Tissue metabolism network research method for toxic effect of atmospheric particulate matters
A technology of atmospheric particulate matter and toxic effects, applied in medical science, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as damage to organisms, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
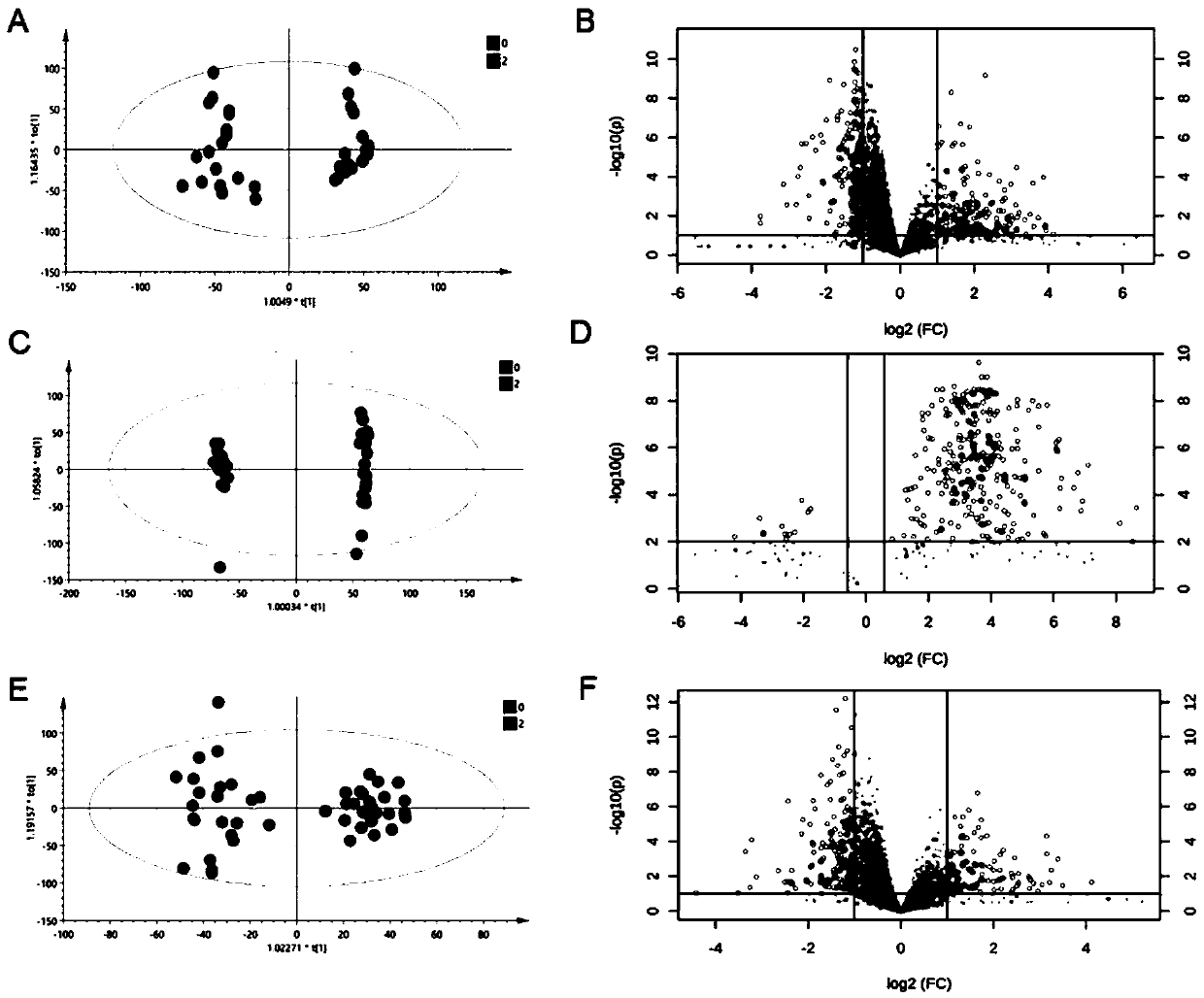
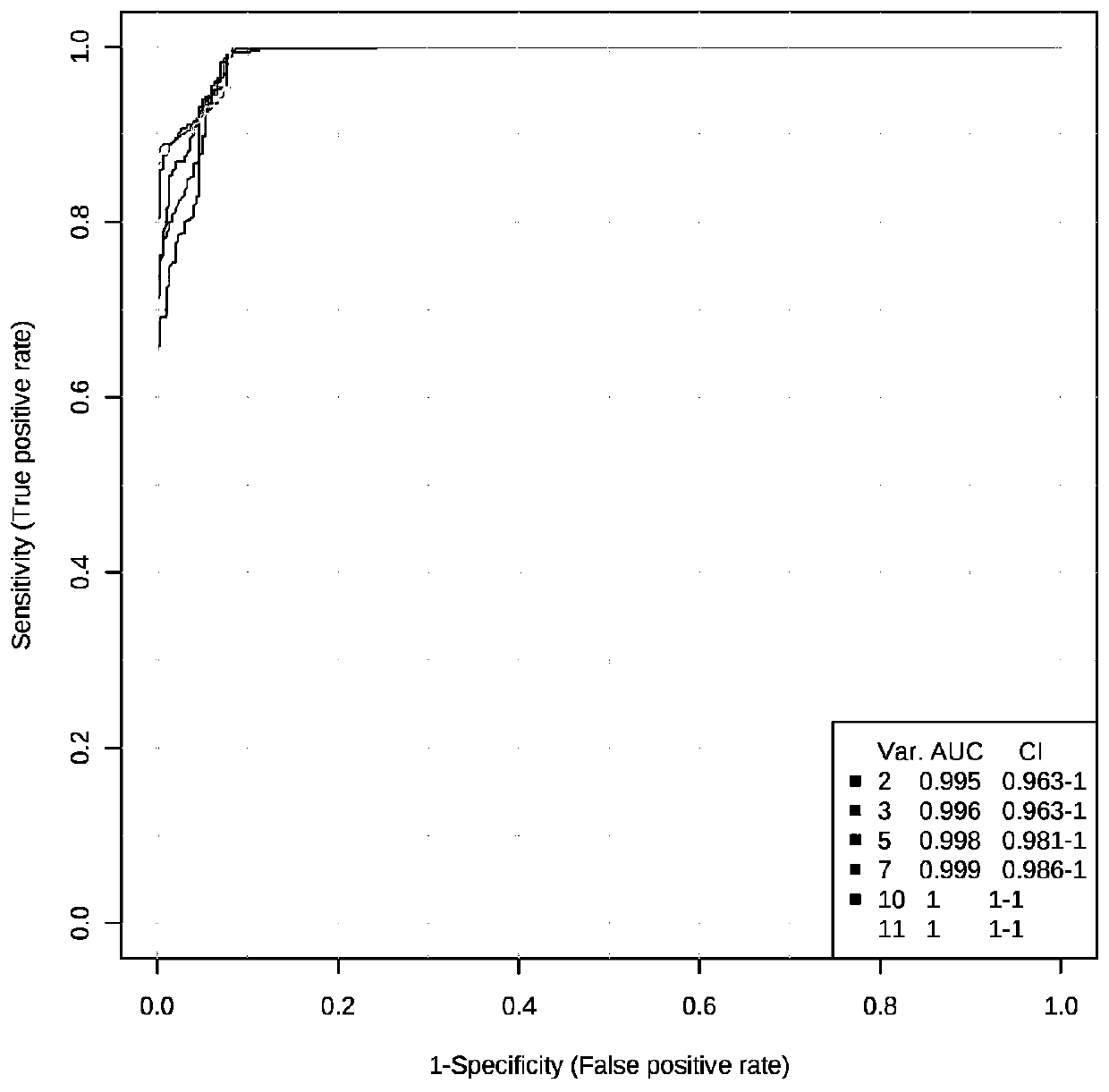
[0038] The design of this example is based on the evaluation of the systemic toxicity effect and the screening of key metabolic markers under the exposure of PM2.5 in the real environment of mice. The specific exposure steps are as follows:
[0039] 1. Exposure experiment of mice in actual environment PM2.5
[0040] Atmospheric fine particle sampler is used to trap PM2.5 particles on the filter membrane, and the obtained particle samples and buffer solution (phosphate buffer or saline) are ultrasonically prepared into a suspension with a certain concentration for tracheal instillation, PM2 .5 The concentration of the suspension is converted according to the Chinese air quality standard and the average body weight of the mice. Mice were exposed to atmospheric particulate matter by tracheal instillation after a period of adaptive feeding.
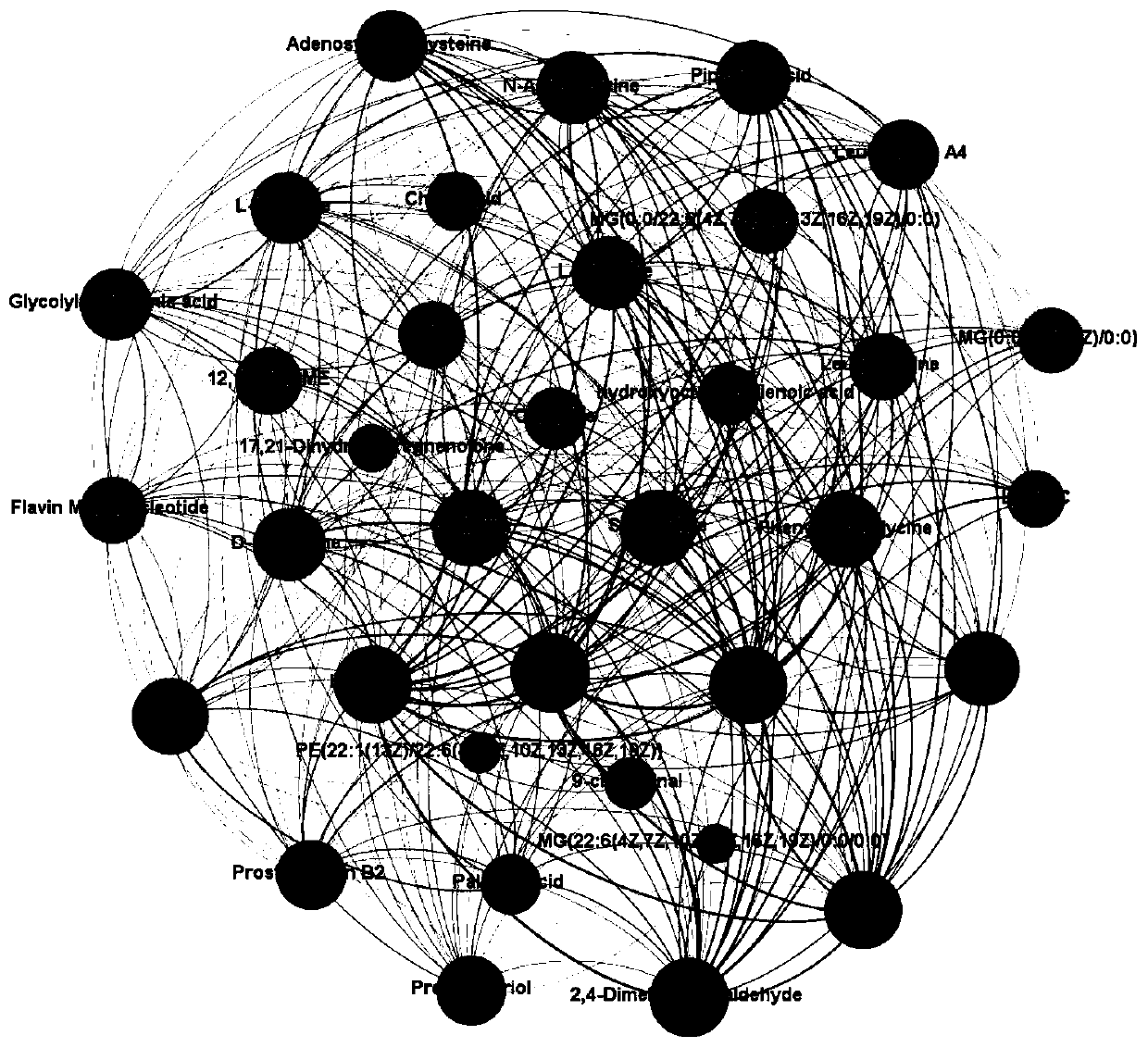
[0041] 2. Sample pretreatment of mouse tissue metabolome
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com