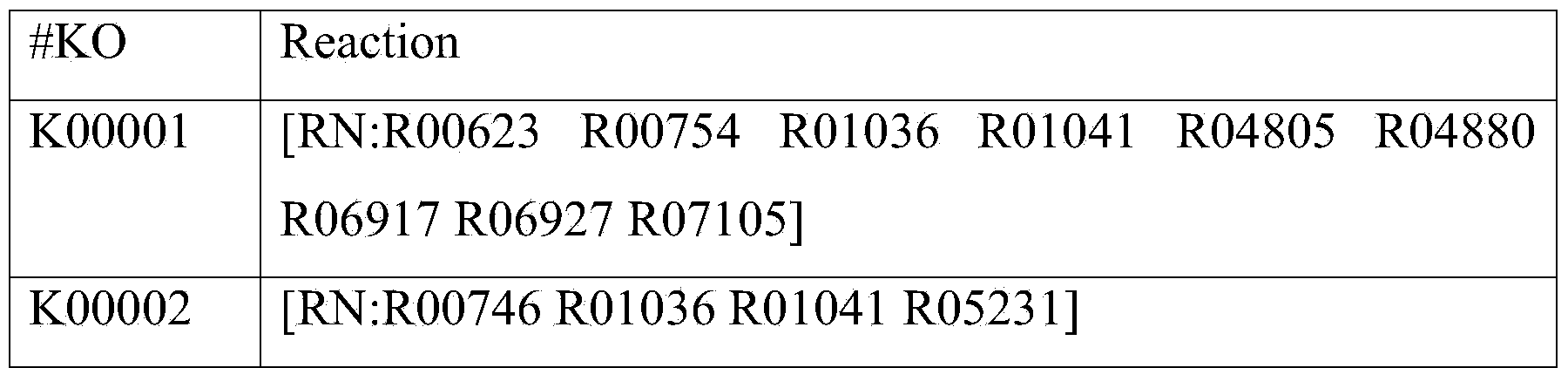
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Metabolic network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell. As such, these networks comprise the chemical reactions of metabolism, the metabolic pathways, as well as the regulatory interactions that guide these reactions.
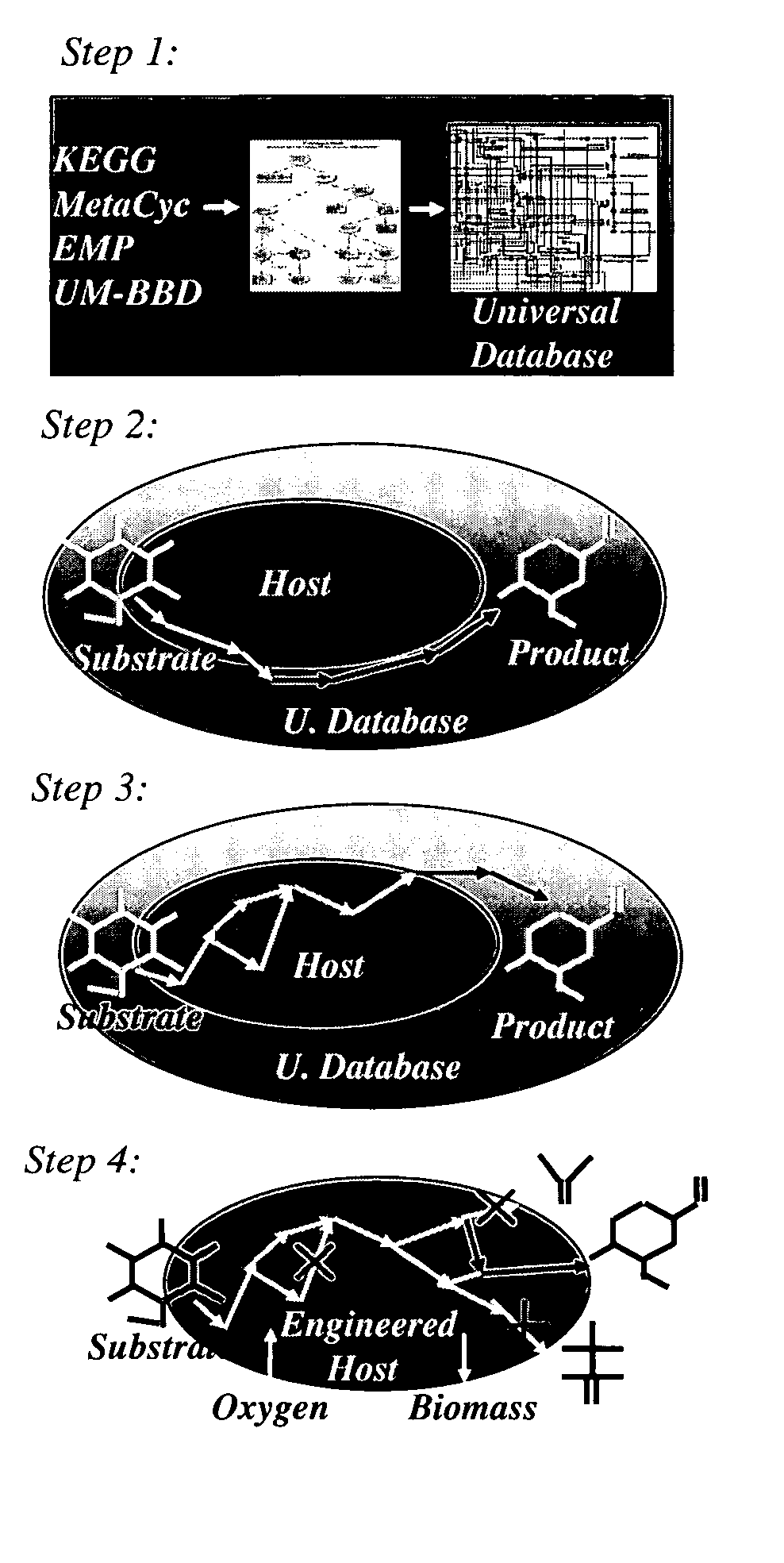
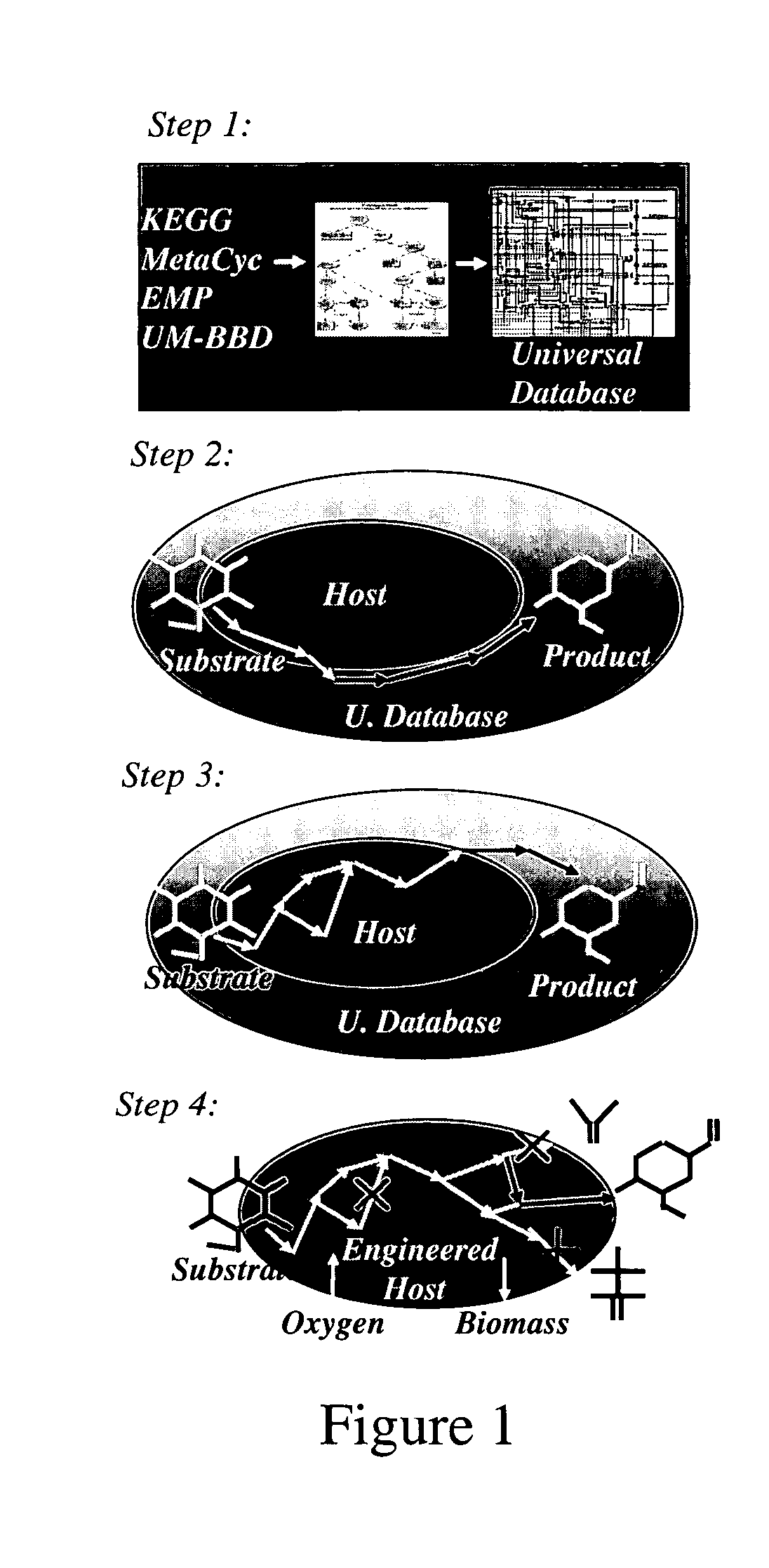
Method for redesign of microbial production systems
ActiveUS20050079482A1Solve complexityIncreased production objectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMicroorganismBiological body
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
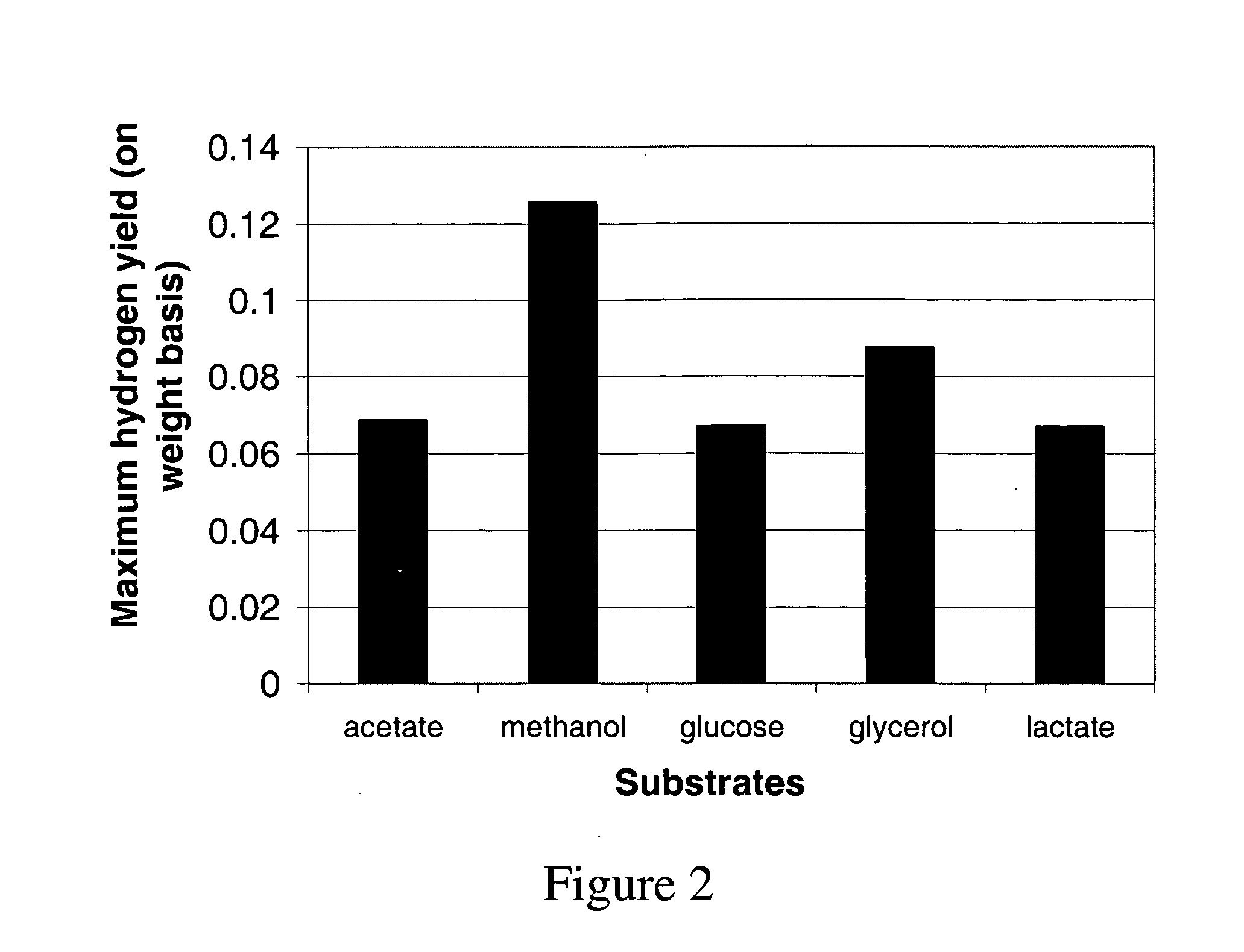
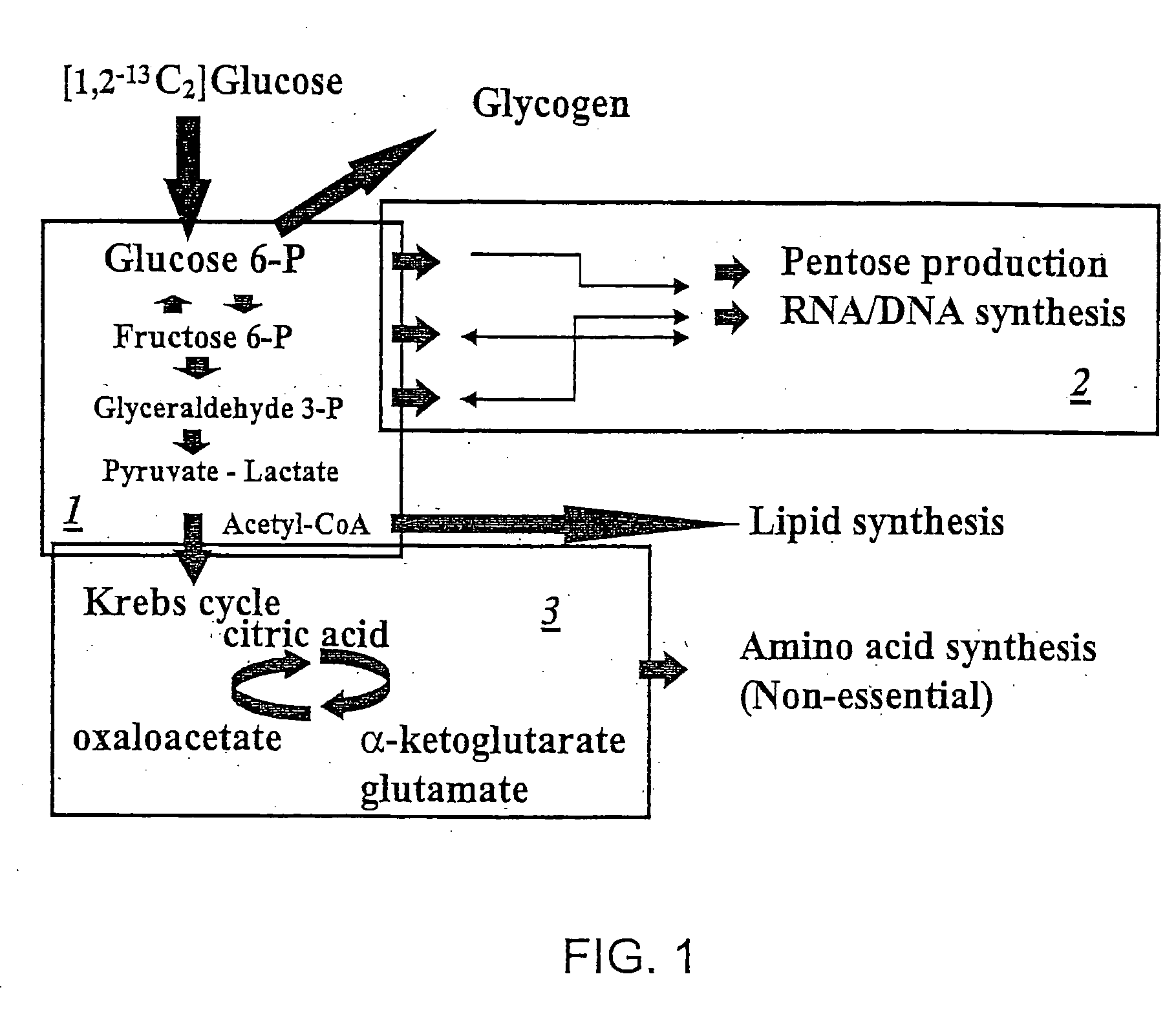
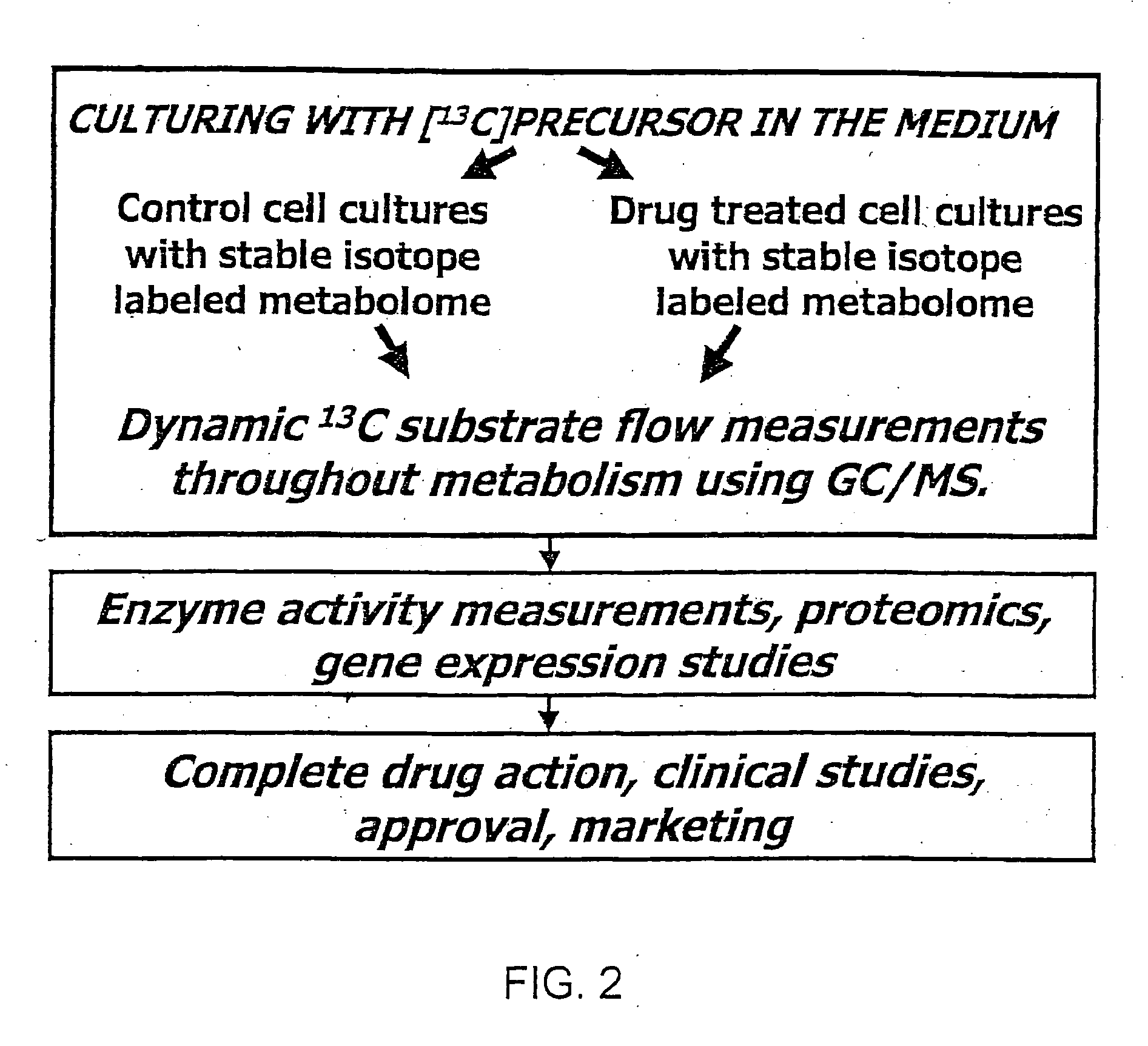
Stable isotope based dynamic metabolic profiling of living organisms for characterization of metabolic diseases, drug testing and drug development
The metabolic processes involved in the formation of any glucose-based metabolite of a metabolic network are determined. A precursor molecule is labeled with a stable carbon (13C) isotope at specific positions. The label is allowed to distribute and rearrange in the system. Metabolites are recovered and analyzed against a control system to determine a set of metabolic pathway substrate fluxes caused by changes to the test system relative to the control system such as the addition of compound being tested as a potential drug.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Method for redesign of microbial production systems
A computer-assisted method for identifying functionalities to add to an organism-specific metabolic network to enable a desired biotransformation in a host includes accessing reactions from a universal database to provide stoichiometric balance, identifying at least one stoichiometrically balanced pathway at least partially based on the reactions and a substrate to minimize a number of non-native functionalities in the production host, and incorporating the at least one stoichiometrically balanced pathway into the host to provide the desired biotransformation. A representation of the metabolic network as modified can be stored.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-arginine and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110964683AShorten the growth cycleClear genetic backgroundBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCarbamyl Phosphate
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-arginine and a construction method and application thereof. According to the invention, a gene for encoding carbamyl phosphate synthetase and a gene for encoding L-arginine biosynthetic pathway enzyme are integrated in escherichia coli; a synthetic route of arginine in escherichia coli and metabolic flux related to argininein a whole amino acid metabolic network are analyzed and reconstructed to obtain genetically engineered bacteria which are clear in genetic background, do not carry plasmids, are not mutated and canstably and efficiently produce L-arginine; and the genetically engineered bacteria have good L-arginine production capacity.
Owner:NINGXIA EPPEN BIOTECH
Streptomyces and multi-antibiotics metabolic regulation fermentation process
ActiveCN102643764AImprove fermentation titerGood control effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptomyces aureochromogenesInorganic salts
The invention discloses a streptomyces and a multi-antibiotics metabolic regulation fermentation process. According to the method, nutrient media components are optimized, inorganic salt is added to disturb a metabolic network of streptomyces aureochromogenes, and a target production way is strengthened, so that the generation of products is promoted. Meanwhile, the multi-antibiotics fermentationprocess is optimized, and a method of flowing-feeding glucose is adopted for a feed supplement batch fermentation method, so that the fermentation unit and the production output are greatly improved,and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for information mining of genome metabolic network preliminary model
InactiveCN103399948AEasy to compareLabor savingSpecial data processing applicationsGenome scaleInformation mining
The invention provides a method for information mining of a genome metabolic network preliminary model. The method comprises the steps as follows: as for the KEGG website, extracting a corresponding relation among gene, protein and reaction, that is, determining the GPR relation by adopting a website script semantic analysis technology on the basis of webpage key content priori position information, and establishing an excel table to show the GPR relation information, so as to obtain the genome metabolic network preliminary model. The model constructed by adopting the method unifies the reaction form, and is convenient in comparison with other models and convenient in reference. The method has been applied to construction of a scheffersomyces stipitis CBS6054 genome-scale metabolic network, and compared with the construction of a traditional network preliminary model based on the KEGG database, a great amount of labor and time are saved, and the construction efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
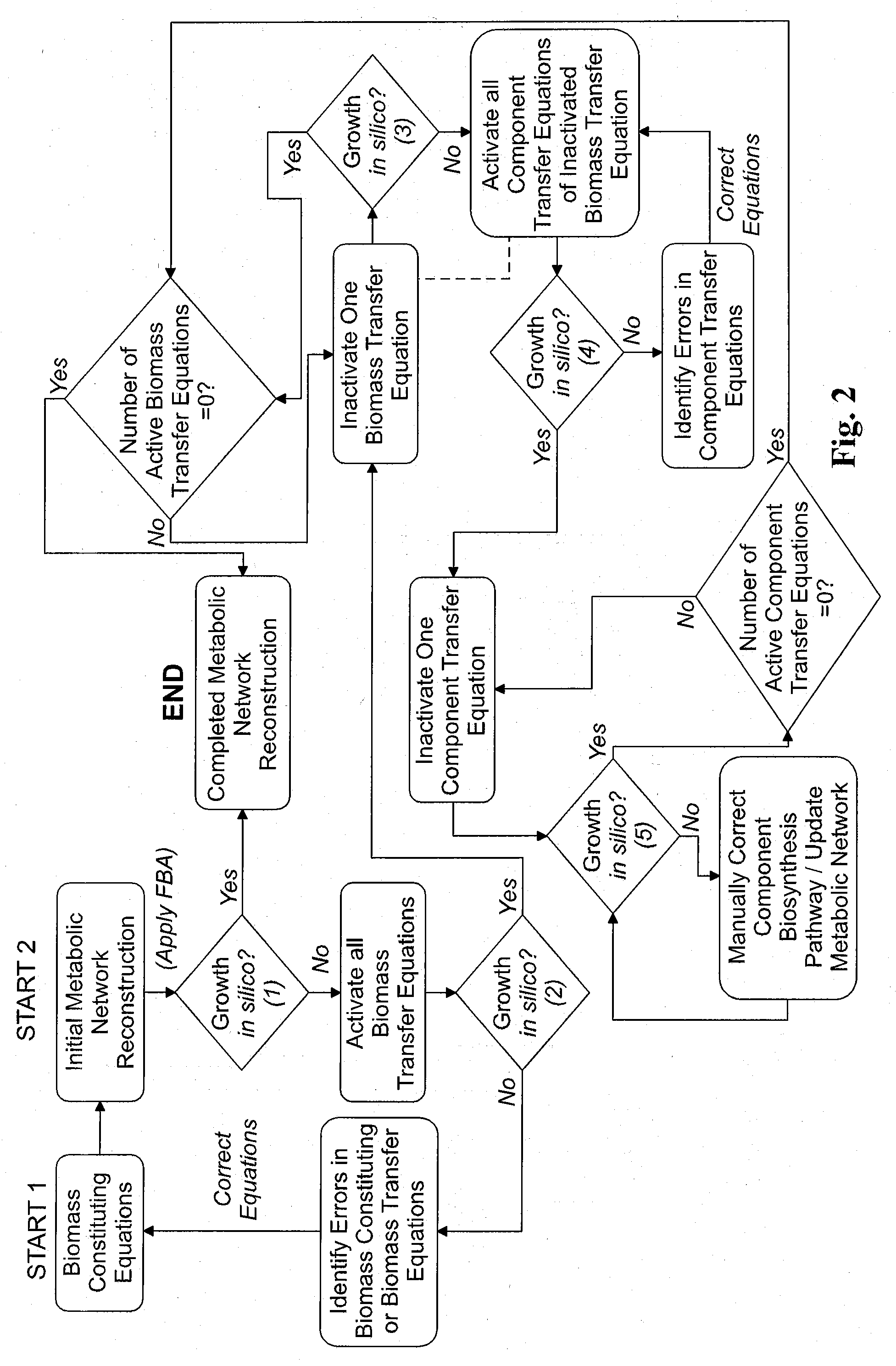
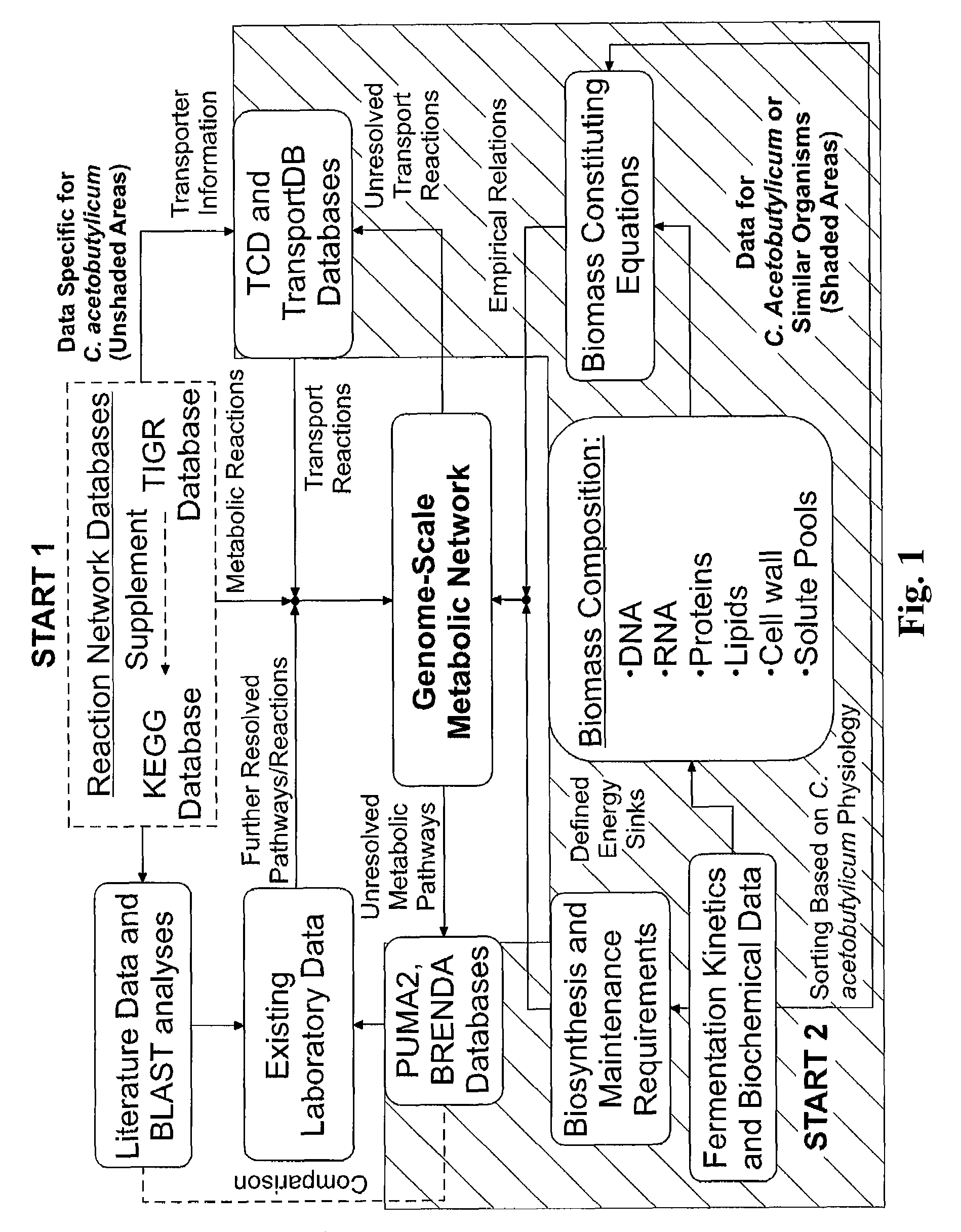
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS20090259451A1Reduce in quantityAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingUnderdetermined systemIn silico
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
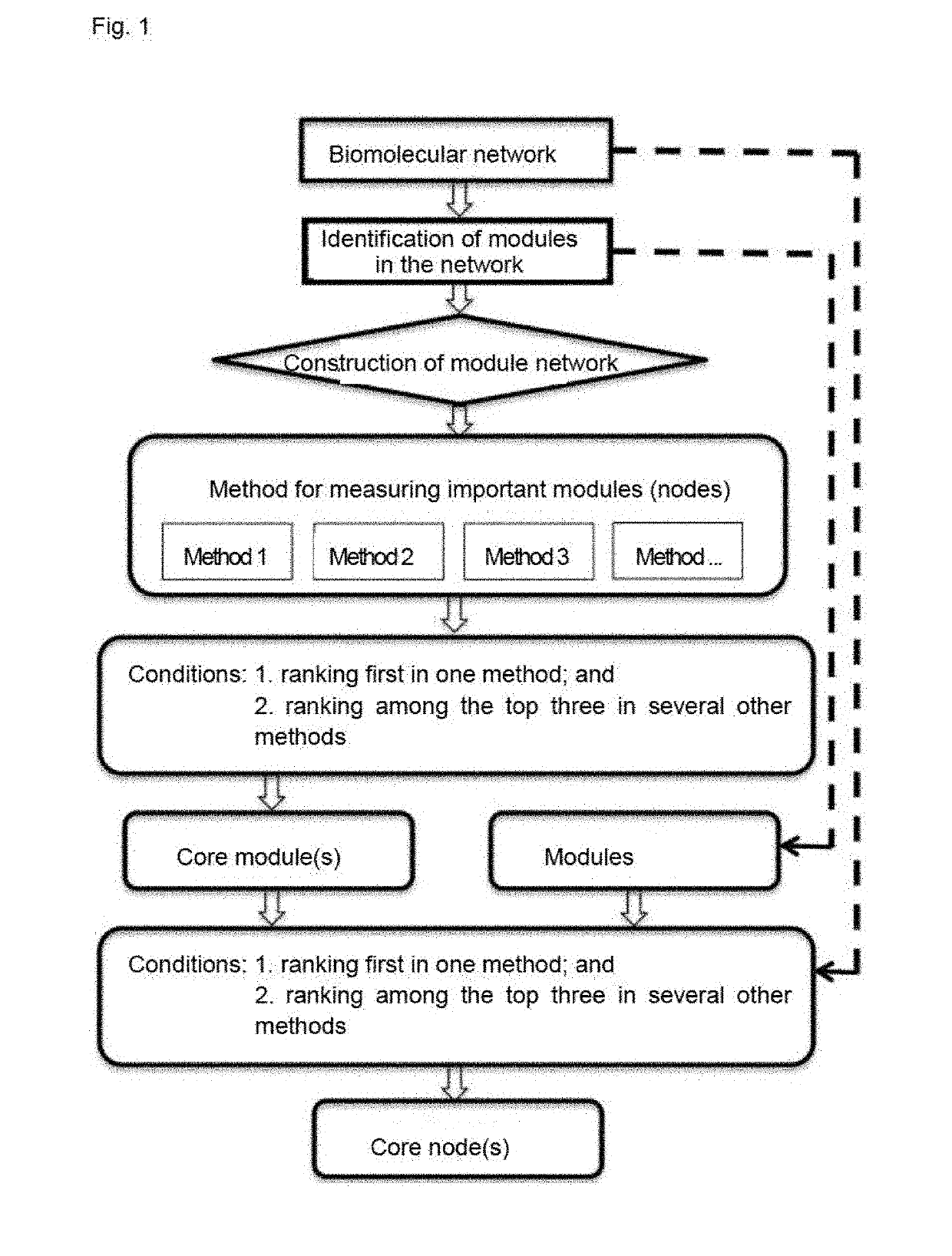
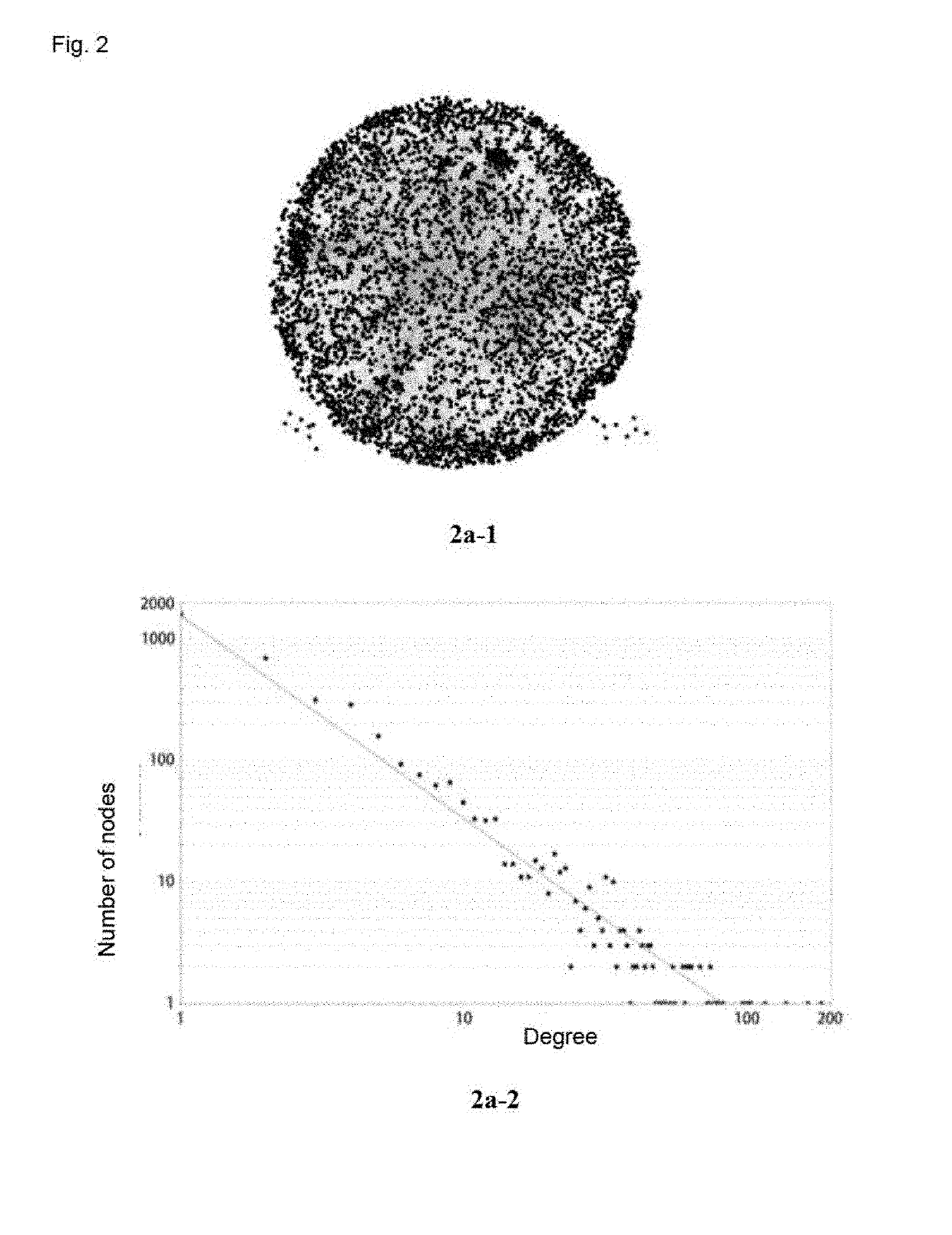
Method for identifying key module or key node in biomolecular network
PendingUS20190139621A1Strong integrationData visualisationBiostatisticsRegulation of gene expressionStructure of Management Information
A method for identifying a key module and a key node of a biomolecular complex network by fusing multiple methods on the basis of a topological structure of the biomolecular complex network which may be such as a protein-protein interaction network, a gene expression regulation network, a biological metabolism network, an epigenetic network, a phenotypic network or a signaling network, comprising the following main steps: according to the biomolecular network and a module division for the network, comprehensively and quantitatively identifying the key module and key node on the basis of the topological structure by various measuring methods from multi-angle.
Owner:WANG ZHONG +1
High-yield 3-Methionol saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103409331AIdentify key metabolic nodesOptimizing Fermentation MediumFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneMetabolic network
The invention relates to high-yield 3-Methionol saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological preparation of food flavors. According to the high-yield 3-Methionol saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and the preparation method and application thereof, the engineering bacteria is designed and constructed through the coupling excessive expression of an aminotransferase gene (ARO9) and a decarboxylase gene (ARO10) and the knock-out of a methylthio lyase gene (CY3) in the anabolic pathway of Methionol by taking Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c as an original strain; the expression of two key enzyme genes in a main synthetic pathway is enhanced, and the expression of the CY3 gene in a side reaction pathway is reduced or eliminated; the bred engineering bacteria (converter) is subjected to multiple-time passage and stable in inheritance, so that the metabolic network and metabolic pathway of the biological synthesis of the Methionol are optimized, and the metabolic flux and yield of the Methionol are obviously increased; a Methionol flavor prepared by fermenting and converting the engineering bacteria is single in structure and chirality and high in fragrance quality.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
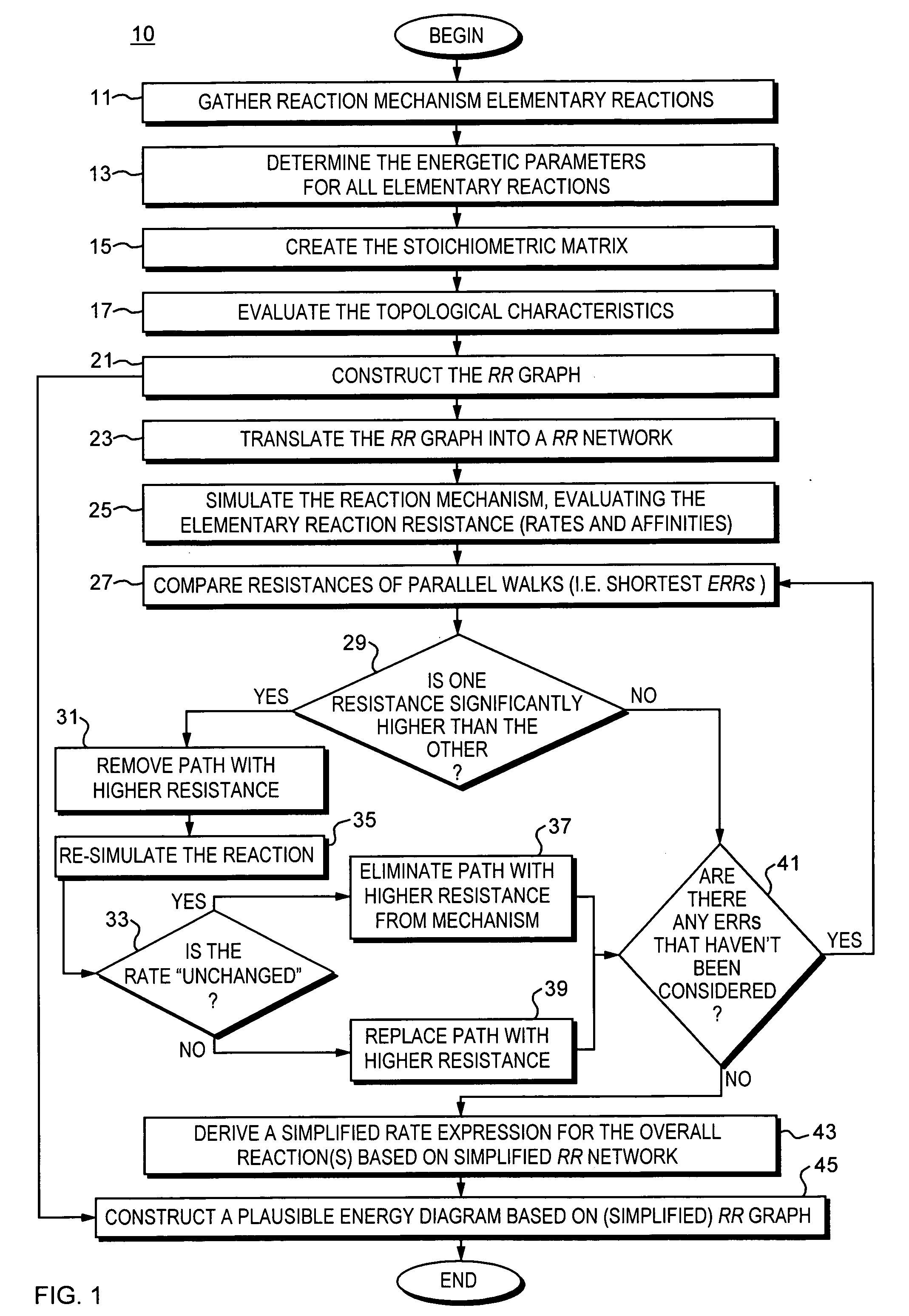
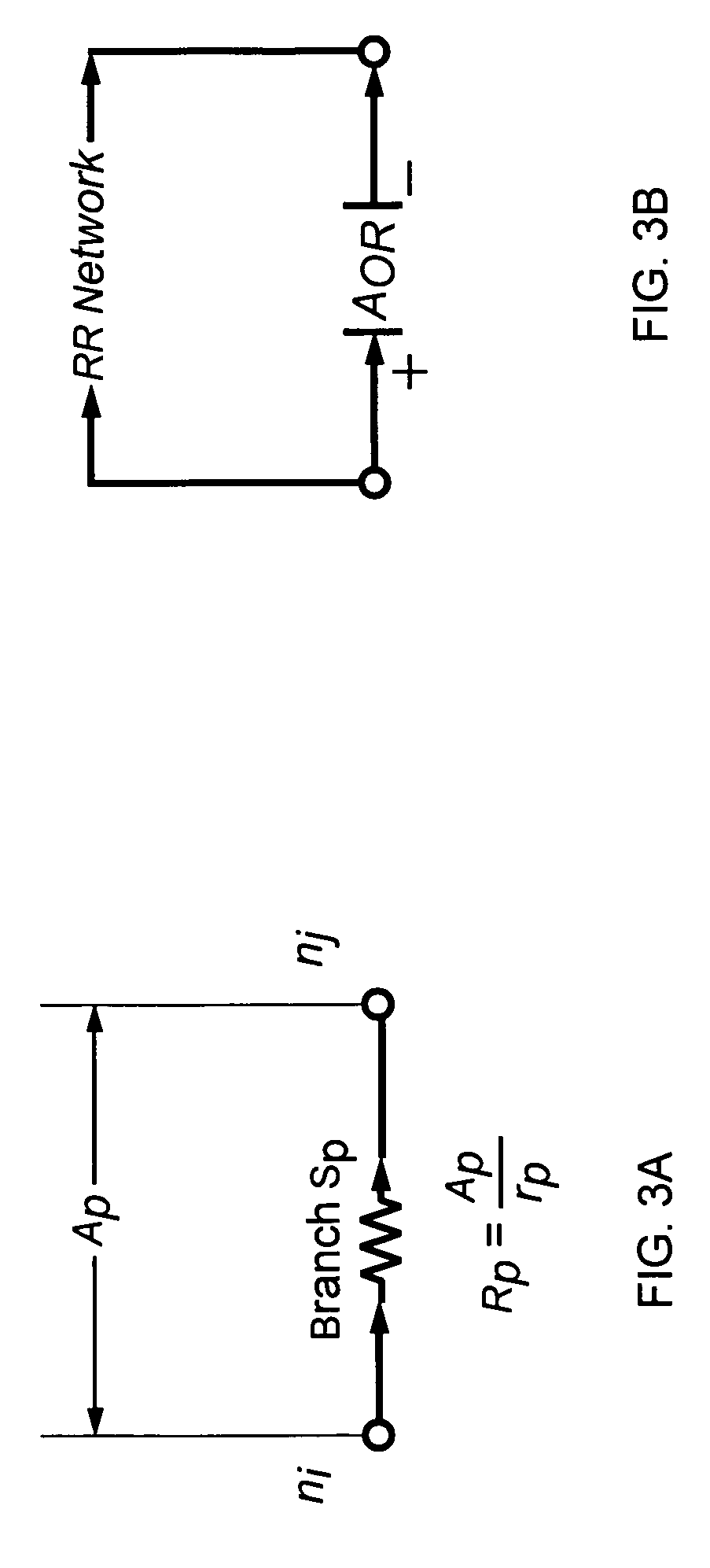
Method and apparatus for reaction route graphs for reaction mechanism and kinetics modeling
InactiveUS20050251346A1Intuitive evaluationMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical processes analysis/designPower gridCombined use
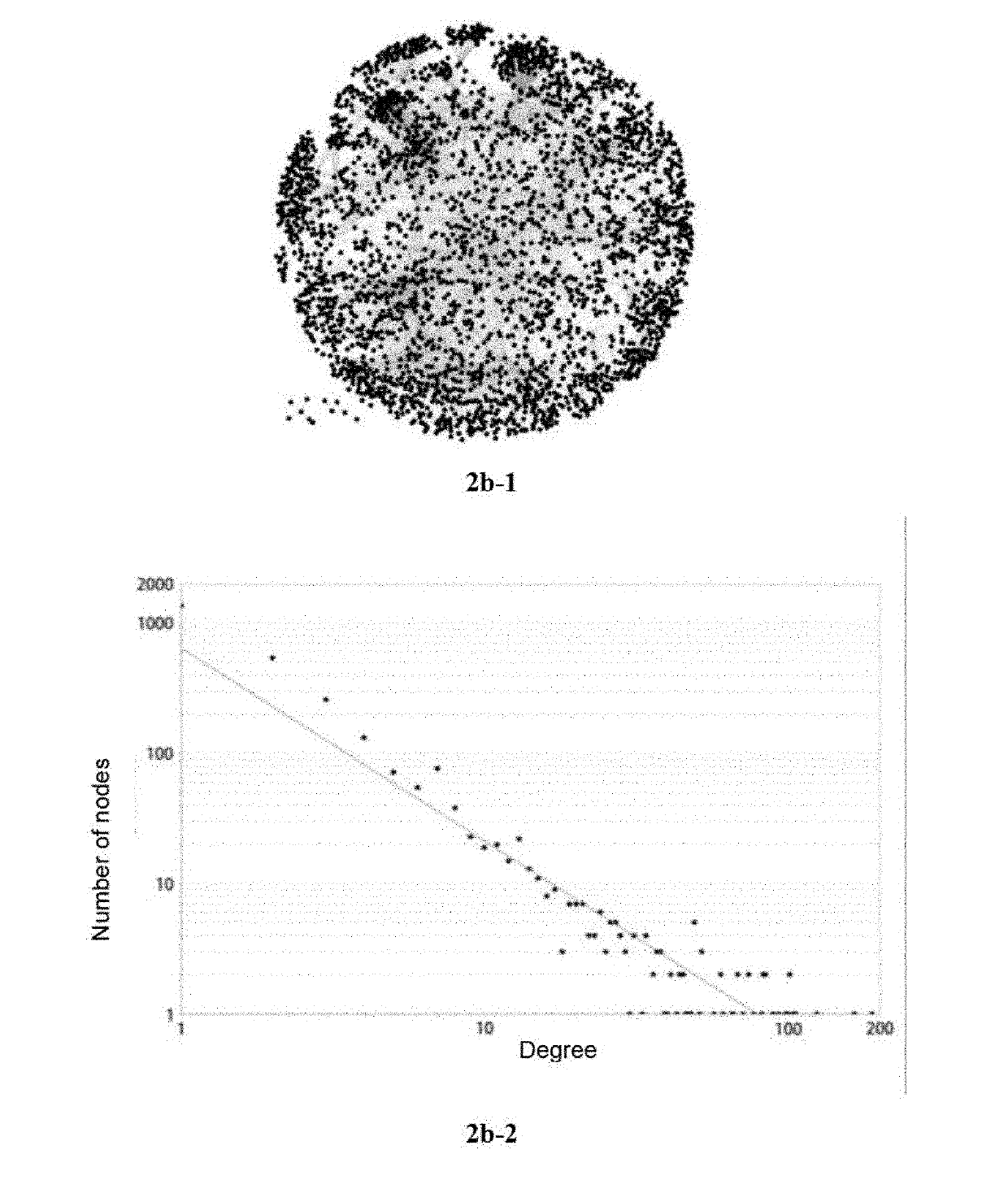
A method and apparatus for reaction route (RR) network analysis is provided in analogy with electrical networks and is based on the combined use of RR theory, graph theory, and Kirchhoff's laws. The result is a powerful new approach of “RR graphs” that is useful in not only topological representation of complex reactions and mechanisms but, when combined with techniques of electrical network analysis, is able to provide revealing insights into the mechanism as well as the kinetics of the overall reactions involving multiple elementary reaction steps including the effect of topological constraints. Unlike existing graph theory approaches of reaction networks, the present invention approach is suitable for linear as well as non-linear kinetic mechanisms and for single and multiple overall reactions. The methodology has broad applicability including atmospheric networks, metabolic networks, and catalytic reaction mechanisms.
Owner:VOLTA ENERGY
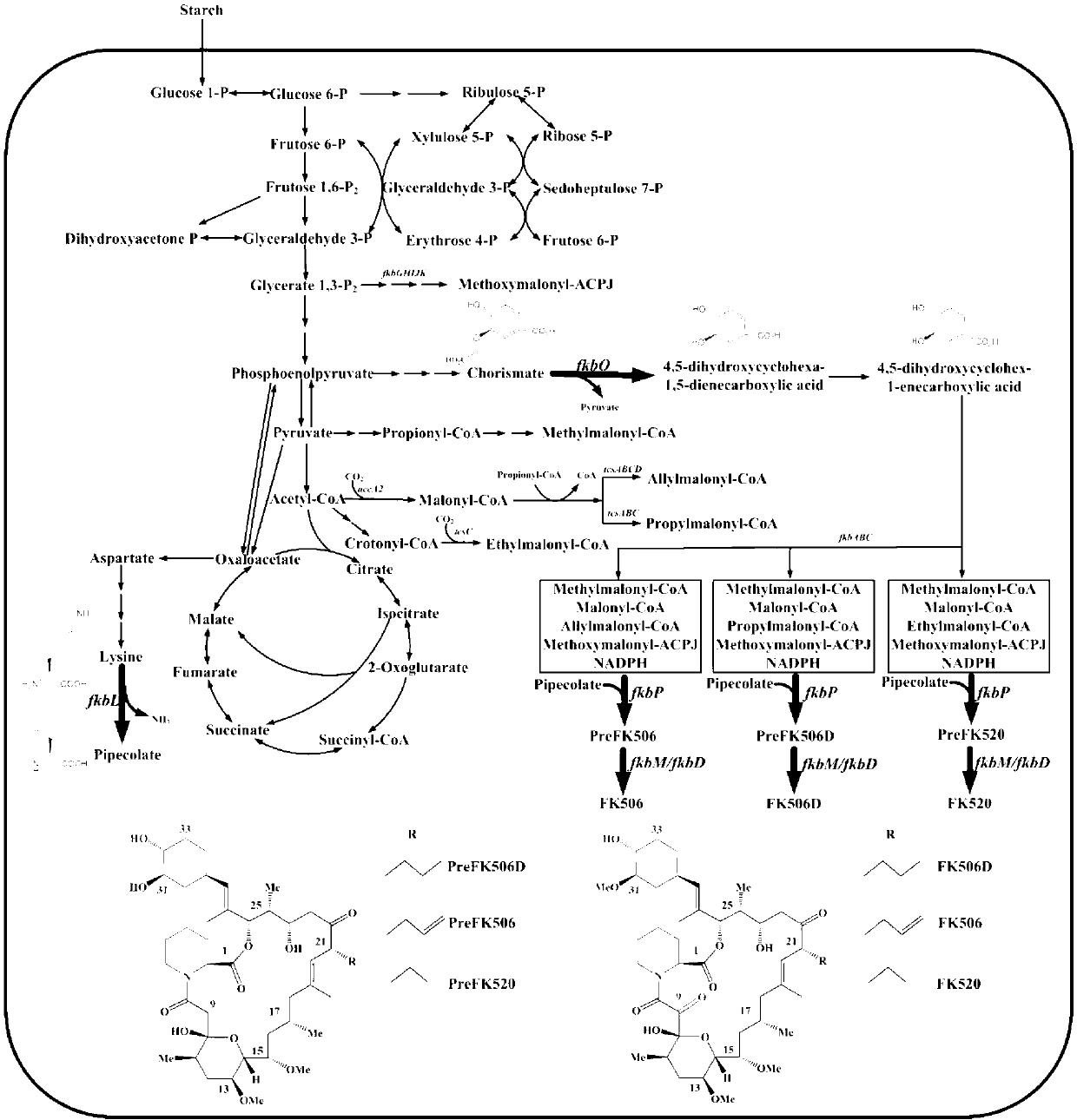
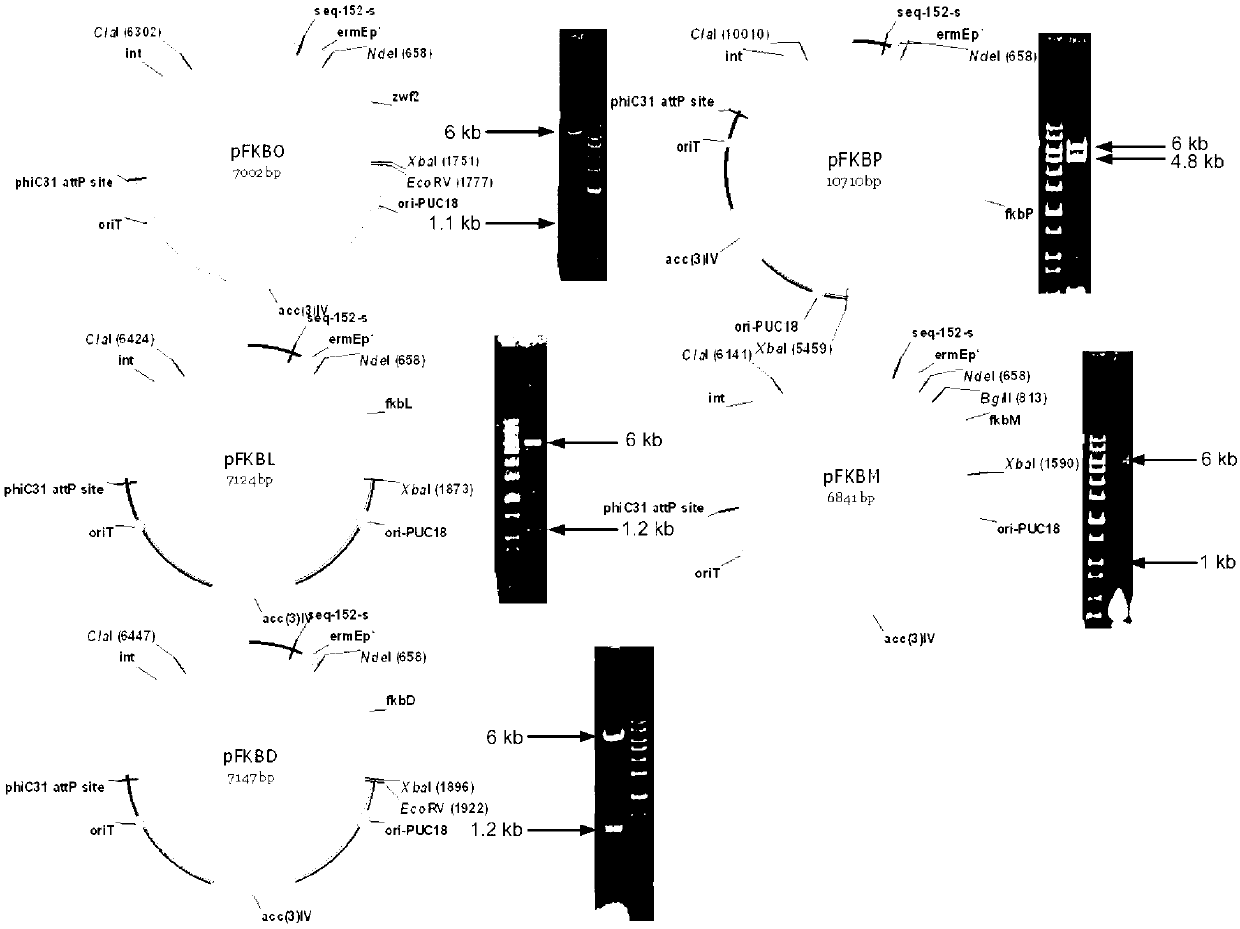
Secondary approach transformation method based on instruction of FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN103279689AIncrease production levelsImprove the experimental effectSpecial data processing applicationsMicroorganismGene cluster
The invention discloses a secondary approach transformation method based on an instruction of an FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model. The model is based on annotation genes and physiology and biochemistry information. By comparing and analyzing the model with a streptomyces coelicolor genome, metabolic genes are found being highly conservative. Metabolic flux analysis is performed on a genome scale metabolic network, and therefore the model predicts a mutation bacterium secondary approach gene cluster transformation strategy for improving a production level. According to the secondary approach transformation method based on the instruction of the FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model, the transformation method utilizes the genome scale metabolic network model to predict special structural genes in an FK506 bacterial strain secondary approach gene cluster, the production level of bacterial strains after transformation is improved by 20 percent to 90 percent, the special structural genes in the gene cluster are augmented to improve production capacity, and large application value is achieved in secondary approach rational transformation of microorganism immunosuppressor production bacterial strains. The high-efficiency and systematic method is provided for optimizing of the bacterial strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Application of composition containing fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in preparation of antitumor drugs
ActiveCN107375934AIncrease aggressivenessIncreased efficacy of anticancer drugsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTricarboxylic acidMetabolic network
The invention provides application of a composition containing fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) in preparation of antitumor drugs. A proportion of the FBP to metabolic regulators are determined according to respective efficacy doses; the metabolic regulators are different in doses, so that the proportion of the FBP to one metabolic regulator is determined according to the effective dose of the specific metabolic regulator. The composition prevents and cures tumors by damaging activity of a tumor metabolic network. The drugs with the composition as an active ingredient have stronger anticancer efficacy compared with FBP and other metabolic regulators in exclusive use. The composition can completely reverse tumor metabolic characteristics and destroy the tumor metabolic network, prominently featured by blocking glycolysis and an intermediate product of a tricarboxylic acid cycle from biosynthesis while promoting nutriments to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation so as to damage an oxidation-reduction system. The composition is highly safe, and further improves the anticancer efficacy of the FBP.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and methods for measuring at least one metabolic rate of a plurality of cells
A system and methods for calculating at least one unknown metabolic flux of a plurality of cells. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of constructing a metabolic network having a plurality of reaction components, the reaction components representing at least glycolysis, reduction of pyruvate to lactate, TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, measuring at least two metabolic rates of a plurality of cells corresponding to at least two of the metabolic network reactions, and calculating metabolic fluxes of a plurality of cells for the rest of the metabolic network reactions from at least two measured metabolic rates of a plurality of cells corresponding to at least two of the reactions.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Plant whole-genome multilevel biological network reconstruction method based on multi-omics data integration
InactiveCN107862176ARealize 3D visualizationSpecial data processing applicationsReconstruction methodMetabolic network
The invention discloses a plant whole-genome multilevel biological network reconstruction method based on multi-omics data integration. The method carries out integration on a rice gene regulation andcontrol network, a protein interaction network and a metabolic network to finish the construction of a rice multilevel regulation and control network; and meanwhile, through the integration of expression profile data in different tissue growth processes of the rice, according to the constructed rice multilevel regulation and control network, a specific tissue multilevel gene regulation and control network is constructed so as to construct a first high-quality rice genome scale multilevel biological network of which the current data level is most integral. A new thought is provided for the construction of the plant multilevel biological network, and a constructed rice multilevel gene regulation and control network database realizes the 3D (Three-Dimensional) visualization of the multilevelregulation and control network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optimized process for producing enramycin through fermenting streptomyces
InactiveCN102250993AImprove fermentation titerTake advantage ofMicroorganism based processesFermentationInorganic saltsStreptomyces
The invention discloses an optimized process for producing enramycin through fermenting streptomyces. In the method, the formation of the enramycin is promoted through optimizing components of a culture medium, adding inorganic salt and low-molecular active substances (amino acid), disturbing the metabolic network of the streptomyces, and enhancing a formation approach of the target product; and the culture process is optimized through transforming the fermentation process and adopting a feed culture method. The optimized process for the fermentation of the enramycin, provided by the invention, is mainly used for greatly improving the fermentation potency of the enramycin and increasing the utilization rate of equipment and raw materials through optimizing the components of the culture medium and the feed process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
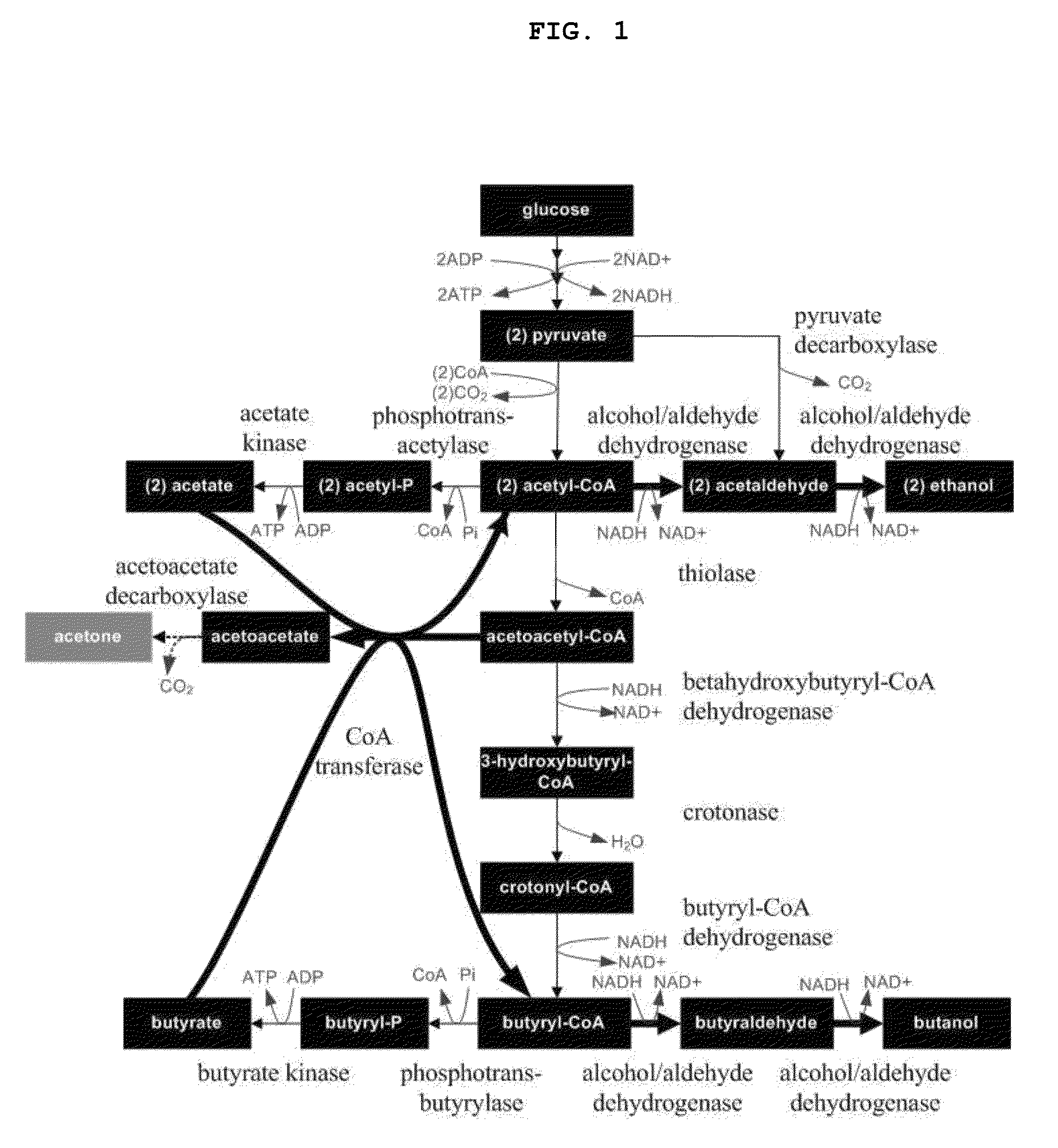
Recombinant microorganisms having increased ability to produce butanol and method of producing butanol using the same
The present invention relates to recombinant microorganisms having an increased ability to produce butanol, and a method of producing butanol using the same. More specifically, the invention relates to recombinant microorganisms whose ability to produce butanol was increased by manipulation of their metabolic networks, and a method of producing butanol using the same. The recombinant microorganisms having an increased ability to produce butanol comprise a deletion of a gene, which encodes an enzyme that converts acetyl CoA to acetate, in host microorganisms having genes that encode enzymes involved in acetyl CoA and butyryl CoA biosynthetic pathway. The recombinant microorganisms obtained by manipulating the metabolic flux of microorganisms are able to selectively produce butanol with high efficiency, and thus are useful as microorganisms for producing industrial solvents and transportation fuels.
Owner:GS CALTEX CORP
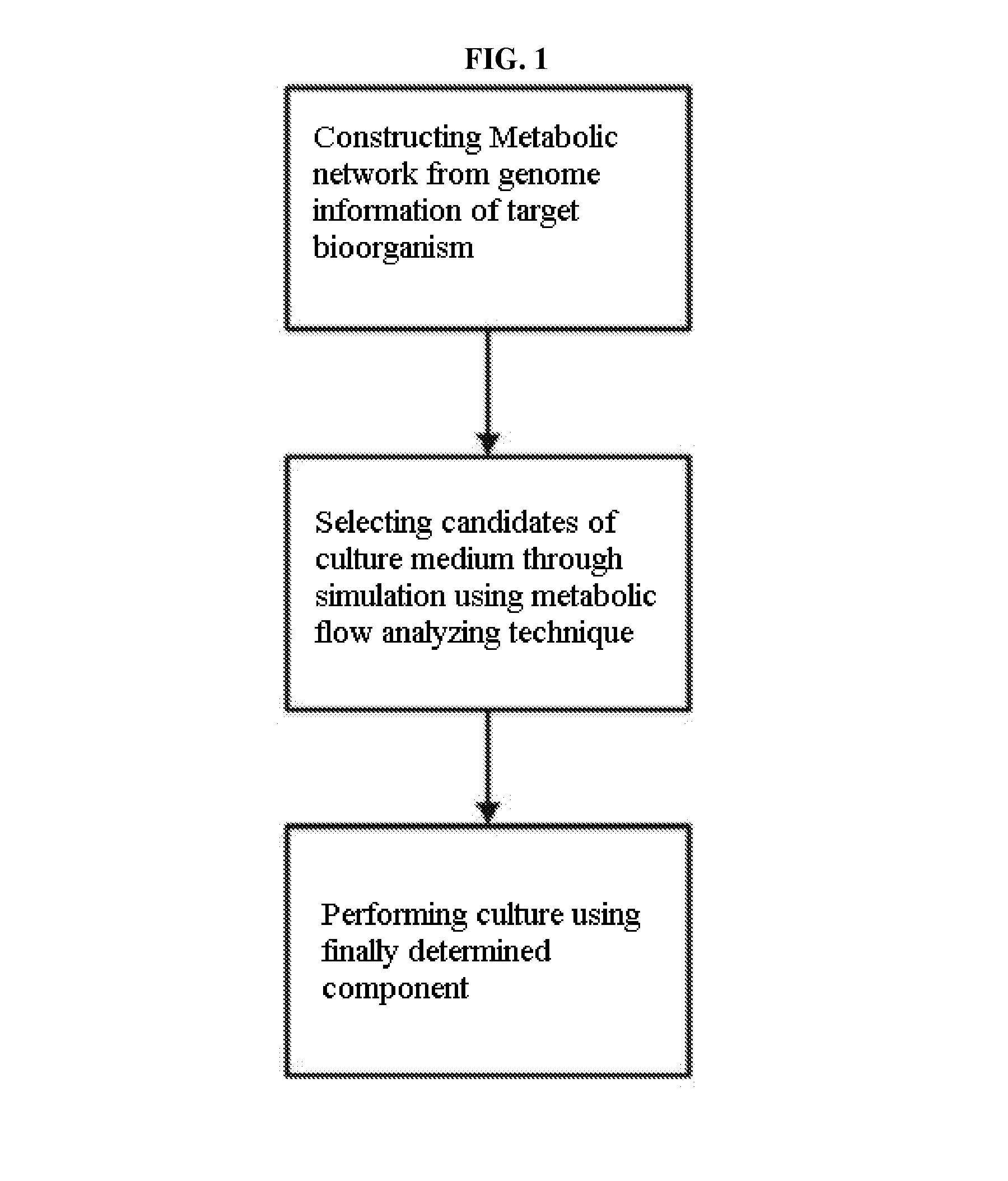
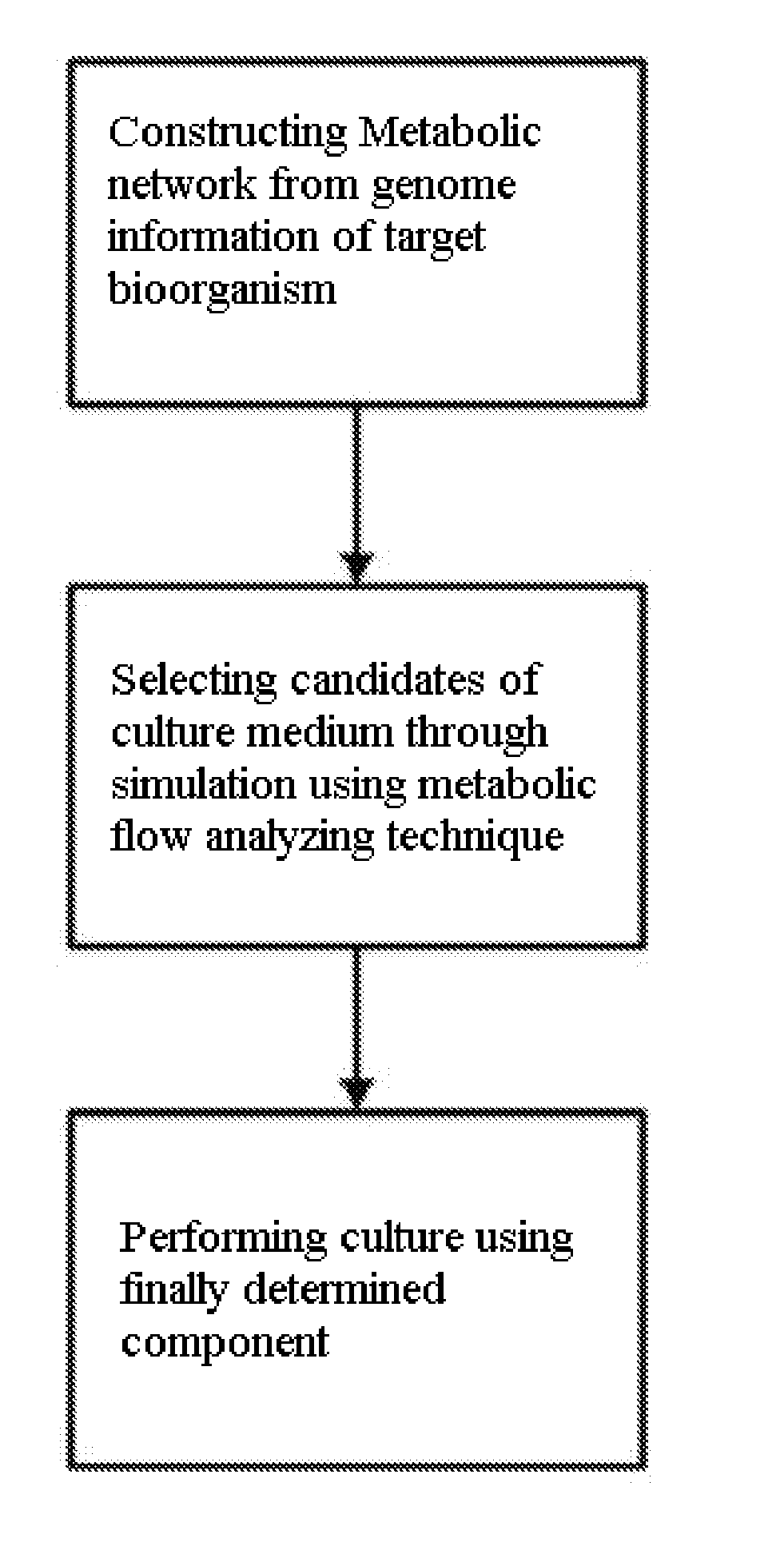
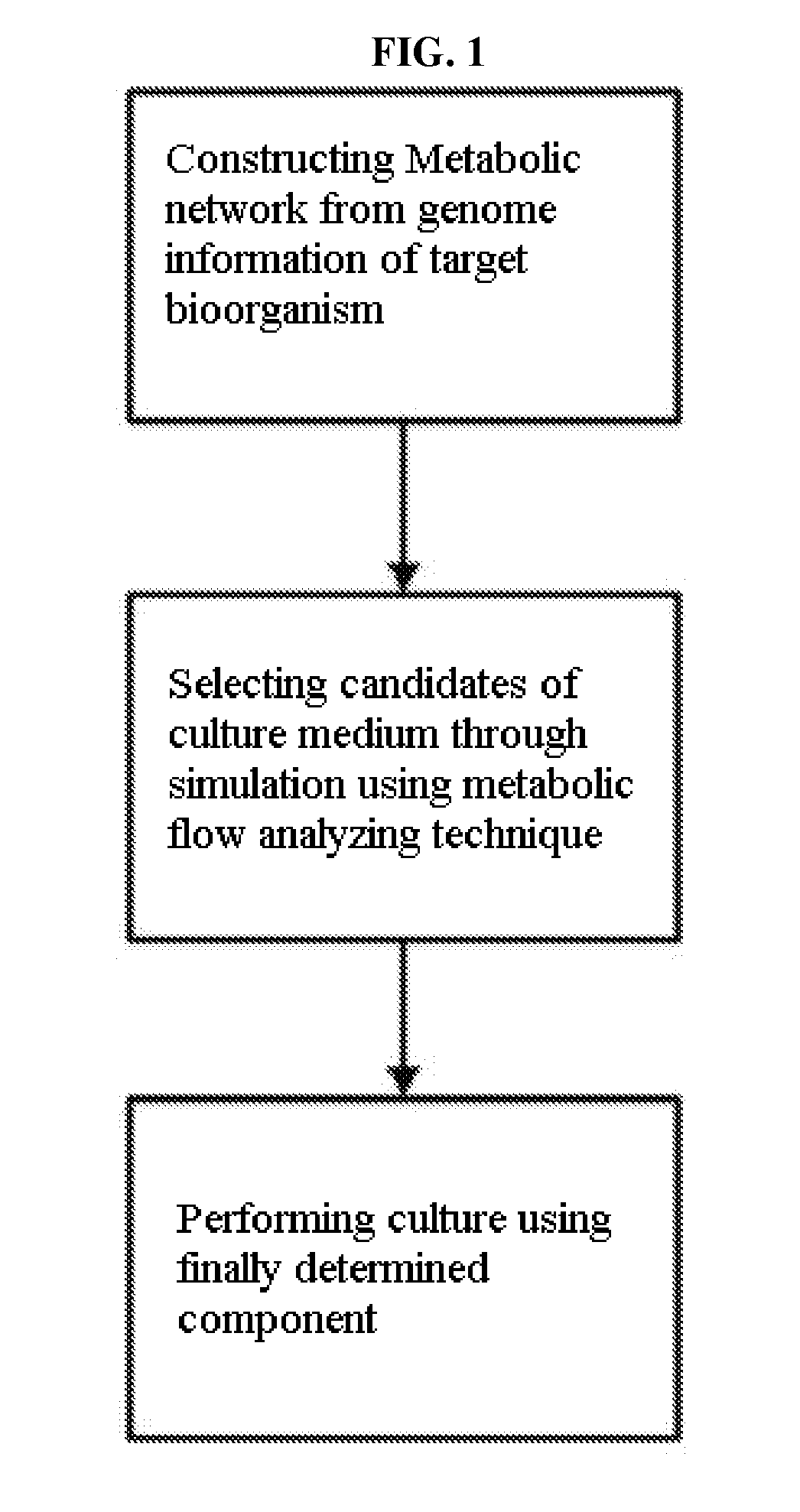
Method for developing culture medium using genome information and in silico analysis
A method for developing a culture medium using genome information and in silico analysis. In one implementation, the method involves developing a minimal synthetic medium, including the steps of constructing a metabolic network using genome information of prokaryotic cell or eukaryotic cell, selecting components of the minimal synthetic medium removing any one among external metabolites from the constructed metabolic network and conducting metabolic flux analysis using in silico simulation, and determining a final culture medium by actual culture.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Cold-coagulation-blood-stasis-syndrome-resistant differential metabolite metabolic pathway and study method of Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction
InactiveCN110794074AHigh diagnostic valueEfficient revealComponent separationEndogenous metabolismDisease
The invention discloses a cold-coagulation-blood-stasis-syndrome-resistant differential metabolite metabolic pathway and study method of a Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction. The method comprises: detecting and analyzing endogenous metabolites changed at different time points after cold-coagulation blood-stasis symptoms forming of a female rat under an ice-water bath and epinephrine induction and Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction intervention by using an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry so as to obtain a fingerprint spectrum; with a multivariate variable statistical analysis method, carrying out screening from a plurality of variables and identifying 21 significantly changed metabolites; and enriching eight metabolic pathways related to different development stages of the cold-coagulation blood-stasis symptom by using ametaboanalyst open-source online metabonomics analysiswebsite. According to the invention, the related metabolic changes in the occurrence and development process of the old-coagulation blood-stasis symptoms and the treatment process of the Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction are studied by using a dynamic analysis method; the disease occurrence and development mechanisms at different time points can be revealed;and the abnormal metabolic network regulated and controlled by medicines in the treatment process can be clarified.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
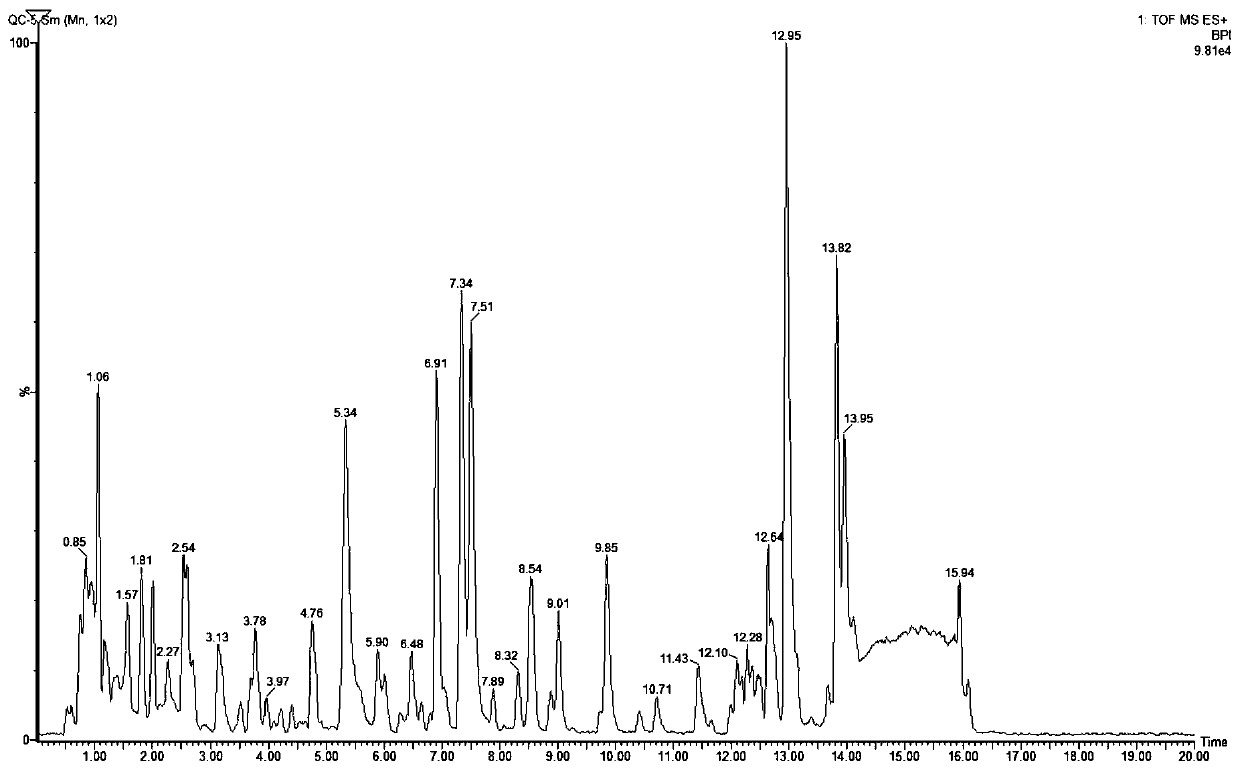
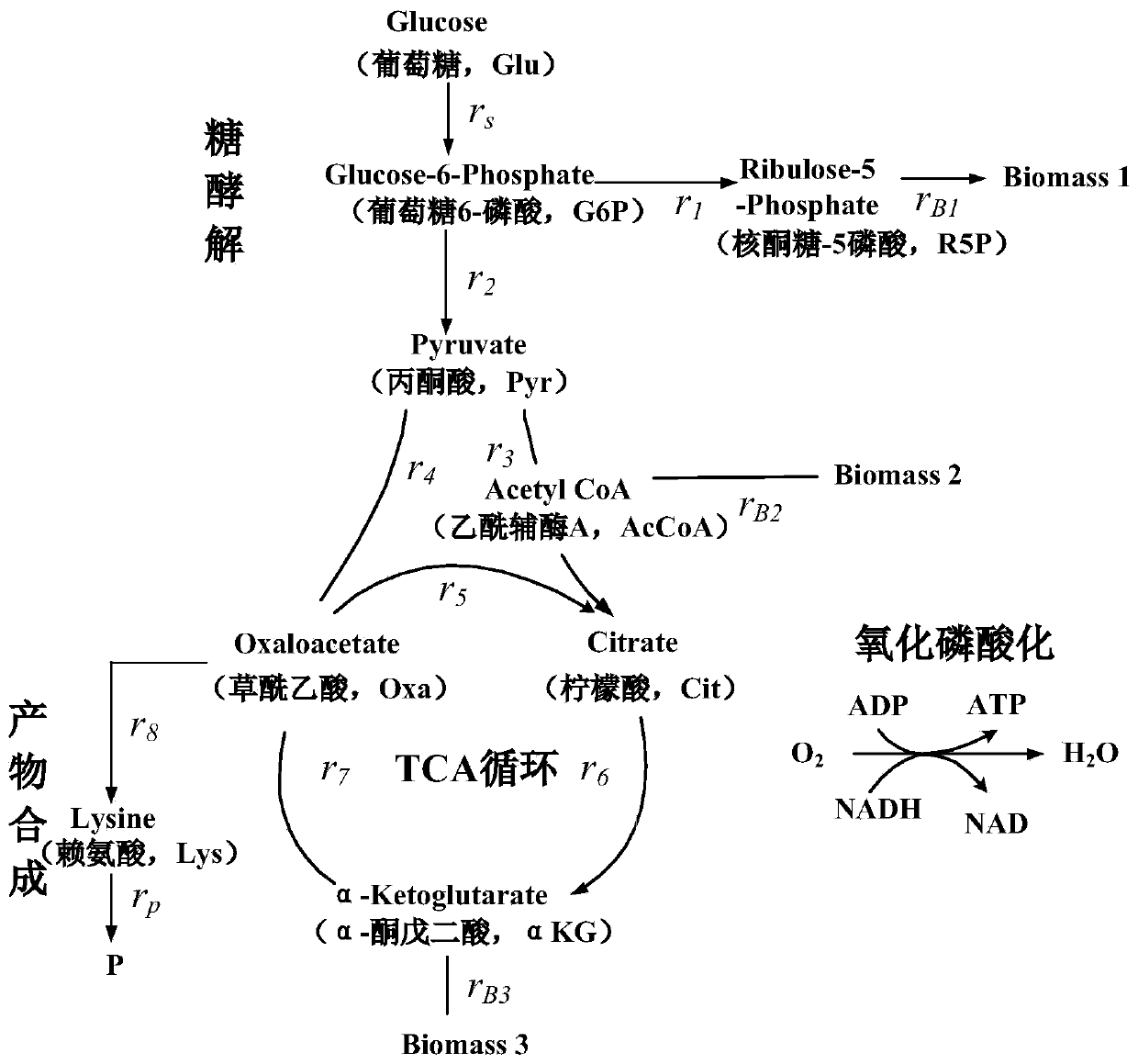
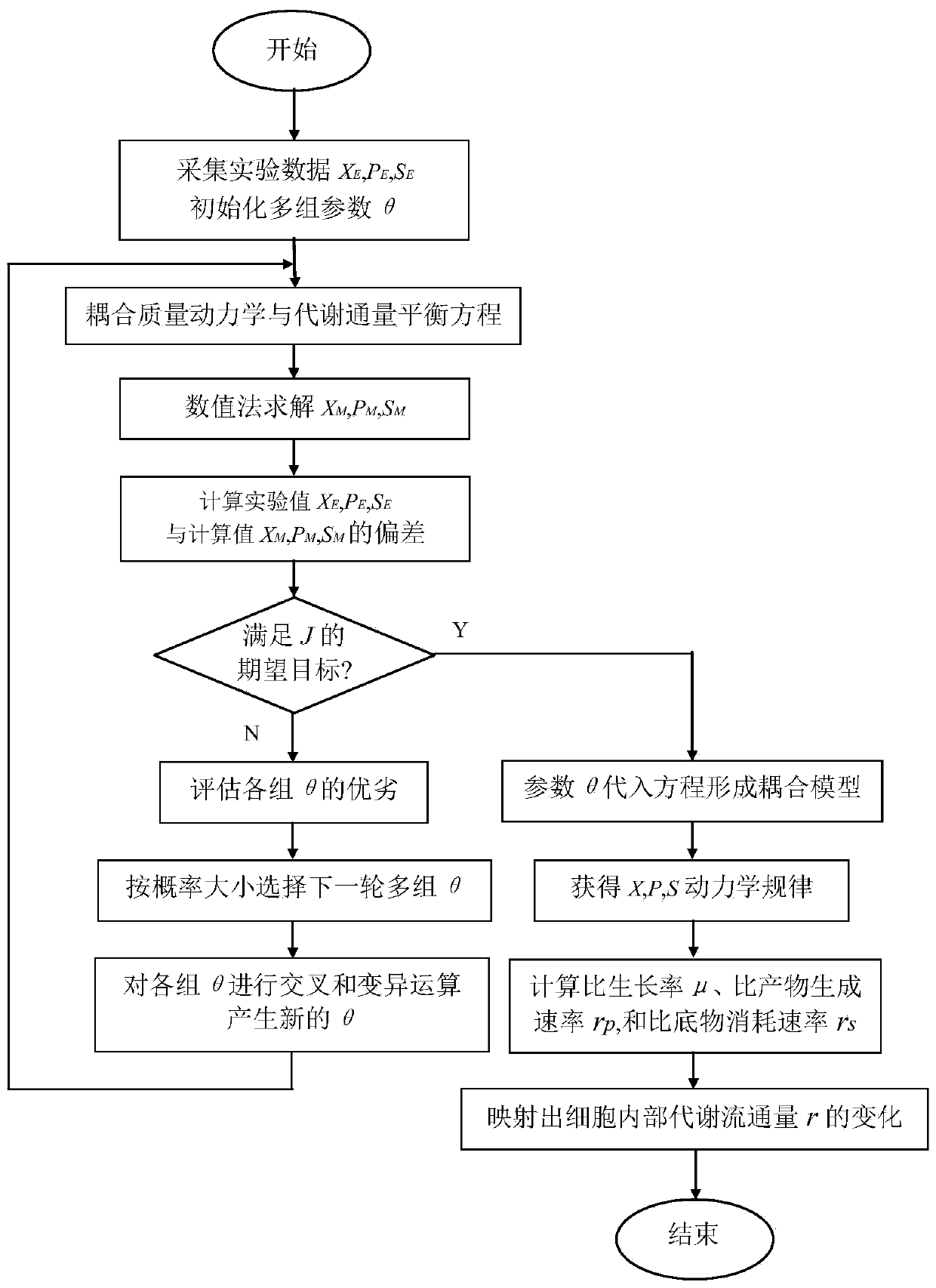
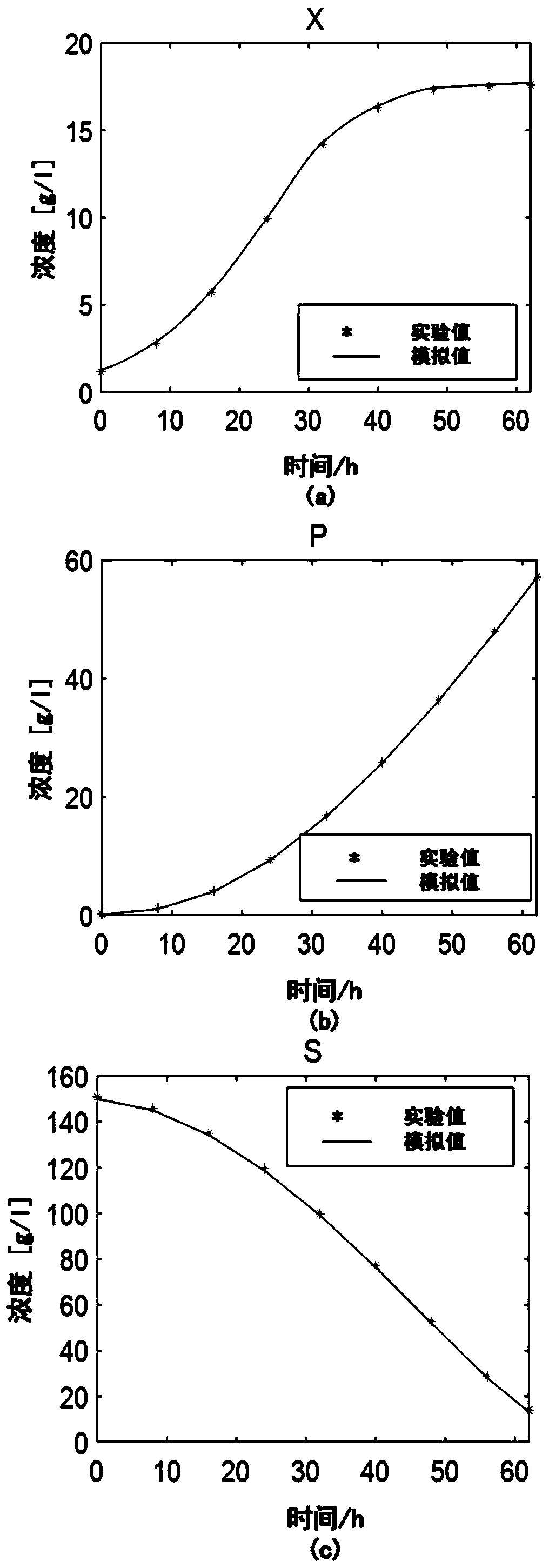
Macrodynamics and cell metabolic flux coupling modeling method in lysine biological manufacturing
The invention provides a macrodynamics and cell metabolic flux coupling modeling method in lysine biological manufacturing, belongs to the field of industrial microorganism manufacturing process modeling technologies and application, and relates to a modeling method combining fermentation dynamics expressed by a differential equation with cell metabolic flux described by chemometrics. Through reduction of a complex lysine metabolic network, correlation between key metabolic flux and external measurable variables is established, and coupling of a metabolic flux balance equation and concentration change kinetics of glucose, lysine and biomass is achieved; a coupling model parameter identification method utilizing an intelligent random optimization algorithm is provided, so that not only canthe change of extracellular macroscopic variable concentration be described, but also the dynamic change of intracellular metabolic flux can be described; compared with a common kinetic model, the model precision is high, and means are provided for exploring micromechanism information and metabolic characteristics in microbial cells.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
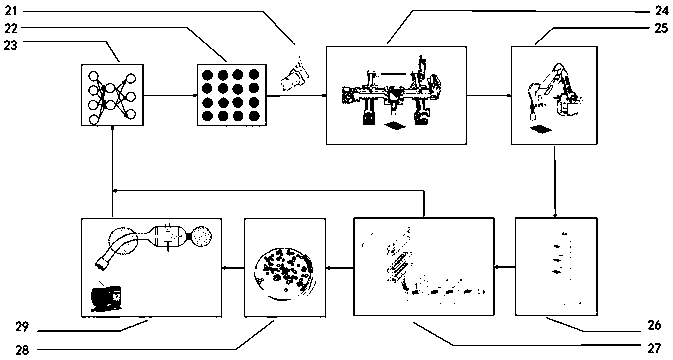
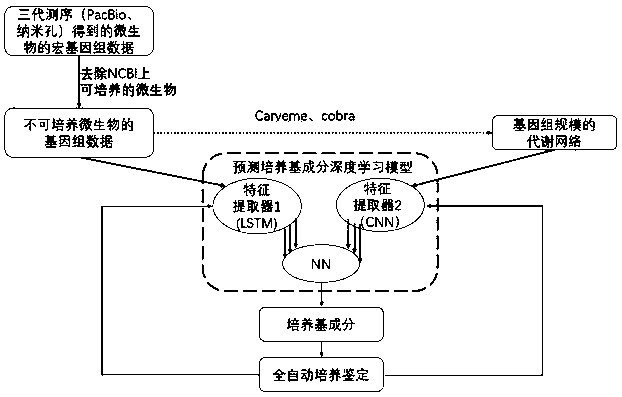
Non-culturable microorganism screening system based on generative adversarial network principle
The invention discloses a non-culturable microorganism screening system based on a generative adversarial network principle, which performs data processing on non-culturable microorganisms to obtain metabolic network and genome data, inputs the metabolic network and genome data into a model shown in figure 1 to obtain a series of culture medium components, and performs automatic sampling, plate sealing, cultivation and detection to obtain a cultivation result. The results are input into a training network to improve a parameter optimization model. Data distribution difference exists between non-culturable microorganisms and culturable microorganisms, the system utilizes migration learning and based on the generative adversarial network principle, the non-culturable microorganisms are takenas a target domain data set, the culturable microorganism data set is taken as a source domain data set, the characteristic space distribution difference between a source domain and a target domain is reduced through a discriminator principle of the generative adversarial network, knowledge migration from the culturable microorganisms to the non-culturable microorganisms is completed, the automation system is enabled to be more complete, and the purpose of improving the accuracy of predicting a culture medium formula is achieved.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Tissue metabolism network research method for toxic effect of atmospheric particulate matters
The invention provides a tissue metabolism network research method for a toxic effect of atmospheric particulate matters, wherein the method includes the following steps: S1, collecting atmospheric particulate matters in a research area and preparing an atmospheric particulate matter suspension; S2, carrying out intratracheal instillation on the atmospheric particulate matter suspension into a tested animal body to simulate the exposure of a human body to the atmospheric particulate matters; S3, after the end of the experiment period, collecting the liver, lung and serum of the tested animal;S4, carrying out metabolome analysis of the liver, lung and serum through a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry combined platform, and determining labeled metabolites of the liver, lung and serumrespectively; and S5, determining key metabolic network through the correlation analysis and the network analysis, and determining key labeled metabolites by the network node centrality evaluation. With use of network analysis, key metabolic markers of multiple tissues are determined through a network model, a method is provided for identifying key marker metabolites in multiple tissue metabolismdata under different phenotypes, and the accuracy of identification of the metabolic markers is improved.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Microbial growth phenotype predication method based on control-metabolic network integration model
InactiveCN105184049AEasy to predictHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsMicroorganismMetabolic network
The present invention discloses a microbial growth phenotype predication method based on a control-metabolic network integration model. The method comprises: firstly, constructing a gene control network, running multiple linear regression based on a large number of gene expression profile data so as to deduce a linear equation of expression variation of each target gene with a transcription factor, and calculating a fault discovery rate (FDR); and then taking a control relation (the FDR is less than or equal to 0.05) as a global control network, finding out transcription factors of control metabolic genes in the control network, calculating a reaction flow value F corresponding to a growth rate during a knockout period of the transcription factors according to the types of the transcription factors, performing same flow equilibrium analysis by an original metabolic network so as to obtain a maximal cell growth rate Fmax, and predicating growth phenotype changes of microorganisms during the knockout period of the transcription factors by calculating F / Fmax. The method provided by the present invention enables analysis precision to be improved, so that a growth phenotype of the microorganisms can be better predicted.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
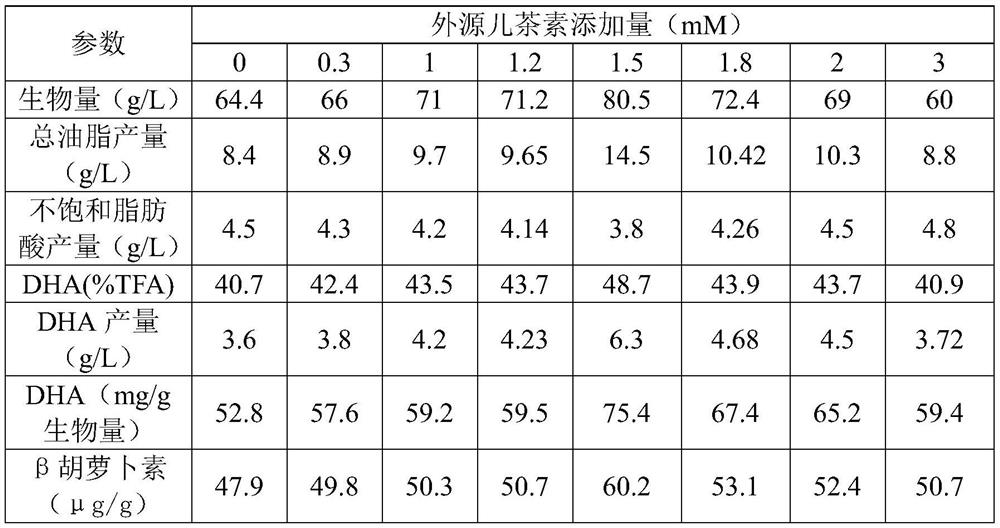
Application of catechinic acid in improving DHA grease yield of schizochytrium limacinum
The invention discloses application of catechin in improvement of DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) grease yield of schizochytrium limacinum, the grease yield is improved by culturing the schizochytrium limacinum with the catechin, and a small amount of catechin in a specific proportion is added to a schizochytrium limacinum fermentation system to inhibit generation of PEPC (polyepichlorohydrin) enzyme.Therefore, a metabolic network is disturbed to reduce biosynthesis of carbon flowing to lipid, the content of grease produced by schizochytrium limacinum fermentation can be effectively increased, theDHA yield is increased by 70% or above, the ratio of DHA to biomass is increased by 40% or above, the total grease is increased by 70% or above, and the beta carotene yield is also remarkably increased. Through simple fermentation regulation and control, the contents of DHA grease and beta carotene in the microbial schizochytrium limacinum can be remarkably increased, so that the production costis reduced, and the method has economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for constructing dynamic metabolic network based on topological structure of elementary reactions
ActiveCN108021787AAccurate quantitative descriptionEasy to automateSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsRate equationReaction rate
The invention discloses a constructing method for a dynamic metabolic network. The method comprises the steps that (a), for the dynamic metabolic network to be constructed, all isolated reactions andregulation reactions are found out, the number of redundant elementary reaction rate constants in each isolated reaction is determined; (b), Michaelis Menten kinetic parameters of all the isolated reactions and the regulation reactions are obtained from in vitro experiments or from existing enzymology databases; (c / d), for each isolated reaction and regulation reaction, absolute values and / or relative values of all the other basic reaction rate constants are calculated; (e) by steps (c) and (d), the rate constants of the elementary reactions are obtained, by computers, a dynamic metabolic network of an elementary reaction topological structure is constructed. The method does not need to deduce the analytical formulas of the Michaelis Menten kinetic rate equations one by one, under the premise of the thermodynamic equilibrium constants, the method is easy to obtain the elementary reaction rate constants involved in the regulation reactions, and suitable for constructing a large-scalemetabolic network by computers.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Volume dissolved oxygen transfer coefficient staged control method based on citric acid metabolic network
InactiveCN102443610AIncrease productionWidely producedMicroorganism based processesFermentationMetabolic networkOxygen
The invention discloses a volume dissolved oxygen transfer coefficient staged control method based on a citric acid metabolic network. The metabolic flow direction is controlled through controlling the dissolved oxygen of citric acid at different fermentation stages, so the yield of the citric acid is improved. In the whole fermentation process of the citric acid, seed liquid is inoculated into a fermentation tank at the inoculation quantity of 8 percent, the temperature is maintained at 37 DEG C, the tank pressure is 0.05 MPa, the stirring speed is maintained at 84 rpm / min, and the air introduction quantity is controlled to be maintained to be 40m<3> / min in the fermentation beginning period, about 48m<3> / min in the fermentation medium period (the fermentation is started for about 2 to 3 hours) and 40m<3> / min in the fermentation later period. When the fermentation is carried out for about 58 hours, the reducing sugar content is detected, and the fermentation can be stopped when the reducing sugar content is reduced to a value lower than 5 percent. The dissolved oxygen transfer coefficient staged control is realized through optimizing the air introduction quantity at different fermentation stages, the improvement for improving the citric acid yield based on the metabolic network is realized, the process is simple and convenient and is easy to operate, the requirement on equipment is low, the energy consumption is little, and the method can be widely applied to citric acid production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel algorithm for building cellular metabolism network
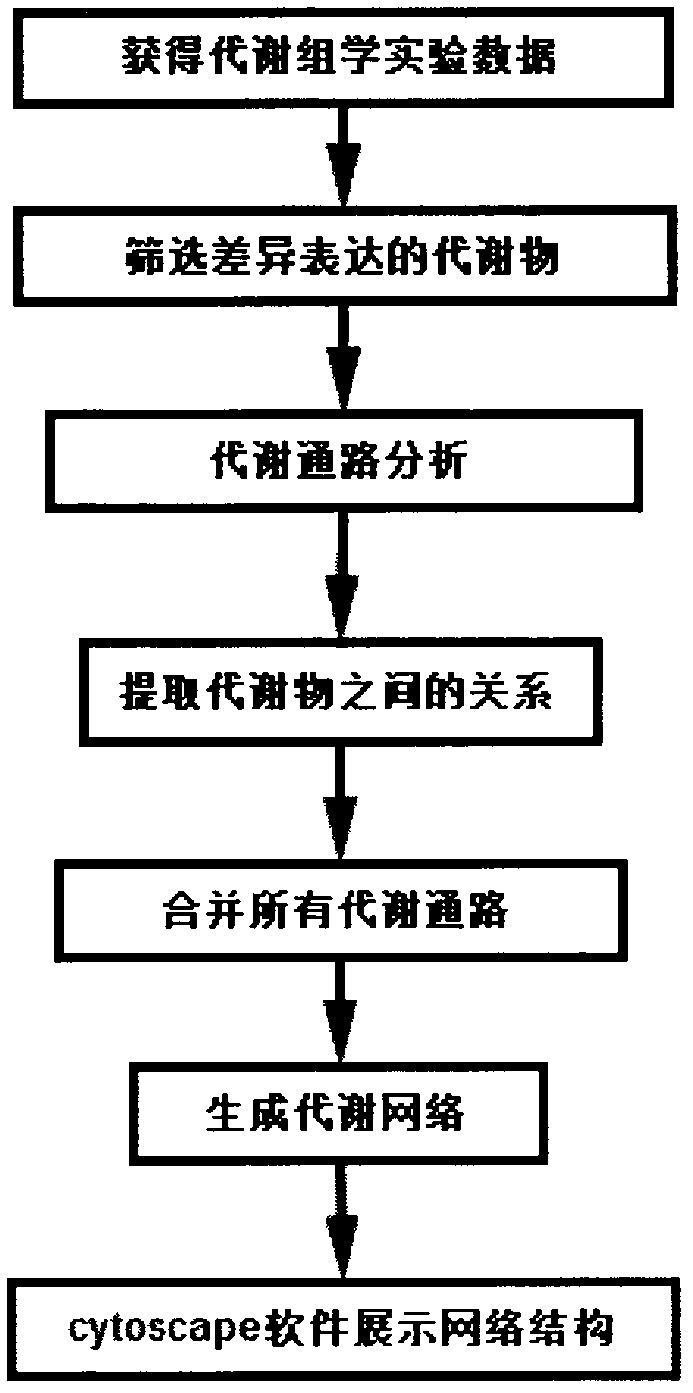
InactiveCN103186718AComprehensive interrelationshipComprehensive and intuitive resultsData visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsMetaboliteMetabolic network
The invention discloses a novel algorithm for building a cellular metabolism net. In the invention, according to a known metabolic pathway, a complete metabolic network is produced through integration. The metabolite relation can be observed globally, so as to play a guiding significance to mutual action of a metabolic pathway. In the invention, the following steps are included: step 1: obtaining experiment data of metabonomics; 2: selecting metabolites with differential expression; 3, metabolic pathway analysis is performed on metabolin; step 4: separating the relations of metabolins in each metabolic pathway; step 5: building a metabolic network: and step 6: using cytoscape software to generate a final network result.
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS8311790B2Analogue computers for chemical processesSystems biologyInformation repositoryMetabolic network
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
System for reproducing in vivo reaction in vitro
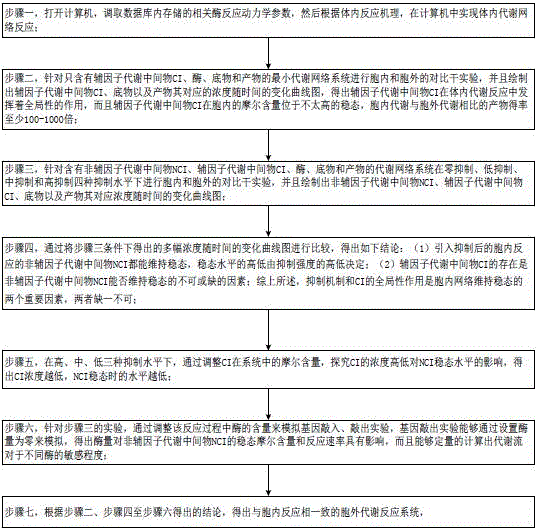
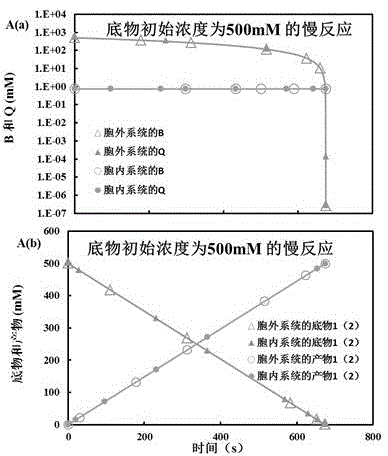
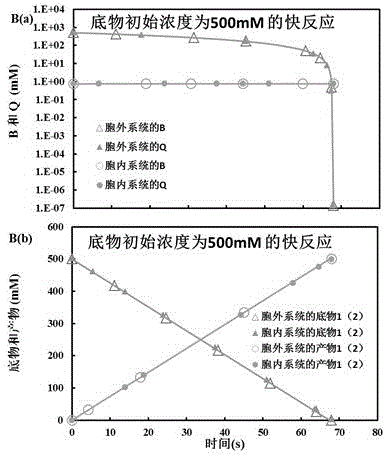
InactiveCN105574358ASolve energy problemsSolve environmental problemsSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsReaction rateMetabolic network
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological metabolism, and provides a system for reproducing an in vivo reaction in vitro. The system comprises the following steps: opening a computer, and dispatching kinetic parameters of related in vivo metabolism stored in a database; carrying out an intracellular and extracellular comparative dry experiment on a minimal metabolic network system only containing a cofactor metabolic intermediate CI, an enzyme, a substrate and a product; carrying out an intracellular and extracellular comparative experiment on an unrestraint metabolic network system containing a non-cofactor metabolic intermediate NCI, the cofactor metabolic intermediate CI, the enzyme, the substrate and the product; obtaining the influence of the concentration level of CI on the steady state level of NCI at high, middle and low inhibition levels; and simulating a gene knock-in and knock-out experiment by adjusting the enzyme content in the reaction process to obtain the result that the enzyme content has influence on the NCI and the reaction rate and that the inhibition mechanism, the cofactor metabolic intermediate CI, the enzyme content and the non-cofactor metabolic intermediate NCI have influence on intracellular reactions, and then an extracellular metabolic reaction system is obtained. The system provided by the invention makes up the blank of the industry.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Time sequence data processing method based on dynamic network diagram analysis
The present invention provides a time sequence data processing method based on dynamic network diagram analysis. The method comprises: analyzing metabonomics queue data from the perspective of a network; analyzing a correlation among variables; constructing a metabolic network according to a dynamic change of the correlation among the variables; and analyzing and determining warning information of occurrence of diseases (such as a malignant tumor) according to a dynamic concentration change and a change of a network topology structure. The time sequence data processing method based on the dynamic network diagram analysis eliminates a disadvantage that characteristic dynamic change information is ignored when a static analysis method is adopted to process time sequence data of metabonomics. Moreover, compared with an algorithm of focusing on finding a monomolecule marker, in the method provided by the present invention, the change of the correlation among the variables over time is considered, and key turns of diseases are analyzed and determined, thereby facilitating a study on pathogenic mechanisms of diseases, and laying a foundation for early diagnosis and a prognostic study of diseases.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for developing culture medium using genome information and in silico analysis
A method for developing a culture medium using genome information and in silico anlaylsis. In one implementation, the method involves developing a minimal synthetic medium, including the steps of constructing a metabolic network using genome information of prokaryotic cell or eukaryotic cell, selecting components of the minimal synthetic medium removing any one among external metabolites from the constructed metabolic network and conducting metabolic flux analysis using in silico simulation, and determining a final culture medium by actual culture.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com