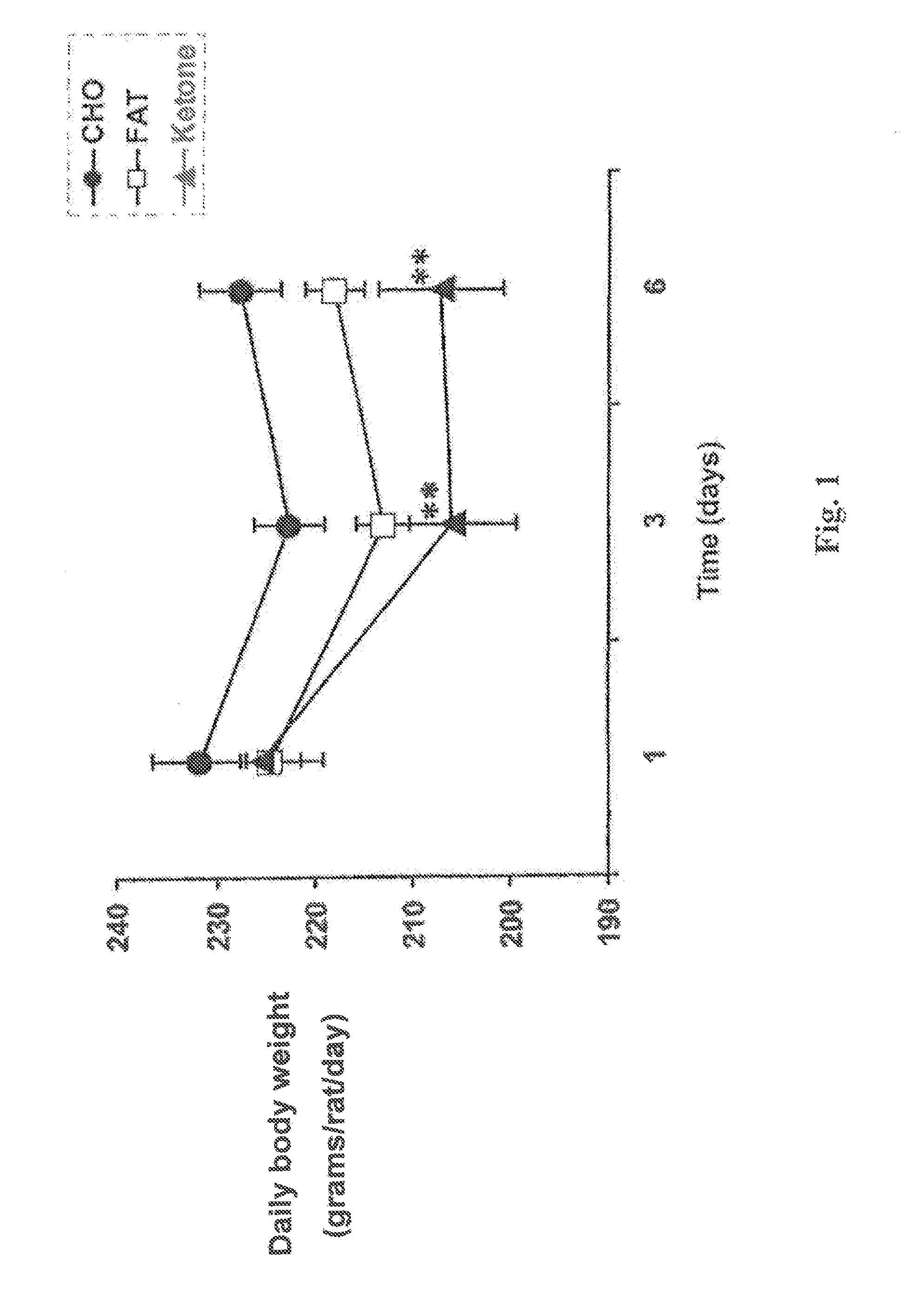
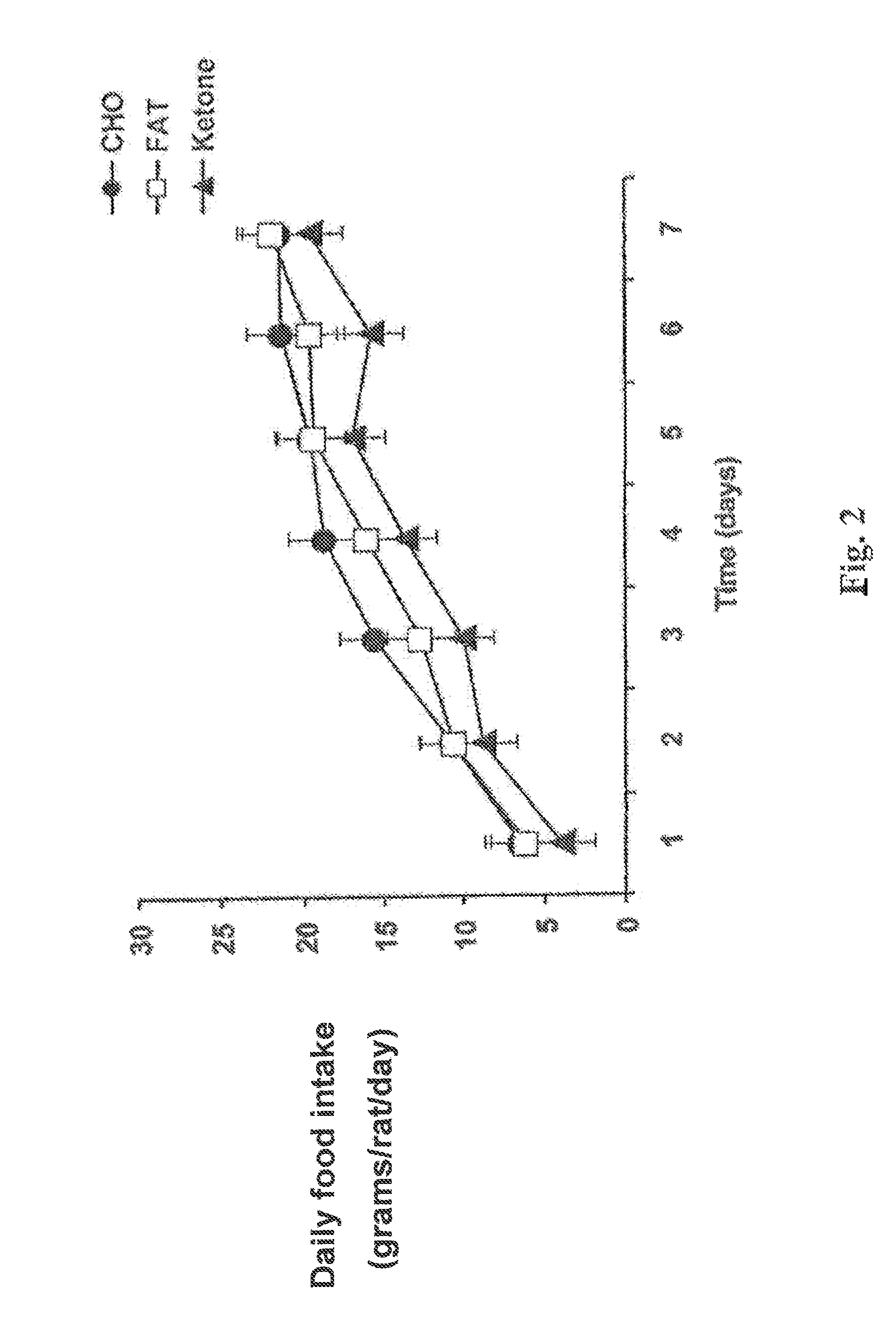
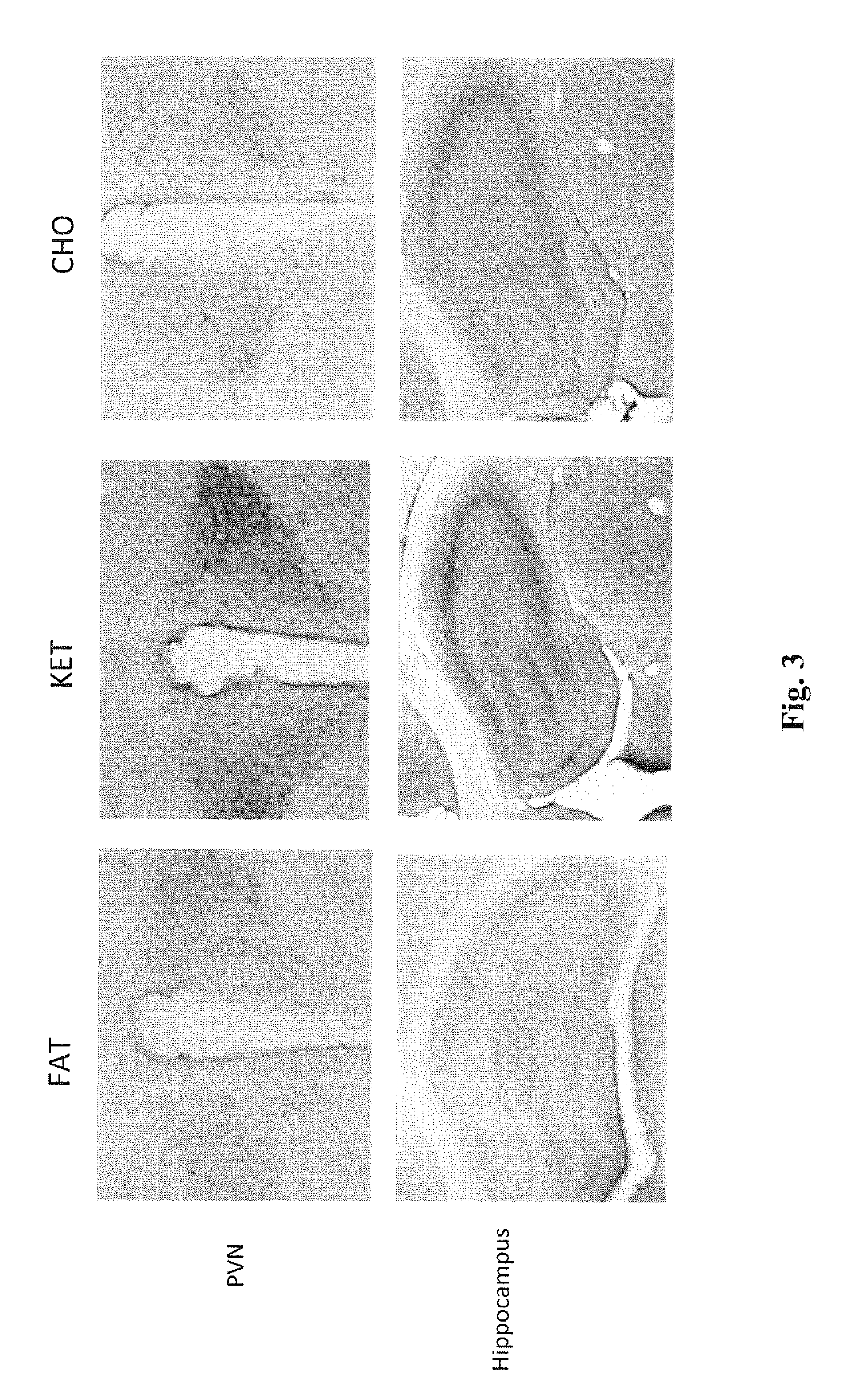
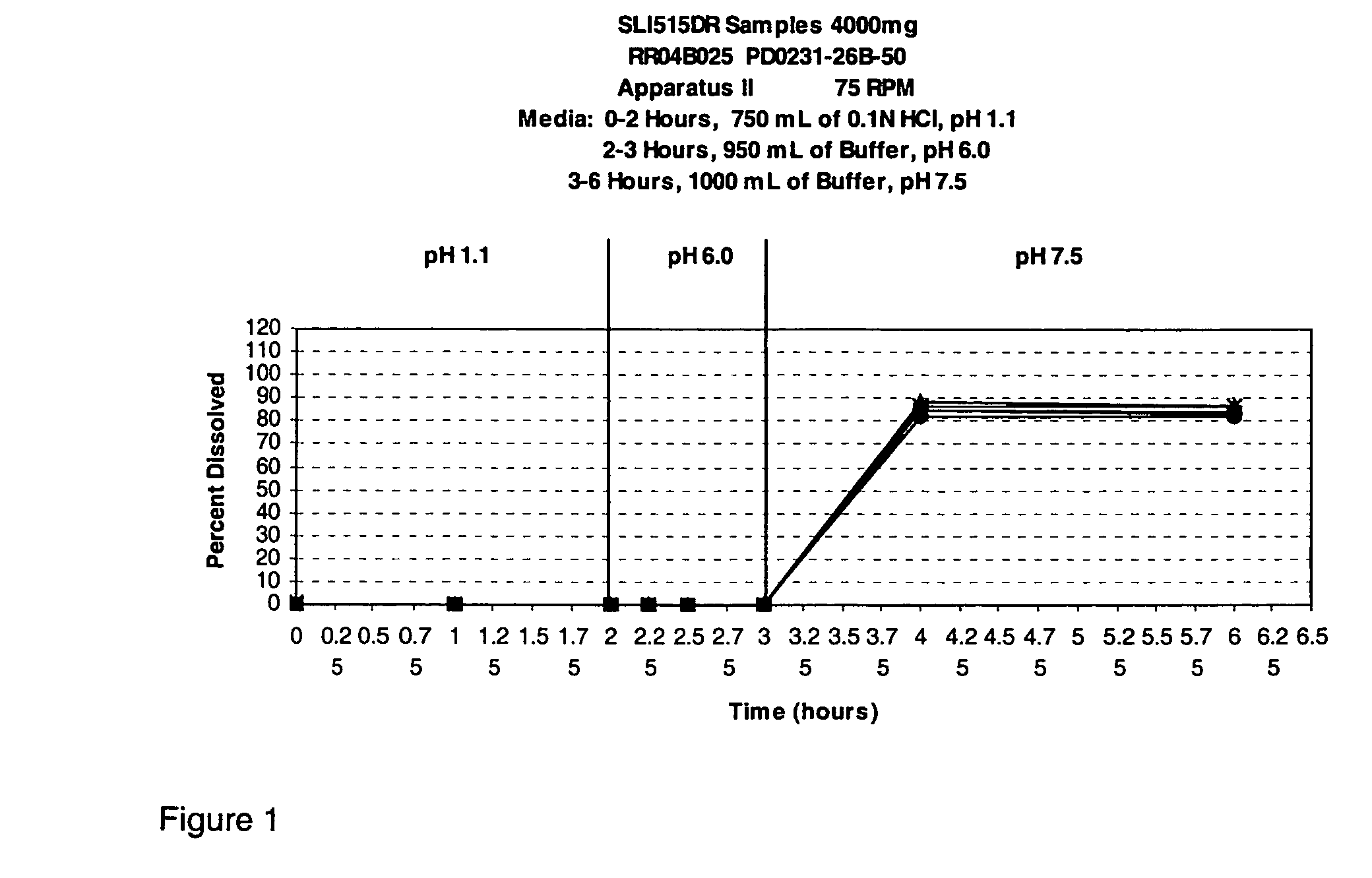
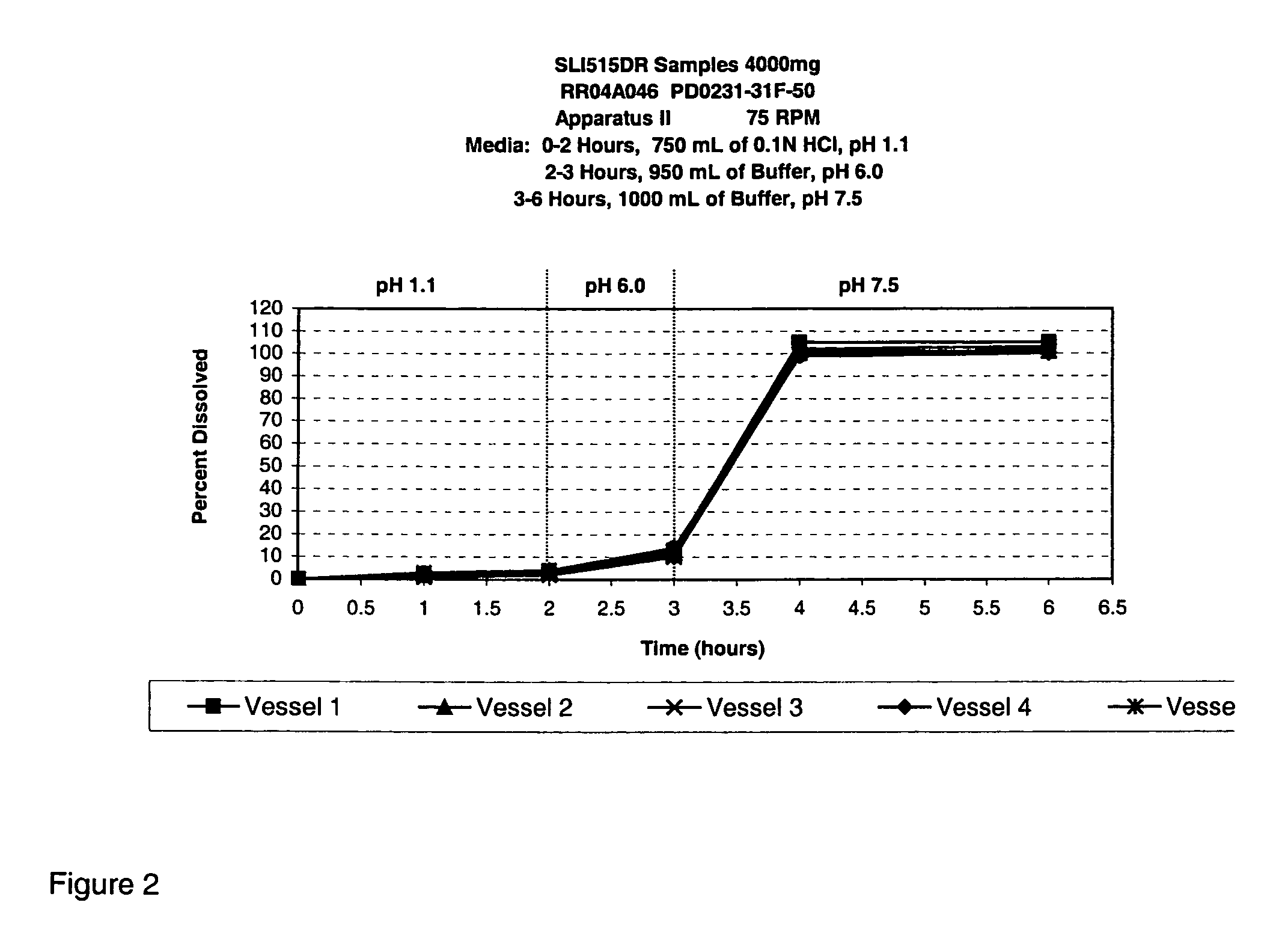
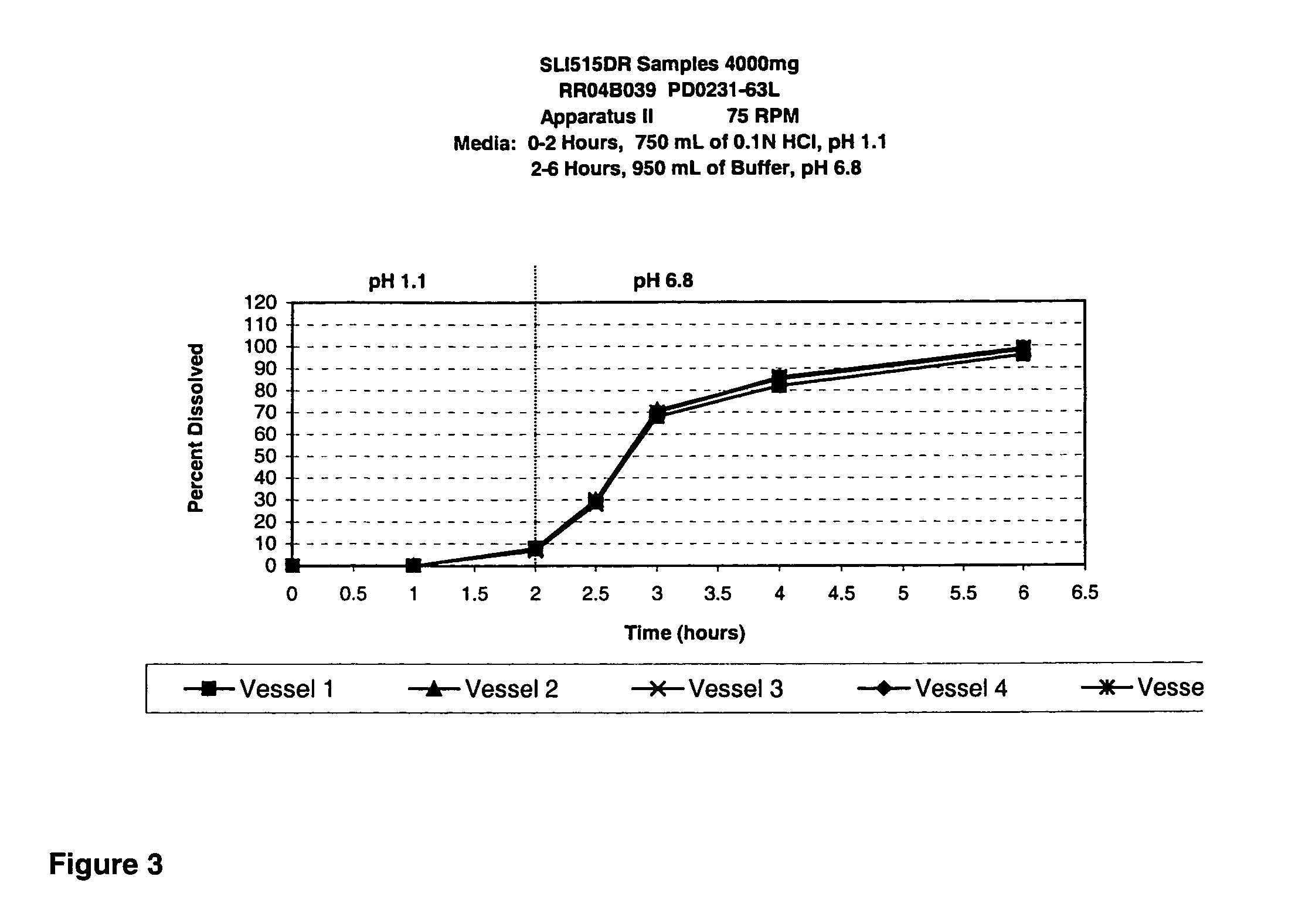
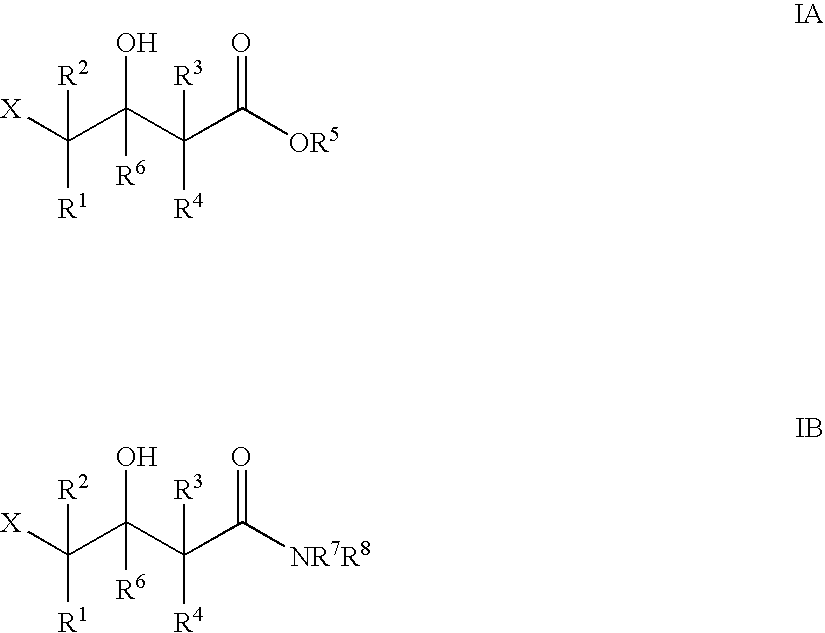
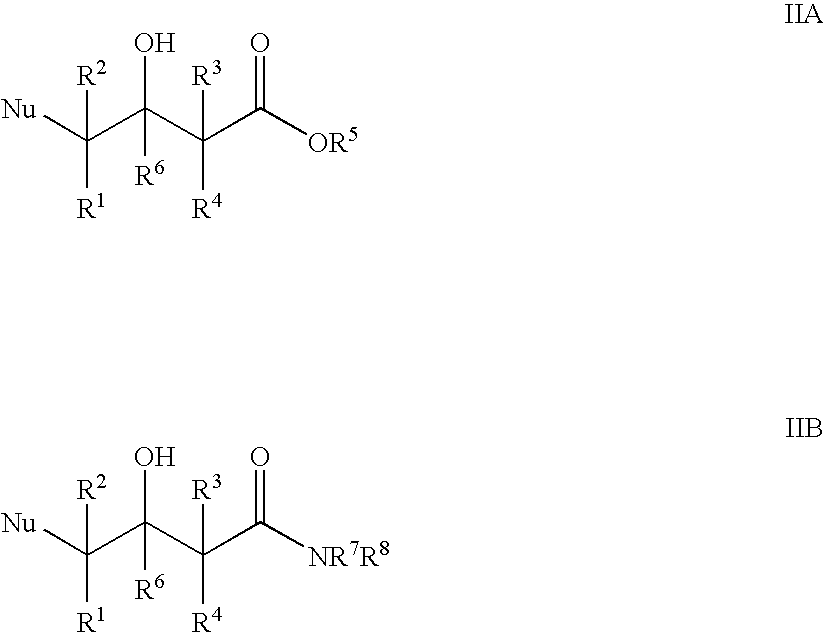
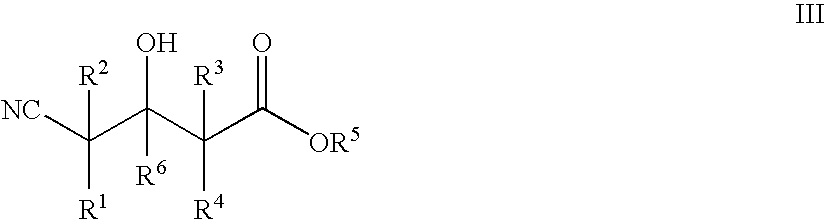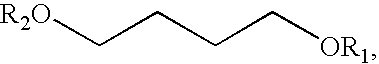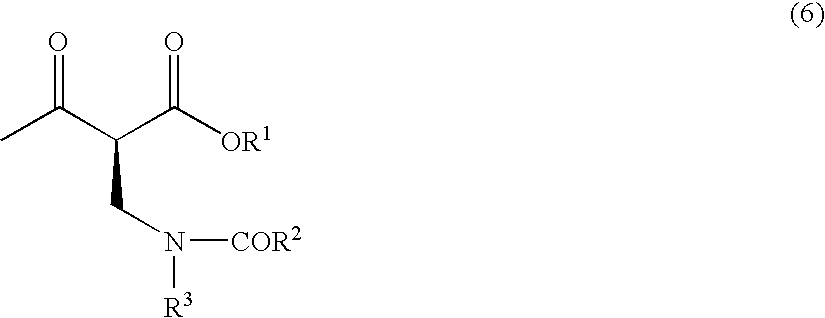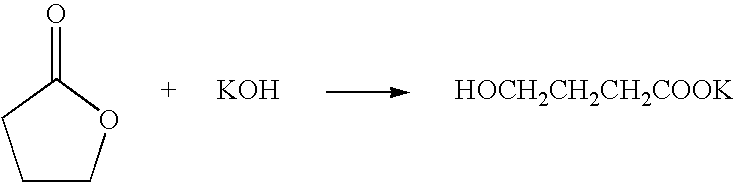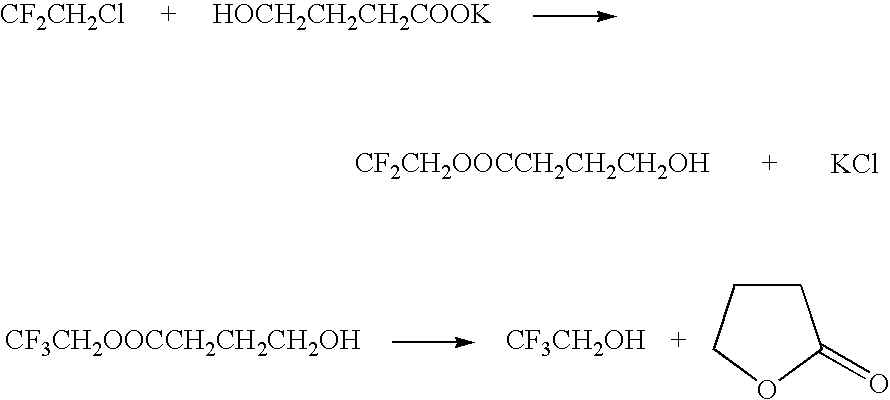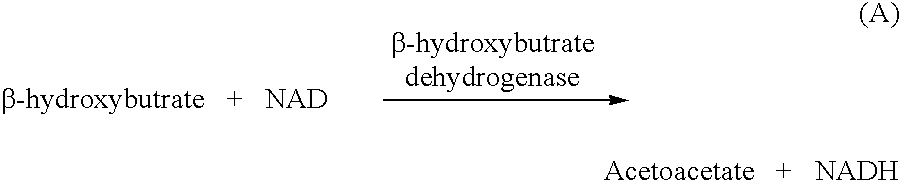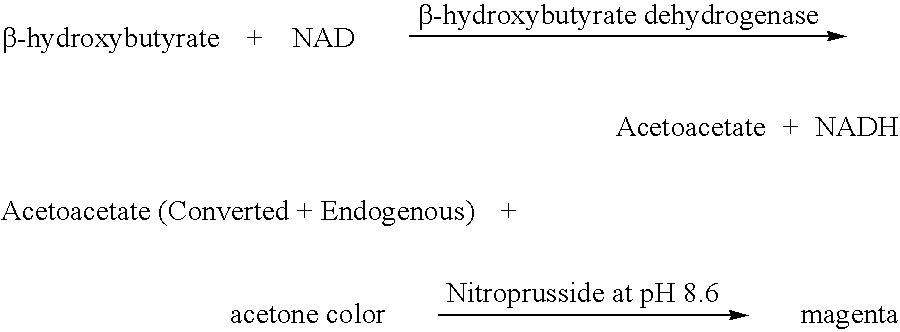Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
547 results about "Hydroxybutyric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydroxybutyric acid is a group of four-carbon organic compounds that have both hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functional groups. They can be viewed as derivatives of butyric acid. The carboxylate anion and the esters of hydroxybutyric acids are known as hydroxybutyrates.
Hydroxybutyrate ester and medical use thereof
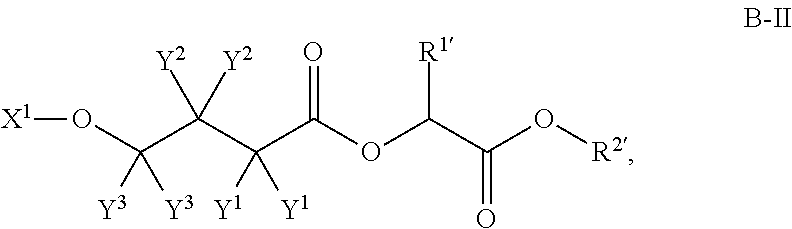
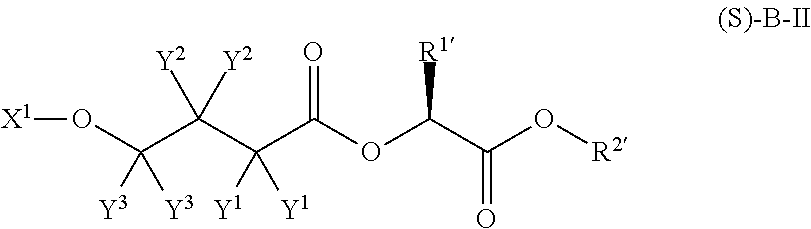
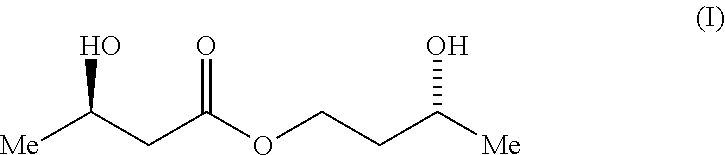
A compound which is 3-hydroxybutyl 3-hydroxybutyrate enantiomerically enriched with respect to (3R)-hydroxybutyl (3R)-hydroxybutyrate of formula (I) is an effective and palatable precursor to the ketone body (3R)-hydroxybutyrate and may therefore be used to treat a condition which is caused by, exacerbated by or associated with elevated plasma levels of free fatty acids in a human or animal subject, for instance a condition where weight loss or weight gain is implicated, or to promote alertness or improve cognitive function, or to treat, prevent or reduce the effects of neurodegeneration, free radical toxicity, hypoxic conditions or hyperglycaemia.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Controlled release compositions of gamma-hydroxybutyrate
ActiveUS8193211B2Reduce in quantityReduce the possibilityBiocideNervous disorderControl releaseImmediate release
The present invention is directed to oral pulse-release pharmaceutical dosage form containing an immediate release component of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid, and one or more delayed / controlled release components of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid.
Owner:SUPERNUS PHARM INC
Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxy substituted carboxylic acid esters
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by halohydrin dehalogenase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for preparing 4-halo-3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives by ketoreductase-catalyzed conversion of 4-halo-3-ketobutyric acid derivatives The present invention also provides methods and compositions for preparing vicinal cyano, hydroxyl substituted carboxylic acid esters.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Compositions and methods for producing elevated and sustained ketosis
ActiveUS20140350105A1Rapid and sustained elevationImprove metabolic healthBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsKetoneSignificant elevation
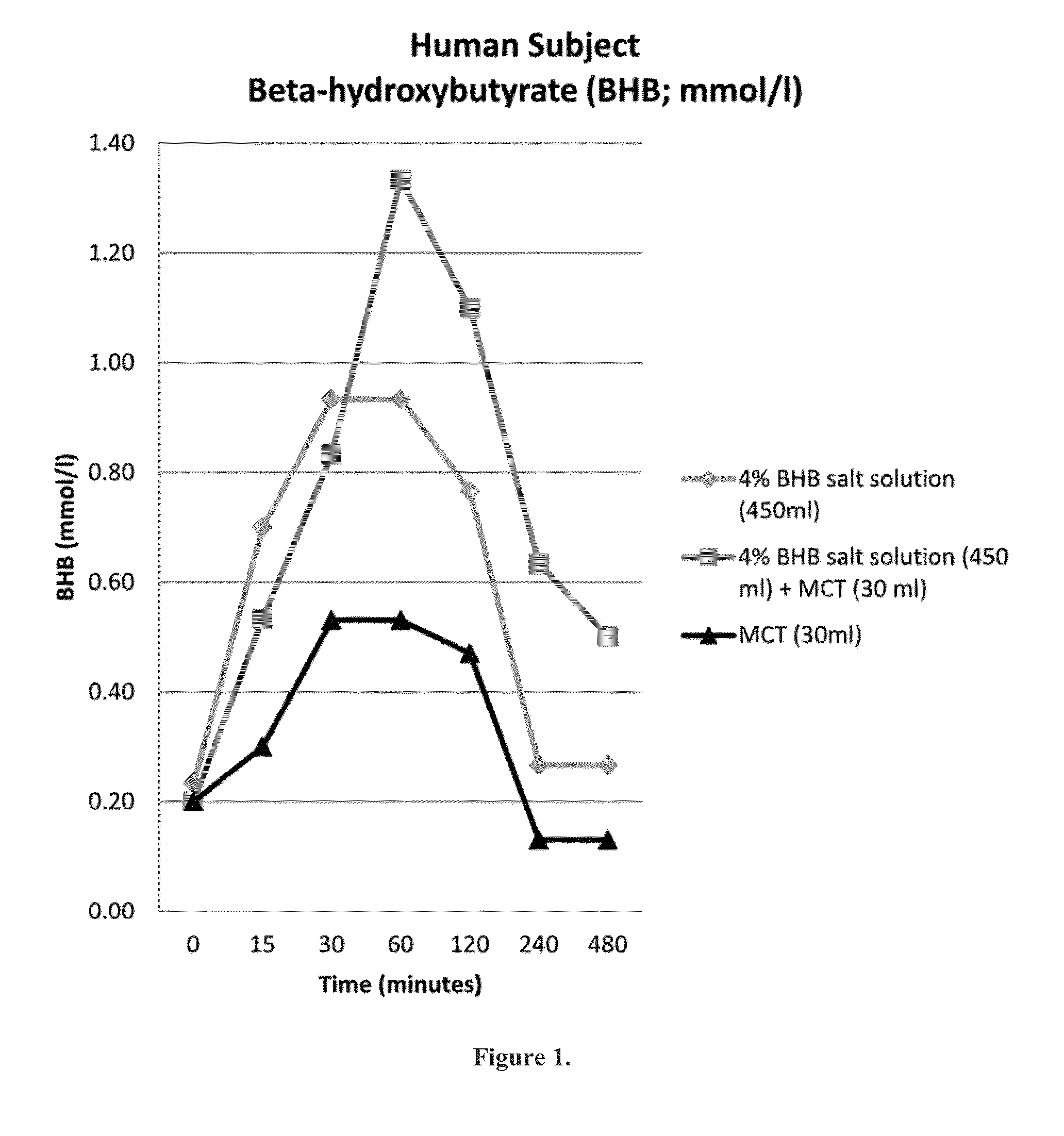
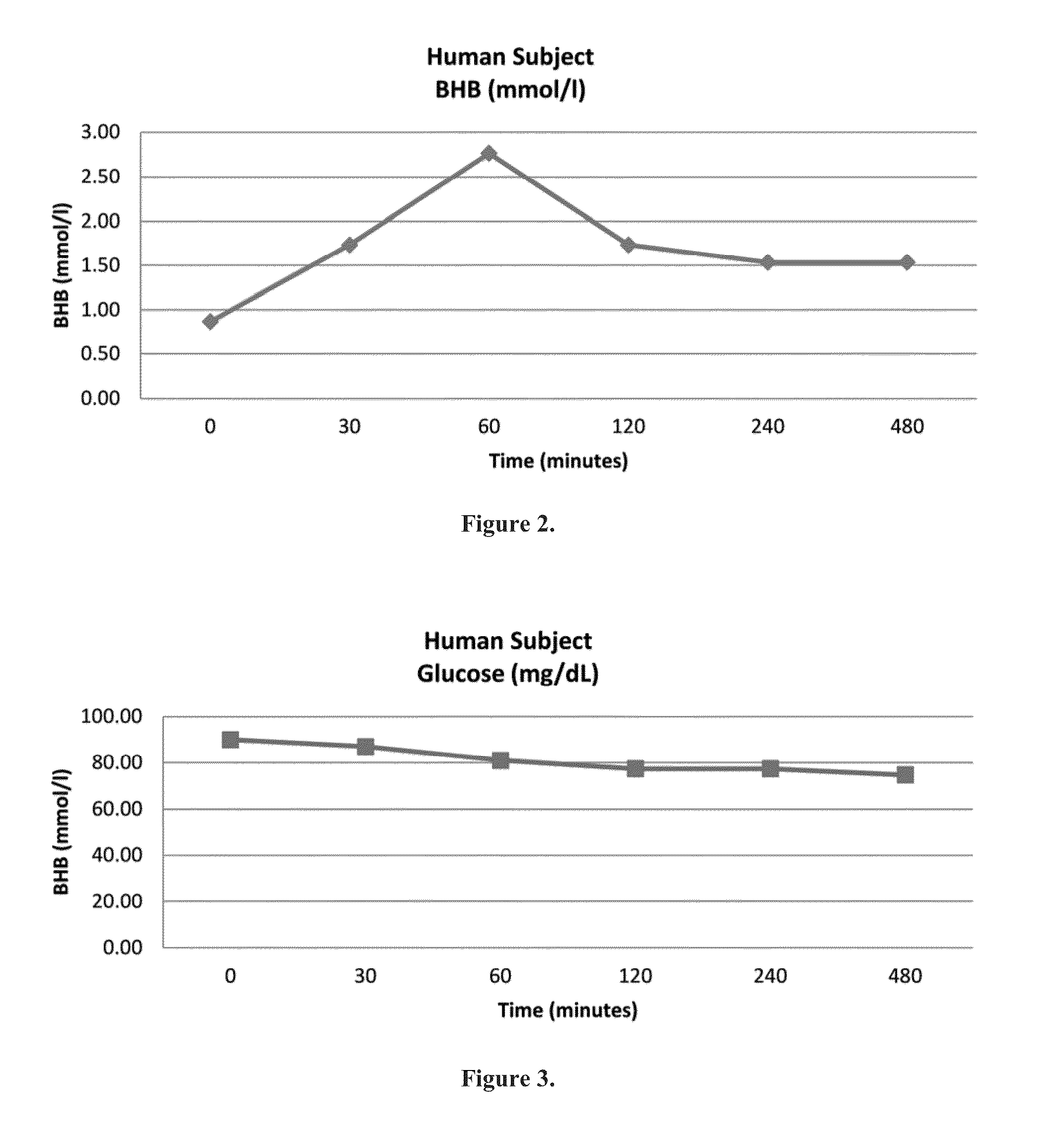
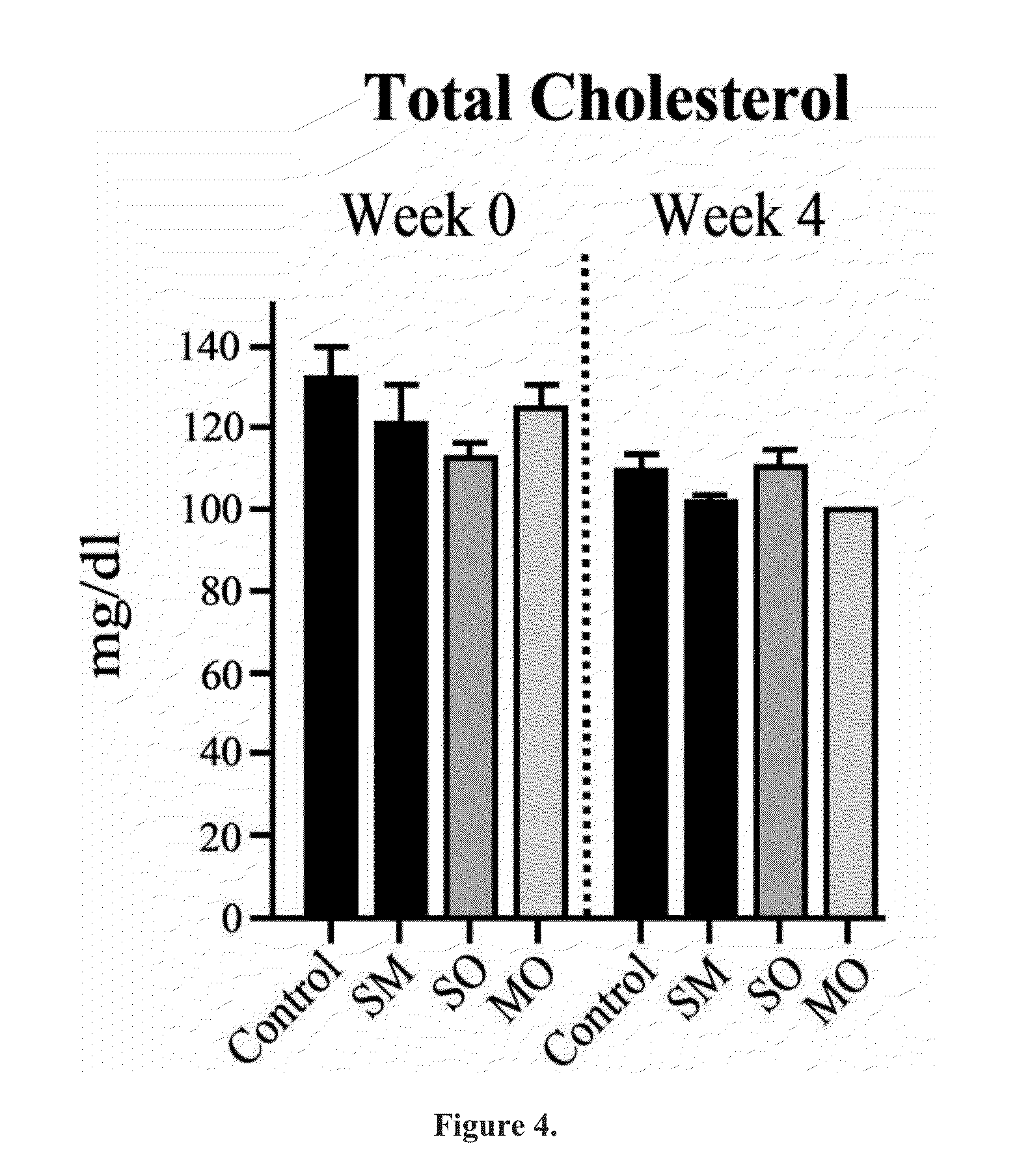
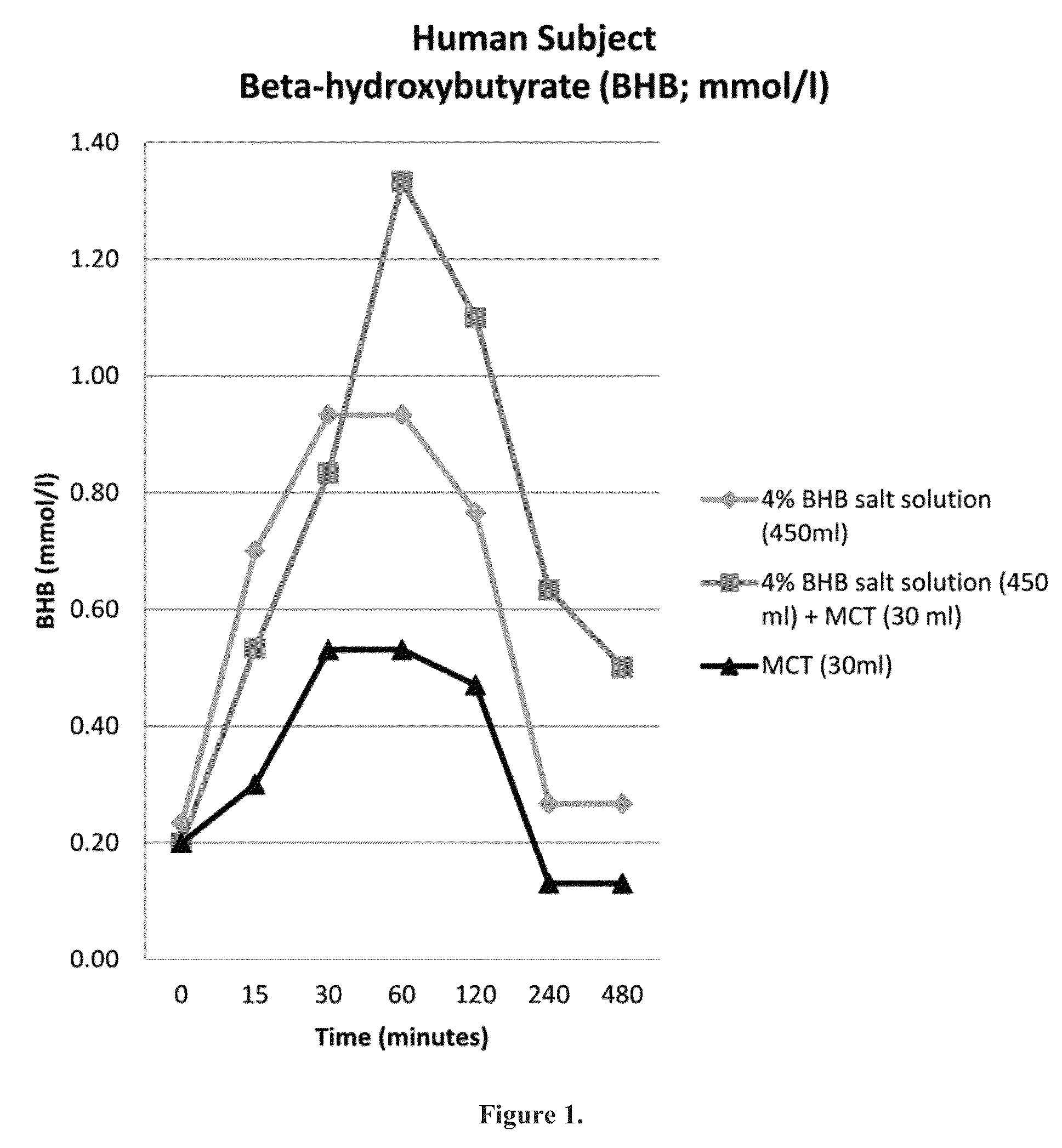
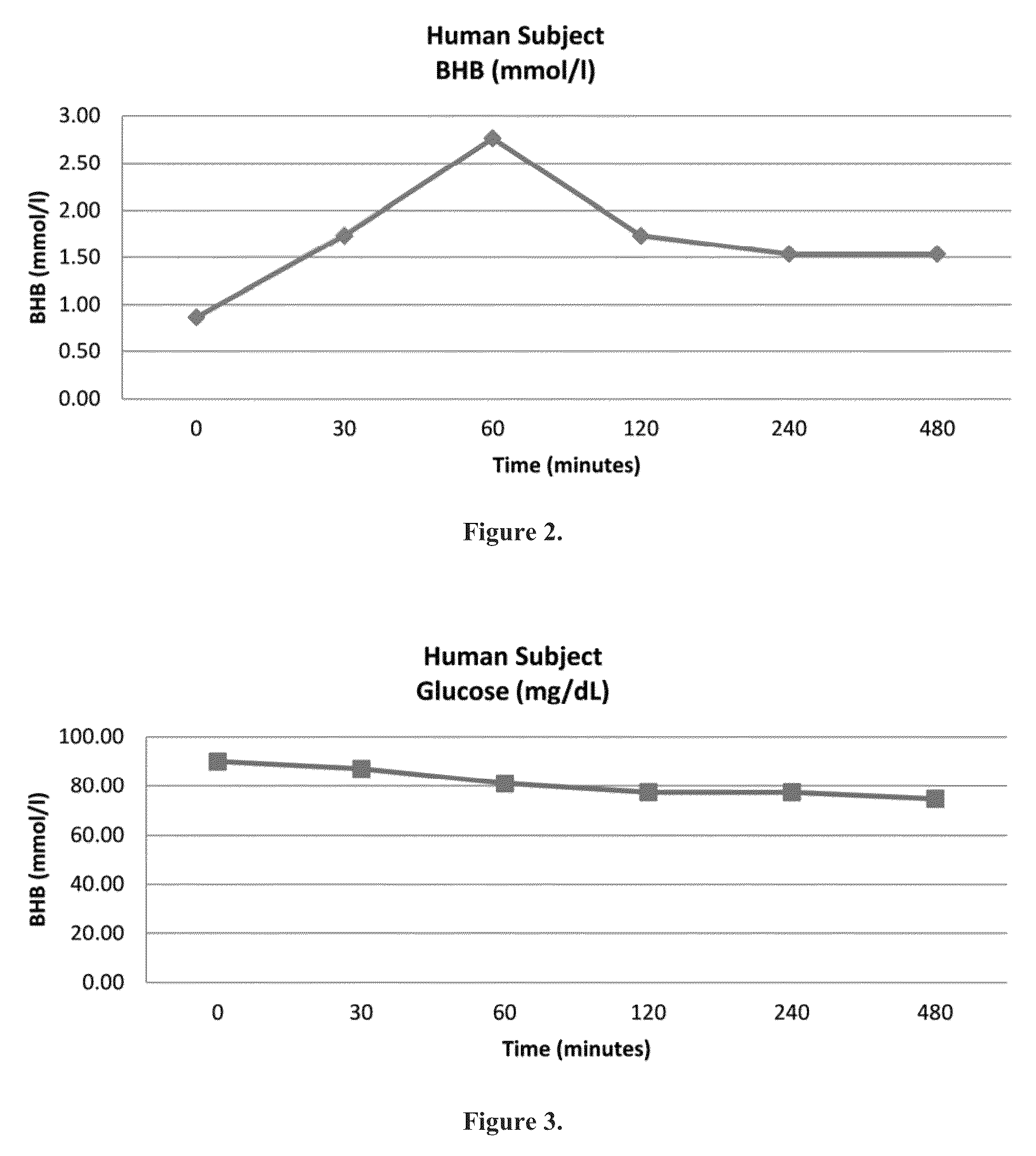
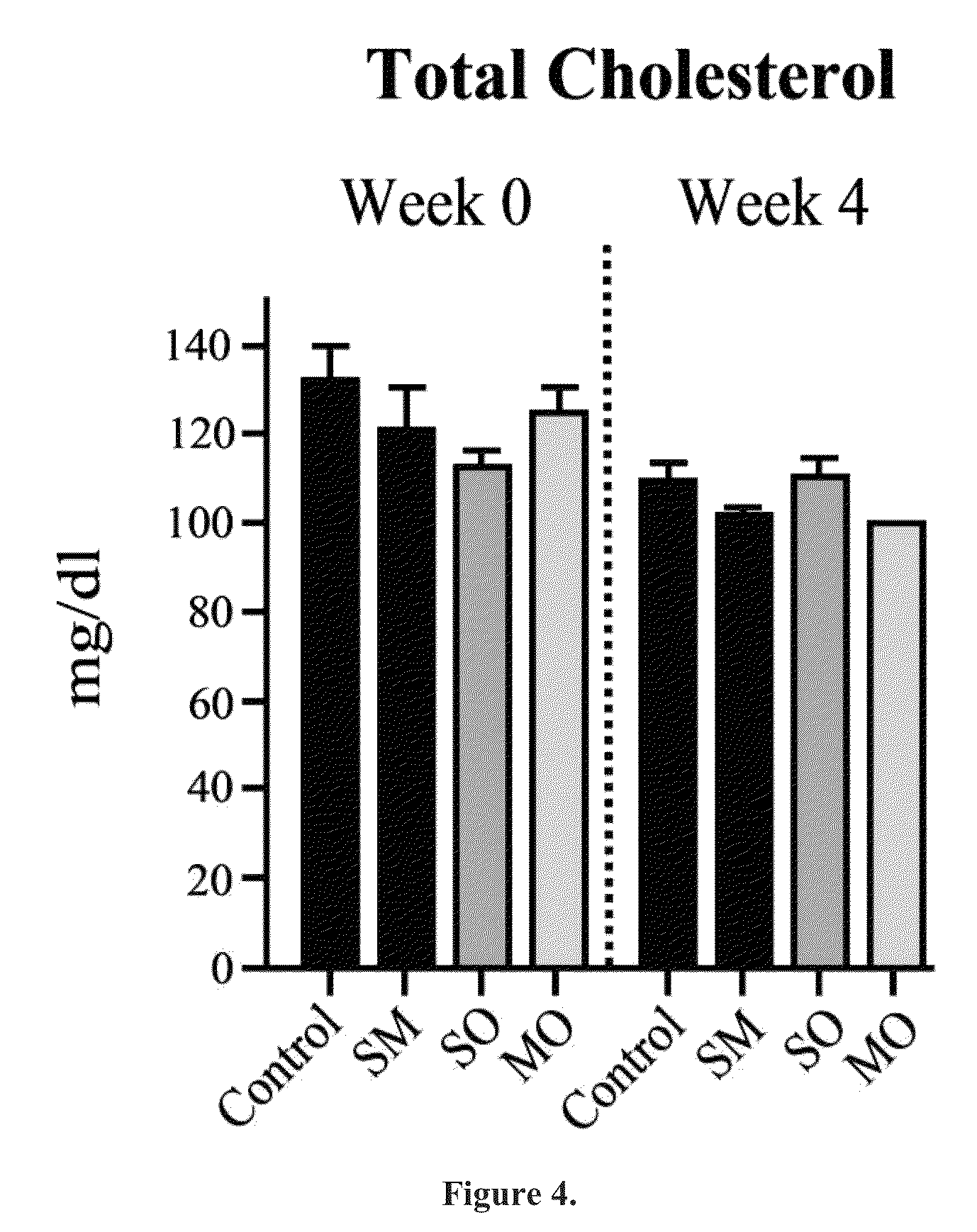
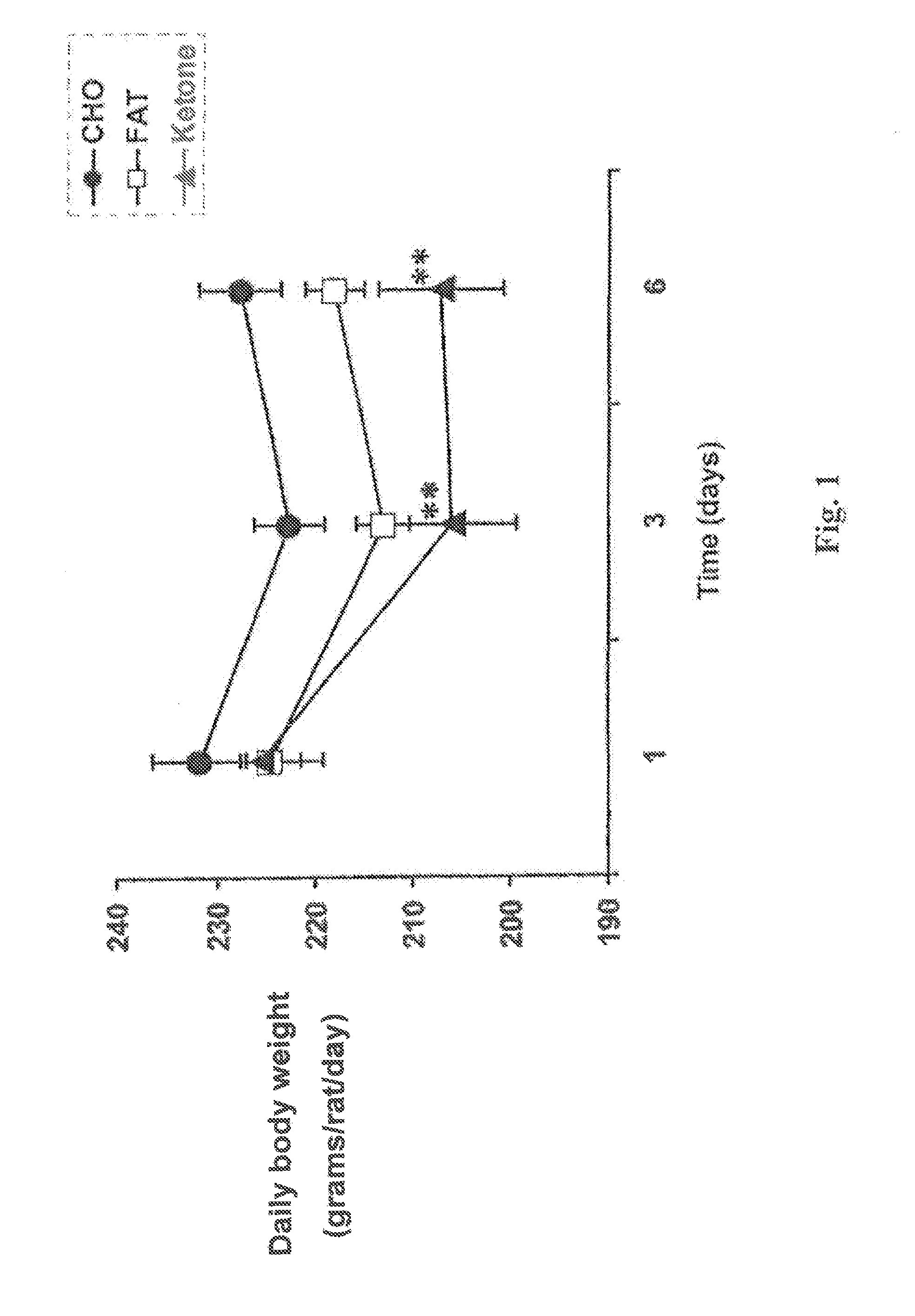
Beta-hydroxybutyrate mineral salts in combination with medium chain fatty acids or an ester thereof such as medium chain triglycerides were used to induce ketosis, achieving blood ketone levels of (2-7 mmol / L), with or without dietary restriction. The combination results in substantial improvements in metabolic biomarkers related to insulin resistance, diabetes, weight loss, and physical performance in a short period of time. Further, use of these supplements to achieve ketosis yields a significant elevation of blood ketones and reduction of blood glucose levels. Use of these substances does not adversely affect lipid profiles. By initiating rapid ketosis and accelerating the rate of ketoadaptation, this invention is useful for the avoidance of glucose withdrawal symptoms commonly experienced by individuals initiating a ketogenic diet, and minimizes the loss of lean body mass during dietary restriction.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Compositions and methods for producing elevated and sustained ketosis
ActiveUS9138420B2Rapid and sustained elevationImprove the level ofHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSignificant elevationKetogenic diet
Beta-hydroxybutyrate mineral salts in combination with medium chain fatty acids or an ester thereof such as medium chain triglycerides were used to induce ketosis, achieving blood ketone levels of (2-7 mmol / L), with or without dietary restriction. The combination results in substantial improvements in metabolic biomarkers related to insulin resistance, diabetes, weight loss, and physical performance in a short period of time. Further, use of these supplements to achieve ketosis yields a significant elevation of blood ketones and reduction of blood glucose levels. Use of these substances does not adversely affect lipid profiles. By initiating rapid ketosis and accelerating the rate of ketoadaptation, this invention is useful for the avoidance of glucose withdrawal symptoms commonly experienced by individuals initiating a ketogenic diet, and minimizes the loss of lean body mass during dietary restriction.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Hydroxybutyrate ester and medical use thereof
ActiveUS20110237666A1Increase alertnessImprove cognitive functionBiocideNervous disorderFatty acidAnimal subject
A compound which is 3-hydroxybutyl 3-hydroxybutyrate enantiomerically enriched with respect to (3R)-hydroxybutyl (3R)-hydroxybutyrate of formula (I) is an effective and palatable precursor to the ketone body (3R)-hydroxybutyrate and may therefore be used to treat a condition which is caused by, exacerbated by or associated with elevated plasma levels of free fatty acids in a human or animal subject, for instance a condition where weight loss or weight gain is implicated, or to promote alertness or improve cognitive function, or to treat, prevent or reduce the effects of neurodegeneration, free radical toxicity, hypoxic conditions or hyperglycaemia.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Methods and Compositions for Treating Arg
InactiveUS20080293698A1BiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsHydroxybutyric acidAcquired resistance
The invention provides dilute and concentrated, aqueous, pharmaceutical compositions comprising gamma-hydroxybutyric acid or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; gamma-butyryl lactone; 1,4-butanediol; 4-hydroxyl pentanoic acid or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; 4-hydroxyl pentanoic acid lactone, or combinations thereof, and a coloring agent and / or flavoring agent that is useful in preventing sexual assault or date rape. Methods of treating conditions responsive to the administration of gamma-hydroxyl butyric acid and / or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts; gamma-butyryl lactone; 1,4-butanediol; 4-hydroxyl pentanoic acid and / or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts; and 4-hydroxyl pentanoic acid lactone are also described. The invention provides methods for treating patients with acquired resistance to GABAnergic agents.
Owner:JOHNSON JOSEPH
Microemulsions with adsorbed macromolecules and microparticles
InactiveUS8206749B1Powerful toolStimulate immune responseAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemHydroxybutyric acidAdjuvant
Microparticles with adsorbent surfaces, methods of making such microparticles, and uses thereof, are disclosed. The microparticles comprise a polymer, such as a poly(α-hydroxy acid), a polyhydroxy butyric acid, a polycaprolactone, a polyorthoester, a polyanhydride, and the like, and are formed using cationic, anionic, or nonionic detergents. The surface of the microparticles efficiently adsorb biologically active macromolecules, such as DNA, polypeptides, antigens, and adjuvants. Also provided are compositions of an oil droplet emulsion having a metabolizable oil and an emulsifying agent. Immunogenic compositions having an immunostimulating amount of an antigenic substance, and an immunostimulating amount of an adjuvant composition are also provided. Methods of stimulating an immune response, methods of immunizing a host animal against a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection, and methods of increasing a Th1 immune response in a host animal by administering to the animal an immunogenic composition of the microparticles, and / or microemulsions of the invention, are also provided.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method for the production of D-(-)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by recombinant esherichia coli
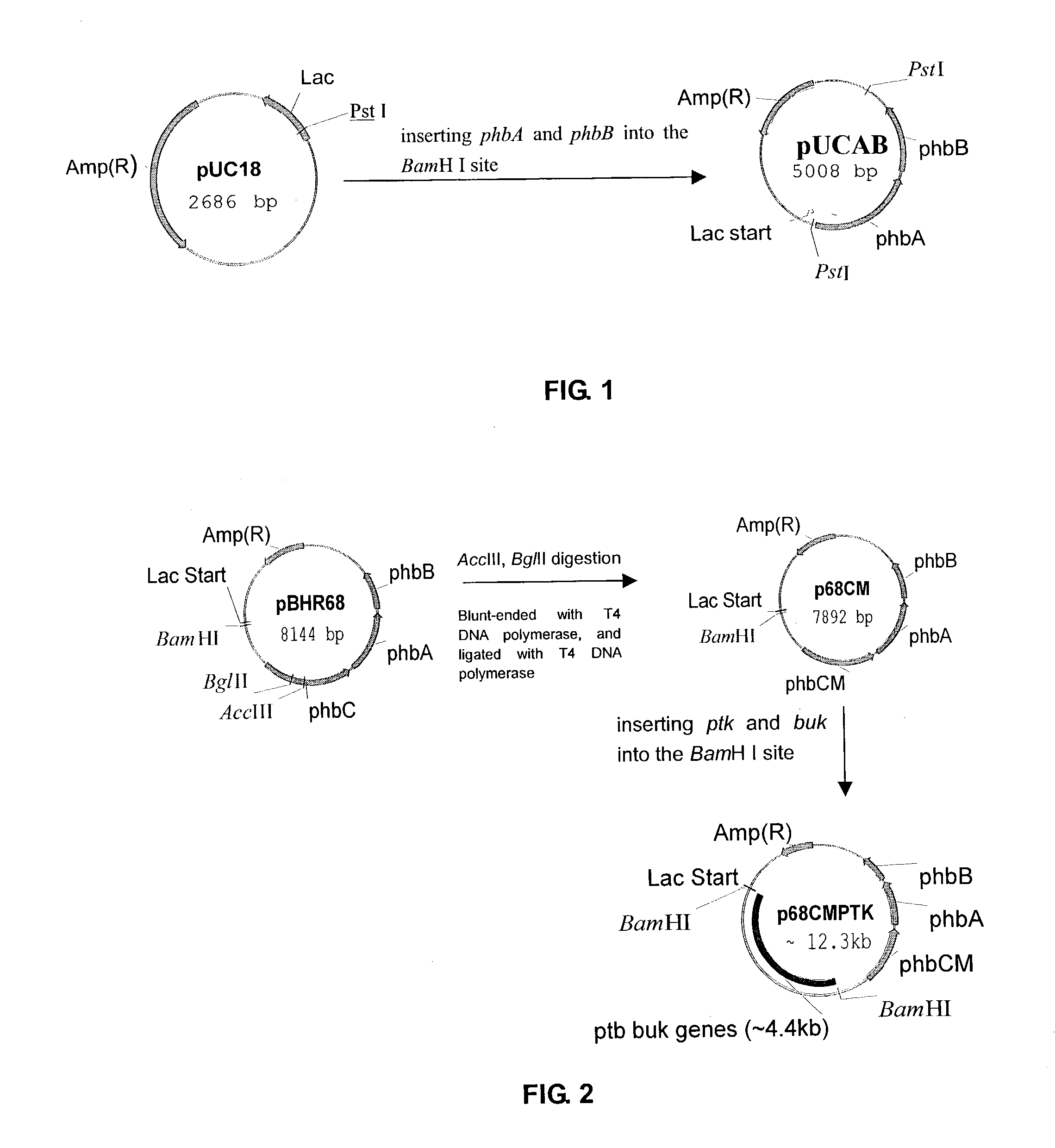
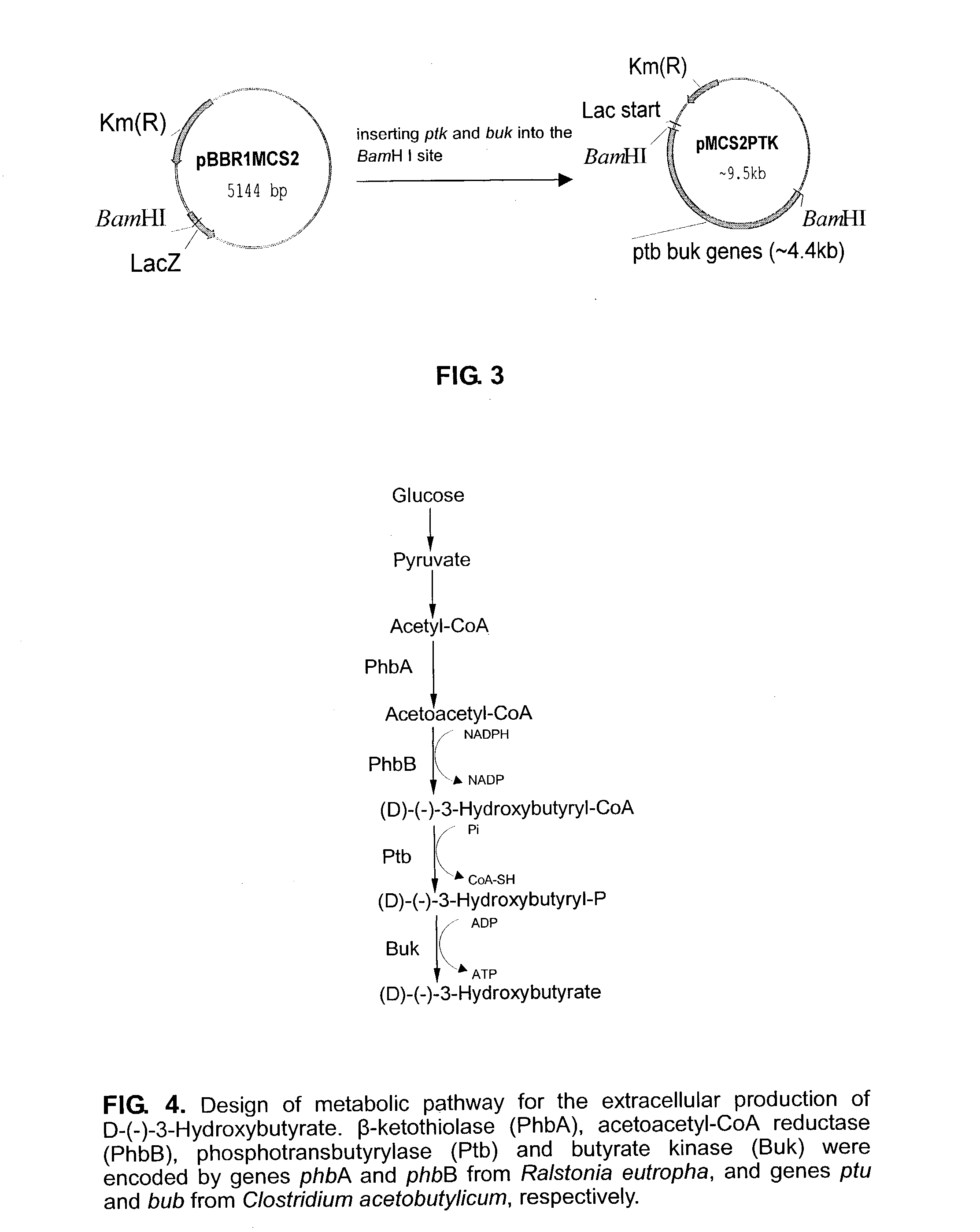
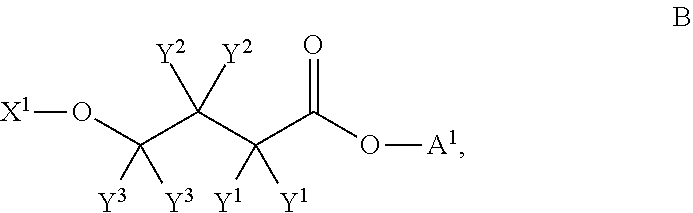
This invention relates to a method for the production of D-(-)-3-hydroxybutyric acid, comprising the step of culturing a recombinant strain containing genes phbA, phbB, ptb and buk by fermentation. Preferably, the recombinant strain is a strain of E. coli. The method of the invention is simple, avoiding the technique of degrading polymer to produce D-(-)-3-hydroxybutyric acid. The present method also provides improved efficiency, lowers the complicated requirement for facilities as used in traditional chemical synthesis, simplifies the complicated technique flow, and omits the complicated chiral separation step. Therefore, the present method greatly reduces the costs associated with D-(-)-3-hydroxybutyric acid production. Also, with this invention, the problems such as environmental pollution of chemical synthesis and chiral separation are overcome.
Owner:CHEN GUOQIANG +2
4-hydroxybutyric acid analogs
This invention relates to novel derivatives of 4-hydroxybutyric acid and prodrugs thereof, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the foregoing. This invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of this invention and the use of such compositions in methods of treating narcolepsy, fibromyalgia, other disorders or conditions that are beneficially treated by improving nocturnal sleep or by administering sodium oxybate.
Owner:SUN PHARMA IND INC
Composition based on gamma-hydroxybutyric acid
ActiveUS8529954B2Increasing apparent half life and bioavailabilityReduce doseBiocideNervous disorderHydroxybutyric acidSolid core
The present invention relates to a granule of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid or of one of its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, characterized in that it comprises a solid core on which the gamma-hydroxybutyric acid or one of its salts is supported.
Owner:DEBREGEAS & ASSOCIES PHARMA
Polishing pad comprising biodegradable polymer
The invention is directed to a polishing pad for use in chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a biodegradable polymer. The biodegradable polymer comprises a repeat unit selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, lactic acid, hydroxyalkanoic acids, hydroxybutyric acid, hydroxyvaleric acid, caprolactone, p-dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, butylene succinate, butylene adipate, monosaccharides, dicarboxylic acid anhydrides, enantiomers thereof, and combinations thereof. The invention is further directed to methods of its use.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Polishing pad comprising biodegradable polymer
The invention is directed to a polishing pad for use in chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a biodegradable polymer. The biodegradable polymer comprises a repeat unit selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, lactic acid, hydroxyalkanoic acids, hydroxybutyric acid, hydroxyvaleric acid, caprolactone, p-dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, butylene succinate, butylene adipate, monosaccharides, dicarboxylic acid anhydrides, enantiomers thereof, and combinations thereof. The invention is further directed to methods of its use.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for producing optically active 2-(n-substituted aminomethyl)-3-hydroxybutyric acid ester
The present invention relates to a method for producing optically active 2-(N-substituted aminomethyl)-3-hydroxybutyric acid esters wherein a 2-(N-substituted aminomethyl)-3-oxobutyric acid ester is treated with an enzyme source capable of stereoselectively reducing said ester to the corresponding optically active 2-(N-substituted aminomethyl)-3-hydroxybutyric acid ester having the (2S,3R) configuration. The present invention provides an efficient method for industrially producing optically active 2-(N-substituted aminomethyl)-3-hydroxybutyric acid esters, in particular such compounds having the (2S,3R) configuration, which are useful as intermediates for the production of medicinal compounds, among others.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for producing 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol
InactiveUS7208641B2MinimizationEffectively removing/separatingOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHydroxybutyric acidSolvent
A method for producing 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol in which a γ-hydroxybutyric acid salt is reacted with 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane to generate 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol is provided. This method leads to increased yields of 2,2,2 -trifluoroethanol, facilitates the separation of salt byproducts and allows the recycling of an aprotic polar solvent.The present invention concerns a method for producing 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol in which a γ-hydroxybutyric acid salt is reacted with 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane in an aprotic polar solvent to generate 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol. This method is characterized in that the γ-hydroxybutyric acid salt used contains no more than 6 wt % of 4,4′-oxybis(butyric acid).
Owner:TOSOH F TECH INC
Process For The Preparation of (3R)-Hydroxybutyl (3R) -Hydroxybutyrate By Enzymatic Enantioselective Reduction Employing Lactobacillus Brevis Alcohol Dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20120064611A1Preparation from ketenes/polyketenesOxidoreductasesHydroxybutyric acidLactobacillus brevis
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD +1
GHB compositions
InactiveUS20060069040A1Reduce cataplexyReduce daytime sleepinessBiocideNervous disorderCompound (substance)In vivo
The invention provides a combination of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) or a prodrug or an analog thereof, with a compound that inhibits the metabolism of the GHB or GHB analog in vivo, thus prolonging or enhancing the bioactivity thereof.
Owner:ORPHAN MEDICAL INC +1
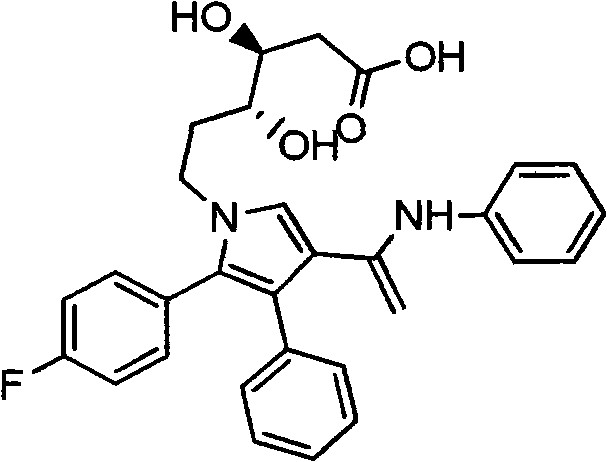
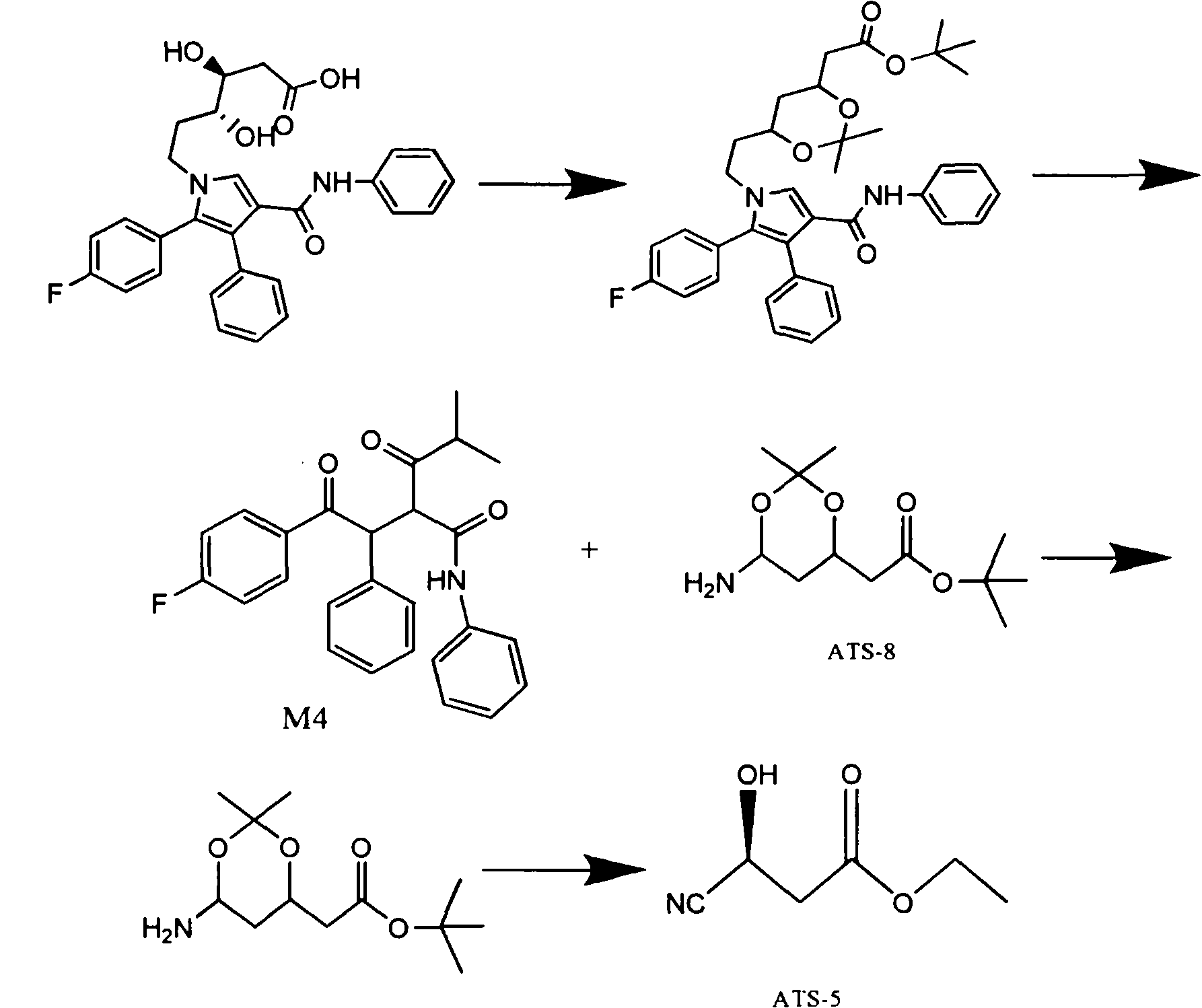
Manufacturing method of atorvastatin intermediate (R)-(-)-4-nitrile-3-hydroxybutyrate
InactiveCN101838221AIncrease profitEmission reductionPreparation by cyanide reactionState of artEnantiomer
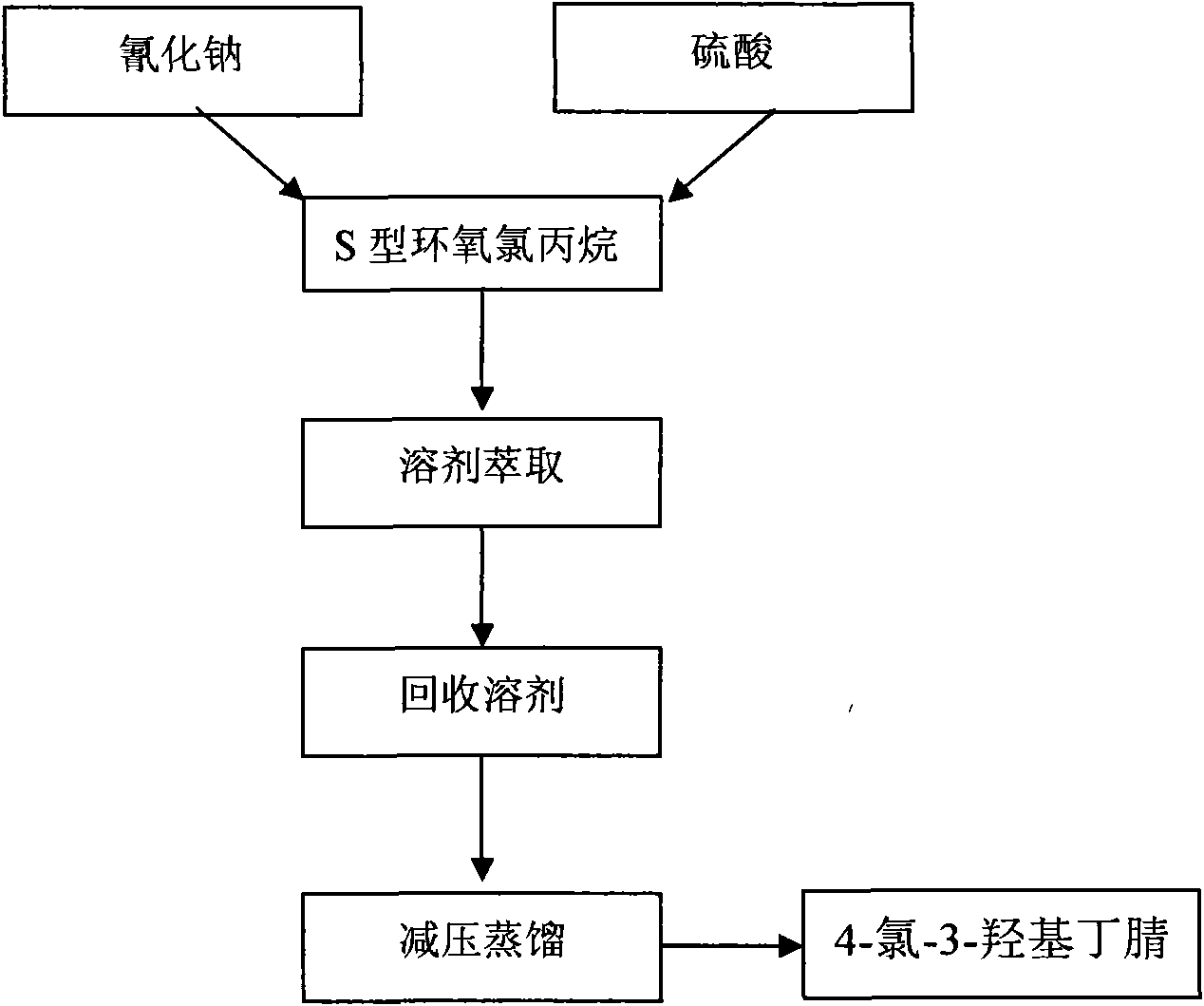
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of atorvastatin intermediate (R)-(-)-4-nitrile-3-hydroxybutyrate (ATS-5), which solves the problems of high cost, expensive raw material price and the like of the prior art. The manufacturing method is characterized in that the atorvastatin intermediate is prepared from epichlorohydrin as a raw material through ring-opening addition, glycolysis esterification, cyaniding substitution synthesis and refining. The invention has simple synthesis route, abundant raw material resources, low equipment requirements and no high-temperature high-pressure reaction; the content of produced ATS-5 is more than 98 percent, the content of water is lower than 0.2 percent, and the content of enantiomer is less than 1.0 percent. The manufacturing method is a mature production process for manufacturing the intermediate of medicine atorvastatin and is applicable to medium-sized and small enterprises.
Owner:HUANGGANG HUAYANG PHARMA
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
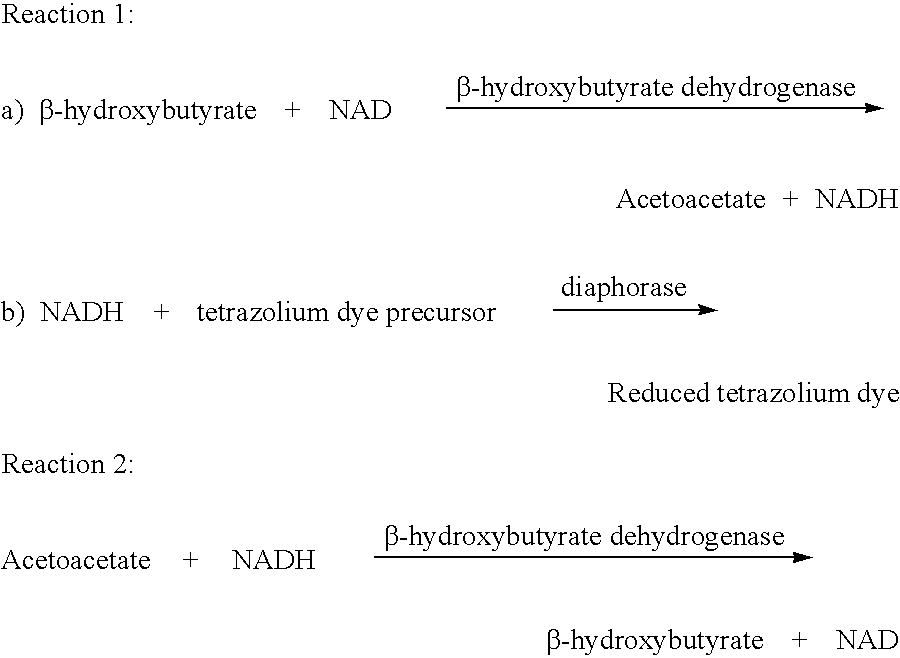
Method and test strips for the measurement of fat loss during weight loss programs
InactiveUS20040043376A1Great advantageEasy to manufactureMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
Disposable test strips and a wet chemistry method for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate or total ketone bodies (i.e., beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) in human bodily fluid samples, including but not limited to urine, saliva or sweat are described. The test strips need only be dipped in the sample and can be used by anyone in almost any milieu. Measurement can be made electrochemically, spectrophotometrically, fluorometrically or by comparision to a color standard. Combined acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate which account for 97-98% of total ketone bodies and may be measured in a cyclic reaction that occurs at pH about 7.0 to about 8.3 with beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, (beta-HBD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a tetrazolium dye precursor and an electron mediator. Using this reaction, false positive results obtained from urine samples taken from patients on sulfhydryl drugs are avoided. beta-HBD from some sources was found to cause false negative results in samples (e.g. urine) containing high chloride content due to chloride inhibition of beta-HBD. Using a simple test for chloride inhibition, it was found that beta-HBD from Alcaligenes is not so inhibited. Using either beta-HBD that is not inhibited by chloride or using 10-20 times the normal concentration of this enzyme eliminates false negatives in samples having substantial chloride content, such as urine, both in the reaction described above and in other reactions disclosed for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate and total ketone bodies, all of which reactions occur in the pH range of about 8.6 to about 9.5.
Owner:GUPTA SURENDRA
Application of alcohol dehydrogenase in catalytic generation of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate
InactiveCN103160547AHigh yieldHigh optical activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses application of alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction. By using alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst, ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate as a substrate and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) as a cofactor, asymmetric reduction is carried out to prepare the ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate. The invention applies the alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction for the first time, and has favorable effect. The enzyme activity is up to 5.6 U / mg, the yield of the substrate is up to 94%, and the enantiomeric excess value of the product is 100%. The yield is high, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
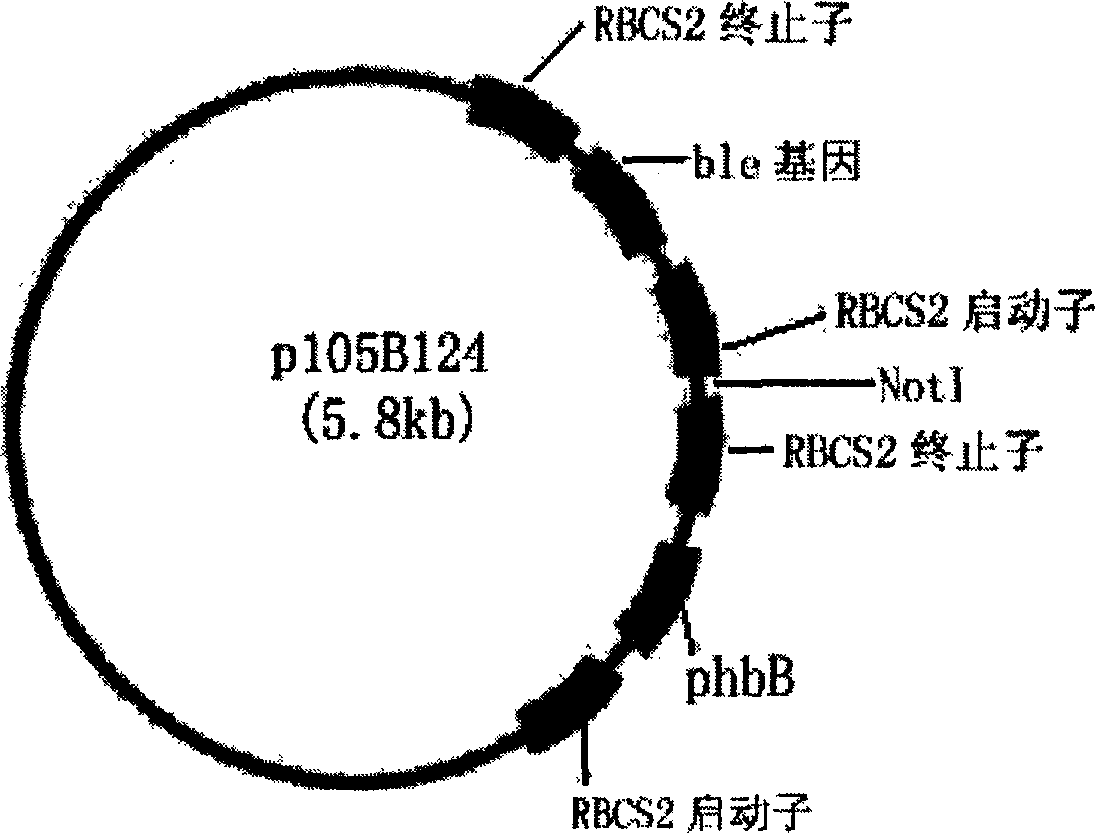
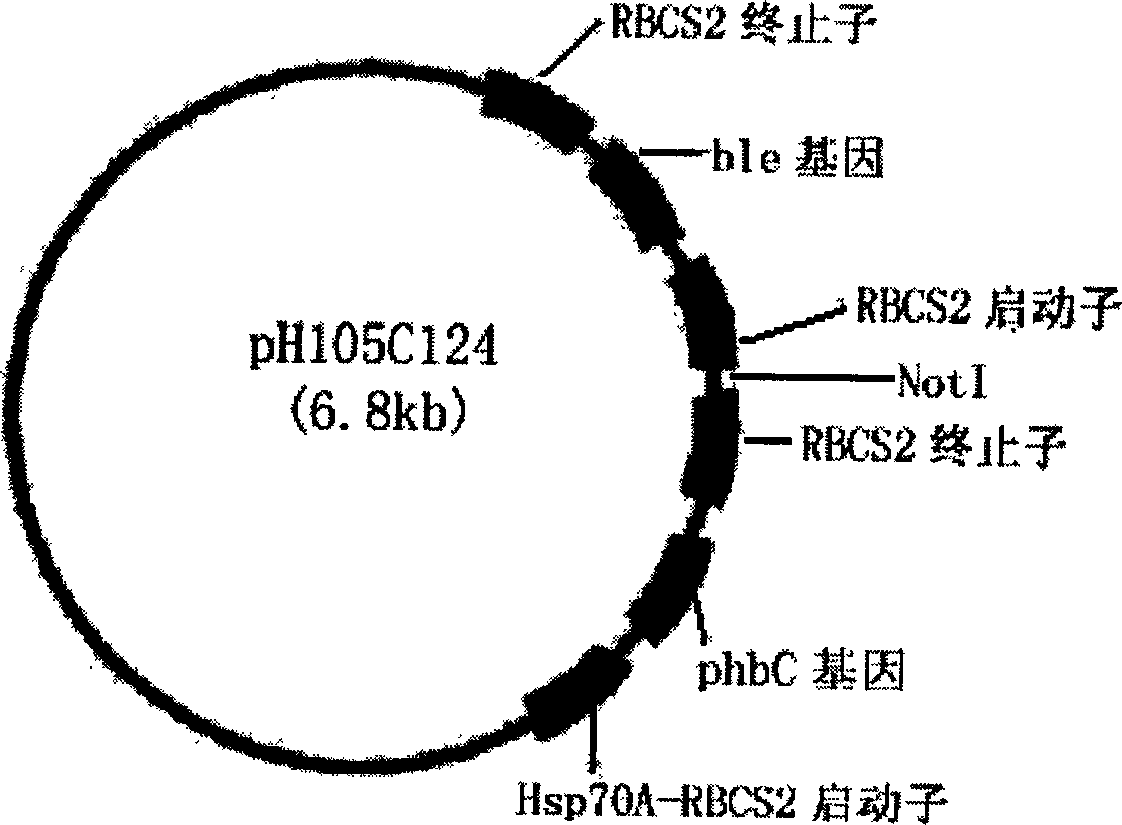
Exogenous gene expression system of Chlamydomonasreinhardtii and method for constructing and producing PHB transgenic algae
ActiveCN1807649AImprove expression efficiencyIncrease productionUnicellular algaeFermentationHydroxybutyric acidChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses an expression system and constructing PHB transgene algae method of rhine chlamydomonas exogenesis gene, which comprises the following parts: promotor, exogenesis-goal gene, screening badge and rhine chlamydomonas acceptor algae strain, wherein the method comprises the following: A, selecting and cultivating acceptor algae strain; B, cloning key enzyme gene by PHB biosynthesizing; C, expressing carrier of PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme rhine chlamydomonas; D, using PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme to lead in rhine chlamydomonas from fungus Bacillus alcaligenes with bead-milling method, gene-gun method or electrization; obtaining bivalence or transgene Chlamydomonas of producing PHB by screen selecting and molecule detecting. The poly-hydroxybutyric acid is compounded by acting in conjunction of PHB compounding key enzyme of phbA, phbB and phbC gene coding, which uses acetylcoenzyme A as substrate by photosynthesis. The method simplifies the operating, which reduces cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Novel composition based on gamma-hydroxybutyric acid
ActiveUS20110293729A1Reduced average total daily doseIncreasing apparent half lifeBiocideNervous disorderHydroxybutyric acidSolid core
The present invention relates to a granule of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid or of one of its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, characterized in that it comprises a solid core on which the gamma-hydroxybutyric acid or one of its salts is supported.
Owner:DEBREGEAS & ASSOCIES PHARMA
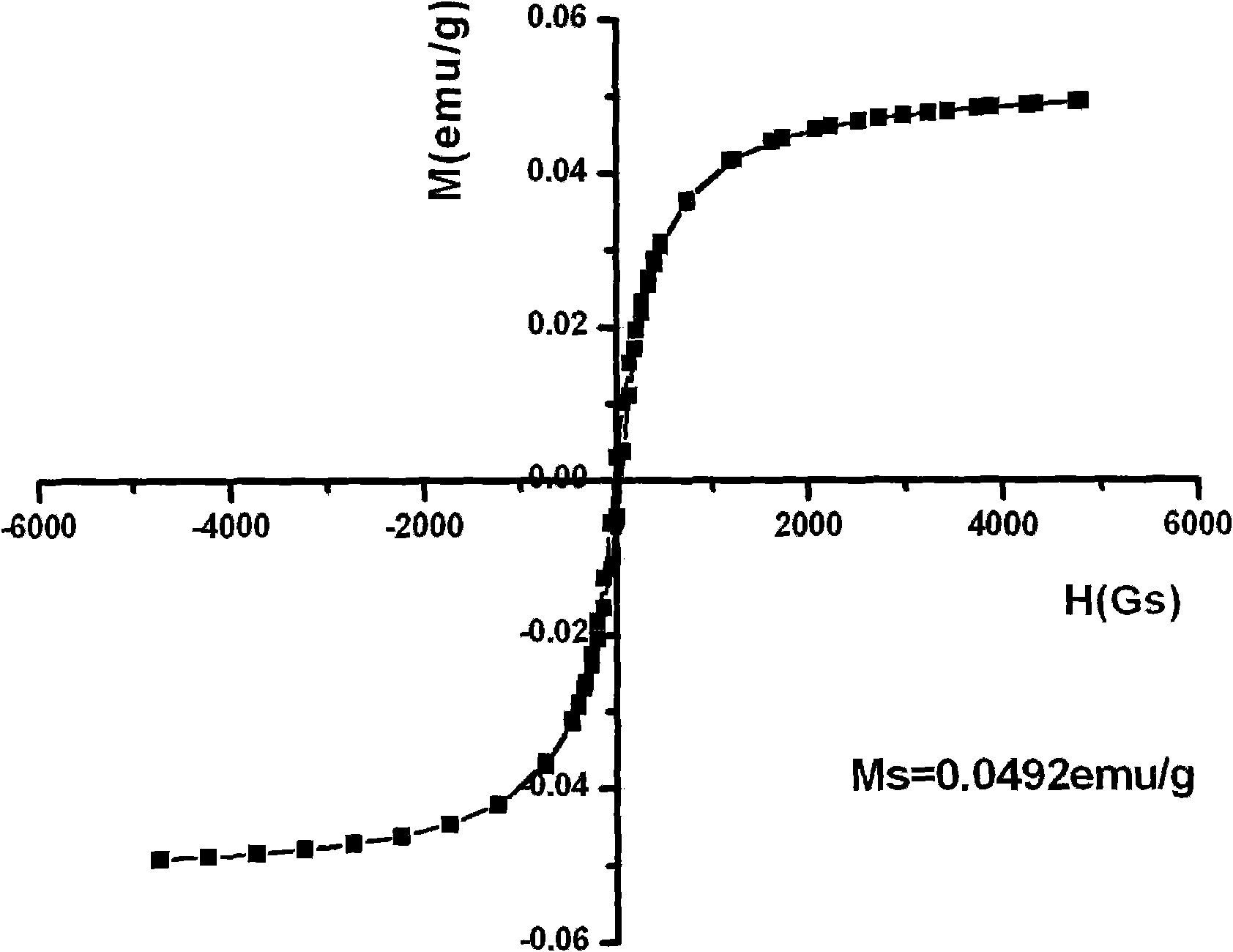
Magnetic composite material and application thereof in regeneration and repair of bone tissues
ActiveCN102049066AHas superparamagnetic propertiesGood biocompatibilityTissue regenerationProsthesisHydroxybutyric acidPolyamide
The invention discloses a magnetic composite material and an application thereof in regeneration and repair of bone tissues, as well as a method for preparing the magnetic composite material and a product prepared by the magnetic composite material, wherein the magnetic composite material comprises the following components: a) 10-50g of polymer material calculated by 100ml of organic solvent, wherein the polymer material is selected from polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, polycaprolactone, polyamide or poly-hydroxybutyric acid; b) 10g of hydroxyapatite nano-particles calculated by 100ml of the organic solvent; and c) 2.5g of gamma-Fe2O3 nano-particles calculated by 100ml of organic solvent, wherein the organic solvent is selected from tetrahydrofuran (THF), dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethylacetamide (DMAc), chloroform or dioxane.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Reversible inhibitors of SAH hydrolase and uses thereof
1. The present invention provides compositions and methods for reversibly inhibiting S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) hydrolase. The compounds of the present invention can be used as an anti-hemorrhagic viral infection agent, an immunosuppressant, a homocysteine lowering agent, or an anti-neoplasm agent. The compositions and methods of the present invention can be used for the prevention and treatment of hemorrhagic virus infection, autoimmune diseases, autograft rejection, neoplasm, hyperhomocysteineuria, cardiovascular disease, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis or diabetes. The compound of the present invention and / or used in the present invention has the formula (I):wherein Z is selected from the group consisting of carbon and nitrogen,R1 and R2 are the same or different, and are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, alkoxy, amino, aryl, heteroaryl, and halogen;R3 and R4 are the same or different and are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, acetyl, alkenyl, aryl, and heteroaryl;X is selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur; andY is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, a C1-10 alkyl group, alkenyl, vinyl, aryl, and heteroaryl, provided that the compound is not (4-adenine-9-yl)-2-hydroxybutanoic acid.
Owner:NINGBO ZIYUAN PHARMA INC
Use of carbonyl reductase in (S)-4-chloro-3 hydroxy butyric ether production
The invention discloses an application of carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 to prepare (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester by asymmetric reduction of 4-chloracetyl ethyl acetate. The carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is taken as a catalyst, the ethyl 4-chloracetyl ethyl acetate is taken as a substrate, and NADPH is taken as a cofactor, and the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester is prepared by the asymmetric reduction. The carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is applied to preparing the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester by the asymmertric reduction of the 4-chloroacetyl ethyl acetate for the first time, which produces good effect; the yield of the substrate is up to 95%, and the enantiomer excess value of the product is 100%, the yield is high, and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Resource-renewable and biodegradable conductive fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102936761ARealize conductive functionLower percolation thresholdElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiber3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The invention discloses resource-renewable and biodegradable conductive fiber and a preparation method thereof. The fiber consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-70 parts of polylactic acid (PLA), 30-70 parts of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid-co-3-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) and 0.05-8 parts of conductive filler. The preparation method of the conductive fiber comprises the following steps of: (1) proportionally pre-mixing PHBV (if PLA is not less than 50 parts) or PLA (if PLA is less than 50 parts) and the conductive filler, and performing melt blending and granulation to obtain the conductive master batch of the PHBV or PLA; (2) proportionally pre-mixing the PLA or PHBV and the conductive master batch of the PHBV or PLA, and performing melt blending and granulation to obtain composite conductive mater batches; and (3) spinning and drafting the composite conductive master batches one by one to obtain the conductive fiber. The conductive fiber disclosed by the invention can be used as the material for electrodes, static resistance, low-temperature heating, electromagnetic shielding, thermal sensitivity, gas sensitivity and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microparticles with adsorbed polypeptide-containing molecules
ActiveUS7501134B2Easy to produceSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsHemagglutininLactide
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Method for the production of D-(-)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by recombinant Escherichia coli
InactiveUS7262037B2Simple technologyImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliHydroxybutyric acid
This invention relates to a method for the production of D-(−)-3-hydroxybutyric acid, comprising the step of culturing a recombinant strain containing genes phbA, phbB, ptb and buk by fermentation. Preferably, the recombinant strain is a strain of E. coli. The method of the invention is simple, avoiding the technique of degrading polymer to produce D-(−)-3-hydroxybutyric acid. The present method also provides improved efficiency, lowers the complicated requirement for facilities as used in traditional chemical synthesis, simplifies the complicated technique flow, and omits the complicated chiral separation step. Therefore, the present method greatly reduces the costs associated with D-(−)-3-hydroxybutyric acid production. Also, with this invention, the problems such as environmental pollution of chemical synthesis and chiral separation are overcome.
Owner:CHEN GUOQIANG +2
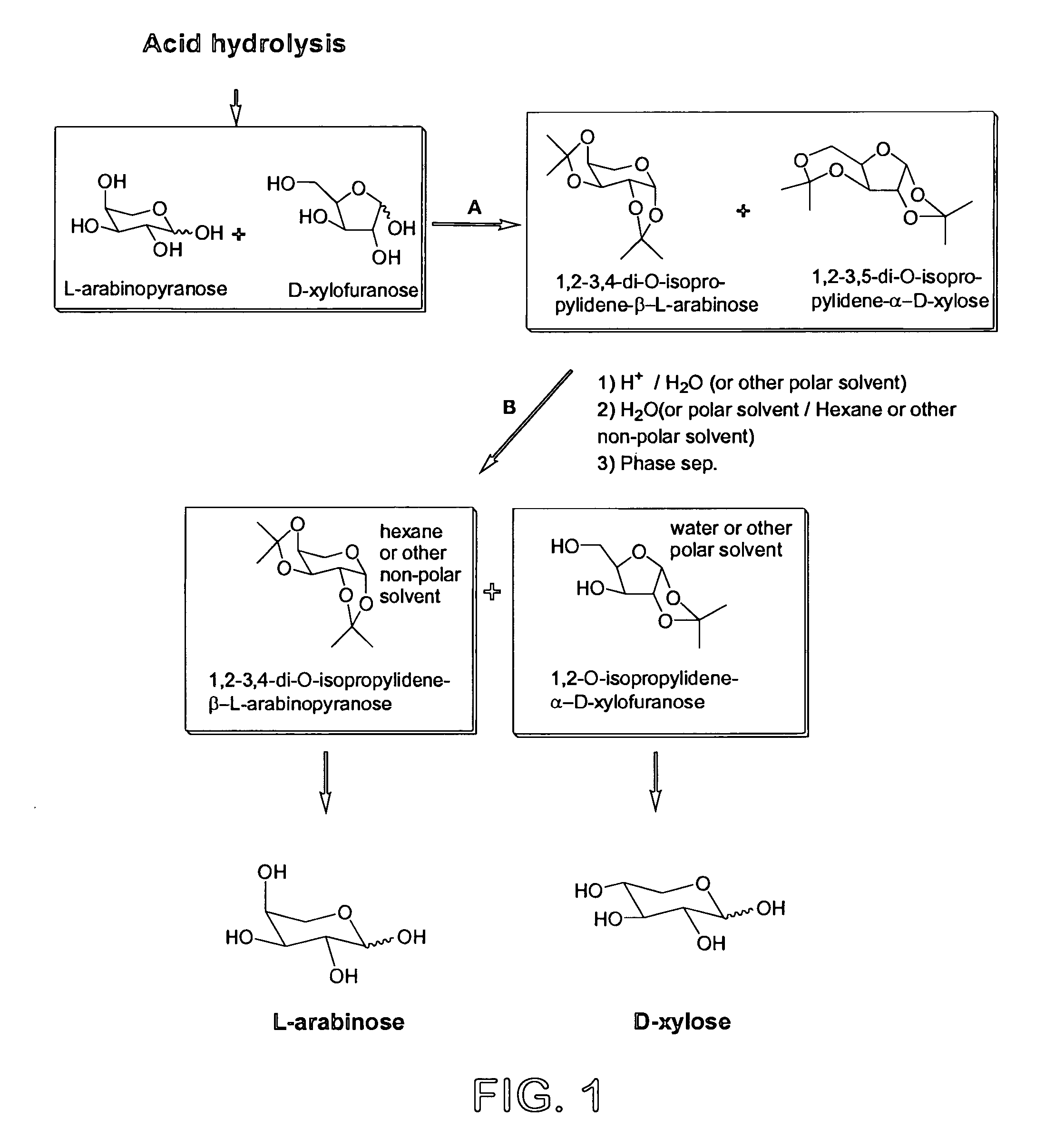
Process for the preparation and separation of arabinose and xylose from a mixture of saccharides
InactiveUS7498430B2Low costAid acetalizationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCombinatorial chemistryArabinose
A process for the preparation and separation of the pentoses, xylose and arabinose from mixtures of saccharides by forming acetals is described. D-xylose is a precursor to xylitol, a sweetener, and L-arabinose is a precursor to the drug intermediate (R)-3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid, carnitine and agrichemicals.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com