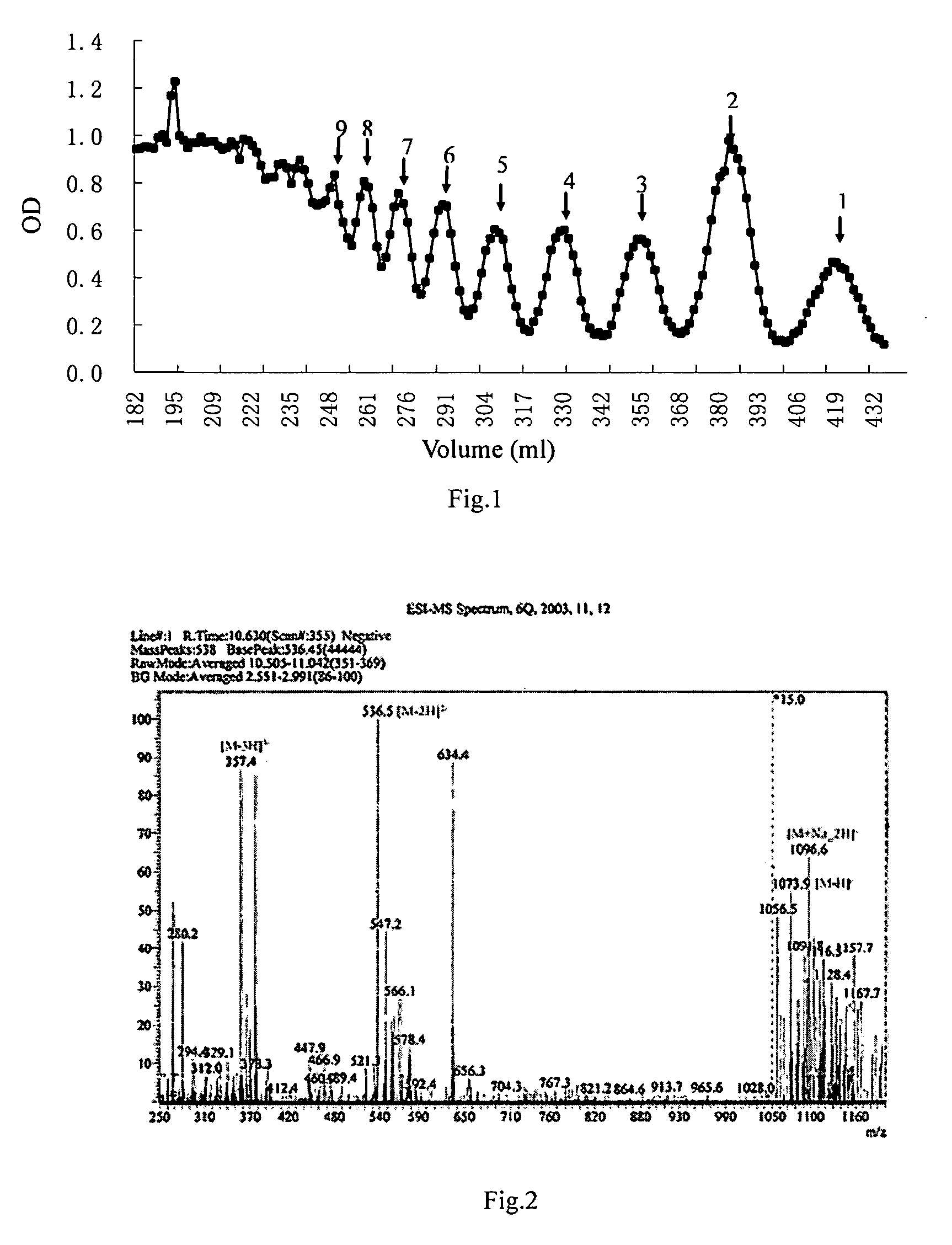
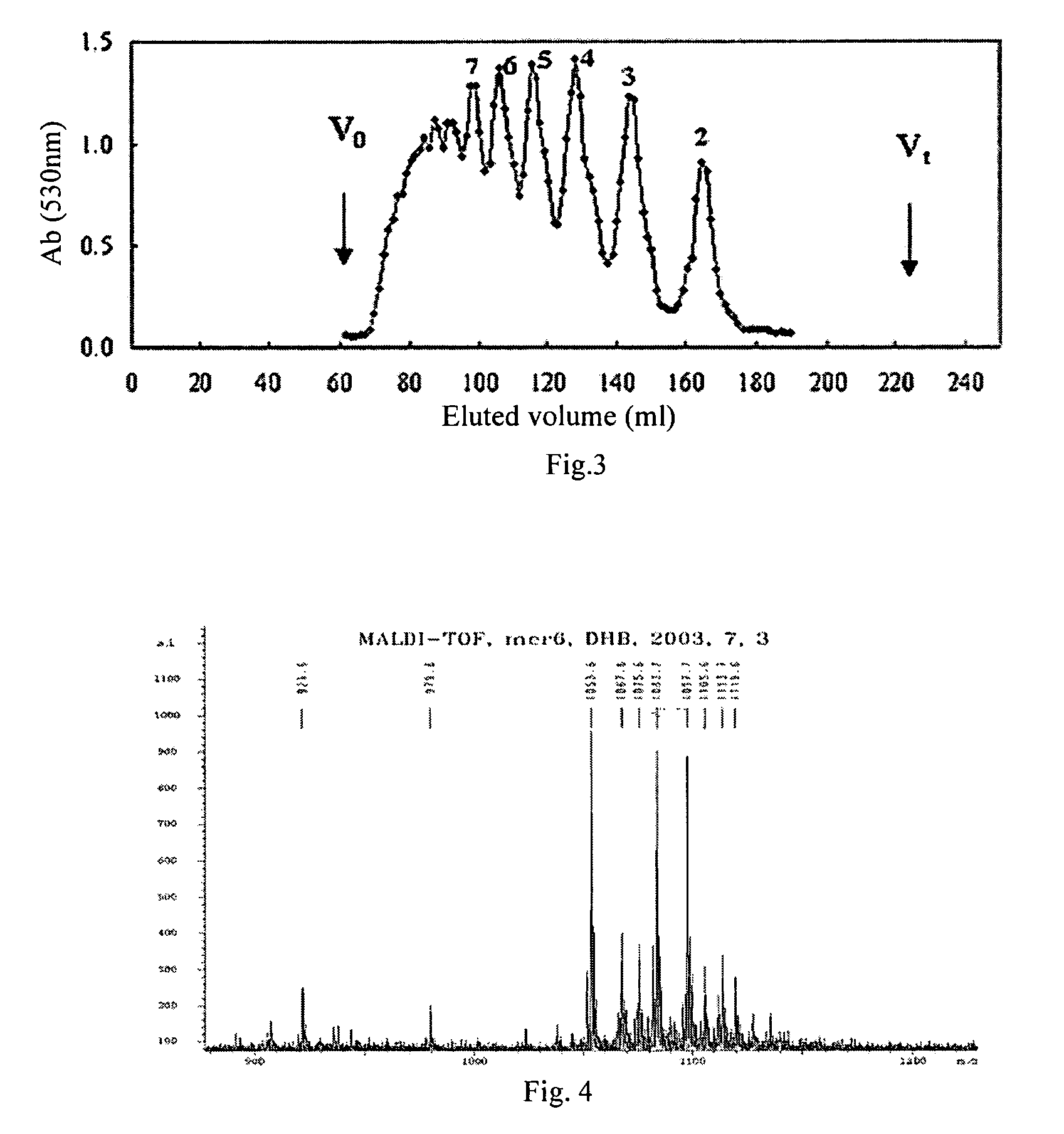
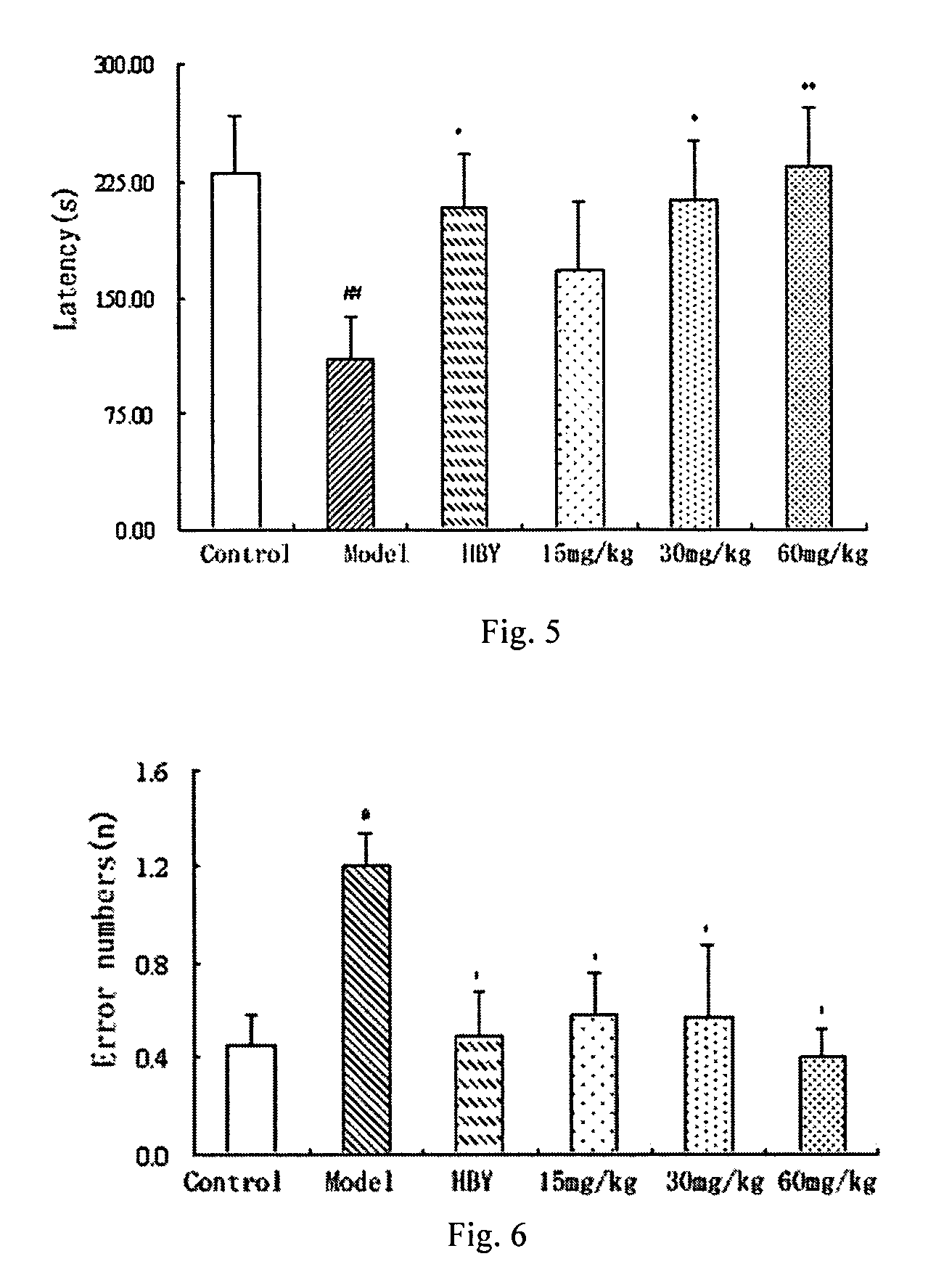
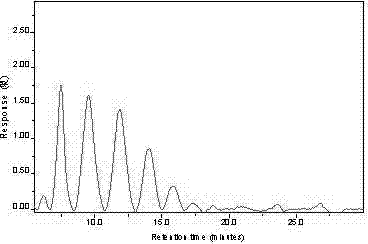
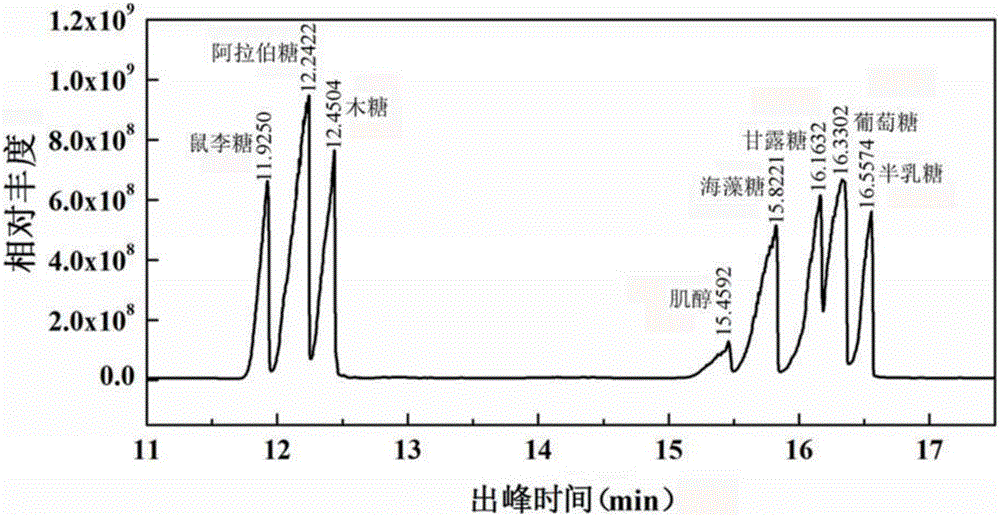
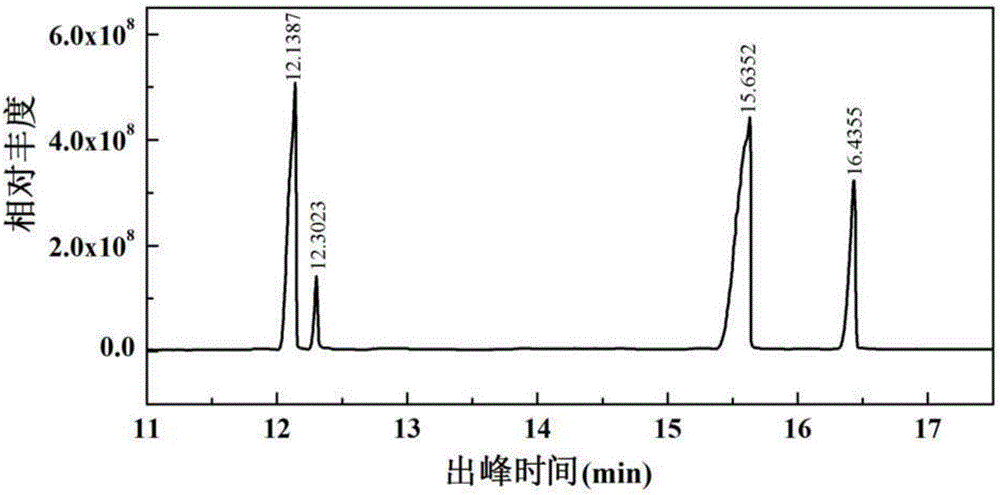
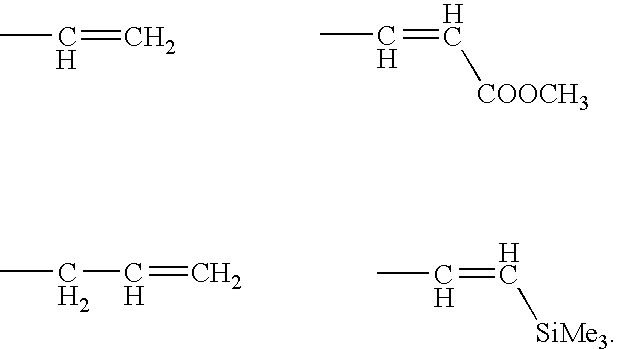
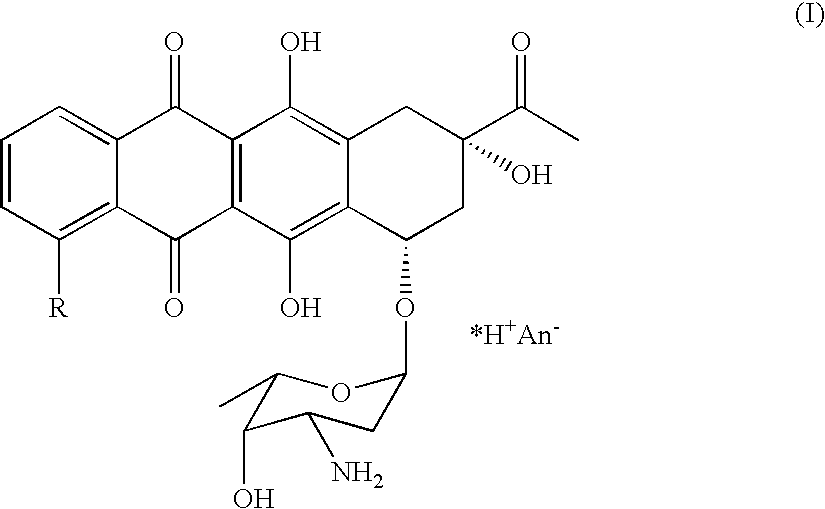
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
593 results about "Glycosidic bond" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
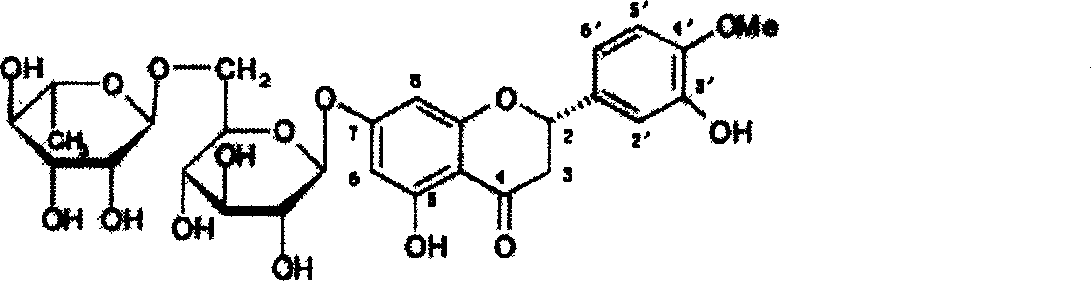
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate. A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide (or a molecule derived from a saccharide) and the hydroxyl group of some compound such as an alcohol. A substance containing a glycosidic bond is a glycoside.
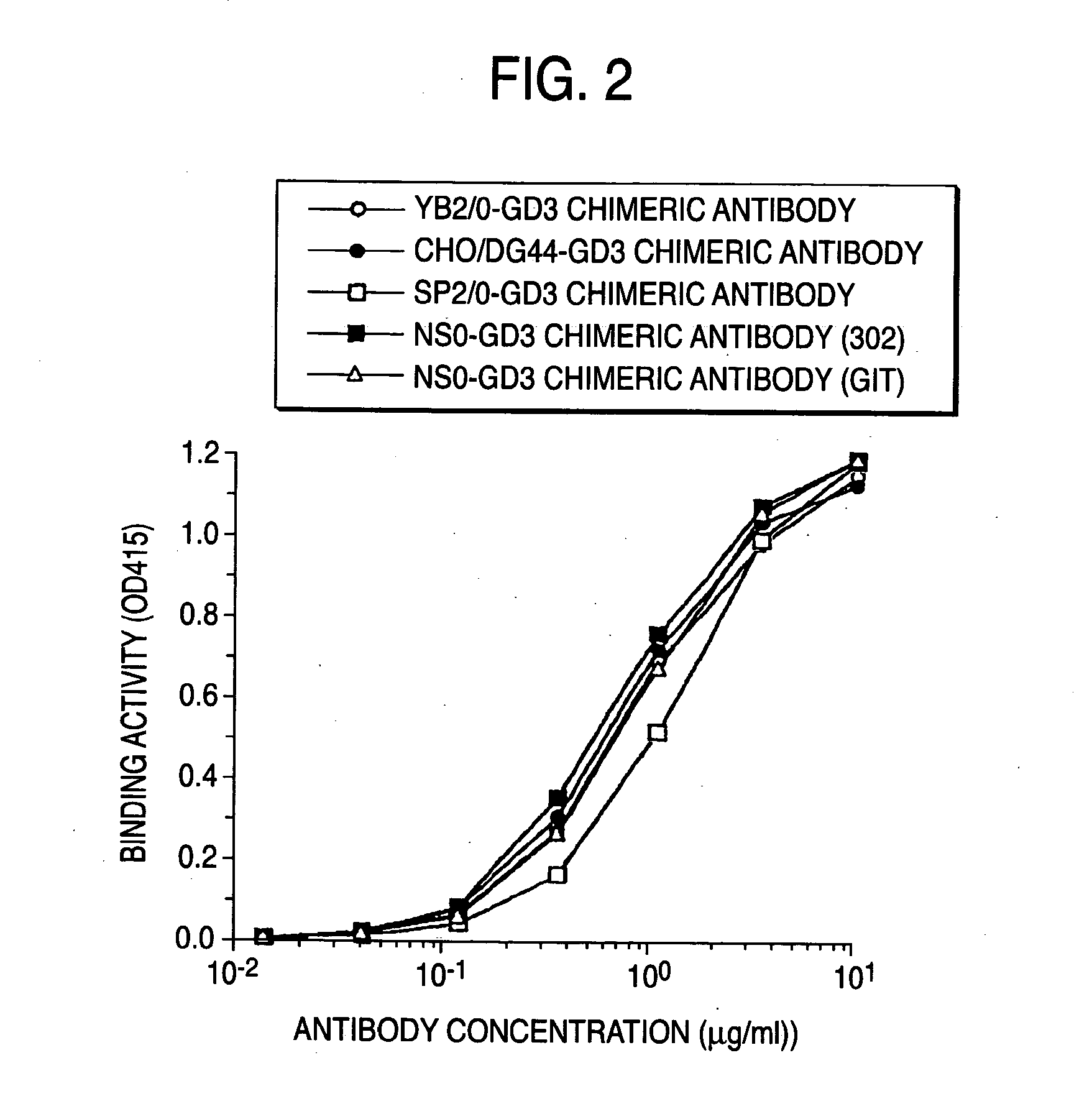
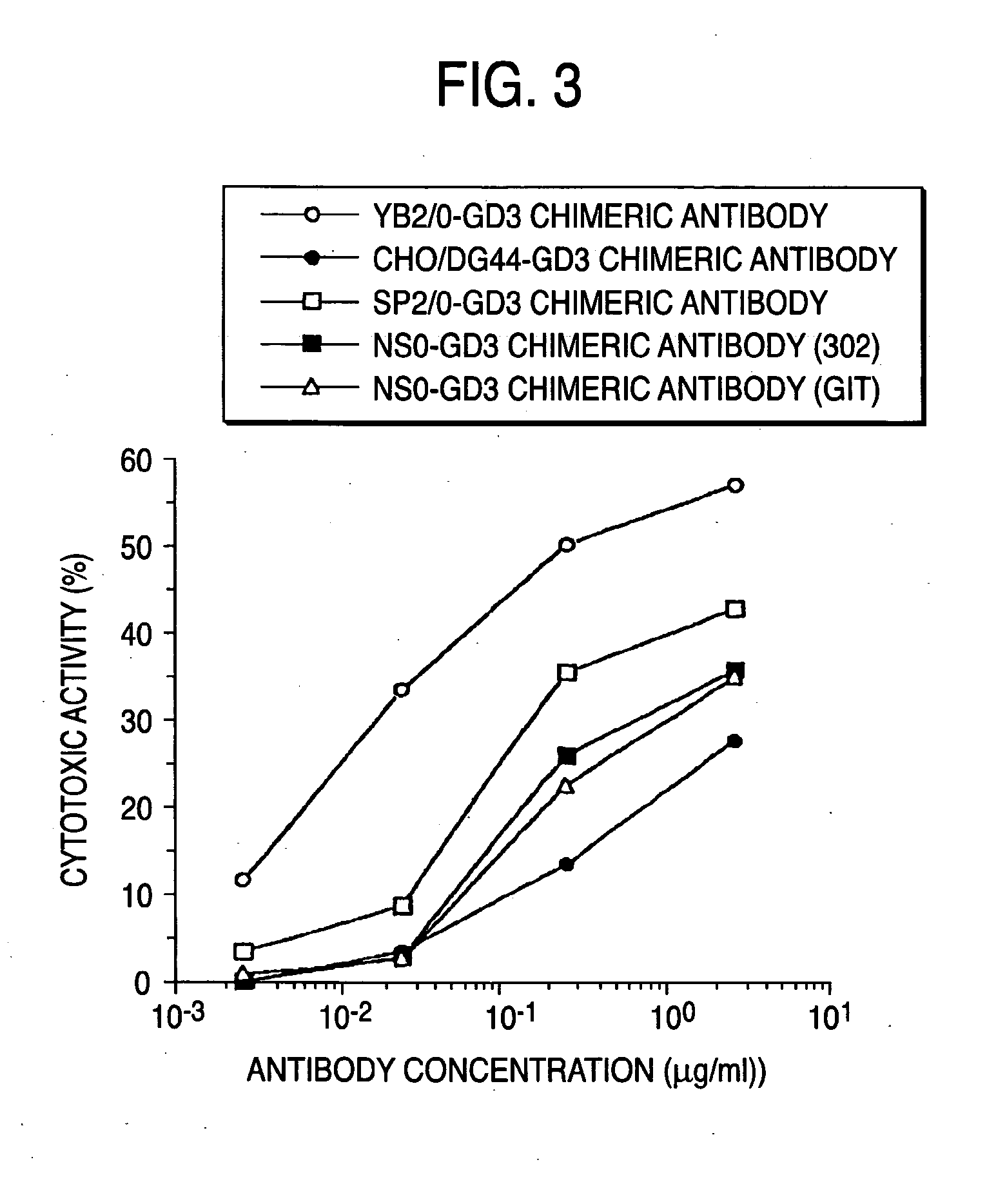
Method of enhancing of binding activity of antibody composition to Fcgamma receptor IIIa
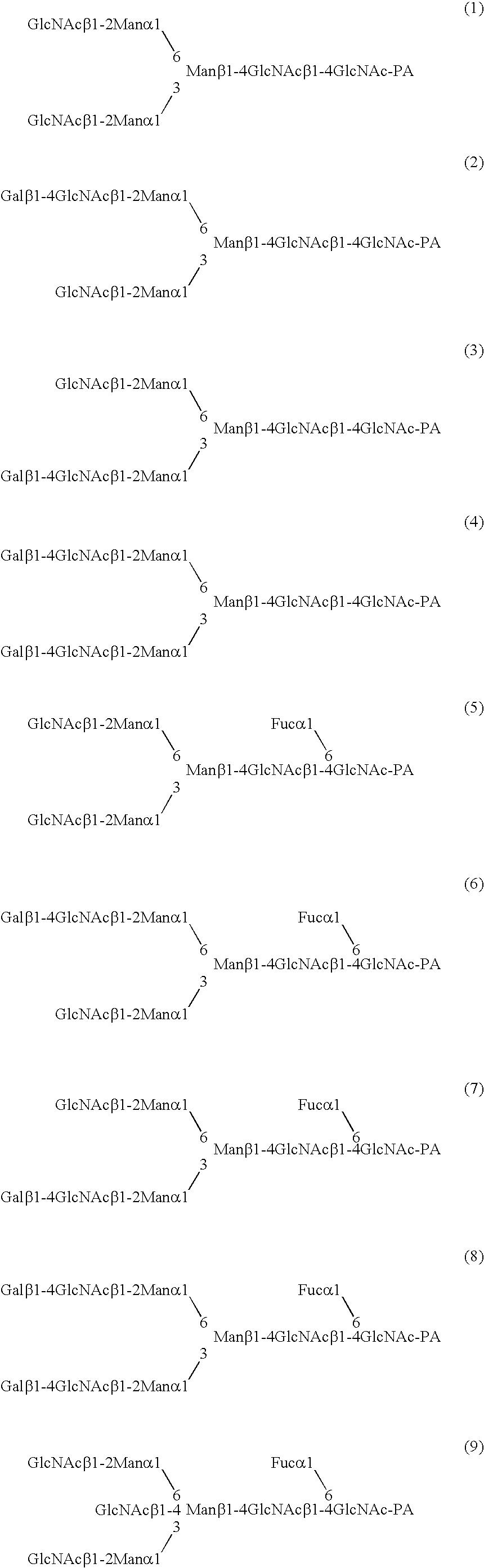
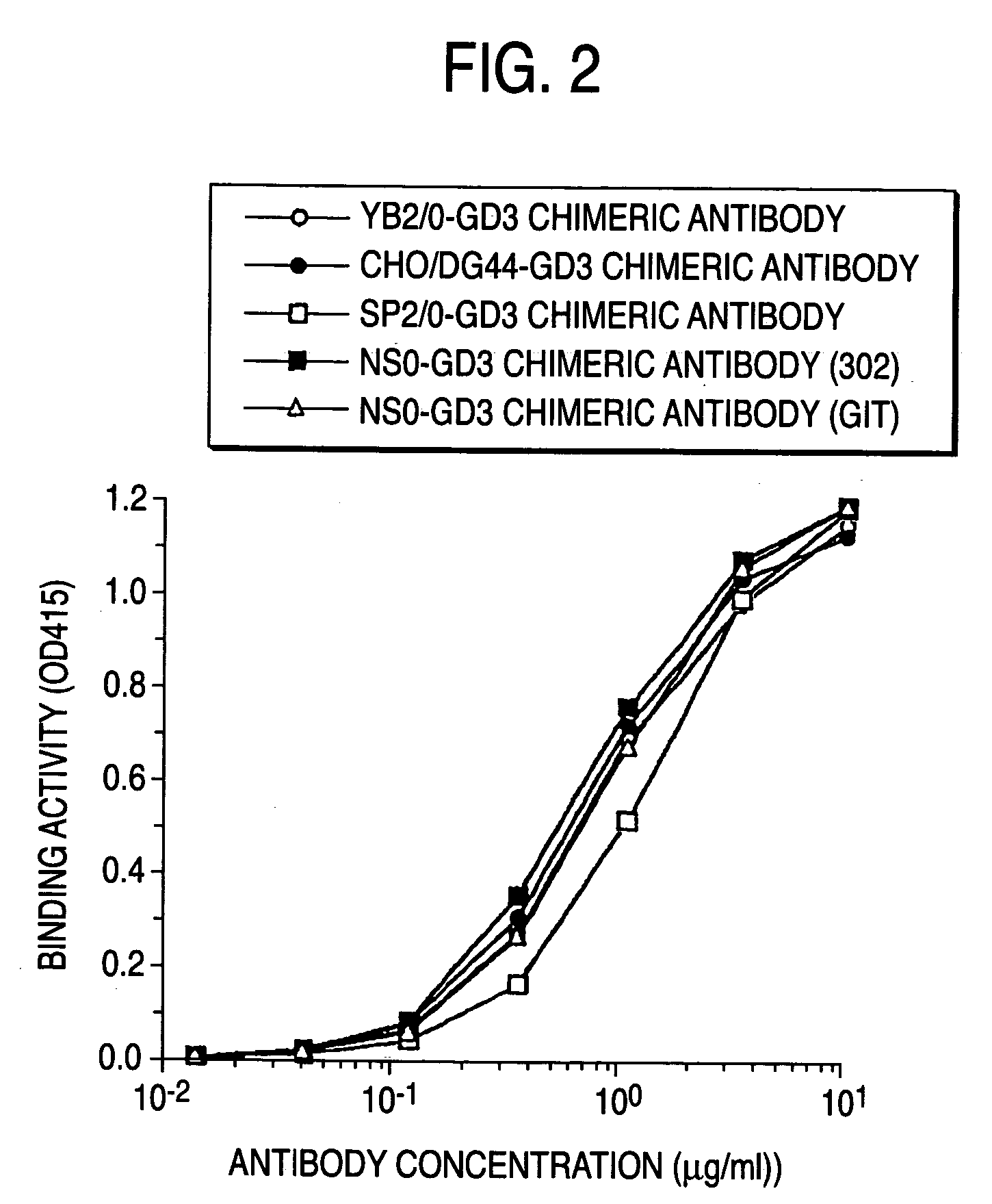
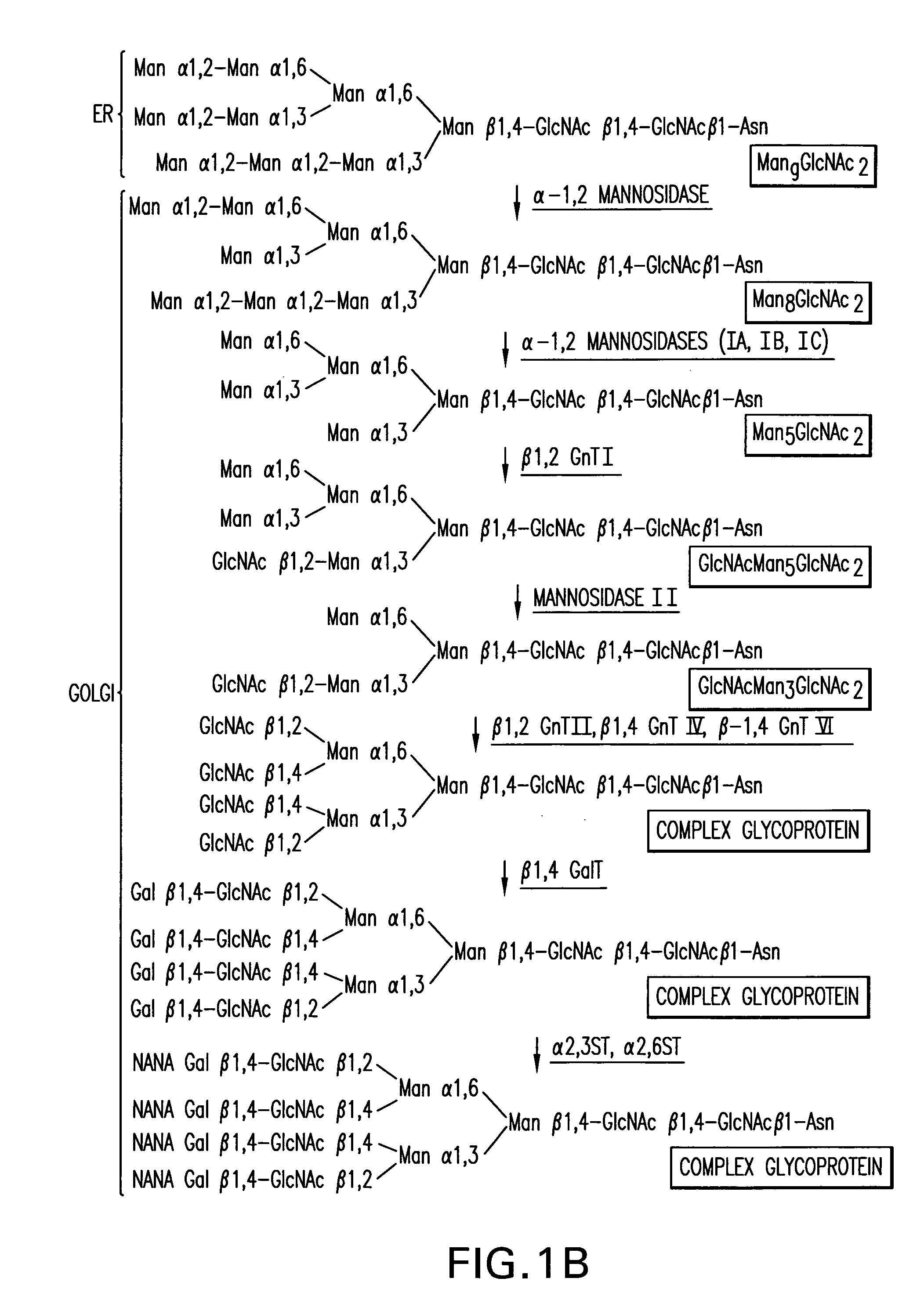
A method for enhancing a binding activity of an antibody composition to Fcgamma receptor IIIa, which comprises modifying a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain which is bound to the Fc region of an antibody molecule; a method for enhancing an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of an antibody composition; a process for producing an antibody composition having an enhanced binding activity to Fcgamma receptor IIIa; a method for detecting the ratio of a sugar chain in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chain among total complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chains bound to the Fc region in an antibody composition; an Fc fusion protein composition produced by using a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through alpha-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain; and a process for producing the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
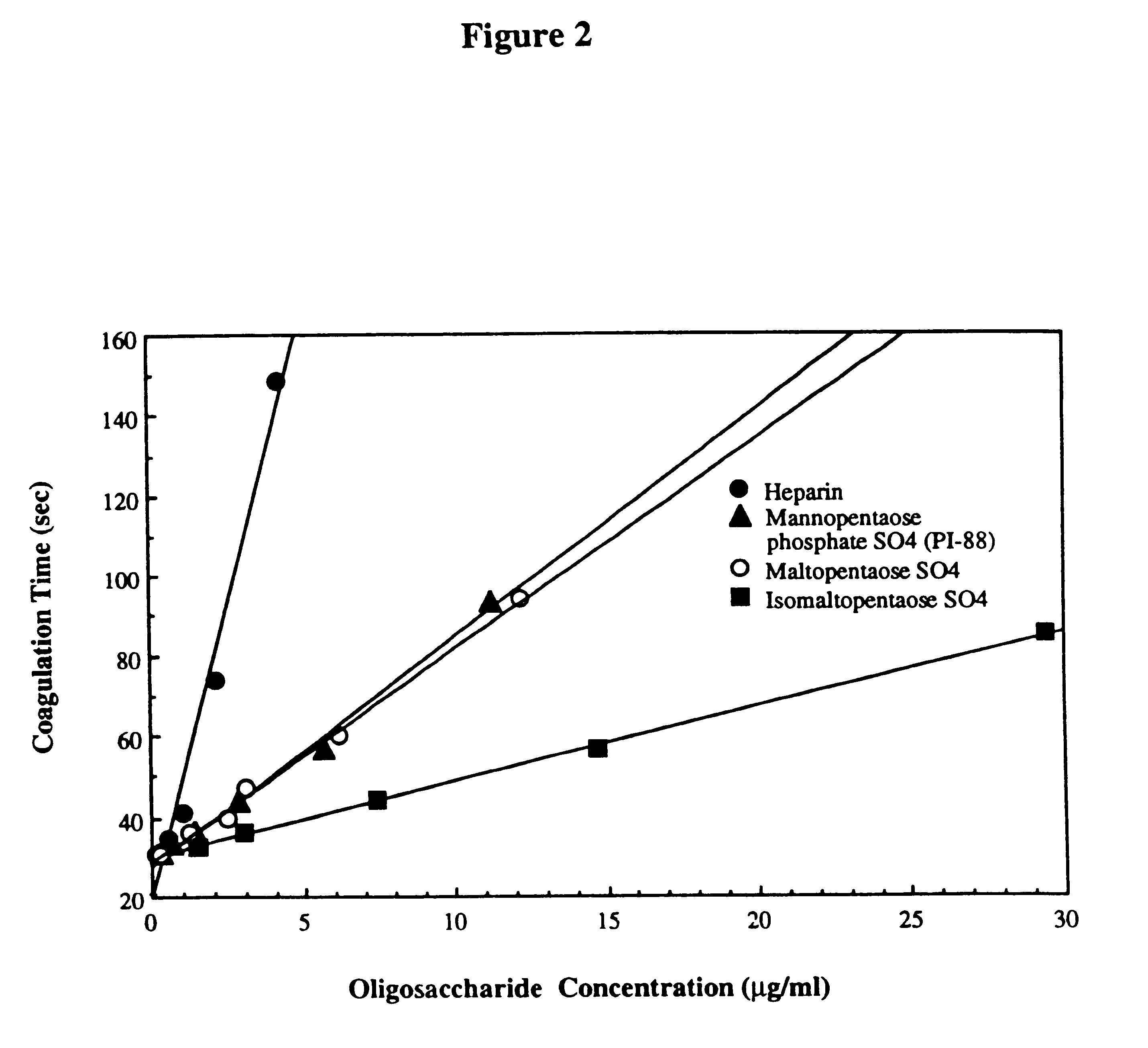
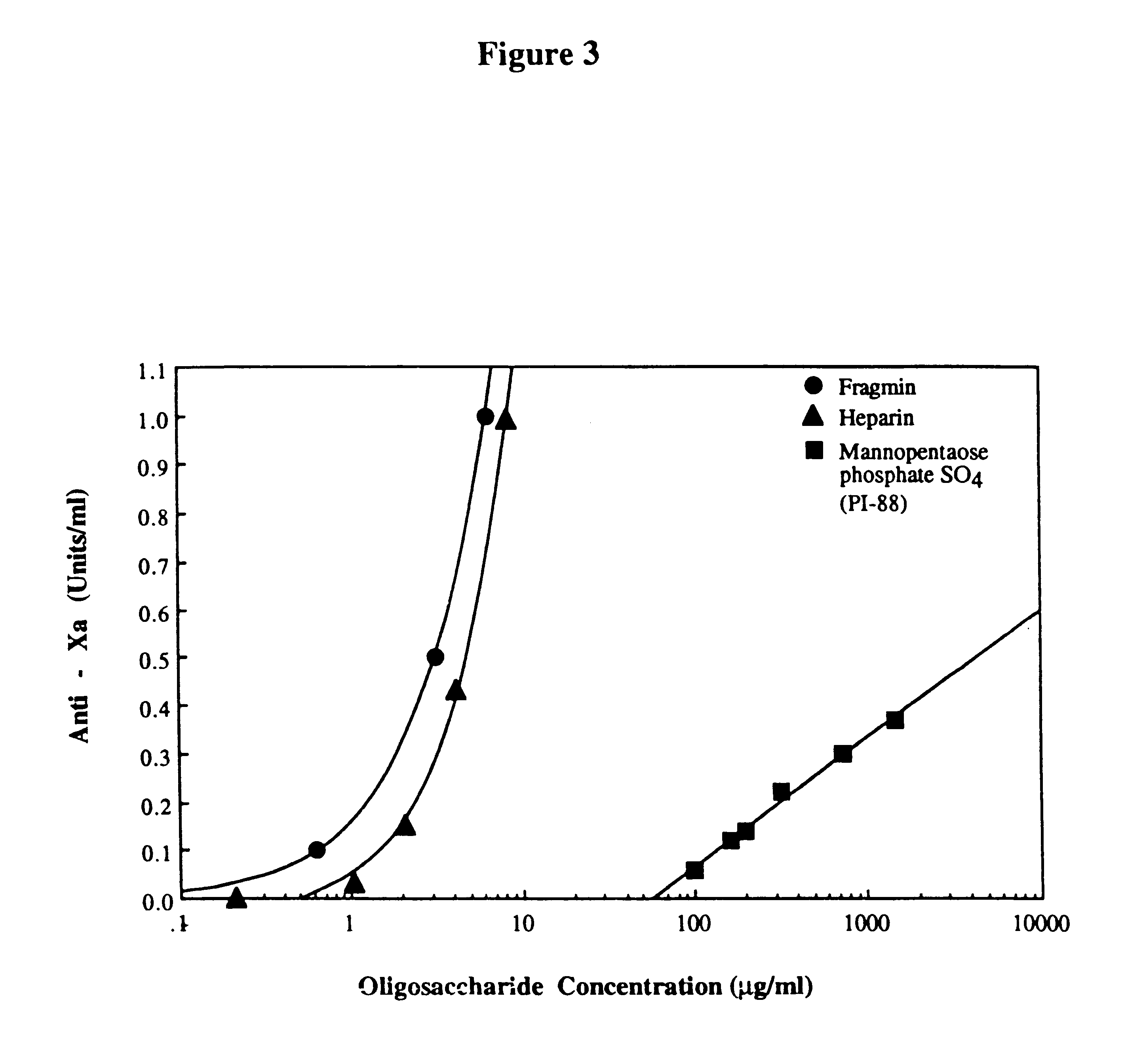
Preparation and use of sulfated oligosaccharides
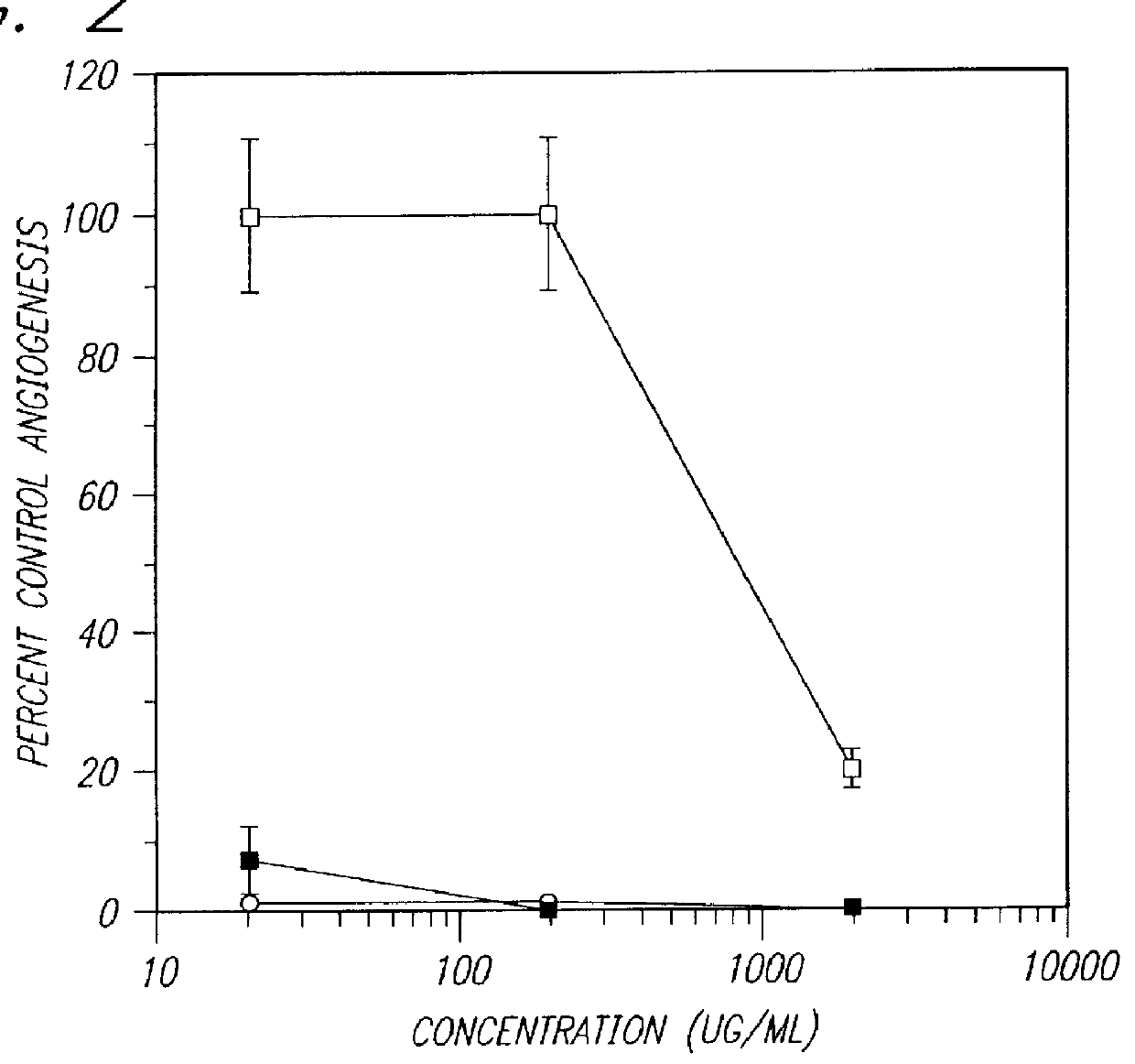
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00238 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 33726 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 31, 1996Sulfated oligosaccharides, wherein the oligosaccharide has the general formula I:R1-(Rx)n-R2(I)wherein R1 and R2 and each Rx represents a monosaccharide unit, all of which may be the same or different, adjacent monosaccharide units being linked by 1->2, 1->3, 1->4 and / or 1->6 glycosidic bonds and n is an integer of from 1 to 6, and use thereof as anti-angiogenic, anti-metastatic and / or anti-inflammatory agents.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Leaf fertilizer composition comprising sodium alginate oligosaccharide and application of leaf fertilizer composition
ActiveCN103011968AWide variety of sourcesLow priceOrganic fertilisersLiquid fertilisersManganeseUronic acid
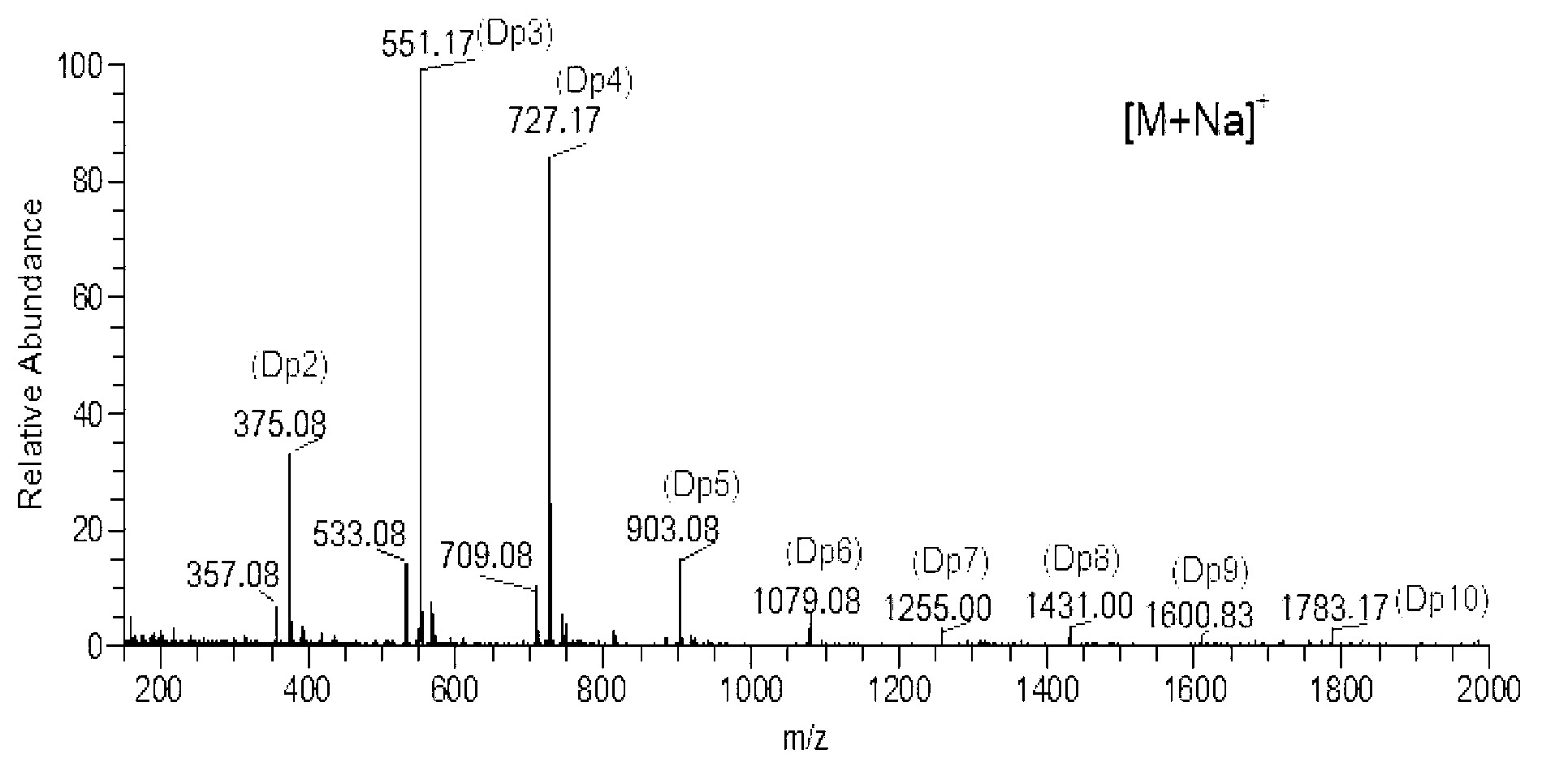
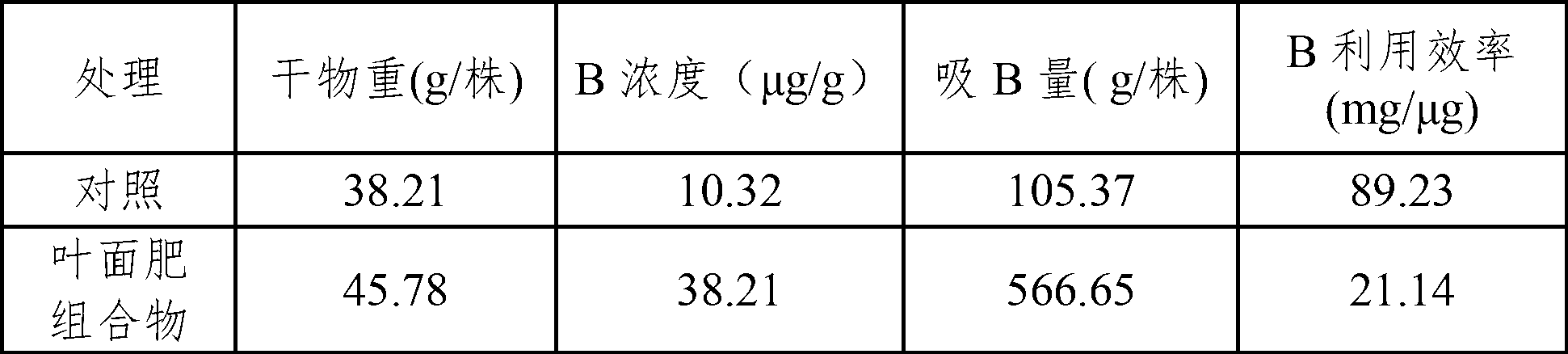
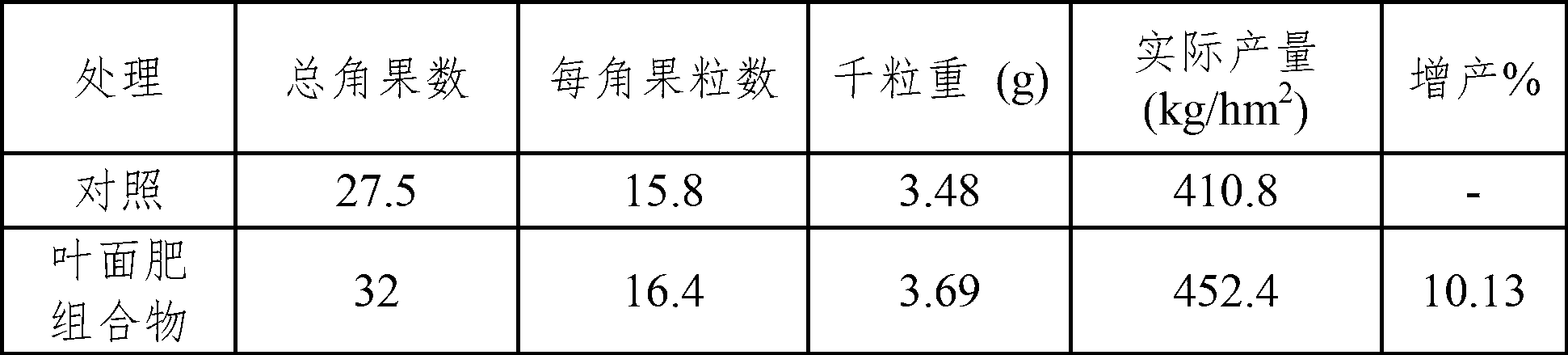
The invention discloses a leaf fertilizer composition comprising sodium alginate oligosaccharide, which is characterized in that the composition comprises sodium alginate oligosaccharide, amino acid and microelements that can promote plant growth significantly, wherein sodium alginate oligosaccharide is also known as sodium alginate, sea-tangle glue and algin, is natural polysaccharide carbohydrate extracted from sea tangle, and is a copolymer comprising a-L-mannuronic acid (M), b-D-guluronic acid (G) connected with a-L-mannuronic acid (M) by 1,4-glycosidic bond, and different GGGMMM fragments; a molecular formula is (C6H7O6Na)n; the degree of polymerization is 2-10; the uronic acid constitution M / G is equal to 7:3; the uronic acid content is greater than 90%, and is 2-3% of the total content; the content of a microelement leaf fertilizer is 2-20%; and the microelement leaf fertilizer comprises at least two of sulfur, boron, ferrum, manganese, copper, zinc and molybdenum. The composition is mainly applicable to industrial crops, fruit and vegetable crops, grain crops, economic trees, flowers, lawns and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof as well as the manufacture and the use of the same
The present invention provides an alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives with the degree of polymerization ranging from 2 to 22. The alginate oligosaccharide is composed of β-D-mannuronic acid linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. The derivatives with the reduced terminal in position 1 of carboxyl radical can be prepared by oxidative degradation. The present invention also provides a process for preparing the alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives, which includes the procedures that an alginate solution is reacted for 2 to 6 h in an autoclave at pH 2-6 and the temperature of 100-120° C., and pH is adjusted to 7 after the reaction is stopped, after which the resultant oligosaccharide is oxidized in the presence of an oxidant to obtain an oxidative degradation product. The alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives of the invention can be used in the manufacture of a medicament for the prophylaxis and treatment of AD and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Application of chitosanoligosaccharide and derivatives thereof in plant cold resisting
InactiveCN102771476AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePlant growth regulatorsBiocideGuanidine derivativesO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention discloses a wide-spectrum plant cold-resisting agent for plants such as food crops, economic crops, vegetables, fruit trees, economic trees, flowers, and lawns. The active component of the agent is chitosanoligosaccharide or a derivative thereof. The chitosanoligosaccharide is oligosaccharide of glucosamine linked through beta-1,4-glucosidic bond, and has a molecular weight of 300-10000Da, and a deacetylation degree of 50-100%. The chitosanoligosaccharide derivatives are chitosanoligosaccharide sulfuric acid derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide hydrochloric acid derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide phosphoric acid derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide sulfonamide derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide acyl isothiocyanate derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide phosphoric derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide guanidine derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide nicotinicacyl isothiocyanate derivative, chitosanoligosaccharide-cerium (IV) complex, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Algin oligose and derivative thereof and producing method and use thereof
ActiveCN100508985CAvoid difficultiesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlycosideDiabetes mellitus
The present invention provides algin oligosaccharides having polymerized degree of 2-22 and the derivatives thereof, such algin oligosaccharides are made of mannuronic acid bonded by [proportional to]-1,4 glycosidic bond. The derivatives which the reduced terminal in position-1 is carboxyl radical can be obtained by oxidation. The invention also provides the manufacture of algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof, which includes the alginate solution in water reacts in the reactor under the condition of high press, 100-120 DEG C, pH2-6, for 2-6 hours, after the reaction completed, its pH value was adjusted to 7. The result oligosaccharides are oxidated in presence of the oxidant, and then produces the oxidated products. The algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof of the invention can be used in the manufacture of medicaments for preventing Alzheimer's dementia and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Glucanases, Nucleic Acids Encoding Them and Methods for Making and Using Them
InactiveUS20110117067A1Low viscosityImprove textureAntibacterial agentsFungiNucleotideExoxylanase activity
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability, including thermotolerance or thermostability, at increased or decreased pHs and temperatures.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Wetting system
A wetting agent which does not present an overall sweet taste, and processes for making and using it. The wetting agent comprises i) at least 40 wt. % or higher of solids, based on total solids in the binder, of one or more fibrous ingredient and ii) at least 1 wt. % of a compound which includes glycerol and / or fatty acid moieties. In a preferred embodiment, the fibrous compound comprises dextrin, most preferably wheat dextrin. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, the wetting agent includes one or more fibrous ingredients having fewer than 70% glucosidic 1,4 linkages, more than 15% glucosidic 1,6 linkages, especially from 25% to 50%, at least 5% each of glucosidic 1,2 linkages and glucosidic 1,3 linkages and less than 5 wt. % mono- and disaccharides. The wetting agent is useful particularly for savory food bars. The invention is also directed to a process of using the wetting agent by applying it to dried food ingredients to rehydrate the foods and to the rehydrated food ingredients per se.
Owner:SLIM FAST FOODS
Expression of class 2 mannosidase and class III mannosidase in lower eukaryotic cells
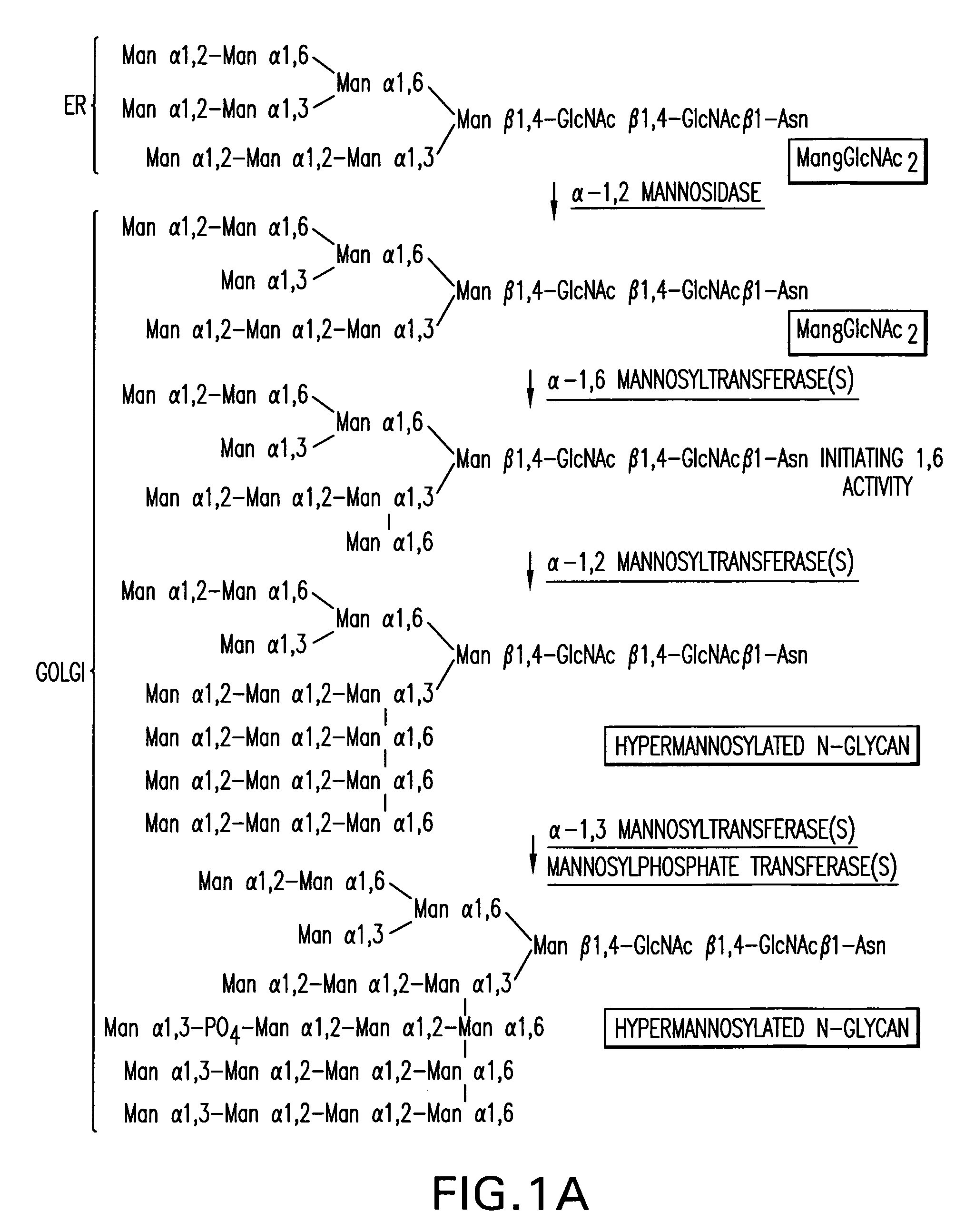
A method for producing human-like glycoproteins by expressing a Class 2 α-mannosidase having a substrate specificity for Manα1,3 and Manα1,6 glycosidic linkages in a lower eukaryote is disclosed. Hydrolysis of these linkages on oligosaccharides produces substrates for further N-glycan processing in the secretory pathway.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide
ActiveCN105061617AHigh purityThe preparation method is fineMetabolism disorderGlucose degradationPrecipitation
The invention discloses an extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD). The process includes: water extraction and alcohol precipitation, protein removal by a Sevage reagent, dialysis, passing of a column with DEAE cellulose as the filler and other steps, thus obtaining finer polysaccharide (PGPSD). The PGPSD can be dissolved in water at room temperature, and is formed by connection of arabinose, mannose and galactose through a glycosidic bond. The peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD) prepared by the process provided by the invention can reinforce the expression of insulin related transcription factors and glucose degradation key enzyme, has no toxicity to mice, and can significantly lower the blood glucose of diabetic mice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
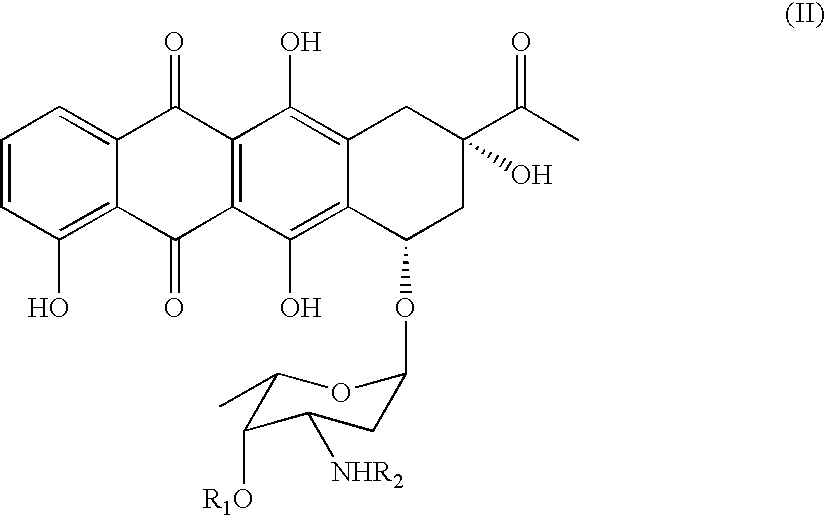
Method of preparing 4-R-substituted 4-demethoxydaunorubicin
ActiveUS7053191B2Reduce in quantityImprove processing yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPtru catalystAcyl group
A method of synthesizing 4-R-substituted anthracyclines and their corresponding salts from 4-demethyldaunorubicin includes the steps of treating 4-demethyldaunorubicin with a sulfonylating agent to form 4-demethyl-4-sulfonyl-R3-daunorubicin. 4-Demethyl-4-R3-sulfonyl-daunorubicin is then subject to a reducing agent in the presence of a transition metal catalyst in a temperature range of about 30° C. to about 100° C. in a polar aprotic solvent in an inert atmosphere. Protected 4-demethoxy-4-R-daunomycin then undergoes hydrolysis in a basic solution to form the 4-R-substituted anthracyclines. The novel method lacks the step of forming a stereospecific glycoside bond between aglycone and aminoglycoside. The method also increases the yield of the final product up to 30 to 40%.
Owner:SYNBIAS PHARMA
Method of Enhancing of Binding Activity of Antibody Composition to FcGamma Receptor IIIa
A method for enhancing a binding activity of an antibody composition to Fcγ receptor IIIa, which comprises modifying a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain which is bound to the Fc region of an antibody molecule; a method for enhancing an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of an antibody composition; a process for producing an antibody composition having an enhanced binding activity to Fcγ receptor IIIa; a method for detecting the ratio of a sugar chain in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chain among total complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chains bound to the Fc region in an antibody composition; an Fc fusion protein composition produced by using a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain; and a process for producing the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Preparation method for soluble dietary fiber with apple pomace as raw material
The invention discloses a preparation method for a soluble dietary fiber with apple pomace as a raw material. According to the method, an expanding method and an enzymatic hydrolysis method are combined. By the application of an expansion process, the structures of cellulose molecules become loose, and partial glycosidic bonds are broken, so that partial insoluble dietary fibers are transformed into soluble ones. After separation of the insoluble dietary fibers and the soluble dietary fibers, the expanded insoluble dietary fibers, which have the loose molecular structures, are hydrolyzed by utilizing a cellulase; and then the insoluble dietary fibers are further transformed into soluble dietary fibers. According to the invention, the modification of the insoluble dietary fibers in the apple pomace enables the insoluble dietary fibers to become high-quality soluble dietary fibers, so that an achievement rate of the soluble dietary fibers can substantially be enhanced as well as water binding capacity and expansibility of dietary fibers can also be improved. According to the test, the achieve rate of the soluble dietary fibers can reach 21.2%; the water binding capacity and expansibility can be enhanced by 110.3% and 7.0% respectively.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Sulfated oligosaccharides having anticoagulant/antithrombotic activity
A method for the anticoagulant and / or antithrombotic treatment of a human or other warm-blooded animal patient in need of such treatment, comprises administration to the patient of an effective amount of at least one sulfated oligosaccharide, wherein the oligosaccharide has the general formula I:wherein R1 and R2 and each Rx represents a monosaccharide unit, all of which may be the same or different, adjacent monosaccharide units being linked by 1->2, 1->3, 1->4 and / or 1->6 glycosidic bonds andn is an integer of from 1 to 6.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Microorganisms or/and biological enzyme extracting method for plant anthocyanin
InactiveCN101760497AEfficient use ofMake full use ofOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIntestinal microorganisms
The invention relates to a Microorganisms or / and biological enzyme extracting method for plant anthocyanin, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying plants containing anthocyanin for smashing, adsorbing water, freezing the plants, heating the plants for thawing, pressing the plants, filtering for making juice, cracking and degrading the anthocyanin by the microorganisms or / and the biological enzyme cracking anthocyanin glycosidic bond, utilizing an anion active agent for precipitation reaction, degrading the precipitate by the microorganisms, and carrying out precipitation separation and evaporation concentration. Cation anthocyanin with the real content of more than 95%, namely color primitive but not the anthocyanin can be obtained by the technology of the invention. The cation anthocyanin made by the invention does not need human intestinal microorganisms for degrading, and is directly adsorbed and utilizedby a human body or directly goes into human blood. The medical care value of the plant anthocyanin is much higher than that of the anthocyanin.
Owner:安徽天紫花青素科技有限公司
Water-soluble Chitooligosaccharide preparation method
InactiveCN1544479AImprove anti-tumor activitySimple processSemi-permeable membranesUF - UltrafiltrationGlycosidic bond
The invention relates to a process for preparing water-soluble chitooligosacchrides, which is prepared by utilizing the difference of recognition capability and disengagement capability of enzymes to different glycosidic bonds and the inhomogeneous distribution of acetylaminos in chitosan raw material. The invention realizes simple process, wherein at the same time of preparing Chitosan oligosaccharide, 8-200 polymerization degree of water-soluble chitooligosacchride can be achieved simultaneously through the method of ultrafiltration membrane separation. The product obtained thereby has exhibites antineoplastic action and immunologic enhancement.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Process for the preparation of homopolysaccharides
ActiveUS20110151517A1High specific viscosityReduce contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMembranesHomopolysaccharideGlycoside formation
A process for the preparation of aqueous solutions of glucans having a β-1,3-glycosidically-linked main chain and side groups having a β-1,6-glycosidic bond by fermentation of fungal strains. The fungal strains secrete the glucans into the fermentation broth, in an aqueous culture medium, and the separation of the glucans from the fermentation broth is effected using asymmetrical filter membranes.
Owner:WINTERSHALL HLDG
α-Isomaltosyltransferase, process for producing the same and use thereof
InactiveUS7192746B2Easy to collectSatisfactory thermalCosmetic preparationsDough treatmentGlycosideD-Glucopyranose
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
Method for hydrolytic preparing biological tangeritin by enzyme
InactiveCN101089187AControl the hydrolysis processEasy to separate and purifyFermentationNaringinCitrus Bioflavonoids
In the invented method, citrus bioflavonoid and corresponding enzyme are used as raw materials, being dissolved in organic solvent, adding glucoside solution at concentration of 1-100g / L, under pH value of 3.0-7.0 and temperature of 20-65 deg.C for 20-60 min. After separation and purification, obtained is citrus bioflavonoid monoglycoside. With this invention, naringoside enzymolysis and cirmtim enzymolysis method for production of naringen in monoglycoside and hesperetin monoglycoside, compared with chemical method, has advantages of:easily to be controlled of enzymolysis, mild reaction, less by-products and easy to be separated of products. By using this invented method, the enzymolysis of naringoside and cirmtim for production of naringenin monocoside and hesperetin monoglycoside can be effectively controlled, and only the first glycosidic bond is broken, so obtained is highest yield of naringenin monoglycoside, hesperetin monoglycoside and rhamnose.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Beta-glucosidase as well as preparation method and application thereof
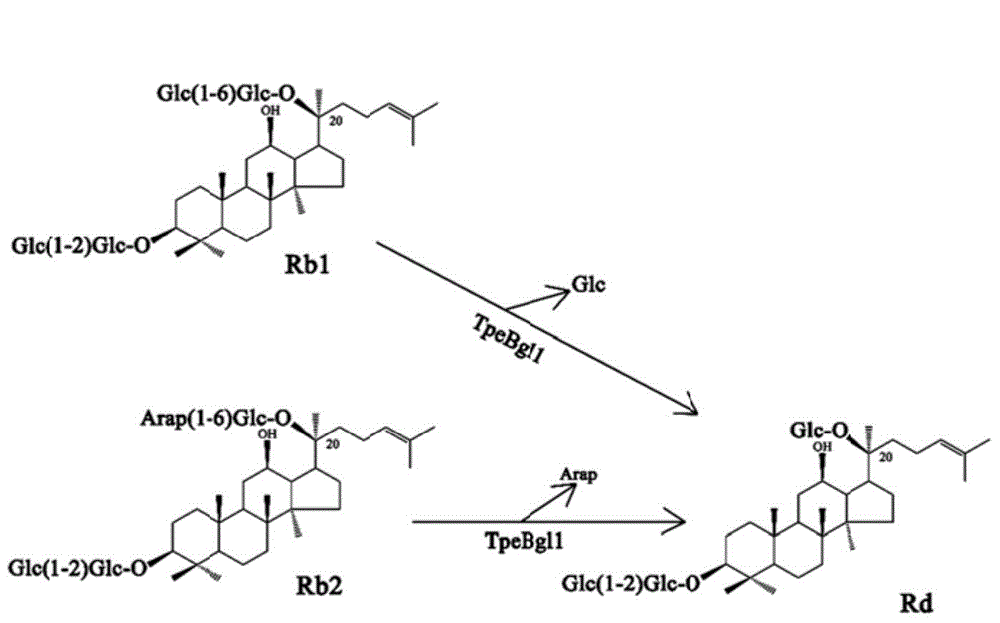
ActiveCN104611313AGood thermal stabilityStrong conversion abilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAlgluceraseGinsenoside Rb1
The invention provides a beta-glucosidase as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of beta-glucosidase is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The beta-glucosidase has excellent thermal stability, can resist high temperature, has higher beta-1,6-glucosidic bond hydrolysis capacity as well as higher alpha-1,6-arabinopyranoside bond hydrolysis capacity and has higher transformation capacity for ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2. After the beta-glucosidase is incubated with the ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 for certain period, ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 are almost transformed into ginsenoside Rd completely. According to a preparation method of TPEBGL1, high-efficiency expression can be realized without an inducer IPTG (isopropyl beta-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside).
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Probiotics and prebiotic compound preparation
PendingCN106617091ARapid stimulation of reproductionIncrease vitalityFood ingredient functionsOligosaccharide food ingredientsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHENGDANGNIAN BIO TECH CO LTD
Carbon-based solid acid, catalyst comprising the solid acid, and reaction using the solid acid as catalyst
InactiveUS8013130B2High total acid contentMinimizationOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbonizationSolid acid
A carbon-based solid acid which has high activity and high thermal stability and is useful as an acid catalyst for various reactions such as hydration of olefins.The carbon-based solid acid for use as a catalyst is obtained by carbonization and sulfonation of an organic substance, which has a reduction rate of 10 mol % or less of acid content as measured by immersing the solid acid in hot water at 120° C. for 2 hours, is used as the acid catalyst.The organic substance to be used as the raw material for preparing the solid acid is preferably a saccharide having β1-4 glycosidic bond (e.g. cellulose) or lignin. Amylose is also suitable as the raw material. Examples of the reaction for which the solid catalyst can be used include hydration of olefins, etherification of olefins, and acid / alcohol esterification.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP +1
Method for remodelling cell wall polysaccharide structures in plants
InactiveUS20030159178A1Reduce the ratioImprove gel propertiesSurgical adhesivesDead animal preservationReticulum cellNucleotide
Methods for providing transgenic plants and parts hereof that, relative to the wild type state, is modified in a complex cell wall polysaccharide structure including pectins and hemicelluloses, the modification being in the overall glycosidic linkage pattern or the monosaccharide profile, comprising transforming a plant cell with a nucleotide sequence that causes an altered production of a complex cell wall polysaccharide-modifying enzyme such as endo-rhamnogalacturonan hydrolase, an endo-rhamnogalacturonan lyase, an endo-galactanase, an endo-arabinanase, an arabinofuranosidase, a galactosidase such as a beta-galactosidase, a xylosidase and an exo-galacturosidase. The modification can occur in vivo or post harvest, in which latter case the modifying enzyme is separated in the growing plant from its substrate, e.g. by targeting the enzyme to the Golgi, the endoplasmic reticulum or a vacuole, or is in a form that is inactive in the plant. After harvest the enzyme is brought into contact with its substrate or it is activated to provide the desired post harvest modification of the cell wall polysaccharide. The transgenic plant materials have improved functionalities and are useful in food and feed manufacturing and as pharmaceutically or medically active substances.
Owner:POALIS
Preparation method for k-carrageenan oligosaccharide with low polymerization degree
The invention discloses a preparation method for k-carrageenan oligosaccharide with a low-polymerization degree. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out enzymolysis preparation on the k-carrageenan; and separating and purifying the degradation products to obtain pure k-carrageenan oligosaccharide mixing component. The preparation method is characterized in that carrageenan degradative enzyme is obtained from a marine microorganism Cellulophaga lytica strain: N5-2(NCBI (National Center of Biotechnology Information), GENBANKD registry number being GU129978) and used for degrading the k-carrageenan to obtain the k-carrageenan oligosaccharide mixture with the low polymerization degree. The enzyme is an extracellular enzyme, can be acted to beta-1,4 glucosidic bond of the k-carrageenan, wherein the acting sites are respectively octasaccharide and hexaose; and the product is low-polymerization degree oligosaccharide consisting of disaccharide repeating units. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is low in cost and simple. Compared with the methods such as chemical method and a physical method, the obtained product is single, the side products are less and the large-scale production is convenient.
Owner:WEIHAI KANGBOER BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Comprehensive utilization process for marine fish skins
ActiveCN102676619AEfficient extractionImprove utilization efficiencyConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsMarine fishAquatic animal
The invention relates to the field of preparation of marine active substance from byproducts processed by aquatic animals and aims at providing a process for extracting collagen and dermatan sulfate by comprehensively utilizing marine fish skins. The process comprises the steps of fish skin treatment, removal of impure protein of the fish skin, removal of fat of the fish skin, fish skin enzymolysis, collagen salting, collagen collection, collagen dialysis and lyophilization, dermatan sulfate glucosidic bond protection, dermatan sulfate precipitation, dermatan sulfate purification and the like. According to the process disclosed by the invention, the active substances can be extracted from the marine fish skins simply, quickly and efficiently, the aim of cogenerating the collagen with the dermatan sulfate is achieved, the utilization benefits of the fish skins are increased and economic benefits are increased. The process is simple and feasible, high in extraction efficiency and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Exoinulinase Z2-5 with low-temperature activity and gene of exoinulinase Z2-5
The invention relates to exoinulinase Z2-5 with low-temperature activity and a gene of the exoinulinase Z2-5. An amino acid sequence of the exoinulinase Z2-5 from sphingobacterium sp. is shown as SEQIDNO.1. The invention provides the gene Z2-5 encoded with the exoinulinase, and a recombinant vector and a recombinant strain of the exoinulinase gene Z2-5. The exoinulinase has the properties that the optimum pH value is 7; after the exoinulinase is treated by a 0.1 M buffer solution of which the pH value is 9.0 at room temperature for 1 hour, the activity of the exoinulinase also can be kept at over 30 percent; the optimum temperature is 40 DEG C, the enzyme activity of the exoinulinase is about 40 percent at the temperature of 10 DEG C and 50 DEG C, and the enzyme activity of the exoinulinase is about 10 percent at the temperature of below 0 DEG C; after the exoinulinase is treated at the temperature of 50 DEG C for 1 hour, the enzyme activity of exoinulinase also can be kept at over 30percent; and substrates of cane sugar, fructosan and the like can be hydrolyzed, so the exoinulinase belongs to the reaction selectivity of the hydrolysis of a fructose glycosidic bond. By the exoinulinase Z2-5, synanthrin can be hydrolyzed to prepare high fructose corn syrup, so the exoinulinase Z2-5 is used for food industry.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof as well as the manufacture and the use of the same
The invention provides an alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives with the degree of polymerization ranging from 2 to 22. The alginate oligosaccharide is composed of β-D-mannuronic acid linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. The derivatives with the reduced terminal in position 1 of carboxyl radical can be prepared by oxidative degradation. The invention also provides a process for preparing the alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives, which includes the procedure that an alginate solution is reacted for 2 to 6 h in an autoclave at pH 2˜6 and the temperature of 100˜120° C., and adjusted pH to 7 after the reaction is stopped, after which the resultant oligosaccharide is oxidized in the presence of an oxidant to obtain an oxidative product. The alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives of the invention can be used in the manufacture of a medicament for the prophylaxis and treatment of AD and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Aminoalkyl glucosaminide phosphate compounds and their use as adjuvants and immunoeffectors
Aminoalkyl glucosaminide phosphate (AGP) compounds that are adjuvants and immunoeffectors are described and claimed. The compounds have a 2-deoxy-2-amino glucose in glycosidic linkage with an aminoalkyl (aglycon) group. Compounds are phosphorylated at the 4 or 6 carbon on the glucosaminide ring and comprise three 3-alkanoyloxyalkanoyl residues. The compounds augment antibody production in immunized animals as well as stimulate cytokine production and activate macrophages. Compositions and methods for using the compounds as adjuvants and immunoeffectors are also disclosed.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Resistant malt dextrin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the functional food field and in particular relates to resistant malt dextrin and a preparation method thereof. The resistant malt dextrin disclosed by the invention comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 24%-40% of (alpha-1),6-glucosidic bond, 3%-6% of (alpha-1),2-glucosidic bond, 5%-10% of (alpha-1),3-glucosidic bond, and 44%-68% of (alpha-1),4-glucosidic bond. The preparation method of the resistant malt dextrin comprises the following steps: (1), preparing roasted dextrin by roasting starch, and preparing a roasted dextrin aqueous solution; (2), adjusting the pH value of the roasted dextrin aqueous solution to 7.0-8.0, and adding alpha-amylase for carrying out hydrolysis; (3), inactivating the alpha-amylase when the DE (Dextrose Equivalent) value of the roasted dextrin aqueous solution reaches 10-20, and filtering to obtain a hydrolysis intermediate product; and (4), hydrolyzing the hydrolysis intermediate product by starch branching enzyme to prepare the resistant malt dextrin. The resistant malt dextrin disclosed by the invention has an obvious effect in lowering blood sugar, and has obvious advantages in comparison with the similar dietary fiber products.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Sea lettuce polysaccharide, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101328227ANo side effectsHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderAntithrombotic AgentIon exchange
The invention relates to Monostroma nitidum polysaccharide, which is characterized in that: sugar chains of the Monostroma nitidum polysaccharide contain rhamnose groups, xylose groups, glucose groups, galactose groups, mannose groups and glucuronic acid groups, and the rhamnose group polysaccharide is a linear long chain molecule which is connected by alpha-1, 2-glycosidic bonds and alpha-1, 3-glycosidic bonds. Under the condition of preparation, algae frond is immersed into water for homogenate, and then heated and extracted, and a clear solution is separated, concentrated and desalinated; the desalinated solution is concentrated and deproteinized; the deproteinized solution is concentrated, alcohol deposited, dried, dissolved and then separated through an ion exchange chromatographic column and a gel chromatographic column in turn; the collected solution is concentrated and desalinated; and the desalinated solution is concentrated, alcohol deposited, cleaned, dried and crushed. The Monostroma nitidum polysaccharide can be used for preparing a novel anticoagulant or antithrombotic reagent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com