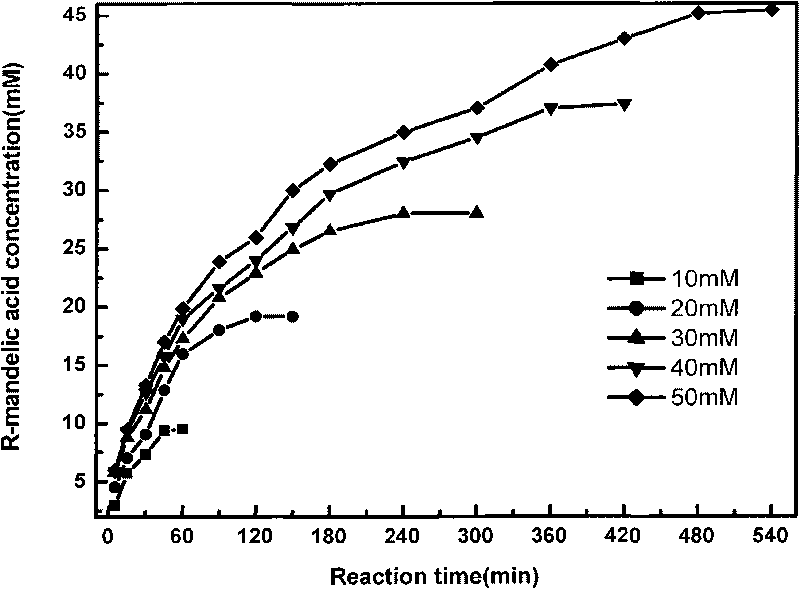
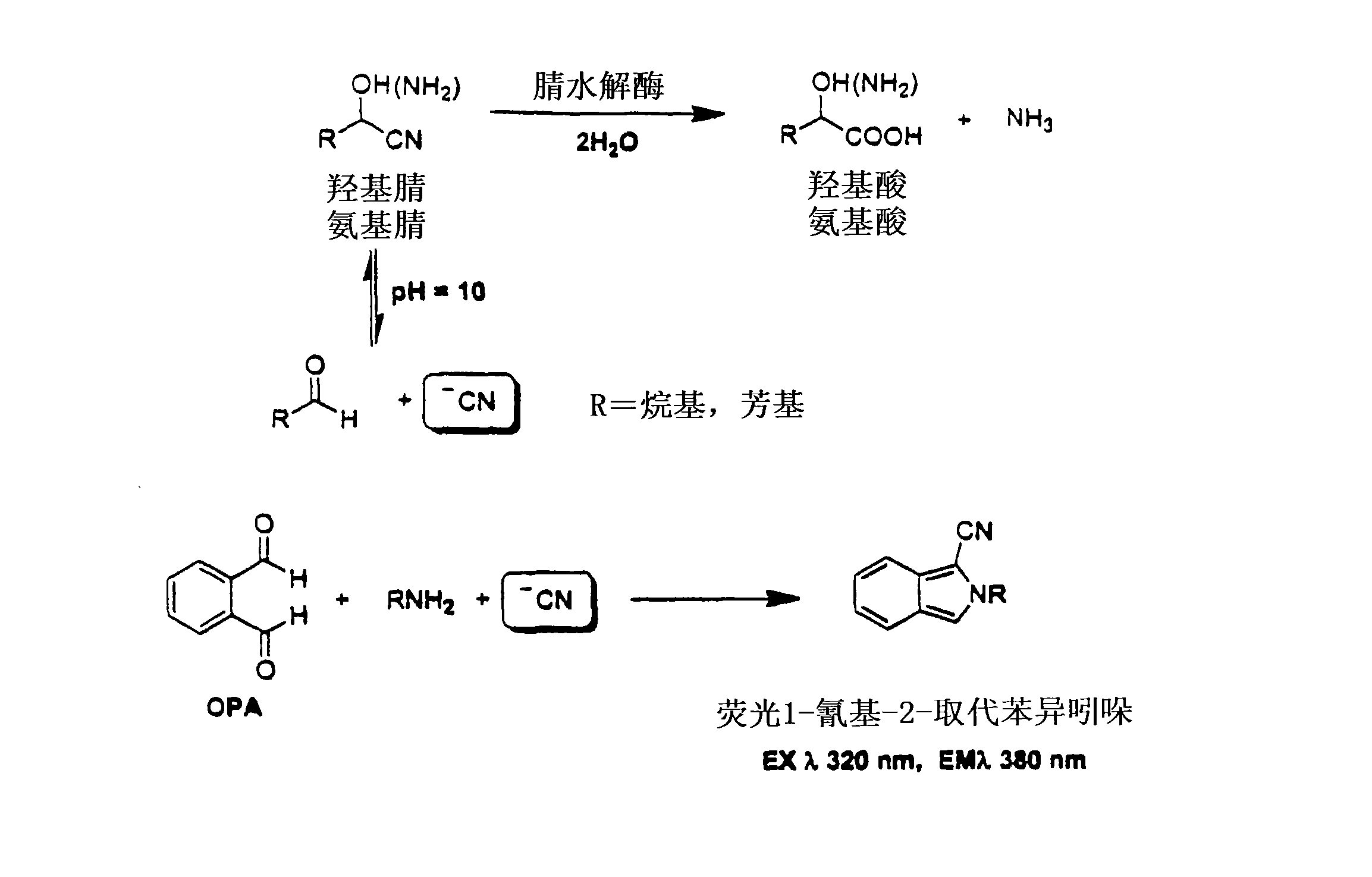
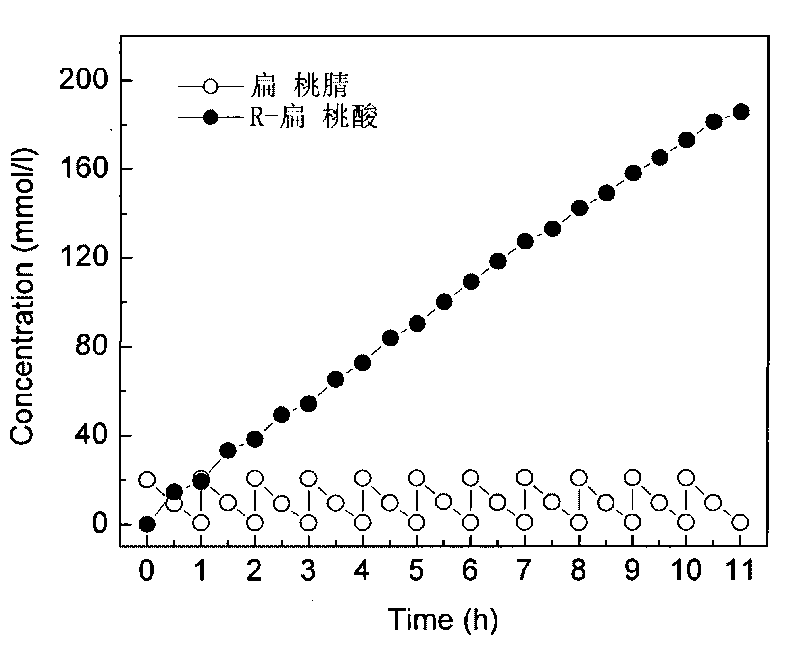
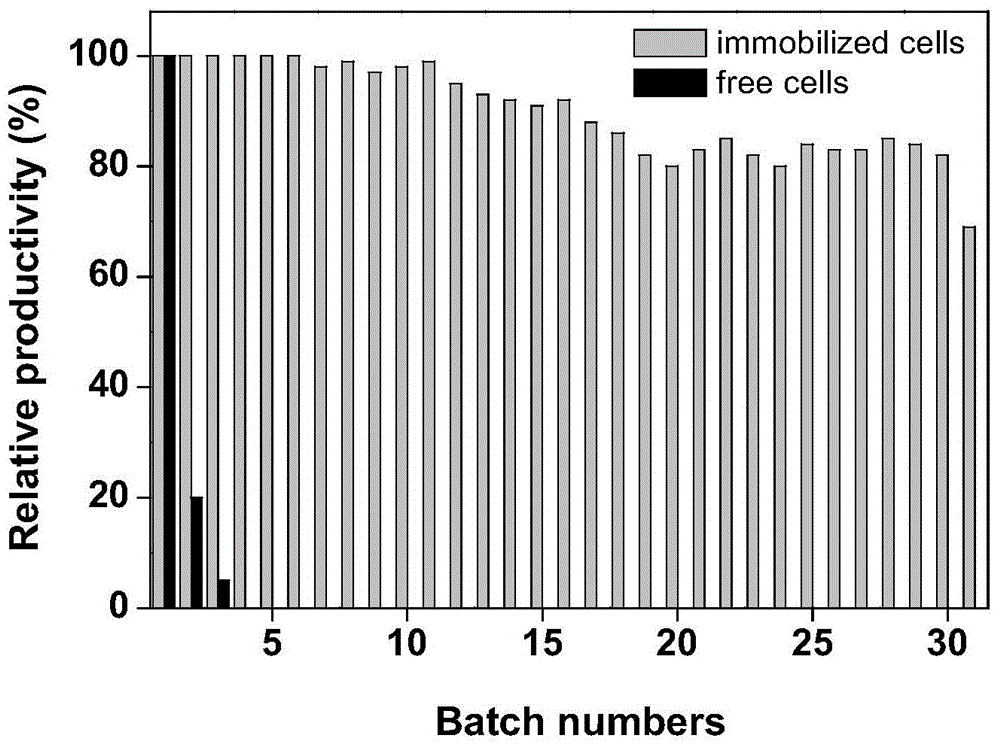
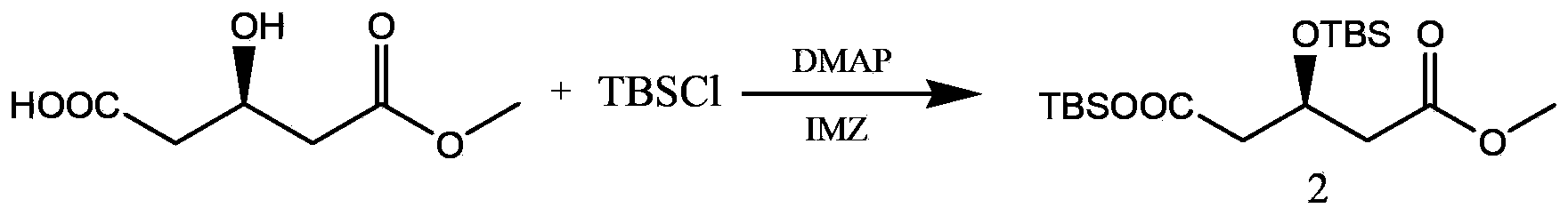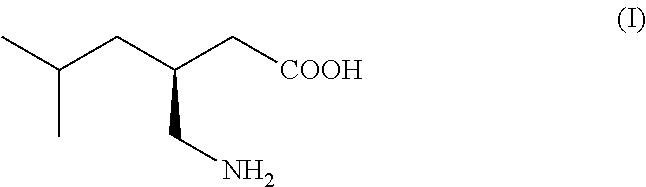Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
191 results about "Nitrilase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
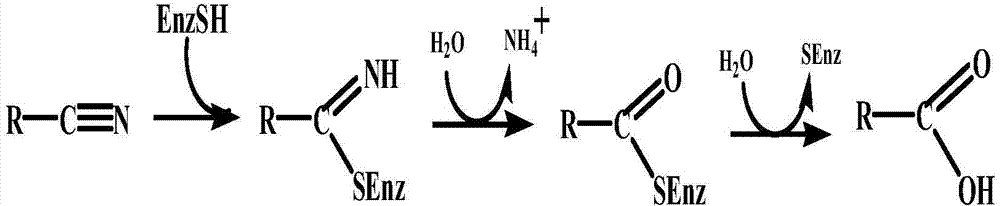
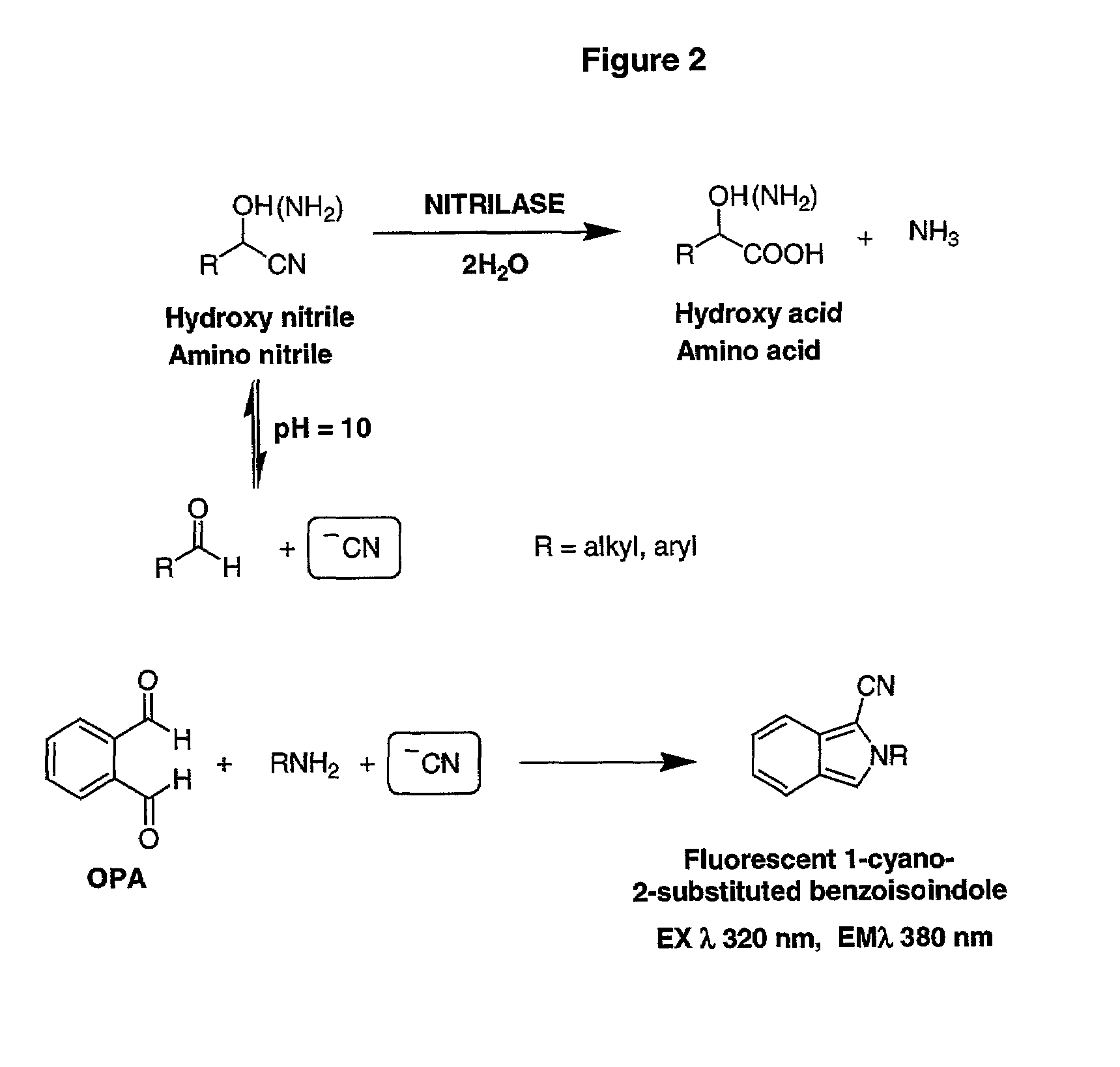
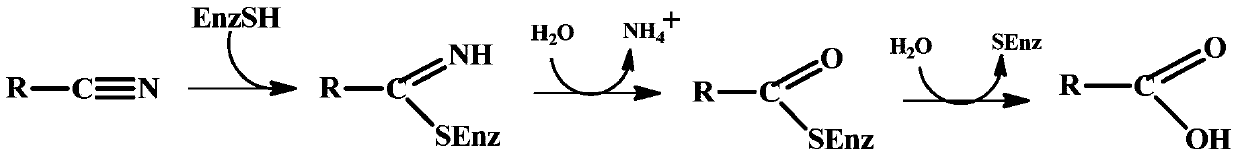
Nitrilase enzymes (nitrile aminohydrolase; EC 3.5.5.1) catalyse the hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids and ammonia, without the formation of "free" amide intermediates. Nitrilases are involved in natural product biosynthesis and post translational modifications in plants, animals, fungi and certain prokaryotes. Nitrilases can also be used as catalysts in preparative organic chemistry. Among others, nitrilases have been used for the resolution of racemic mixtures. Nitrilase should not be confused with nitrile hydratase (nitrile hydro-lyase; EC 4.2.1.84) which hydrolyses nitriles to amides. Nitrile hydratases are almost invariably co-expressed with an amidase, which converts the amide to the carboxylic acid. Consequently, it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish nitrilase activity from nitrile hydratase plus amidase activity.
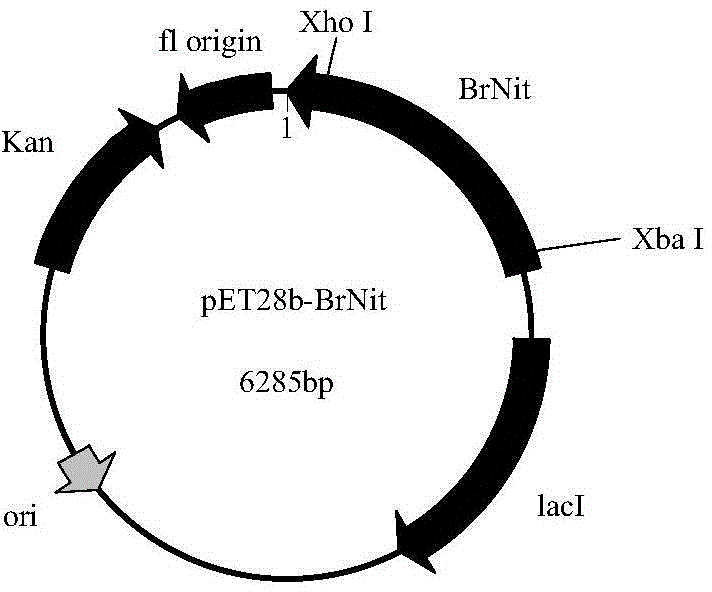
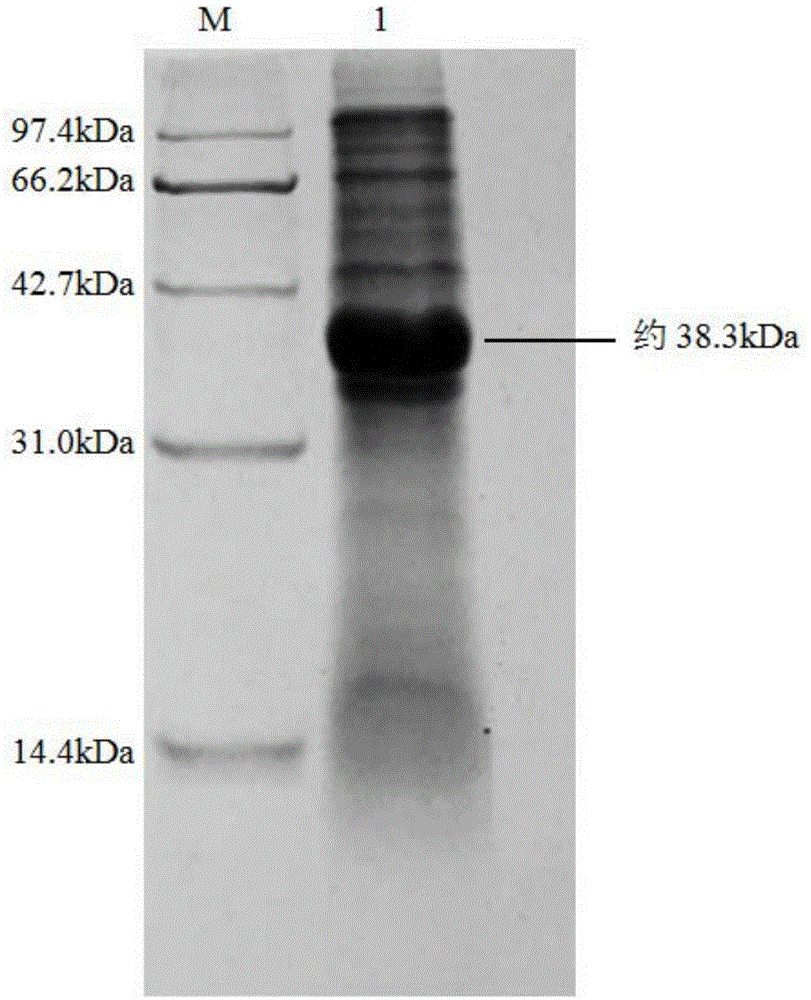
Nitrilase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107177576AImprove thermal stabilityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliProtein molecules
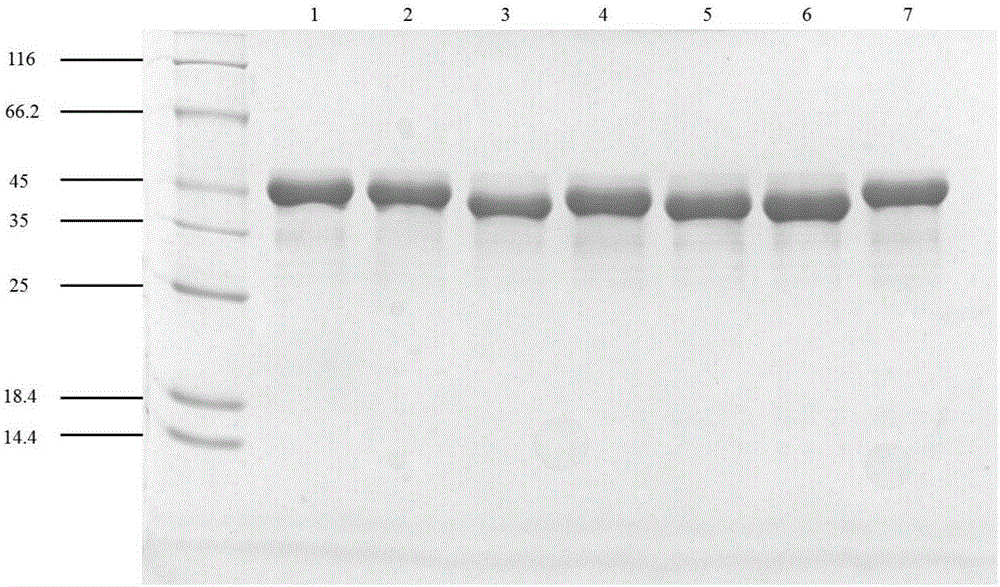
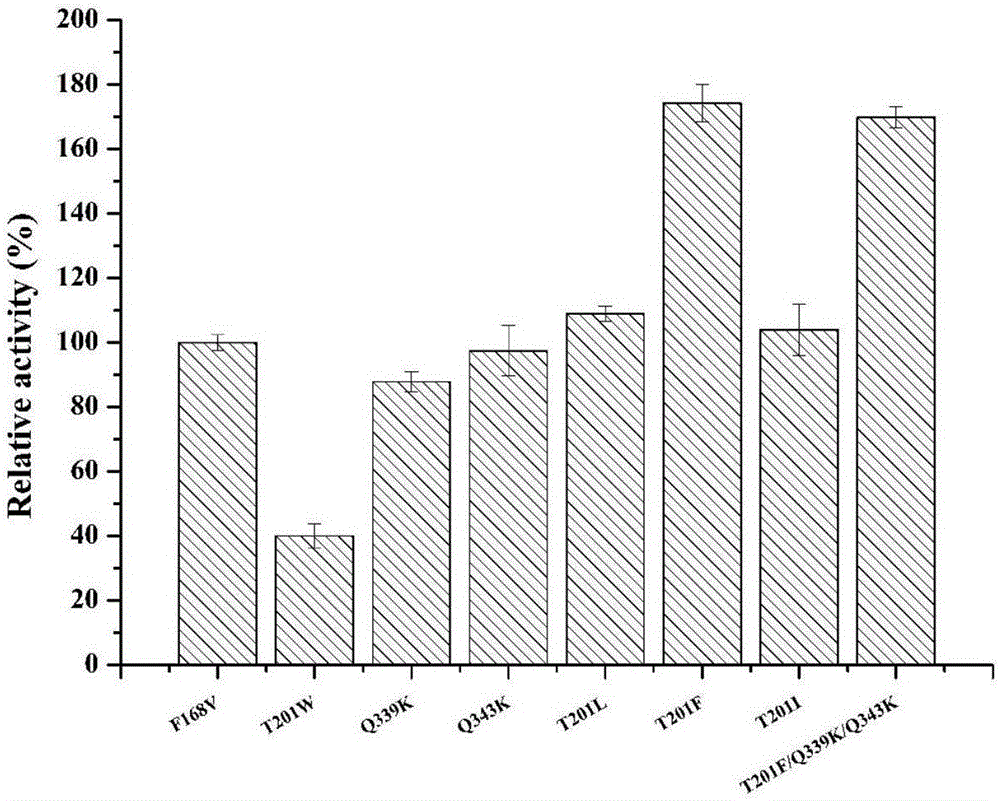
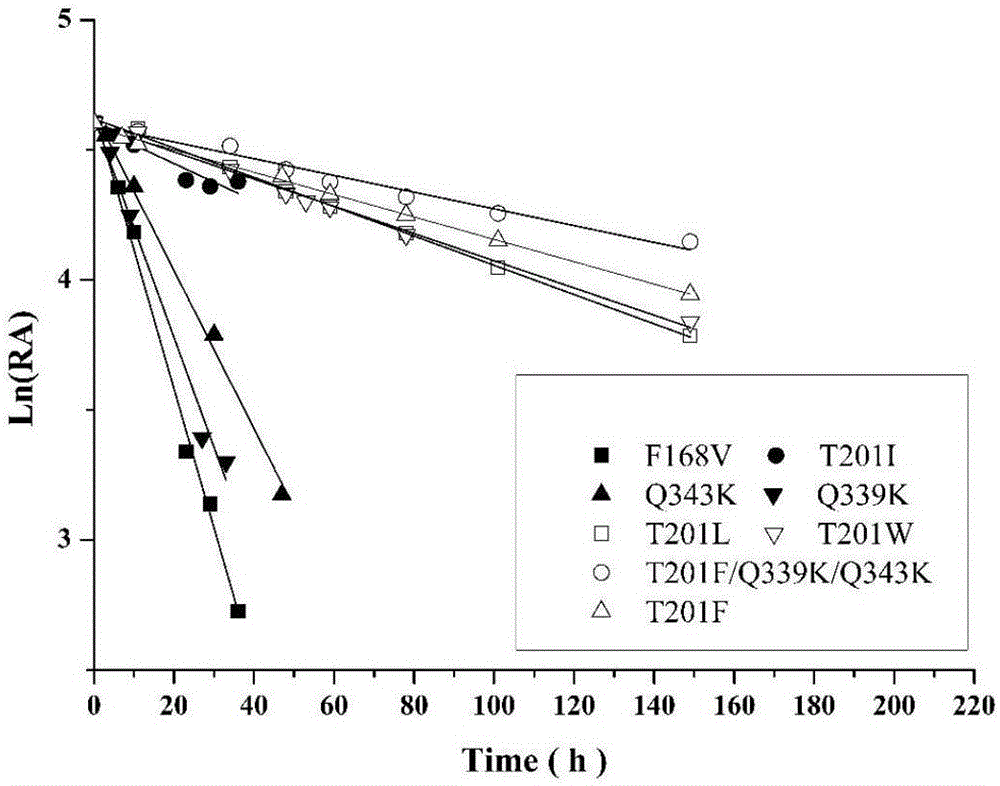
The invention discloses nitrilase mutant and application thereof. The mutant is obtained by carrying out mutation one or more of the sits including 201 site, 339 site and 343 site of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2. By modification of protein molecules, the thermal stability of nitrilase AcN pure enzyme is improved by 14 times to a maximum extent, recombinant escherichia coli which contains the nitrilase mutant is used for hydrolyzing 1-cyanocyclohexane acetonitrile at the high temperature (45 DEG C), and the reaction time is shortened to be one third of the original reaction time. Therefore, the acquired mutant has good application prospect in efficient catalysis of the 1-cyanocyclohexane acetonitrile to synthesize 1-cyanocyclohexane acetic acid as a gabapentin intermediate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
High-density fermentation method of engineering bacteria containing nitrilase
InactiveCN104212785APrevention of waste and other disadvantagesControl growth rateHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHigh concentration
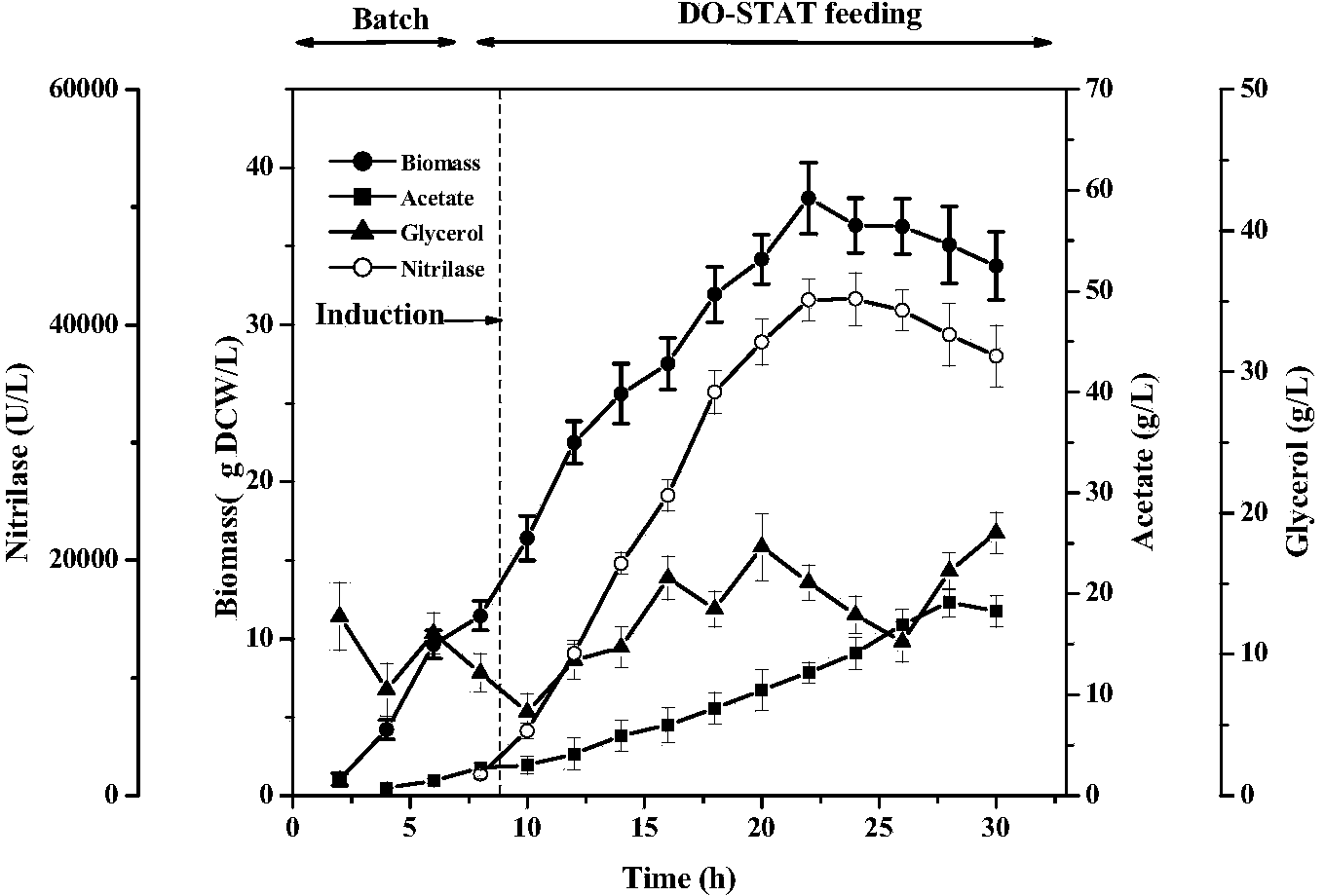
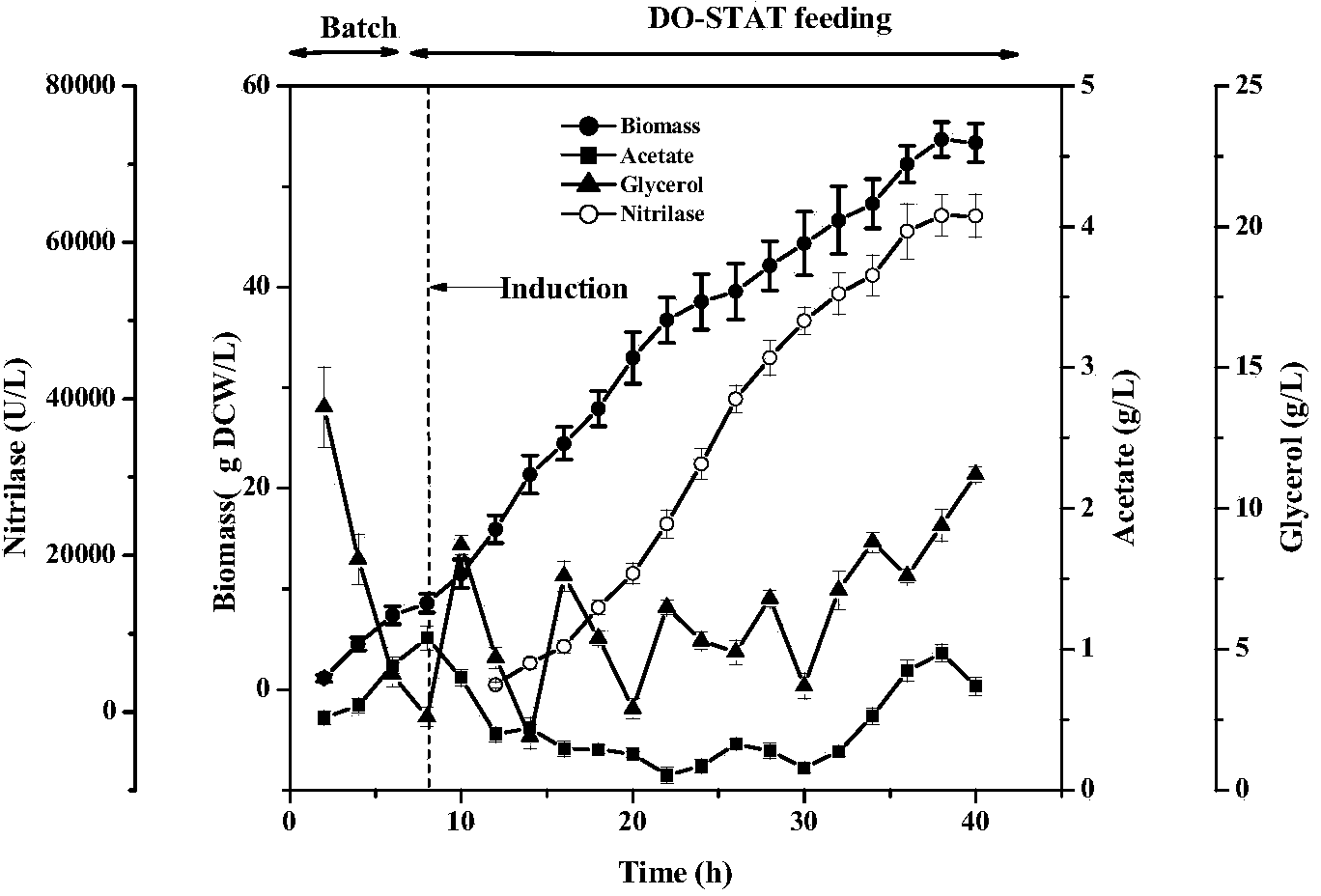
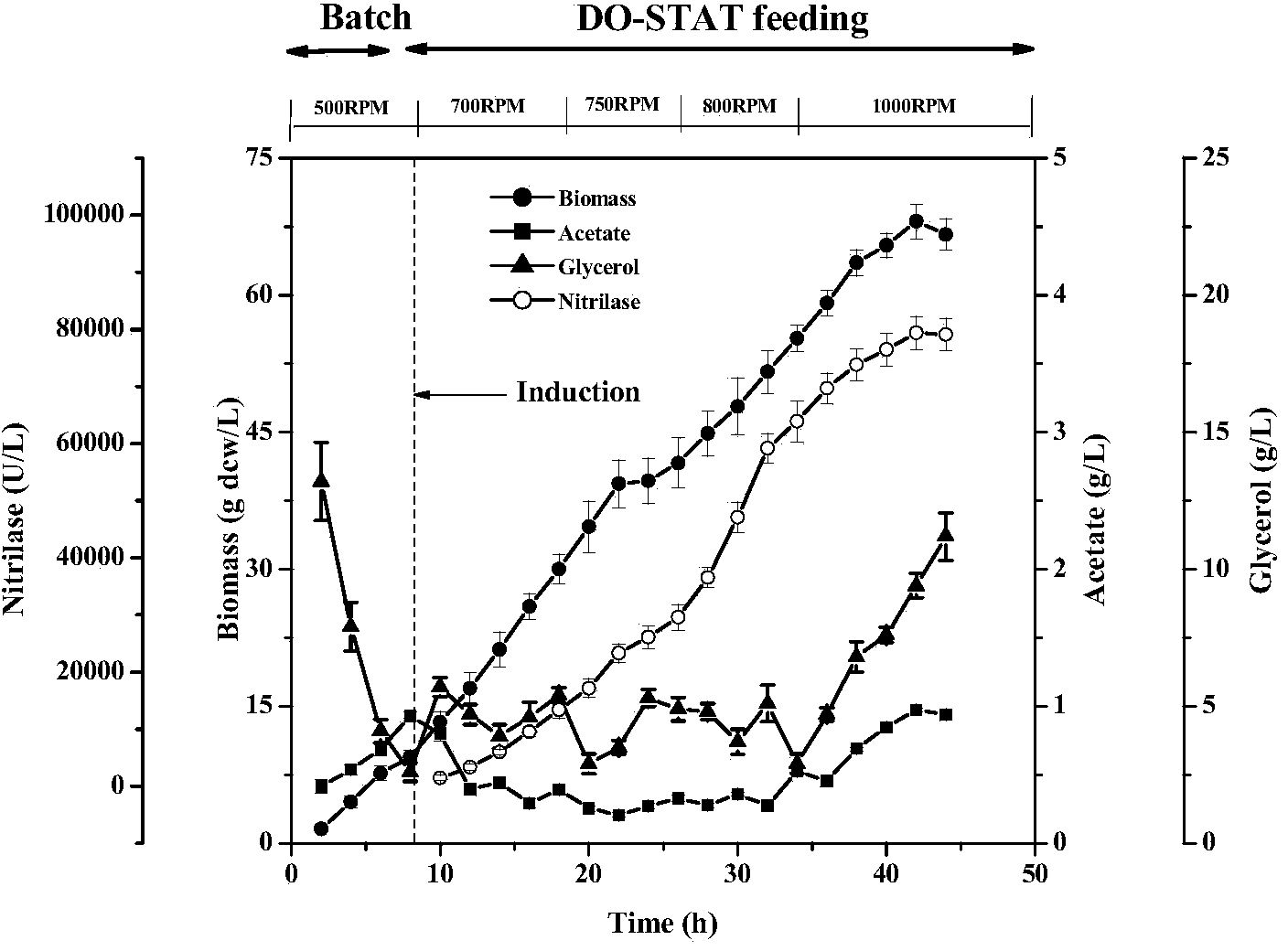
The invention discloses a high-density fermentation method of engineering bacteria containing nitrilase. The method adopts a novel recombinant Escherichia coli fermentation and supplementary material culture medium formula, and uses a method of DO-STAT coupling step-by-step induction and gradual increase of the speed stage by stage. The method not only meets the need for mixing power in the culture process with biomass increase, effectively controls the growth rate of thalli, and prevents disadvantages of produced acid accumulation caused by fast growth of thalli, feedback inhibition and culture medium waste. In addition, the induced mode of batch-by-batch lactose supplement addition avoids the high viscosity of the fermentation broth caused by high concentration of lactose, resulting in resistance of oxygen transfer and mass transfer, but also improves the induction strength. The high-density fermentation technology of the invention increase the biomass of recombinant Escherichia coli from 10.35g DCW / L to 70g DCW / L, volume enzyme activity from 18205U / L to 103530U / L, and the fermentation level by 4.7 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Novel rhodococcus, rhodococcus-origin nitrilase gene, nitrilehydratase gene and amidase gene and process for producing carboxylic acids by using the same
InactiveCN1340101AHigh puritySuitable for industrial productionBacteriaHydrolasesChemical compoundCarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to a novel Rhodococcus bacterium and to a process of hydrolyzing a cyano group of a nitrile compound using a novel Rhodococcus bacterium to produce the corresponding carboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to a process of producing carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids using a transformant transformed with a plasmid containing a nitrilase gene, a nitrile hydratase gene and an amidase gene derived from Rhodococcus bacteria capable of exhibiting particularly excellent position selectivity for the cyano group of aromatic polynitrile compounds, to such a transformant, such a plasmid, to such genes, to a process of producing an enzyme using the transformant, and to enzymes obtained by the process. The carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids obtained by the present invention are useful as starting materials for the synthesis of drugs, agrochemicals, dyestuffand other chemicals.
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Nitrilase and gene and application thereof
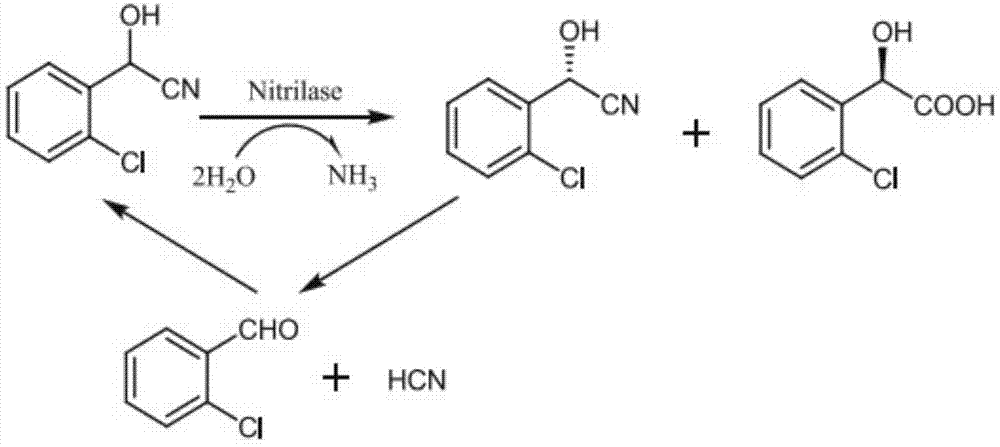
The invention discloses a new nitrilase and gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant containing the gene, a method for preparing the recombinant nitrilase or microbial cell containing the recombinant nitrilase by use of the recombinant expression transformant, and application of the microbial cell in dehydrating ortho-chlorine mandelonitrile or other analogues and producing chiral ortho-chlorine mandelonitrile or other analogues. The recombinant nitrilase disclosed by the invention comes from Labrenzia aggregate and can be used as a catalyst for dehydrating and splitting ortho-chlorine mandelonitrile or other analogues; and the recombinant nitrilase has the advantages of high catalysis efficiency, strong enantioselectivity, mild reaction conditions, environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nitrilase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN104774825AIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesDouble mutationSingle mutation
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant and its application in R-o-chloromandelic acid synthesis. The mutant is obtained by single mutation or double mutation of the 132nd threonine or 189th phenylalanine on the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with non-mutant nitrilase, the enzyme activity is increased by 3.70 times and reaches 1.08U / mg, and the enantioselectivity is up to 99%. Also, the result shows that in a two-phase system (with ratio of toluene to water being 2:8) the nitrilase mutant can catalyze 300mM o-chloromandelonitrile, and the yield is 90.8%. Through fed batch of the substrate, a maximum of 500mM o-chloromandelonitrile can be catalyzed, the yield is 90%, and the enantioselectivity is greater than 99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nitrilase gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
The invention provides a nitrilase gene coding nitrilase, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a recombinant gene engineering bacteria obtained by converting the recombinant vector and application thereof in preparing recombinant nitrilase. The nitrilase gene can be connected with an expression vector for construction to obtain endoenzyme expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene or secretion expression recombinant plasmid, and then the endoenzyme expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene or the secretion expression recombinant plasmid is respectively and correspondingly converted to a colibacillus bacterial strain to obtain recombinant colibacillus; the recombinant colibacillus contains recombinant nitrilase and can recombine colibacillus into an enzyme resource for biological catalysis and conversion. The recombinant nitrilase serves as the enzyme for conversion, and racemisation mandelonitrile, acrylonitrile, iminodiacetonitrile or 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carbonitrile and the like serve as a substrate for converting to react and prepare corresponding R-mandelic acid, crylic acid, iminodiacetic acid or chiral 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane formic acid and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nitrilase, encoding genes, carrier and application
InactiveCN104962540AAtom economy is highHigh potential for industrial applicationHydrolasesFermentationBrassica rapaBirdsrape Mustard
The invention discloses nitrilase from brassica rapa, encoding genes and an application of the encoding genes to the preparation of pregabalin chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid through biocatalysis, and an amino acid sequence of the nitrilase is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention provides novel nitrilase for preparing the (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid with high region and high stereoselectivity through hydrolysis, the concentration of hydrolysis substrates of the nitrilase can reach more than 1 M, and an ee (enantiomeric excess) value is kept more than 99 percent. The pregabalin important chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid can be prepared through the nitrilase; a preparation method of the (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid has the advantages of high atom economy, mild conditions, environmental friendliness and the like and has high industrial application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
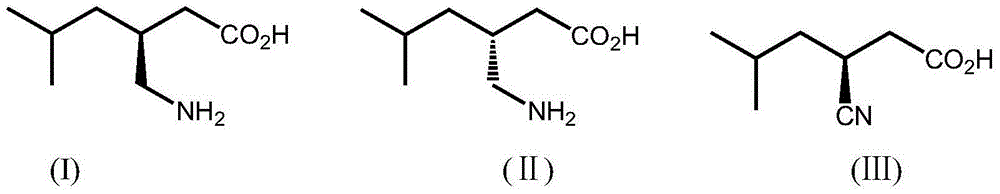
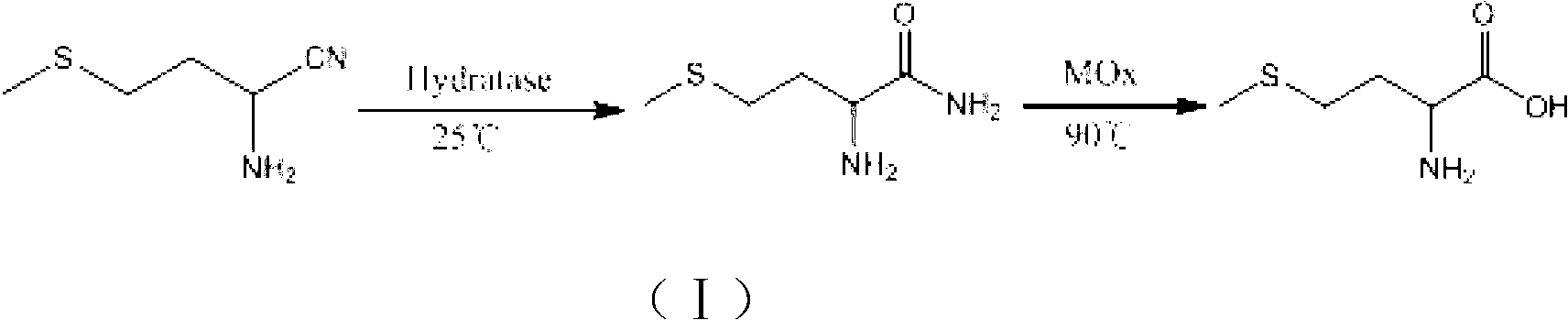
Method for preparing 2-amino-4-methylthio butyric acid by using recombinant nitrilase
InactiveCN102911975AEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWater bathsMethionine biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2-amino-4-methylthio butyric acid by using recombinant nitrilase, which comprises the following steps: performing water bath shaker reaction (25-40 DEG C, 150-200rpm) on an enzyme source and a substrate in a reaction system of a buffer solution with a pH value of 7.0-9.0, wherein the enzyme source is a wet bacterium obtained through the induced culture of a recombinant engineering bacterium containing nitrilase, and the substrate is 2-amino-4-methylthio butyronitrile; and after the reaction is finished, performing post treatment on the reaction liquid to obtain 2-amino-4-methylthio butyric acid. According to the invention, the gene engineering bacterium is used for experiment of methionine production through biological catalysis and can biologically catalyze methionine production effectively, and the 2-amino-4-methylthio butyronitrile conversion rate within 2 hours is up to 80-100%. Thus, the bacterium has wide application prospects in the field of methionine production through biological catalysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing rosuvastatin intermediate
ActiveCN103361386ASolve the problem of low concentration and low conversion rateIncrease concentrationHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acidSubstrate concentration
The invention relates to a method for preparing a rosuvastatin intermediate which is (R)-3-hydroxy-monomethyl glutarate and hydroxyl-protected (R)-3-hydroxy- monomethyl glutarate. According to the method, (R)-4-cyano-3-hydroxy-methyl butyrate which servers as a substrate is subjected to reaction under the action of an enzyme to generate the (R)-3-hydroxy- monomethyl glutarate, and particularly the enzyme is the recombinant nitrilase, and the reaction is carried out in a aqueous-phase buffering solution with the pH value of 7.0-9.0 at the temperature of 25-35 DEG C. Because the specific recombinant nitrilase is adopted by the method, the problems of ultralow concentration of the substrate and low conversion rate in the existing method for preparing the rosuvastatin intermediate through biological catalysis are solved. The method has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions and high reaction efficiency, is easy and convenient to operate and has important industrial application value.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Double knockout recombinant rhodococcus as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105420154AHigh expression activityQuality improvementBacteriaHydrolasesSaccharumLevansucrase
The invention discloses a construction method of double knockout recombinant rhodococcus. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) primers are designed according to nitrile hydratase gene sequence of the rhodococcus for respective amplification of an upstream sequence and a downstream sequence of a nitrile hydratase gene, and an upstream fragment and a downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are obtained; (2) the upstream fragment and the downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are inserted into a suicide plasmid, and a recombinant suicide plasmid is obtained, wherein the suicide plasmid carries a kanamycin resistant gene and a levansucrase gene; (3) competent cells of recombinant rhodococcus of an amidase gene are knocked out through transformation of the recombinant suicide plasmid, and the double knockout recombinant rhodococcus is obtained: first screening is performed through kanamycin resistance, and a first recombinant colony is obtained and subjected to second screening through a sucrose plate. The invention further discloses recombinant rhodococcus with high nitrilase expression, a construction method of the recombinant rhodococcus and a method for preparing acrylamide.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nitrilase mutant and application thereof in preparation of nicotinic acid
ActiveCN106148310AEfficient productionExpansion of microbial resourcesBacteriaHydrolasesWater bathsBacterial strain
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant and application thereof in preparation of nicotinic acid. The mutant can be used for mutating phenylalanine at position 168 of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 into valine and serine at position 192 into phenylalanine. A wet cell obtained by induced expression of a recombinant bacterial strain containing an itrilase mutant encoding gene is used as an enzyme source, 3-cyanopyridine is used as a reaction substrate, and a PBS buffer with pH of 7.0 is used as a reaction medium to form a reaction system, a reaction is carried out in a 40 DEG C water bath, and the nicotinic acid is obtained after the reaction is finished.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for the preparation of pregabalin
ActiveUS20150344919A1Economical and simpleEasy to implementOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAlkaline earth metalMethyl group
The present invention provides an improved process for the preparation of a compound of formula (I), which comprises the steps of: formula (I), (a) reacting isovaleraldehyde of formula (II) and alkyl cyanoacetate of formula (III) optionally in presence of salts of weak acid and weak base or weak base in a suitable solvent to get 2-cyano-5-methyl-hex-2-enoic acid alkyl ester of formula (IV); (b) reacting 2-cyano-5-methyl-hex-2-enoic acid alkyl ester of formula (IV) with a suitable cyanide source in water or in an organic solvent or mixture thereof to get 2-isobutylsuccinonitrile of formula (V); (c) obtaining optionally 2-isobutylsuccinonitrile of formula (V) by reacting isovaleraldehyde of formula (II) and alkyl cyanoacetate of formula (III) in presence of suitable cyanide source in water or in an organic solvent or mixture thereof in single step; (d) converting 2-isobutylsuccinonitrile of formula pa (V) to racemic 3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoic acid or salt thereof of formula (VI) with a genetically modified nitrilase enzyme (Nit pt 9N_56_2) in water or optionally with an organic co-solvent at appropriate pH and temperature; (e) converting racemic 3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoic acid or salt thereof of formula (VI) to racemic alkyl 3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoate of formula (VII) by treatment with alcohol (R3OH) and acidic catalyst or alkyl halide (R3X) in presence of a base in a suitable solvent or a mixture of solvents thereof; (f) obtaining (S)-alkyl 3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoate of formula (VIII) and (R)-3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoic acid or salt thereof of formula (X) by enzymatic enantioselective hydrolysis in water or organic solvent or a mixture thereof from racemic alkyl 3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoate of formula (VII); (g) obtaining optionally the compound of formula (VII) by racemizing unwanted (R)-3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoic acid or salt thereof of formula (X) or substantially enriched (R)-3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoic acid salt thereof of formula (X) in presence of a base in organic solvent or a mixture thereof; (h) converting (S)-alkyl 3-cyano-5-methyl-hexanoate of formula (VIII) to pregabalin of formula (I) by hydrolyzing ester group with suitable alkali or alkaline earth metal base followed by hydrogenation optionally in one pot in a solvent selected from water or other organic solvents or a mixture thereof in presence of a suitable hydrogenation catalyst.
Owner:HIKAL
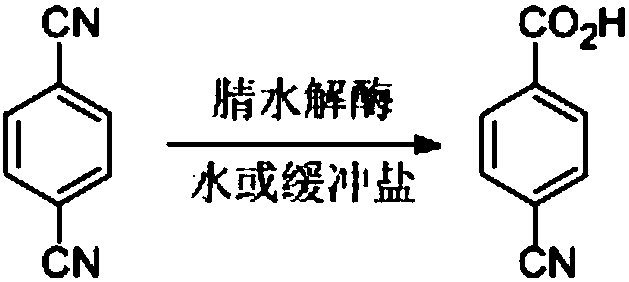
Nitrilase capable of preparing paracyanobenzoic acid by hydrolyzing p-benzenedicarbonitrile
ActiveCN107641622AMild reaction conditionsQuick responseHydrolasesFermentationArabidopsis thalianaPollution
The invention discloses a nitrilase N1 derived from pantoea sp.AS-PWVM4 and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N2 derived from arabidopsis thaliana and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N3 derived from acidovoraxfacilis 72W and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N4 derived from leptolyngbya sp. and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N5 derived from brassica oleracea var.oleracea and a gene thereof and a nitrilase N6 derived from camelina sativa and a gene thereof, and a method for preparing paracyanobenzoic acid as p-aminomethylbenzoic acid intermediate by using the nitrilase as a biological catalyst; resting cells ofthe corresponding nitrilases can be used for catalyzing 100g / L of substrate; the conversion rate is greater than 99%; the method has the obvious characteristics of mild reaction conditions, no pollution and simple process route, and has broad industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plant nitrilase mutant, coding gene and application of plant nitrilase mutant
ActiveCN110714002AImprove solubilityHigh catalytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesBrassicaceaeArabis alpina
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nitrilase mutant and application thereof in preparation of anti-epileptic drug intermediate
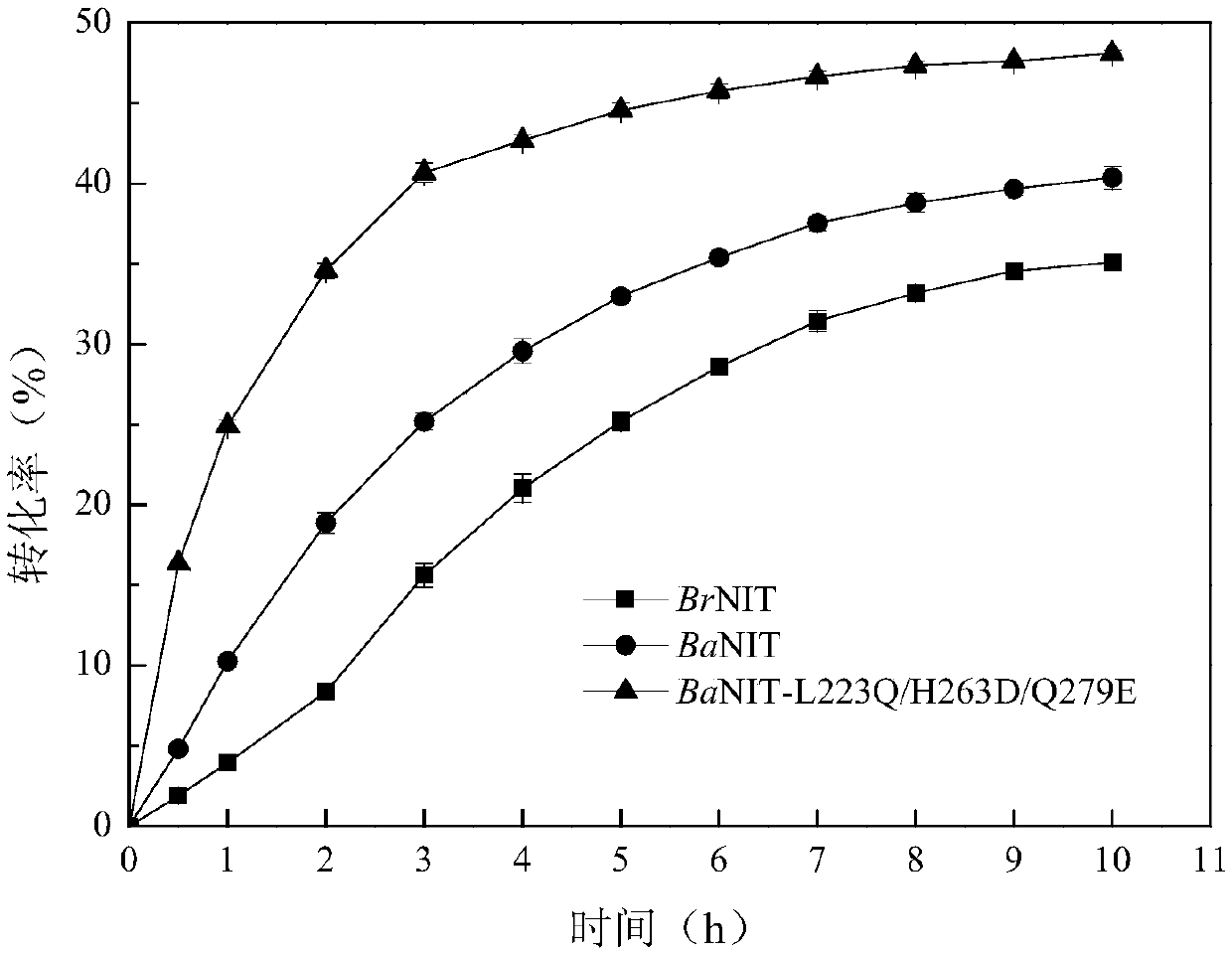
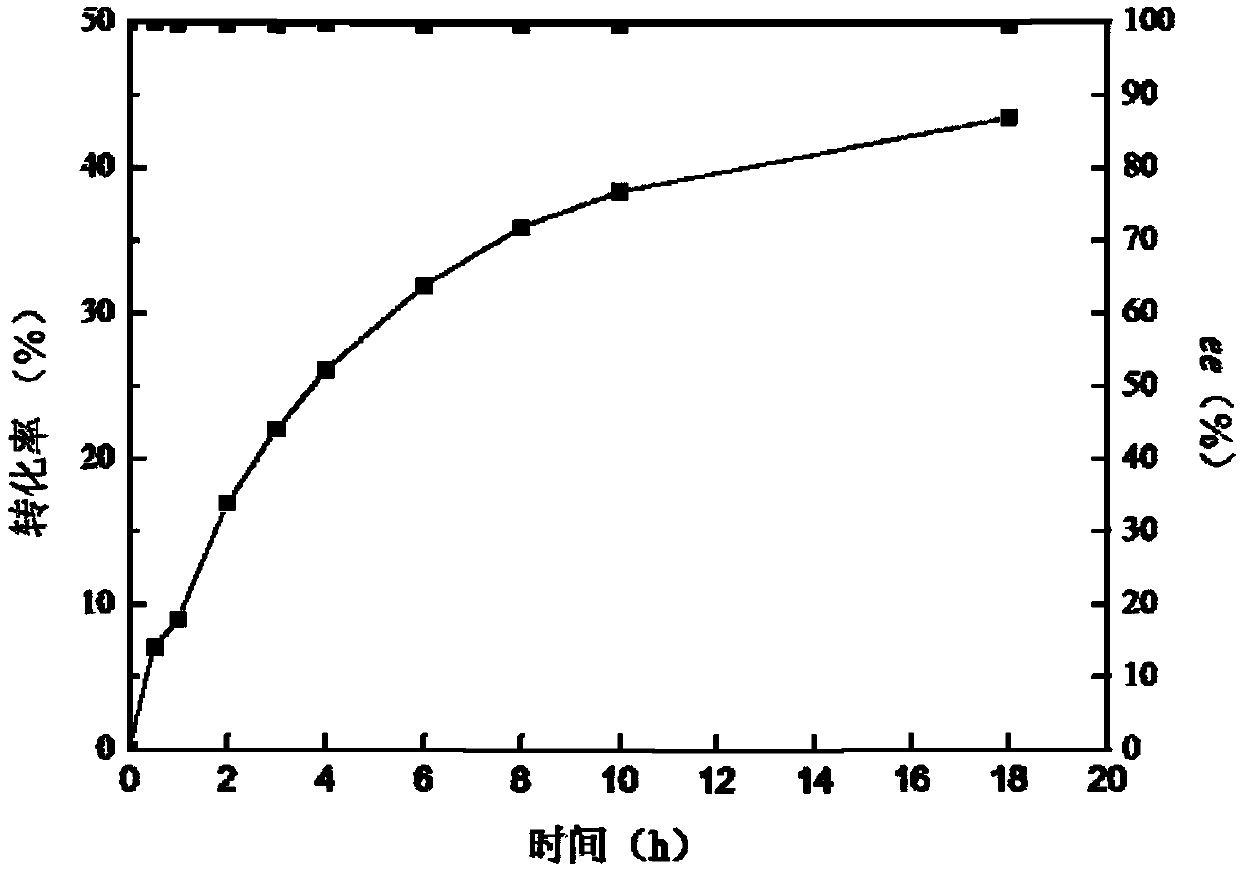
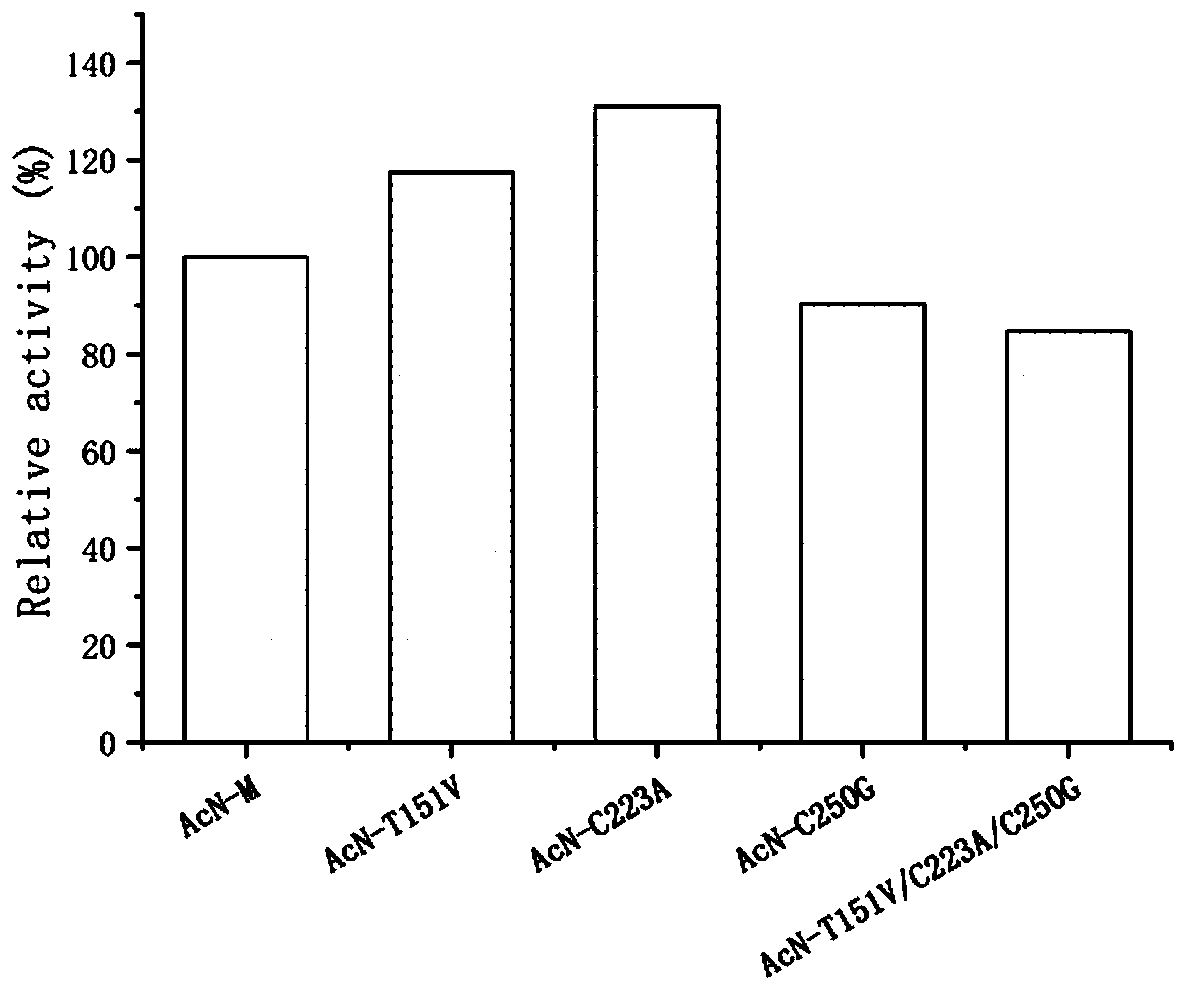
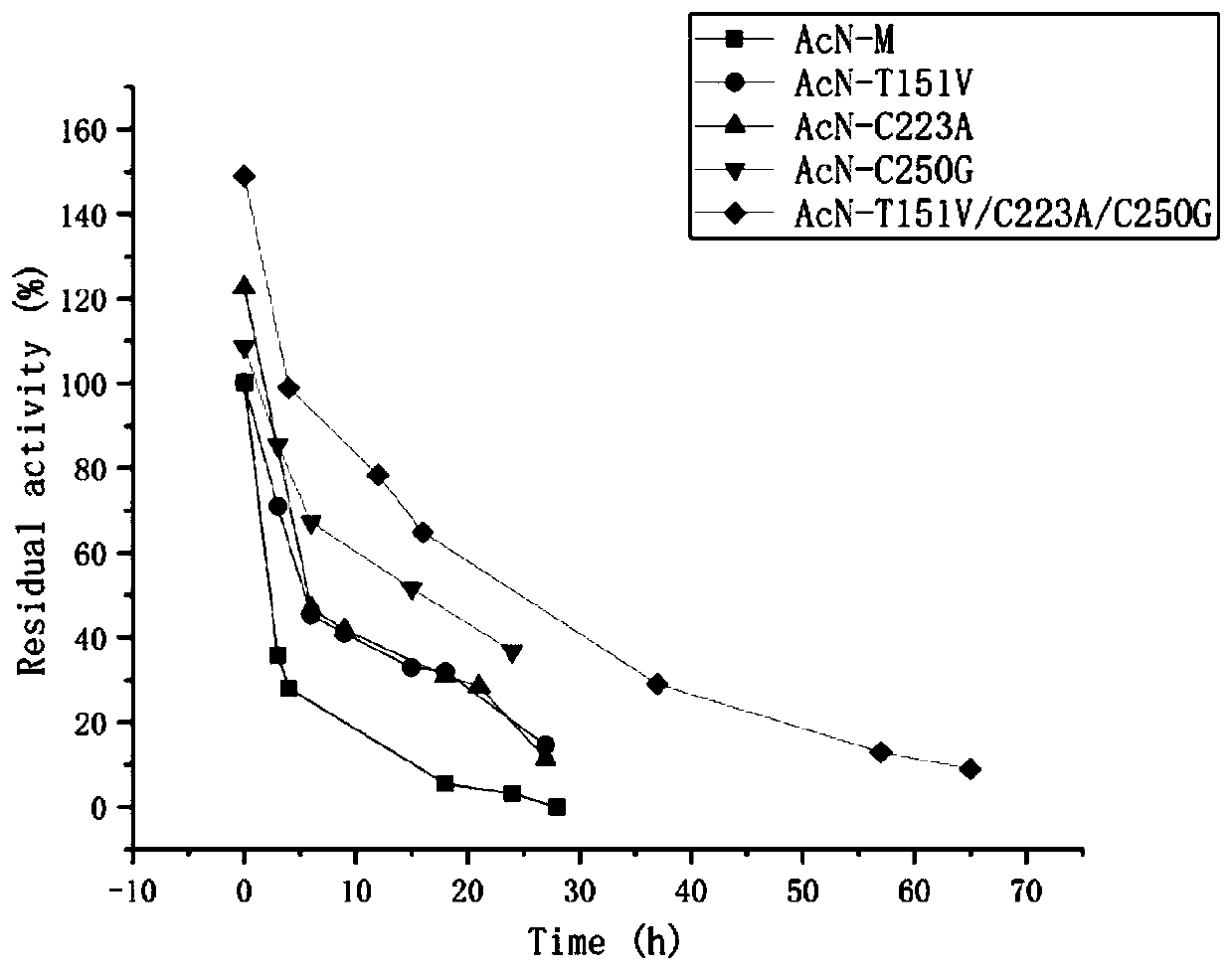
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant and an application thereof in preparation of an anti-epileptic drug intermediate. The mutant is obtained by mutating one or more of 151th amino acid, 223th amino acid and 250th amino acid of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2. The thermal stability of the nitrilase mutant AcN-T151V / C223A / C250G is improved by 1.73 times, 1M 1-cyanocyclohexyl acetonitrile is hydrolyzed by use of recombinant escherichia coli containing the nitrilase mutant at the temperature of 35 DEG C to generate 1-cyanocyclohexylacetic acid, and the yield of a final product reaches 95%. When 1.2 M 1-cyanocyclohexyl acetonitrile is hydrolyzed at the temperature of 35 DEG C, the final yield reaches 97%. Gabapentin is synthesized by use of the nitrilase mutant, and the yieldof the final product reaches 80%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis method of amikacin
ActiveCN106866755AReduce usageHigh activitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAmikacinKanamycin
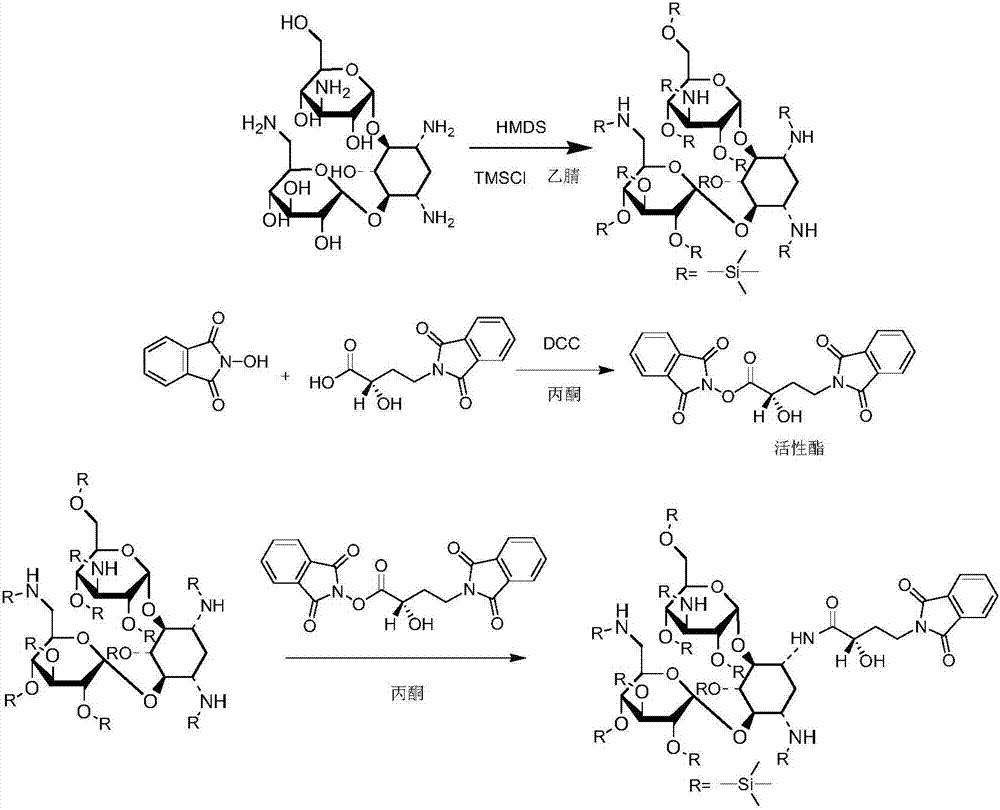
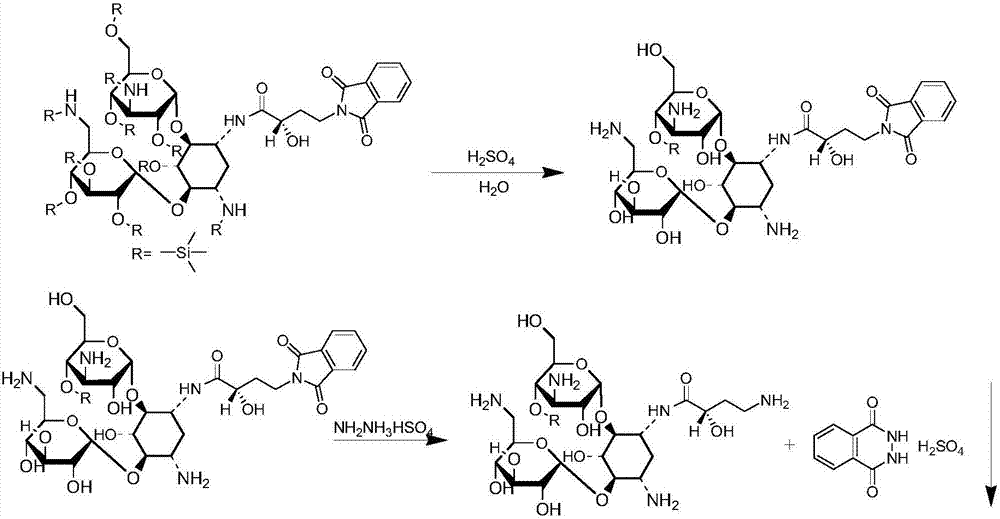
The invention discloses a synthesis method of amikacin. The synthesis method comprises following steps: firstly, a partially silanization protection product of kanamycin A is prepared; dehydration of the partially silanization protection product with PHBA under the action of DCC is carried out so as to obtain a acylated product; the acylated product is subjected to hydrolysis, nitrilase, and column chromatography purification so as to obtain amikacin. According to the synthesis method, NOP is not used, synthesis of an active ester via esterification is avoided, damage on the health of workers is reduced greatly, solid waste generated in production process is reduced greatly, product yield is increased, and the synthesis method is especially suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:山东安信制药有限公司
Self-aggregation short-peptide induction based immobilized nitrilase and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103757042AImprove mechanical stabilityHigh purityHydrolasesChemical industryFreeze-dryingEndoenzyme
The invention discloses a self-aggregation short-peptide induction based immobilized nitrilase and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) splicing connecting peptides and self-aggregation short peptides, so as to construct an expression vector; (2) connecting a nitrilase gene and the expression vector, and transforming into a recipient strain, so as to obtain an engineering strain; (3) carrying out induced expression on the engineering strain, carrying out wall breaking treatment on cells, and centrifuging and / or filtrating to obtain a precipitate, namely a nitrilase endoenzyme aggregate; (4) immobilizing the obtained nitrilase endoenzyme aggregate in alginate, thereby obtaining the immobilized nitrilase. According to the immobilized nitrilase aggregate obtained by the method, the particle diameter of the immobilized nitrilase is about 1mm. According to the immobilized nitrilase, particles can be subjected to freeze-drying preservation, and the enzyme activity is reserved to 90% when the immobilized nitrilase is preserved for 20 days at the temperature of 37 DEG C; the activity of the immobilized nitrilase is high, and the operating flow is simple.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Nitrilases and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS7521216B2Altered biological activityHigh expressionBacteriaSugar derivativesIncrease phStereochemistry
The invention relates to nitrilases and to nucleic acids encoding the nitrilases. In addition methods of designing new nitrilases and method of use thereof are also provided. The nitrilases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Immobilized enzyme as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110964710AEasy to fixImprove recycling efficiencyCarbon-nitrogen lyasesHydrolasesLyaseCross linker
The invention provides an immobilized enzyme as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The immobilized enzyme comprises an enzyme and an amino resin carrier for immobilizing the enzyme, the enzyme is selected from any one of transaminase, ketoreductase, monooxygenase, ammonia lyase, alkene reductase, imine reductase, amino acid dehydrogenase and nitrilase, the amino resin carrieris the cross-linking agent modified amino resin carrier, and a cross-linking agent is a cross-linking agent treated by a high polymer. The amino resin carrier is modified by adopting the cross-linking agent treated by the high polymer, so that enzymes immobilized on the amino resin carrier can form netted cross-linking, the immobilization effect of the enzymes is more stable, and the cyclic utilization efficiency of the enzymes is improved.
Owner:JILIN ASYMCHEM LAB CO LTD
Method for preparing (R)-o-chloromandelic acid through enzyme and application of enzyme
InactiveCN105349583ALow priceSimple processHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesMandelonitrileGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing medical intermediate (R)-o-chloromandelic acid through enzyme. A large amount of nitrilase expressed E. coli is obtained with genetic engineering and biological fermentation methods and produces (R)-o-chloromandelic acid directionally through hydrolysis of o-chloromandelic mandelonitrile racemate. According to the method, the cost of raw materials is low, the process is simple, the reaction condition is mild, the energy consumption is low, few reaction steps are adopted, no conventional toxic reagent participates in a reaction, the method is environment-friendly and pollution-free, the purity and the ee value of prepared (R)-o-chloromandelic acid are both higher than 98%, and the quality requirement of a drug intermediate is met.
Owner:WUHAN WUYAO PHARMA
Nitrilase mutant, gene, carrier, engineering bacteria and application
ActiveCN105505904AHigh selectivityIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesSpecific enzymeMandelonitrile
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant, gene, carrier, engineering bacteria and application in preparation of R-mandelic acid. The nitrilase mutant is obtained by carrying out site-specific mutagenesis on a 190th serine of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The nitrilase mutant (with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.12) disclosed by the invention has the advantages that specific enzyme activity is improved by 3.0 times and enantiomer selectivity is increased to more than 99% from 94% compared with parent nitrilase (with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2). Results show that the nitrilase mutant (with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.12) can completely hydrolyze 100mM mandelonitrile within 30min with a small amount of wet thalli (10g / L), and enantiomer selectivity is more than 99%, so that the nitrilase mutant disclosed by the invention can be applied to industrialized production of a medical intermediate R-mandelic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for converting 3-cyanopyridine into nicotinic acid by using gibberella intermedia CA3-1
ActiveCN102492750AImprove conversion efficiencyExtended half-lifeMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismHalf-life
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a method for converting 3-cyanopyridine into nicotinic acid by using gibberella intermedia CA3-1. The strain is collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a collection number of CGMCC No. 4903. The strain can be used for converting the3-cyanopyridine into the nicotinic acid under the condition of substrate concentration of 5.2 g / L (50 mM), the substrate conversion efficiency reaches up to 98 percent; under the condition of the optimum reaction temperature of 30 DEG C, the half life reaches up to 231.1 h; and the nitrilase of the strain CA3-1 has a broad substrate spectrum, and various single nitrile and double nitrile compounds can be converted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
New method of biologically synthesizing (R)-3-hydroxylglutarate monoester
The invention relates to a new method of biologically synthesizing (R)-3-hydroxylglutarate monoester and more particularly provides a method of preparing the (R)-3-hydroxylglutarate monoester from (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate through halogenohydrin dehalogenase recombinant bacteria and nitrilase recombinant bacteria, or double-enzyme co-expression recombinant bacteria, in a one-pot manner. The (R)-3-hydroxylglutarate monoester is a key intermediate of statin medicines such as fluvastatin, rosuvastatin, pitavastatin and the like. The method is mild in reaction conditions, is free of pollution and is simple in process route.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cell immobilization method of nitrilase producing strain
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering technology application, and in particular relates to a cell immobilization method of a nitrilase producing strain. Sodium alginate / polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400 beads are white, and have the diameter of 1 to 2mm. The cell immobilization method comprises the following steps of: culturing the nitrilase producing strain in liquid to obtain strain liquid, performing centrifugal separation to obtain thalli, suspending the thalli in triisopropylphenylsulfonyl (Tris)-Hcl buffer solution, adding a sterilized blend of alginate and PEG400, uniformly mixing, stably injecting into CaCl2 solution by using an injector, and immobilizing. The cell immobilization method provides a novel way for cell immobilization research and has a certain application value.
Owner:WUXI HENGYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for producing R-mandelic acid and derivates thereof by biocatalysis
ActiveCN101701243AReduce dosageReduce outputMicroorganism based processesFermentationMandelonitrileWastewater
The invention provides a method for producing R-mandelic acid and derivates thereof by biocatalysis. The method comprises performing hydrolysis reaction in a reaction system which takes racemization mandelonitrile compound shown in formula (I) as the zymolyte, and nitrilase obtained by culturing bacillus foecalis alkaligenes (CCTCC No: M 208168) as the catalyst at 20-60 DEG C with pH being 8.0-8.5 to obtain chiral R-mandelic acid and derivates thereof shown in corresponding formula (II). The invention has the beneficial effects that the activity of strain bacillus foecalis alkaligenes is high, the dosage of thallus is little, the produced waste water in the reaction process is little, and pollution is less; the reaction conditions are mild and energy consumption is low; the cost is low, conversion rate is high and yield is high, and the invention is favorable for industrialized production of chiral R-mandelic acid and R-chloro mandelic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing pregabalin chiral intermediate through regio-selective and stereo-selective bio-catalytic synthesis
The invention discloses a preparation method for synthesizing a pregabalin chiral intermediate through regio-selective and stereo-selective bio-catalytic synthesis. The method comprises the followingsteps: reacting racemic isobutyl butyronitrile (IBSN) in a reaction medium at a temperature of 20-50 DEG C in presence of nitrilase and amidase catalysis for 4-10 hours, thereby obtaining (S)-3-cyano-5-methyl hexanoate. The method is mild in reaction conditions, simple and feasible in operation and excellent in regio-selectivity and stereo-selectivity, the conversion rate of the pregabalin key chiral intermediate, namely (S)-3-cyano-5-methyl hexanoate, synthesized from the racemic substrate IBSN through a one-pot process can reach 49.5%, the value e.e. is 99.5%, and the conversion rate is close to a theoretical conversion rate of 50%. Meanwhile, the optical purity exceeds 99%, and the method has obvious application values for simplifying the production process steps of pregabalin and reducing the production cost of the pregabalin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing nicotinic acid and derivative by catalysis of enzyme
InactiveCN101550432AMild reaction conditionsLow equipment requirementsFermentationStrong acidsPyridine
The invention relates to a method for producing nicotinic acid and the derivative, in particular a method for producing nicotinic acid by hydrolyzing nicorinic acid nitrile using nitrilase. The problems of erosion of equipments caused by using strong acid and strong base, complex process and low yield in the current synthetic method of nicotinic acid are solved. The technical scheme is the method for producing nicotinic acid by catalysis of enzyme, taking 3-cyanopyridine as raw material, hydrolyzing 3-cyanopyridine using nitrilase that is produced by fermenting to gain nicotinic acid. The reaction formula of the invention can be represented above.
Owner:SYNCOZYMES SHANGHAI
Nitrilases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using Them
The invention relates to nitrilases and nucleic acids encoding the nitrilases. In addition methods of designing new nitrilases and method of use thereof are also provided. The nitrilases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:BASF ENZYMES
Method for producing R-mandelic acid with biocatalysis and separating and coupling method
ActiveCN101709323ADisinhibition effectHigh catalytic yieldIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationCouplingMandelonitrile
The invention provides a method for producing R-mandelic acid with biocatalysis and separating and coupling method. The method comprises: adding alkaliteit anion exchange resin of 10-50g / L into a reaction system with racemic mandelonitrile as substrate and nitrilase as catalyst after reaction begins 0-1 hour to perform hydrolysis reaction with pH being 8.0-8.5 and temperature being 20-60 DEG C; when the concentration of substrate racemic mandelonitrile in the conversion system is low, further adding racemic mandelonitrile of 10-100mmol / L and alkaliteit anion exchange resin of 10-50g / L into the reaction system to perform hydrolysis reaction of next batch with the same conditions. The invention provides a method for efficiently producing R-mandelic acid, R-mandelic acid is prepared by nitrilase biocatalysis and separating and coupling technology, thus effectively removing inhibitory action of the product; resin is used for absorbing R-mandelic acid to perform coupling conversion, thus the catalysis yield of the nitrilase biocatalyst is greatly enhanced and sequential separation is facilitated; therefore, the inventive technology has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Immobilization method for cells containing nitrilase
InactiveCN104911174ALow costEasy to operateOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierEscherichia coliFiltration
The invention discloses an immobilization method for cells containing nitrilase. The immobilization method comprises the steps that wet vectors obtained by a recombinant genetic engineering strain containing nitrilase genes through fermental cultivation is added into a buffer solution or distilled water to prepare bacterial suspension; a carrier is added into the bacterial suspension, and even stirring is conducted; then polyethyleneimine is added, and stirring for flocculation is conducted for 0.5-2 h; then glutaraldehyde is added to conduct crosslinking, and after stirring and crosslinking are conducted at 10-25 DEG C by 0.5-2 h, liquid supernatant is discarded; after vacuum filtration, cells containing nitrilase are obtained. The immobilization method for cells containing nitrilase has the advantages that the cost is low, operation is easy, and reusability is good; prepared immobilization recombinant escherichia coli whole cells producing nitrilase are used for catalyzing 1-cyanocyclohexane acetonitrile to produce 1-cyanocyclohexane acetic acid; after conversion is continuously conducted by 30 times, the conversion yield is still more than 80%; and a good industrialized application prospect is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com