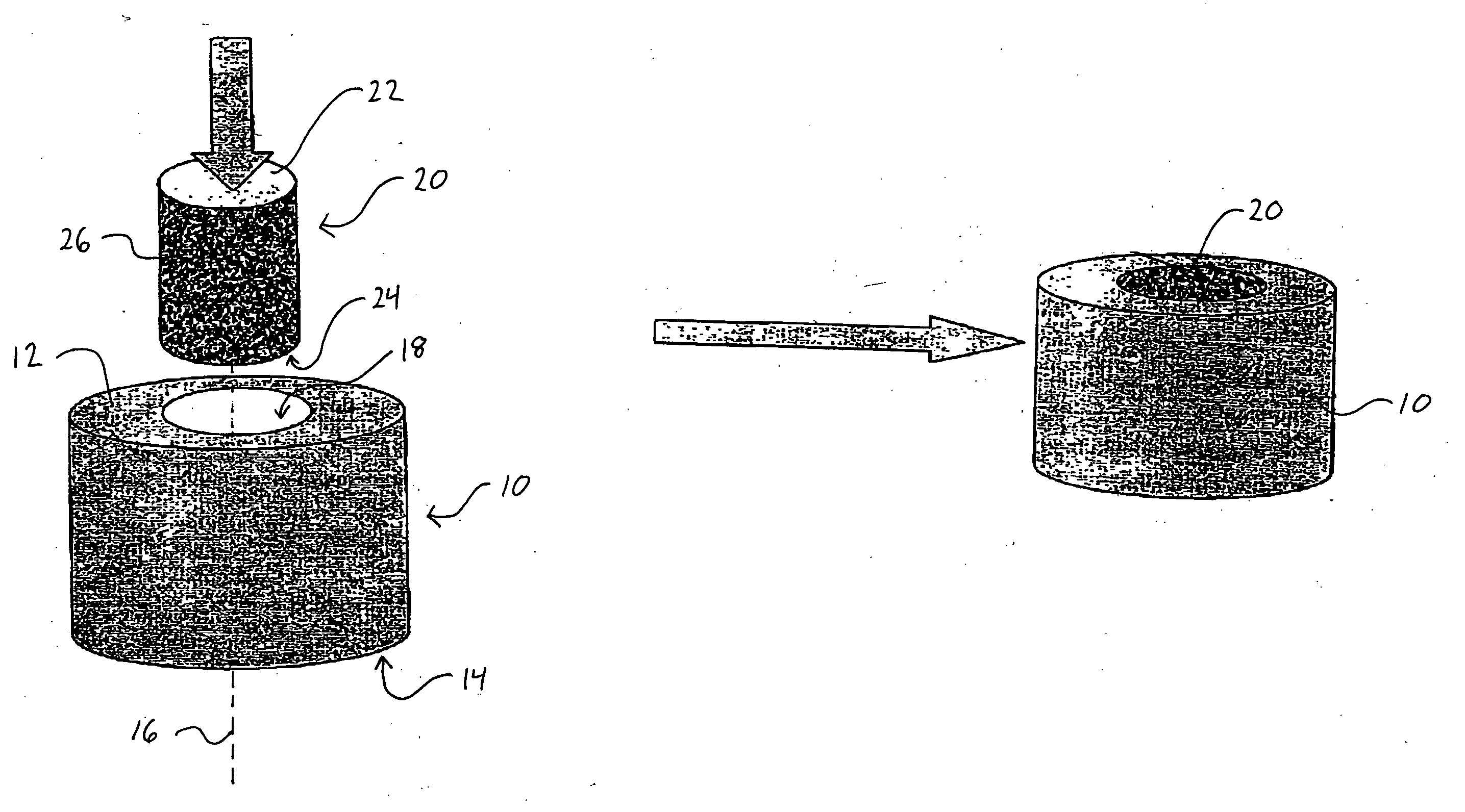
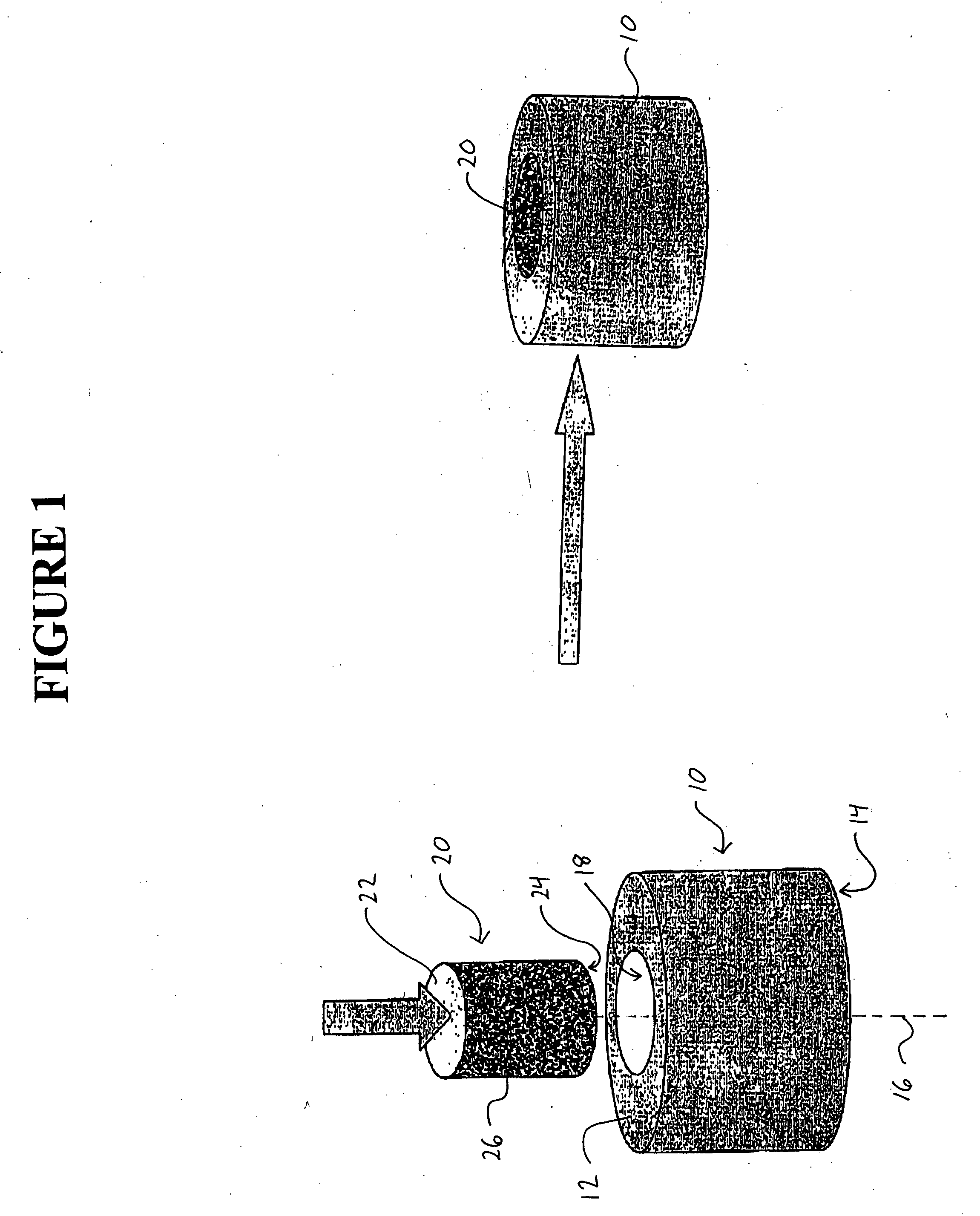
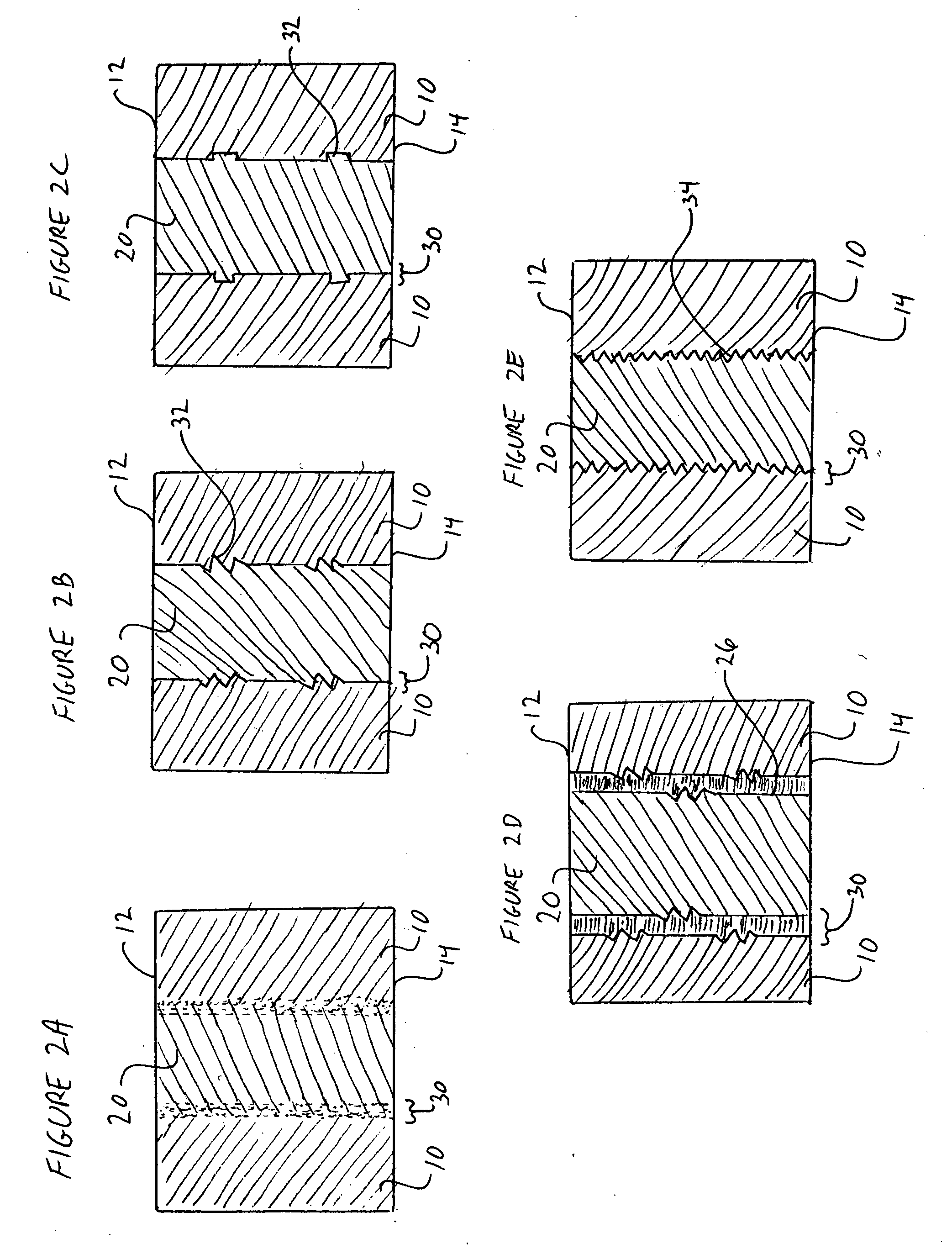
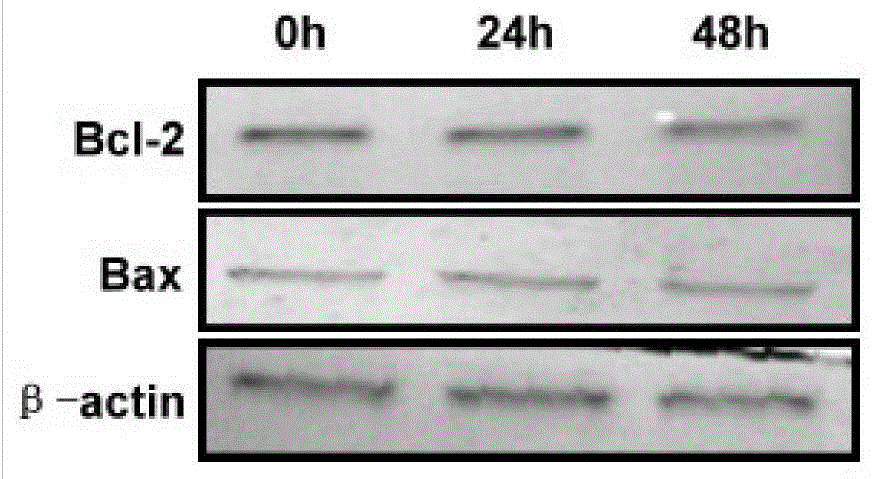
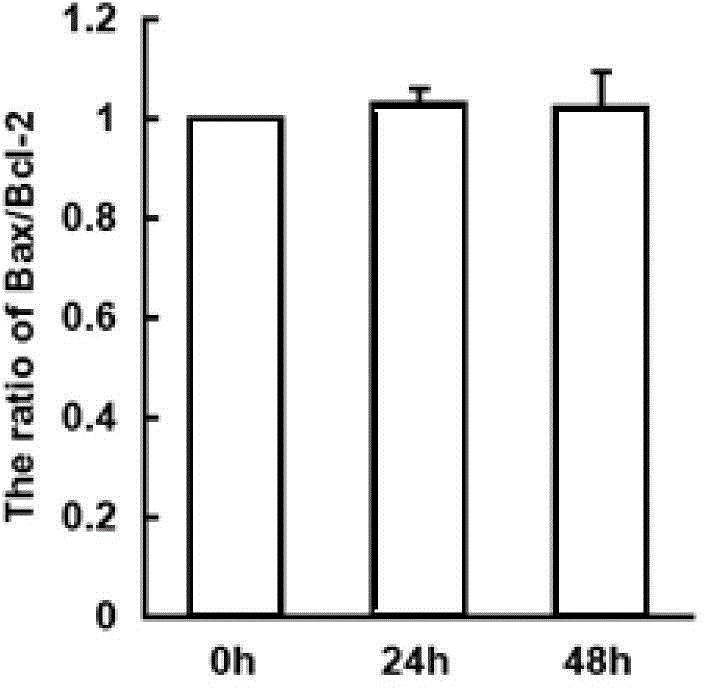
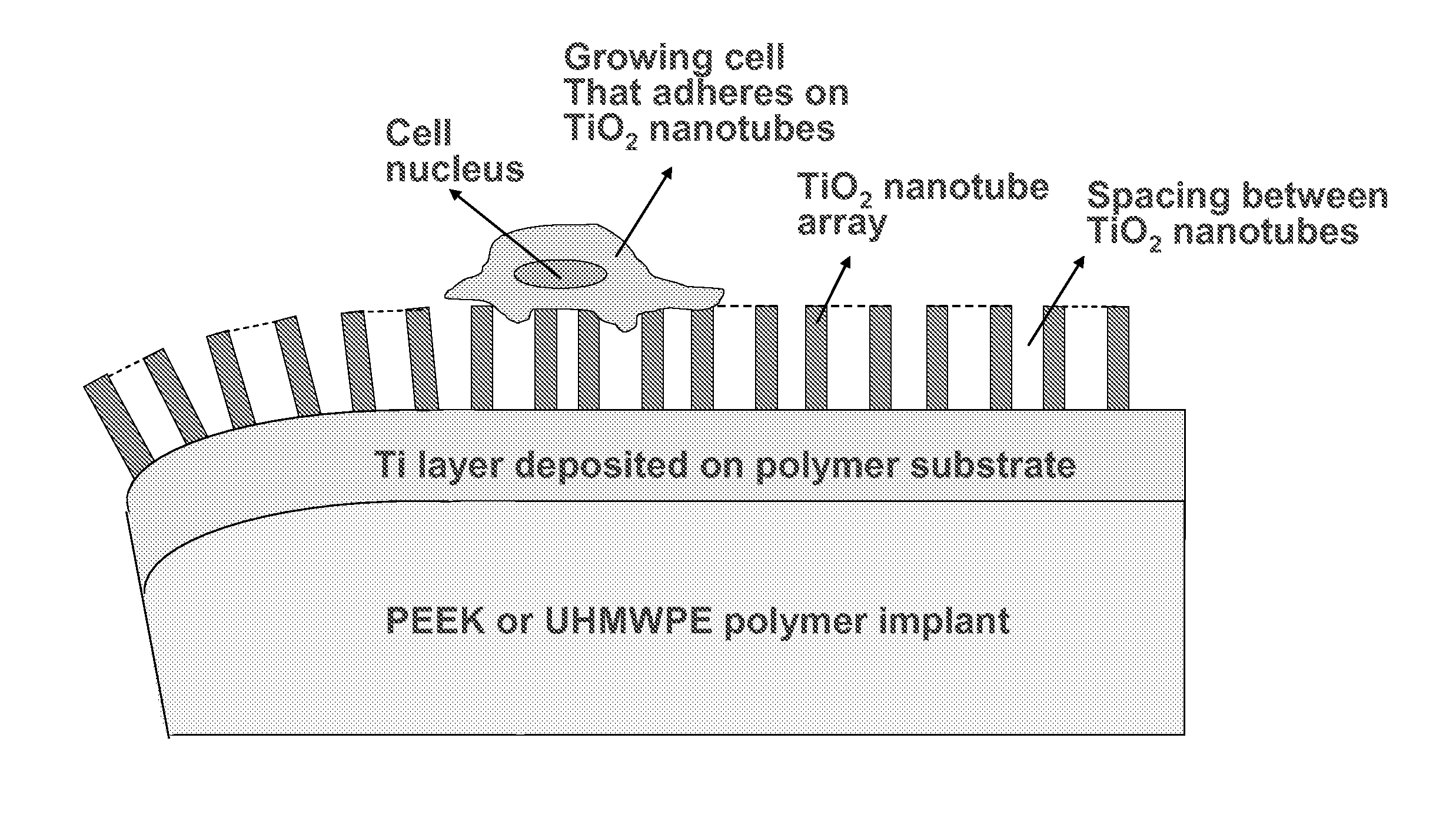
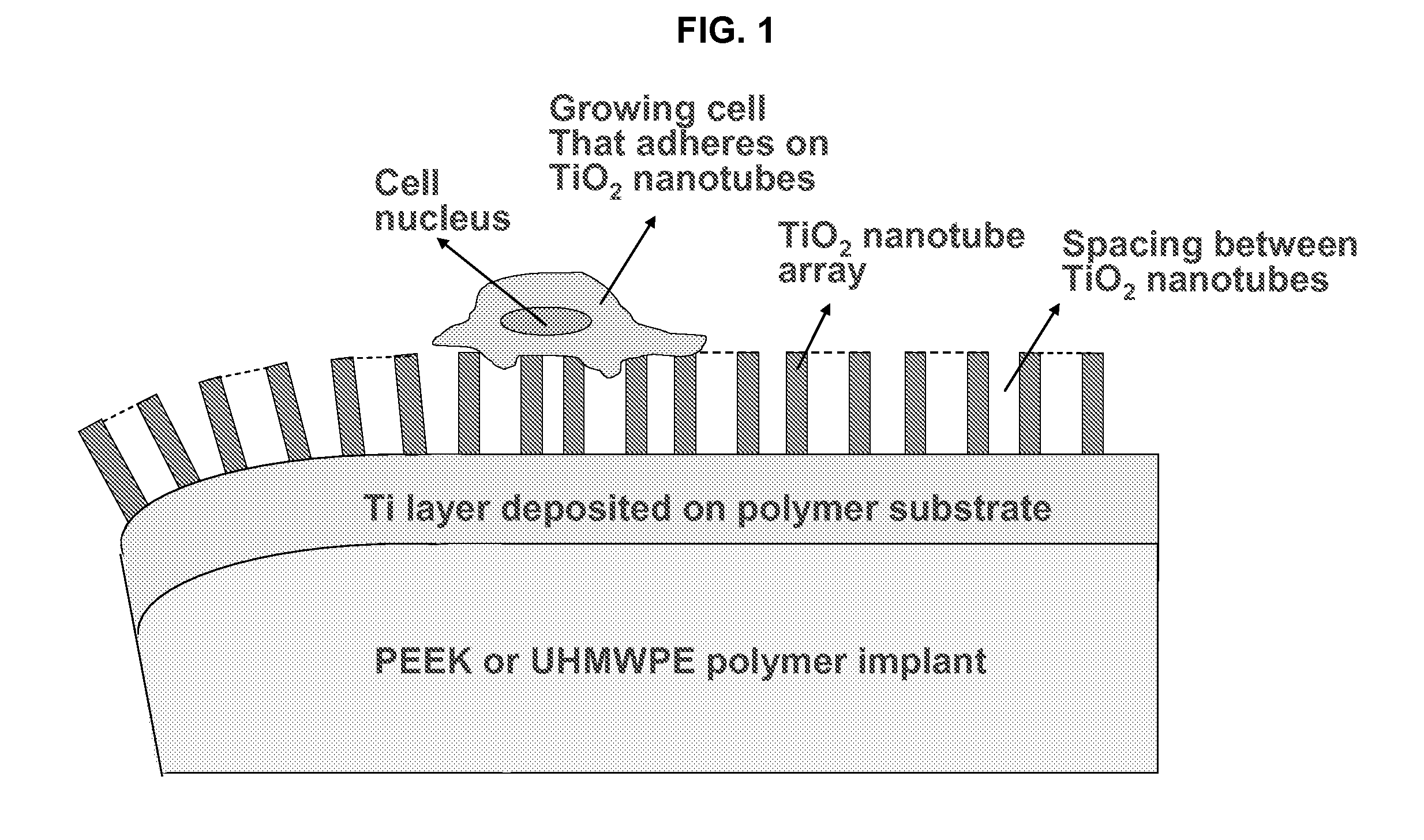
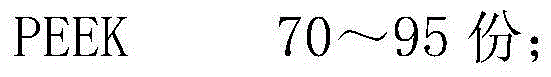Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1564 results about "Polyether ether ketone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a colourless organic thermoplastic polymer in the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family, used in engineering applications. It was originally introduced by Victrex PLC, then Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) in the early 1980s.
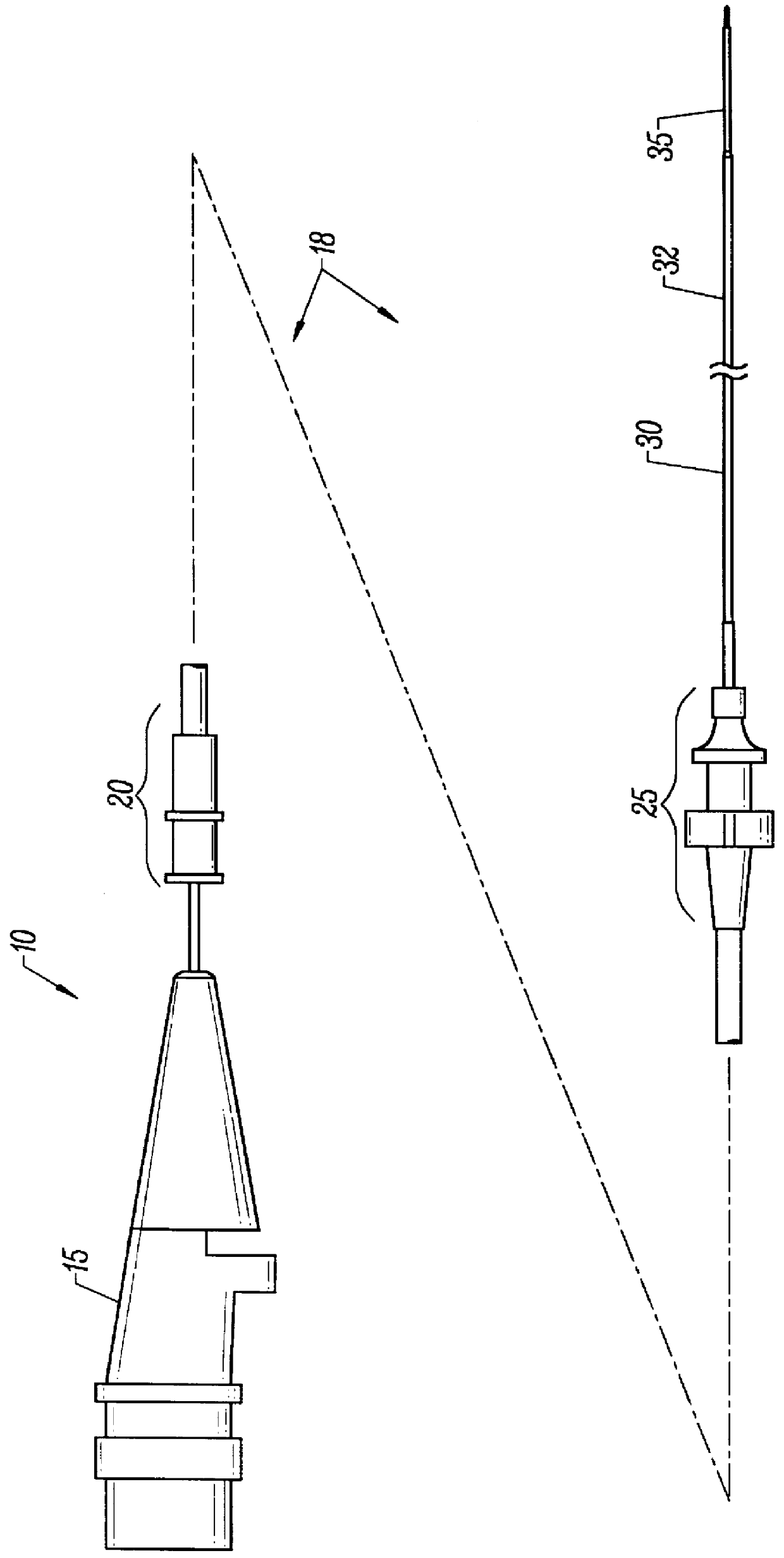
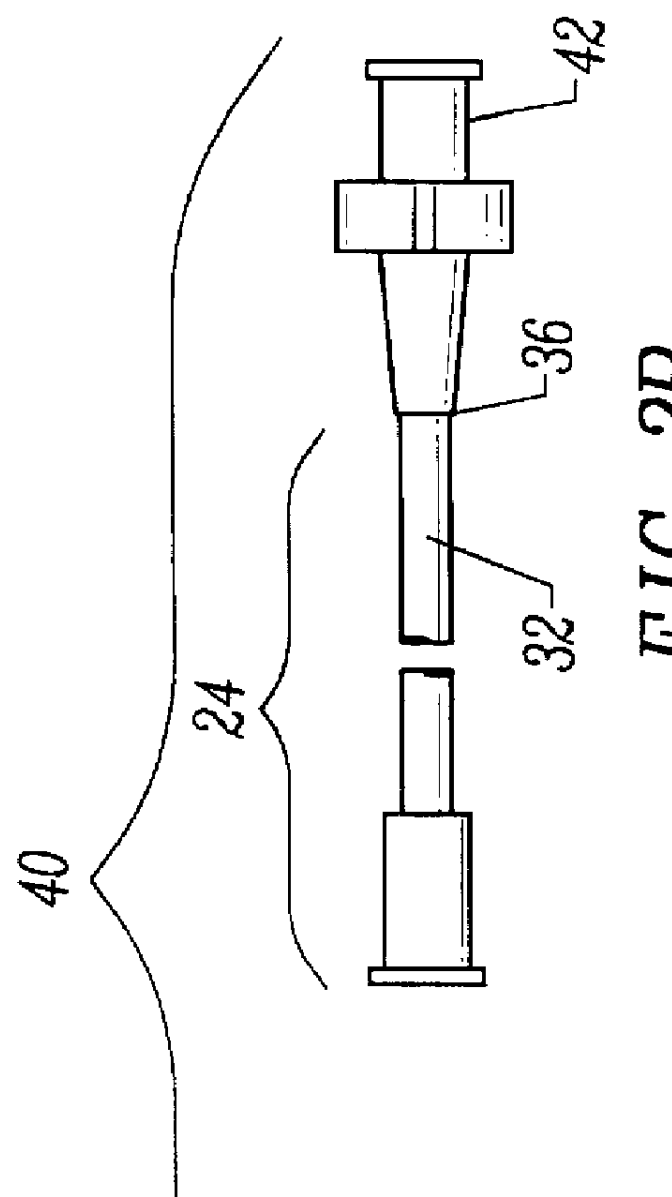
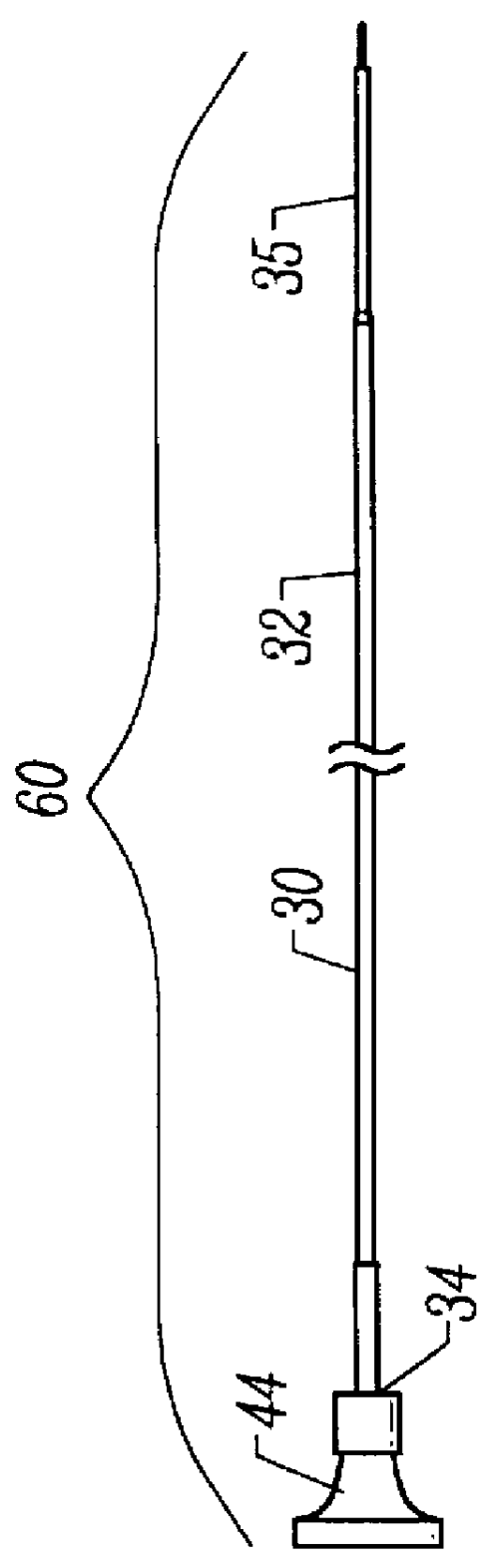
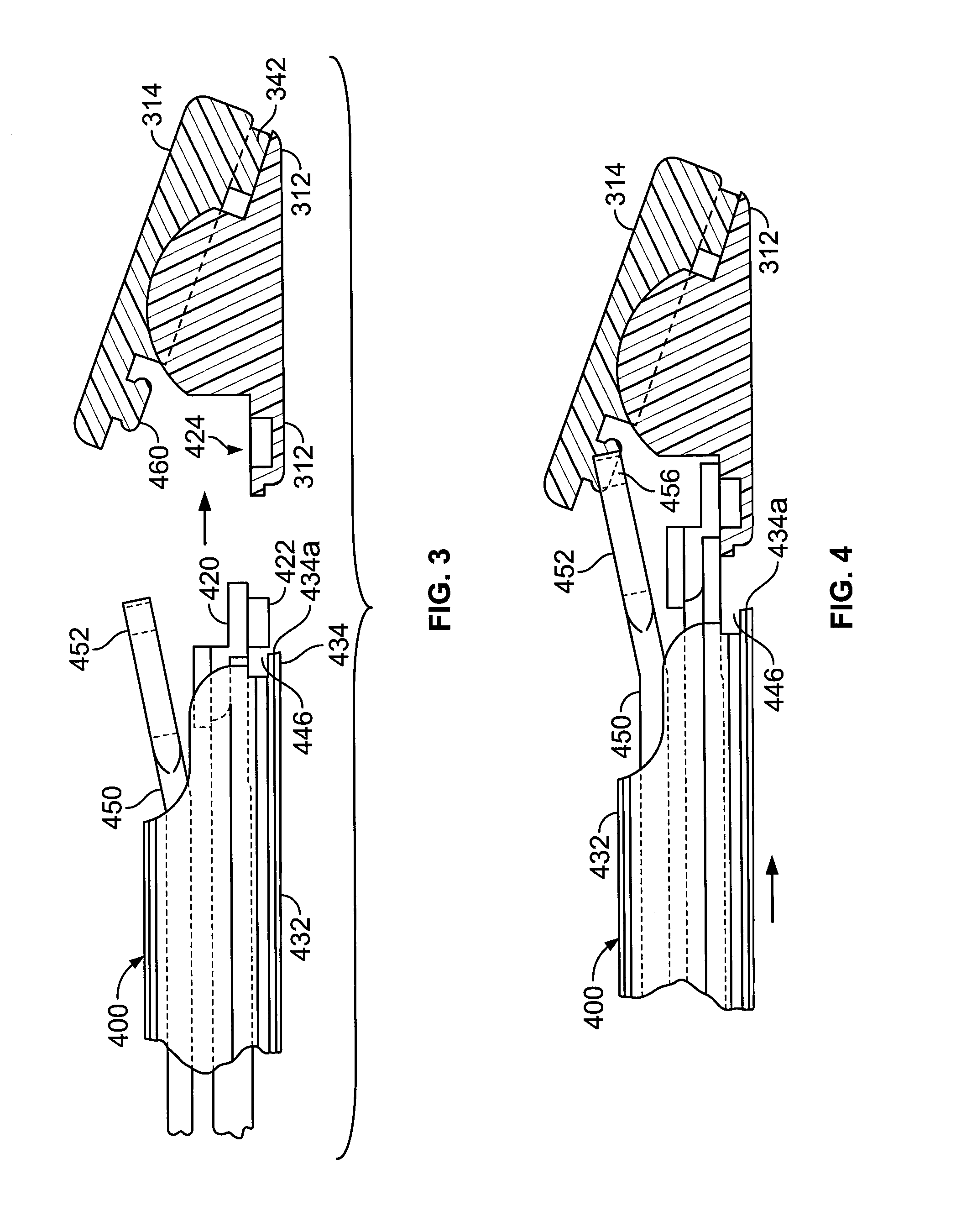
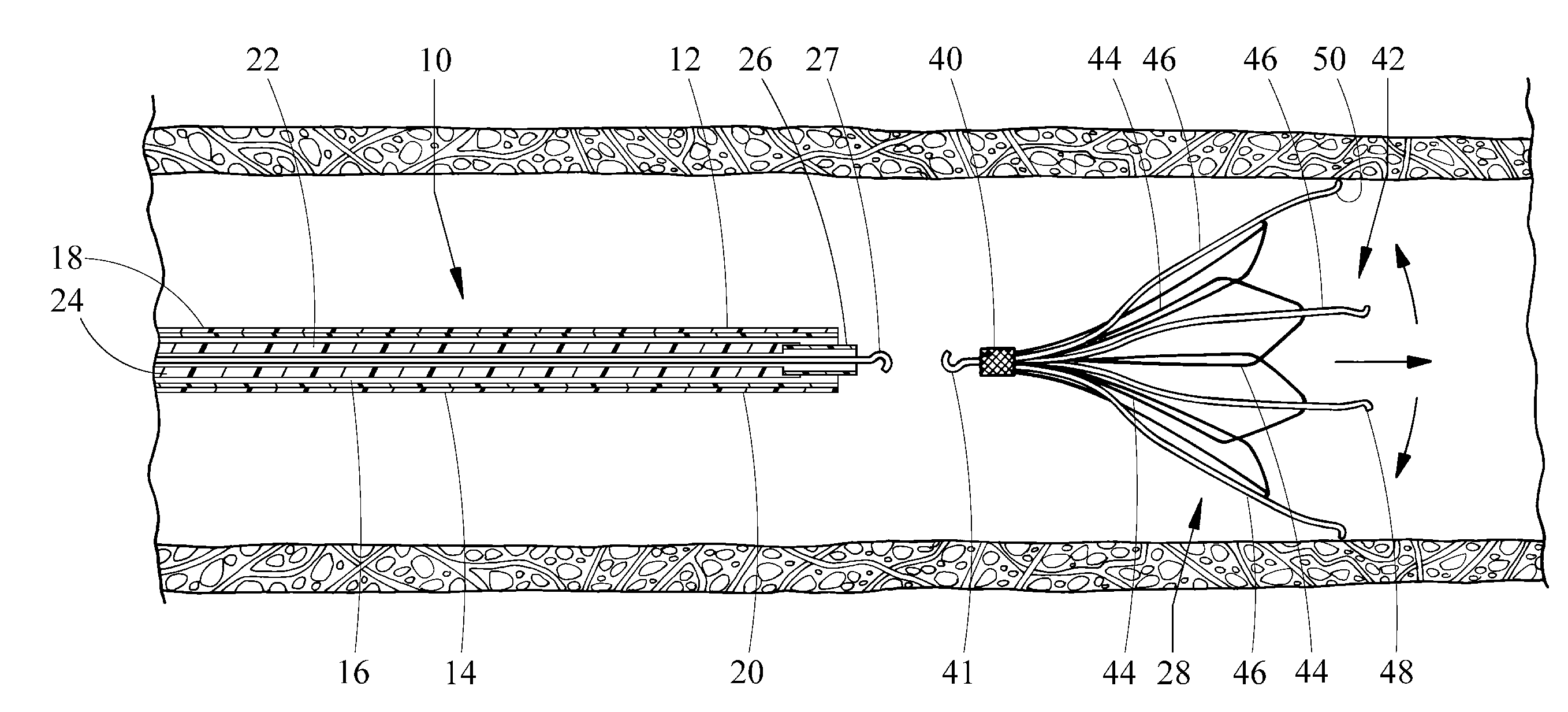
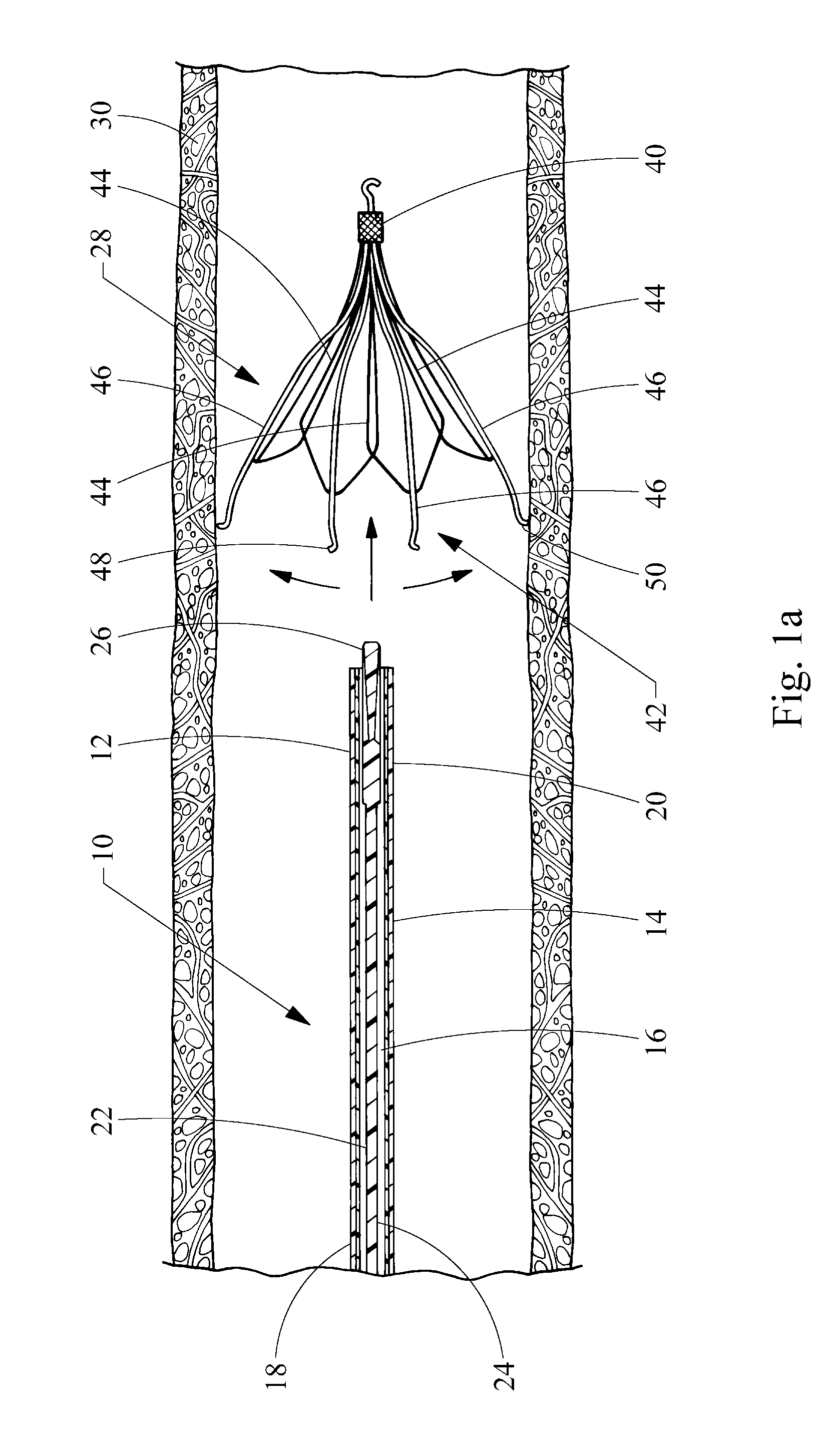
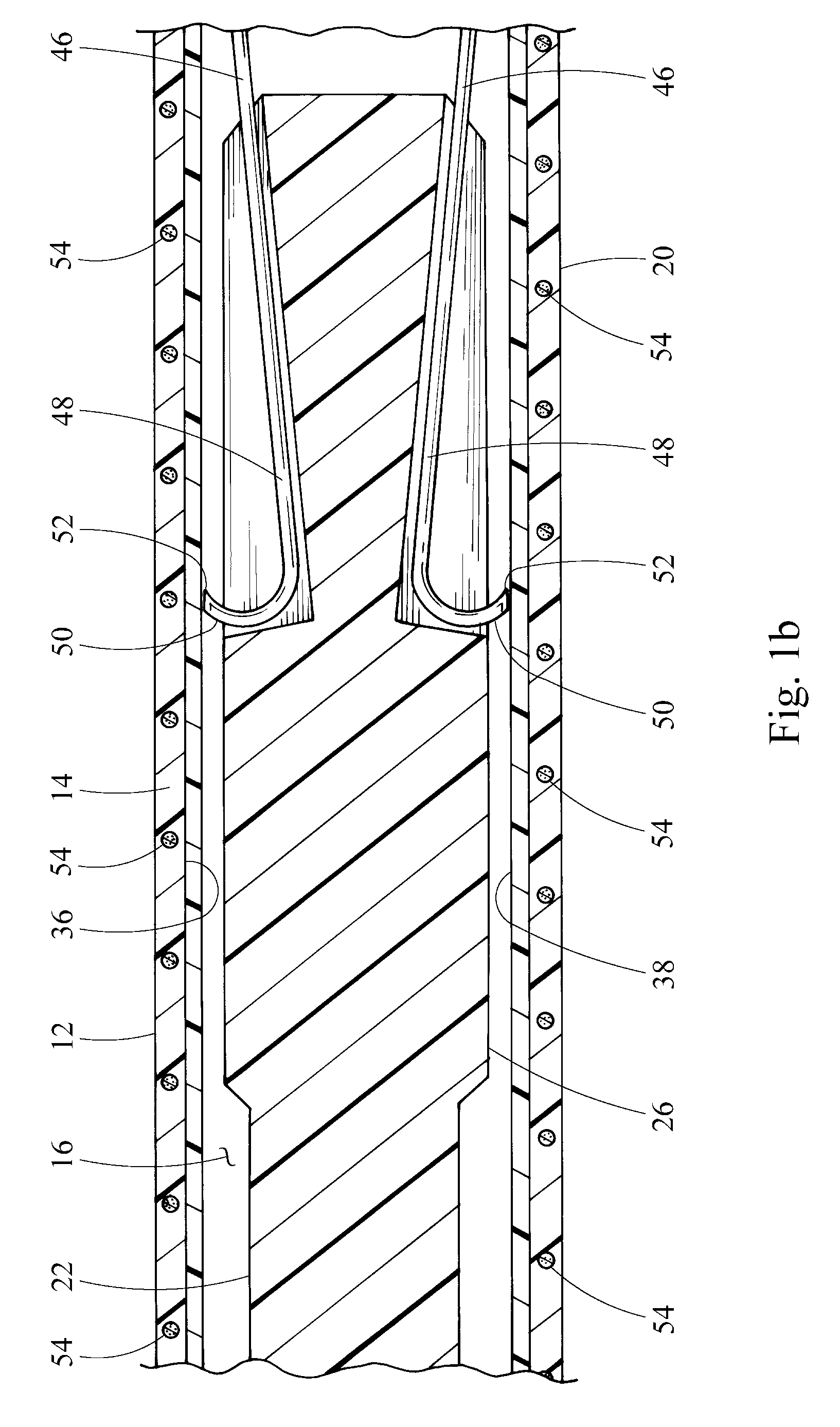
Catheher system having connectable distal and proximal portions
InactiveUS6050949AEnhanced hoop strengthBending stiffnessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPlastic materialsUltrasonic imaging
A vascular catheter system comprises a catheter body having a proximal and distal portion and a single common lumen therebetween. The catheter body includes a first connector secured to the distal end of the proximal portion and a second connector secured to the proximal end of the distal portion. The connectors can be selectively connected to each other to join the lumens of the proximal and distal portions together in a continuous, axially fixed relationship. Disposed within the lumens, when the proximal and distal portions are joined together, is a drive cable. The drive cable may be movably, rotatable about its own longitudinal axis and carries at its distal end, a work element, which is typically an ultrasonic imaging transducer or interventional device. The lumen carrying the cable will be sufficiently large along a proximal portion to permit preferential collapse of the cable should rotation of the distal end become impeded. The catheter body may be made of a polymer or plastic material, such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK), which provides adequate bonding stiffness and resistance to kinking from large hoop stresses.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Composite spinal fixation systems
InactiveUS20060247638A1Adjustable stiffnessAdjustable flexibilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPolyether ether ketoneMaterials science
Embodiments provide composite components for use in spinal fixation systems. The composite components may comprise polyetheretherketone (PEEK) or another non-resorbable or resorbable polymeric material and at least one metal. Incorporation of PEEK or another non-resorbable or resorbable polymeric material into the components allows average or mean physical properties (e.g., tensile strength, modulus of elasticity, etc.) of the components to be modulated. The composition and orientation of the composite components can be advantageously chosen to produce components with desired physical characteristics.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Joint Arthroplasty Devices Having Articulating Members
InactiveUS20080109081A1Improve wear resistanceAvoid Strength LossAnkle jointsJoint implantsJoint arthroplastyPolyether ether ketone
Articulating devices for replacing damaged or degenerated weight bearing joints are provided. The devices may have two or more surfaces that articulate against one another that are coated or fully formed of PEEK or similar materials to provide improved wear capabilities while maintaining sufficient strength to operate in a weight bearing capacity.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
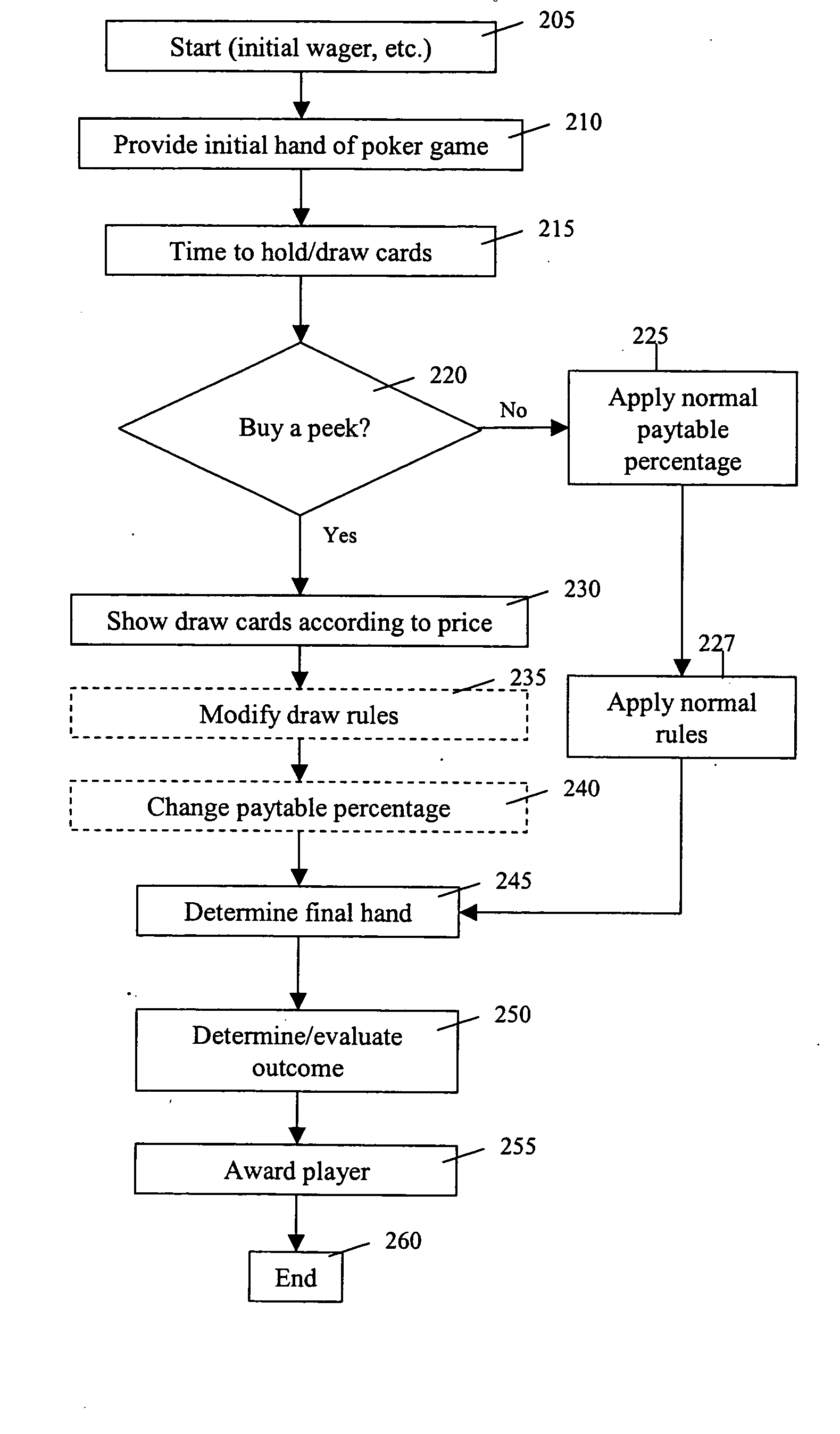
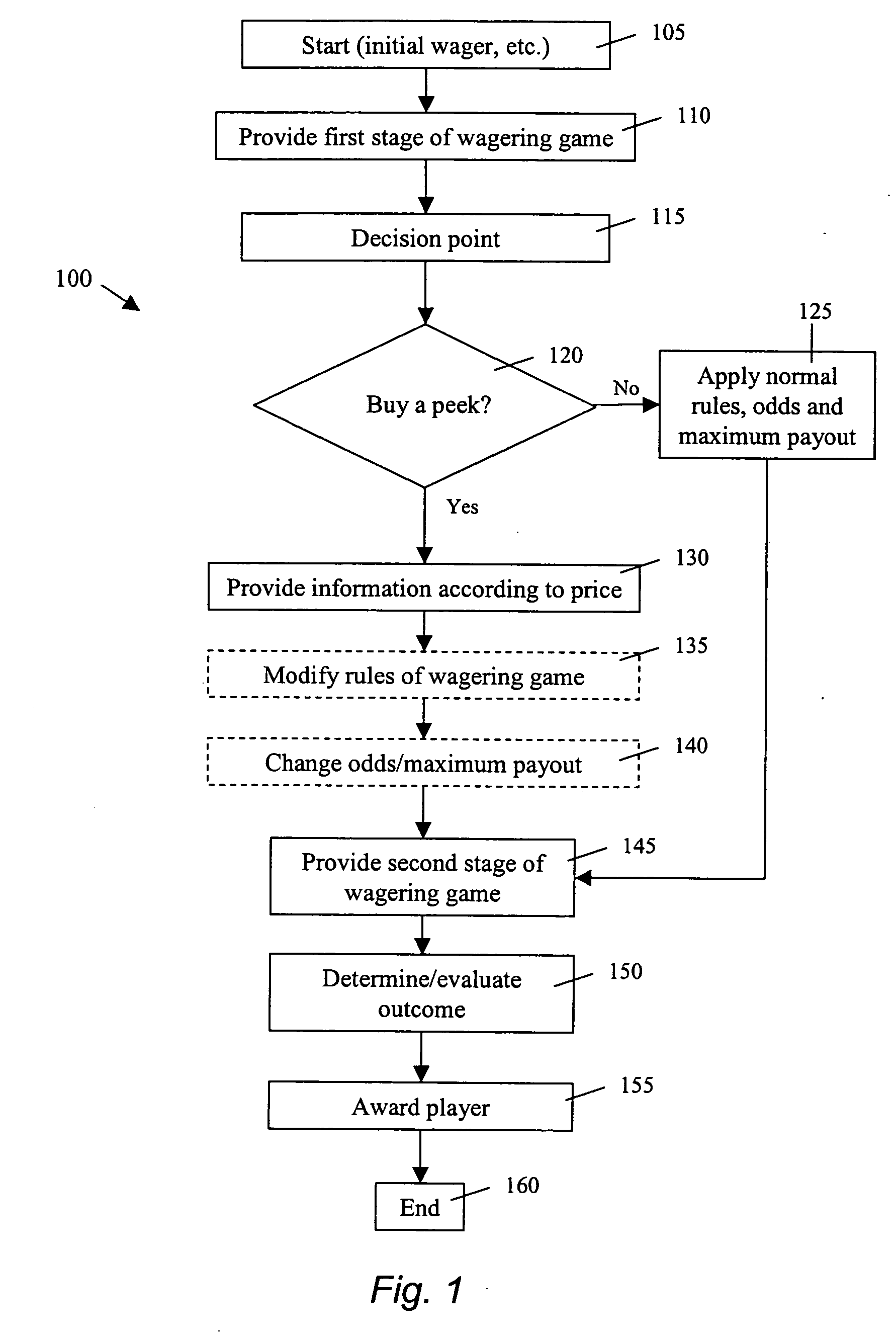
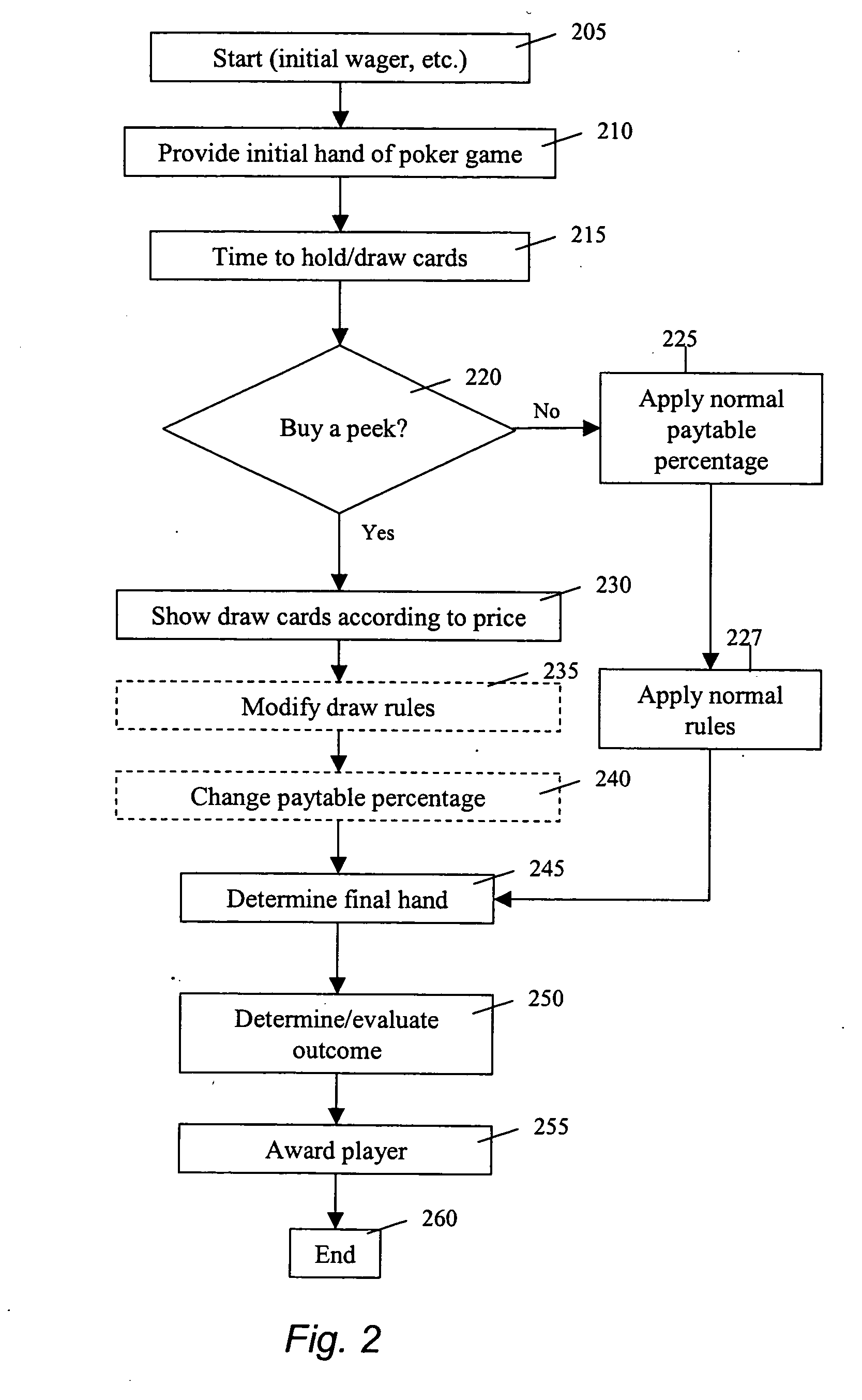
"Buy a peek" gaming methods and devices
ActiveUS20060025193A1Reducing player 's oddsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesPolyether ether ketoneMultimedia
Owner:IGT
Osteoconductive integrated spinal cage and method of making same
The spinal cage comprises a structural component having sufficient strength to withstand the compressive loading between vertebral bodies. The structural component is integrated with an osteoconductive component to facilitate bone growth between the vertebral bodies. The structural component may comprise any of PEEK, PEKK, or other structural material. The osteoconductive component may comprise any of allograft, natural bone, tricalcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite or a blend of calcium carbonate, calcium lactate and other calcium salts. A method for making the spinal cage involves molding polymers around an osteoconductive component, heat staking, and may further include ultrasonically welding, snap fit or mechanically assembling and / or adhesively bonding components.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
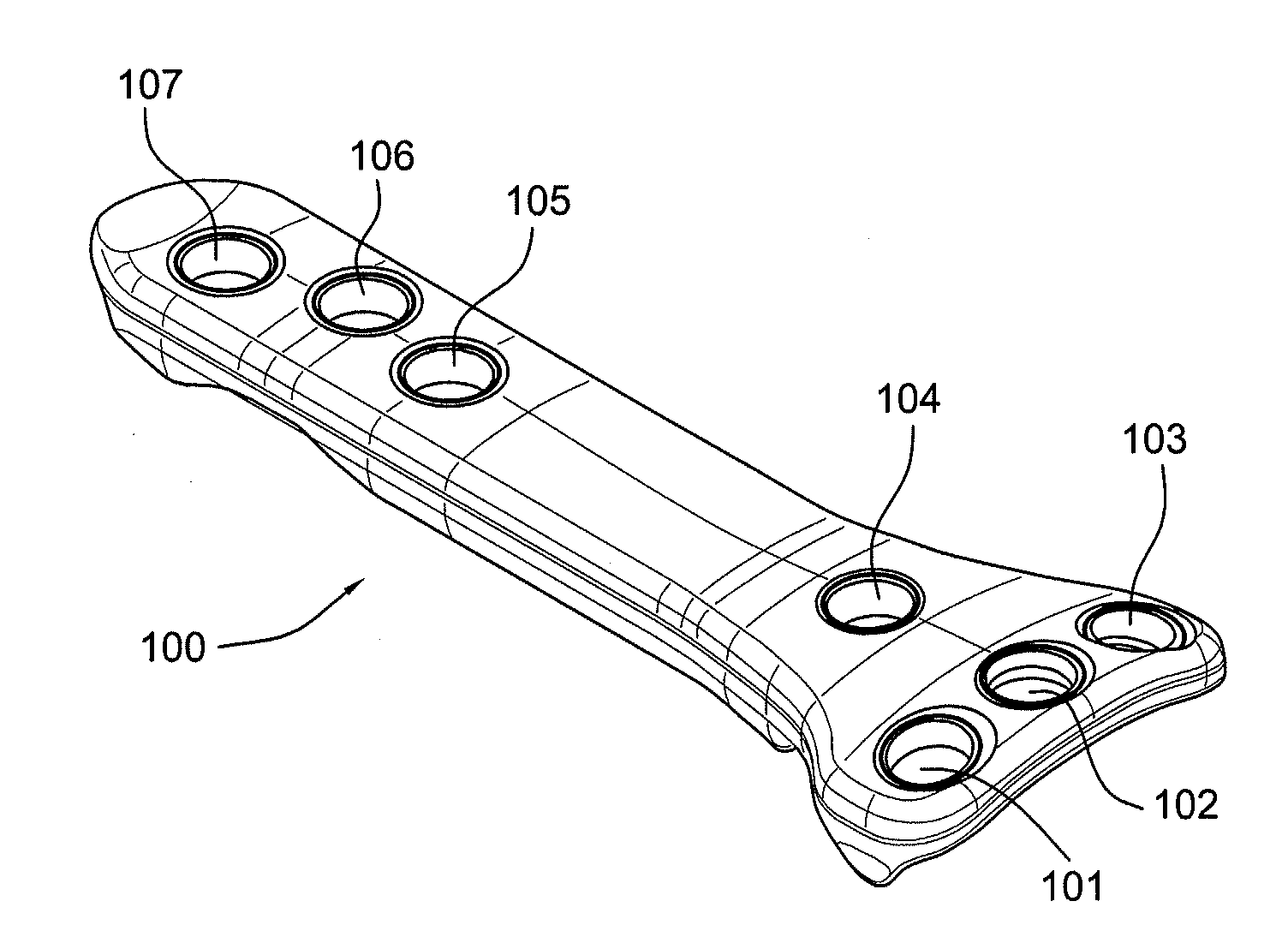
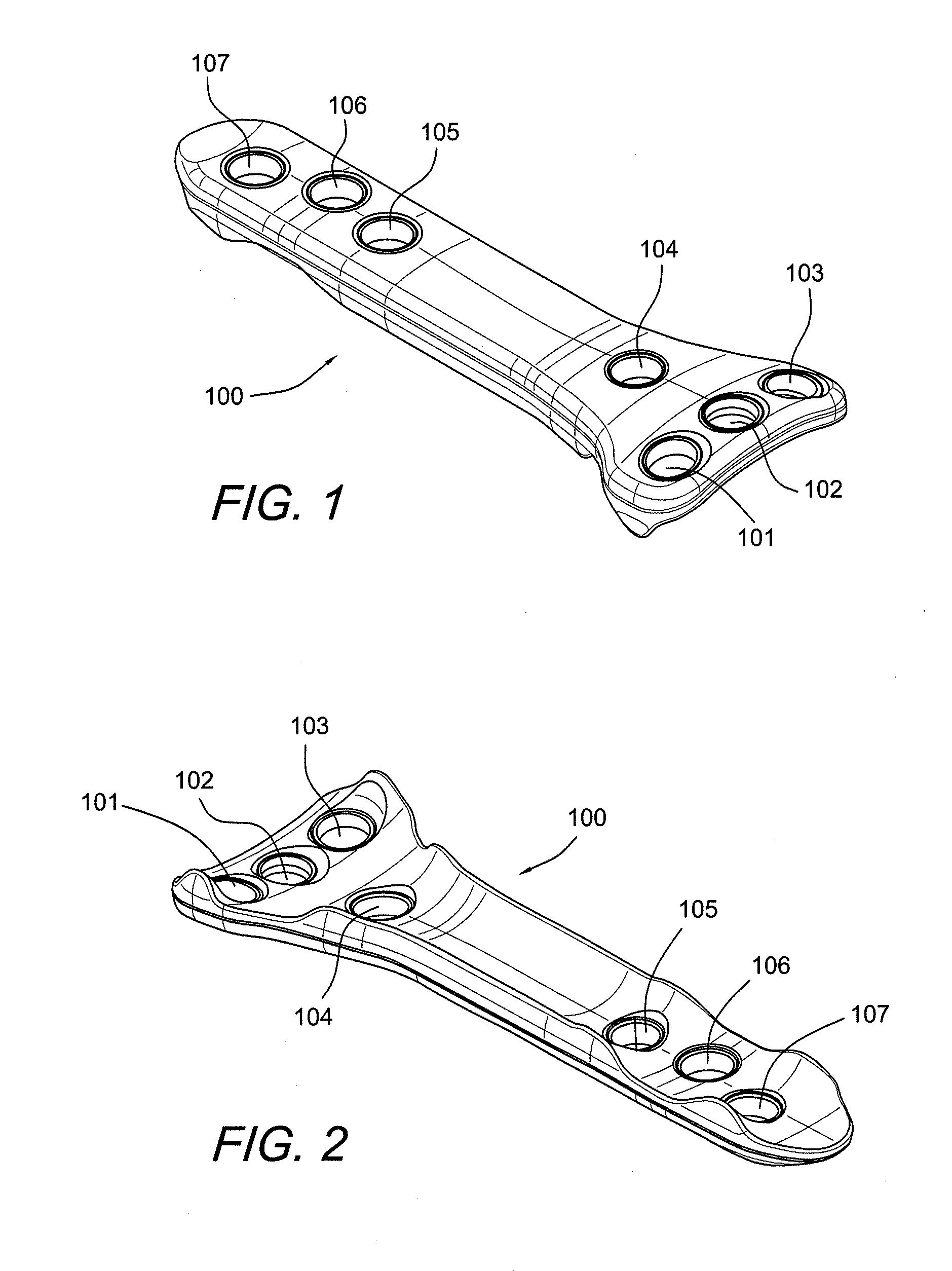
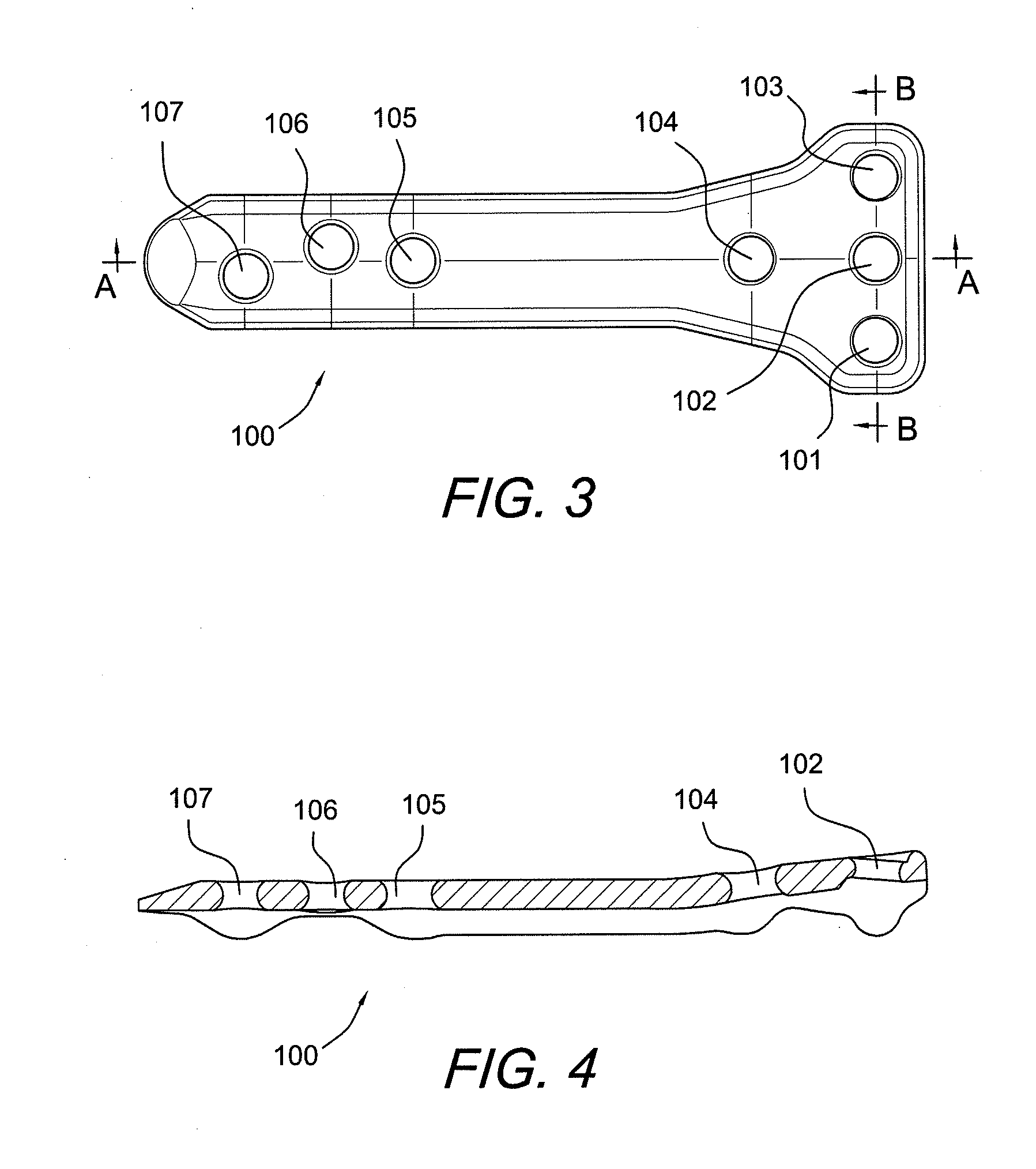
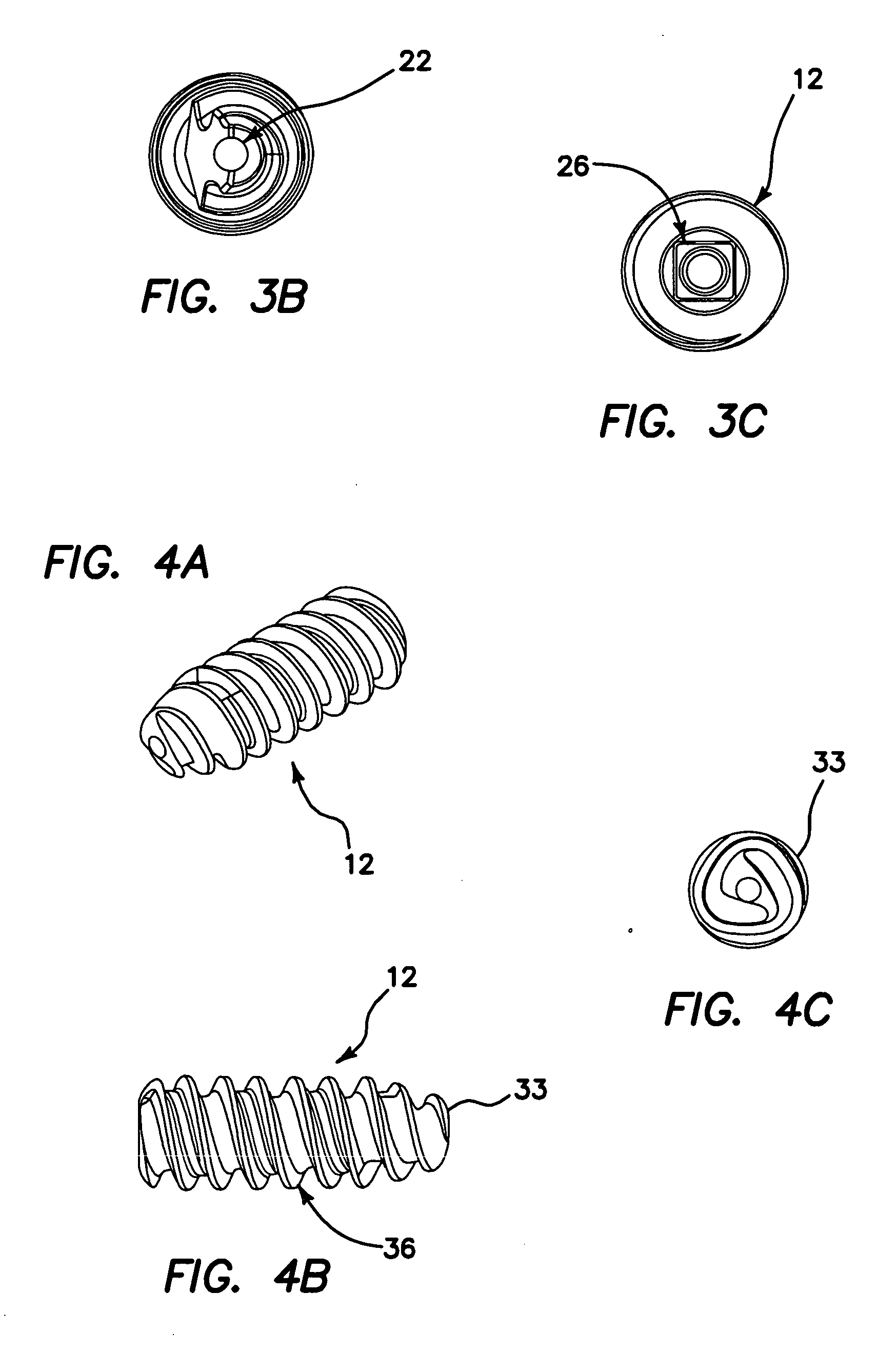
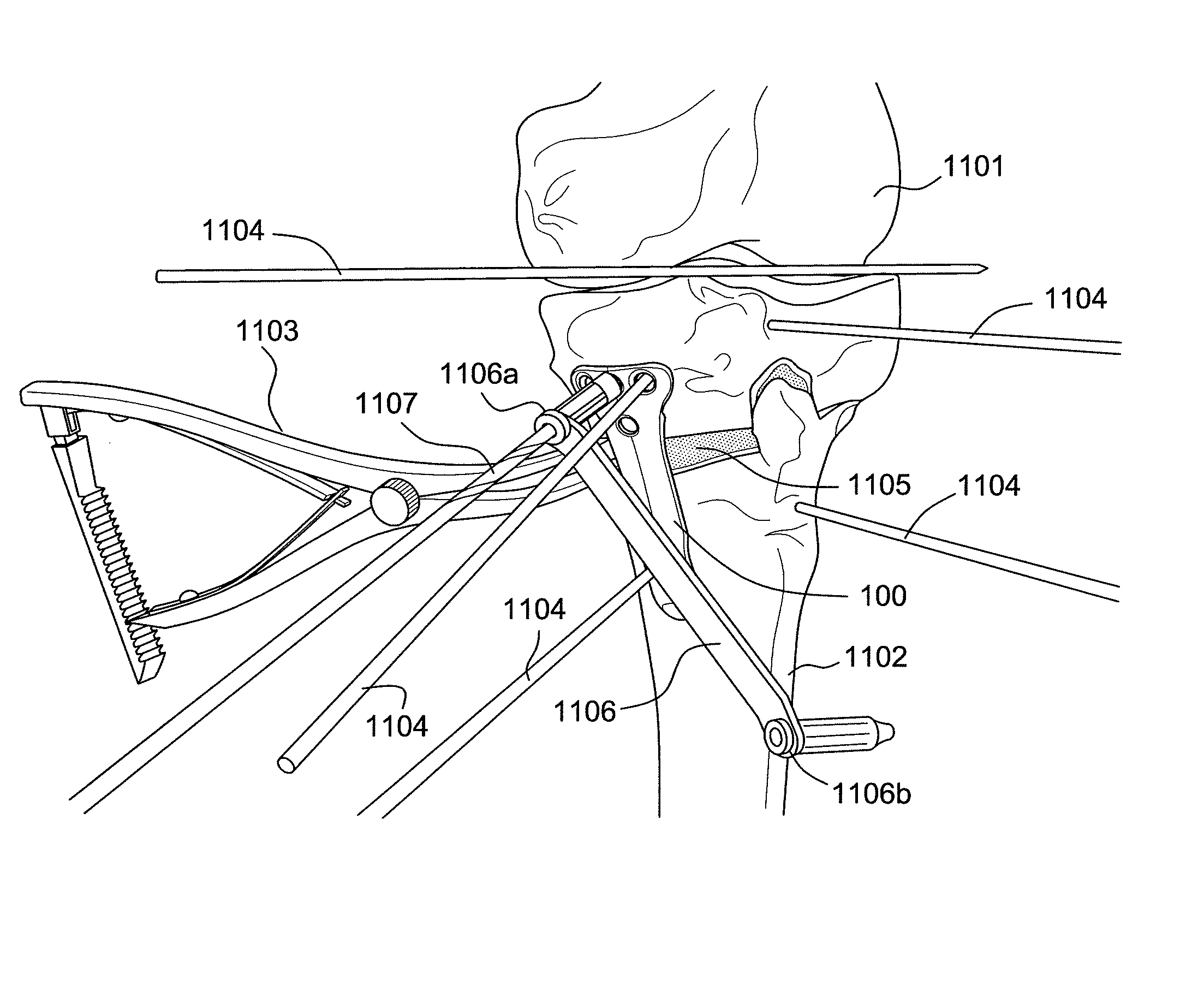
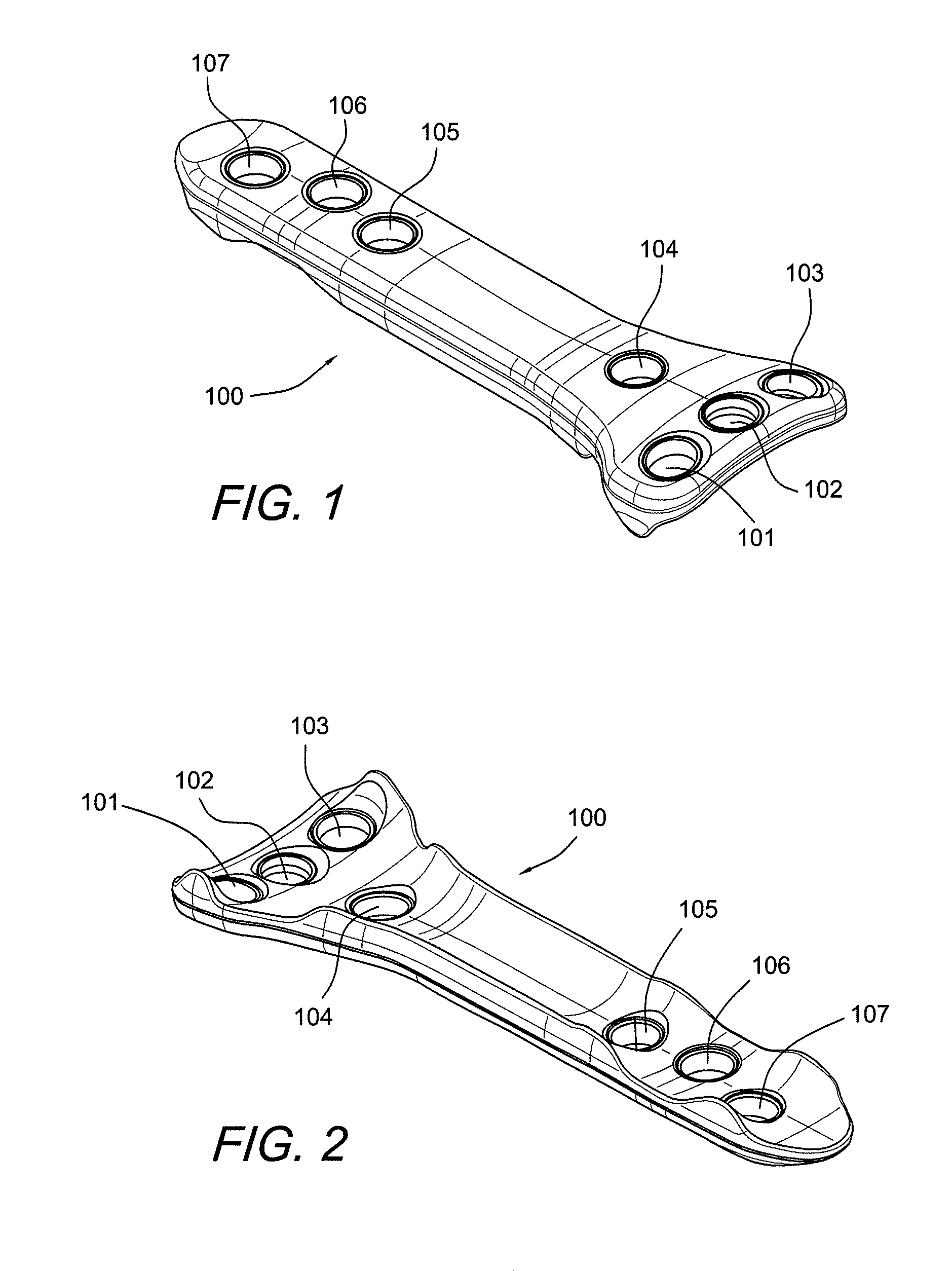
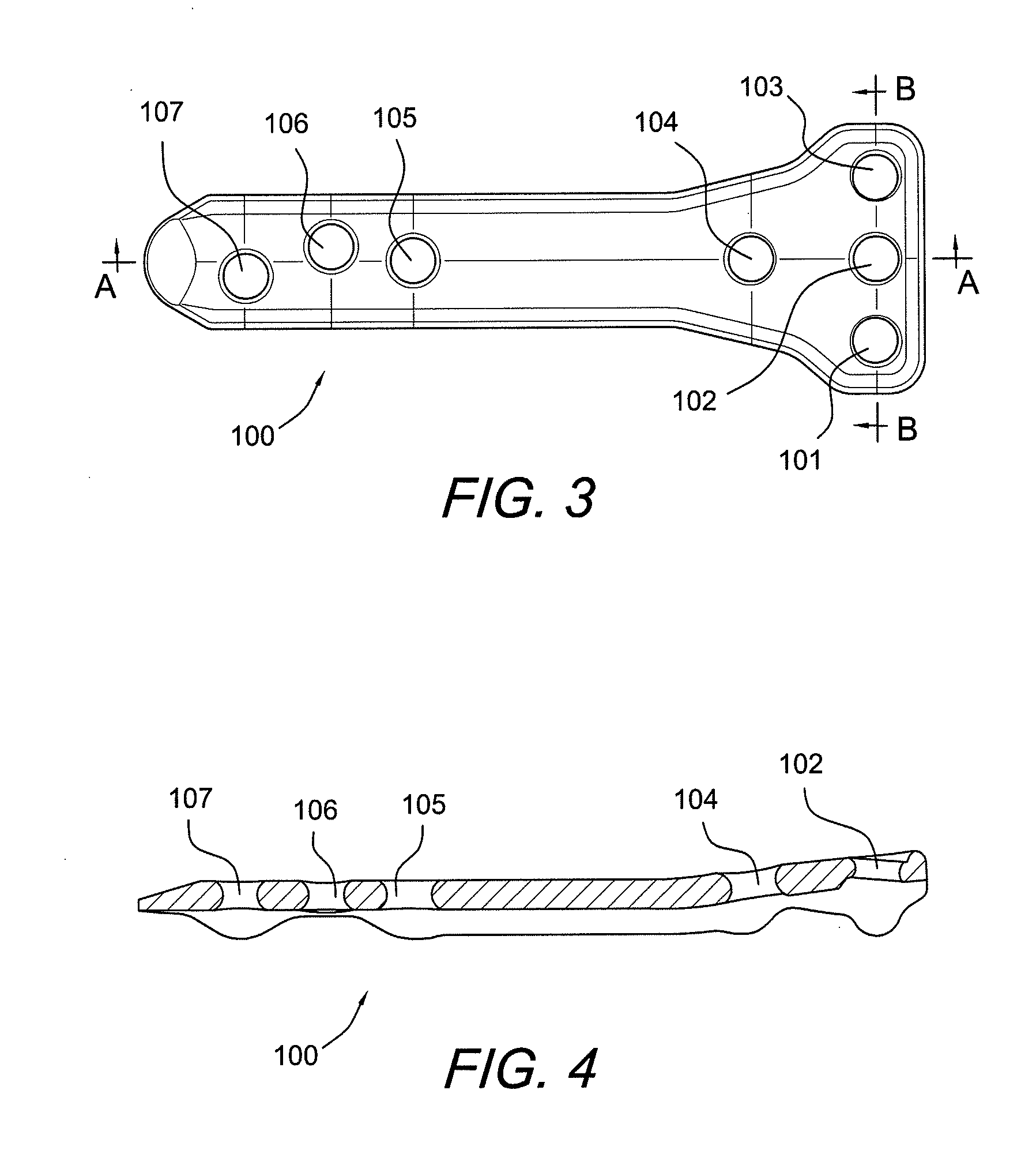
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Peek Bone Plate With Titanium Fixation Screws
Apparatus and methods for tissue fixation using a bone plate configured to accommodate fixation devices (such as screws, for example) inserted at various angles. The bone plate is formed of a material softer than the material of the fixation devices, and is provided with fixation holes with rounded, curved interior walls (i.e., non-threaded holes) that allow the fixation devices to be inserted at various angles. The fixation holes have a diameter smaller than that of the fixation devices. As a result of the difference between the materials of the plate and of fixation devices, and of the difference between the diameters of the fixation holes and of the fixation devices, the fixation devices deform the interior walls of the fixation holes, therefore self-threading the holes at an advantageous angle.
Owner:ARTHREX
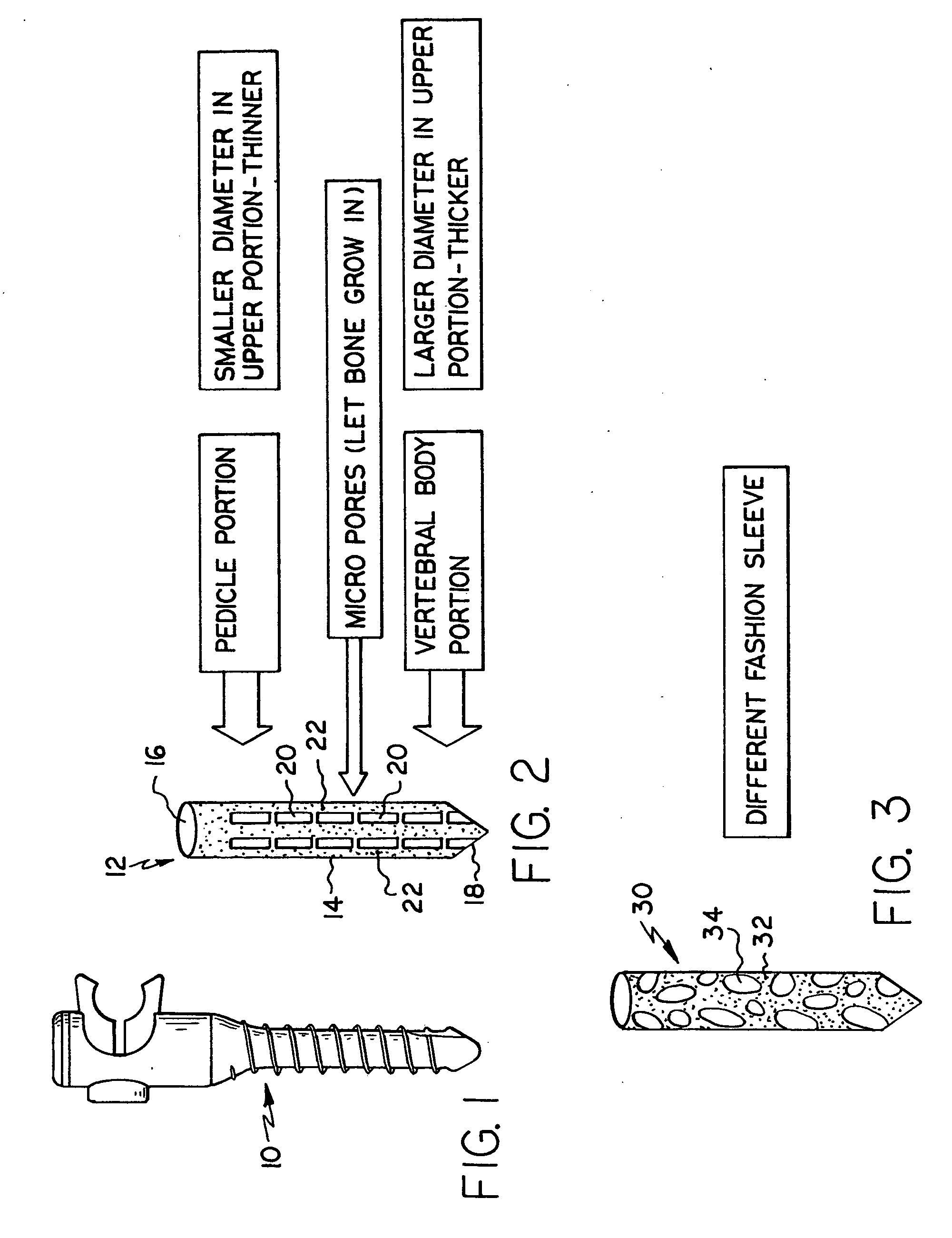
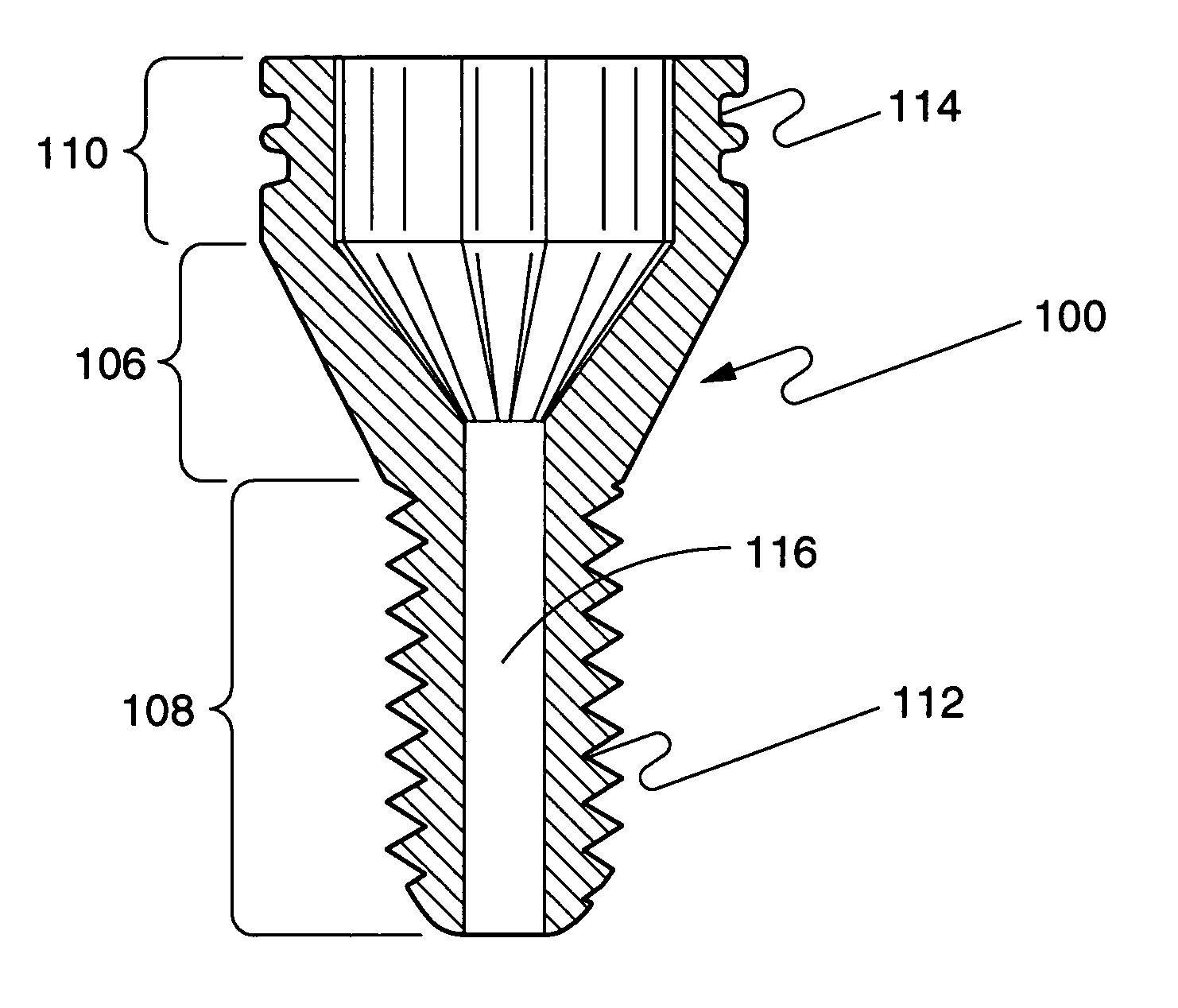
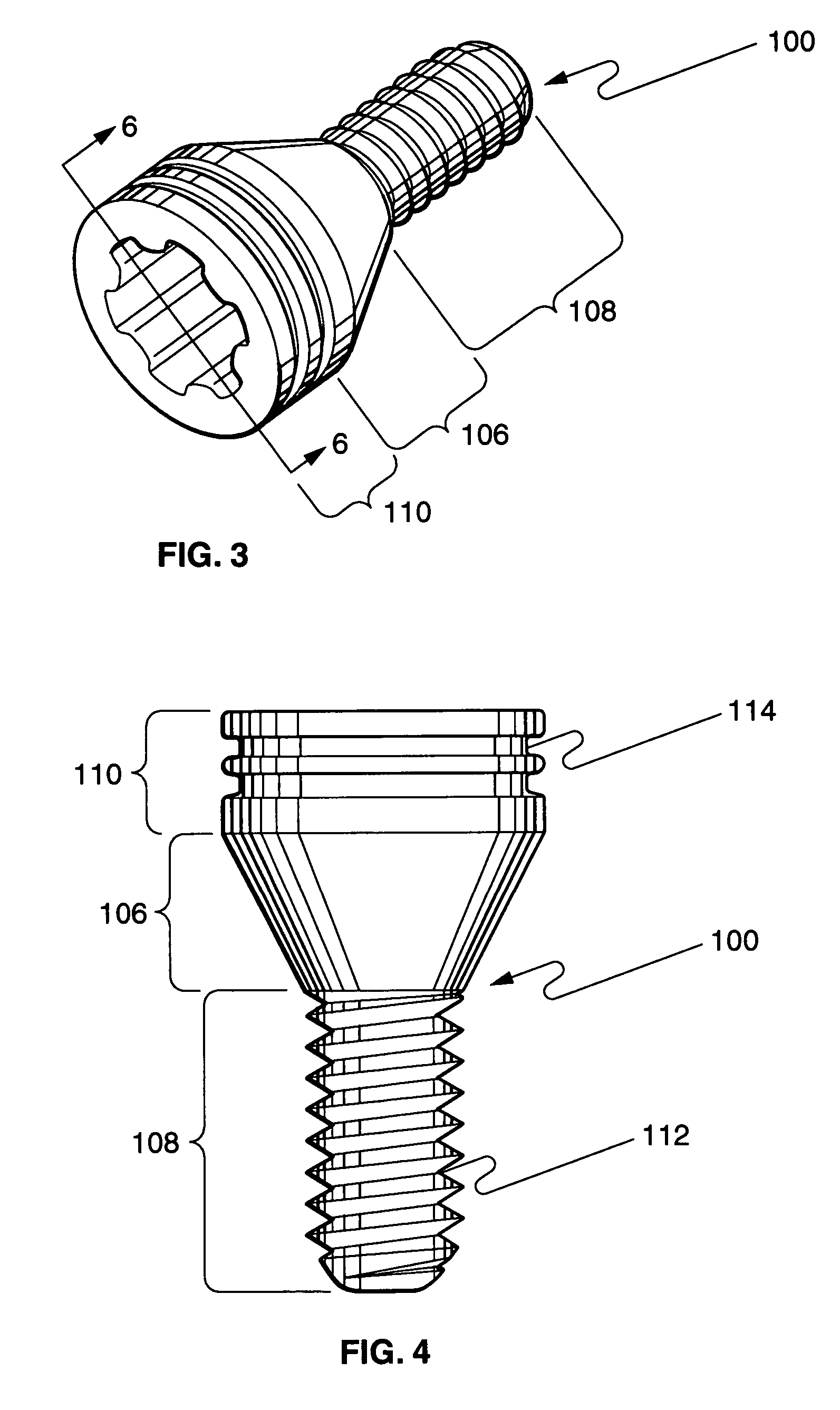
Screw sleeve made of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for augmentation of bone screw insertion in osteoporotic or revision lumbar spine instrumentation
InactiveUS20060129148A1Excellent mechanical propertiesImprove interferenceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisOrthopaedic deviceBone tissue
An orthopaedic device comprising an orthopaedic bone screw and a sleeve of polyetheretherketone material in which the orthopaedic bone screw is received for increasing interference between the screw and bone tissue to increase strength of fixation when the device is installed in bone.
Owner:SIMMONS EDWARD +1
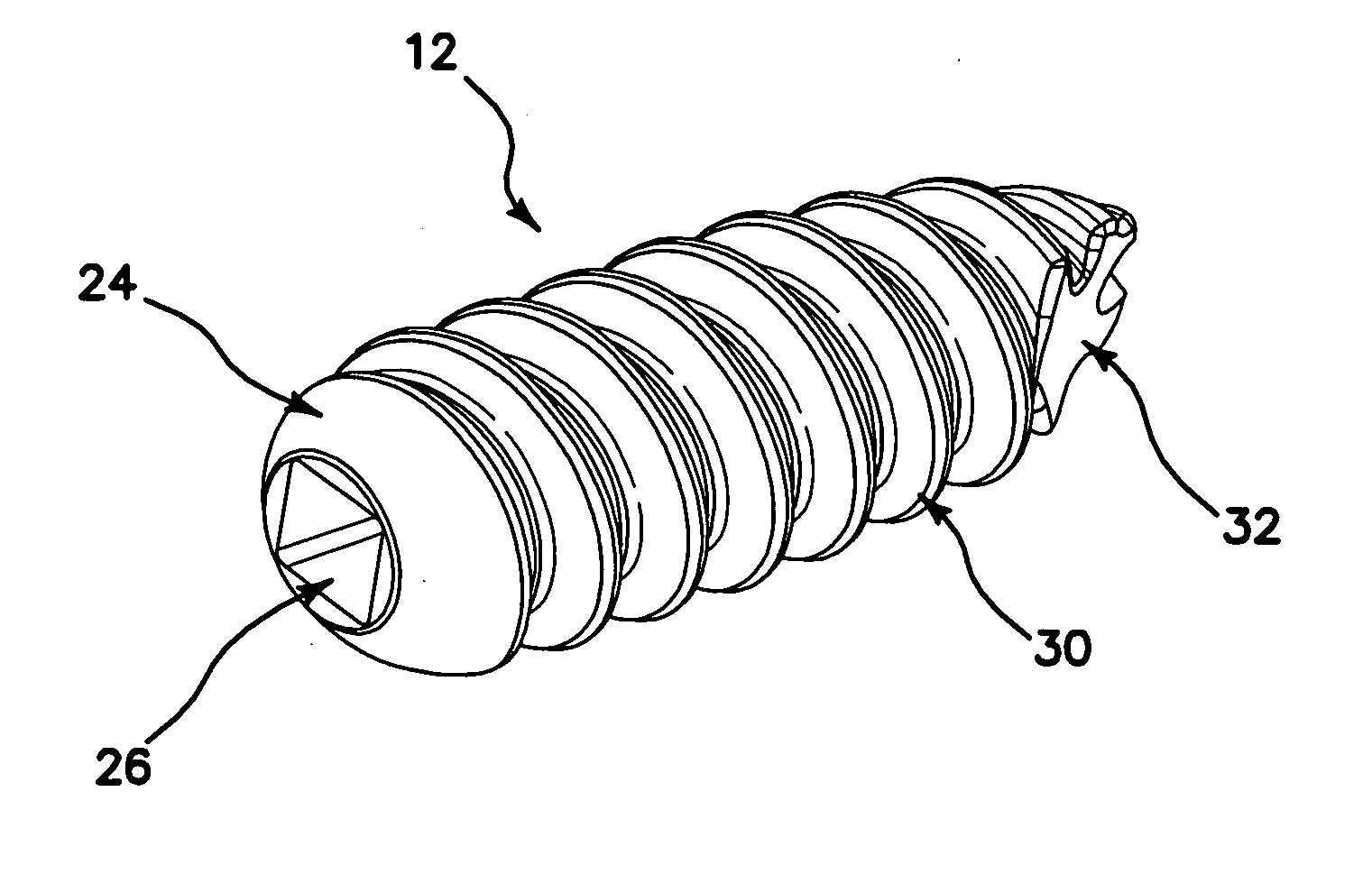
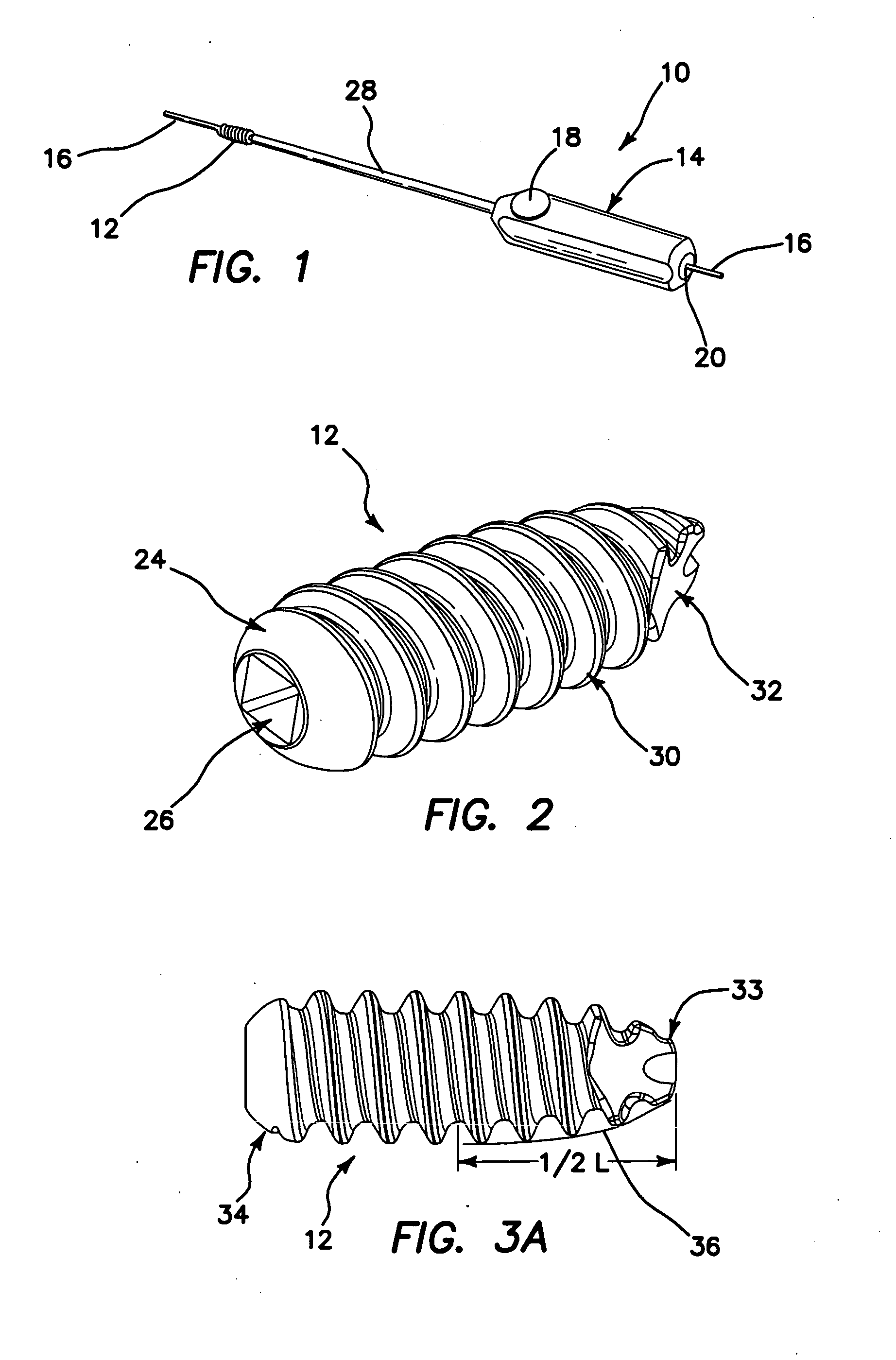
Peek threaded suture anchor
A threaded suture anchor formed of a material comprising polyether-ether ketone (PEEK) has a suture loop that is disposed internally within the suture anchor. The suture loop can extend through a substantial length of the anchor body with the ends of the suture loop secured at the distal end of the anchor and the proximal end of the loop being flush with or recessed just below the proximal surface of the proximal end of the anchor. The anchor body can be threaded and have a tapered distal portion.
Owner:ARTHREX
Self-tapping biocompatible interference bone screw
A biocompatible interference screw for soft tissue or bone-to-bone fixation comprises a screw body extending from a screw head to a distal tip of the screw. The screw body has an outer surface, and comprises polyether-ether-ketone (PEEK) material. Advantageously, the body outer surface has a textured surface finish for substantially improving pull-out strength of the interference screw. The textured surface finish is textured, in preferred embodiments, with a minimum of approximately 16 micro inches of surface roughness. The screw head comprises a tapered square keyhole for receiving a distal end of a driver instrument. The screw comprises a series of threads, which have a relatively smooth profile, in order to prevent graft tissue laceration as the screw is being inserted. The distal tip of the screw body comprises a narrow tip, and a distal end of the screw body is angled inwardly toward the narrow distal tip.
Owner:CAYENNE MEDICAL INC
Carbon fiber reinforced peek bone plate with titanium fixation screws
Apparatus and methods for tissue fixation using a bone plate configured to accommodate fixation devices (such as screws, for example) inserted at various angles. The bone plate is formed of a material softer than the material of the fixation devices, and is provided with fixation holes with rounded, curved interior walls (i.e., non-threaded holes) that allow the fixation devices to be inserted at various angles. The fixation holes have a diameter smaller than that of the fixation devices. As a result of the difference between the materials of the plate and of fixation devices, and of the difference between the diameters of the fixation holes and of the fixation devices, the fixation devices deform the interior walls of the fixation holes, therefore self-threading the holes at an advantageous angle.
Owner:ARTHREX
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20070099081A1Improve reliabilityHigh charge and discharge capacityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsPolyetherimidePolyamide
A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery including a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator interposed between the positive and negative electrodes, and a non-aqueous electrolyte. The negative electrode includes composite particles and a binder. Each of the composite particles includes: a negative electrode active material including an element capable of being alloyed with lithium; carbon nanofibers that are grown from a surface of the negative electrode active material; and a catalyst element for promoting the growth of the carbon nanofibers. The binder comprises at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyimide, polyamide imide, polyamide, aramid, polyarylate, polyether ether ketone, polyether imide, polyether sulfone, polysulfone, polyphenylene sulfide, and polytetrafluoroethylene.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Peek mode and graphical user interface (GUI) experience
ActiveUS20130328914A1Input/output for user-computer interactionUsing electrical meansGraphicsGraphical user interface
A tablet device determines a spatial relationship between the tablet device and a protective cover. The tablet device operates in accordance with the spatial relationship.
Owner:APPLE INC
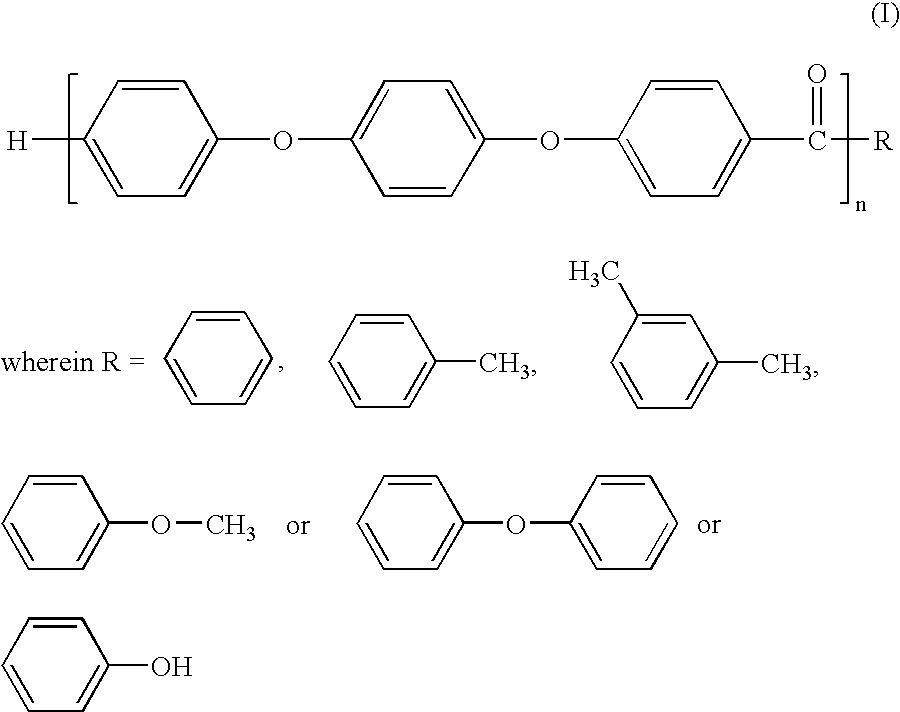
Melt processible polyether ether ketone polymer
InactiveUS6881816B2Easy to processReduce the temperatureChemical recyclingMethane sulfonic acidEnd-group
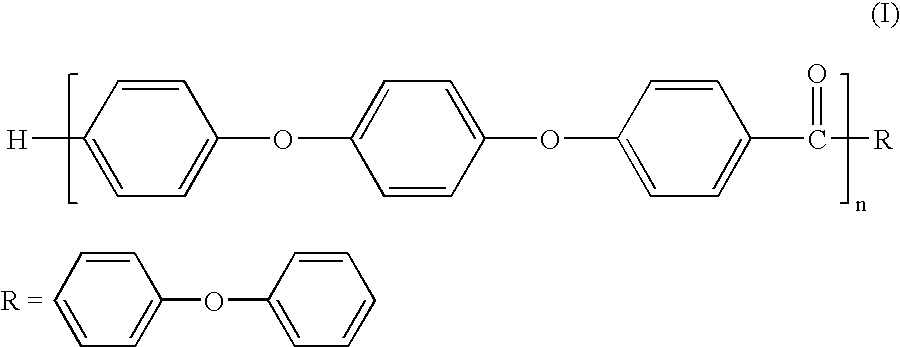
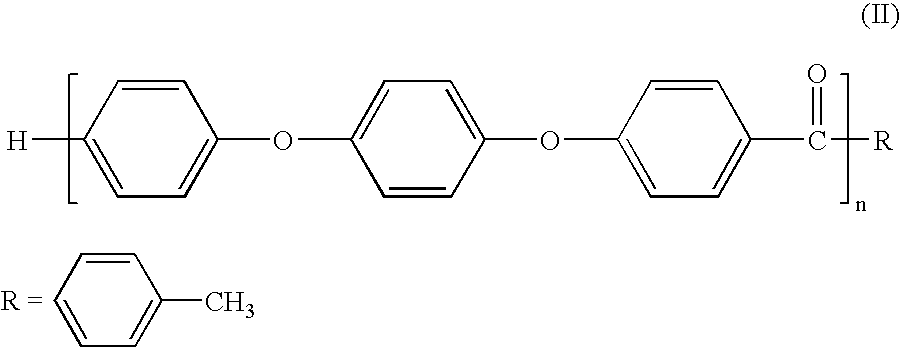
A melt processible Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) polymer with novel end-group structure is synthesized electrophilically using Methane Sulfonic Acid containing Methane Sulfonic Anhydride or Phosphorous Pentoxide. The product so obtained shows controlled structure with elimination of reactive end group like —COOH and is therefore melt processible by conventional techniques and exhibits high thermal and mechanical properties making it useful high temperature engineering and specialty plastics. It can be extruded into a rod, film and can also be molded into commercially useful products.
Owner:GHARDA CHEM LTD
Multi-layer low friction and low wear polymer/polymer composites having compositionally graded interfaces
InactiveUS20060029795A1Reduce wearReduce frictionLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer sciencePolyether ether ketone
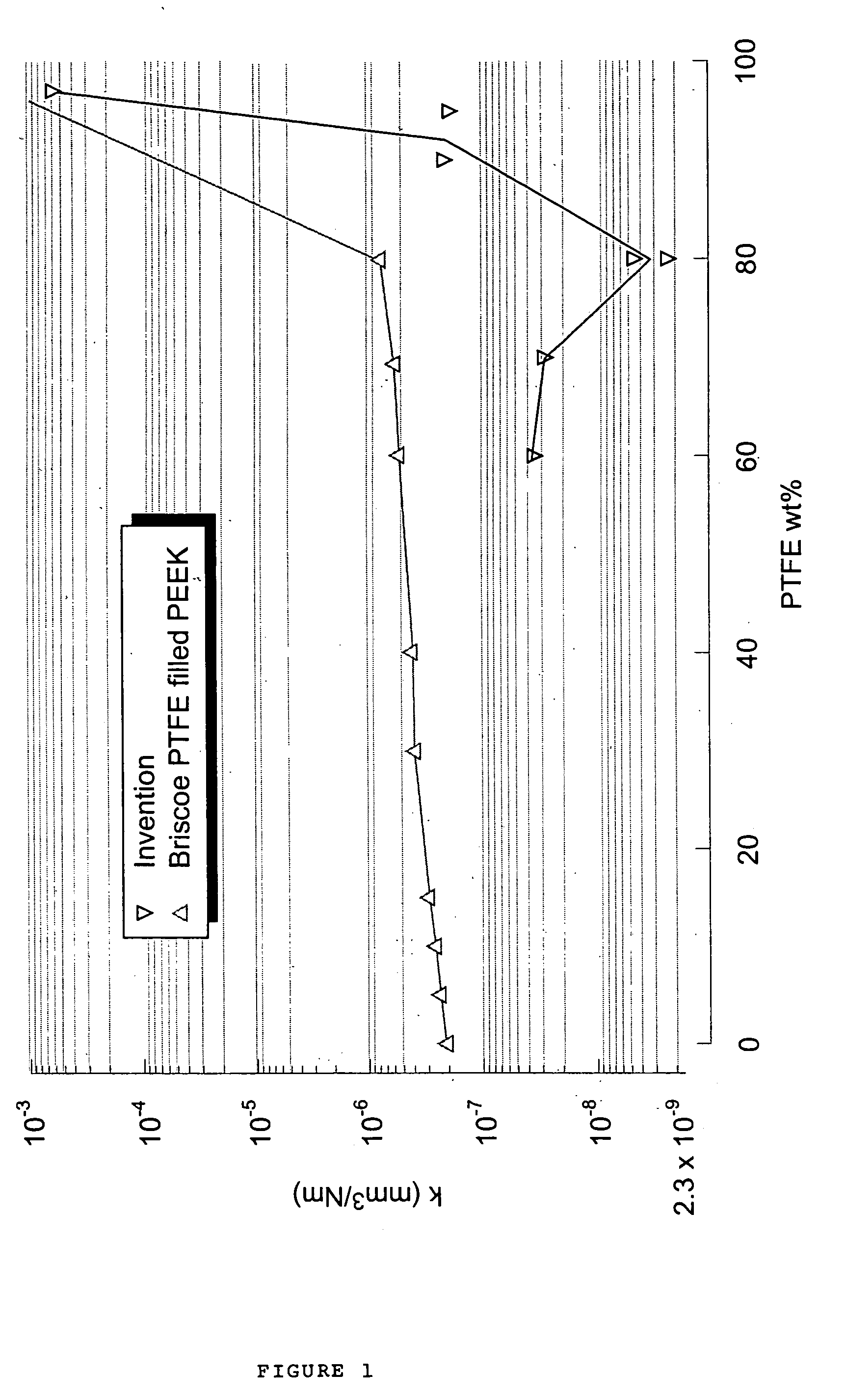
A high strength multi-layer polymeric article having a low wear surface includes a base polymer layer, and a polymer composite capping layer disposed on the base polymer layer. The capping layer includes a first polymer including a transfer film forming polymer, and a second polymer different from the first polymer for strengthening this polymer composite mixed with the first polymer. The first polymer provides at least 10 weight % of the composite capping layer. A transition layer composite including the first and second polymer is interposed between the capping layer and the base polymer layer, at least a portion of the transition layer providing a non-constant first or second polymer concentration. A wear rate of the article is <10−7 mm3 / Nm. The first polymer can be PTFE and the second polymer can be a polyaryletherketone (PEEK).
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Multi-layered foamed polymeric objects and related methods
ActiveUS20090104420A1Large levelIncrease in sizeClosuresClosure using stoppersPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention disclosed herein relates to relates to foamed thermoplastic material objects and articles of manufacture having an internal layered cellular structure, as well as to methods of making the same. In one embodiment, the invention is directed to a multi-layer foamed polymeric article of manufacture, comprising: a non-laminated multi-layer thermoplastic material sheet, wherein the multi-layer thermoplastic material sheet has first and second discrete outer layers sandwiching a plurality of discrete inner foamed layers, and wherein the two outer layers and plurality discrete inner foamed layers are integral with one another. The thermoplastic material may be a semi-crystalline polymer such as, for example, PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PEEK (polyetheretherketone), PEN (polyethylene napthalate), PBT (polybutylene terephthalate), PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), PLA (polylactide), polyhydroxy acid (PHA), thermoplastic urethane (TPU), or blends thereof. The two outer layers may be unfoamed skin layers having smooth outer surfaces, and the discrete inner foamed layers may be microcellular.
Owner:DART CONTAINER +1
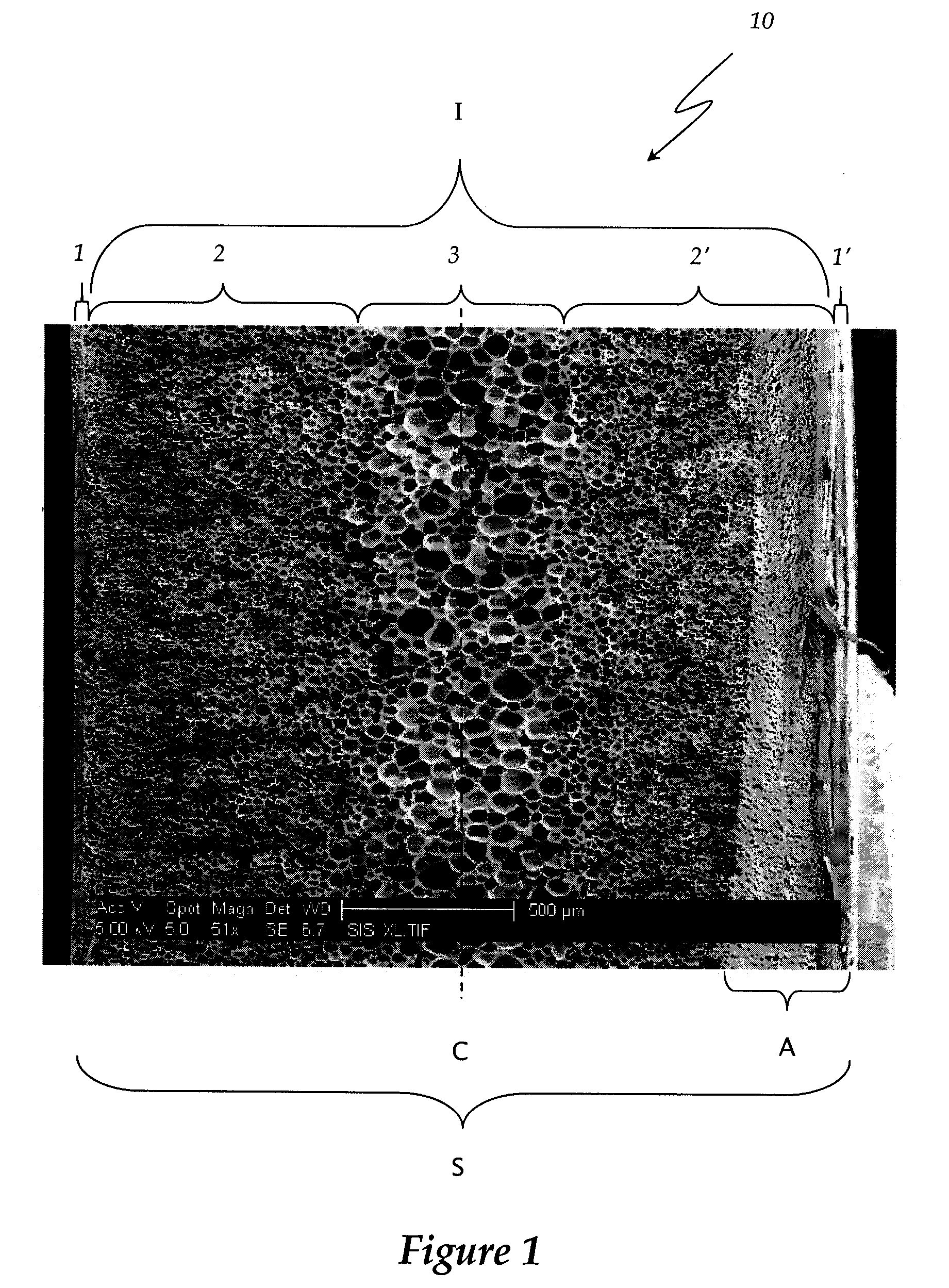
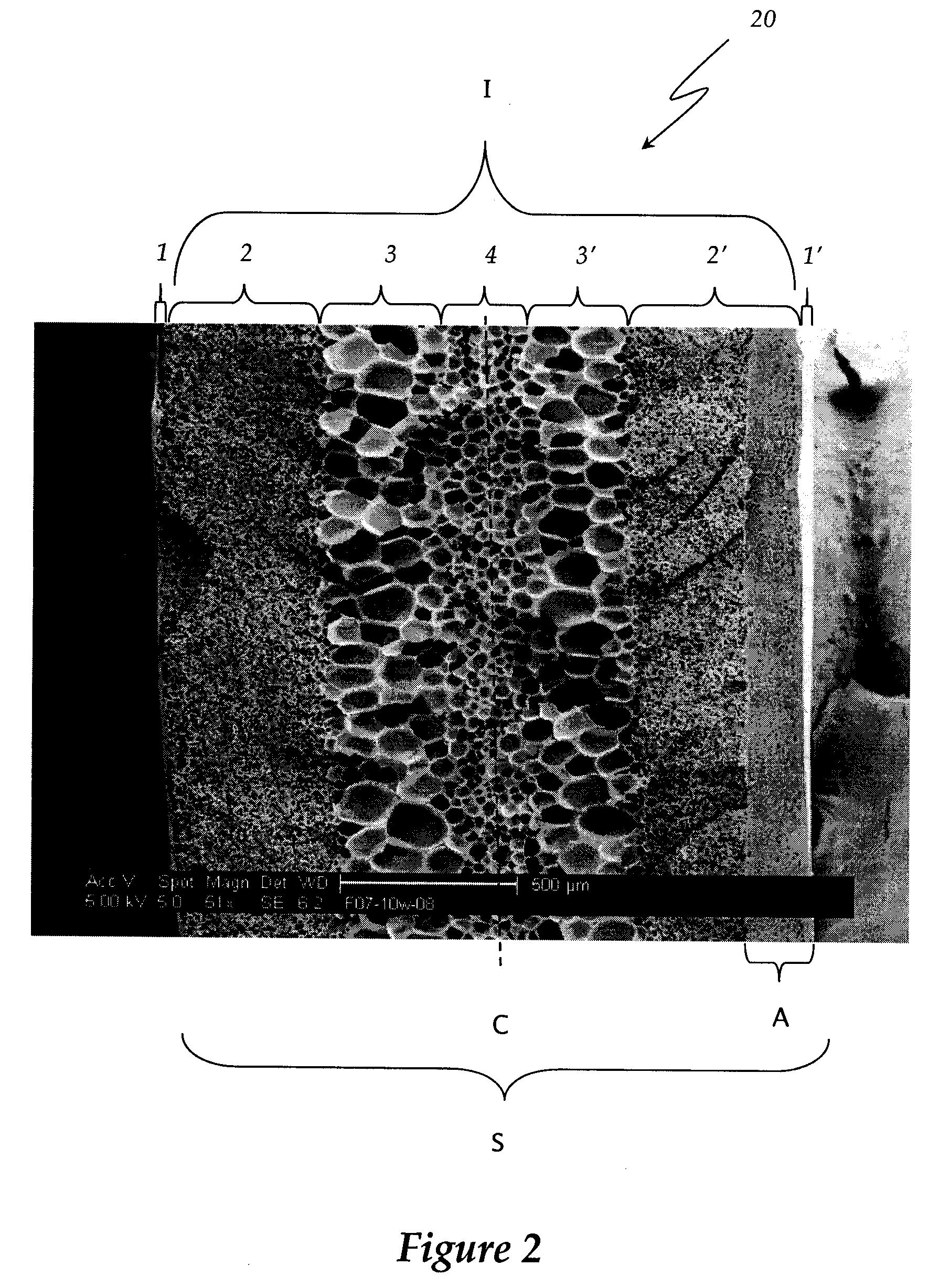
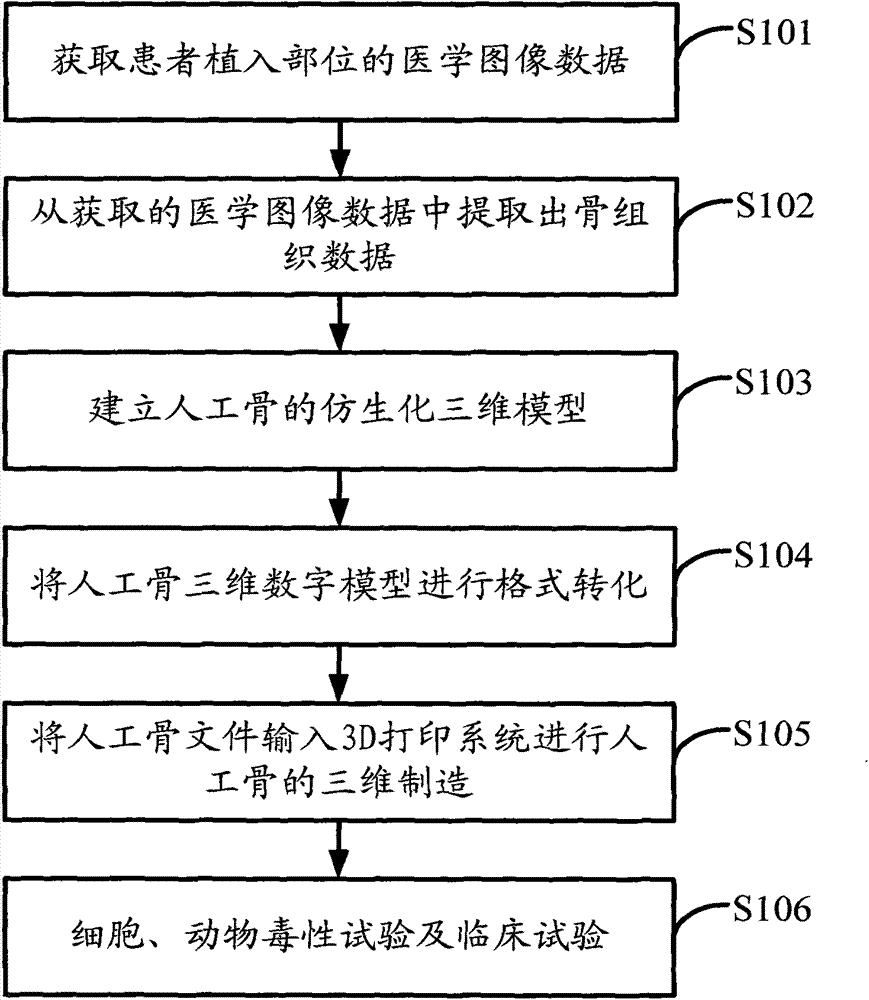
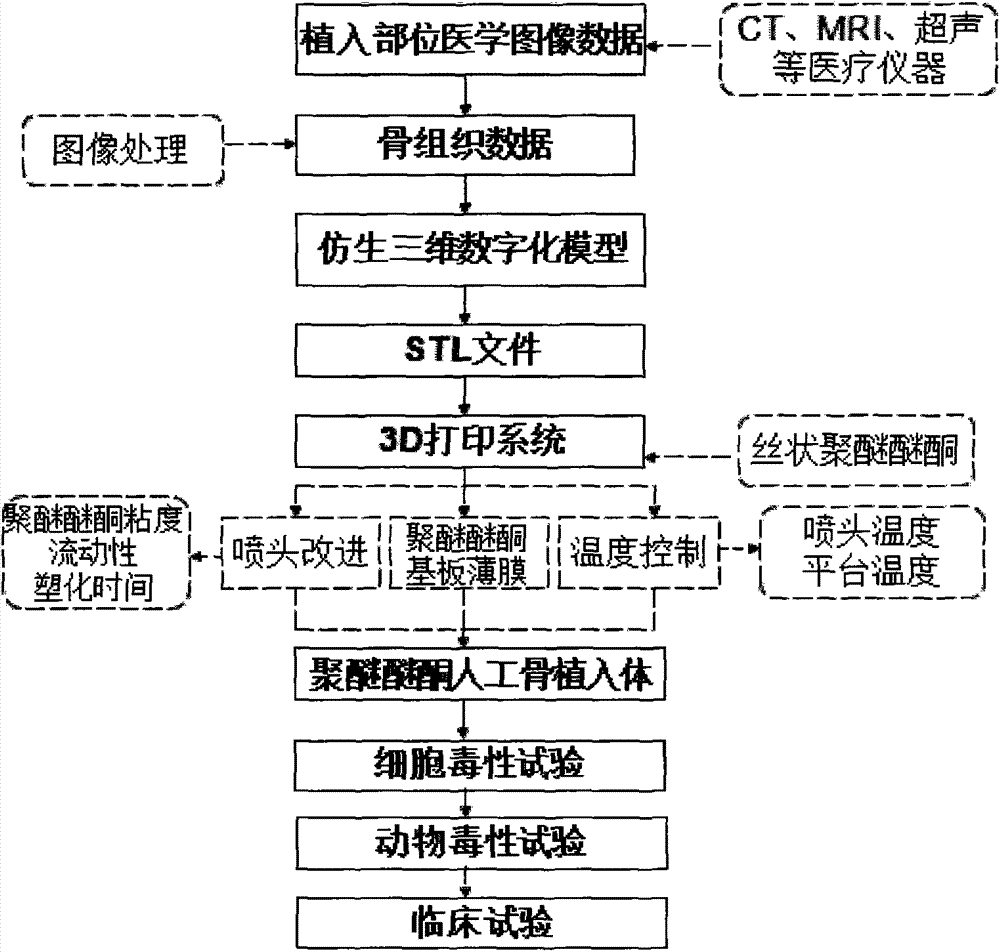
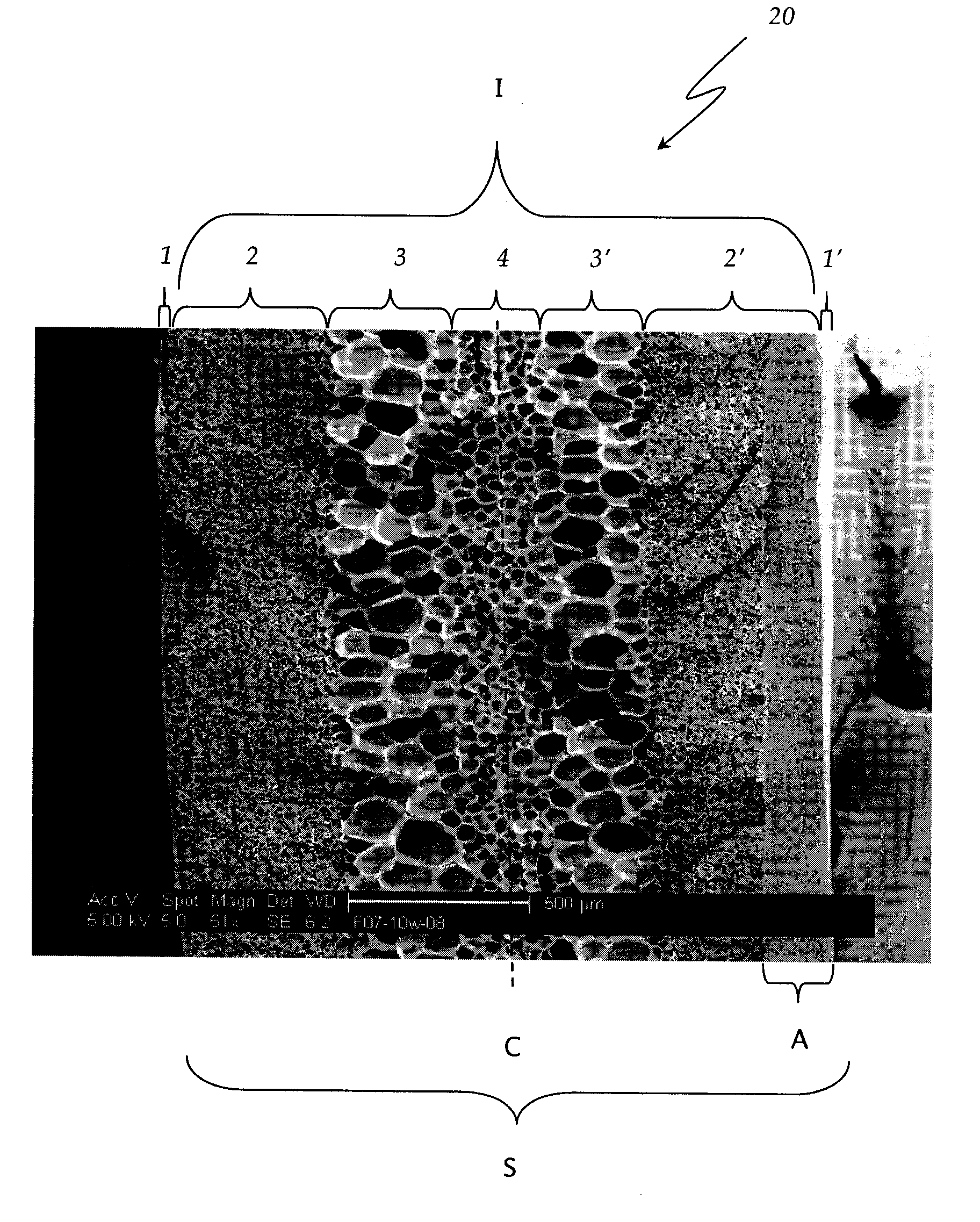
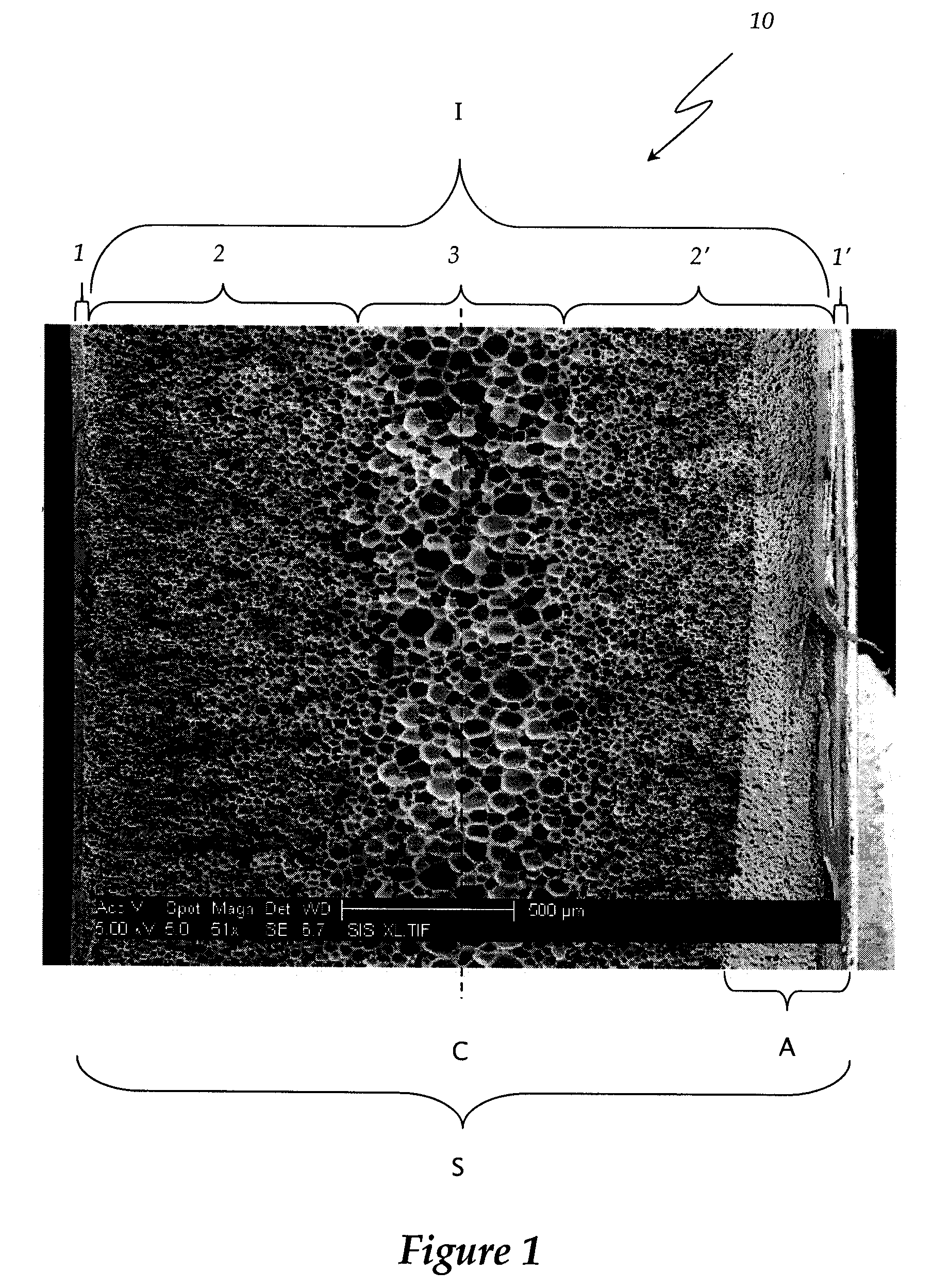
Polyether-ether-ketone biomimetic artificial bone 3D printing manufacturing method
ActiveCN103707507ASave timeSave costSpecial data processing applications3D modellingBiocompatibility TestingArtificial bone
The invention discloses a polyether-ether-ketone biomimetic artificial bone 3D printing manufacturing method, wherein the artificial bone can replace metal and has an excellent biocompatibility. The method comprises the following steps: first, collecting the bone tissue image data of the part, which is about to be implanted with an artificial bone, of a patient by using a medical instrument; secondly, establishing a three-dimensional digital model of the artificial bone on the basis of the collected data; thirdly, carrying out a format conversion on the three-dimensional digital model of artificial bone, inputting the converted file into a 3D printing system to manufacture the artificial bone; and finally carrying out cell toxicity tests, animal tests, and clinical tests. The invention utilizes a self-made polyether-ether-ketone 3D printing system to manufacture artificial bones, thus the time and cost for manufacturing moulds are saved, the manufacture period is shortened; at the same time, the shape of parts can be adjusted at any time according to the setting of the forming software; so that an crystalline polymer polyether-ether-ketone artificial bone, which has excellent biocompatibility, can be implanted into the human body, and has the advantages of high melting point, large viscosity, and bad fluidity, can be manufactured through the 3D printing method.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
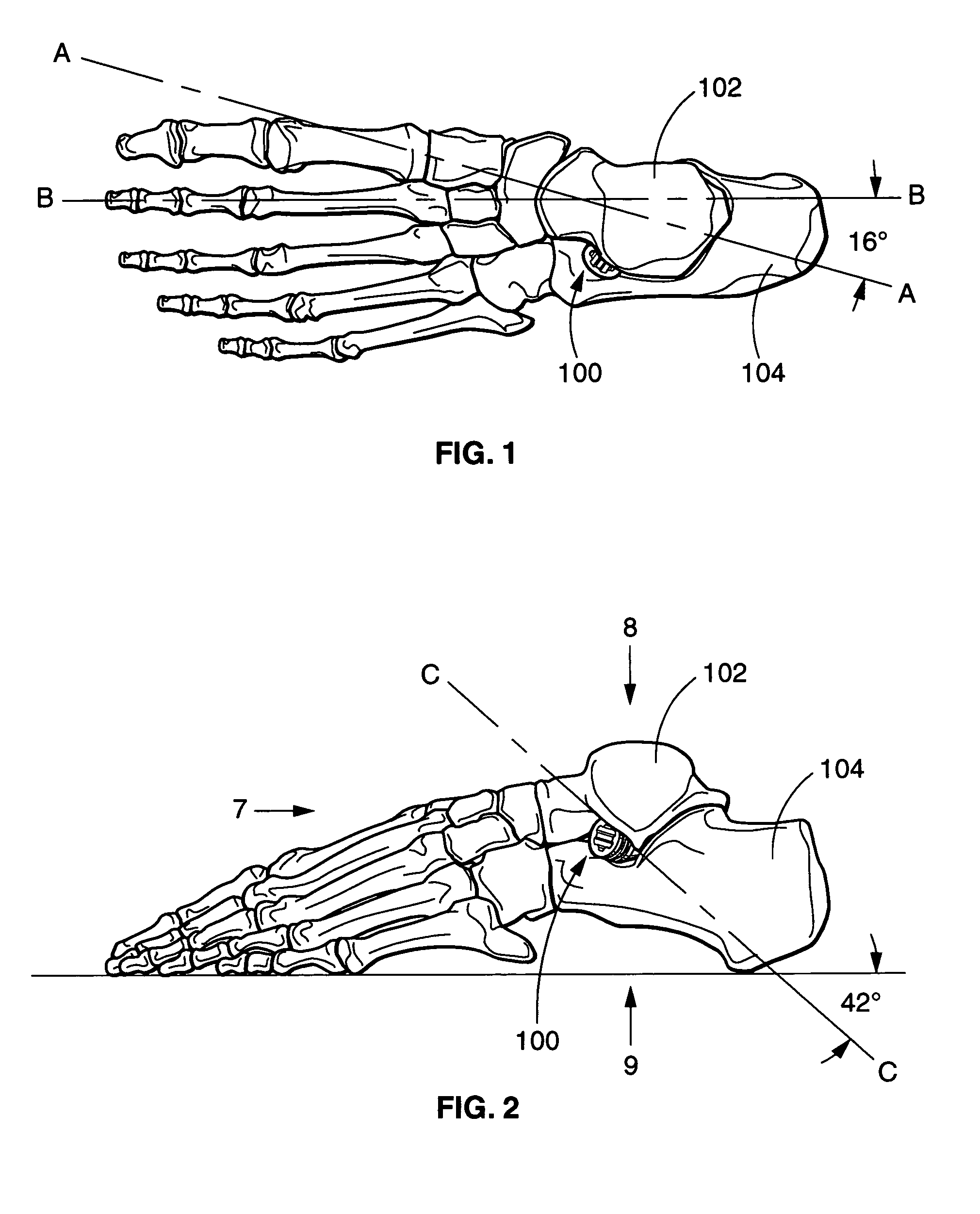
Sinus tarsi implant
An arthroeresis-prosthesis (endorthosis) system comprising a sinus tarsi implant for the purpose of blocking abnormal motion between the talus and calcaneus while allowing normal motion and alignment. In a preferred embodiment, the prosthetic device is composed of a non-metallic, specialized medical grade polymer (polyetheretherketone-PEEK) that is a combination of a frustum of a right cine and an axially extending cylinder that is cannulated and partially structured on the exterior surface.
Owner:GRAHAM MEDICAL TECH LLC
Composite Spinal Fixation Systems
InactiveUS20070190230A1Internal osteosythesisPharmaceutical containersPolyether ether ketoneMaterials science
Embodiments provide composite components for use in spinal fixation systems. The composite components may comprise polyetheretherketone (PEEK) or another non-resorbable or resorbable polymeric material and at least one metal. Incorporation of PEEK or another non-resorbable or resorbable polymeric material into the components allows average or mean physical properties (e.g., tensile strength, modulus of elasticity, etc.) of the components to be modulated. The composition and orientation of the composite components can be advantageously chosen to produce components with desired physical characteristics.
Owner:TRIEU HAI H +1
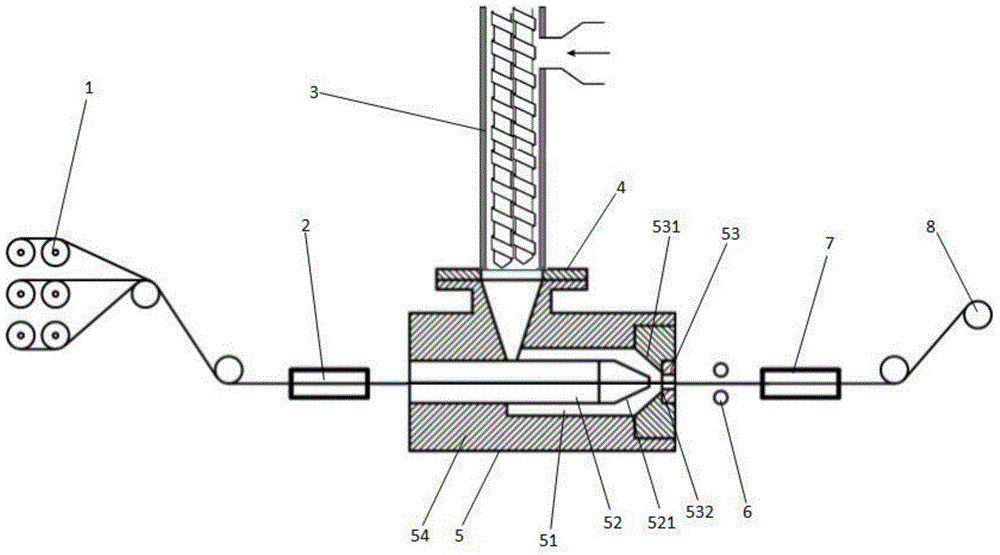
Method and equipment for preparing continuous fiber-reinforced polyether-ether-ketone composite material prepreg tape
ActiveCN104629254AGuaranteed continuous productionImprove performanceFiber bundlePolyether ether ketone
The invention discloses a method and equipment for manufacturing a continuous fiber-reinforced polyether-ether-ketone composite material prepreg tape. The method comprises the following steps: (1) splitting; (2) preheating; (3) cladding, namely, feeding the preheated continuous fiber bundle into a dipping mold to be mixed with modified PEEK resin melt extruded from a twin-screw extruder in the dipping mold, and cladding the modified PEEK resin melt on the continuous fiber bundle under the pressure action; and (4) winding. The equipment comprises a splitting device, a heating box, a material mixing device and a winding device which are arranged from left to right, wherein the material mixing device comprises the twin-screw extruder and the dipping mold; the dipping mold is connected with the twin-screw extruder and is used for cladding the resin melt flowing from a resin runner on the continuous fiber bundle under the pressure action; and the winding device is used for winding the prepreg tape which is discharged from the dipping mold. According to the method and the equipment, continuous production of the prepreg tape is ensured; blending modification and fiber dipping are integrated; the technological processes are reduced; and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-layered foamed polymeric objects and related methods
ActiveUS7807260B2ClosuresClosure using stoppersPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate
Owner:DART CONTAINER +1
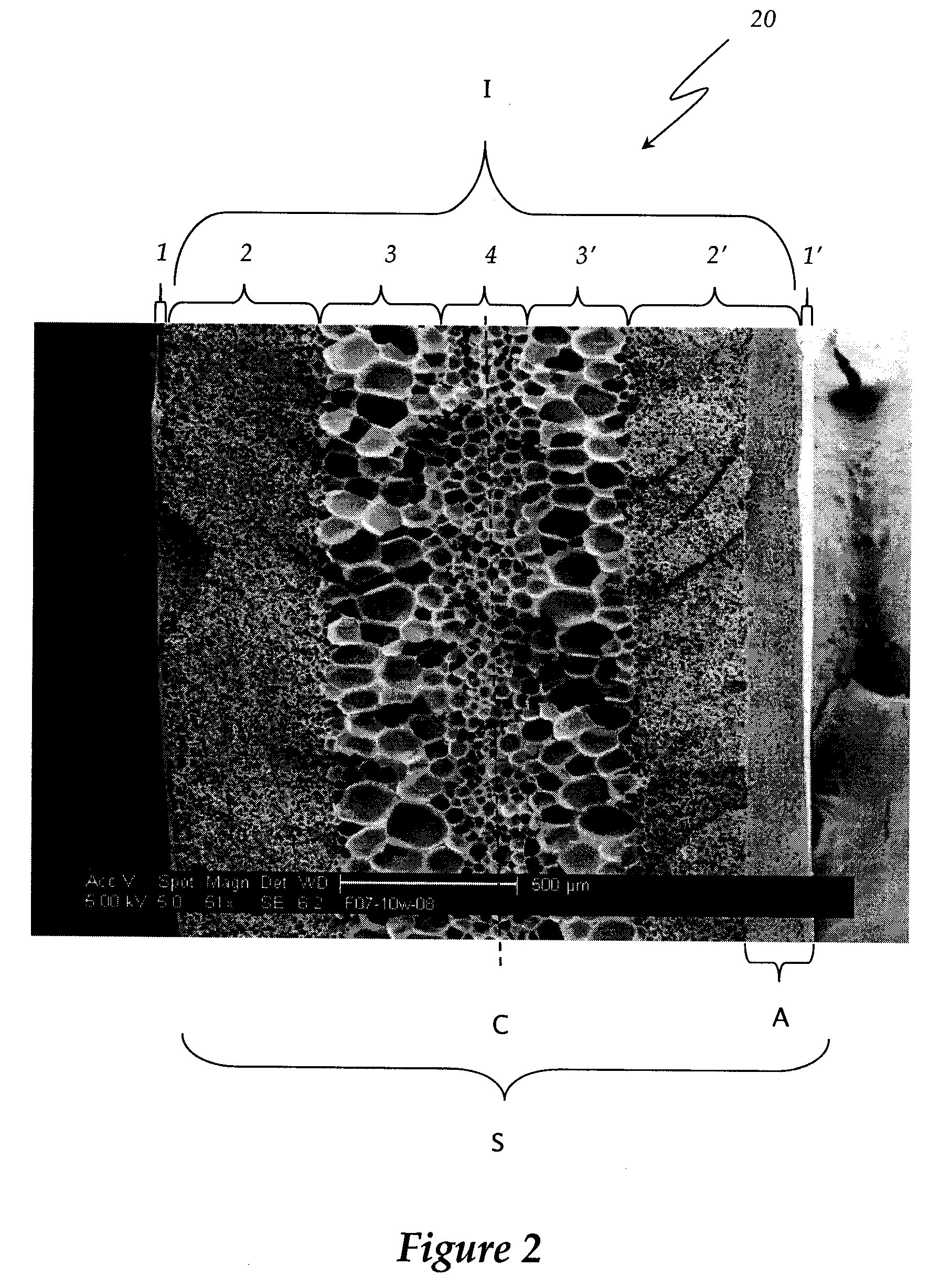
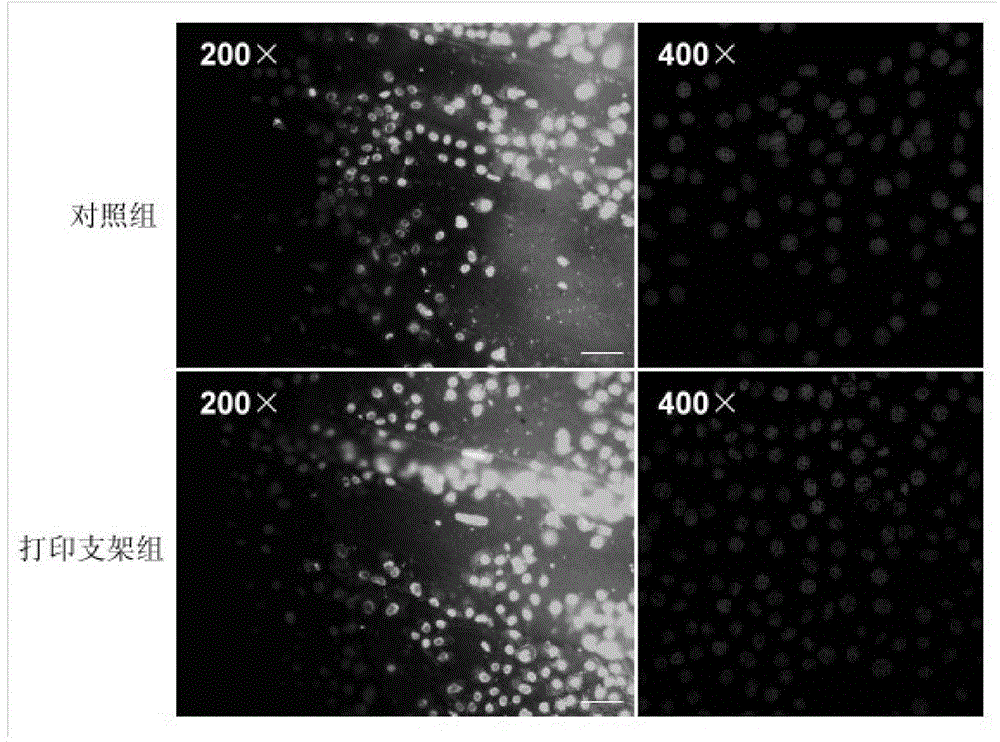
3D printing manufacturing method for tantalum-coated hierarchical pore polyether-ether-ketone artificial bone scaffold
The invention discloses a 3D printing manufacturing method for a tantalum-coated hierarchical pore polyether-ether-ketone artificial bone scaffold. The method comprises the steps of scanning bone tissues of a human injured part through CT (computed tomography) to ensure that the tissue structure of symmetrical parts can be scanned at the bone tissues of the deficient part, acquiring injured bone image data, importing the data into Mimics software, and establishing a three-dimensional bone model of a human specified part; controlling the software through a 3D printing system to generate a motion locus code; printing a polyether-ether-ketone artificial bone scaffold by using the 3D printing system till the manufacturing process of the whole artificial bone scaffold is completed, putting the dried artificial bone scaffold into the cavity of a sputtering chamber of a magnetron sputtering instrument, bonding the artificial bone scaffold to an objective table by using silver colloid, and plating a tantalum coating on the artificial bone scaffold by adopting a magnetron sputtering technology; discharging gas from the sputtering chamber after the tantalum coating is plated, taking the artificial bone scaffold out, and disinfecting the tantalum-coated hierarchical pore polyether-ether-ketone scaffold to complete all the steps. The artificial bone scaffold is manufactured through 3D printing, so that the method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the manufactured scaffold is harmless to the human body.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Inorganically surface-modified polymers and methods for making and using them
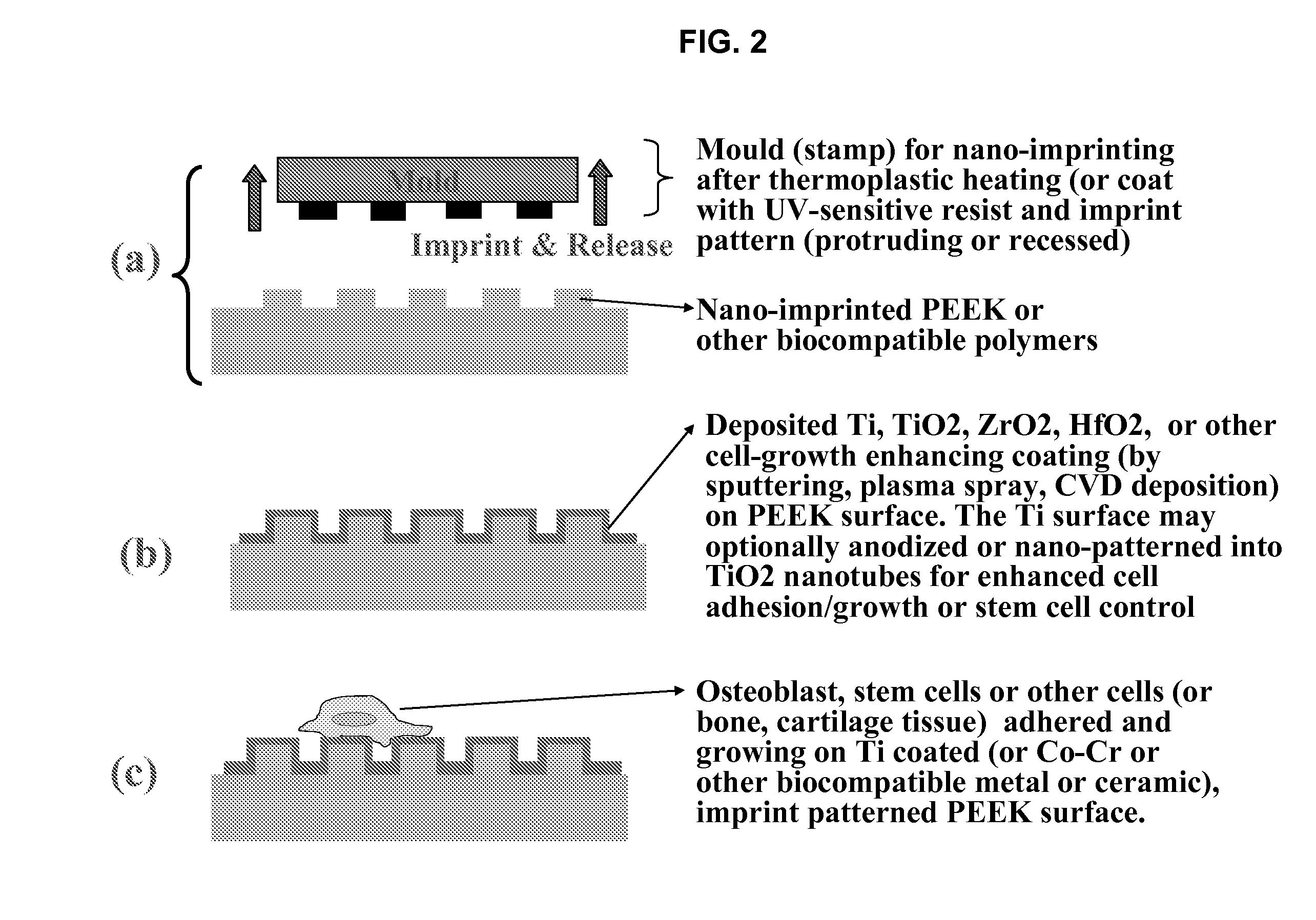
In alternative embodiments, the invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising PolyEther EtherKetone (PEEK) surface-modified (surface-nanopatterned) to exhibit nanostructured surfaces that promote osseointegration and bone-bonding for, e.g., joint (e.g., knee, hip and shoulder) replacements, bone or tooth reconstruction and / or implants, including their use in making and using artificial tissues and organs, and related, diagnostic, screening, research and development and therapeutic uses, e.g., as primary or ancillary drug delivery devices. In alternative embodiments, the invention provides biocompatible nanostructures that promote osseointegration and bone-bonding for enhanced cell and bone growth and e.g., for in vitro and in vivo testing, restorative and reconstruction procedures, implants and therapeutics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
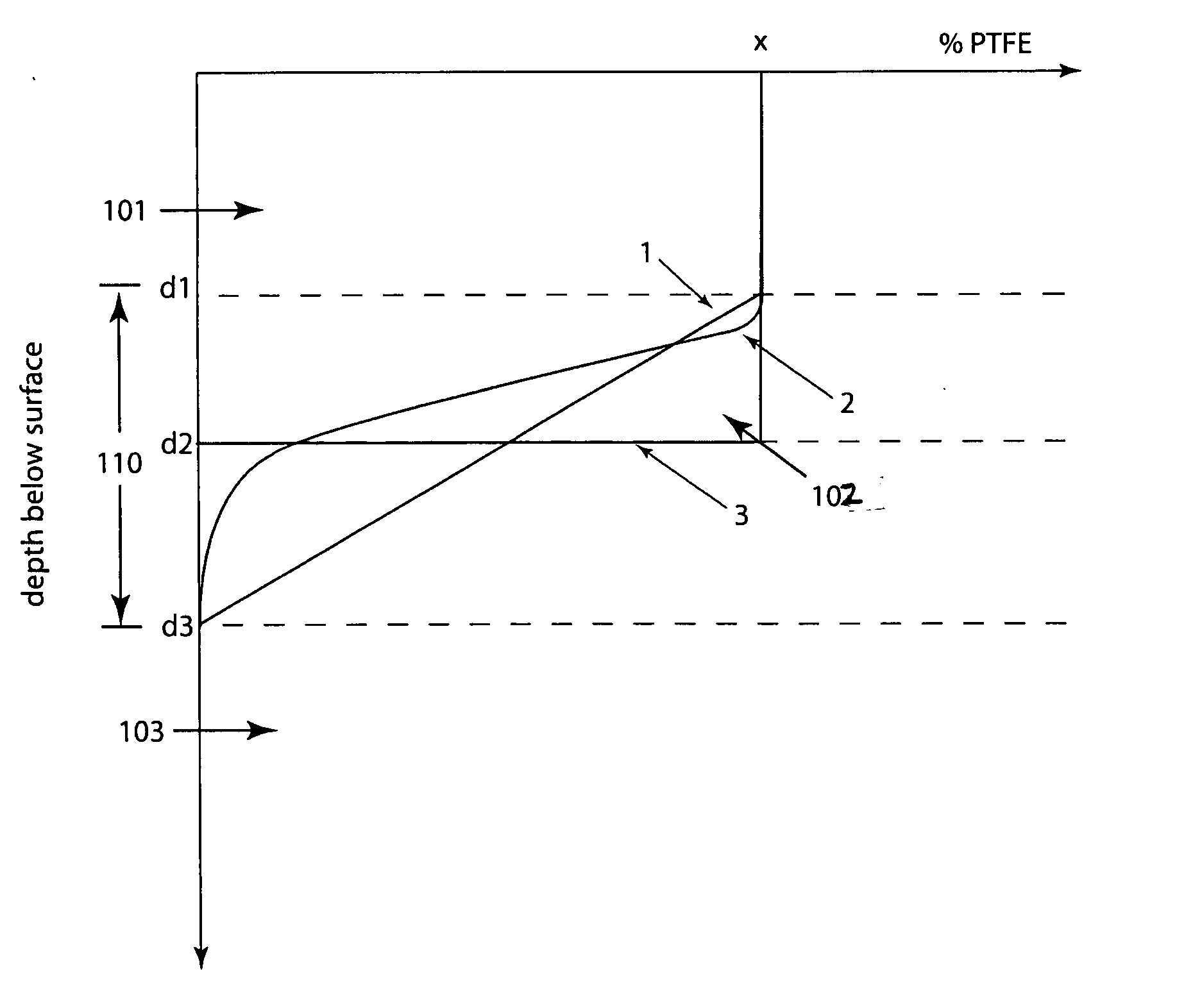
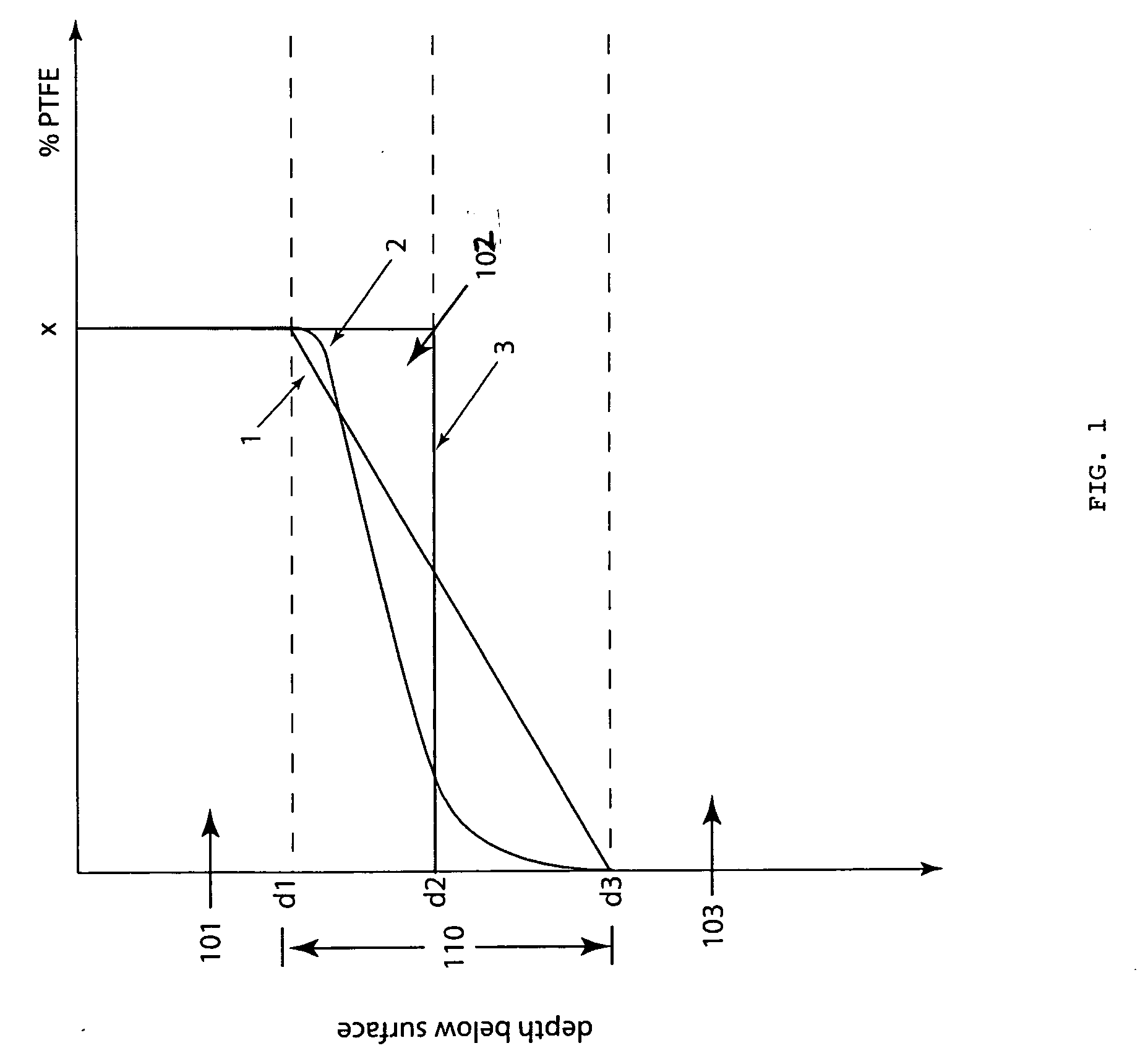
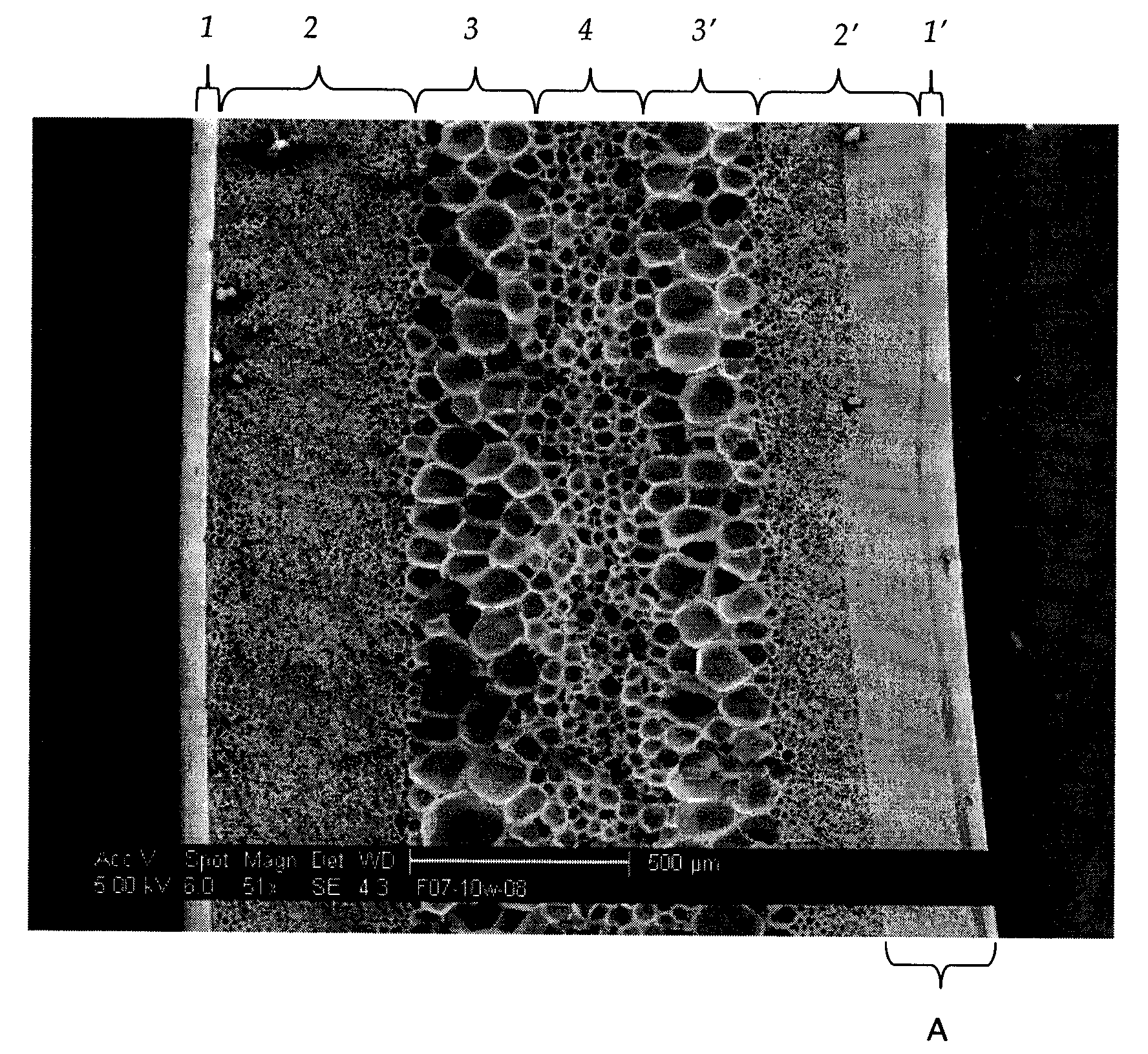
Novel polyetheretherketone self-lubricating hard wearing compound material and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101580753AImprove wear resistanceImprove the lubrication effectLubricant compositionFiberTetrafluoroethylene
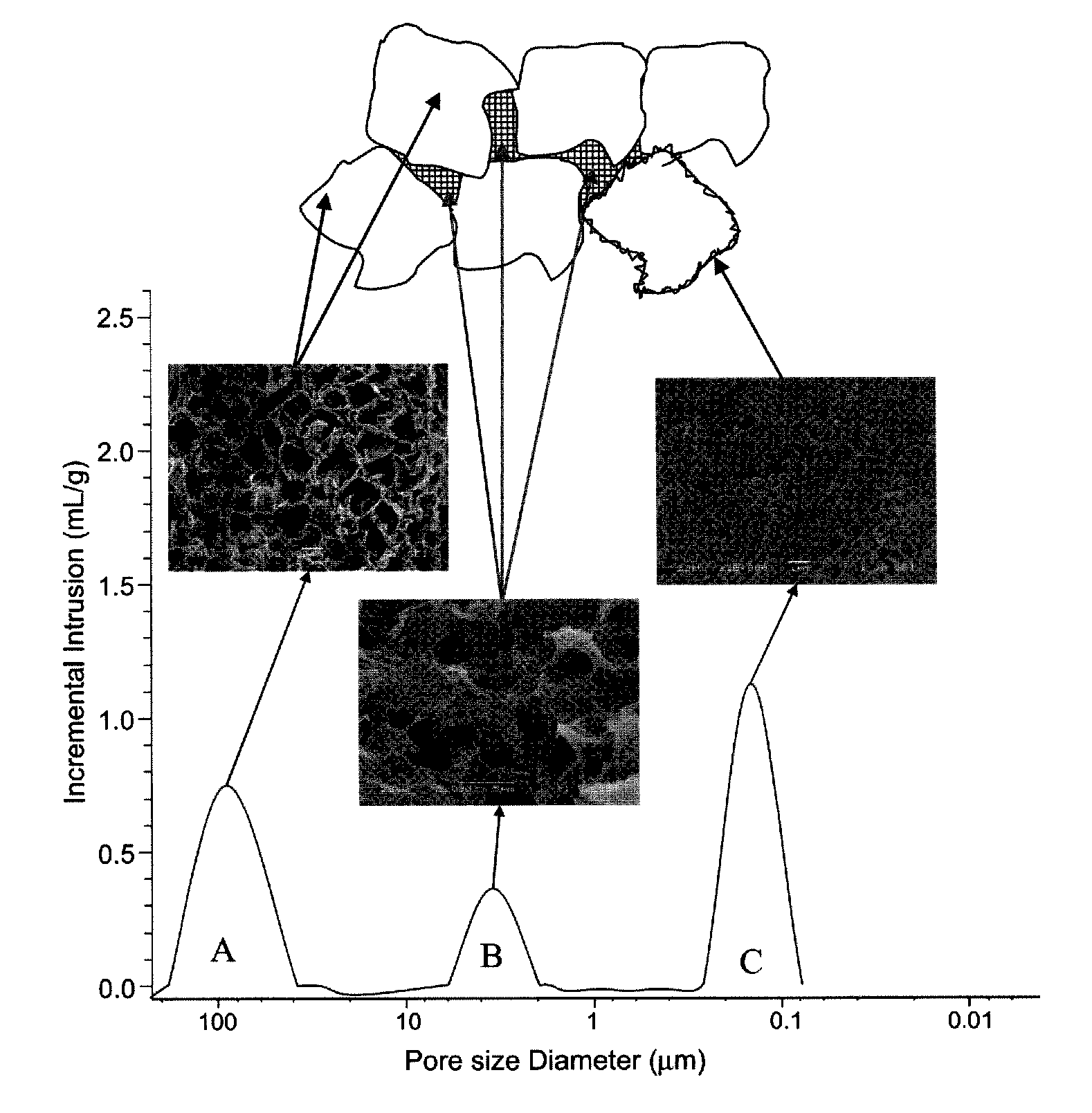
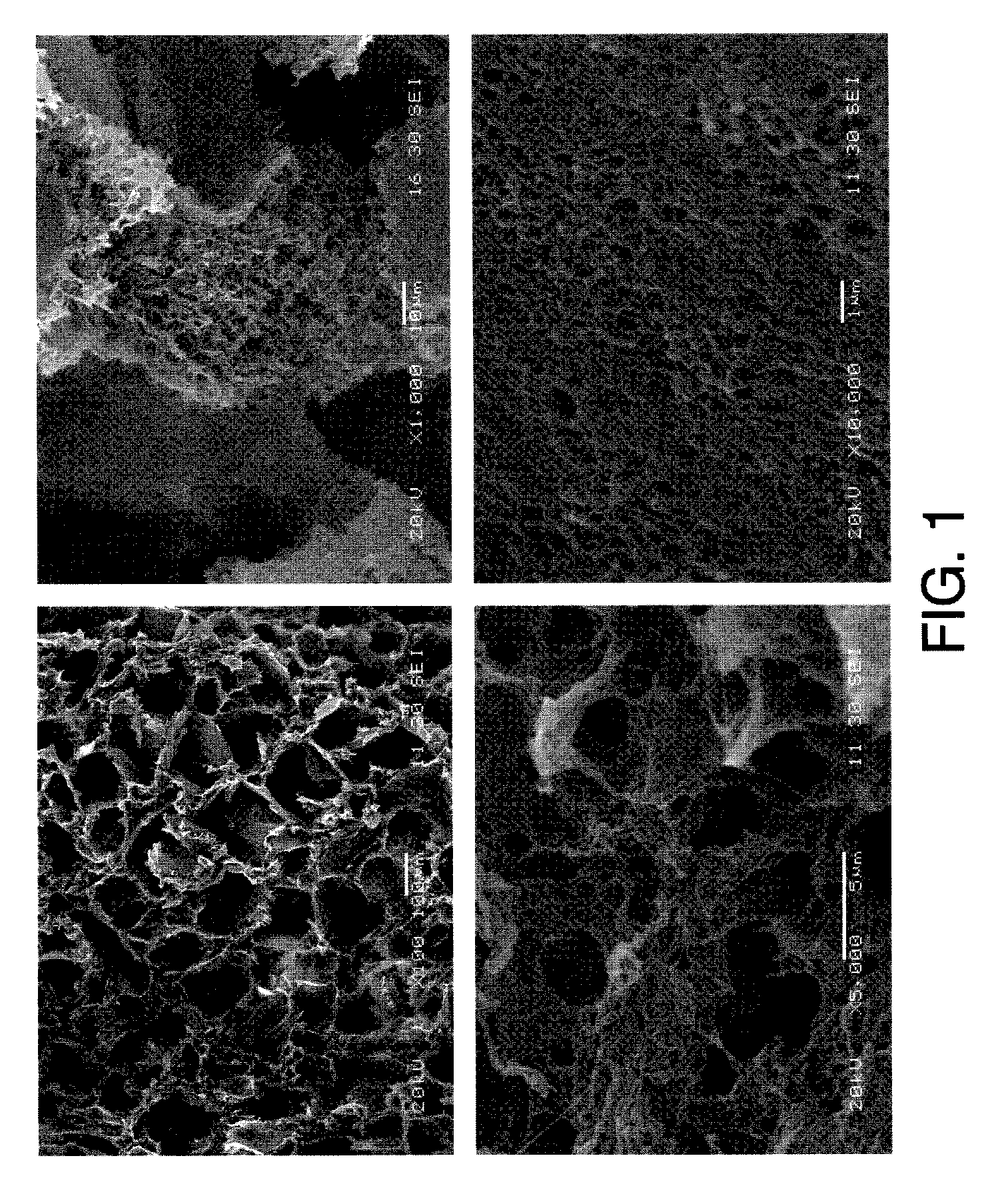
The invention provides a novel polyetheretherketone (PEEK) compound material which is prepared by taking the porous PEEK compound material as matrixes and filling the pores thereof with lubricating grease; wherein, the porous PEEK matrix is prepared from the following components by the weight percentage: 45% to 90% of PEEK powder, 0% to 30% of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) powder, 5% to 40% of reinforcing fiber and 5% to 49% of pore-forming agent; the porosity of the matrix is 5% to 35%, the pore diameter ranges from 0.05 mum to 10 mum, the average pore size is 1.0 mum, and the tensile strength thereof is 45MPa to 90MPa. The invention further provides a method for preparing the PEEK compound material. By forming a lubricating oil film on friction surfaces of the material so as to have good lubricating effect, thereby remarkably reducing the friction coefficient thereof and improving the wear resistance thereof; and the material is suitable for reducing and resisting friction within high-temperature, vacuum, radiation, corrosion and other special environments and capable of greatly prolonging the service life of devices.
Owner:DAQING GASOLINEEUM INST
Low friction and low wear polymer/polymer composites
InactiveUS20060030681A1Improve tribological propertiesReduce wearCoatingsSpecial surfacesPolymer sciencePolyether ether ketone
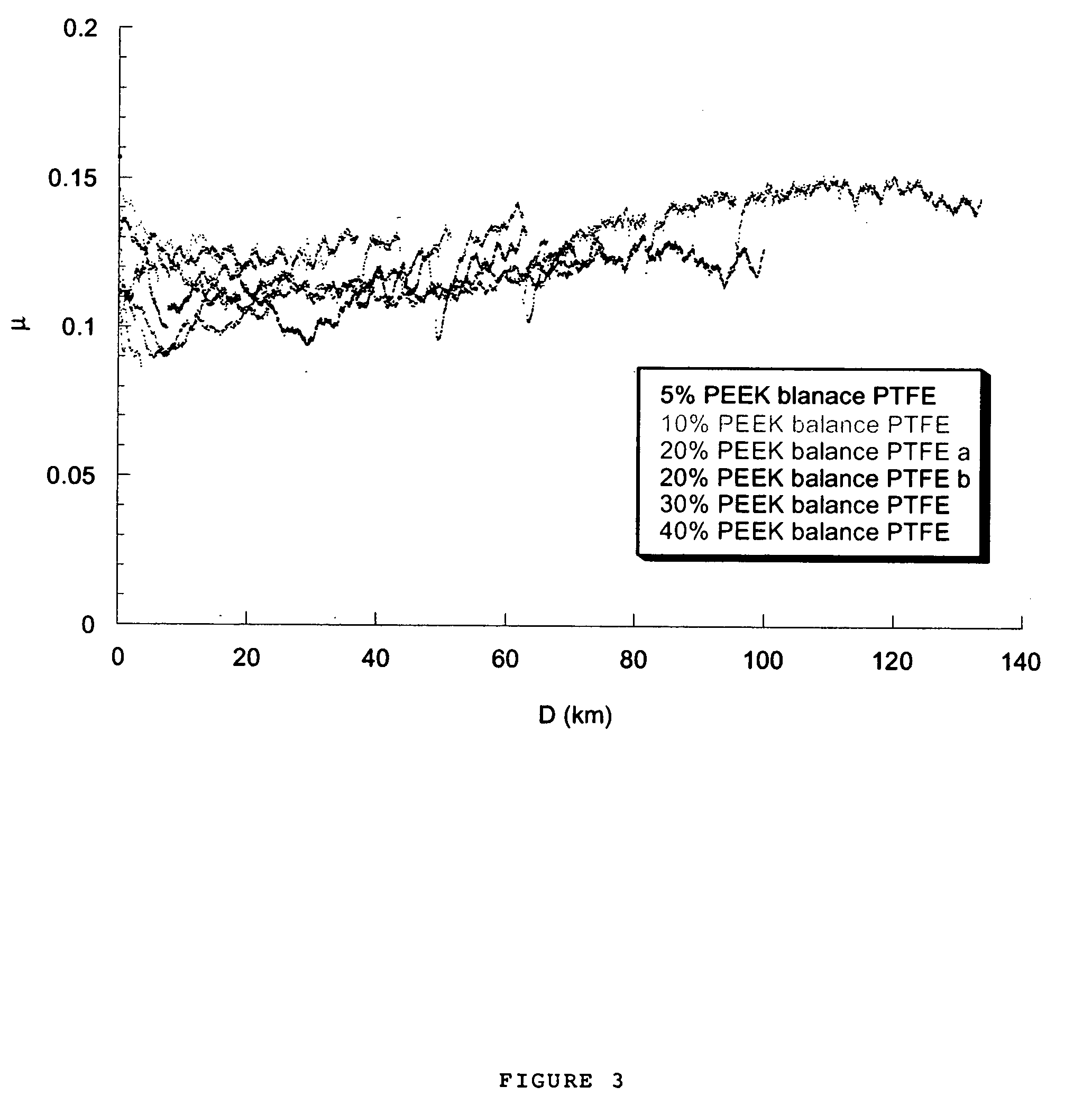
A composite material having superior tribological properties includes a first polymer being a transfer film forming polymer and a second polymer mixed with the first polymer. The first polymer is at least 10 weight % of the composite and the composite provides a wear rate of <10−7 mm3 / Nm and an average friction coefficient of said composite no more than 0.15. The first polymer can be PTFE and the second polymer a polyaryletherketone (PEEK). A method of forming composites includes the steps of providing a plurality of transfer film forming polymer particles and second polymer particles, and molding or extruding the particles at a temperature sufficient to allow softening and mobilization of at least one of the transfer film forming polymer particles and the plurality of strengthening phase polymer particles to form an interconnected network, wherein the composite formed provides a wear rate of <10−7 mm3 / Nm.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Insulated cylinder liner for a marine engine
InactiveUS7191770B1High glass transition temperatureCylinder headsCylindersPolyethylene terephthalateEngineering
An engine is made by providing a layer of material between the outer surface of a cylinder liner and the inner surface of the cylinder opening within an engine block. The material can be a polymer or a ceramic. Polyether ether ketone or polyethylene terephthalate can be a polymer used for these purposes. Zirconia or yttria can be ceramic used for these purposes. An electro-deposited paint can serve as the layer of thermally insulative material.
Owner:BRUNSWICK CORPORATION
Porous peek article as an implant
The present invention refers to a porous PEEK-type polymer article comprising a porous PEEK-type polymer structure and presenting at least a trimodal pore distribution. The invention describes a process for the production of said porous PEEK-type polymer article comprising: a) contacting a PEEK-type polymer with a composition comprising at least a organic solvent, b) heating at a temperature at which the PEEK-type polymer is dissolved, c) adding at least a porogen agent, d) cooling the mixture obtained in c) at a temperature at least equal or lower than the temperature at which the PEEK-type polymer precipitates, e) forming said cooled mixture into a shaped article, f) removing the organic solvent and the porogen agent, and g) recovering the PEEK-type polymer article.
Owner:FUNDACION TECNALIA RES & INNOVATION
Peek threaded suture anchor
InactiveUS20070135841A1Prevents suture abrasionAvoid abrasionsSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuture anchorsDistal portion
A threaded suture anchor formed of a material comprising polyether-ether ketone (PEEK) has a suture loop that is disposed internally within the suture anchor. The suture loop can extend through a substantial length of the anchor body with the ends of the suture loop secured at the distal end of the anchor and the proximal end of the loop being flush with or recessed just below the proximal surface of the proximal end of the anchor. The anchor body can be threaded and have a tapered distal portion.
Owner:ARTHREX
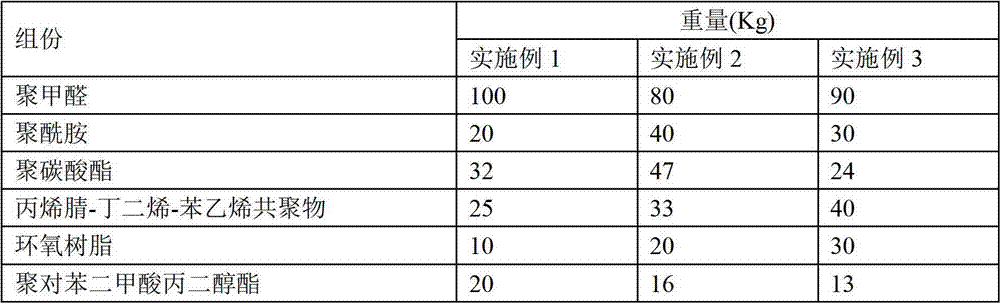
Engineering plastic with high wearing resistance
InactiveCN102875956AGood mechanical propertiesReduce wear ratePolyethylene glycolPolymethyl methacrylate
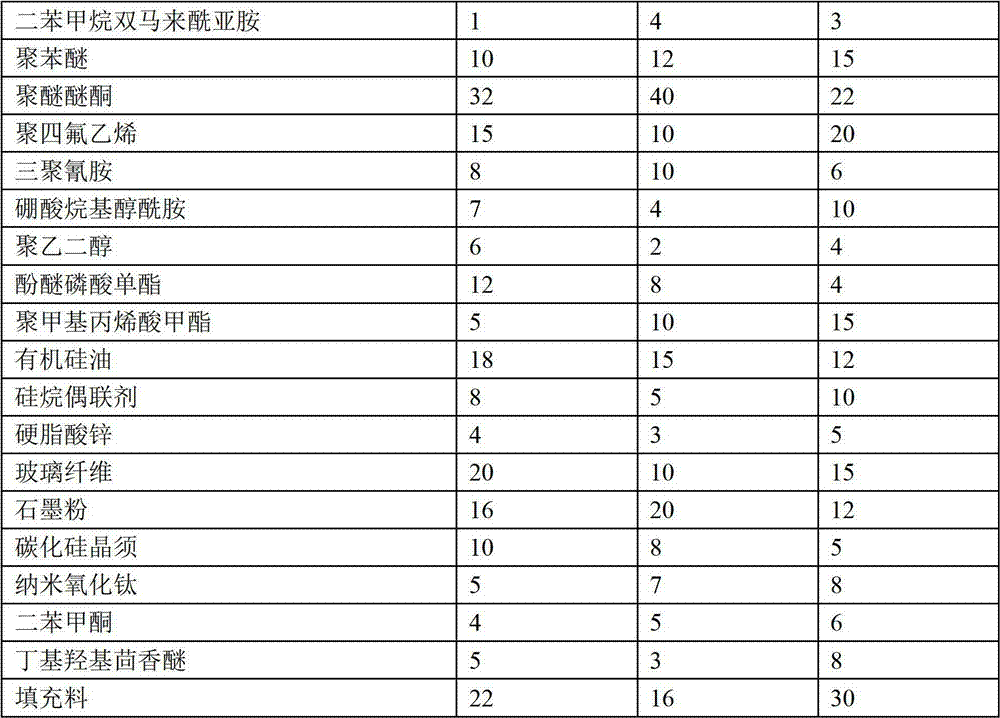
The invention provides an engineering plastic with high wearing resistance. The engineering plastic is made from the following raw materials by weight: 80-100 parts of polyformaldehyde, 20-40 parts of polyamide, 20-50 parts of polycarbonate, 25-40 parts of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer, 10-30 parts of epoxy resin, 12-20 parts of polytrimethylene terephthalate, 1-5 parts of diphenylmethane bismaleimide, 10-15 parts of polyphenyl ether, 20-40 parts of polyether-ether-ketone, 10-20 parts of polytetrafluoroethylene, 5-10 parts of melamine, 4-12 parts of boric acid alkanolamide, 2-6 parts of polyethylene glycol, 4-12 parts of phenolic ether phosphomonoester, 5-15 parts of polymethyl methacrylate, 10-20 parts of organic silicone oil, 5-10 parts of silane coupling agent, 3-5 parts of zinc stearate, 10-20 parts of glass fibre, 12-20 parts of graphite, 5-10 parts of silicon carbide whisker, 5-8 parts of nanometre titanium oxide, 4-6 parts of diphenyl ketone, 3-8 parts of butylated hydroxyanisole and 15-30 parts of filler. The engineering plastic provided by the invention has a good wear-resisting property.
Owner:SUZHOU YUNYUAN NETWORK TECH
Puncture and abrasion resistant sheath
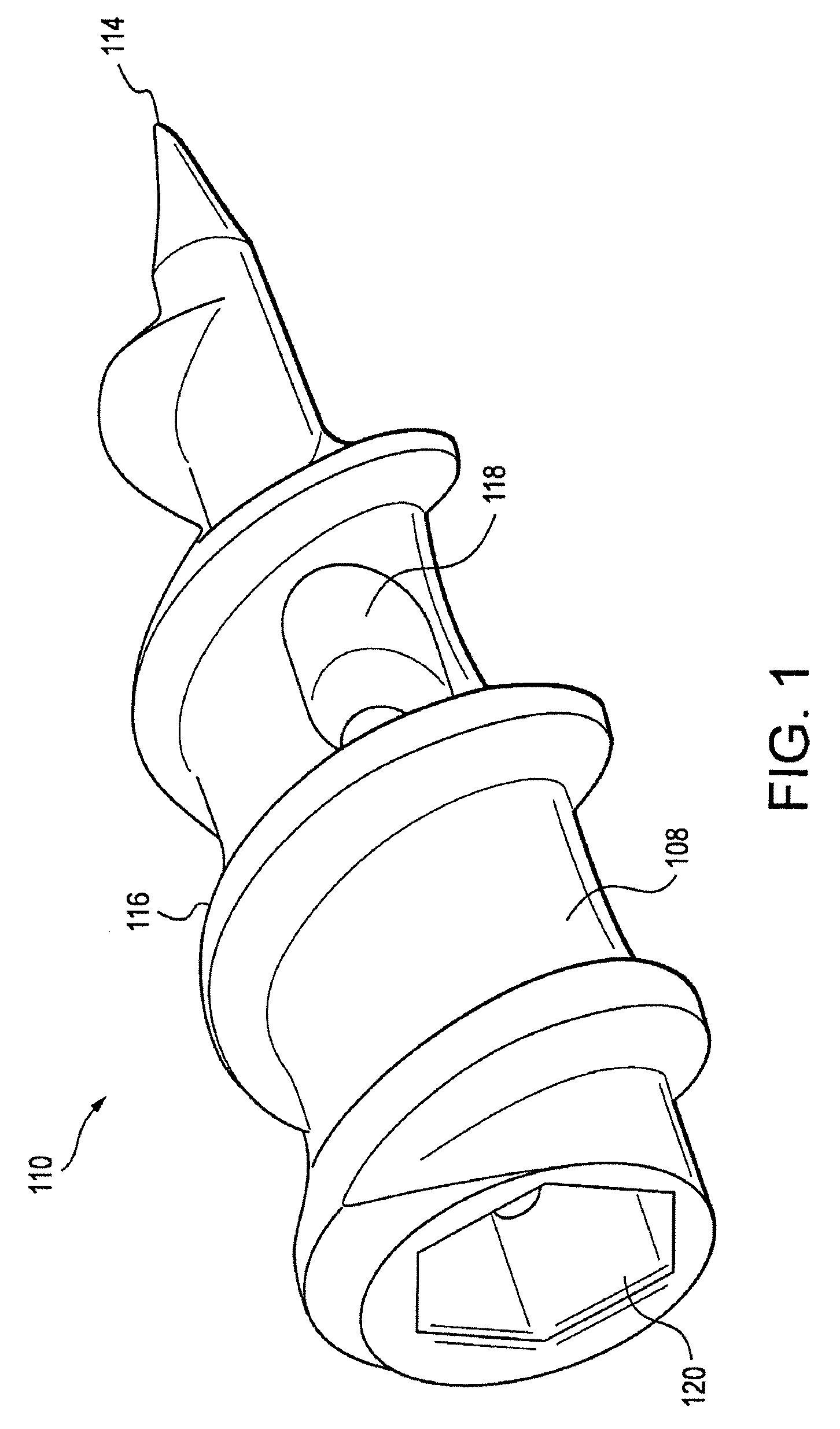
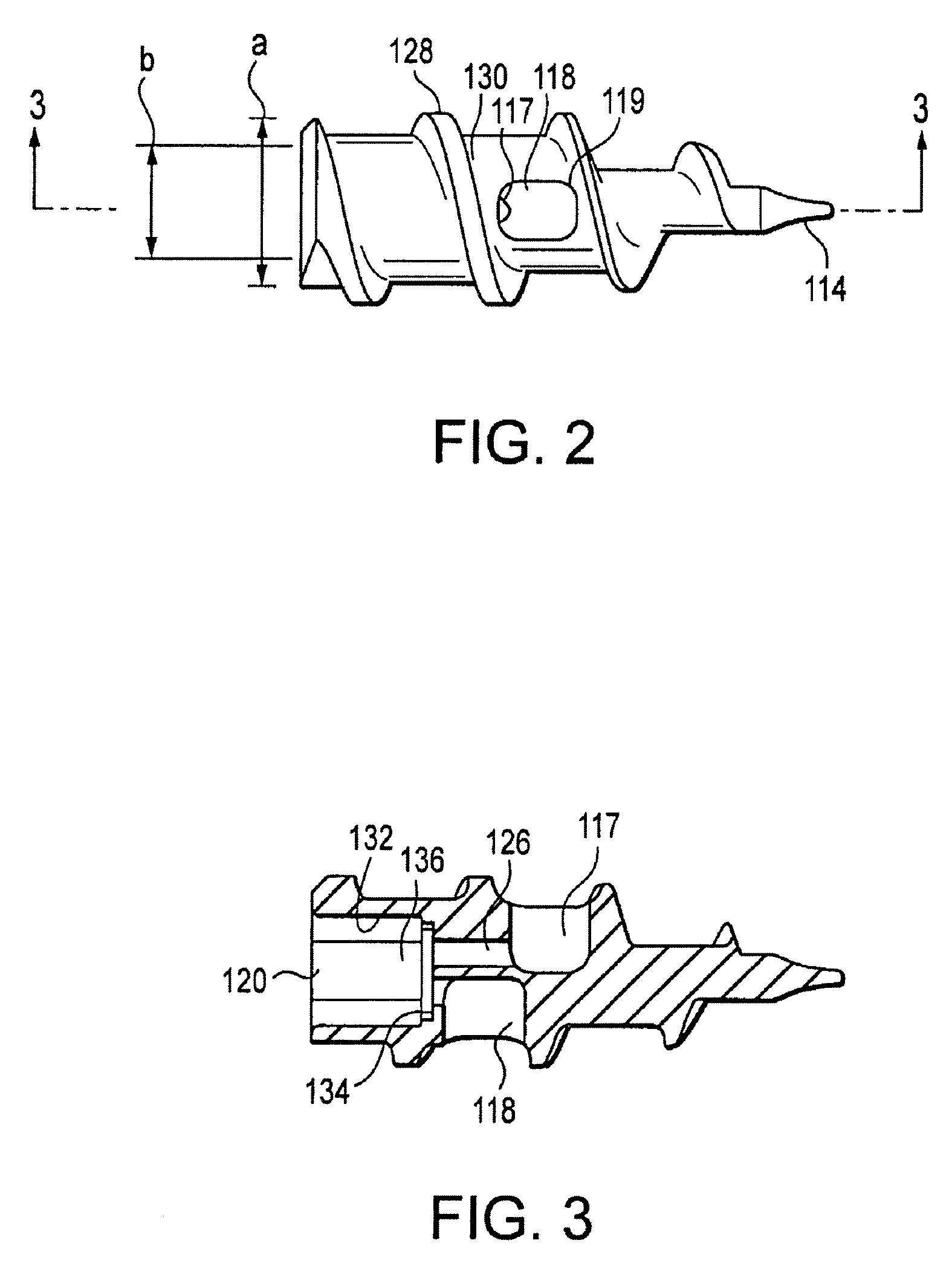
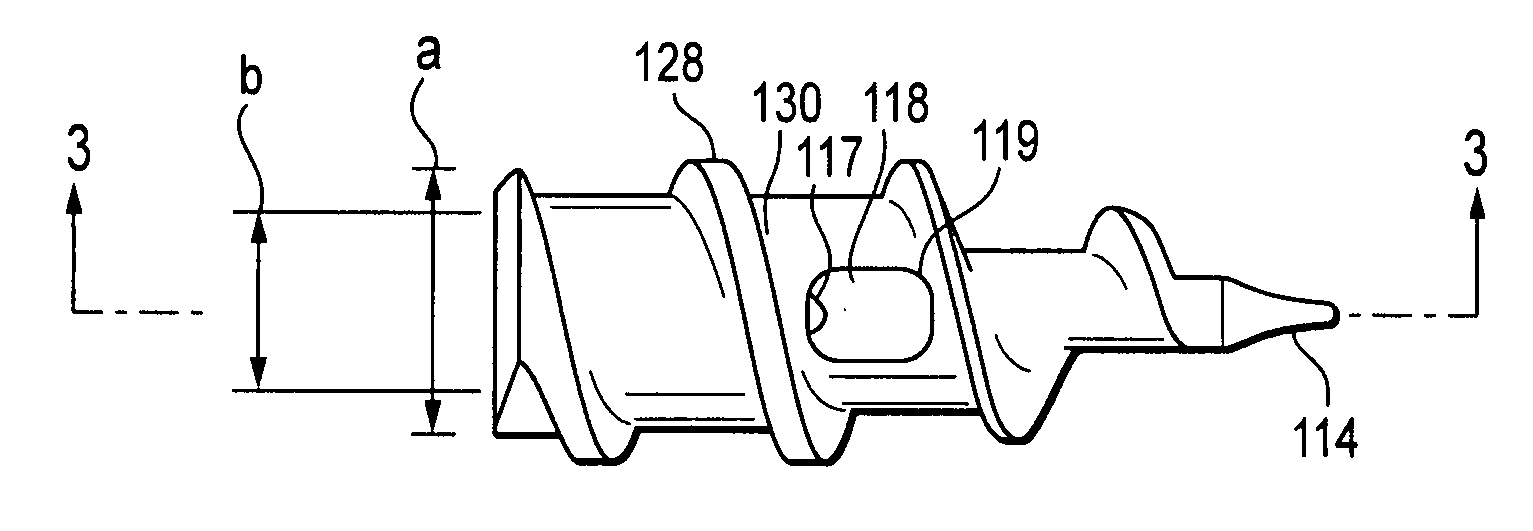
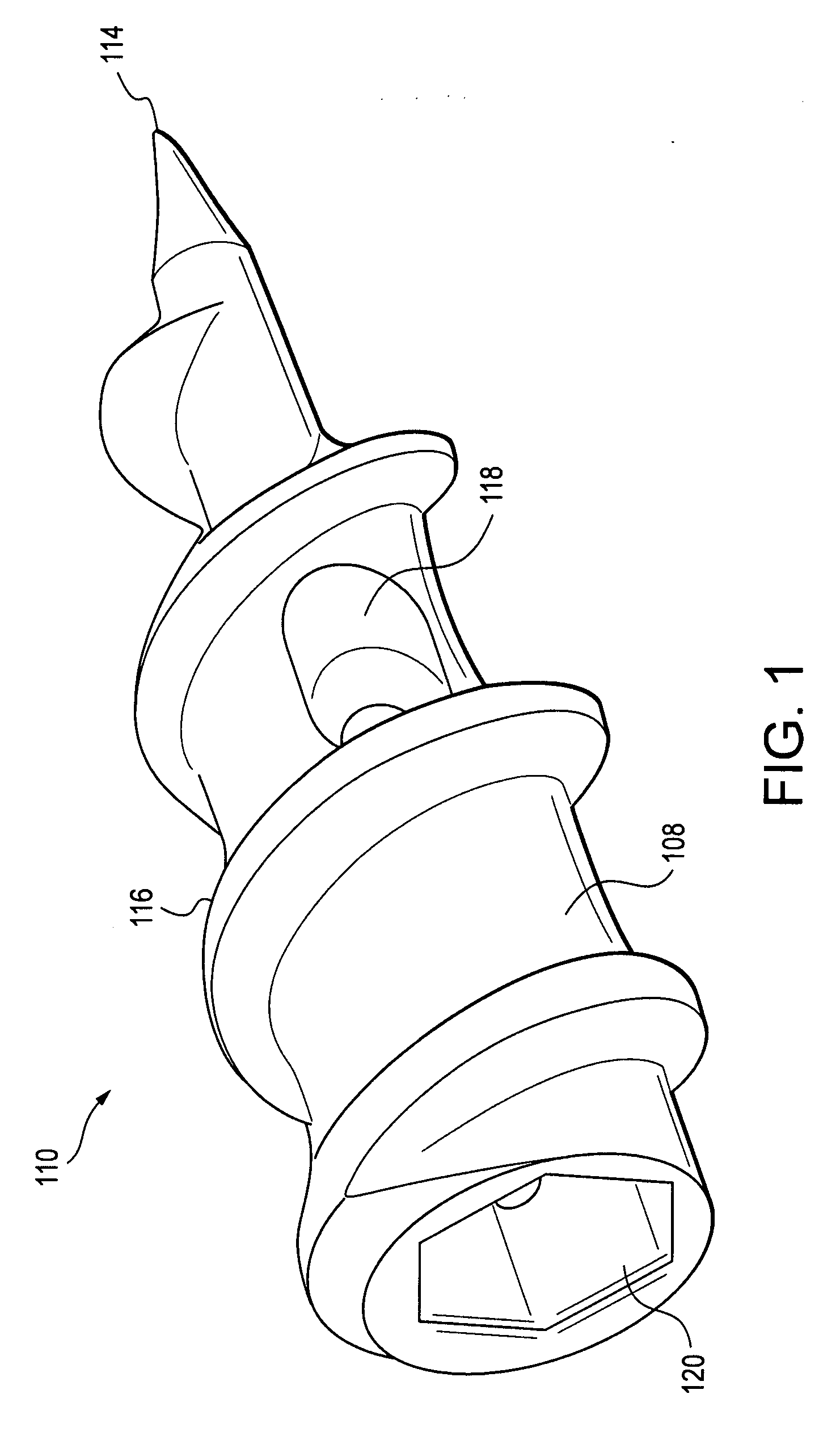
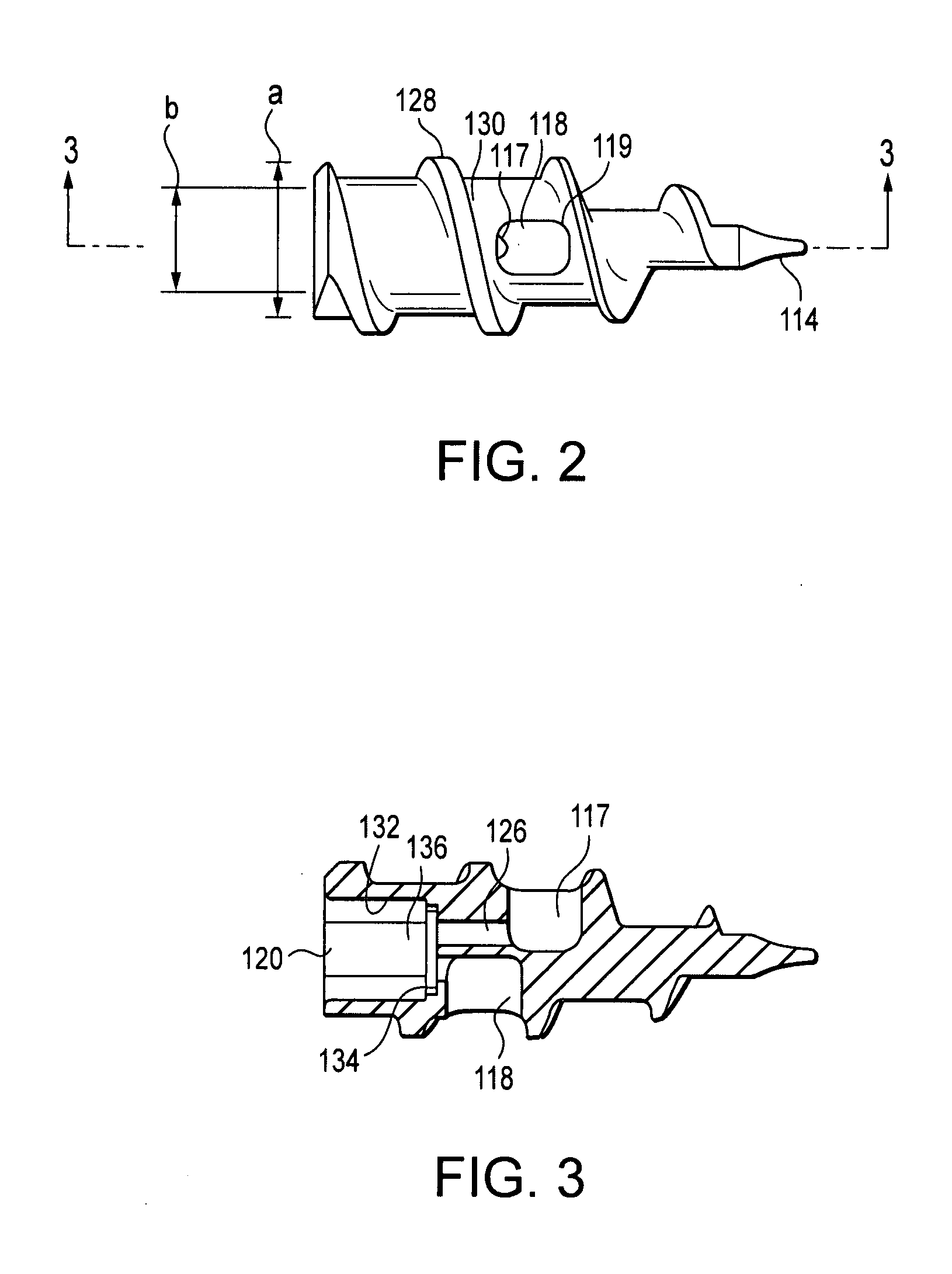
InactiveUS20080119867A1Excellent abrasion resistanceImprove puncture resistanceGuide needlesEar treatmentDistal portionPolyether ether ketone
A delivery apparatus for introducing an implant, such as a vena cava filter, for capturing emboli in a body vessel. The apparatus includes an outer sheath having a tubular wall defining a lumen formed therethrough and having a proximal end extending to a distal end. The tubular wall includes an inner surface and may also include optional reinforcing members. A radiopaque marker band is disposed about the inner surface adjacent the distal end, and a tubular liner is disposed along the inner surface. The tubular liner comprises at least one of polyimide, PEEK, and PVDF. An inner catheter is slidably disposed within the lumen of the outer sheath and has a distal portion configured to engage and deliver the implant through the distal end of the outer sheath in the body vessel.
Owner:COOK INC
Wear-resistant carbon fiber modified polyether-ether-ketone composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wear-resistant carbon fiber modified polyether-ether-ketone composite material, which is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 40 to 60 parts of polyether-ether-ketone resin, 10 to 30 parts of polyfluortetraethylene resin, 8 to 20 parts of polyimide resin, 2 to 5 parts of carbon fiber, 5 to 10 parts of vermiculite, 5 to 15 parts of parithenolide, 4 to 8 parts of orthoclase powder and 1 to 2 parts of compatilizers. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the composite material. The composite material has the advantages that the wear-resistant performance is good; the high-temperature-resistant performance is excellent; the processing is easy; the anti-impact performance is good; the intensity is high; the composite material can be widely applied to the field of mechanical part preparation; in addition, the preparation method is simple; the cost is low.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHENZHAN TECHCAL MATERIAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com