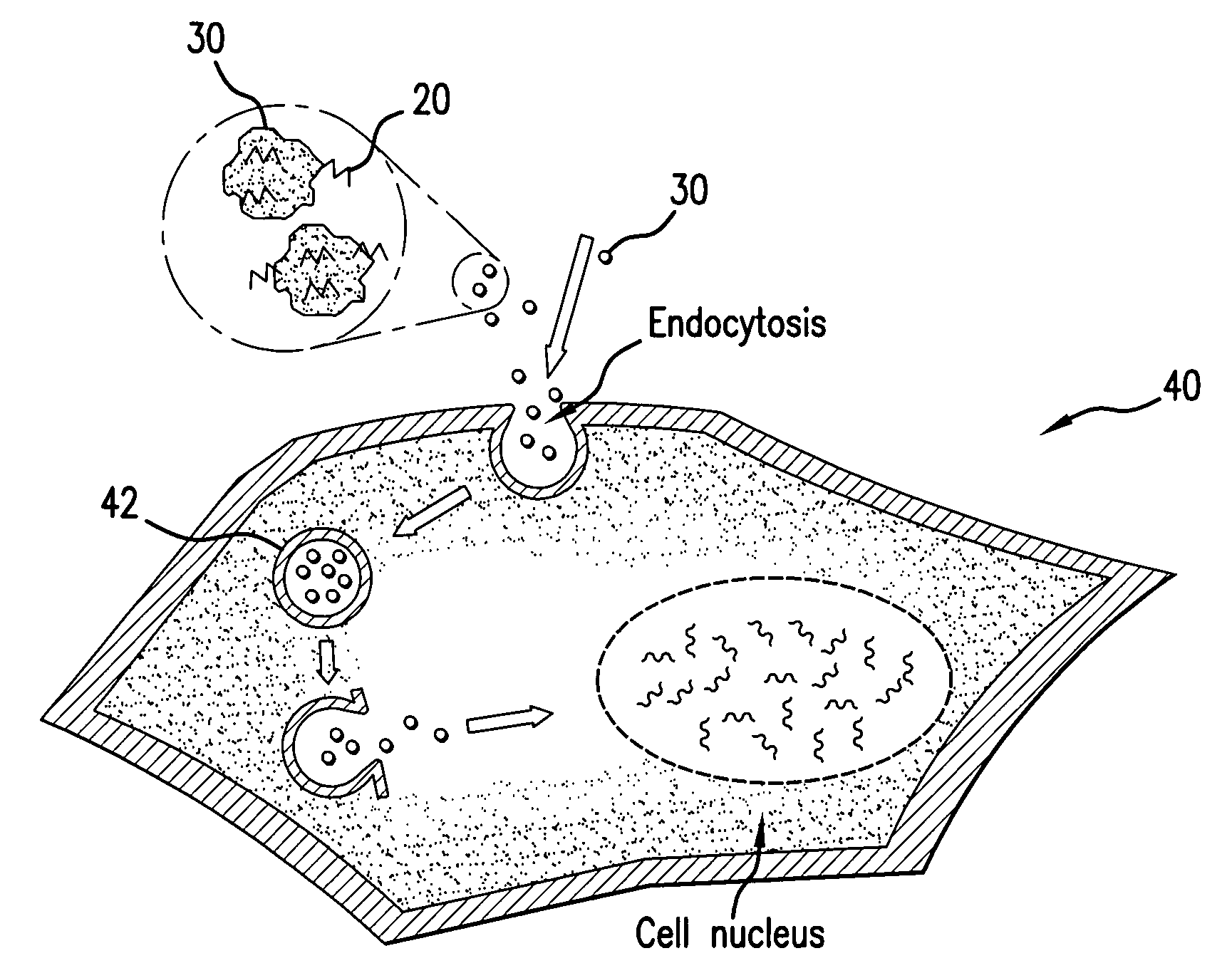
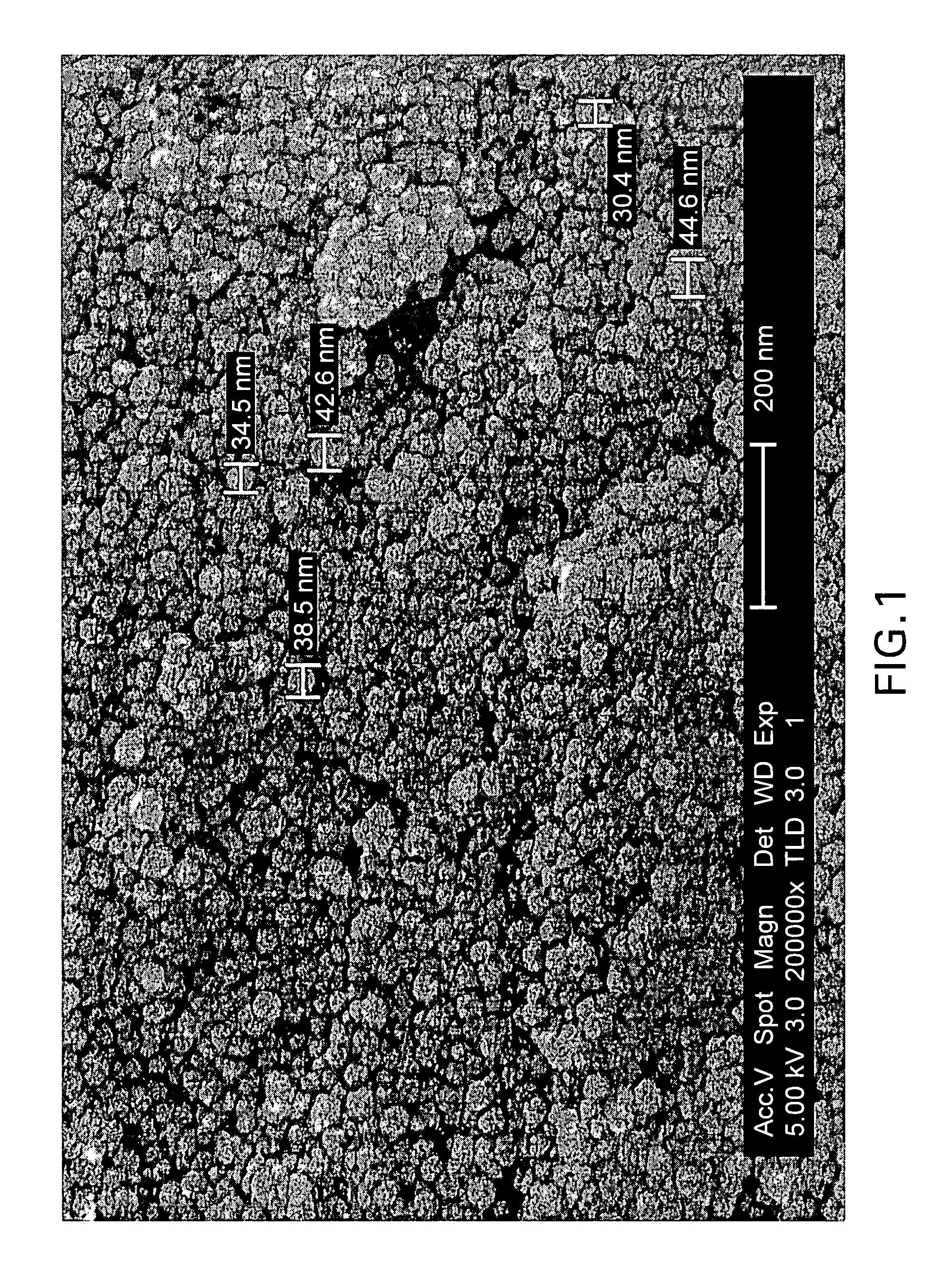
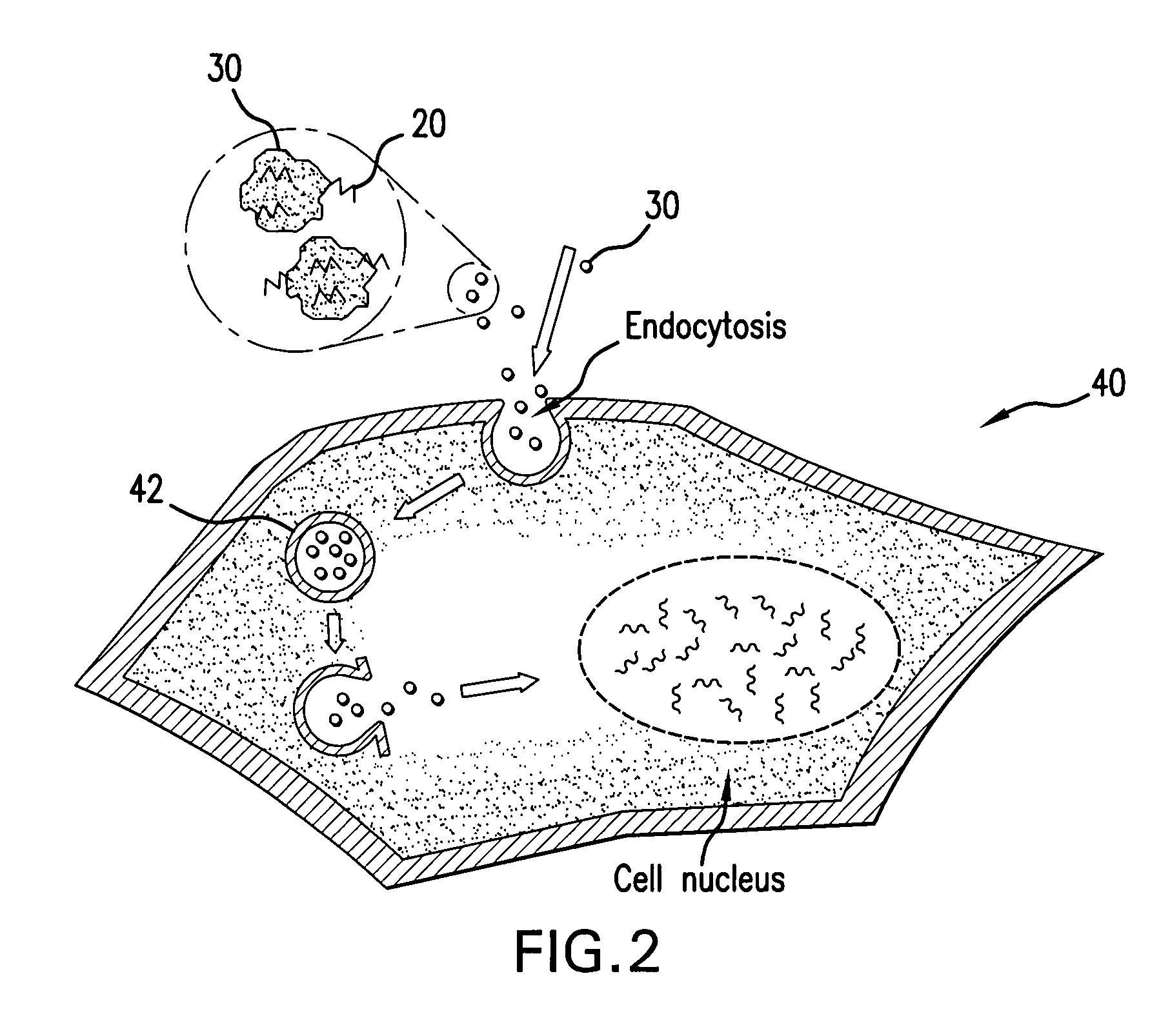
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Biodegradable metal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioresorbable (also called biodegradable or bioabsorbable) metals are metals or their alloys that degrade safely within the body. The primary metals in this category are magnesium-based and iron-based alloys, although recently zinc has also been investigated.
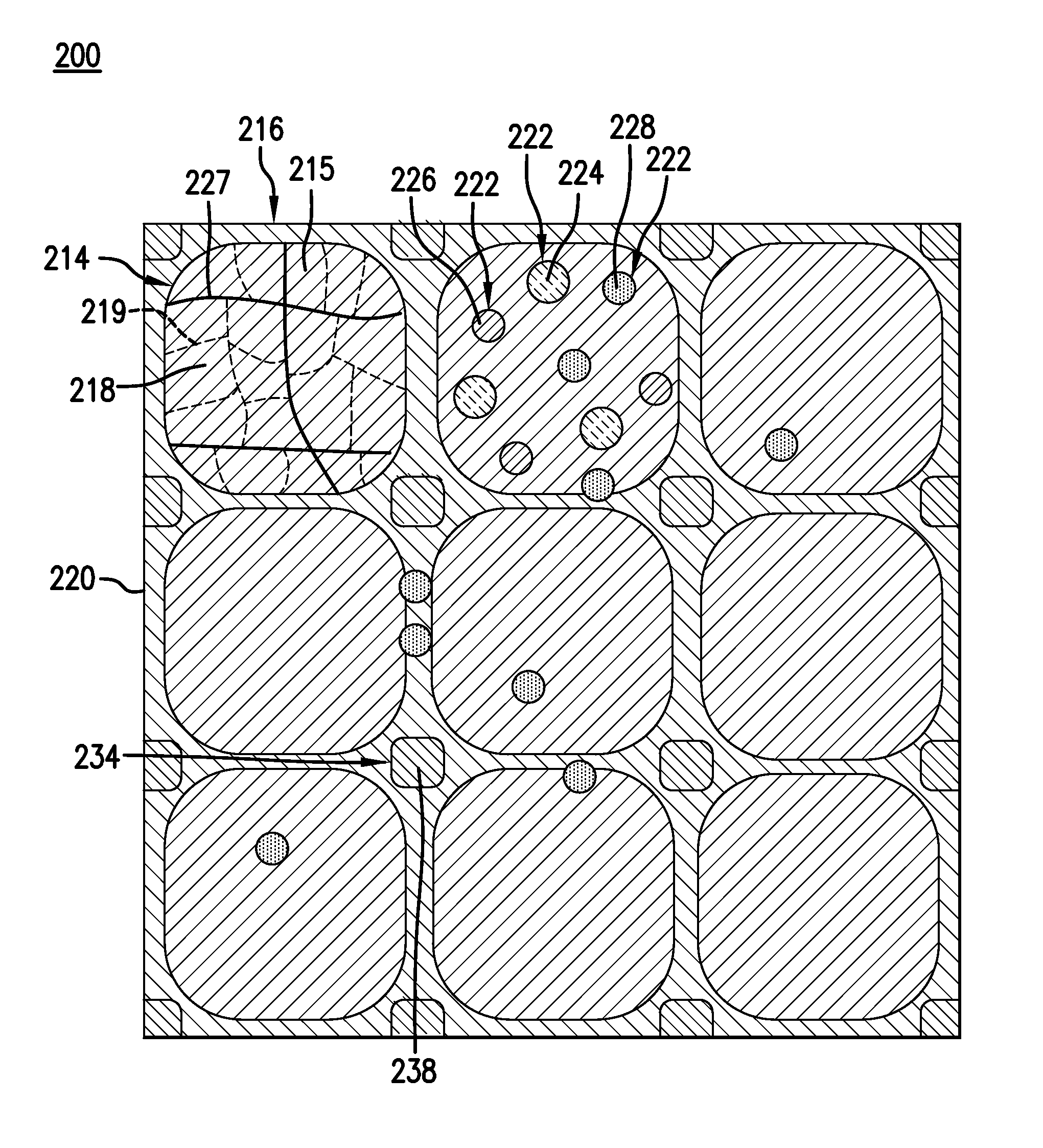
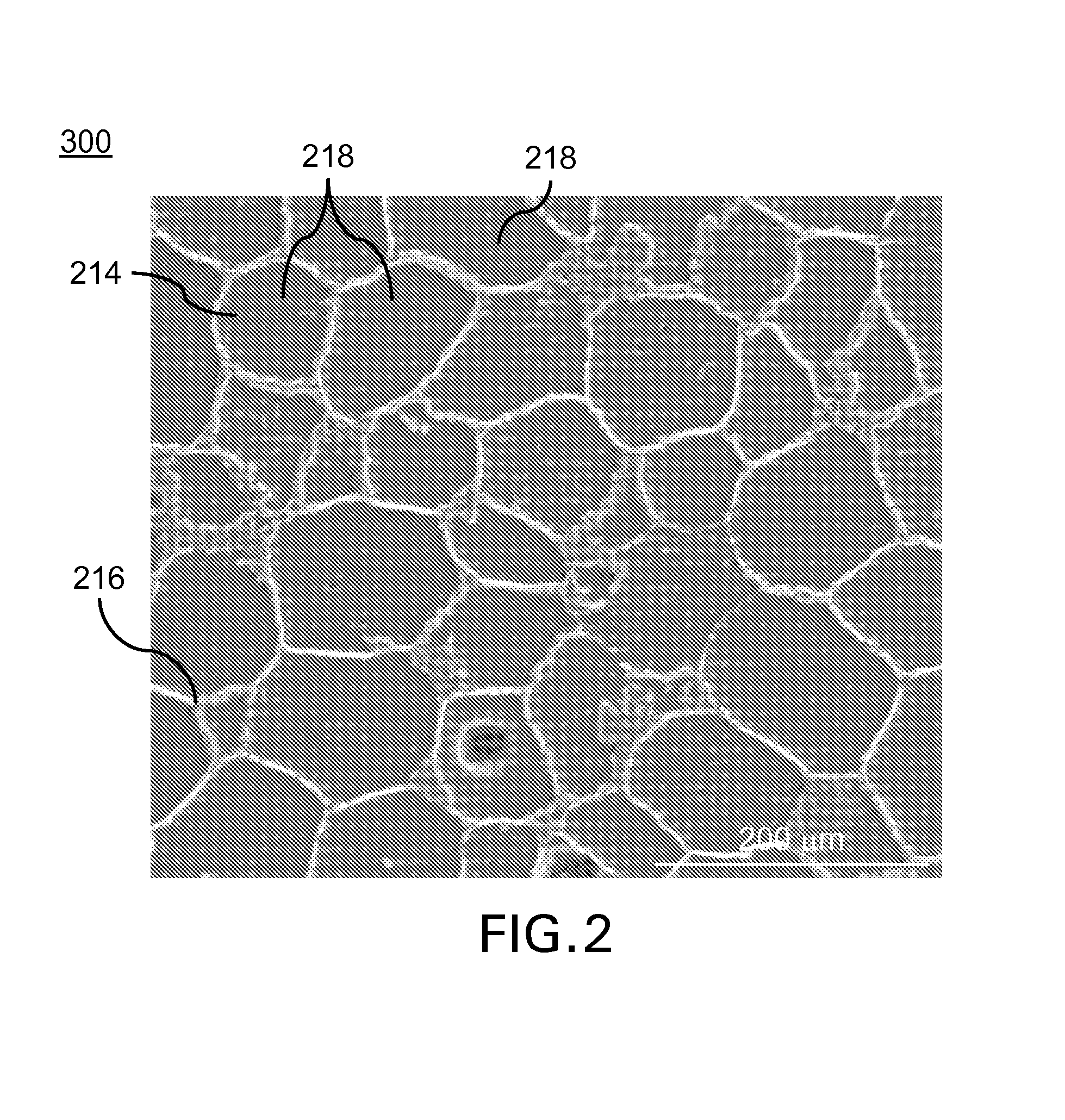
Corrosion resistant coatings for biodegradable metallic implants
InactiveUS20070224244A1Corrosion controlControl corrosion rateSurgeryCoatingsMedical deviceMaterials science
According to an aspect of the invention, implantable medical devices are provided which contain at least one biodegradable metallic region and a polymeric corrosion resistant coating over the biodegradable metallic region. The polymeric corrosion resistant coating slows the rate of corrosion of the biodegradable metallic region upon implantation into a subject.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
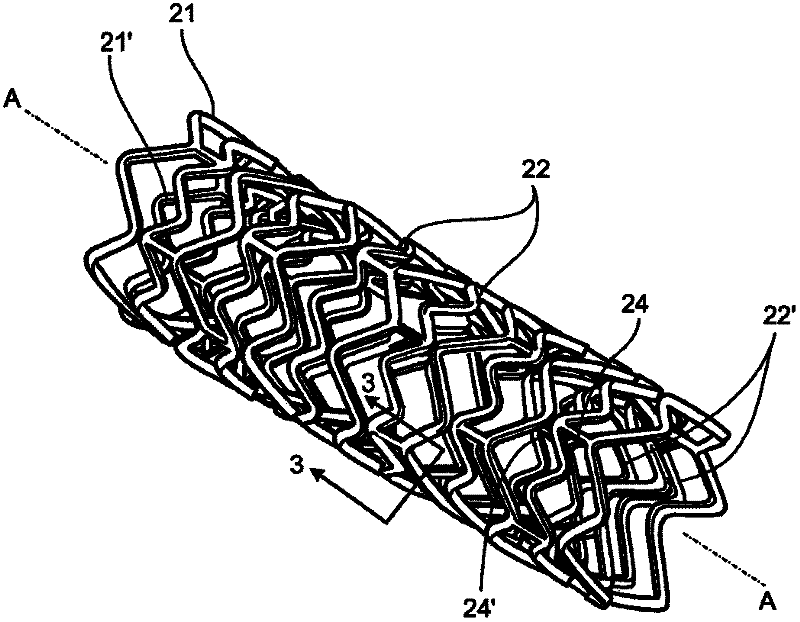
Biodegradable vascular support
The embodiments described herein are directed to biodegradable stents comprising an inner biodegradable metal scaffold and an outer polymeric coating. The biodegradable coating consists preferentially of biodegradable polymers and may additionally include at least one pharmacologically active substance such as an anti-inflammatory, cytostatic, cytotoxic, antiproliferative, anti-microtubuli, antiangiogenic, antirestenotic (anti-restenosis), antifungicide, antineoplastic, antimigrative, athrombogenic and / or antithrombogenic agent.
Owner:HEMOTEQ AG
Porous, degradable implant made by powder molding
InactiveUS20080175885A1Sufficient pore volumeSufficient volumeDental implantsTransportation and packagingDecompositionEvaporation
The exemplary embodiment of the present invention are provided which relate to at least partially degradable implants and methods for the manufacture thereof which can use powder molding techniques. For example, a suspension can be provided comprising a plurality of first particles of at least one organic polymer, a plurality of second particles of at least one metal-based material which is at least partially biodegradable in-vivo, and at least one solvent. The first and second particles can be substantially insoluble in the solvent. The suspension can be molded to form a green body comprising the first particles embedded in a matrix of compressed second particles. The first particles may be removed from the green body by thermally induced decomposition and / or evaporation. Further, the green body can be sintered to form the implant. The first particles may be removed during the sintering procedure.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Biodegradable Metal Barrier Layer for a Drug-Eluting Stent
InactiveUS20080243240A1Reduce and prevent cell proliferationReduce and prevent and inflammationStentsSurgeryAnti mitoticMedical treatment
An implantable medical device includes a substrate, a drug-impregnated layer deposited over the substrate, and a barrier layer at least partially covering the drug-impregnated layer. The barrier layer may be a biodegradable metal, biodegradable metal oxide, or biodegradable metal alloy, such as, magnesium, a magnesium oxide or a magnesium alloy. The drug-impregnated layer includes a therapeutic substance, such as, antineoplastic, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet, anticoagulant, fibrinolytic, thrombin inhibitor, antimitotic, antiallergic, and antiproliferative substances.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Implants comprising biodegradable metals and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100075162A1High strengthImprove interface strengthDental implantsInternal osteosythesisUltimate tensile strengthBiodegradable magnesium
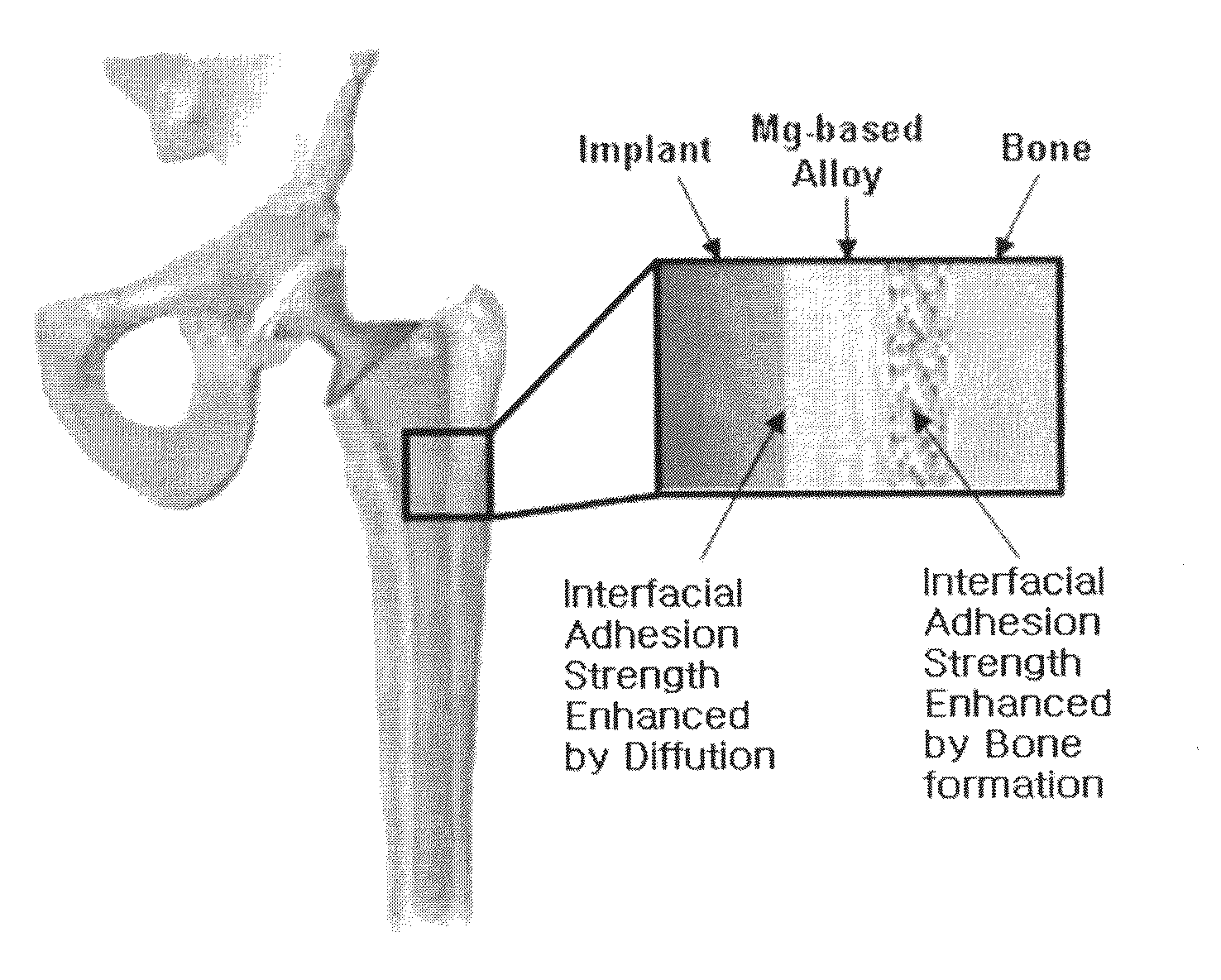
The present invention provides an implant consisting of a biodegradable magnesium-based alloy or partially applied with the magnesium-based alloy, and a method for manufacturing the same. The implant according to the present invention is biodegradable, in which its biodegradation rate can be easily controlled, and the implant has excellent strength and interfacial strength to an osseous tissue.
Owner:U & I INC
Biodegradable vascular support
ActiveCN101636187AAvoid decompositionAvoid breakingSurgeryCoatingsBiodegradable coatingMetal framework
The invention relates to biodegradable vascular supports consisting of an inner biodegradable metal skeleton and an outer polymeric coating. The biodegradable coating preferably consists of biodegradable polymers and can also contain at least one pharmacologically active substance such as an anti-inflammatory, cytostatic, cytotoxic, anti-proliferative, anti-microtubule, anti-angiogenic, anti-restenotic (anti-restenosis), anti-fungicidal, anti-neoplastic, anti-migrative, athrombogenic and / or antithrombogenic active ingredient.
Owner:HEMOTEQ AG
Magnesium-Based Biodegradable Metallic Material
ActiveUS20090171452A1Possibility of degradationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSurgeryMetallic materialsImplanted device
As a novel biodegradable metallic material the degradation speed of which in vivo can be controlled over a broad scope while achieving desired mechanical properties such as strength, work hardening and ductility without restricting the shape of an implant device, it is intended to provide a magnesium-based biodegradable metallic material which comprises Mg containing Mg as the major composition and having a concentration of inevitable impurities equal to or less than 0.05 atomic %, is free from precipitates or intermetallic compounds, and has an average grain size being regulated to equal to or less than ¼ of the minimum part of the material.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Medical implant
InactiveUS20090192595A1Limited decomposition rateHigh strengthUrinary bladderStentsBiomedical engineeringBiodegradable polymer
Disclosed herein is a medical implant including an implant body of which at least a part is comprised of a biodegradable metal, wherein the part comprised of the biodegradable metal has a crystal grain diameter of not more than 10 μm.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Partially biodegradable stent
Owner:TAEWOONG MEDICAL CO LTD
Vascular prosthesis
A vascular prosthesis comprising a tubular shaped expandable ECM member and at least one anchoring mechanism. In one embodiment, the anchoring mechanism comprises proximal and distal single or dual-ring anchors. In one embodiment, the anchoring mechanism comprises a multiple-ring anchor. The anchors preferably comprise a biodegradable metal, such as magnesium. The anchors can also comprise a shape memory alloy, such as nitinol, and a cross-linked ECM material. In some embodiments, the ECM member includes a pharmacological agent.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Medical devices having nanostructured coating for macromolecule delivery
A medical device having a biodegradable coating comprising an inorganic material complexed to macromolecules. Biodegradation of the biodegradable coating releases nanoparticles of the inorganic material with macromolecules complexed to the released nanoparticles. The inorganic material may be applied directly onto the medical device as a nanostructured coating or be dispersed within or under a layer of biodegradable polymer. The medical device body may comprise a biodegradable metallic material. Also provided is a method of delivering macromolecules to body tissue using the medical device of the present invention.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Biodegradable stent composite
InactiveCN105169496ADoes not lower pHDoes not cause inflammationSurgeryCoatingsAcetic acidTrimethylene carbonate
The invention discloses a biodegradable stent composite. The biodegradable stent composite is prepared from biodegradable medical polyurethane and a biodegradable metal material. The weight ratio between the biodegradable medical polyurethane and the biodegradable metal material is 0.1-99%:1-99.9%, preferably 5-90%:10-95%. To regulate the hardness of the material, other high molecular materials, such as polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, poly-p-dioxanone and copolymers thereof (PPDO and P(LA-PDA)), poly trimethylene carbonate, polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer, polycaprolactone-trimethylene carbonate copolymer, polyglycolic acid and polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, can be added, so that clinical usage is facilitated.
Owner:COMSCAFFOLDS NANJING MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Implants comprising biodegradable metals and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101516292AExcellent interface strengthSuitable for maintaining initial stabilityDental implantsInternal osteosythesisUltimate tensile strengthBiodegradable polymer
The present invention provides an implant consisting of a biodegradable magnesium-based alloy or partially applied with the magnesium-based alloy, and a method for manufacturing the same. The implant according to the present invention is biodegradable, in which its biodegradation rate can be easily controlled, and the implant has excellent strength and interfacial strength to an osseous tissue.
Owner:U & I INC
Non-phosphate non-nitrogen easy-to- biodegrade metal spent meal and preparing method
InactiveCN101381876AEnsure mixing uniformityGuaranteed production efficiencySurface cleaningPhosphate
The invention discloses phosphor-free nitrogen-free biodegradable metal spent meal and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of surface cleaning of a metal material. The spent meal comprises the following compositions and content ( weight portion): 10 to 50 portions of sodium carbonate, 5 to 30 portions of sodium orthosilicate, 0.1 to 10 portions of gluconic acid sodium salt, 0.1 to 5 portions of sodium citrate, 0.1 to 5 portions of peregal 0-20, and 1 to 20 portions of linear alkyl polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate. The spent meal is prepared in certain feeding sequence, the compositions are fully and evenly mixed at normal temperature and normal pressure at the stirring speed of 10 to 100 revolutions / minute. At normal temperature, the spent meal has the advantages of fast oil removing, good effect, no phosphor or nitrogen, easy biodegradability, environmental pollution prevention, requirement accordance of energy conservation and discharge reduction, convenient transportation and storage, production and application cost conversation.
Owner:HUBEI DE MEI TECH
Biodegradable metallic medical implants, method for preparing and use thereof
A medical implant includes a metal composite that contains a cellular nanomatrix having a metallic nanomatrix material and a metal matrix disposed in the cellular nanomatrix, the medical implant being configured to disintegrate in response to contact with a fluid. A method for repairing tissue includes disposing an implant in a patient, the implant including a metal composite which contains: a cellular nanomatrix having a metallic nanomatrix material; and a metal matrix disposed in the cellular nanomatrix; contacting tissue of the patient with the implant, the tissue being in need of repair; and non-operatively removing the implant to repair the tissue.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Biodegradable metal-chelating polymers and vaccines
InactiveUS20100004390A1Powder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMetal chelateBiodegradable polymer
The invention provides metal-chelating poly(ether amide) polymers useful in preparation of polymer compositions for delivering a variety of cargo molecules, such as bioactive agents. In solution metal ions and cargo molecules, such as vaccine epitopes, that include metal avid amino acids can be loaded into the polymer compositions and held in a non-covalent complex. Nanoparticles of such polymer compositions can also be prepared directly from the solution.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Biodegradable metal alloys
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Implants comprising biodegradable metals and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN102512711AExcellent interface strengthSuitable for maintaining initial stabilityDental implantsImpression capsUltimate tensile strengthBiodegradable polymer
The present invention provides an implant consisting of a biodegradable magnesium-based alloy or partially applied with the magnesium-based alloy, and a method for manufacturing the same. The implant according to the present invention is biodegradable, in which its biodegradation rate can be easily controlled, and the implant has excellent strength and interfacial strength to an osseous tissue.
Owner:U & I INC
Biodegradable metal drawing lubricating oil and method for producing same
InactiveCN101705136AImprove protectionSolve non-renewable problemsBase-materialsAntioxidantEmission standard
The invention discloses biodegradable metal drawing lubricating oil, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 35 to 50 percent of colza oil, 7 to 25 percent of lard oil, 8 to 15 percent of oleic acid, 5 to 12 percent of rosin, 4 to 10 percent of triethanolamine, 3.5 to 8 percent of 30 percent NAOH solution, 6 to 12 percent of dilution, 3 to 6 percent of stabilizer, 0.5 to 1 percent of defoaming agent and 0.01 to 0.06 percent of antioxidant. The method for producing the metal drawing lubricating oil comprises the following steps: reacting the rosin and the oleic acid with the 30 percent NAOH solution in the presence of the colza oil and the lard oil to obtain saponified solution (I); performing saponification reaction on the oleic acid and the triethanolamine in the presence of the dilution, and adding the colza oil and the lard oil to perform reaction to obtain saponified solution (II); and evenly mixing the saponified solution (I) and (II) and adding the stabilizer, the defoaming agent and the antioxidant into the mixed solution to obtain the drawing oil. The drawing oil has the advantages of reproducibility, good liquidity, excellent cleaning performance, good lubricating effect, high safety, environment protection, no pollution, no toxicity or harm of the product, capacity of meeting the emission standard after use and the like.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Vascular prosthesis
A vascular prosthesis comprising a tubular shaped expandable ECM member and at least one anchoring mechanism. In one embodiment, the anchoring mechanism comprises proximal and distal single or dual-ring anchors. In one embodiment, the anchoring mechanism comprises a multiple-ring anchor. The anchors preferably comprise a biodegradable metal, such as magnesium. The anchors can also comprise a shape memory alloy, such as nitinol, and a cross-linked ECM material. In some embodiments, the ECM member includes a pharmacological agent.
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Method for improving biodegradation rate of pure iron or iron alloy and application thereof
InactiveCN102912171AMeet Medical Design RequirementsGood biocompatibilityProsthesisMetallic materialsBiocompatibility Testing
The invention aims to provide a method for improving the biodegradation rate of pure iron or iron alloy, which is characterized in that: pore structures are produced in the pure iron or iron alloy so that the degradation rate of the pure iron or iron alloy in the physiological environment is improved. Due to the adoption of the method, the problem that the degradation rate of the pure iron or iron alloy which develops as the biodegradable metal material is too low is solved. According to the principle of crevice corrosion, various types of pore structures are produced on the iron-based biodegradable material to achieve the purpose of improving the degradation rate of the material. Compared with the materials without the pore structures, the degradation rate of the iron-based biodegradable material is improved markedly, and the original biocompatibility is kept.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Implant and Method for Manufacturing
ActiveUS20100161053A1Improve the degradation problemImprove deformationSurgeryPharmaceutical containersHydrogenMetallic materials
The present invention proposes an implant, in particular an intraluminal endoprosthesis, having a body, comprising at least one at least largely biodegradable metallic material, in particular magnesium or a magnesium alloy. To improve the degradation behavior, the implant has a first layer on at least a portion of its body surface, said layer containing a hydrogen-binding material, preferably palladium. Furthermore, methods for producing such an implant are given.
Owner:BIOTRONIK
Biodegradable metallic medical implants, method for preparing and use thereof
A medical implant includes a metal composite that comprises a cellular nanomatrix comprising a metallic nanomatrix material and a metal matrix disposed in the cellular nanomatrix, the medical implant being configured to disintegrate in response to contact with a fluid. A method for repairing tissue includes disposing an implant in a patient, the implant comprising a metal composite which comprises: a cellular nanomatrix comprising a metallic nanomatrix material; and a metal matrix disposed in the cellular nanomatrix; contacting tissue of the patient with the implant, the tissue being in need of repair; and non-operatively removing the implant to repair the tissue.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Drug eluting medical implant with porous surface
An implant is proposed, in particular made from a base material including a biodegradable metal and / or a biodegradable metal alloy, wherein the implant includes a coating made of crystalline calcium phosphate and / or amorphous calcium phosphate.
Owner:BIOTRONIK VI PATENT
Biodegradable metal alloys
The invention relates to biodegradable, metal alloy-containing compositions, methods for their preparation and applications for their use. The compositions include magnesium and other components, such as yttrium, calcium, silver, cerium, and zirconium; or zinc, silver, cerium, and zirconium; or aluminum, zinc, calcium, manganese, silver, yttrium; or strontium, calcium, zinc. The compositions are prepared by vacuum induction / crucible melting together the components and casting the melted mixture in a preheated mild steel / copper mold. In certain embodiments, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful for forming medical devices for implantation into a body of a patient.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Bioerodible endoprosthesis
InactiveCN102458315AFavorable mechanical propertiesFavorable biodegradabilityStentsProsthesisMedicineInsertion stent
A stent includes a first tubular element formed of a first bioerodible metal composition and second tubular element formed of a second biodegradable metal composition. The first and second tubular elements are concentrically arranged; and the first and second bioerodible metal compositions are different
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Biodegradable metal rust inhibitor
InactiveCN107033646AImprove adhesionImprove rust resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsFatty alcoholEthyl acrylate
The invention discloses a biodegradable metal rust inhibitor. The biodegradable metal rust inhibitor is prepared from styrene acrylic emulsion, modified filler, a modified reinforcing agent, modified anti-rust reinforcing agent, methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate, ammonium persulfate, styrene, ethyl acrylate, epoxy resin, epoxy acrylic resin, benzotriazole, zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate, sodium tripolyphosphate, naphthenic base oil, diethylene glycol propyl ether, octadecylamine, alkyl sodium sulfonate, sulfamic acid, hexamine, barium alkylsulfonate, thia fatty acid ester, fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether, propenyl alcohol amine, sodium carboxymethyl starch, arabic gum, maleic-methyl acrylate copolymer, potassium dihydrogen sulfate and sodium molybdate. The metal rust inhibitor has excellent anti-rust performance and can be degraded.
Owner:TIANCHANG RUNDA METAL ANTIRUST AUX
Biodegradable metal alloys
The invention relates to biodegradable, metal alloy-containing compositions, methods for their preparation and applications for their use. The compositions include magnesium and other components, such as yttrium, calcium, silver, cerium, and zirconium; or zinc, silver, cerium, and zirconium; or aluminum, zinc, calcium, manganese, silver, yttrium; or strontium, calcium, zinc. The compositions are prepared by vacuum induction / crucible melting together the components and casting the melted mixture in a preheated mild steel / copper mold. In certain embodiments, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful for forming medical devices for implantation into a body of a patient.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Polymer Metal and Composite Implantable Medical Devices
A device and a method of manufacturing an implantable medical device, such as a stent, are described herein. The device includes a metallic region composed of a bioerodable metal and a polymer region composed of a biodegradable polymer contacting the metallic region. The metallic region may erode at a different rate when exposed to bodily fluids than the polymer region when exposed to bodily fluids. In certain embodiments, the polymer region is an outer layer and the metallic region is an inner layer of the device. A further aspect of the invention includes device and a method of manufacturing the device that includes a mixture of a biodegradable polymer and bioerodable metallic particles. The mixture may be used to fabricate an implantable medical device or to coat an implantable medical device. In some embodiments, the metallic particles are metallic nanoparticles.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
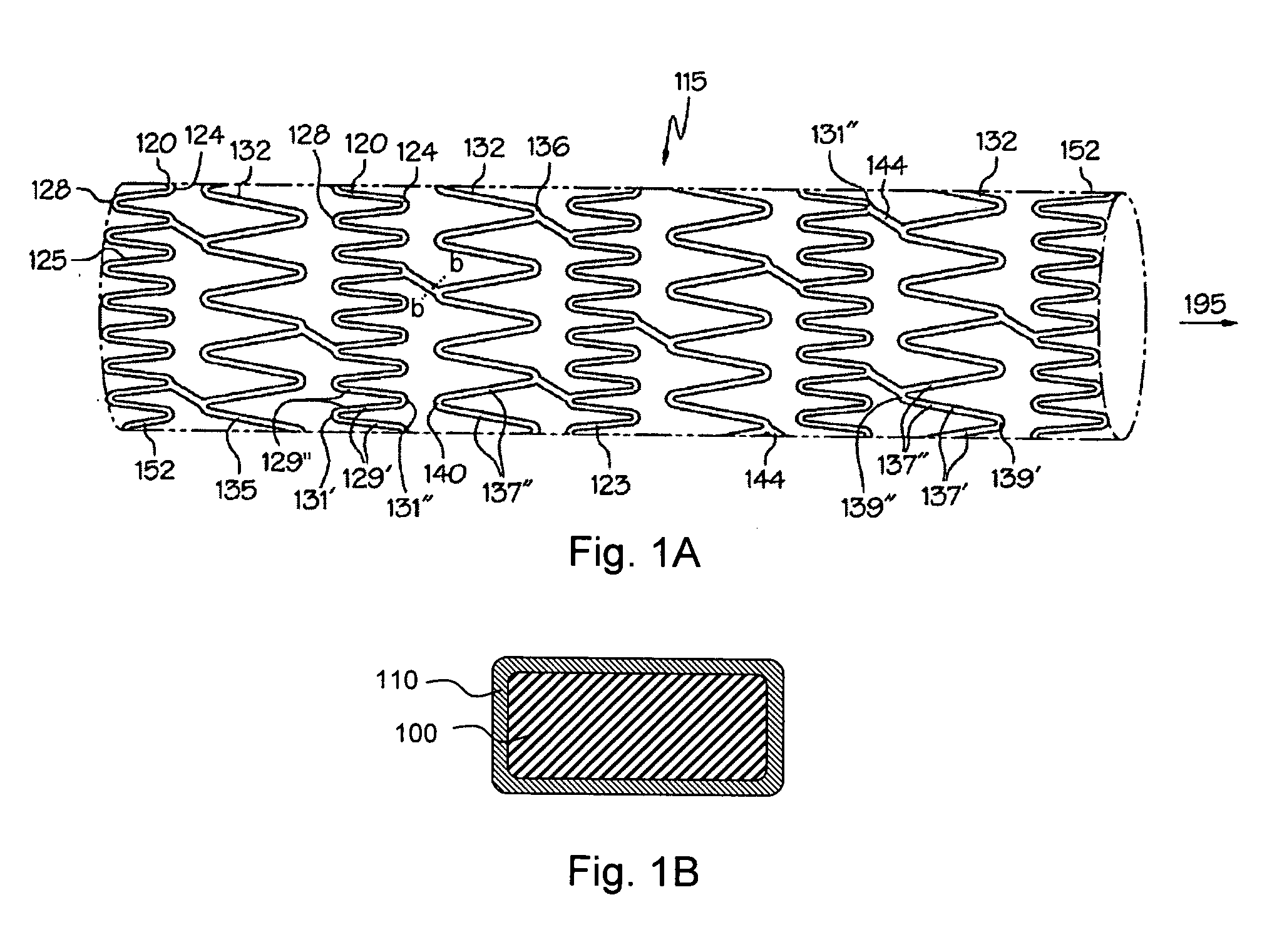
Degradable biliary duct drug-eluting stent
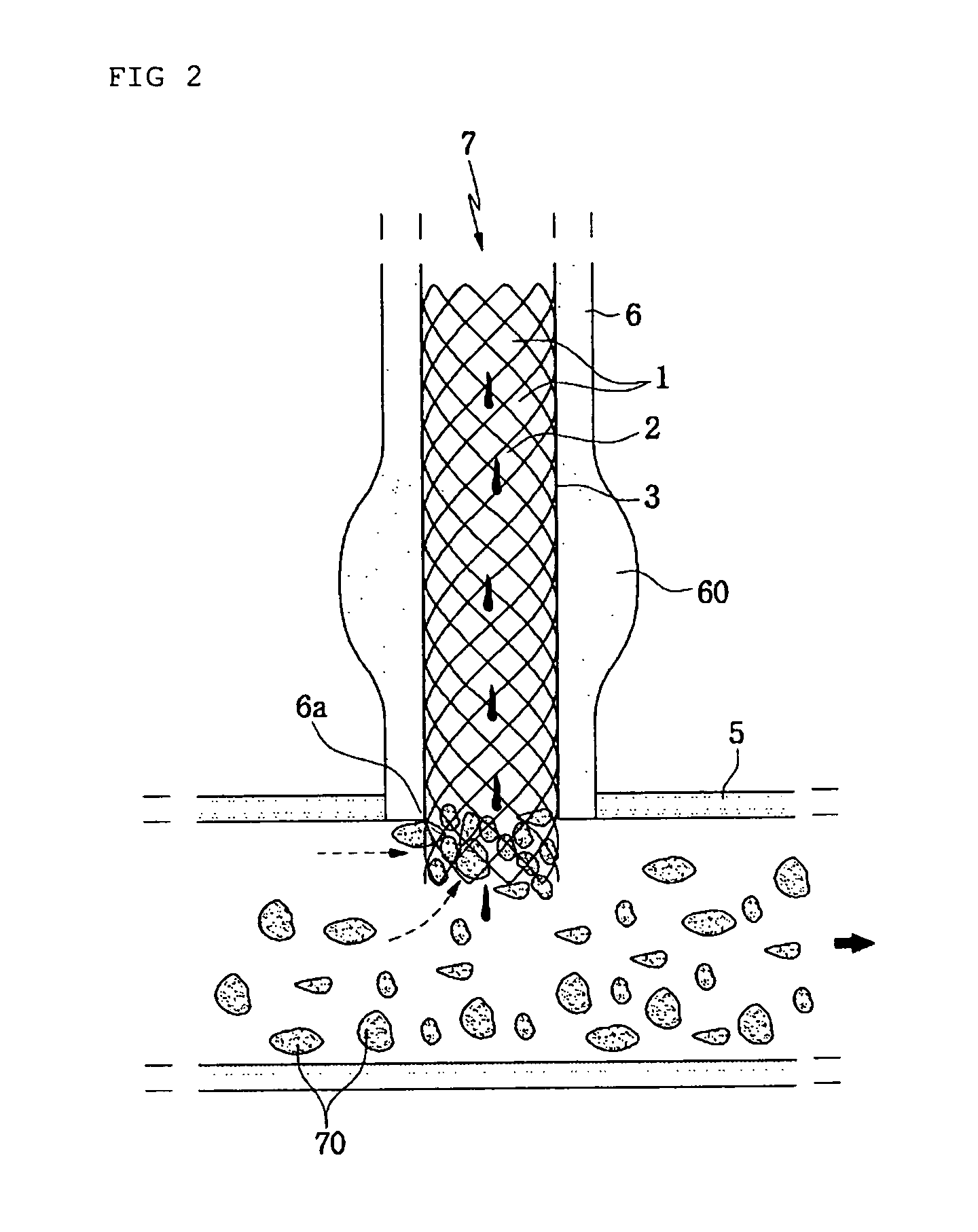
The invention discloses a degradable biliary duct drug-eluting stent, which consists of a biliary duct stent body and a biodegradable high-molecular polymer coating arranged on the surface of the biliary duct stent body. The biliary duct stent body is formed by mixed braiding of biodegradable metal wires and biodegradable high-molecular material silk threads. The biliary duct stent body is of a tubular structure. The two ends of the biliary duct stent body are shaped like trumpets that are open outwardly. The surface of the biliary duct stent body is a netted surface. The biodegradable high-molecular polymer coating carries drugs. The degradable biliary duct drug-eluting stent plays a mechanical supporting effect in a short period, is completely degraded after a treatment effect disappears, prevents tube wall tissues from being stimulated for a long period of time, effectively prevents the wall tissues from narrowing again after an operation, enables drug loaded fiber films to evenly wrap the surface of the stent body, and makes the drugs release slowly.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUHUI DISTRICT DAHUA HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com