Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
174 results about "Amorphous calcium phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
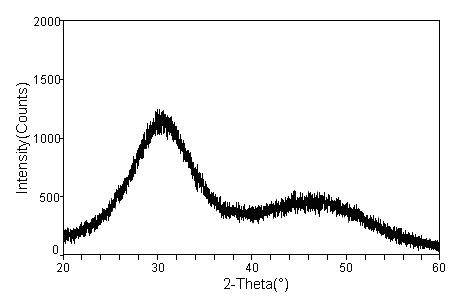
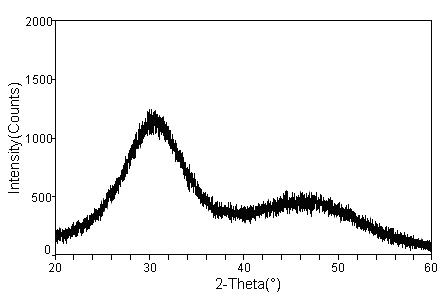
Amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP or ATCP) is a glassy precipitate of variable composition that is formed in double decomposition reactions involving a soluble phosphate and calcium salts (e.g. (NH₄)₂HPO₄ + Ca(NO₃)₂) performed under carefully controlled pH conditions. The precipitate will either be "amorphous tricalcium phosphate", ATCP, or calcium deficient hydroxypatite, CDHA, Ca₉(HPO₄)(PO₄)₅(OH), (note that CDHA is sometimes termed apatitic calcium triphosphate). The composition of amorphous calcium phosphate is CaₓHy(PO₄)z·nH₂O, where n is between 3 and 4.5. Precipitation from the moderately supersaturated and basic solution containing magnesium produces amorphous magnesium calcium phosphate (AMCP) in which magnesium incorporated into the ACP structure.
Calcium phosphate bone graft material, process for making same and osteoimplant fabricated from same
A calcium phosphate bone graft material comprising an amorphous calcium phosphate glassy phase of from about 30 to about 100 volume % is obtained by plasma spraying calcium phosphate-containing powder onto a target to produce a deposited layer and removing the deposited layer from the target to provide the calcium phosphate bone graft material.
Owner:OSTEOTECH INC
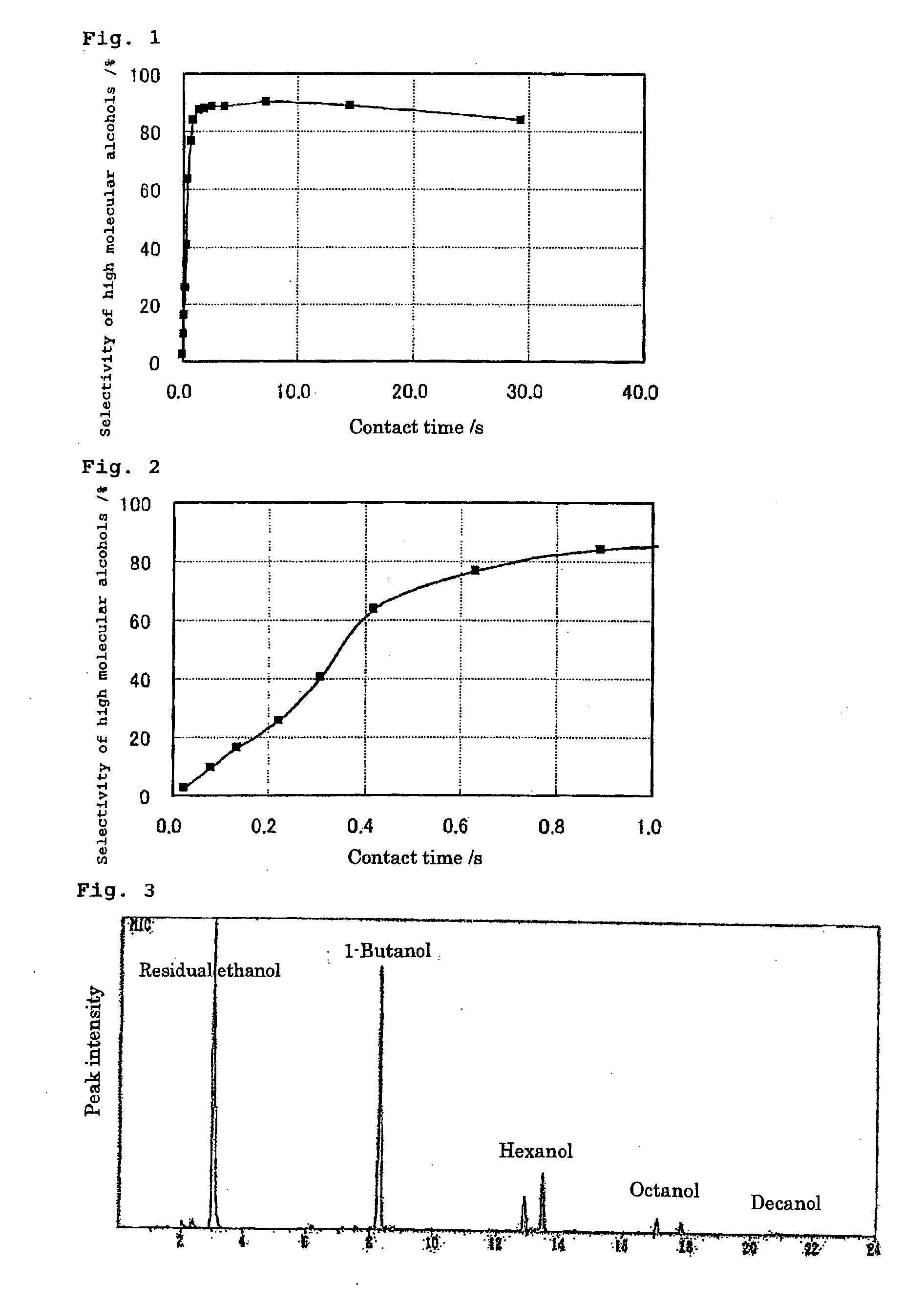
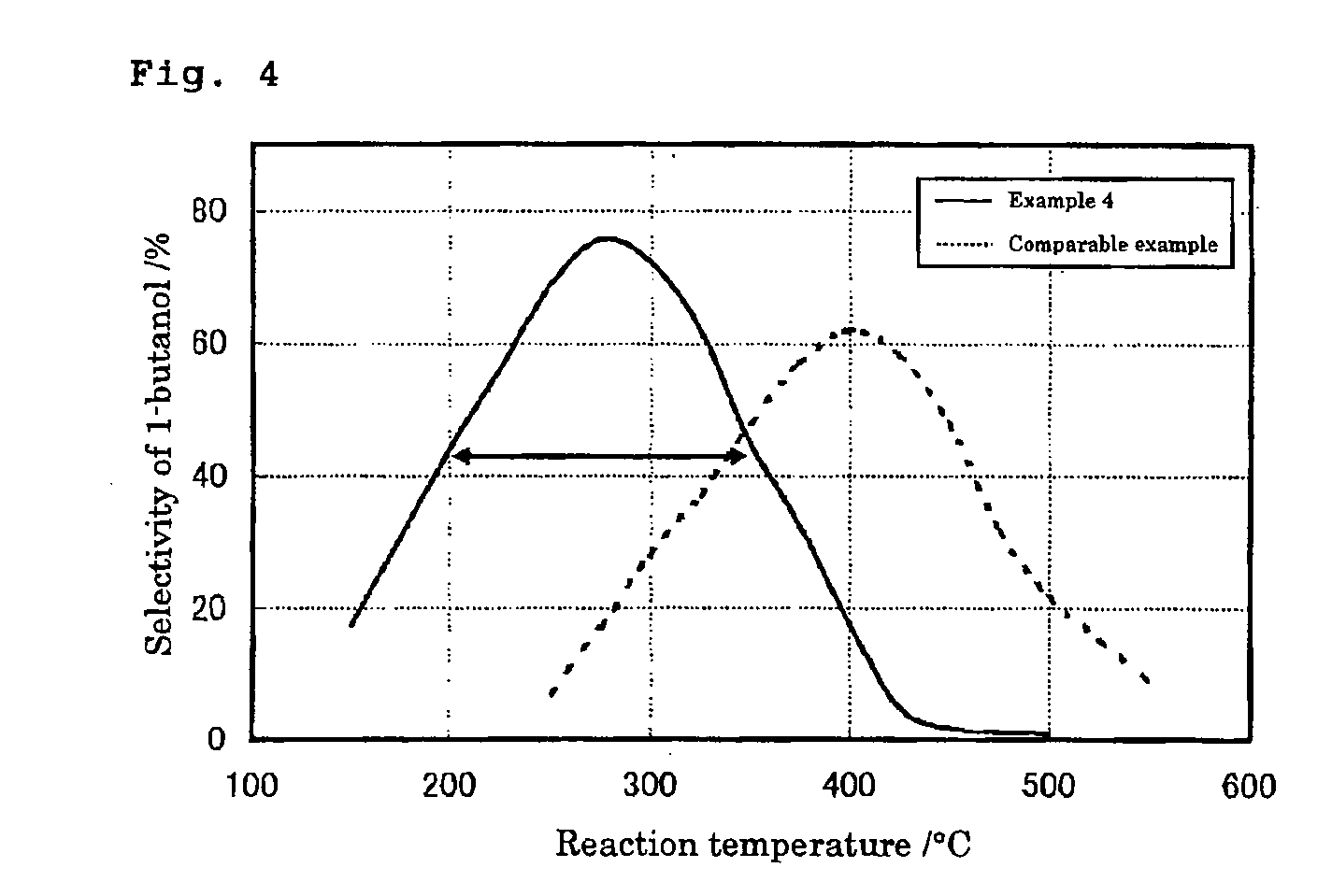
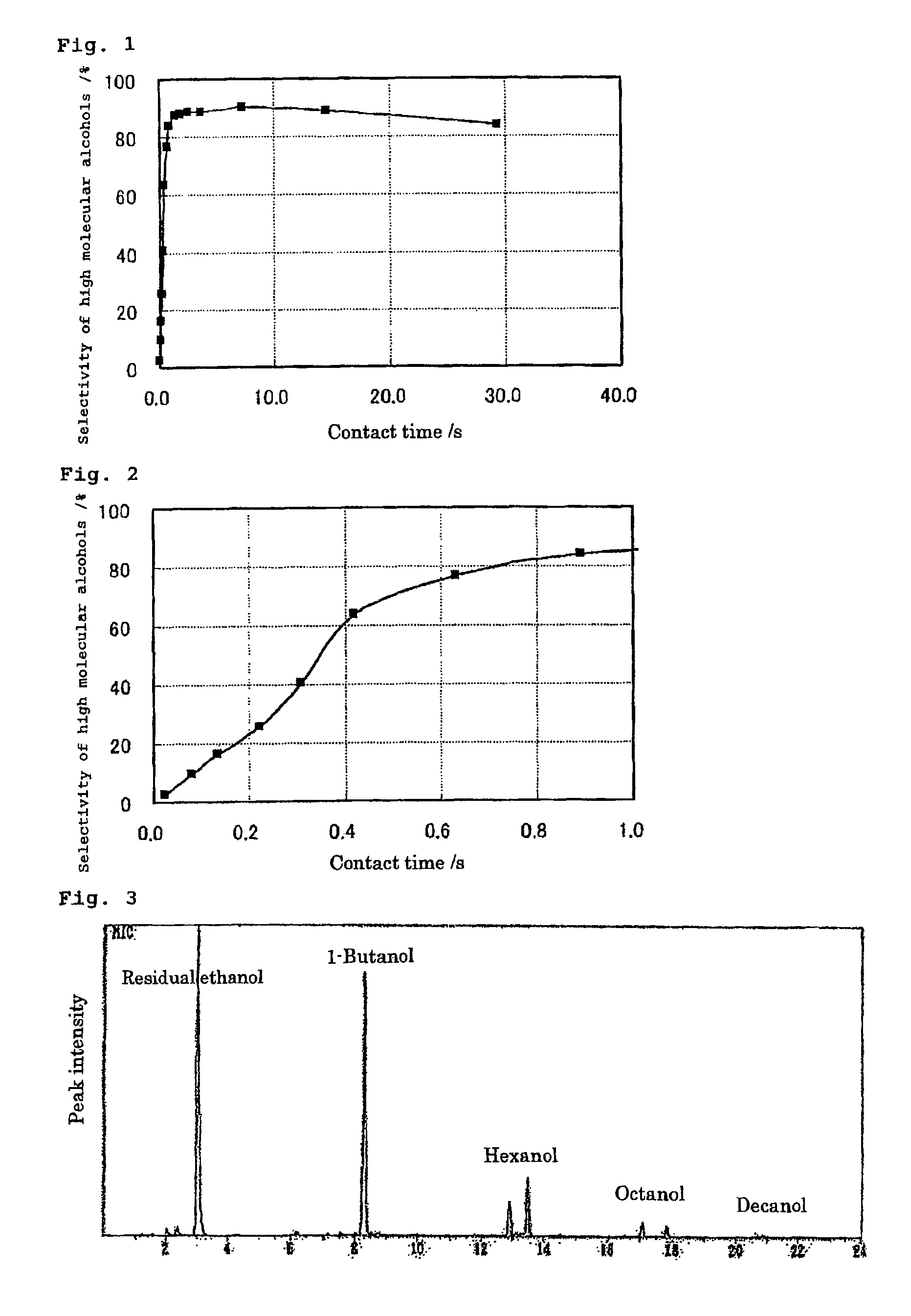
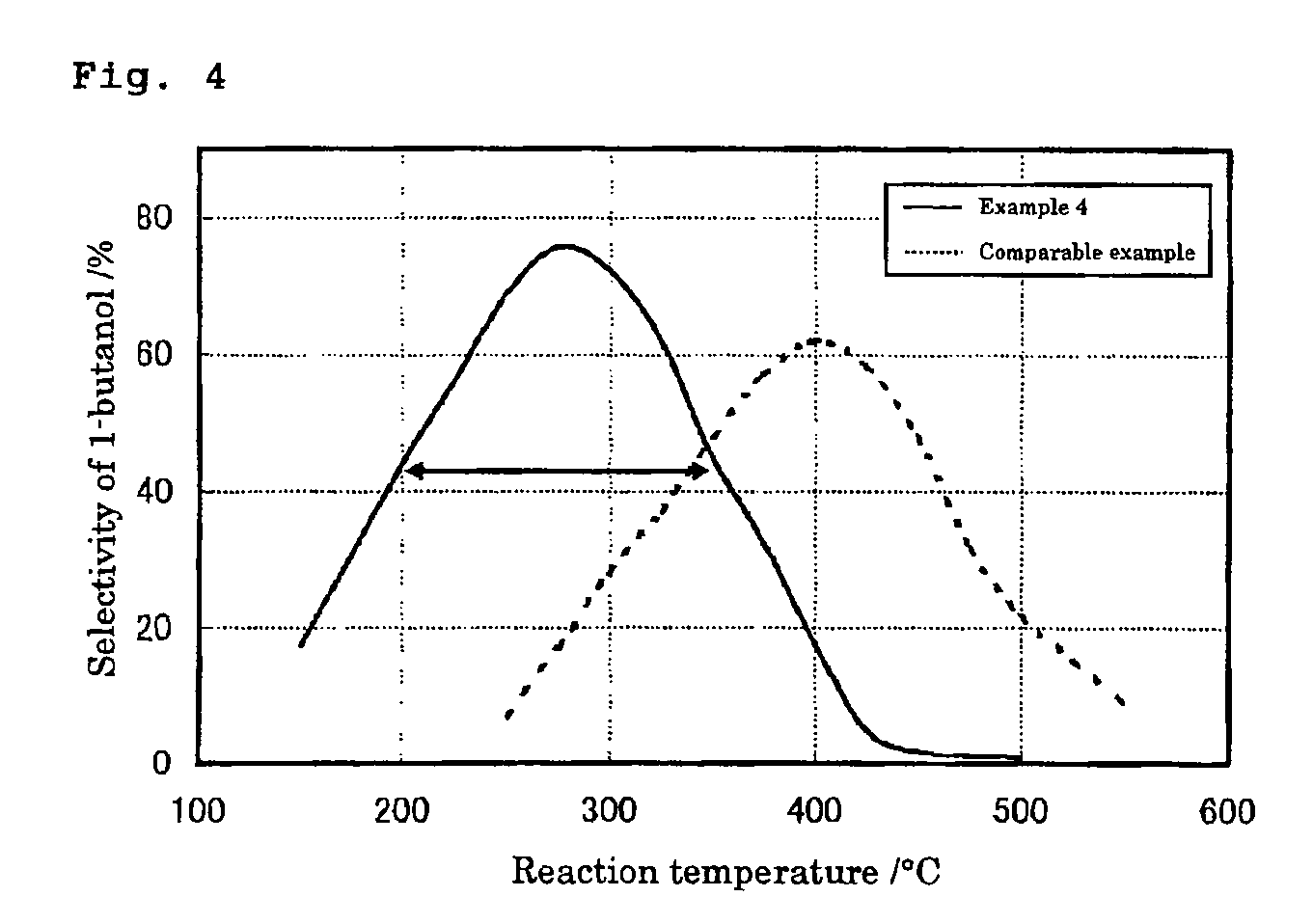
Method of Synthesizing Higher-Molecular Alcohol
ActiveUS20070255079A1Efficient collectionIncreased ethanol productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationOctanolSynthetic Polymeric Macromolecules
The present invention provides a production method with which high molecular alcohols having an even number of carbon atoms such as 1-butanol, hexanol, octanol and decanol, and a mixture of these are efficiently collected through clean processes with the use of ethanol as a raw material. High molecular alcohols are produced from ethanol by using calcium phosphate-based compounds such as hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2, calcium monohydrogen phosphate CaHPO4.(0˜2)H2O, calcium diphosphate Ca2P2O7, octacalcium phosphate Ca8H2(PO4)6.5H2O, tetracalcium phosphate Ca4(PO4)2O or amorphous calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2.nH2O as a catalyst, using ethanol as a starting material, and setting a contact time at 0.4 second or longer.
Owner:SANGI CO LTD
Composition for caries prevention
InactiveUS20050089481A1Excellent composition for preventionInhibition is effectiveCosmetic preparationsImpression capsCementum cariesPhosphopeptide
To obtain a composition for caries prevention, which has effects for efficiently suppressing demineralization and promoting remineralization and stability in keeping for a long time, 0.01 to 10% by weight of sodium carboxymethylcellulose having the etherification degree of 0.7 to 1.0 is used in a composition blended with a casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate complex (CPP-ACP) and / or a casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate complex (CPP-ACFP), a sodium carboxymethylcellulose, a viscosity regulator and water.
Owner:GC CORP
Hollow ball shaped nanometer hydroxylapatite material and the preparing method
InactiveCN101032630ALight weightLarge specific surface areaSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsApatiteHydroxylapatite
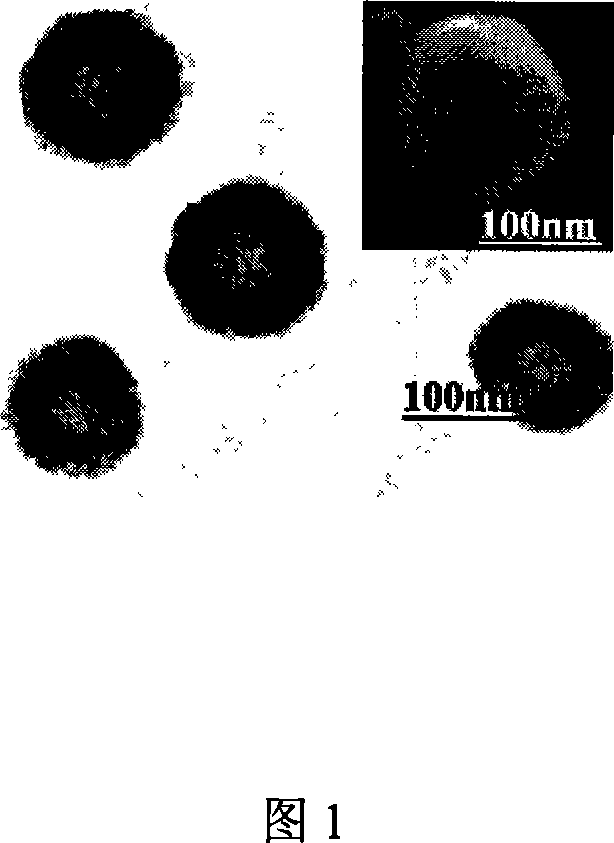
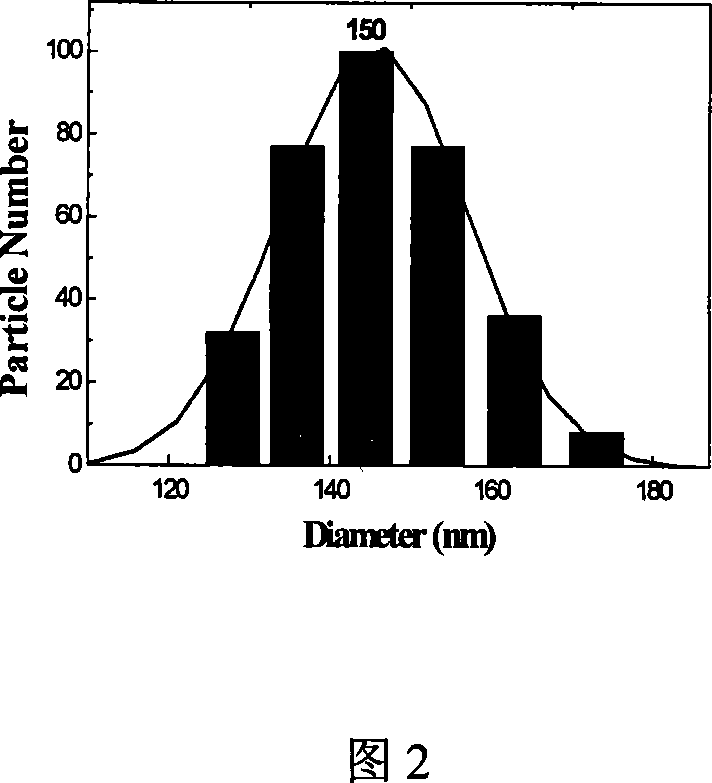
The present invention is one kind of nanometer hollow spherical granular hydroxyapatite and its preparation process. The nanometer hollow spherical granular hydroxyapatite has diameter of 130-170 nm, wall thickness of 40-50 nm, crystalline hydroxyapatite content of 40-60 % and amorphous calcium phosphate for the rest. The preparation process includes the following steps: dropping calcium salt solution slowly into solution containing phosphate radical and CTAB as template agent at certain temperature and in ultrasonic condition, dropping ammonia water solution to regulating the solution pH value to 9-10 and obtain milk white suspension, filtering, washing and low temperature vacuum drying. The nanometer hollow spherical granular hydroxyapatite has simple preparation process, light weight, great specific surface area and important application foreground in medicine release controlling carrier, medicated tissue engineering rack, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
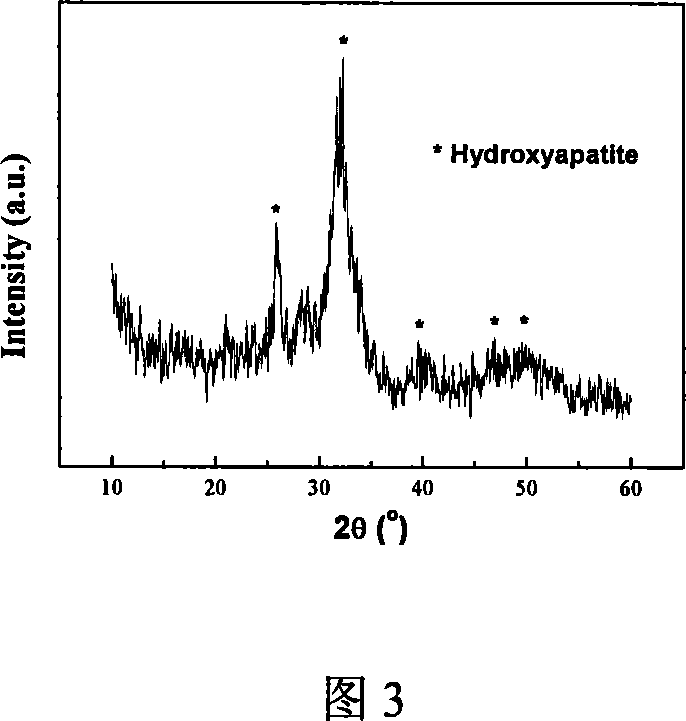
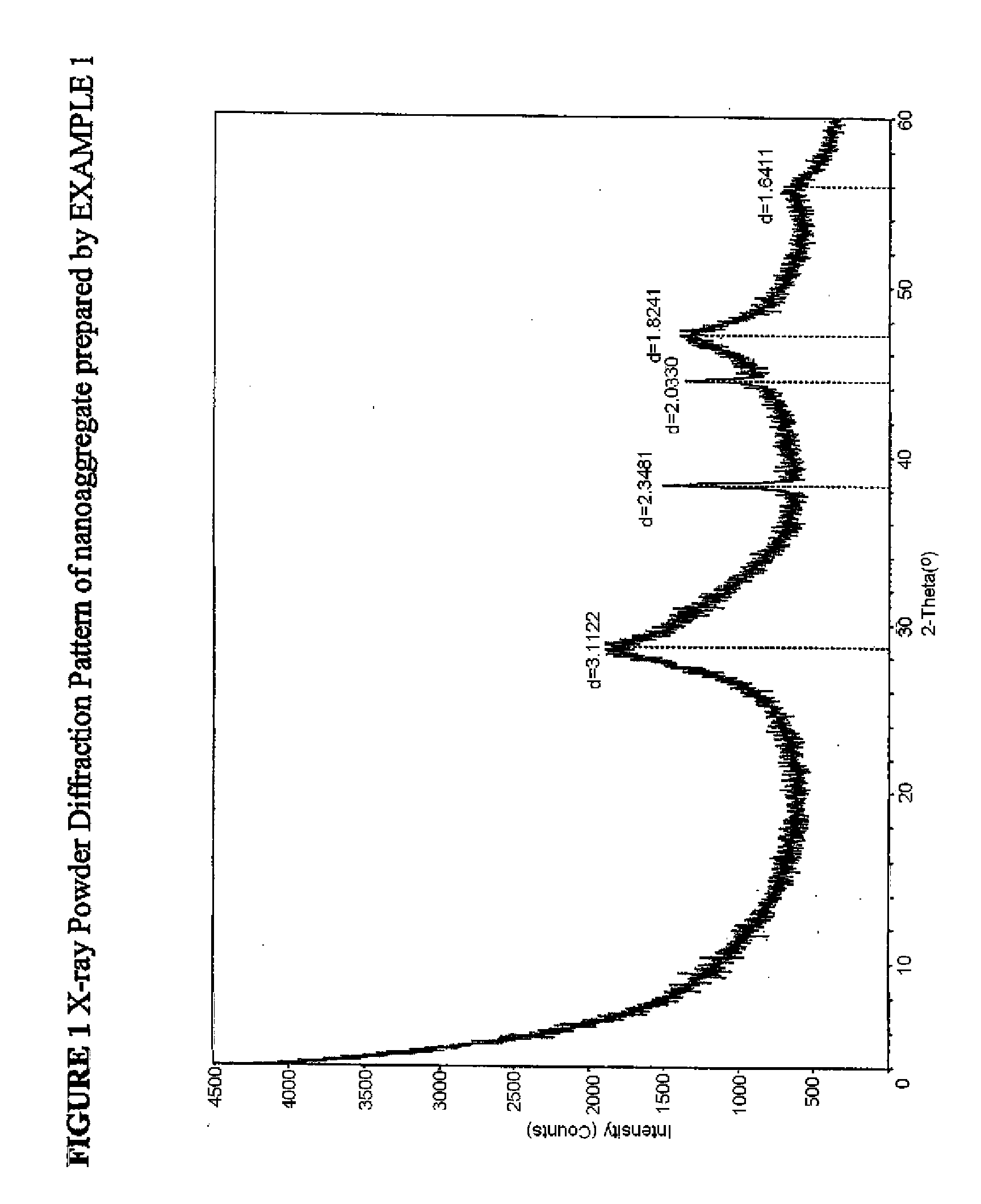
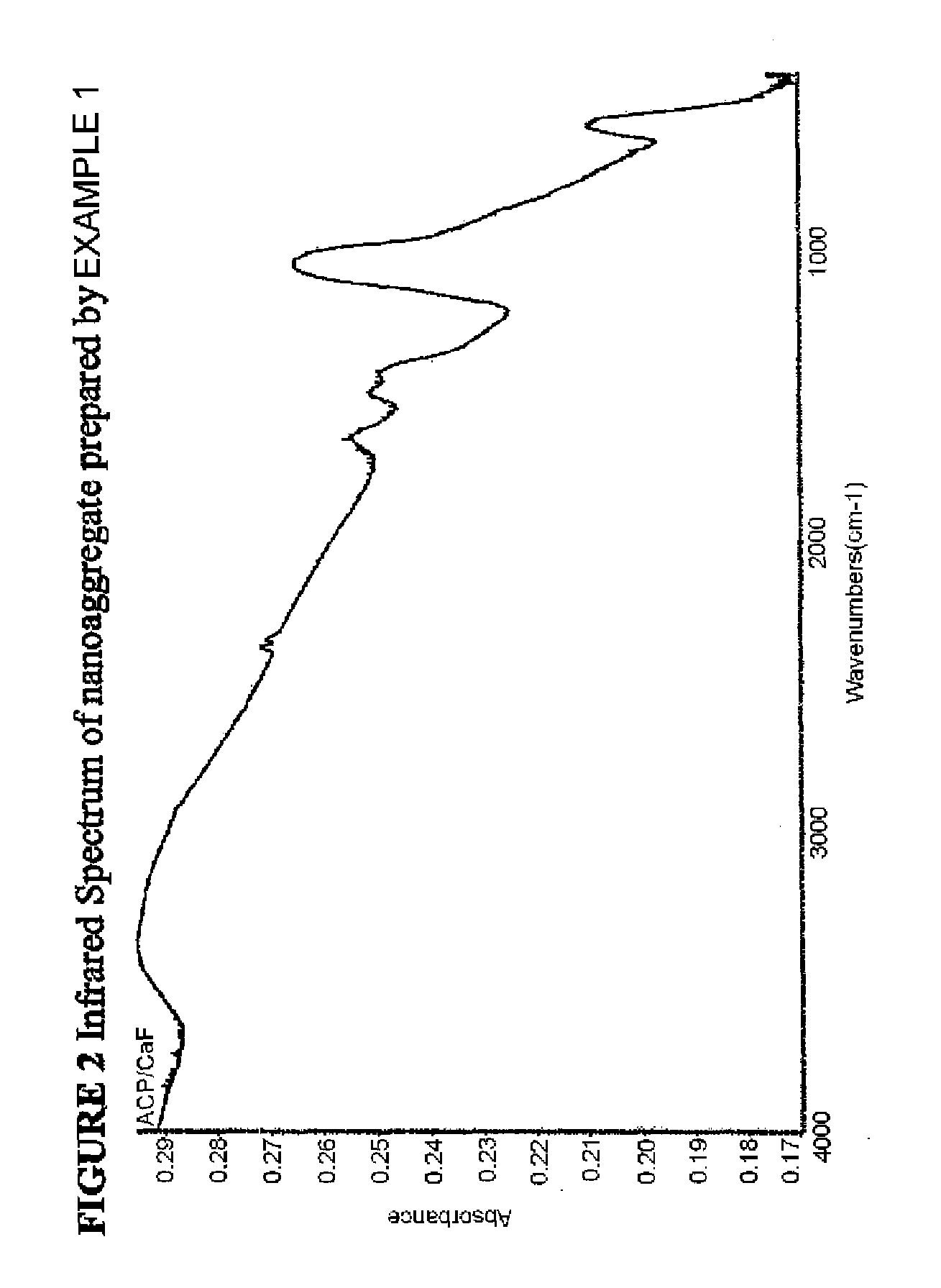
Tooth fluoridating and remineralizing compositions and methods, based on nanoaggregate formation
ActiveUS20080292565A1Well formedAvoid repairsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNano compositesWhitening Agents
Compositions and methods for forming, in an aqueous environment, a nanoaggregate of calcium fluoride and amorphous calcium phosphate-containing compound, such as amorphous calcium phosphate fluoride or amorphous calcium carbonate phosphate fluoride are described. The nanoaggregate (or nanocomposite) can release calcium, phosphate, and fluoride, and ultimately convert to the tooth mineral, fluorapatite. One method for forming such a nanoaggregate involves applying a non-aqueous (e.g., varnish-based) composition (e.g., a suspension), containing solid particles of water soluble salts of calcium, phosphate, and fluoride, to the aqueous environment of the mouth. This results in rapid solubilization of the salts, precipitation of the nanoaggregate, and tooth remineralization. Tooth fluoridation and remineralization may also be carried out by applying to the tooth a non-aqueous carrier containing the nanoaggregate. Whitening agents can also be added to these compositions and methods.
Owner:ADA FOUND
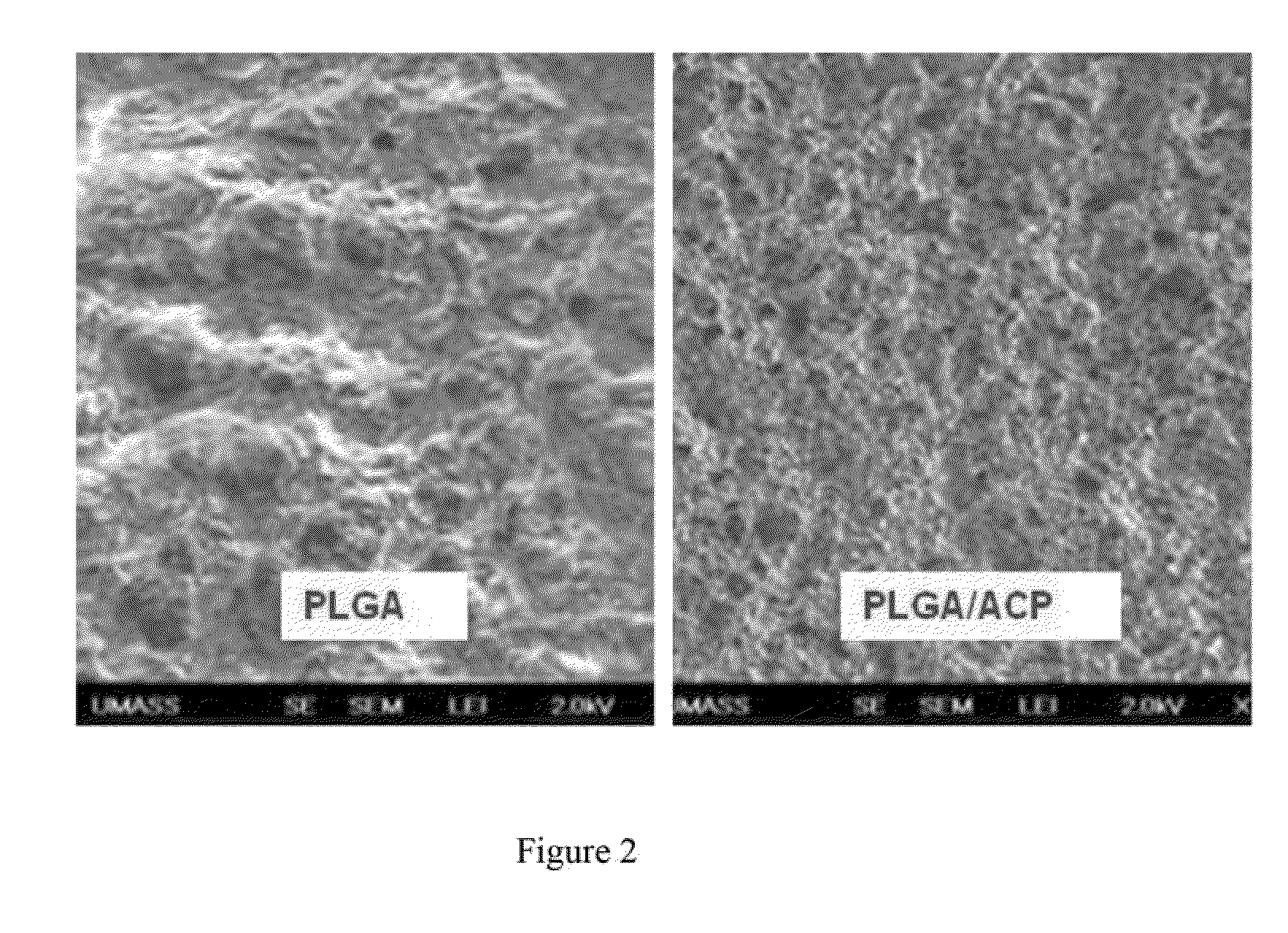
Polymeric bioresorbable composites containing an amorphous calcium phosphate polymer ceramic for bone repair and replacement
A bioresorbable composite of a non-crystalline calcium phosphate ceramic synthesized within an encapsulating microspheres of bioresorbable polymeric material for use in bone repair and replacement is provided. Also provides are methods for producing these composites as well as porous, 3-dimensional scaffold produced by sintering together microspheres of this bioresorbable composite.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Dental restorative materials
Owner:MELBOURNE UNIV OF THE
Dentinal tubule sealant and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20130189337A1Impart caries resistanceSubstance may accumulateCosmetic preparationsImpression capsCalcium biphosphateDentinal Tubule
A dentinal tubule sealant comprises poorly-soluble calcium phosphate particles (A), a phosphorus-free calcium compound (B), and water (C), wherein the particles (A) are at least one member selected from the group consisting of dicalcium phosphate anhydrous [CaHPO4] particles, α-tricalcium phosphate [α-Ca3(PO4)2] particles, β-tricalcium phosphate [β-Ca3(PO4)2] particles, amorphous calcium phosphate [Ca3(PO4)2.nH2O] particles, calcium pyrophosphate [Ca2P2O7] particles, calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate [Ca2P2O7.2H2O] particles, octacalcium phosphate pentahydrate [Ca8H2(PO4)6.5H2O] particles, and dicalcium phosphate dihydrate [CaHPO4.2H2O] particles, and the dentinal tubule sealant contains 30 to 76% by weight of the particles (A), 0.001 to 4% by weight of the compound (B), and 23 to 69% by weight of the water (C). Thus, there is provided a dentinal tubule sealant capable of sealing dentinal tubules of an exposed dentin and also remineralizing the surrounding dentin after the sealing.
Owner:KURARAY NORITAKE DENTAL
Dental Mineralization
A method is provided for mineralizing a dental surface or subsurface including contacting the dental surface with a protein disrupting agent and stabilized amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) or amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP).
Owner:MELBOURNE UNIV OF THE
Amorphous calcium phosphate nanoball and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102795610APromote degradationGood biological propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus compoundsCalcium biphosphateSolubility
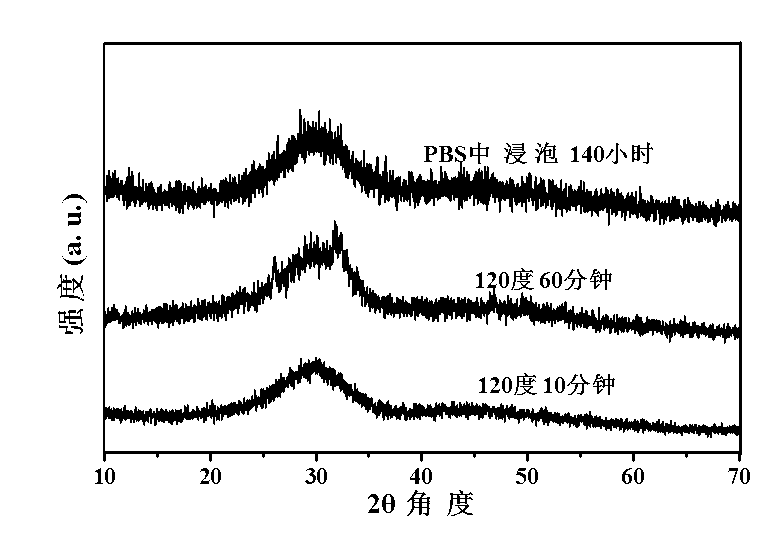
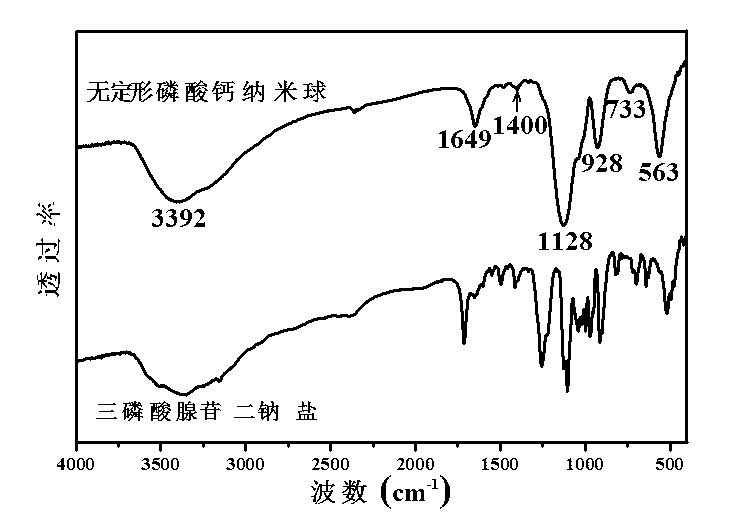
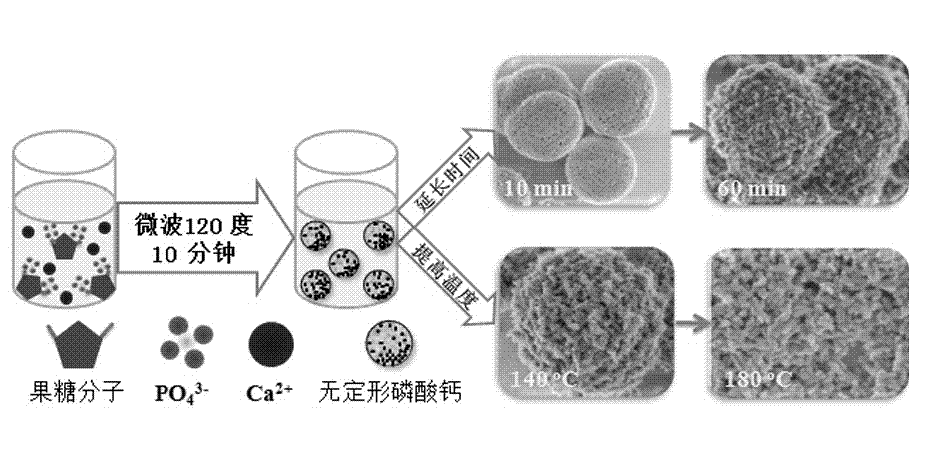
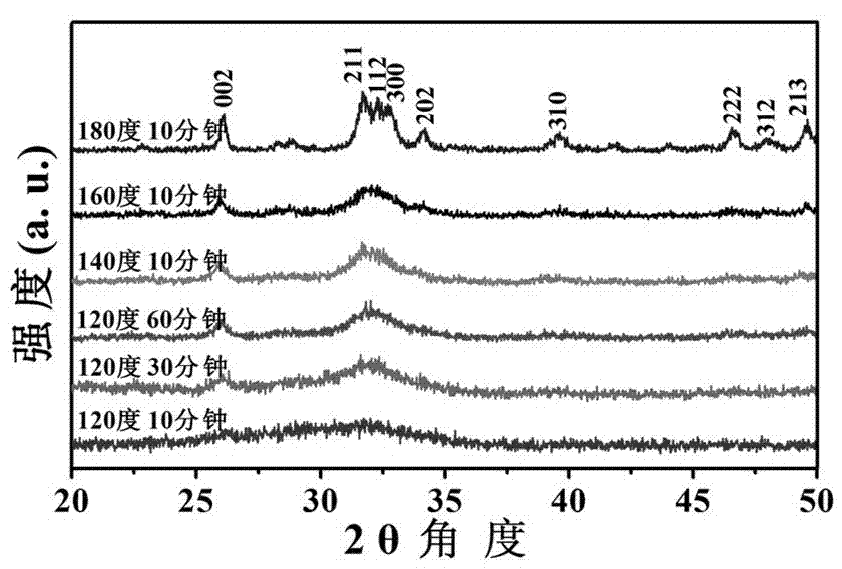
The invention relates to an amorphous calcium phosphate nanoball and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following step of: with water-solubility calcium salt as a carbon source and phosphorus-containing biologic molecules as a phosphorus source, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction under assistance of microwaves to prepare the amorphous calcium phosphate nanoball. The amorphous calcium phosphate nanoball prepared by the method disclosed by the invention can stably exist in an aqueous solution for more than 140 hours, and can improve the biologic performance of the amorphous calcium phosphate and enhance the medicine loading capability of the calcium phosphate.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Calcium phosphopeptide complexes
InactiveUS20050037948A1Prevent demineralisationInhibition formationAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsDietary supplementDelivery vehicle
Phosphopeptides containing the Ser(P) cluster sequence motif Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Glu-Glu- can stabilise their own weight in amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) [Ca3(PO4)1.87(HPO4)0.2xH2O] and amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP) [Ca8(PO4)5FxH2O]. The amorphous phases stabilised by the phosphopeptides are an excellent delivery vehicle to co-localise Ca, F, and phosphate at the tooth surface in a slow-release amorphous form producing superior anticaries efficacy. These amorphous phases stabilised by the phosphopeptides also have utility as dietary supplements to increase calcium bioavailability and to help prevent diseases associated with calcium deficiencies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Calcium phosphopeptide complexes
InactiveUS7312193B2Prevent demineralisationInhibition formationAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseDietary supplement
Phosphopeptides containing the Ser(P) cluster sequence motif Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Glu-Glu- can stabilize their own weight in amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) [Ca3(PO4)1.87(HPO4)0.2xH2O] and amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP) [Ca8(PO4)5F x H2O]. The amorphous phases stabilised by the phosphopeptides are an excellent delivery vehicle to co-localise Ca, F, and phosphate at the tooth surface in a slow-release amorphous form producing superior anticaries efficacy. These amorphous phases stabilised by the phosphopeptides also have utility as dietary supplements to increase calcium bioavailability and to help prevent diseases associated with calcium deficiencies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Biodegradable stent formed with polymer-bioceramic nanoparticle composite and method of making the same
The present invention relates to biodegradable medical devices such as stents manufactured from biodegradable polymeric-bioceramic nanoparticle composites. The invented medical devices include at least one bioceramic nanoparticle dispersed in at least one biodegradable polymer, wherein the said biodegradable polymers include biodegradable polyesters. The device and methods to disperse one or more bioceramic nanoparticle, wherein the said bioceramic nanoparticle include, but are not limited to, amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP), dicalcium phosphate (DCP), tricalcium phosphate (TCP), pentacalcium hydroxyl Apatite (HAp), tetracalcium phosphate monoxide (TTCP) and combinations or analogues thereof. Other embodiments include methods of fabricating biodegradable stent with said polymeric-nanoparticle composites.
Owner:DR TIM WU
Degradable nanometer composite material for biological and medical use
A nanometer-grade medical decomposable composite material and its preparation method. By different Ca / P, different crystallizing states in the inorganic phase, the composite material adjusts decomposing rate, recombines with decomposable polymer, thus the biological decomoposing rate of the whole composite material is adjustable. The inorganic phase is selected from one or two of amorphous calcium phosphate, ª‡- tricalcium phosphate, ª‰- tricalcium phosphate, phosphorite and calcium phosphate dibasic. The preparation method comprises selecting organic solvents for uniformly dispersing calciumphosphate powder in a decomposable polymer matrix, then obtaining nanometer-grade composite material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of bionic mineralized collagen scaffold
The invention provides a preparation method of a bionic mineralized collagen scaffold. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1), preparing a bionic mineralized liquid: adjusting the pHvalue of carboxymethyl chitosan-amorphous calcium phosphate (or amorphous strontium phosphate or amorphous strontium carbonate) nanocomposite liquid to be lower than an isoelectric point of CMC; 2),preparing the bionic mineralized collagen scaffold: mixing the bionic mineralized liquid and acid-dissolved type-I collagen, then putting into a dialysis bag, sealing, then putting into a PBS buffer liquid, self-assembling and mineralizing for 2-5 days, then adding an alkaline CMC / ACP (ASP or ASC) liquid into the dialysis bag, and changing the PBS buffer liquid; 1-3 days later, putting the dialysis bag into deionized water for dialyzing for 10-72h, changing the deionized water for several times, centrifuging the liquid in the bag to obtain collagen gel, and performing freeze drying to obtain the bionic mineralized collagen scaffold. By the preparation method, collagen self-assembly and mineralization are cooperatively performed, intra-collagen fiber mineralization is achieved at relativelyhigh efficiency, and osteogenic ability-promoting strontium is integrated into the collagen scaffold, so that the preparation method has a wide clinical application prospect.
Owner:博纳格科技(天津)有限公司
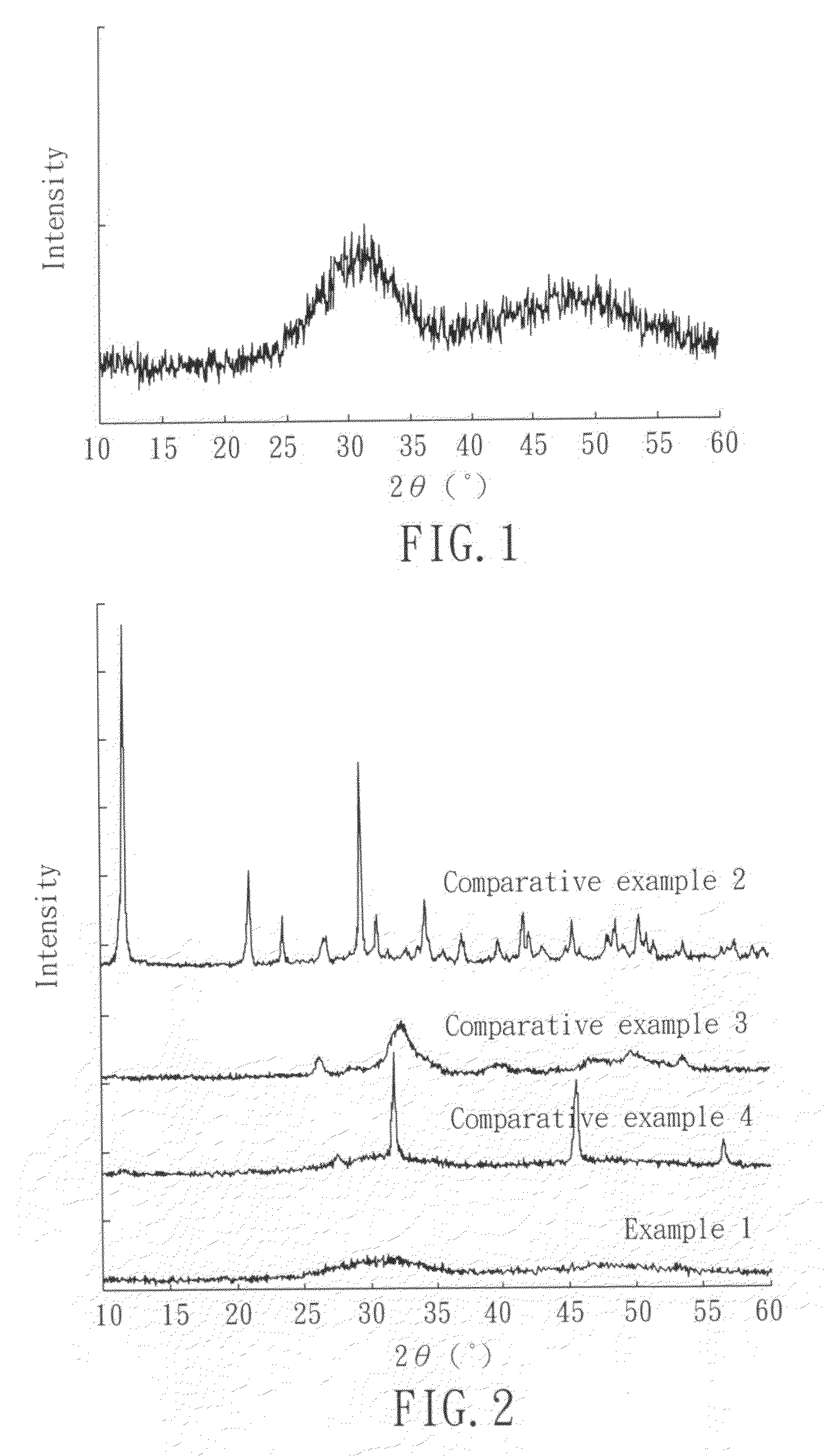
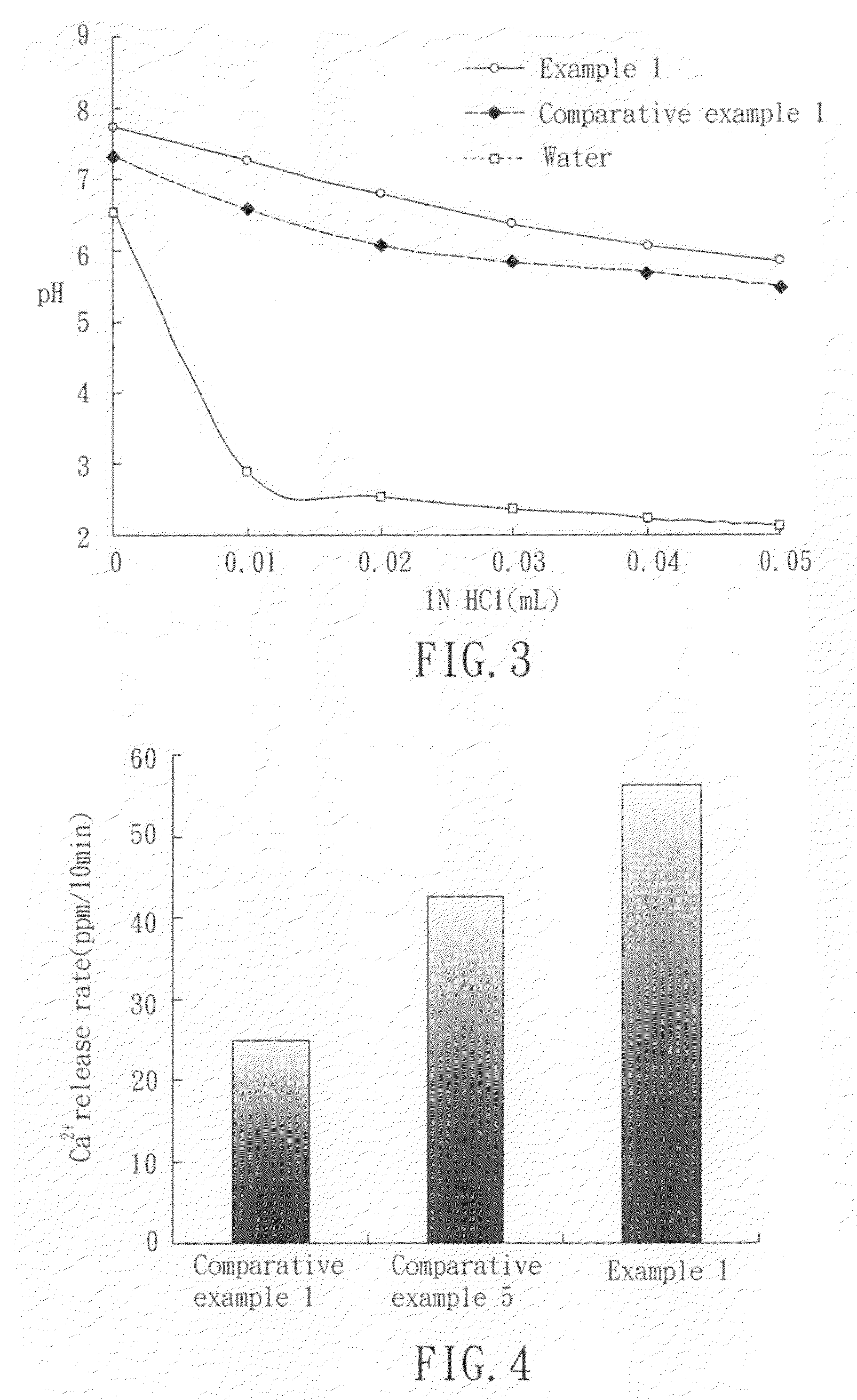
Method for preparing amorphous calcium phosphate and oral care composition containing amorphous calcium phosphate prepared by the same
InactiveUS20100143271A1Simple and low-cost and green productionAvoid carryingCosmetic preparationsPhosphatesTrace elementDental health
A method for preparing amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) and oral care composition containing ACP prepared by the same are disclosed, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (a) cleaning and pulverizing the oyster shells; (b) sintering the oyster shells to obtain a calcium-containing powder; (c) dissolving the calcium-containing powder in water to obtain a calcium-containing solution; and (d) mixing the calcium-containing solution with a other phosphate-containing solution, to produce amorphous calcium phosphate.The method of the present invention not only can simplify the process and reduce the cost, but also can solve the problem of environment pollution resulting from wasted oyster shells. In addition, the ACP prepared in accordance with the method of the present invention further comprises some trace elements, such as strontium (Sr) and fluoride (F), which can improve dental health.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
Method of synthesizing higher-molecular alcohol
ActiveUS8080695B2Efficient collectionIncreased ethanol productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationSynthetic Polymeric MacromoleculesOctanol
The present invention provides a production method with which high molecular alcohols having an even number of carbon atoms such as 1-butanol, hexanol, octanol and decanol, and a mixture of these are efficiently collected through clean processes with the use of ethanol as a raw material. High molecular alcohols are produced from ethanol by using calcium phosphate-based compounds such as hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2, calcium monohydrogen phosphate CaHPO4.(0˜2)H2O, calcium diphosphate Ca2P2O7, octacalcium phosphate Ca8H2(PO4)6.5H2O, tetracalcium phosphate Ca4(PO4)2O or amorphous calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2. nH2O as a catalyst, using ethanol as a starting material, and setting a contact time at 0.4 second or longer.
Owner:SANGI CO LTD
Composite material for tooth hard tissue remineralization
ActiveCN103655209ATo remineralizeNo inhibitionCosmetic preparationsImpression capsSimulated body fluidBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a composite material for tooth hard tissue remineralization. The composite material comprises a simulation body fluid, and is improved in that the simulation body fluid is added with 0.1+ / -0.001% by weight of carboxymethyl chitosan and 0.025+ / -0.005% by weight of an amorphous calcium phosphate component. According to the present invention, after using the composite material, the remineralization effect can be provided for the demineralized tooth tissue, characteristics of no toxicity, no irritating, good biocompatibility and low allergenicity are provided, good inhibition effects are provided for oral cariogenic bacteria such as Streptococcus mutans, and the use effect is good.
Owner:STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Calcium phosphate nano-structures and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102897734APromote degradationShape is easy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus compoundsNanostructureNanorod
The invention relates to calcium phosphate nano-structures and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, water-soluble calcium salt serving as a calcium source and phosphorous biomolecules serving as as a phosphor source are prepared into a calcium phosphate nano-structure powder through a microwave assisted hydrothermal reaction, wherein the phosphorous biomolecules are phosphofructose or fructose diphosphate. The three different nanostructures, namely amorphous calcium phosphate porous nano-spheres, hydroxyapatite nano-rods and amorphous calcium phosphate / hydroxyapatite composite nano-spheres, prepared by the preparation method can be widely applied to biomedicine, tissue engineering and other fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nano-complexes for enamel remineralization
The invention relates to nano-sized complexes formed by associating or attaching amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) and / or amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP) with an amphiphilic polymer surfactant (APS) and a bioadhesive polymer. The bioadhesive polymer may serve as a connector or an anchor to attach the nano ACP-APS or ACFP-APS to the tooth surface and to chemically bond the calcium in the enamel to the calcium ions in the nano ACP-APS or ACFP-APS complexes, thus allowing for more controlled release of remineralizing components into the oral cavity. Methods of use of the composition and kits are also disclosed.
Owner:PAC DENT INC
Synthesizing method of amorphous calcium phosphate
InactiveCN102320586AThe preparation method is mildLow costPhosphorus compoundsCalcium nitrate tetrahydrateCalcium biphosphate
The invention relates to a synthesizing method of amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP). According to the invention, tetrahydrated calcium nitrate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate are prepared into a solution; the solution is precipitated under an ultrasonic condition with a temperature of 0 DEG C; and the precipitate is vacuum-filtered and is dried, such that ACP powder is obtained. According to the method, no stabilizer is needed, and the method is simple and applicable. With the method, calcium phosphate powder with an adjustable Ca / P ratio and good bioactivity can be prepared. The prepared ACP powder can be applied in the field of biomedical materials.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of quickly repairing demineralized dentine
ActiveCN105267046AGood mineral contentGood hierarchyImpression capsDentistry preparationsPortland cementALLYL SUCROSE
The invention relates to a method of quickly repairing demineralized dentine. An existing method of repairing demineralized dentine uses two dentine non-collagen analogs, repairing is implemented by the aid of a Portland cement slow-release system, but this method is too complex and takes as long as four months to achieve full mineralization. According to the method of the invention, polyacrylic acid simple and easy to obtain is used as a regulator, calcium ions and phosphorus ions are used as raw materials, and fluidic amorphous calcium phosphate particles 15-20 nm in size are synthesized; glutamic acid is then used as a mineralization accelerator to mineralize the demineralized dentine again within 2 days, the natural hierarchical structure of the demineralized dentine is repaired, and the mechanical properties of the re-mineralized dentine also close to those of natural dentin. Compared with existing re-mineralization techniques, the method has the advantages that on the basis of achieving equivalent repaired hierarchical structure and mechanical properties, an apparatus is simple, time consumption is low, and the problem of re-mineralizing the demineralized dentine is more effectively solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bonding-assisting biological mineralization material and applications thereof in biomimetic mineralization
InactiveCN106473933ASimple preparation processEasy to storeImpression capsDentistry preparationsAdhesiveBiological materials
The invention provides a bonding-assisting biological material and applications of the bonding-assisting biological material in biomimetic mineralization, for promoting the remineralization of type I collagen, demineralized enamel and dentin. The bonding-assisting biological mineralization material is the synthetized amorphous calcium phosphate particles stabilized by non-collagenous protein analogue. According to the applications of the bonding-assisting biological mineralization material in biomimetic mineralization, the assisting mineralization material is mixed with a self-etching adhesive, thus the bonding-assisting biological mineralizer is prepared, the bonding-assisting biological mineralizer coats the surfaces of single-layer recombinant type I collagen, the demineralized enamel and the dentin, and then the mineralization property of the biological mineralizer for the single-layer recombinant type I collagen, the demineralized enamel and the dentin is studied. The existing biological mineralization mode (solutions and paste are adopted, namely, gargling or local coating is adopted) is changed, the assisting mineralization material is mixed with the adhesive, after curing, the liquid state is converted into the solid state, then the adhesive anti-caries coating is formed, and the adhesive anti-caries coating can be adhered to the part needing mineralization for a long term, so that the acting time with teeth is prolonged, the use is simple and convenient, and the self-repairing of the demineralized teeth is promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for fixing soil heavy metal ion in situ by nanometer amorphous calcium phosphate
InactiveCN101961727AEasy to implementEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationSoil heavy metalsPrecipitation
The invention discloses a method for fixing soil heavy metal ions in situ by nanometer amorphous calcium phosphate. According to the method, the nanometer amorphous calcium phosphate is applied to the heavy metal polluted soil the amount of which accounts for 0.1%-0.6% of the weight of water-free soil and then the mixture is fully and evenly blended. After being applied to the heavy metal polluted soil,the nanometer amorphous calcium phosphate can noticeably reduce biological effectiveness and mobility of the heavy metal in the soil by reactions with the heavy metal elements such as adsorption, coordination, precipitation and the like. The method of the invention has the advantages of low cost, simple use, high fixing efficiency to heavy metal and capability of improving soil fertility and realizing in-situ remediation without leading to secondary pollution, thus being a safe and effective method for remedying heavy metal polluted soil.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Material for desensitizing teeth by sealing dentinal tubules
ActiveCN107569395AReasonable structural designEasy to prepareImpression capsDentistry preparationsBiocompatibility TestingDipotassium phosphate
The invention provides a material for desensitizing teeth by sealing dentinal tubules. The material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of carboxymethyl chitosan, 5-10 parts of dipotassium phosphate, 10-20 parts of calcium chloride, 24-48 parts of lysozyme and 12-24 parts of water. Through an electrostatic acting force between the carboxymethyl chitosan and the lysozyme, a carboxymethyl chitosan and lysozyme containing nanogel is formed, the nanogel stabilizes calcium ions and hydrogen phosphate ions in a calcium phosphate solution, and the formed desensitizing material is in the form of rigid solid spheres containing nanometer amorphous calcium phosphate particles. Experiments prove that the desensitizing material is simple and convenient in preparation method and can penetrate into the dentinal tubules to achieve rapid desensitization and mineral crystals are formed and are firmly combined with the surfaces of the teeth; the newly formed crystals cancover the dentinal surfaces; the desensitizing material is good in biocompatibility, low in allergenicity, non-toxic, non-irritant, wide in clinical application range and ideal in using effect.
Owner:STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Stable oral compositions comprising casein phosphopeptide complexes and fluoride
The present invention relates to oral care compositions, especially toothpastes, comprising: a safe and effective amount of phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate complex (“PP-ACP”); a safe and effective amount of a fluoride ion source; a pharmaceutically-acceptable topical, oral carrier, and a safe and effective amount of a calcium chelator, wherein the composition has improved fluoride stability. This invention further relates to a method of maintaining the fluoride levels in an oral care composition comprising a safe and effective amount of PP-ACP, a safe and effective amount of a fluoride ion source, and a pharmaceutically-acceptable topical, oral carrier, by adding, to the composition, a safe and effective amount of a calcium chelator.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Dental mineralization
ActiveUS8673363B2Improve mineralizationBiocideCosmetic preparationsNuclear chemistryAmorphous calcium phosphate
A method is provided for mineralizing a dental surface or subsurface including contacting the dental surface with a protein disrupting agent and stabilized amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) or amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP).
Owner:MELBOURNE UNIV OF THE
Stabilized stannous compositions
ActiveUS20160317404A1Reduced bioavailabilityReduced activityCosmetic preparationsHeavy metal active ingredientsPhosphopeptidePhases of clinical research
The present invention relates to improved complexes of amorphous calcium phosphate and / or amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate stabilised by phosphopeptides / phosphoproteins by addition of stannous ions. These complexes have anticariogenic properties useful to protect tooth structures as they remineralize (repair) early stages of dental caries and have other dental / medical applications (including anti-calculus, anti-erosion / corrosion and anti-dentinal hypersensitivity). Methods of making the complexes of the invention and of treatment or prevention of various dental conditions including dental caries, dental calculus, dental erosion / corrosion and dental hypersensitivity are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Drug eluting medical implant with porous surface
An implant is proposed, in particular made from a base material including a biodegradable metal and / or a biodegradable metal alloy, wherein the implant includes a coating made of crystalline calcium phosphate and / or amorphous calcium phosphate.
Owner:BIOTRONIK VI PATENT
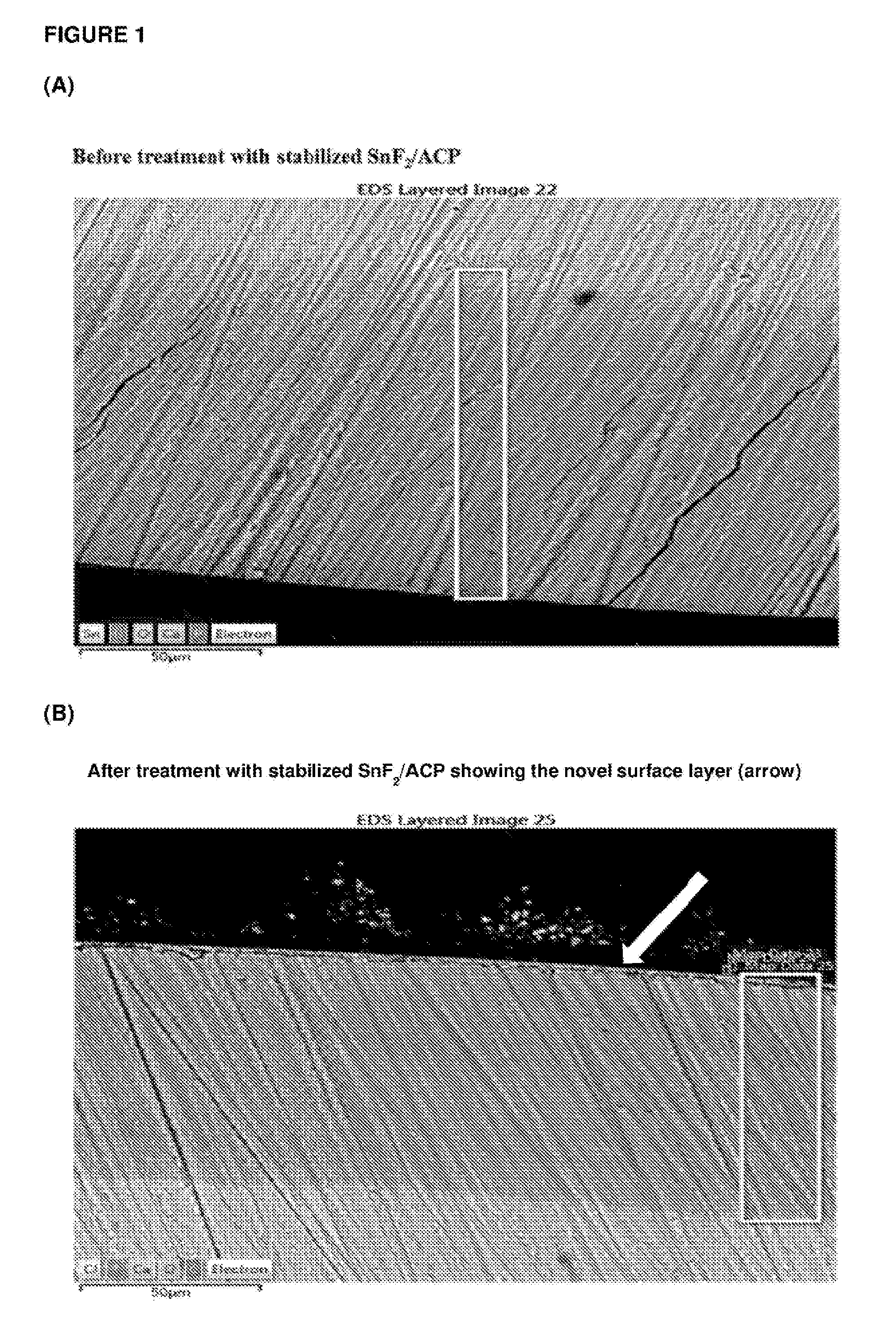
Apparatus and methods for visual demonstration of dental erosion on simulated dental materials
Comparative effectiveness of various oral care products such as dentifrices on preventing dental erosion may be demonstrated using simulated enamel. A substrate is prepared. A mineral layer to simulate dental enamel is nucleated by solution growth on the substrate surface. Alternatively, the mineral layer may be nucleated on a template comprising a self-assembled monolayer formed on a gold layer deposited on the substrate surface. The mineral layer may comprise a homogeneous layer of hydroxyapatite or a thin veneer of hydroxyapatite on a layer of amorphous calcium phosphate. The simulated enamel is then optionally treated with an oral care product and subjected to an acid challenge. The amount of mineral layer remaining after the acid challenge dramatically illustrates the effectiveness or non-effectiveness of the oral care product at preventing dental erosion.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com