Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1744 results about "Radioactive waste" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radioactive waste is waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is usually a by-product of nuclear power generation and other applications of nuclear fission or nuclear technology, such as research and medicine. Radioactive waste is hazardous to most forms of life and the environment, and is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment.
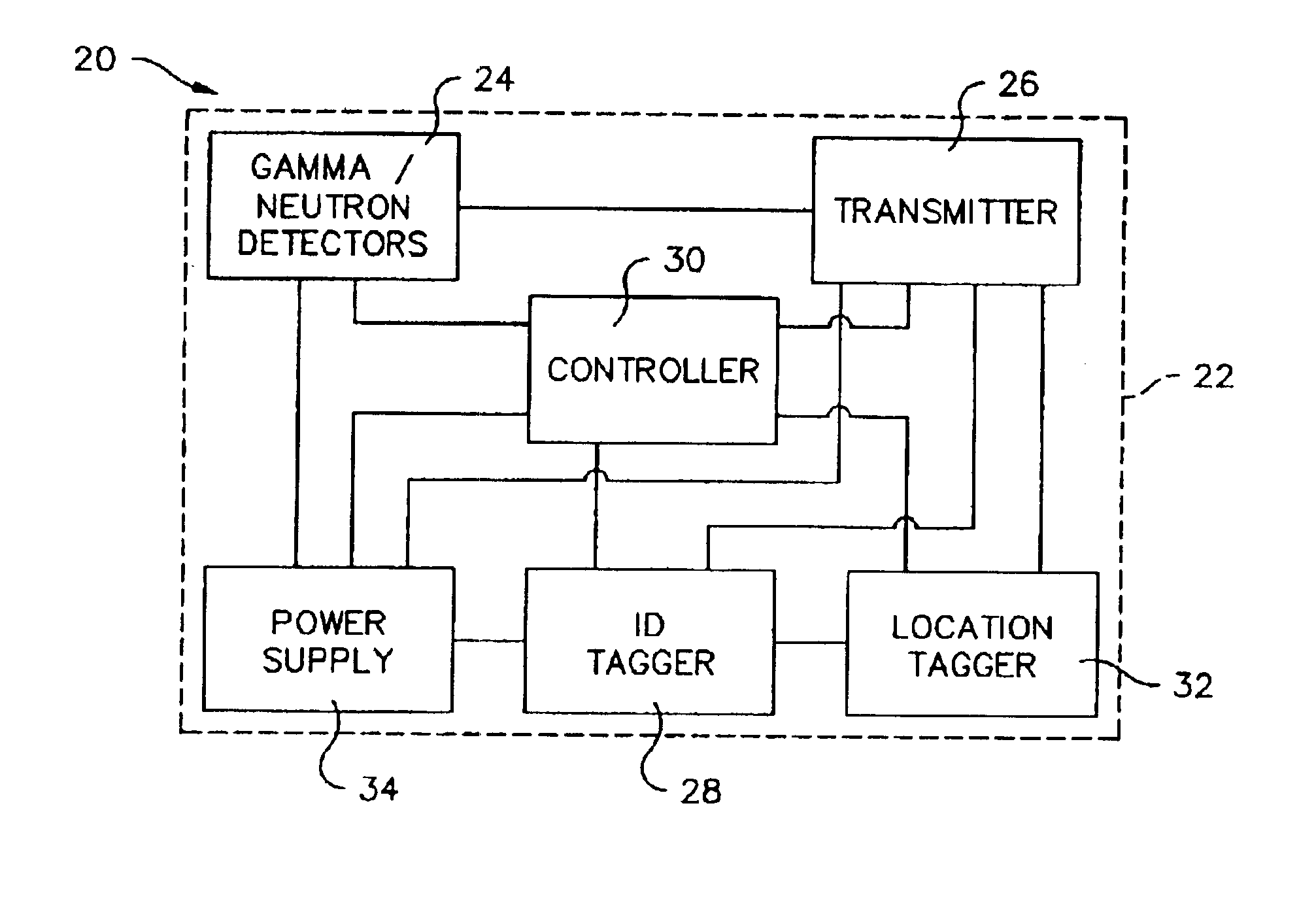
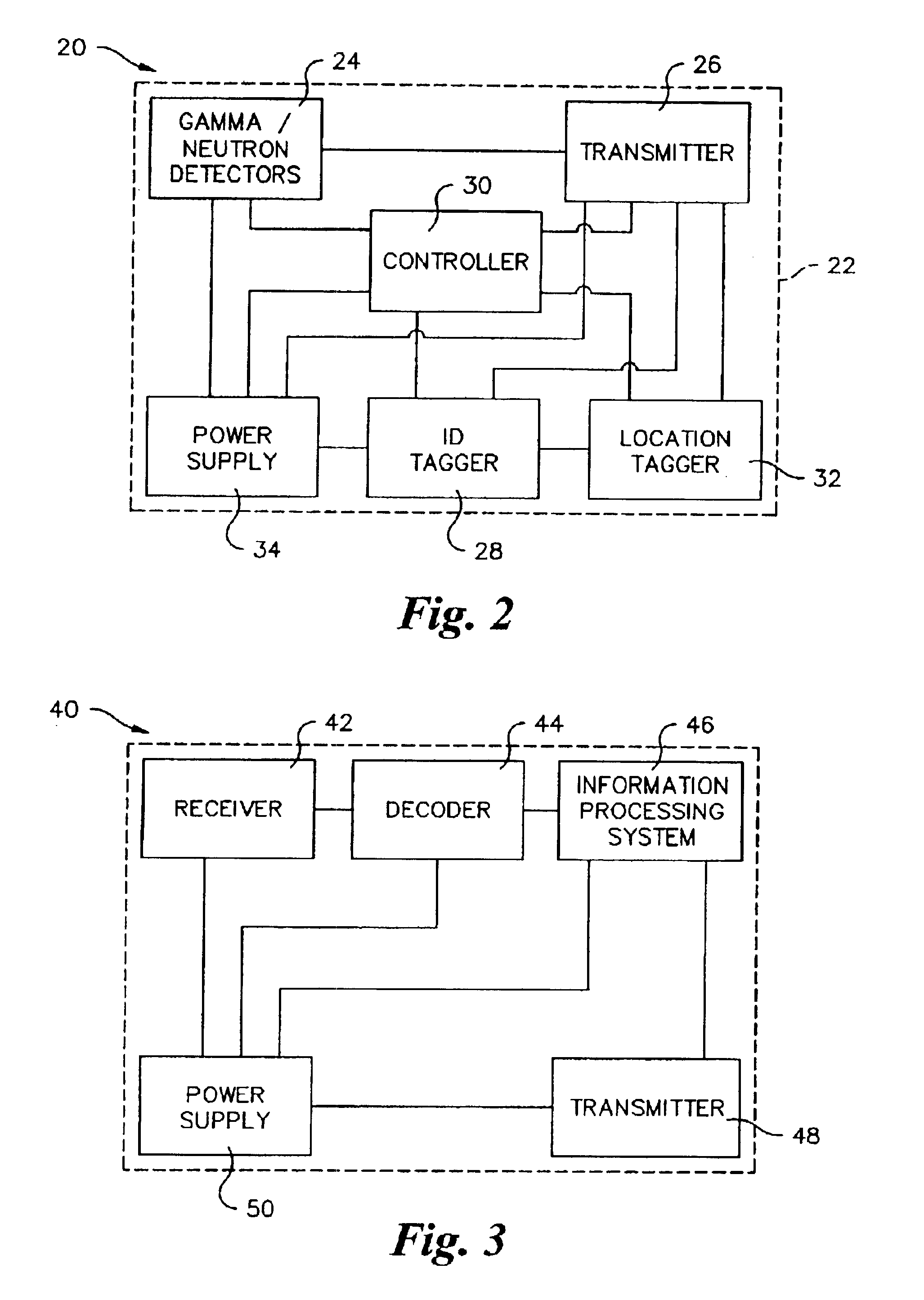
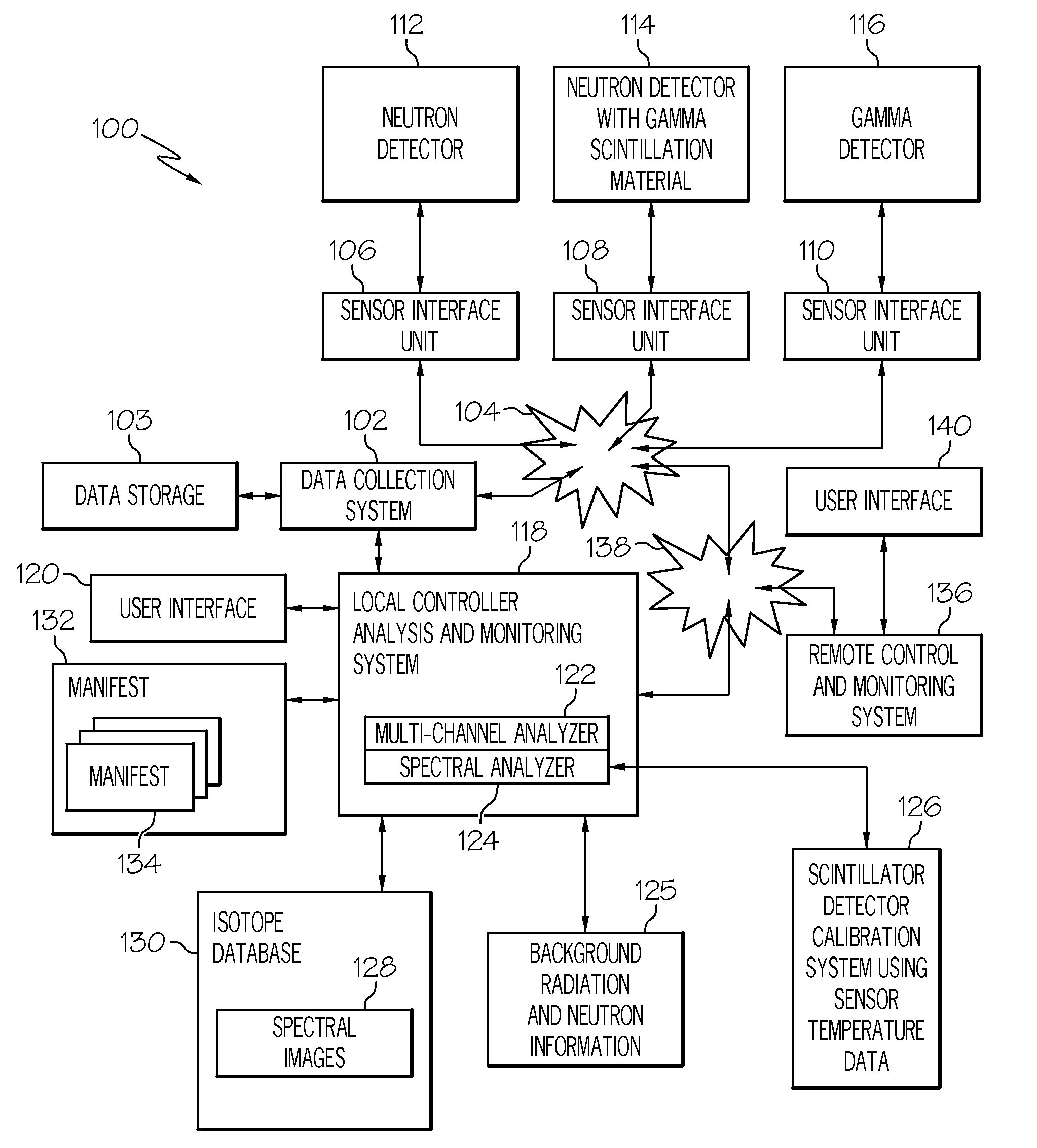
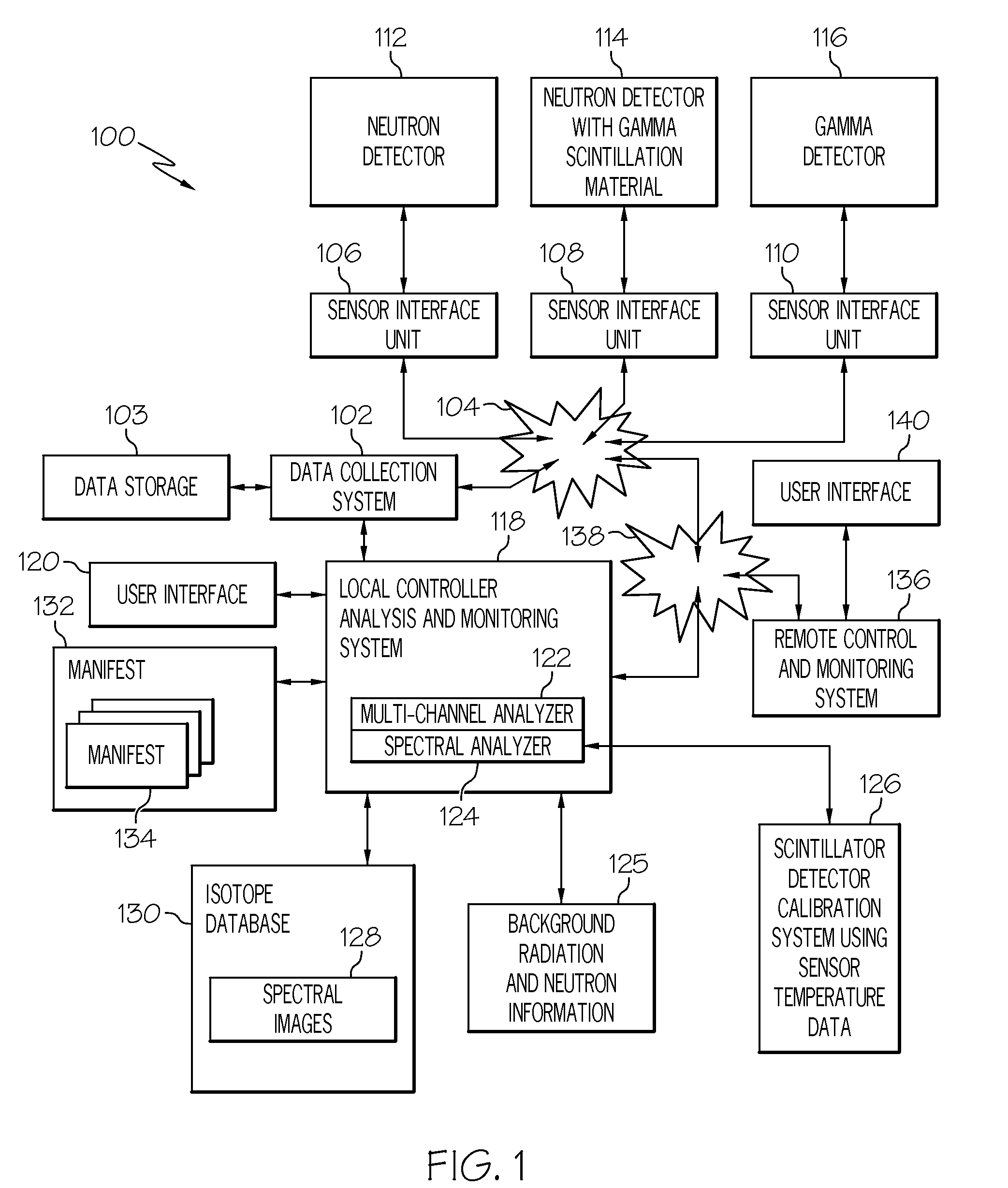
Method and apparatus for detection of radioactive material
ActiveUS6891470B2Electric testing/monitoringRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A radioactive material detection apparatus includes a transmitter, a radiation sensor and a controller. The transmitter is capable of transmitting information in correspondence with a signal. The radiation sensor has a sensor output and is configured to detect radiation over a predetermined period of time. The controller is configured to receive the sensor output from the radiation sensor and to send the signal to the transmitter for transmission.
Owner:QUINTELL OF OHIO
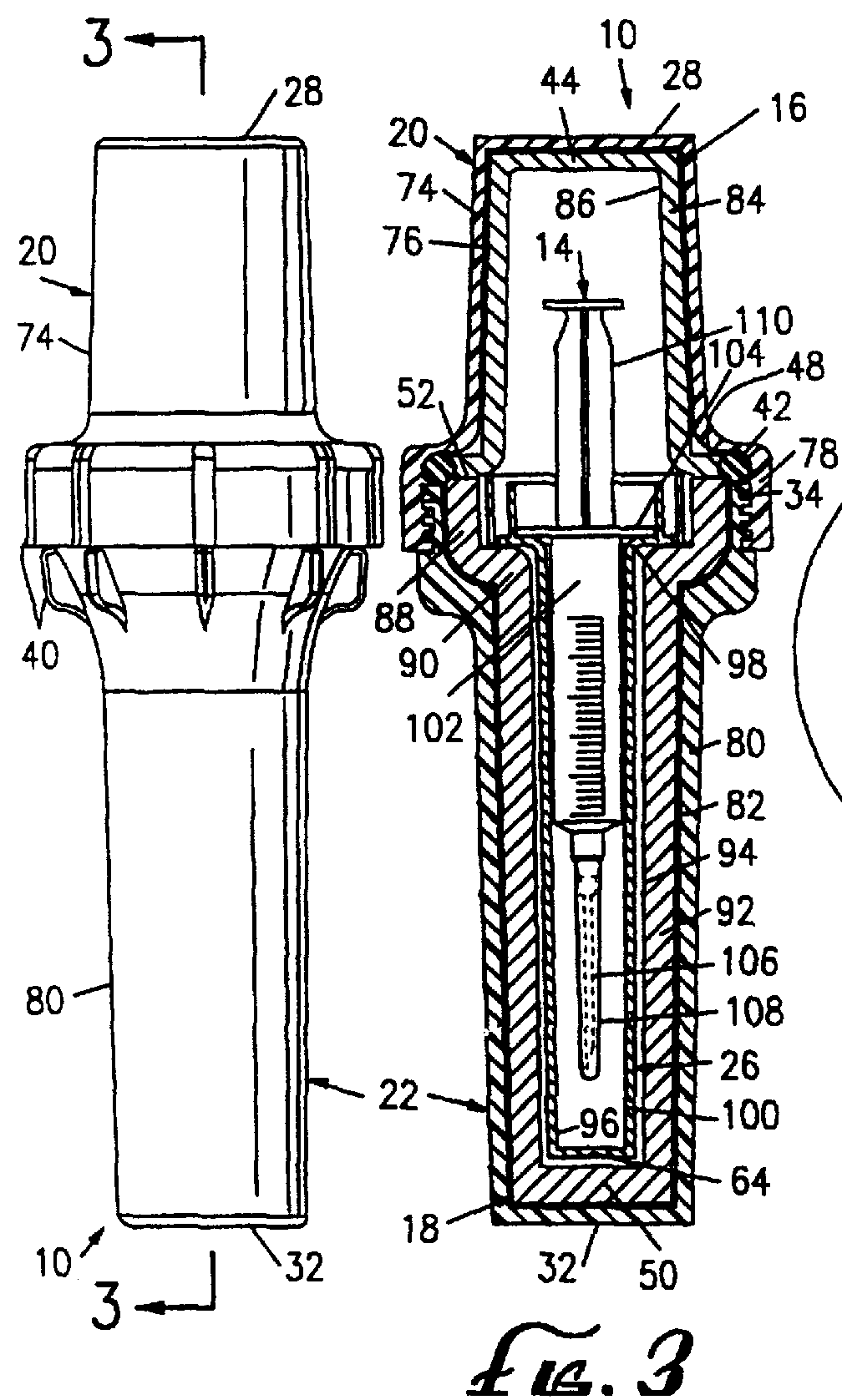
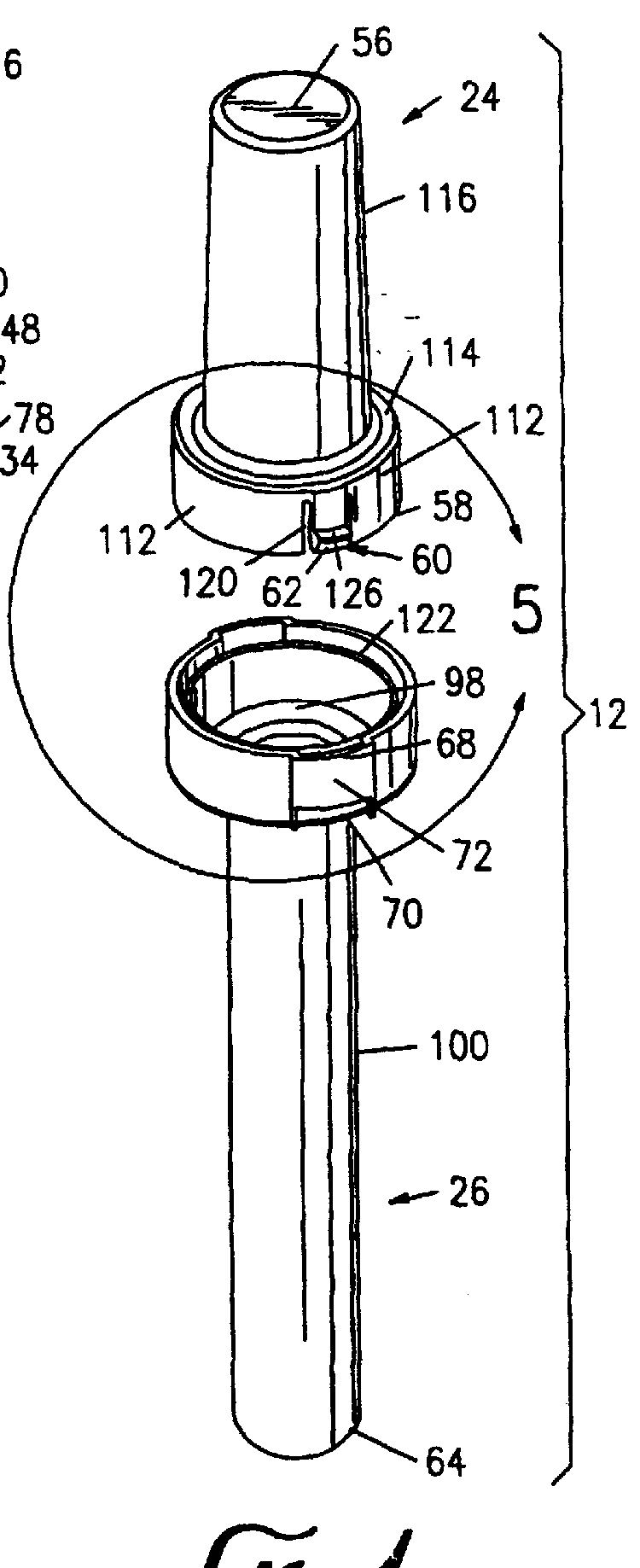
Container and method for transporting a syringe containing radioactive material
InactiveUSRE36693E1Reduced Possibility of ContaminationDurable shellDispensing apparatusOther accessoriesRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A method and apparatus for transporting syringes containing radioactive material. The apparatus includes a radiopharmaceutical pig having an inner chamber in which a sharps container can be secured. The sharps container has a housing and an attachable cap. The method includes assembling the radiopharmaceutical pig so that the chamber of the radiopharmaceutical pig contains the syringe in the sharps container housing. The radiopharmaceutical pig is disassembled, where upon the syringe is removed, discharged, and then replaced in the sharps container housing. The cap of the sharps container is affixed to the housing of the sharps container, thus enclosing the contaminated syringe therein. The radiopharmaceutical pig is assembled so that its chamber contains the sharps container and the syringe. The radiopharmaceutical pig is transported to a disposal area, where it is disassembled and the sharps container containing the syringe is placed in a particular disposal container.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH INC
Assembly for transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material
InactiveUS6233299B1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationRadioactive agentTechnetium-99
A new transmutation assembly permits an efficient transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material (long-lived FP nuclides such as technetium-99 or iodine-129) which was produced in the nuclear reactor. Wire-type members of a long-lived radioactive material comprised of metals, alloys or compounds including long-lived FP nuclides are surrounded by a moderator material and installed in cladding tubes to form FP pins. The FP pins, and nothing else, are housed in a wrapper tube to form a transmutation assembly. The wire-type members can be replaced by thin ring-type members. The transmutation assemblies can be selectively and at least partly loaded into a core region, a blanket region or a shield region of a reactor core in a fast reactor. From a viewpoint of reducing the influence on the reactor core characteristics, it is optimal to load the transmutation assemblies into the blanket region.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
Method and system for high-speed, 3D imaging of optically-invisible radiation and detector and array of such detectors for use therein
InactiveUS20050017181A1Reduce exposureStrong applicationElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesHuman exposureSpectroscopy
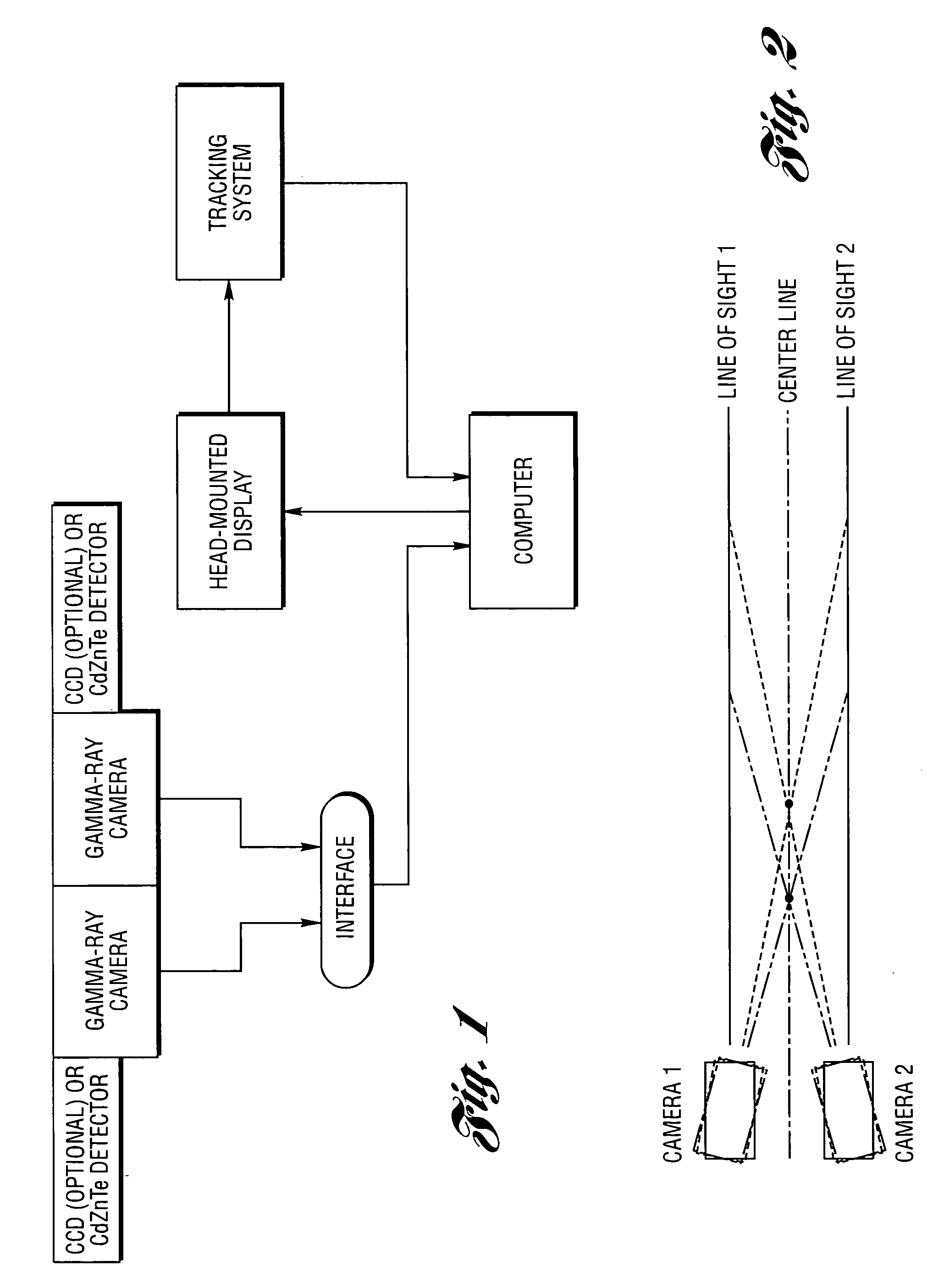
A high-speed, three-dimensional, gamma-ray imaging method and system as well as a detector and array of such detectors for use therein are provided which characterize radioactivity distributions in nuclear and radioactive waste and materials facilities by superimposing radiation images on a view of the environment using see-through display screens or shields to provide a stereoscopic view of the radiation. The method and system provide real-time visual feedback about the locations and relative strengths of radioactive sources. The method and system dynamically provide continuous updates to the displayed image illustrating changes, such as source movement. A pair of spaced gamma-ray cameras of a detector subsystem function like “gamma eyes”. A pair of CCD cameras may be coupled to the detector subsystem to obtain information about the physical architecture of the environment. A motion tracking subsystem is used to generate information on the user's position and head orientation to determine what a user “sees”. The invention exploits the human brain's ability to naturally reconstruct a 3D, stereoscopic image from 2D images generated by two “imagers” separated by a known angle(s) without the need for 3D mathematical image reconstruction. The method and system are not only tools for minimizing human exposure to radiation thus assisting in ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) planning, but also are helpful for identifying contamination in, for example, laboratory or industrial settings. Other optically-invisible radiation such as infrared radiation caused by smoldering fires may also be imaged. Detectors are manufactured or configured in curvilinear geometries (such as hemispheres, spheres, circles, arcs, or other arrangements) to enable sampling of the ionizing radiation field for determination of positional activity (absolute or relative amounts of ionizing radiation) or spectroscopy (energy distributions of photons). More than one detector system may be used to obtain three-dimensional information. The detector systems are specifically suitable for direct visualization of radiation fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Nuclear Assisted Hydrocarbon Production Method
InactiveUS20100105975A1Reduced availabilityMinimized in sizeFluid removalShieldingHydrogenFormation fluid
A method is disclosed for the temporary or permanent storage of nuclear waste materials comprising the placing of waste materials into one or more repositories or boreholes constructed into an unconventional oil formation. The thermal flux of the waste materials fracture the formation, alters the chemical and / or physical properties of hydrocarbon material within the subterranean formation to allow removal of the altered material. A mixture of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and / or other formation fluids are produced from the formation. The radioactivity of high-level radioactive waste affords proliferation resistance to plutonium placed in the periphery of the repository or the deepest portion of a borehole.
Owner:BAIRD JAMES RUSSELL
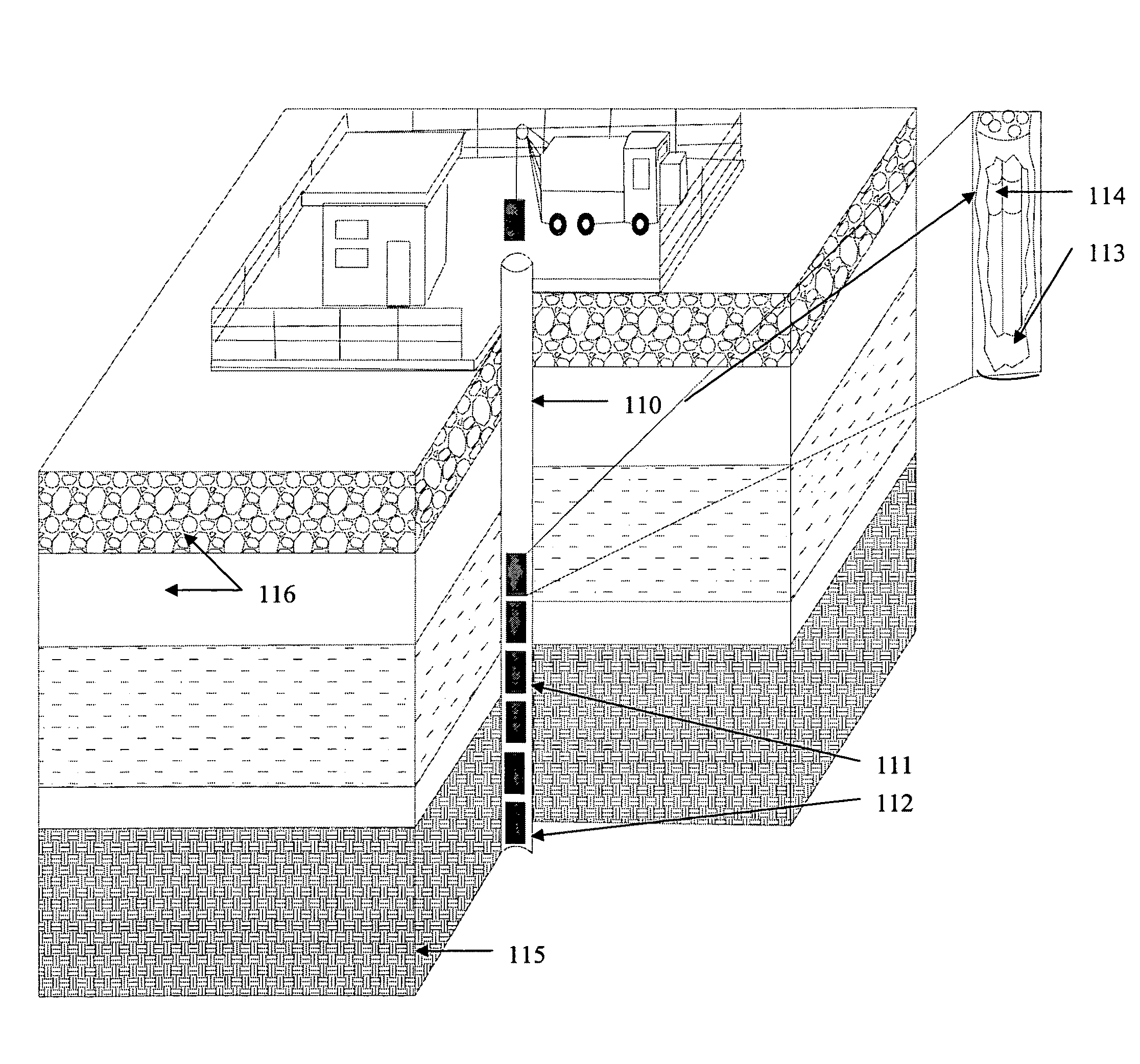
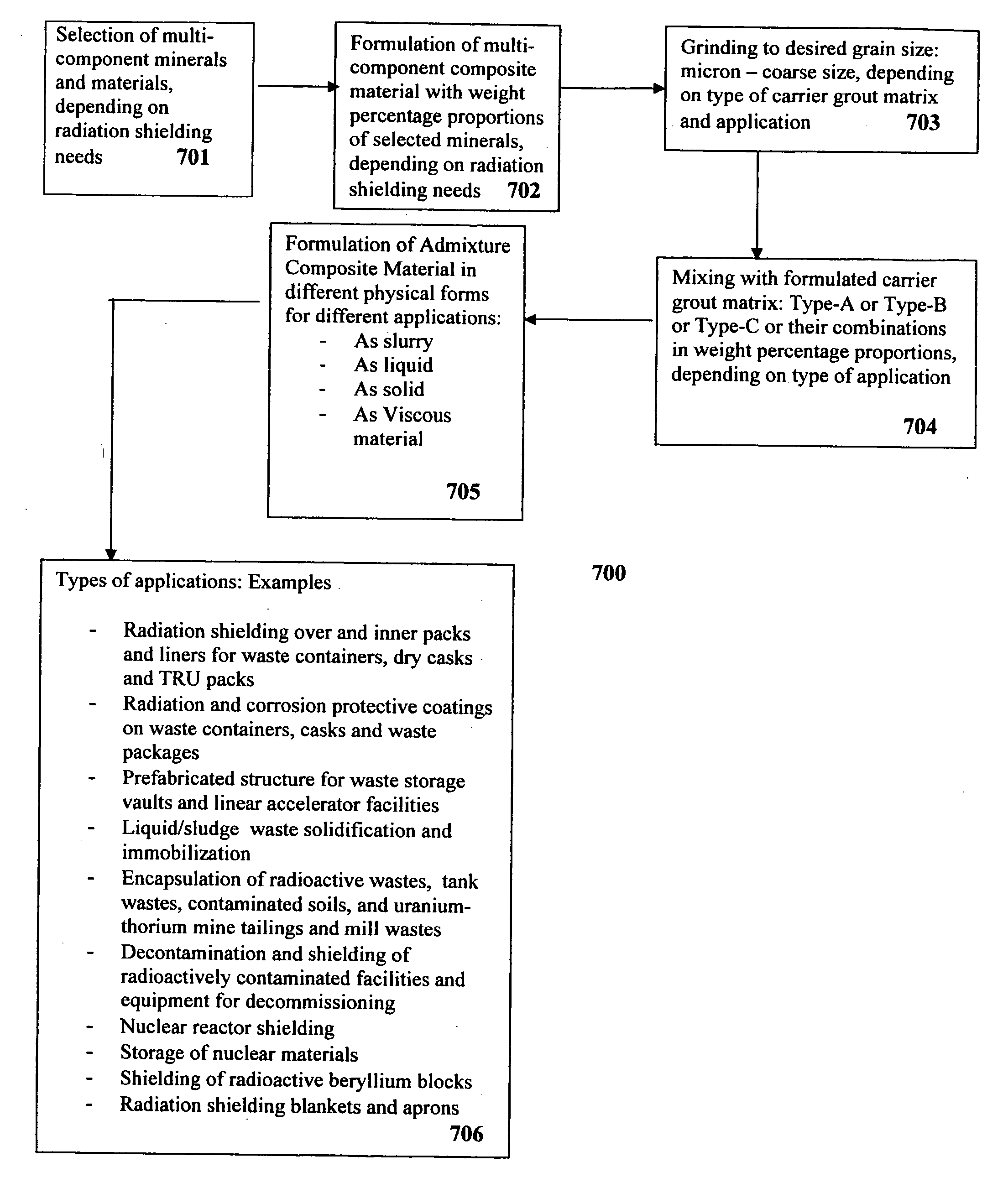
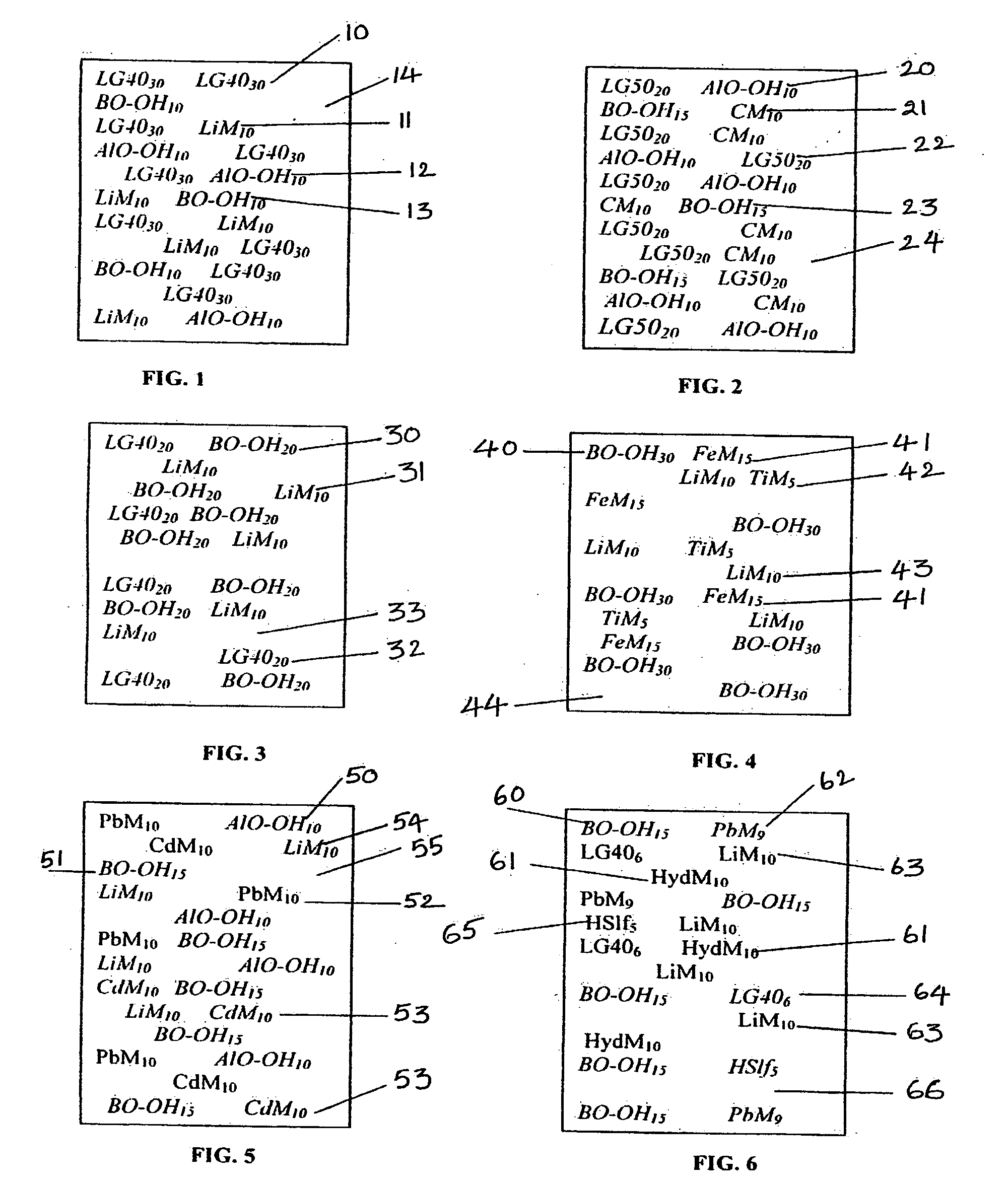
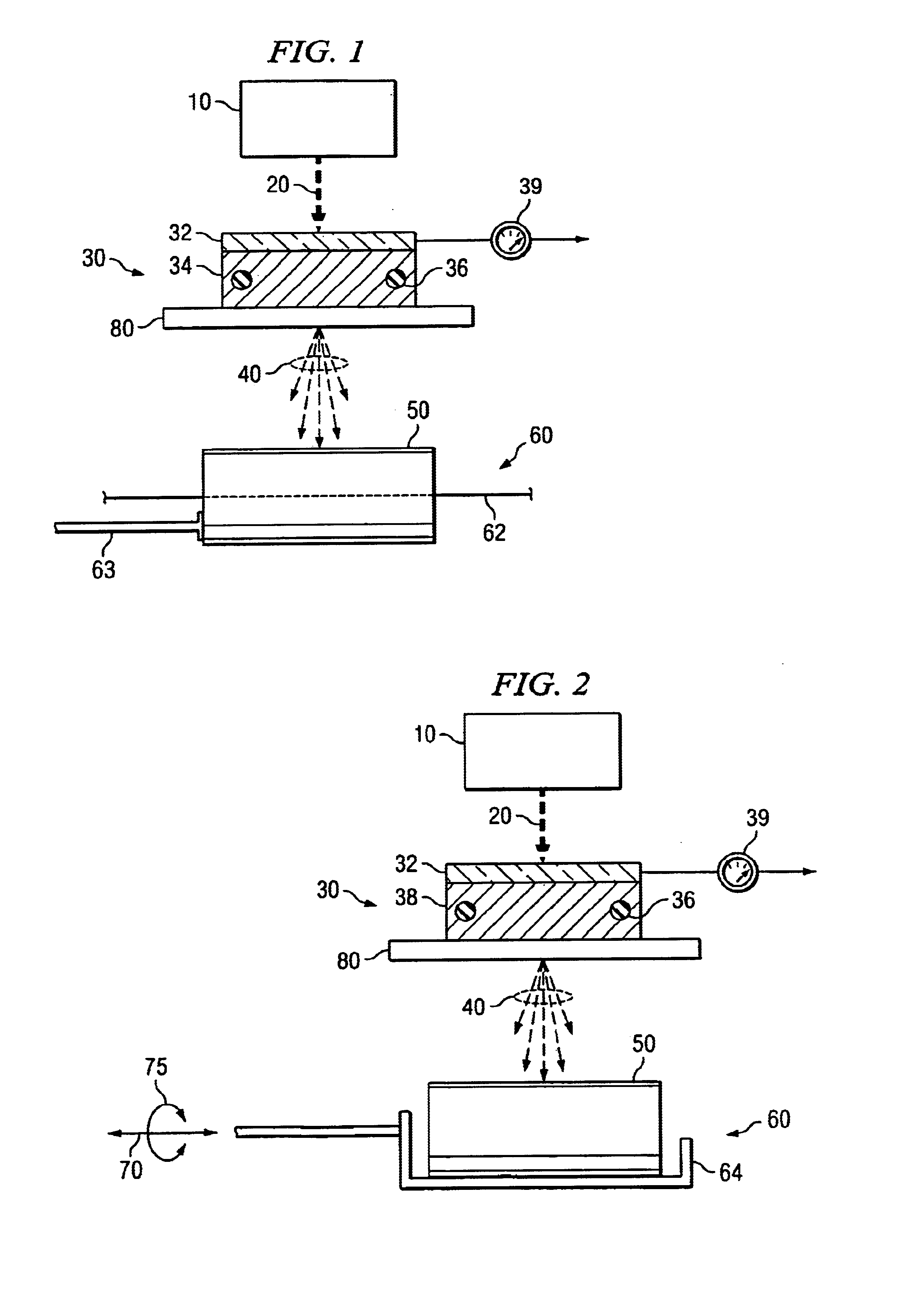
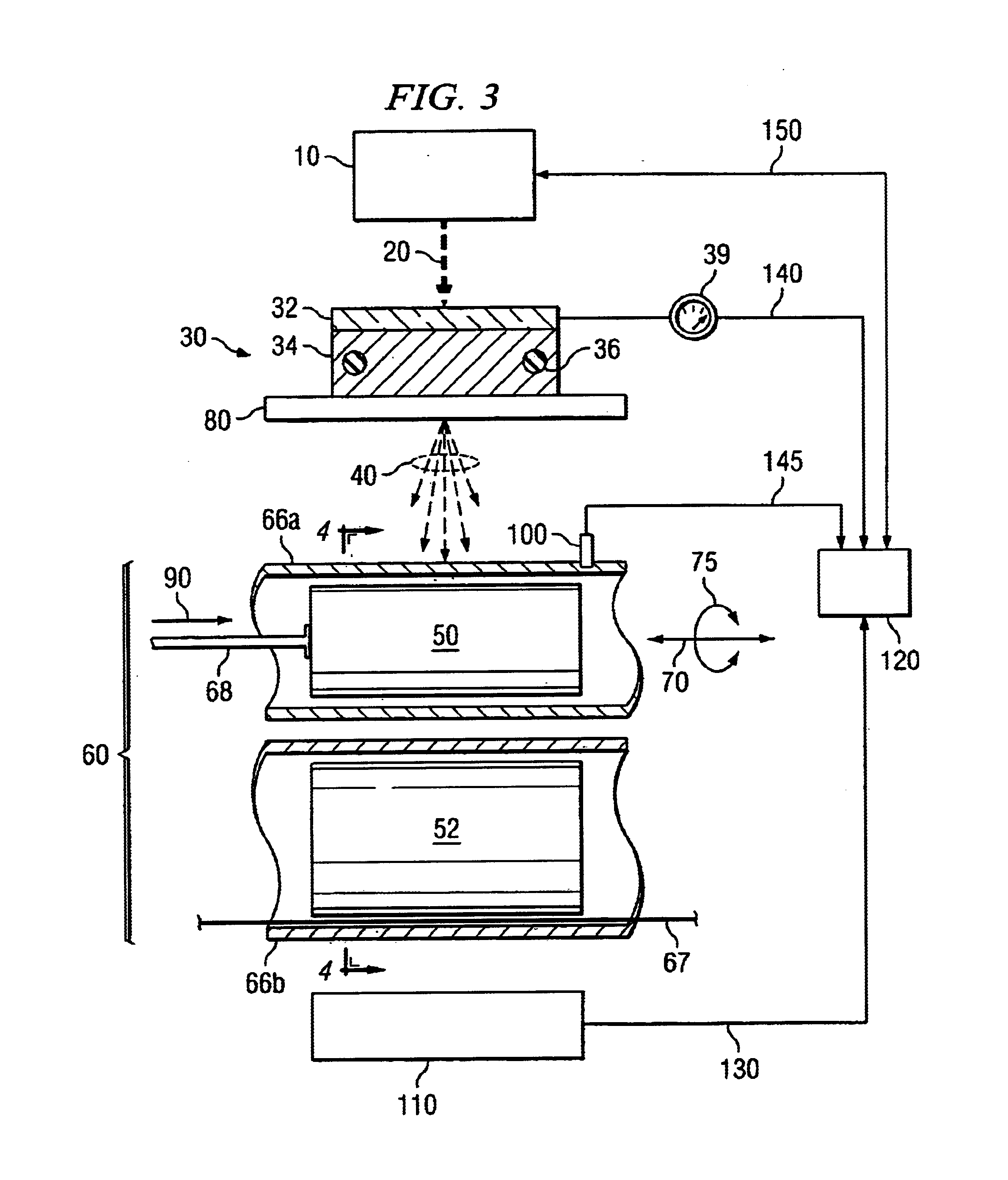
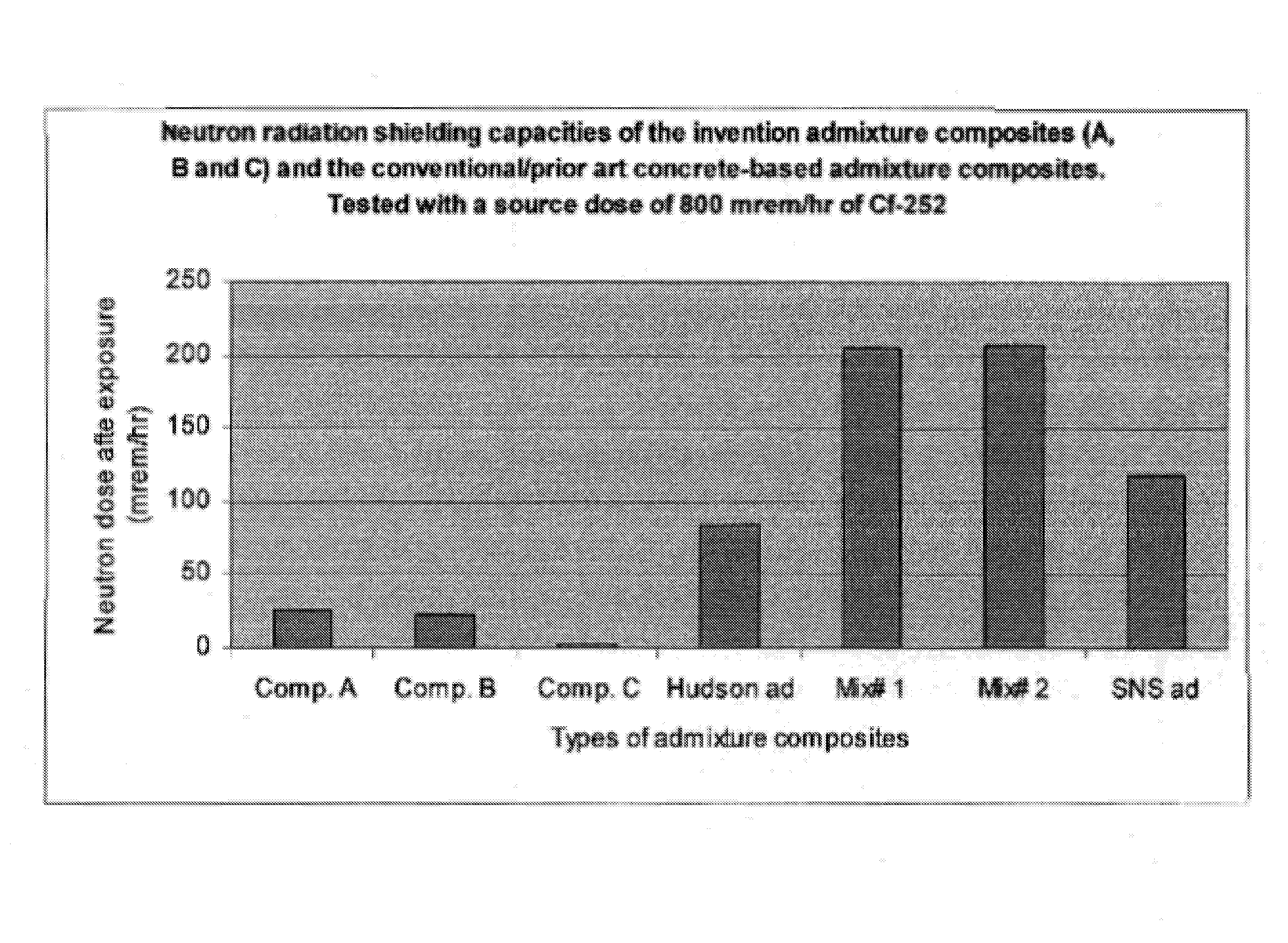
Composite materials and techniques for neutron and gamma radiation shielding
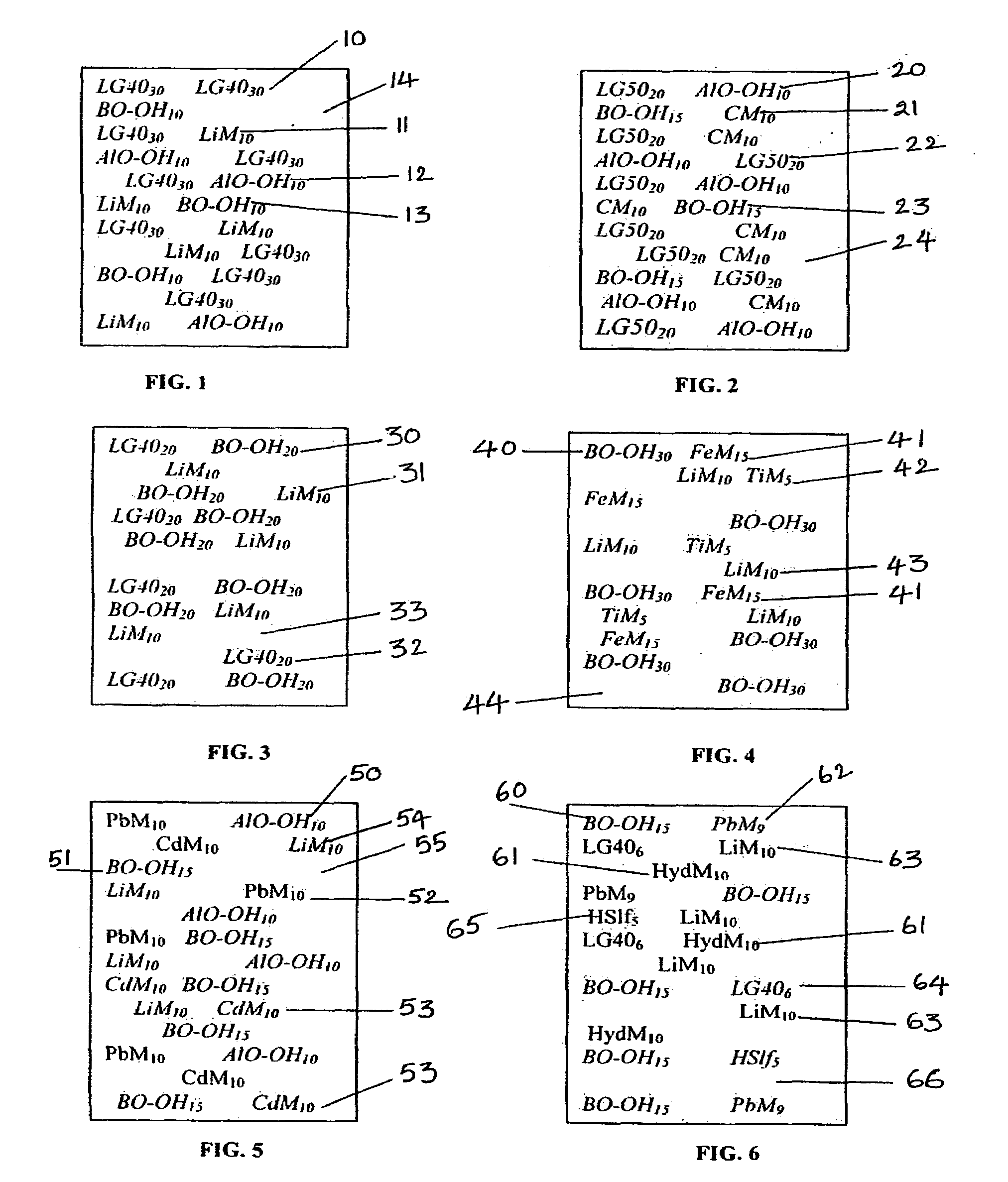
ActiveUS20050258405A1Safe and cost-effective managementIncrease volumeDiffusing elementsNuclear engineering solutionsPolymer modifiedRadioactive waste
This invention deals with multi-component composite materials and techniques for improved shielding of neutron and gamma radiation emitting from transuranic, high-level and low-level radioactive wastes. Selective naturally occurring mineral materials are utilized to formulate, in various proportions, multi-component composite materials. Such materials are enriched with atoms that provide a substantial cumulative absorptive capacity to absorb or shield neutron and gamma radiation of variable fluxes and energies. The use of naturally occurring minerals in synergistic combination with formulated modified cement grout matrix, polymer modified asphaltene and maltene grout matrix, and polymer modified polyurethane foam grout matrix provide the radiation shielding product. These grout matrices are used as carriers for the radiation shielding composite materials and offer desired engineering and thermal attributes for various radiation management applications.
Owner:SAYALA DASHARATHAM
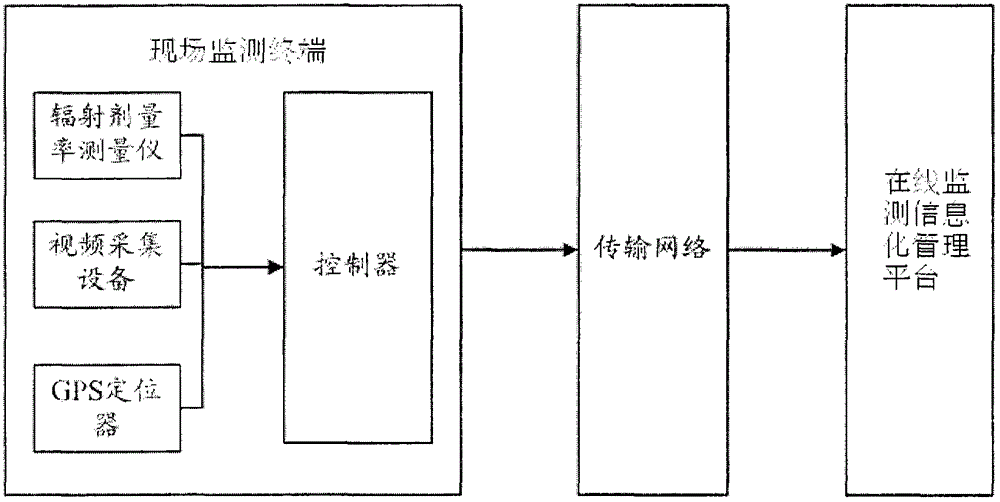
Radioactive source on-line monitoring system based on Internet of Things technology
ActiveCN104808237AComprehensive monitoringImprove monitoring efficiencyDosimetersInformatizationMeasuring instrument
The invention provides a radioactive source on-line monitoring system based on an Internet of Things technology. The radioactive source on-line monitoring system comprises RF (radio frequency) cards, field monitoring terminals, a transmission network and an on-line monitoring informatization management platform, wherein the RF card is fixedly arranged in each monitoring site with a preset distance from a radiation source, unique identity information of a radiation source, approved geographical position information and the standard radiation dose rate are stored in the RF cards, each field monitoring terminal is arranged in the corresponding monitoring site, and comprises an RF card reader-writer, a radiation dose rate measuring instrument, video collecting equipment, a GPS (global positioning system) positioning device, a controller, an in-site warning device, a communication interface and a power supplying power supply, and the processor is respectively connected with the RF card reader-writer, the radiation dose rate measuring instrument, the video collecting equipment, the GPS positioning device, the field warning device, the communication interface and the power supplying power supply. The radioactive source on-line monitoring system has the advantages that the radiation source can be comprehensively monitored, then, through a communication network, the monitoring information can be remotely obtained in time, and the monitoring efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SOS TECH
Method for preparing ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres and application thereof
InactiveCN102079823AWide variety of sourcesEasy to makeOther chemical processesMagnetic liquidsMicrosphereWastewater
The invention relates to a method for preparing ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres and application thereof. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: mixing acidic aqueous solution of chitosan and a water-based magnetofluid first, then crosslinking by using glutaraldehyde, then adjusting the pH value to form a gelatinous precipitate, then modifying by using ethylenediamine and epichlorohydrin, and washing and drying to obtain a final product. The product has good absorption effect on radionuclide aranium and metal ions such as heavy metal Pb, Cr and the like; the removal rate reaches over 95 percent when the initial concentration of various ions is within the range of 200mg / L; and the product has quick absorption rate and good regeneration performance. The ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres can be used for metal recovery and pollution remediation in mines, radioactive waste water, smelteries, electronics factories and waste water of electroplating factories.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Apparatus for providing additional radiation shielding to a container holding radioactive materials, and method of using the same to handle and/or process radioactive materials
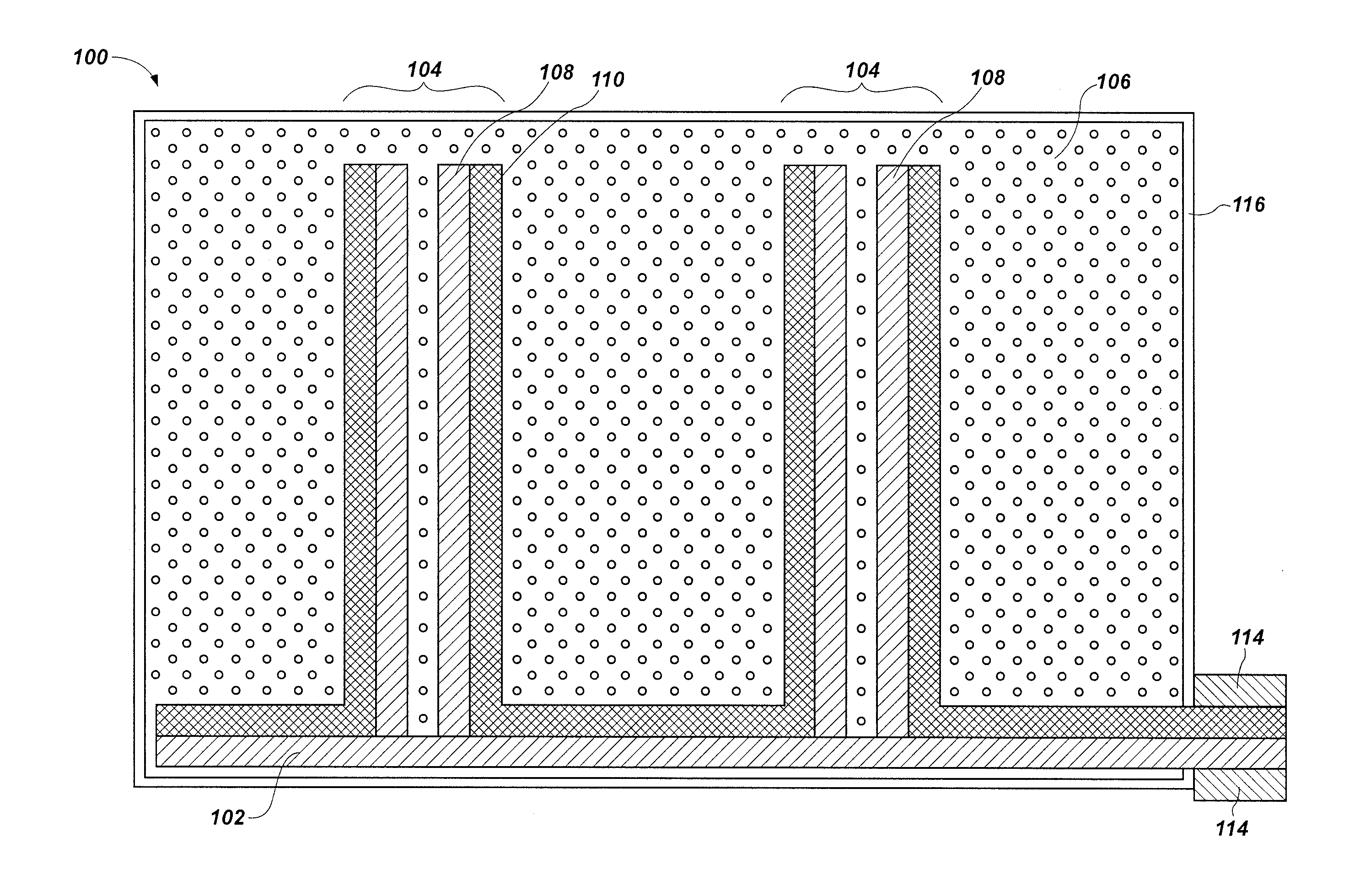
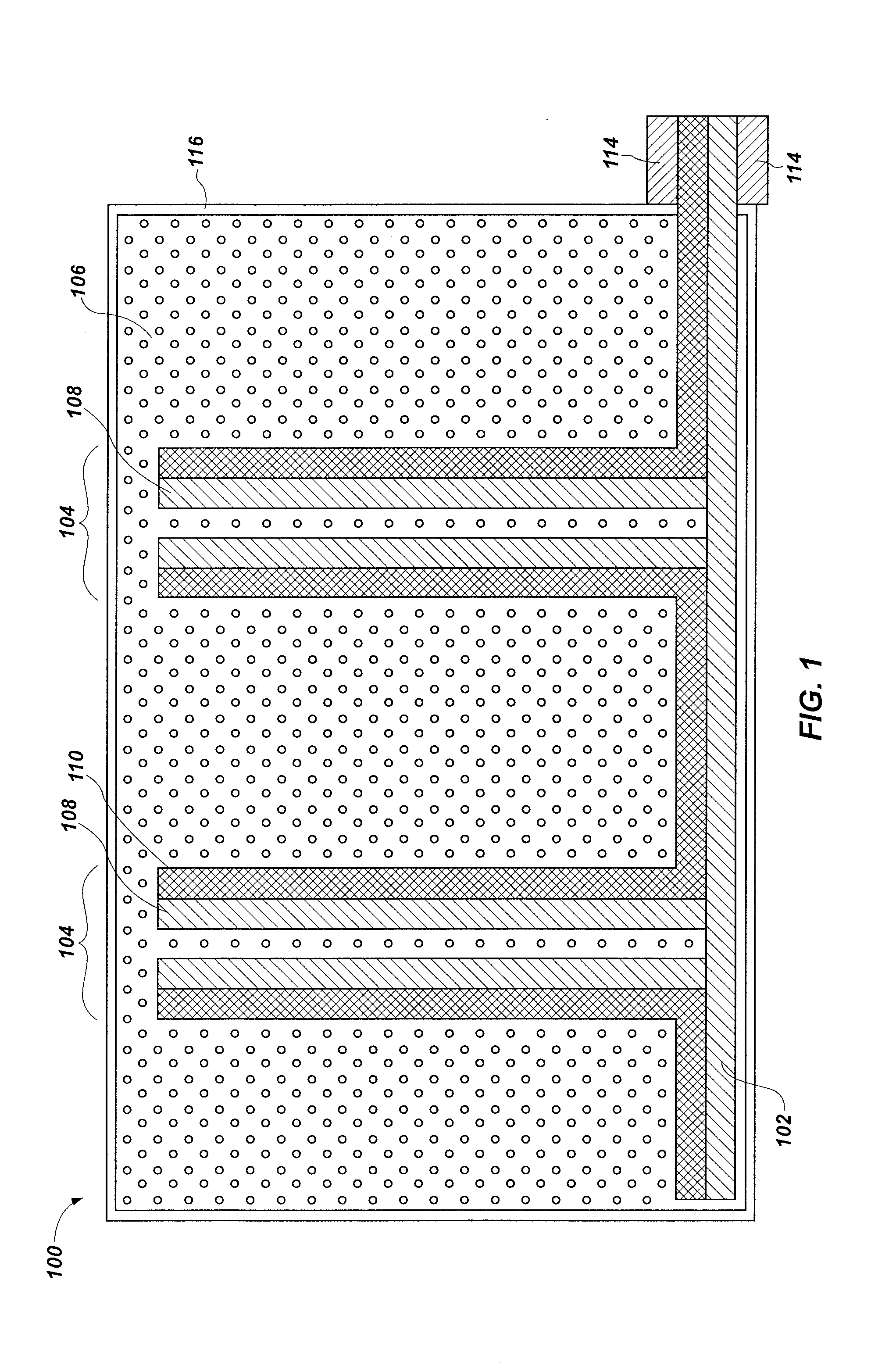
ActiveUS20080265182A1Quantity maximizationIncreasing transfer procedure cycle timeNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsLifting capacityRadar-absorbent material
A system, method and apparatus for providing additional radiation shielding to a container holding radioactive materials. The invention utilizes a sleeve-like structure that is slid over a container holding high level radioactive materials to add radiation shielding protection. Because the sleeve-like structure and container are non-unitary and slidably separable from one another, crane lifting capacity is not affected. In one aspect, the invention is an apparatus comprising: a tubular shell constructed of a gamma radiation absorbing material and having an inner surface that forms a cavity having an axis, the cavity having an open top end and an open bottom end; a plurality of spacers extending from the inner surface of the shell toward the axis of the cavity, the spacers extending a first height from the inner surface of the tubular shell; and one or more flange members located at or near the open top end of the cavity extending from the tubular shell toward the axis of the cavity, the flange member extending a second height from the inner surface of the shell, the second height being greater than the first height.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
Localization of a Radioactive Source
InactiveUS20090127459A1Reduce biological effectHigh sensitivitySurgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive wasteRadioactive source
An angle-responsive sensor, comprising:a radiation detector adapted to detect ionizing radiation;at least one radiation absorbing element arranged to block radiation from reaching said detector in a manner dependent on a relative orientation of a radiation source, said detector and said element, said detector and said element defining an aim for said sensor; andcircuitry coupled to said detector and which generates an output signal which varies as a function of said relative orientation,wherein said detector and said element are arranged to have a working volume of at least 10 cm in depth and having an angular width, such that said signal defines an accuracy of better than 3 mm within one standard deviation, over said working volume.
Owner:NAVOTEK MEDICAL
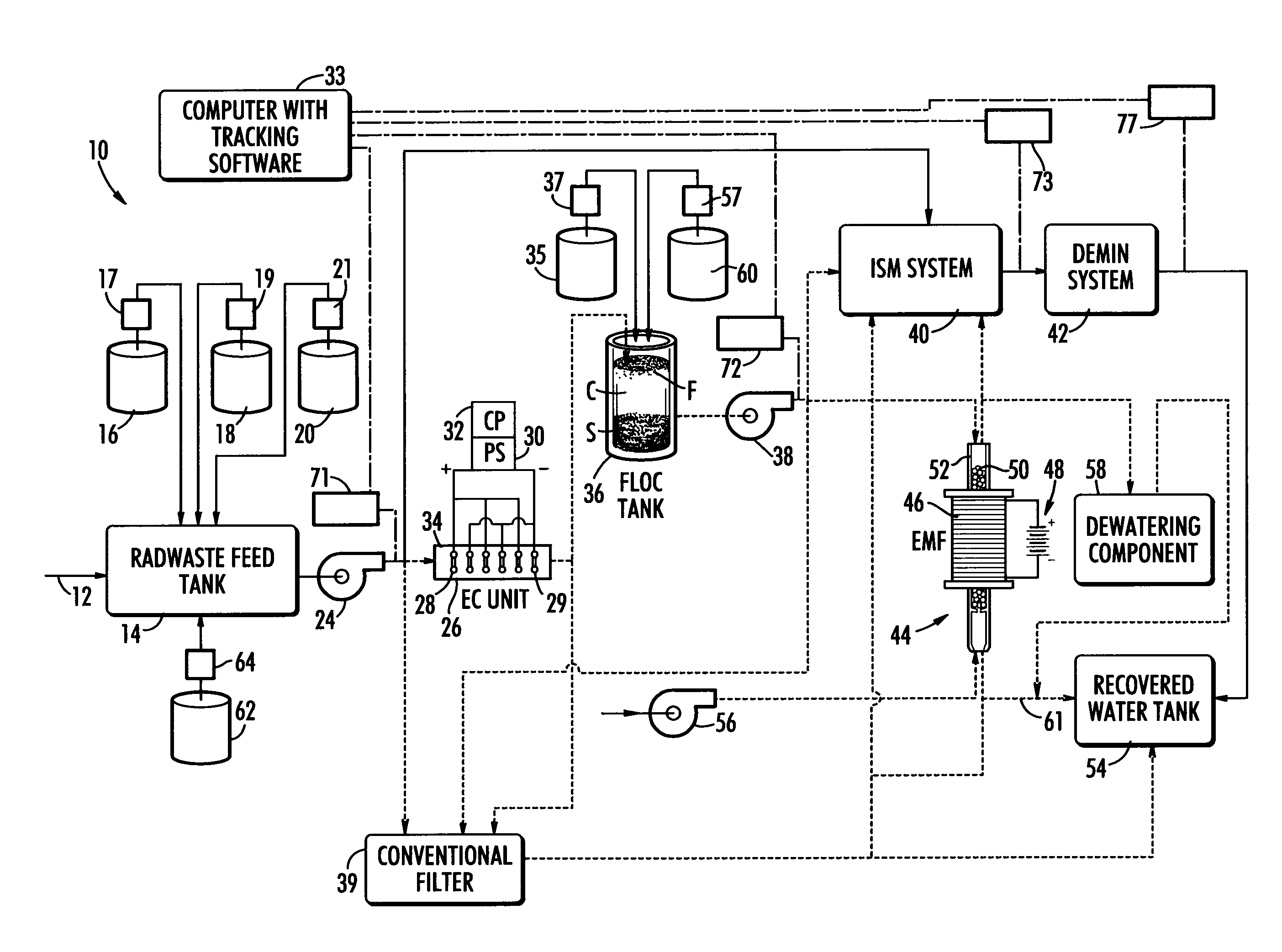
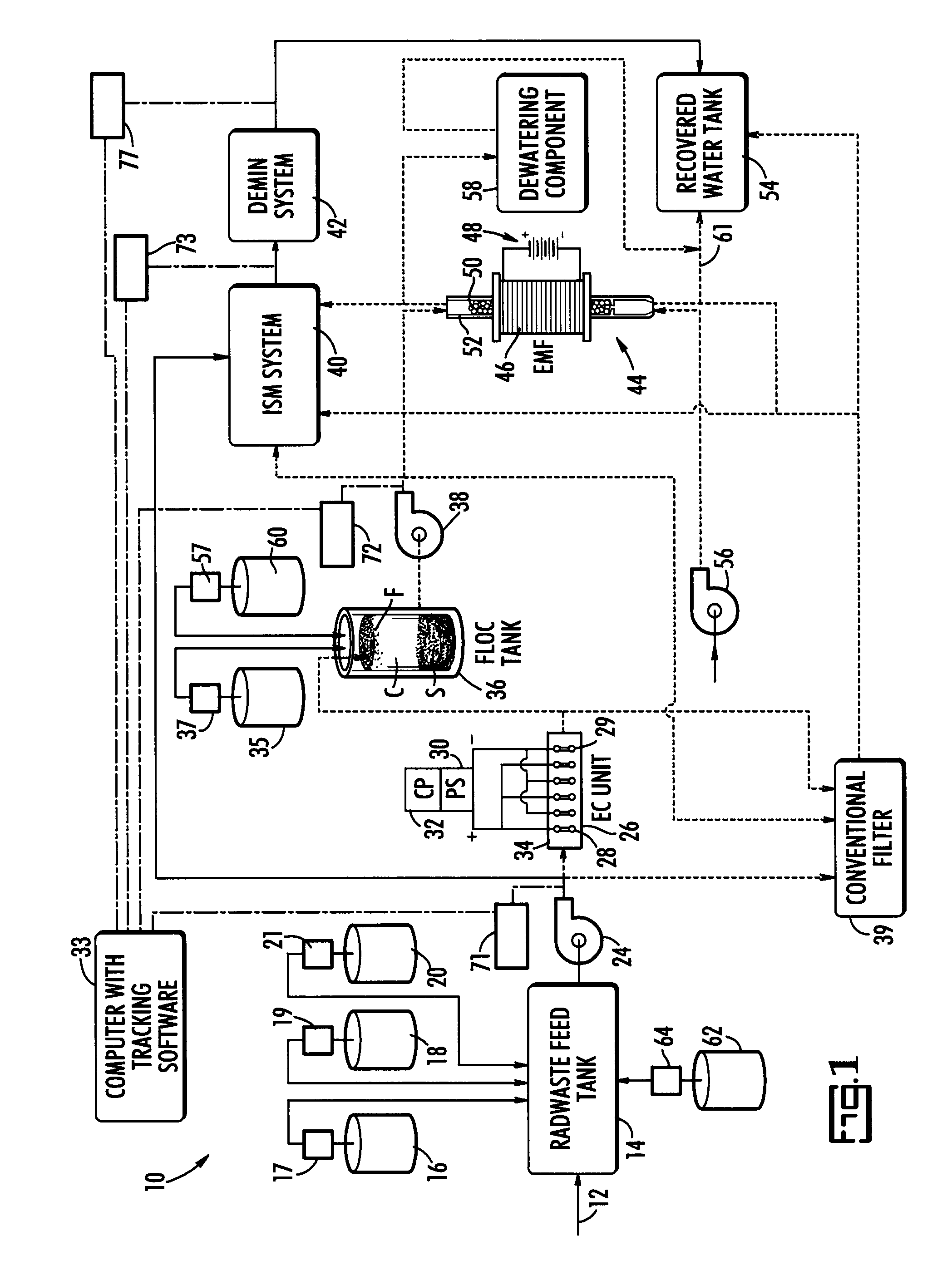
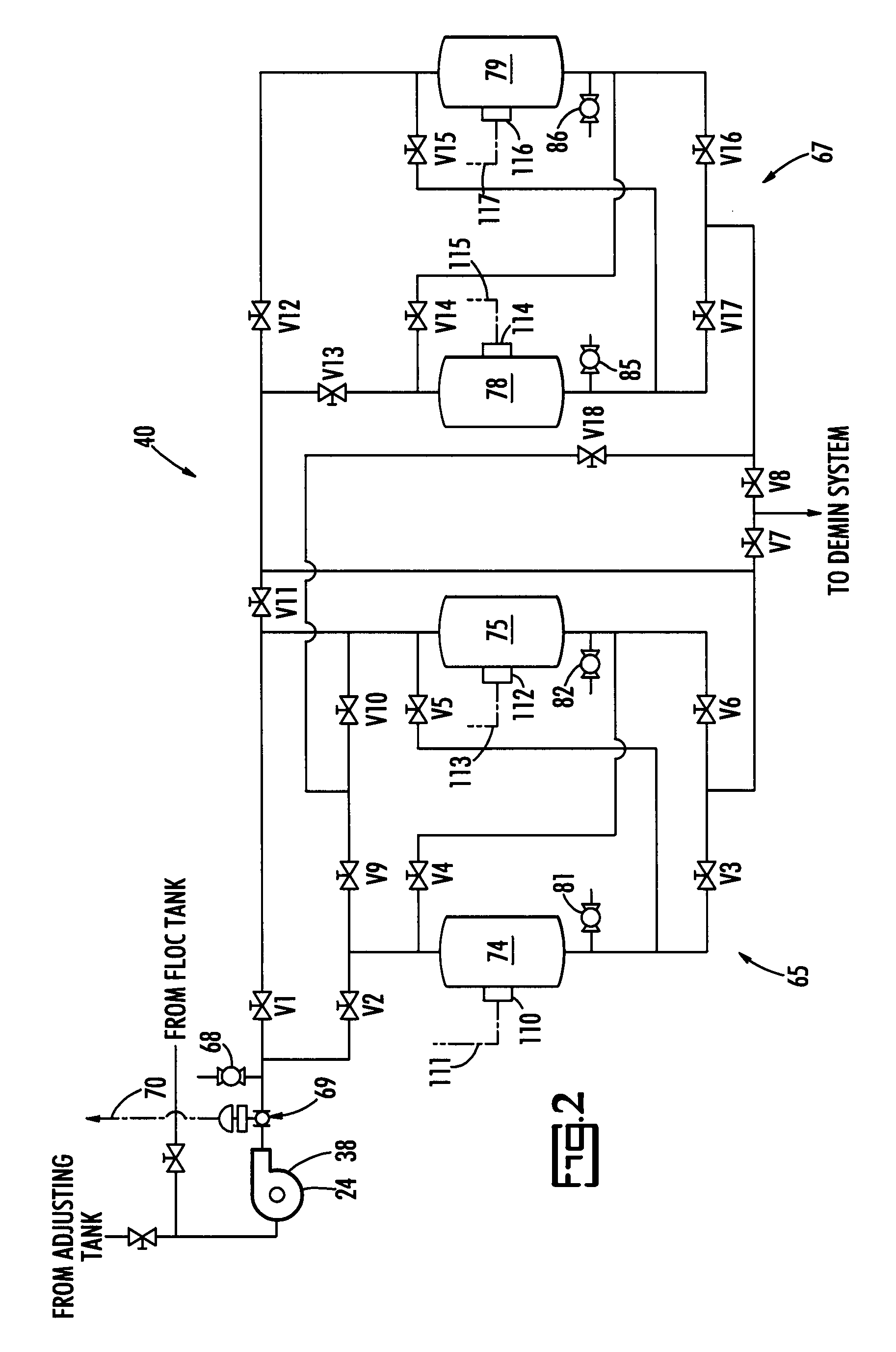
Method and system for treating radioactive waste water
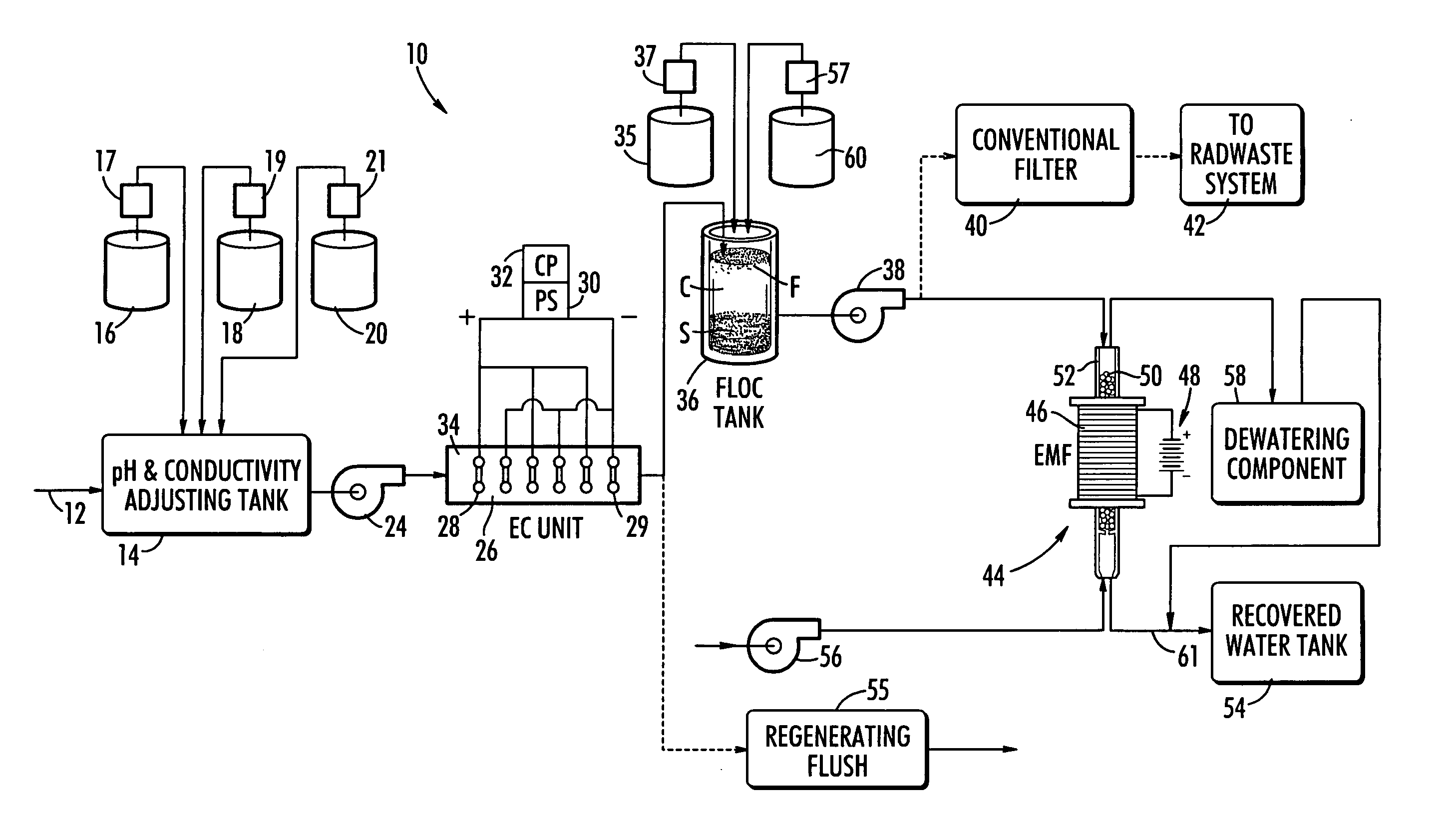
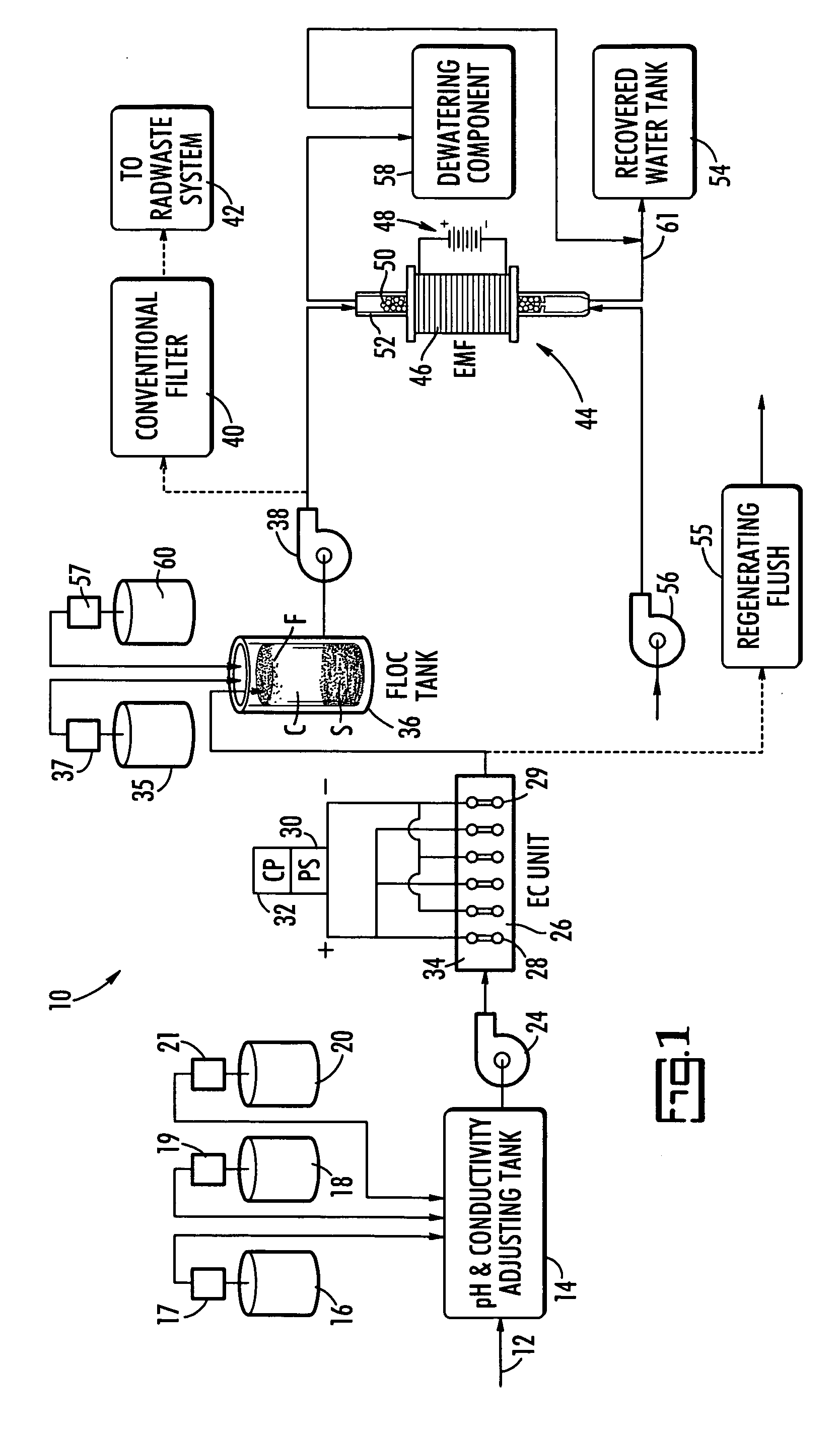
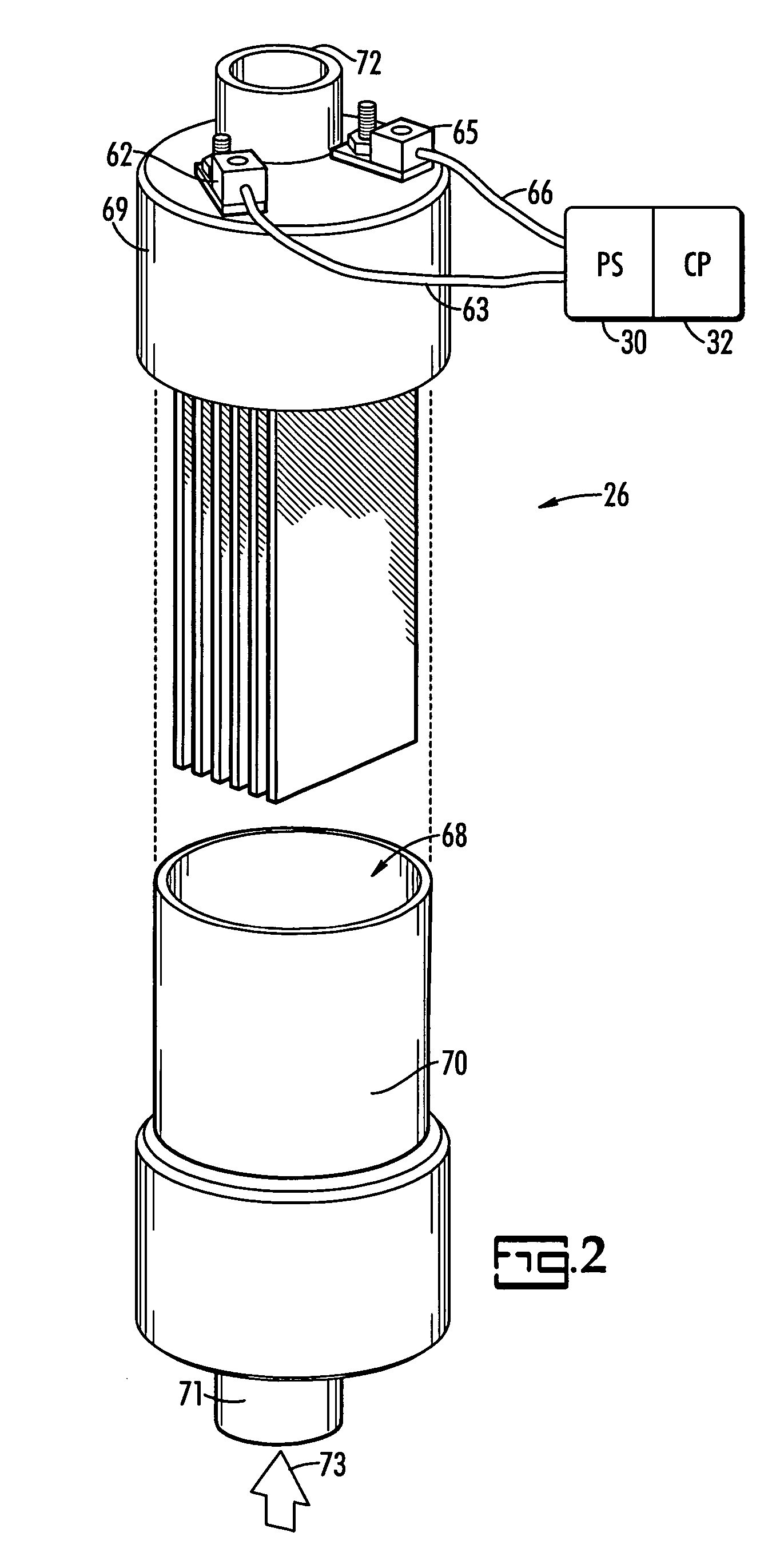
ActiveUS20070131621A1Easy to useLoss in efficiencyElectrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricityFiltrationElectro coagulation
A method and apparatus for treating radioactive waste water containing contaminating ions, colloids and suspended solids having like (usually negative) charges preventing their precipitation. An electric current is passed through the waste water in an EC assembly to cause electro-coagulation of the contaminants and anodes of this assembly are made of a metal that dissolves to provide cations for neutralizing the negative charges and forming precipitates containing neutralized contaminants. Precipitates are then separated from waste water by an electro-magnetic or other filtering unit. The water pH and conductivity may be adjusted before the EC assembly and additives may be introduced into its effluent for enlargement of precipitate particles, improvement of filtration, improvement of dewaterability, and / or enhancement of magnetism.
Owner:ENERGYSOLUTIONS LLC
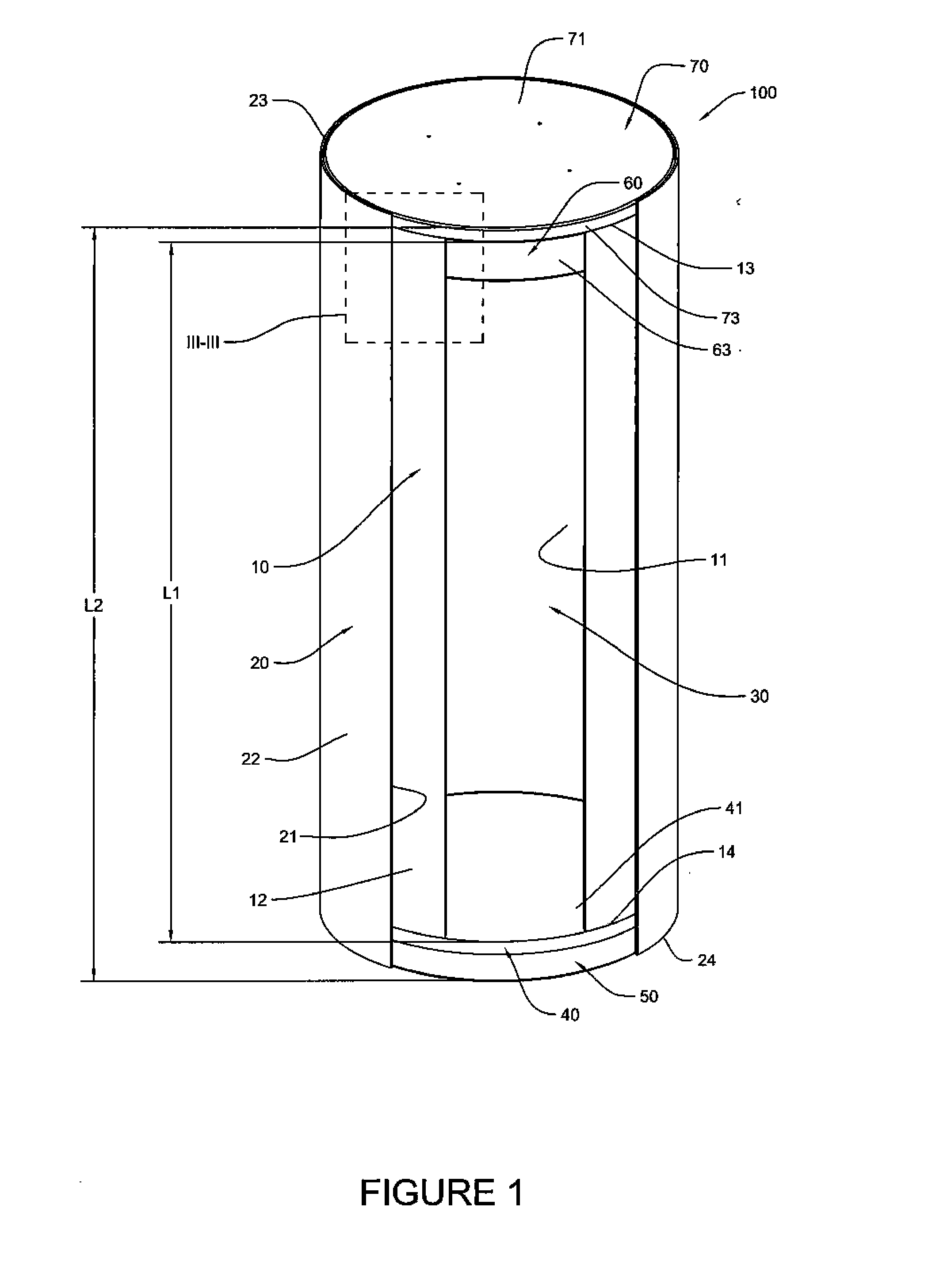
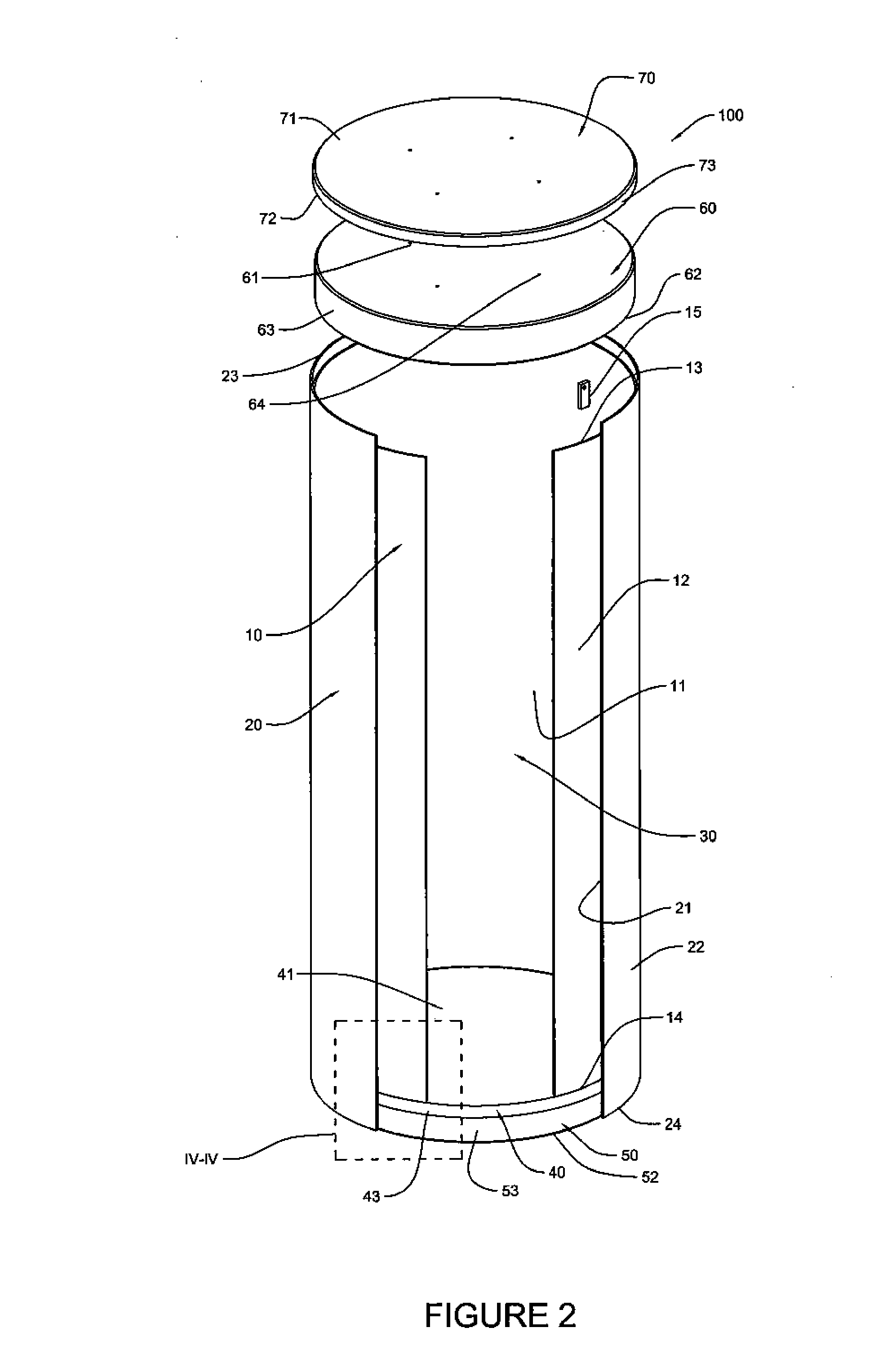
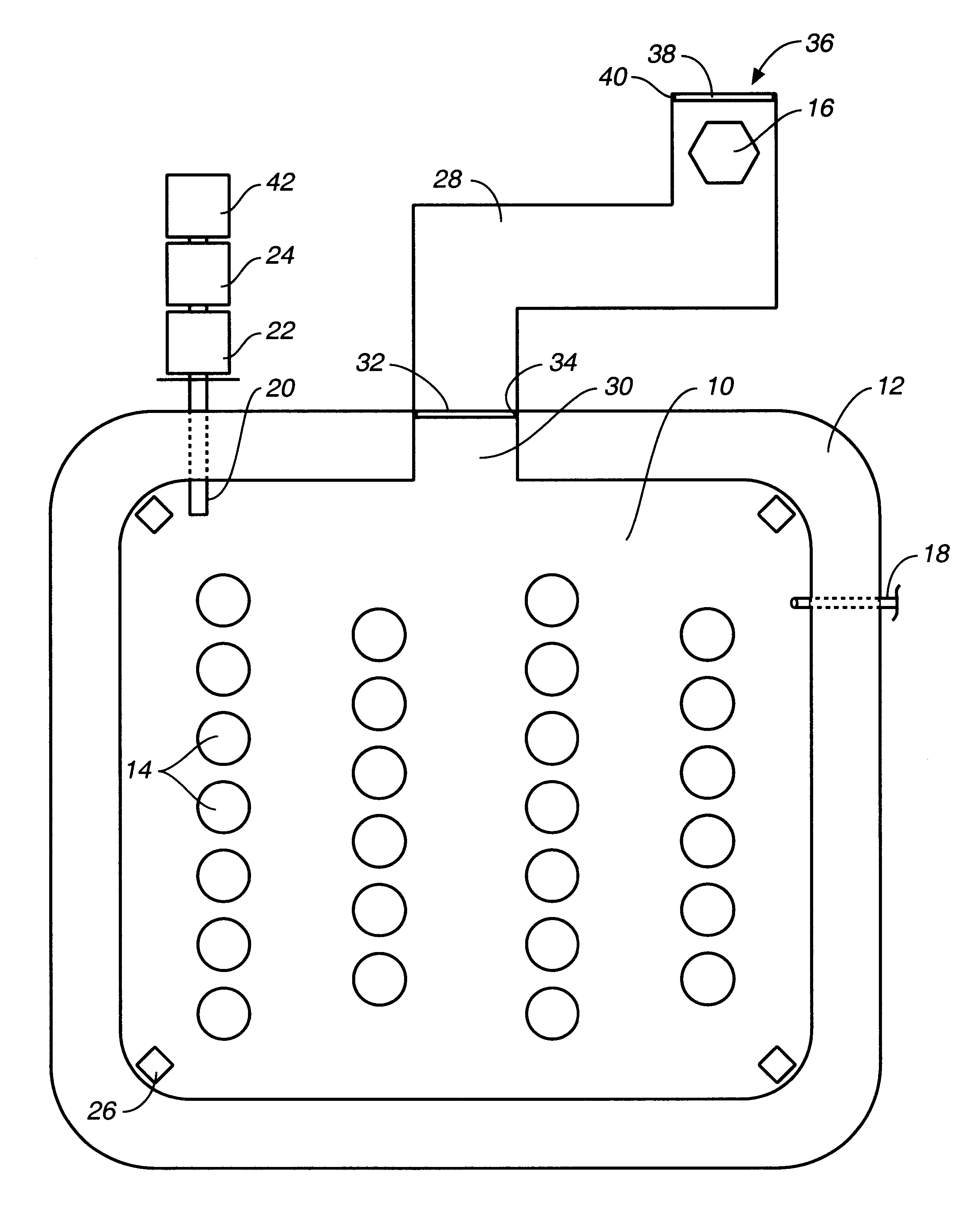
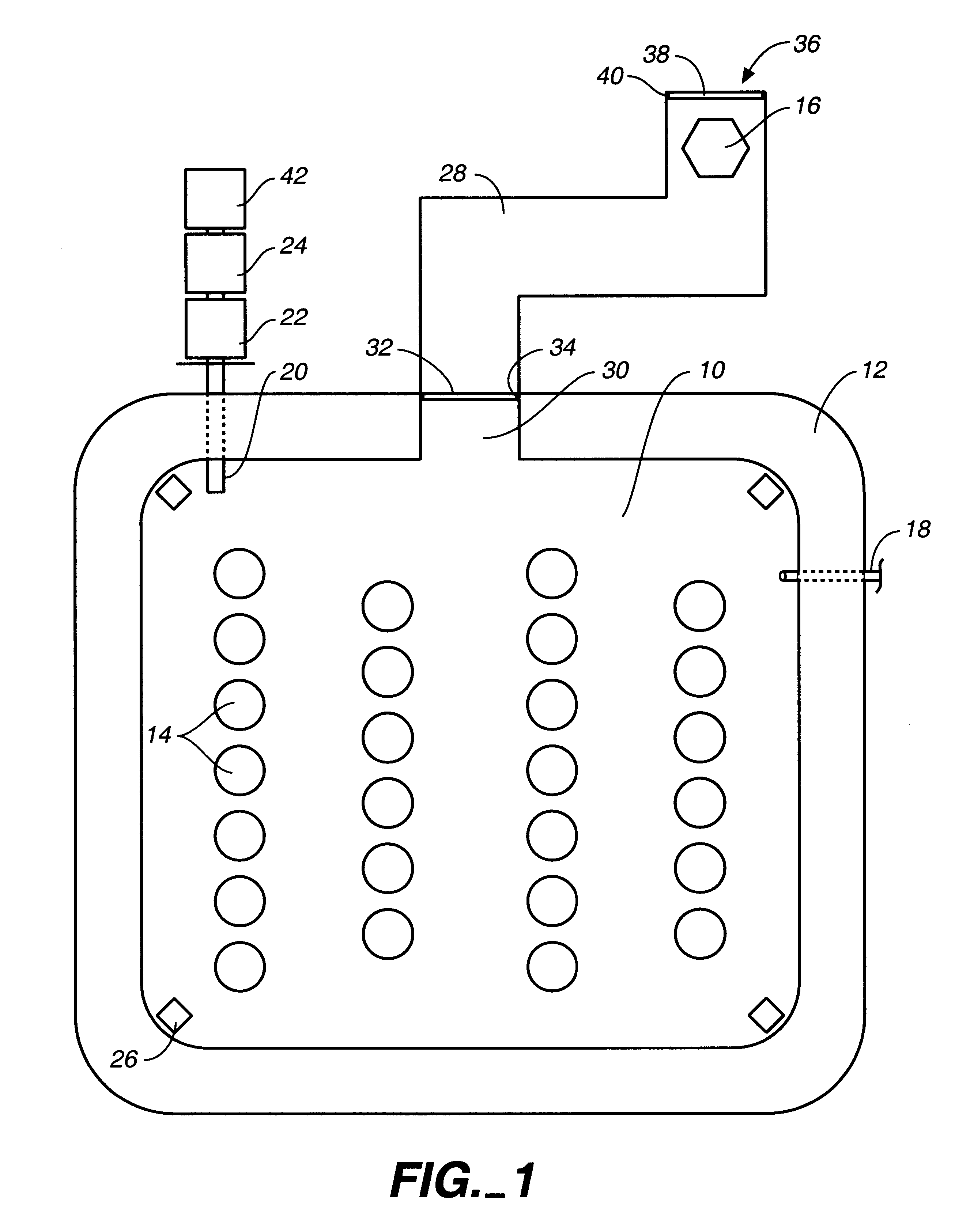
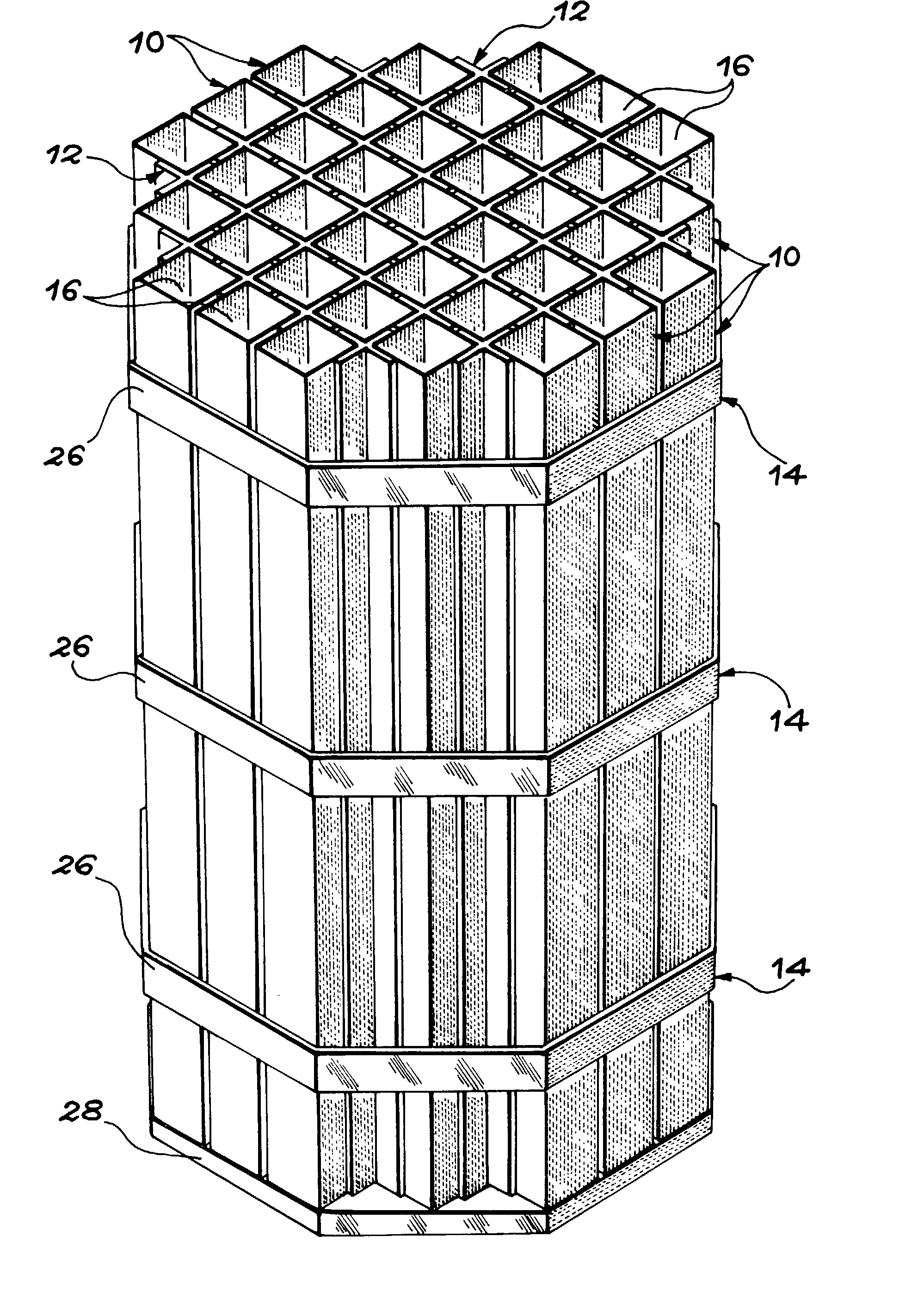
Canister apparatus and basket for transporting, storing and/or supporting spent nuclear fuel
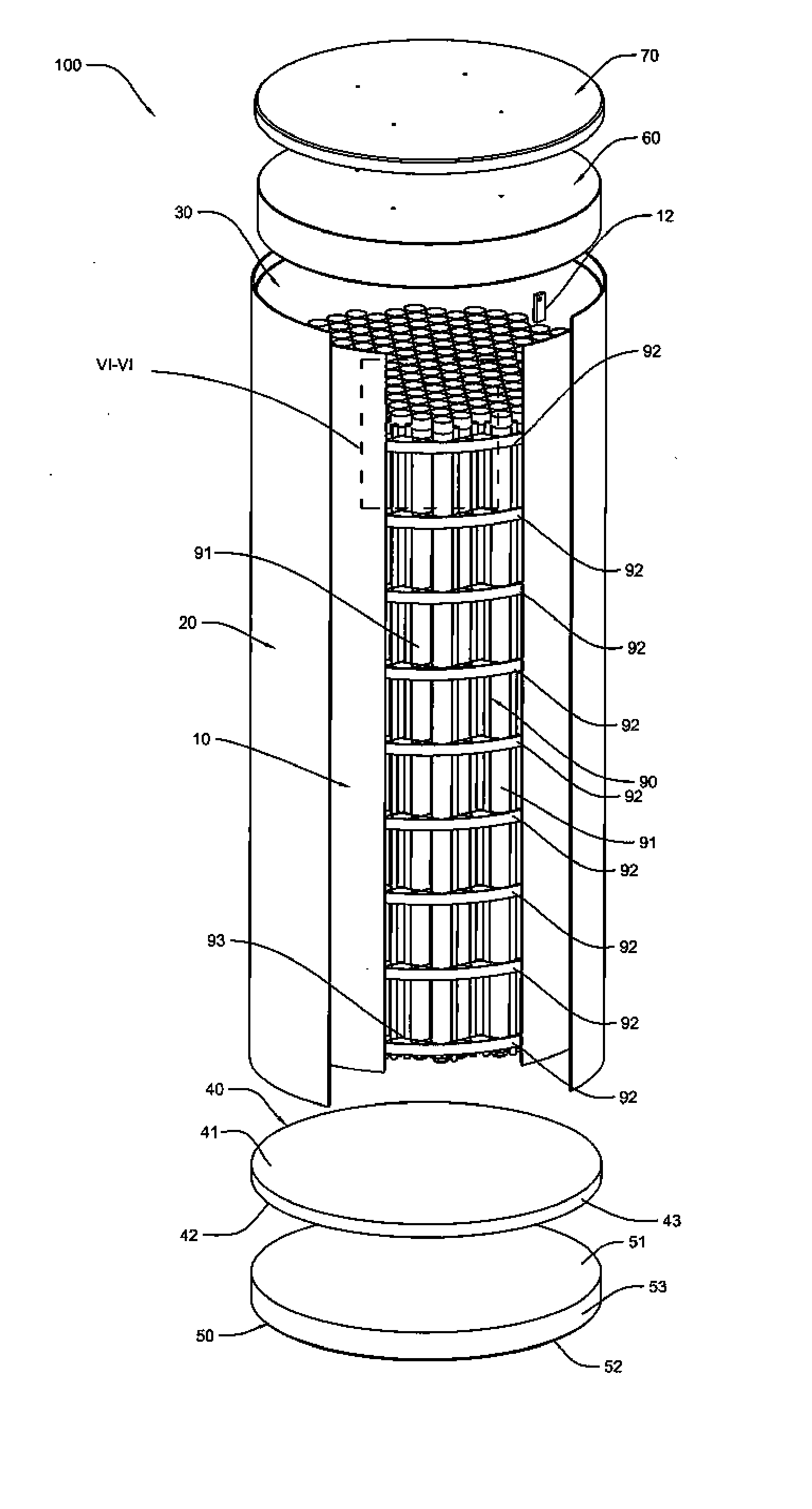
ActiveUS20080069291A1Efficiently accommodate both poison rodEfficiently spent nuclear fuelNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsRadioactive wasteEngineering
A canister apparatus, basket apparatus and combinations thereof for transporting and / or storing high level radioactive waste, such as spent nuclear fuel. The canister apparatus comprises a cavity for receiving the spent nuclear fuel that is surrounded by two independent gas-tight containment boundaries. The structures that form the two independent gas-tight containment boundaries are in substantially continuous surface contact with one another, thereby facilitating sufficient heat removal from the cavity. In another aspect, the invention is a basket apparatus having a plurality of disk-like grates arranged in a stacked and spaced arrangement so that the cells of the disk-like grates are aligned. In still another aspect, the invention can be a basket apparatus having a disk-like grate having a ring-like structure encompassing a gridwork of beams specially arranged to achieve a unique cell configuration.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
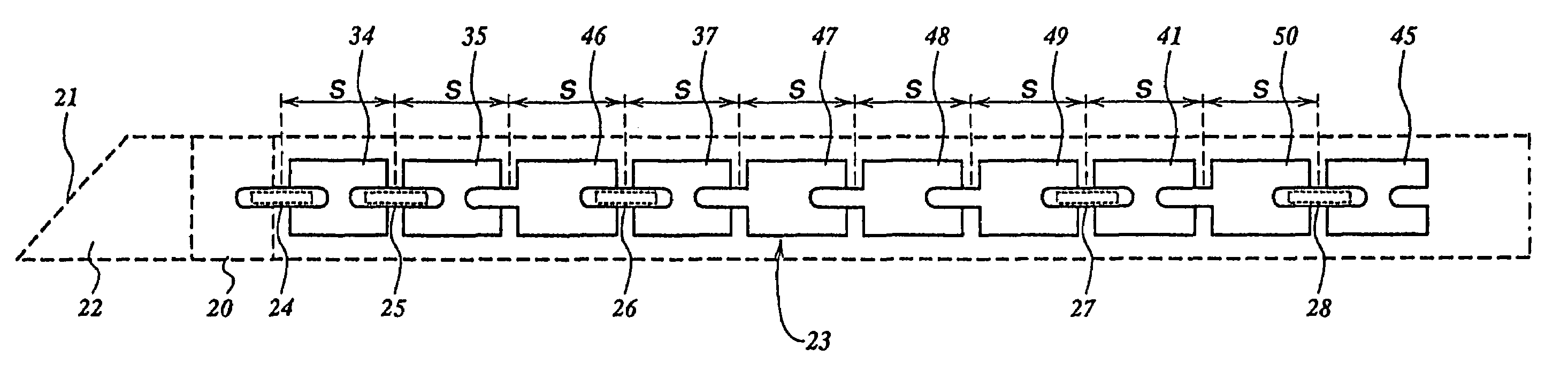
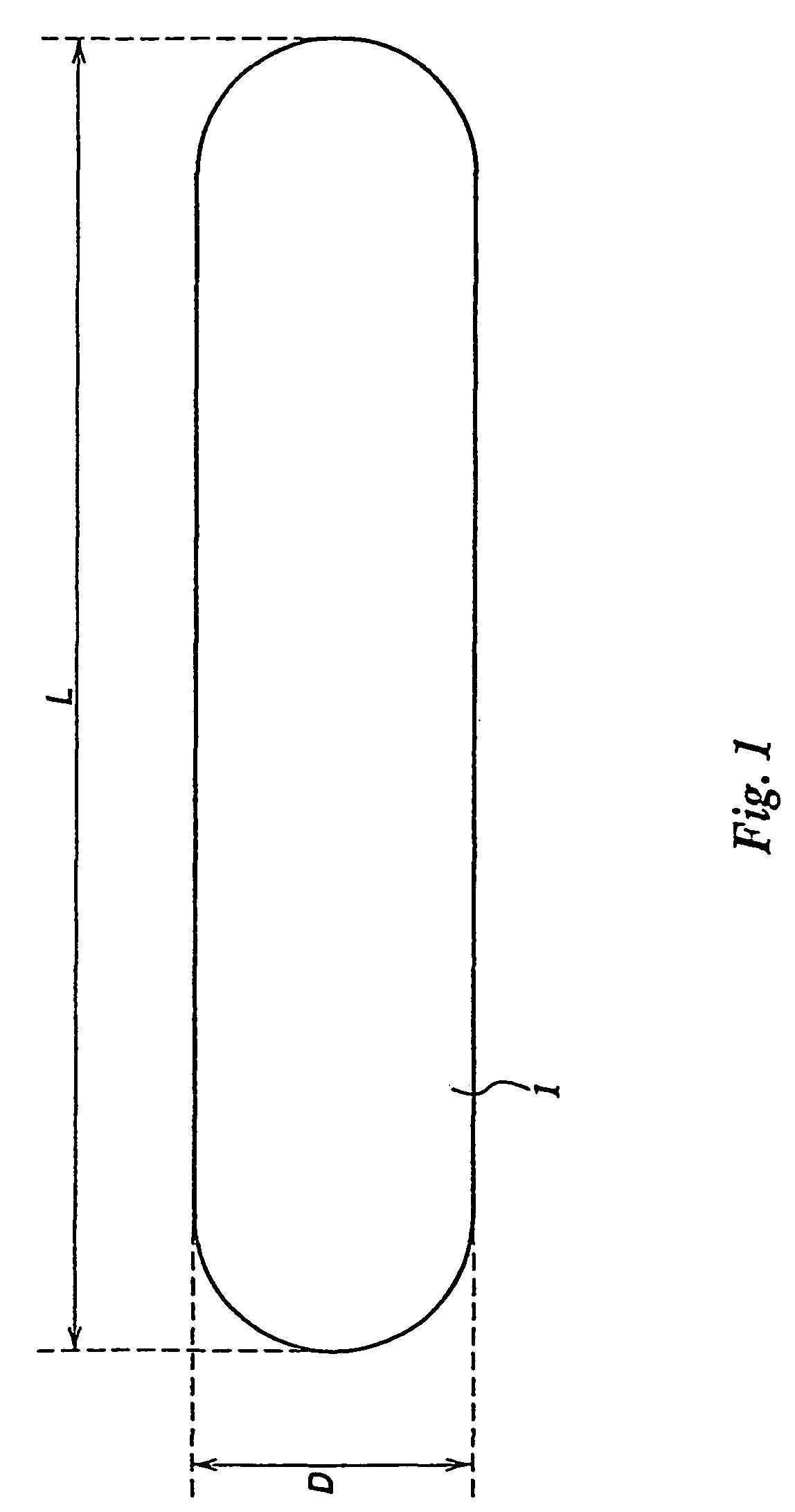
Row of radioactive seeds and non-radioactive spacers and connector therefore
InactiveUS7008367B2Ensure flexibilityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadioactive wasteEngineering
An arranged row of radioactive seeds and non-radioactive spacers with a predetermined pitch can be provided with physical coherence by applying connectors between the separate seeds and spacers. In a first embodiment the connectors are elongated with introversions at both ends, in a second embodiment a connector also forms a spacer and is provided at one end with an introversion and at another end with a projection in the form of a seed.
Owner:NUCLETRON OPERATIONS
Method of removing radioactive materials from a submerged state and/or preparing spent nuclear fuel for dry storage
ActiveUS20090069621A1Quantity maximizationIncreasing transfer procedure cycleNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A system, apparatus and method of processing and / or removing radioactive materials from a body of water that utilizes the buoyancy of the water itself to minimize the load experienced by a crane and / or other lifting equipment. In one aspect, the invention is a method comprising: a) submerging a container having a top, a bottom, and a cavity in a body of water having a surface level, the cavity filling with water; b) positioning radioactive material within the cavity of the submerged container; c) raising the submerged container until the top of the containment apparatus is above the surface level of the body of water while a major portion of the container remains below the surface level of the body of water; and d) removing bulk water from the cavity while the top of the container remains above the surface level of the body of water and a portion of the container remains submerged. The bulk water can be added back into the cavity to add neutron shielding after the container is placed in a staging area and prior to personnel performing the desired operations to the container. As a result, gamma radiation and neutron shielding of the container can be maximized for any crane capacity.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
Device for loading radioactive seeds
InactiveUS6926657B1Quickly and easily and accurately prepareX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadioactive wasteAdemetionine
Owner:MEDI PHYSICS IN
Acidified zeolite
The invention discloses an acidified zeolite. The technical scheme is as follows: the acidified zeolite is composed of zeolite, attapulgite clay, magnesia, hydrochloric acid, instant sodium silicate, polyvinyl alcohol, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and sodium carbonate. The acidified zeolite materials are input into a mill and milled, and the milled powder is the acidified zeolite. The production method of acidified red mud adopts acidification before composite proportioning, thereby avoiding the chemical reaction between the sulfuric acid and the instant sodium silicate, polyvinyl alcohol, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and sodium carbonate; and the acidified zeolite can effectively remove ammonia, iron, fluorine, phosphides and micro pollutants in domestic sewage, and can be used for removing or recovering heavy metal ions and treating radioactive waste. The acidified rear has the characteristics of favorable thixotropy, favorable heat stability, favorable plasticity and favorable binding property, and is suitable for producing drying agents, adsorptive separation agents, molecular sieves, catalysts, defluorination soil improvers, deodorizers and firefighting products.
Owner:江苏世澳非金属应用科技有限公司
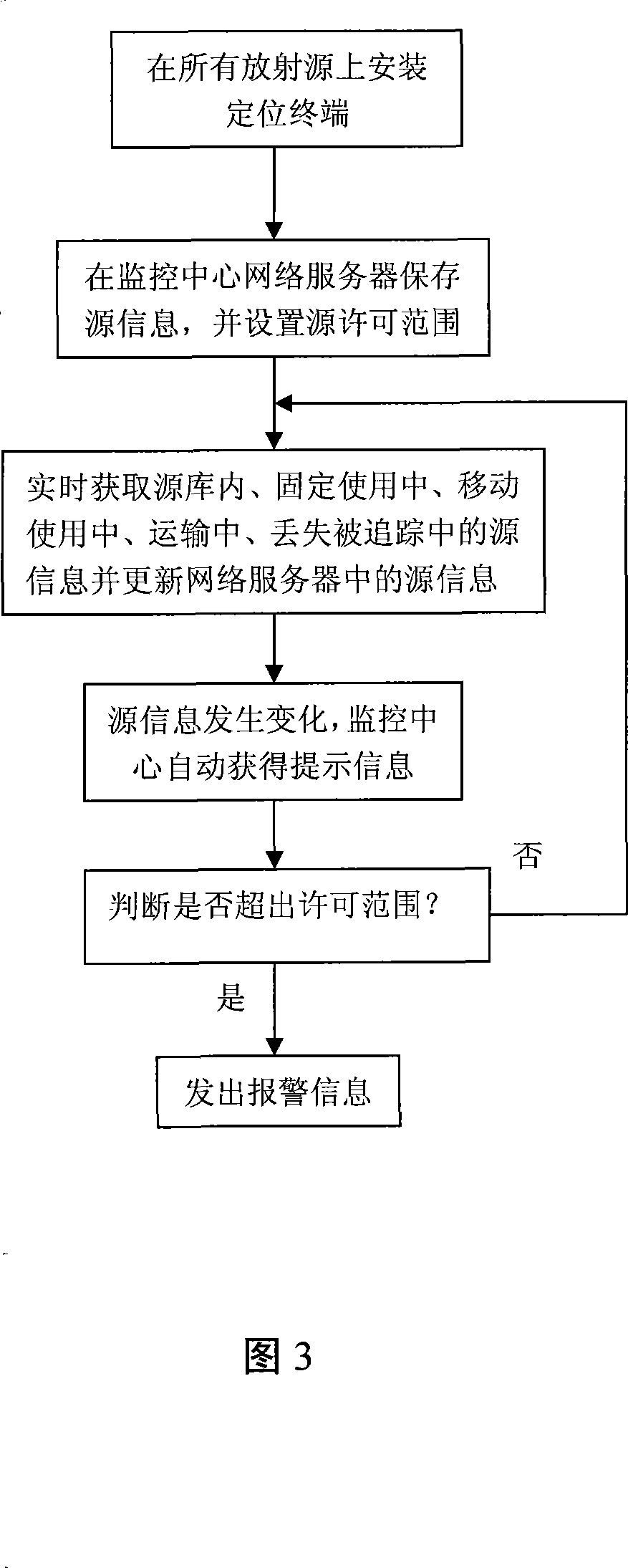
Method and system for automatically monitoring and real time monitoring radioactive source
ActiveCN101221685AAvoid managementAutomate regulationAlarmsTransmissionComputer terminalRadioactive waste
The invention relates to a radioactive source automatic supervision and real-time monitoring method and a system. The method mainly comprises the following steps: a positioning terminal in which a GPS positioning unit and a CDMA network positioning unit are arranged and source file information is solidified is arranged on a radioactive source; the source file information is stored in a network server of a monitoring center and a source admission range is set up; source position information and source file information is acquired at real time and corresponding source information in the network serve is updated at real time; when the source information stored in the network server changes, the monitoring center automatically obtains prompting information and judges whether the change of the source information is beyond the admission range; when the change of the source information exceeds the admission range, automatic alarm is carried out. The system realizing the method comprises a positioning terminal assembly device, a source information storing device, a source information updating device, a source information monitoring device and a real-time alarm device. The method and the system realize automatic supervision and real-time monitoring of all links of the radioactive source, thereby putting an end to severe security accidents like loss of the radioactive source, etc.
Owner:BEIJING HUALIXING SCI TECH DEV
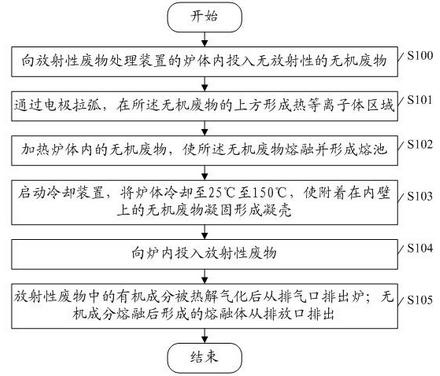
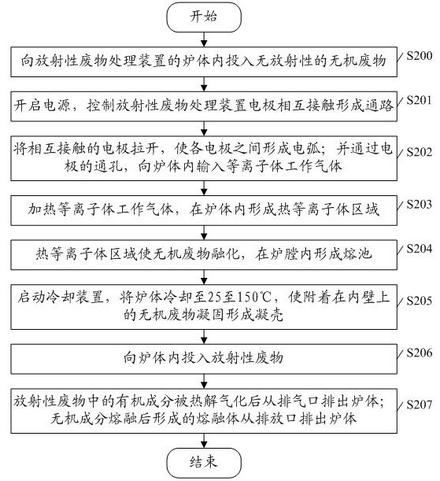
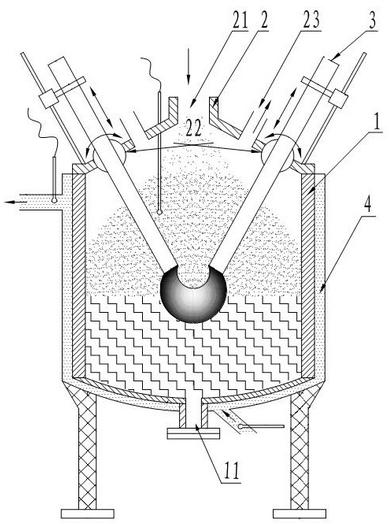
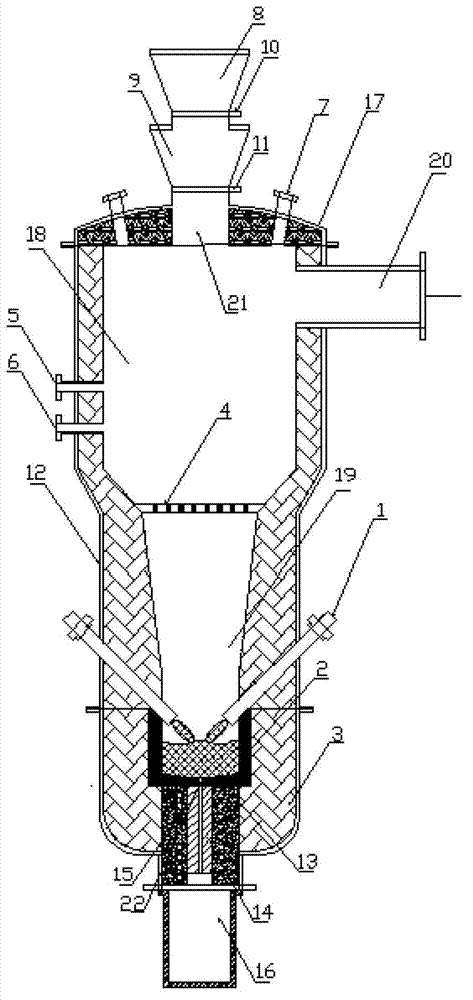
Method and device for treating radioactive wastes
ActiveCN102157215AAvoid pollutionImprove corrosion resistanceRadioactive decontaminationPlasma techniqueRefractoryRadioactive waste
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for treating radioactive wastes. The method comprises the following steps of: putting nonradioactive inorganic wastes into a furnace body of a radioactive waste treatment device to form a thermal plasma area above the inorganic wastes by electrode arcing, and heating the putted inorganic wastes to form a molten pool; starting a coolingdevice to cool down the furnace body to a temperature of 25-150 DEG C so as to make the inorganic wastes attached to the inner wall of the furnace body be solidified to form a shell; putting radioactive wastes into the furnace body to pyrolyze organic elements of the radioactive wastes, and then exhausting the generated gas from the furnace body; and charging inorganic elements of the radioactivewastes into the molten pool to be molten, and discharging the molten inorganic elements out of the furnace body. During the implementation of the method and device disclosed by the invention, the furnace body does not need refractory materials, and the molten body is solidified in an area near the inner wall of the furnace to form the shell, thus the inner wall of the furnace does not directly contact with the molten body, radioactive nuclides are prevented from polluting the inner wall of the furnace, the device can be used for treating various wastes, the service life of the device is long and the amount of residual wastes is small.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD
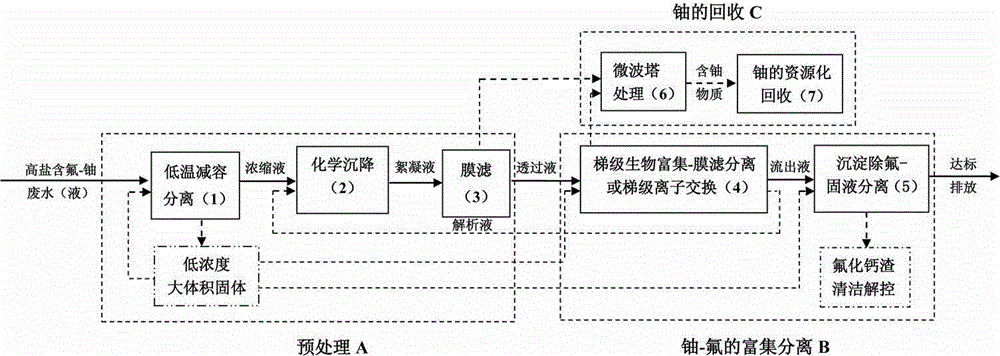
Method for deeply purifying and recovering hyperhaline fluoric-u radioactive waste solution
ActiveCN104835545AReduce lossesImprove efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisLiquid wasteRecovery method
The invention discloses a method for deeply purifying and recovering hyperhaline fluoric-U radioactive waste solution. The method comprises three sequent treatment phases including pretreatment, enrichment and separation of U-F and recovery of U, and can be further finely divided into 7 treatment units, including lower temperature reduction separation, chemical sedimentation, film filtering, step-grade organism enrichment-film filtering separation or step ion exchange, deposit fluorine removal solid-liquid separation, microwave tower treatment and resource recovery of U; under the condition that the salinity of waste solution to be treated is 0.1-10%, the initial U concentration is 0.1-1000mg / L, and the fluorine concentration is 0.01-15g / L, after treatment, the concentration of U is not larger than 0.05mg / L, the concentration of the fluorine is not higher than 10mg / L, and the recovery rate of U is larger than 90%. The method for deeply purifying and recovering hyperhaline fluoric-U radioactive waste solution is suitable for treating hyperhaline fluoric-U radioactive waste solution and the resource recovery of radioactive U.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for producing radioactive materials for medical treatment using x-rays produced by an electron accelerator
InactiveUS6907106B1Effective interceptionImprove cooling effectConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesHigh energyX-ray
An apparatus and method for irradiating target objects, especially medical stents for in vivo implantation. A linear accelerator provides a high energy electron beam that impinges upon and is received by an x-ray conversion target. The x-ray conversion target is activated by either a static or dynamically moveable electron beam to generate and emit an x-ray flux so as to efficiently intercept the target object. The x-ray flux is directed to the target object for a desired time period and is of sufficiently high energy to efficiently impart radioactive properties to the target object. Alternatively, the target object is positioned within the path of the x-ray flux or is translated within the path during irradiation. Mechanical transport assemblies such as a carousel, rotational and / or linear translator and / or movement tube system also may be provided.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Composite materials and techniques for neutron and gamma radiation shielding
ActiveUS7250119B2Increase volumeWaste loadingDiffusing elementsNuclear engineering solutionsPolymer modifiedCement grout
Owner:SAYALA DASHARATHAM
Primary voltaic sources including nanofiber schottky barrier arrays and methods of forming same
ActiveUS20140021827A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanosensorsSolid carbonRadioactive waste
Primary voltaic sources include nanofiber Schottky barrier arrays and a radioactive source including at least one radioactive element configured to emit radioactive particles. The arrays have a semiconductor component and a metallic component joined at a metal-semiconductor junction. The radioactive source is positioned proximate to the arrays such that at least a portion of the radioactive particles impinge on the arrays to produce a flow of electrons across the metal-semiconductor junction. Methods of producing voltaic sources include reacting at least one carbon oxide and a reducing agent in the presence of a substrate comprising a catalyst to form a solid carbon product over the substrate. Material is disposed over at least a portion of the solid carbon product to form a nanofiber Schottky barrier array. A radioactive source is disposed adjacent the nanofiber Schottky barrier array.
Owner:SEERSTONE
Mixed nuclide gamma point source volume sample efficiency calibration method
InactiveCN103135122AGuarantee the traceability of the quantity valueAvoid complexityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCalibration resultRadioactive waste
The invention belongs to the ionizing radiation measurement technology, in particular to a mixed nuclide gamma point source volume sample efficiency calibration method. Measurement results of solid mixed nuclide gamma point source around a detector are adopted and the monte carlo simulation calculation is combined to determine the detection efficiency of the detector to arbitrary axisymmetric shape volume samples. Through the measurement results of solid mixed nuclide gamma point source around the detector, a volume sample detection efficiency curve can be determined. Under the premise that the traceability of calibration result values is guaranteed, the problems that complex manufacturing process and occurrence of radioactive wastes which are brought by other calibration methods ( such as standard volume sample calibration) are avoided.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Preparation method of vitrification substrate for radioactive nuclear waste
ActiveCN101826376AImprove stabilityImprove radiation stabilityRadioactive decontaminationVitrificationRadioactive waste
The invention relates to a preparation method of a vitrification substrate for radioactive nuclear wastes, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: mainly taking (NH4) H2PO4, Fe2O3 and H3BO3 as raw materials, proportioning, mixing, melting for 2-3.5 hours at the temperature of 1100-1250 DEG C, forming, and annealing, thereby preparing a vitrification body with glass of an iron-boron-phosphorus system as the substrate. The invention combines the advantages of high irradiation stability of the vitrification body of the borosilicate system and large waste-loading capacity of thevitrification body of the iron phosphate system. The prepared vitrification body has the advantages of excellent chemical stability and good thermal stability. Moreover, the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process and easy engineering, and can be widely applied in the curing treatment of radioactive nuclear wastes.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process and System for Treating Radioactive Waste Water to Prevent Overloading Demineralizer Systems
ActiveUS20090038961A1Easily backflushedAvoid disposition problemsTreatment involving filtrationSolid sorbent liquid separationWastewaterRadioactive waste
A process and system for treating waste water containing contaminants to prevent excessive accumulation on demineralizer media of a driver contaminate capable of such accumulation before another contaminant can reach a predetermined level of accumulation. The waste water is treated upstream of the demineralizer media with removal means for specifically removing the driver contaminant while leaving the other contaminant for subsequent removal by the demineralizer media. The amount of accumulation on the demineralizer media of the other contaminant is monitored, and the supplying of treated waste water to the demineralizer media is terminated when its accumulation reaches the predetermined level.
Owner:ENERGYSOLUTIONS LLC
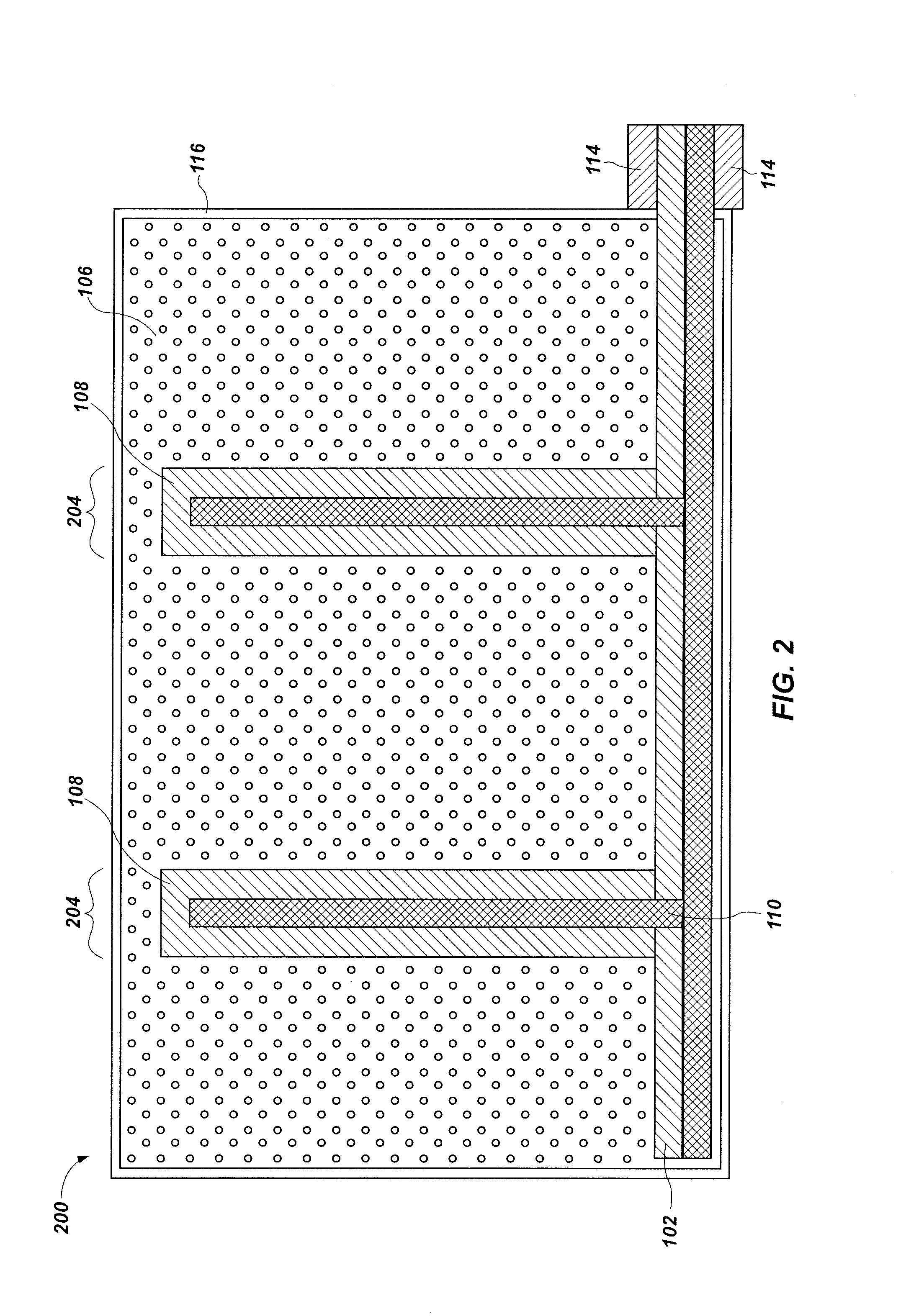
High performance neutron detector with near zero gamma cross talk
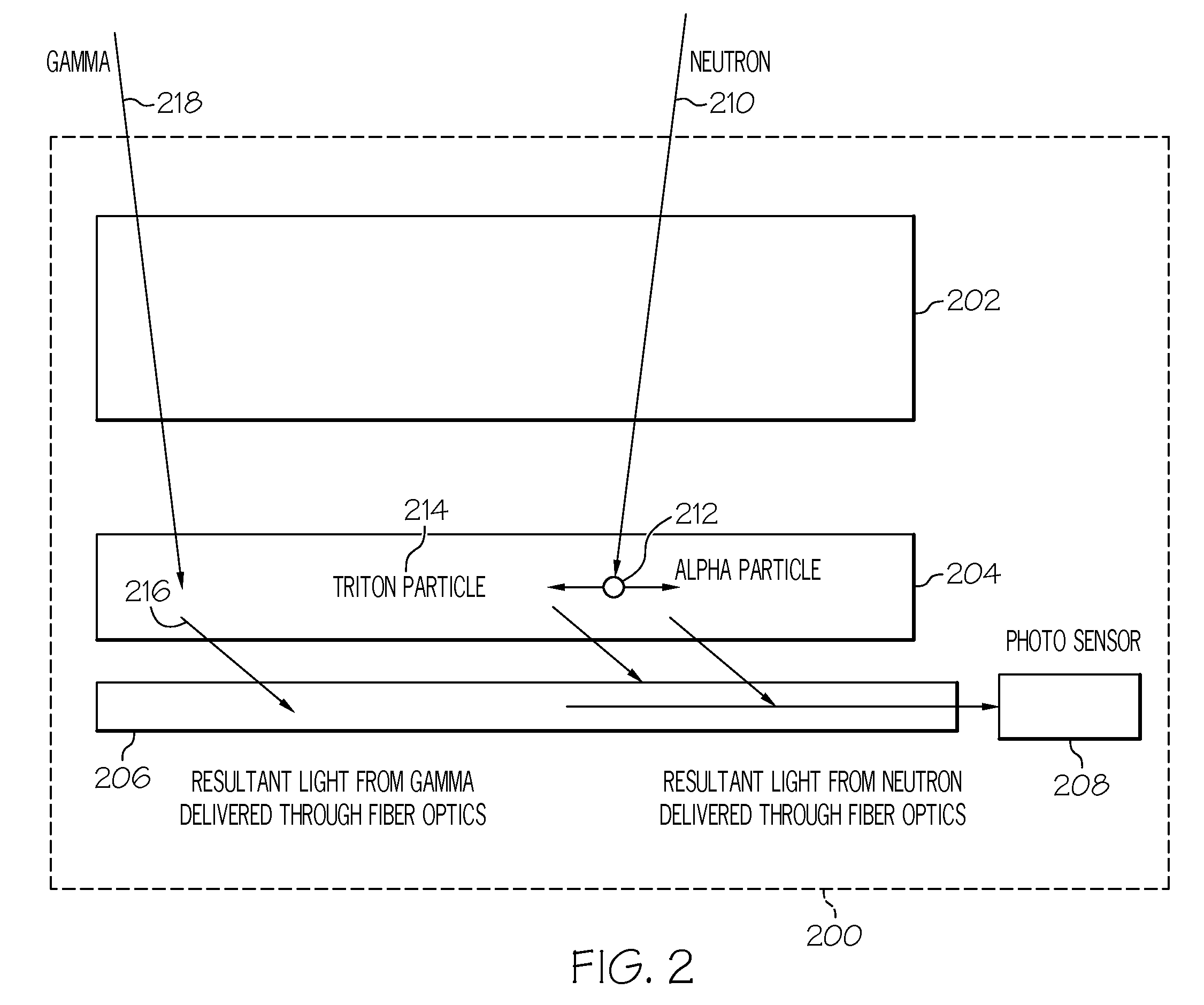
InactiveUS20100294943A1Light transmissionReduce manufacturing costMeasurement with scintillation detectorsPhotometryFiberRadioactive agent
A scintillator system is provided to detect the presence of fissile material and radioactive material. One or more neutron detectors include scintillator material, and are optically coupled to one or more wavelength shifting fiber optic light guide media that extend from the scintillator material to guide light from the scintillator material to a photosensor. An electrical output of the photosensor is connected to an input of a pre-amp circuit designed to provide an optimum pulse shape for each of neutron pulses and gamma pulses in the detector signals. Scintillator material as neutron detector elements can be spatially distributed with interposed moderator material. Individual neutron detectors can be spatially distributed with interposed moderator material. Detectors and moderators can be arranged in a V-shape or a corrugated configuration.
Owner:EMR RESOURCES +2
Method of using nuclear waste to produce heat and power
A method of using nuclear waste material and exploiting heat generated by radioactive decay of said radioactive waste, comprising the steps of incorporating solid nuclear waste into glass, ceramic, or cementitious blocks, covering the blocks in heat absorbing sealed containers, placing the sealed containers in a columnar arrangement in a gas tight containment room, circulating a heat exchange gas around said containers, passing the heated gas through a sealed heat exchanger, and using the heated water for useful work.
Owner:SNYDER STUART
Boron-containing radioactive spent resin cement solidification method
InactiveCN101456715AImprove processing efficiencySolid waste managementPressurized water reactorPortland cement
The invention discloses a method for cement solidification of a boron-containing radioactive waste resin, which belongs to the technical field of cement solidification of the boron-containing radioactive waste resin of a pressurized water reactor nuclear power station. The method comprises the following steps: the boron-containing radioactive waste resin of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station, ordinary Portland cement, a water reducing agent, zeolite, lime and water are taken as raw materials, the mixture ratio of the raw materials comprises that the boron-containing radioactive waste resin of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station: the ordinary Portland cement: the water reducing agent: the zeolite: the lime: the water is equal to 300-500L: 800-1,000kg: 4-5kg: 40-50kg: 25-30kg: 90-110kg, and the raw materials are weighed; and the materials are added into a C1 solidification barrel with a volume of 1 cubic meter and are stirred evenly to obtain a cement solidification body. The adoption of each solidification drum with the volume of 1 cubic meter can solidify 300 to 500L of radioactive resin, and remarkably improve the treatment efficiency of boron-containing radioactive waste resins of pressurized water reactors.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
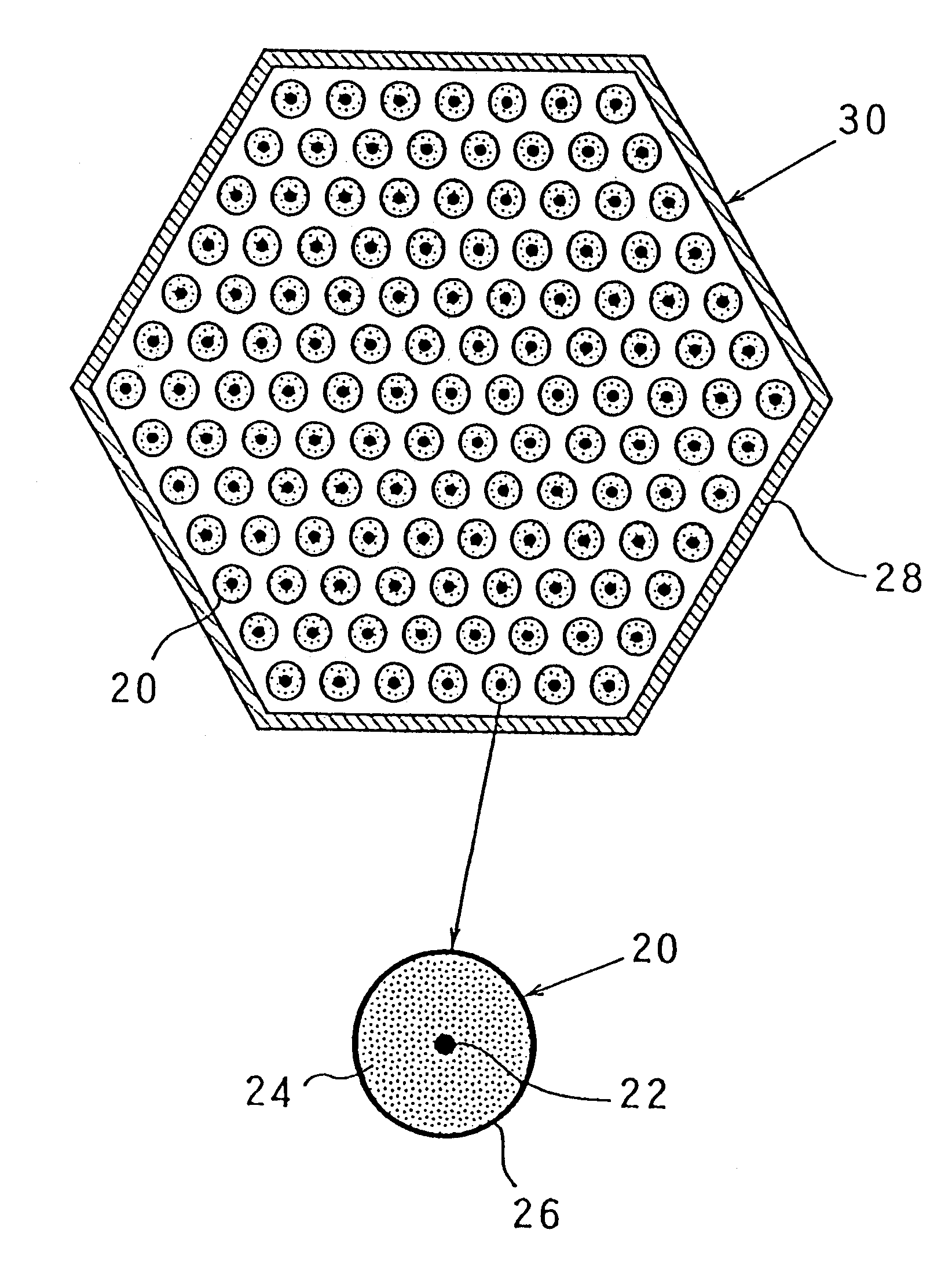
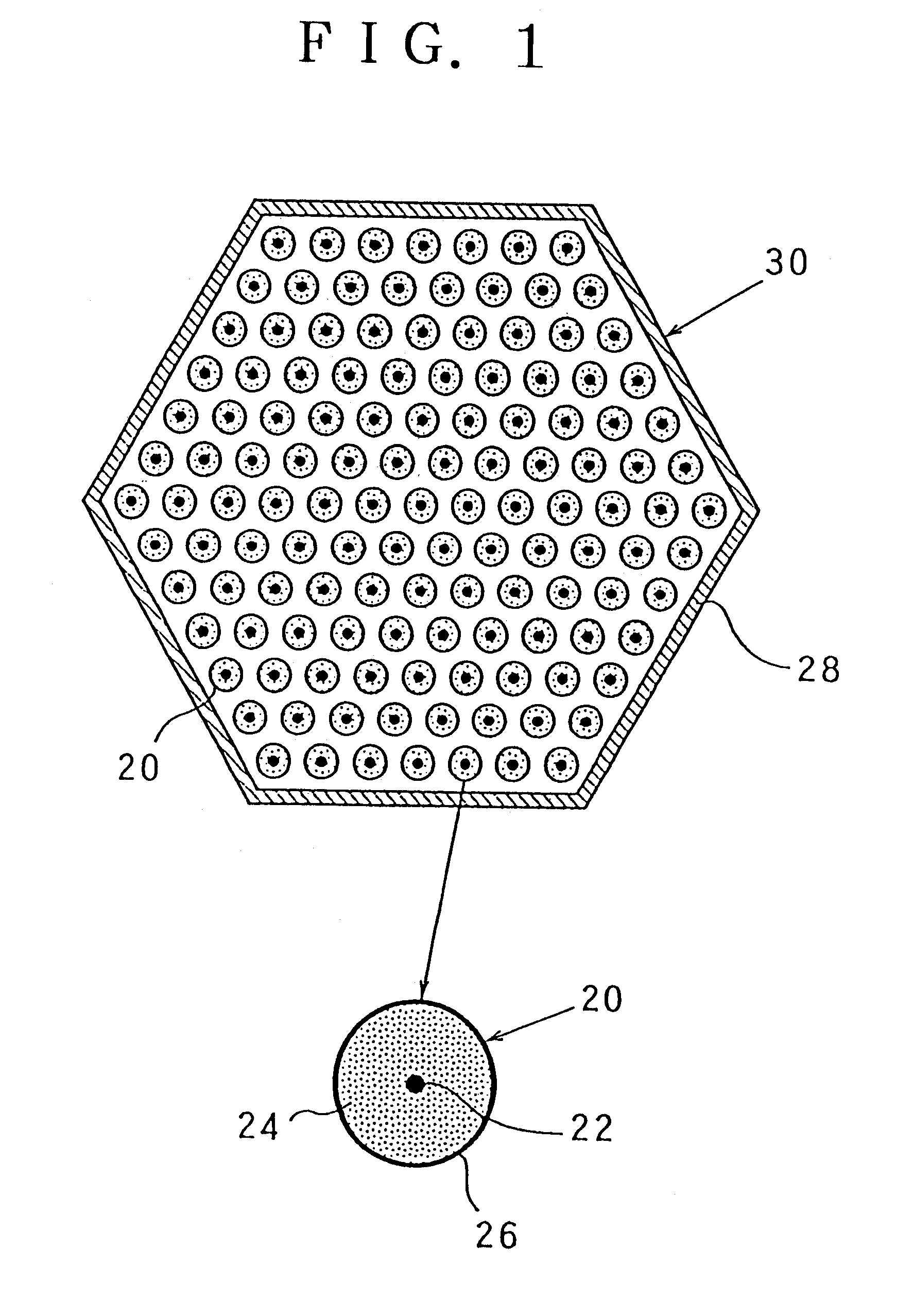
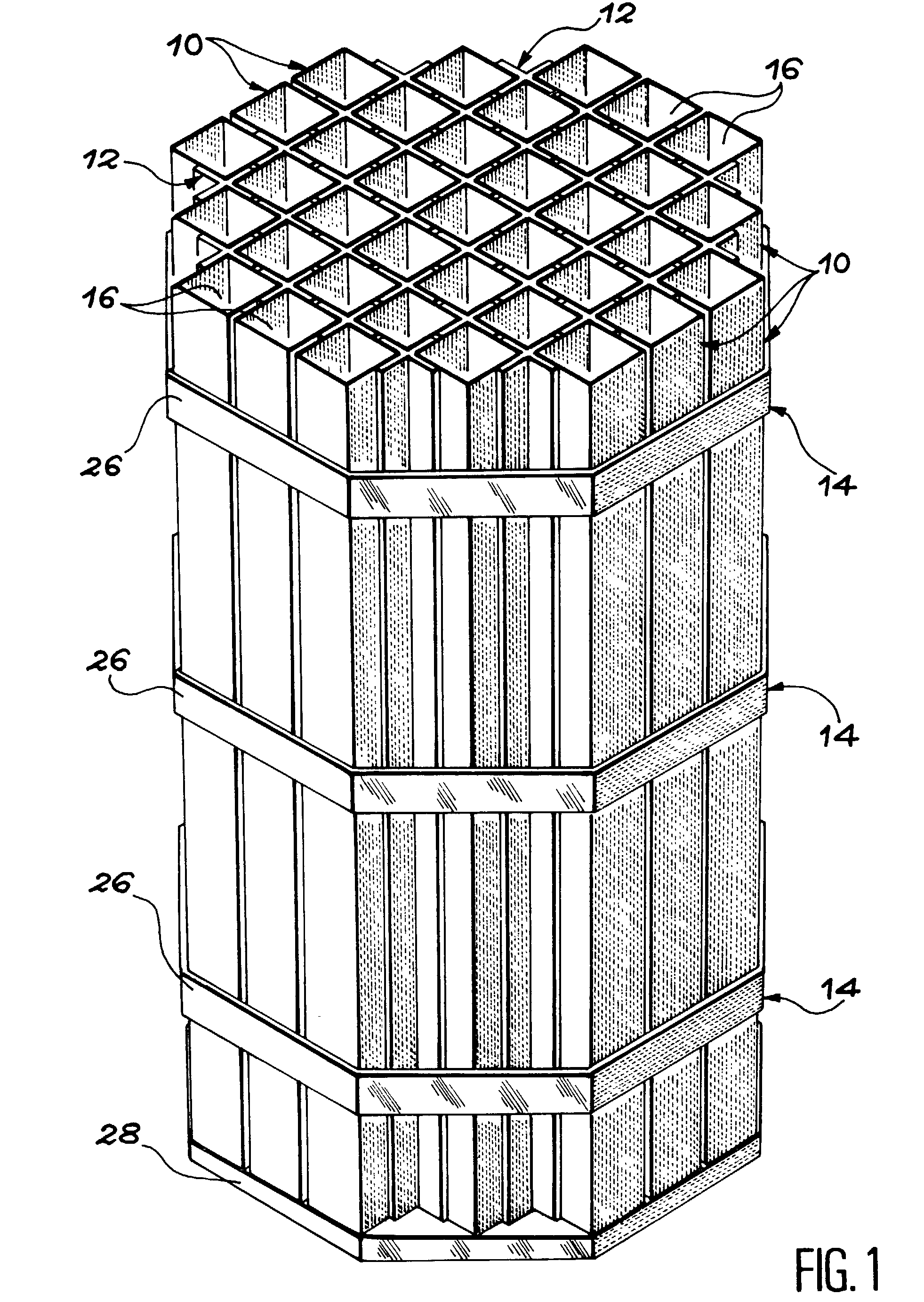
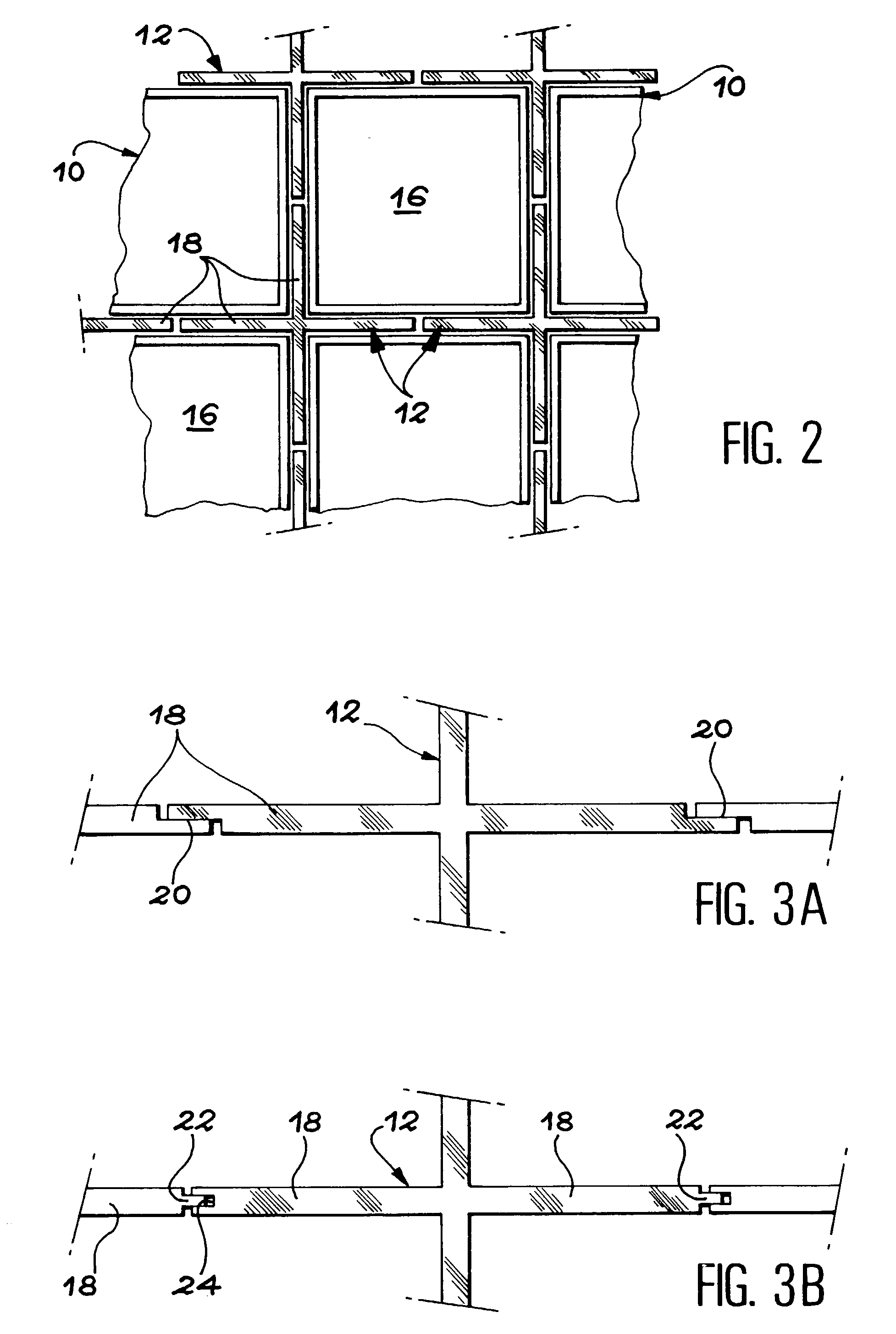
Storage container for radioactive materials
The basket comprises a bundle of tubes (10) connected to each other by an assembly structure (14) so as to form a regular network of compartments (16). Cross pieces (12) are placed between the tubes (10) so as to define a second wall approximately continuous around each compartment (16) surrounding the first wall materialized by tubes (10) and at least partially in contact with this wall. Thus, baskets with compartments with arbitrarily shaped cross sections, and particularly square, rectangular, hexagonal or circular cross sections, can be made for a limited cost.
Owner:SOC POUR LES TRANSPORTSDE LINDUSTRIE NUCLEAIRETRANSNUCLEAIRE
Device and method for disposing low and medium-radioactivity solid waste by hot plasmas
InactiveCN102831945AReduce disposal storage spaceTo minimizeRadioactive decontaminationFlue gasEmission standard
The invention discloses a device and a method for disposing low and medium-radioactivity solid waste by hot plasmas. The device comprises a plasma melting gasification furnace, a hot plasma generator, a working gas preparation supply device, a cooling water supply device, a feeding device, a glass solidified body discharging and receiving device, a tail gas purification treatment device and corresponding measuring, controlling and monitoring systems. Organic and inorganic carbonaceous compositions in the waste are gasified by the hot plasmas in a low-temperature area of a hearth, generated ash and inorganic substances in the waste are melted in a high-temperature area of the hearth, added glass organizers are regulated so that radioactive nuclides are stably fixed in glass organizers, and flue gas meets emission requirements of air quality standards after being subjected to purification treatment. Besides, the device and the method for disposing the low and medium-radioactivity waste are environment-friendly, a disposal process is safe and reliable, disposal storage space for radioactive waste can be greatly reduced, national emission standards are met, and the purpose of minimized and stabilized disposal for the radioactive waste is achieved.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com