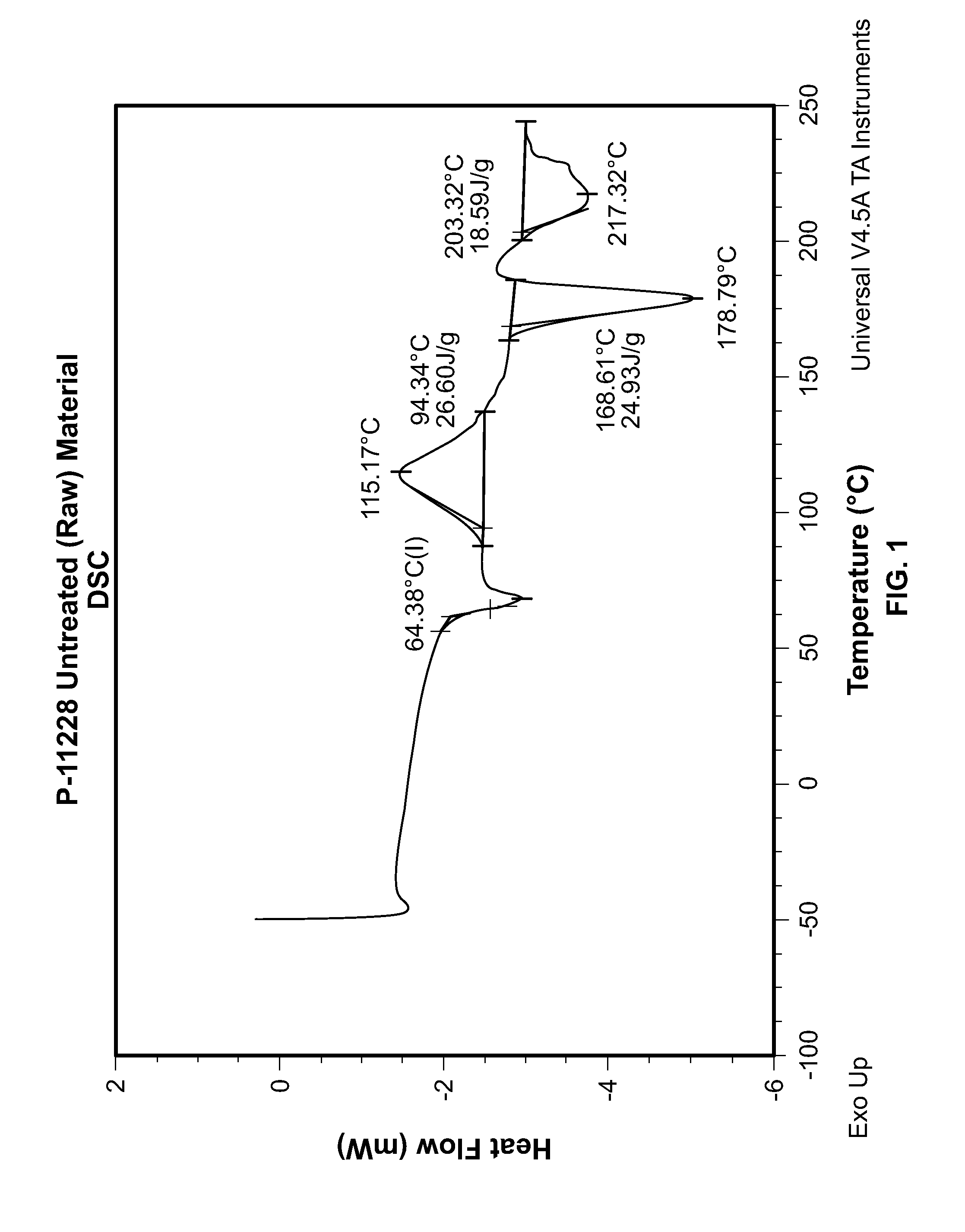
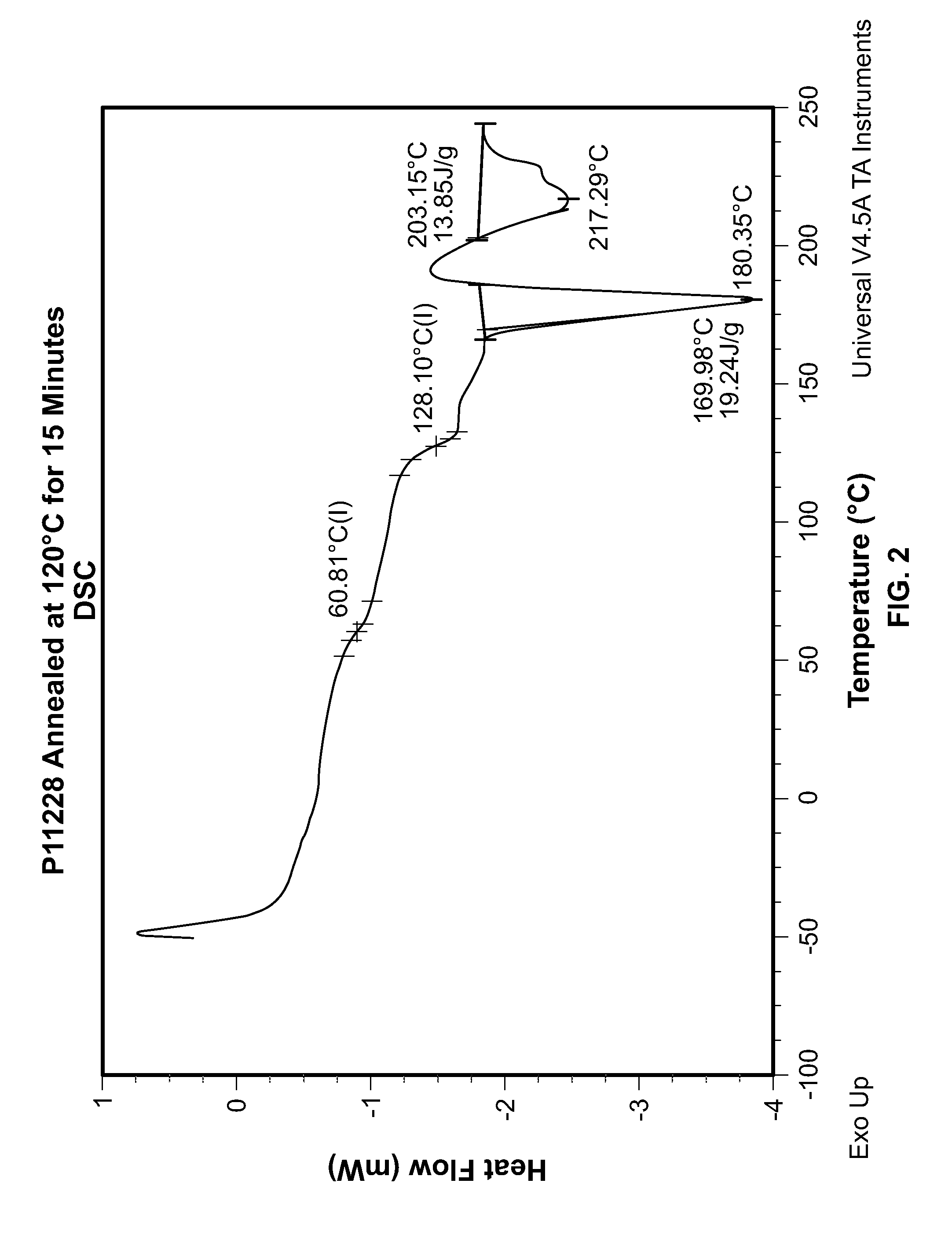
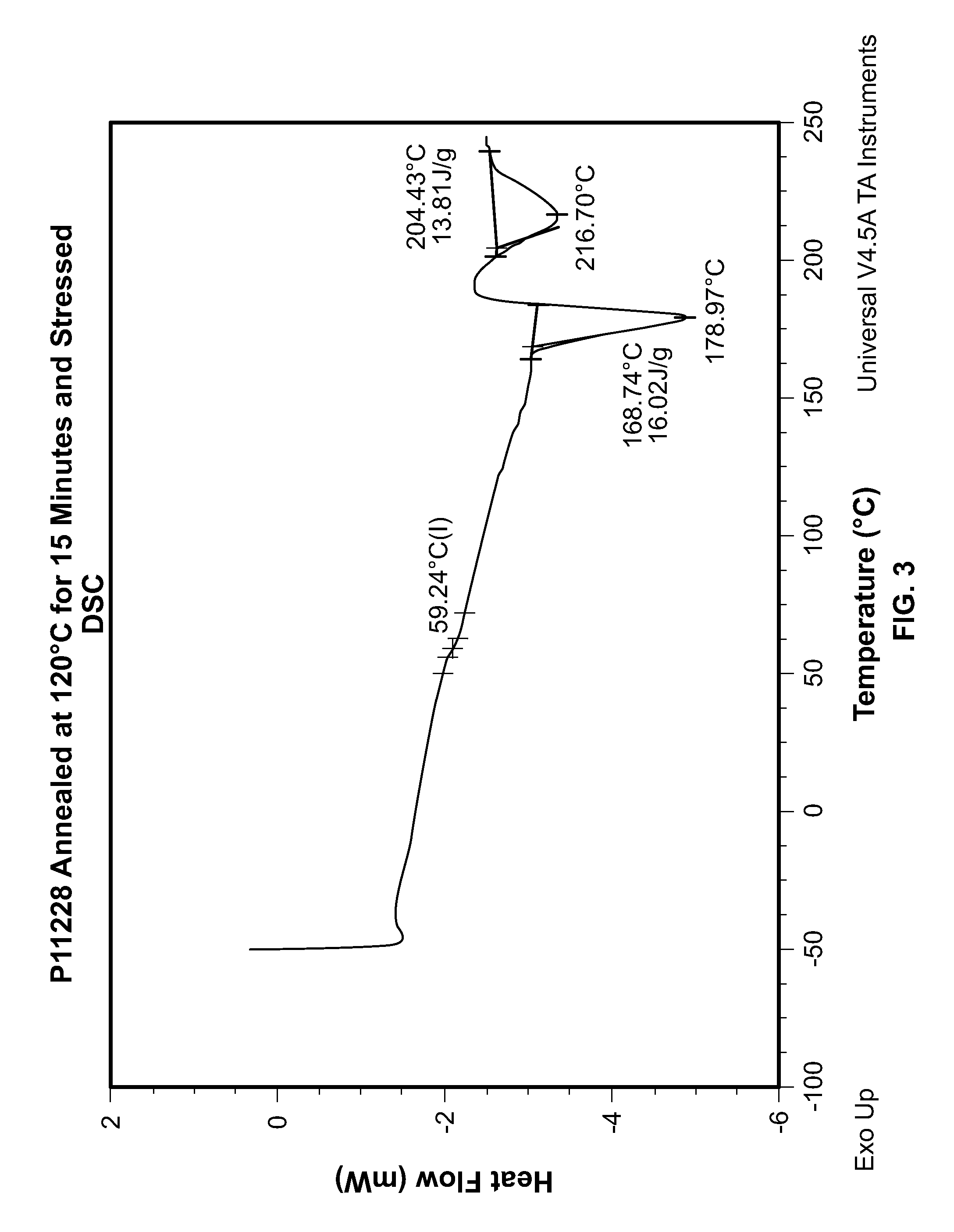
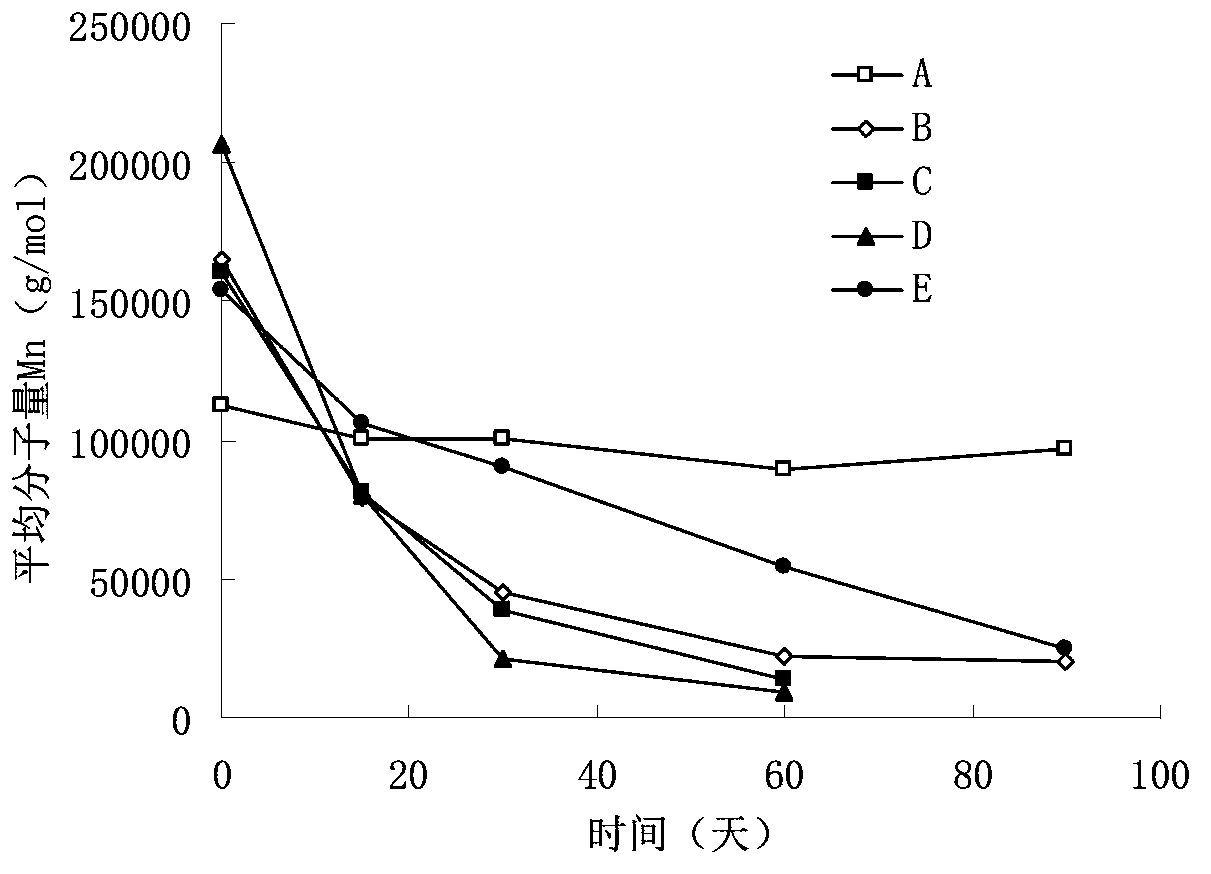
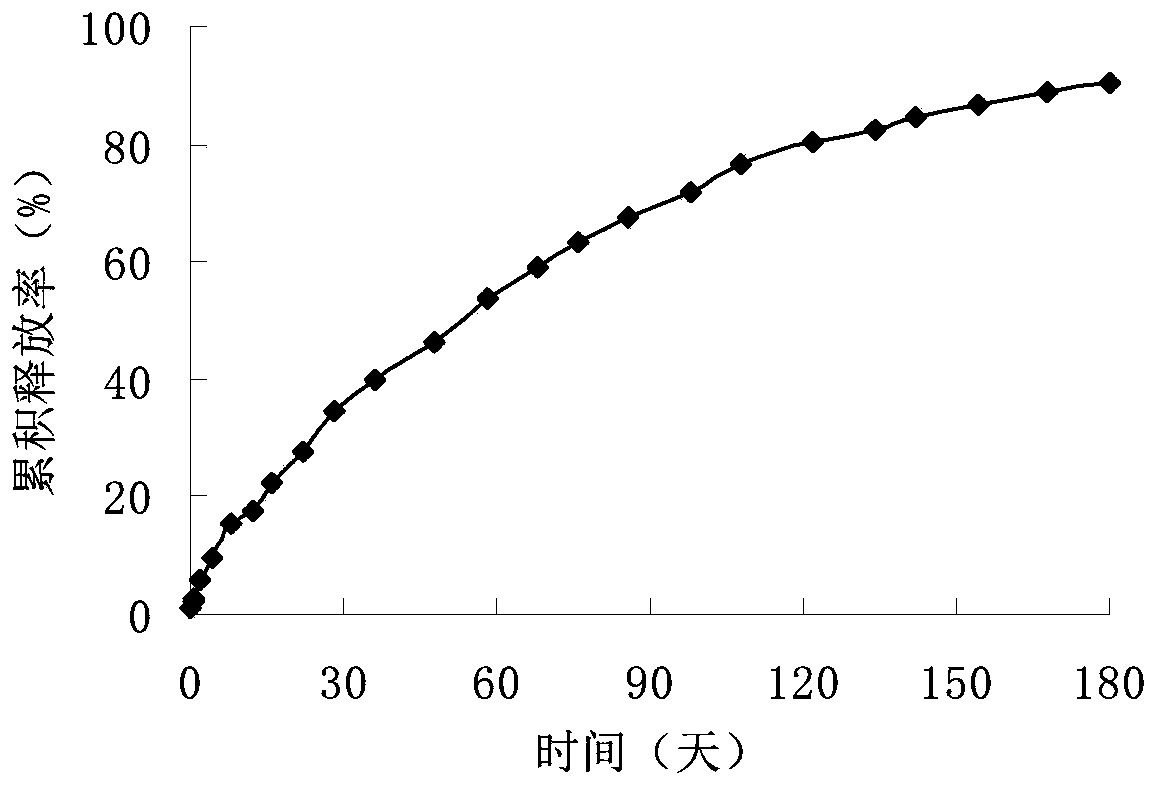
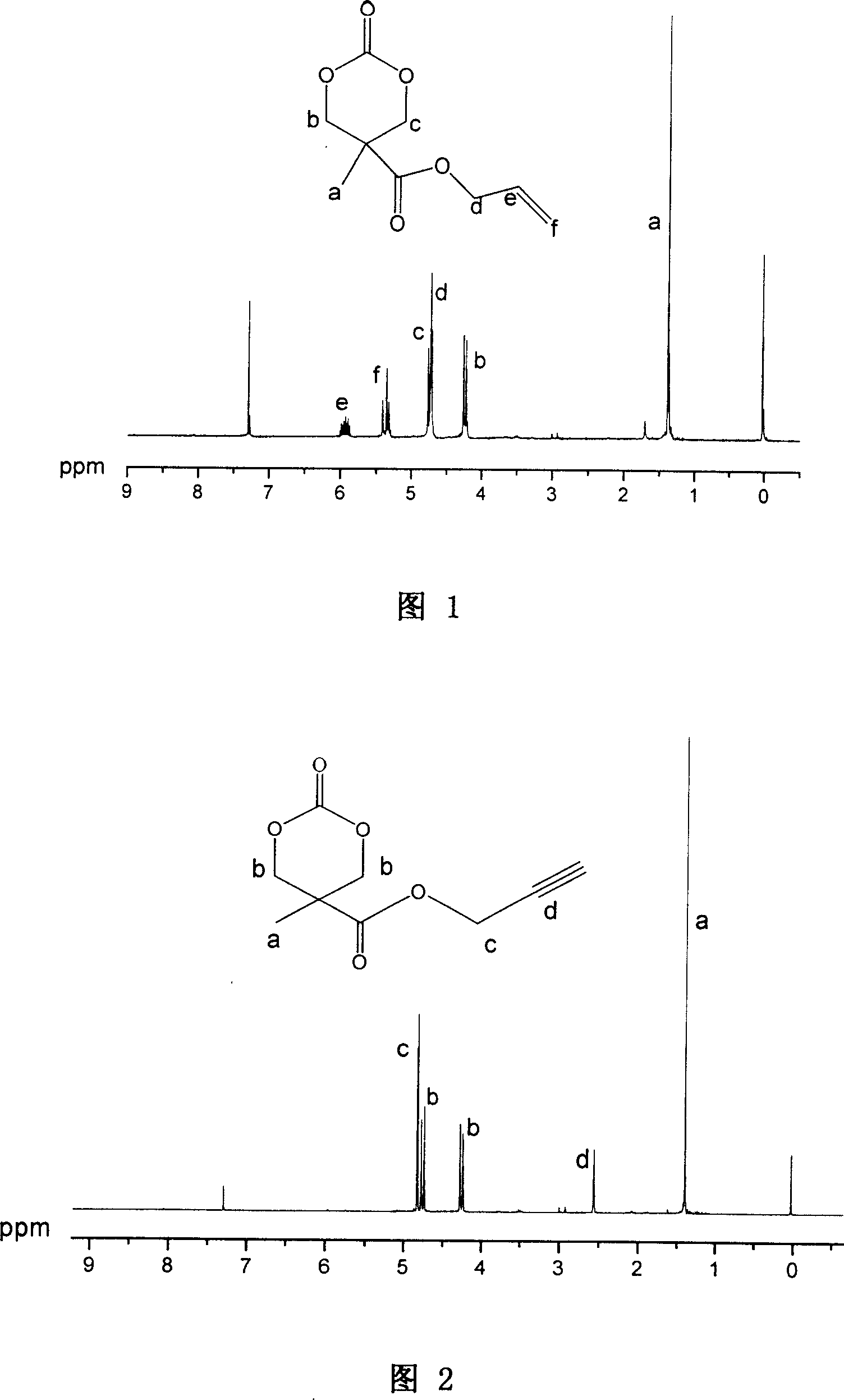
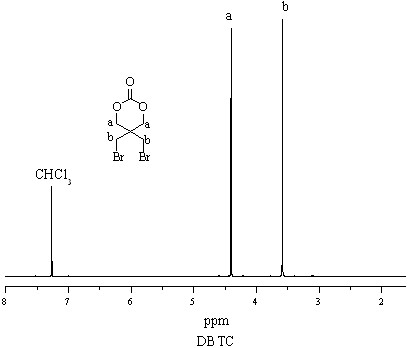
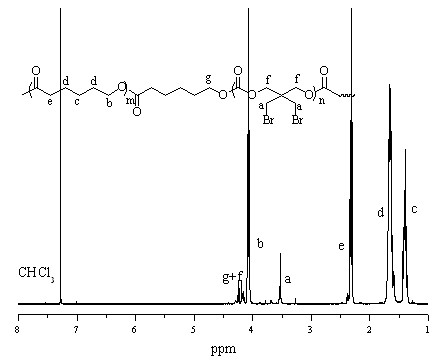
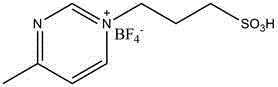
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "Trimethylene carbonate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Trimethylene carbonate or 1,3-propylene carbonate is a 6-membered cyclic carbonate ester. It is a colourless solid that upon heating or catalytic ring-opening converts to the poly(trimethylene carbonate). Such polymers are called aliphatic polycarbonates are of interest for potential biomedical applications. An isomeric derivative is propylene carbonate, a colourless liquid that does not spontaneously polymerize.
Bioabsorbable blends and surgical articles therefrom
InactiveUS7138441B1Excellent flexibiltyExcellent Adhesive PropertiesSuture equipmentsSurgical adhesivesCyanoacrylatePolymer science
Blends made of bioabsorbable materials including glycolide, lactide, caprolactone, dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, alkylene glycols, esteramides, etc., and polymers and copolymers thereof with cyanoacrylates are described. Processes for making the polymers and surgical articles made totally or in part from such polymers, including sutures, are also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
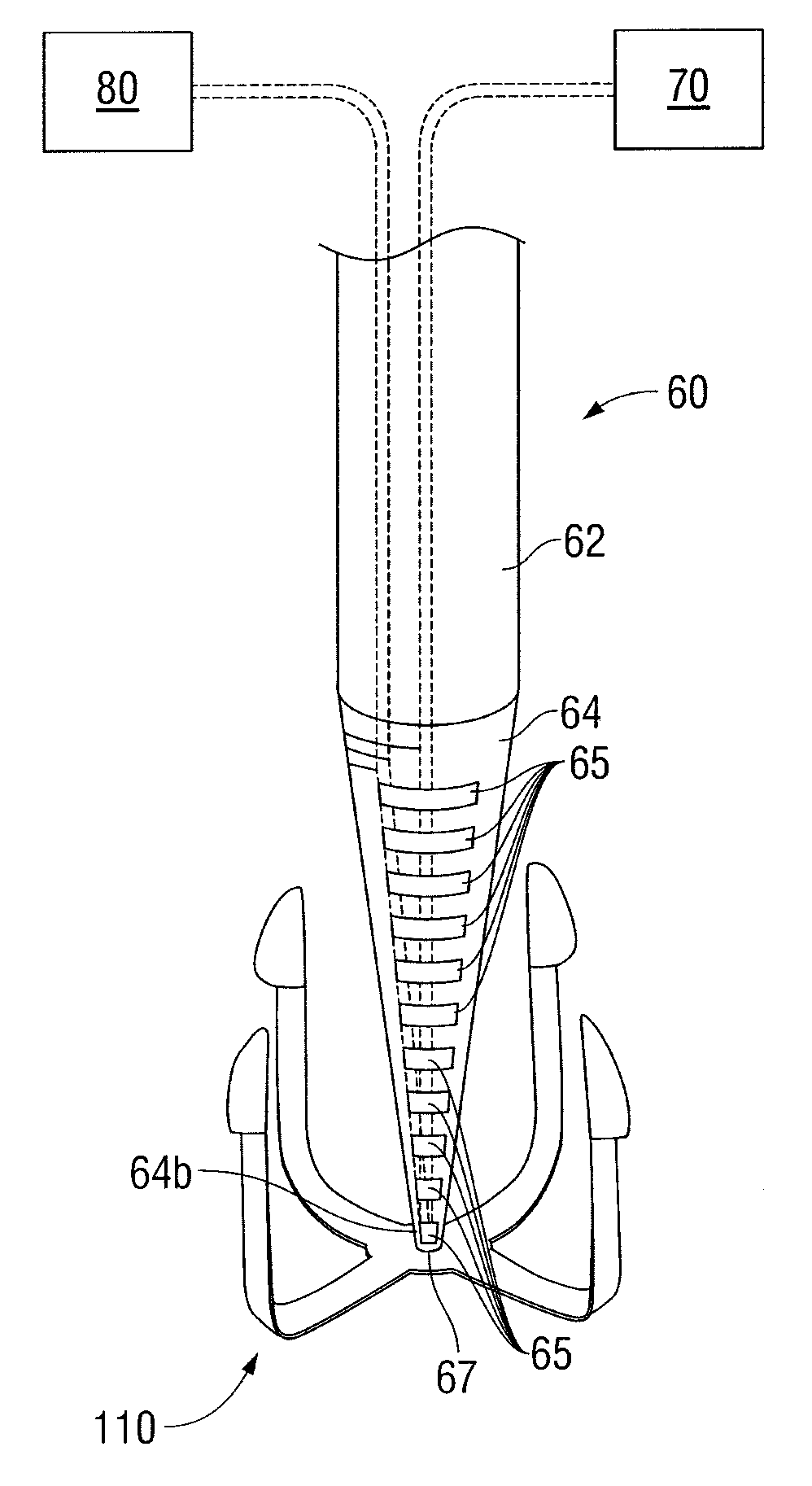
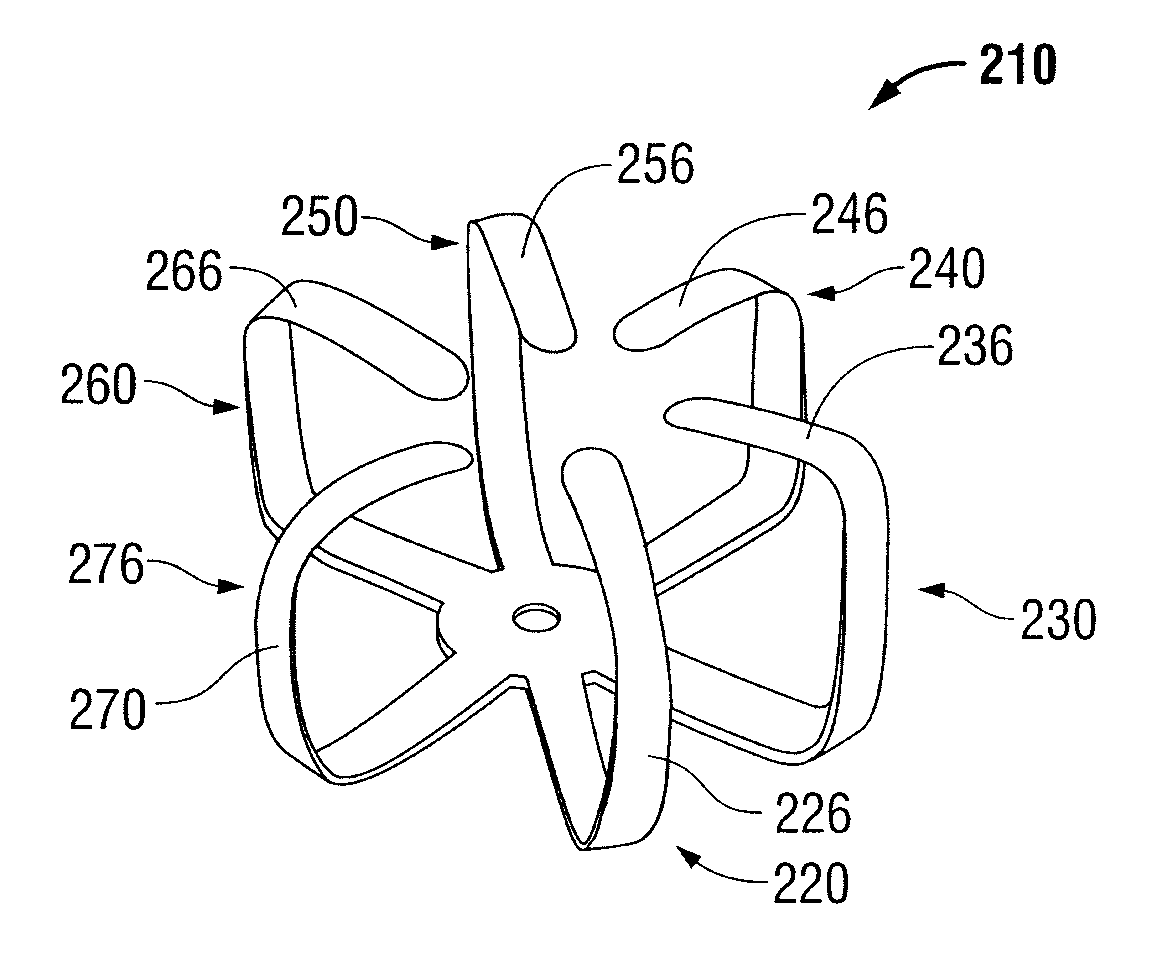
Shape memory fasteners and method of use
ActiveUS9295463B2DiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTrimethylene carbonateBiological activation
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
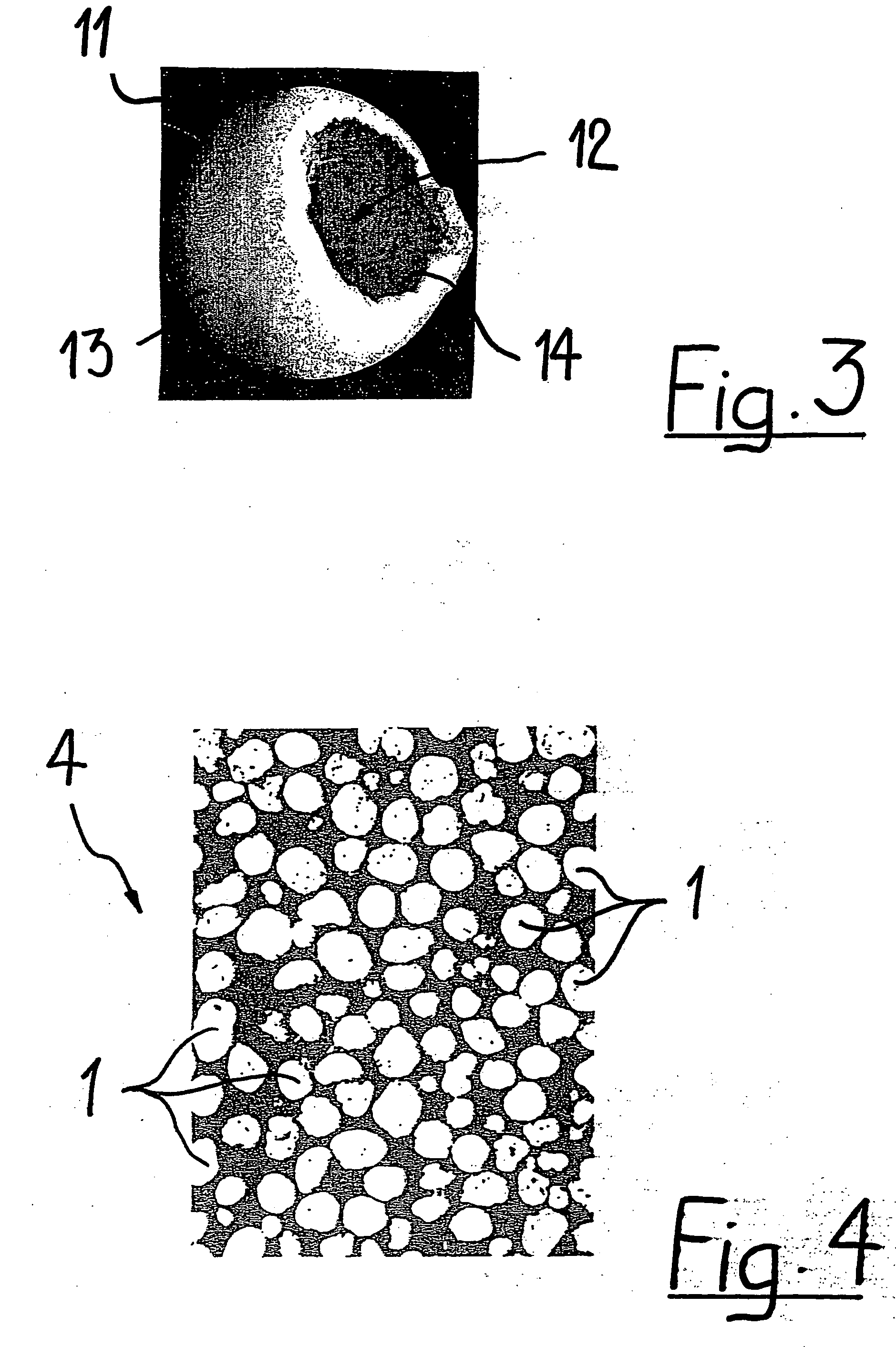
Porous biocompatible implant material and method for its fabrication
a biocompatible and biodegradable implant for a cavity in a bone of a living organism is made of a biocompatible and biodegradable granules which are selected from the group including biopolymers, bioglasses, bioceramics preferably calcium sulfate, calcium phosphate such as monocalcium phosphate monohydrate, monocalcium phosphate anhydrous, dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, dicalcium phosphate anhydrous, tetracalcium phosphate, calcium orthophosphate phosphate, α-tricalcium phosphate, β-tricalcium phosphate, apatite such as hydroxyapatite, or a mixture thereof. The biocompatible and biodegradable granules are provided with a coating, which comprises at least one layer of a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer which is selected from the group including poly((α-hydroxyesters), poly(orthoesters), polyanhydrides, poly(phosphazenes), poly(propylene fumarate), poly(ester amides), poly(ethylene fumarate), polylactide, polyglycolide, polycaprolactone, poly(glycolide-co-trimethylene carbonate), polydioxanone, co-polymers thereof and blends of those polymers. The biocompatible and biodegradable implants are obtained by fusing together the polymer-coated granules through polymer-linkage of the polymer coatings of neighboring granules.
Owner:COLLAGEN MATRIX
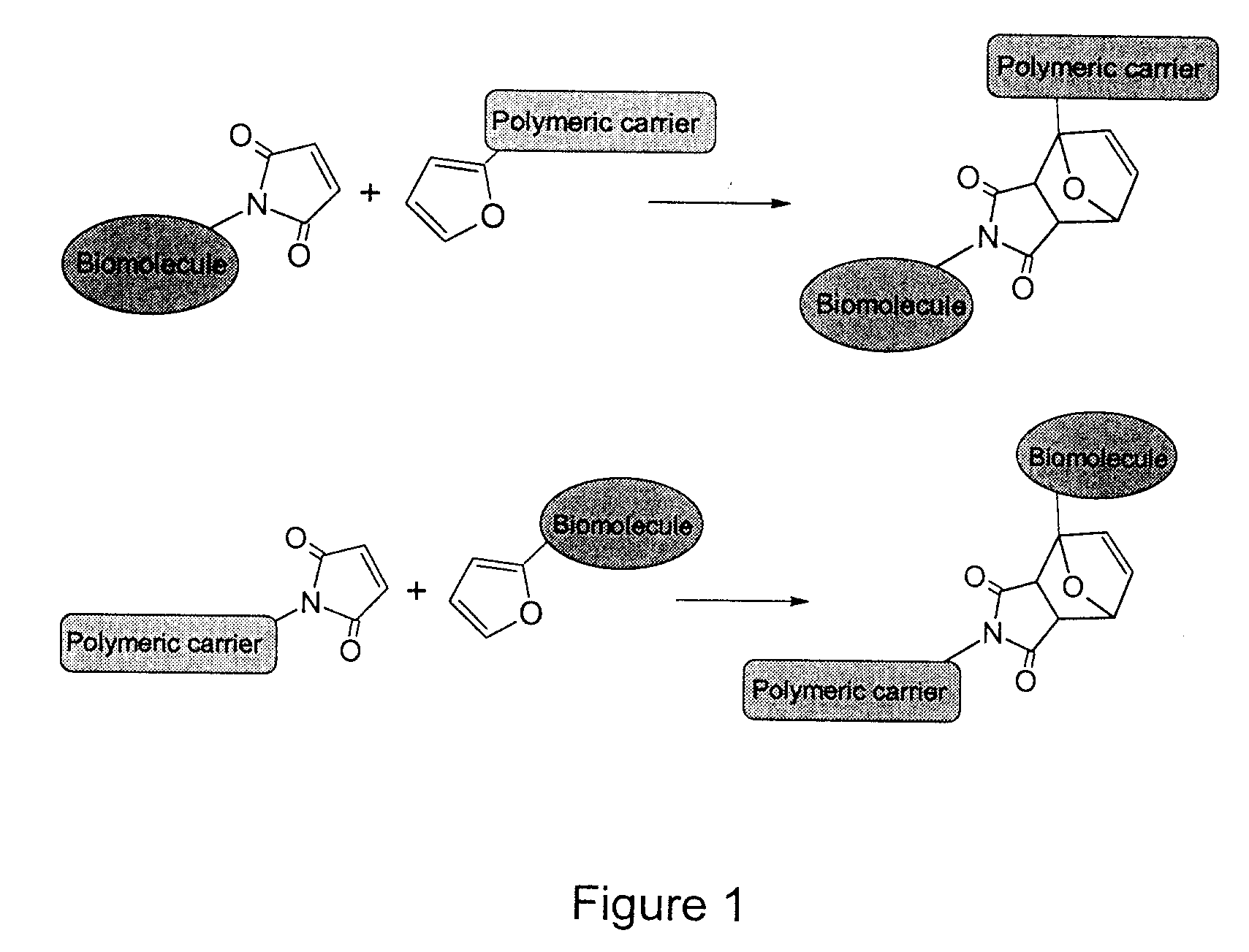
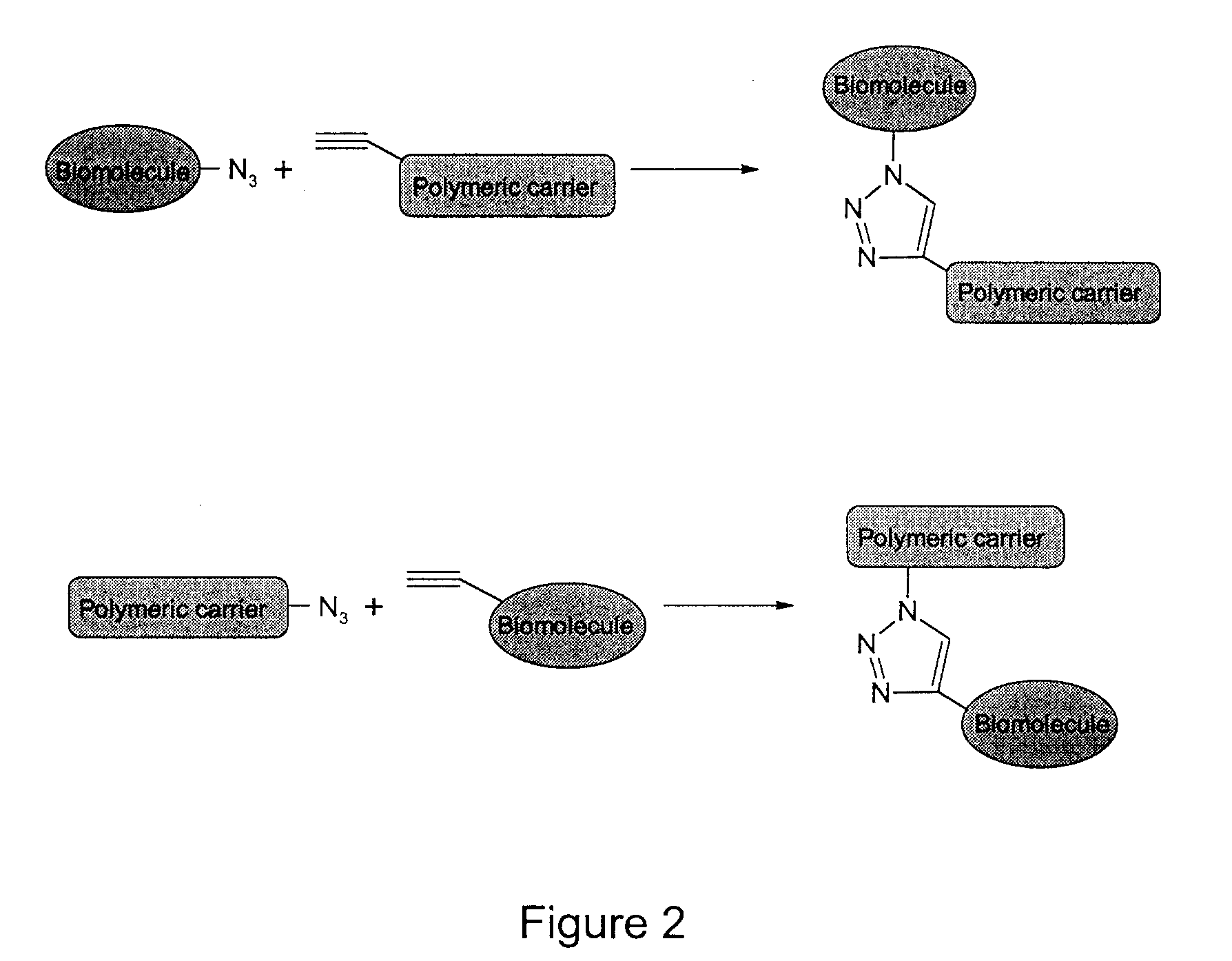
Method of Biomolecule Immobilization On Polymers Using Click-Type Chemistry
ActiveUS20090297609A1Improve efficiencyProcess environmental protectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFuranAlkyne
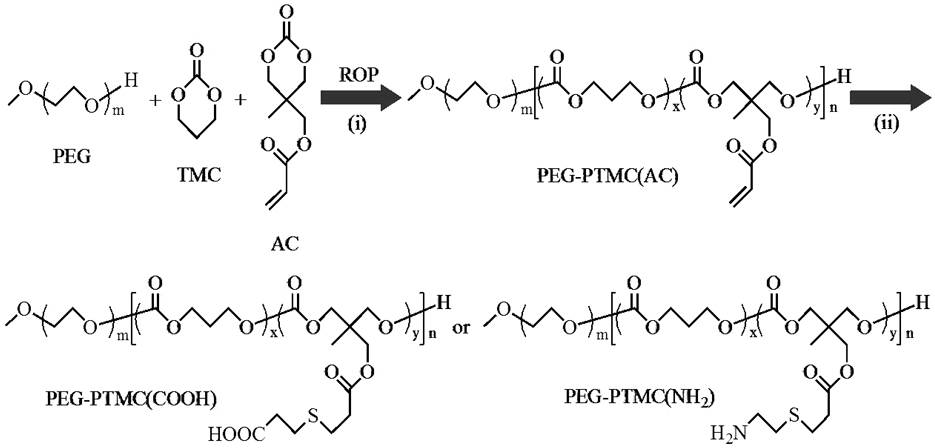
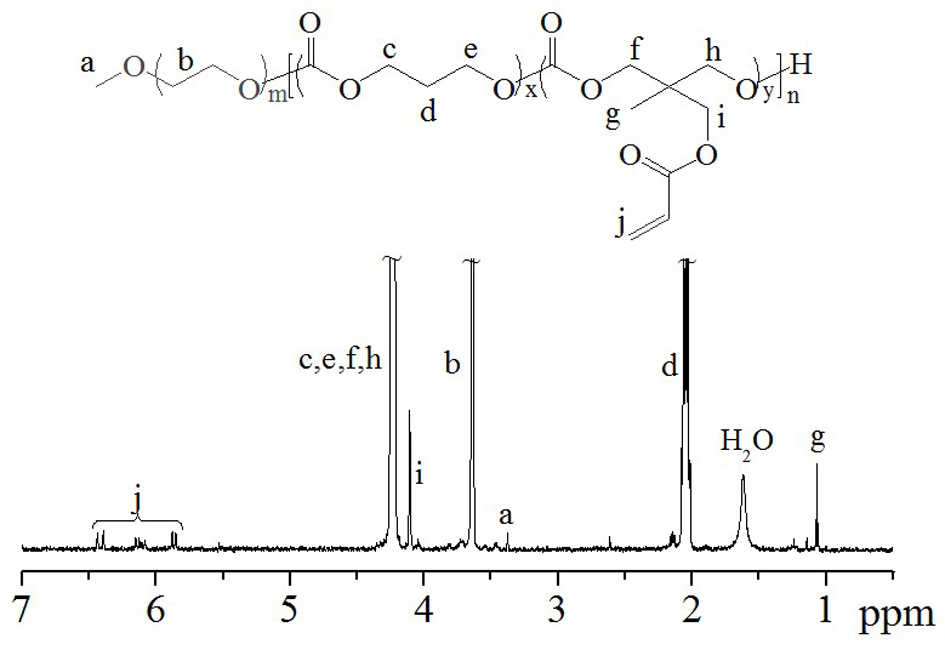
The present invention provides a method for the covalent immobilization of biomolecules on polymers for delivery of the biomolecules, which has the advantage of being simple, highly efficient, environmentally friendly and free of side products relative to traditional immobilization techniques. The invention provides a modified micro / nanoparticle system, which uses a functionalized polymer formed into micro or nanoparticles to bind a molecule to the particles using uses facile chemistry, the Diels-Alder cycloaddition between a diene and a dienophile with the polymer being functionalized with one of them and the molecule with the other, or the Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between a terminal alkyne and an azide to bind the molecule to the particle. The molecules and / or other therapeutic agents may be encapsulated within the polymer particles for intravenous therapeutic delivery. The invention also provides a novel synthetic biodegradable polymer, a furan / alkyne-functionalized poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC)-based polymer, whose composition can be designed to meet the defined physical and chemical property requirements. In one example, the particle system self-aggregates from functionalized PTMC-based copolymers containing poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) segments. The composition of the copolymers can be designed to meet various particle system requirements, including size, thermodynamic stability, surface PEG density, drug encapsulation capacity and biomolecule immobilization capacity.
Owner:SHOICHET MOLLY S +2
Method for improving water resistance of polyvinyl alcohol film by using poly(trimethylene carbonate) and poly(p-dioxanone)
The invention discloses a method for improving water resistance of a polyvinyl alcohol film by using poly(trimethylene carbonate) and poly(p-dioxanone). The method comprises the following steps of (1) adding poly(trimethylene carbonate), diisocyanate, a catalyst and a solvent into a drying reactor, and reacting while stirring at the temperature of 50-55 DEG C to obtain end-NCO group contained poly(trimethylene carbonate); (2) adding end-NCO group contained poly(trimethylene carbonate), polyvinyl alcohol, a solvent and a catalyst into the drying reactor, and reacting while stirring at the temperature of 50-55 DEG C to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol and poly(trimethylene carbonate) grafted copolymer; (3) adding the polyvinyl alcohol and poly(trimethylene carbonate) grafted copolymer, poly(p-dioxanone) and a solvent into the drying reactor, stirring and mixing at the temperature of 40-50 DEG C, filming by using a tape casting method and drying to obtain a target product required by the invention. The method is simple in preparation process and easy to master, and the water resistance of the obtained modified film is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
High strength fibers of L-lactide copolymers epsi-caprolactone and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 25%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.4 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yarns of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
High strength fibers of l-lactide copolymers, epsilon-caprolactone, and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably ε-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yams of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Shape Memory Fasteners And Method Of Use
ActiveUS20110087277A1DiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTrimethylene carbonateBiological activation
A surgical fastener configured to close an opening in tissue is provided. The surgical fastener includes a base defining a central axis at least one pair of legs extending from the base. Each of the legs includes a base portion and a tissue engaging portion. When in a first position, each of the tissue engaging portions is arranged to define an insertion direction and when in a second position, each of the tissue engaging portions extends inward towards the central axis. The surgical fastener is at least partially formed from a shape memory material including a combination of Polydioxanone and Poly(L-lactide) or a combination of Trimethylene Carbonate and Poly(L-lactide). The pair of legs are configured to move from the first position to the second position upon activation of the shape memory material.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Thickened paint and coating remover
InactiveUS6239090B1Low toxicityImprove efficacyInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsChemical paints/ink removersAlcoholTrimethylene carbonate
A thickened composition and process useful for removing paint, comprising: a carbonate such as propylene carbonate or ethylene carbonate, a thickener such as polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), hydrogen peroxide and water. The composition may include additional cosolvents such as glycol ethers and alcohols such as benzyl alcohol, and / or dibasic ester (DBE).
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC
Coated, slow-absorbing textile constructs for sutures and tissue engineering
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Disclosed are coated surgical constructs including sutures made of multifilament yarns of the present copolymers and coated with nitrogenous copolyesters which will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Preparation and characterization of polyethyleneglycol/polyesters as biocompatible thermo-sensitive materials
InactiveUS20070218099A1Reduce molecular weightWell formedPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention relates to a biocompatible and thermosensitive poly(ethylene glycol) / polyester block copolymer and a method of its preparation thereof, and particularly to a multi-functional intelligent hydrogel polymer comprising a hydrophilic part of a poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) having a low molecular weight and a hydrophobic part comprising an ester-based caprolactone (CL) segment as an essential ingredient and further comprising a para-dioxanone (PDO) segment, a trimethylene carbonate (TMC) segment or a PDO / TMC copolymer containing the PDO and the TMC segments in a predetermined ratio, which easily forms a desired-shaped gel and decomposes or disperses without necessitating the operation process for removing the gel due to the temperature-dependent phase transition caused by the coagulation and the expansion of polymer micelles comprising a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic part, thus being applicable to a drug delivery system or a porous support for tissue engineering purpose.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
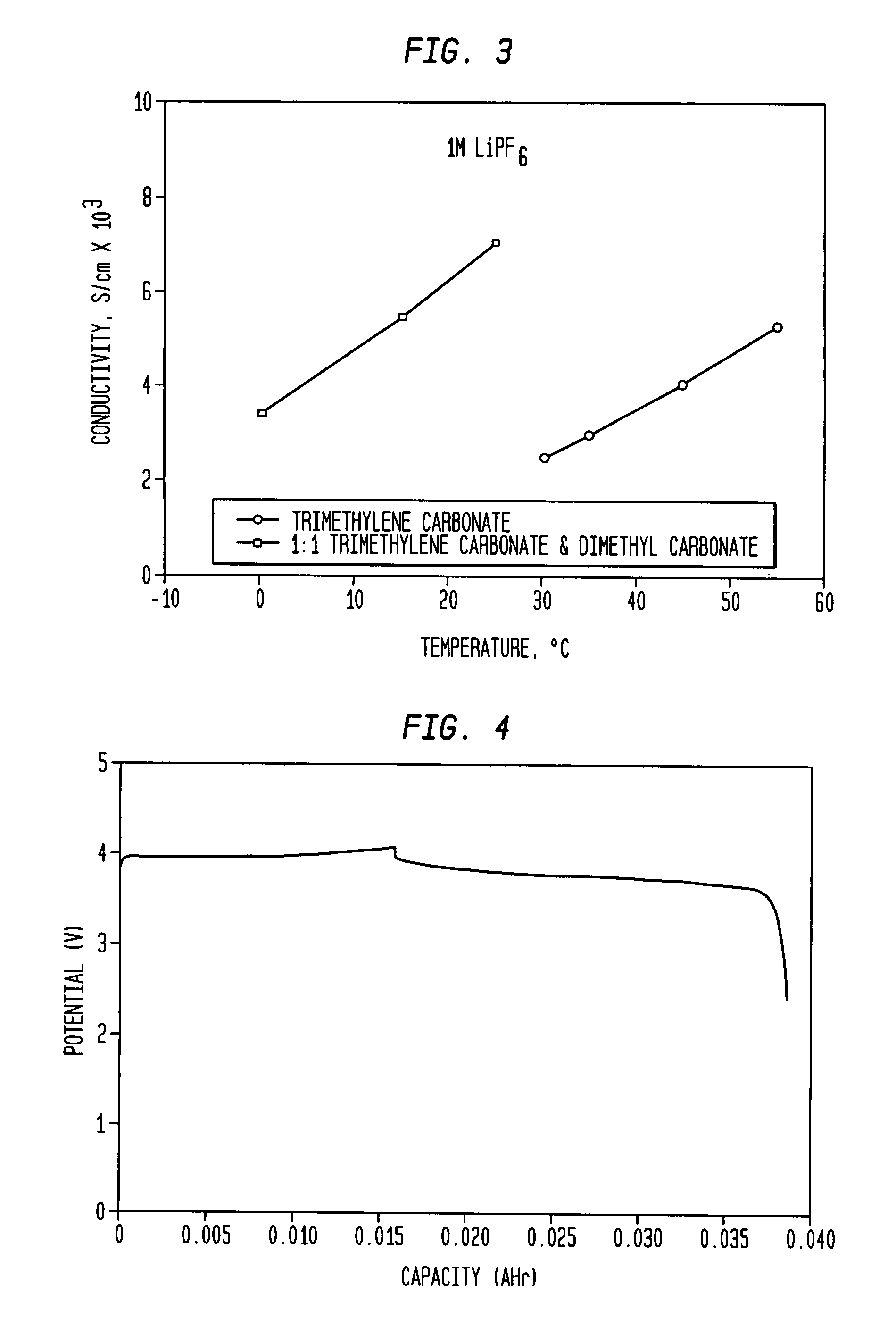
Carbonate solvent for electrolytes in lithium and lithium ion cells
InactiveUS8021791B1Inhibition formationImprove battery performanceOrganic electrolyte cellsSolid electrolyte cellsOrganic solventTrimethylene carbonate
An electrochemical cell includes an anode composed of a salt, a cathode insulated from the anode and a non-aqueous electrolyte in contact with the anode. The electrolyte may include an organic solvent that comprises at least approximately one percent by volume trimethylene carbonate.
Owner:ARMY SEC OF THE THE
Polishing pad comprising biodegradable polymer
The invention is directed to a polishing pad for use in chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a biodegradable polymer. The biodegradable polymer comprises a repeat unit selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, lactic acid, hydroxyalkanoic acids, hydroxybutyric acid, hydroxyvaleric acid, caprolactone, p-dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, butylene succinate, butylene adipate, monosaccharides, dicarboxylic acid anhydrides, enantiomers thereof, and combinations thereof. The invention is further directed to methods of its use.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Absorbable vessel ligature clamp and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102973988AImprove hydrophobicityChange the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicitySurgerySurgical operationPolyester
The invention provides an absorbable vessel ligature clamp for surgical operation and a preparation method thereof. The vessel ligature clamp is prepared from a biodegradable aliphatic polyester material, wherein the biodegradable aliphatic polyester material is a homopolymer of any one of monomers or a copolymer of any two type of monomers, namely dioxanone, glycolide, lactide, caprolactone and trimethylene carbonate, and the vessel ligature clamp can be prepared by virtue of the modification and injection molding of amino acid. The vessel ligature clamp is good in biocompatibility, adjustable in degradation time, and capable of being matched with the vessel healing period after the surgical operation.
Owner:HANGZHOU MEDZONE BIO-TECH CO LTD
Polishing pad comprising biodegradable polymer
The invention is directed to a polishing pad for use in chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a biodegradable polymer. The biodegradable polymer comprises a repeat unit selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, lactic acid, hydroxyalkanoic acids, hydroxybutyric acid, hydroxyvaleric acid, caprolactone, p-dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, butylene succinate, butylene adipate, monosaccharides, dicarboxylic acid anhydrides, enantiomers thereof, and combinations thereof. The invention is further directed to methods of its use.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Biodegradable stent composite
InactiveCN105169496ADoes not lower pHDoes not cause inflammationSurgeryCoatingsAcetic acidTrimethylene carbonate
The invention discloses a biodegradable stent composite. The biodegradable stent composite is prepared from biodegradable medical polyurethane and a biodegradable metal material. The weight ratio between the biodegradable medical polyurethane and the biodegradable metal material is 0.1-99%:1-99.9%, preferably 5-90%:10-95%. To regulate the hardness of the material, other high molecular materials, such as polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, poly-p-dioxanone and copolymers thereof (PPDO and P(LA-PDA)), poly trimethylene carbonate, polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer, polycaprolactone-trimethylene carbonate copolymer, polyglycolic acid and polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, can be added, so that clinical usage is facilitated.
Owner:COMSCAFFOLDS NANJING MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Bioabsorbable Polymeric Compositions and Medical Devices
The bioabsorbable polymers and compositions of the present invention may be formed into medical devices such as stents that can be crimped onto a catheter system for delivery into a blood vessel. The properties of the bioabsorbable polymers allow for both crimping and expansion of the stent. The crystal properties of the bioabsorbable polymers may change during crimping and / or expansion allowing for improved mechanical properties such as tensile strength and slower degradation kinetics. Typically, bioabsorbable polymers comprise aliphatic polyesters based on lactide backbone such as poly L-lactide, poly D-lactide, poly D,L-lactide, mesolactide, glycolides, lactones, as homopolymers or copolymers, as well as formed in copolymer moieties with co-monomers such as, trimethylene carbonate (TMC) or ε-caprolactone (ECL).
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Copolymerization of propylene oxide and carbon dioxide and homopolymerization of propylene oxide
Copolymers of propylene oxide and carbon dioxide and homopolymers of propylene oxide are made using two dimensional double metal cyanide complexes having the formula Co[M(CN)4] or hydrated or partially dehydrated form thereof. There is no propylene carbonate by product in the copolymerization.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Vesicles consisting of amphiphilic polymer and application of vesicles
InactiveCN102657873AEasy to packEfficient packagingGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBackbone chainDouble bond
The invention discloses vesicles consisting of amphiphilic polymer and application of the vesicles. A main chain of the amphiphilic polymer consists of a hydrophilic chain segment and a biodegradable hydrophobic chain segment, wherein the molecular weight of the hydrophilic chain segment is 4 to 6kDa; the molecular weight of the hydrophobic chain segment is 3 to 5 times that of the hydrophilic chain segment; the hydrophobic chain segment is formed by performing random copolymerization on a monomer A and a monomer B in a molar ratio of (5-20):1; the monomer A is trimethylene carbonate or cyclic carbonate; the monomer B is acrylate-based carbonate or vinyl sulfone-based carbonate; the hydrophobic chain segment is grafted with a short branched chain; the grafting position is a double bond of the monomer B; a monomer forming the short branched chain is 3-mercaptopropionic acid, cysteamine hydrochloride or cysteine; and the grafting rate is 0.3 to 1. The vesicles are directly prepared from the amphiphilic polymer in an aqueous solution and used as a carrier and a release system of a protein medicine, the encapsulating efficiency and bioavailability of the protein medicine can be improved, and the stability of the encapsulated protein is enhanced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for improving hydrophily and flexibility of polypeptide membrane by poly(trimethylene carbonate) and polyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for improving the hydrophily and flexibility of a polypeptide film by poly(trimethylene carbonate) and polyethylene glycol. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding carboxy terminated poly(trimethylene carbonate) monododecyl ether, a solvent, a condensing agent and a polypeptide homopolymer into a dried reactor, and reacting for 3-4 days to obtain a polypeptide-poly(trimethylene carbonate) segmented copolymer; (2) adding carboxy terminated poly(trimethylene carbonate) monododecyl ether, a solvent, a condensing agent and amino terminated methoxy polyethylene glycol into a dried reactor, and reacting for 2-3 days to obtain a polyethylene glycol-poly(trimethylene carbonate) segmented copolymer; (3) adding the polypeptide-poly(trimethylene carbonate) segmented copolymer, the polyethylene glycol-poly(trimethylene carbonate) segmented copolymer and a solvent into a dried reactor, mixing for 40-50 minutes, forming a film by a tape casting method, and drying to obtain the target object. The preparation process is simple, and the hydrophily and flexibility of the modified film can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
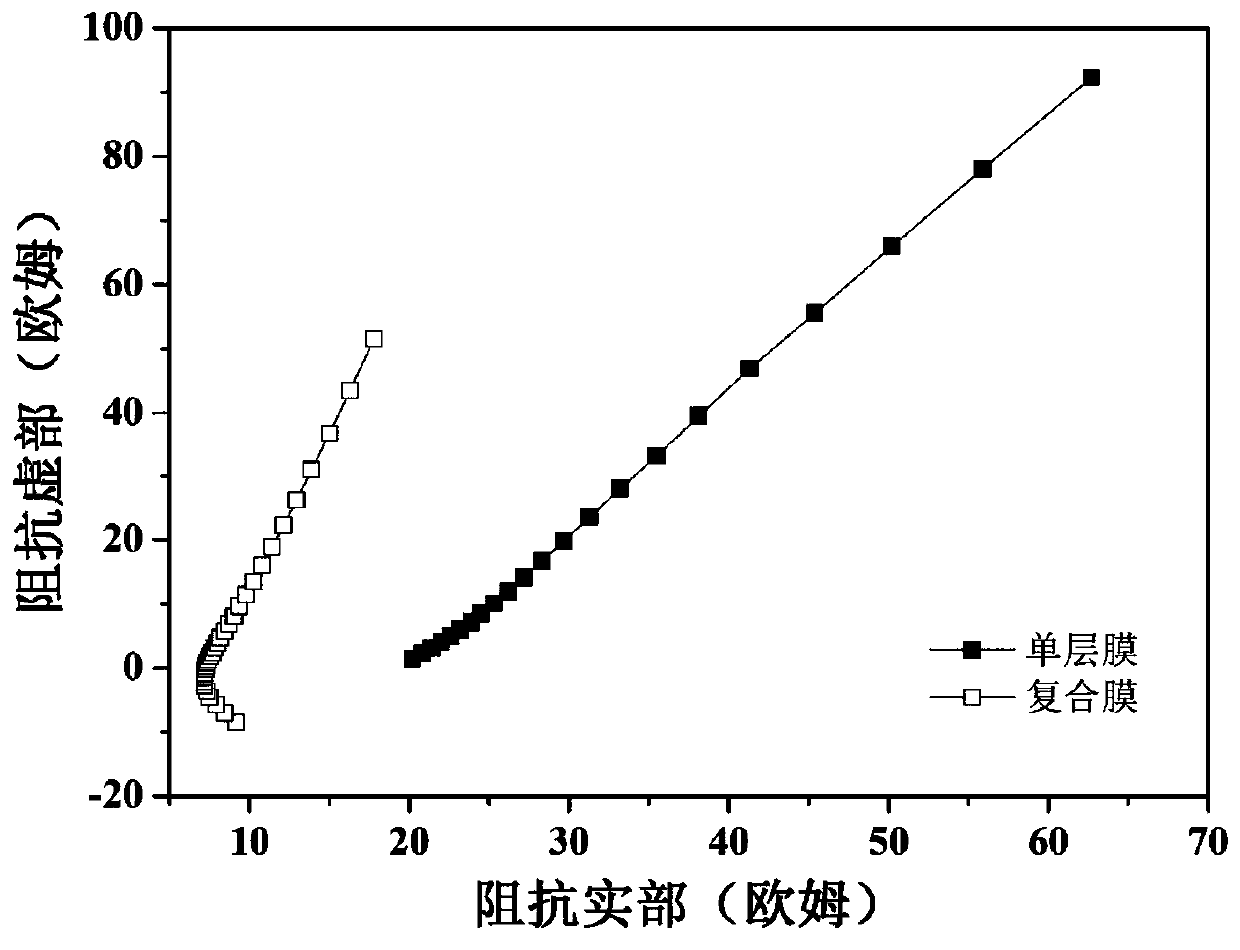
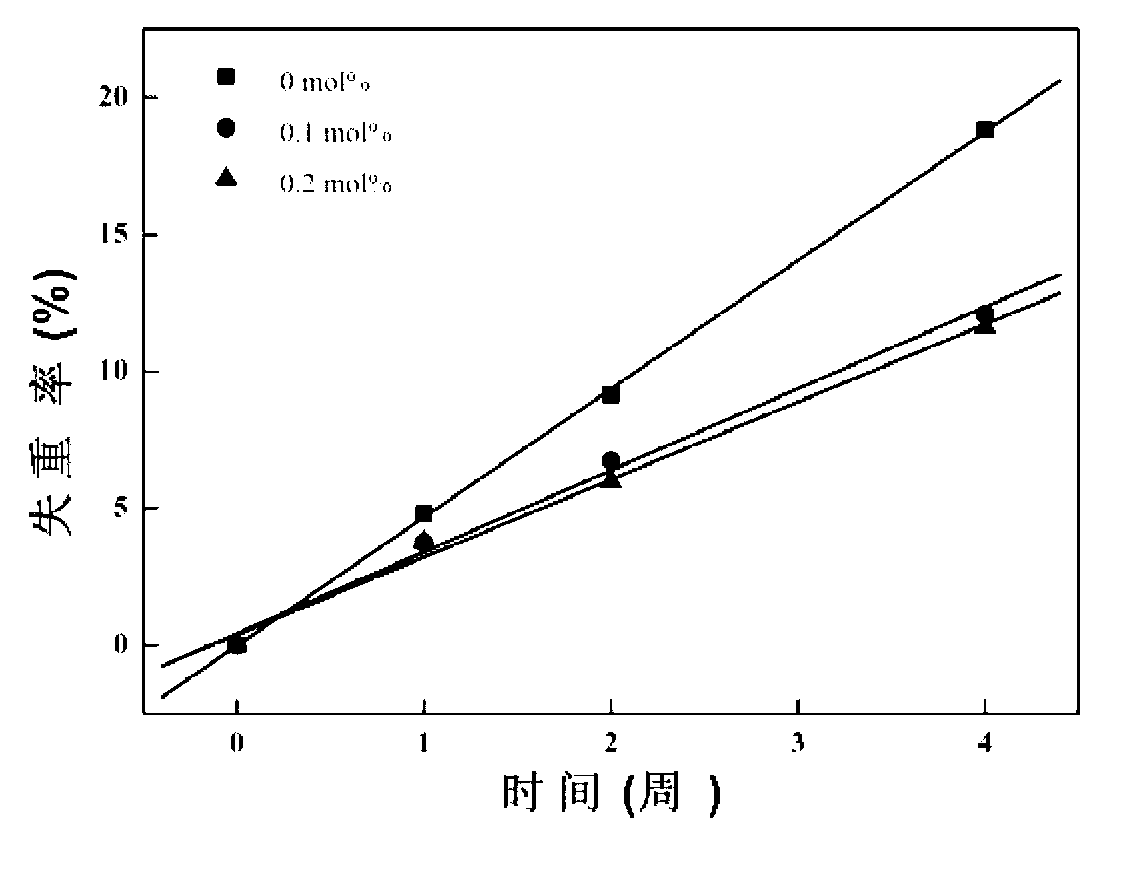
Composite solid-state electrolyte membrane, preparation method and solid-state lithium battery
InactiveCN111430788AImprove cycle stabilityImprove capacity playMaterial nanotechnologySolid electrolytesSolid state electrolytePolyvinyl chloride
The invention discloses a composite solid-state electrolyte membrane, a preparation method and a solid-state lithium battery. The composite solid-state electrolyte membrane comprises a support membrane, an organic-inorganic composite coating A coated on the surface of the positive electrode side of the support membrane, and an organic-inorganic composite coating B coated on the surface of the negative electrode side of the support membrane, wherein the coating A comprises an organic polymer A, a lithium salt and a nano inorganic solid electrolyte, and the organic polymer A is one or more thantwo of polyvinylidene fluoride, a polyvinylidene fluoride copolymer, polyacrylonitrile and polyvinyl chloride; the coating B comprises an organic polymer B, a lithium salt and a nano inorganic solid electrolyte; and the organic polymer B is one or more than two of polyoxyethylene, polypropylene carbonate, polycarbonate and poly trimethylene carbonate. Aiming at different requirements of positive and negative electrode layers in the solid-state lithium battery on the electrolyte membranes, the graphene oxide membrane is used as a support, and the electrolyte membranes containing different polymer groups are designed on the two sides of the graphene oxide membrane respectively so that the comprehensive performance of the battery is further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE POWER SOURCES
Biodegradable medical polymer tubing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102989044AMechanical property regulationAvoid or eliminate inflammationSurgeryCatheterP-dioxanoneLactide
The invention relates to a biodegradable medical polymer tubing and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a biodegradable medical polymer tubing with adjustable diameter and controllable wall thickness and a preparation method thereof. The tubing is made from biodegradable medical polymer material, and has inner diameter of 0.5-20 mm and thickness of 0.05-10 mm; and the biodegradable medical polymer material is one of a homopolymer, a copolymer, a star-shaped polymer and a crosslinking polymer of trimethylene carbonate, p-dioxanone, lactide, caprolactone and glycollide.
Owner:杨立群
Polishing pad comprising biodegradable polymer
The invention is directed to a polishing pad for use in chemical-mechanical polishing comprising a biodegradable polymer. The biodegradable polymer comprises a repeat unit selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, lactic acid, hydroxyalkanoic acids, hydroxybutyric acid, hydroxyvaleric acid, caprolactone, p-dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, butylene succinate, butylene adipate, monosaccharides, dicarboxylic acid anhydrides, enantiomers thereof, and combinations thereof. The invention is further directed to methods of its use.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for improving water resisting property and flexibility of polyvinyl alcohol film by means of poly trimethylene carbonate and poly lactic acid-glycolic acid
The invention discloses a method for improving the water resisting property and flexibility of a polyvinyl alcohol film by means of poly trimethylene carbonate and poly lactic acid-glycolic acid. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, carboxyl end capped poly trimethylene carbonate single lauryl ether, solvent, a condensing agent and polyvinyl alcohol are added into a reactor, and after reaction, polyvinyl alcohol-poly trimethylene carbonate grafted copolymer is obtained; secondly, the polyvinyl alcohol-poly trimethylene carbonate grafted copolymer, carboxyl end capped poly lactic acid-glycolic acid single lauryl ether, solvent and a condensing agent are added into the reactor, and after reaction, polyvinyl alcohol-poly trimethylene carbonate poly lactic acid-glycolic acid bi-grafted copolymer is obtained; thirdly, the polyvinyl alcohol-poly trimethylene carbonate poly lactic acid-glycolic acid bi-grafted copolymer, poly trimethylene carbonate single lauryl ether and solvent are added into the reactor and mixed to form the film, and the target object is obtained. The preparing technology is simple and easy to grasp, and the water resisting property and flexibility of the modified film are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
In-situ gel injection implant
ActiveCN103446043AEasy to makeEasy to useAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryControl releaseOrganic solvent
The invention mainly provides an in-situ gel injection implant. The implant is mainly composed of drugs, homopolymers or copolymers taking lactide, caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate as the monomers, and an organic solvent, which is mutually soluble with water. The drug transmission system can be injected into the subcutaneous parts, muscles, or diseased regions, and then a solid, namely an in-situ controlled-release implant, is formed through the solvent exchange. Through adjusting the ratios and molecular weights of each monomer and the prescription composition, the drugs can be released from one month to one year.
Owner:LIAONING RES INST OF FAMILY PLANNING
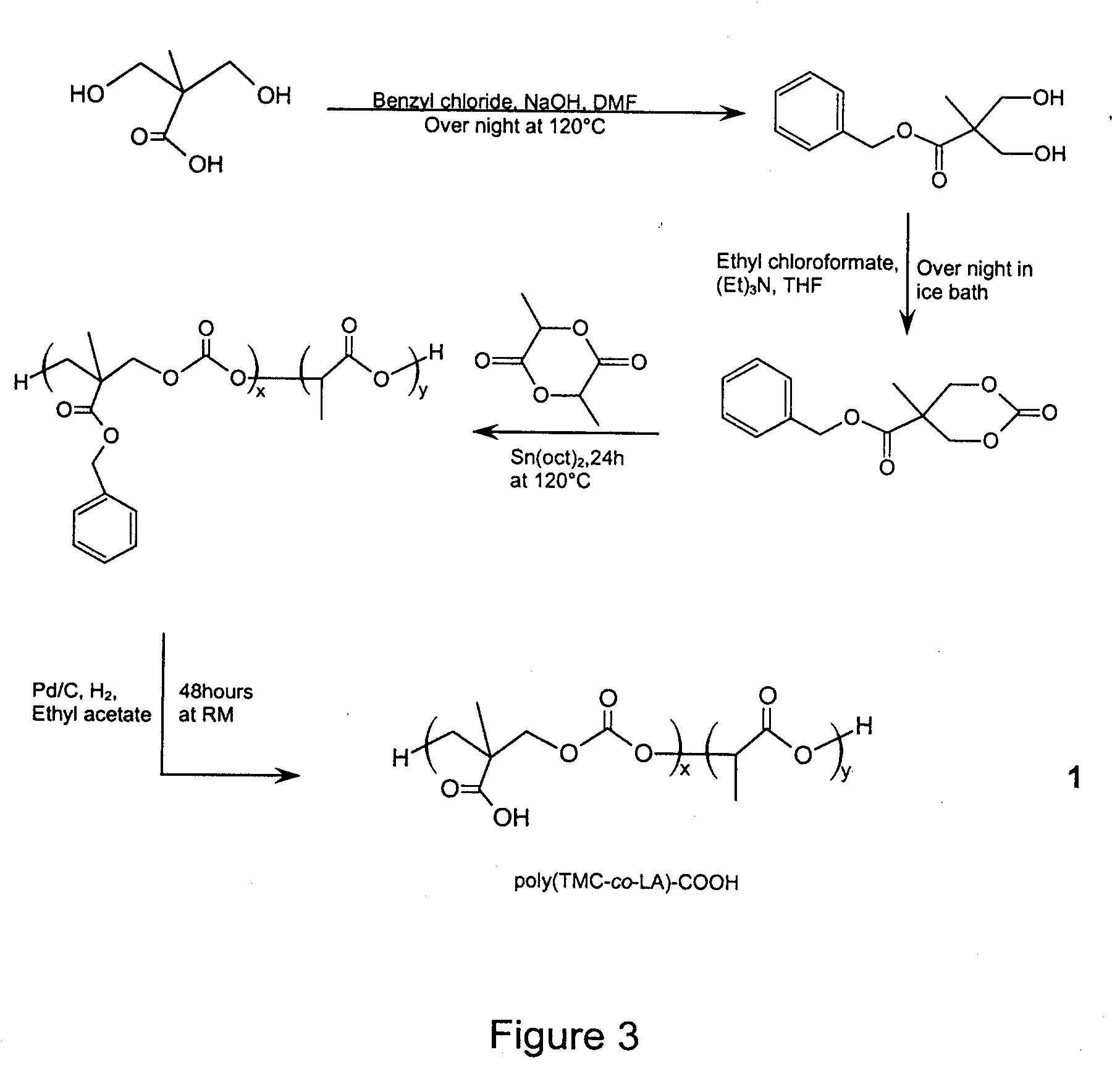
Synthesizing process and use of unsaturation cyclic aliphatic carbonate monomer and its polymer
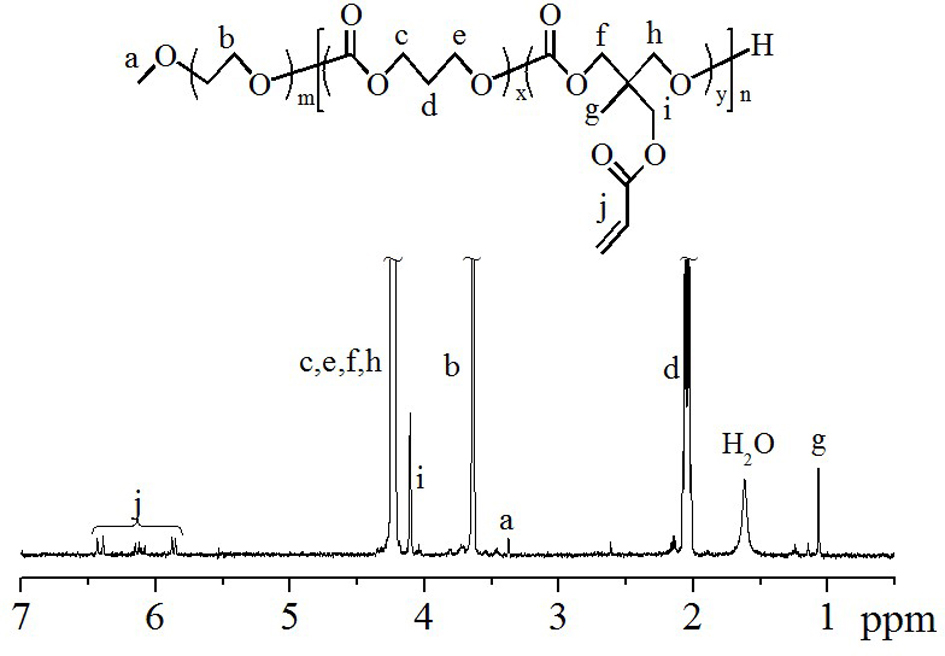
This invention involves unsaturated cyclic aliphatic carbonate monomer and polymer synthesis and uses, and is biomedical polymer materials. From 2,2 - dimethylolpropionic acid departing, to synthesize 2-methyl-2-allyl-oxygen carbonyl trimethylene carbonate and 2-methyl-2-propargyl oxygen carbonyl trimethylene carbonate, and then through ring-opening polymerization or aliphatic monomers cycloate monomer opening loop and copolymerization, gain copolymer of aliphatic polycarbonate or aliphatic polyester-carbonate that side group contains double and Triple bond. Such polymer has advantage of both aliphatic polyester and carbonate, is biodegradable, degradation products is non-toxic. Use the functional side group of Double and Triple bond can connect drugs, active peptides or other bioactive elements with the polymer, improving the biocompatibility and biological activity of polymer, which may has real application in controlled-release drug, polymer pro-drug and tissue engineering fields.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for the preparation of propylene carbonate
ActiveUS7728164B2Easy to operateChemical recyclingPreparation by hydrolysisTrimethylene carbonatePropylene carbonate
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Preparation method of quaternary degradable antibacterial agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a quaternary degradable antibacterial agent, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: homopolymerizing cyclic aliphatic carbonate monomers containing bromine functional groups, namely 2,2-dibromo-methyl trimethylene carbonate (DBTC) monomers or copolymerizing the 2,2-dibromo-methyl trimethylene carbonate monomers with aliphatic cyclic ester, or copolymerizing the 2,2-dibromo-methyl trimethylene carbonate monomers with the aliphatic cyclic ester or dihydroxy polyethylene glycol, or copolymerizing the 2,2-dibromo-methyl trimethylene carbonate monomers with the aliphatic cyclic ester or single methoxy polyethylene glycol; and further reacting an obtained polymer with alkylamine, thus obtaining the quaternary degradable polyester antibacterial agent with antibacterial performance. The antibacterial agent provided by the invention integrates the advantages of biocompatibility and degradability and not only has good antibacterial performance, but also has no harm to an environment, thereby being an environment-friendly antibacterial material; as an additive, the antibacterial agent provided by the invention has potential application prospects in food packaging materials, fibers, coatings, medical field and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Catalyst for polylactone preparation
The invention discloses a catalyst for polylactone preparation. A raw material lactone monomer undergoes ring-opening polymerization under the action of a difunctional group ionic liquid catalyst to obtain polylactone, and the catalyst is 1-(4-sulfo)butyl-3-methylpyrazinyltetrafluoroborate or 1-(4-sulfo)butyl-3-methylimidazolyltetrafluoroborate. The catalyst can catalyze lactone ring-opening polymerization to obtain polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, poly(trimethylene carbonate) or other degradable polymers.
Owner:YUNNAN MINZU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com