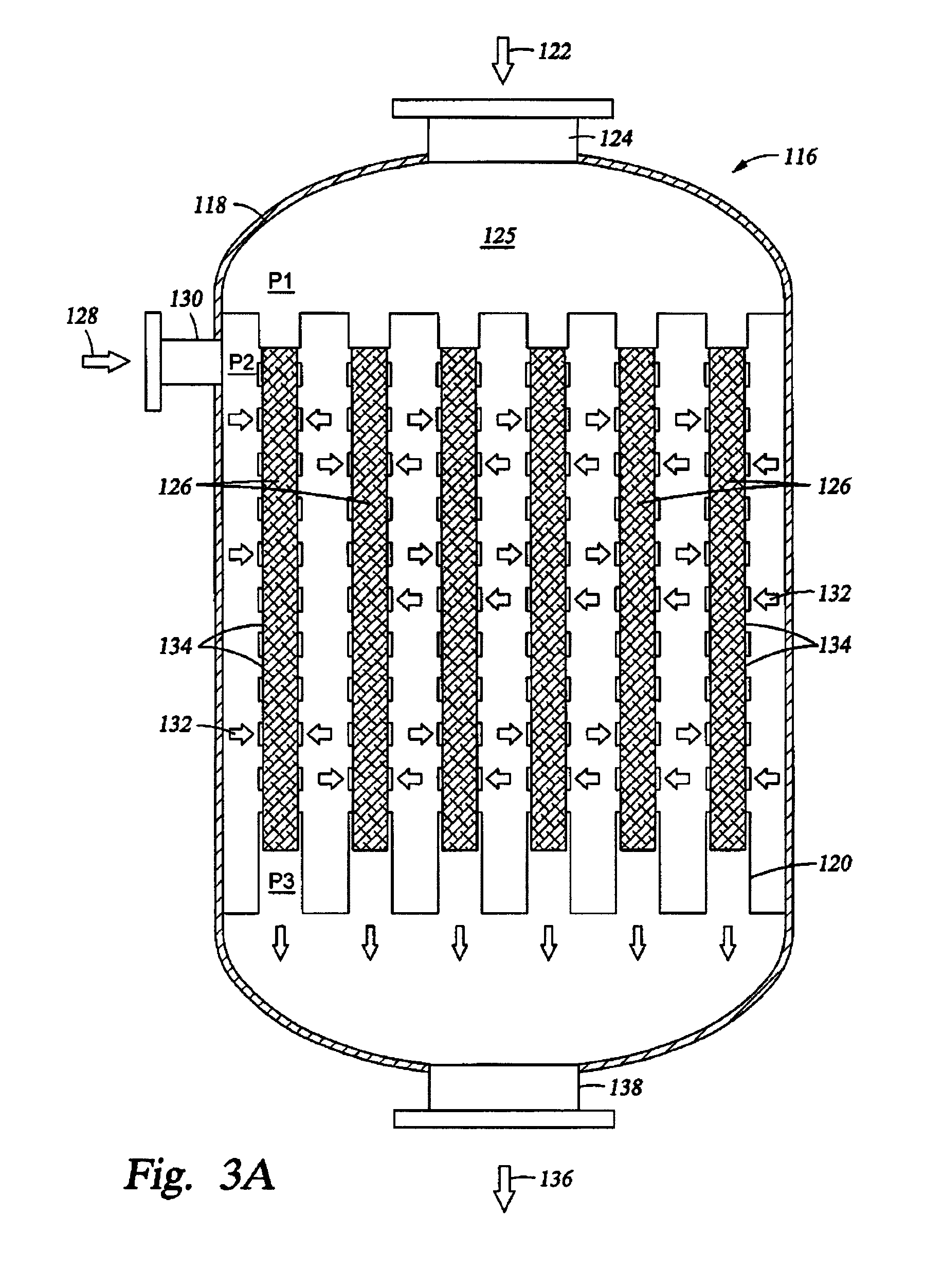
Synthesis gas process comprising partial oxidation using controlled and optimized temperature profile
ActiveUS7261751B2Low selectivityRisk of explosion can be minimizedHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisPartial oxidationFixed bed
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
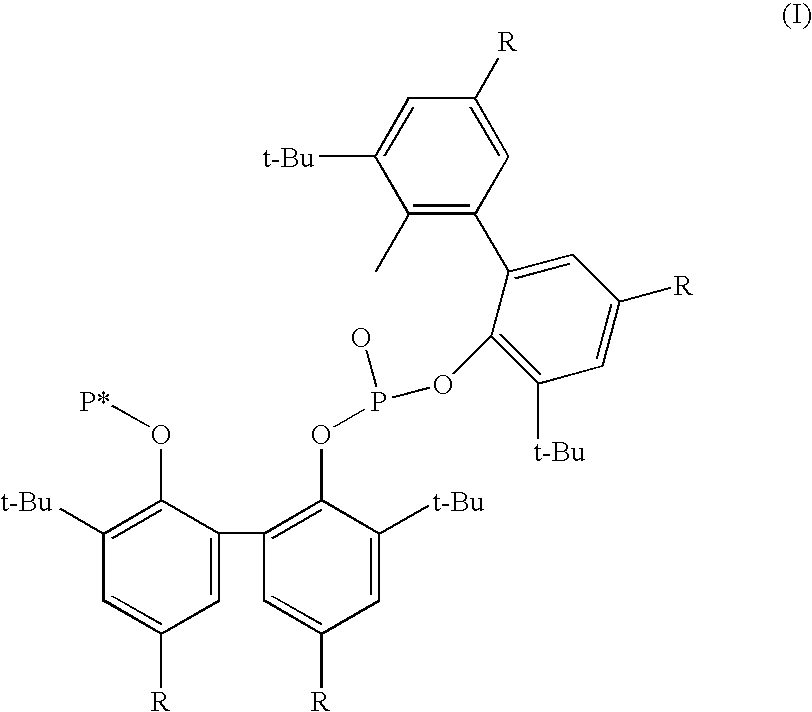
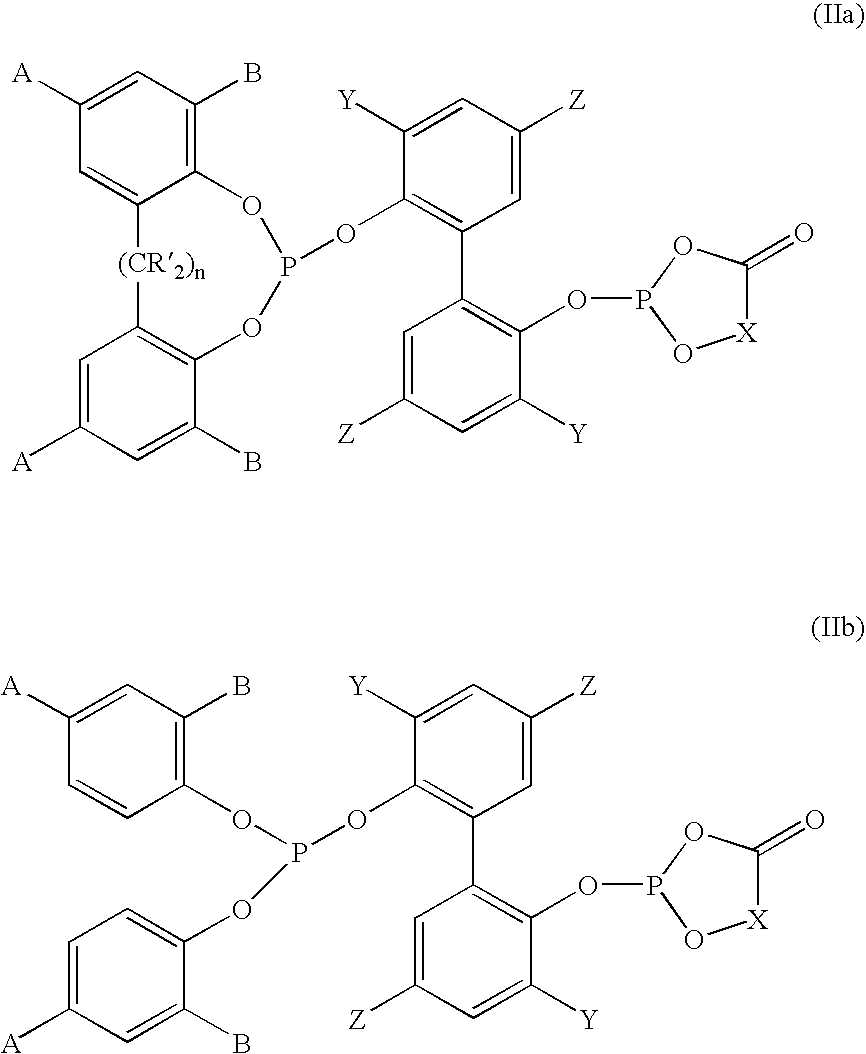
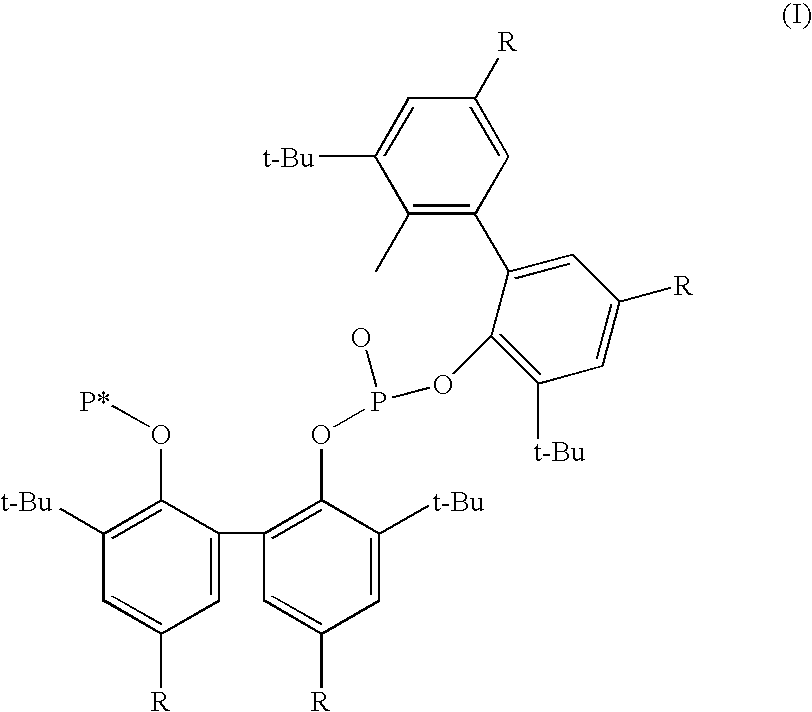
Phosoxophite ligands and use thereof in carbonylation processes
ActiveUS7196230B2High activityHigh selectivitySilicon organic compoundsRhodium organic compoundsCarbonylationProtein carbonyl
A novel organophosphorus composition and synthesis thereof, the composition being characterized by one phosphite moiety, one phosoxophite moiety, and a plurality of sterically bulky substituents. The novel composition finds utility as a ligand in Group VIII transition metal phosoxophite complex catalysts and complex catalyst precursors that are used in carbonylation processes, preferably, hydroformylation processes. Additionally, there is disclosed a novel method of preparing a phosphoromonochloridite composition that finds utility as a precursor to the novel phosoxophite composition.
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Lithium-containing composite oxide and its production method
ActiveUS20090258296A1Low amountExcellent propertyElectrode manufacturing processesActive material electrodesComposite oxideHigh weight
To provide a lithium / nickel / cobalt / manganese-containing composite oxide powder which has a high weight capacity density, a high packing property, an excellent cycle property, an excellent discharge rate property and an excellent safety, and which has little content of free alkalis and is free from gelation at a time of producing a slurry.A lithium / nickel / cobalt / manganese-containing composite oxide powder represented by the formula LipNixCoyMnzMqO2-aFa (wherein M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, Ge, Sn, alkaline earth metal elements and transition metal elements other than Co, Mn and Ni, 0.9≦p≦1.1, 0.2≦x≦0.5, 0.2≦y≦0.5, 0.1≦z≦0.4, 0≦q≦0.05, 1.9≦2-a≦2.1, p+x+y+z+q=2, and 0≦a≦0.02), characterized in that when the powder is classified into small particle size-classified particles with an average particle size of 2 μm≦D50≦8 μm and large particle size-classified particles with an average particle size of 10 μm≦D50≦25 μm, the ratio of (% by weight of the small particle size-classified particles) / (% by weight of the large particle size-classified particles) is from 15 / 85 to 40 / 60, the molar ratio (ps) of lithium to the total of nickel, cobalt, manganese and the M element contained in the small particle size-classified particles is smaller than the molar ratio (pl) of lithium to the total of nickel, cobalt, manganese and the M element contained in the large particle size-classified particles.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Membrane scaffold proteins
InactiveUS20050182243A1Increase stability and monodispersityImprove purification effectBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsNative structurePhospholipid
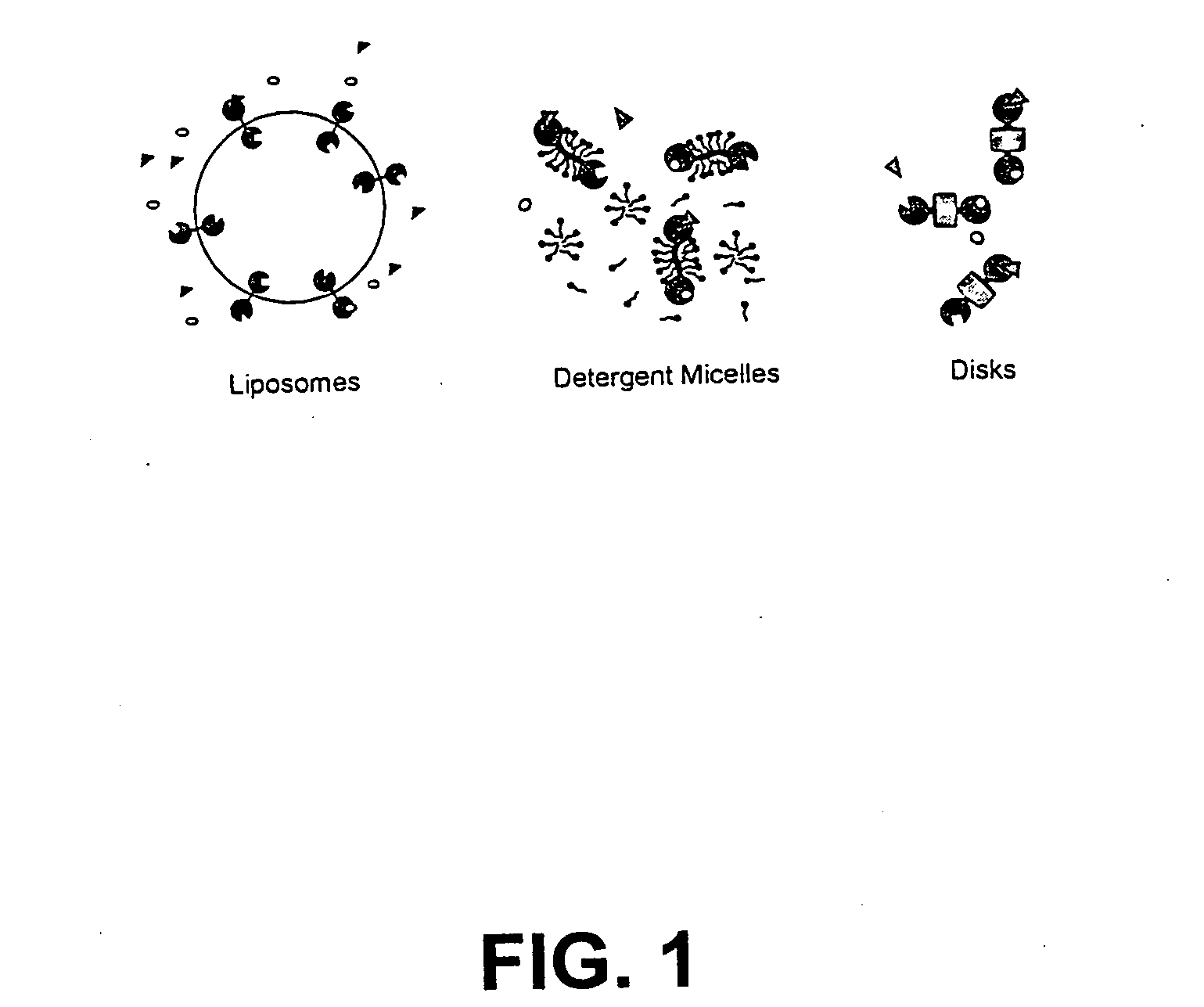
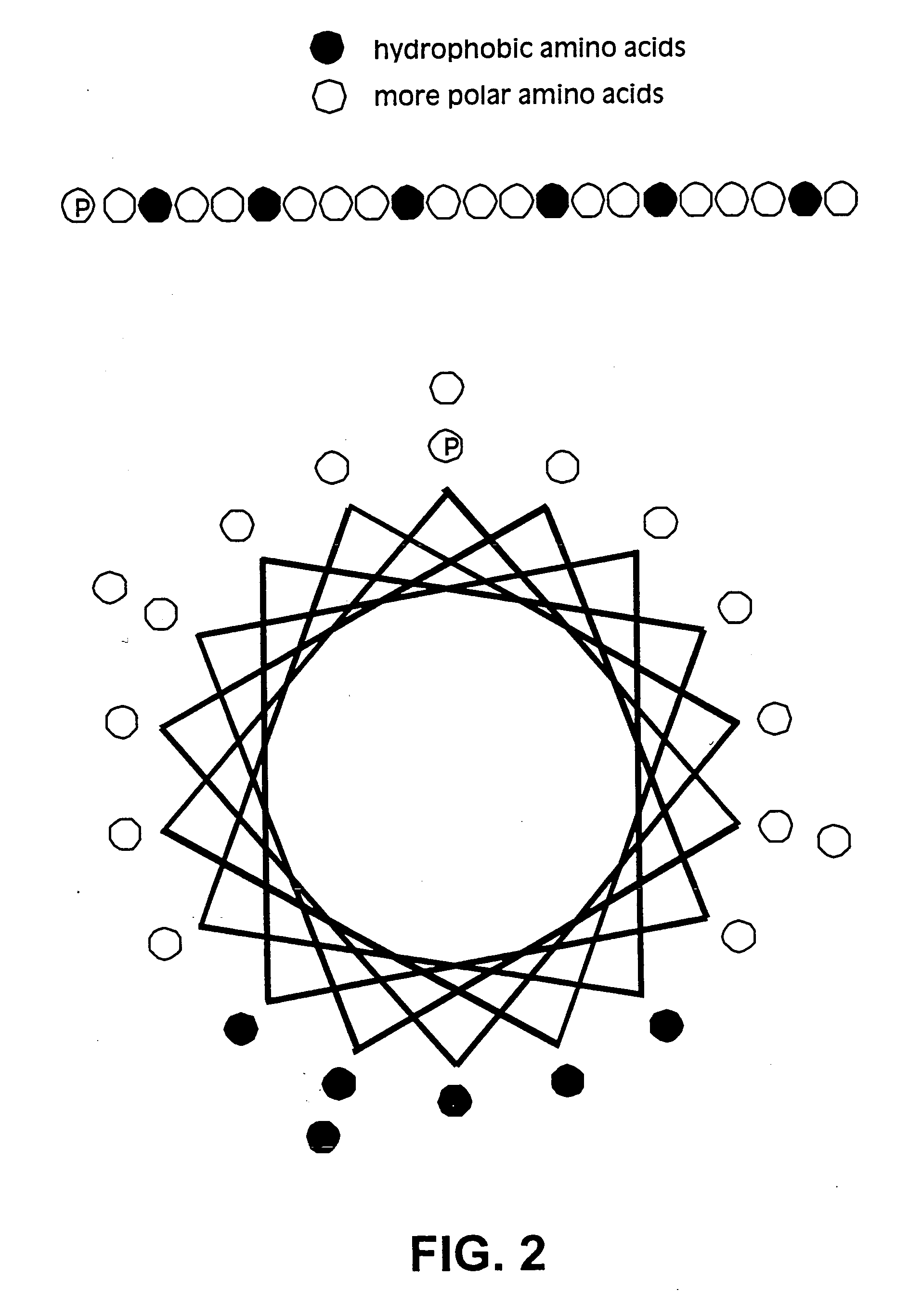
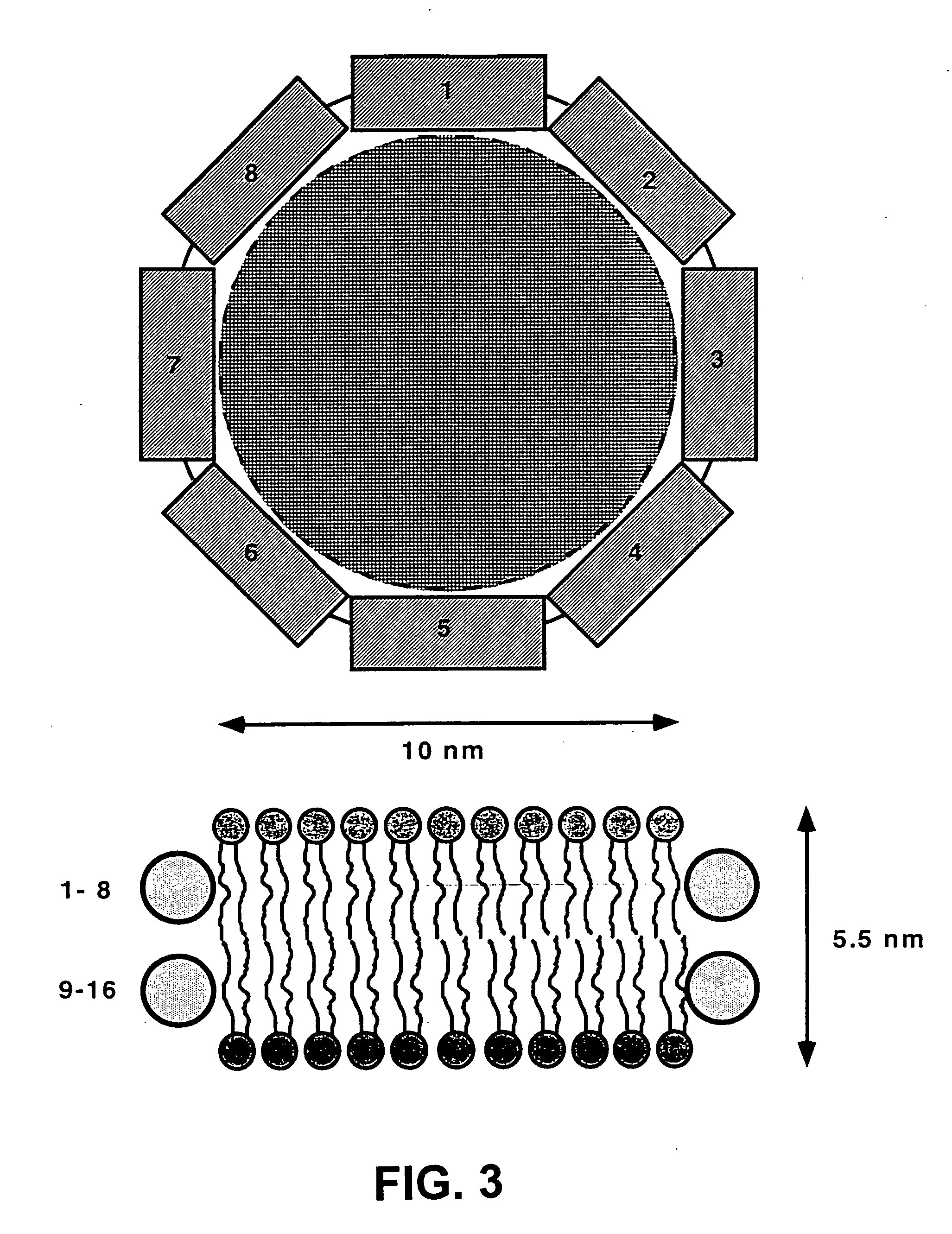
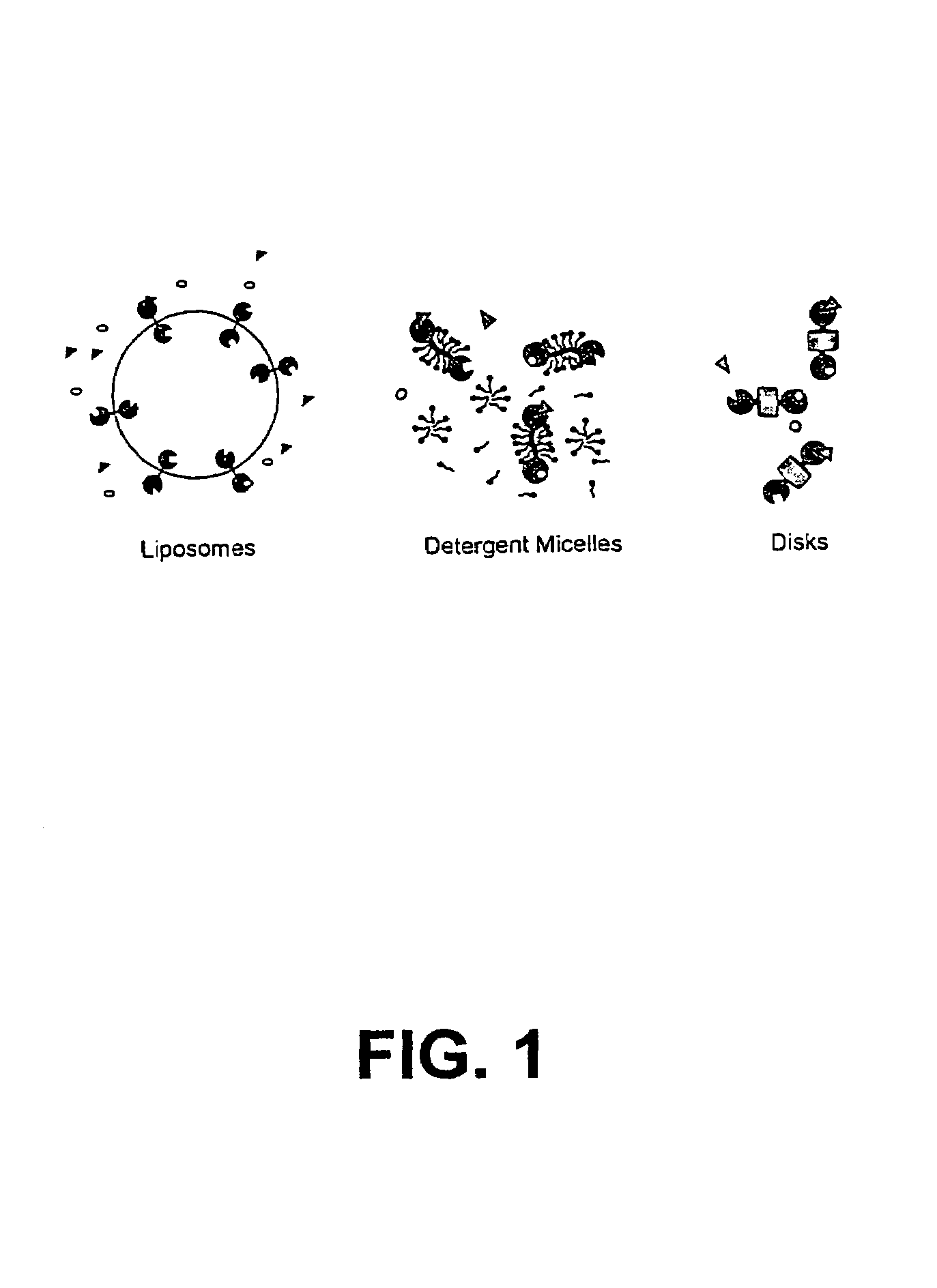
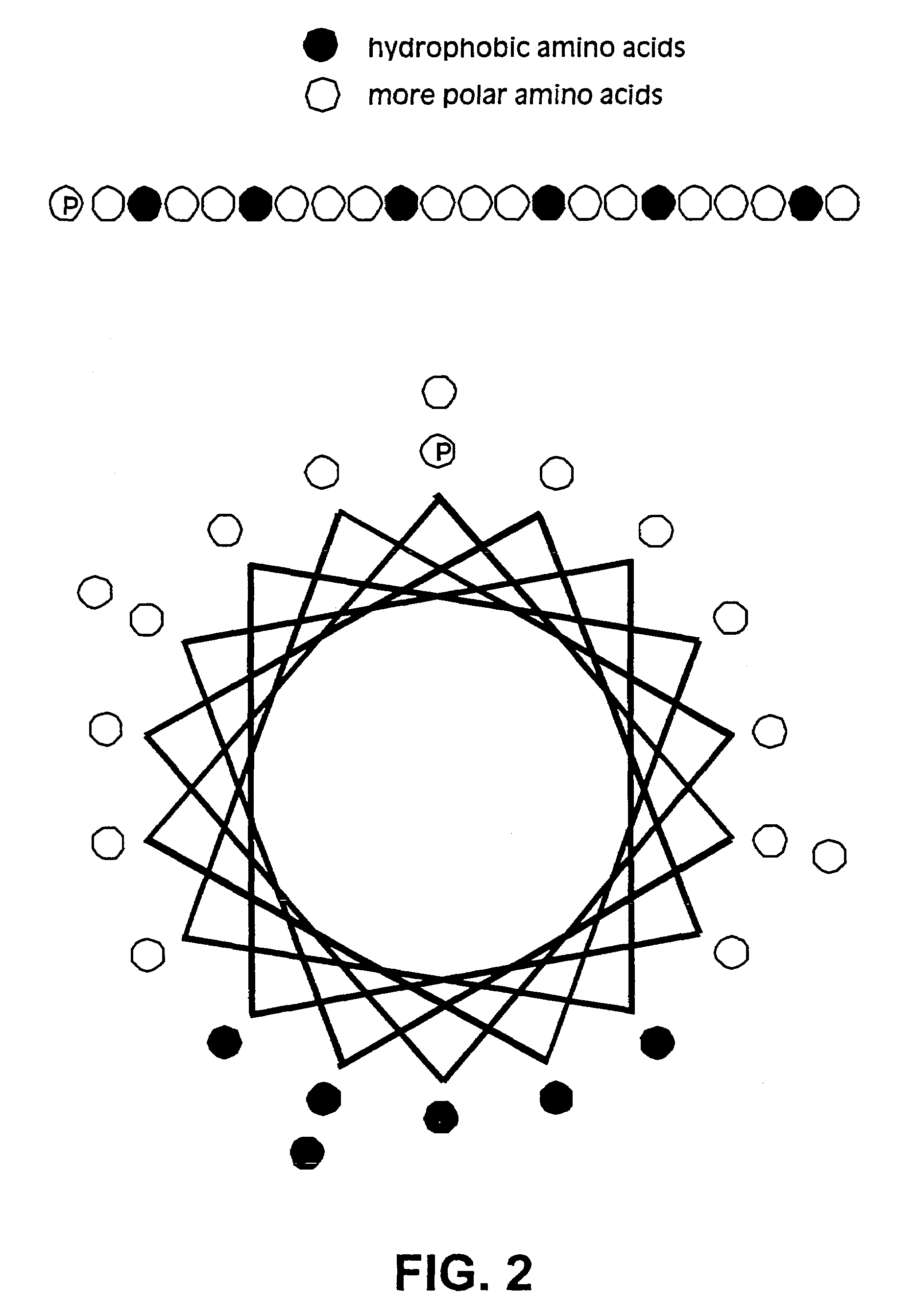
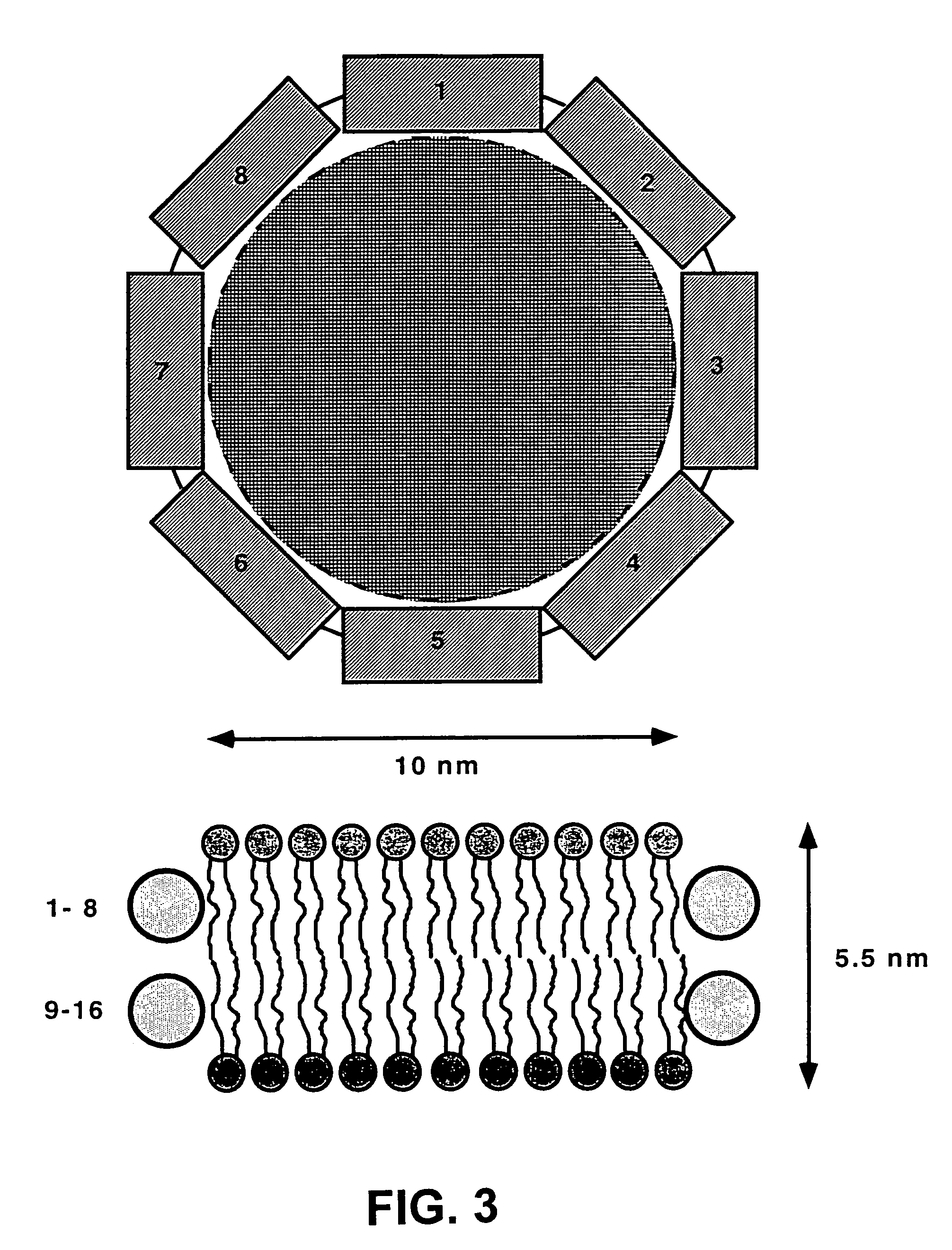
The membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) of the present invention assemble with hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles, in terms of stability and preservation of biological activity and native conformation. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles, which are robust in terms of integrity and maintenance of biological activity of incorporated proteins, facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlations, structure determinations, bioseparations, and drug discovery.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS THE A BODY & POLITIC OF THE STATE OF ILLINOIS
Aromatic aklylating agent and an aromatic production apparatus
InactiveUS20110178354A1Increase the molar ratioIncrease valueHydrocarbonsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon condensationAlkaneMethylating Agent
One exemplary embodiment can be a process using an aromatic methylating agent. Generally, the process includes reacting an effective amount of the aromatic methylating agent having at least one of an alkane, a cycloalkane, an alkane radical, and a cycloalkane radical with one or more aromatic compounds. As such, at least one of the one or more aromatic compounds may be converted to one or more higher methyl substituted aromatic compounds to provide a product having a greater mole ratio of methyl to phenyl than a feed.
Owner:UOP LLC
Transdermal and transmucosal preparations
InactiveUS20070166362A1Promote absorptionIncrease the molar ratioOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAdditive ingredientHydroxyapatites
Transdermal and transmucosal preparations are often insufficiently absorbed. Thus, there is a need for additives that can enhance the transdermal and / or transmucosal absorption of various drugs. The present invention provides compositions for enhancing transdermal and / or transmucosal absorption, comprising a hydroxyapatite and essential ingredients. The hydroxyapatite has a maximum particle size of 1 μm or less, preferably 0.1 μm or less, and the content of the hydroxyapatite relative to a drug to be formulated ranges from 0.1 to 1000 weight percent.
Owner:SANGI CO LTD
Carboxamide derivative, processes for producing the same, and detergent composition
InactiveUS20070010680A1Reduced amide ester contentGood low temperature stabilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsBetaineFormamide
To provide: a carboxamide derivative having reduced content of amide ester; a method for producing thereof; and a detergent composition containing the carboxamide derivative and having excellent low-temperature stability. One method for producing a carboxamide derivative is to react carboxamide, produced with a manufacturing method of carboxamide including 0.02% by weight to 0.18% by weight of amide ester, with hydrogen peroxide, wherein the method includes a carboxamide synthesis process to synthesize carboxamide by reacting diamine with fatty acid ester at a molar rate of 1.20 to 1.60. Another method for producing a carboxamide derivative is to react the carboxamide with monohaloalkylcarboxylic acid or a salt thereof. A carboxamide derivative is produced by the method for producing a carboxamide derivative. A detergent composition includes the carboxamide derivative. The carboxamide derivative is preferably amidoamine oxide or amide betaine.
Owner:LION AKZO
Production of light olefins and aromatics
InactiveUS20100331590A1Increase the molar ratioIncrease valueCatalytic crackingHydrocarbonsCarbon numberCyclic alkane
Processes for the conversion of both straight- or branched-chain (e.g., paraffinic) as well as cyclic (e.g., naphthenic) hydrocarbons of a hydrocarbon feedstock into value added product streams are disclosed. The processes involve the use of both dehydrogenation and olefin cracking to produce both light olefins and aromatics in varying proportions depending on the feedstock composition and particular processing scheme. The processes are especially applicable to naphtha feedstocks comprising paraffins and naphthenes in the C5-C11 carbon number range.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for producing bisphenol a
InactiveUS6429343B1Lower conversion rateIncrease the molar ratioOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationThiolIon-exchange resin
The present invention provides a process for producing bisphenol A which is capable of prolonging the life of an acid-type ion exchange resin partially modified with a sulfur-containing amine compound as catalyst, and increasing the yield of bisphenol A per unit quantity of the catalyst. There is disclosed a process for producing bisphenol A by reacting acetone with phenol in the presence of an acid-type ion exchange resin partially modified with a sulfur-containing amine compound as catalyst and alkylmercaptan as co-catalyst, said process comprising:conducting said reaction using a multi-stage reaction apparatus comprising at least two individual reactors connected in series to each other, wherein the molar ratio of total alkylmercaptan to total acetone and the molar ratio of total acetone to phenol are increased as the conversion rate of the phenol is decreased.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Process for increasing a mole ratio of methyl to phenyl
InactiveUS20110178356A1Increase the molar ratioIncrease valueHydrocarbon by isomerisationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsMethylating AgentMethyl group
One exemplary embodiment can be a process for increasing a mole ratio of methyl to phenyl of one or more aromatic compounds in a feed. The process can include reacting an effective amount of one or more aromatic compounds and an effective amount of one or more aromatic methylating agents to form a product having a mole ratio of methyl to phenyl of at least about 0.1:1 greater than the feed.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for increasing methyl to phenyl mole ratios and reducing benzene content in a motor fuel product
InactiveUS20110174692A1Increase the molar ratioIncrease valueCatalytic naphtha reformingHydrocarbonsBenzeneMethyl group
One exemplary embodiment can be a process for increasing a mole ratio of methyl to phenyl of one or more aromatic compounds in a feed. The process can include reacting an effective amount of one or more aromatic compounds and an effective amount of one or more non-aromatic compounds to convert about 90%, by weight, of one or more C6+ non-aromatic compounds.
Owner:UOP LLC
Membrane scaffold proteins
InactiveUS7592008B2Increase stability and monodispersityImprove purification effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNative structurePhospholipid
The membrane scaffold proteins (MSP) of the present invention assemble with hydrophobic or partially hydrophobic proteins to form soluble nanoscale particles which preserve native structure and function; they are improved over liposomes and detergent micelles, in terms of stability and preservation of biological activity and native conformation. In the presence of phospholipid, MSPs form nanoscopic phospholipid bilayer disks, with the MSP stabilizing the particle at the perimeter of the bilayer domain. The particle bilayer structure allows manipulation of incorporated proteins in solution or on solid supports, including for use with such surface-sensitive techniques as scanning probe microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. The nanoscale particles, which are robust in terms of integrity and maintenance of biological activity of incorporated proteins, facilitate pharmaceutical and biological research, structure / function correlations, structure determinations, bioseparations, and drug discovery.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS THE A BODY & POLITIC OF THE STATE OF ILLINOIS
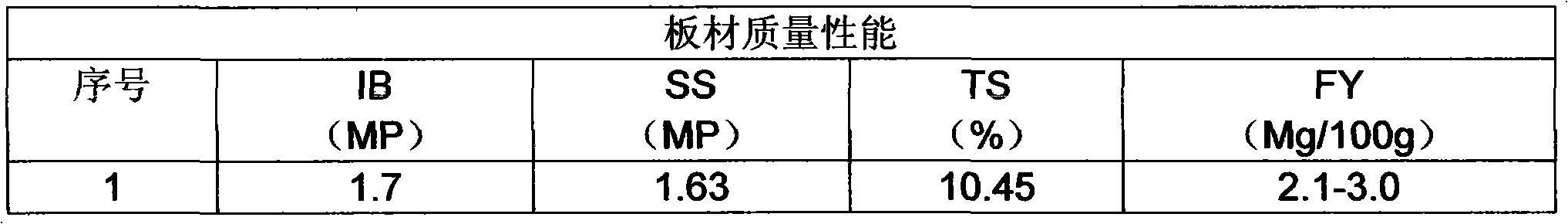
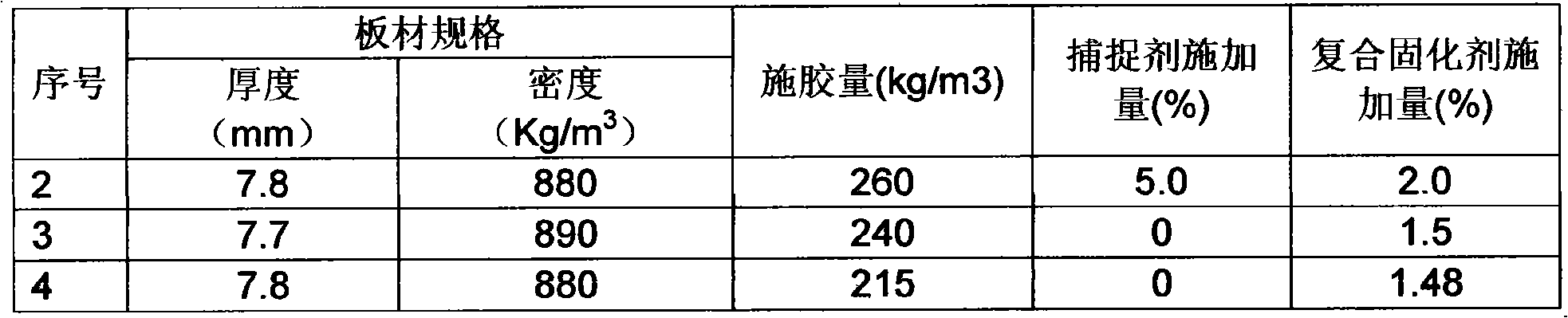
Method for manufacturing low-oxymethylene-releasing high-density fibreboard
ActiveCN101306553AStable and excellent physical and mechanical propertiesThe release amount is stable and does not reboundNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesFiberHigh density
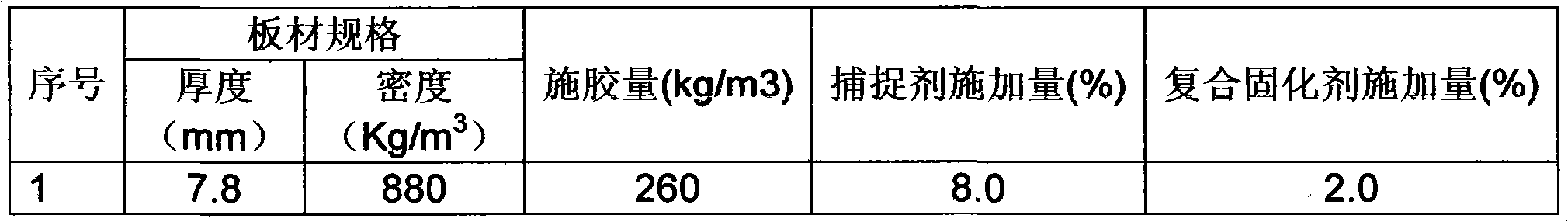
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a low formaldehyde release quantity high density fiberboard, which comprises sizing procedures. The method is characterized in that in the sizing procedure, E1 or E0 grade fiberboard used synthetic resin, a compound curing agent and a formaldehyde capture agent are adopted; sizing quantity accounts for 30-35% of fiber quantity; the application quantity of the compound curing agent accounts for 1.48-2.5% of the synthetic resin; and the application quantity of the formaldehyde capture agent accounts for 0.0-10.0%. According to the method, the whole mol ratio of urea formaldehyde resin is controlled in the range of 1.05-0.93; and with the addition of the formaldehyde capture agent, E1 or E0 grade fiberboards can be produced. The method has the advantages of low production cost, flexible production technique and strong adaptability. The produced fiberboard has the advantages of stable and excellent performance, and low free formaldehyde release quantity, and the formaldehyde release quantity can be flexibly controlled according to the users' requirements.
Owner:DARE WOOD BASED PANEL GRP
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
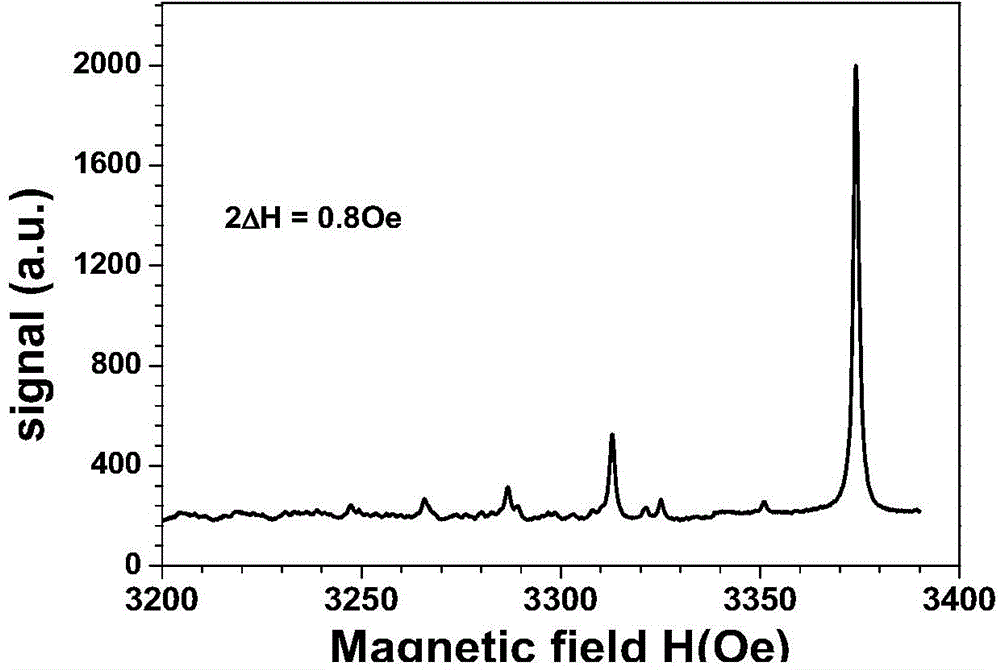
Yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104831357AFerromagnetic resonance linewidthThe ferromagnetic resonance linewidth is very narrowPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSingle crystalElectronic materials
The present invention provides an yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film and a liquid-phase epitaxy preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of electronic materials. According to the present invention, the component of the yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film is La[x]Y[3-x]Fe5O12, wherein x is 0.01-0.05; 0.44% by mass of Y2O3, 10.31% by mass of Fe2O3, 0.06% by mass of La2O3, 87.44% by mass of PbO and 1.75% by mass of B2O3 are adopted as raw materials; the liquid-phase epitaxy method is used to grow the single-crystal film; the ferromagnetic resonance line width of the obtained yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film is narrow and achieves less than or equal to 1 Oe; and the roughness, the lattice matching, the film stress, the lead content, the impure phase and the like of the film are improved.
Owner:成都威频科技有限公司
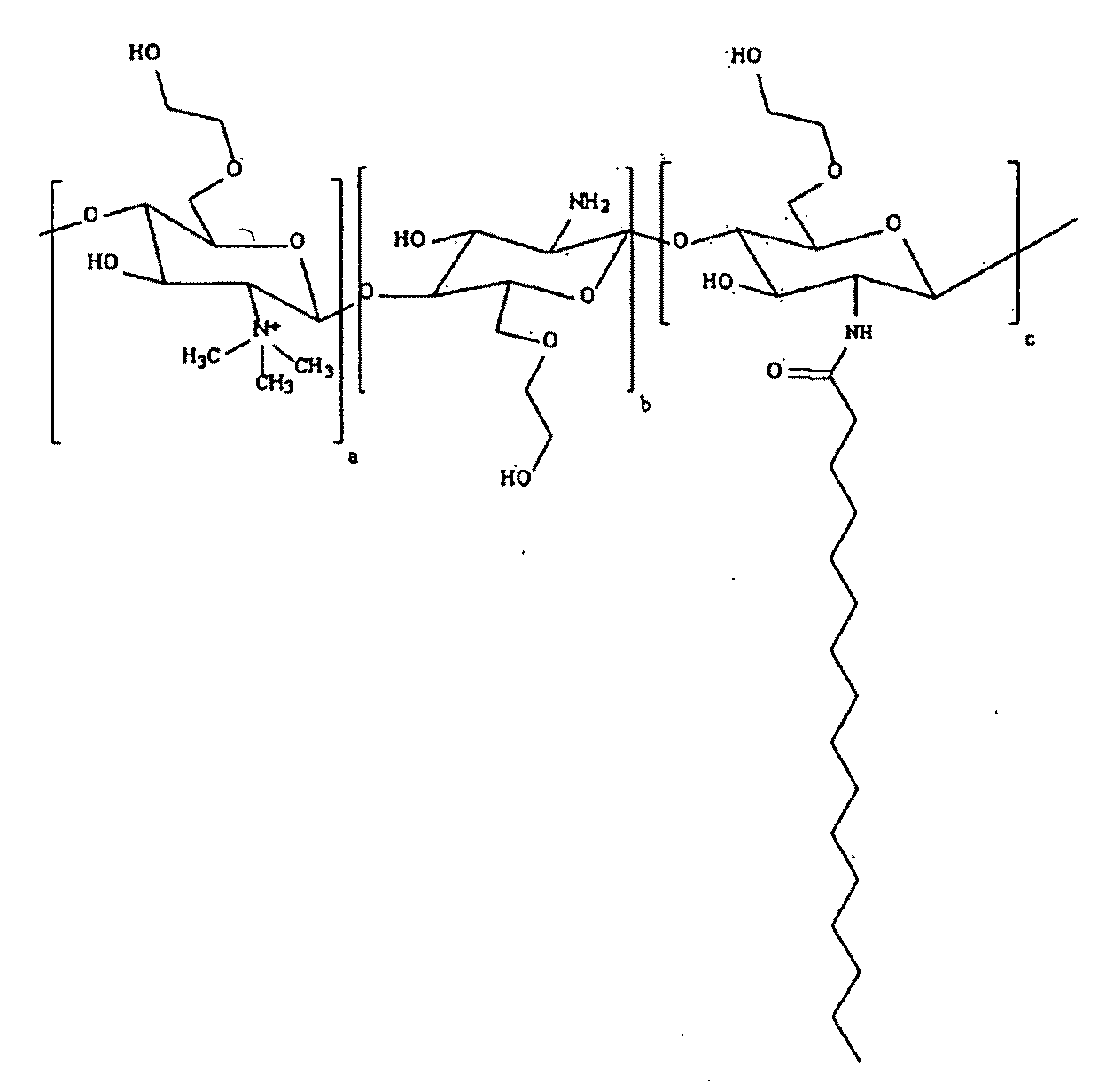
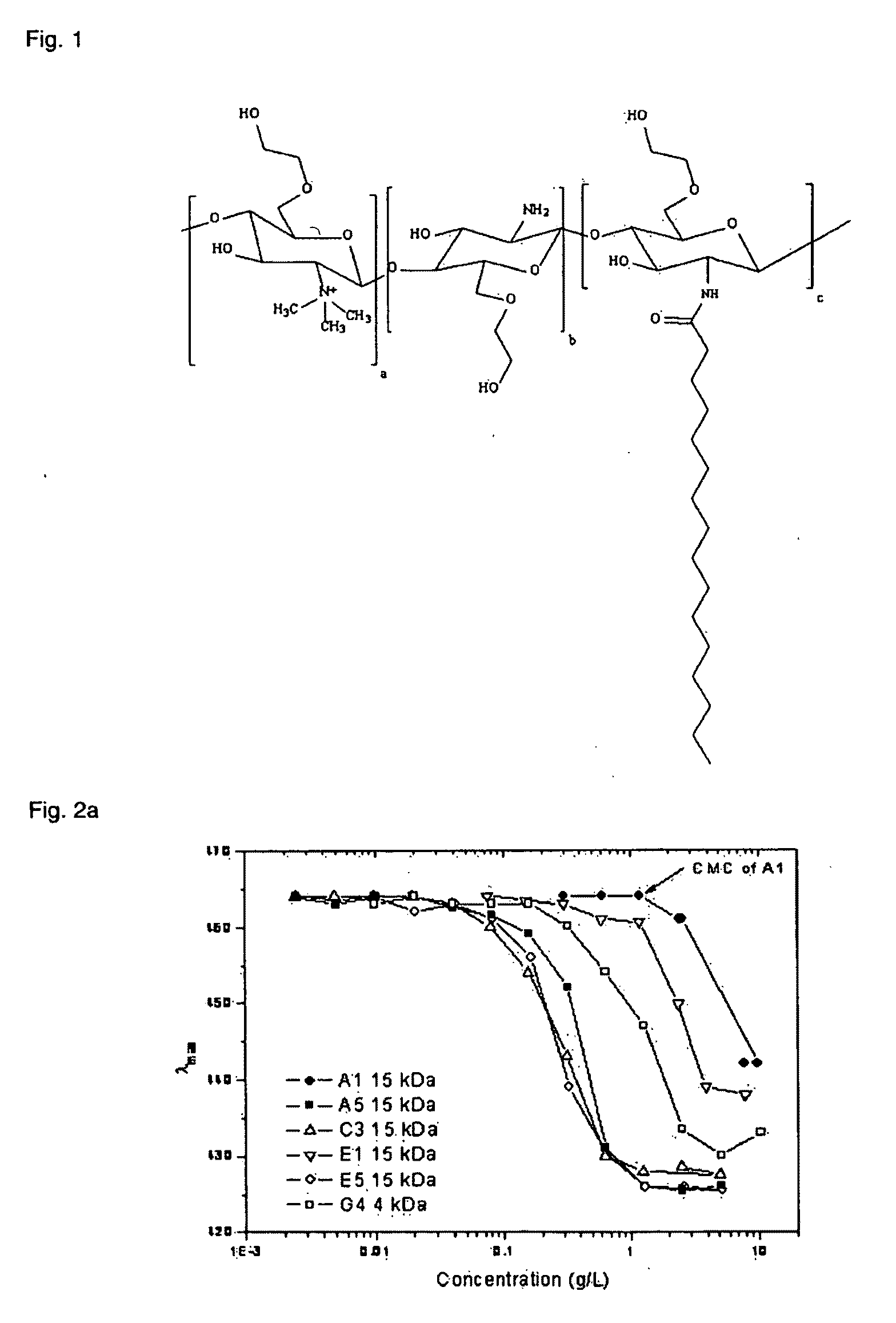
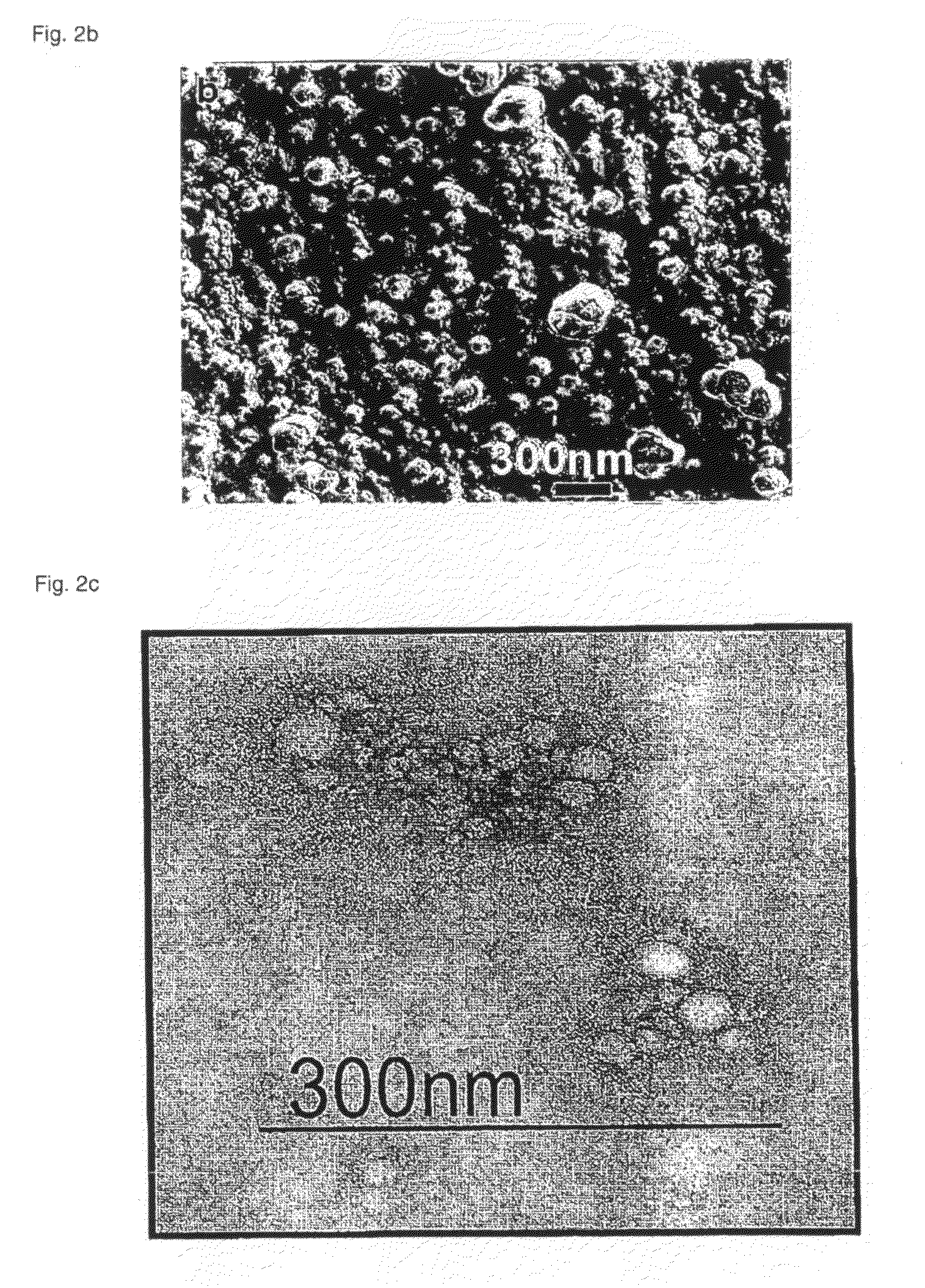
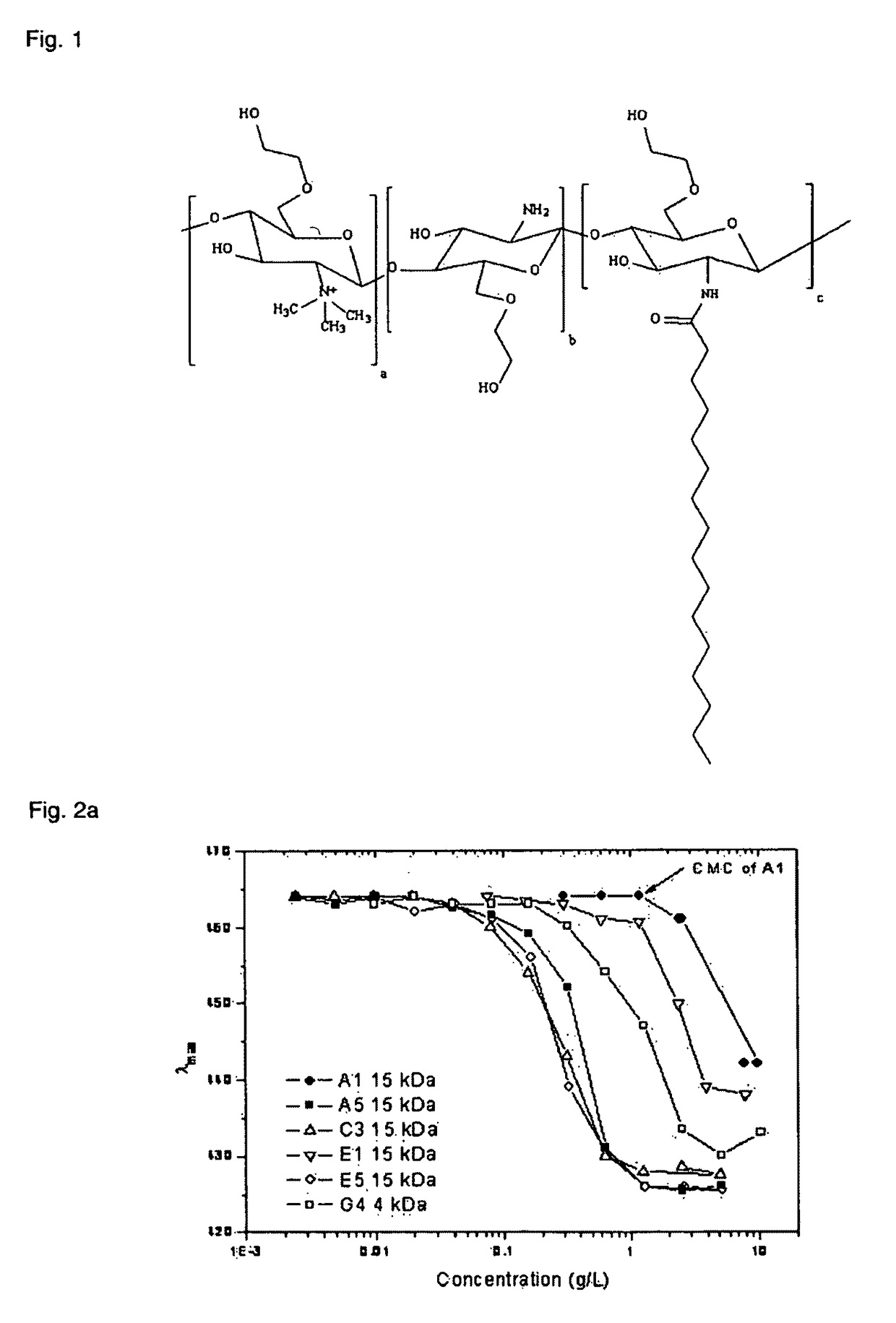
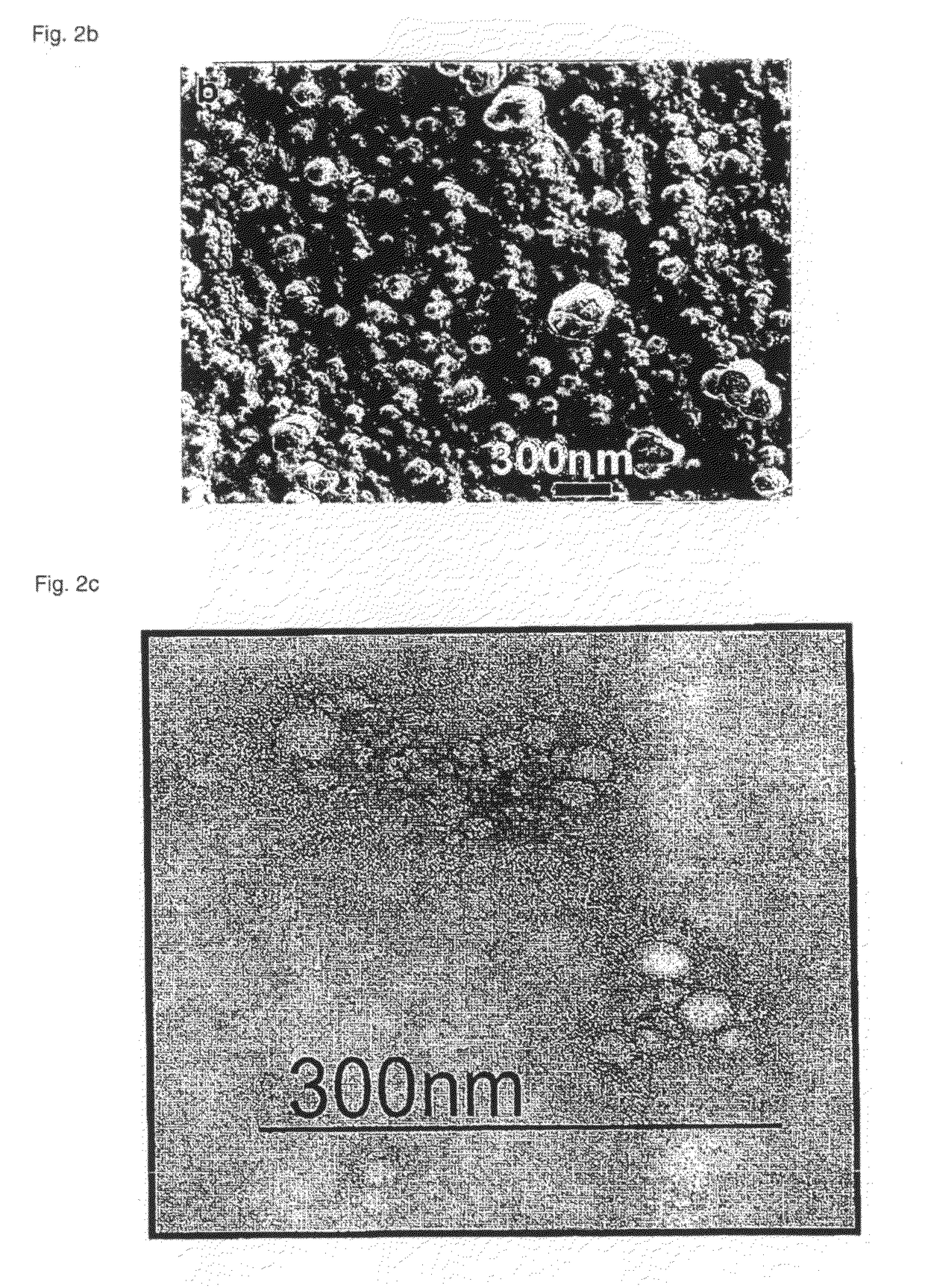
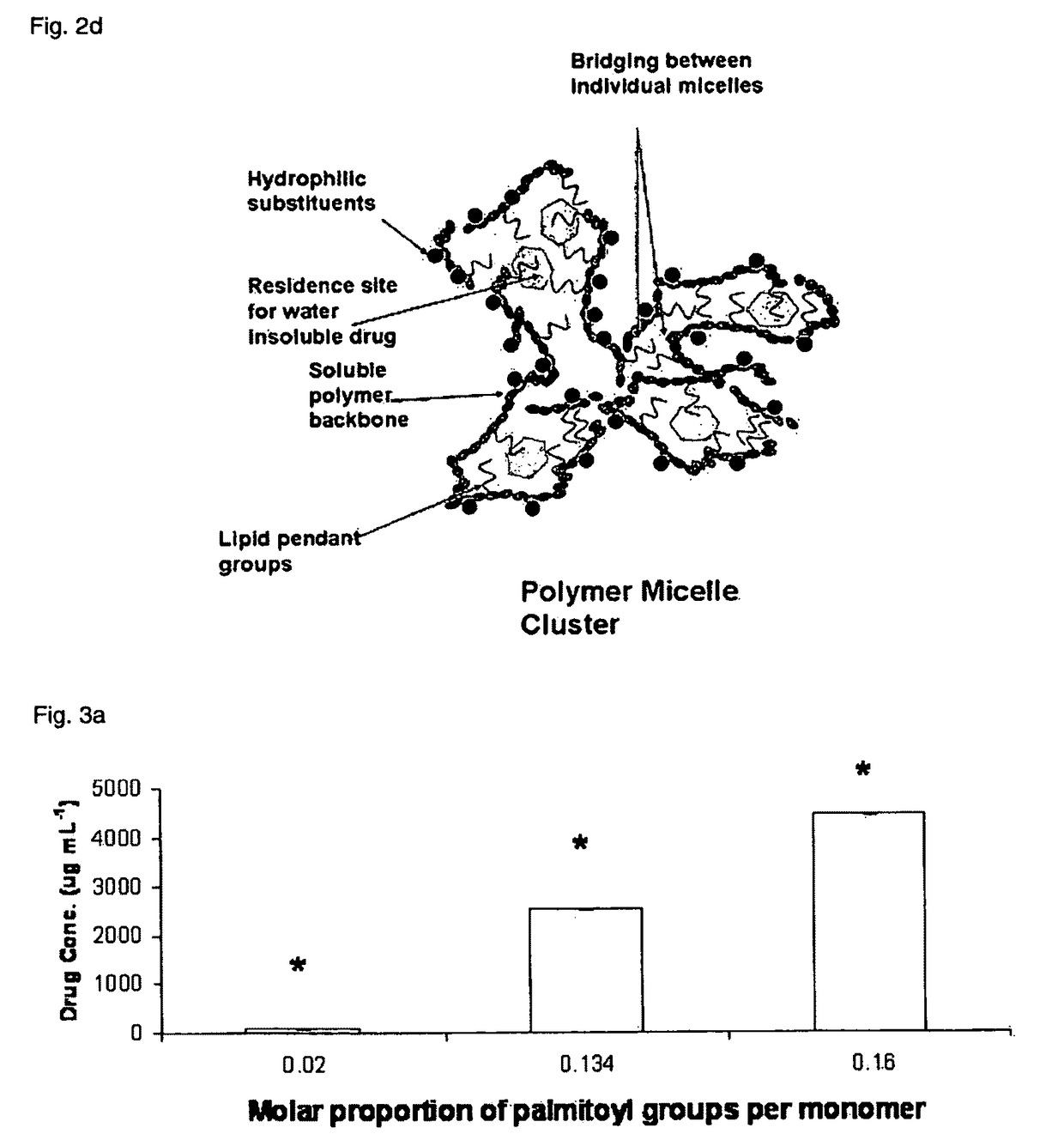
Polymeric micellar clusters and their uses in formulating drugs
ActiveUS20100159014A1Low water solubilityRaise transfer toAntibacterial agentsBiocideAmphiphileCrystallography
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
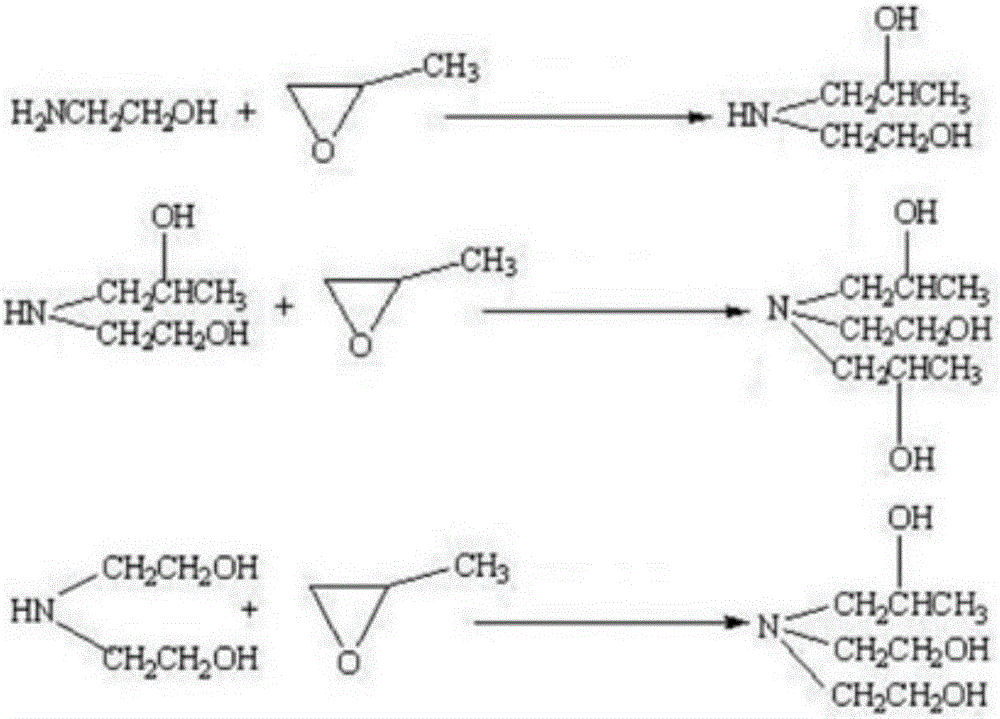
Preparation method of novel isopropanolamine
InactiveCN106631836AIncrease the molar ratioHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationMolecular sieveAlcohol
The invention provides a preparation method of novel isopropanolamine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a catalyst; (2) preparing diethanol amine; (3) synthesizing diethanolisopropanolamine. In the method, liquid ammonia, ethylene oxide and propylene oxide are taken as raw materials, and the diethanolisopropanolamine is synthesized in two steps; when the liquid ammonia and the ethylene oxide are used for synthesizing the diethanol amine, a molecular sieve catalyst is adopted, so that the generation of triethanolamine is inhibited effectively, the production of monoethanolamine is reduced by increasing the molar ratio of ethylene oxide to the liquid ammonia, the yield of the diethanol amine is increased, and the yield of the diethanolisopropanolamine is increased. Since byproducts in a final product are all alcohol amine substances which can be used directly in the production of a cement grinding aid, thereby simplifying the production process and lowering the production cost.
Owner:北京德博莱化工产品销售有限公司
Polymeric micellar clusters and their uses in formulating drugs
ActiveUS8470371B2Low water solubilityRaise transfer toAntibacterial agentsBiocideCrystallographyAmphiphile
Polymeric micellar clusters formed from amphiphilic carbohydrate polymers and their uses in formulating drugs is disclosed, and in particular the finding that amphiphilic carbohydrate polymers are capable of self assembling to form micellar clusters in which the carbohydrate amphiphiles aggregate into hierarchically organized micellar clusters of individual aggregates. The micellar clusters may be transformed into stable nanoparticles with drugs, especially hydrophobic drugs that have poor aqueous solubility, and may improve the transfer of hydrophobic drugs across biological barriers.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Carboxamide derivative, processes for producing the same, and detergent composition
InactiveUS7718816B2Reduced amide ester contentGood low temperature stabilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsBetaineFormamide
To provide: a carboxamide derivative having reduced content of amide ester; a method for producing thereof; and a detergent composition containing the carboxamide derivative and having excellent low-temperature stability. One method for producing a carboxamide derivative is to react carboxamide, produced with a manufacturing method of carboxamide including 0.02% by weight to 0.18% by weight of amide ester, with hydrogen peroxide, wherein the method includes a carboxamide synthesis process to synthesize carboxamide by reacting diamine with fatty acid ester at a molar rate of 1.20 to 1.60. Another method for producing a carboxamide derivative is to react the carboxamide with monohaloalkylcarboxylic acid or a salt thereof. A carboxamide derivative is produced by the method for producing a carboxamide derivative. A detergent composition includes the carboxamide derivative. The carboxamide derivative is preferably amidoamine oxide or amide betaine.
Owner:LION AKZO
Forming crosslinked-glutathione on nanostructure
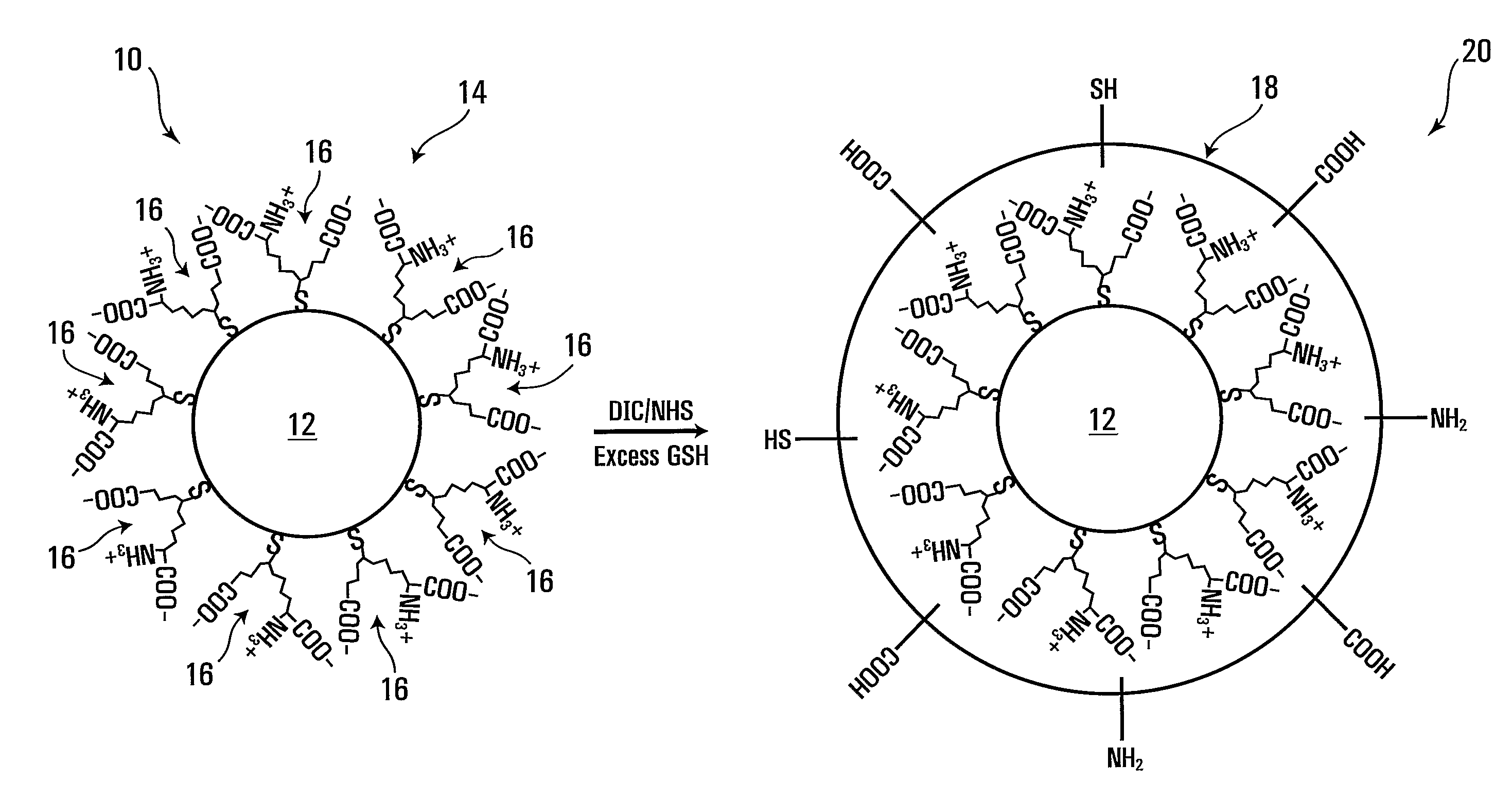
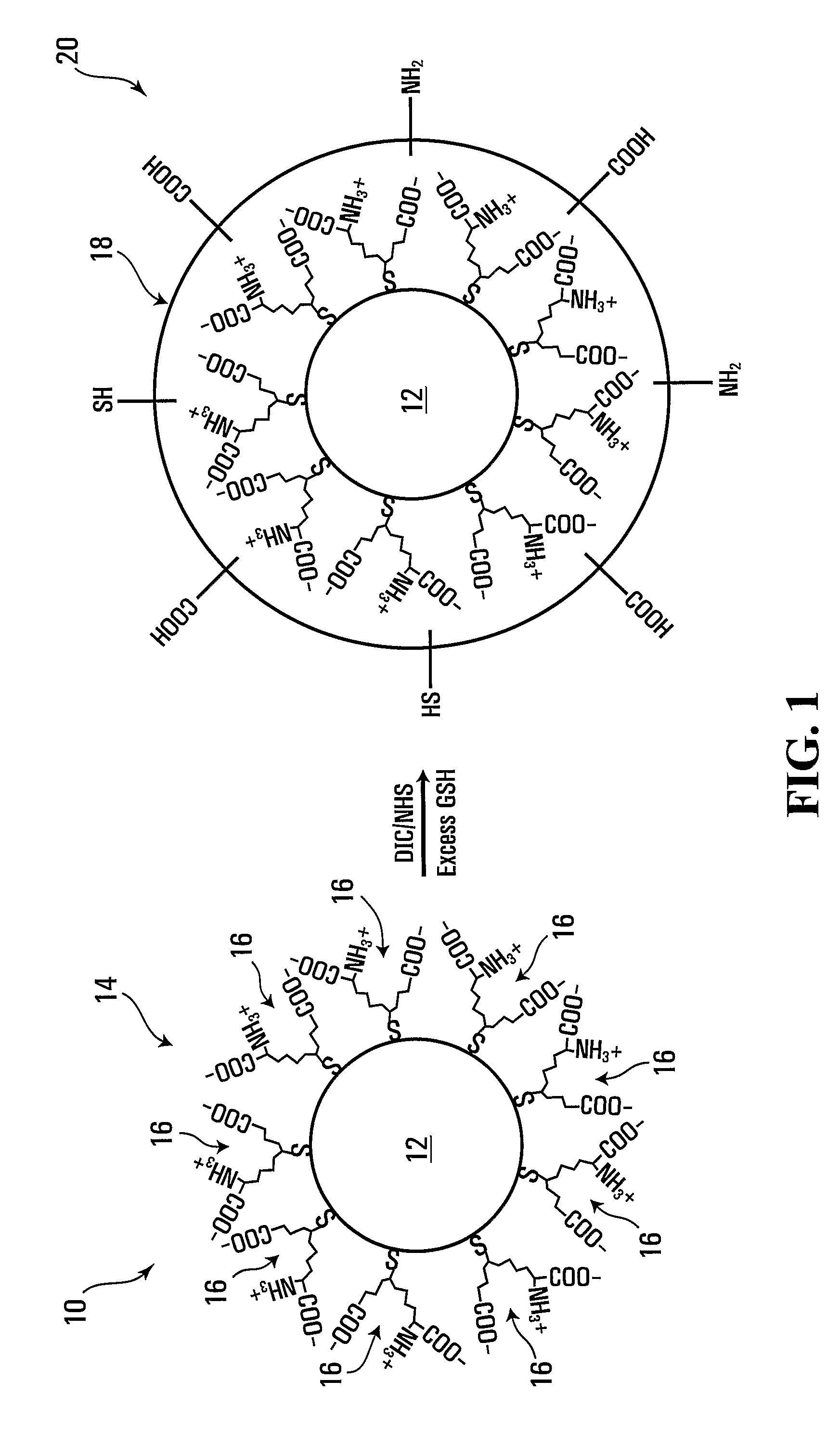
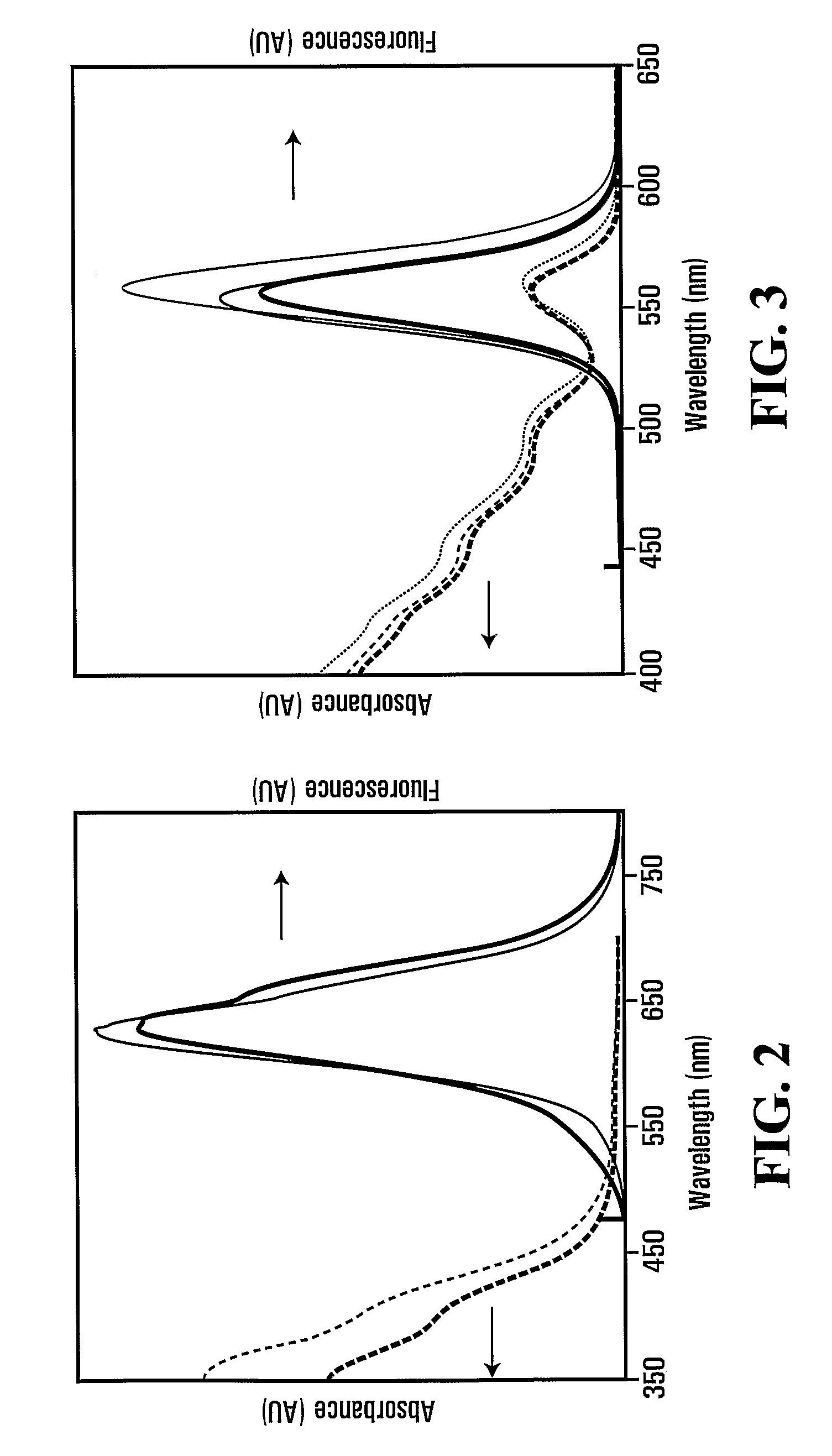
InactiveUS20100117029A1Increase the molar ratioLiquid surface applicatorsNanosensorsQuantum dotNanostructure
In a method of forming a light emissive nanostructure, a quantum dot is provided and a crosslinked-glutathione layer around the quantum dot is formed. The light emissive nanostructure thus comprises a quantum dot and a crosslinked-glutathione layer around the quantum dot. In another method, a metal-based nanostructure is provided, and a crosslinked-glutathione layer coated on a surface of the metal-based nanostructure is formed. The metal-based nanostructure is thus coated with a crosslinked-glutathione layer. To promote crosslinking and stability, the glutathione layer may be crosslinked in the presence of an activating agent and sufficient amount of free glutathione.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
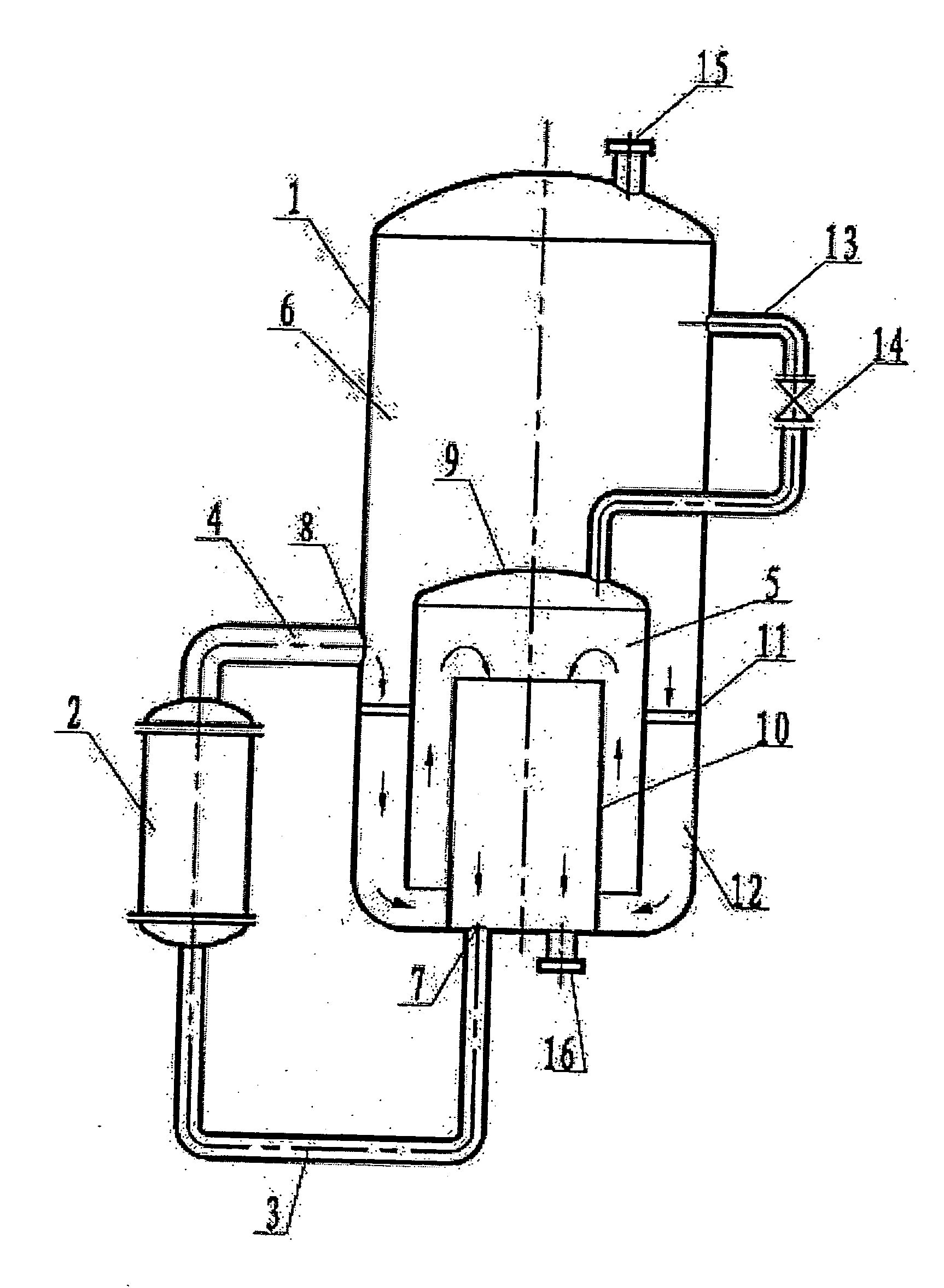
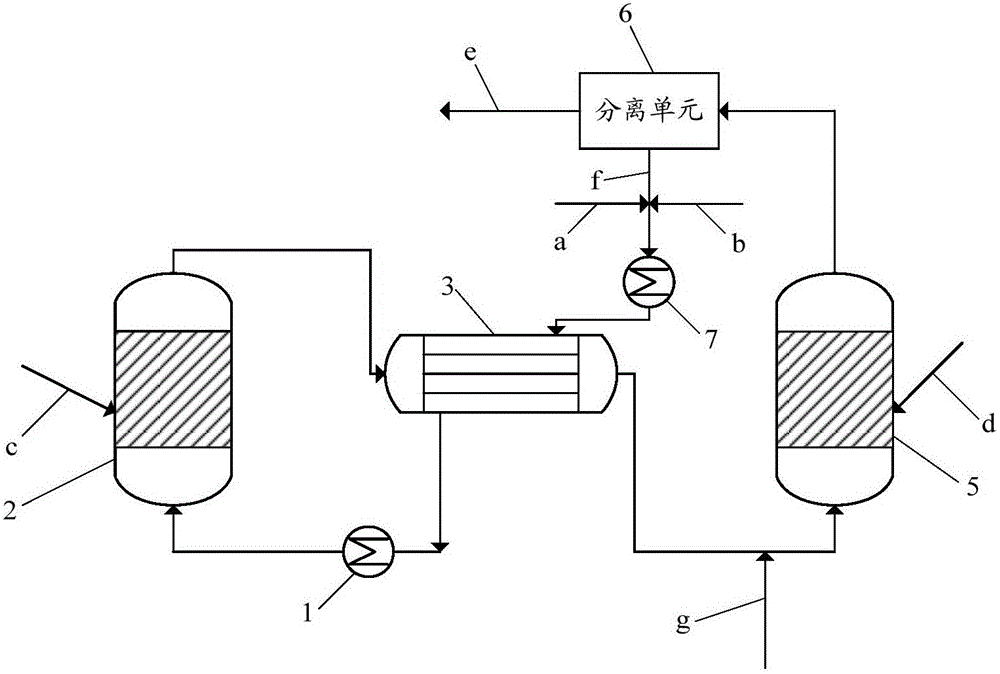
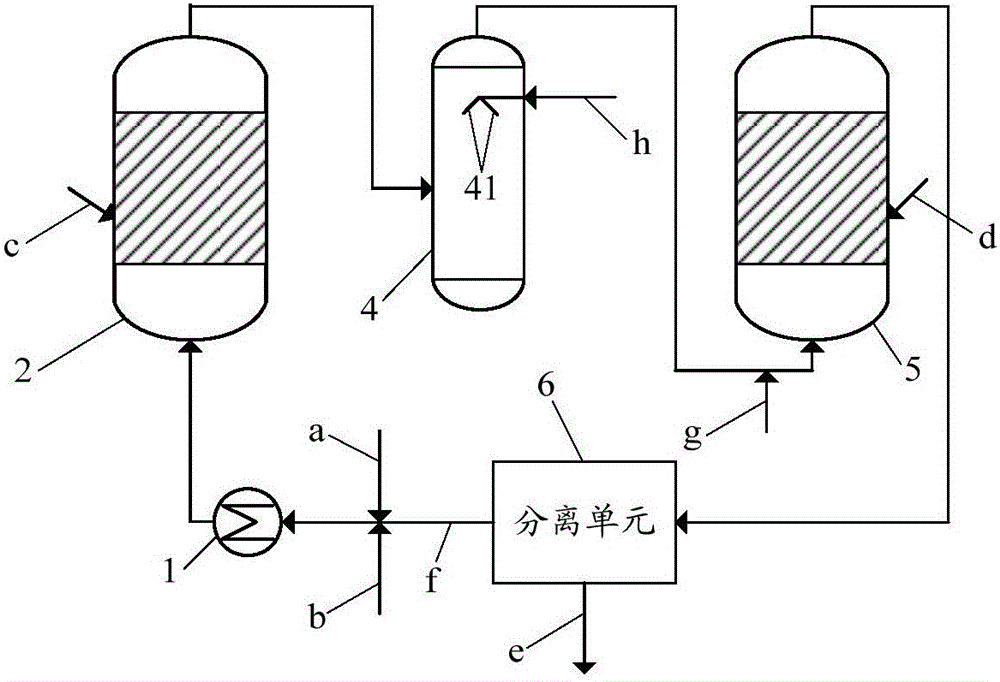
Device for reaction or separation and a continuous esterification process using the device
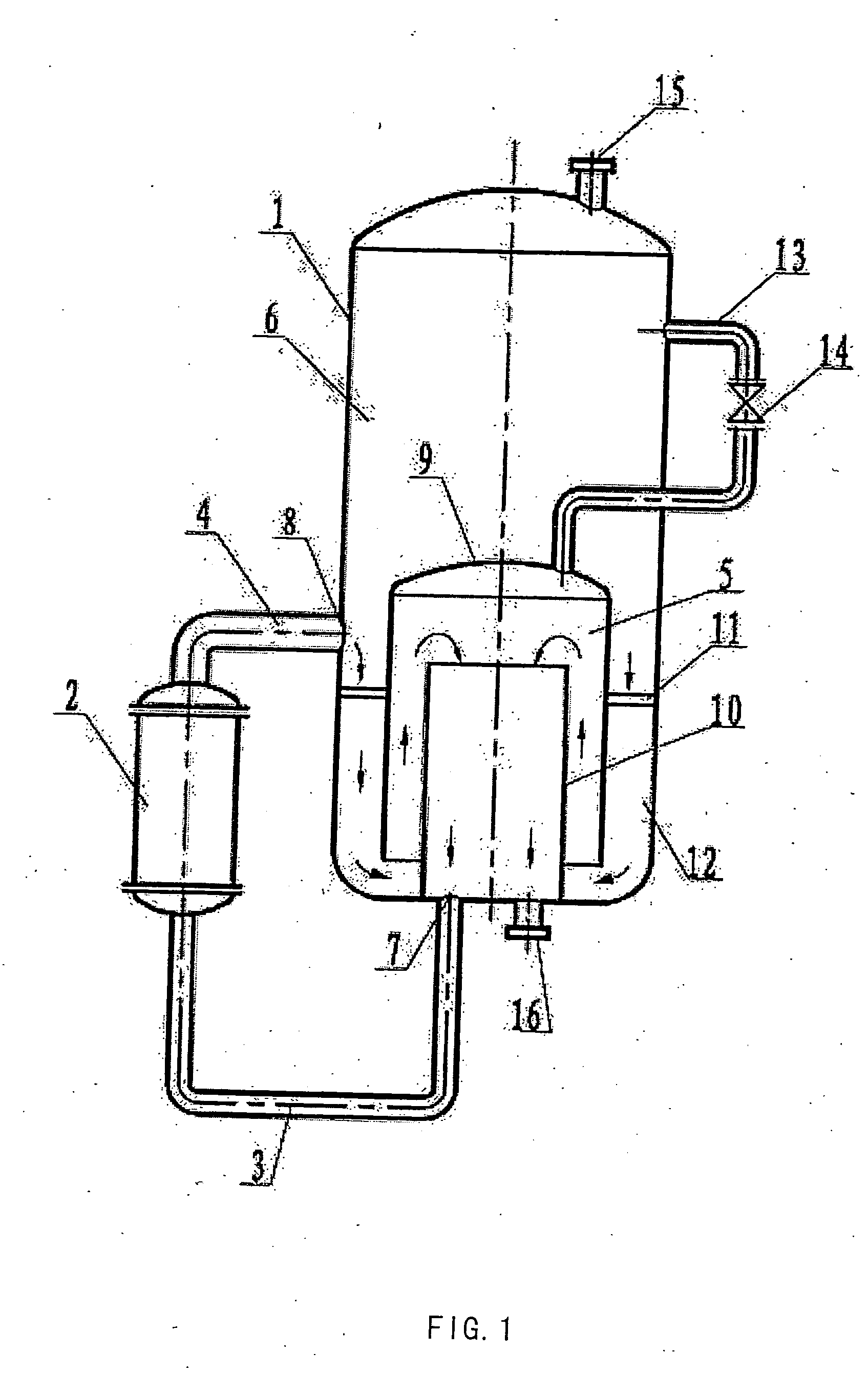
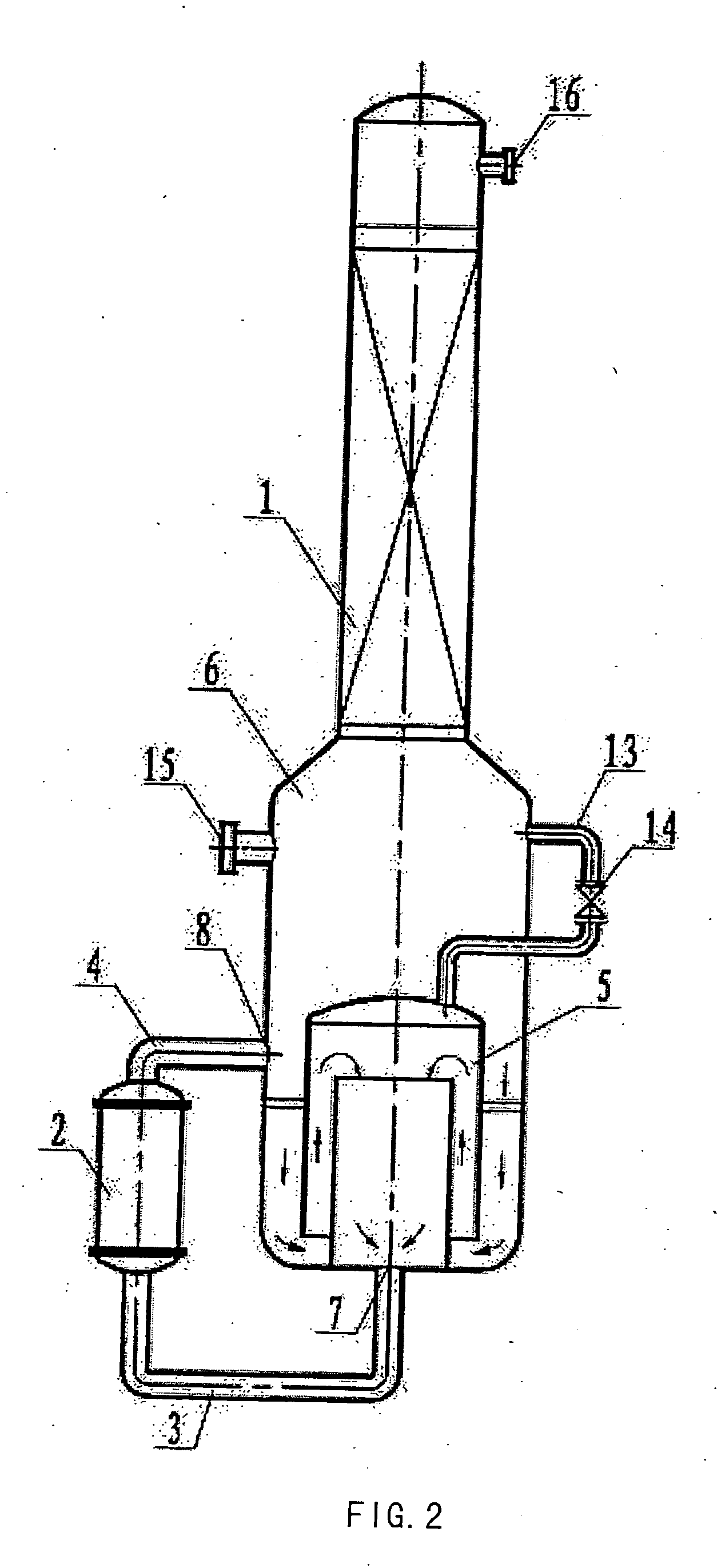
ActiveUS20070100126A1Easy to driveIncrease the molar ratioGaseous chemical processesOrganic chemistryEngineeringReaction conditions
The present invention relates to a reaction or separation device, wherein the materials circularly flow in a container and a pipe. Said device contains a container and an external circular pipe, wherein the container is a double-chamber structure. The inner chamber consists of an outer cylinder and an inner cylinder with the latter being jacketed by the former, and there is a space between the walls of the outer cylinder and the inner cylinder. The lower end of the outer cylinder is open and higher than the bottom of the container, and the outer cylinder is fixed to the wall or bottom of the container. The upper end of the inner cylinder is open and its lower end connects with the external circular pipe through the feed outlet. A continuous passage is sequentially formed from the spaces between the wall of the outer cylinder and that of the container, between the lower end of the outer cylinder and the bottom of the container, between the wall of the outer cylinder and that of the inner cylinder, and in the inner cylinder. The external circular pipe connects with the bottom of the container and leads to the inner chamber, and connects with the sidewall at the lower part of the container and leads to the outer chamber, respectively. The present invention also relates to a continuous esterification process, which comprises feeding liquid reaction materials to the reaction device and carrying out reaction under reaction conditions.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +2
Curable liquid acryloyl group containing resin composition
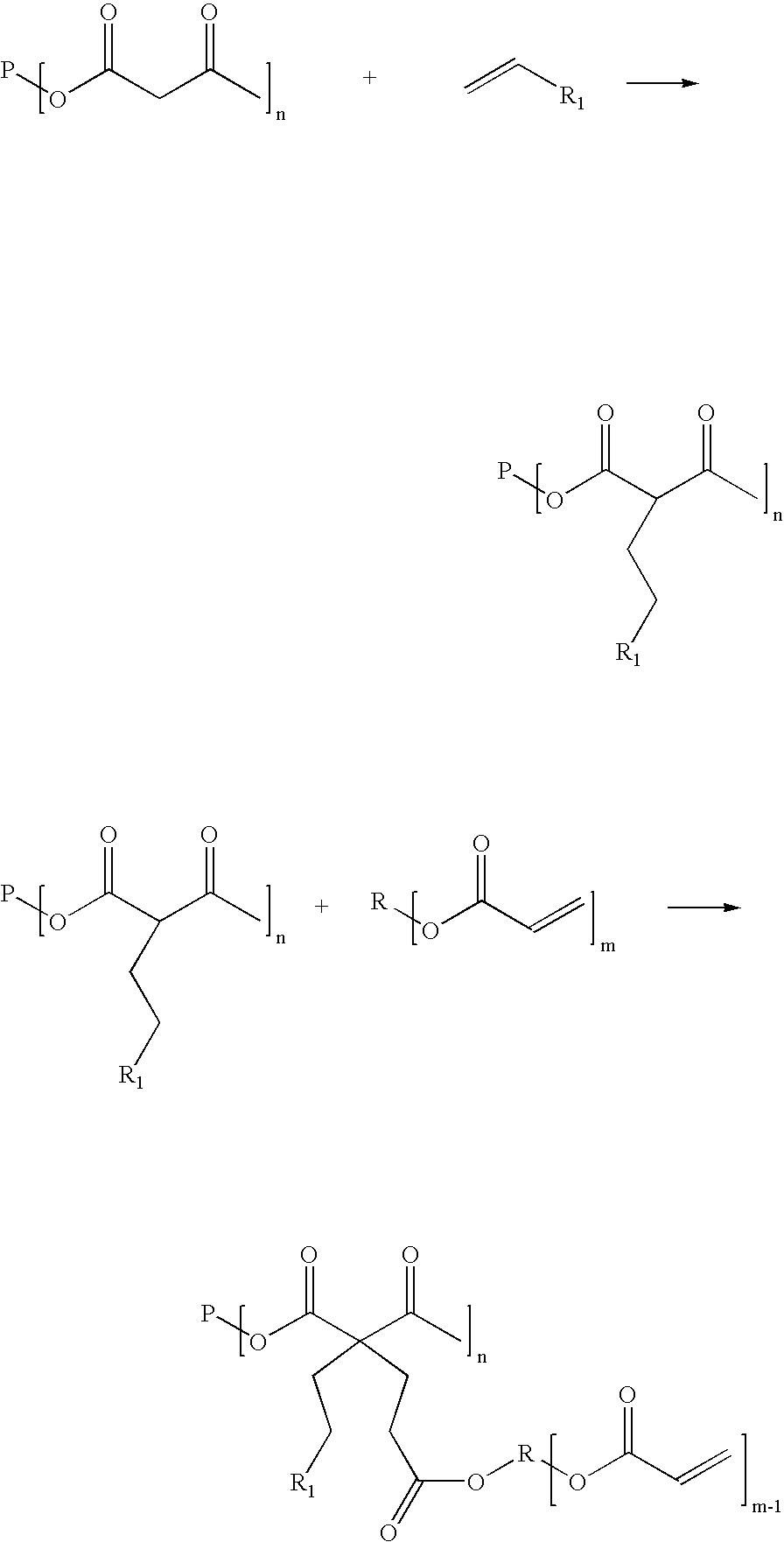
ActiveUS20060148924A1Less influenceIncrease the molar ratioPhotosensitive materialsPretreated surfacesPolymer scienceMeth-
The invention describes curable liquid acryloyl group containing compositions, which are produced by reacting monofunctional vinyl compounds and multifunctional acrylic esters with β-dicarbonyl group containing compounds having two activated hydrogen atoms in its methylene position. These material can be polymerized or crosslinked by free radical polymerization, UV (ultraviolet) or electron-beam radiation. The curable liquid compositions are suitable for producing curable coatings, printing inks, adhesives, or moulding compositions.
Owner:SUN CHEM CORP
Nanometer hydroxyapatite/chitosan porous composite scaffold material as well as bionic dialysis mineralization preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108478880AGood biocompatibilityHigh biosecurityTissue regenerationProsthesisFreeze-dryingPorous composite
The invention belongs to the technical field of bone tissue engineering, and discloses a nanometer hydroxyapatite / chitosan porous composite scaffold material as well as a bionic dialysis mineralization preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps that (1) chitosan is dissolved in an acetic acid solution to obtain a chitosan solution; the chitosan solution isput into a container for freezing; freeze drying is performed to obtain an early-period chitosan porous scaffold; (2) the early-period chitosan porous scaffold is soaked in alkali liquid; water washing is performed until the pH is 7 to 8; freeze drying is performed to obtain a chitosan porous scaffold; (3) the chitosan porous scaffold is soaked in an alkaline phosphatase solution; then, the chitosan porous scaffold and the alkaline phosphatase solution are charged into a dialysis bag; the dialysis bag is put into a mixed solution of calcium glycerophosphate and CaCl2; constant-temperature constant-speed stirring is performed for mineralization; taking out, washing and freeze drying are performed to obtain the nanometer hydroxyapatite / chitosan porous composite scaffold material. The nanometer hydroxyapatite / chitosan porous composite scaffold material can be applied to the field of bone tissue engineering, particularly the bone defect repair.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of polystyrene-based mesoporous silica film
InactiveCN102050955AFacilitate depositionIncrease the molar ratioElectrophoretic coatingsPolystyreneMesoporous silica
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polystyrene-based mesoporous silica film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out surface sulfonation modification on a polystyrene slice; mixing and stirring water (H2O), ammonia water (NH3) and tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) in a mole proportion of 1:0.008:0.012 to prepare a sol solution, wherein the ammonia water serves as a catalyst, and the tetraethoxysilane serves as a silicon source; putting two electrode pads in the sole solution, deviating a polystyrene matrix to an anode plate, applying an electric field at two ends of the electrode pads, and applying an electric field at the two ends of the electrode pads for 4 hours-7 hours by using a voltage of 2.8V-4.0V; and obtaining a polystyrene-based mesoporous silica deposition film, drying and then obtaining the polystyrene-based mesoporous silica film. The film is even in thickness, the surface is smooth and has no crack, and vermicule-like mesoporous pore canals are formed and have a certain order. The preparation method in the invention is low in cost, simple to operate and easy to control, the required equipment is simple, and the large-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Soil remediation process
InactiveUS20110182670A1Mitigating minimising damageIncrease the molar ratioIndividual molecule manipulationContaminated soil reclamationPlant rootsSoil remediation
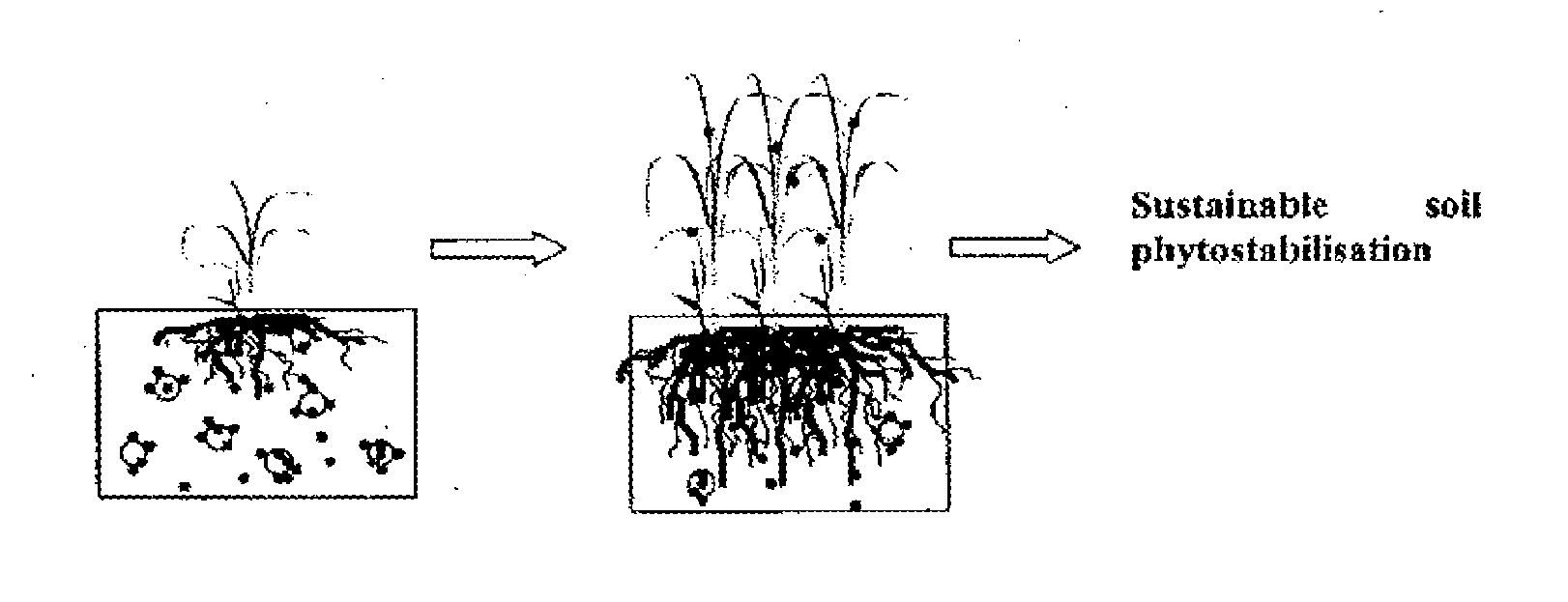
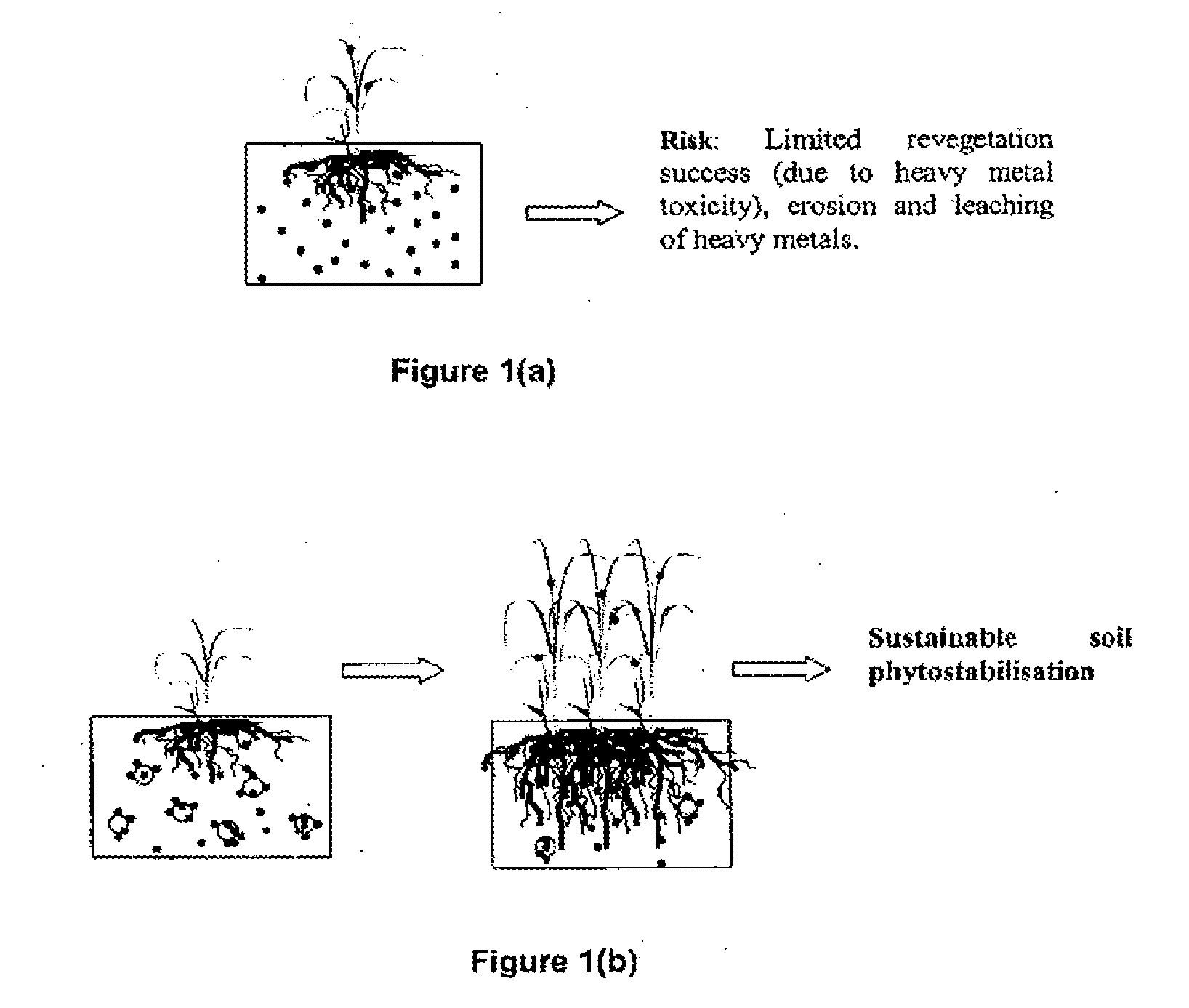
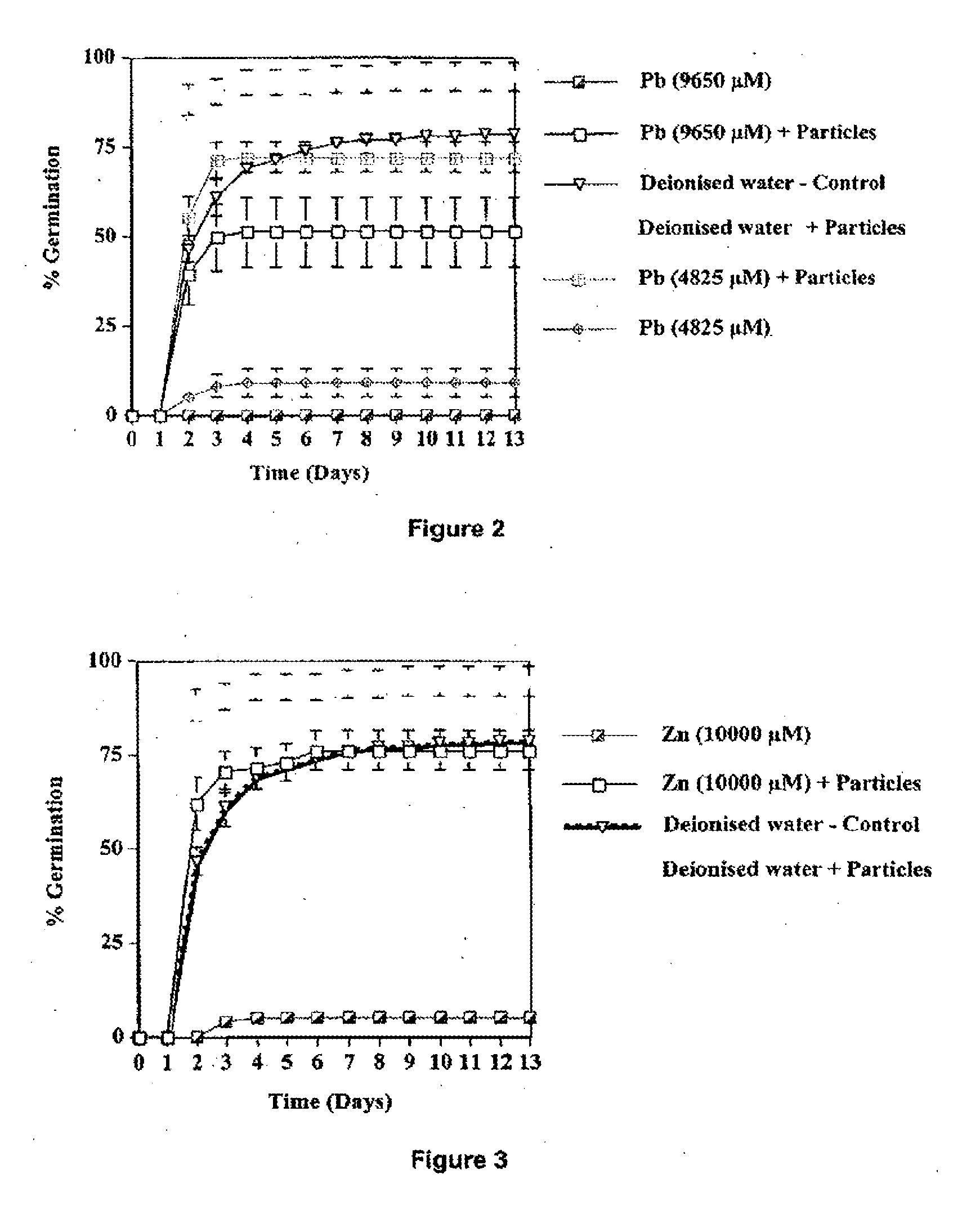
The invention provides a process for remediation of sites contaminated with metals such as former industrial sites and mines. In particular the invention provides a process for site remediation comprising the steps of: (a) adding metal-binding particles to a site containing one or more metal contaminants such that at least some of the one or metal contaminants are sequestered by the particles, and (b) populating the site with plants. The use of the particles of the present invention in association with plants, and microbiota associated with the plant roots can achieve sustainable phytostabilisation of contaminated sites.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Novel phosoxophite legands and use thereof in carbonylation processes
ActiveUS20060100453A1High activityHigh selectivitySilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationCarbonylationProtein carbonyl
A novel organophosphorus composition and synthesis thereof, the composition being characterized by one phosphite moiety, one phosoxophite moiety, and a plurality of sterically bulky substituents. The novel composition finds utility as a ligand in Group VIII transition metal phosoxophite complex catalysts and complex catalyst precursors that are used in carbonylation processes, preferably, hydroformylation processes. Additionally, there is disclosed a novel method of preparing a phosphoromonochloridite composition that finds utility as a precursor to the novel phosoxophite composition.
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Process for making monomenthyl esters
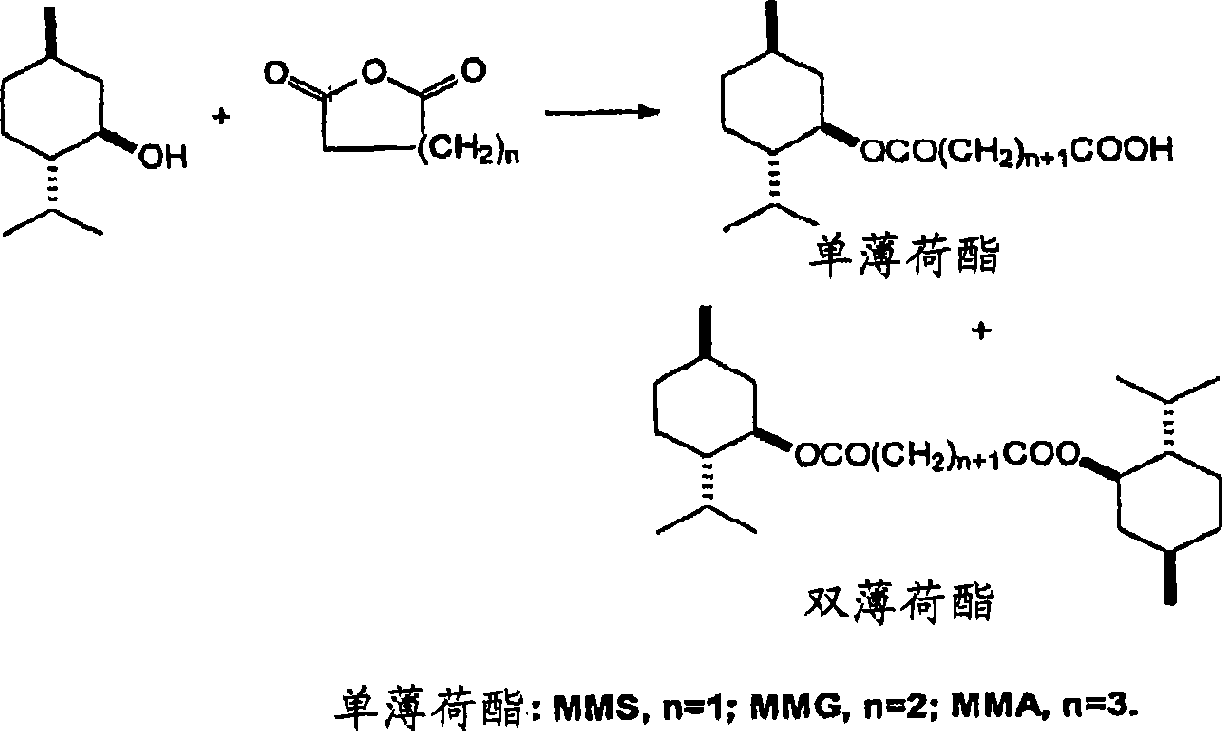
ActiveCN101389588AIncrease the molar ratioEfficient manufacturingOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationMentholAlkaline earth metal
A process for making monomenthyl esters of dicarboxylic acids is disclosed. Menthol reacts with a saturated, cyclic anhydride in the presence of a base catalyst under conditions effective to produce a mixture of mono- and bis-menthyl esters in which the molar ratio of mono- to bis-menthyl esters is enhanced compared with the ratio of esters produced in a similar uncatalyzed process.
Owner:利安德巴塞尔调味香料和芳香有限责任公司
Silicon tetrachloride hydrogenation method
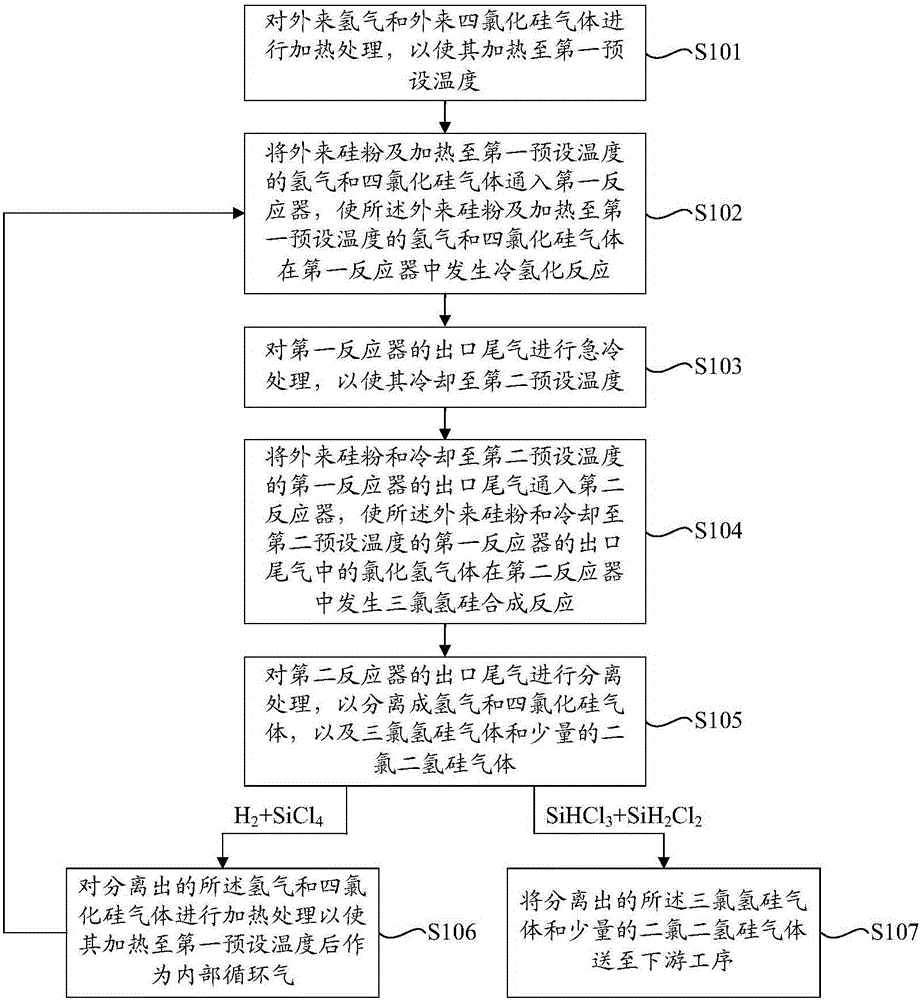
ActiveCN106395832AHigh yieldEfficient recyclingHalogenated silanesHydrogenation reactionDichlorosilane
The invention provides a silicon tetrachloride hydrogenation method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) heating external hydrogen gas and external silicon tetrachloride gas to a first preset temperature; 2) introducing external silicon powder and the hydrogen gas and the silicon tetrachloride gas which are heated to the first preset temperature into a first reactor, and carrying out a cold hydrogenation reaction; 3) cooling the outlet tail gas of the first reactor to a second preset temperature; 4) introducing the external silicon powder and the outlet tail gas which is cooled to the second preset temperature into a second reactor, and carrying out a trichlorosilane synthesis reaction; and 5) subjecting the outlet tail gas of the second reactor to separation treatment, heating the separated hydrogen gas and the silicon tetrachloride gas to the first preset temperature and then returning to the step 2), and conveying the separated trichlorosilane gas and a small amount of dichlorosilane gas to a downstream process. The silicon tetrachloride hydrogenation method does not need a complex reactor and can increase the yield of the existing trichlorosilane and the one-way conversion rate of the existing silicon tetrachloride.
Owner:XINTE ENERGY
Preparation method of water purification carbon composite material with low nano zero-valent iron and nano-silver loading capacities
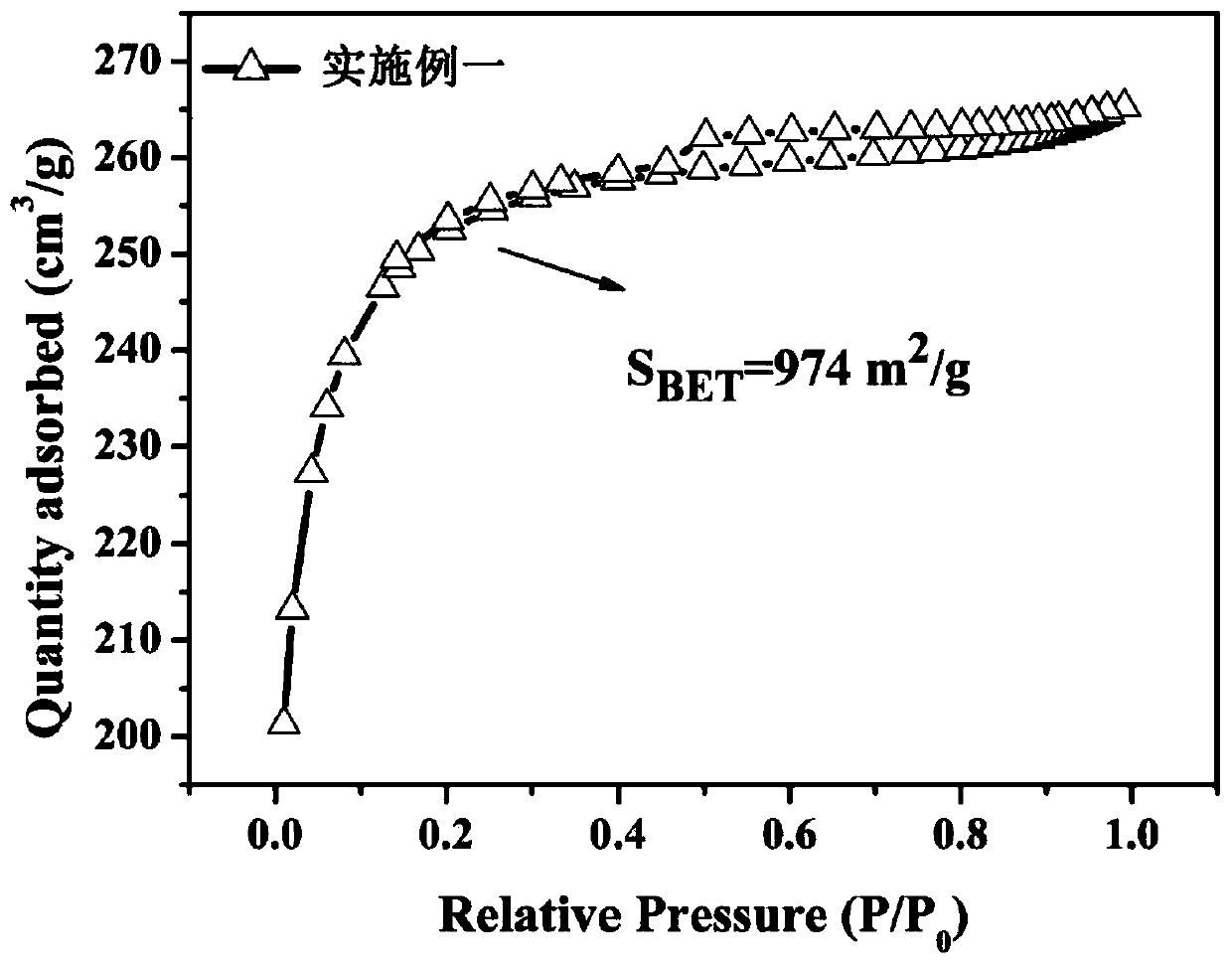
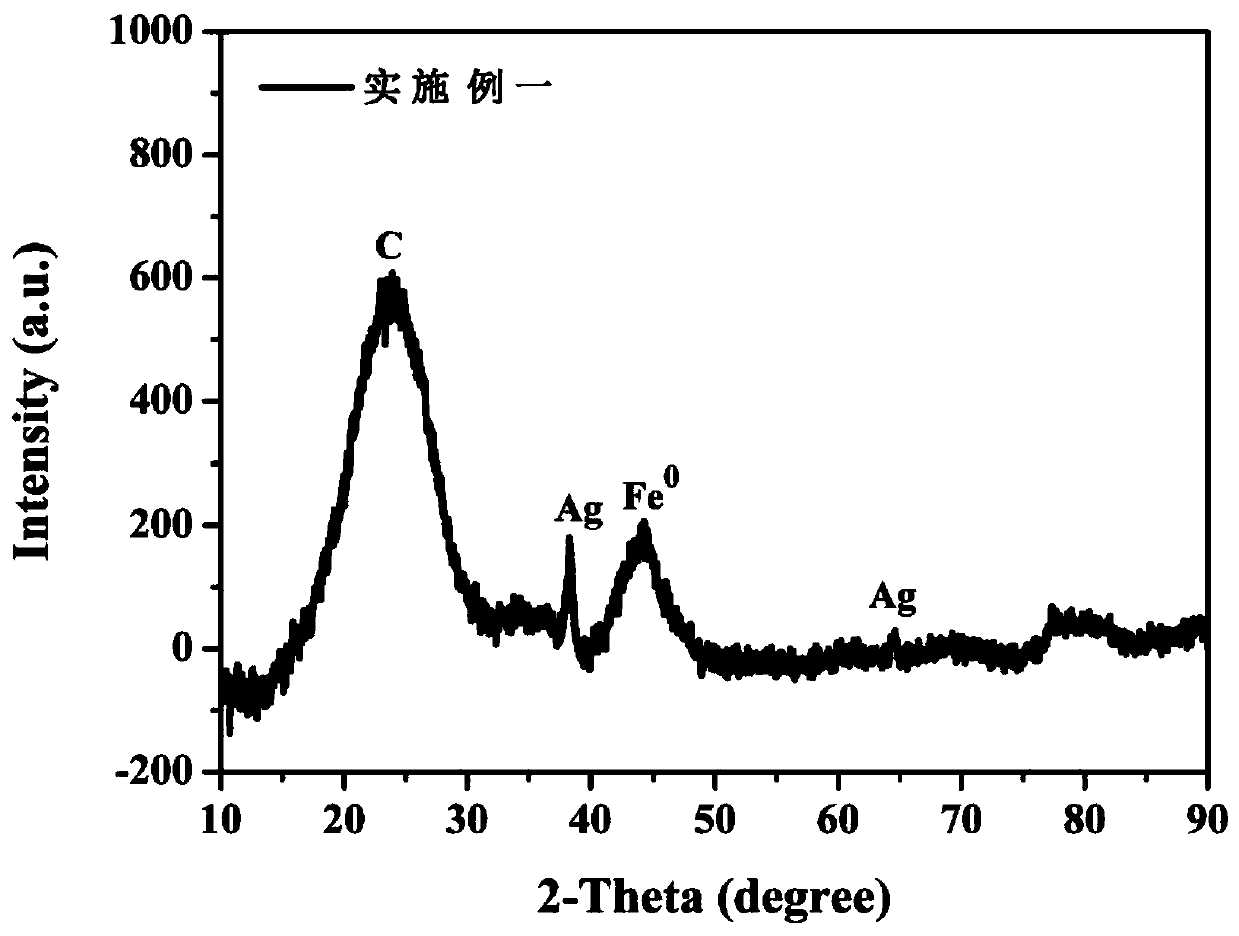
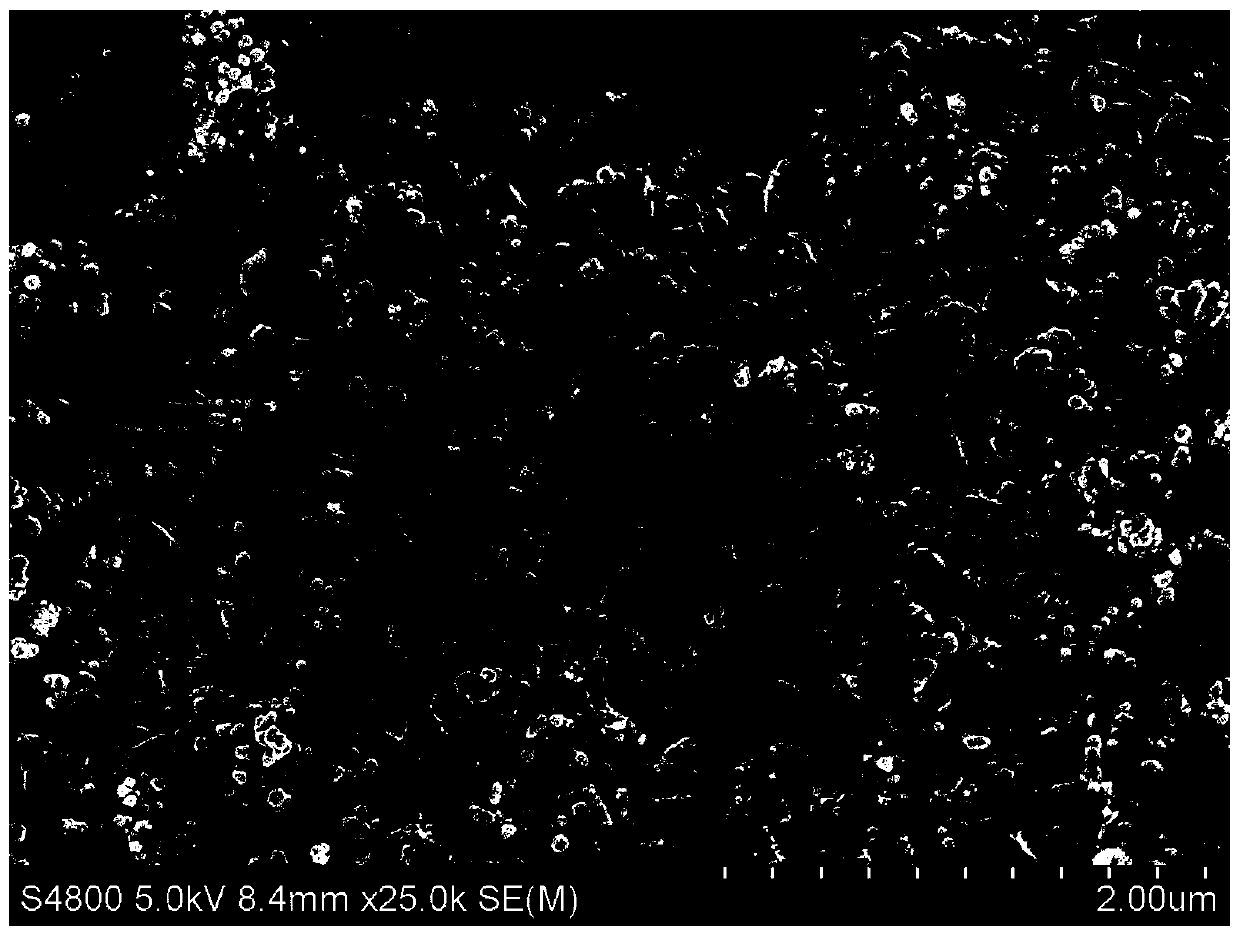
PendingCN110559990ALarge specific surface areaSmall specific surface areaOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCarbon compositesMulti pollutant
The invention relates to a preparation method of a water purification carbon composite material with low nano zero-valent iron and nano-silver loading capacities. The water purification carbon composite material with the low nano zero-valent iron and nano-silver loading capacities, which is prepared by the preparation method, has a high specific surface area; the loading capacity of iron and the loading capacity of silver in the composite material are low; the particle size of nano zero-valent iron and the particle size of nano silver are both smaller than 20nm; the water purification carbon composite material can adsorb, convert or degrade various pollutants in drinking water at the same time; the release amount of iron and silver is extremely low; and the water purification carbon composite material is a water purification material with extremely high application values.
Owner:KETAN XIAMEN NEW CARBON MATERIAL CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com