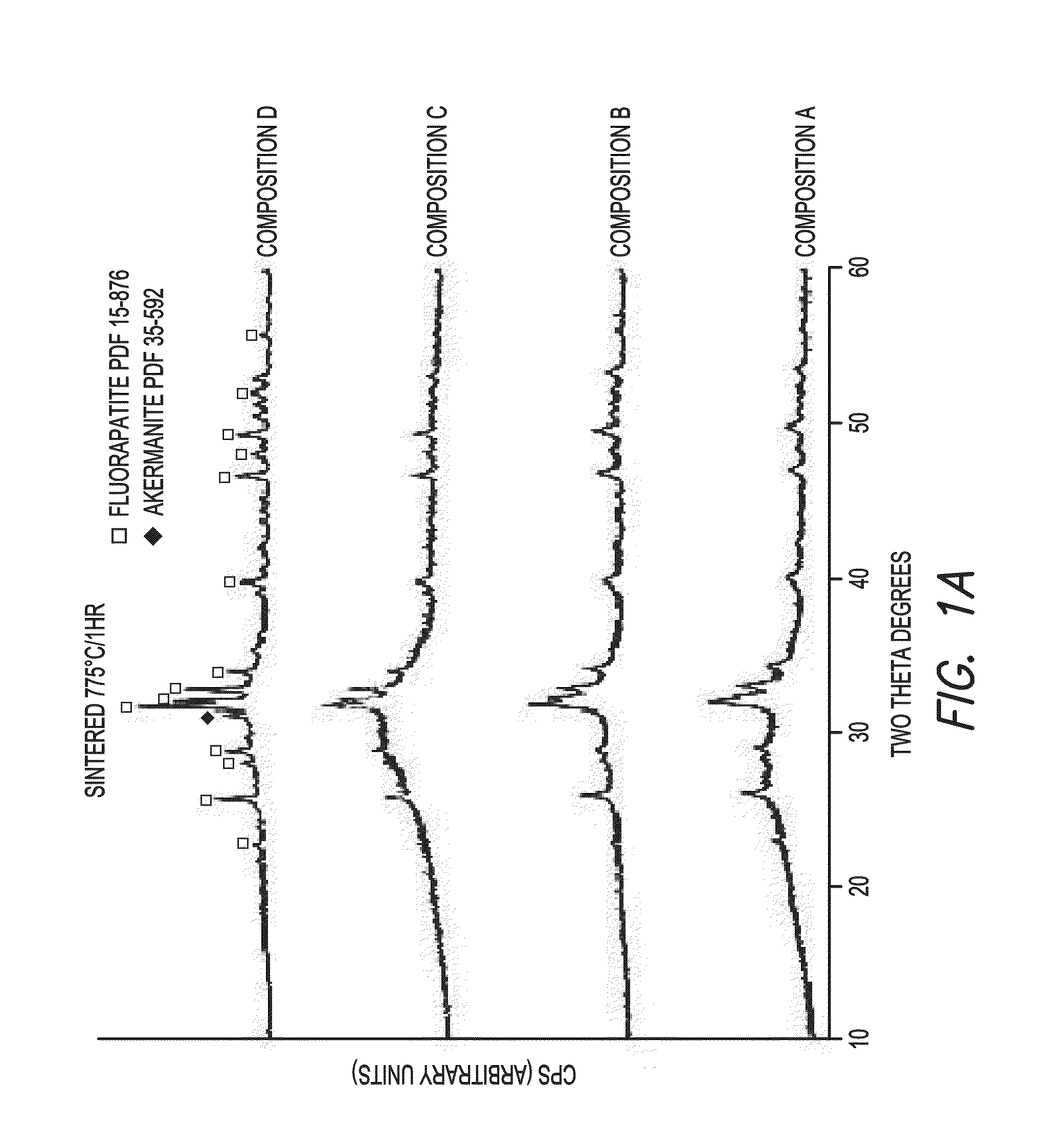
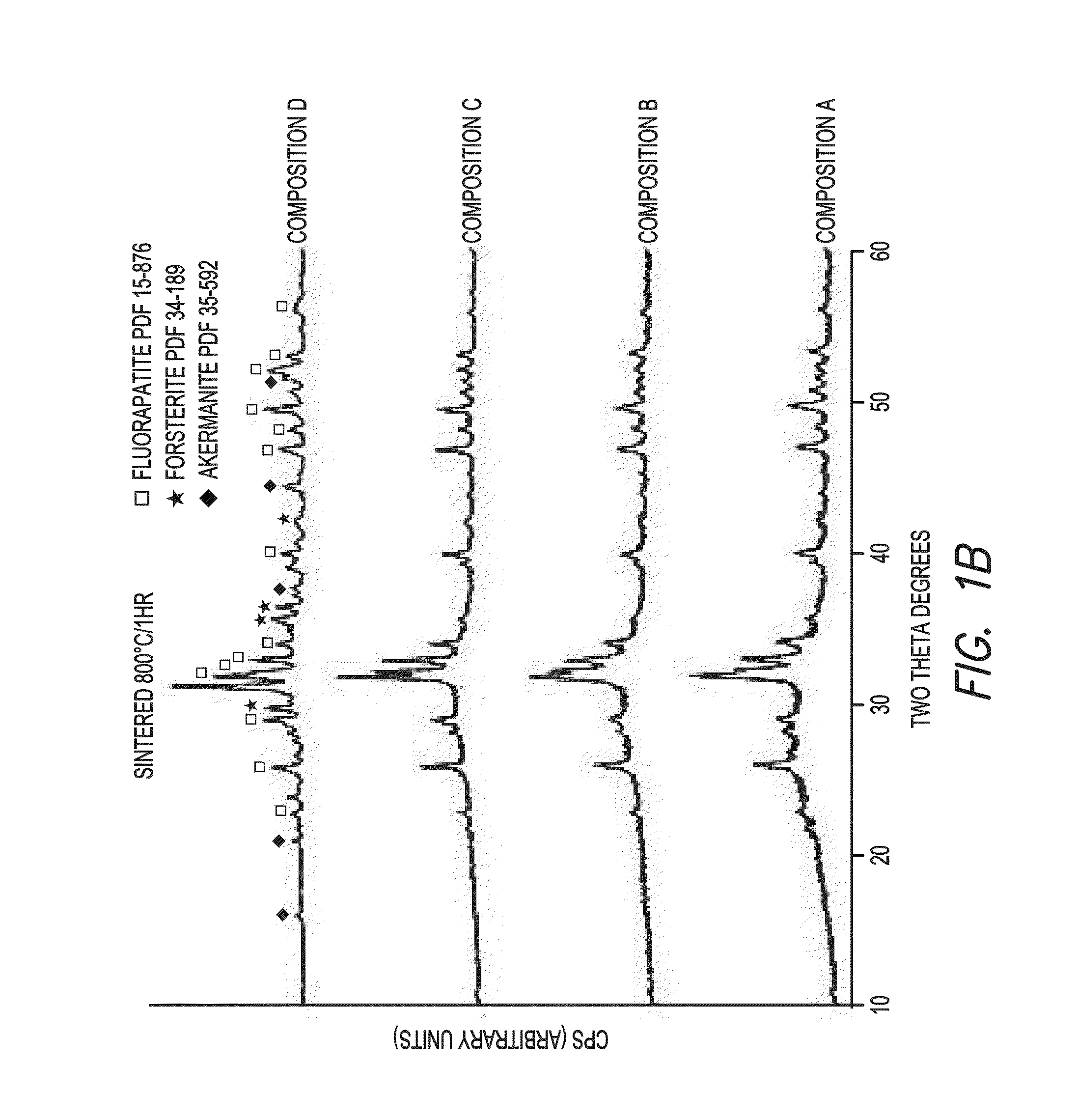
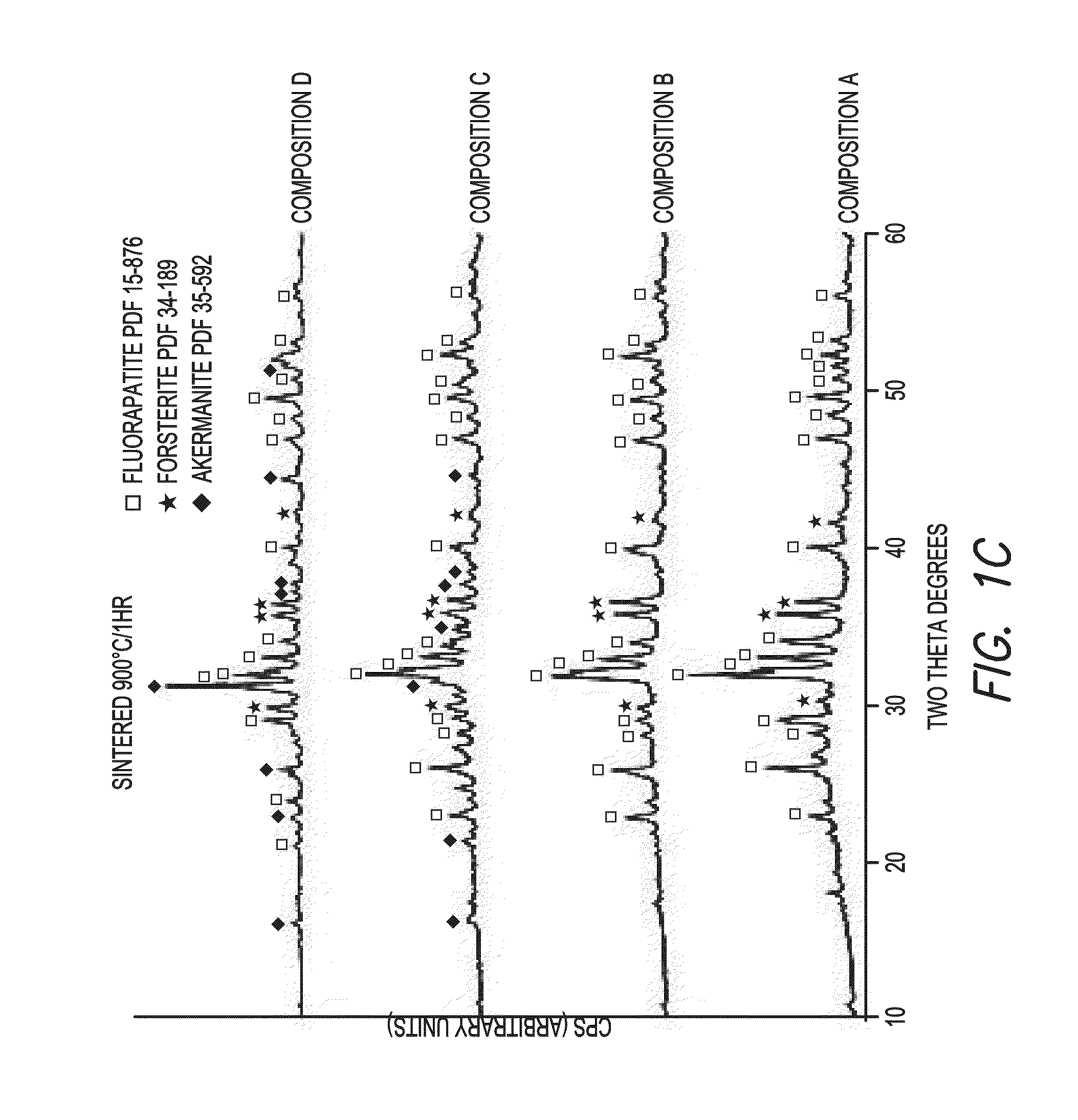
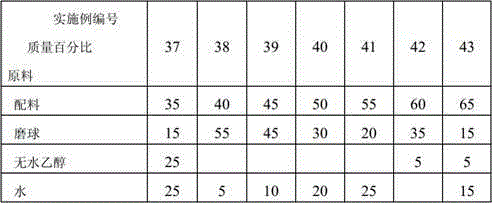
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Fluorapatite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorapatite, often with the alternate spelling of fluoroapatite, is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca₅(PO₄)₃F (calcium fluorophosphate). Fluorapatite is a hard crystalline solid. Although samples can have various color (green, brown, blue, yellow, violet, or colorless), the pure mineral is colorless as expected for a material lacking transition metals. Along with hydroxylapatite, it can be a component of tooth enamel.
Porous bioceramics for bone scaffold and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050113934A1High of bioactivityHigh propertiesBone implantPretreated surfacesOsseointegrationBiocompatibility Testing
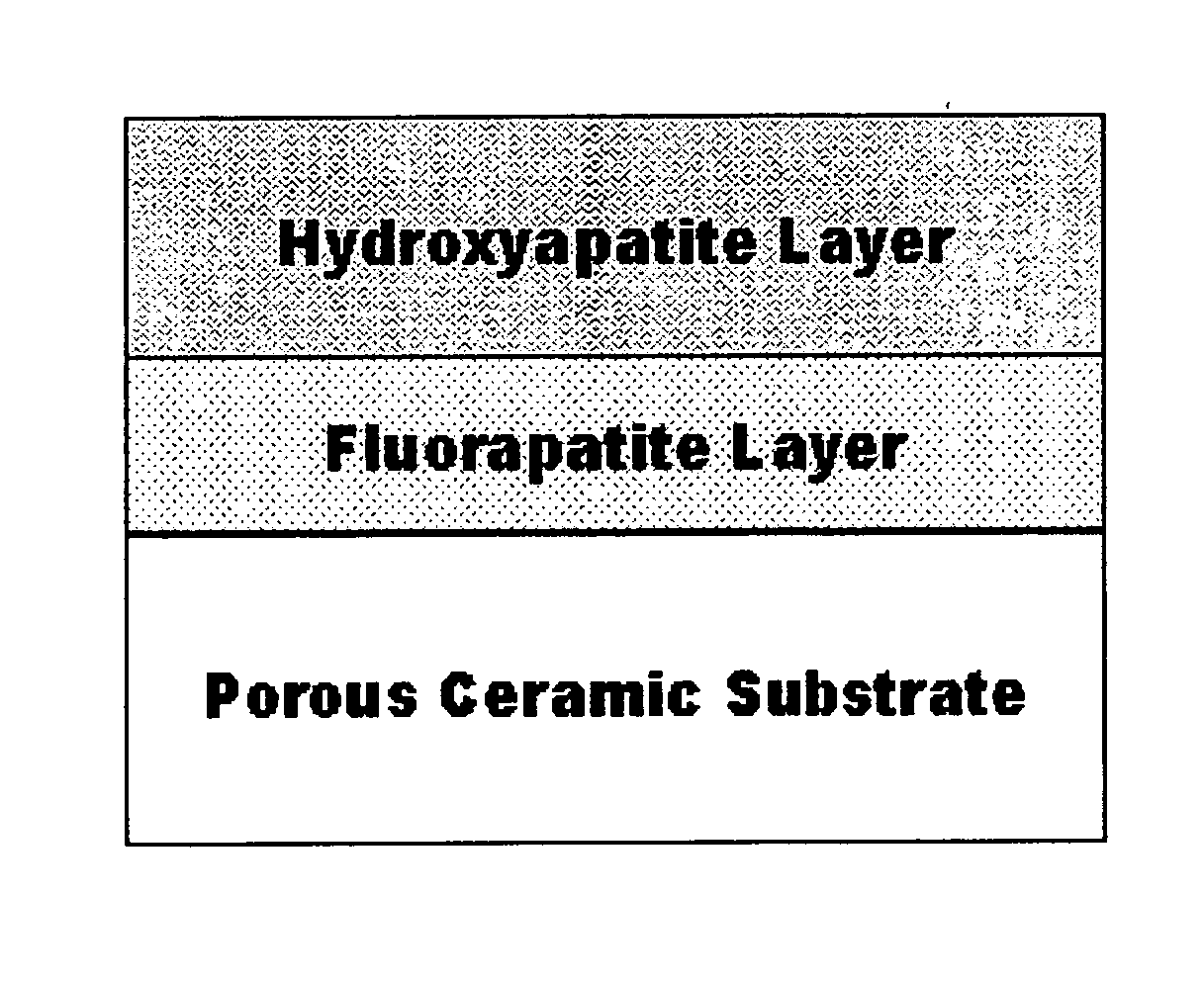
The present invention provides a porous bioceramics for bone scaffold. The porous bioceramics according to the present invention comprises a biocompatible porous ceramic substrate having the property to thermal-decompose hydroxyapatite in contact with it; a fluorapatite (FA) inner layer formed on said porous ceramic substrate; and a hydroxyapatite (HA) outer layer formed on said fluorapatite inner layer. The insertion of FA intermediate layer can prevent the thermal reaction between ZrO2 and HA. Therefore, the present invention can provide the implant material into human body having excellent mechanical properties of zirconia as well as the biocompatibility, bioaffinity and bioactivity of HA. The present invention can also provide the implant material to promote osteoconduction and osteointegration in human body.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
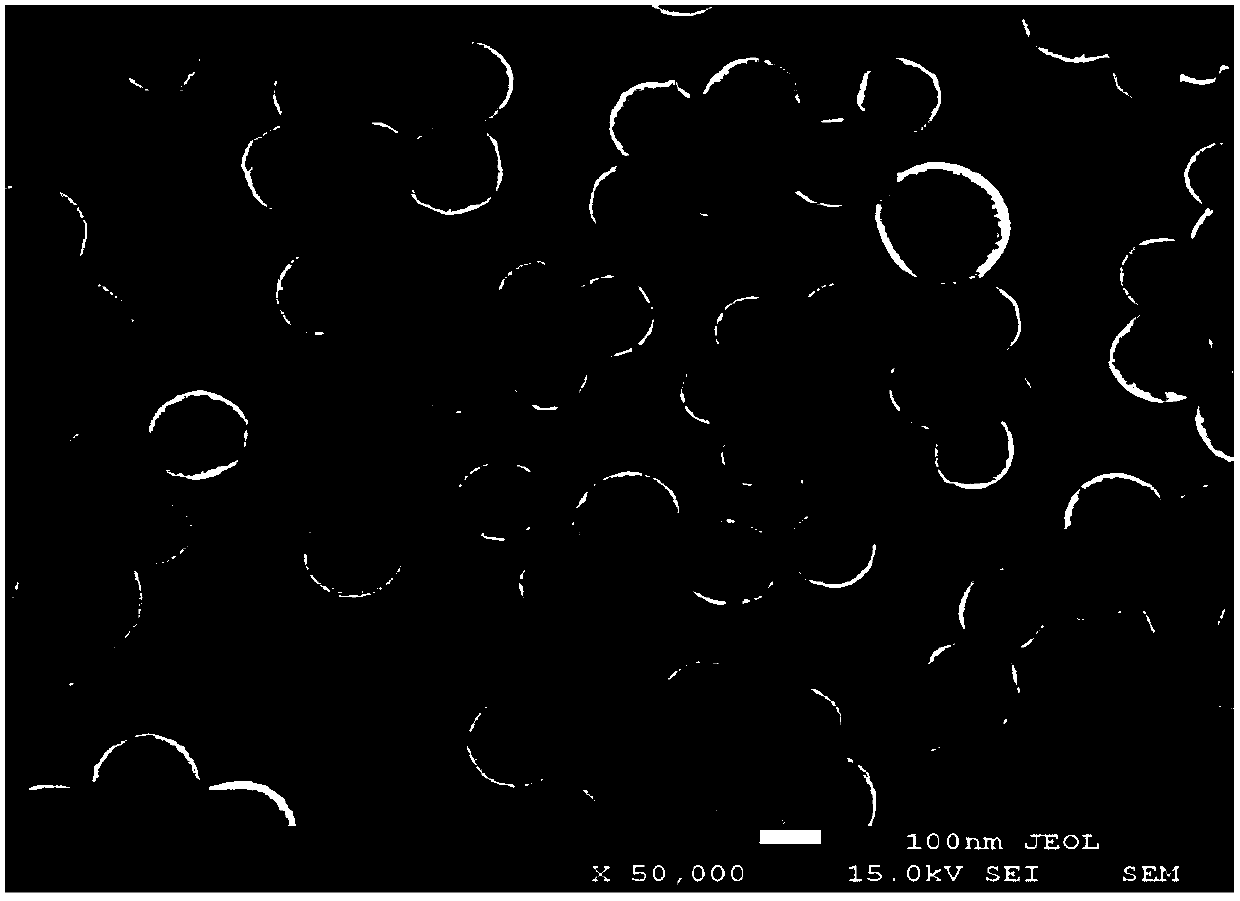
Tooth fluoridating and remineralizing compositions and methods, based on nanoaggregate formation
ActiveUS20080292565A1Well formedAvoid repairsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNano compositesWhitening Agents
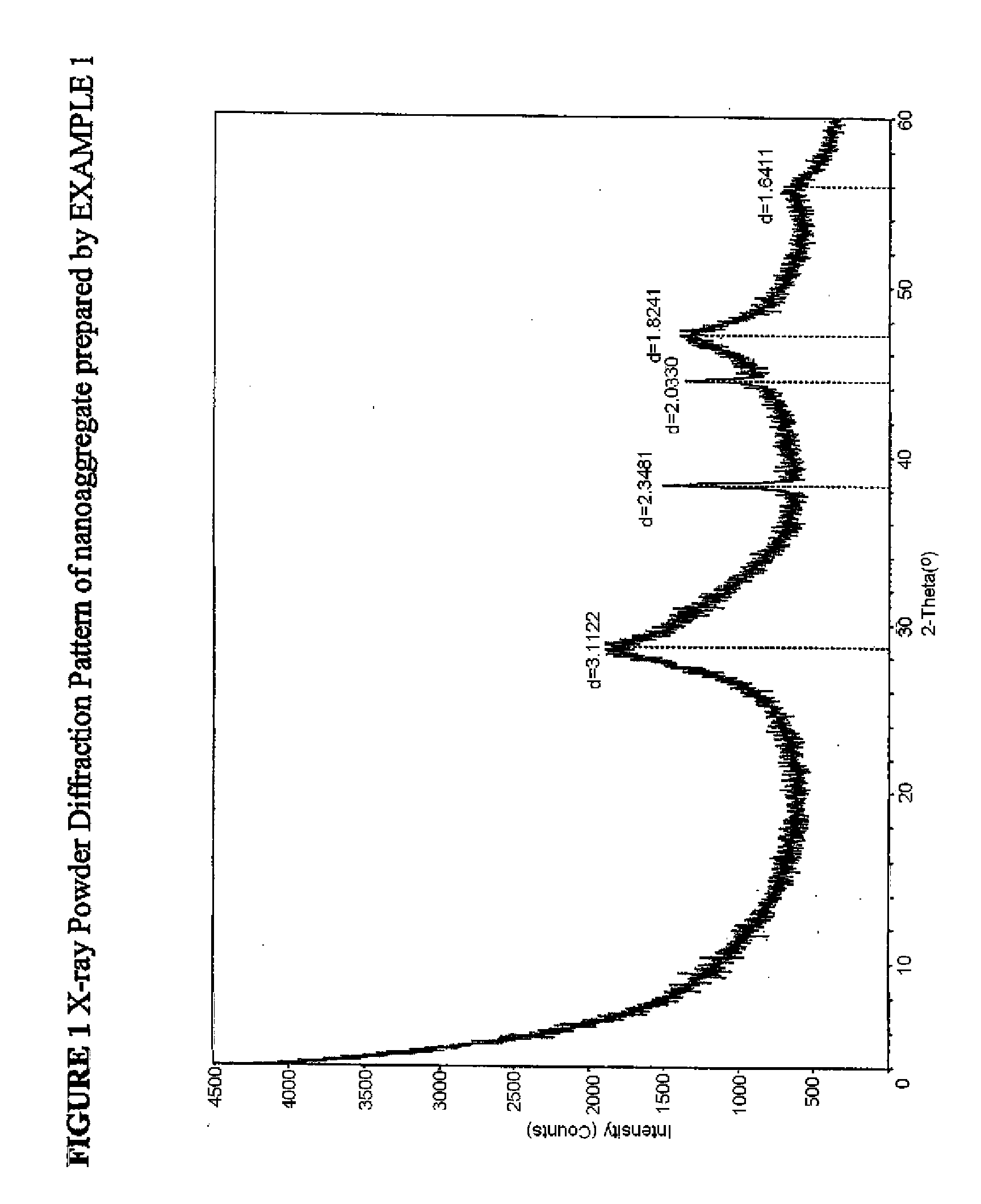
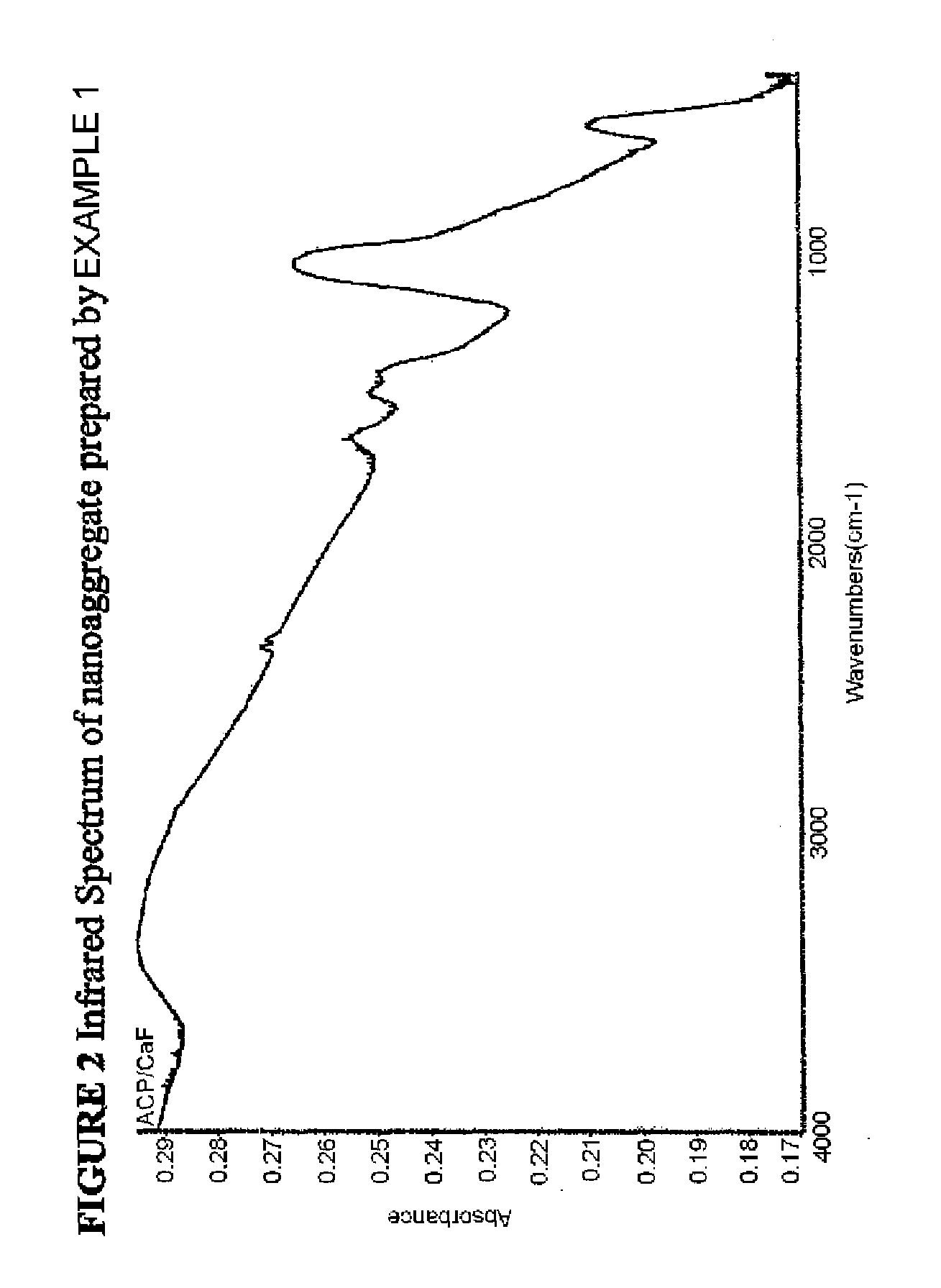
Compositions and methods for forming, in an aqueous environment, a nanoaggregate of calcium fluoride and amorphous calcium phosphate-containing compound, such as amorphous calcium phosphate fluoride or amorphous calcium carbonate phosphate fluoride are described. The nanoaggregate (or nanocomposite) can release calcium, phosphate, and fluoride, and ultimately convert to the tooth mineral, fluorapatite. One method for forming such a nanoaggregate involves applying a non-aqueous (e.g., varnish-based) composition (e.g., a suspension), containing solid particles of water soluble salts of calcium, phosphate, and fluoride, to the aqueous environment of the mouth. This results in rapid solubilization of the salts, precipitation of the nanoaggregate, and tooth remineralization. Tooth fluoridation and remineralization may also be carried out by applying to the tooth a non-aqueous carrier containing the nanoaggregate. Whitening agents can also be added to these compositions and methods.
Owner:ADA FOUND
Glass ceramic scaffolds with complex topography
InactiveUS20110081396A1Improve propertiesHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologyBone implantCrystallinityUltimate tensile strength
A bioactive and bioresorbable scaffold including a glass-ceramic material including fluoroapatite and hydroxyapatite doped with about 1-5 wt.% niobium oxide that is shaped into a scaffold is described. The glass-ceramic material has high crystallinity and a complex topography which provide it with greater structural strength and bioresorbability. Methods of preparing the bioactive and bioresorbable scaffold and methods of using the scaffold for musculoskeletal engineering are also provided.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Polyether-ether-ketone composite material containing fluorapatite and titanium dioxide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101879332AReinforcement and toughnessEnhanced mechanical compatibilityProsthesisCalcium fluorophosphateMechanical property
The invention discloses a polyether-ether-ketone composite material containing fluorapatite and titanium dioxide and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of biomedical composite materials. The composite material is a bone restoration material prepared from a polyether-ether-ketone composite material with enhanced fluorapatite and titanium dioxide and is prepared by blending fluorapatite, titanium dioxide and polyether-ether-ketone in a fusion way, wherein the fluorapatite and the titanium dioxide are respectively 10-30 percent of the total weight of the composite material, and the balance is the components of the polyether-ether-ketone. The composite material prepared from the fluorapatite, the titanium dioxide and the polyether-ether-ketone in the invention realizes good strength and toughness and consistent elastic modulus with a human bone, has bone-substitute material with bioactivity, and can overcome the defect that the traditional metal and ceramic bone-substitute material has the mechanical property which is not matched with the human bone.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Tinct adjustable stomatic bioactive divitrified glass and its prepn
InactiveCN1349944AHigh strengthGood biocompatibilityArtificial teethLeuciteUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to an oral cavity bio-active nucleated glass with adjustable colour and its rpeparation method. Its preparation method includes the following steps: firstly, uniformly mixing raw materials according to a certain mixing ratio, melting for 3 hr. at 1400-1550 deg.C, pouring the molten glass inti mould and forming to obtain blank, cooling to room temp., heating glass blank and heat-insulating to make glass nucleate, continuously heating and heat-insulating to make glass crystallize to obtain the bio-active nucteated glass using apatite and fluorophlogopite as main crystal phase. Said nucleated glass uses TiO2 / ZrO2 as crystal nucleus agent, and contains a certain crystal phase formed from leucite and calc-silicate stone to raise its strength, and said product possesses good bio-compatibility, machinability and beautifulness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Process for upgrading raw phosphate ore
InactiveUS20040067187A1High-purity phosphorusIncrease productionPhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesO-Phosphoric AcidSludge
Fluorapatite mineral deposits in middle Tennessee were formerly beneficiated by washing out most of the clay, but some of the clay remained in the beneficiated ore. The ore was agglomerated by heating to temperatures high enough to melt clay remaining in the ore thereby obtaining a fluid phase for agglomeration in rotary kilns. The agglomerated phosphatic material was mixed with silica rock and metallurgical coke and the mixture was smelted in electric furnaces to produce elemental phosphorus. The feedstock had a percent P O in the phosphate-plus-silica of about 25.7. Phosphate ore deposits amenable tp beneficiation by washing were used up. Furthermore, mud ponds containing the washed-out clay polluted ground water and water courses. An endeavor was made to smelt feedstock prepared from raw phosphate ore but the percent P O in the feedstock was too low for smelting. The present invention is a process for upgrading feedstock prepared from raw phosphate ore. Phosphorus sludge is burned to produce impure phosphoric acid and the acid is combined with beneficiated phosphate ore to prepare anhydrous monocalcium phosphate. Feedstock prepared from raw phosphate ore is blended with anhydrous monocalcium phosphate to upgrade the feedstock.
Owner:JAMES C BARBER & ASSOCS
Coated magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104623739APromote growthSatisfy the requirement of strong fixed timeSurgeryMetallic material coating processesElemental compositionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses coated magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws. The magnesium alloy consists of Mg of which the purity is more than 99.99wt%, Zn and adding elements, wherein the adding elements refer to one, two or three in Zr, Sr, Ca and Ag; and the magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 3 percent of Zn, 0.2-1.0 percent of Zr, 0-1.0 percent of Sr, 0-1.0 percent of Ca, 0.0-1.0 percent of Ag and the balance of Mg. The coated magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws have the advantages that after being subjected to comprehensive treatment, the magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws have reasonable degradation rate, capacity of promoting new bone growth in the living body and high biocompatibility; particularly, after the bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws are treated by the mixed aqueous solution of hydrofluoric acid and calcium and phosphorus compounds, the corrosion rate can be regulated by virtue of the thickness of the surface fluorides and fluorapatite layer, and the requirement on rigid fixation time of the bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws before internal fracture fixation within 3 months can be met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method of producing fluoroapatite, fluoroapatite, and adsorption apparatus
ActiveUS20090060814A1Improve acid resistanceLarge specific surface areaPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesHydrogen fluorideO-Phosphoric Acid
A method of producing fluoroapatite by using a calcium-based compound containing calcium, hydrogen fluoride and phosphoric acid is provided. The method can be produced fluoroapatite having improved acid resistance by reducing an amount of an impurity derived from a raw material to a low or very low level, and ability capable of separating a large amount of a protein due to a large specific surface area thereof. Further, fluoroapatite having high acid resistance and a large specific surface area is also provided. Furthermore, an adsorption apparatus using such fluoroapatite is also provided.
Owner:HOYA CORP
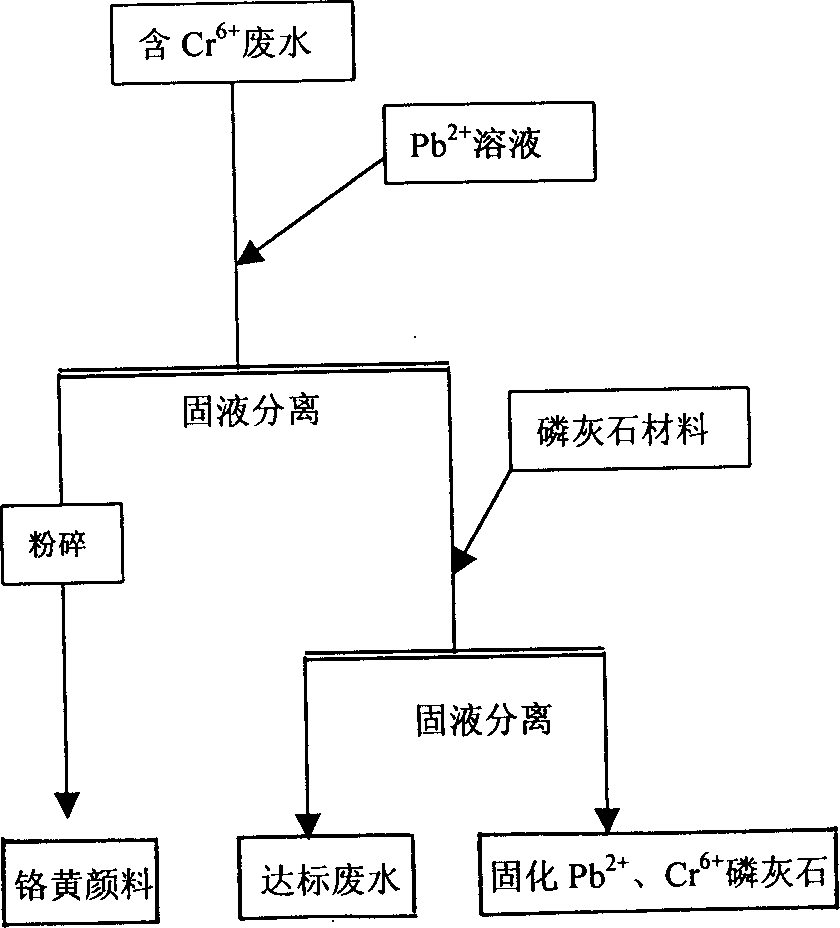
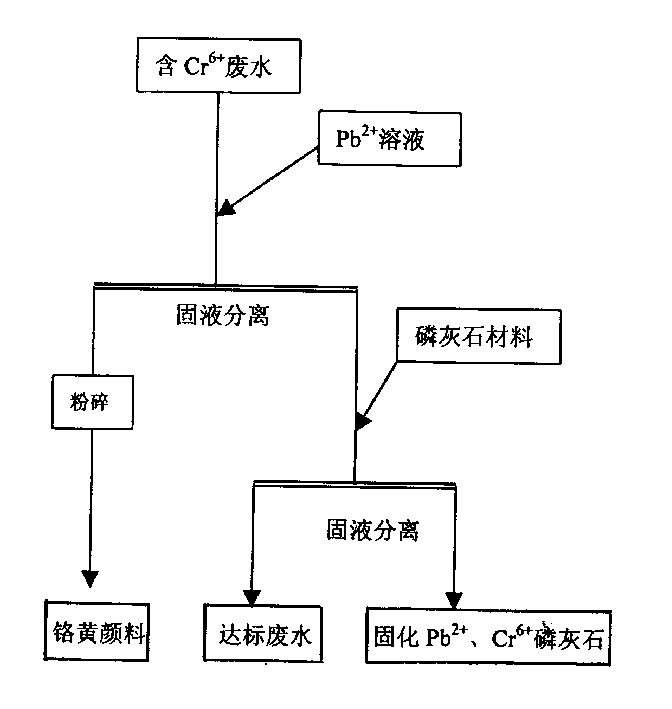
Process for recovering chrome yellow from chrome containing sewage
InactiveCN1373094AAvoid secondary pollutionOptimal treatment processPigmenting treatmentChromates/bichromatesWastewaterSewage
A process for recovering chrome yellow from the Cr-containing waste water and removing metallic ions includes adding the solution containing Pb (2+) ions to said waste water to generate PbCrO4 precipitate and reduce the Cr (6+) concentration to lower than 0.5 mg / L, solid-liquid separation, drying the solid, cooling, pulverizing to obtain chrome yellow powder, adding francolite to the liquid to adsorb Cr (6+) and Pb (2+) ions, solid-liquid separation, and draining the liquid.
Owner:WUHAN CHEM COLLEGE
Porous bioceramics for bone scaffold and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7416564B2High of bioactivityHigh propertiesBone implantPretreated surfacesHuman bodyOsseointegration
The present invention provides a porous bioceramics for bone scaffold. The porous bioceramics according to the present invention comprises a biocompatible porous ceramic substrate having the property to thermal-decompose hydroxyapatite in contact with it; a fluorapatite (FA) inner layer formed on said porous ceramic substrate; and a hydroxyapatite (HA) outer layer formed on said fluorapatite inner layer. The insertion of FA intermediate layer can prevent the thermal reaction between ZrO2 and HA. Therefore, the present invention can provide the implant material into human body having excellent mechanical properties of zirconia as well as the biocompatibility, bioaffinity and bioactivity of HA. The present invention can also provide the implant material to promote osteoconduction and osteointegration in human body.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Polyether-ether-ketone composite material containing fluorine phosphorus lime, preparation method and usage thereof
InactiveCN101899193AEnsure initial fixationGood biocompatibilityProsthesisBinding forceDrug biological activity
The present invention provides a polyether-ether-ketone composite material with fluorine phosphorus lime, a preparation method and usage thereof. The preparation method of the composite material comprises the following steps of: melting and blending the raw material fluorine phosphorus lime and the polyether ether ketone, and then cooling, wherein the dosage of the fluorine phosphorus lime takes 10-50wt% of the total weight of the raw material, and the dosage of the polyether ether ketone takes 50-90% of the total weight of the raw material. The composite material is featured by good mechanical compatibility, reducing stress resistance, greatly increasing binding force between interfaces, reducing shearing stress, reducing tender movement and vertical displacement, and guaranteeing initial fixing of the composite material. Besides, the composite material has the advantages of good biological compatibility and biological activity, capable of promoting bone tissue growth, realizing biological fixing and being used as substitute of metal or ceramic bone substitute material.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of manufacturing implant and method of manufacturing artificial dental root
ActiveUS20100243429A1Low biocompatibilitySophisticated crystal structureDental implantsTeeth fillingBiocompatibility TestingHardness
A method for producing an implant whose surface is roughened by the sandblast method using shot material containing fluoroapatite. Fluoroapatite, compared to hydroxyapatite, has poor biocompatibility, but is superior in hardness. It also has a property of being dissolved in acid. As a result, by the sandblast method using shot material containing fluoroapatite, the surface roughening is performed quite effectively, and shot materials remained on the surface can easily be removed by acid.
Owner:YAMAHACHI DENTAL MFG
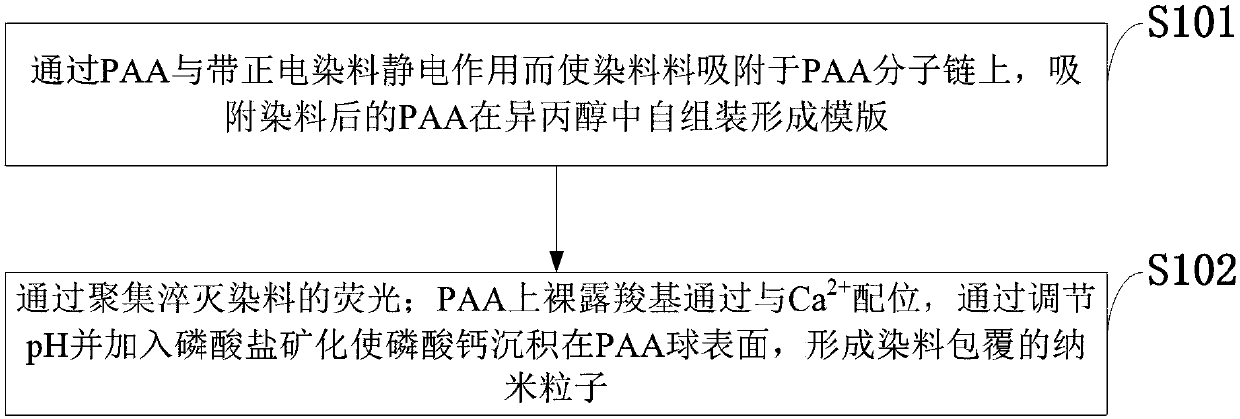
PH (potential of hydrogen)-responsive type ultra-sensitive nanometer fluorescent probe and method for preparing same
InactiveCN107638572AAccurate imagingEnables ultra-sensitive detectionPowder deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsUltra sensitiveMicro environment
The invention belongs to the field of molecular imaging technologies, and discloses a pH (potential of hydrogen)-responsive type ultra-sensitive nanometer fluorescent probe and a method for preparingthe same. The pH-responsive type ultra-sensitive nanometer fluorescent probe comprises pH-responsive matrix materials and fluorescent organic small-molecule dye. The pH-responsive matrix materials comprise calcium phosphate, hydroxy calcium phosphate, fluorapatite, calcium carbonate and ZIF series; the fluorescent organic small-molecule dye is positively charged dye or negatively charged dye. Themethod includes coating the positively charged dye with the negatively charged matrix materials; coating the negatively charged dye with the negatively charged matrix materials; coating the negativelycharged dye with the positively charged matrix materials. The pH-responsive type ultra-sensitive nanometer fluorescent probe and the method have the advantages that the fluorescent imaging sensitivity and specificity can be greatly improved as compared with the traditional small-molecule fluorescent dye, and response of tumor micro-environments can be detected in an ultra-sensitive manner; the pH-responsive type ultra-sensitive nanometer fluorescent probe which is a specific responsive probe prepared for unique properties of the tumor micro-environments is high in targeting, few in backgroundsignals and high in signal-to-noise ratio, small tumor can be detected in an ultra-sensitive manner, and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Phosphosilicate Glass Ceramic
ActiveUS20110021336A1Reduction factorLow pressing temperatureOther chemical processesGlass drawing apparatusNatural toothOptical property
A phosphosilicate glass ceramic with nanoscale fluoroapatite and leucite crystals. The glass ceramic is very similar to natural tooth material in terms of its optical properties. The glass ceramic has a low linear thermal expansion coefficient and a low pressing temperature and is therefore particularly suitable for pressing on metal alloys to produce dental restoration.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Low-temperature-resistant high-voltage power transmission porcelain insulator and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a low-temperature-resistant high-voltage power transmission porcelain insulator and a preparation method thereof. The porcelain insulator comprises a porcelain part of the porcelain insulator. The porcelain part of the porcelain insulator comprises the following raw materials: aluminum oxide, calcined bauxite, potassium feldspar, a zirconium dioxide / kaolin composite material, fluorapatite, cerium oxide / lanthanum oxide-coated nano-boron nitride and a sintering aid. A reinforcing layer and a self-cleaning layer are sequentially arranged outside the porcelain part of the porcelain insulator. A coating for the reinforcing layer is prepared by mixing the following raw materials: nano-aluminum oxide sol, a cerium oxide / SiO2-coated graphene oxide composite material, aluminum dihydrogen phosphate, nano-attapulgite and nano-boron nitride. A coating for the self-cleaning layer is prepared by mixing the following raw materials: lanthanum / cerium co-doped titanium dioxide sol, nano-aluminum oxide sol, acicular wollastonite and tetrapod-like zinc oxide whiskers. The porcelain insulator prepared in the invention has good weatherability, is suitable for long-term use in extremely cold areas, and has strong anti-pollution performance and excellent mechanical properties.
Owner:湖南兴诚电瓷电器有限公司
Fluoroapatite dried particles and adsorption apparatus
InactiveUS20090087369A1Avoid separationImprove acid resistancePhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesHydrogen fluorideHydroxy compound
Fluoroapatite dried particles are obtained by reacting hydroxyapatite primary particles having hydroxyl groups and hydrogen fluoride molecules having fluorine atoms so that at least one of hydroxyl groups of hydroxyapatite primary particles are substituted by the fluorine atoms of the hydrogen fluoride molecules. The fluoroapatite dried particles can exhibit superior acid resistance. Further, an adsorption apparatus using such fluoroapatite dried particles is provided.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Cutable bioactive devitrified glass and its prepn
The invention relates to a machinable bio-active nucleated glass and its preparation method. Said preparation method includes the following steps: firstly, uniformly mixing raw materials according toa certain proportion, melting them at 1400-1550 deg.C for 2-4 hr., pouring the molten glass liquor into mould and forming to make blank, cooling to room temp., heating and heat-insulating to make glass nucleate, continuously heating and heat-insulating to make gas crystallize to obtain biological nucleated glass using apatite and fluorophlogopite as main crystal phase. Said product also contains a certain reinforced phase formed fronm leucite and wollastonite, and possesses good biological compatibility, machinability and beautifulness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Anticorrosive rubber material
The invention discloses an anticorrosive rubber material composed of the raw materials of, by weight, 0.2-0.6 parts of 8-10% sulfuric acid, 26-30 parts of melamine, 5-8 parts of a 37% formaldehyde solution, 7-10 parts of urea, 6-10 parts of microcrystalline cellulose, 1-1.2 parts of isopropanol, 2-3 parts of sulfur, 3-4 parts of maleic anhydride, 210-230 parts of neoprene S40V, 4-6 parts of methylparaben, 0.6-1 parts of triterpenoid saponin, 2-4 parts of calcium propionate, 2-3 parts of sodium diacetate, 1-3 parts of N-methylpyrrolidone, 4-5 parts of nano-grade calcium phosphate, 0.8-1 part of sodium sorbate, 40-54 parts of fluorapatite, and 2-4 parts of an anti-aging agent RD. according to the invention, with the crosslinking effect of maleic anhydride, microcrystalline cellulose forms a closer network structure in melamine resin formed by melamine, urea and formaldehyde, such that resin viscosity and tensile deformation resistance are well improved, and certain reinforcement and tackification effects are performed in the rubber material. Rubber flexure cracking resistance, hot air aging resistance and stability are improved. With the added anticorrosive dispersion liquid, the anticorrosive property of the rubber product can be effectively improved, and the service life of the rubber material can be prolonged.
Owner:FUYANG ANGU BOILER PRESSURE VESSEL MFG
Coating of dental prosthetic surfaces comprising distinct layer of synthetic hydroxyapatite
InactiveCN107530145AReduce the risk of peripheral inflammationDental implantsBone implantTooth lossHydroxylapatite
The invention relates to prosthetic moulded parts which comprise, at least in regions on the surface thereof, at least one layer of biomimetic apatite selected from fluorapatite, hydroxylapatite or mixtures thereof, wherein the surface of the moulded parts comprises, at least in said region, micromechanical anchoring locations for improving the mechanical binding of apatite on the surface. The invention also relates to moulded parts for use in dental prosthetic provision in the event of tooth loss, in particular, for cellular attachment of cells on prosthetic moulded parts. The invention further relates to the method for producing the prosthetic moulded parts.
Owner:古萨有限公司
Fluorapatite coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101856511AImprove biological activityGood biocompatibilityCoatingsGel preparationBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a fluorapatite coating which is prepared by ion coated gel preparation, shielding layer gel preparation and biomineralization process. The fluorapatite coating has higher bioactivity, biocompatibility and synostosis capability, and effectively overcomes the defects of the existing implanted materials.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of producing fluoroapatite, fluoroapatite, and adsortion apparatus
InactiveUS20100130353A1Improve acid resistancePhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesOther chemical processesSlurryImpurity
A method of producing a fluoroapatite is provided. The method comprises preparing a slurry containing a hydroxyapatite which has at least one hydroxyl group, preparing a hydrogen fluoride-containing solution containing a hydrogen fluoride, mixing the hydrogen fluoride-containing solution with the slurry to obtain a mixture to thereby adjust a pH of the mixture in the range of 2.5 to 5, and reacting the hydroxyapatite with the hydrogen fluoride in the mixture in a state that the pH of the mixture is adjusted within the above range to thereby obtain the fluoroapatite by substituting the at least one hydroxyl group of the hydroxyapatite with fluorine atom of the hydrogen fluoride. The method can produce the fluoroapatite having improved acid resistance by reducing an impurity, such as ammonia, derived from a raw material to a low or very low level. Further, a fluoroapatite having high acid resistance is also provided. Furthermore, an adsorption apparatus using such a fluoroapatite is provided.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorapatite glass-ceramics
InactiveUS20140271565A1Increase depositionPromote growthBiocideSurgical adhesivesMedicineGlass-ceramic
The present invention provides a highly-sintered fluorapatite glass-ceramic comprising a high Ca / Al or Sr / Al mole-ratio, that possesses a microstructure that induces apatite / bone deposition.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Method of producing fluoroapatite, fluoroapatite, and adsorption apparatus
ActiveUS20090148376A1High crystallinityImprove acid resistancePhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesFluoride preparationHydrogen fluorideSlurry
A method of producing a fluoroapatite is provided. The method comprises preparing a slurry containing a hydroxyapatite which has at least one hydroxyl group, preparing a hydrogen fluoride-containing solution containing a hydrogen fluoride, mixing the hydrogen fluoride-containing solution with the slurry to obtain a mixture to thereby adjust a pH of the mixture in the range of 2.5 to 5, and reacting the hydroxyapatite with the hydrogen fluoride in the mixture in a state that the pH of the mixture is adjusted within the above range to thereby obtain the fluoroapatite by substituting the at least one hydroxyl group of the hydroxyapatite with fluorine atom of the hydrogen fluoride. The method can produce the fluoroapatite having improved acid resistance by reducing an impurity, such as ammonia, derived from a raw material to a low or very low level. Further, a fluoroapatite having high acid resistance is also provided. Furthermore, an adsorption apparatus using such a fluoroapatite is provided.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Chemical stability evaluating method of fluorapatite ceramic solidification body
ActiveCN105004681AEvaluation of Chemical StabilityChoose reasonableAnalysis by thermal excitationColor/spectral properties measurementsDeep geological repositoryOperability
The invention discloses a chemical stability evaluating method of a fluorapatite ceramic solidification body. The chemical stability evaluating method is characterized by comprising the steps that the fluorapatite ceramic solidification body with simulation time actinide nuclide is prepared; a hydrothermal reaction kettle with an outer shell made of stainless steel and a liner made of polytetrafluoroethylene is adopted as a leaching container; deionized water is adopted as a leaching agent, and the pH value is adjusted to 5-9; leaching is carried out at the temperature of 100 DEG C to 200 DEG C and the pressure of 0.101 MPa to 1.554 MPa, the conductivity of the leaching agent is tested, the concentration of ions in the leaching liquid is analyzed, the normalized leaching rate of the simulation time actinide nuclide is calculated, the phase changes before and after leaching of the solidification body are analyzed, and the chemical stability of the fluorapatite ceramic solidification body under the coupling action of heat, water, force and chemistry is evaluated. The method is simple and practical, high in operability, reasonable and visual in evaluation index, and accurate and reliable in evaluation result, and effective experiment bases and technical supports can be provided for evaluating the long-term stability and safety of the high-level waste solidification body in the deep geological disposal environment.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Radioactive waste organic solvent tributyl phosphate pyrolyzing furnace ash treatment method
ActiveCN109824355ARealize local materialsIncrease in sizeRadioactive decontaminationRadioactive wasteSolvent
The invention discloses a radioactive waste organic solvent tributyl phosphate pyrolyzing furnace ash treatment method which is characterized in that calcium pyrophosphate, calcium hydroxide, uranyl nitrate and calcium fluoride serve as raw materials and are ball-milled and dried to prepare powder, the powder is pressed on a tablet press and a cold isostatic press and pretreated to prepare a greenbody, and the green body is sintered by a flash burning technology to prepare a fluorapatite ceramic solidified body. The flash burning technology is applied to treatment of radioactive waste organicsolvent tributyl phosphate pyrolyzing furnace ash, and the prepared fluorapatite ceramic solidified body has the advantages of high mineralogical phase purity and compactness, low leaching rate and the like. Compared with existing other radioactive waste organic solvent tributyl phosphate pyrolyzing furnace ash treatment methods, the flash burning treatment method has the advantages of simple equipment, time-saving property, high efficiency, high technical controllability, economical efficiency, energy conservation, high practicability and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fluorophlogite/fluoroapatite glass ceramics and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to fluorophlogite / fluoroapatite glass ceramics and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of glass ceramics. The method for preparing the fluorophlogite / fluoroapatite glass ceramics includes the steps of evenly mixing fluorophlogite and fluoroapatite to obtain a mixture; hot-pressing the mixture at 600-900 DEG C for 60-120 min, cooling with a furnace,and obtaining the fluorophlogite / fluoroapatite glass ceramics. According to the preparation method, the sintering temperature is reduced to be within 900 DEG C, the ultra-high temperature process ofa traditional casting method is omitted, the controllability of material properties is effectively ensured, the requirements on production devices are significantly reduced, and the production processis simplified. The preparation method greatly reduces the manufacturing difficulty, facilitates industrialized production, saves energy, is environmentally friendly and is a very promising fluorophlogite / fluoroapatite glass ceramics preparation method.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of producing fluoroapatite, fluoroapatite, and adsorption apparatus
ActiveUS7740820B2Improve acid resistancePhosphorus oxidesPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesHydrogen fluorideSlurry
A method of producing a fluoroapatite is provided. The method comprises preparing a slurry containing a hydroxyapatite which has at least one hydroxyl group, preparing a hydrogen fluoride-containing solution containing a hydrogen fluoride, mixing the hydrogen fluoride-containing solution with the slurry to obtain a mixture to thereby adjust a pH of the mixture in the range of 2.5 to 5, and reacting the hydroxyapatite with the hydrogen fluoride in the mixture in a state that the pH of the mixture is adjusted within the above range to thereby obtain the fluoroapatite by substituting the at least one hydroxyl group of the hydroxyapatite with fluorine atom of the hydrogen fluoride. The method can produce the fluoroapatite having improved acid resistance by reducing an impurity, such as ammonia, derived from a raw material to a low or very low level. Further, a fluoroapatite having high acid resistance is also provided. Furthermore, an adsorption apparatus using such a fluoroapatite is provided.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Dental repairing and filling composition, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106214496AStable appearance and high color stabilityGood mechanical propertiesImpression capsDentistry preparationsBenzoyl peroxidePhosphorylcholine
The invention discloses a dental repairing and filling composition and the preparation method thereof. The dental repairing and filling composition is prepared from the following components: fluorapatite, calcium phosphite, epoxy acrylate, diethyl(2-oxopropyl)phosphonate, poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, HEDP, tobermorite, hyaluronic acid, polyether-ether-ketone, strontium hydrogen phosphate, bismuth oxide, beryllium oxide, talcum powder, barium sulfate, benzoyl peroxide, methylated beta-cyclodextrin, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, gelatin, phosphorylcholine and boron trifluoride amine. The bending intensity of the dental repairing and filling composition can reach 86-94 MPa, the flexural modulus can reach 9.8-11.3 GPa, the modulus of compression can reach 6.9-7.5 MPa, the mechanical property is excellent, appearance and color stability to strong tea is higher than 4.5, the appearance beauty can be kept enduringly, the comprehensive performance is excellent, and the dental repairing and filling composition is very suitable for serving as a dental repairing and filling material to be popularized and used extensively.
Owner:林春梅
Fluorapatite purification method and method for preparing fluorohydroxyapatite bioceramic thereof
InactiveCN109909058AReduce manufacturing costSimple processWet separationPurification methodsFluorohydroxyapatite
The invention discloses a fluorapatite purification method and a method for preparing a fluorohydroxyapatite bioceramic, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The fluorapatite purification method comprises the following steps that the fluorapatite ore is ground, stirred and slurried, adjusted to pH value, added with an inhibitor and a collector, and inflated for rough selectionto obtain a coarsely selected concentrate and a coarsely selected tailings; the coarsely selected concentrate is slurried, adjusted to pH value, and added with the inhibitor for selection to obtain afluoroapatite concentrate and a selected tailings; and the fluoroapatite concentrate is added with water and slurried and then added with phosphoric acid leaching, solid-liquid separation is carriedout, and the purified fluoroapatite is obtained after drying. The purified fluoroapatite is added with water and stirred to remove the agent, concentrated nitric acid is added to dissolve, NaOH is added to carry out hydroxy reaction, and after calcination and crystallization, the fluorohydroxyapatite bioceramic is obtained. The method obtains the synthesized fluorohydroxyapatite which is used as ahuman body hard tissue substitute material, and the method has the characteristics of being low in production cost, simple in process, easy to operate and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Phosphoric acid desulphurization or/and defluorination method for ammonium biphosphate industrial production
InactiveCN103641093AImprove oxidation capacityEasy to removePhosphatesSulfate radicalsAluminium hydroxide
The invention provides a phosphoric acid desulphurization or / and defluorination method for ammonium biphosphate industrial production. The invention relates to an inorganic chemical technology field. The method comprises: according to an amount of 100-105%, adding calcium oxide or calcium hydrate required by reacting sulfate radical and fluorinion respectively with calcium hydrate, into dilute phosphoric acid obtained in the reaction of sulfuric acid with fluor apatite for the ammonium biphosphate industrial production, stirring at medium and high speed in 800-3000 r / min, filtrating to separate gypsum, calcium fluoride or / and metasilicic acid, magnesium hydroxide, iron hydroxide and aluminium hydroxide, and carrying out desulphurization and / or defluorination. The method is applied in industrial production of an ammonium biphosphate agricultural composite fertilizer.
Owner:耿兆翔
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com