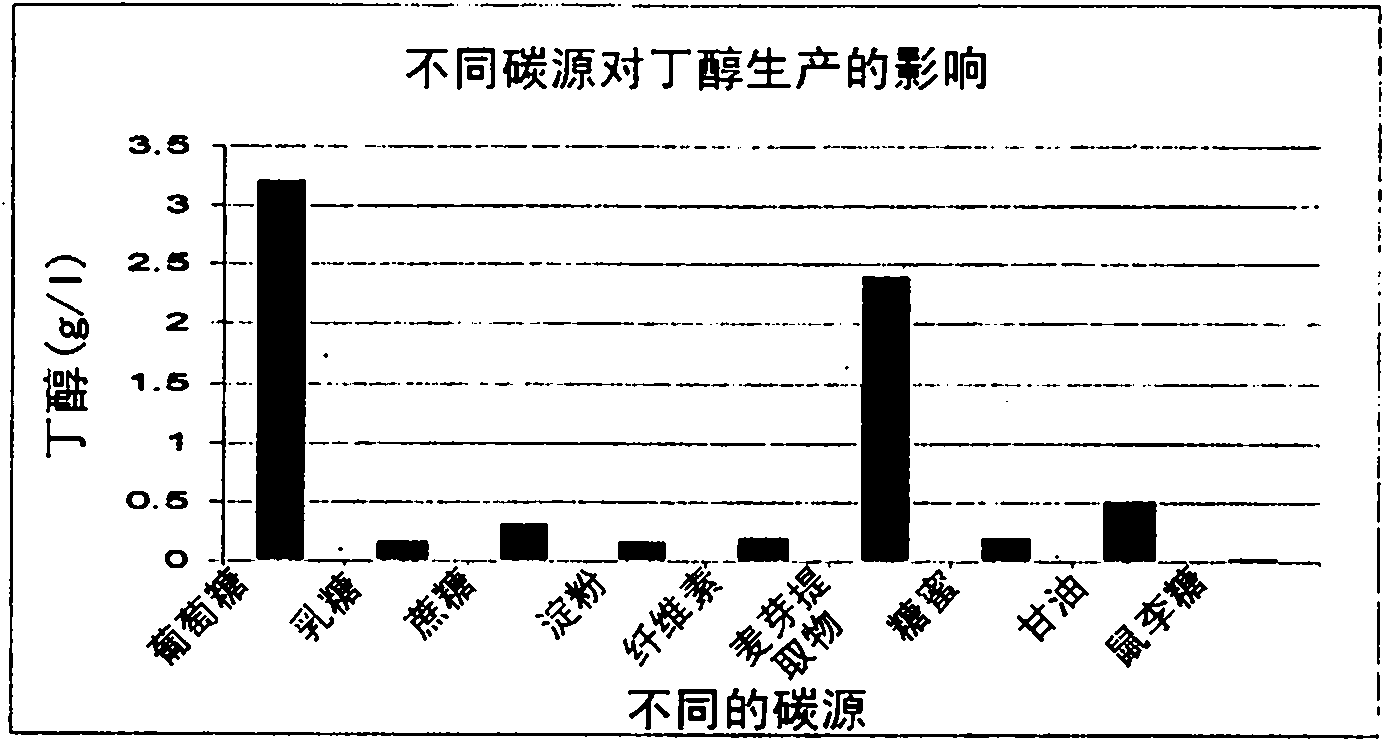
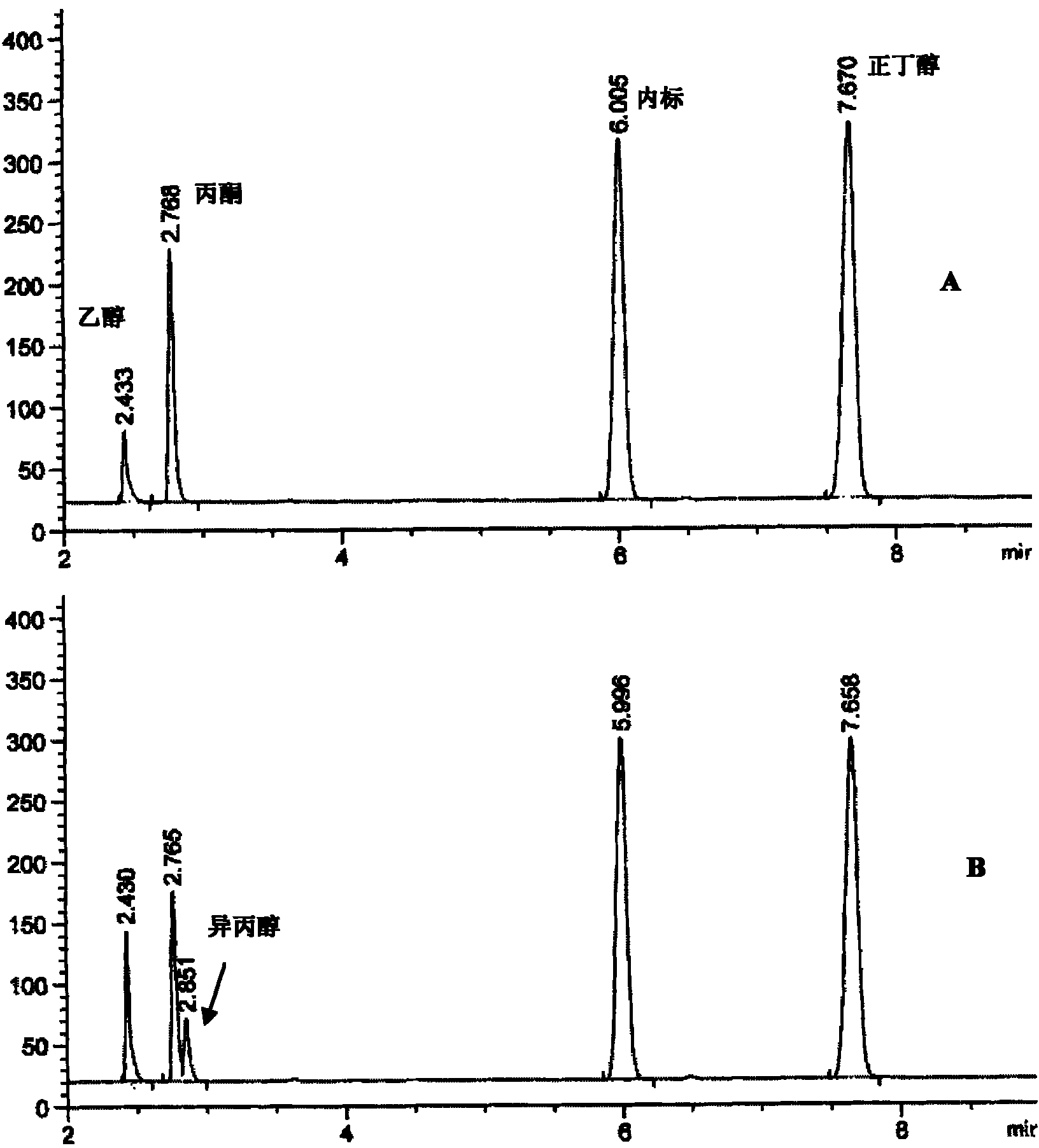
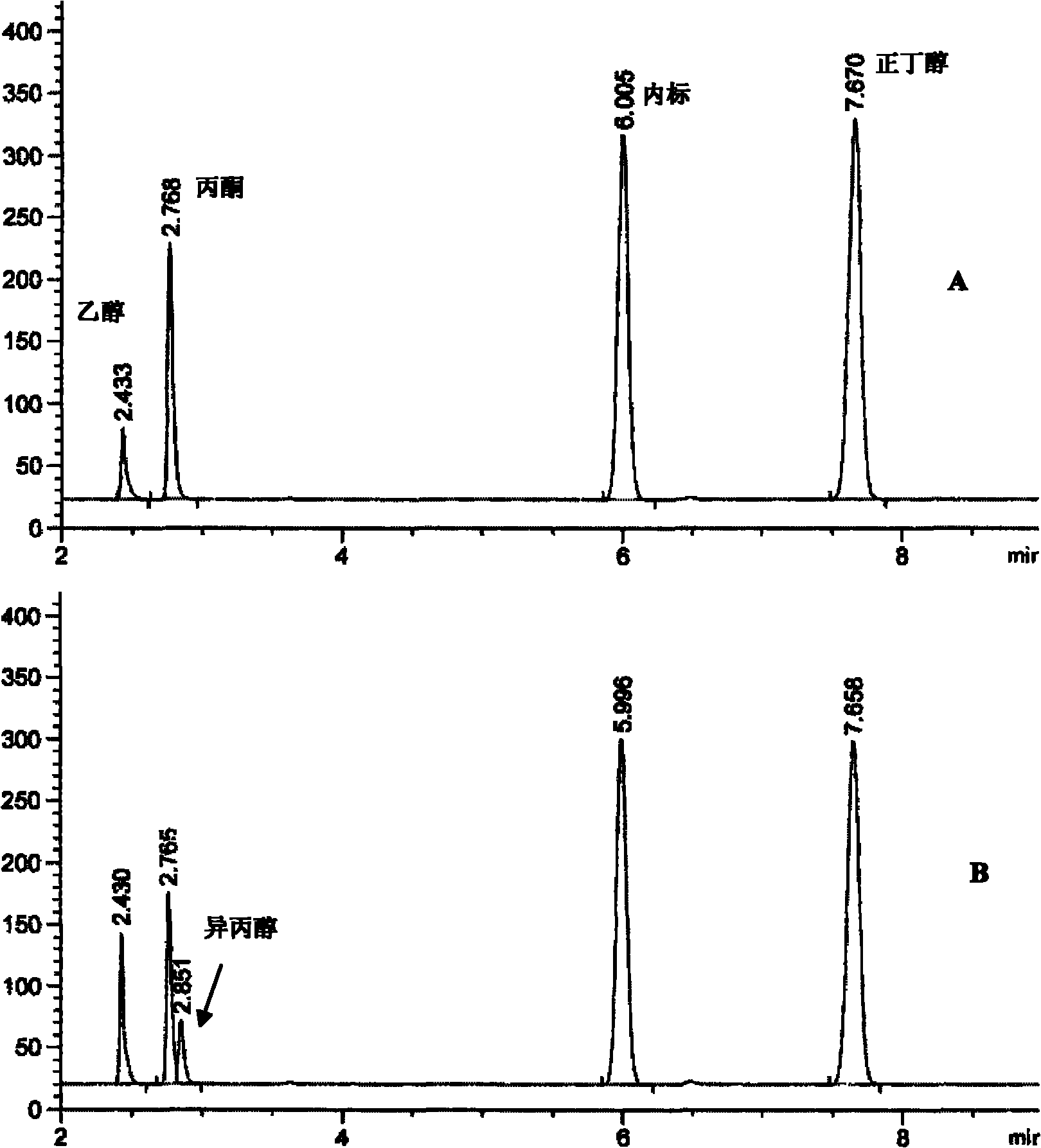
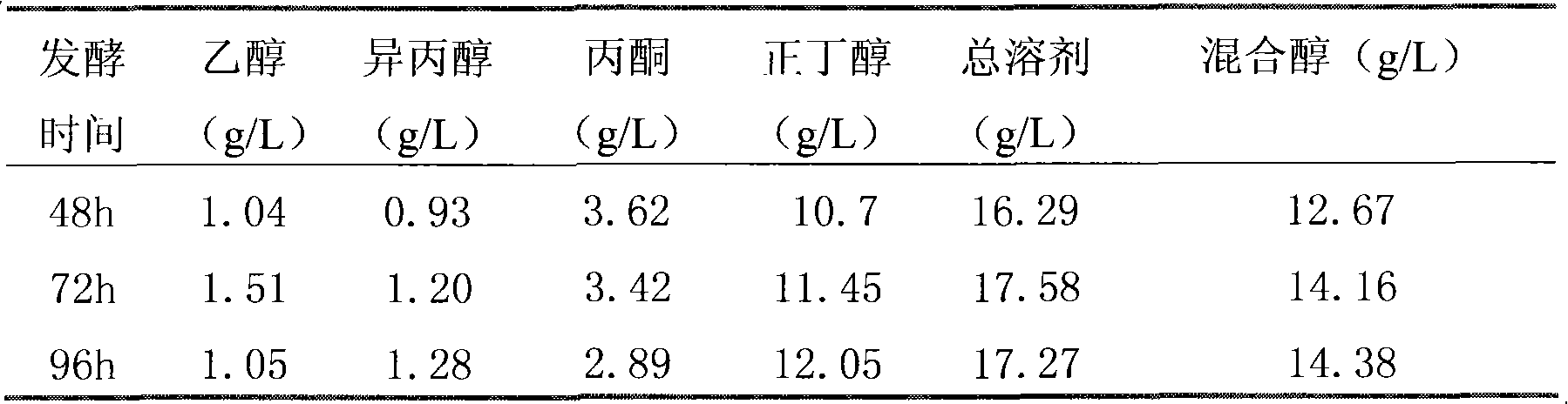
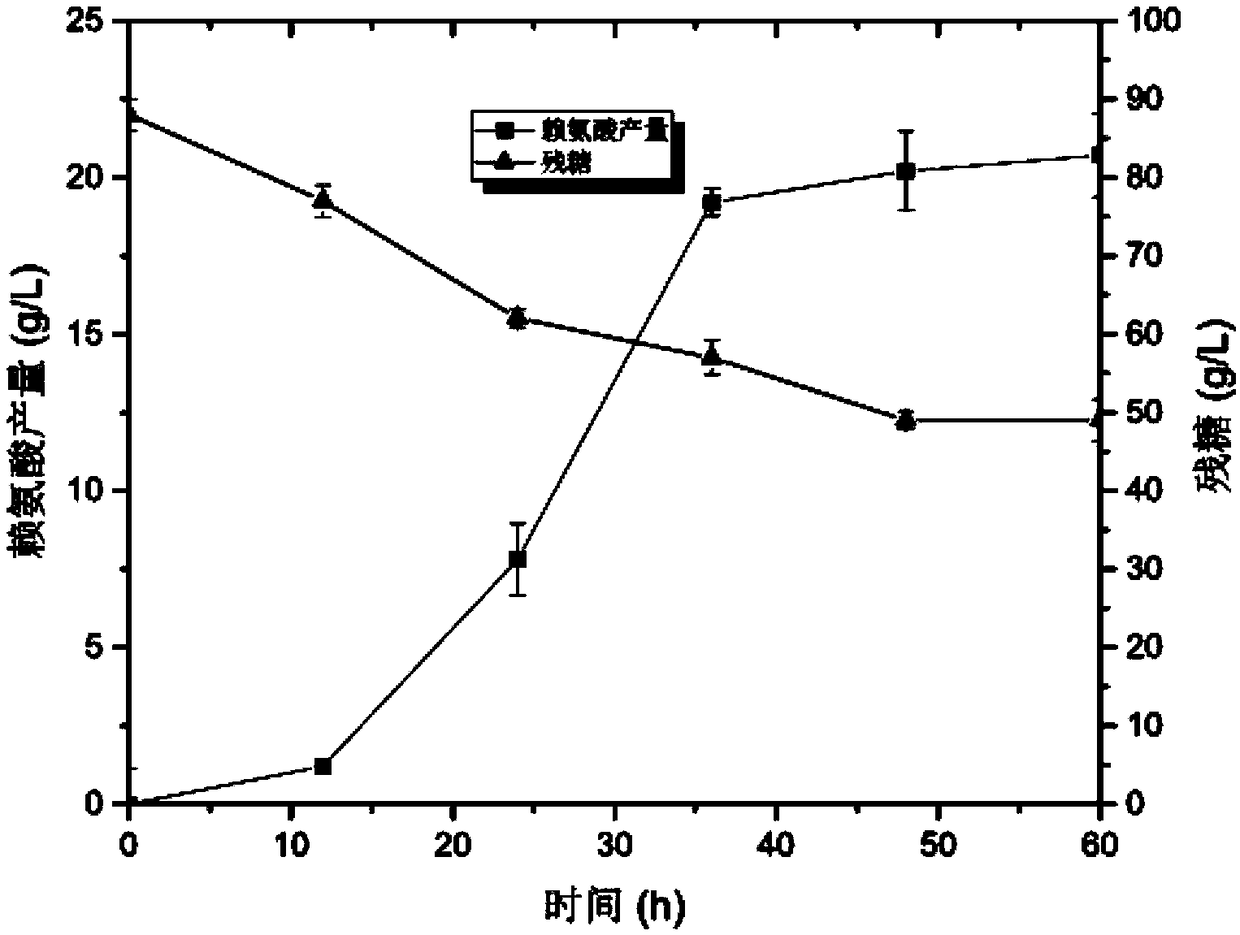
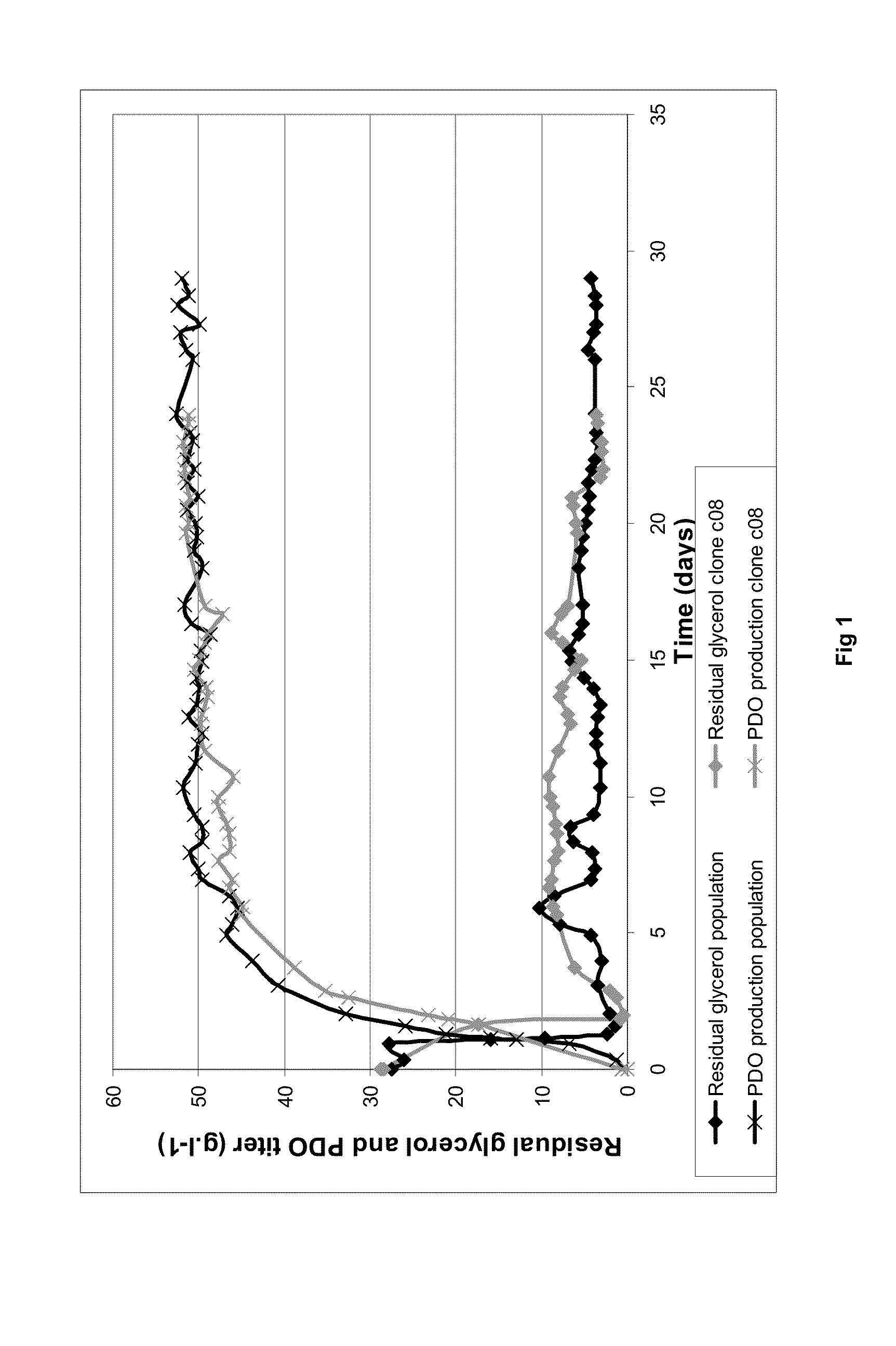
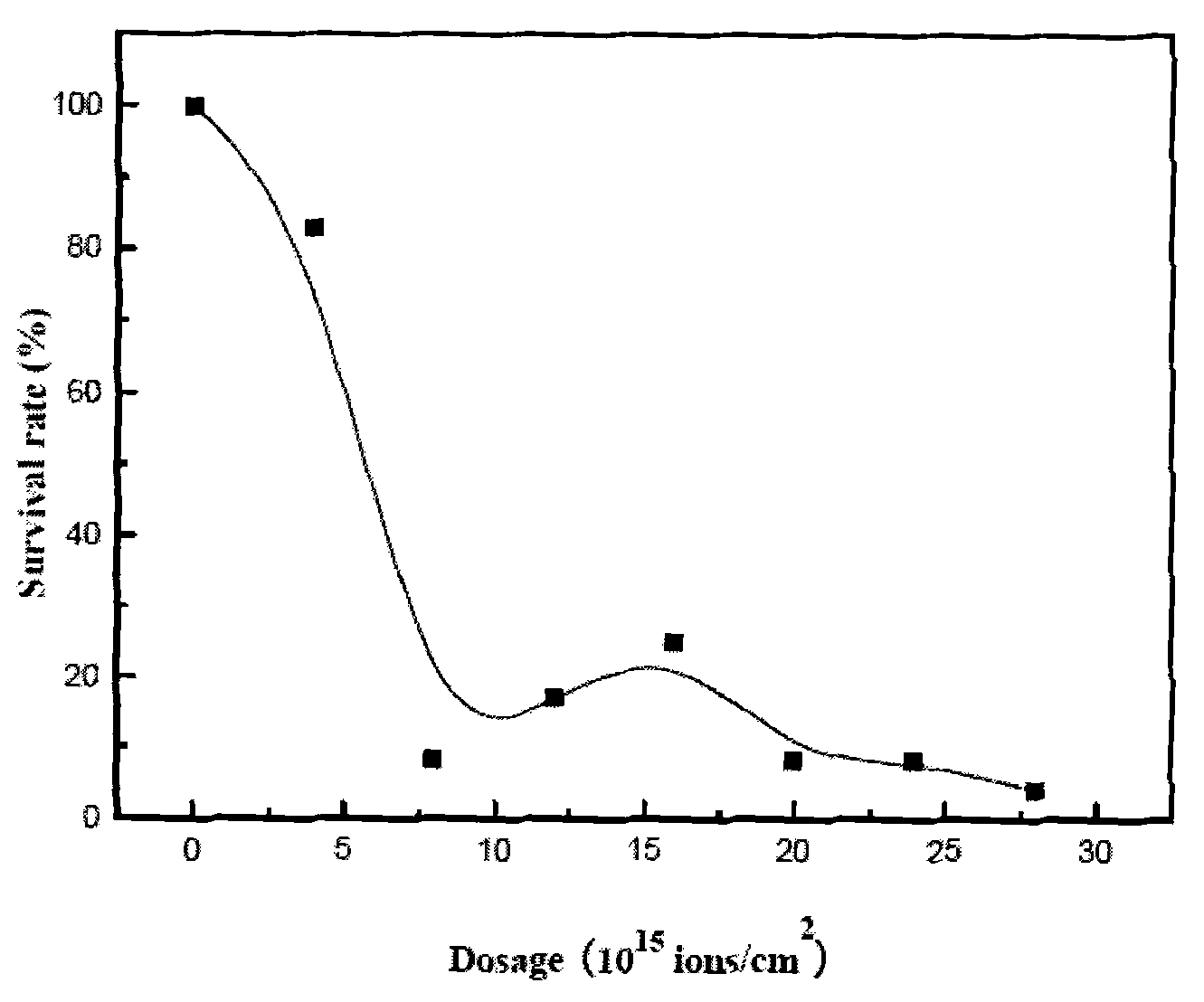
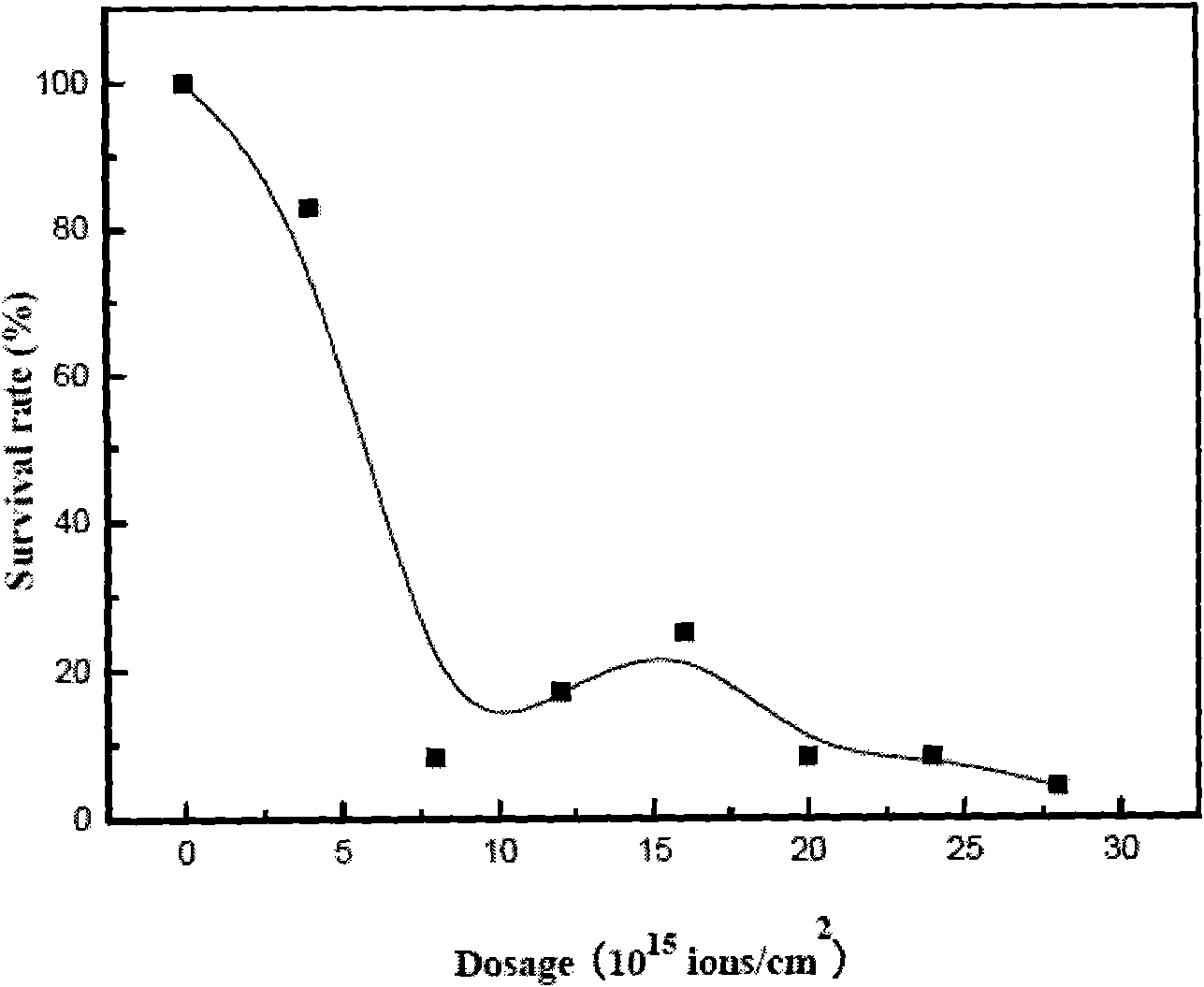
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Clostridium acetobutylicum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clostridium acetobutylicum, ATCC 824, is a commercially valuable bacterium sometimes called the "Weizmann Organism", after Jewish-Russian-born Chaim Weizmann. A senior lecturer at the University of Manchester, England, he used them in 1916 as a bio-chemical tool to produce at the same time, jointly, acetone, ethanol, and butanol from starch. The method has been described since as the ABE process, (Acetone Butanol Ethanol fermentation process), yielding 3 parts of acetone, 6 of butanol, and 1 of ethanol. Acetone was used in the important wartime task of casting cordite. The alcohols were used to produce vehicle fuels and synthetic rubber.
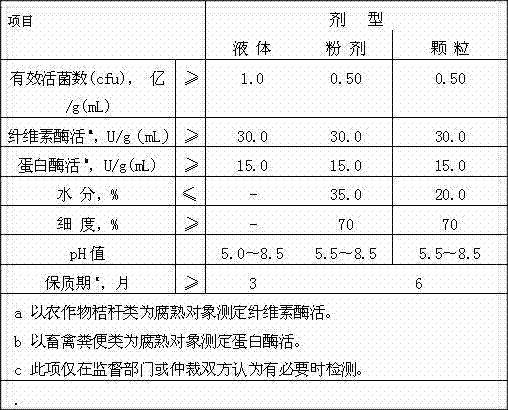
Special microorganism composite bacterial agent for directly decomposing and fermenting crops straws to generate marsh gas and application method thereof
InactiveCN101775359AGood degradation activityEasy to storeFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisVaccination
The invention discloses a special microorganism composite bacterial agent for directly decomposing and fermenting crops straws to generate marsh gas and application method thereof. The special microorganism composite bacterial agent is liquid or solid, and is formed by fermenting, culturing, combining and compositing one or a plurality of bacillus cereus, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus megaterium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus circulans, bacillus sphaerieus, clostridium sporogenes, clostridium acetobutylicum, clostridium barati, clostridium beijerinckii, clostridium thermocellum, trichoderma viride, trichodermareesei and aspergillus niger. Simultaneously, by taking the special microorganism composite bacterial agent as a vaccination bacterial agent, the invention provides an application method for decomposing the crops straws and accelerating the ferment to generate marsh gas; and the microorganism composite bacterial agent-treated crops straws have fast ferment speed, large marsh gas generation quantity, low treating cost and no secondary pollution, can be fermented to generate the marsh gas under the condition of no faeces of poultry, and have very wide application range.
Owner:刘相梅 +1
Clostridium acetobutylicum and applications thereof
ActiveCN103320335AStrong oxygen resistanceHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEconomic benefitsGrowth regulator
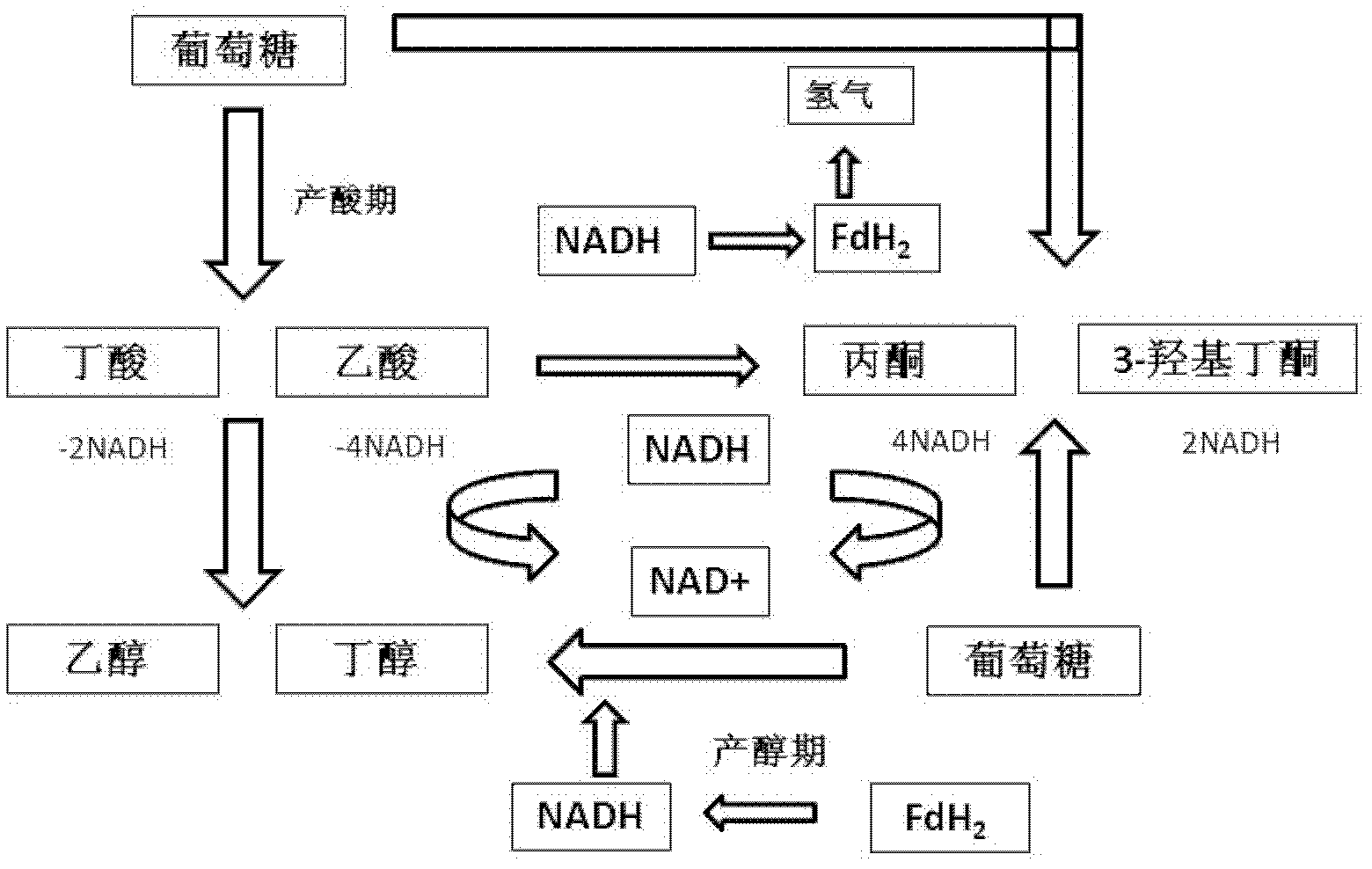
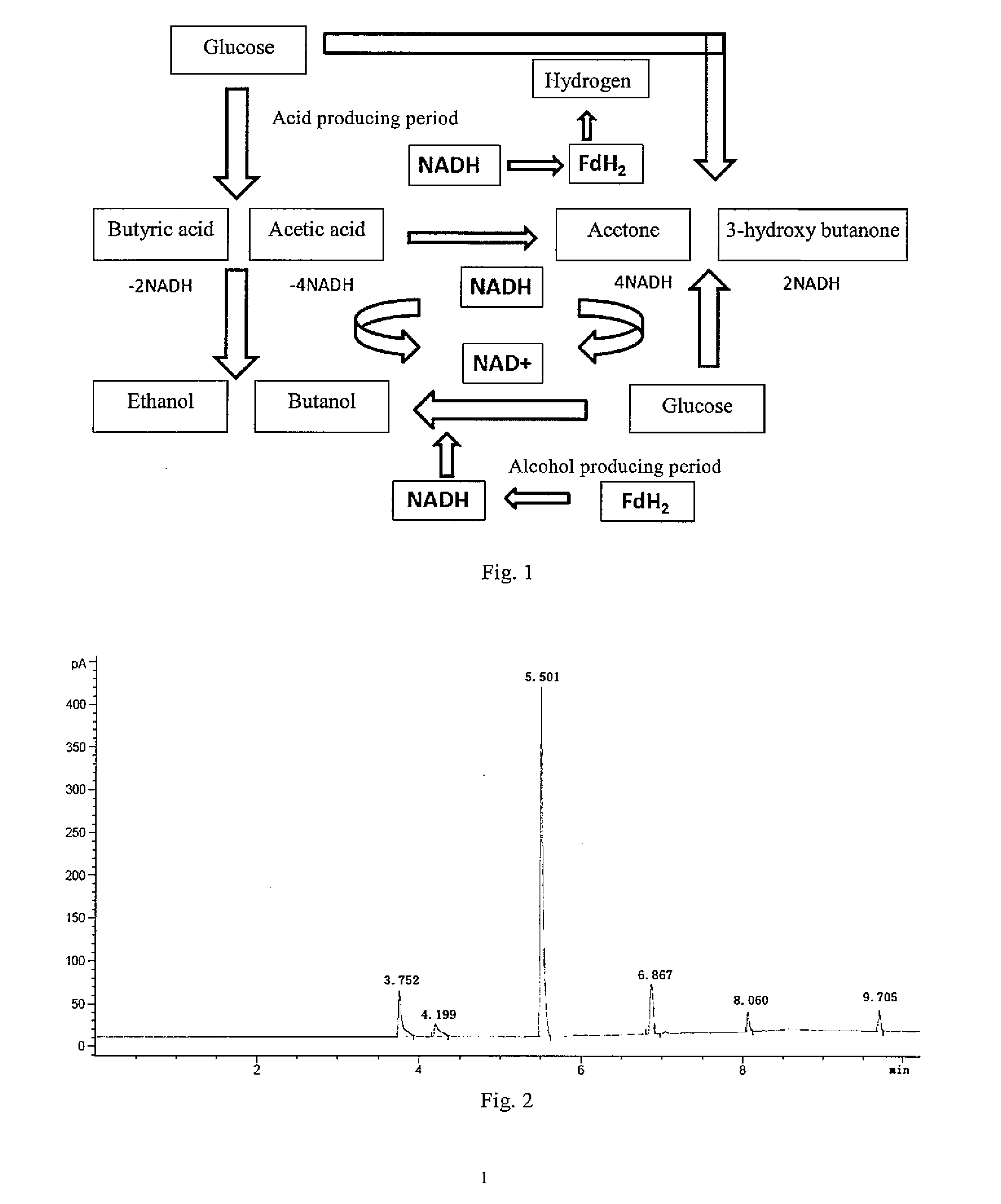
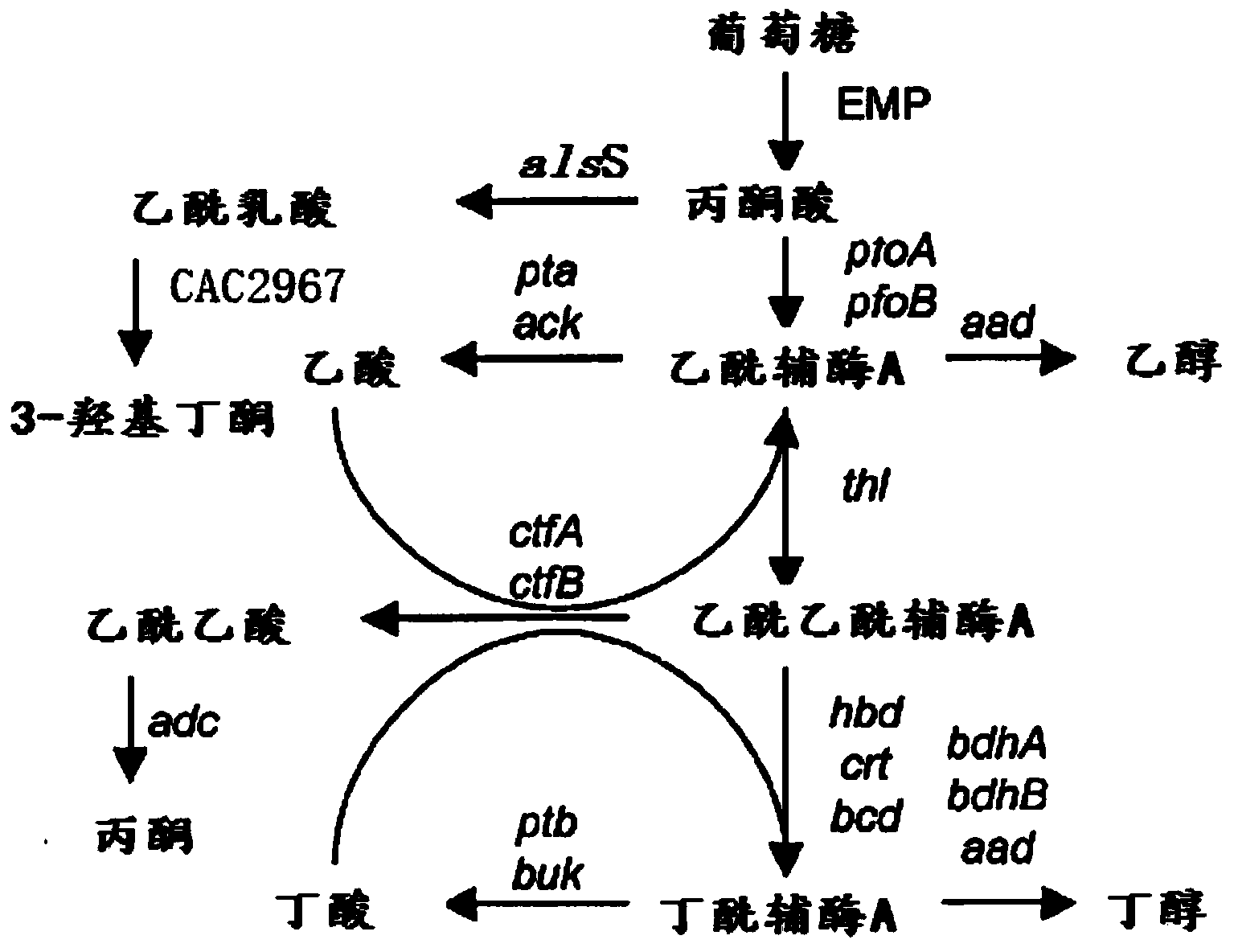
The invention provides a Clostridium acetobutylicum and applications thereof. The accession number of the Clostridium acetobutylicum provided by the invention is CGMCC No. 5234. The Clostridium acetobutylicum can be used to simultaneously produce acetone, butanol, ethanol and 3-hydroxybutanone through fermentation, so that economic benefits of butanol fermentation are increased. Coupled regeneration of NAD+ can be achieved by adding metabolism or growth regulators, which increases product yields and, at the same time, can flexibly adjust the yields of coproduction products to adapt to market demand.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A strain of Clostridium acetobutylicum, screening method and use thereof
ActiveCN101353632AQuick useReduce CODBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodCorn meal
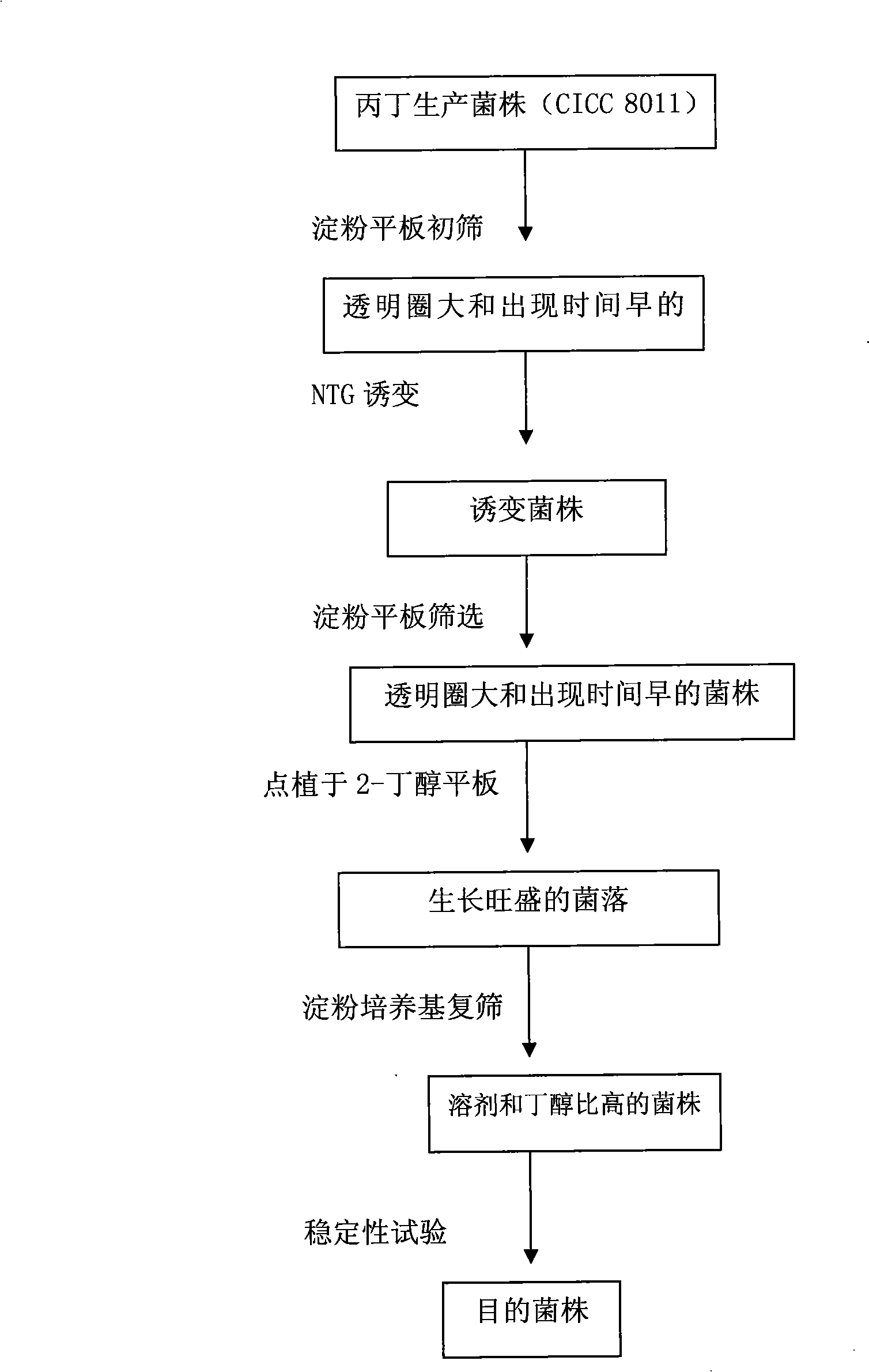
The invention relates to the technical field of bio-fermentation, in particular to a clostridium acetobutylicum which can quickly use amylofermentation to produce biological butanol, and a screening method and application thereof; the invention discloses a strain of the clostridium acetobutylicum, which belongs to the mutant strain of the clostridium acetobutylicum CICC 8011 with the preservation number of CTCC M207199. The invention obtains the strain which can quickly use amylofermentation to produce biological butanol by NTG mutagenesis and double flat plate screening of starch transparent ring and analogs of the butanol, has high butanol rate, solves the problem that in the traditional technique, the waste mash COD is high by adopting the corn meal as materials and is more friendly to environment.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +1
Method for improving sugar utilization rate of clostridium acetobutylicum in fermentation of mixed sugar
ActiveCN102796692AElimination of inhibitory effectsImprove xylose utilizationBacteriaTransferasesHigh concentrationWild type
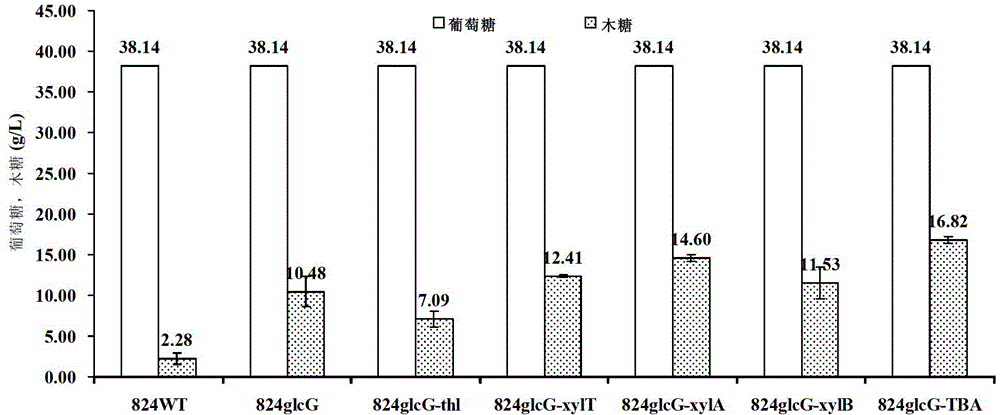
The invention discloses a method for improving the sugar utilization rate of clostridium acetobutylicum in fermentation of mixed sugar. The method comprises the following steps of: performing gene engineering modification on clostridium acetobutylicum, so that compared with wild type clostridium acetobutylicum, the clostridium acetobutylicum has the advantages that expression of g1cG gene can be inhibited, and the expression and activity of xylose transportprotein, xylose isomerase, and / or xylulokinase can be improved; and applying the obtained clostridium acetobutylicum which is subjected to gene engineering to fermentation of sugar. By the method, more xylose and arabinose can be used by clostridium acetobutylicum in the fermentation of the mixed sugar, a solvent product with high concentration can be produced, and the product yield can be improved; and the method has excellent industrial application prospect.
Owner:南京食气生化科技有限公司
Method for producing ethanol, butanol and acetone by utilizing segmented and mixed fermentation of mixed sugar containing pentose and hexose
ActiveCN103409470ASolve the five-carbon sugar fermentation problemSolve the problem of low conversion rateBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesCelluloseAgricultural residue
The invention discloses a method for producing ethanol, butanol and acetone by utilizing segmented and mixed fermentation of mixed sugar containing pentose and hexose. According to the method, ethanol, butanol and acetone is produced by using mixed sugar containing pentose and hexose as a raw material to perform segmented and mixed fermentation with acetone butanol through saccharomyces cerevisiae, the problems of pentose fermentation of the traditional cellulose fuel ethanol and low conversion rate of total solvent produced by co-fermentation of clostridium acetobutylicum pentose and hexose can be solved, the conversion rate of the total solvent is improved by 5-50%, forestry and agricultural residues can be comprehensively utilized, environmental pollution can be reduced, diversification of the energy structure in China can be promoted, and the method has a positive meaning to the liquid fuel safety of China.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing butanol by continuous solid state fermentation of restaurant-kitchen garbage
InactiveCN102174595AImplement preprocessingImprove degradation rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSolventCulture mediums
The invention discloses a method for producing butanol by continuous solid state fermentation of restaurant-kitchen garbage. The method comprises the following basic steps of: (1) performing liquid-solid separation on the restaurant-kitchen garbage by using a centrifugal dehydrator; (2) performing steam explosion pretreatment on the dehydrated restaurant-kitchen garbage; (3) adding saccharification enzyme into the treated restaurant-kitchen garbage according to the weight, and delivering the cellulase to a continuous solid state fermentation reactor; (4) continuously inoculating the cultured clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution to a culture medium; (5) continuously delivering the raw materials to the reactor under set conditions to perform continuous butanol fermentation and extraction; (6) rectifying the condensed solvent to obtain pure products of acetone, ethanol and butanol; and (7) further drying the fermentation residue through a continuous dryer till the water content is less than 14 percent to prepare an organic fertilizer. By adopting the continuous solid state fermentation process, wastewater treatment is avoided, the treatment efficiency is increased, the energy consumption is reduced, and the production cost of the butanol is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
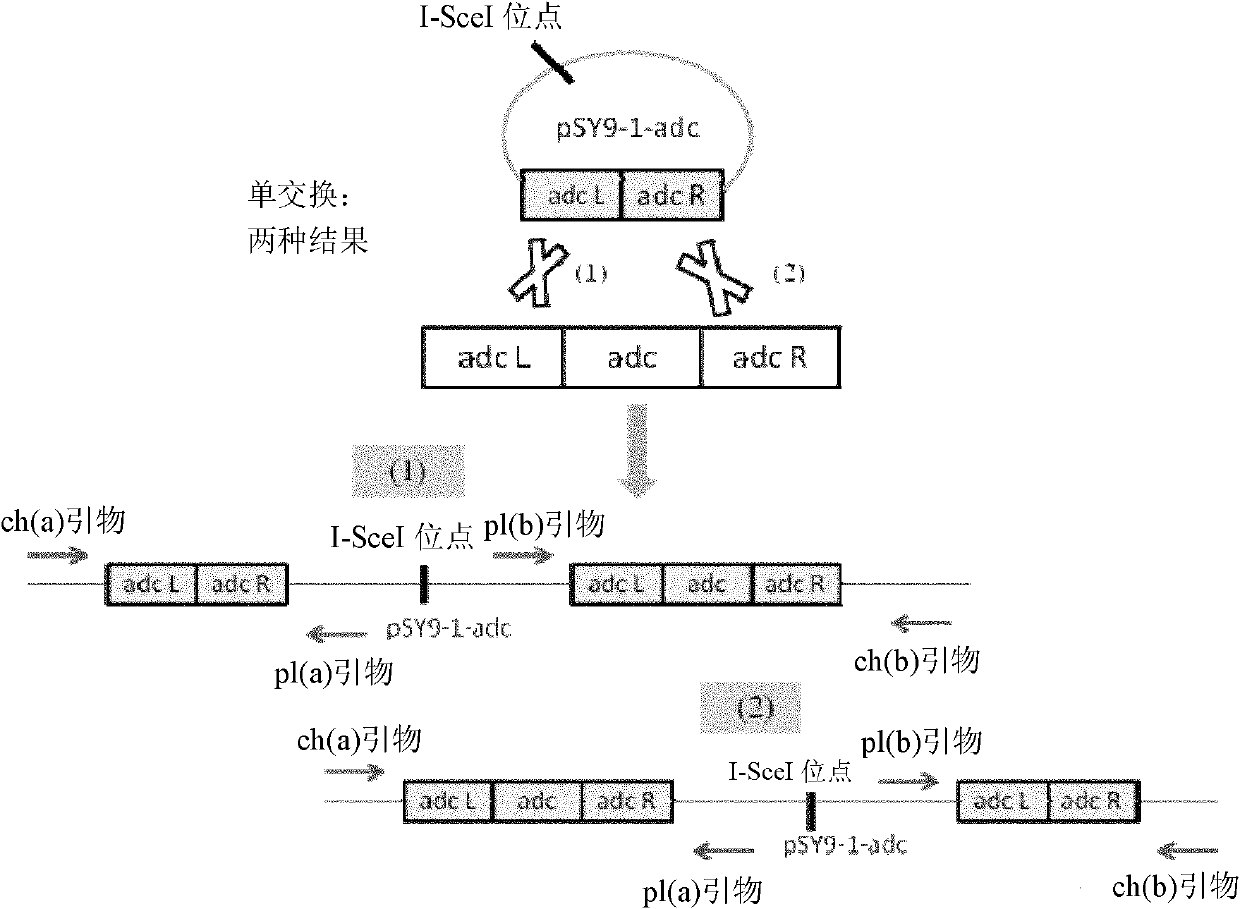
Recombinant plasmid for acetone-butanol clostridium gene disruption
InactiveCN101328486AIncrease insertion efficiencyImprove the imperfect situationVector-based foreign material introductionPlasmid VectorGenetics manipulation
The invention provides a recombinant plasmid, a preparation method thereof, an application, two knockout recombinant plasmid vectors pSY6-buk and pSY6-solR which are prepared by taking the recombinant plasmid as a starting plasmid, a method for preparing the recombiant plasmid vectors pSY6-buk and pSY6-solR, and an application. The recombinant plasmid can be taken as a knonckout starting plasmid of an acetone and butanol, can perform the gene knockout efficiently and rapidly, and can be evolved into a novel genetic manipulation system in order to improve the imperfect condition of the prior manipulation system in the current research on the clostridium acetobutylicum, thereby providing convenience for the research on the metabolic engineering of the clostridium acetobutylicum. The recombinant plasmid vectors pSY6-buk and pSY6-solR can be directly applied to establishing knockout strains of the clostridium acetobutylicum buk and solR genes.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium acetobutylicum and application thereof
InactiveUS20150093796A1Strong oxygen resistanceAvoid measuringBacteriaBiofuelsEconomic benefitsCogeneration
The present invention provides Clostridium acetobutylicum and an application thereof. A preservation number of the Clostridium acetobutylicum provided in the invention is CGMCC No. 5234. The Clostridium acetobutylicum provided in the present invention can be used for cogeneration of acetone, butanol, ethanol, and 3-hydroxy butanone through fermentation, so as to improve the economic benefit of butanol fermentation. NAD+ coupling and regeneration can be implemented by adding metabolism or growth regulating substances, so as to improve the product yield, and at the same time, the yield of cogeneration products can be flexibly adjusted, so as to cater for the market demand.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing acetoin as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103436479AIncrease productionIncreased acetoin productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenetically engineered
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing acetoin. The genetically engineered bacterium is clostridium into which a coding gene of acetolactate decarboxylic reaction enzyme is imported. The invention also discloses a construction method and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium. By adopting the method, the average yield of acetoin produced from clostridium acetobutylicum is about 5g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bacillus series straw fast rotting agent and using method thereof
InactiveCN102876607ACorrupted Time ReductionShorten the durationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a bacillus series straw fast rotting agent and a using method thereof. The fast rotting agent comprises bacillus licheniformis, bacillus circulans, bacillus subtilis, clostridium pasteurianum, bacillus megatherium, jelly-like bacillus, clostridium acetobutylicum, bacteria macerans, bacillus polymyxa and nutrient solution and is used for treating straws to make biological organic fertilizer. The using method comprises the following steps: stacking the straws into a walkway with the width of 40 cm and the height of 30 to 50 cm; uniformly spraying 1.25 kilograms of the fast rotting agent into per ton of straws; controlling the water content of the straws to be 40 to 60 wt%; and rotting at normal temperature for 1 to 2 weeks, wherein when the straws change into brown or black brown, the wet straws are flexible and elastic when being held by hands and the dry straws are crisp and easy to break, a straw decomposition agent product with the nutrient substance content up to 59 weight percent is obtained and can direct serve as fertilizer. By adoption of the fast rotting agent, the straw rotting time is reduced from 15-20 days at present to 7-10 days.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
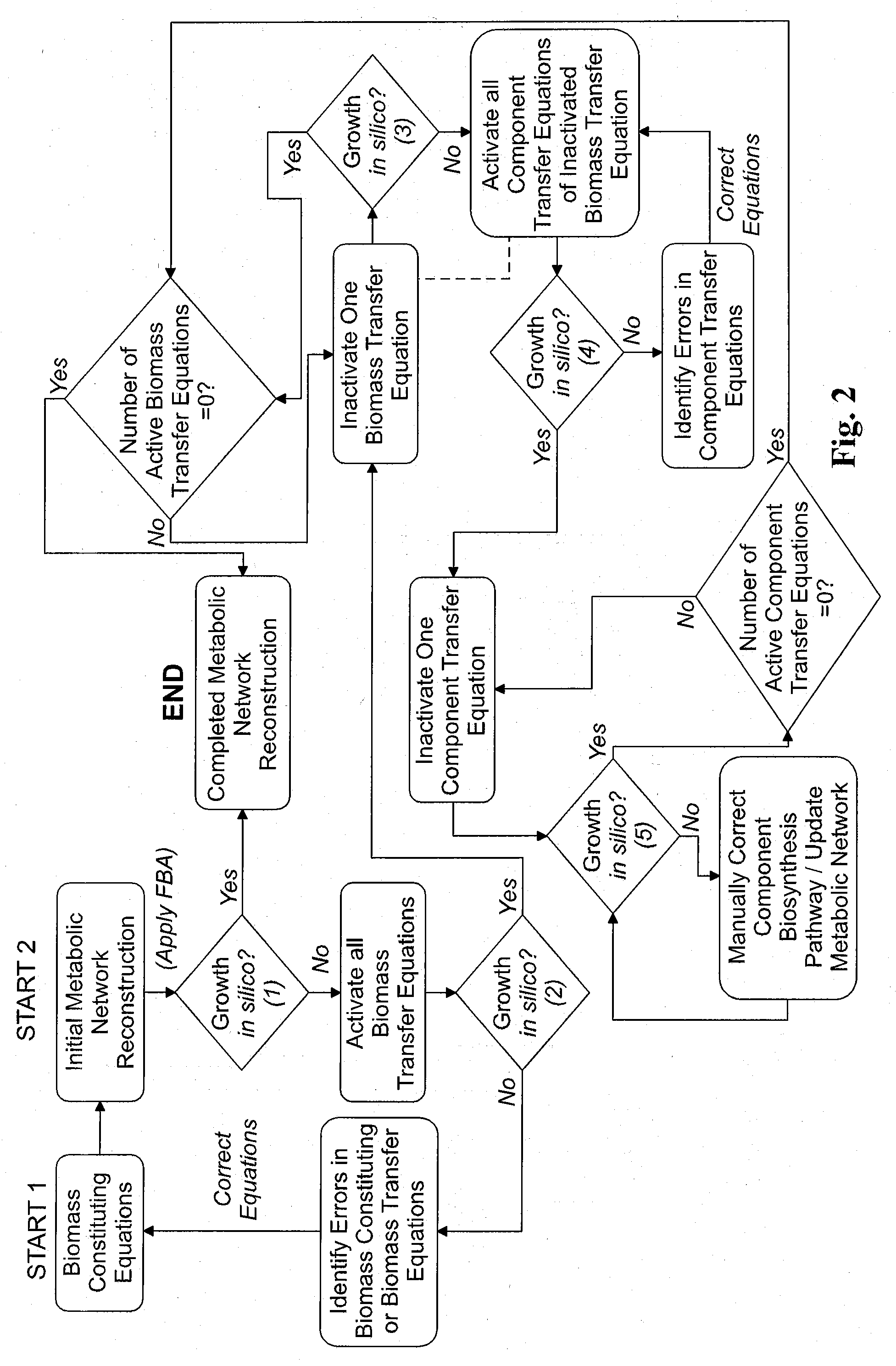
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS20090259451A1Reduce in quantityAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingUnderdetermined systemIn silico
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Method for ex-situ preparation of methane and combined production of humic acid, and composite microbial agent used in same
InactiveCN105274178AIncrease productionImprove extraction efficiencyOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesCelluloseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for ex-situ preparation of methane and combined production of humic acid, and a composite microbial agent used in the same, belonging to the field of recycling of brown coal. The composite microbial agent is composed of fermentation broth of four bacteria, i.e., Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, Penicillium decumbens and Clostridium acetobutylicum. The composite microbial agent has strong degradation capability on a variety of celluloses, hydrocarbons, asphaltene and a variety of carbonaceous macro-molecules. As coal is treated by the composite microbial agent, anaerobic digestion time can be shortened, output of methane gas is increased and extraction efficiency of humic acid is improved; moreover, the synergistic effect of the above-mentioned four microbial strains is superior to the effect of any one microbial strain or any two microbial strains.
Owner:创盛量子科技(温州)有限公司
Method for regulating and controlling synthesis of EPS (extracellular polymeric substance) of clostridium acetobutylicum
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling synthesis of an extracellular polymeric substance of clostridium acetobutylicum. The method is characterized in that an intron sequence is interpolated into a gene Spo0A of the clostridium acetobutylicum by using a type II intron gene knockout technology. The invention provides a simple and efficient method for regulating and controlling EPS (Extracellular Polymeric Substance) synthesis; a recombinant strain obtained based on the method is relatively good in regulating and controlling effect on the EPS; in case of taking glucose as a carbon source, when cultivated in an anaerobic bottle with the volume of 100 ml by using a slide biomembrane cultivation method, a clostisdium acetobutylicum biomembrane is 5.81 mum in thickness, and the thickness of a strain biomembrane cultivated under the same condition is 24.6 mum.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Microbial agent for sewage treatment, attachment carrier of microbial agent and preparation method of microbial agent
The invention discloses a microbial agent for sewage treatment. The microbial agent comprises, by weight, 8-10 parts of clostridium acetobutylicum, 12-16 parts of bacillus licheniformis, 16-20 parts of bacillus subtilis, 5-7 parts of lactobacillus acidophilus, 5-7 parts of methanosarcina, 3-5 parts of methanosaeta, 6-8 parts of rhodopseudomonas palustris, 4-6 parts of cellulomonas flavigena, 8-10parts of streptococcus thermophilus, 8-10 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 3-5 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 2-4 parts of bacillus nitrosomonas, 1-3 parts of issatchenkia orientalis and 3-5 partsof streptomyces bullis. Besides, the invention further discloses an attachment carrier of the microbial agent and a preparation method of the microbial agent. The microbial agent can be effectively attached to the carrier and accordingly has better activity. The microbial agent is reasonable in strain preparation and can be effectively attached to the attachment carrier to treat sewage, and the method for sewage treatment is simple, good in treatment effect and worthy of popularization.
Owner:ANJIEYU BEIJING OILFIELD TECHNICAL SERVICES CO LTD
Clostridium acetobutylicum strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102226163AStrong conversion rateStrong outputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationSolvent
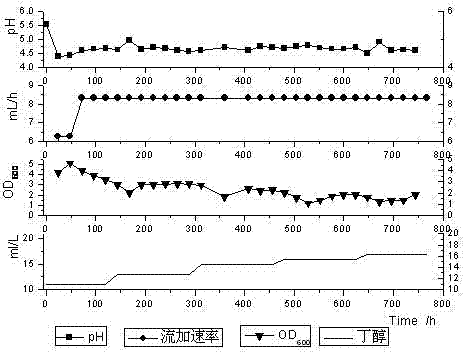
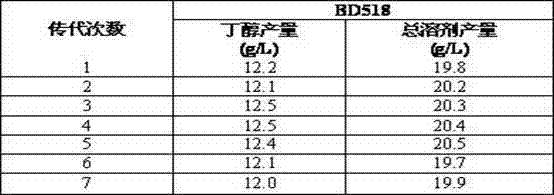
The invention relates to a Clostridium acetobutylicum strain and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biofermentation. The classification designation of the Clostridium acetobutylicum strain provided by the invention is Clostridium acetobutylicum BD518, and the preservation registration number is CCTCC NO:M2010308. The high-concentration butanol-tolerant strain BD518 is obtained by continuous culture, domestication and screening, and the butanol tolerance is up to 18g / L and is increased by 38.5% in comparison with the original strain (13g / L). When glucose is used as a carbon source, the total solvent and butanol yields in a 5L fermentation tank are respectively up to 21.1g / L and 13.2g / L and are respectively increased by 16.6% and 15.8% in comparison with the original strain. The Clostridium acetobutylicum strain has high butanol tolerance, high solvent yield and good repeatability, thereby having significant social meanings and economic values.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of peanut soy
The invention relates to a preparation method of peanut soy, belonging to the technical field of preparation methods of soy. The peanut soy provided by the invention adopts groundnut kernels as a raw material, bacillus licheniformis, brevibacterium flavum, clostridium acetobutylicum and rhamnose lactobacilli are taken as composite fermentative bacteria of a peanut fungi solution; the special proportional aspergillus oryzae, aspergillus niger and monascus are utilized as fermenting aspergillus of a peanut yeast, and a preparation process of natto soy is adopted. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that the fermentation period is shortened, natto kinase is generated after fermenting of groundnut kernels, the kinase can restrain the browning of the soy in preservation, a maillard reaction is reduced, the nutritive values of the groundnut kernels are high, the flavor is unique, and the color, the aroma and the taste of the prepared soy are good; the content amino acid nitrogen is improved by 43.9%, the full nitrogen content is improved by 17.5%, a soluble salt-free solid is improved by 18.8%, and the preparation method is especially used for preparing ideal soy of pickles.
Owner:松原北大荒食品科技有限公司
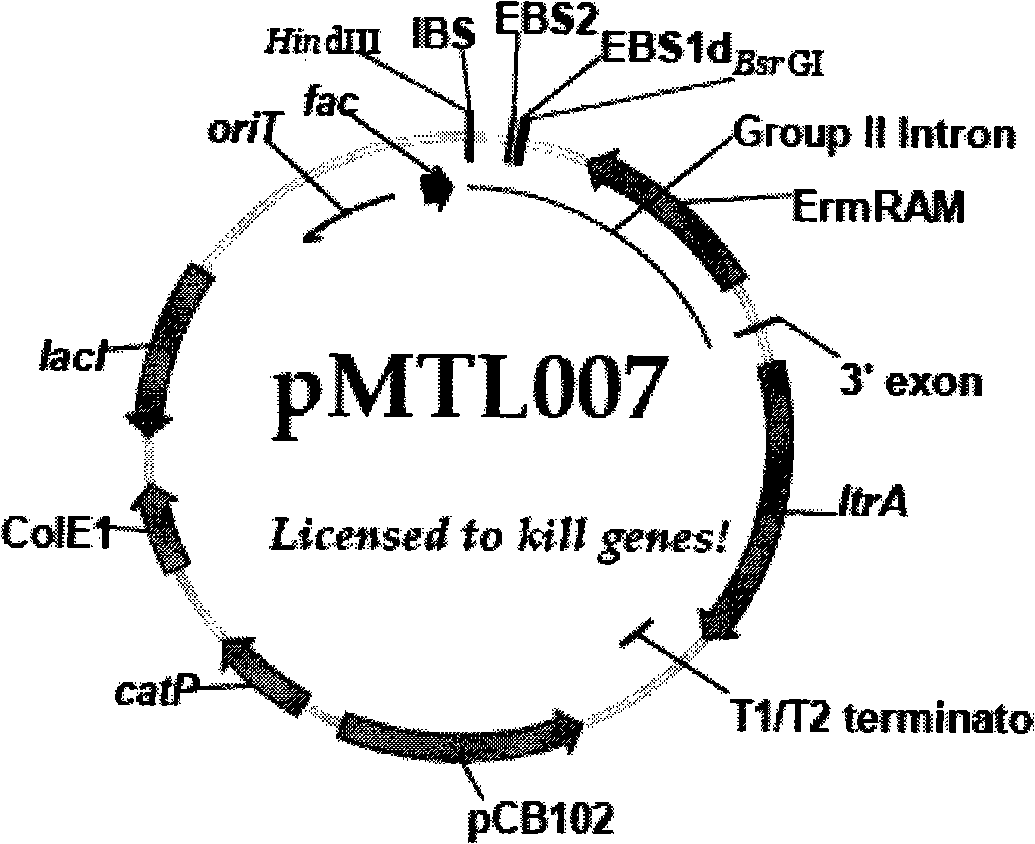
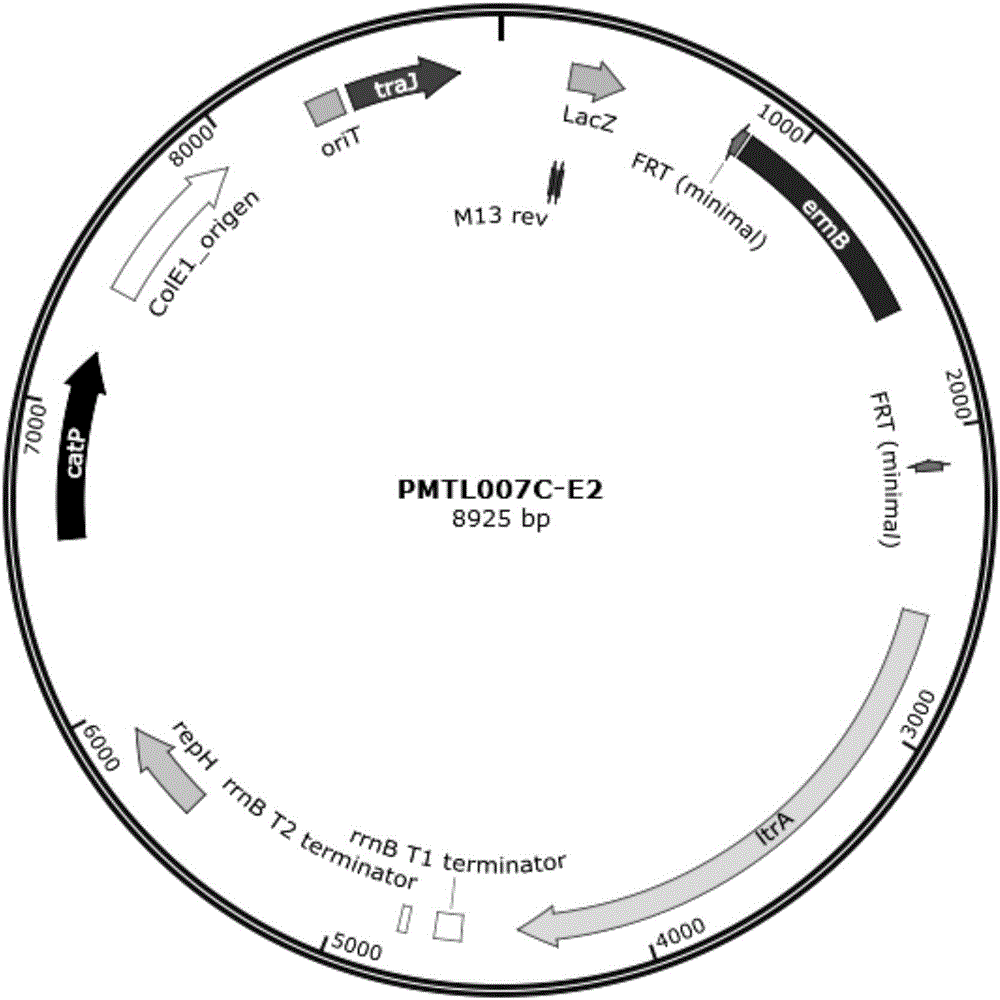
Method for knocking out gene in clostridium acetobutylicum
The invention relates to a method for realizing gene knock out, exogenous gene introduction, point mutation and large fragment knock out in clostridium, polynucleotide sequences containing a sequence shown by SEQ ID NO: 1, constructions and the like which are used in the method, and the application of the polynucleotide sequences and the constructions to realization of the gene knock out, the exogenous gene introduction, the point mutation and the large fragment knock out in the clostridium. The invention also relates to the clostridium prepared by the adoption of the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
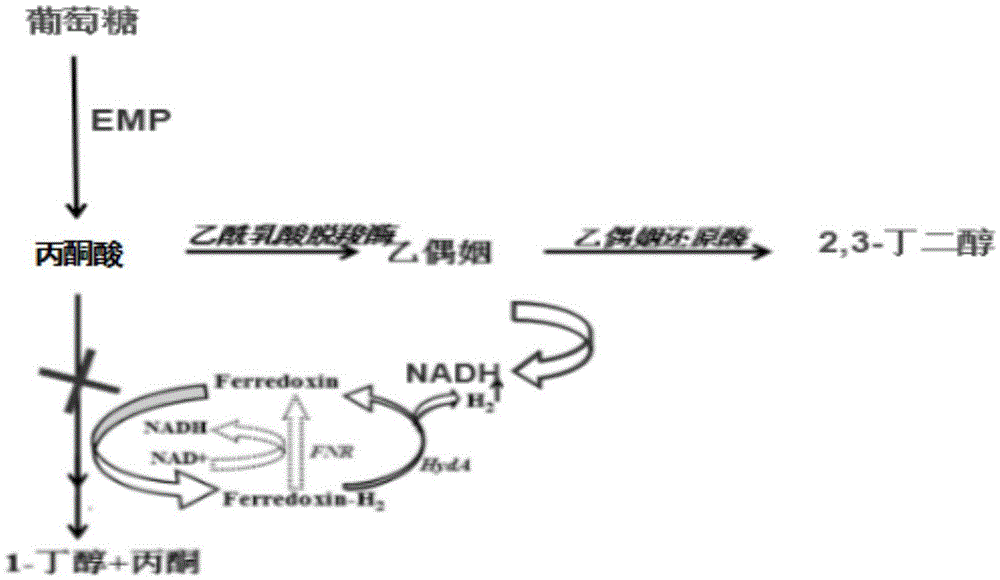
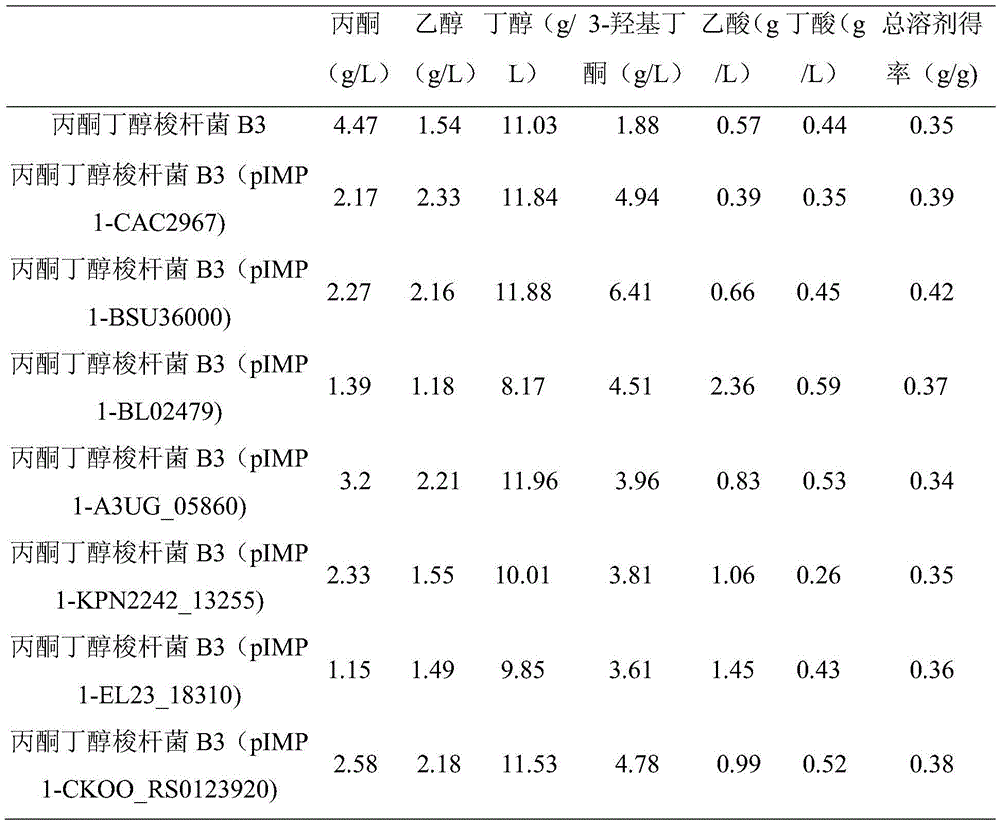
Genetically engineered bacterium for co-generating butanol and 2,3-butanediol and construction method and application thereof
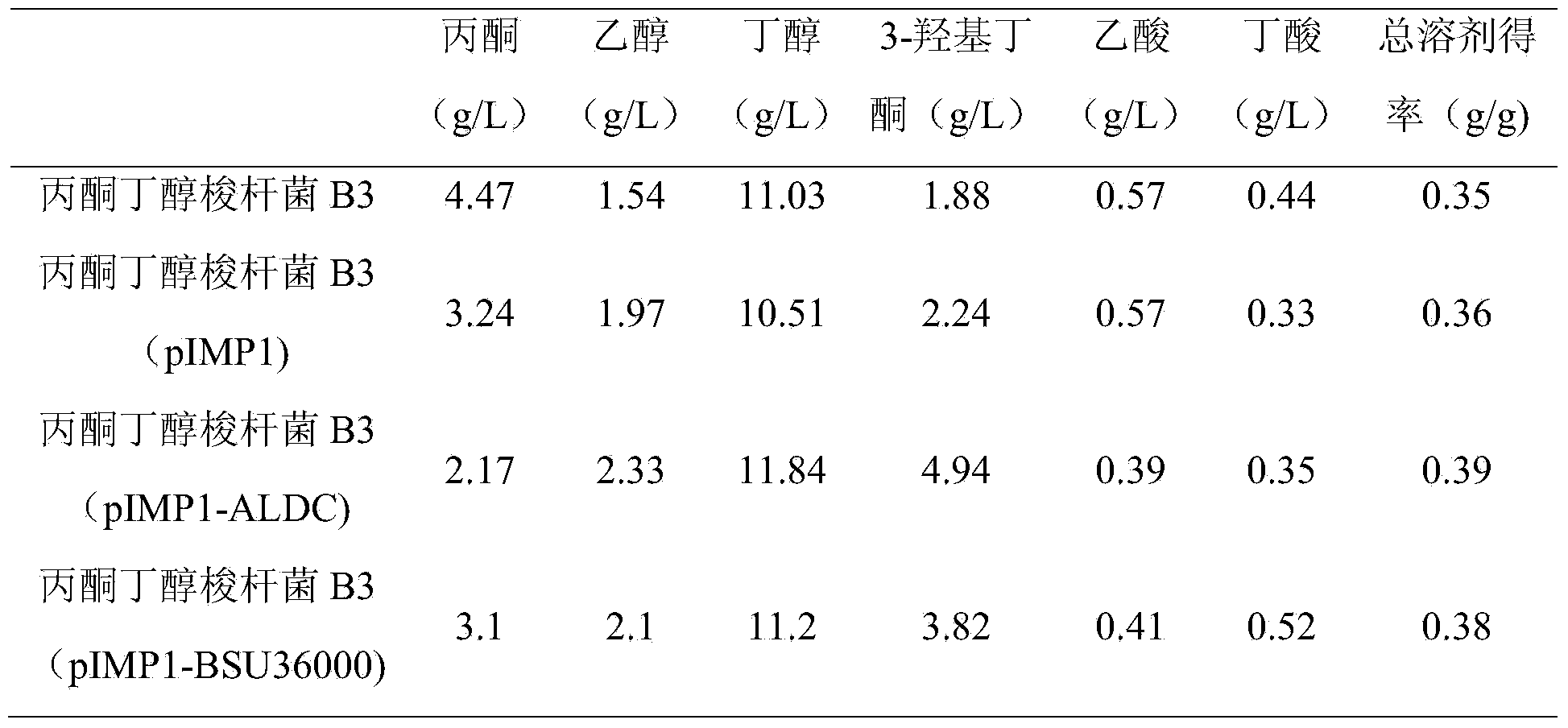
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for co-generating butanol and 2,3-butanediol. The genetically engineered bacterium is a butanol generating clostridium to which an acetoin reductase gene is introduced or a butanol generating clostridium to which an acetolactic acid decarboxylase gene and the acetoin reductase gene are introduced. The nucleotide sequence of the acetolactic acid decarboxylase gene is any one of nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1-7, and the nucleotide sequence of the acetoin reductase gene is any one of nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:8-11. An acetolactic acid decarboxylic reaction is enhanced in a clostridium acetobutylicum, the yield of 3-hydroxy butanone is greatly increased to about 6.4 g / L from initial about 1.8 g / L, and then acetoin is converted into 2,3-butanediol reaching up to 8.05 g / L under the effect of acetoin reductase; acetone is reduced to 2.2 g / L from about 4.5 g / L, and economic benefits of fermentation of the clostridium acetobutylicum are remarkably increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
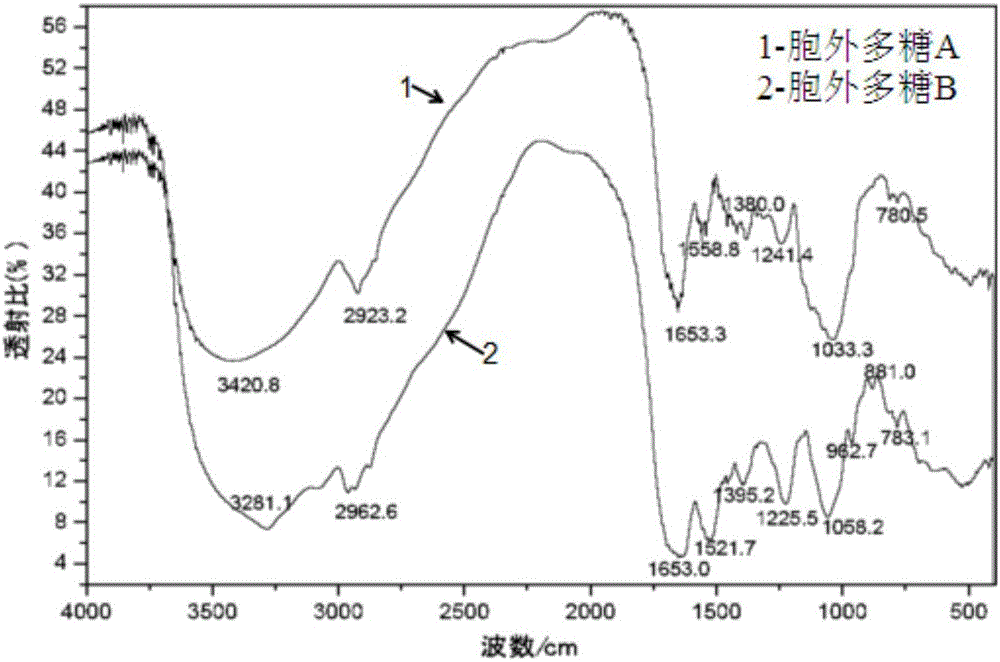
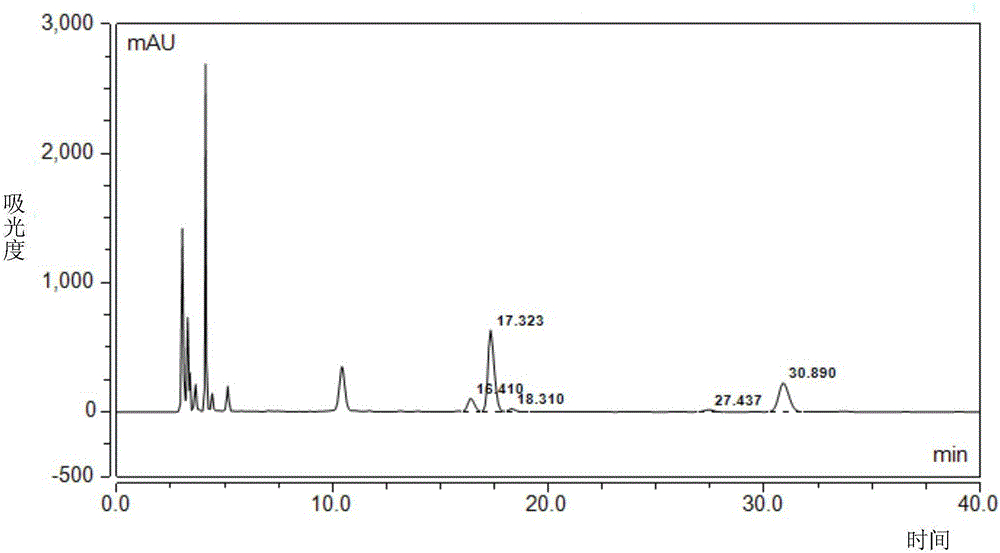
Method for extracting and isolating clostridium acetobutylicum exopolysaccharide
The invention provides a method for extracting and isolating clostridium acetobutylicum exopolysaccharide, comprising the following steps: (1), inoculating clostridium acetobutylicum seed liquid to a fermentation tank, adding mobilizing material, culturing until the surface of the mobilizing material is fully covered by clostridium acetobutylicum biofilm; (2), dissolving clostridium acetobutylicum biofilm with alkaline solution, centrifuging to remove bacterial precipitate, adding an organic solvent into supernate so that the organic solvent is 30-90% by weight, the organic solvent being ethanol, acetone or butanol, centrifuging, and collecting precipitate; adding an acid to adjust pH to 3.5-10.0, and collecting precipitate, the precipitates collected twice being the exopolysaccharide. The method provided herein has the advantages of low cost and good operation simplicity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for production and quantitation of high yield of biobutanol
InactiveCN101932716AShorten the timeEffective monitoringBiofuelsFermentationChemical industryBiofuel
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Clostridium acetobutylicum for producing butanol by utilizing manihot as raw materials and application thereof
The invention discloses clostridium acetobutylicum for producing butanol by utilizing manihot as raw materials and application thereof. The clostridium acetobutylicum is preserved in China Center for Type CultureCollection with the number of CCTCC M 2011280. The clostridium acetobutylicum is capable of fermenting to produce the butanol, and particularly, the fermentation volume of the butanol in a fermentation medium taking the manihot as the raw materials can reach 13.07 g / L.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium acetobutylicum and construction method and purposes thereof
The invention discloses a clostridium acetobutylicum p1147 (CGMCCNo3686) which is prepared by the protoplast fusion of clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. The strain can be used for fermenting and producing polydiol which contains isopropanol. The strain provided by the invention has the advantages of rapid growth, high reproduction, short cycle and stability, and the polydiol fermented and produced by the strain has high yield and good quality.
Owner:NORTH CHINA PHARMA GROUP CORP
Method for preparing n-butyl alcohol in fermentation mode by hydrolyzing lignocellulose through mixed cellulose crude enzyme
ActiveCN104004794AReduce consumptionReduce dependenceMicroorganism based processesFermentationLiquid glucoseN-Butyl Alcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing n-butyl alcohol, in particular to a method for preparing n-butyl alcohol in a fermentation mode by hydrolyzing lignocellulose through mixed cellulose crude enzymes. According to the method, the problems that in the existing process that the n-butyl alcohol is produced by biological fermentation, a substrate is high in cost, the production cost is increased due to the use of commercial enzymes in the hydrolytic process of the lignocellulose, and the enzyme activity is reduced due to an unbalanced proportion of a cellulose system of the single kind of culture are solved. The method comprises the steps that the preprocessed lignocellulose is applied to the mixed cellulase crude enzymes of trichoderma viride and aspergillus niger and hydrolysis is conducted according to a biological enzyme method; after a nitrogen source, inorganic salt and vitamins are added to obtained liquid glucose, nitrogen is added to the liquid for deoxygenization; a clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution is inoculated for anaerobic fermentation, and therefore the n-butyl alcohol is generated. According to the method, the activity of biological enzymes is improved in the cellulose enzymolysis process, cost of the substrate and the enzymatic hydrolysis in the process that the n-butyl alcohol is produced by biological fermentation is reduced, the problems of device losses and environment pollution are solved, and the saccharity hydrolysis efficiency of the mixed crude enzymes reaches 75%.
Owner:黑龙江茂全马铃薯生物技术有限公司
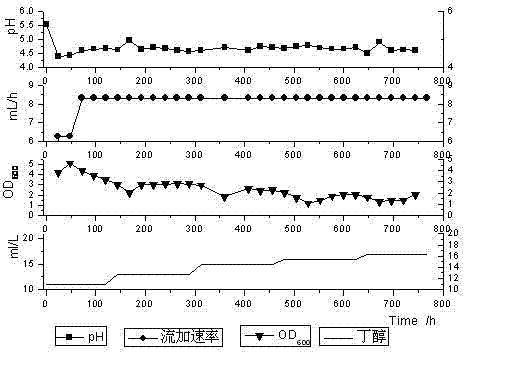
Method for immobilizing clostridium acetobutylicum by use of bacterial cellulose membrane
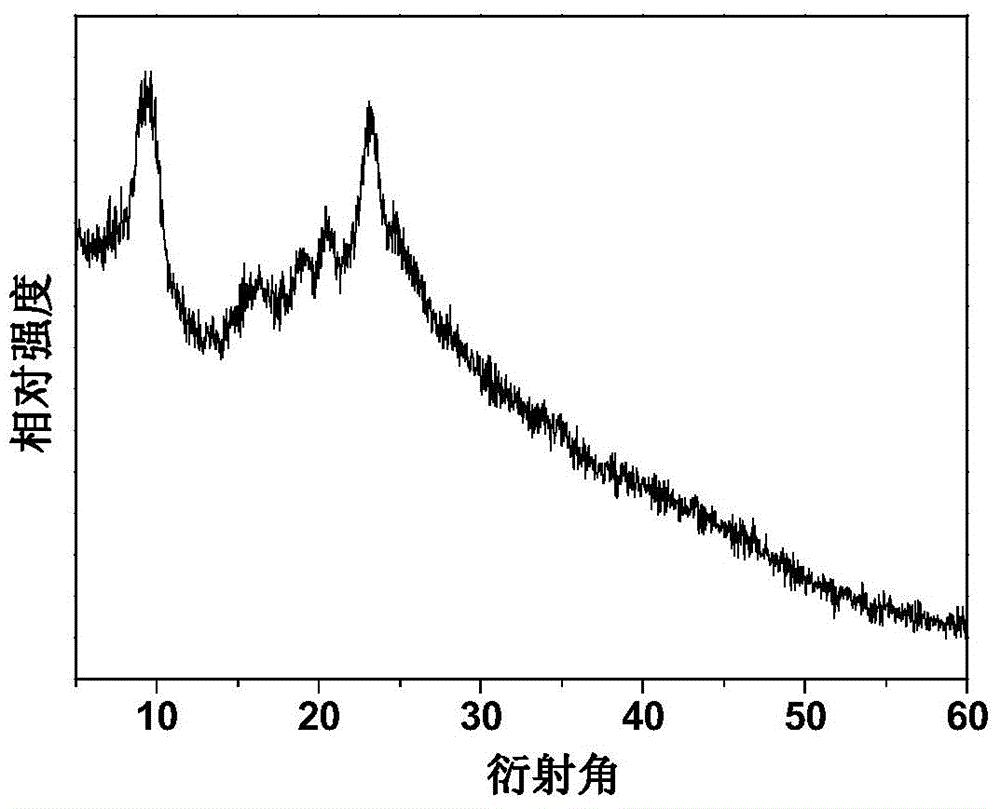
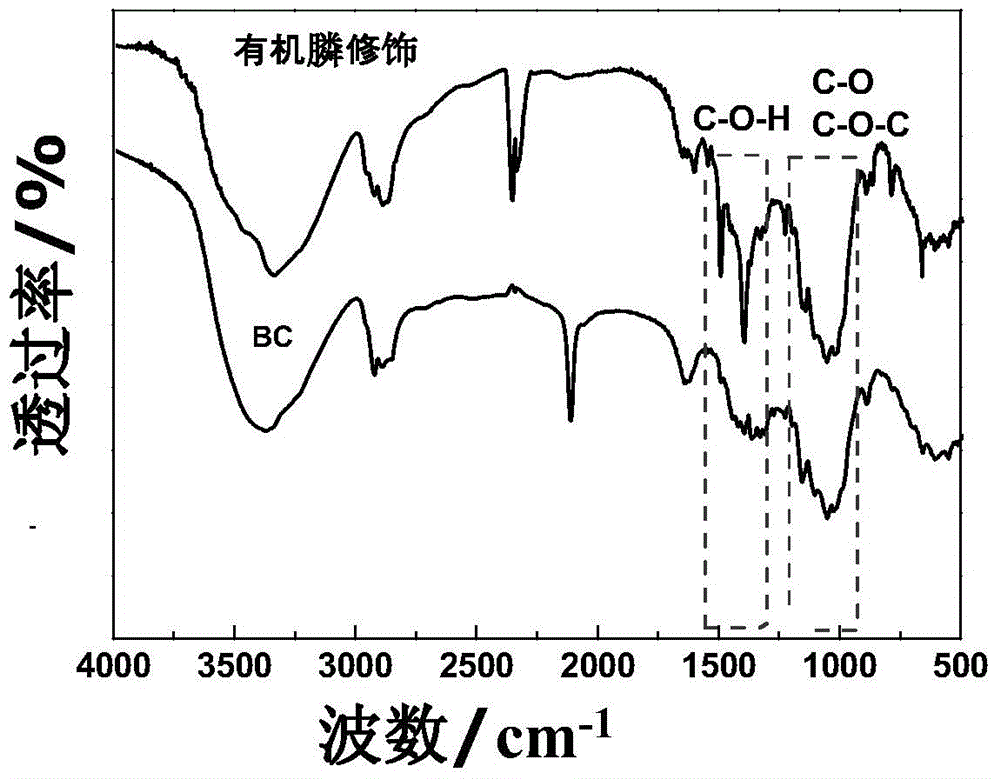
ActiveCN104894096AIncrease concentrationEasy to separateBacteriaOn/in organic carrierMicrobiologyClostridiales
The invention discloses a method for immobilizing clostridium acetobutylicum by use of a bacterial cellulose membrane. The method comprises the following steps: (1) hydrophobic modification of a bacterial cellulose membrane: conducting acid treatment on the bacterial cellulose membrane, and then cleaning and drying to obtain a bacterial cellulose membrane A; conducting alkaline treatment on the bacterial cellulose membrane A, and then cleaning and drying to obtain a bacterial cellulose membrane B; conducting acetylation, esterification, silane-coupling, polymeric modification or organic phosphate coupling on the surface of the bacterial cellulose membrane B to prepare a modified bacterial cellulose membrane; (2) immobilization of clostridium by use of the modified bacterial cellulose membrane: fixing the modified bacterial cellulose membrane obtained in the step (1) in a continuous fermentation tank, pumping in a clostridium acetobutylicum bacterial suspension for self-circulation culture to enable clostridium acetobutylicum to be adsorbed onto the bacterial cellulose membrane so as to obtain clostridium acetobutylicum immobilized onto the bacterial cellulose membrane. According to the method, after hydrophobic modification, clostridium is immobilized for continuous fermentation, the production efficiency is improved and the cost is lowered.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Medicinal-residue fermentation bacterial group and medicinal-residue fermentation technology
InactiveCN104017755APlay a role in decompositionPromote decompositionBio-organic fraction processingFungiBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention relates to a medicinal-residue fermentation bacterial group and a medicinal-residue fermentation technology. The medicinal-residue fermentation bacterial group is prepared from the following bacterial strains in parts by weight: 25-35 parts of bacillus subtilis, 20-25 parts of clostridium acetobutylicum, 15-20 parts of lactobacillus, 10-15 parts of nematspora gossypii, 5-10 parts of micromonospora echinospora, 3-8 parts of white rot fungus and 1-2 parts of pichia pastoris. A solid fermentation manner is employed for preparing protein feed from traditional Chinese medicine residue, so that environment pollution caused by traditional Chinese residue is avoided, and traditional Chinese residue becomes a new resource of protein feed, and wastes are changed into valuables. Also, through multiple-test research on the technology, the fermentation technology has the advantages of simple and practicable preparation technology, obvious effect and high practicability.
Owner:郑州市三维配电设备有限公司
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum in high L-lysine yield and construction method thereof
ActiveCN109370974AIncrease supplyReduce accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousCorynebacterium efficiens
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum in high L-lysine yield and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum disclosed by the invention, a phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase encoding gene gapC derived from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824 is heterogeneously expressed bytaking corynebacterium glutamicum CICC 23604 as an original strain and adopting CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology, and supply of intracellular NADPH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) isincreased; a homoserine kinase encoding gene thrB is knocked out, accumulation of a byproduct-threonine during a fermentation process is reduced, corynebacterium glutamicum genetically engineered bacteria with the accumulation of L-lysine can be obtained, the yield is up to 42g / L, and foundation is laid for producing the L-lysine through further metabolism engineering reform of the corynebacterium glutamicum.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microorganisms for 1,3-propanediol production using high glycerine concentration
The present invention is related to a population of Clostridium acetobutylicum useful for the production of 1,3-propanediol (PDO), wherein said population comprises at least one strain of a Clostridium acetobutylicum sp. comprising mutations selected among the mutations identified in table 1, wherein relative percentages of said mutations are selected among specific genes.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Method for immobilizing cell for producing Clostridium acetobutylicum
InactiveCN101475932AStable productionImprove efficiencyOn/in inorganic carrierContinuous fermentationSolvent
A cell immobilization method of producing butanol clostridium adopts the butanol clostridium liquor at exponential growth phase to produce immobilized cells through the adsorption of straw. The method includes main steps as follows: A) crushing the corn stalk into small pieces, bathing in the dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid at 80-100 DEG C for boiling 10-60 minutes, cleansing, and drying to a constant weight; B) immerging the corn stalk processed by the step A into a butanol clostridium cell culture fluid at exponential growth phase, static adsorption at 30 -40 DEG C for 12-48 hours. The inventive immobilization method has features of low cost, effective cell-rich effect, high activity of immobilized cells, and high production efficiency during continuous fermentation.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
Clostridium acetobutylicum strain and screening method and application thereof
InactiveCN101864389AStrong reductionGreat social significanceBacteriaMutant preparationBromocresol greenScreening method
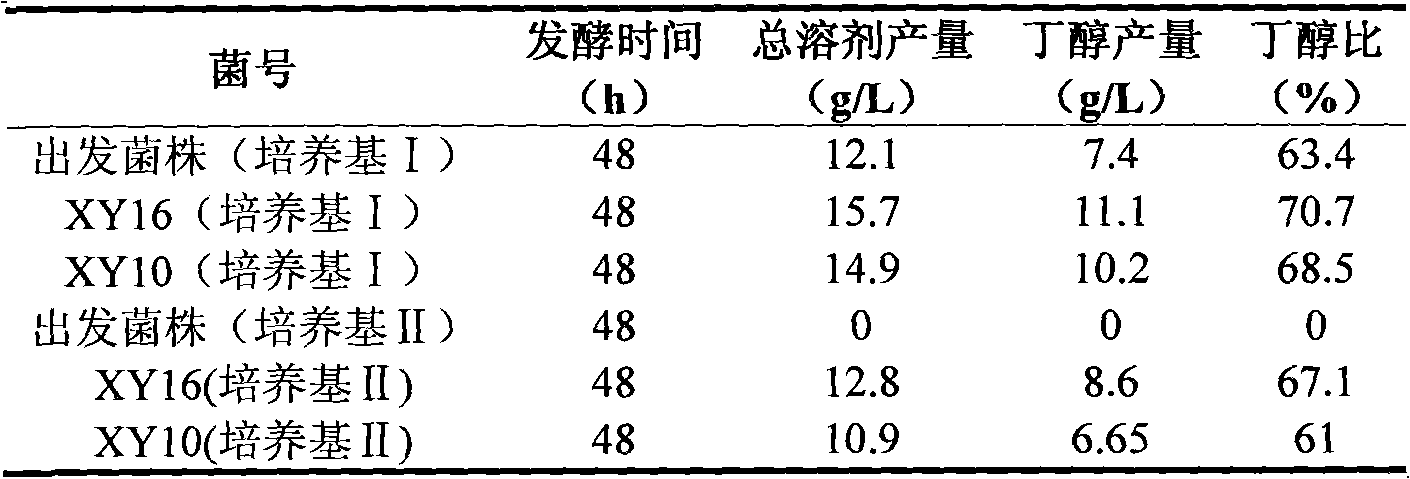
The invention relates to a Clostridium acetobutylicum strain capable of quickly generating butanol by fermenting xylose and starch, and a screening method and application thereof. The invention discloses Clostridium acetobutylicum, which is classified and named Clostridium acetobutylicumXY16 with the preservation and registration number of CCTCC NO:M2010011. The strain obtained by ion beam mutation and screening of a xylose plate, a 2-deoxy-D-glucose plate, a bromocresol green plate and a resazurin plate can quickly and efficiently generate the butanol by fermenting xylose and starch, has the advantages of high yield of total solvent, high butanol ratio and good repeatability, and is a good strain suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
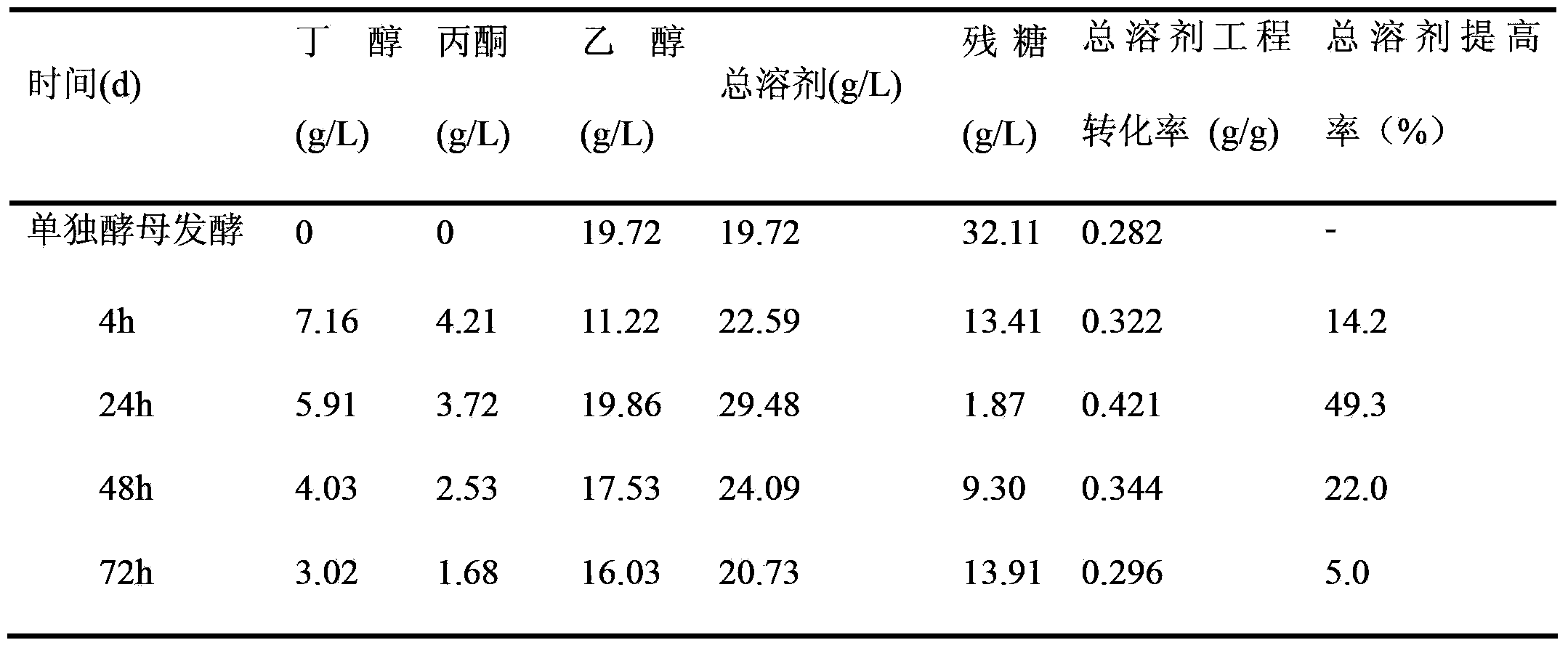
Method for producing acetone, butanol and ethyl alcohol through mixed-bacterial fermented cassava
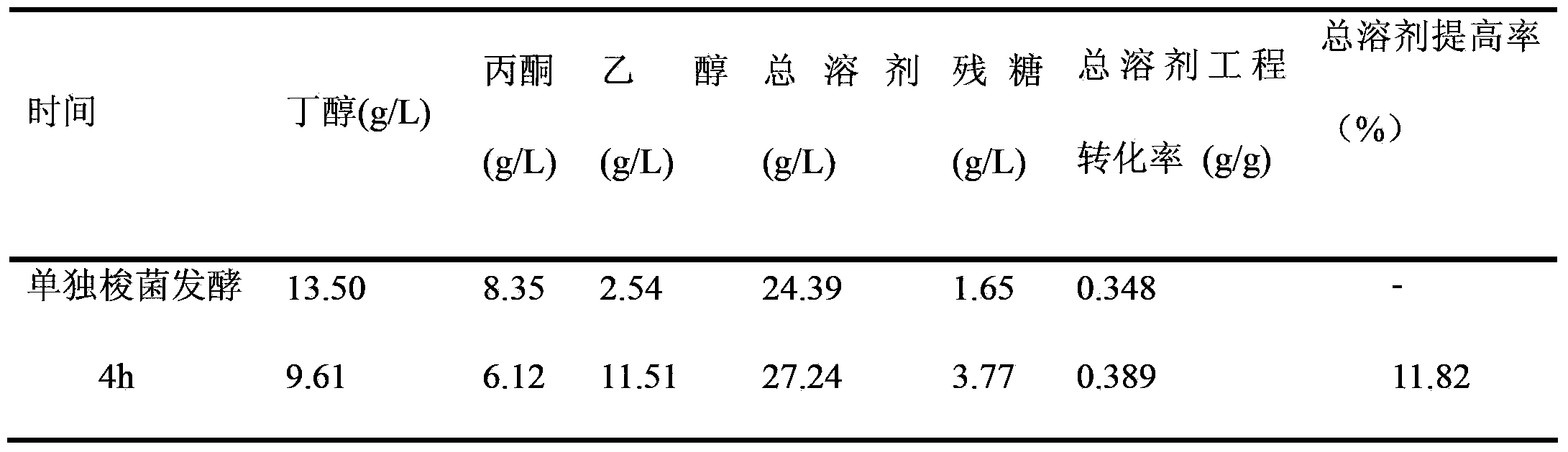
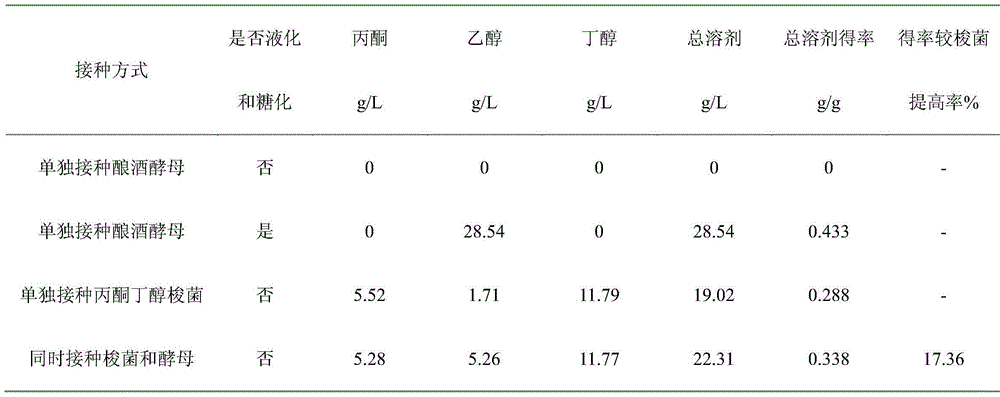
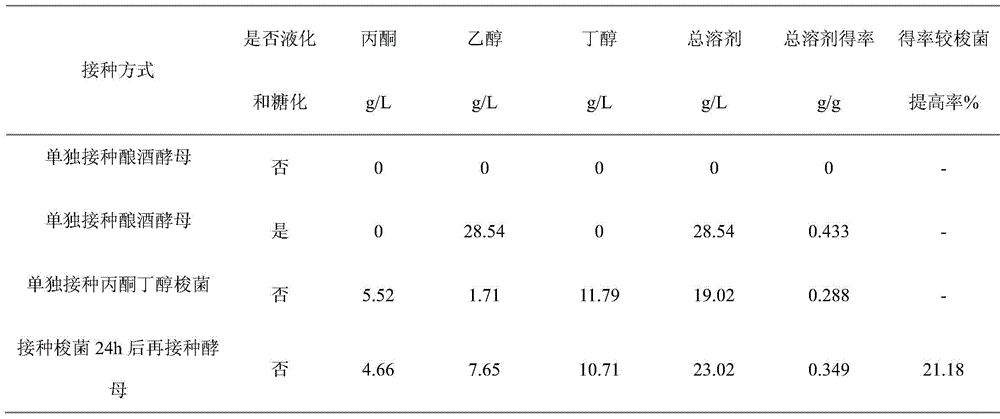
The invention discloses a method for producing acetone, butanol and ethyl alcohol through mixed-bacterial fermented cassava. The method includes: taking the cassava as a carbon source, adding nitrogen and phosphorus source and preparing a cassava fermentation medium via size mixing and sterilizing; generating amylase and saccharifying enzyme by the aid of clostridium acetobutylicum, and saccharifying the cassava fermentation medium to obtain saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation sugar so as to avoid high cost brought by commercial amylase and saccharifying enzyme; meanwhile, generating the acetone, the butanol and the ethyl alcohol through the saccharomyces cerevisiae fermented sugar saccharified by the saccharomyces cerevisiae fermented cassava to realize clostridium acetobutylicum and the saccharomyces cerevisiae cooperated mixed fermentation, wherein yield of solvent is obviously increased. The acetone, the butanol and the ethyl alcohol are produced by taking the cassava as raw materials by means of fermentation, non-staple crop fermentation production of the acetone, the butanol and the ethyl alcohol is realized, and great significance is achieved for production research of non-staple crop liquid biofuels.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com