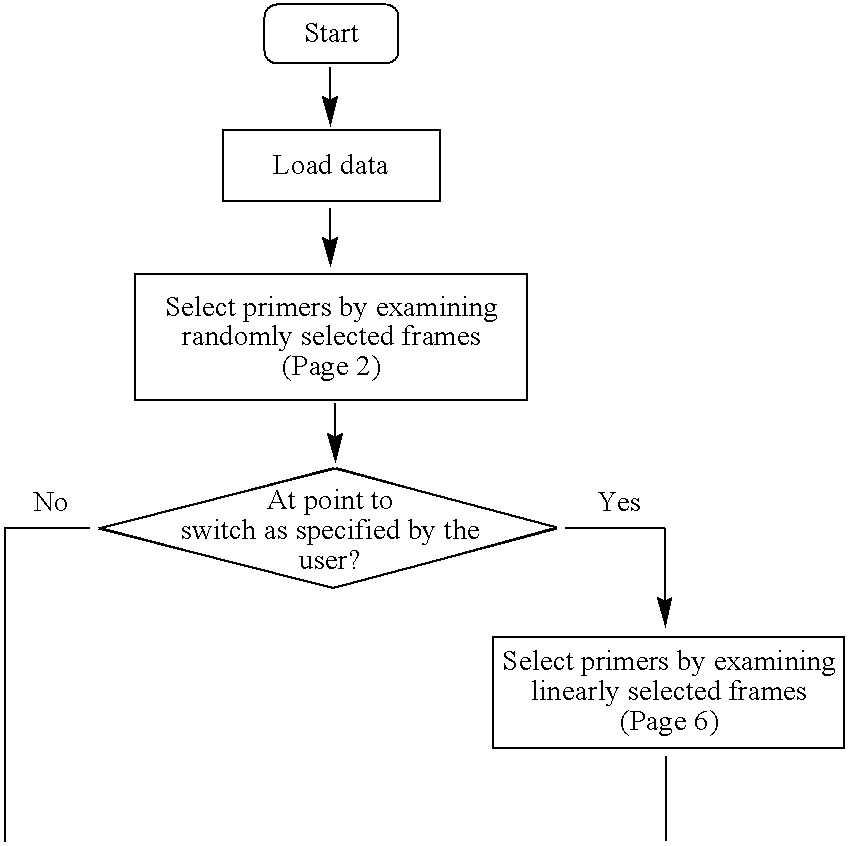
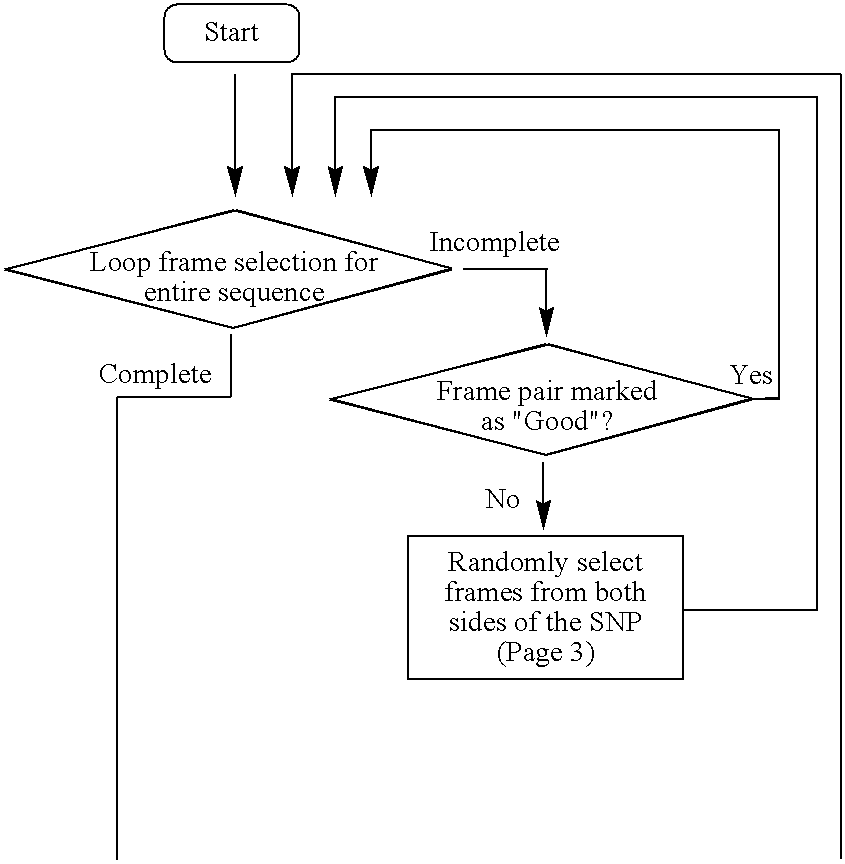
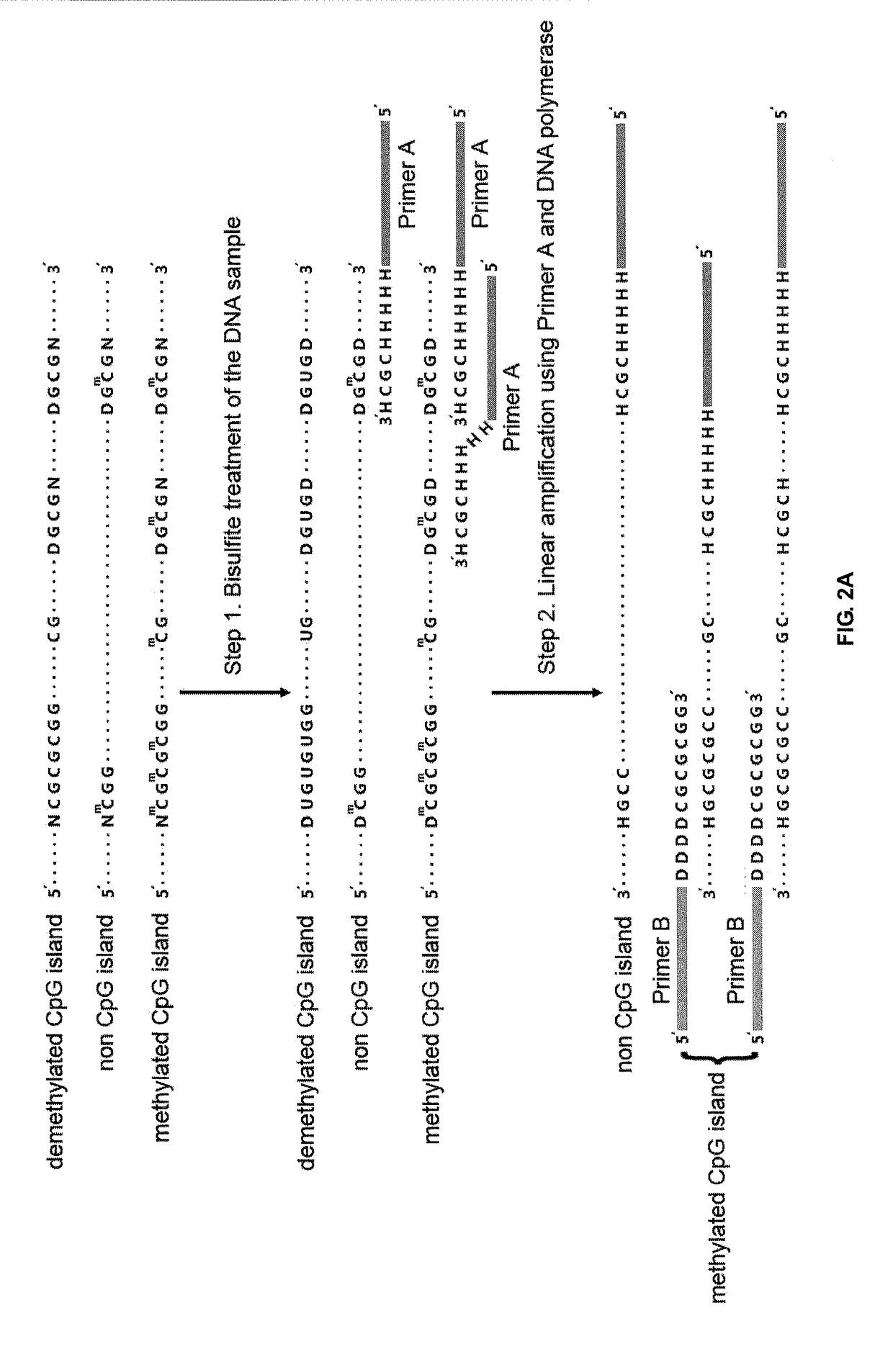
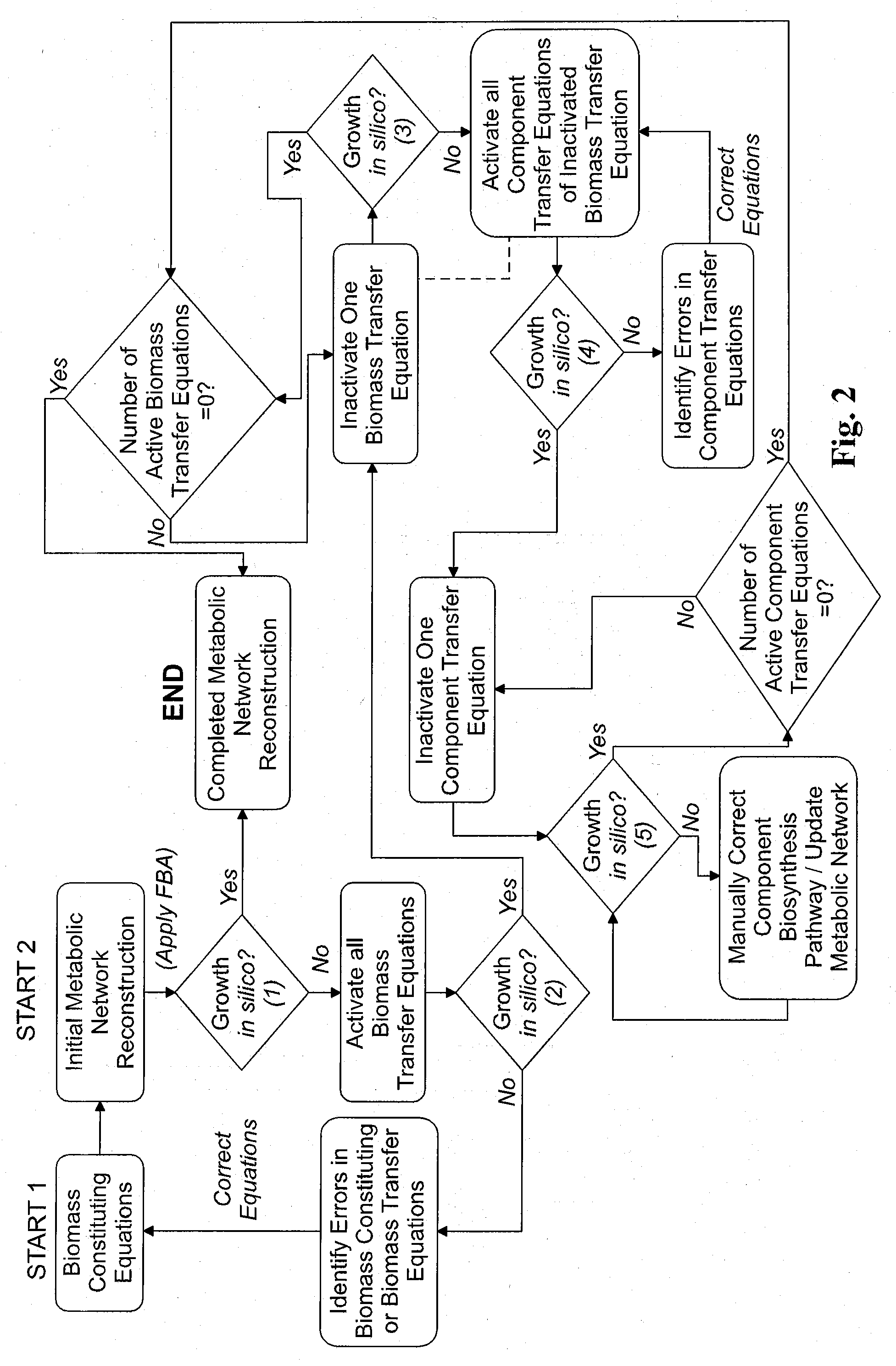
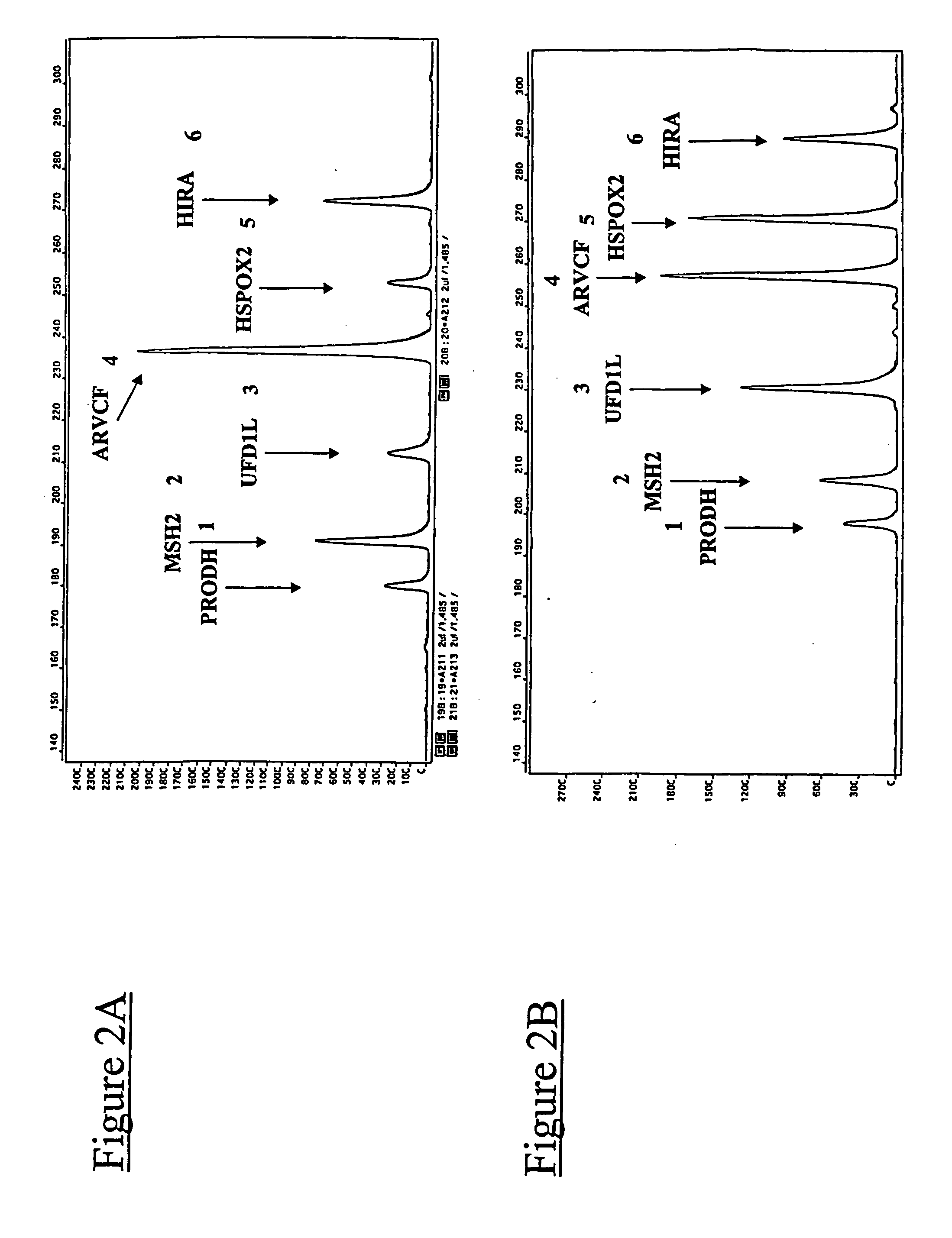
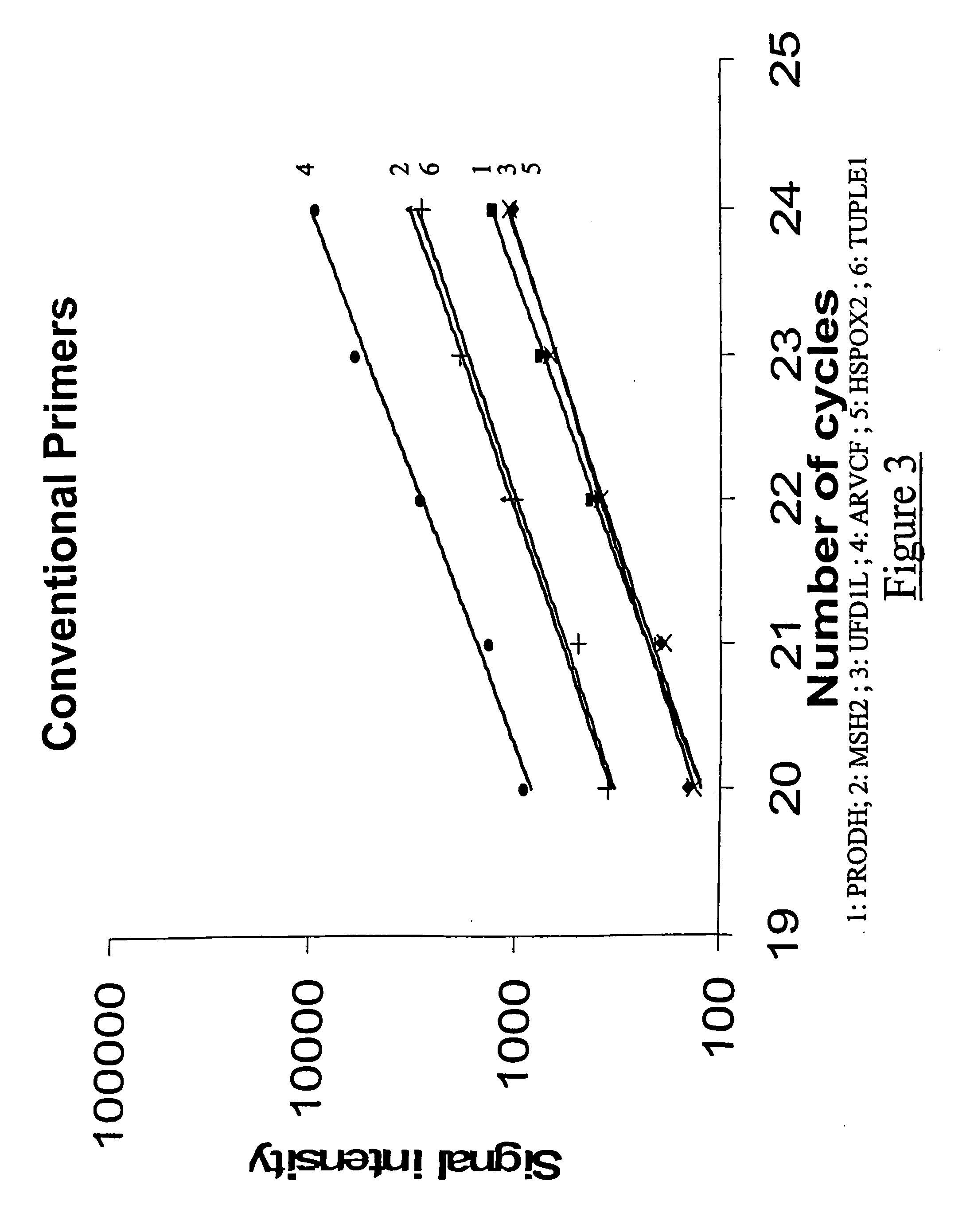
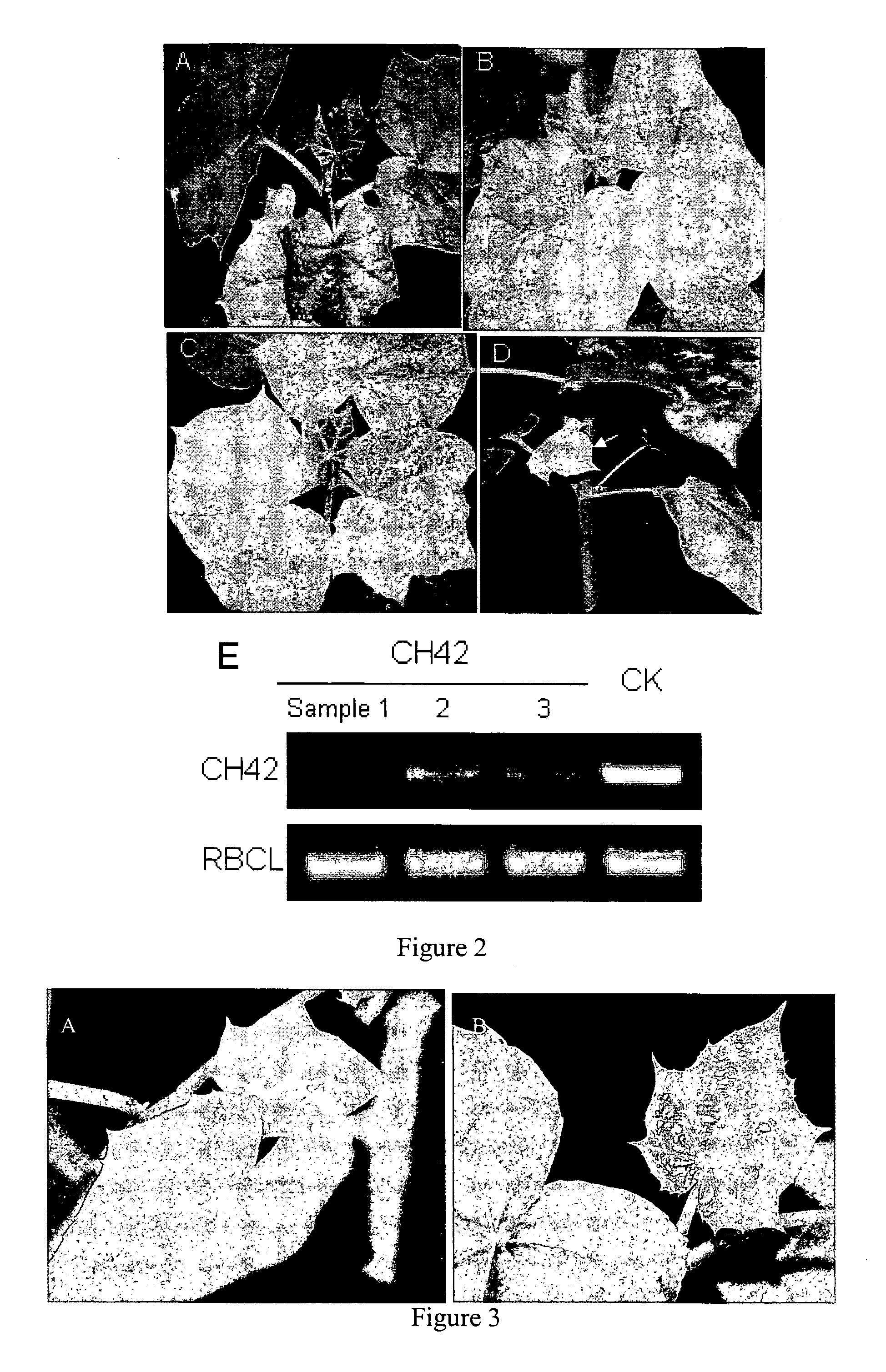
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Genome scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High throughput multiplex DNA sequence amplifications
InactiveUS20060281105A1Efficient and simultaneous amplificationMinimize formationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHigh throughput genotypingGenome scale
The present invention provides methods of designing PCR primers that allow the efficient and simultaneous amplification of a large number of different desired DNA fragments in a single multiplex PCR and minimize the formation of nonspecific extensions of undesired DNA fragments. The present invention allows a multiplex PCR to use at least 50 pairs of primers and produce at least 50 DNA fragments of interest. The present invention significantly broadens the application of multiplex PCR in the identification of multiple genes related to multifactorial diseases, the genome-scale detection of genetic alterations, the studies in large-scale pharmacogenetic reactions, the genotyping genetic polymorphism in a large population, the gene expression profiling in various samples, and high throughput genotyping technologies.
Owner:LI HONGHUA +1
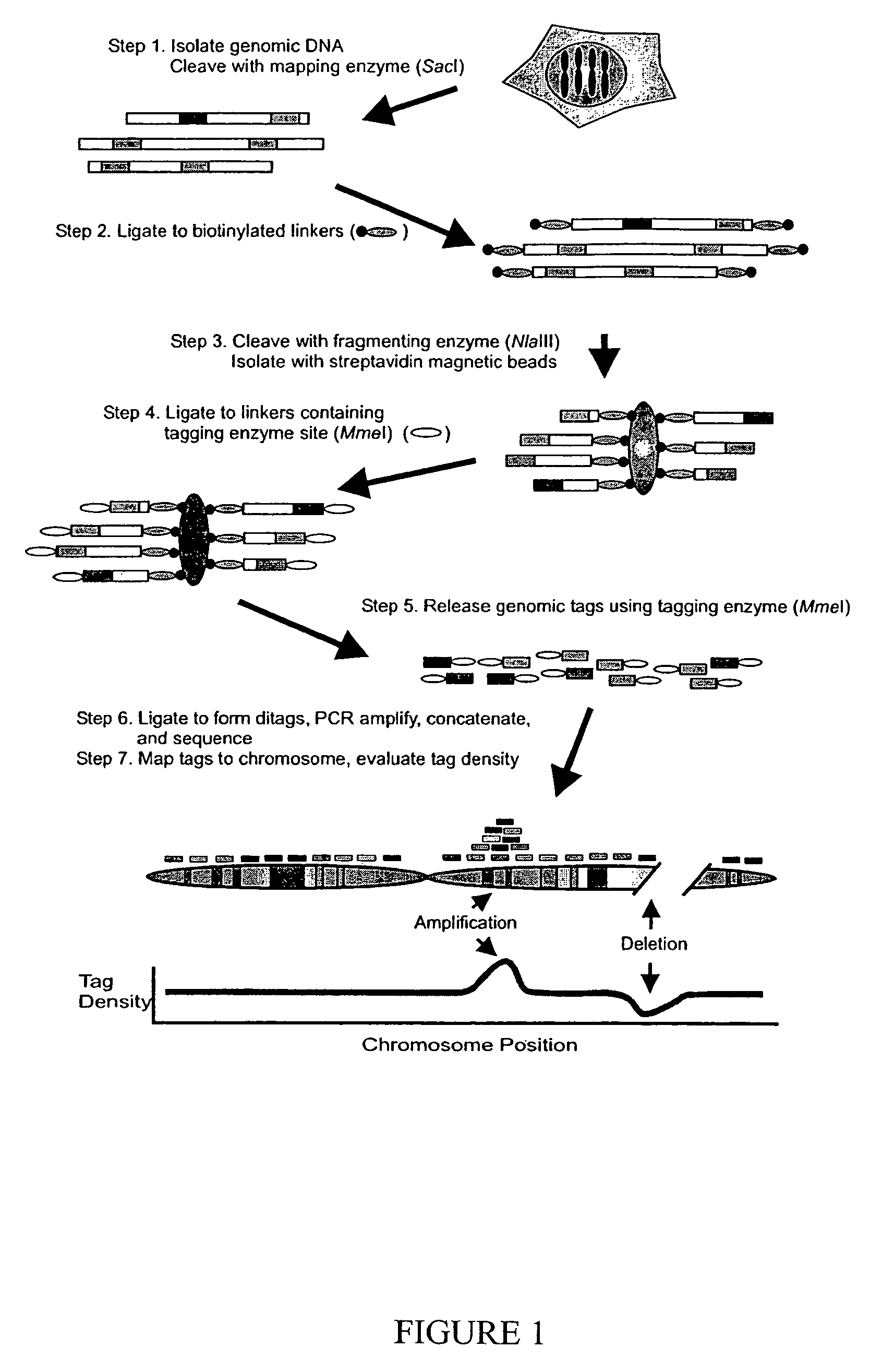
Digital karyotyping
ActiveUS7704687B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHuman DNA sequencingHuman cancer
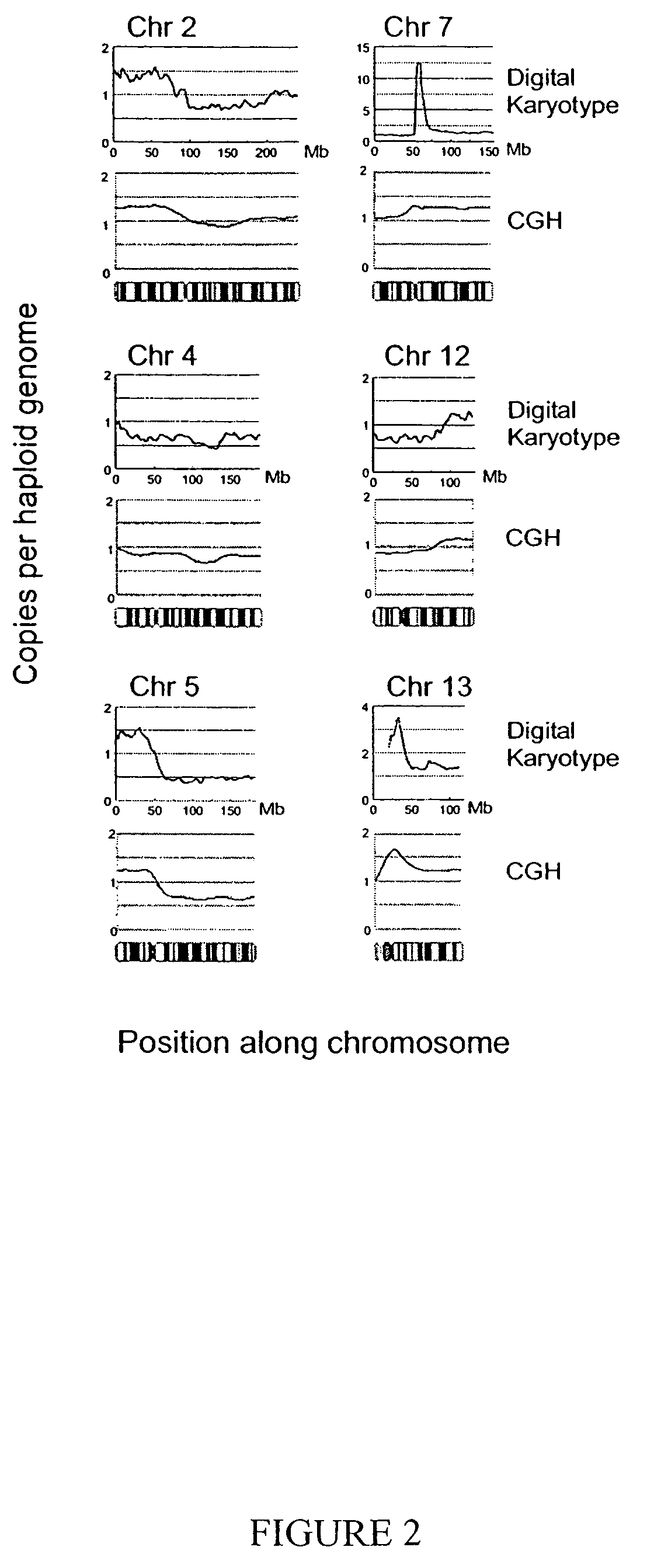
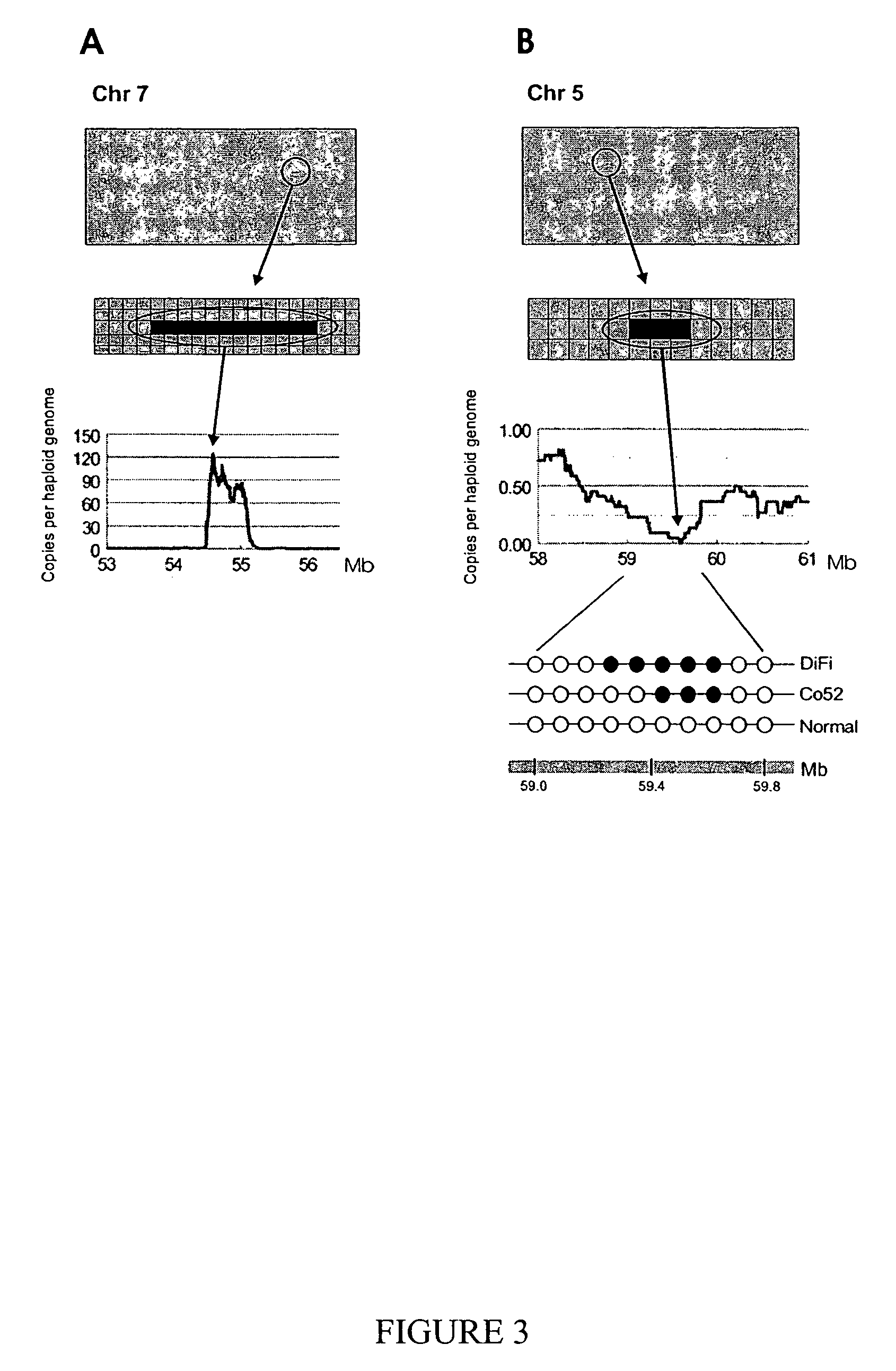
Alterations in the genetic content of a cell underlie many human diseases, including cancers. A method called Digital Karyotyping provides quantitative analysis of DNA copy number at high resolution. This approach involves the isolation and enumeration of short sequence tags from specific genomic loci. Analysis of human cancer cells using this method identified gross chromosomal changes as well as amplifications and deletions, including regions not previously known to be altered. Foreign DNA sequences not present in the normal human genome could also be readily identified. Digital Karyotyping provides a broadly applicable means for systematic detection of DNA copy number changes on a genomic scale.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Functional genomics using crispr-cas systems, compositions, methods, screens and applications thereof
ActiveUS20160251648A1Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesStable introduction of DNAScreening processGenome scaleGenomics
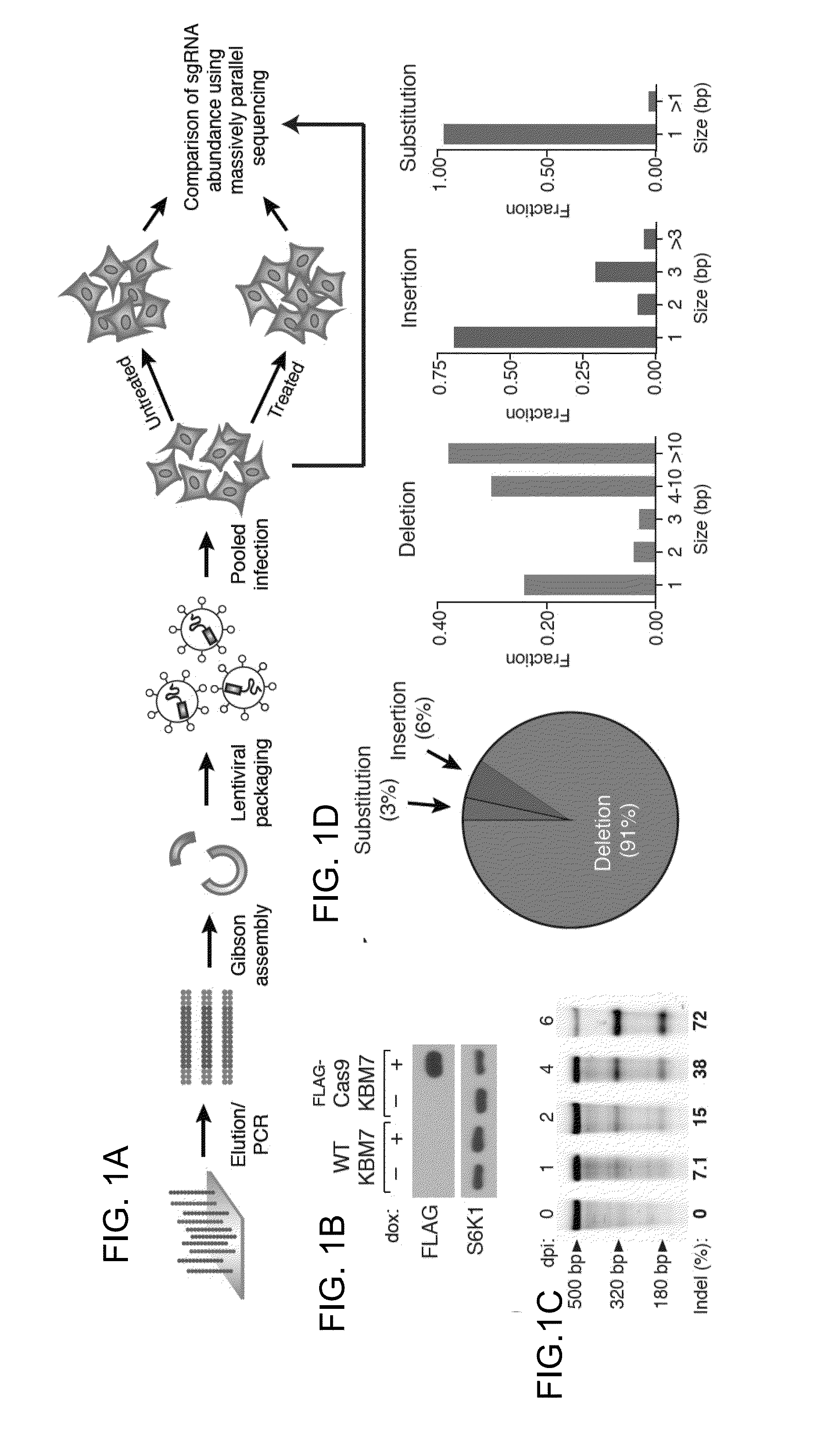
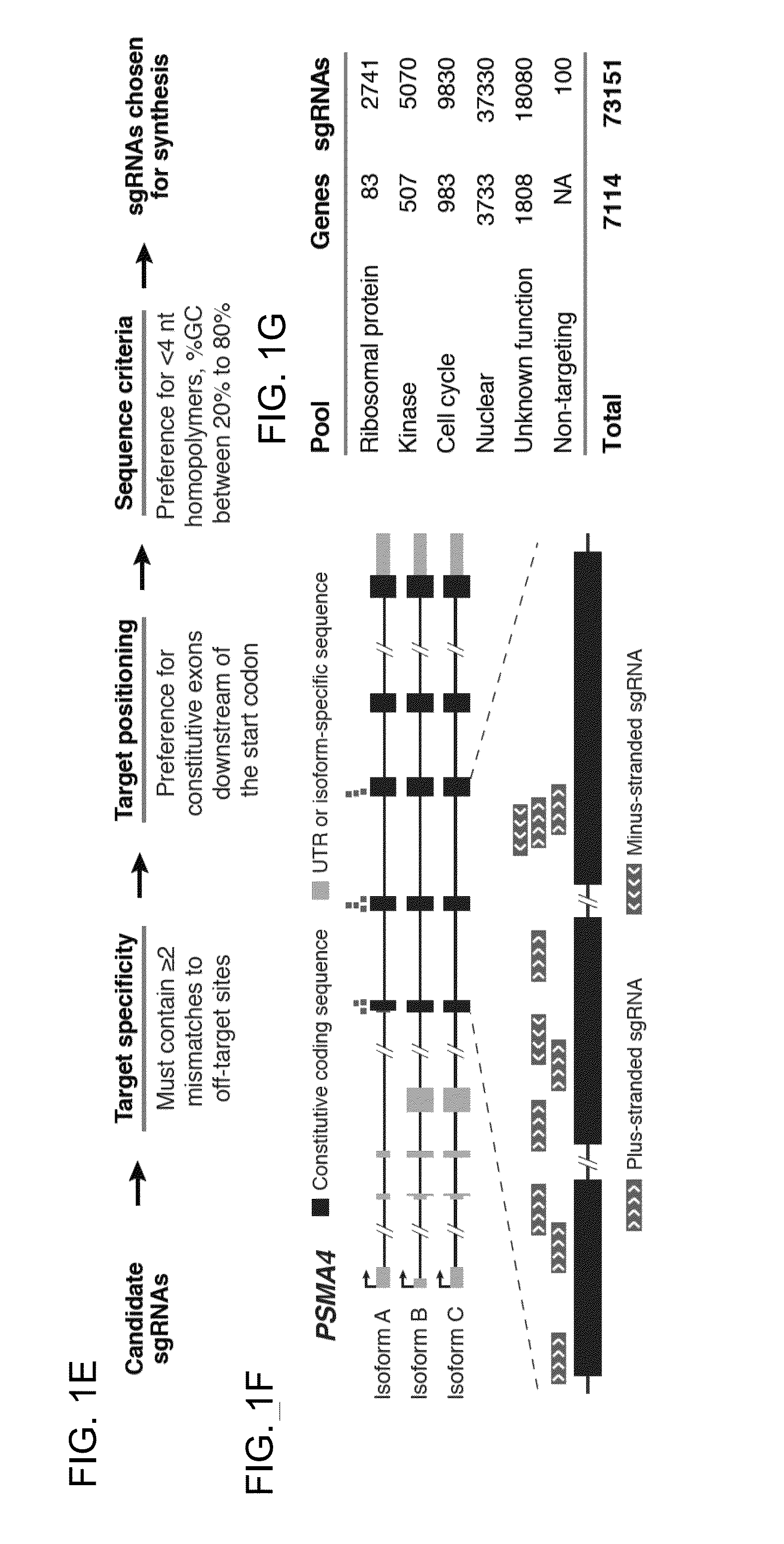
The present invention generally relates to libraries, kits, methods, applications and screens used in functional genomics that focus on gene function in a cell and that may use vector systems and other aspects related to Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems and components thereof. The present invention also relates to rules for making potent single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for use in CRISPR-Cas systems. Provided are genomic libraries and genome wide libraries, kits, methods of knocking out in parallel every gene in the genome, methods of selecting individual cell knock outs that survive under a selective pressure, methods of identifying the genetic basis of one or more medical symptoms exhibited by a patient, and methods for designing a genome-scale sgRNA library.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
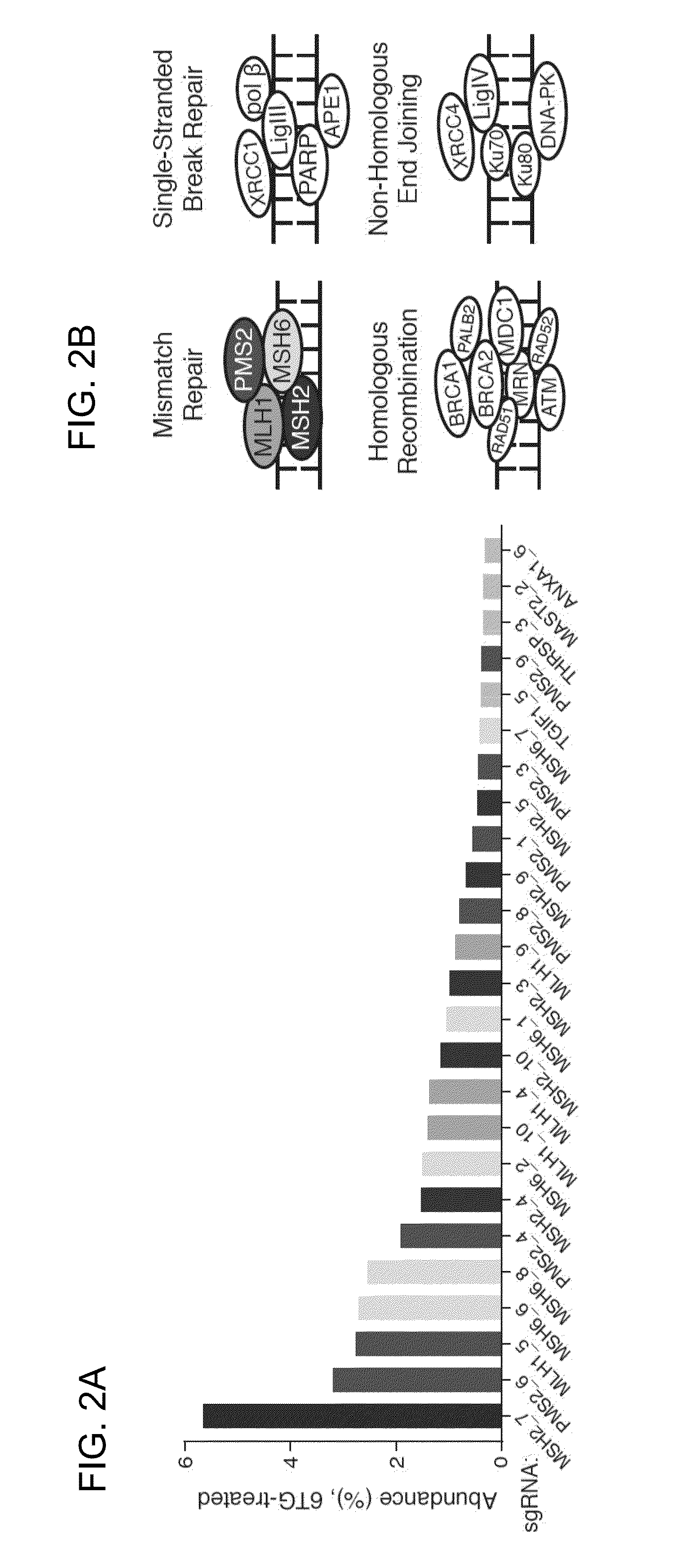
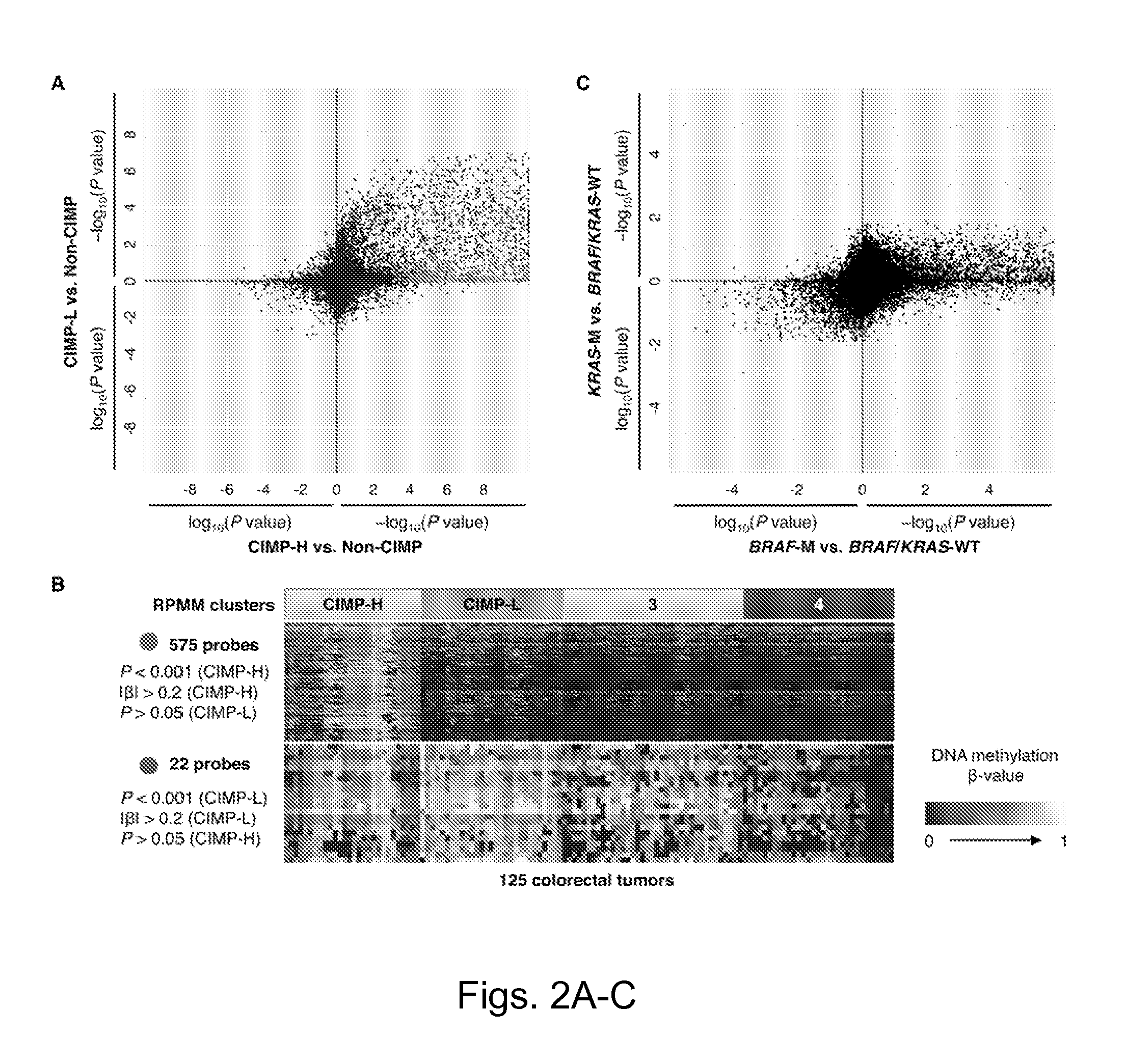
Genome-scale analysis of aberrant DNA methylation in colorectal cancer
Particular aspects provide methods and compositions (e.g., gene marker panels) having substantial utility for at least one of diagnosis, identification and classification of colorectal cancer (CRC) (e.g., tumors) relating to distinctive DNA methylation-based subgroups of CRC including CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) groups (e.g., CIMP-H and CIMP-L) and non-CIMP groups. Exemplary marker panels include: B3GAT2, FOXL2, KCNK13, RAB31 and SLIT1 (CIMP marker panel); and FAM78A, FSTL1, KCNC1, MYOCD, and SLC6A4 (CIMP-H marker panel). Further aspects relate to genetic mutations, and other epigenetic markers relating to said CRC subgroups that can be used in combination with the gene marker panels for at least one of diagnosis, identification and classification of colorectal cancer (CRC) (e.g., tumors) relating to distinctive CIMP and non-CIMP groups.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
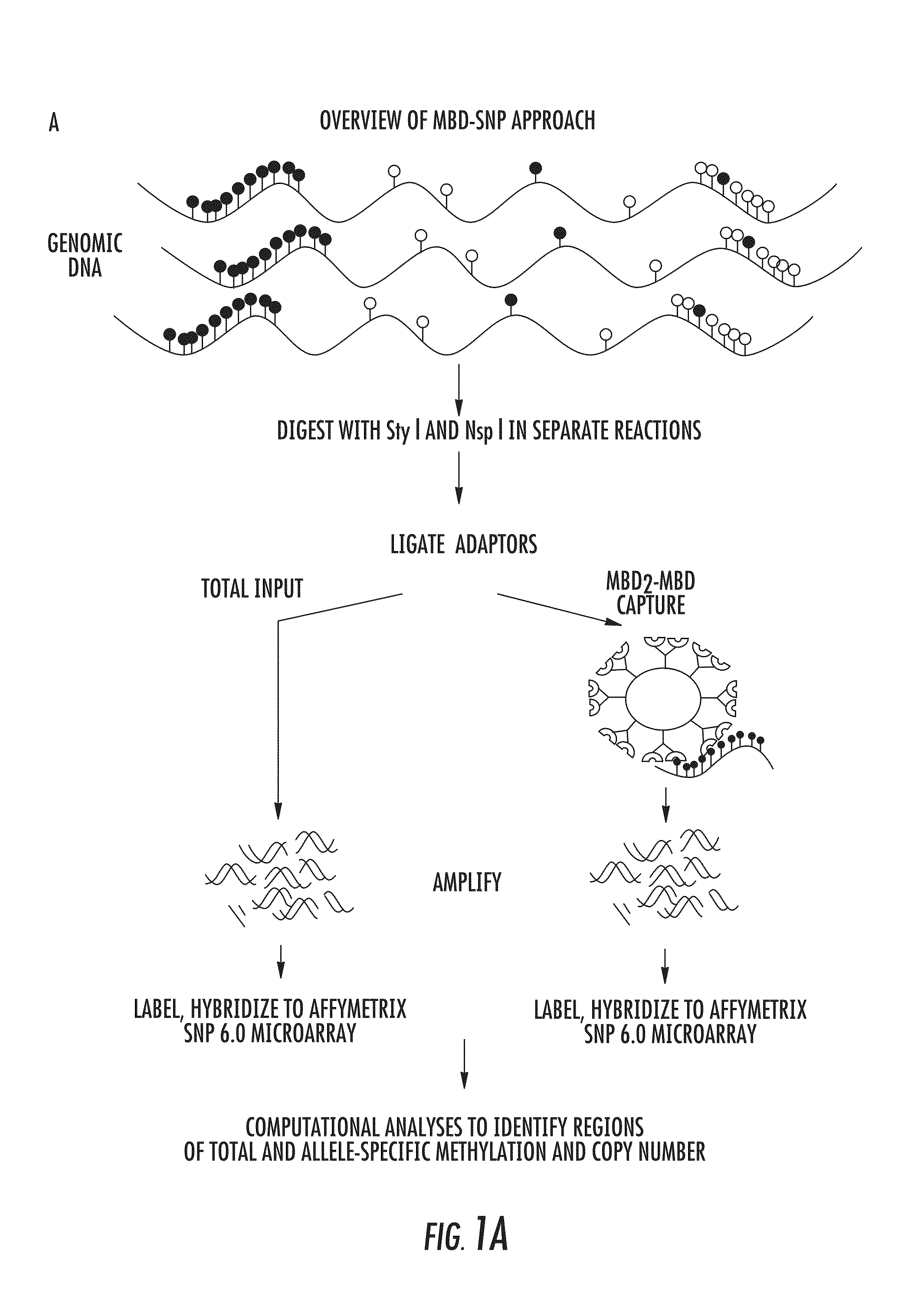
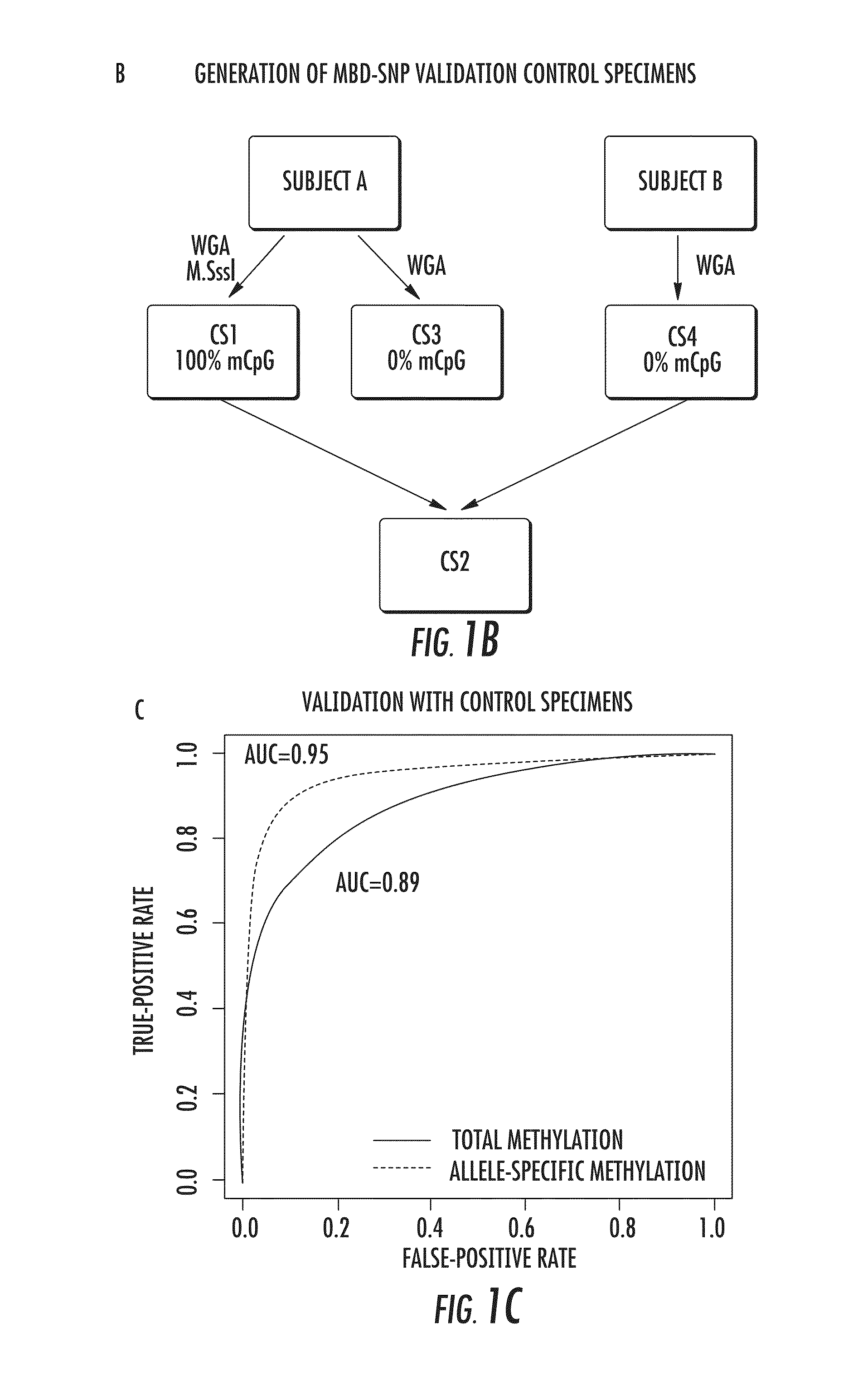
DNA methylation markers for metastatic prostate cancer
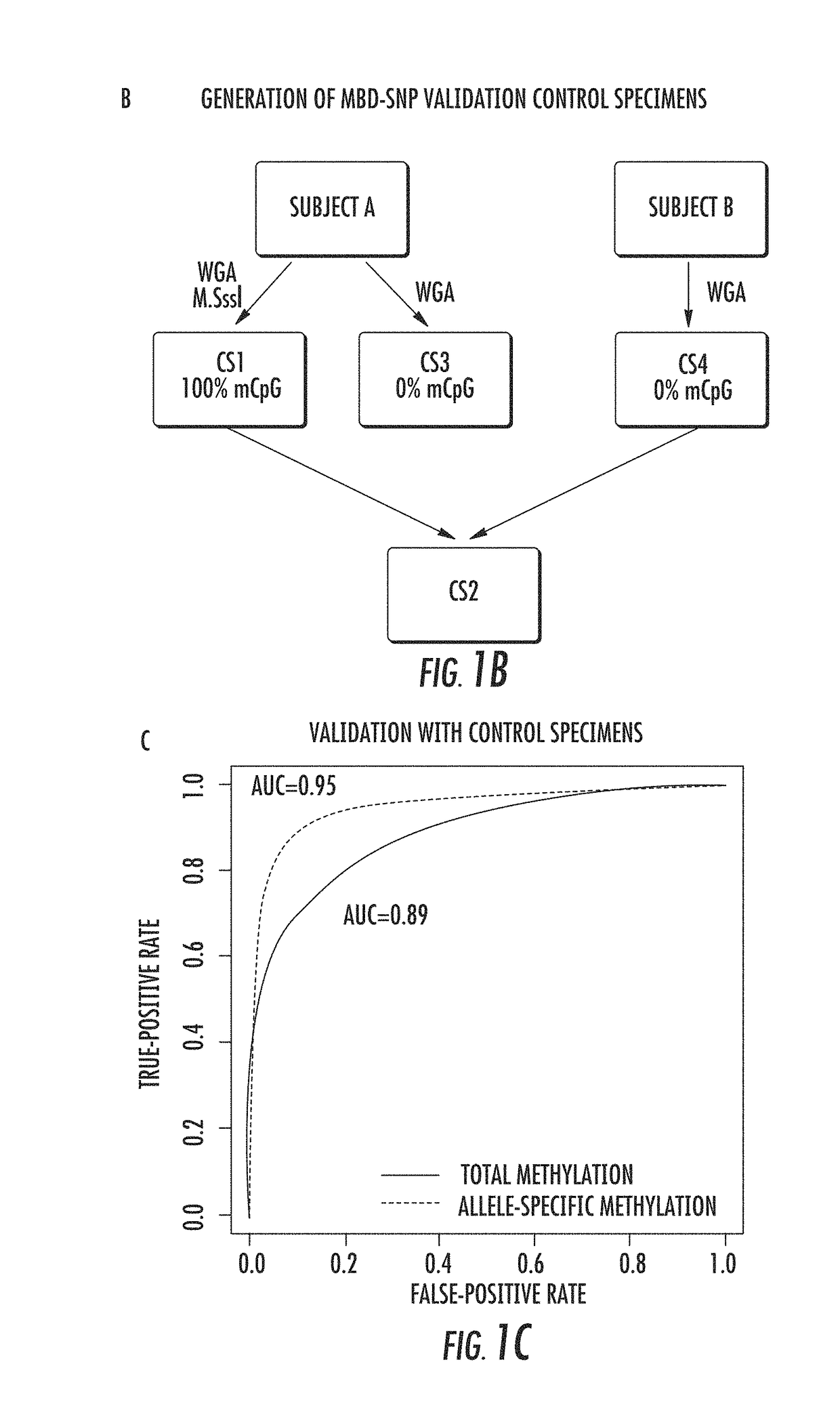
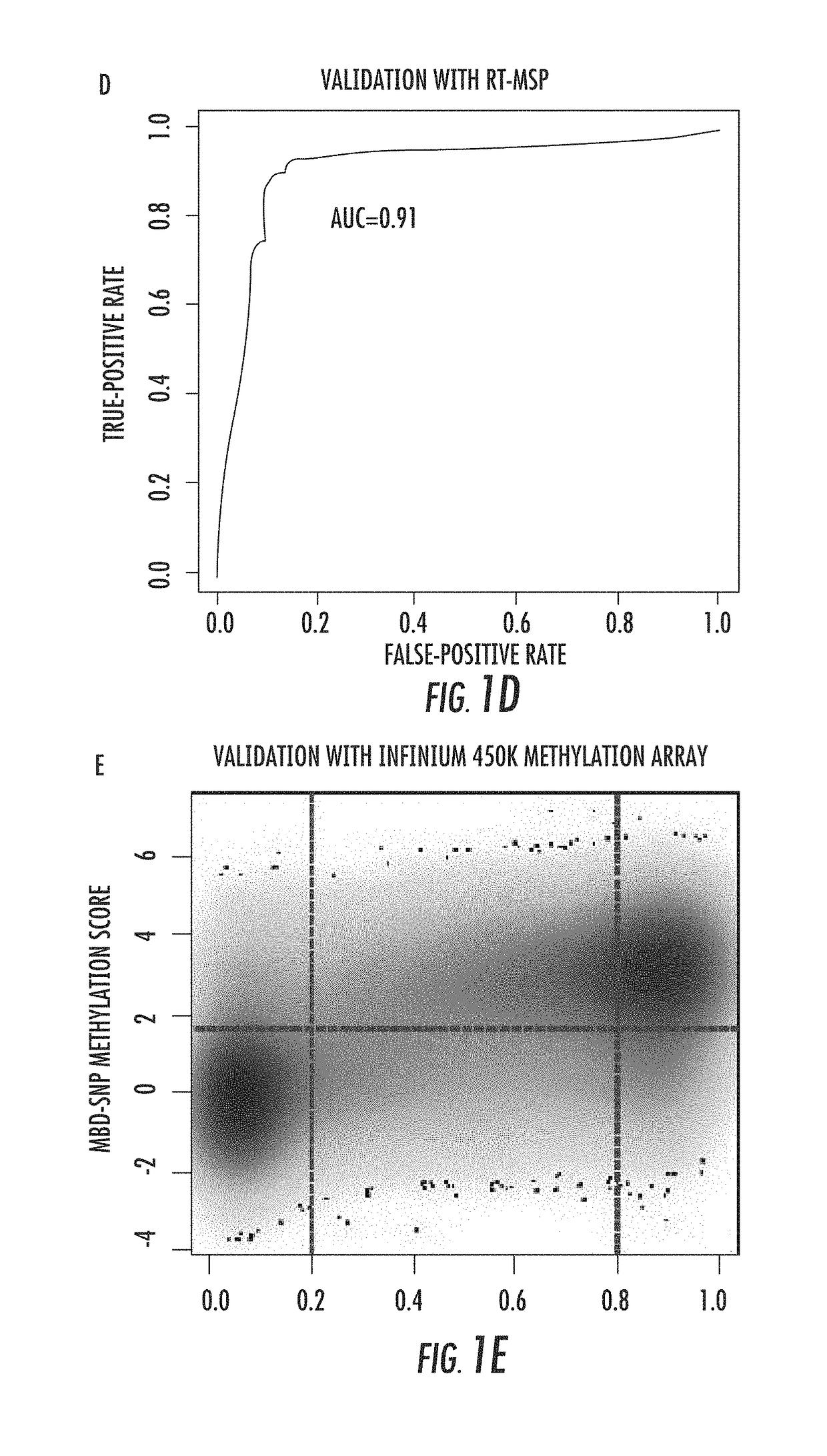
InactiveUS20140274767A1Rapid and cost-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationGenome scale
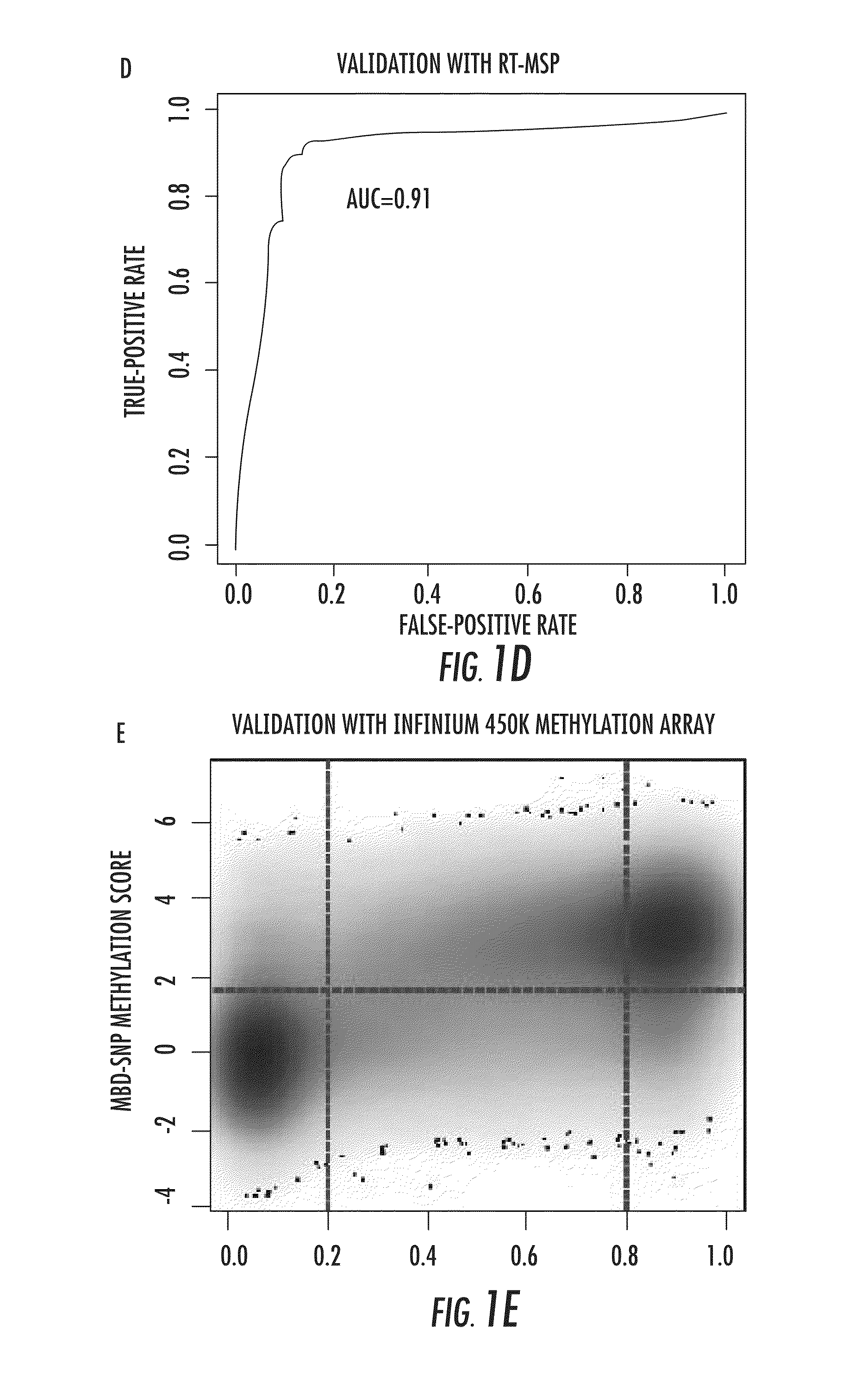
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions useful for assessing prostate cancer. In a specific embodiment, present inventors have developed and applied a new technology and associated computation methods enabling simultaneous genome-scale analysis of genetic (copy number) and epigenetic (total methylation (TM) and allele-specific methylation (ASM) alternation, This method, called MBD-SNP, features affinity enrichment or methylated genomic DNA fragments using a methyl-binding domain polypeptide.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Genome-scale analysis of replication timing
InactiveUS20120322675A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenome scaleReplication timing
Methods for identifying and / or distinguishing a homogeneous population of cells based on their replication domain timing profile using high resolution genomic arrays or sequencing procedures are provided. These methods may be used to compare the replication timing profile for a population of cells to another replication timing profile(s), a replication timing fingerprint, and / or one or more informative segments of a replication timing fingerprint, which may be simultaneously or previously determined and / or contained in a database, to determine whether there is a match between them. Based on such information, the identity of the population of cells may be determined, or the identity of the population of cells may be distinguished from other populations of cells or cell types. Methods for determining a replication timing fingerprint for particular cell types are also provided.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Method for information mining of genome metabolic network preliminary model
InactiveCN103399948AEasy to compareLabor savingSpecial data processing applicationsGenome scaleInformation mining
The invention provides a method for information mining of a genome metabolic network preliminary model. The method comprises the steps as follows: as for the KEGG website, extracting a corresponding relation among gene, protein and reaction, that is, determining the GPR relation by adopting a website script semantic analysis technology on the basis of webpage key content priori position information, and establishing an excel table to show the GPR relation information, so as to obtain the genome metabolic network preliminary model. The model constructed by adopting the method unifies the reaction form, and is convenient in comparison with other models and convenient in reference. The method has been applied to construction of a scheffersomyces stipitis CBS6054 genome-scale metabolic network, and compared with the construction of a traditional network preliminary model based on the KEGG database, a great amount of labor and time are saved, and the construction efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting differentially methylated cpg islands associated with abnormal state of human body
InactiveUS20180143198A1Reduce tearingReduce wearNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyHepatocellular carcinoma
Disclosed is a method for detecting differentially methylated CpG islands associated with an abnormal state of a human body, characterized by detecting very minute amounts of methylated CpG short tandem nucleic acid sequences in highly fragmented DNA samples with genome scale, identifying differentially methylated CpG islands associated with abnormal state of human body and determining the corresponding abnormal state of human body. Sequencing libraries are constructed by using CpG short tandem sequences as primers to perform three steps of PCR reactions on DNAs which are conversed by nodifiers, and detections of very minute amounts of methylated CpG short tandem nucleic acid sequences are implemented with high throughput sequencing technology. A group of genome sequences and methylation patterns of differentially methylated CpG islands which are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma are also disclosed; they may be used for distinguishing between hepatacellular carcinoma and non-cancerous state.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method
InactiveCN103774241AReduce masking effectLow costLibrary member identificationLibrary creationCDNA libraryGenome scale
The invention discloses a library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method. The method takes a genome-grade cDNA as the bait to screen the genome-grade cDNA library. In the application process of the method, the cDNA library is subjected to a homogenization treatment so as to reduce the masking effect of the high-abundance interaction proteins to the low-abundance interaction proteins, and thus the screening efficiency is improved; and moreover the characteristic of yeast URA3 gene is utilized so as to automatically remove the sequences, which have the self-activating function, in bait cDNA. The invention establish a library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method, which has the advantages of high feasibility, low cost, low requirements on experiment conditions, and low workload; and successfully applies the method to a screening of pathogen-host plant interaction proteins.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS20090259451A1Reduce in quantityAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingUnderdetermined systemIn silico
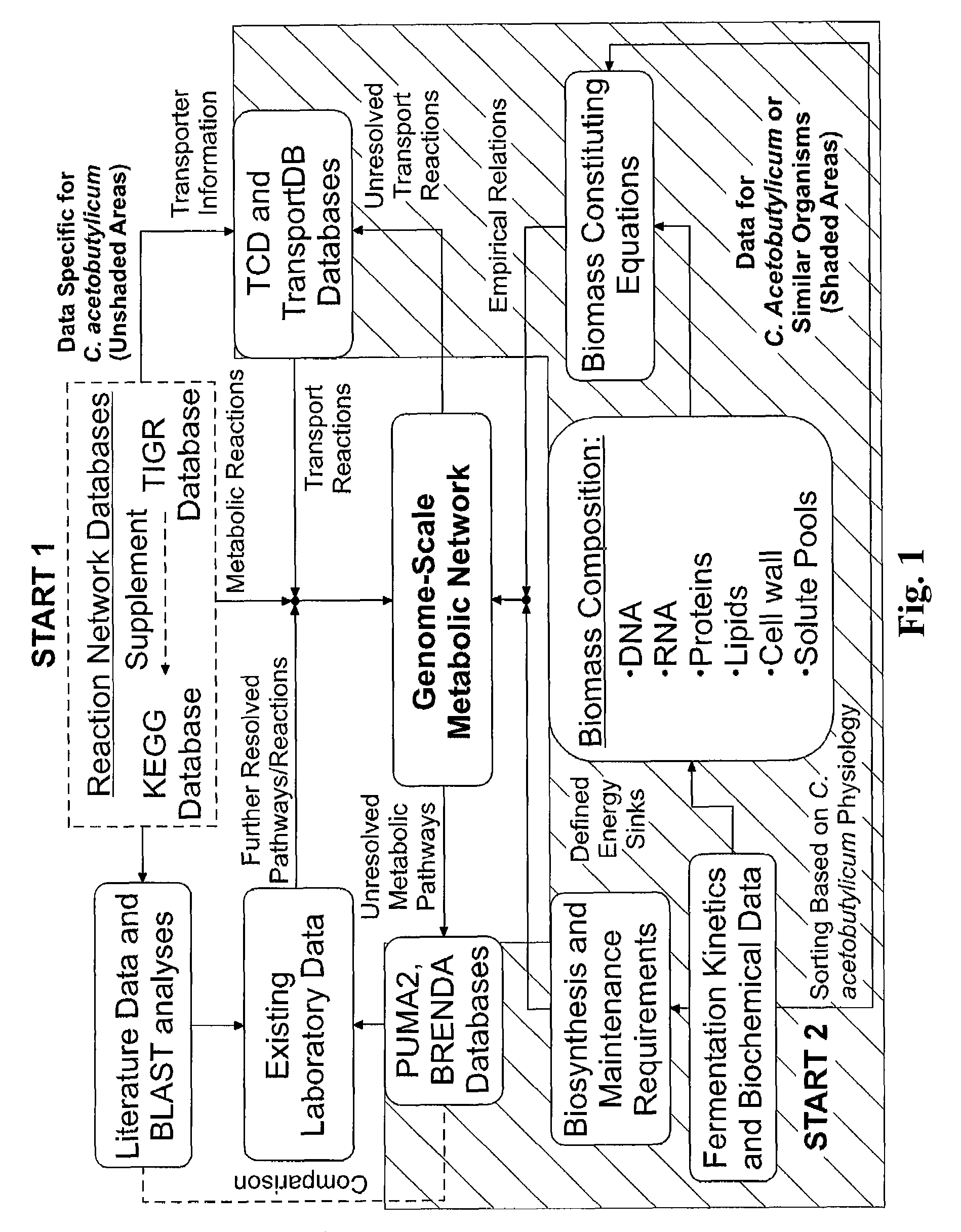
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Quantitative multiplex amplification on a genomic scale, and applications for detecting genomic rearrangements
InactiveUS20050244830A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingMultiplex
The present application relates to novel composite primers which make it possible to amplify in multiplex at a quantitative level of precision, and to the application of these composite primers for detecting gnomic rearrangements in general and cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in particular. These composite primers contain a tag the sequence of which is absent from or poorly represented in the genome analyzed, and which exhibits a very low propensity to form stable pairings. The composite primers, which contain them, make it possible to carry out multiplex amplifications with quantitative precision on the scale of a genome such as the human genome.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Homology retrieval system, homology retrieval apparatus, and homology retrieval method
InactiveUS20100205204A1Improve accuracyExact searchDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGenome scaleHigh homology
A homology retrieval can be performed with higher accuracy than conventional technologies when comparing a query sequence with a target sequence, and retrieving a similar location in the target sequence. The sequence information of a query sequence and a genomic-scale target sequence is acquired, the acquired information is compressingly converted into a compressed query sequence and a compressed target sequence in each of which a homopolymer region including two or more consecutive identical bases is replaced with a single base of the bases, the two sequences are compared, and a refining search is performed for a compressed target partial sequence that matches the compressed query sequence in the compressed target sequence. For the refined compressed candidate sequence and the query sequence, based on the information on the number of consecutive identical bases in the each of the sequences before compression, the number of consecutive bases is compared between the two compressed sequences for each corresponding base, and the degree of similarity indicating homology of the candidate sequence with the query sequence is computed from a degree of match or a degree of mismatch in the number of consecutive bases. By ranking and selecting an arbitrary number of candidate sequences having relatively high homology with the query sequence from this degree of similarity, it is possible to avoid the influence of the number of consecutive identical bases in a homopolymer region, thereby performing a homology retrieval accurately.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST RES ORG OF INFORMATION & SYST
Network construction and analysis method for oxidized bacterium gluconicum genome scale metabolism
The invention discloses a network construction and analysis method for oxidized bacterium gluconicum genome scale metabolism. The method comprises the steps of utilizing annotation information of oxidized bacterium gluconicum and biochemistry information of corresponding enzymes in the KEGG database to construct a reaction list sketch; modifying the sketch; adding reactions of biomass synthesis, transport and exchangeto form a metabolism network; converting the metabolism network to an SBML format, utilizing Matlab and Bobara Toolbox to debug the metabolism network, analyzing gaps and ineffective cycles and making correction according to the result of debugging; inthe light of the metabolism network, drawing a metabolism diagram by using Pagek and analyzing the network topology structure; and according to the metabolism network, analyzing one or more of the robustness, gene essentiality and flux changeability by utilizing the Matlab and Cobra Toolbox. The metabolism network can be used for analyzing the different metabolism states of oxidized bacterium gluconicum when the oxidized bacterium gluconicum produces dihydroxy acetone, vitamin C and glucose acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Plant whole-genome multilevel biological network reconstruction method based on multi-omics data integration
InactiveCN107862176ARealize 3D visualizationSpecial data processing applicationsReconstruction methodMetabolic network
The invention discloses a plant whole-genome multilevel biological network reconstruction method based on multi-omics data integration. The method carries out integration on a rice gene regulation andcontrol network, a protein interaction network and a metabolic network to finish the construction of a rice multilevel regulation and control network; and meanwhile, through the integration of expression profile data in different tissue growth processes of the rice, according to the constructed rice multilevel regulation and control network, a specific tissue multilevel gene regulation and control network is constructed so as to construct a first high-quality rice genome scale multilevel biological network of which the current data level is most integral. A new thought is provided for the construction of the plant multilevel biological network, and a constructed rice multilevel gene regulation and control network database realizes the 3D (Three-Dimensional) visualization of the multilevelregulation and control network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Variability single nucleotide polymorphisms linking stochastic epigenetic variation and common disease
InactiveUS20130296182A1Increase risk of diseaseLittle riskNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease riskNucleotide
Provided are methods and models for an alternative source of disease risk, which identifies not genetic variants for a phenotype per se, but variants for variability itself. Also provided are methods and models for a genome-scale, gene-specific analysis of DNA methylation in the same individuals over time, in order to identify a personalized epigenomic signature that may correlate with common genetic disease. Also provided are methods and models for simulating stochastic epigenetic variation as a driving force of development, evolutionary adaptation, and disease.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Functional Analysis of Jatropha Genes
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Methods and systems for genome-scale kinetic modeling
ActiveUS8301393B2Maximize and minimize objective functionBiological testingSystems biologyGenome scaleProteomics
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to the construction, analysis, and characterization of dynamical states of biological networks at the cellular level. Methods are provided for analyzing the dynamical states by constructing matrices using high-throughput data types, such as fluxomic, metabolomic, and proteomic data. Some embodiments relate to an individual, while others relate to a plurality of individuals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for identification and monitoring of epigenetic modifications
The present invention provides novel methods for identifying and monitoring epigenetic modifications, such as imprinted genes, using microarray based technology. Specifically, the invention detects imprinted genes by the presence of overlapping closed and open chromatin markers. The invention also discloses a method for detecting the loss of imprinting on a genome-wide scale, which is indicative of a variety of medical conditions. Diagnostic assays and chromatin structure markers for identifying gene imprinting and loss thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:NIMBLEGEN SYST
Construction method of fringed iris gene silencing system
PendingCN113736819AStrong resistanceLess susceptibleSsRNA viruses positive-senseOxidoreductasesIris PlantGene silencing
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and aims to provide a construction method of a fringed iris gene silencing system. According to the construction method of the fringed iris gene silencing system, the TRV-VIGS system is applied to the gene function research of fringed iris for the first time. By establishing a rapid and efficient fringed iris virus-mediated gene silencing system, the optimal fringed iris infection receptor, the optimal bacterial liquid concentration and the optimal infection part are determined, fringed iris plants are infected by adopting a leaf back cross cutting injection method, so that the efficiency of agrobacterium infection and gene silencing is remarkably improved, and high-throughput and functional analysis of iris plant gene functions in monocotyledonous plants on a genome scale are realized. The fringed iris gene silencing system is simple, convenient, rapid and efficient, and can lay a foundation for analyzing a molecular mechanism of important characters of fringed iris.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for acquiring specific expressed genes of peanut seeds in whole genome scale and application thereof
InactiveCN108707651ALower Sequencing CostsReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGenome scalePlant tissue
The invention provides a method for acquiring specific expressed genes of peanut seeds in a whole genome scale and application thereof. According to the method provided by the invention, the specificexpressed genes of the peanut seeds can be screened in the whole genome scale, and the specific expressed genes of the peanut seeds can be arranged according to the magnitude of expression quantities;the method is capable of dividing plant tissues into seed tissues and non-seed tissues, so that the expenditure for transcriptome sequencing is greatly reduced, and the accuracy of acquiring the specific expressed genes of the peanut seeds is improved. The application of the method for acquiring the specific expressed genes of the peanut seeds in the whole genome scale in identifying specific expressed promoters of the peanut seeds is beneficial for screening and acquiring the specific expressed promoters of the peanut seeds in the genome scale. The method and the application, provided by theinvention, have important application value on cloning and identification of specific promoters of high-expression seeds of peanuts and other plants and also have important application value in acquisition of the specific expressed genes of other tissues of the peanut and the specific expressed genes of other plant tissues.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS8311790B2Analogue computers for chemical processesSystems biologyInformation repositoryMetabolic network
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Method to determine transcriptional regulation pathways in organisms
InactiveUS8306752B1Microbiological testing/measurementDigital data processing detailsBiological bodyGene targets
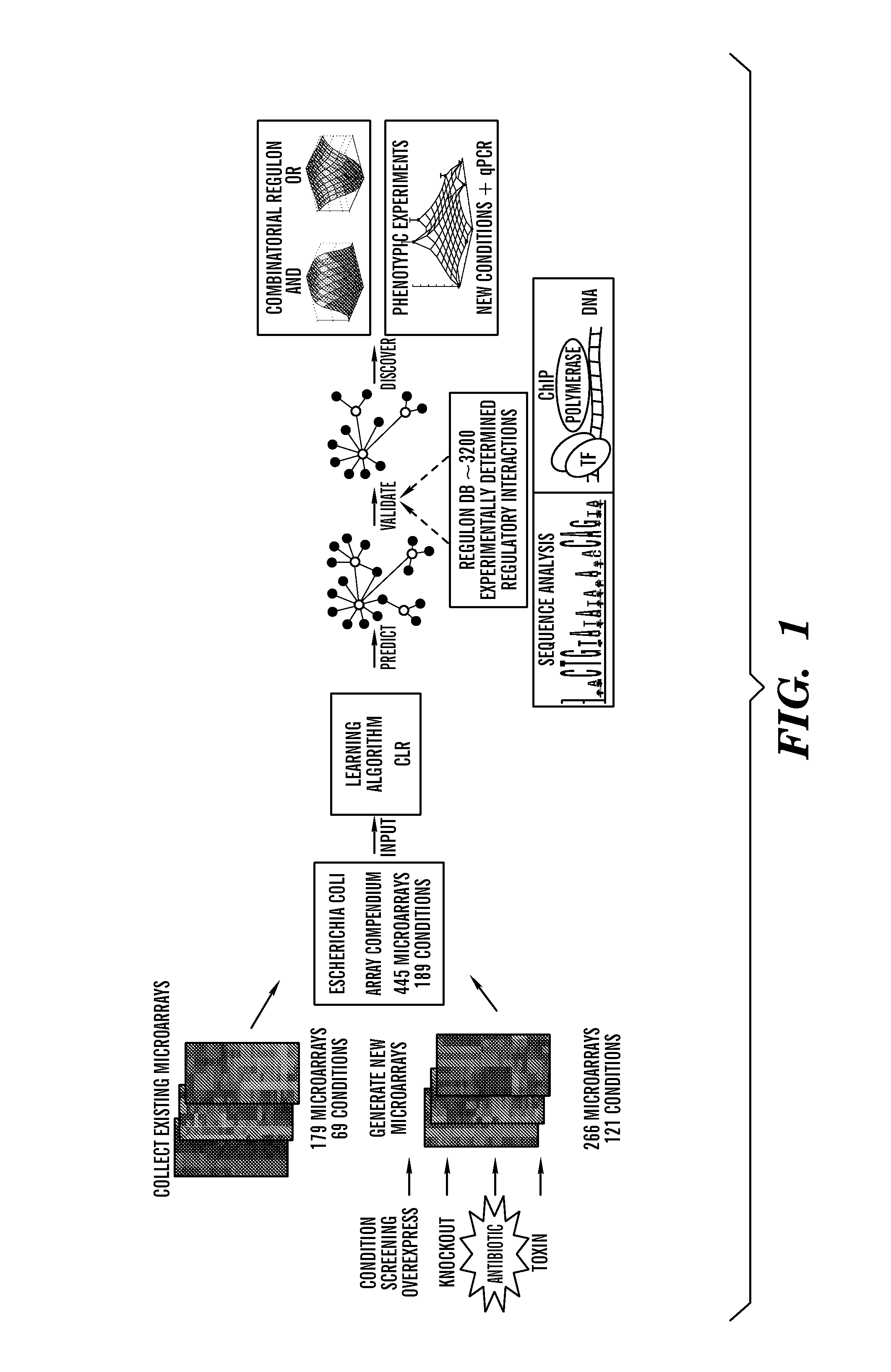
The invention relates to computer-implemented methods and systems for identifying regulatory relationships between expressed regulating polypeptides and targets of the regulatory activities of such regulating polypeptides. More specifically, the invention provides a new method for identifying regulatory dependencies between biochemical species in a cell. In particular embodiments, provided are computer-implemented methods for identifying a regulatory interaction between a transcription factor and a gene target of the transcription factor, or between a transcription factor and a set of gene targets of the transcription factor. Further provided are genome-scale methods for predicting regulatory interactions between a set of transcription factors and a corresponding set of transcriptional target substrates thereof.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method
InactiveCN103774241BReduce masking effectLow costLibrary member identificationLibrary creationCDNA libraryProtein insertion
The invention discloses a library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method. The method takes a genome-grade cDNA as the bait to screen the genome-grade cDNA library. In the application process of the method, the cDNA library is subjected to a homogenization treatment so as to reduce the masking effect of the high-abundance interaction proteins to the low-abundance interaction proteins, and thus the screening efficiency is improved; and moreover the characteristic of yeast URA3 gene is utilized so as to automatically remove the sequences, which have the self-activating function, in bait cDNA. The invention establish a library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method, which has the advantages of high feasibility, low cost, low requirements on experiment conditions, and low workload; and successfully applies the method to a screening of pathogen-host plant interaction proteins.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Functional genomics using CRISPR-Cas systems, compositions, methods, screens and applications thereof
ActiveUS11149267B2Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesStable introduction of DNAScreening processGenomicsGenome scale
The present invention generally relates to libraries, kits, methods, applications and screens used in functional genomics that focus on gene function in a cell and that may use vector systems and other aspects related to Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems and components thereof. The present invention also relates to rules for making potent single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for use in CRISPR-Cas systems. Provided are genomic libraries and genome wide libraries, kits, methods of knocking out in parallel every gene in the genome, methods of selecting individual cell knock outs that survive under a selective pressure, methods of identifying the genetic basis of one or more medical symptoms exhibited by a patient, and methods for designing a genome-scale sgRNA library.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Method for thoroughly designing valid and ranked primers for genome-scale DNA sequence database
A method for designing all coverage of valid primer pairs, which satisfy various filtering constraints provided by users with respect to a given sequence database and has validated specificity to given sequences, is provided. By screening all suitable primer pairs present on a given DNA sequence database without omitting any one primer pair and also screening all primers having a coverage of 1 or more as well as primers having a coverage of 1, a user can be allowed to give rankings to the primers in order to easily select the primers having a high success rate in biological experiments from the resulting primers.
Owner:DAEGU GYEONGBUK INST OF SCI & TECH
Bacterial Metastructure and Methods of Use
Although metabolic networks have been reconstructed on a genome-scale, the corresponding reconstruction and integration of governing transcriptional regulatory networks has not been fully achieved. Here such an integrated network was constructed for amino acid metabolism in Escherichia coli. Analysis of ChlP-chip and gene expression data for the transcription factors ArgR, Lrp, and TrpR showed that 19 / 20 amino acid biosynthetic pathways are either directly or indirectly controlled by these regulators. Classifying the regulated genes into three functional categories of transport, biosynthesis, and metabolism leads to elucidation of regulatory motifs constituting the integrated network's basic building blocks. The regulatory logic of these motifs was determined based on the relationships between transcription factor binding and changes in transcript levels in response to exogenous amino acids. Remarkably, the resulting logic shows how amino acids are differentiated as signaling and nutrient molecules. This reveals the overarching regulatory principles of the amino acid stimulon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Functional analysis of jatropha curcas genes
InactiveUS20110265223A1Similar efficiencyImprove fuel performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesGenome scaleJatropha platyphylla
The present invention relates to the field of functional analysis of Jatropha genes on a genomic scale. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for high-throughtput functional analysis of Jatropha curcas genes on a genomic scale using virus-induced gene silencing. The method involves use of the tobacco rattle virus (TRV).
Owner:JOIL S
DNA methylation markers for metastatic prostate cancer
ActiveUS20180100196A1Rapid and cost-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationGenome scale
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions useful for assessing prostate cancer. In a specific embodiment, present inventors have developed and applied a new technology and associated computation methods enabling simultaneous genome-scale analysis of genetic (copy number) and epigenetic (total methylation (TM) and allele-specific methylation (ASM) alternation, This method, called MBD-SNP, features affinity enrichment or methylated genomic DNA fragments using a methyl-binding domain polypeptide.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
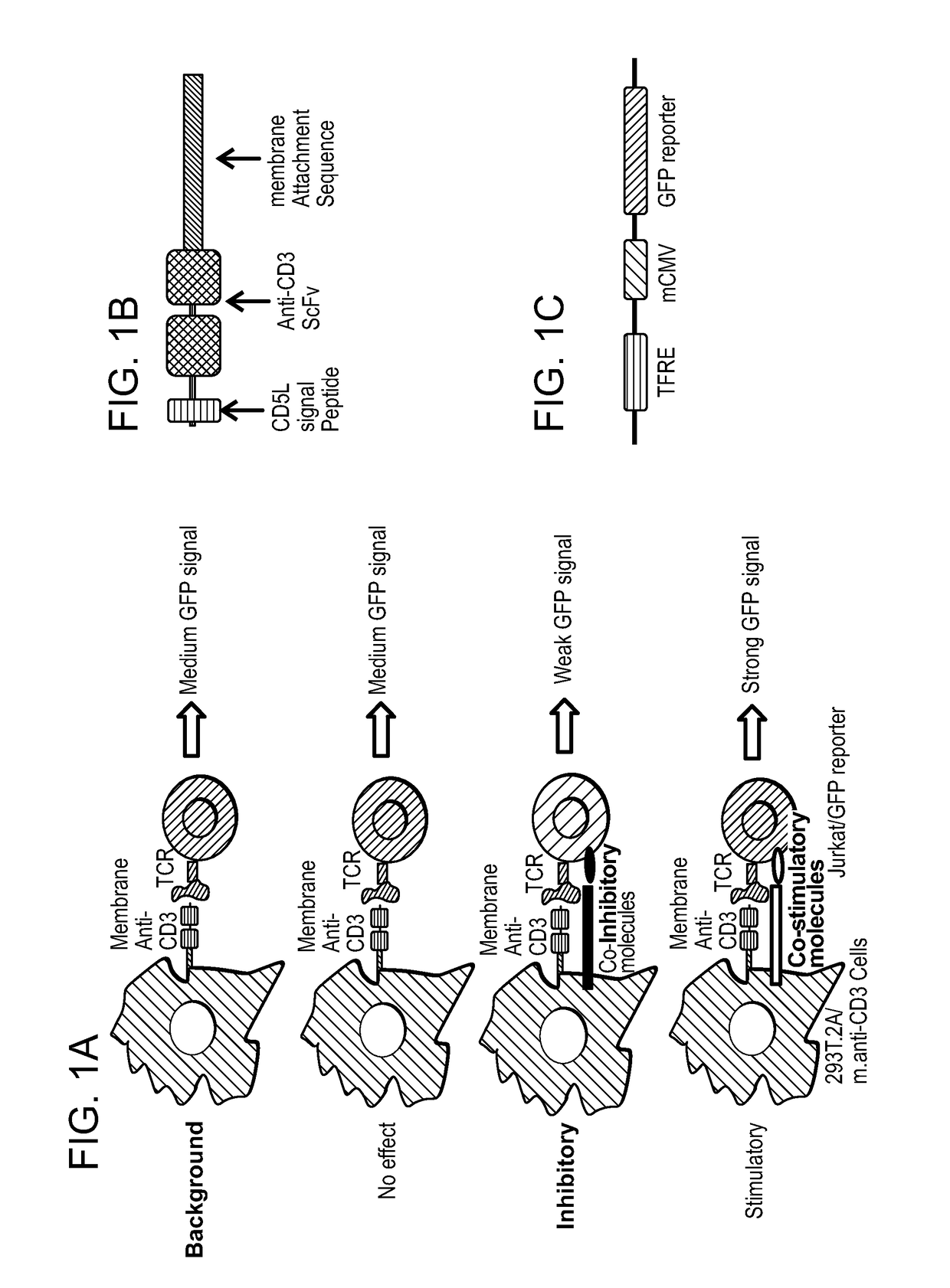
Genome-scale t cell activity array and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20180306778A1Assisted identificationComprehensive understandingBiological material analysisLaboratory glasswaresGenome scaleImmune Modulators
The present invention provides Genome-Scale T Cell Activity Arrays (GS-TCAA), as well as methods of making these arrays and methods of using them to identify immune modulators.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Whole-genome random mutation method based on CRISPR-Cas system and application of whole-genome random mutation method
PendingCN112680450AHigh mutation rateVariety of mutation typesFungiHydrolasesMutation screeningSaccharomyces
The invention discloses a whole-genome random mutation method based on a CRISPR-Cas system and application of the whole-genome random mutation method. The whole-genome random mutation method is based on the CRISPR-Cas system, through the guidance of a random gRNA library, the whole genome of a living body is subjected to scattered bullet type random cutting, and random mutation on the whole genome scale is triggered under the non-fidelity type DNA repair effect. The whole-genome random mutation method can be used for directed evolution and iterative evolution, saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for producing beta-carotene to serve as a verification model, seven rounds of iterative mutation screening are completed within two months, and an evolved strain with the yield increased to 10.5 times is obtained. The omics analysis shows that about 122 mutations can be introduced into each operation on average, the transcription level of about 50% of genes is remarkably changed, it shows that deep remodeling occurs in saccharomyces metabolism through mutation evolution, and experiments prove that the method is a simple and controllable new genome variation technology.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com