Method for immobilizing clostridium acetobutylicum by use of bacterial cellulose membrane
A technology of bacterial cellulose membrane and Clostridium acetobutylicum, applied in the direction of immobilized on/in organic carriers, bacteria, fermentation, etc., can solve the problem of poor thermal stability and mechanical stability affecting the stability of immobilized materials, bacteria Single cellulose structure, unfavorable bacteria adsorption and other problems, to achieve the effect of shortening fermentation time, reducing production cost and increasing product concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
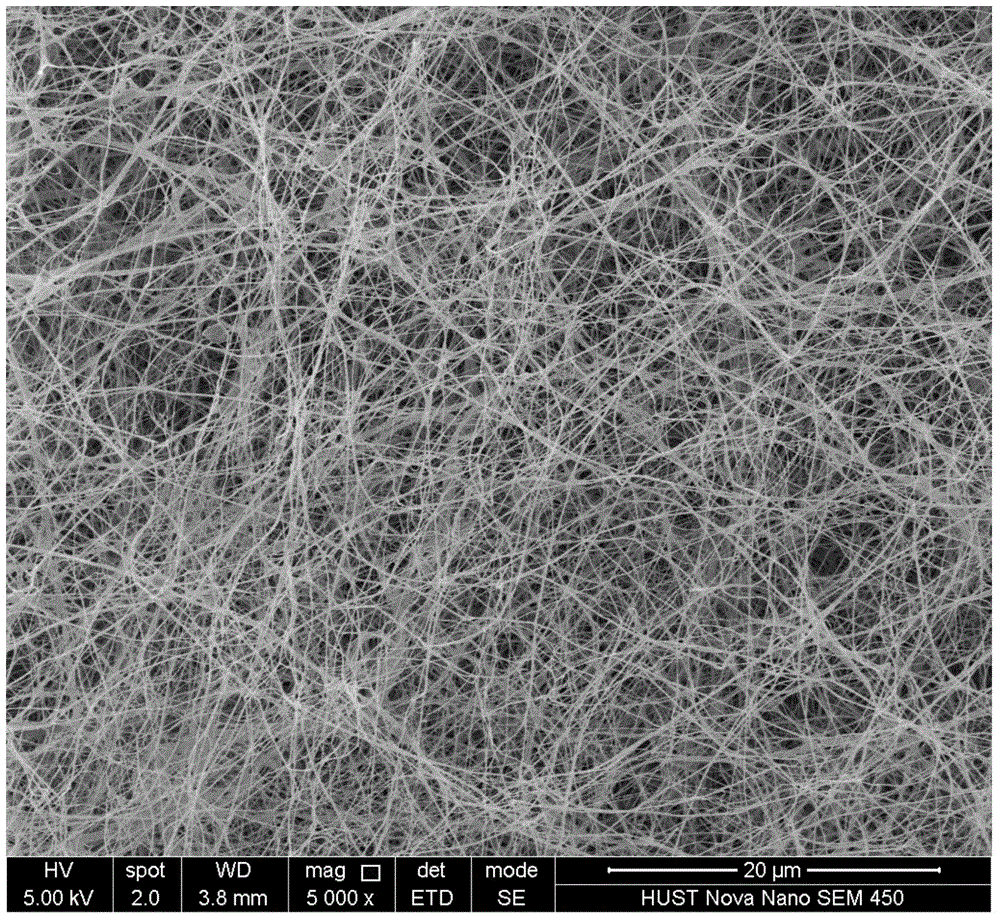
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Acetobacter xylinum preserved at -80°C (purchased from ATCC, the number of the bacterium is ATCC 23769) was inoculated on the slant medium, and the slant medium was: glucose 100g / L, yeast powder 10g / L, calcium carbonate 20g / L, agar 15g / L, pH=6.8; at 30°C, culture statically for 24 hours, after the bacterial lawn grows, scrape a ring and transfer it to 100ml seed medium, the seed medium is: glucose 20g / L, peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, disodium hydrogen phosphate 2.7g / L, citric acid 1.2g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.25g / L, pH6.0, high temperature sterilization for 15min, 150r / min , 30°C, cultured for 18 hours; inoculated into 200ml fermentation medium with 5% inoculum size, the fermentation medium was: glucose 20g / L, peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, disodium hydrogen phosphate 2.7g / L, citric acid 1.2g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.25g / L, pH 6.0, 30°C, static culture for 72h, until the bacterial cellulose film is formed, take out the bacterial cellulose film, rinse with distilled...
Embodiment 2
[0058] According to the methods shown in Table 1, the modified bacterial cellulose membranes modified by acetylation, esterification, silane coupling agent, polymer and organic phosphine were prepared respectively. The addition amount of bacterial cellulose in the following modification method is 0.5g.
[0059] Table 1 Modification method of bacterial cellulose membrane
[0060]
[0061]
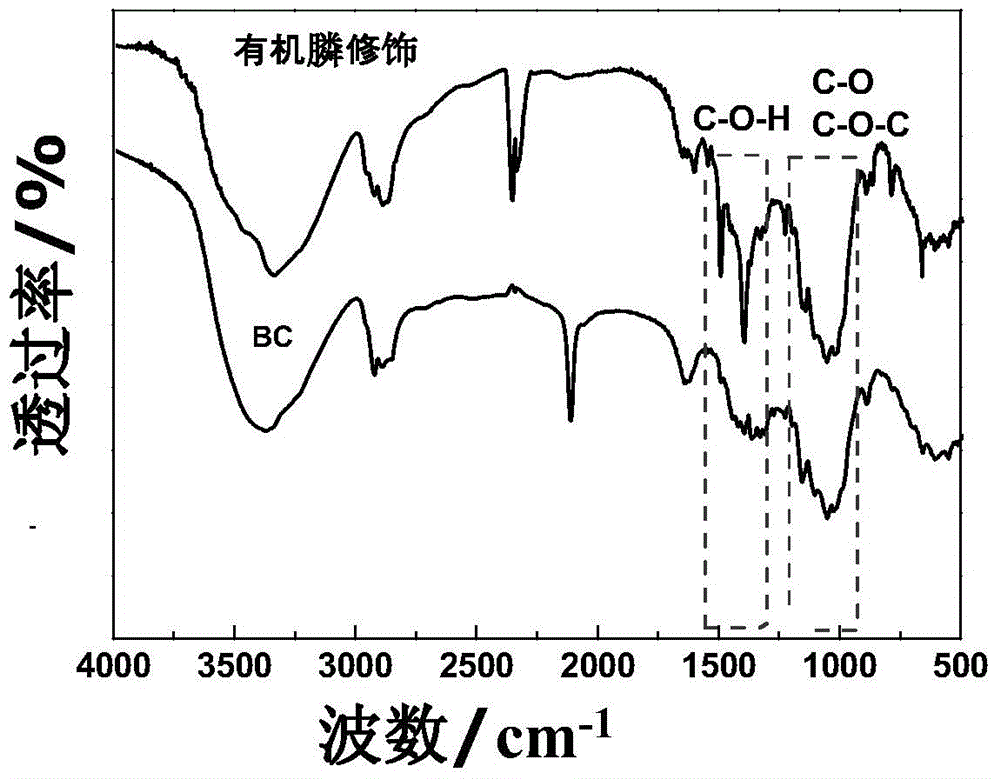
[0062] See the experimental results image 3 , 4 .
[0063] Such as image 3 , It can be seen from the characteristic peaks in the infrared spectrum: the characteristic peak of bacterial cellulose is 3450nm, O—H stretching vibration, 2920nm, CH2—CH stretching vibration, 900nm, glycosidic bond, 1059nm, C=O stretching vibration .
[0064] After organic phosphine modification, the peak at 2100nm disappeared, the peaks at 1500nm and 1400nm appeared, and the peak at 1000-1300nm was enhanced, indicating that the phosphoester bond appeared and strengthened. CO at 2400nm 2 absorption pe...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Preparation of Clostridium acetobutylicum cell liquid: Clostridium acetobutylicum B3 (CGMCC No.5234) preserved at -80°C was inoculated on the plate medium, and the plate medium was: glucose 5g / L, Peptone 5g / L, yeast powder 3g / L, ammonium acetate 2g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 3g / L, NaCl 2g / L, K2HPO4 1g / L, KH2PO4 1g / L, FeSO4 7H 2 O 0.1g / L, agar powder 15-20g / L, pH 6.0, 121°C, sterilized for 15 minutes; at 37°C, anaerobic culture for 24 hours, after the bacterial lawn grows, scrape the bacterial lawn and transfer to another plate After 12 hours, transfer again, scrape the lawn after 12 hours of cultivation, and transfer to 100ml seed medium, the seed medium is: glucose 5g / L, peptone 5g / L, yeast powder 3g / L, acetic acid Ammonium 2g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 3g / L, NaCl 2g / L, K2HPO4 1g / L, KH2PO4 1g / L, FeSO4 7H 2 O 0.1g / L, pH 6.0, high temperature sterilization for 15min, 37°C, static culture for 12h; inoculate 100ml fermentation medium with 10% inoculum size, the fermentation medium is: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com