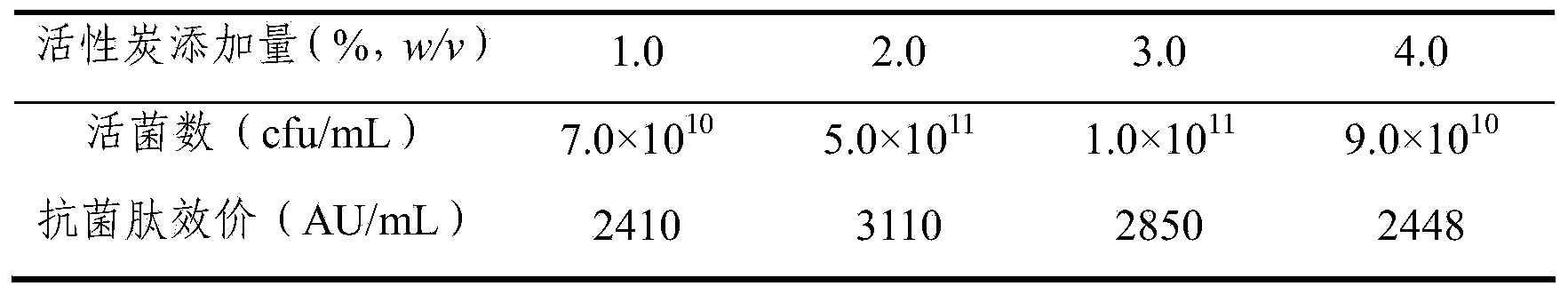Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141results about How to "Disinhibition effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
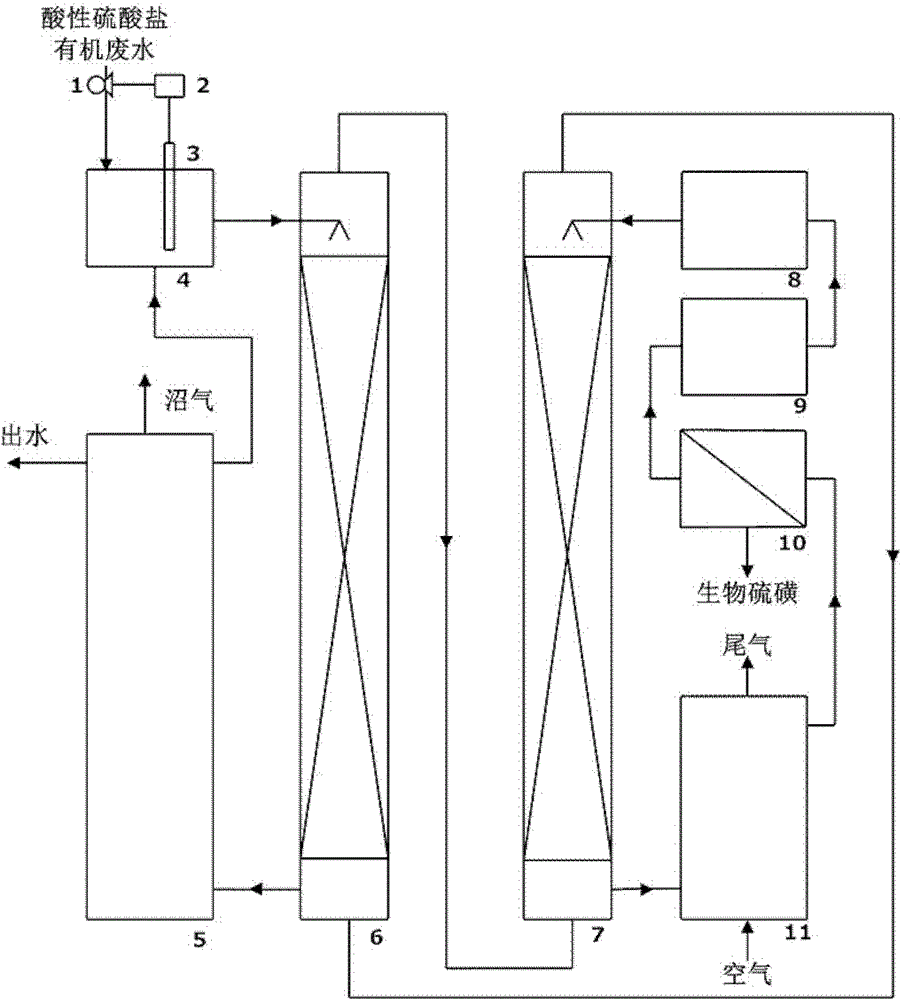
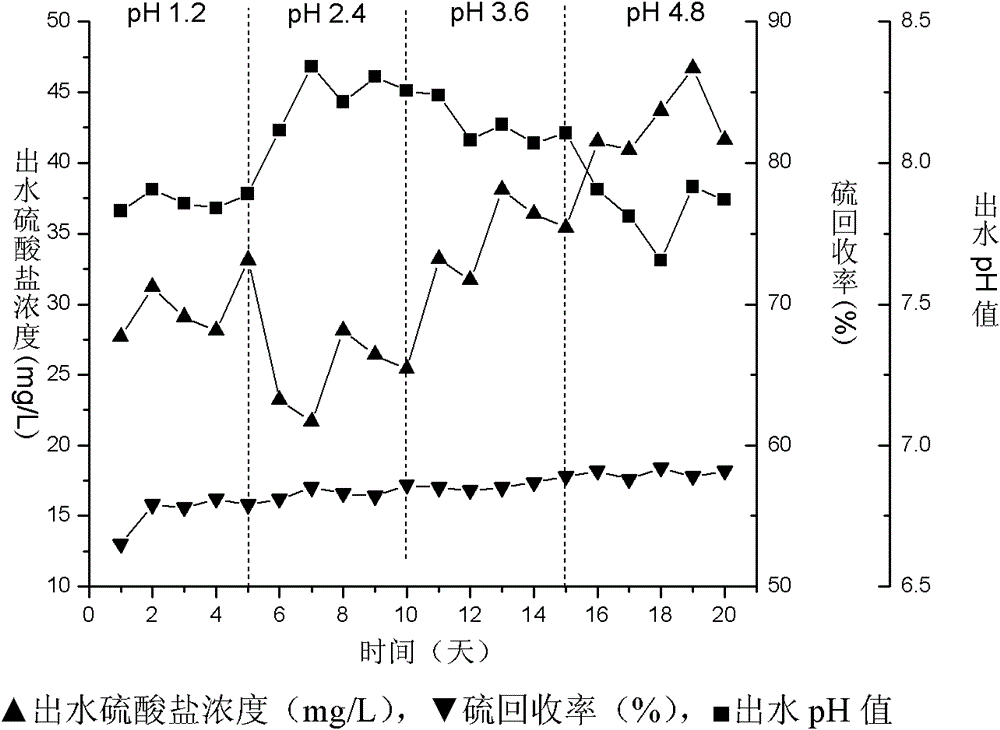
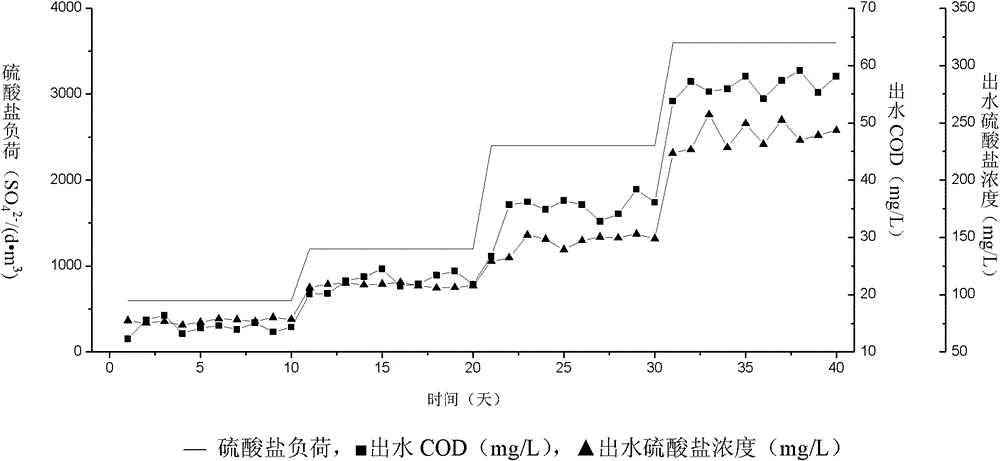
Device and method for comprehensively treating acidic sulfate organic waste water based on biological desulfurization
InactiveCN102795739AAchieving processing powerFacilitate conversion and strippingMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater basedSulfate-reducing bacteria
The invention belongs to the field of environmental engineering, and in particular relates to a device and a method for comprehensively treating acidic sulfate organic waste water based on biological desulfurization. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, reducing sulfate in the organic waste water, blowing hydrogen sulfide off, namely (1-1) mixing the acidic sulfate organic waste water and sulfide-containing recirculation water in an anaerobic digestion reactor, controlling the pH of the mixture to be 5.0 to 6.0, and thus obtaining a hydrogen sulfide-containing acidic mixed solution, and (1-2) introducing inert gas, blowing the hydrogen sulfide off, adding sulfate reducing bacteria, reducing the sulfate to form sulfide, obtaining the sulfide-containing recirculation water and returning to the step (1-1); and 2, absorbing, oxidizing and recycling the hydrogen sulfide, namely (2-1) absorbing the hydrogen sulfide blown off in the step (1-2) by using a weak alkaline solution, adding sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, oxidizing the hydrogen sulfide to form elemental sulfur, separating to obtain the elemental sulfur and effluent, and (2-2) treating the effluent for recycling. By the device and the method, sulfate innocent treatment and resource recovery treatment are realized.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treatment of lysosomal storage disorders and other proteostatic diseases
InactiveUS20110237538A1Increase half-lifeInhibitory effectBiocideNervous disorderAcid CeramidaseAcid beta-galactosidase
Described are various compounds, in particular iminosugars, and methods for the treatment of proteostatic diseases, in particular lysosomal storage disorders. The compound may be a pharmacoperone of an enzyme selected from: (a) Acid alpha-glucosidase; (b) Acid beta-glucosidase; (c) glucocerebrosidase; (d) alpha-Galactosidase A; (e) Acid beta-galactosidase; (f) beta-Hexosaminidase A; (g) beta-Hexosaminidase B; (h) Acid sphingomyelinase; (i) Galactocerebrosidase; (j) Acid ceramidase; (k) Arylsulfatase A; (l) alpha-L-Iduronidase; (m) Iduronate-2-sulfatase; (n) Heparan N-sulfatase; (o) alpha-N-Acetylglucosaminidase; (p) Acetyl-CoA: alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase; (q) N-Acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase; (r) N-Acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase; (s) Acid beta-galactosidase; (t) Arylsulfatase B; (u) beta-Glucuronidase; (v) Acid alpha-mannosidase; (w) Acid beta-mannosidase; (x) Acid alpha-L-fucosidase; (y) Sialidase; and (z) alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase.
Owner:SUMMIT
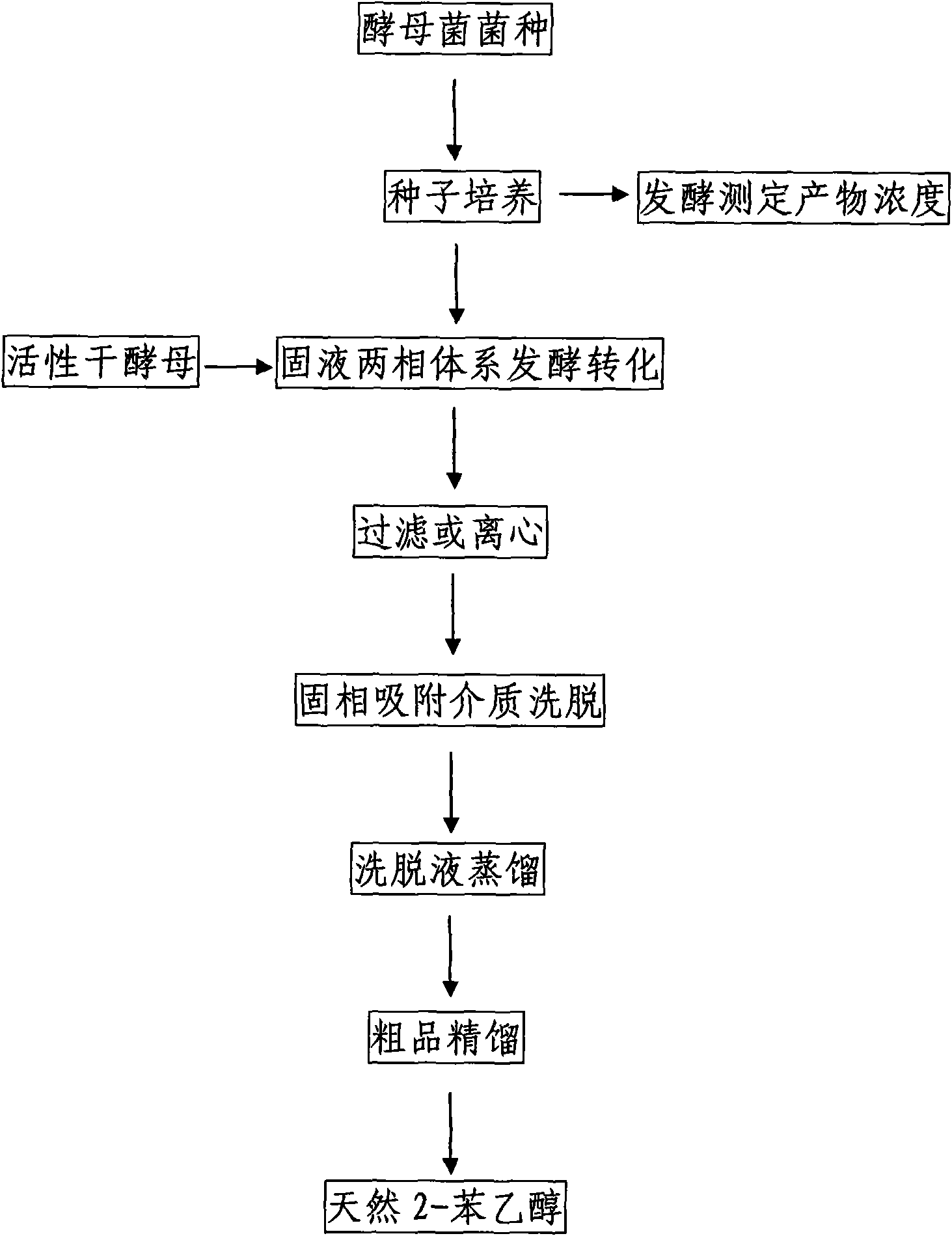
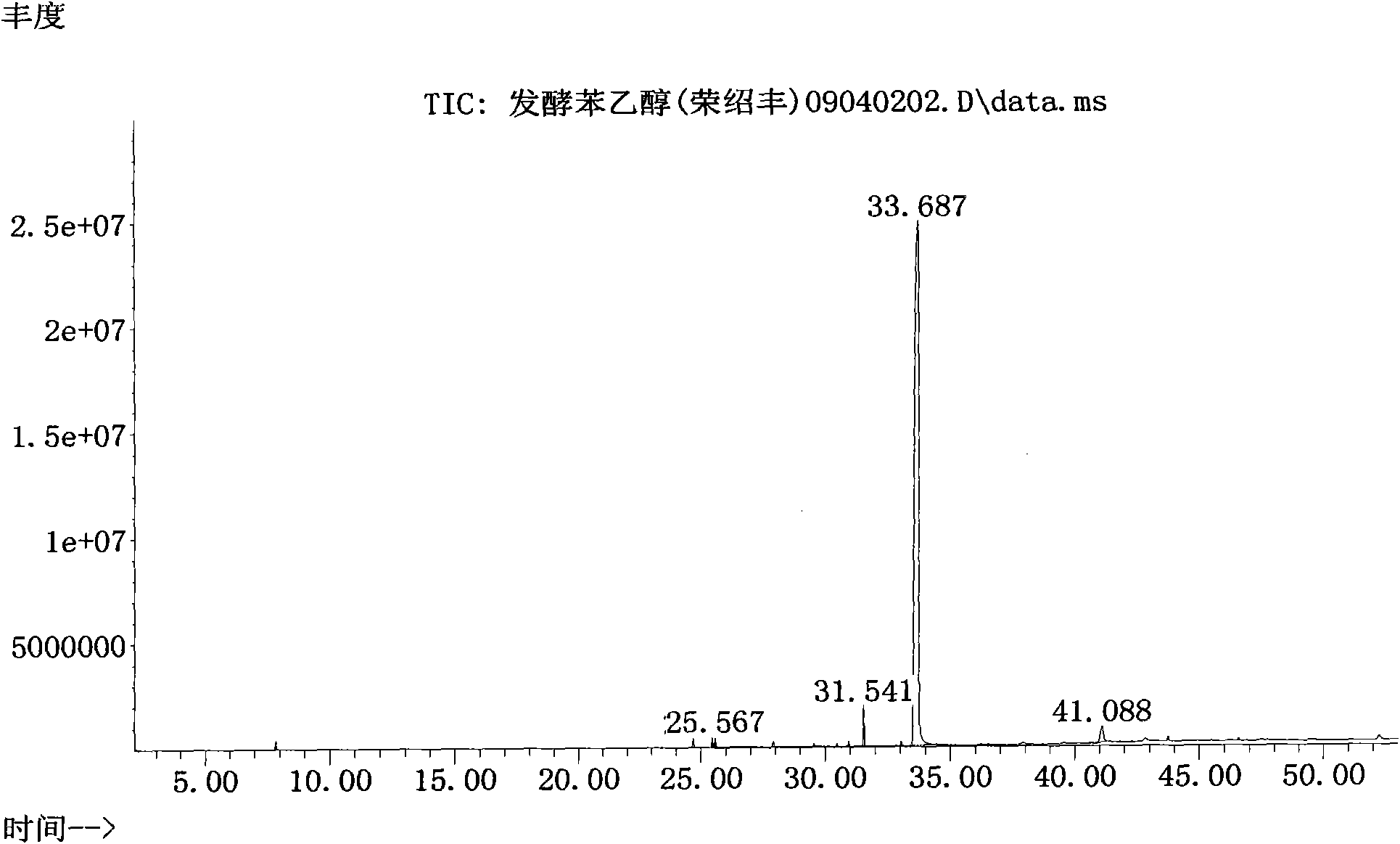
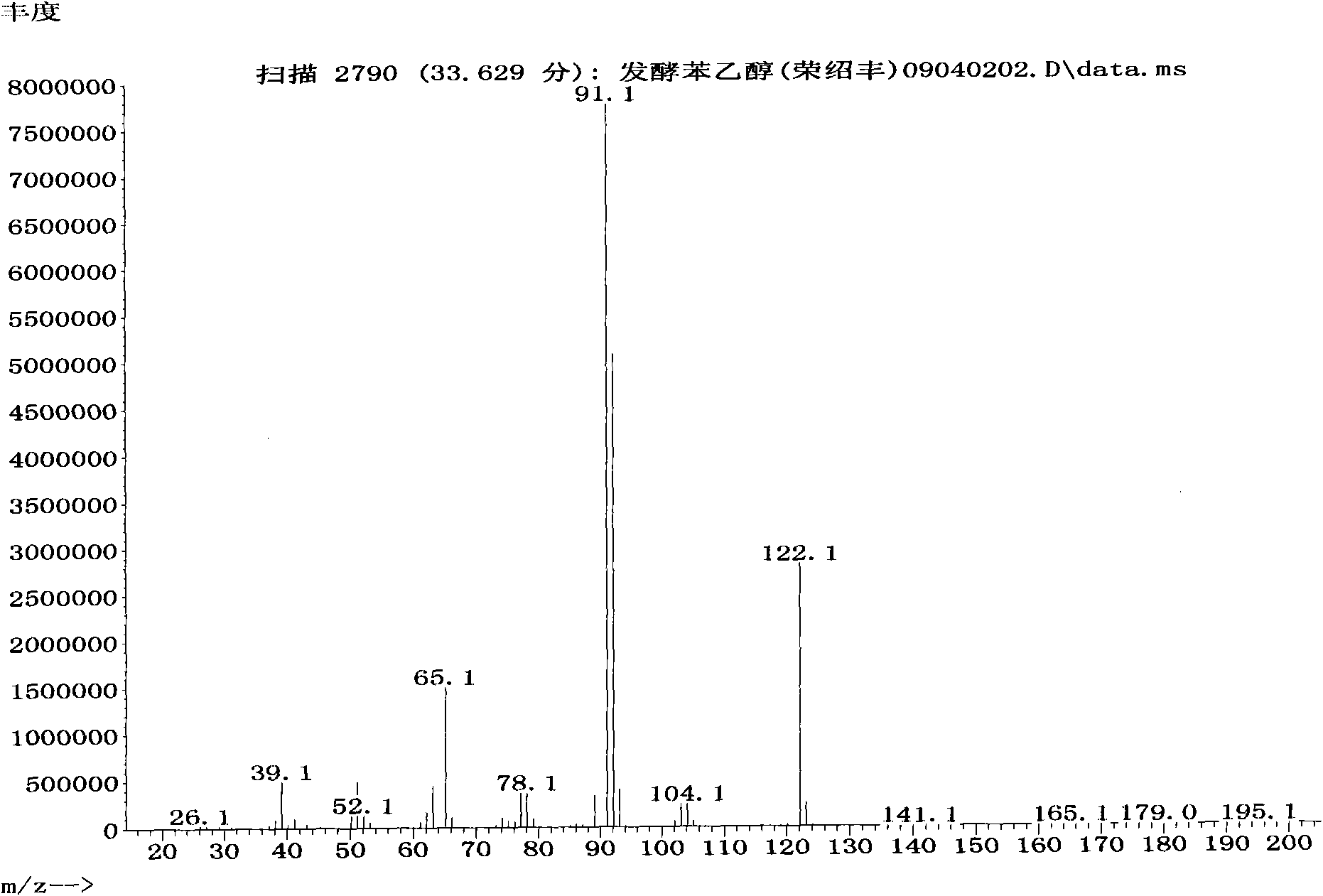
Preparation method of natural spice 2-phenethyl alcohol
InactiveCN101608190ADisinhibition effectDetoxifyMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiltrationPhenethyl alcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of natural spice 2-phenethyl alcohol, which is implemented by selecting Candida drusei, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces marxianus, inoculating cultivated seed liquid or active dried yeast powder into fermentation culture medium, taking L-PHE produced by fermentation method or enzyme method as substrate, performing liquid aerobic fermentation in a fermentation shake flask or a fermentation tank, adding solid phase absorption medium, L-PHE and glucose in the process of fermentation, obtaining the solid phase absorption medium in a filtration or centrifugation manner, then adopting an elution solvent to carry out elution on the absorption medium, further distilling the eluent to obtain the natural 2-phenethyl alcohol with purity of 97.5-99.5%. The invention combines the fermentation and absorption separation of 2-phenethyl alcohol, has low production cost and excellent aroma quality of the product.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its application
InactiveCN101020919AImprove solubilityPromote biotransformationMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolubilityMicroorganism
The present invention belongs to the field of biological sterol transforming technology, and is especially biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its derivative and its preparation. In a transforming system, cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain amount is added, or substrate and cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain ratio are made to form inclusion compound, so as to facilitate transformation. The process of the present invention is especially suitable for microbial transformation of hydrophobic compound, and can raise the solubility of reaction substrate in water solution, raise the substrate utilizing rate and reaction rate, release substrate and product inhibition and raise product converting rate. When the substrate concentration is 3-20g / L, the present invention has conversion period shorted to 3-4 days, conversion rate of 50-95 % and high industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
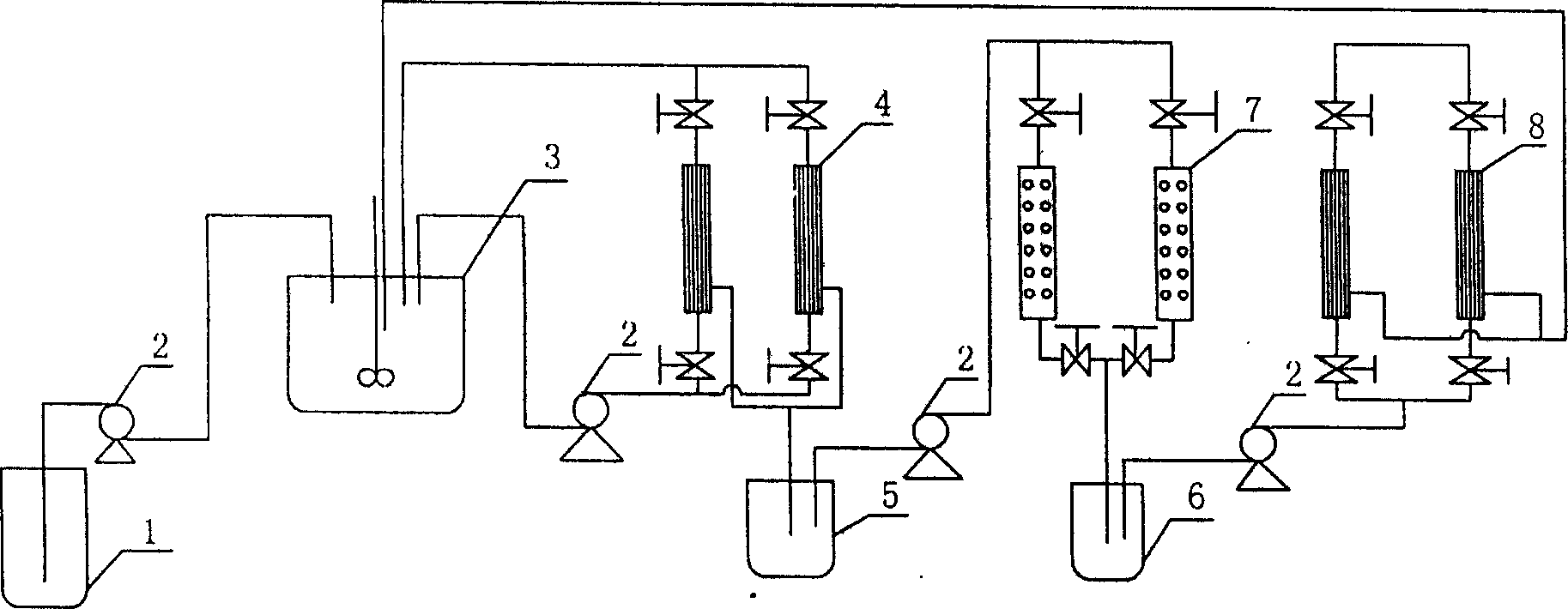
Method of realizing microorganism in situ separation and fermentation employing inorganic film
InactiveCN1908176AIncrease growth rateIncrease concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPeristaltic pumpFiber
the invention discloses a realizing method of microbe original separating fermenting method through inorganic film in the high-density fermenting domain, which comprises the following parts: ferment tank, inorganic film component, chromatographic column, hollow fiber film component or extracting device, compensating tank, liquid reserving tank and peristaltic pump. the invention can separate object product or side-product from fermenting system, which inhibits microbe seriously.
Owner:天津市新星兽药厂
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase and applications thereof
The invention provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase, which is named Saccharomyces cerevisiae 102SB, and preserved with a Preservation No. of CGMCC No. 7450 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 11, 2013. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention can continuously and efficiently secrete beta-glucosidase in a complex non-selective medium, and the extracellular enzyme activity can reach 1005.3 U / g (dry weight). By using a characteristic that the maximum specific growth rate of cellobiose is consistent with that of glucose, the strain reaches 0.29 h<-1> under the condition of limited oxygen. In SSF taking a cellulose material as a substrate, the yield of ethanol taking microcrystalline cellulose as a substrate is increased by 110%, and the yield of ethanol taking acid-hydrolyzed corncobs as a substrate is increased by 89%. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain disclosed by the invention is of great importance in reducing the production cost of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in the process of cellulosic ethanol production, and simplifying the production process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing natural medicines by coupling glycosidase catalysis and salting-out extraction
InactiveCN102094052AEasy to produceIncrease productivityFermentationNatural productEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing natural medicines by coupling glycosidase catalysis and salting-out extraction, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method is characterized in that enzymatic hydrolysis reaction is coupled with salting-out extraction of a product. Glycosidase and the natural product are added into a salting-out extraction system, and the glycosidase is utilized to convert the natural product containing glycosyl into an active ingredient of which the glycosyl is removed; meanwhile, the product and a substrate are separated through the extracting capacity of the system. The invention has the advantages of developing a novel reaction and separation coupled method easy for industrial production, and improving production efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing antimicrobial peptide through fermentation of brevibacillus laterosporu
ActiveCN104004803AImprove securityRealize multiple reuseMicroorganism based processesFermentationActivated carbonDesorption
The invention provides a method for producing antimicrobial peptide through fermentation of brevibacillus laterosporu. In fermentation of the brevibacillus laterosporu, when the yield of the antimicrobial peptide is no longer increased, active carbon is directly added into the fermentation liquor; as the active carbon adsorbs the fermentation product, the inhibiting effect of the product is relieved, and the density of the thallus and the yield of the antimicrobial peptide are greatly improved. According to the method, the active carbon is taken as an adsorption stripping coupling agent, has low cost, is environmentally friendly, and can be directly added in the fermentation process without being activated in advance; the antimicrobial peptide can be adsorbed without regulating the pH value of the fermentation liquor; and the method is simple and easy to promote, and the active carbon can be regenerated through desorption after fermentation, thus being recycled repeatedly, and lowering the production cost.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
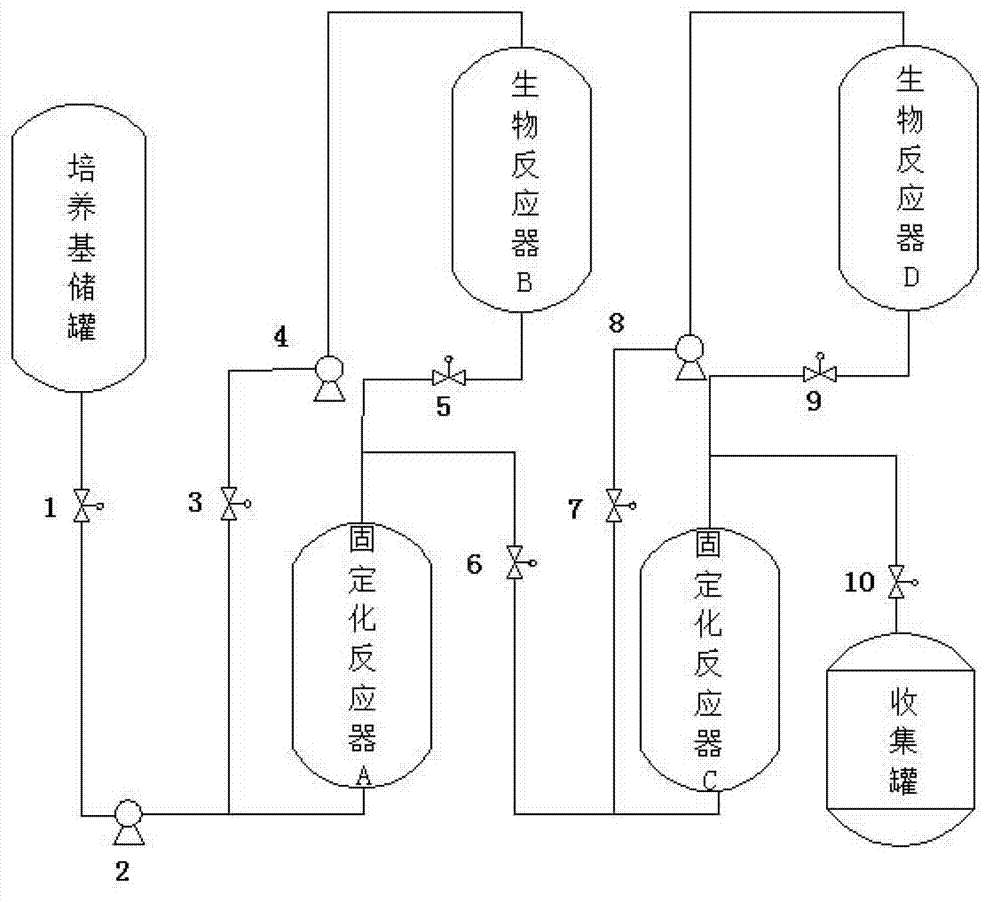
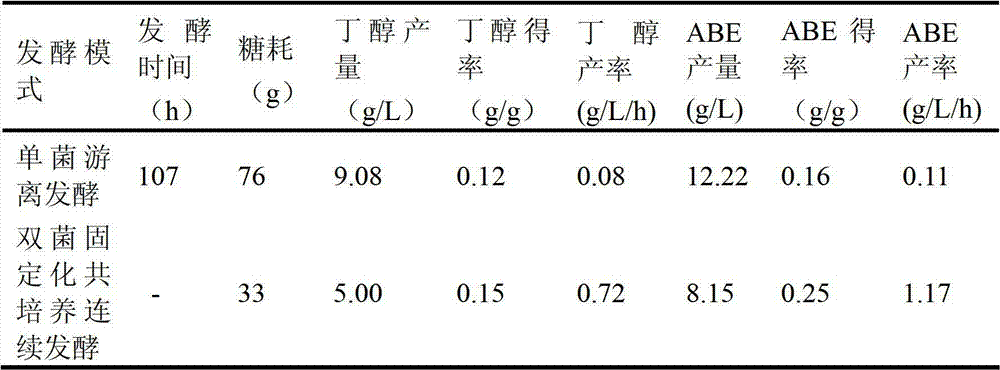
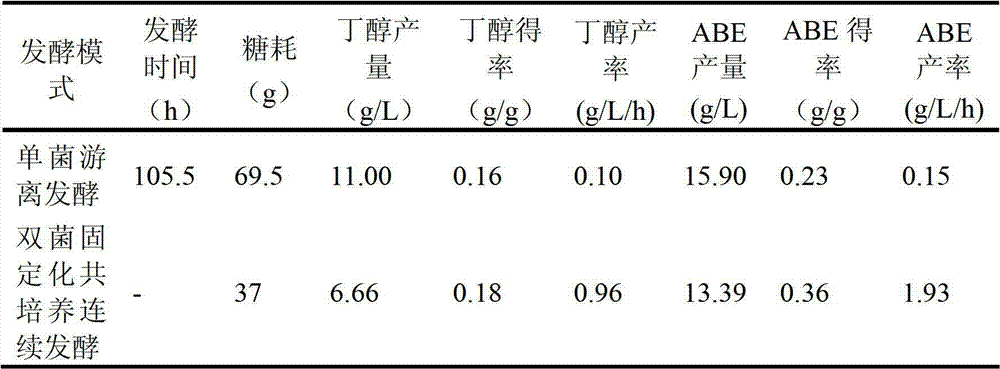
Apparatus and method for butanol production through dual bacteria immobilization anaerobic fermentation
ActiveCN102952745AShorten the fermentation cycleImprove yield and productivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemistryButanol
The present invention discloses an apparatus and a method for butanol production through dual bacteria immobilization anaerobic fermentation, wherein the apparatus comprises a fermentation culture medium storage tank, a butyric acid production immobilization reactor A, a butanol production immobilization reactor C, and a product collection tank, wherein the devices are sequentially connected in series through pipelines. According to the present invention, butyric acid production anaerobic bacteria and butanol production anaerobic bacteria are respectively immobilized in the butyric acid production immobilization reactor A and the butanol production immobilization reactor C to carry out dual bacteria immobilization, and a fermentation culture medium is controlled to flow from the fermentation culture medium storage tank, sequentially flows through the butyric acid production immobilization reactor A and the butanol production immobilization reactor C to carry out continuous anaerobic fermentation, and finally flows into the product collection tank, wherein the butyric acid production anaerobic bacteria adopts a substrate to produce butyric acid, and the butanol production anaerobic bacteria adopts the butyric acid as a substrate to produce butanol. With the method, a fermentation period can be substantially shortened, and substrate conversion rate and yield of the butanol can be increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
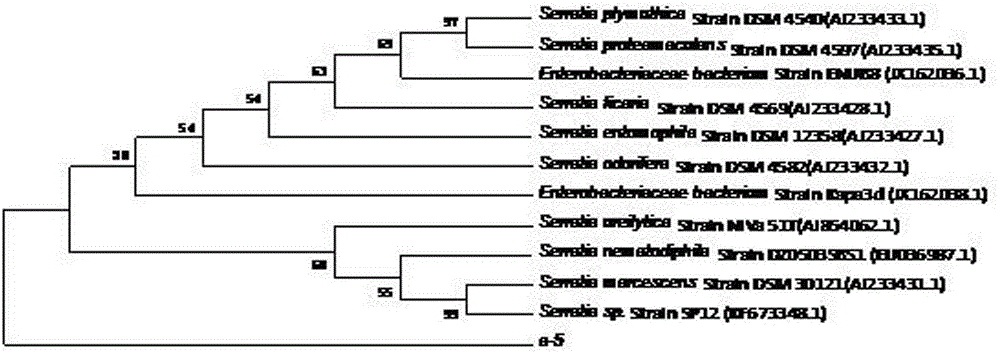
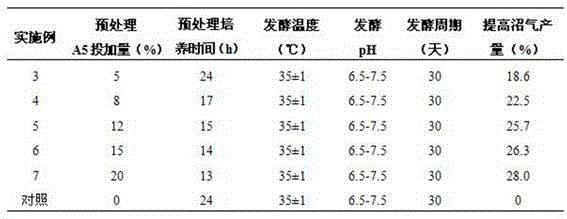
Serratia sp. A5 and uses thereof
ActiveCN104371951ADisinhibition effectImprove hydrolysis efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyOil and grease
The present invention relates to Serratia sp. A5 and applications thereof. The Serratia sp. A5 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 28, 2014, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.9621. According to the present invention, the Serratia sp. A5 is isolated from soil, the suitable growth temperature is 25-35 DEG C, the pH value is 7.0-7.5, and the Serratia sp. A5 has the lipase production ability; and the Serratia sp. A5 can be applied for degrading grease, relieving the inhibition effect of the grease in food waste anaerobic fermentation, increasing the biogas yield by 15-30%, and effectively increasing anaerobic fermentation hydrolysis and biogas production efficiency of other waste containing fat and the like or waste water, and further provides important significance for promotion of harmless, resource and energy utilization of organic waste.
Owner:河北绿茵生化科技有限公司
Method for perstraction of fermented microbial intracellular product with non-ionic surfactant
ActiveCN102443605AChange in permeabilityDisinhibitionMicroorganism based processesEnzymesMicrobial enzymesSecondary metabolite
The invention discloses a method for perstraction of a fermented microbial intracellular product with a non-ionic surfactant. Specifically, during fermentation of a microbial intracellular product, a non-ionic surfactant micellar solution formed by addition of the non-ionic surfactant concentration or a cloud point system formed thereby is adopted as a microbial fermentation medium, by which the intracellular product can be penetrated to an extracellular environment so as to improve the product level of microbial fermentation. Simultaneously, perstraction and fermentation of the microbial intracellular product can be realized. The method of the invention is especially suitable for the fermentation process of an intracellular product, such as production of intracellular microbial enzymes, production of intracellular organic small molecule substances as well as production of intracellular oil compounds, etc. The method provided in the invention effectively eliminates intracellular product inhibition, enhances the concentration of a microbial fermentation product, and adjusts the composition of a microbial fermentation secondary metabolite, thus improving the volume yield of microbial fermentation as well as the efficiency of intracellular product fermentation, product release and other processes.
Owner:JECHO BIOPHARM CO LTD
Biological transformation method by utilizing hydrophobic compound of cyclodextrin
InactiveCN101168765AImprove conversion rateIncrease the rate of conversion reactionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismReaction rate
The invention discloses a bioconversion method by using cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof, belongs to the bioconversion technical field, in particular relates to the bioconversion method by using the cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof, and provides the bioconversion method by using the cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof. The method of the invention is particularly suitable for the microbial conversion of hydrophobic compounds, can effectively improve the dissolubility of reaction substrate in aqueous solution, improve the utilization rate and the reaction rate of the substrate, release the inhibition of the substrate and the product to a certain extent, and improve the conversion rate of the product. The invention adopts a conversion system including the cyclodextrin, the special structure of the cyclodextrin ensures the cyclodextrin to have a certain solubilizing power, and strengthens the bioavailability of the substrate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adsorption separation coupling fermentation process with high nisin yield,
ActiveCN104212858AEasy to separate and purifyReduce concentrationMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesCouplingLactococcus lactis
The invention discloses an adsorption separation coupling fermentation process with high nisin yield. A certain amount of resin is added in the logarithmic growth phase to adsorb the nisinin fermentation on the resin, thus on the one hand reducing concentration of nisin in the fermentation liquid to relieve the inhibitory effect on cell growth and product synthesis and on the other hand effectively improving the fermentation concentration of nisin. The nisin concentration in the invention reaches above 10000U / mL, which is significantly higher than the concentration of nisin in a general fermentation method. In addition, Lactococcus lactis CQ0422 with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.8090 is used as a fermentation strain, which has the yield of synthesized nisin at least 4.5 times of that of the general Lactococcus lactis, so as to play an important role in improving the nisin yield. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low production cost, concentration and high yield of nisin, etc.
Owner:西藏天虹科技股份有限责任公司
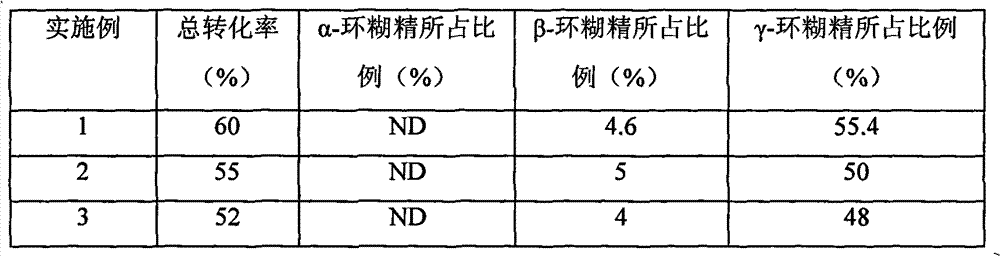
Production process for producing gamma-cyclodextrin by biological method
ActiveCN102827900AImprove conversion rateEasy to produceMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic solventGram
The invention relates to a production process for producing gamma-cyclodextrin by a biological method and belongs to the technical field of cyclodextrin production. The production process solves the technical problems to provide the process for producing gamma-cyclodextrin by the biological method, and the production cost of the gamma-cyclodextrin is reduced. The production process has the technical scheme that the gamma-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase from alkalophilic bacillus is adopted for producing the gamma-cyclodextrin, the starch pulp regulation is carried out according to the concentration being 10 percent, the materials are stirred for 5 to 15 minutes under the condition being 60 to 90 DEG C, the temperature is set to be 40 to 60 DEG C, the pH is regulated to be about 10.0, the gamma-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase is added according to a quantity of 1 to 10 units for one gram of starch, after 2 to 5 percent (w / v) organic solvents are added, the sufficient reaction is carried out for 8 to 10 hours, the organic solvents are recovered, and the gamma-cyclodextrin is obtained by adopting a crystallization method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Building and application of engineered strains capable of producing xylitol and ethanol at high temperature simultaneously with high yield
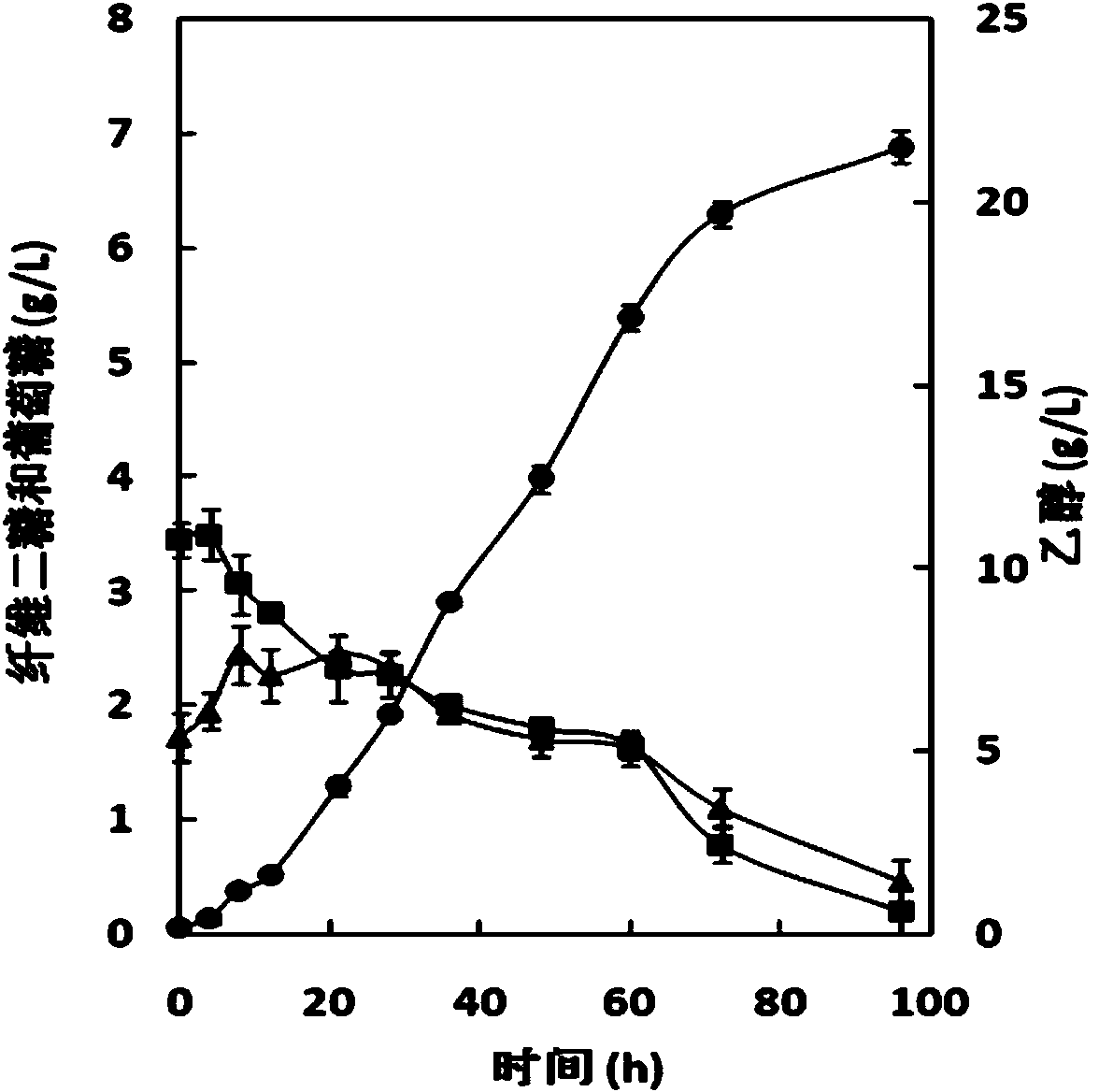
ActiveCN105062907ADisinhibition effectYield is not affectedFungiBiofuelsEnzyme GeneEngineered genetic
The invention relates to building and application of engineered strains capable of producing xylitol and ethanol at a high temperature simultaneously with a high yield. Concretely, N376F mutant genes of saccharomyces cerevisiae galactose permease (hexose transporter protein of hexose for transporting galactose and glucose) (ScGAL2) are effectively expressed in heat-resistant yeast strains YZJ015 by a gene engineering transformation method; meanwhile, K.marxianus glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (KmGPD1) genes are removed to cut off a glycerol production branch, so that the obtained strains YZJ119 obtain good capability of efficiently co-utilizing and fermenting glucose and xylose to produce the ethanol and the xylitol at a high temperature (higher than 42 DEG C). Under the condition of 42 DEG C, the YZJ119 can simultaneously use 43.95g / l of xylose and 83.11g / l of glucose to produce 40.43g / l of xylitol and 34.66g / l of ethanol in 28 hours; the production speed of the xylitol is 1.44g / l / h; the production speed of the ethanol is 1.24g / l / h; the yield of the xylitol is 0.92g / g; and the yield of the ethanol is 0.42g / g.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
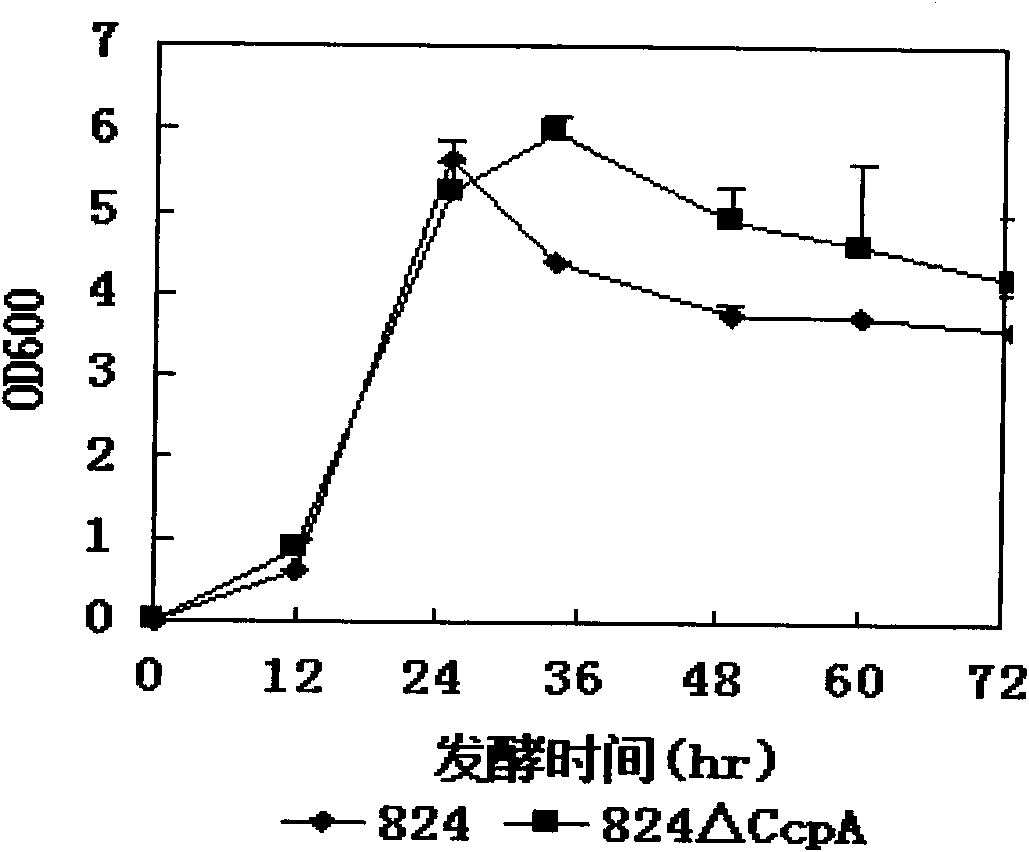
Method for eliminating glucose inhibition effect of clostridium acetobutylicum
InactiveCN102041267AIncreased ABE concentrationDisinhibition effectBacteriaBiofuelsXyloseGene expression
The invention provides a method for eliminating glucose inhibition effect of clostridium acetobutylicum, and a recombinant strain of which the ccpA gene expression of clostridium acetobutylicum is inhibited in a genome. The method for eliminating the glucose inhibition effect of clostridium acetobutylicum is implemented by inhibiting the ccpA gene expression of clostridium acetobutylicum. By using the method provided by the invention, the ccpA gene expression of clostridium acetobutylicum is interrupted. In the strain provided by the invention, after the ccpA gene is subject to insertional inactivation through group II intron, the capability of the strain of synchronously utilizing xylose and glucose is obviously improved, and the concentration of converted ABE is correspondingly increased at the same time. The engineering strain constructed by the invention eliminates the glucose inhibition effect and can synchronously utilize glucose and xylose for fermenting, thus the strain has the potential in acetone-butanol fermentation with hydrolyzate of lignocelluloses.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for fermenting lactic acid bacteria
ActiveCN102134581AShorten the enzymatic digestion timeDisinhibition effectFermentationHigh concentrationRaw material
The invention relates to a method for fermenting lactic acid bacteria. The method comprises the steps of: utilizing celluloses of plant straws, which are treated with partial enzymolysis, as a carbon source for the fermentation of lactic acid bacteria so as to produce lactic acid by fermentation, and causing the sugar content of celluloses of plant straws, which are treated with partial enzymolysis, to range from 1 to 10 in percentage by weight; and partial enzymolysis comprises the steps of: carrying out enzymolysis on the celluloses of plant straws for 12 to 72 hours through cellulose at the temperature from 45 to 55 DEG C so that sugar generated through enzymolysis and celluloses which are not treated with the enzymolysis can be contained in fermentation liquor and the lactic acid can be prepared through enzymolysis and fermentation simultaneously. Compared with the prior art, the production cycle is shortened to 64 hours from 136 hours, the inhibition of high-concentration glucose on lactic acid bacteria fermentation lactic acid is gotten rid off, and the fermentation level is increased to 6.8 from 3.6 in percentage by weight. The method utilizes the plant straws as raw materials for fermentation, makes waste profitable, reduces environmental pollution and has positive significance to guarantee food security.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Transfer factor solution applied in livestock and poultry, its preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN1864742ARaise storage temperatureImprove disease resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunological disordersUltrafiltrationDistilled water
Disclosed is a transfer factor solution for animals, wherein its preparing process consists of washing freeze chicken spleens and chopping, charging distilled water and comminuting cells to homogenate, freezing eight times at minus 30 deg C, centrifuging the homogenated liquid, separating deposition and filtering supernatant fluid with microporous filtering film, carrying out hyperfiltration with ultrafiltration membrane to obtain stock solution, removing viruses, charging niacinamide as stabilizer, filtering and degerming through microporous filtering film, charging glycerine and split charging directly.
Owner:TIANJIN RINGPU BIO TECH
Method for improving 2-keto-L-gluconic acid fermentation efficiency
InactiveCN106434830AIncrease production intensityPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyGluconic acid
The invention relates to a method for improving 2-keto-L-gluconic acid fermentation efficiency. The method is characterized in that in the process of mixed strains fermenting 2-keto-L-gluconic acid, the mixed strains comprise ketogulonigenium vulgare and bacillus megaterium, seed solution cultured to the middle and later periods of logarithmic growth is inoculated into fermentation tank optimum culture media to ferment and culture, sorbose is fed since fermentation time is 0h, and small material culture media are fed at the prior period of the logarithmic growth. According to the method, production intensity of the 2-keto-L-gluconic acid can be improved, efficiency is improved, production capacity is optimized, the content of the 2-keto-L-gluconic acid in fermentation solution can reach 115.6-150.3mg / ml, acid producing rate is 2.89-3.76g.(L.h)-1, and the conversion rate of glucose acid is 87.2-95.0%.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
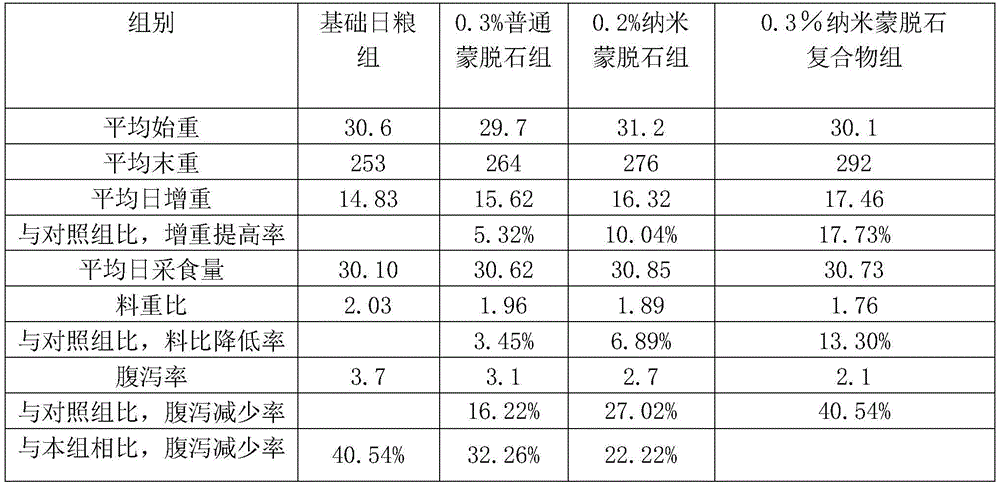
Nanometer montmorillonite feed additive compound for detoxifying and diarrhea prevention of livestock and poultry
InactiveCN105941870AReduce pollutionAvoid the problem of drug resistance caused by abuseAccessory food factorsMontmorilloniteZinc
The invention discloses a nanometer montmorillonite feed additive compound for detoxifying and diarrhea prevention of livestock and poultry, and belongs to the field of animal feed additives. The nanometer montmorillonite feed additive compound is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 54.0-82.8 percent of nanometer montmorillonite, 10-20 percent of organic zinc, 2-10 percent of xylooligosaccharide, 0.2-1.0 percent of glucose oxidase and 5-15 percent glucose. The nanometer montmorillonite feed additive compound has the advantages that the diarrhea of piglets and chicks can be effectively prevented and treated, the growth property of livestock and poultry is improved, the survival rate of livestock and poultry, especially small livestock and poultry, is obviously improved, and the culture benefit is increased.
Owner:重庆新动生物技术有限公司
Mycotoxin detoxification agent
InactiveCN108094832AImprove immunityGood for healthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsYeast MannanMycotoxin
The invention relates to a mycotoxin detoxification agent. The mycotoxin detoxification agent comprises the following components of modified aluminosilicate powder, yeast mannan, a microecological preparation and a plant extract. Compared with the prior art, the mycotoxin detoxification agent disclosed by the invention has treble detoxification efficacy of adsorption, degradation and toxin expelling, unification of the broad-spectrum property and the specificity of the mycotoxin detoxification agent can be realized, and the raising benefits can be effectively increased.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU AONONG ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TECH +2
Method for asymmetrically synthesizing (2S,3R)-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine by one-bacterium multi-enzyme whole cells
ActiveCN110951799ASimple and efficient operationShort reaction timeBacteriaTransferasesMolecular biologyAldehyde formation
The invention provides a method for asymmetrically synthesizing (2S,3R)-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine by one-bacterium multi-enzyme whole cells, which belongs to the field of biocatalysis and enzyme engineering. By simultaneously expressing L-threonine transferase (PsLTTA), ethanol dehydrogenase (ApADH) and formate dehydrogenase (CbFDH) in escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) engineering bacteria, asymmetric efficient biosynthesis of (2S,3R)-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine is realized. The key chiral building block (2S,3R)-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine of the beta-amino alcohol antibiotics can be obtained through one-step reaction at normal temperature and normal pressure, meanwhile, the inhibition effect of a byproduct acetaldehyde on the PsLTTA is relieved, and the method is an efficient green biosynthesis way.
Owner:福建昌生生物科技发展有限公司
Method for enhancing mitsuba seed germination rate
InactiveCN103348801APromote growthIncreased fresh weightSeed arrangmentsSeed immunisationSalt waterBenomyl
The invention relates to a method for enhancing the mitsuba seed germination rate, which comprises the following steps: soaking mitsuba seeds in salt water with the mass concentration of 15 to 18%, clearing floating dopants and shrivelled seeds, cleaning the seeds with clean water, soaking the mitsuba seeds cleaned by the clean water in benomyl of 500 to 1000 times, fishing out, and trickling moisture; soaking the trickled mitsuba seeds in gibberellin solution with the concentration of 150 to 300 mg / L for 11.5 to 12.5 hours at the temperature of 23 to 27 DEG C, then soaking in lukewarm water of which the water temperature falls from 55 DEG C to 35 DEG C gradually for 5.5 to 6.5 hours, placing the mitsuba seeds soaked by the lukewarm water in a breeding plate, and accelerating germination under a temperature alternating condition. The method takes certain process measure to the seeds before the sow to improve the germination rate and the sow quality of the seeds, is good to save the seed dose, meanwhile also promotes the initial grow of the germchit, and enhance the resistance of the plants.
Owner:ZHENJIANG SUIHAN AGRI
Method for increasing expression quantity of Fab antibody
ActiveCN106967658AMature TransformationMakeover special and novelBacteriaHydrolasesProteinase activityMutant
The invention specifically relates to a method for increasing the expression quantity of a Fab antibody in gene engineering, belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: construction of a recombinant plasmid pVEGF-FAB; preparation of specific protease defective cell mutants (delta pepN, delta DegQ, delta dcp and delta pepP); transformation; inducible expression of the Fab antibody; etc. The method provided by the invention is special and innovative in reconstruction of host cell strains; prepared host cell strains can eliminate inhibition or degradation effect on expressed Fab due to deletion of specific protease, so the expression quantity of Fab antibody can be increased; thus, the method has good application value in expression and preparation of specific Fab antibodies, provides good reference for expression and preparation of other antibody proteins, and thus has good practical value and scientific research significance.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of realizing high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine and method for high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine via same
ActiveCN111117940ALow costReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliInducer
The invention relates to an engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of realizing high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine and method for high-yield production of pentamethylene diamine via the same. The engineered Escherichia coli strain is Escherichia coli with an accession number of CGMCC No. 17454. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing engineered Escherichia colistrain TJU-cadA-1 for exogenous expression of L-lysine decarboxylase, wherein the enzyme activity of the L-lysine decarboxylase is about 100 times the enzyme activity of a no-load strain; (2) carryingout permeability treatment on L-lysine decarboxylase-rich whole cells, wherein the enzyme activity of the L-lysine-rich decarboxylase in permeabilized cells is 3-4.5 times the enzyme activity of thewhole cells; and (3) catalyzing L-lysine hydrochloride to produce pentamethylene diamine by using the permeabilized cells, wherein the yield of pentamethylene diamine is 90%-100%, and the concentration of pentamethylene diamine can reach 220 g / L or above. According to the method, the L-lysine hydrochloride is used for efficiently producing the pentamethylene diamine; and compared with the prior art, an expensive IPTG inducer is not needed in the invention, so the method has the advantages that mass transfer efficiency is high, yield is high, production cost is low, and higher economic feasibility and practicability are obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Electrolytic-biological anaerobic reactor and technique thereof
InactiveCN101693577AGuaranteed uptimeDisinhibition effectWater/sewage treatmentTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesNuclear engineeringAnaerobic reactor
The invention discloses an electrolytic-biological anaerobic reactor and a technique thereof. The electrolytic-biological anaerobic reactor comprises a reactor body and support legs, wherein the reactor body is orderly provided with a mud settling chamber, a gradual expansion chamber and an upflow reaction chamber from top to bottom; the outer side on the bottom of the reactor body is provided with a water inlet pipe and an external circulation pipe outlet; the upper part of the gradual expansion chamber is provided with an overflowing conical baffle; a three-phase separator is arranged in the mud settling chamber; the side wall on the upper part of the mud settling chamber is provided with an overflow weir, an overflow weir water outlet pipe and a gas-liquid separator; the upper part of the reactor body is provided with a backflow external circulation outlet; the outflow water flows into an external circulation inlet from the external circulation outlet through an external electrolysis bath; and the cathode and the anode of the electrolysis bath are separated by a cation exchange membrane. Through the electrolysis action of the external circulation, the invention can promote sulfides to be converted and oxidized, relieve the toxicity inhibition of the sulfides to the biological treatment, ensure the efficiency of the reactor for treating anaerobes and relieve the stroma inhibition. The reactor has large potential and strong impact resistance for treating waste water with low carbon-sulfur ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of dynamically regulating 7-deoxycholesterol and vitamin D3
The invention relates to a construction method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of dynamically regulating and controlling 7-deoxycholesterol and vitamin D3. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1, controlling expression of a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain mot3 gene by using a promoter GAL7, and transforming the mot3 gene into original saccharomyces cerevisiae to construct first saccharomyces cerevisiae; S2, constructing a dCas9 system dynamically regulated and controlled by ergosterol, and extracting constructed plasmids; S3, artificially synthesizing a fusion gene segment gal80F-loxT-PTEF1-DHCR24-Tcyc1-PGAP-DIC-TADH1-gal80R, convertingthe fusion gene segment into a first saccharomyces cerevisiae, and carrying out PCR verification, so as to obtain a second saccharomyces cerevisiae; and S4, transforming the plasmids constructed in the step S3 into second saccharomyces cerevisiae, and performing screening to obtain the saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of dynamically regulating and controlling to produce 7-DHC. According to the saccharomyces cerevisiae constructed by the construction method provided by the invention, the reduction of by-products and the increase of the yield of 7-DHC are realized by utilizing an endogenous sterol regulation and control system of the saccharomyces cerevisiae and combining a dCas9 system while the growth state of a strain is not influenced.
Owner:西宝生物科技(上海)股份有限公司
Methods of increasing gene expression through RNA protection
InactiveUS20110009466A1Increase gene expressionHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsTissue cultureTarget mrnaHuman patient
This invention relates to the use of one or more RNA target protectors to inhibit the binding of an RNA, e.g., small RNA, to a target RNA (e.g., a target mRNA), thus increasing the stability of the target RNA and its function (e.g., increasing the gene expression of the gene corresponding to a target mRNA). An RNA target protector may be, for example, an oligonucleotide, e.g., a morpholino, or a small molecule. The invention further relates to the treatment of a human patient in need thereof with one or more RNA target protectors.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for producing energy ethanol by fermentation of waste paper pulp
InactiveCN101358213AHas negative costLarge specific surface areaBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesDistillationPapermaking
The present invention discloses a method for producing energy alcohol by utilizing waste paper pulp fermentation. The method at least includes the following steps: preparation of yeast starter liquor, preparation and sterilization of fermentation medium, synchronous diastatic fermentation and distillation for dehydration. In the step of synchronous diastatic fermentation, after fermentation lasts for 12 to 60 hours, waste paper pulp, corn steep liquor and enzyme are supplemented, so that the alcoholicity of yeast mash of 72 to 96 hours can reach over 40g / L, and fermentation is stopped. Containing fine-particle cellulose and hemicellulose, the waste paper pulp in the present invention, which is the waste of the papermaking industry, has a large specific surface area, which is favorable for enzymolysis and saccharification, so the waste paper pulp can be used for synchronous diastatic fermentation without being preprocessed, and moreover, the waste paper pulp is characterized by negative cost. Consequently, using waste paper pulp fermentation to produce the energy alcohol not only can leave out materials and preprocessing expense, the cost of which ranks first in the process of producing alcohol by cellulose fermentation, thus having economic feasibility, but also can change waste into valuable, thus solving the environment pollution problem of the papermaking industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of beads for evanescent mode casting and expandable resin obtained by using preparation method
ActiveCN105199136ADisinhibition effectHigh yieldFoundry mouldsFoundry coresFoaming agentEvanescent mode
The invention relates to a preparation method of beads for evanescent mode casting, comprising the following steps: S1, dissolving a monomer methyl methacrylate, an initiator, a dispersant and a secondary dispersant into water, polymerizing at the temperature of 75-85 DEG C to obtain an intermediate product; and S2, dissolving the intermediate product, a foaming agent, the dispersant and the second dispersant into water, and dipping at the temperature of 100-150 DEG C at the pressure of 0.5-1.5 MPa to obtain expandable beads. The invention also relates to an expandable resin obtained by the preparation method disclosed by the invention. According to the invention, the initiator is added in the step S1, and the foaming agent is added in the step S2, thus radically eliminating the inhibitory effect of the foaming agent on polymerization reaction of free radicals and improving yield and quality of beads.
Owner:潘敦
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com