Method for improving sugar utilization rate of clostridium acetobutylicum in fermentation of mixed sugar
A technology of Clostridium acetobutylicum and xylulokinase, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering technology and fermentation and can solve problems such as reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0165] Example 1. Construction of pWJ1-glcG plasmid vector
[0166] Amplify the glcG targetron fragment by PCR, then use XhoI and BsrG I to perform double digestion, and connect it to the pWJ1 vector that has also been digested by XhoI and BsrG I, to obtain the interrupted plasmid pWJ1-glcG, in which, PCR amplifies the template of glcG targetron And the primer design method comes from the Targetron of Sigma-Aldrich company TM Gene Knockout System (TA0100) kit, the specific steps are as follows:
[0167] 1.1PCR amplification primers
[0168] ReferenceTargetron TM According to the method provided by the Gene Knockout System (TA0100) kit, primers glcG-IBS (as shown in sequence SEQ ID NO.: 4), glcG-EBS1d (as shown in sequence SEQ ID NO.: 5) and glcG-EBS2 were designed respectively (as shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO.: 6), used to construct the pWJ1-glcG plasmid vector.
[0169] The EBS universal primers (EBS universal) required for PCR amplification were supplied by Target...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Example 2. Construction of Clostridium acetobutylicum glcG Mutant, Detection and Loss of Knockout Plasmid
[0178] After the pWJ1-glcG plasmid was methylated at the Cac8I site by Escherichia coli ER2275 / pANS1, it was electroporated into Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. After recovery overnight, 200 μl of the cell solution was applied to CGM with 20 μg / mL erythromycin On the plate, after culturing in an anaerobic box at 37°C for 48-96 hours, pick a single bacterium for colony PCR verification. The specific process is as follows:
[0179] 2.1 Methylation of pWJ1-glcG plasmid
[0180] In order to prevent foreign DNA from entering Clostridium acetobutylicum and being cleaved and degraded by its restriction system, the pWJ1-glcG plasmid needs to be methylated (Mermelstein, L.D and Papoutsakis, E.T. Appl Environ Microbiol.vol 59.issue 4: p1077-81 ).
[0181] The pANS1 plasmid was treated with CaCl 2 Transform into Escherichia coli ER2275 by heat shock method to obtai...
Embodiment 3824
[0197] Fermentation of embodiment 3.824glcG mutant strain
[0198] Get the Clostridium acetobutylicum strain 824glcG that has interrupted the glcG gene in step 2.5 to ferment in P2 medium, and detect the fermentation broth, the specific process is as follows:
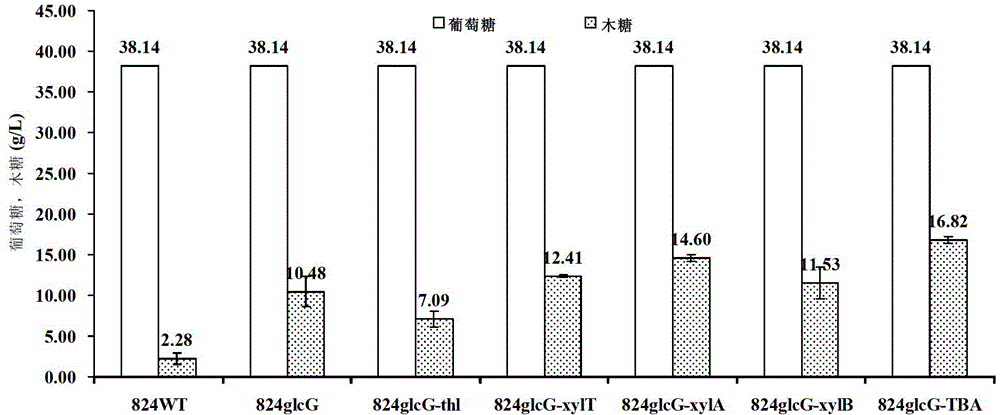
[0199] Pick a single bacterium from the CGM plate and insert it into 5mL CGM liquid medium, cultivate overnight, insert 1% inoculum into 50mL CGM medium, cultivate for 8~10hr, and make the bacterial concentration OD 600 Reach 0.4, insert in P2 substratum with 5% and cultivate and ferment, get fermented liquid and detect residual sugar content (use the sugar-park column of WATERS company to measure through Agela 1200HPLC, the result is as follows figure 1 shown), and Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 was used as a contrast, wherein the following pretreatment was required before the determination of the residual sugar content in the fermentation broth: after the fermentation broth was centrifuged, the supernatant was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com