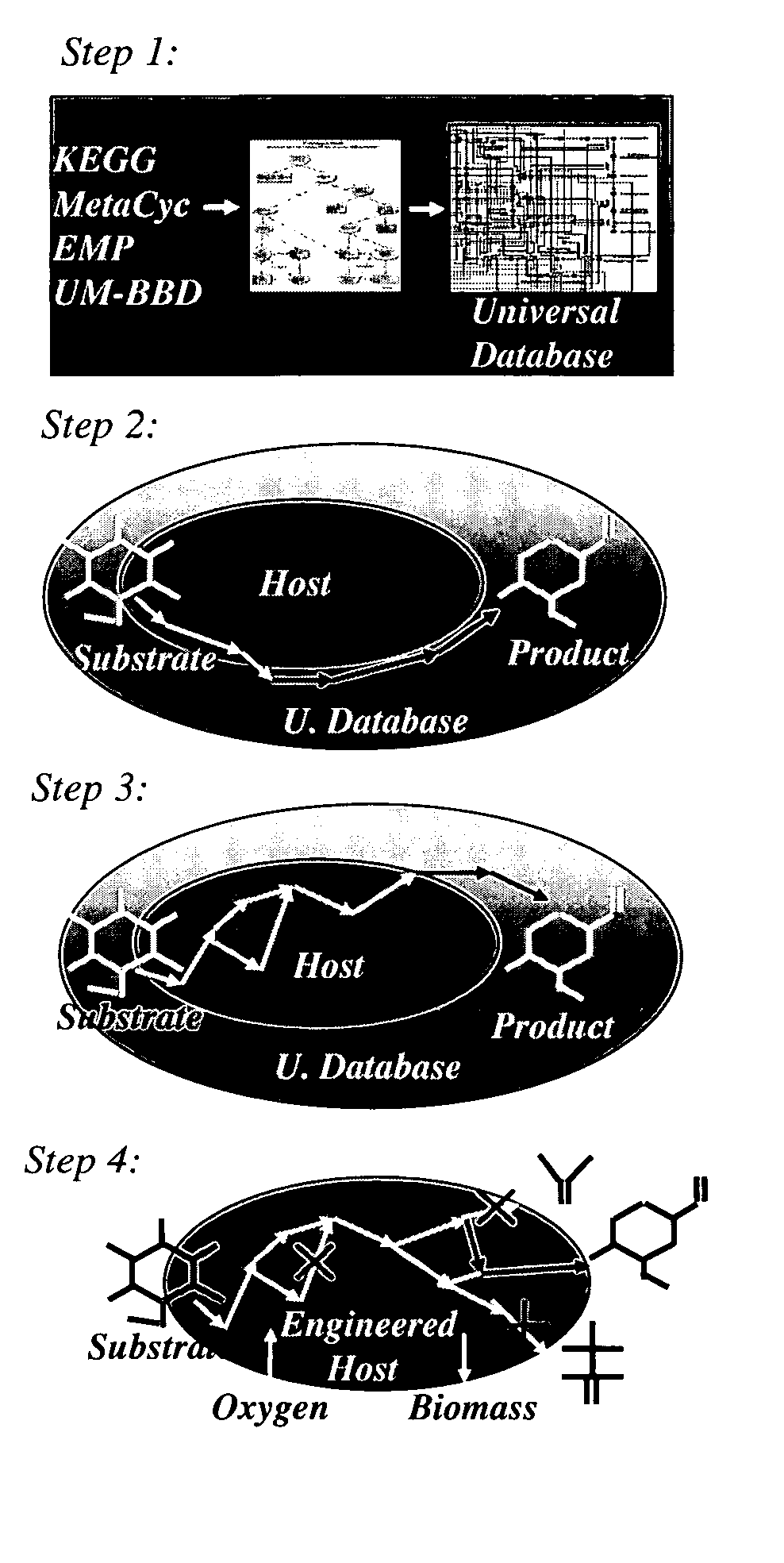
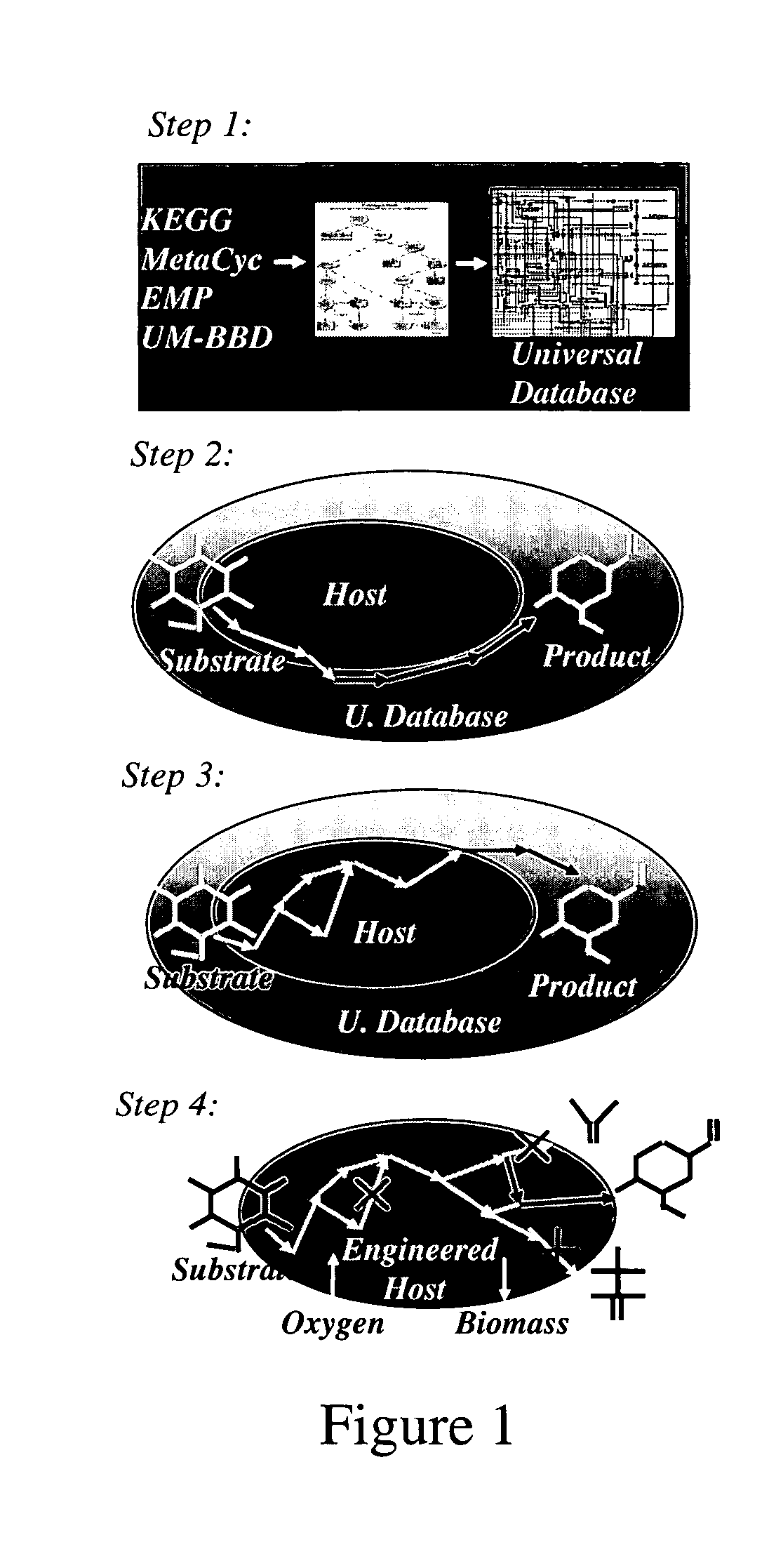
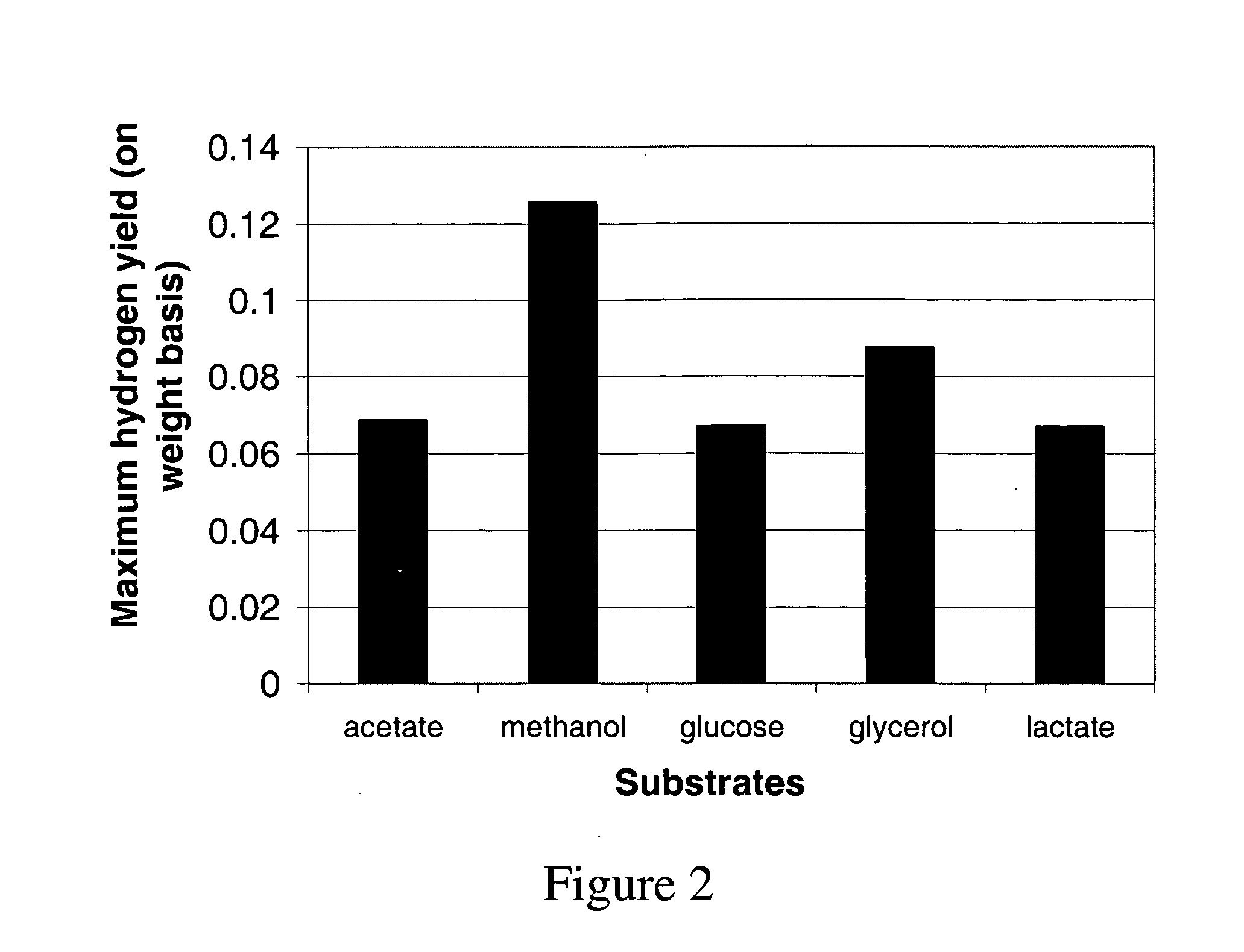
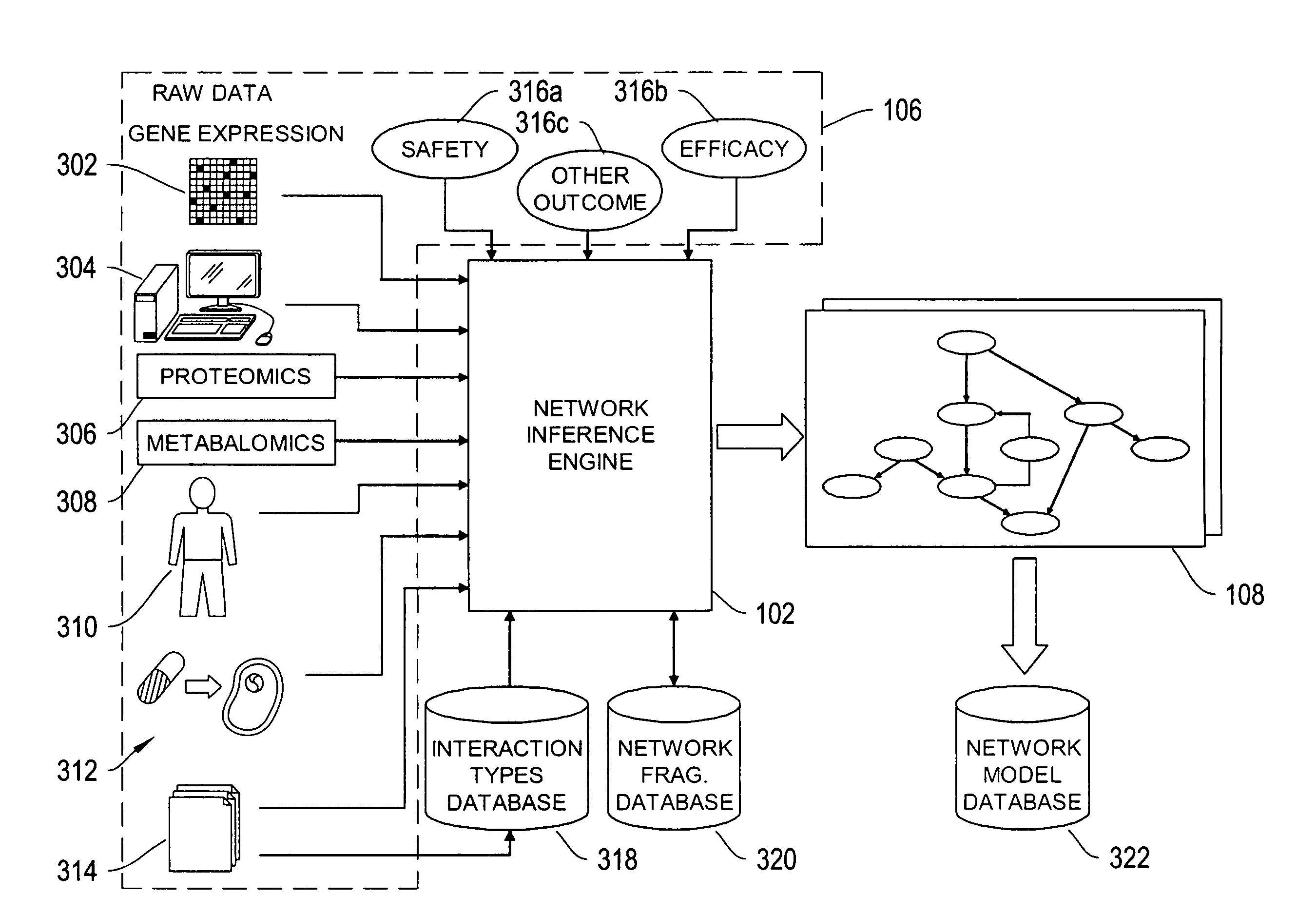
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2271results about "Systems biology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
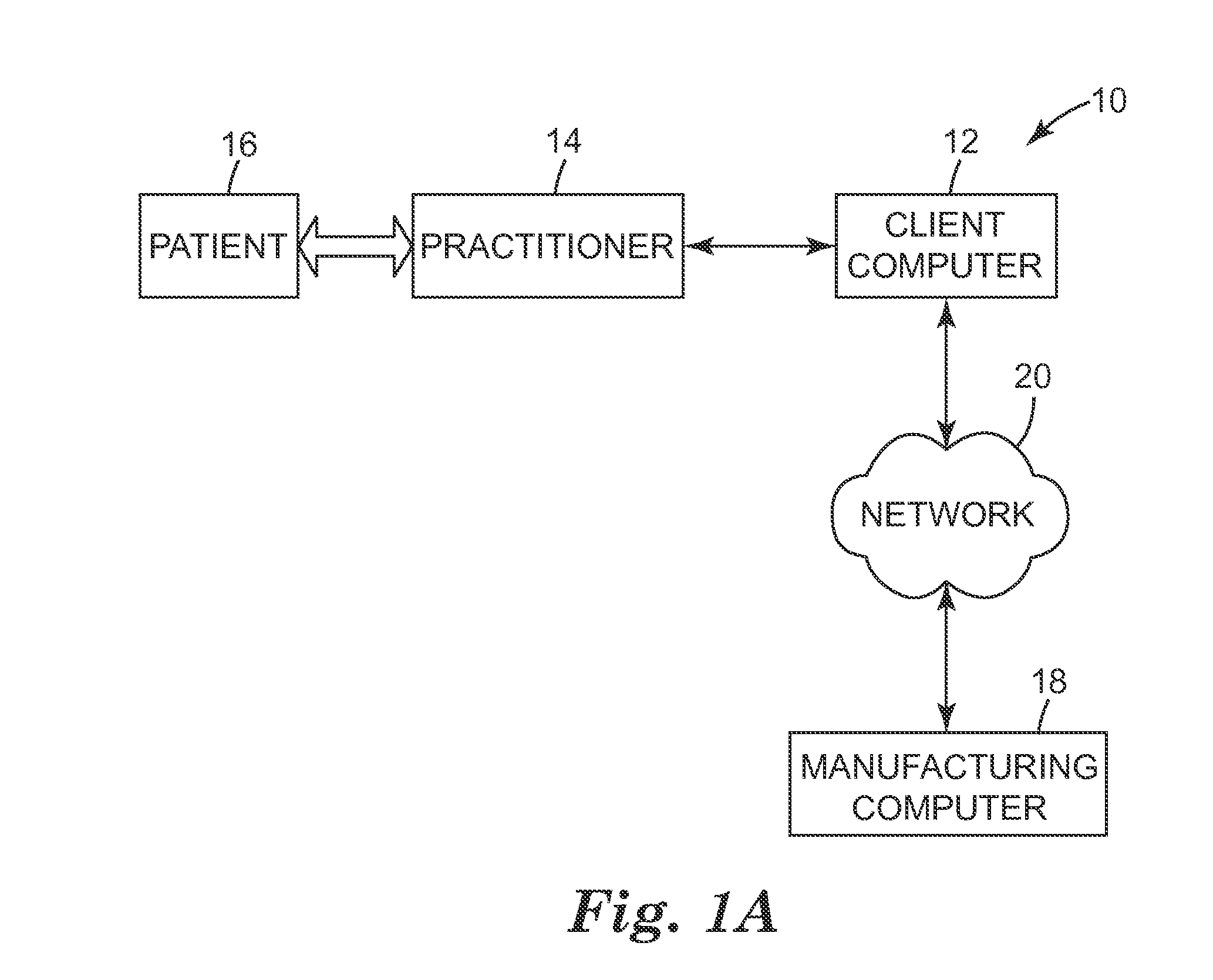
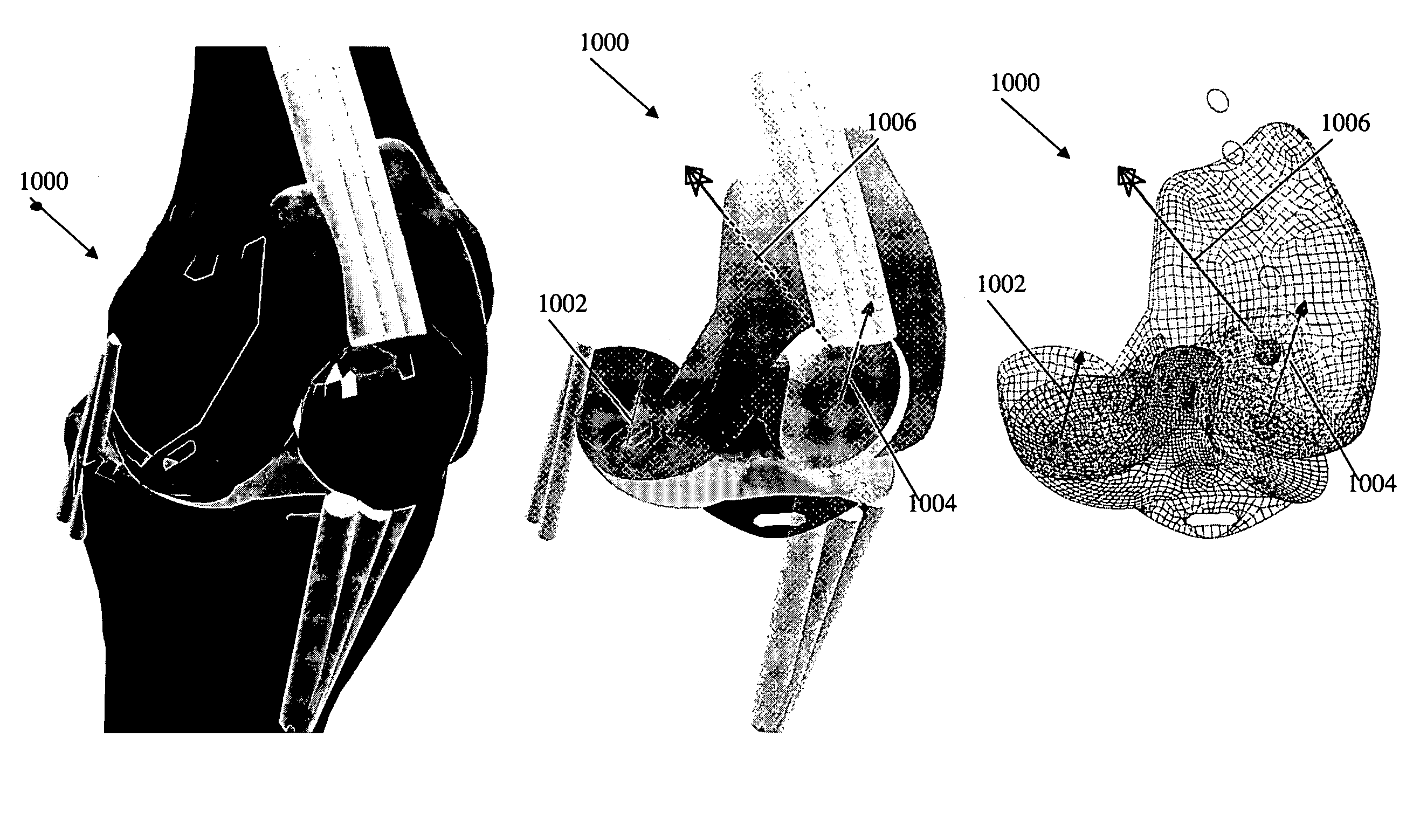
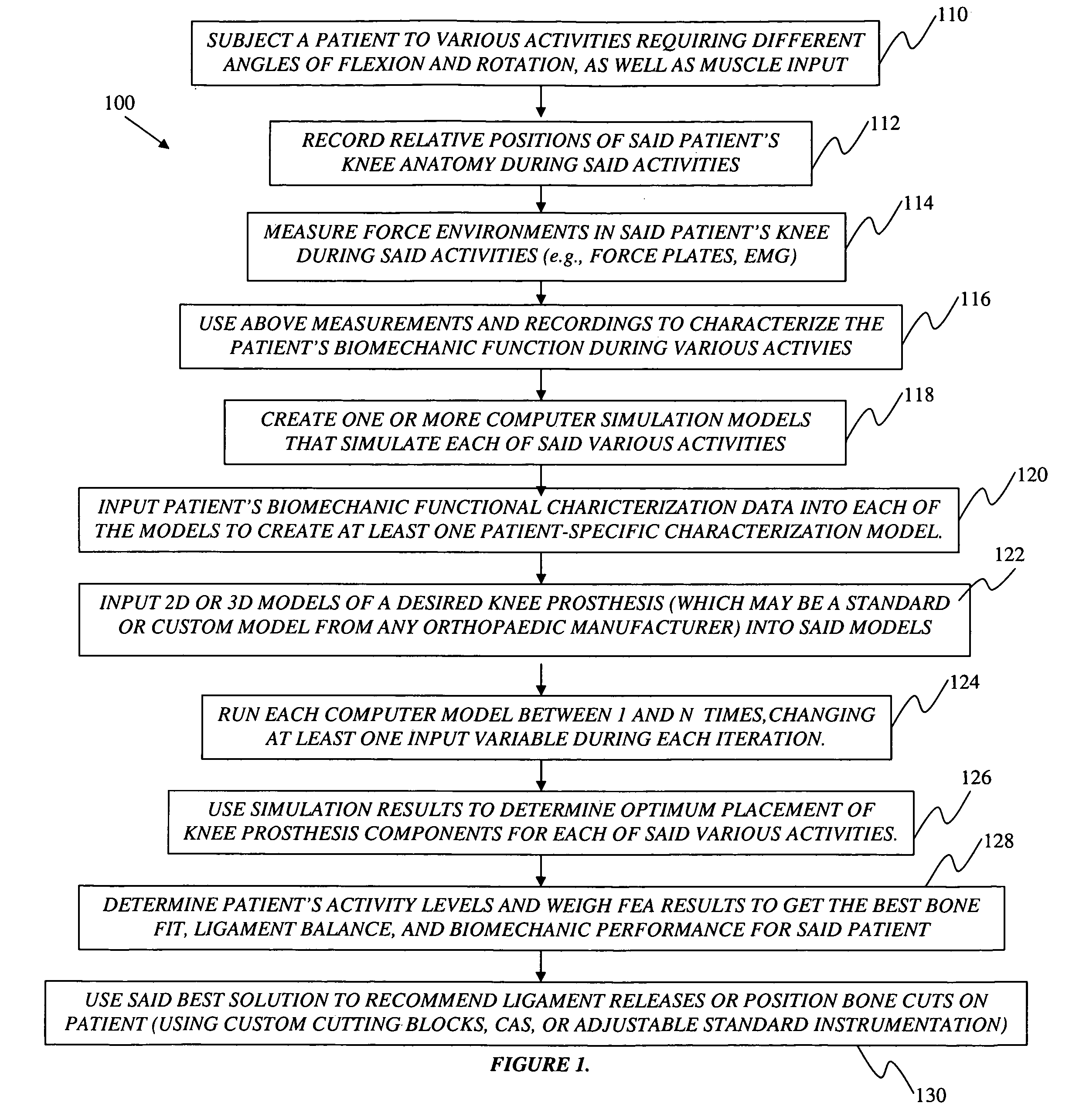
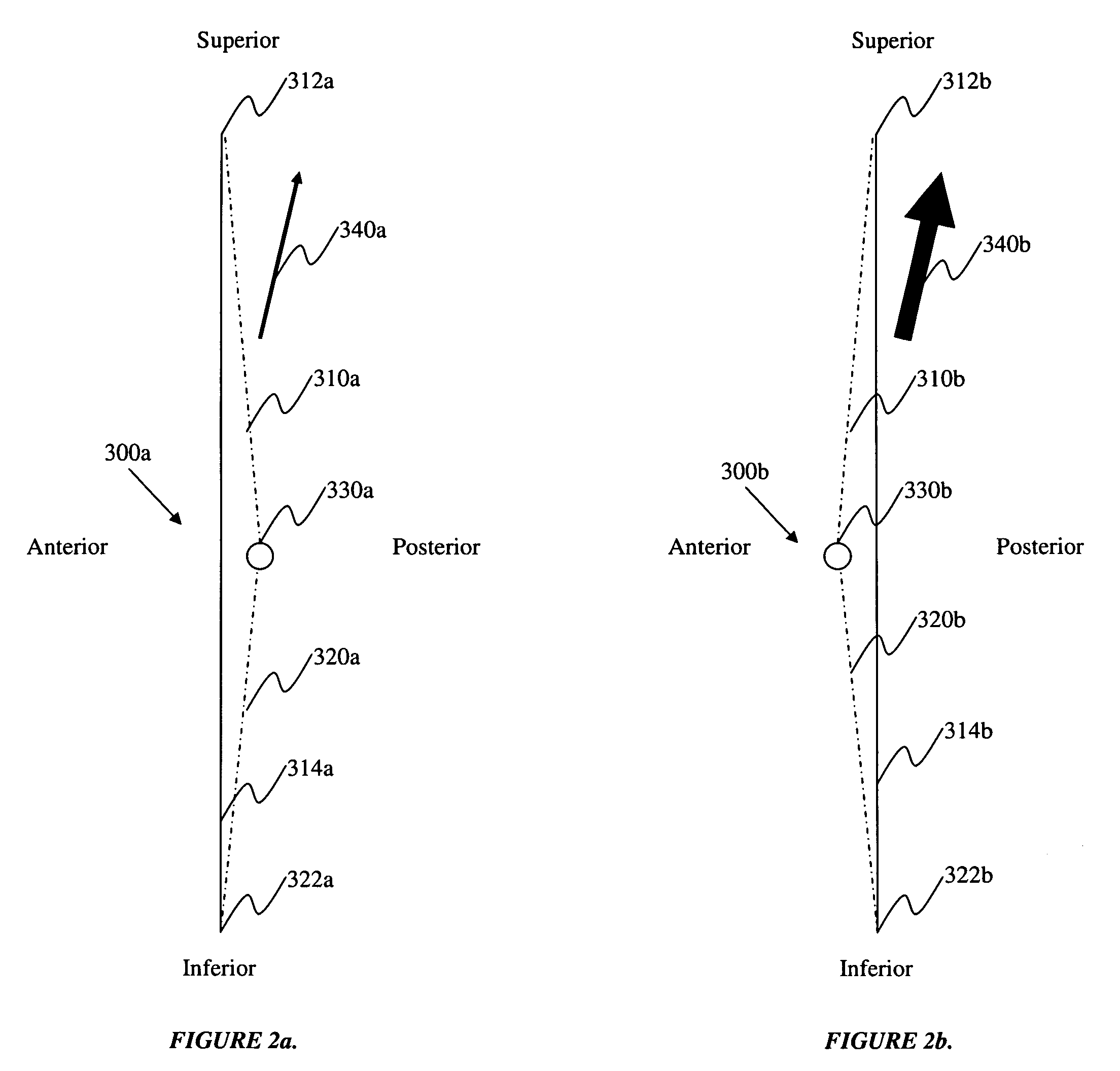
Operatively tuning implants for increased performance
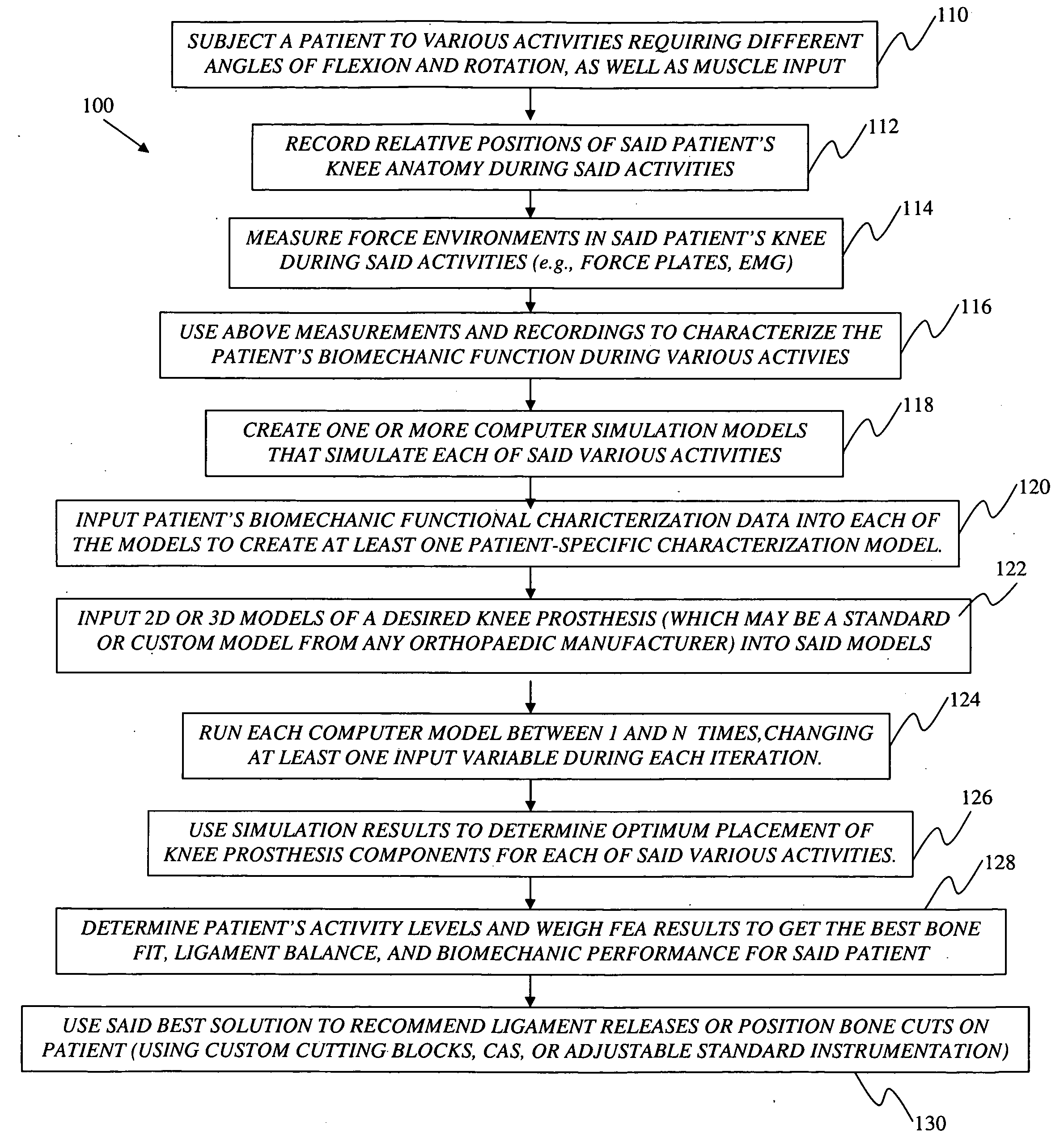
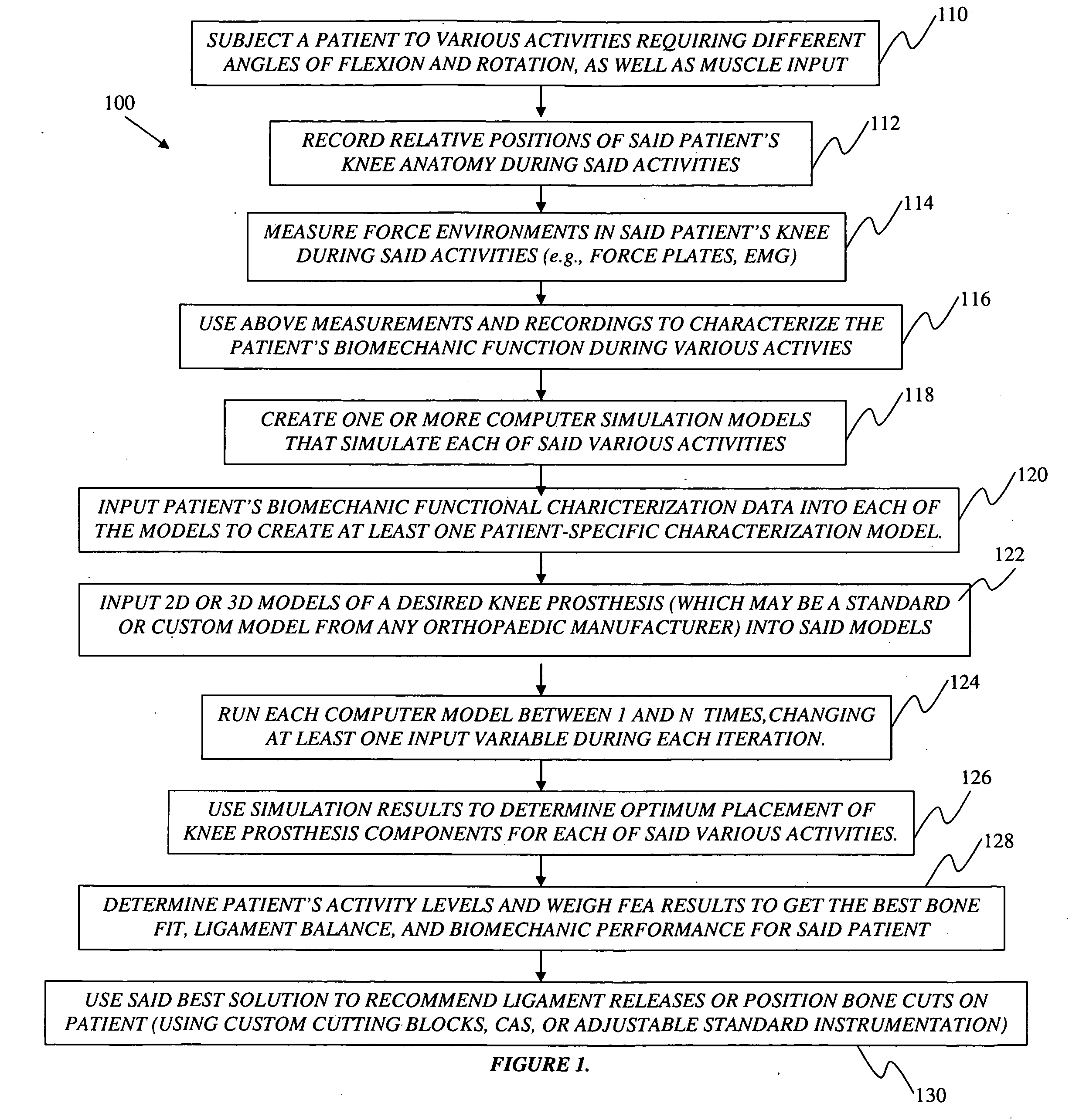
ActiveUS20100076563A1Improve balanceGood postoperative biomechanic functionPhysical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBiomechanicsPatient acceptance
A method for preoperatively characterizing an individual patient's biomechanic function in preparation of implanting a prosthesis is provided. The method includes subjecting a patient to various activities, recording relative positions of anatomy during said various activities, measuring force environments responsive to said patient's anatomy and affected area during said various activities, characterizing the patient's biomechanic function from said relative positions and corresponding force environments, inputting the measured force environments, relative positions of knee anatomy, and patient's biomechanic function characterization into one or more computer simulation models, inputting a computer model of the prosthesis into said one or more computer simulation models, and manipulating the placement of the prosthesis in the computer simulation using said patient's biomechanic function characterization and said computer model of the prosthesis to approximate a preferred biomechanical fit of the prosthesis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
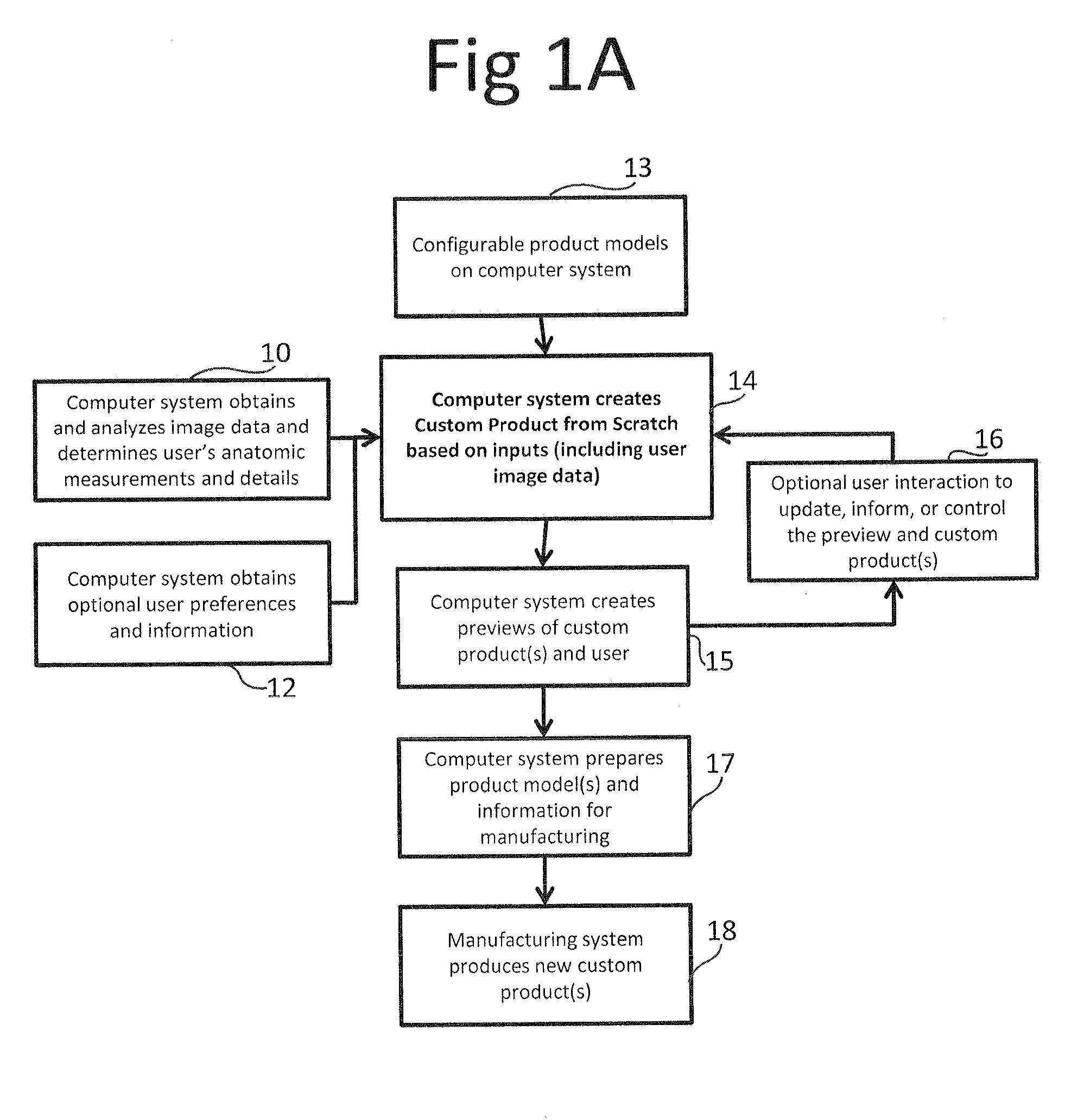
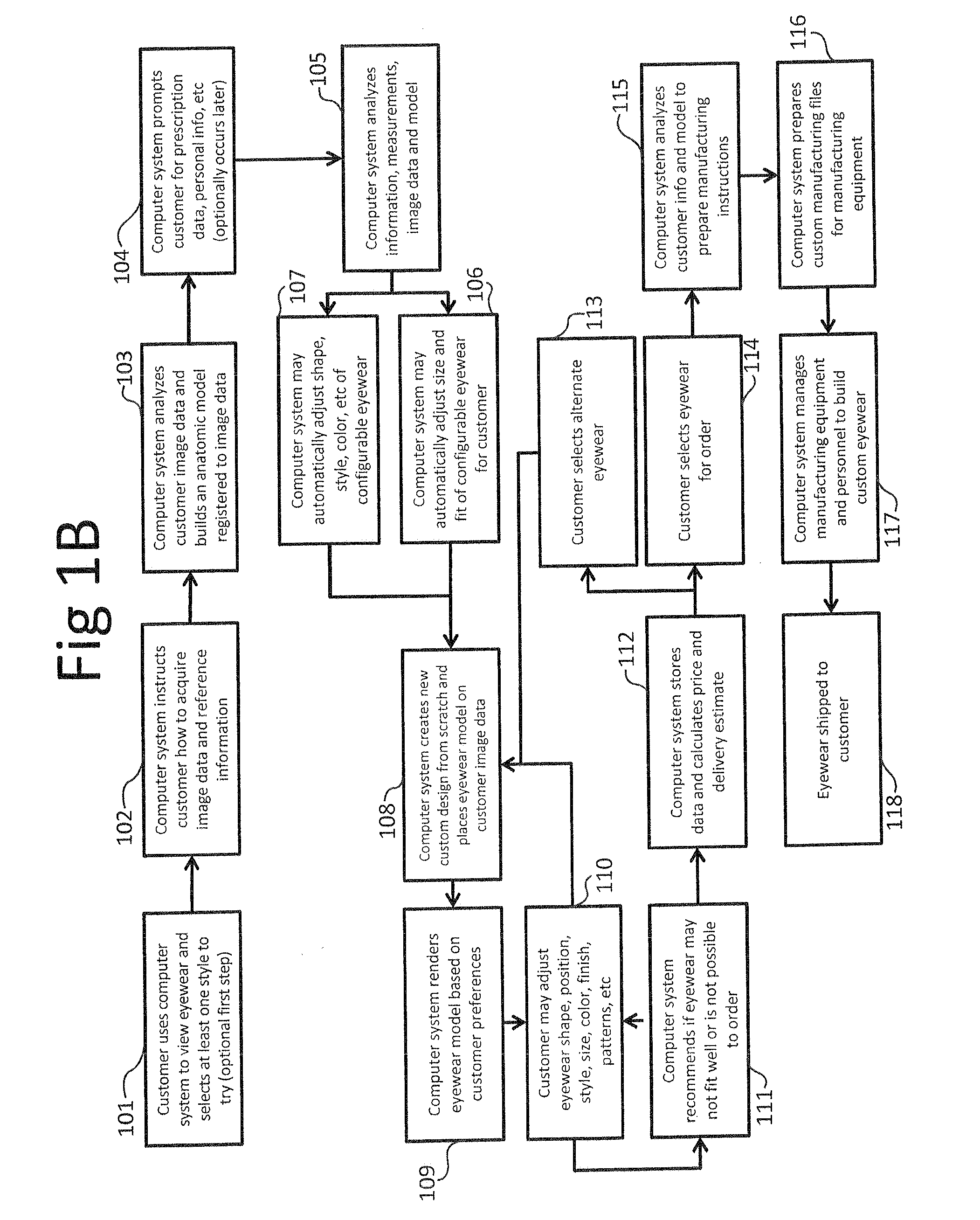
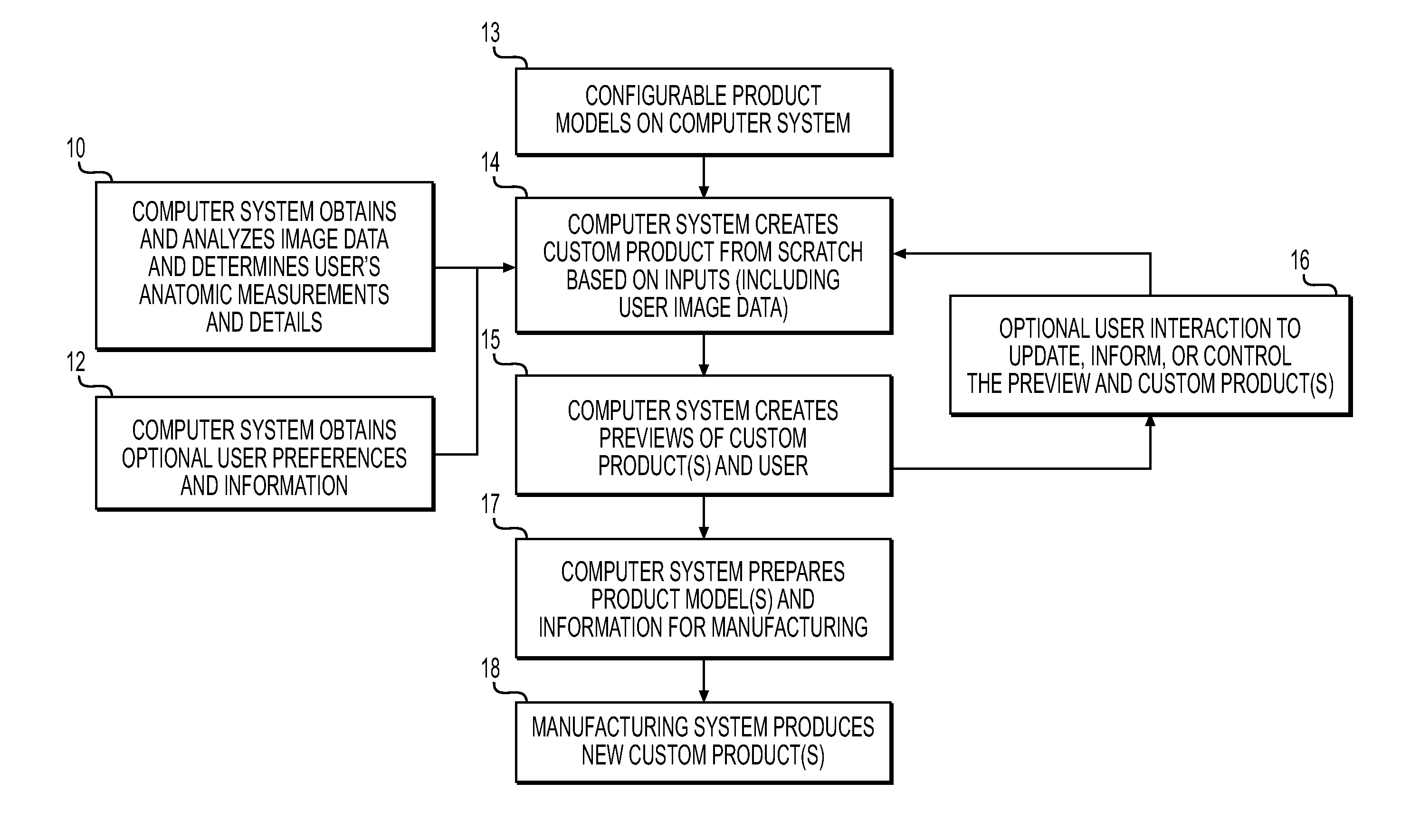
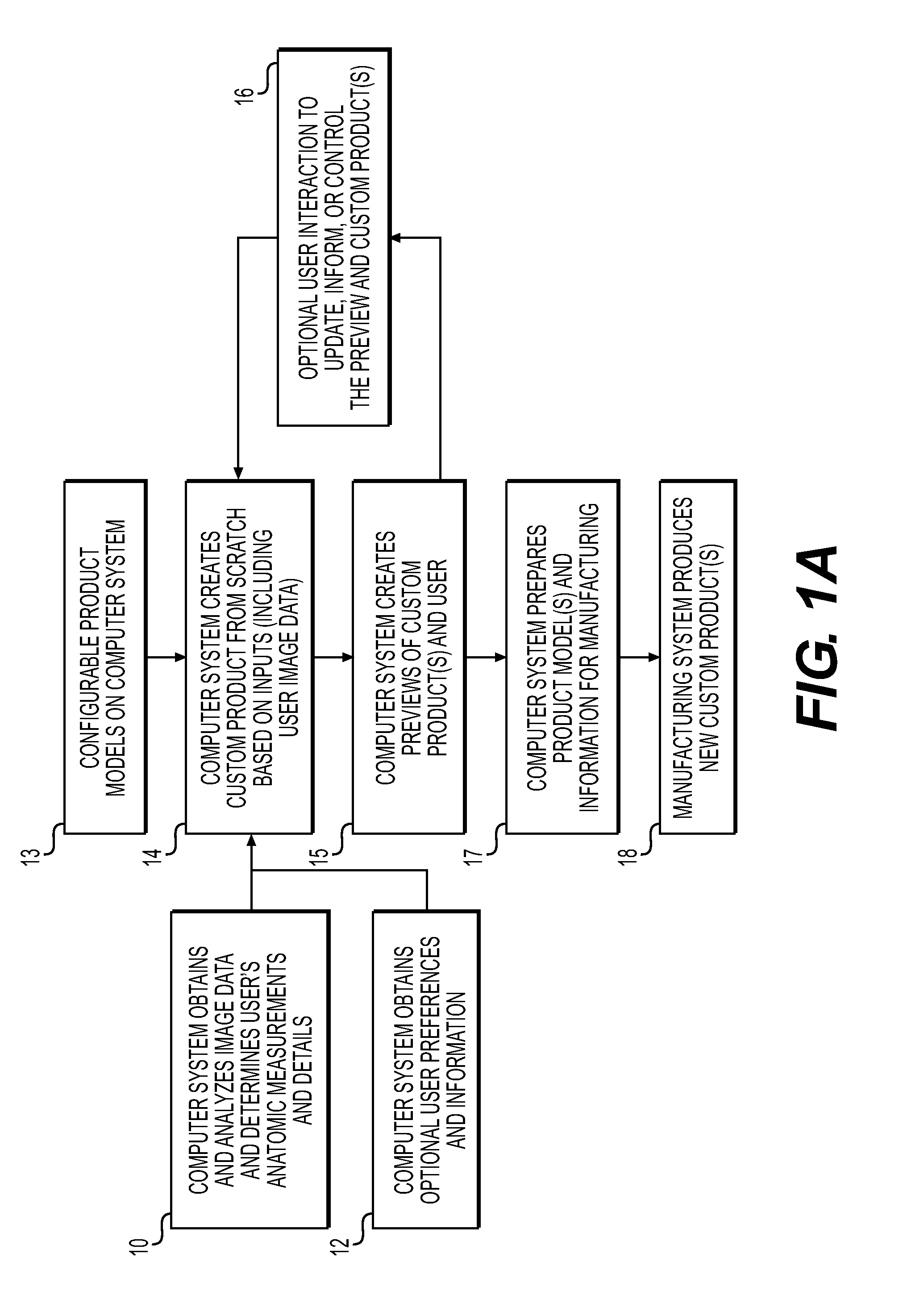
Method and system to create products
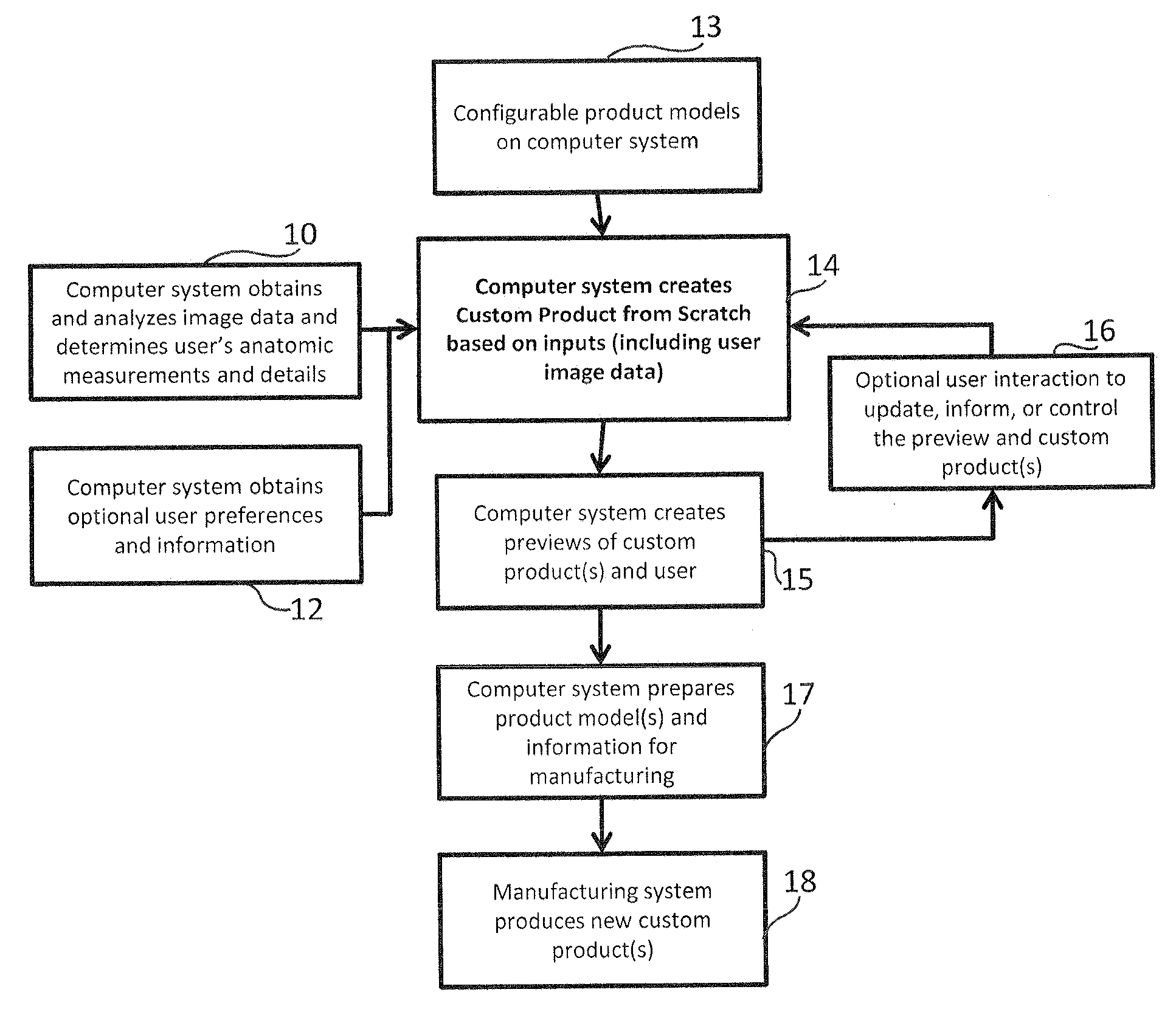
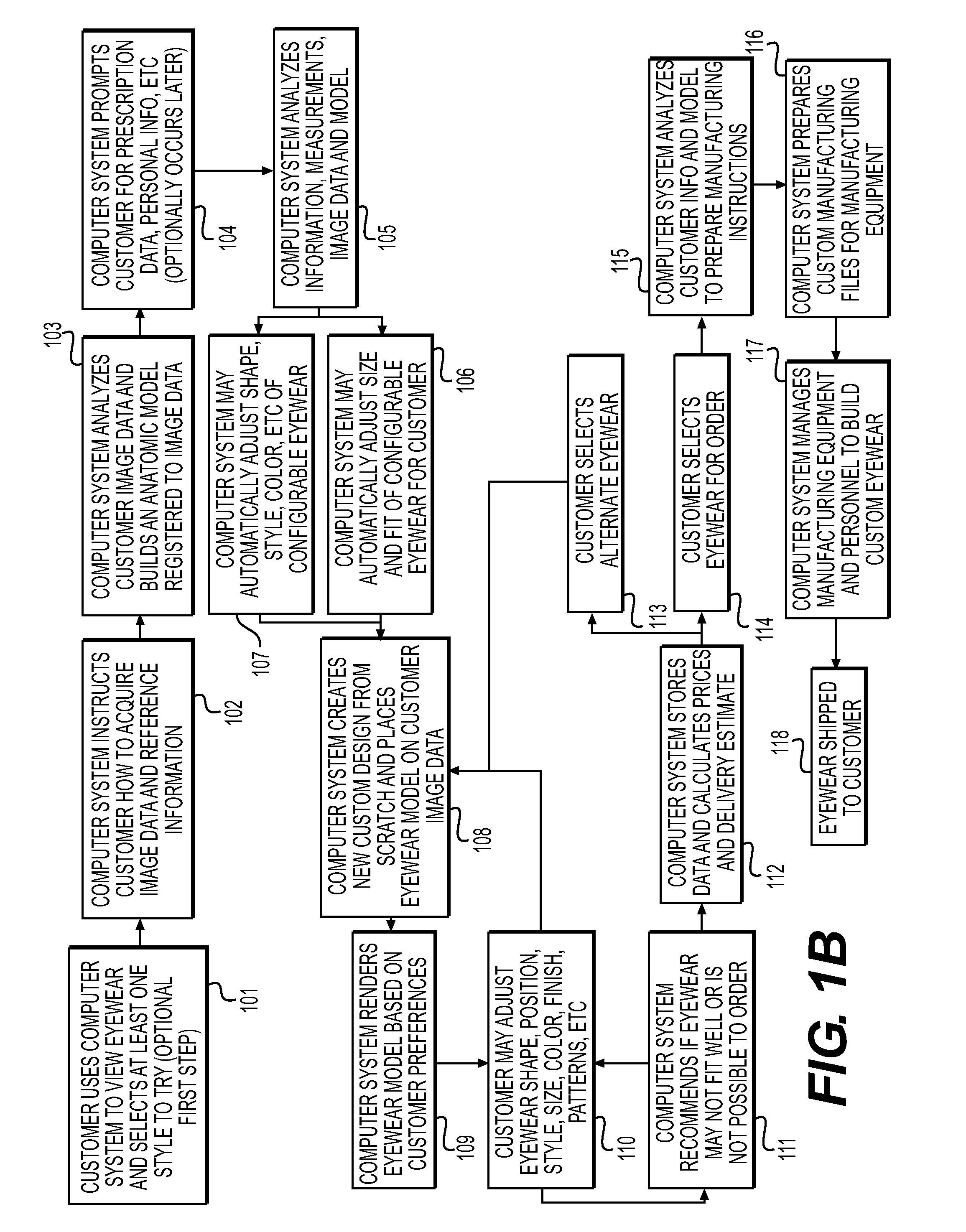
Systems and methods for creating fully custom products from scratch without exclusive use of off-the-shelf or pre-specified components. A system for creating custom products includes an image capture device for capturing image data and / or measurement data of a user. A computer is communicatively coupled with the image capture device and configured to construct an anatomic model of the user based on the captured image data and / or measurement data. The computer provides a configurable product model and enables preview and automatic or user-guided customization of the product model. A display is communicatively coupled with the computer and displays the custom product model superimposed on the anatomic model or image data of the user. The computer is further configured to provide the customized product model to a manufacturer for manufacturing eyewear for the user in accordance with the customized product model. The manufacturing system is configured to interpret the product model and prepare instructions and control equipment for the manufacturing of the customized product.
Owner:BIS
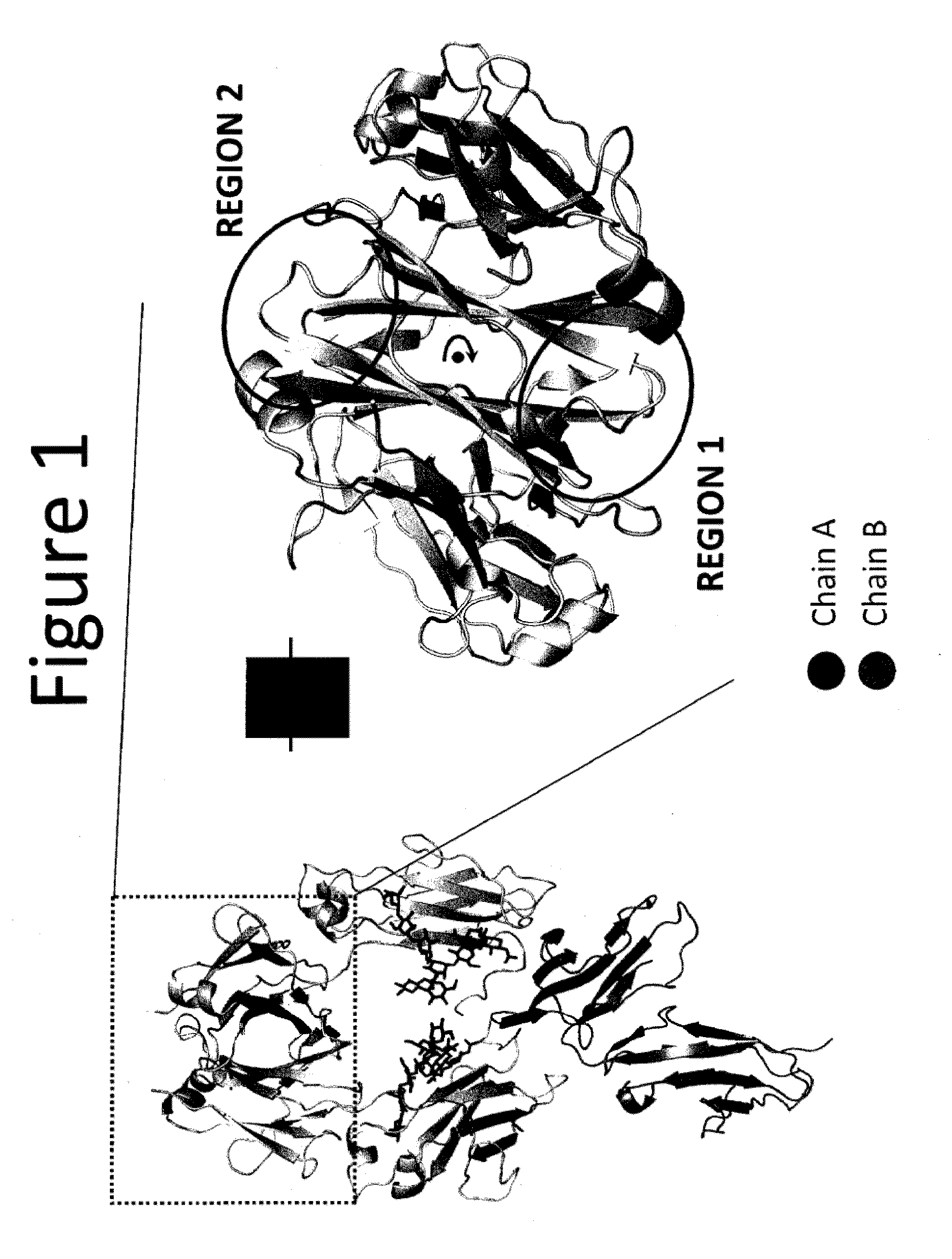
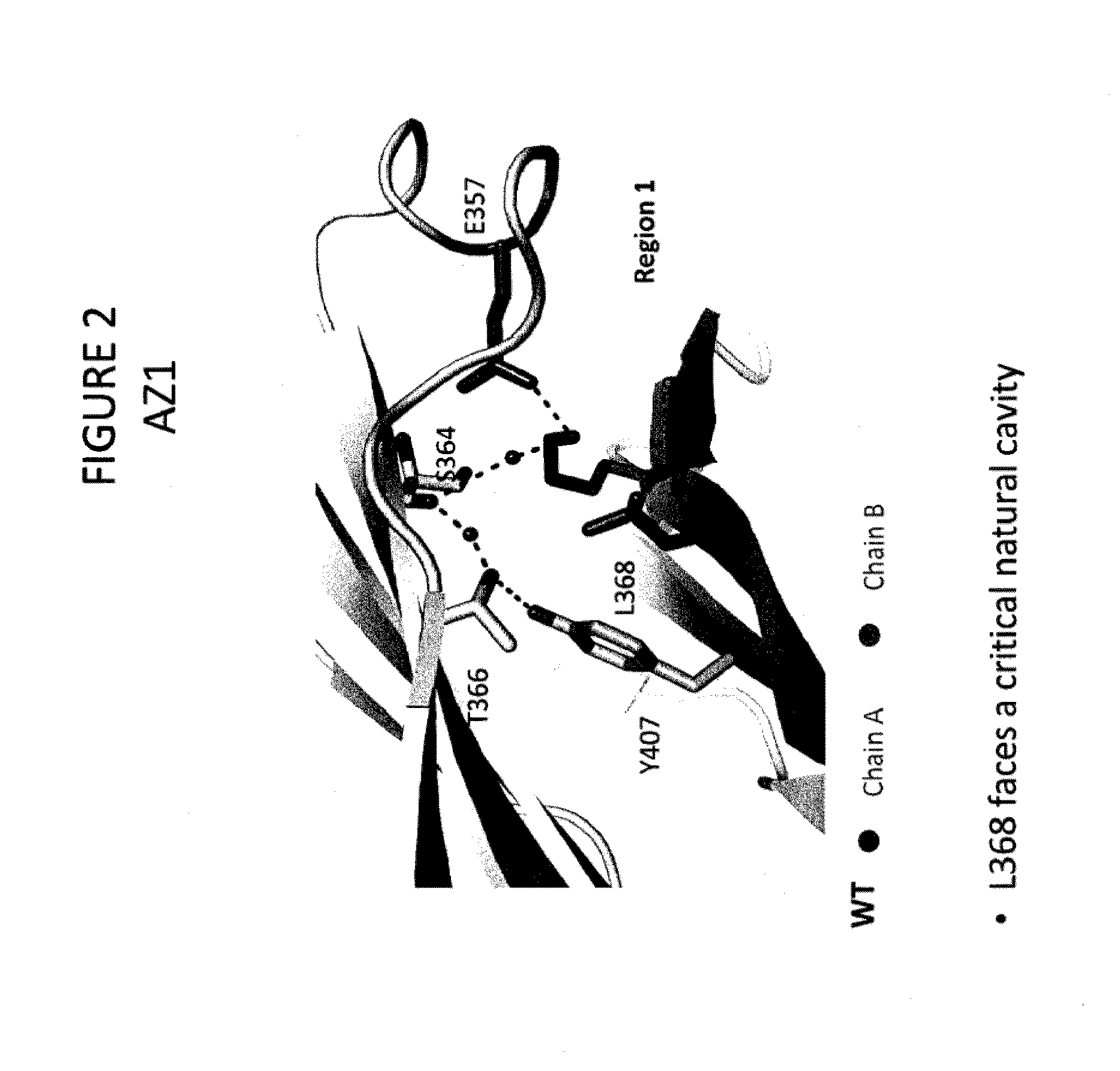
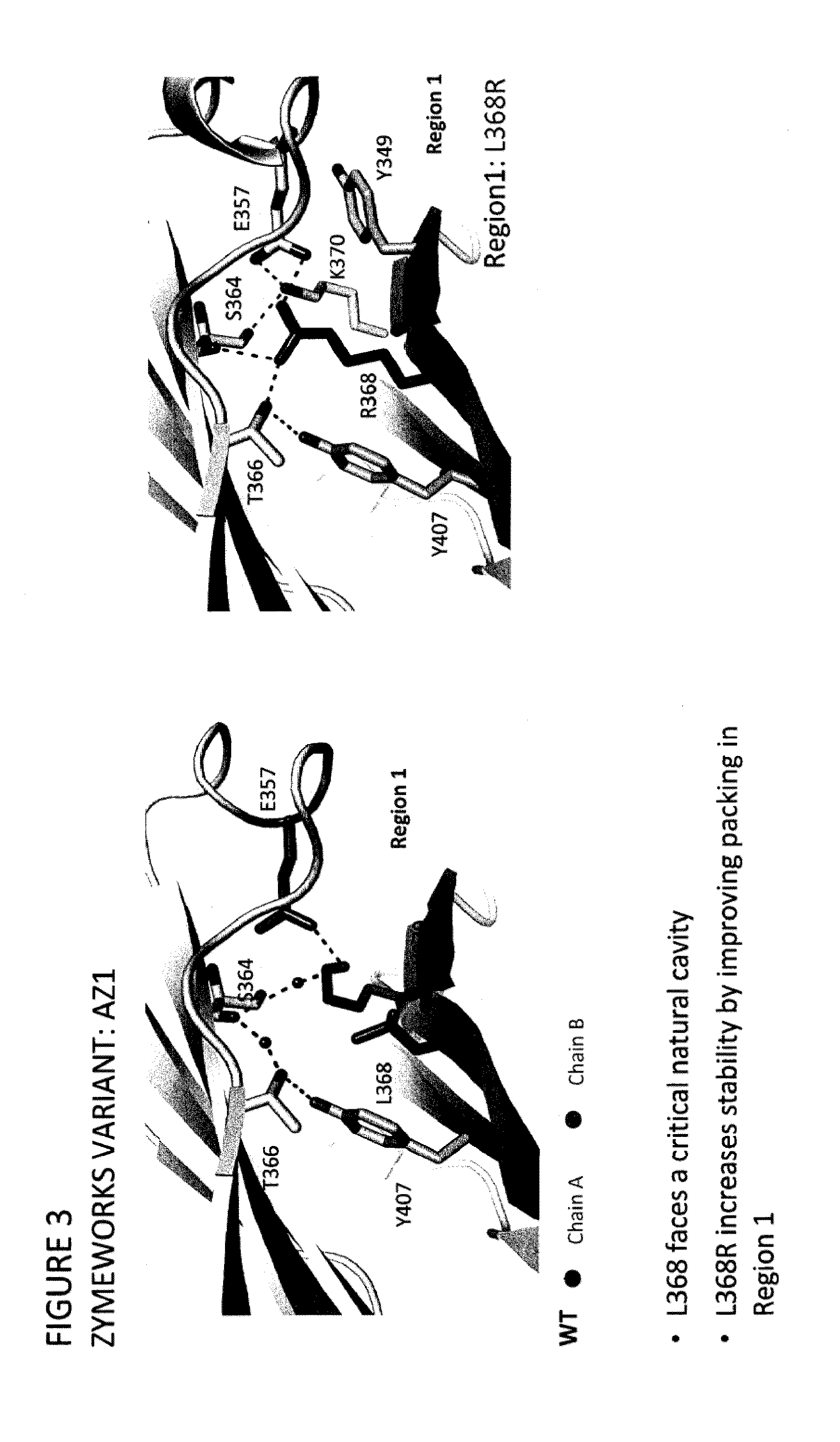
Stable Heterodimeric Antibody Design with Mutations in the Fc Domain
ActiveUS20130195849A1Improve stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunological disordersFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The provided scaffolds have heavy chains that are asymmetric in the various domains (e.g. CH2 and CH3) to accomplish selectivity between the various Fc receptors involved in modulating effector function, beyond those achievable with a natural homodimeric (symmetric) Fc molecule, and increased stability and purity of the resulting variant Fc heterodimers. These novel molecules comprise complexes of heterogeneous components designed to alter the natural way antibodies behave and that find use in therapeutics.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
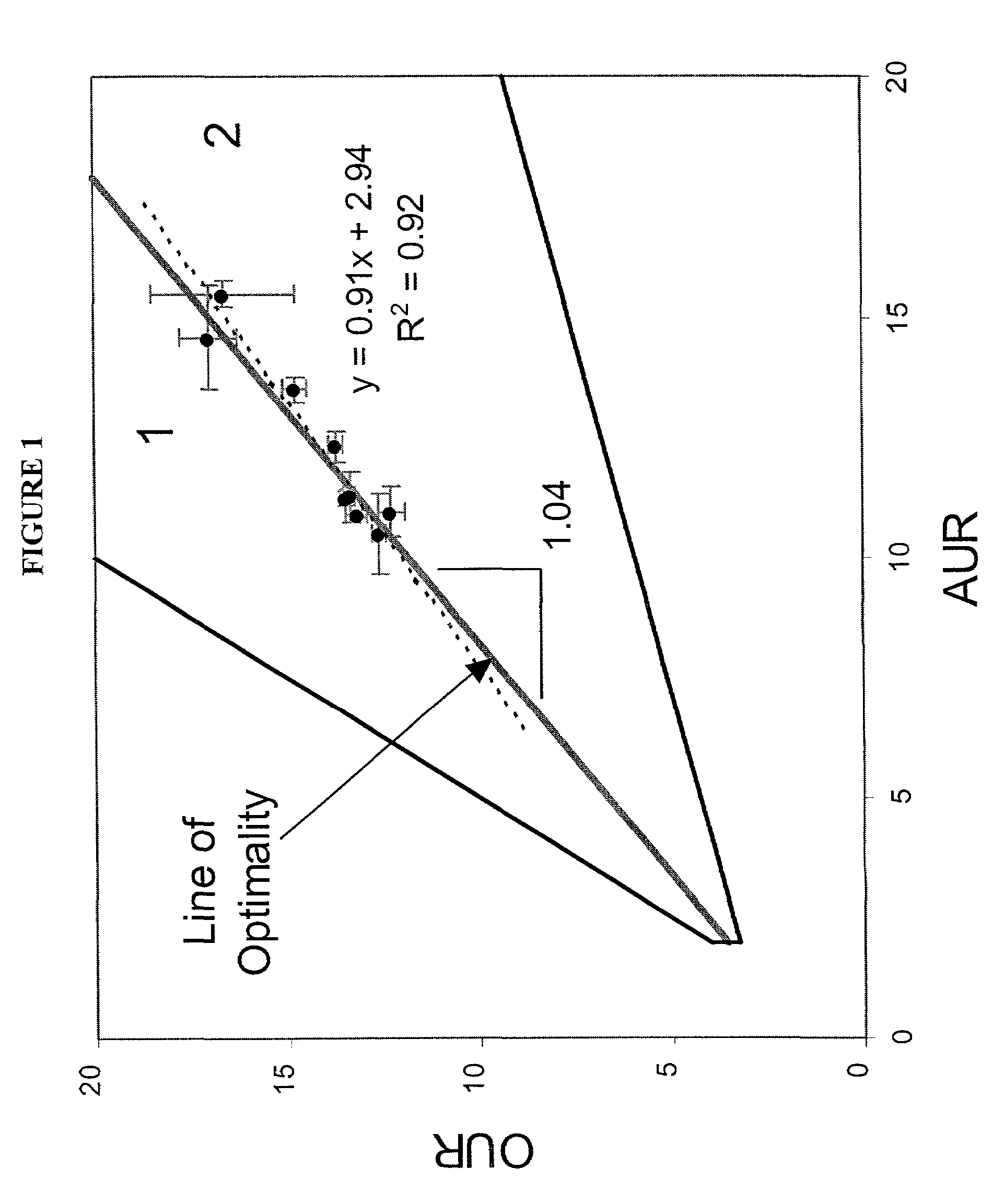
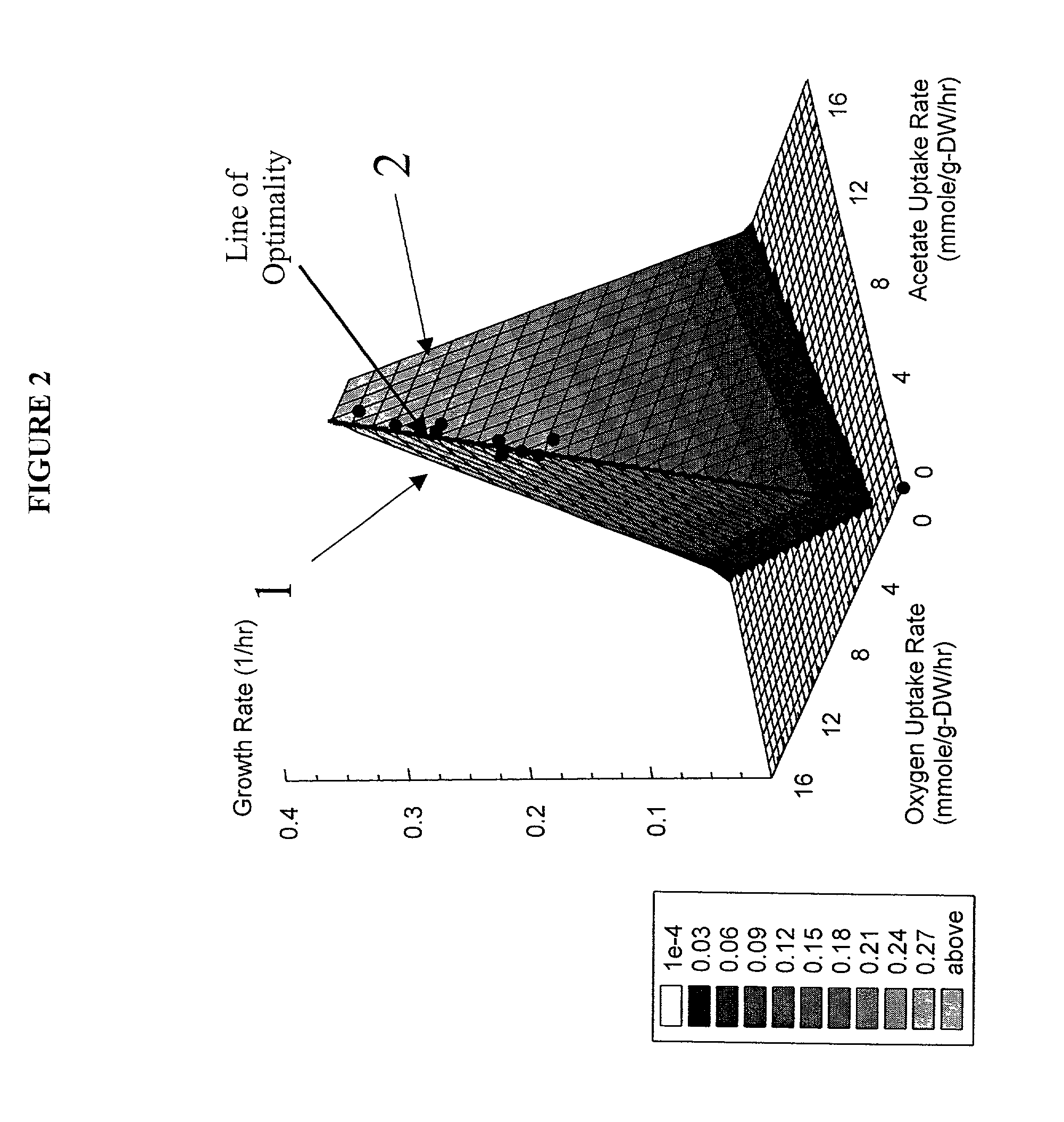
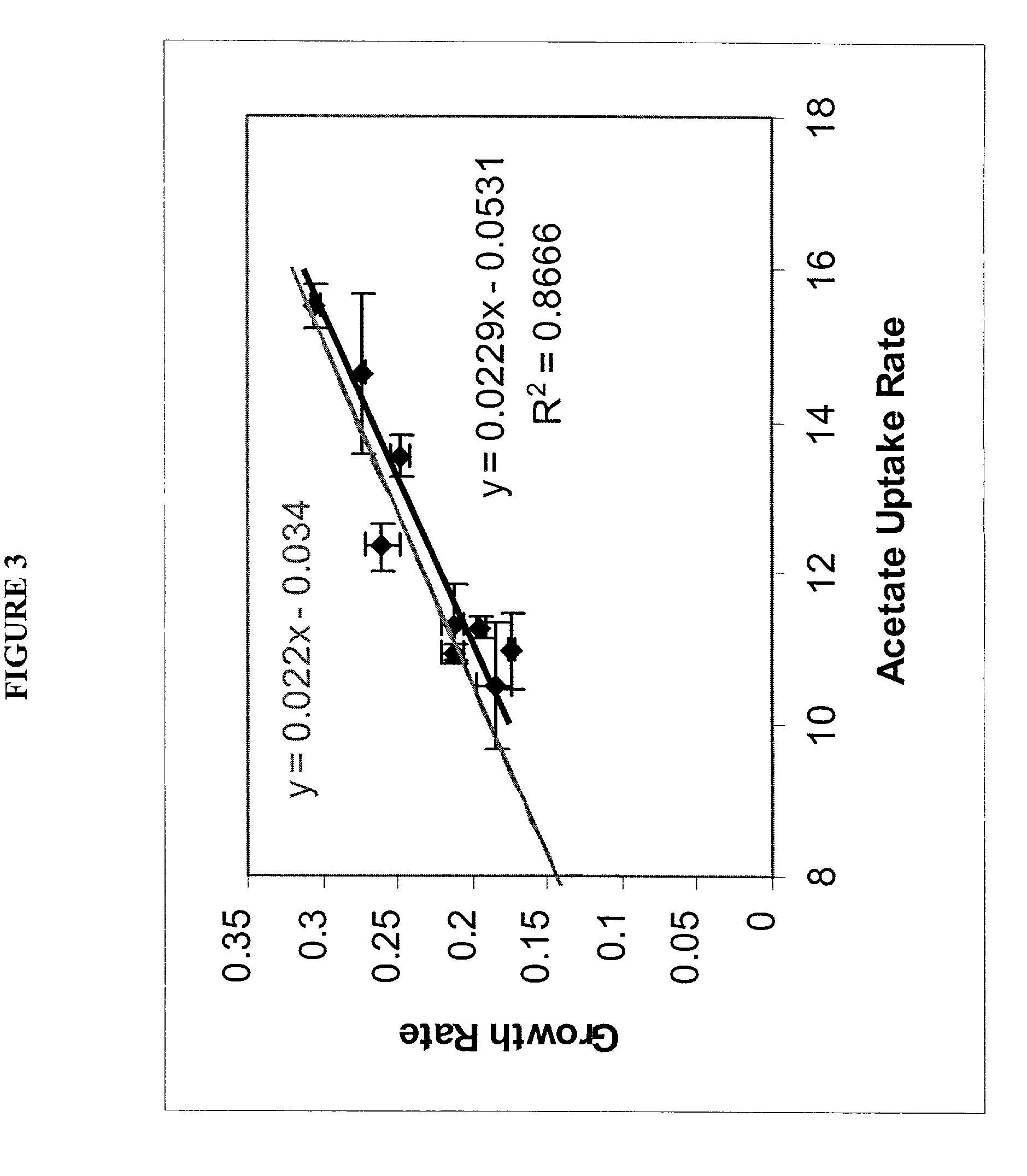
Method for the evolutionary design of biochemical reaction networks
The present invention relates to methods for achieving an optimal function of a biochemical reaction network. The methods can be performed in silico using a reconstruction of a biochemical reaction network of a cell and iterative optimization procedures. The methods can further include laboratory culturing steps to confirm and possibly expand the determinations made using the in silico methods, and to produce a cultured cell, or population of cells, with optimal functions. The current invention includes computer systems and computer products including computer-readable program code for performing the in silico steps of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
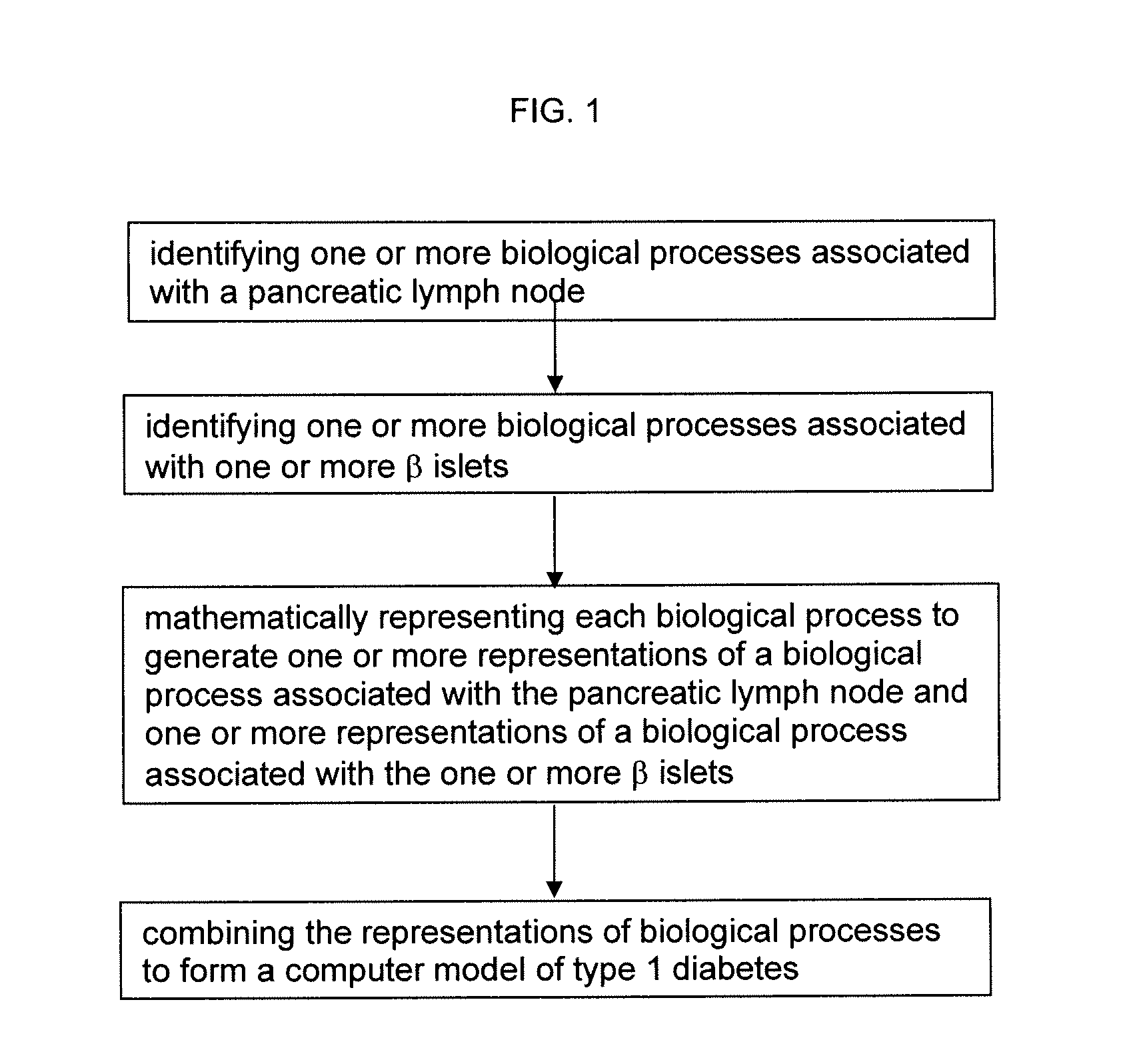
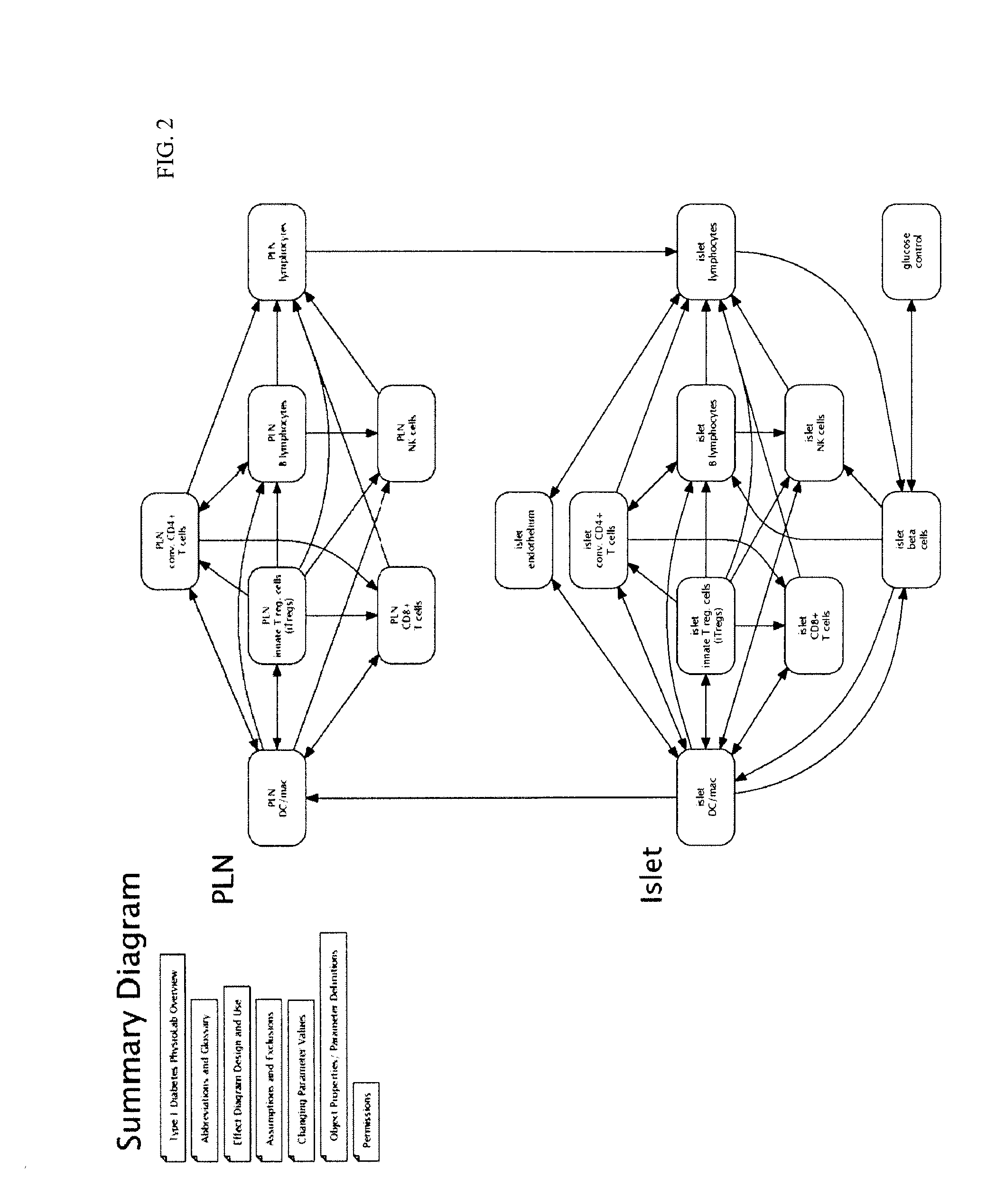
Apparatus and method for computer modeling type 1 diabetes
The invention encompasses novel methods for developing a computer model of type 1 diabetes in a mammal. In particular, the models can include representations of biological processes associated with a pancreatic lymph node and one or more pancreatic islets. Alternatively, the models can include representations of biological processes associated with at least two conditions selected from the group consisting of autoreactive T cell production, autoreactive T cell priming, insulitis and hyperglycemia. The invention also provides methods for developing a computer model of a non-insulin replacement treatment of type 1 diabetes. The invention also encompasses computer models of type 1 diabetes, methods of simulating type 1 diabetes and computer systems for simulating type 1 diabetes and the uses thereof.
Owner:ENTELOS INC
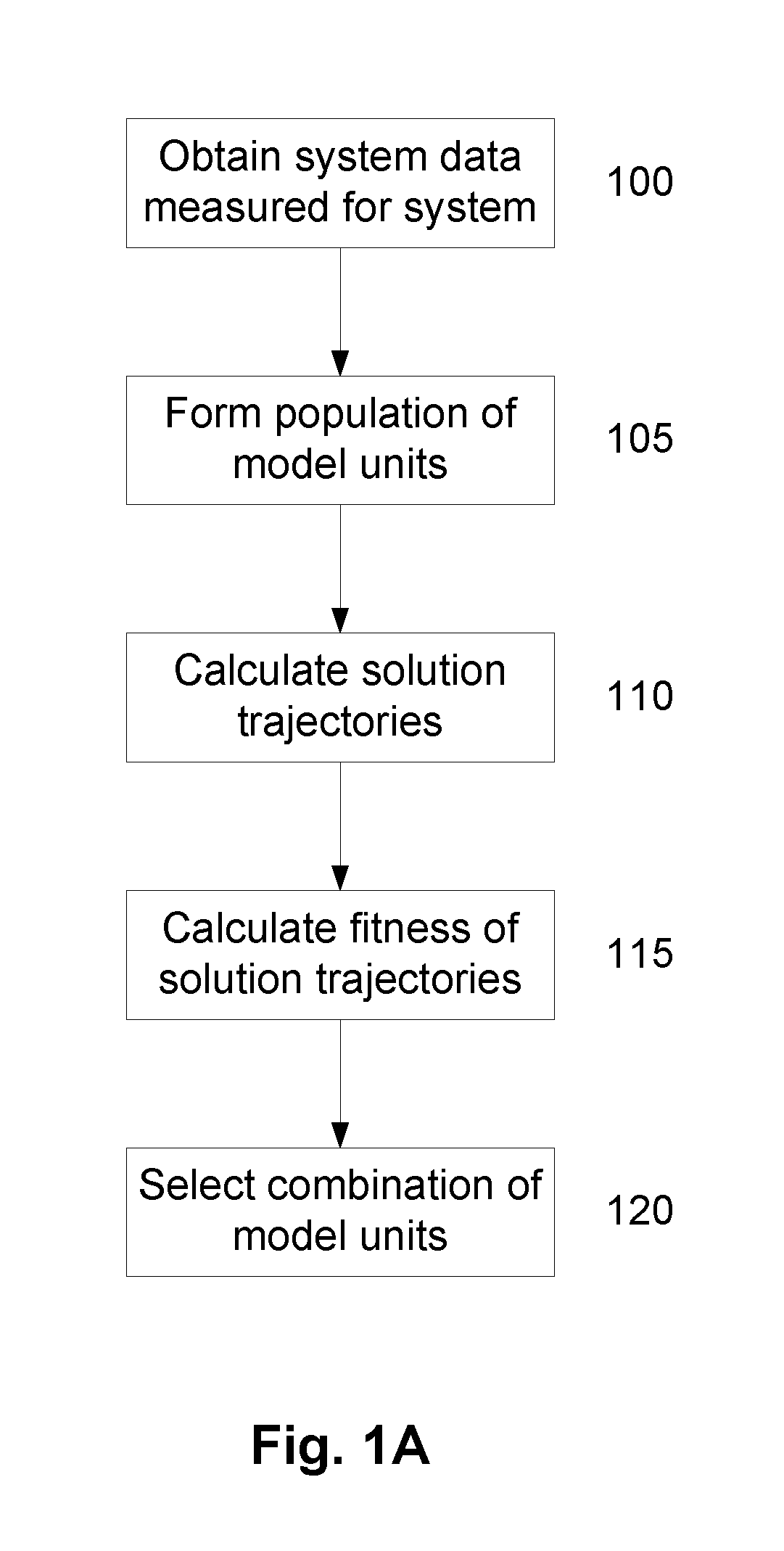
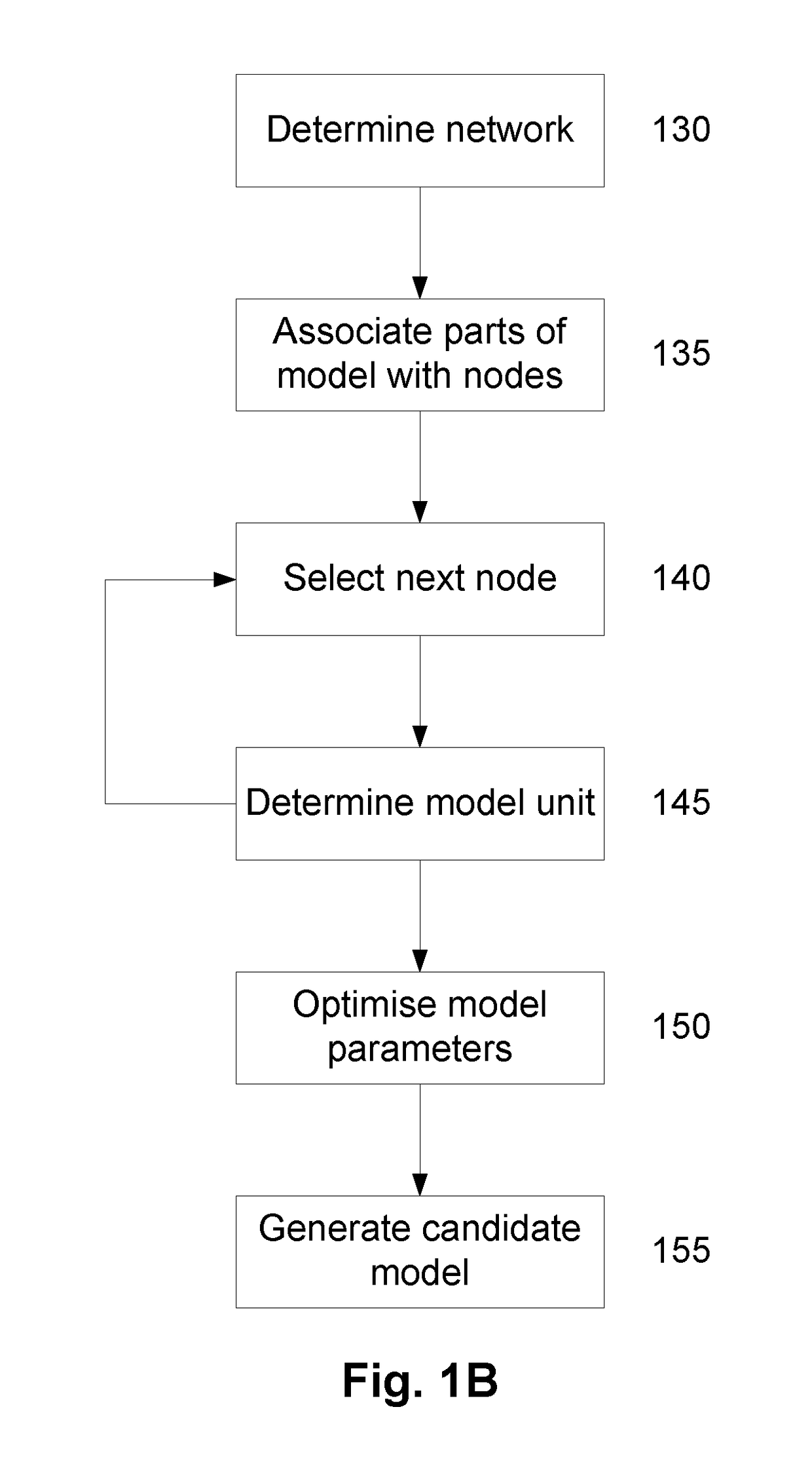
A System and Method for Modelling System Behaviour
ActiveUS20170147722A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMedical simulationDesign optimisation/simulationCollective modelModel system
A method of modelling system behaviour of a physical system, the method including, in one or more electronic processing devices obtaining quantified system data measured for the physical system, the quantified system data being at least partially indicative of the system behaviour for at least a time period, forming at least one population of model units, each model unit including model parameters and at least part of a model, the model parameters being at least partially based on the quantified system data, each model including one or more mathematical equations for modelling system behaviour, for each model unit calculating at least one solution trajectory for at least part of the at least one time period; determining a fitness value based at least in part on the at least one solution trajectory; and, selecting a combination of model units using the fitness values of each model unit, the combination of model units representing a collective model that models the system behaviour.
Owner:EVOLVING MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
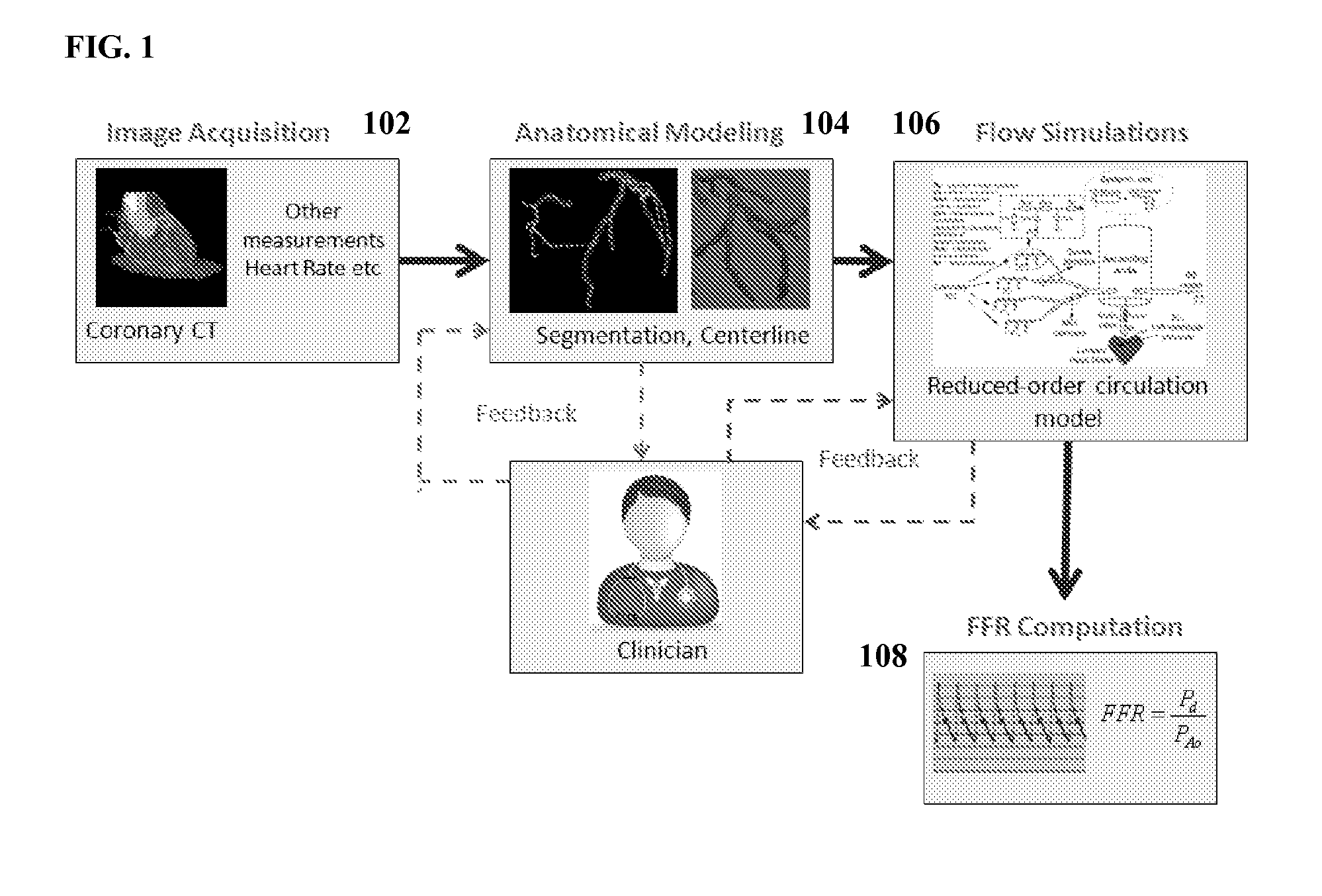
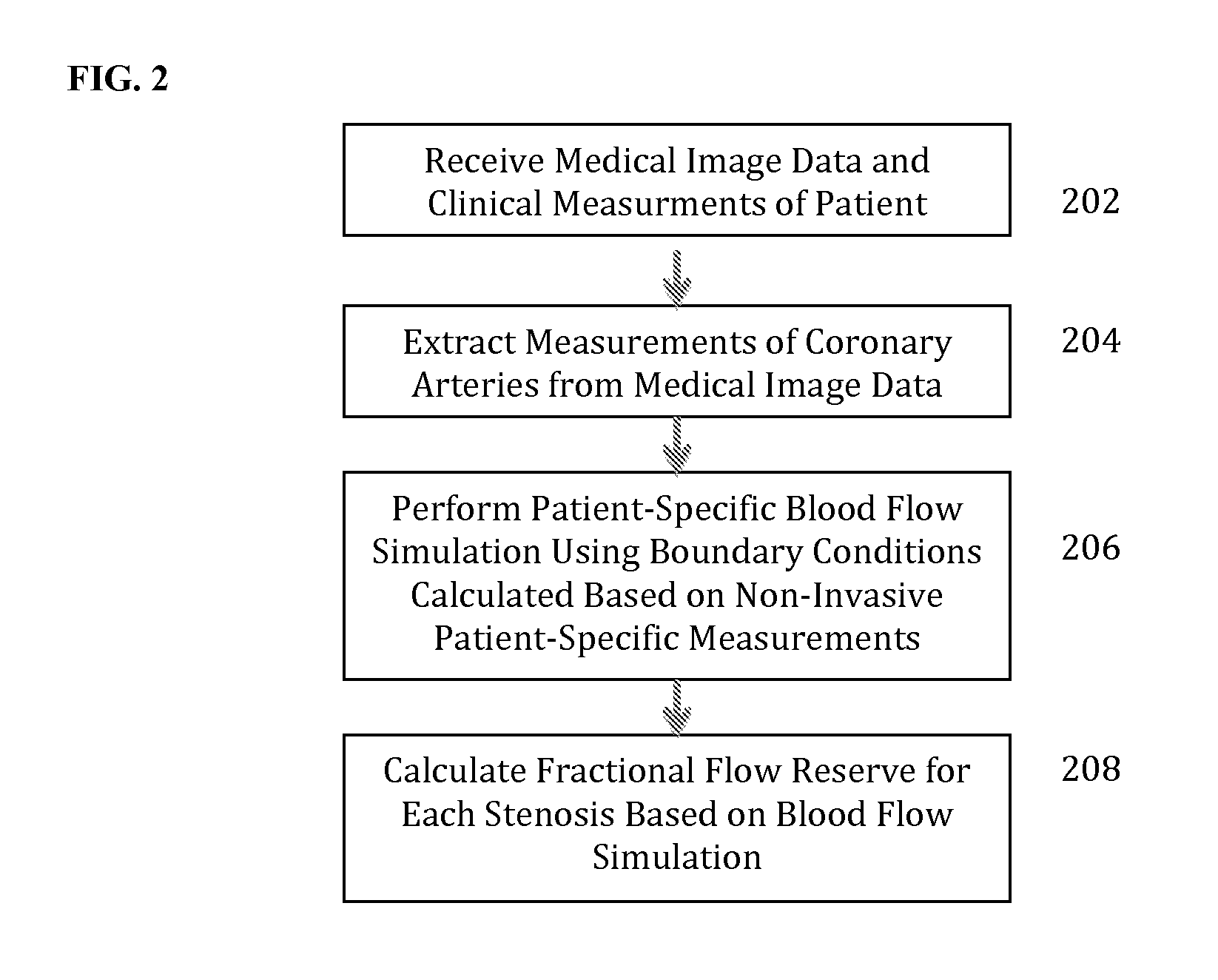
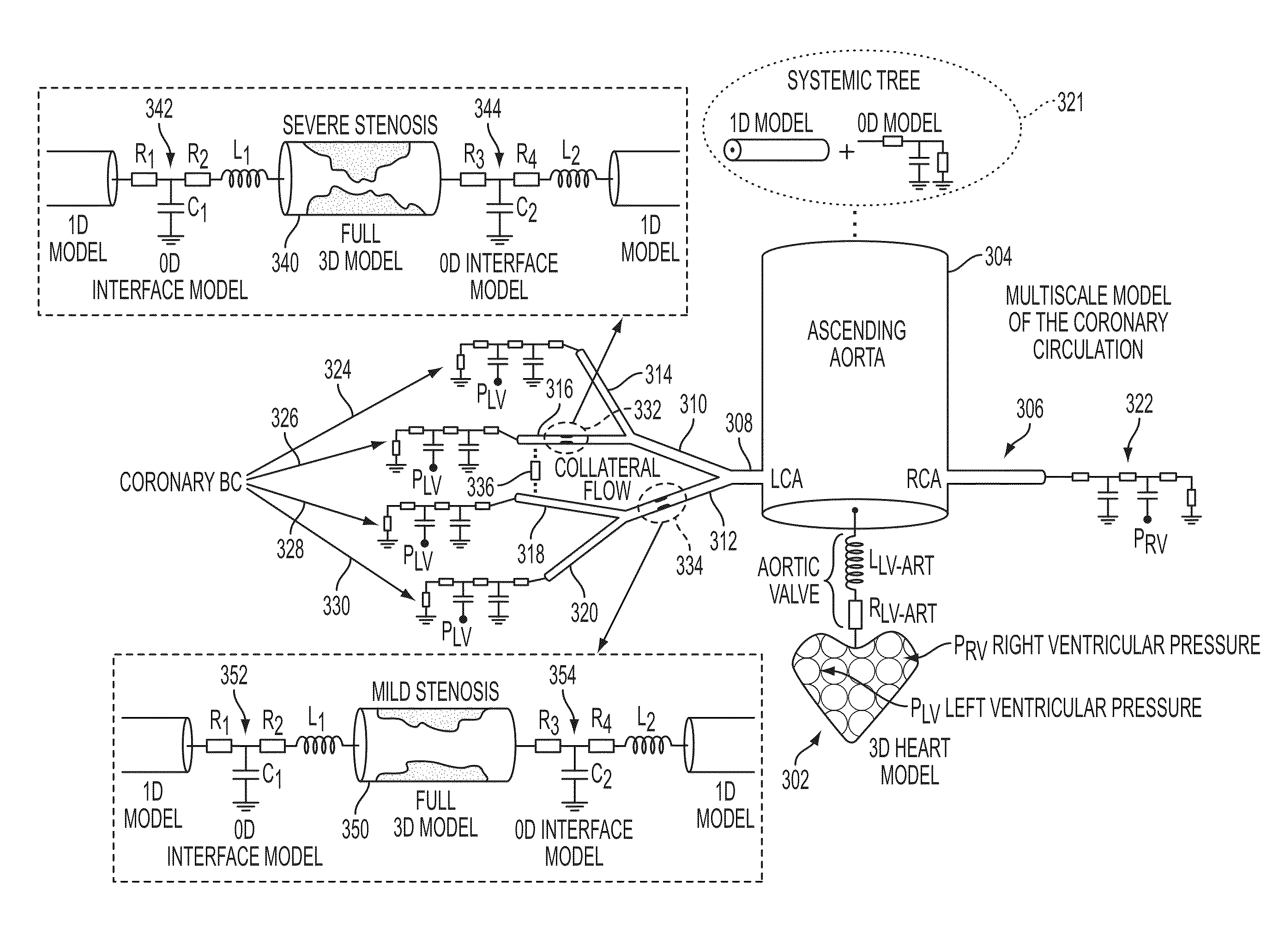
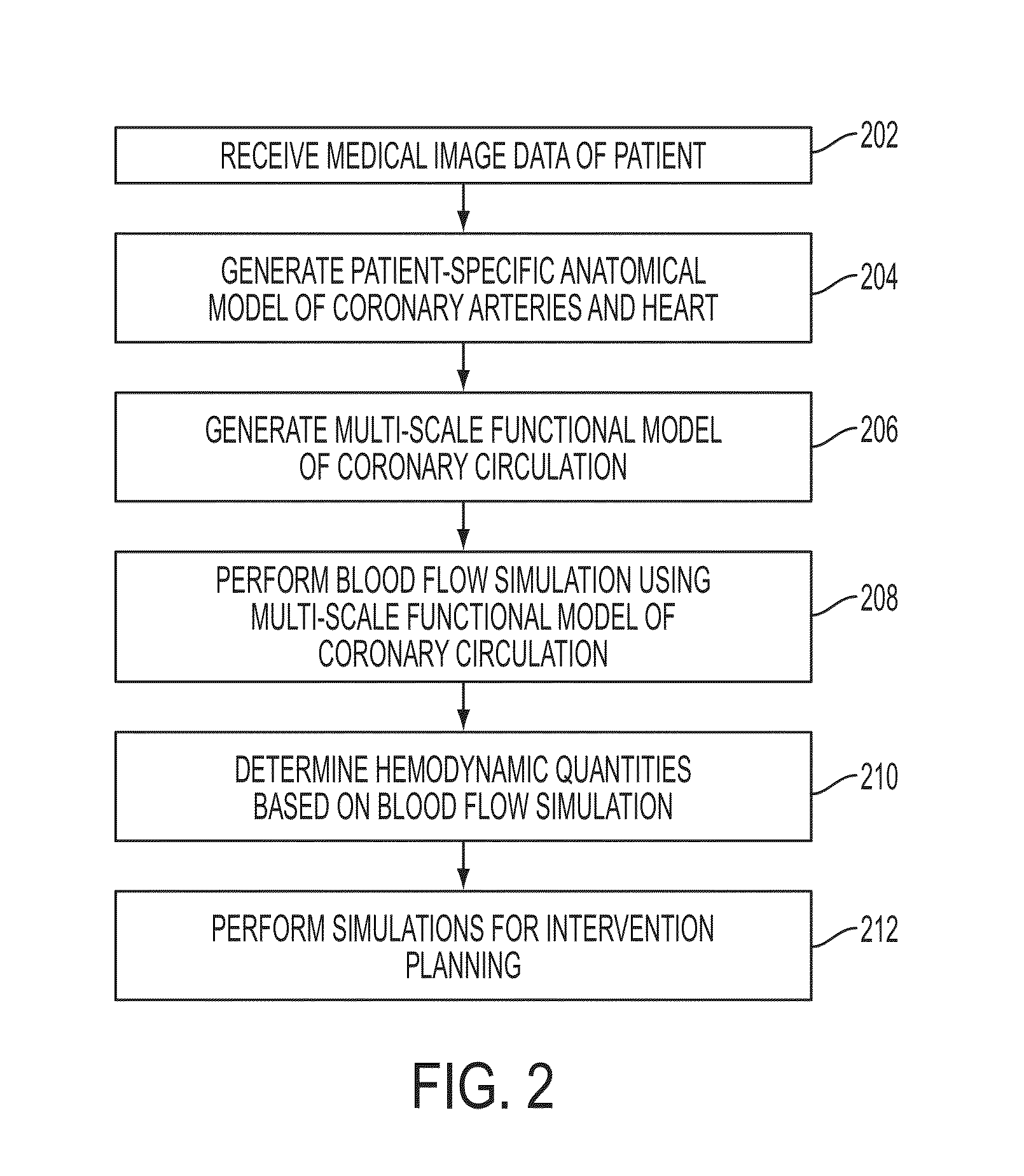
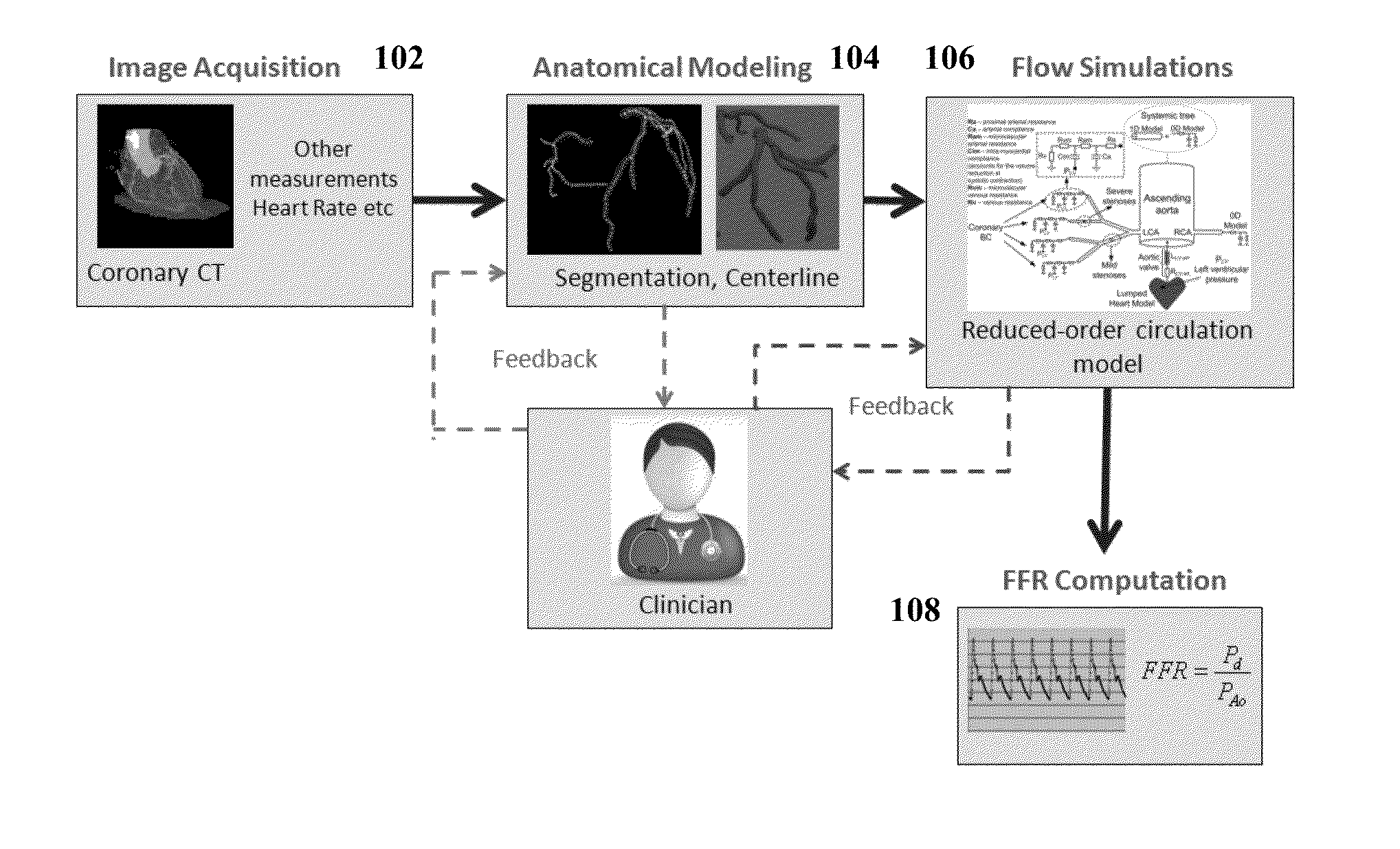
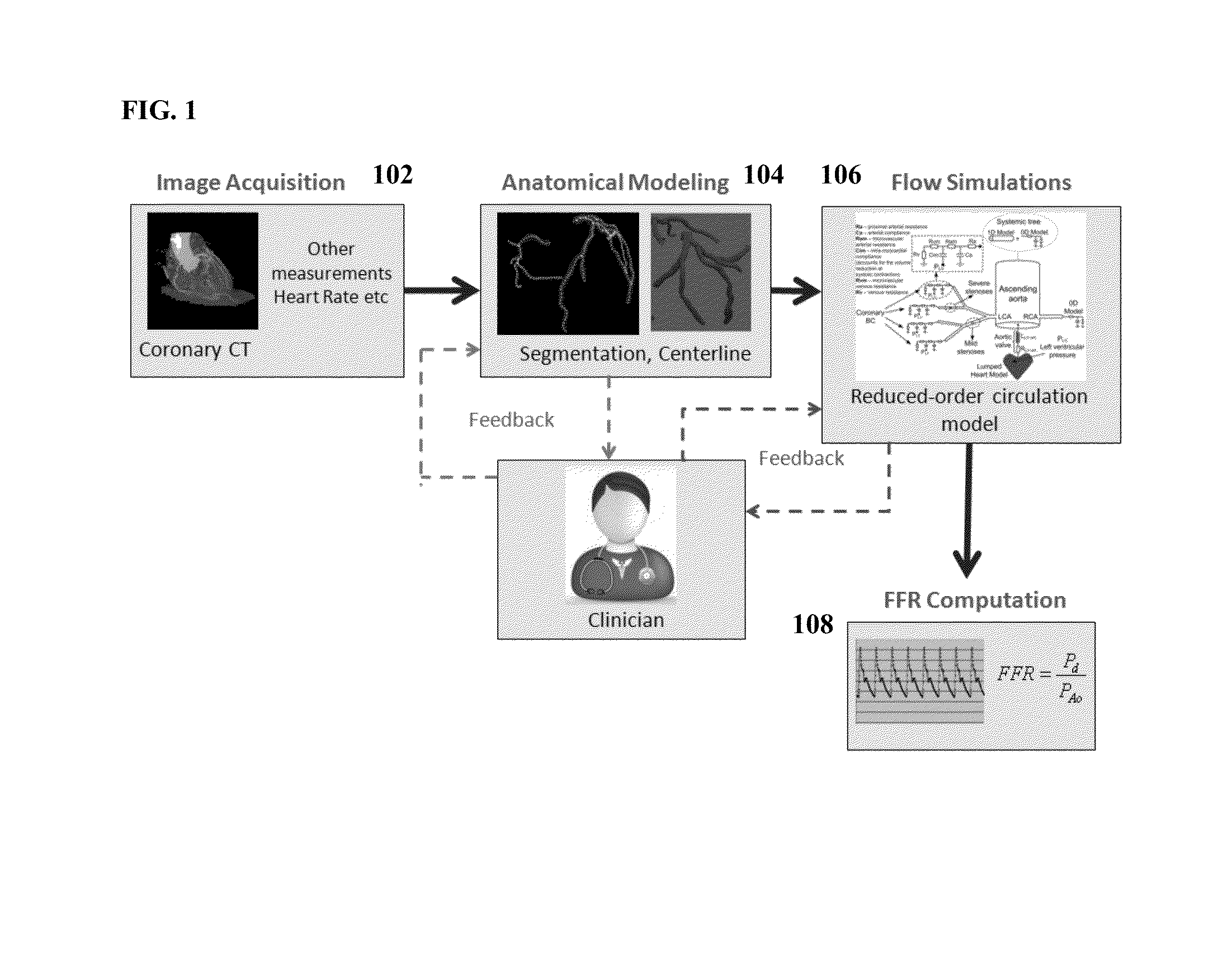
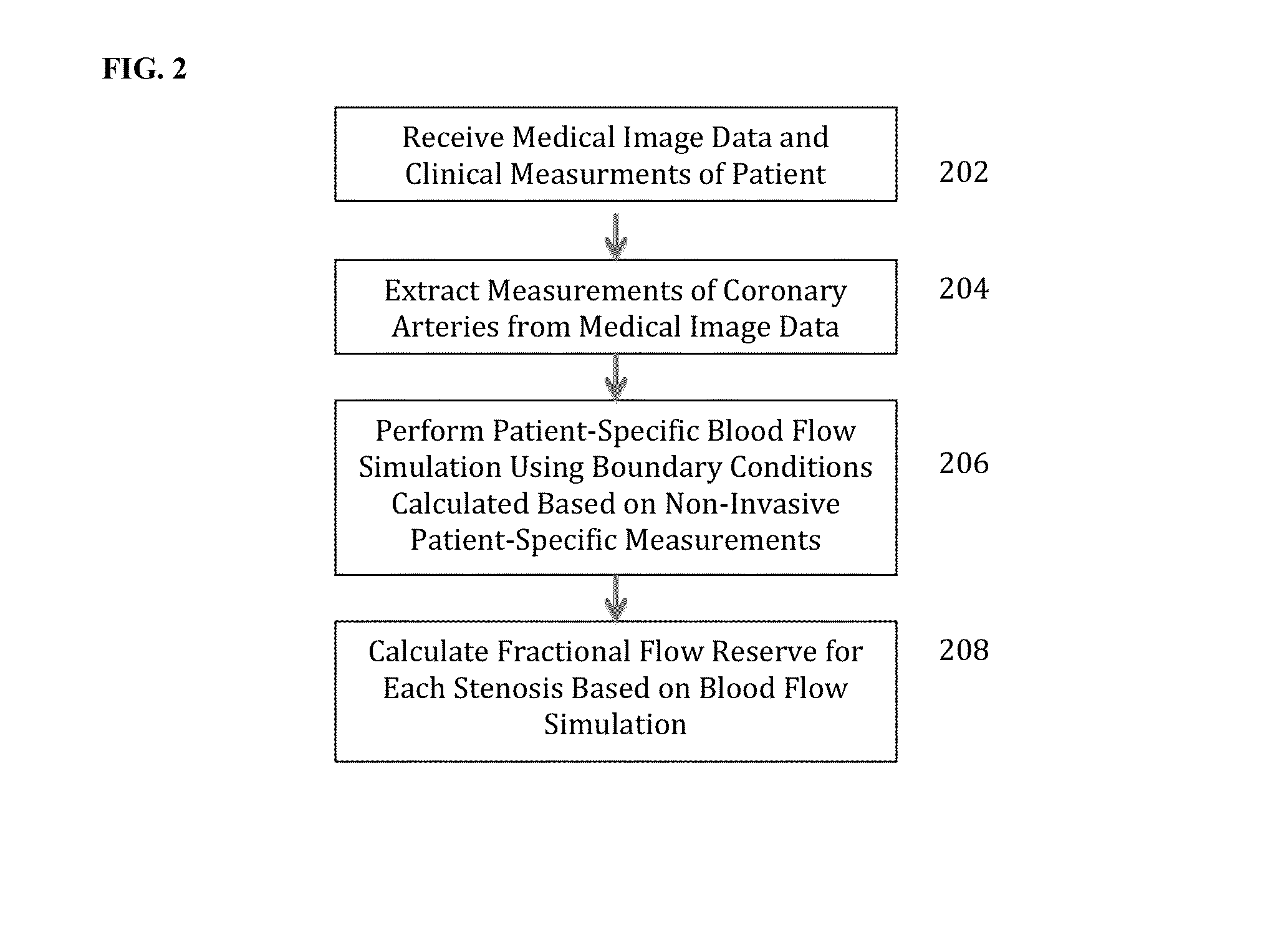
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
InactiveUS20130246034A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
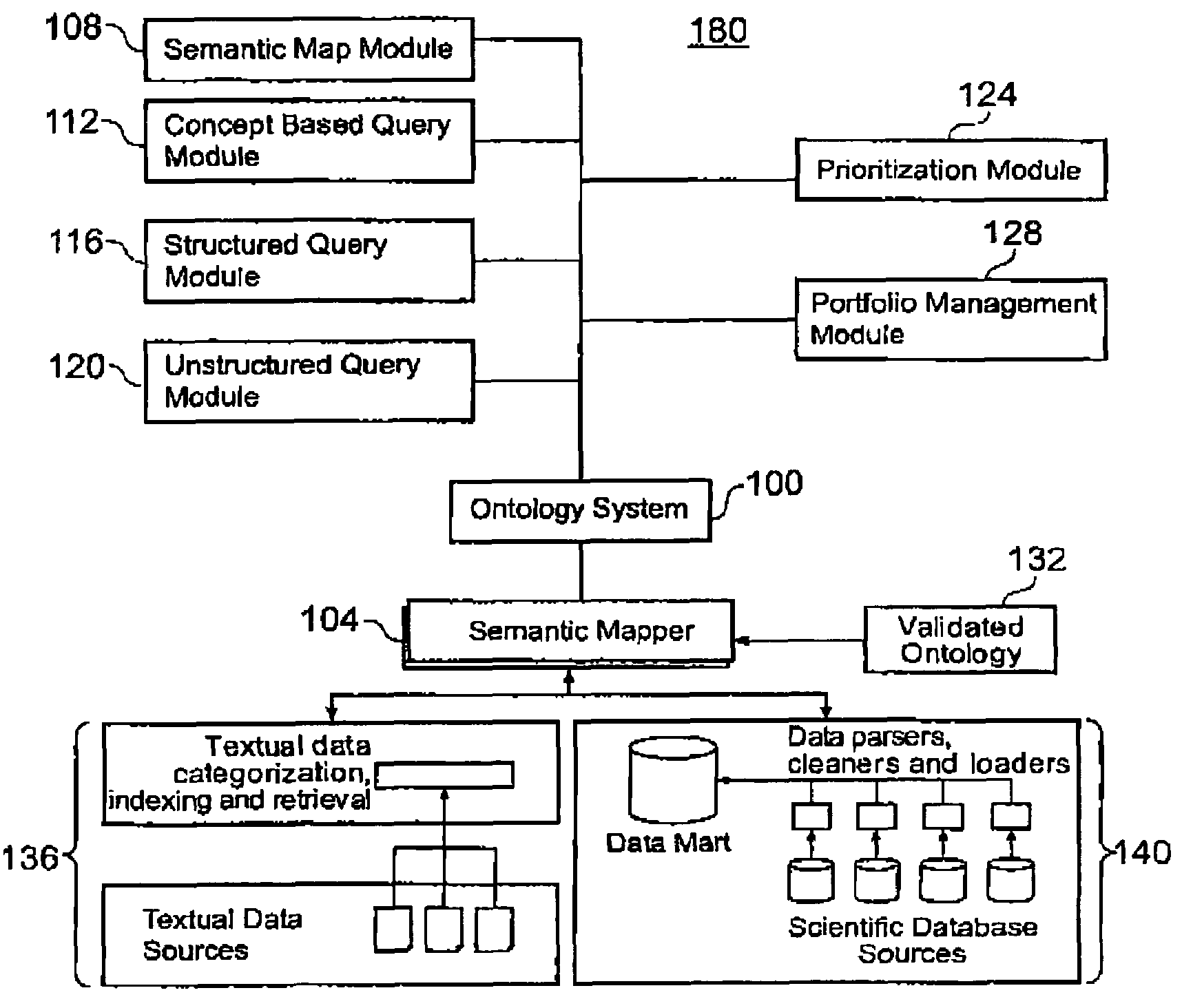
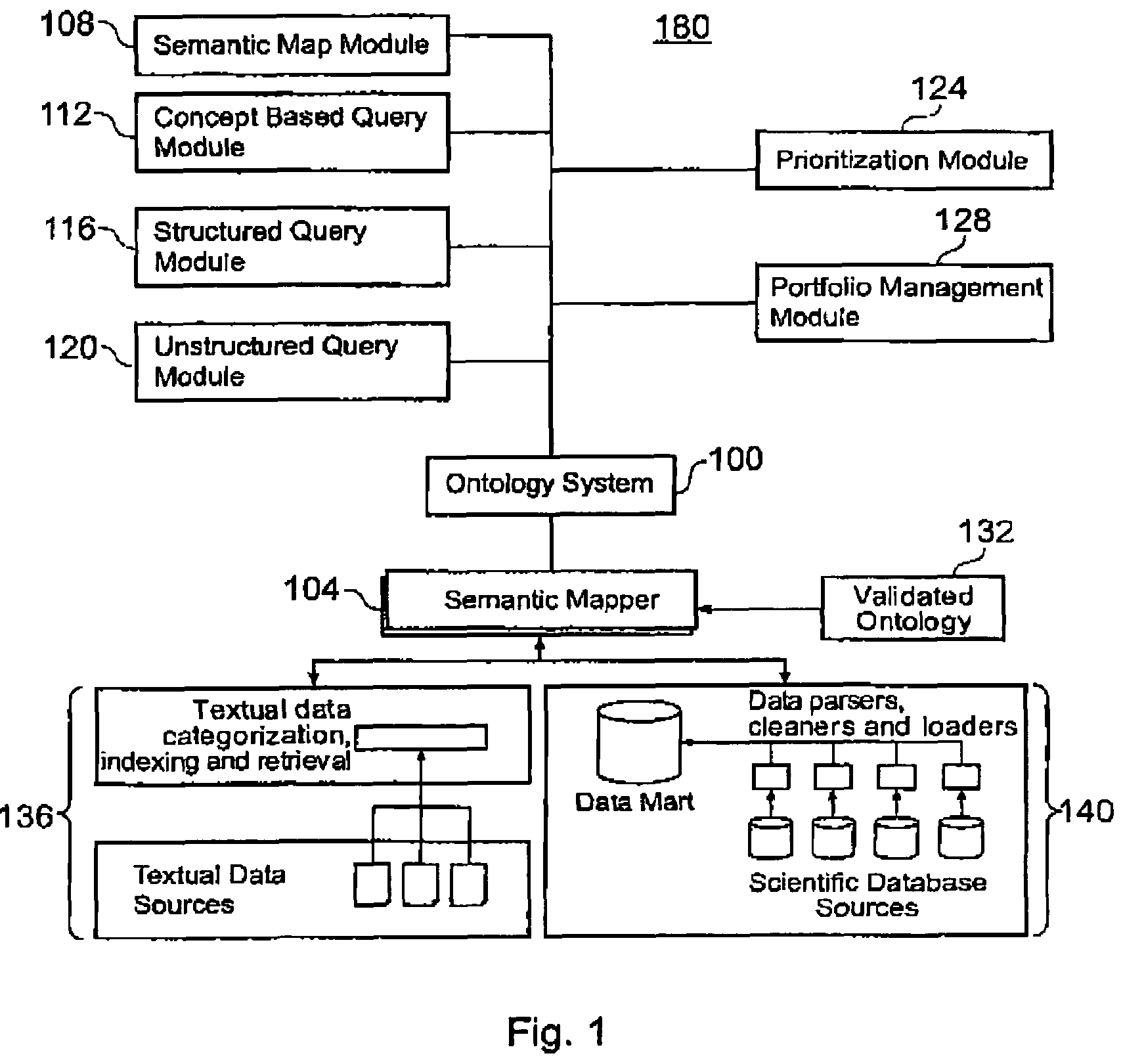
Ontology-based information management system and method
InactiveUS7225183B2Effective syntacticEffective semantic mappingData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformaticsUnstructured data
An information management system and method is provided for integrating structured and unstructured data using an ontological approach, and further comprises processes for creating, validating, augmenting, and combining ontologies for life science informatics and other disciplines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
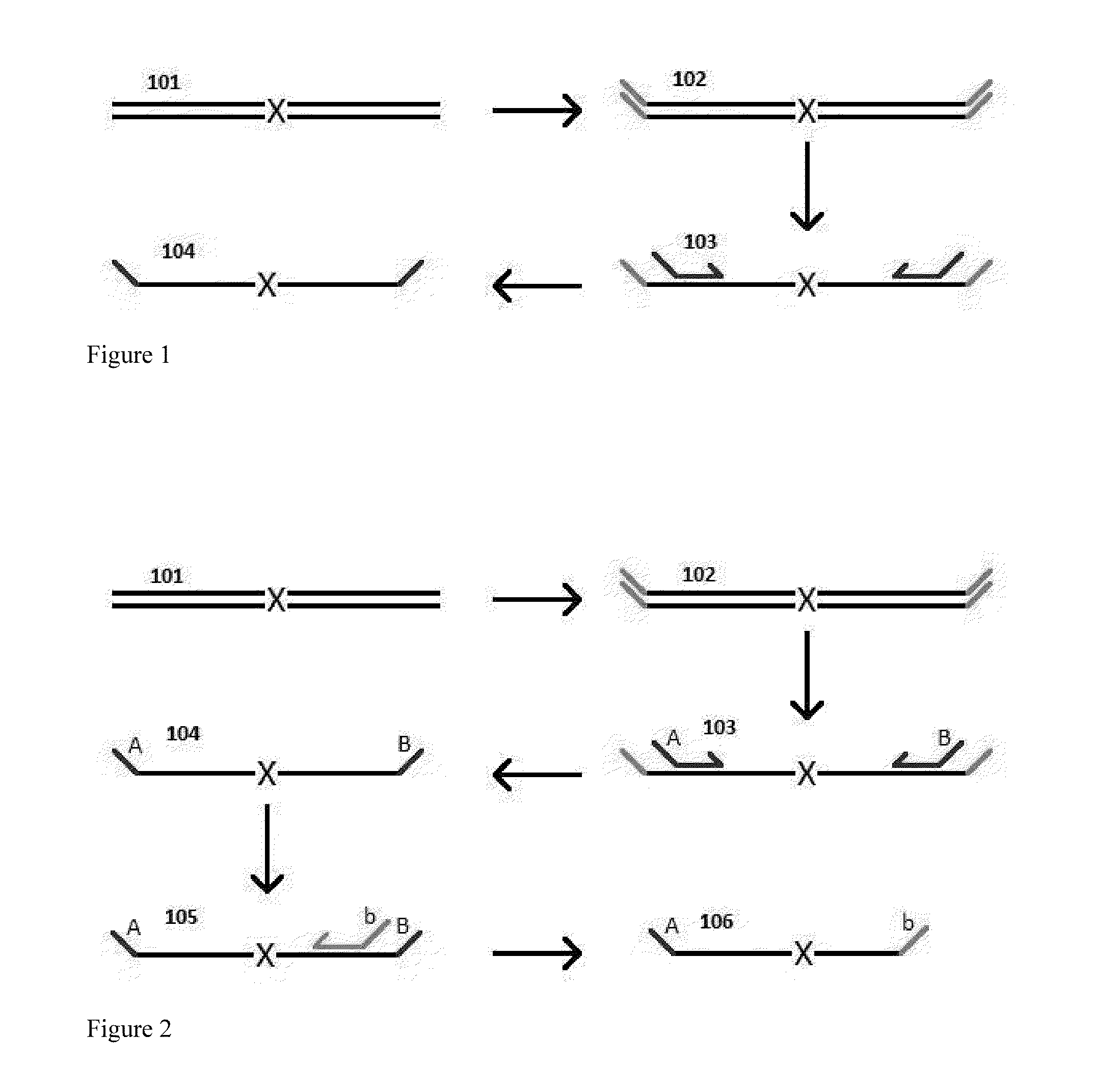
Highly Multiplex PCR Methods and Compositions
InactiveUS20130123120A1Increase opportunitiesHigh copy numberNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexDimer
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
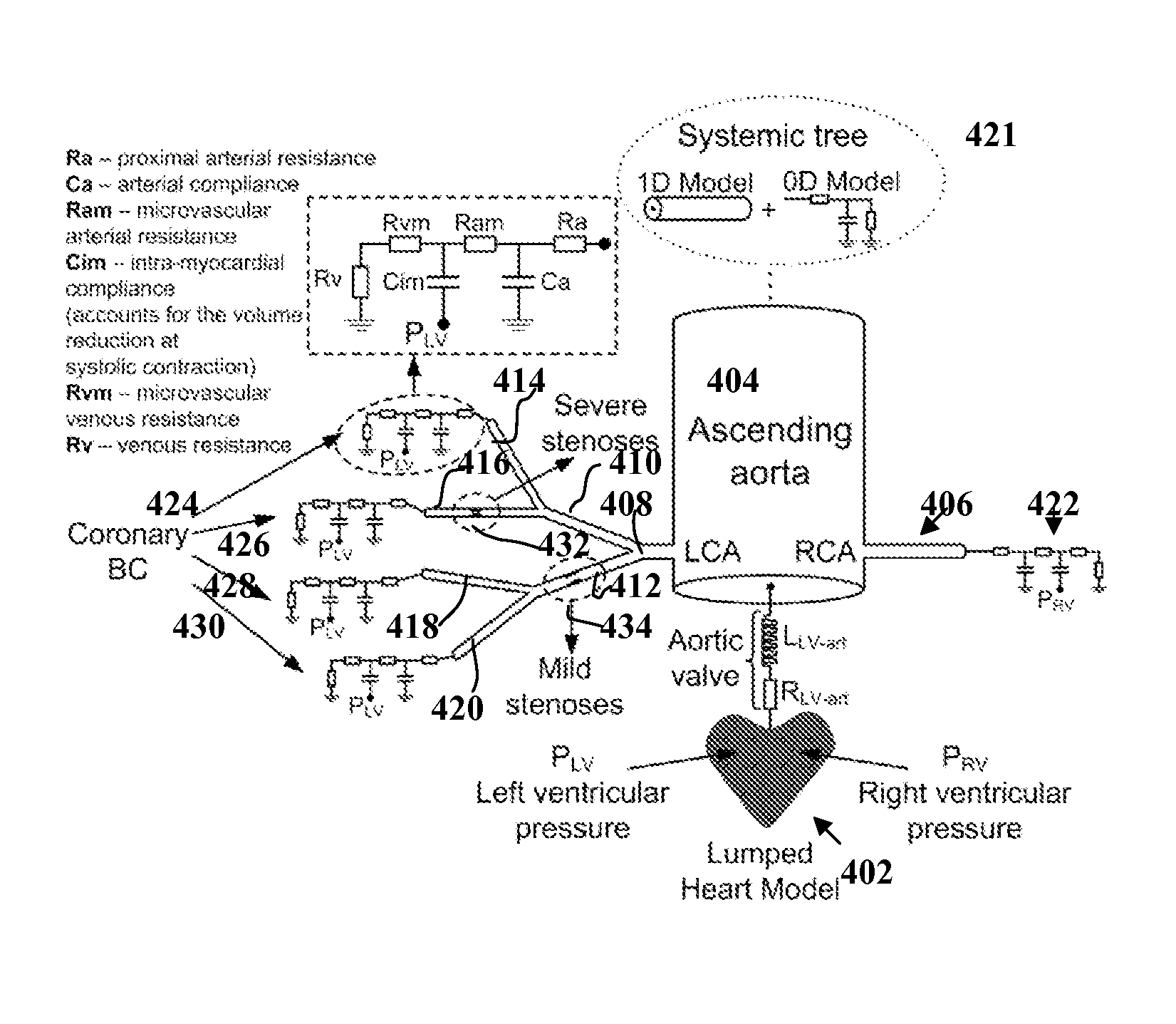
Method and System for Multi-Scale Anatomical and Functional Modeling of Coronary Circulation
ActiveUS20130132054A1Improve predictive performanceImprove clinical managementChemical property predictionChemical structure searchCoronary arteriesIntervention planning
A method and system for multi-scale anatomical and functional modeling of coronary circulation is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of coronary arteries and the heart is generated from medical image data of a patient. A multi-scale functional model of coronary circulation is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model. Blood flow is simulated in at least one stenosis region of at least one coronary artery using the multi-scale function model of coronary circulation. Hemodynamic quantities, such as fractional flow reserve (FFR), are computed to determine a functional assessment of the stenosis, and virtual intervention simulations are performed using the multi-scale function model of coronary circulation for decision support and intervention planning.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
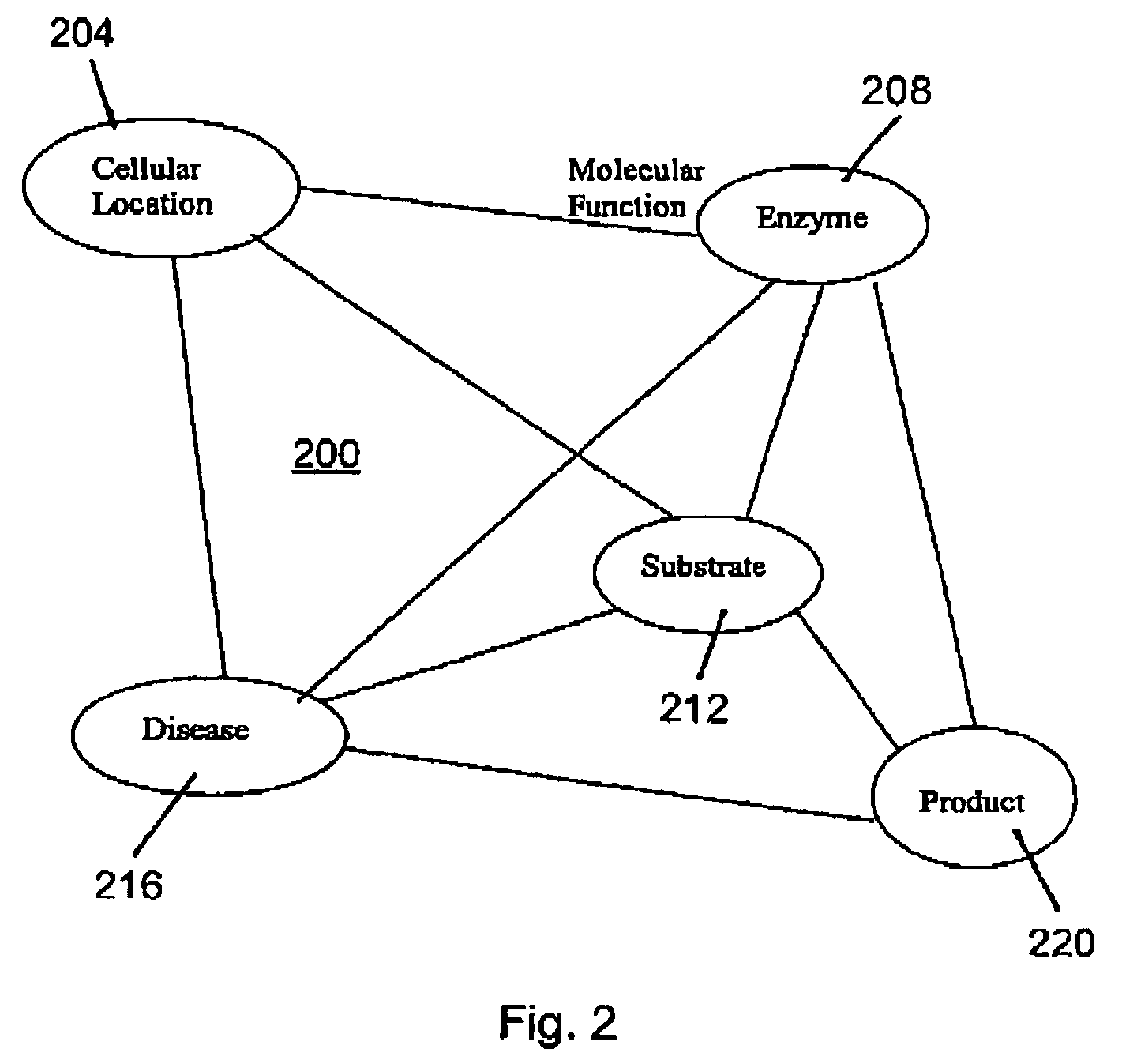
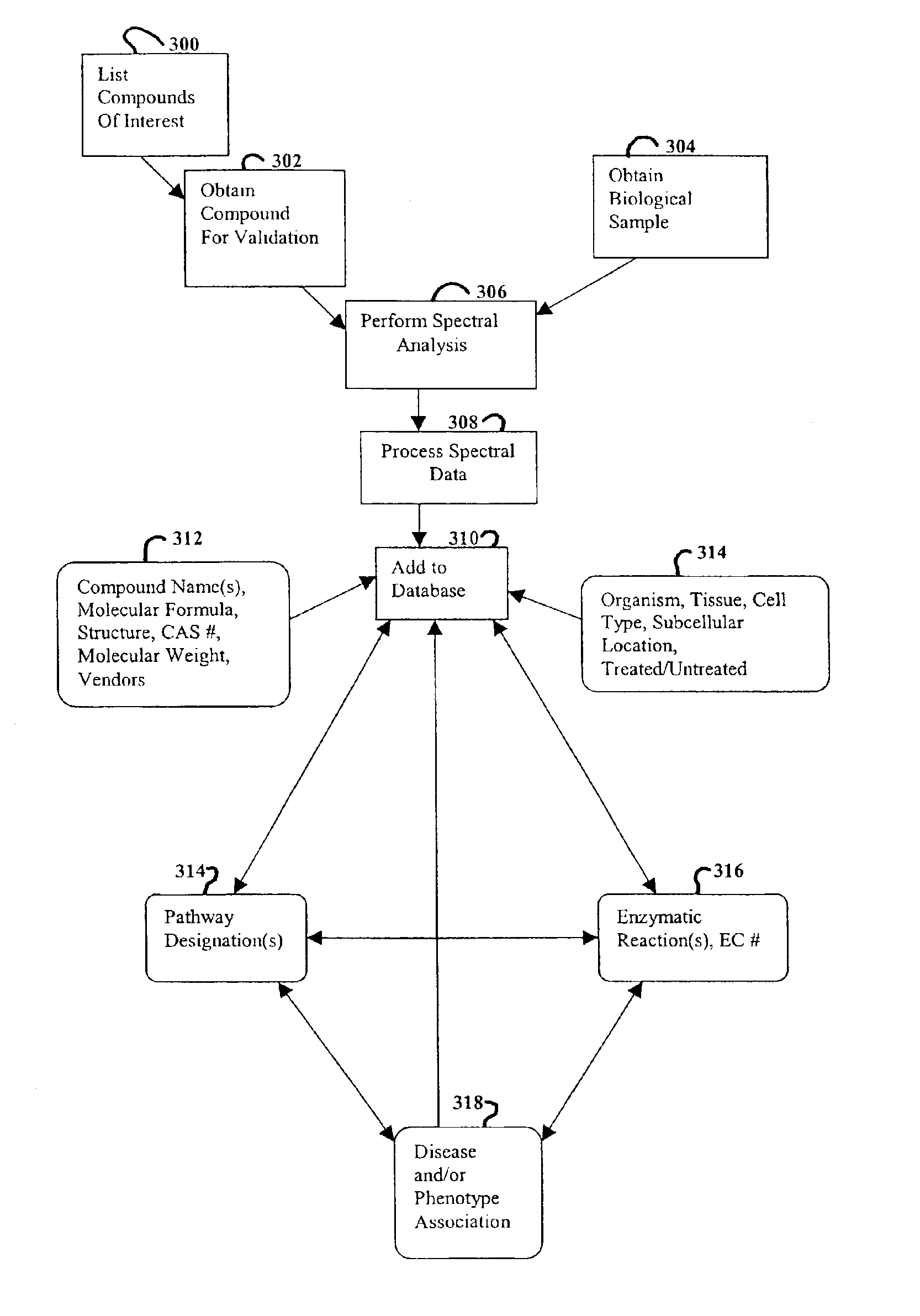
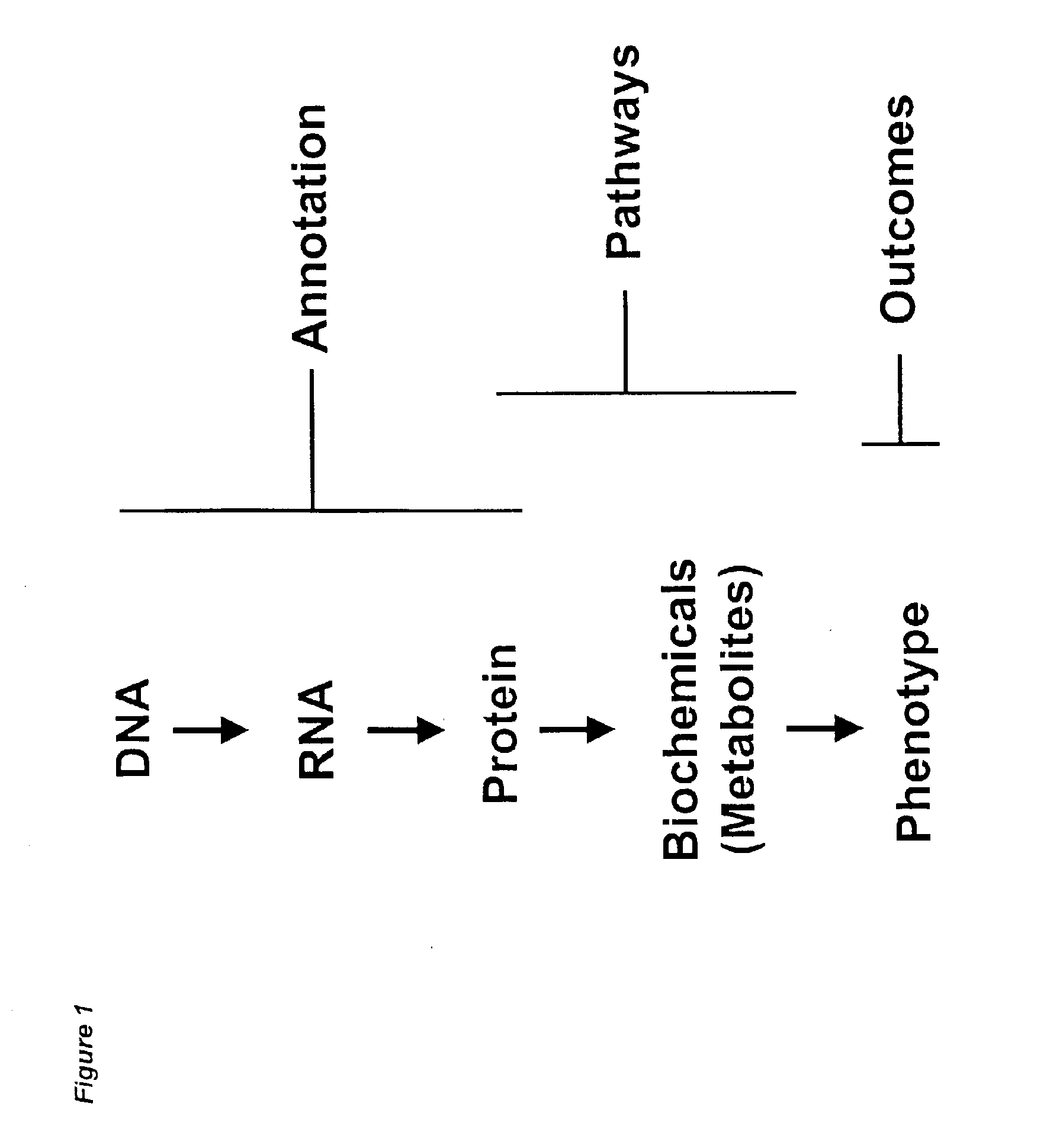
Methods and systems for analyzing complex biological systems
The present invention provides methods and systems for organizing complex and disparate data. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and systems for organizing complex and disparate data into coherent data sets. Coherent data sets resulting from the methods and systems of the present invention serve as models for biological systems. Methods and systems for integrating data and creating coherent data sets are useful for numerous biological applications, such as, for example, determining gene function, identifying and validating drug and pesticide targets, identifying and validating drug and pesticide candidate compounds, profiling drug and pesticide compounds, producing a compilation of health or wellness profiles, determining compound site(s) of action, identifying unknown samples, and numerous other applications in the agricultural, pharmaceutical, forensic, and biotechnology industries.
Owner:METABOLON
Network models of complex systems
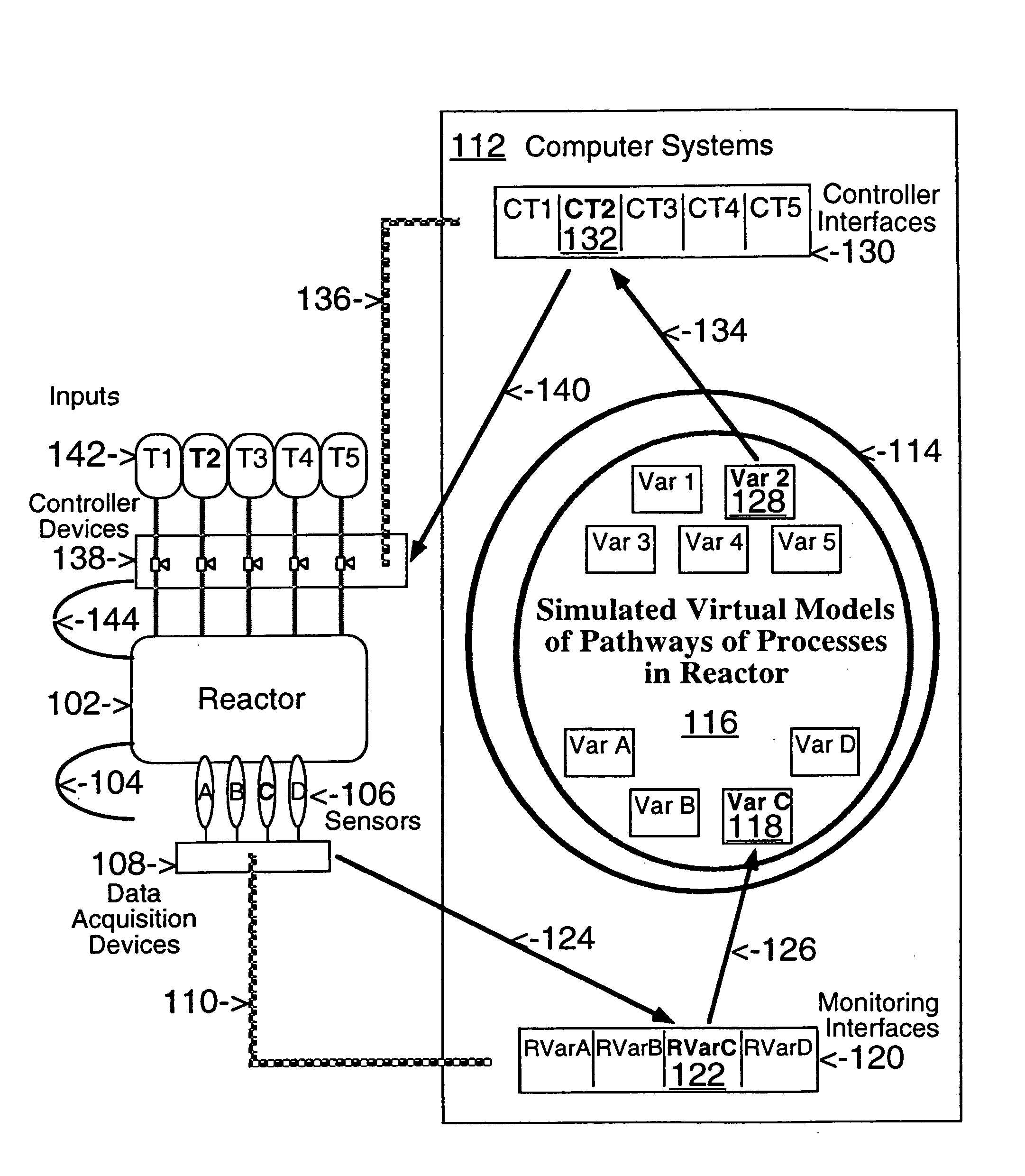
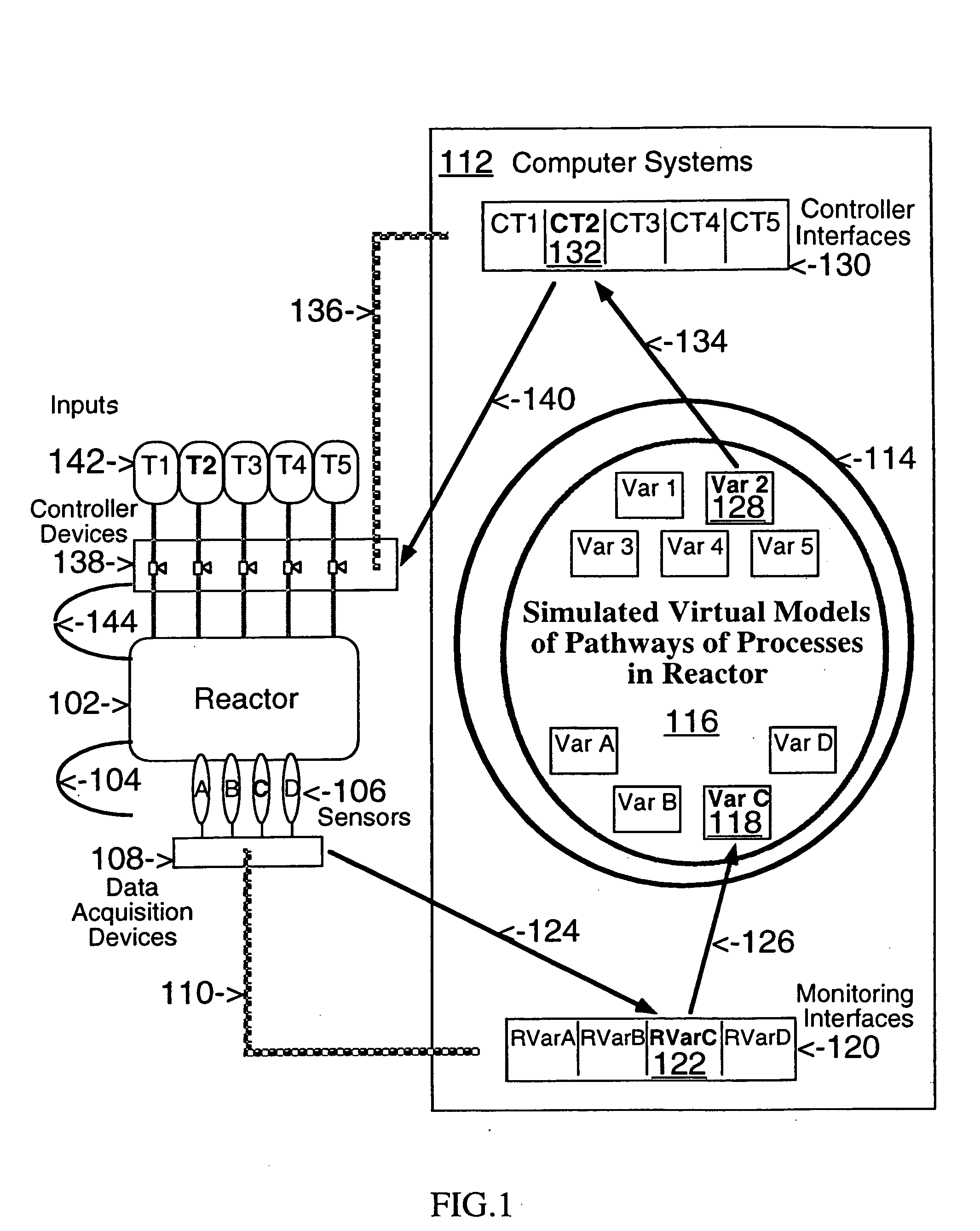
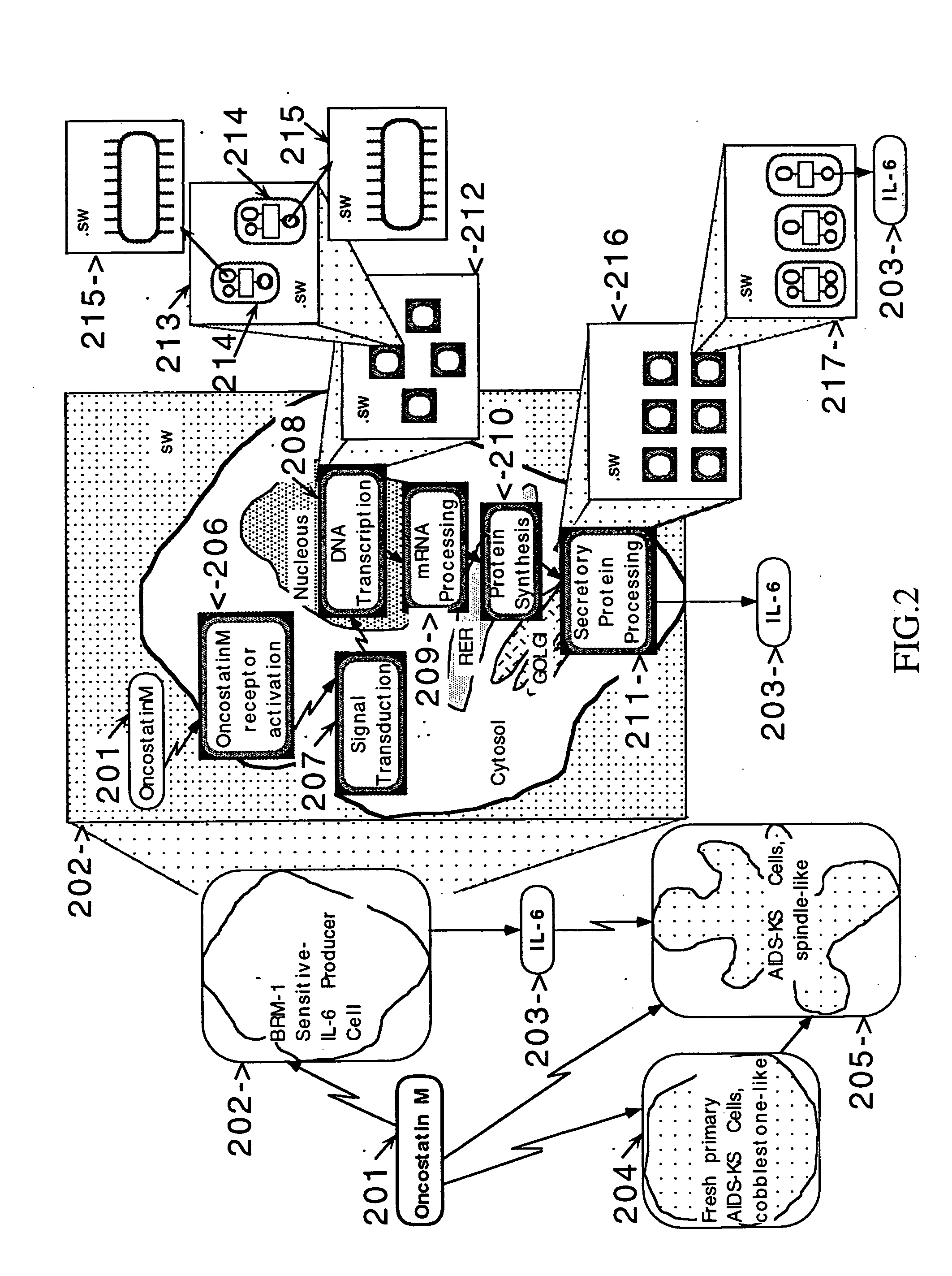
This invention describes computer based virtual models of complex systems, together with integrated systems and methods providing a development and execution framework for visual modeling and dynamic simulation of said models. The virtual models can be used for analysis, monitoring, or control of the operation of the complex systems modeled, as well as for information retrieval. More particularly, the virtual models in the present implementation relate to biological complex systems. In the current implementation the virtual models comprise building blocks representing physical, chemical, or biological processes, the pools of entities that participate in those processes, a hierarchy of compartments representing time-intervals or the spatial and / or functional structure of the complex system in which said entities are located and said processes take place, and the description of the composition of those entities. The building blocks encapsulate in different layers the information, data, and mathematical models that characterize and define each virtual model, and a plurality of methods is associated with their components. The models are built by linking instances of the building blocks in a predefined way, which, when integrated by the methods provided in this invention, result in multidimensional networks of pathways. A number of functions and graphical interfaces can be selected for said instances of building blocks, to extract in various forms the information contained in said models. Those functions include: a) on-the-fly creation of displays of interactive multidimensional networks of pathways, according to user selections; b) dynamic quantitative simulations of selected networks; and c) complex predefined queries based on the relative position of pools of entities in the pathways, the role that the pools play in different processes, the location in selected compartments, and / or the structural components of the entities of those pools. The system integrates inferential control with quantitative and scaled simulation methods, and provides a variety of alternatives to deal with complex dynamic systems and with incomplete and constantly evolving information and data.
Owner:INTERTECH VENTURES
Orthodontic digital setups
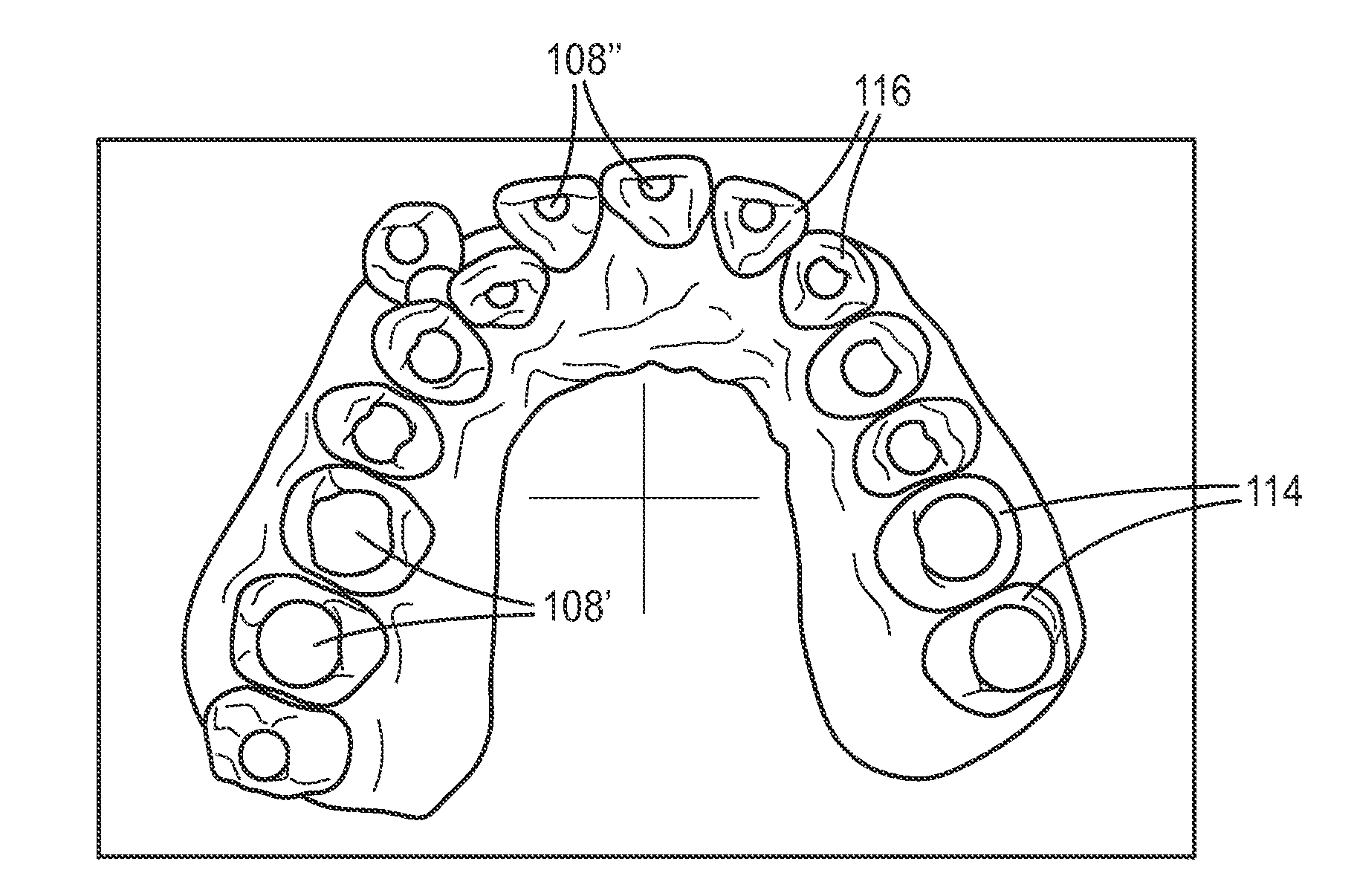
ActiveUS20130325431A1Increase success rateIncrease the amount of calculationMedical simulationOthrodonticsComputer scienceTooth surface
Methods for recognizing a virtual tooth surface, defining a virtual tooth coordinate system, and simulating a collision between virtual teeth are provided. Methods include receiving input data specifying a point on the rendered surface model associated with a tooth, deriving a perimeter on the surface model of the tooth, and analyzing the surface model along a plurality of paths outwardly extending from points on the perimeter. Methods also include receiving point input data, receiving axis input data that defines first and second axes associated with the virtual tooth, computing a substantially normal vector for a portion of the tooth surface surrounding the point, and computing a coordinate system. Methods also include receiving permissible movement input data directed to permissible movement of a first virtual tooth, bringing the first virtual tooth into contact with a second virtual tooth, and displaying data resulting from the simulation.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Energy expenditure
ActiveUS20130191034A1Physical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPeak valueEnergy expenditure
Aspects relate to calculating energy expenditure values from an apparatus configured to be worn on an appendage of a user. Steps counts may be quantified, such as by detecting arm swings peaks and bounce peaks in motion data. A search range of acceleration frequencies related to an expected activity may be established. Frequencies of acceleration data within a search range may be analyzed to identify one or more peaks, such as a bounce peak and an arm swing peak. Novel systems and methods may determine whether to utilize the arm swing data, bounce data, and / or other data or portions of data to quantify steps. The number of peaks (and types of peaks) may be used to choose a step frequency and step magnitude. At least a portion of the motion data may be classified into an activity category based upon the quantification of steps.
Owner:NIKE INC
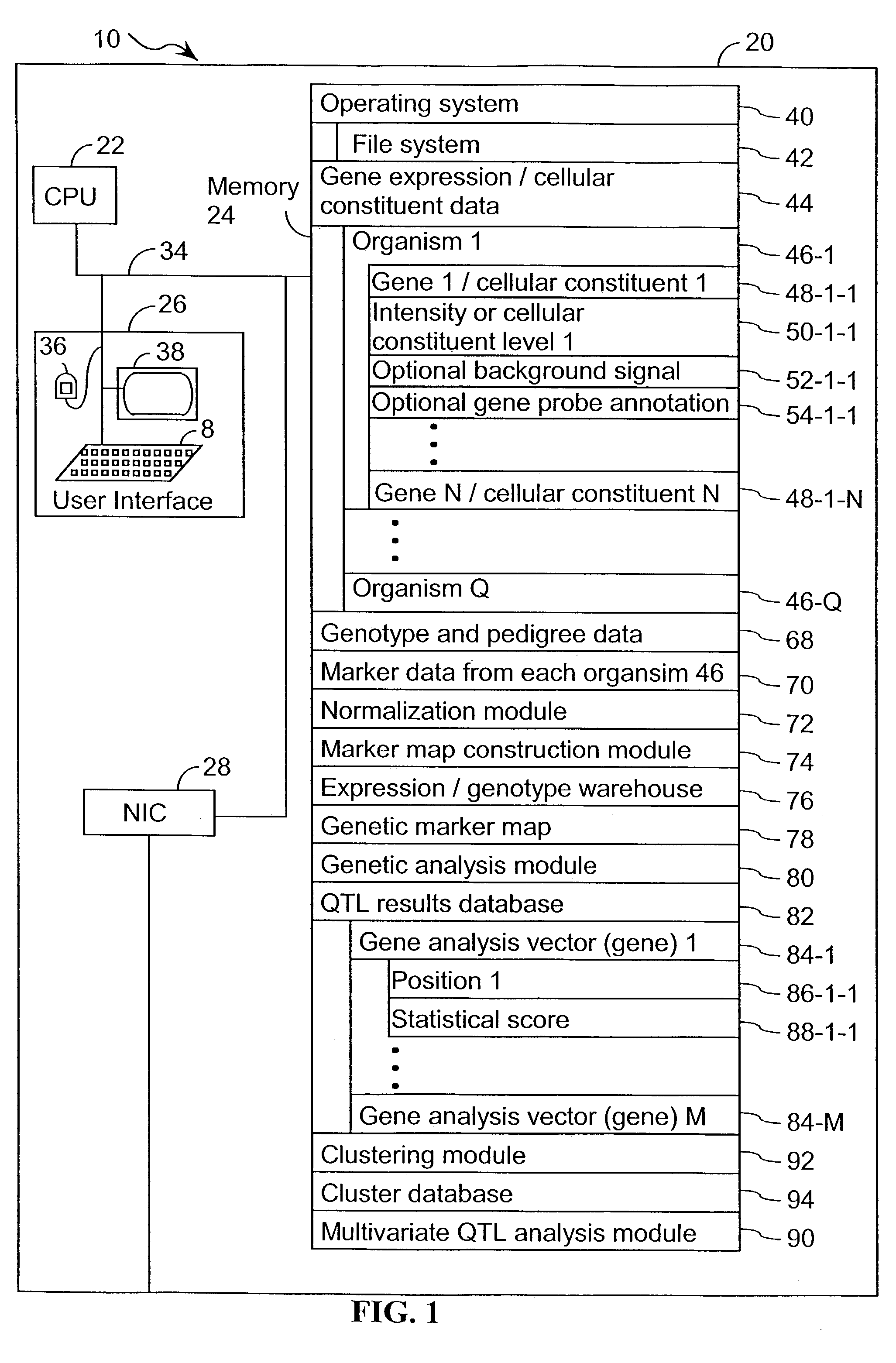
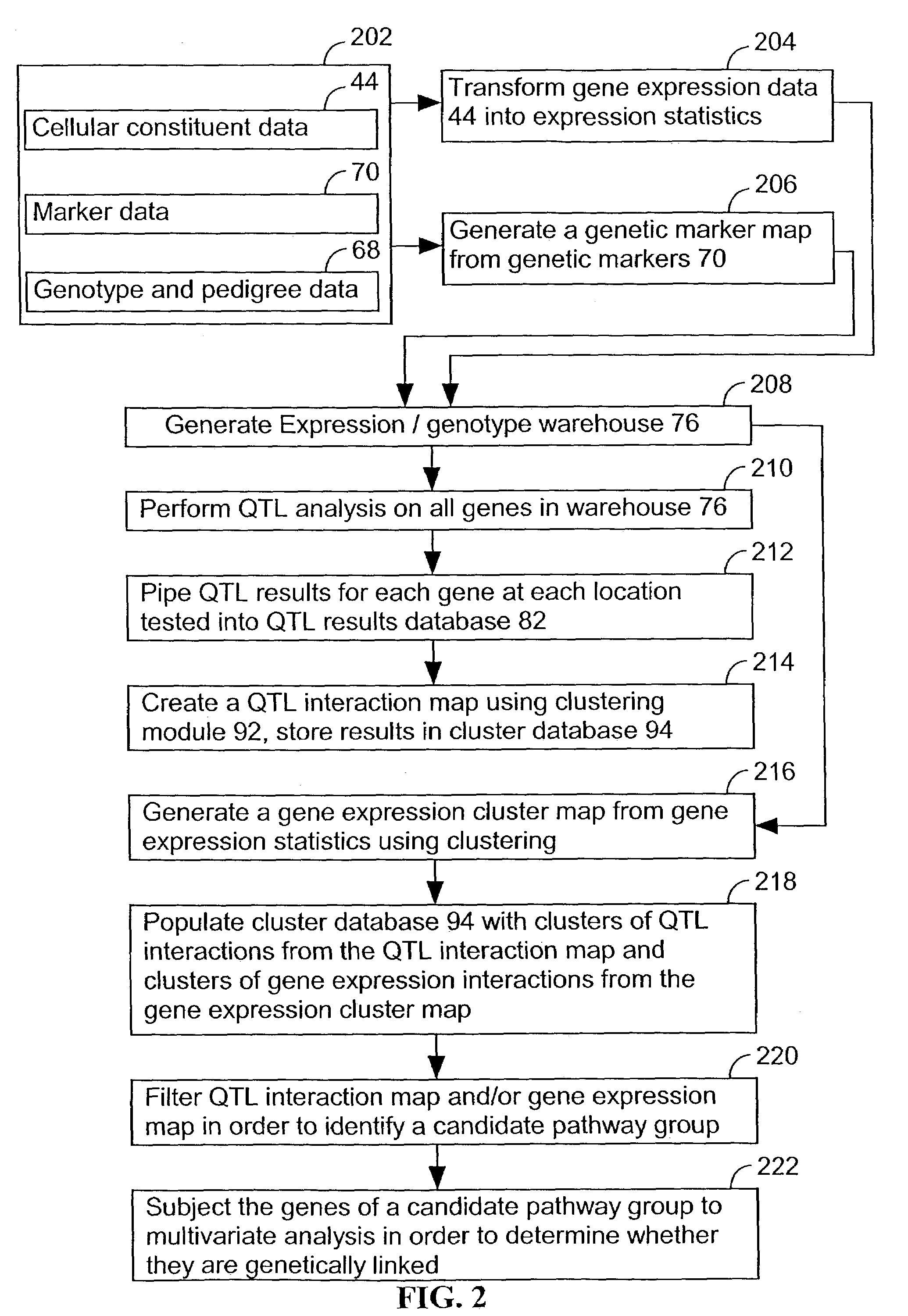
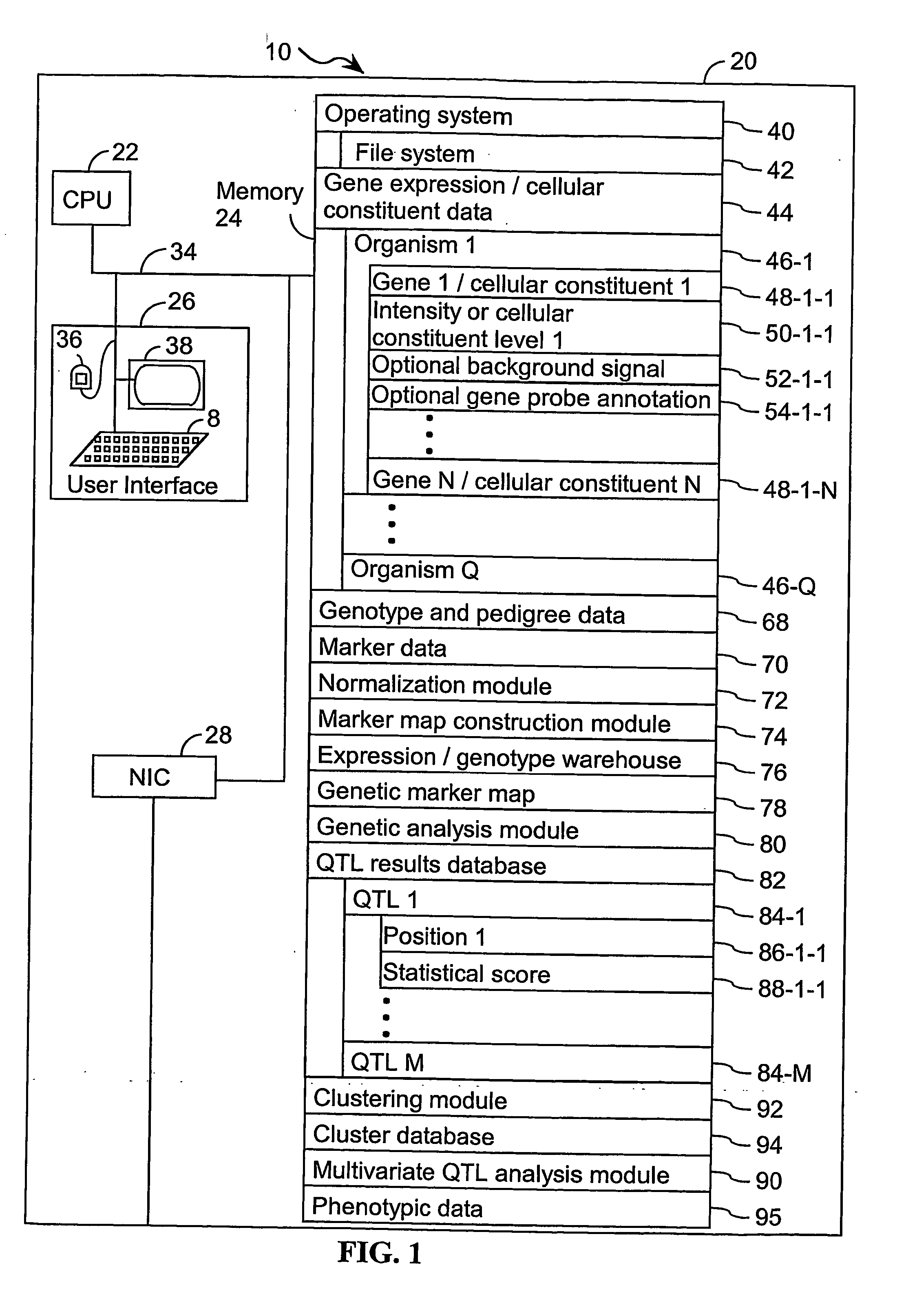
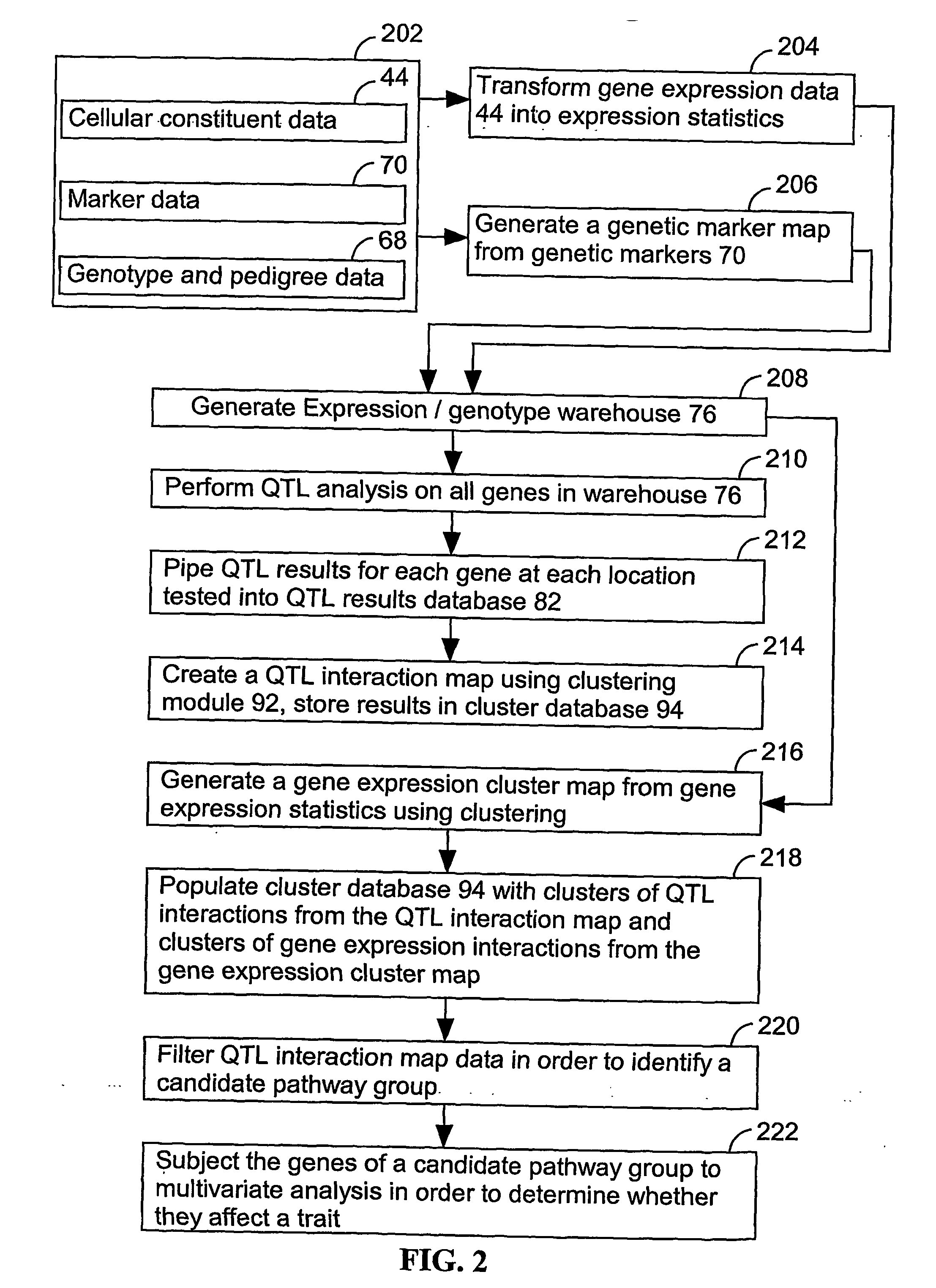
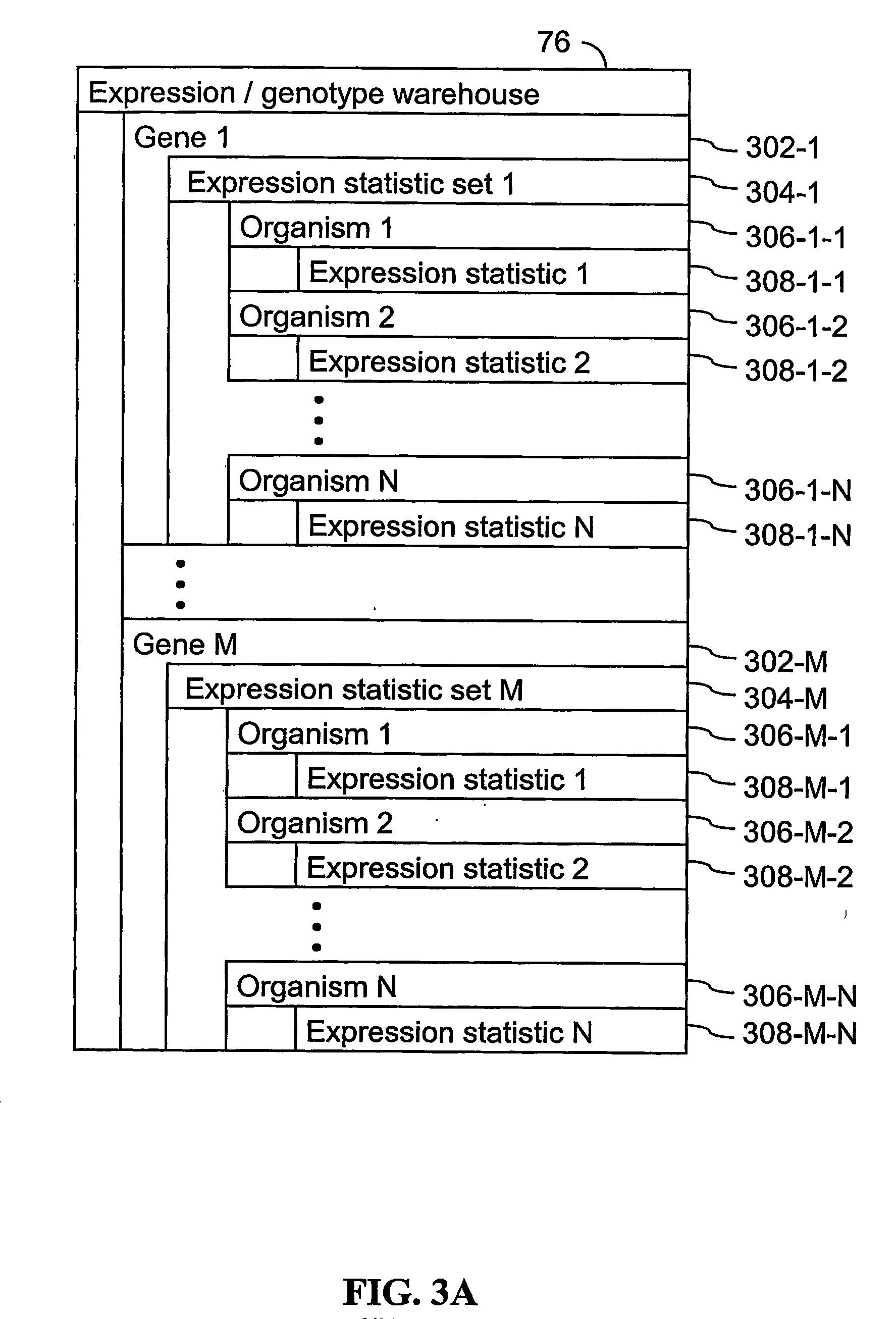
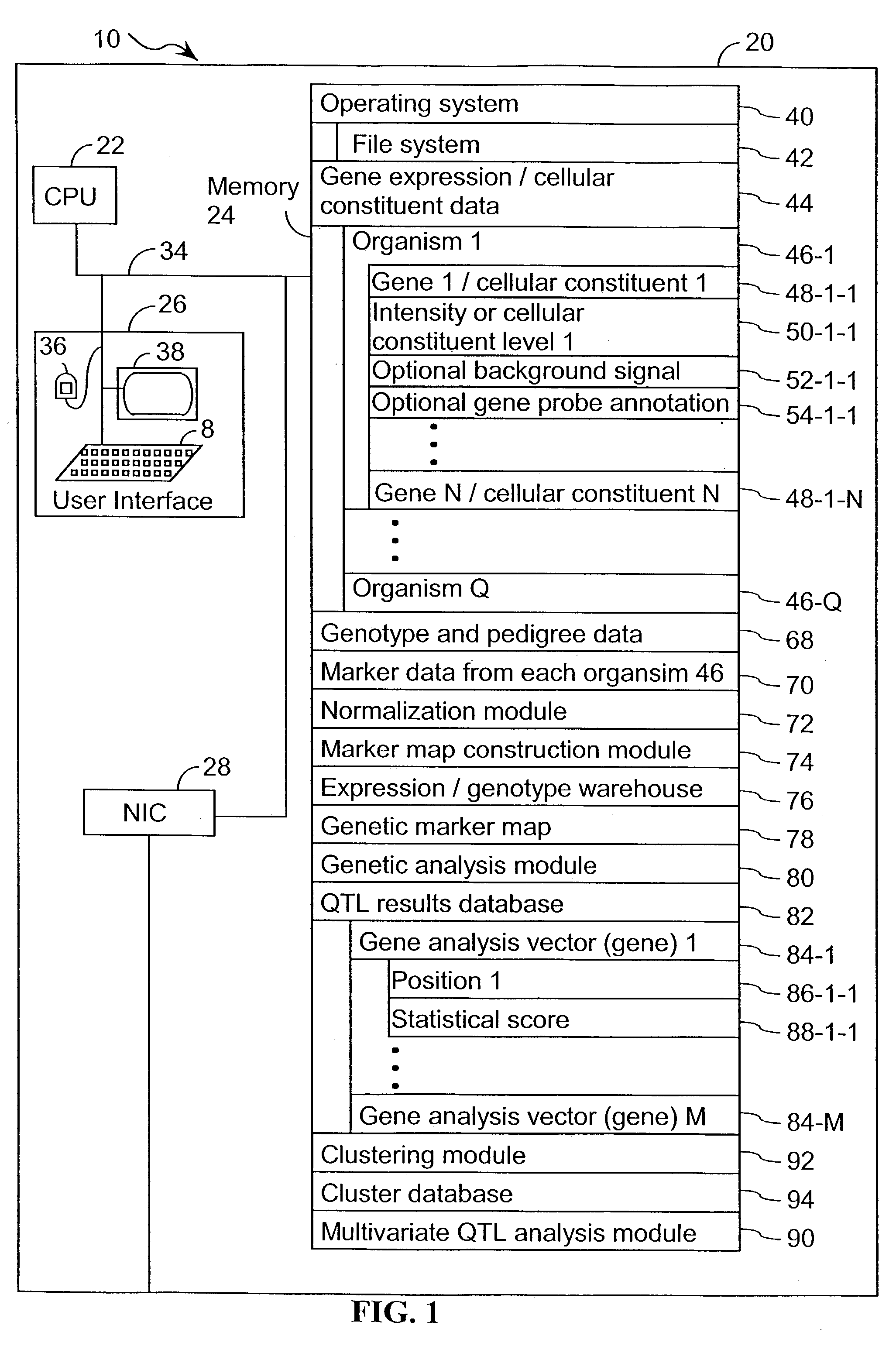
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS7035739B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
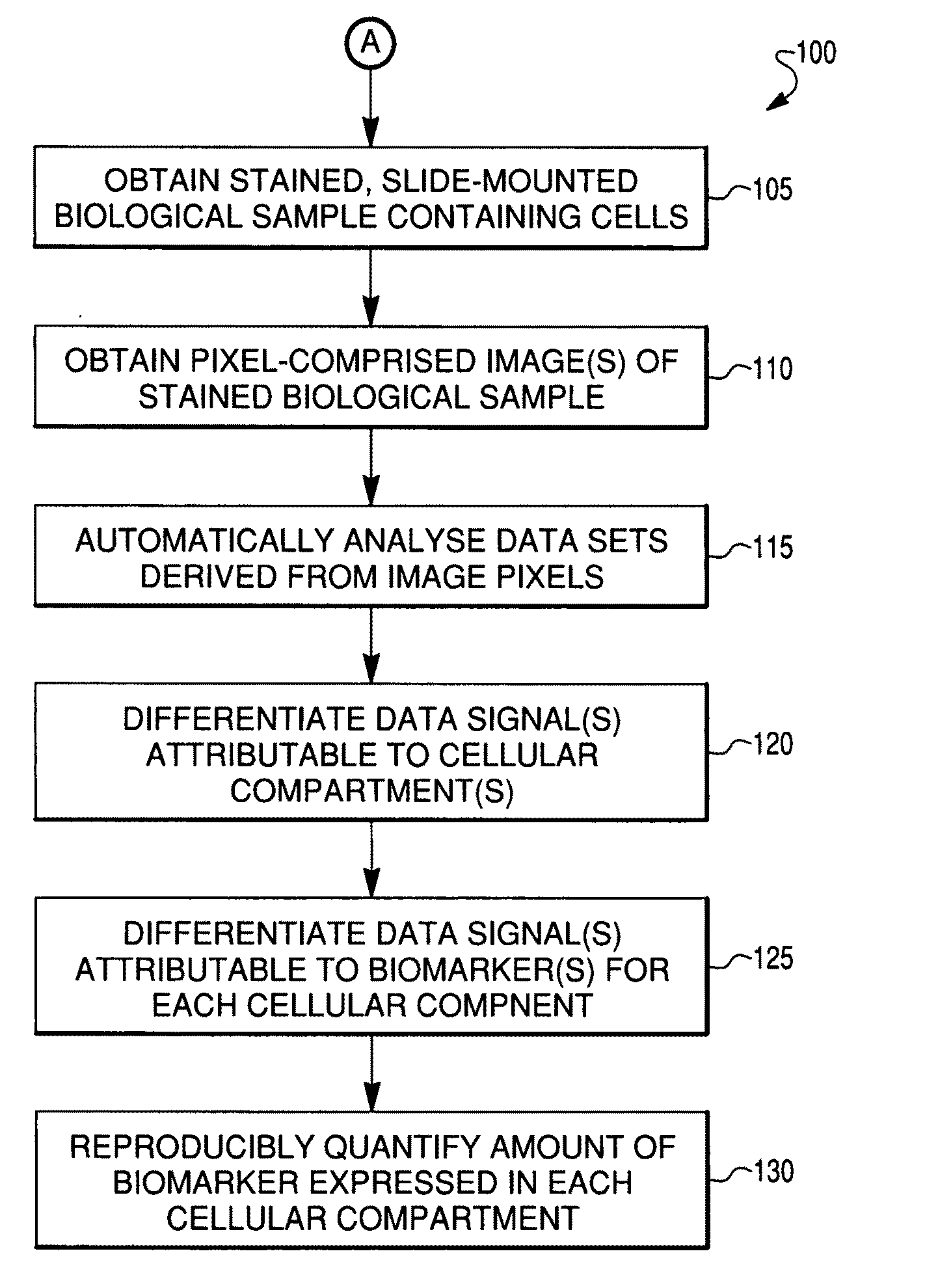
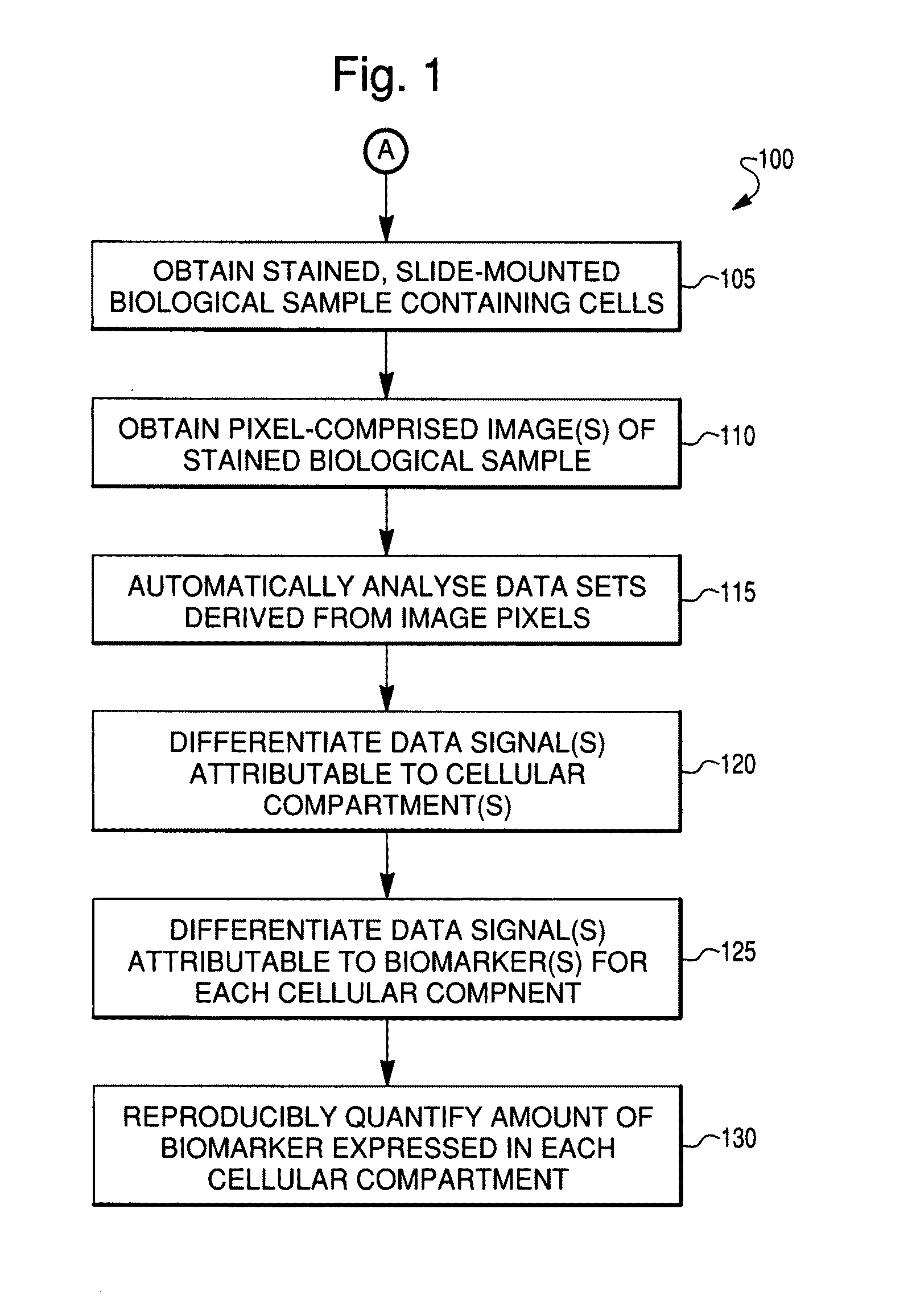
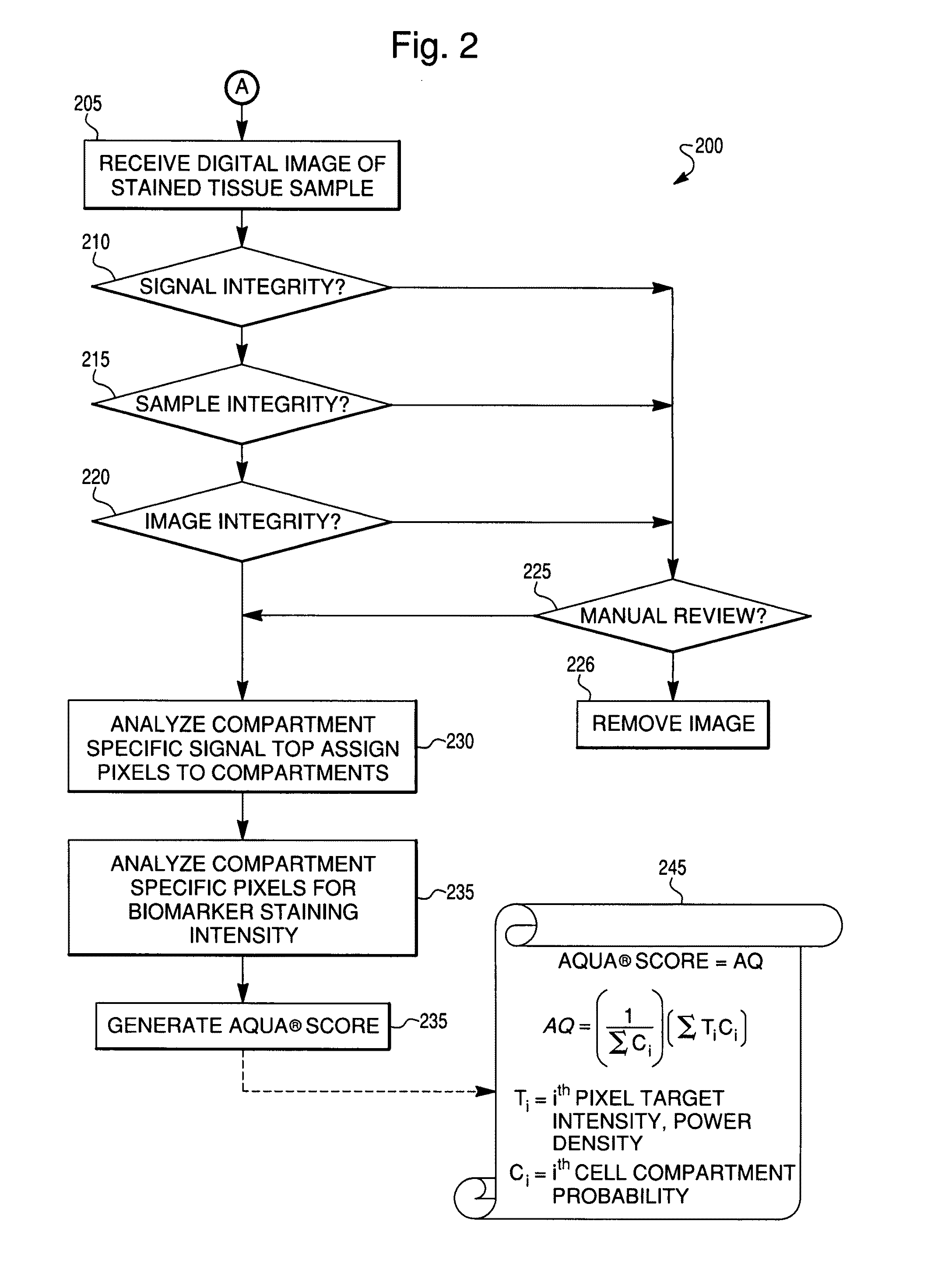
Reproducible quantification of biomarker expression
ActiveUS20100136549A1Low variabilityGood reproducibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementTissue sampleBiologic marker
A method is described for the reproducible quantification of biomarker expression, including biomarker expression in a tissue sample. Methods and systems are described whereby reproducible scores for biomarker expression are obtained independent of instrument, its location, or operator.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
ActiveUS20140058715A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
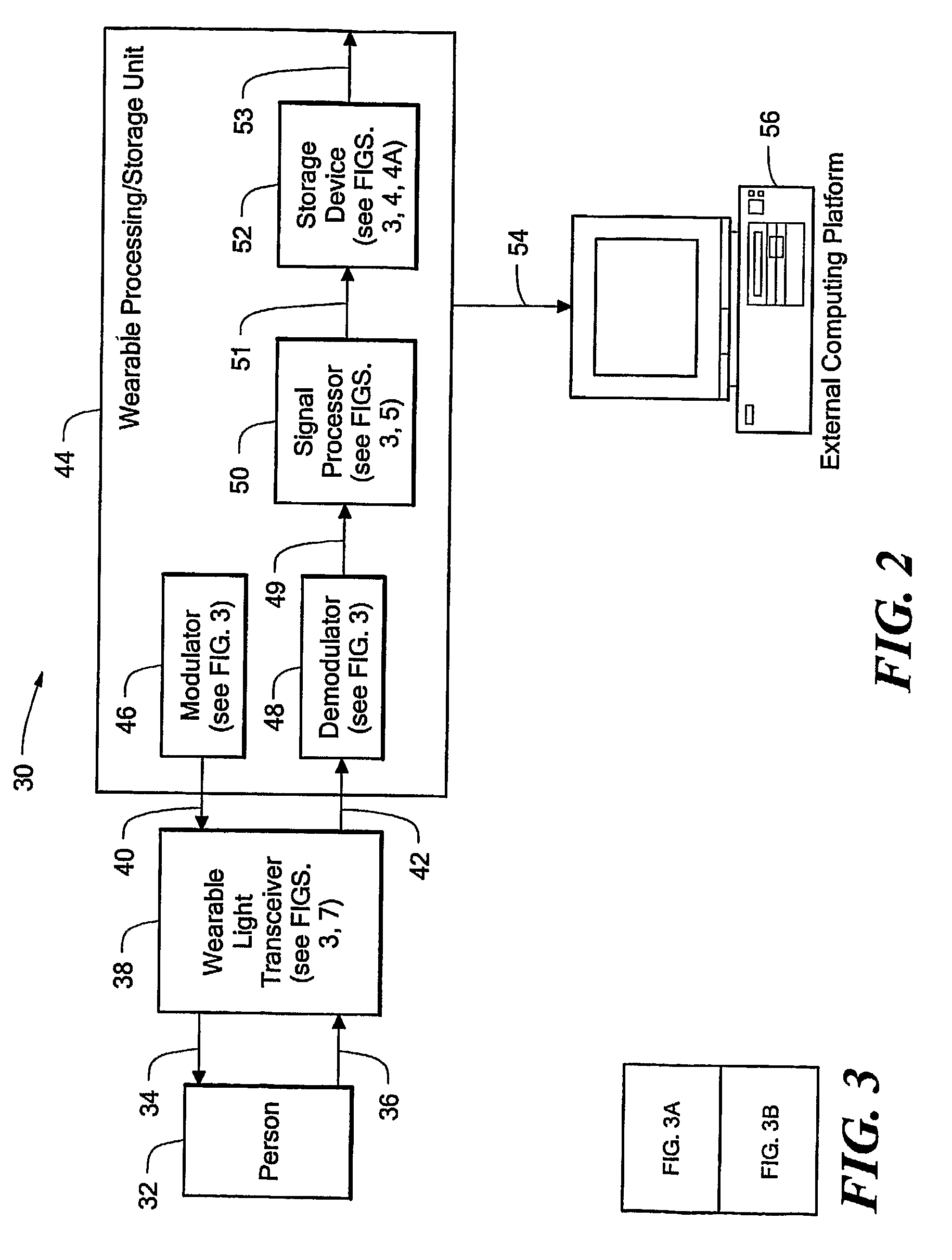
Electro-Optical System, Apparatus, and Method For Ambulatory Monitoring
An electro-optical system, apparatus, and method allow long-term, ambulatory measurements to be made on a patient using light transmitted into the patient and resulting light received from the patient.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Computer systems and methods for associating genes with traits using cross species data
ActiveUS20070166707A1Filtered outImprove bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenome
A method for confirming the association of a query QTL or a query gene in the genome of a second species with a clinical trait T exhibited by the second species. A first QTL or a first gene in a first species that is linked to a trait T′ is found. The trait T′ is indicative of trait T. A region of the genome of the first species that comprises the first QTL or the first gene is mapped to a particular region of the genome of the second species. A query QTL or a query gene in the second species that is potentially associated with the trait T is found. The potential association of the query QTL or the query gene with the clinical trait T is confirmed when the query QTL or the query gene is in the particular region of the genome of the second species.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS20030224394A1Improve artBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
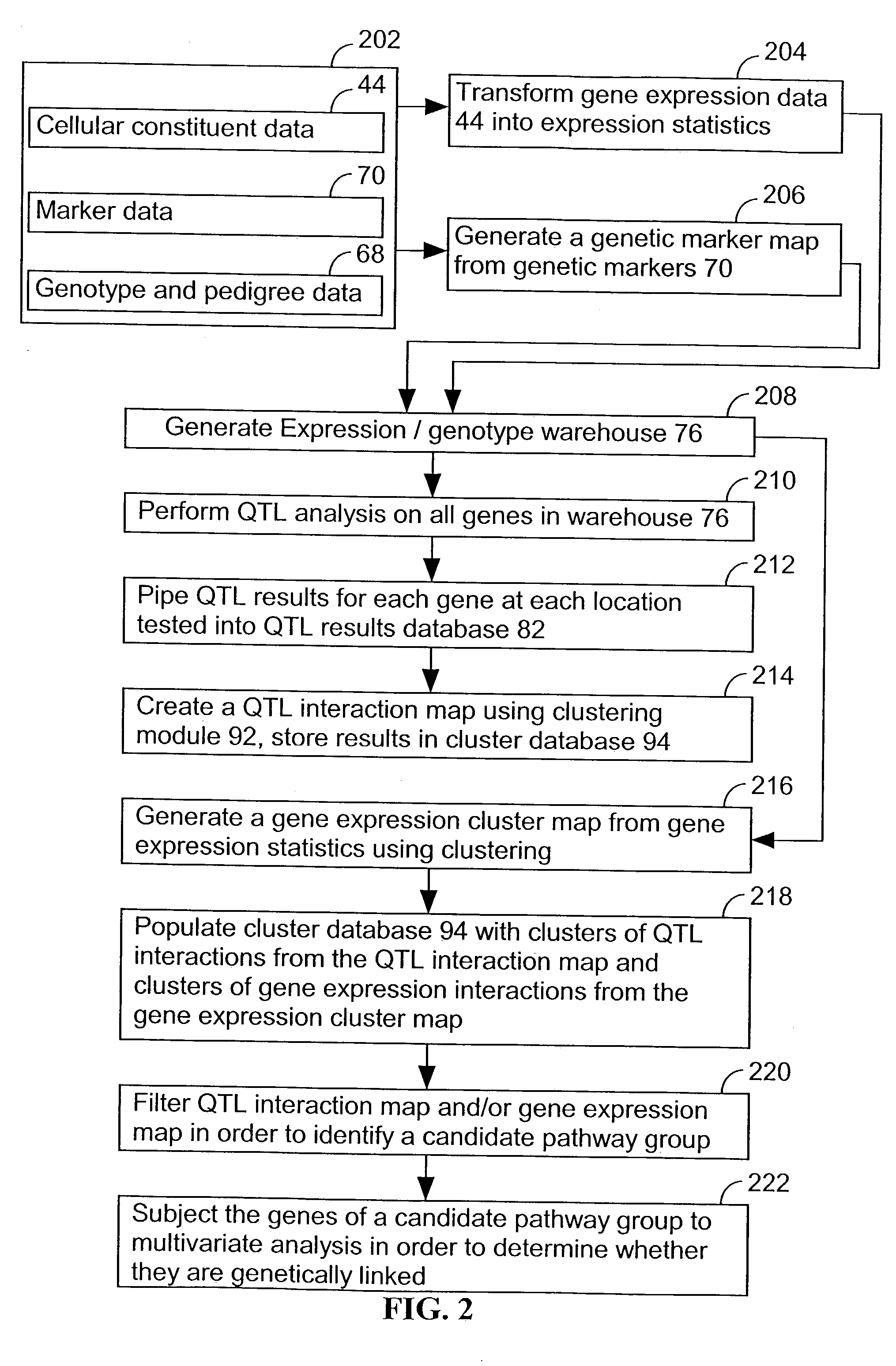
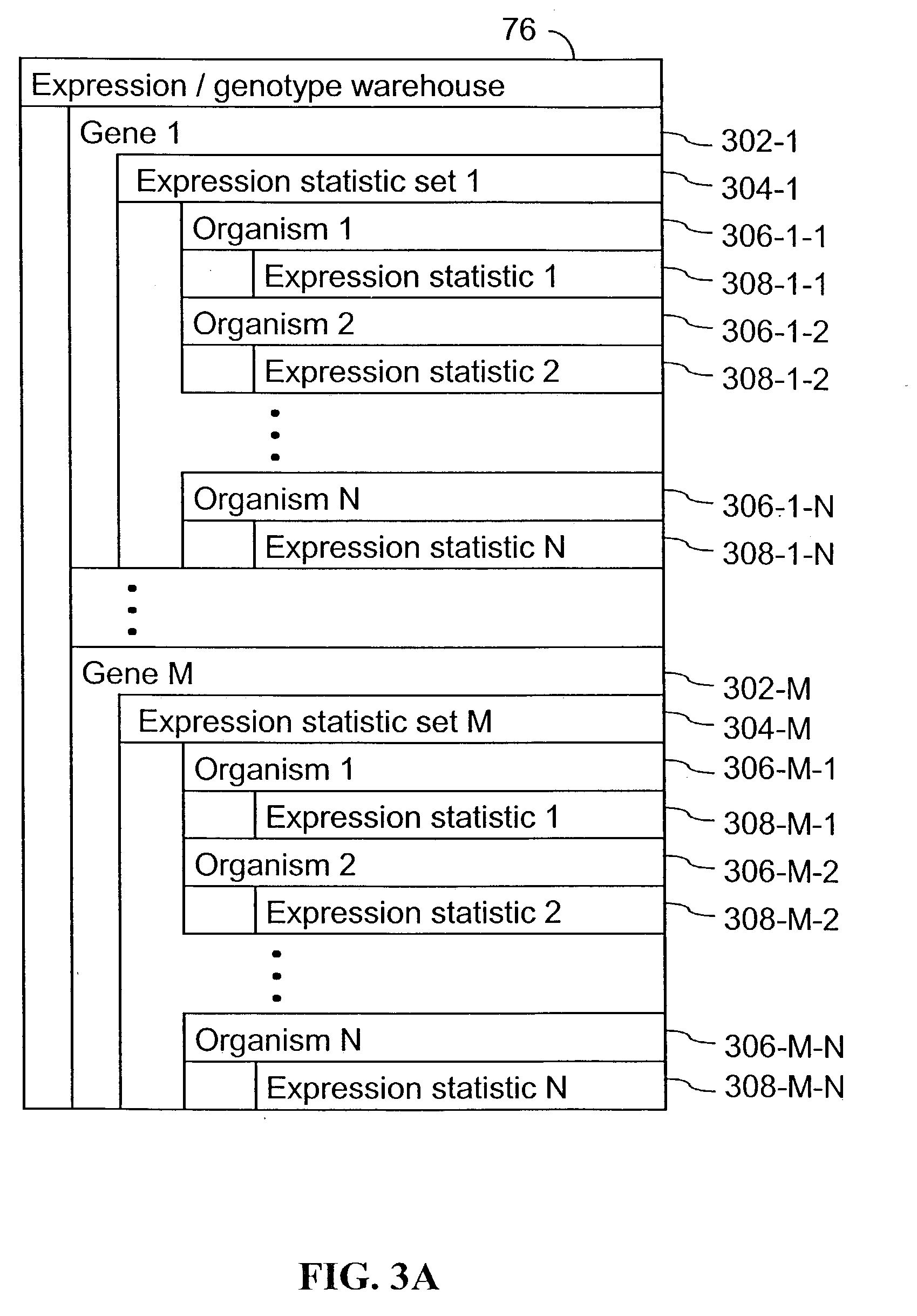
A method for associating a gene with a trait exhibited by one or more organisms in a plurality of organisms from a species. A genetic marker map is constructed from a set of genetic markers associated with the plurality of organisms. For each gene in a plurality of genes, a quantitative trait locus analysis is performed using the genetic marker map and a quantitative trait. The quantitative trait locus analysis produces quantitative trait locus data. A quantitative trait comprises an expression statistic for a gene. The expression statistic for a gene is derived from a cellular constituent level that corresponds to the gene in each organism in the plurality of organisms. The quantitative trait locus data are clustered from each quantitative trait locus analysis to form a quantitative trait locus interaction map. Clusters of genes in the map are identified as a candidate pathway group. An expression cluster map is used to refine the candidate pathway group. Multivariate analysis is used to validate the candidate pathway group as a set of genes that are genetically interacting.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
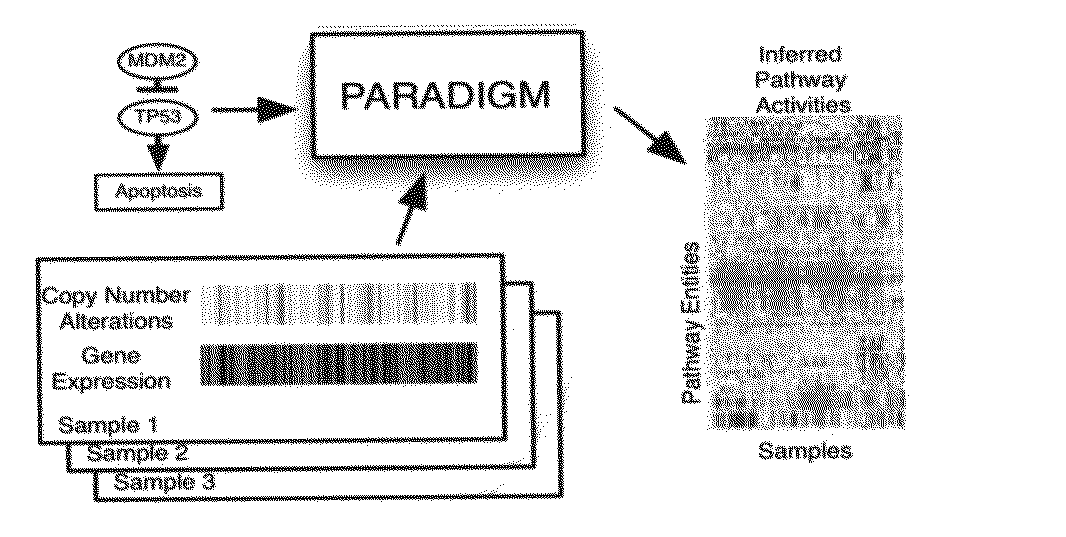
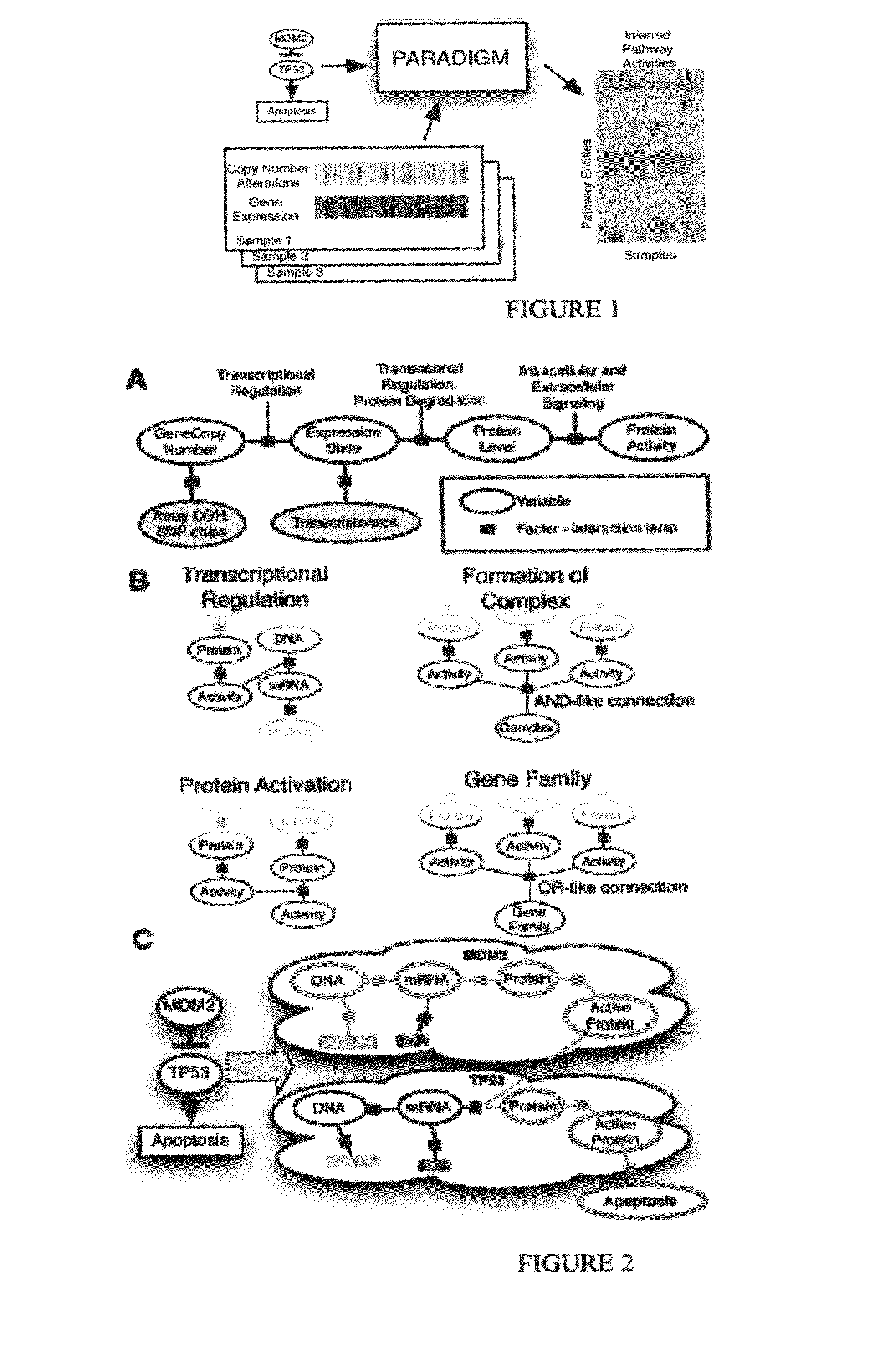
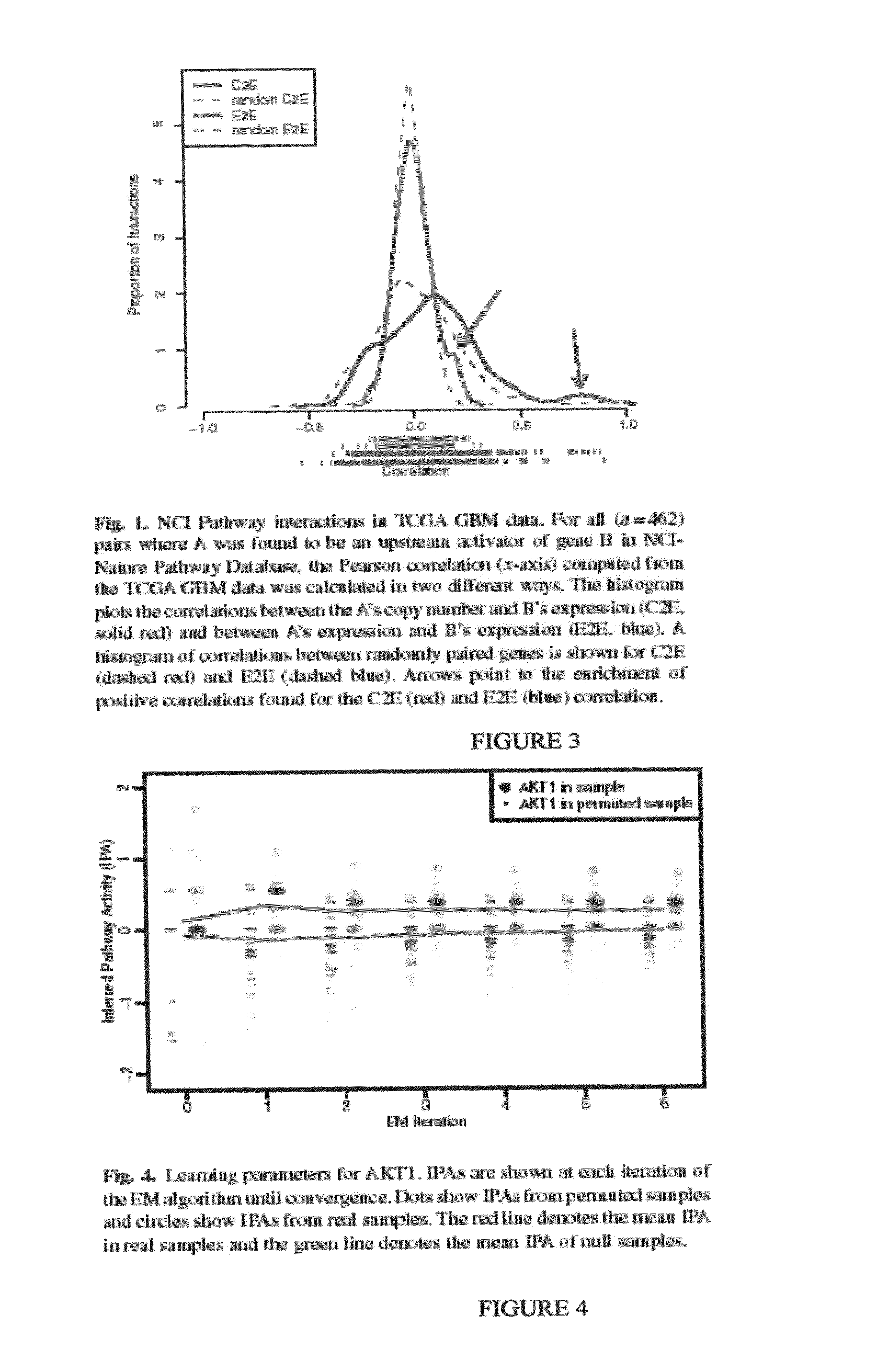
Pathway recognition algorithm using data integration on genomic models (PARADIGM)
ActiveUS20120041683A1Divergent outcomeConducive to survivalData visualisationDigital computer detailsRegimenMedicine
The present invention relates to methods for evaluating the probability that a patient's diagnosis may be treated with a particular clinical regimen or therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Highly multiplex PCR methods and compositions
InactiveUS20140094373A1High copy numberMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMultiplexDimer
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
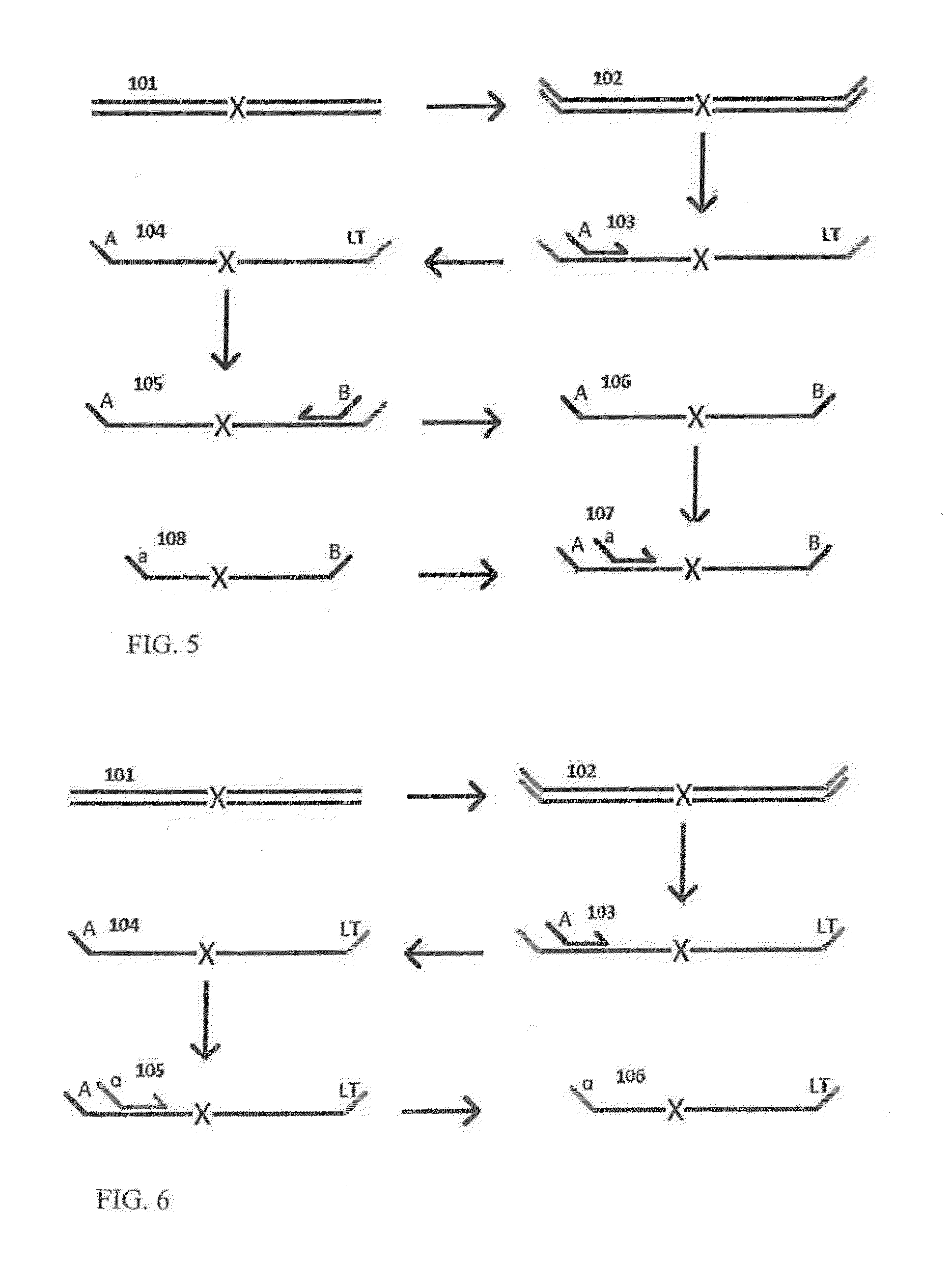
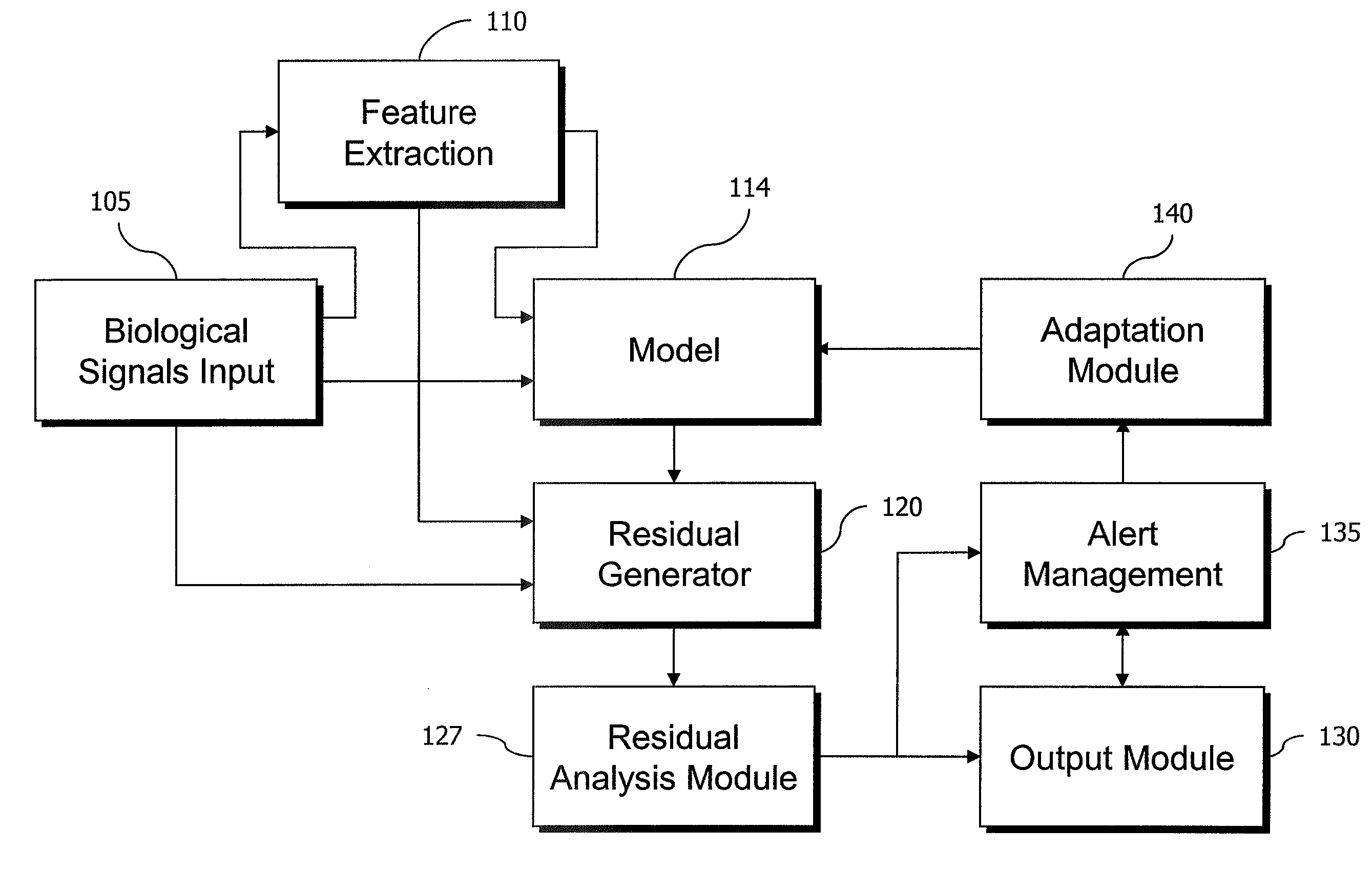
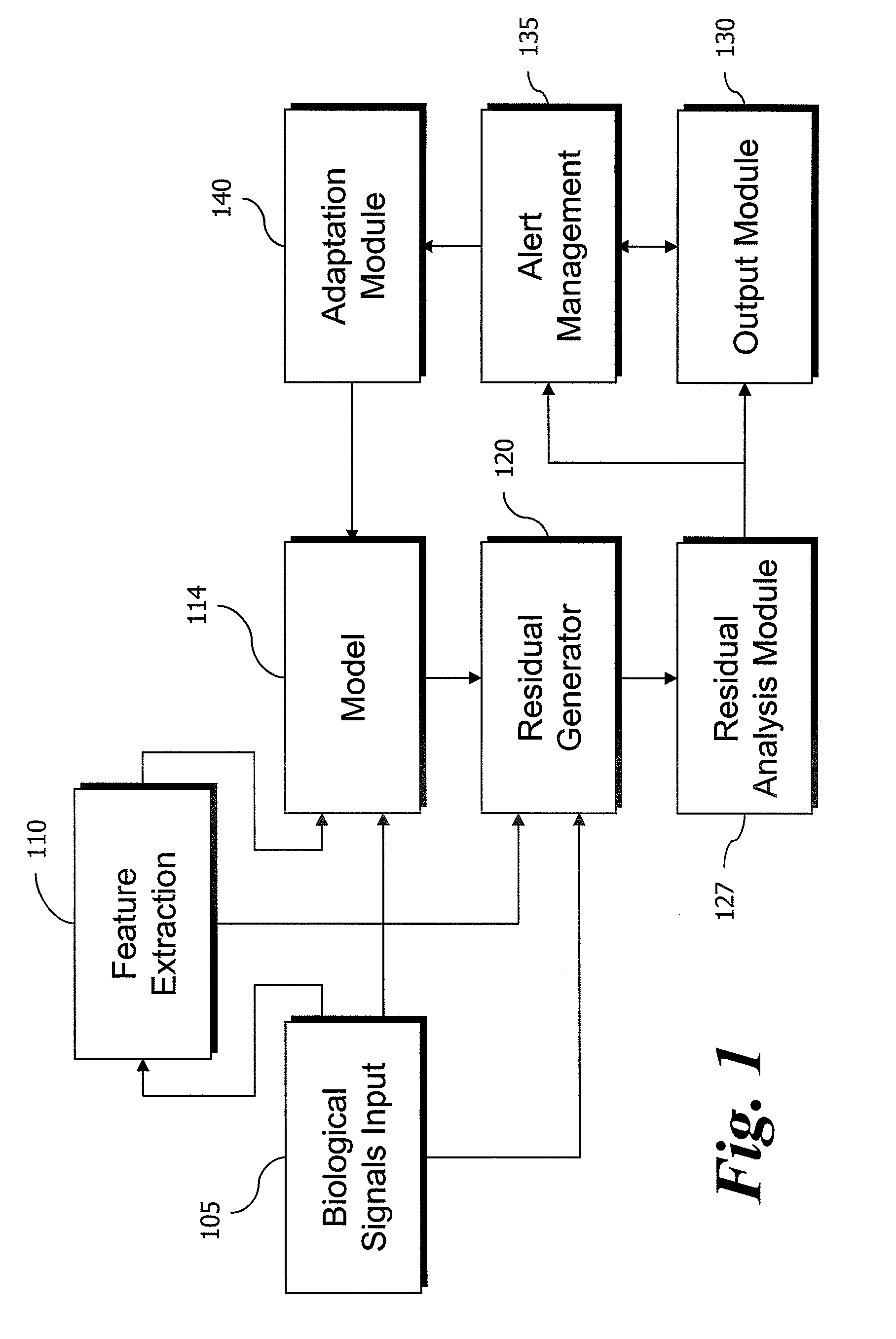
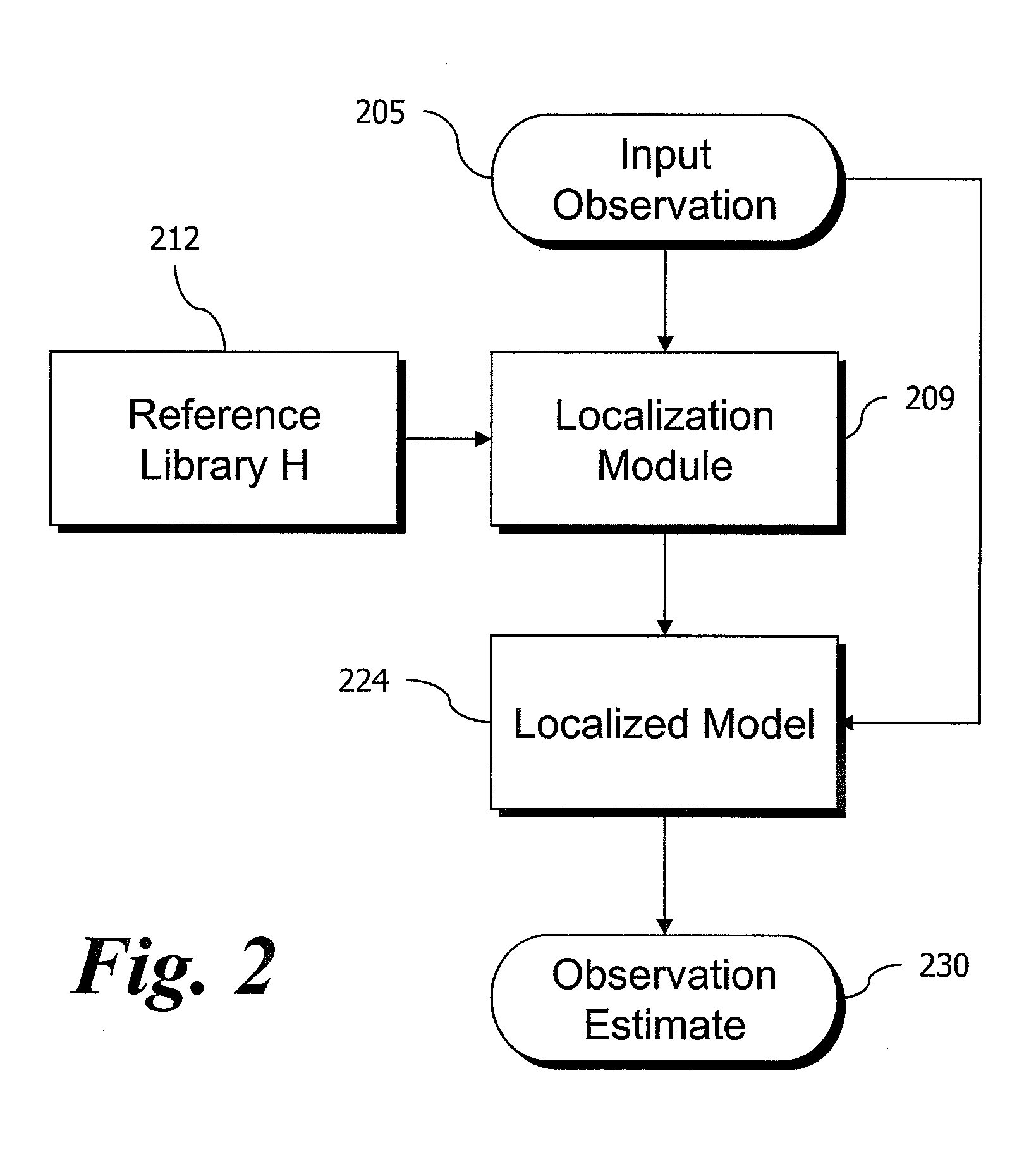
Residual-Based Monitoring of Human Health
ActiveUS20070149862A1Increases patient monitoring loadFacilitates long-termAnalogue computers for chemical processesCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringHuman health
Improved human health monitoring is provided in the context of sensor measurements of typical vital signs and other biological parameters, by a system and method using an empirical model of the parameters and disposed to estimate values of the parameters in response to actual measurements. Residuals resulting from the difference between the estimates and actual measurements are analyzed for robust indications of incipient health issues. Residual analysis is both more robust and more sensitive than conventional univariate range checking on vital signs.
Owner:PHYSIQ
Method for redesign of microbial production systems
ActiveUS20050079482A1Solve complexityIncreased production objectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMicroorganismBiological body
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Systems and methods for modeling and analyzing networks
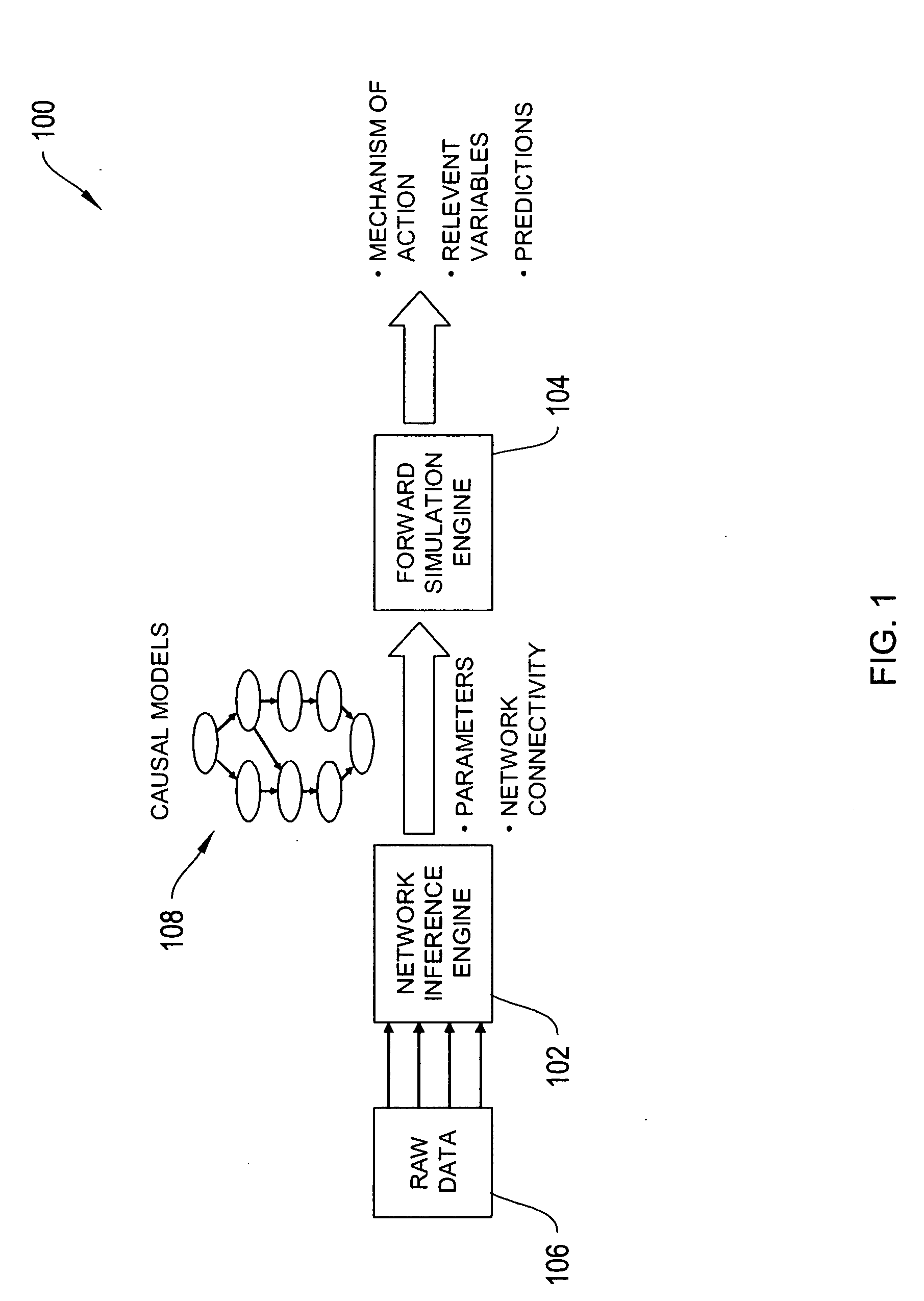
The systems and methods described herein utilize a probabilistic modeling framework for reverse engineering an ensemble of causal models, from data and then forward simulating the ensemble of models to analyze and predict the behavior of the network. In certain embodiments, the systems and methods described herein include data-driven techniques for developing causal models for biological networks. Causal network models include computational representations of the causal relationships between independent variables such as a compound of interest and dependent variables such as measured DNA alterations, changes in mRNA, protein, and metabolites to phenotypic readouts of efficacy and toxicity.
Owner:GENE NETWORK SCI
System, method and apparatus for causal implication analysis in biological networks
InactiveUS20050165594A1Efficient modelingRapidly and efficiently analyzingAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsSystems approachesOrganism
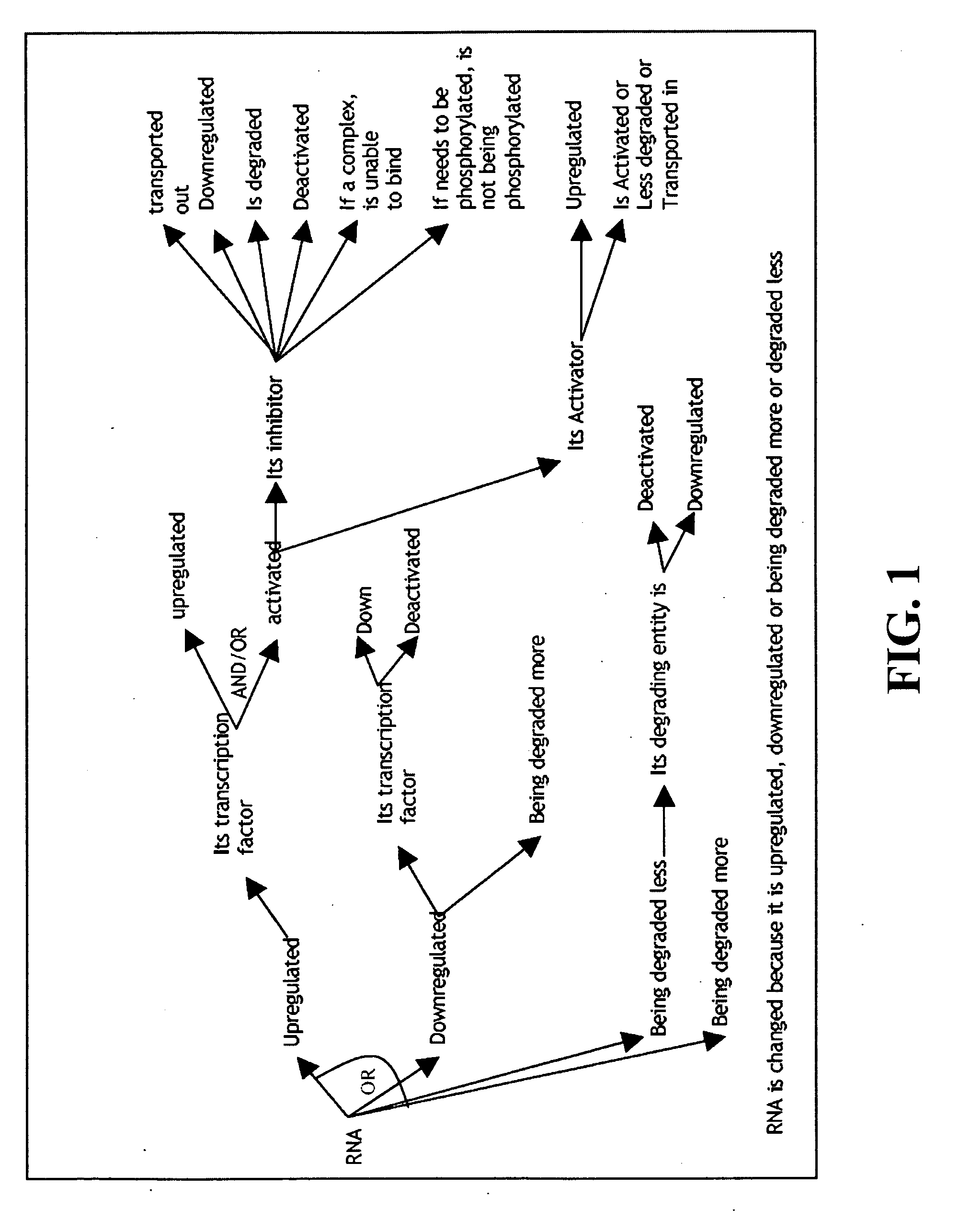
Described are methods, systems and apparatus for hypothesizing a biological relationship in a biological system. A database of biological assertions is provided consisting of biological elements, relationships among the biological elements, and relationship descriptors characterizing the properties of the elements and relationships. A biological element may be selected from the database and a logical simulation may be performed within the biological database, from the selected biological element, through relationship descriptors, along a path defined by potentially causative biological elements to discern a biological element hypothetically responsible for the change in the selected biological element. The logical simulation may be either a backward logical simulation, performed upstream through the relationship descriptors to discern a hypothetical responsible biological element, or a forward logical simulation, performed downstream through the relationship descriptors to discern the extent to which the perturbation generates the observed change in the selected biological element.
Owner:GENSTRUCT
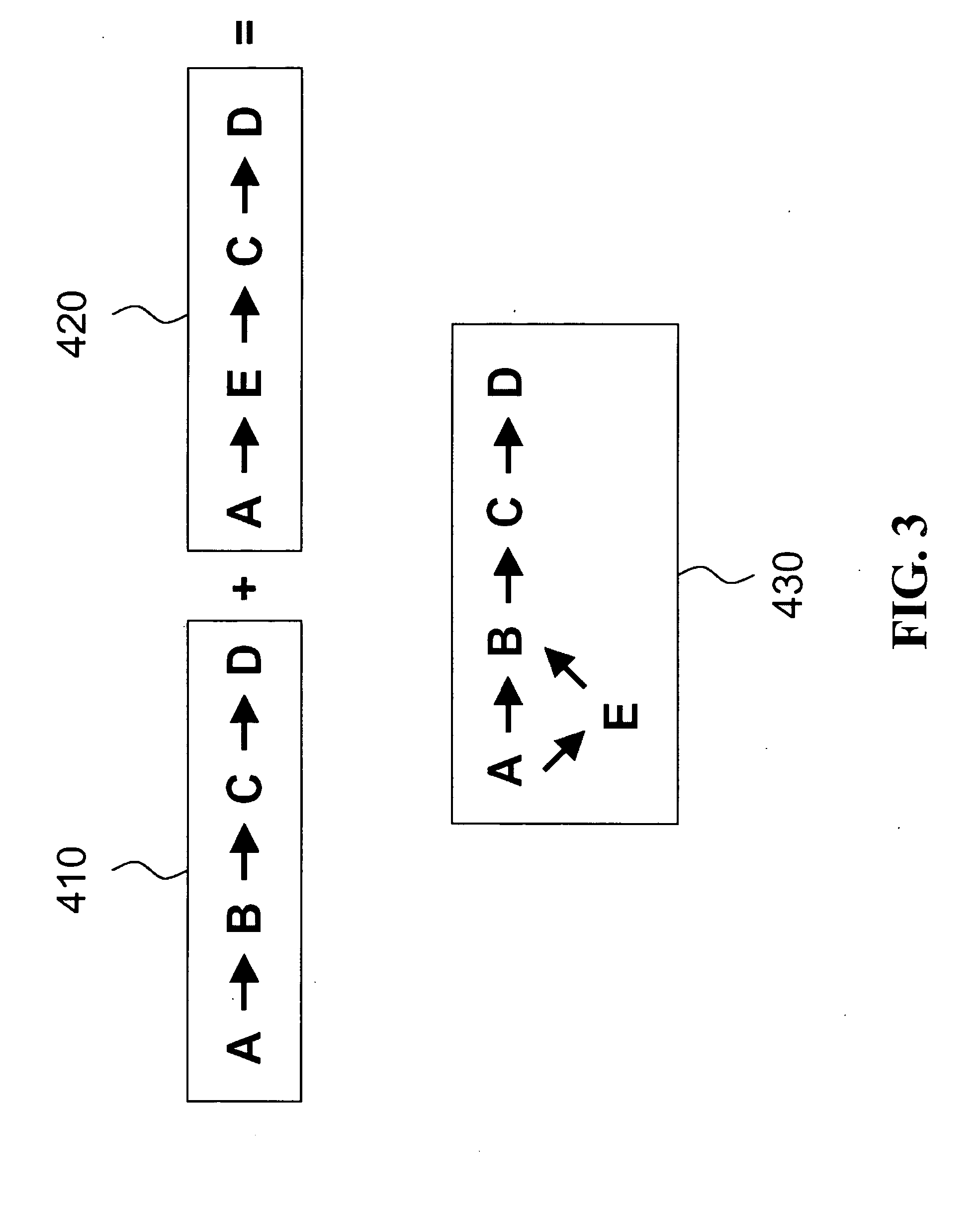
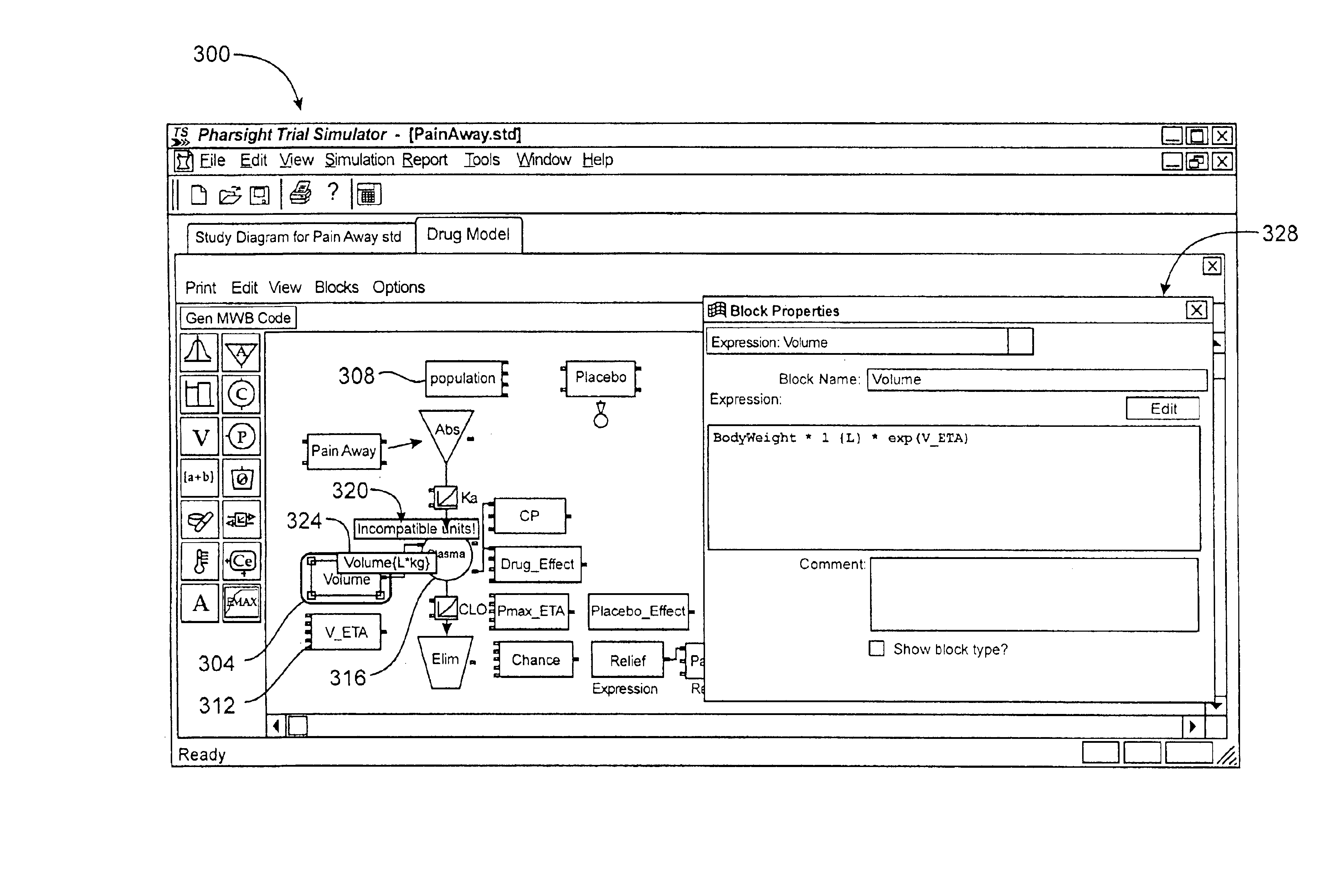
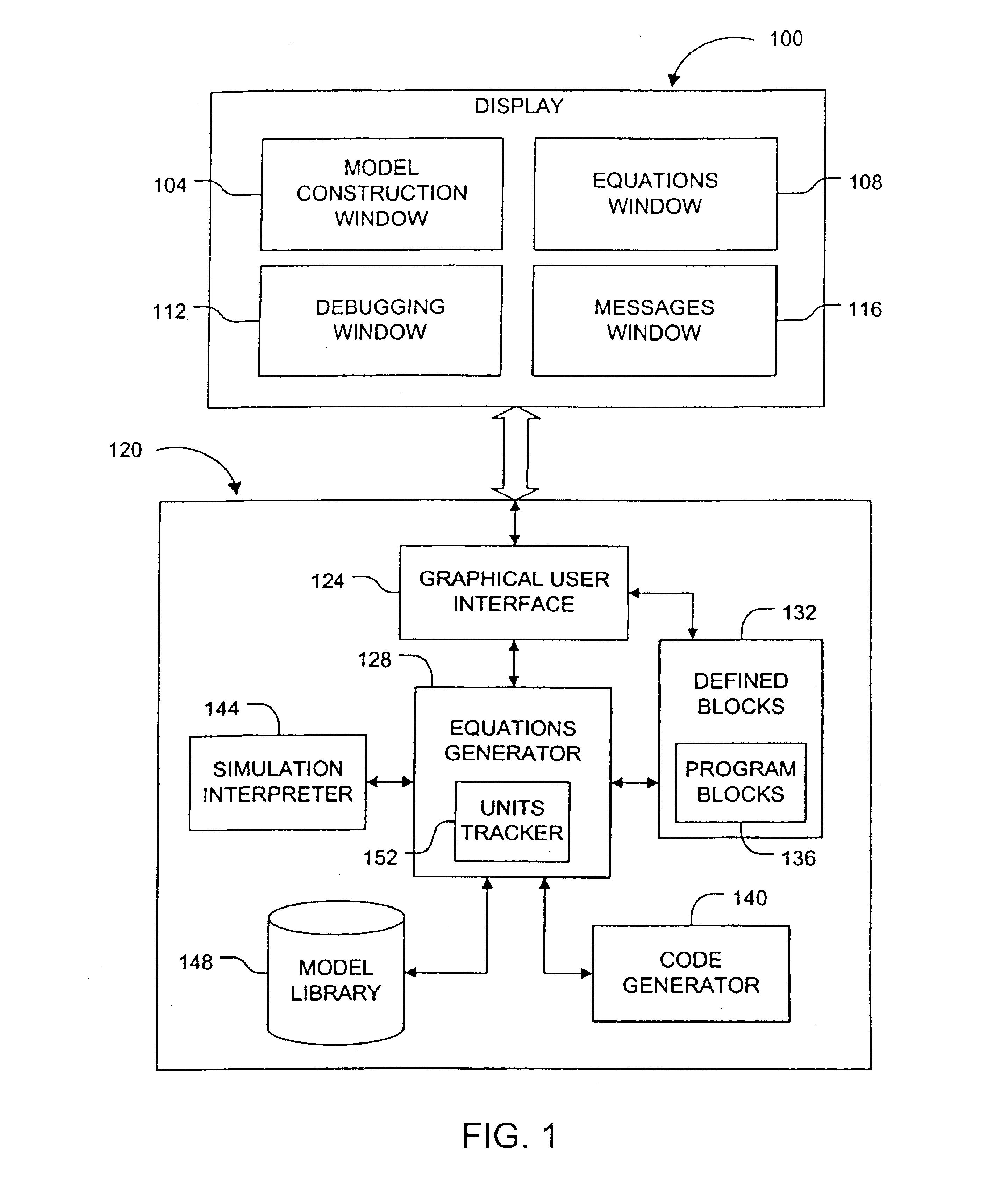
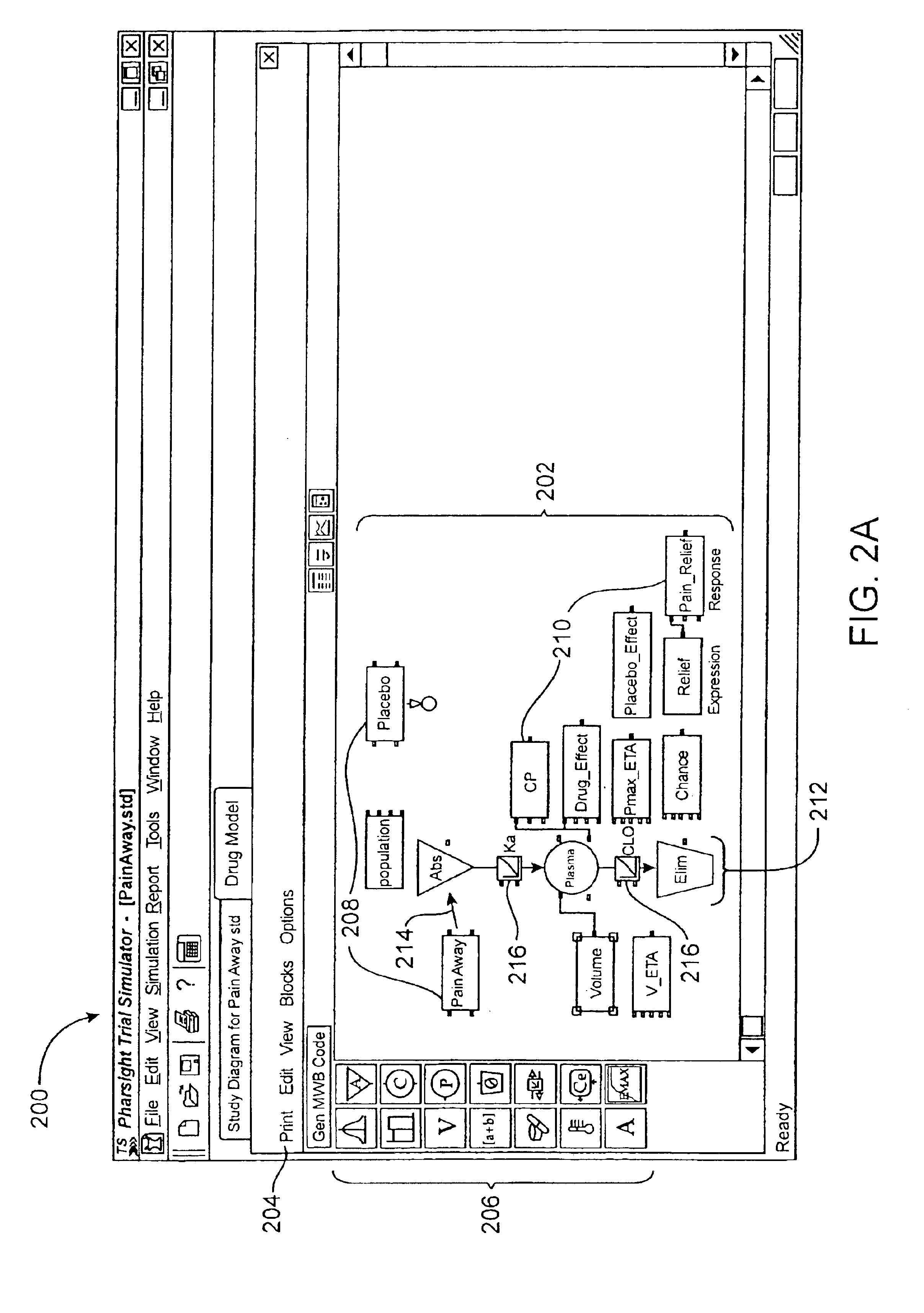
Unit tracking and notification in a graphical drug model editor
InactiveUS6937257B1Accelerating model buildingIncrease the verification processData visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method for maintaining consistent unit relationships during graphical pharmacological computational model construction is disclosed. A graphical user interface is presented through which a user may place and connect objects representing pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic elements. The user may specify units definitions for variables and constants using unit expressions. As the objects are converted into an internal format representing the statements of the corresponding computational model, the unit expressions are included in this internal format as multidimensional data type information. This multidimensional data type information is regularly and automatically propagated for each statement in the internal format to identify inconsistent units. When such inconsistent units are identified, a warning message is generated to notify the user, substantially immediately after the inconsistent units are created.
Owner:CERTARA
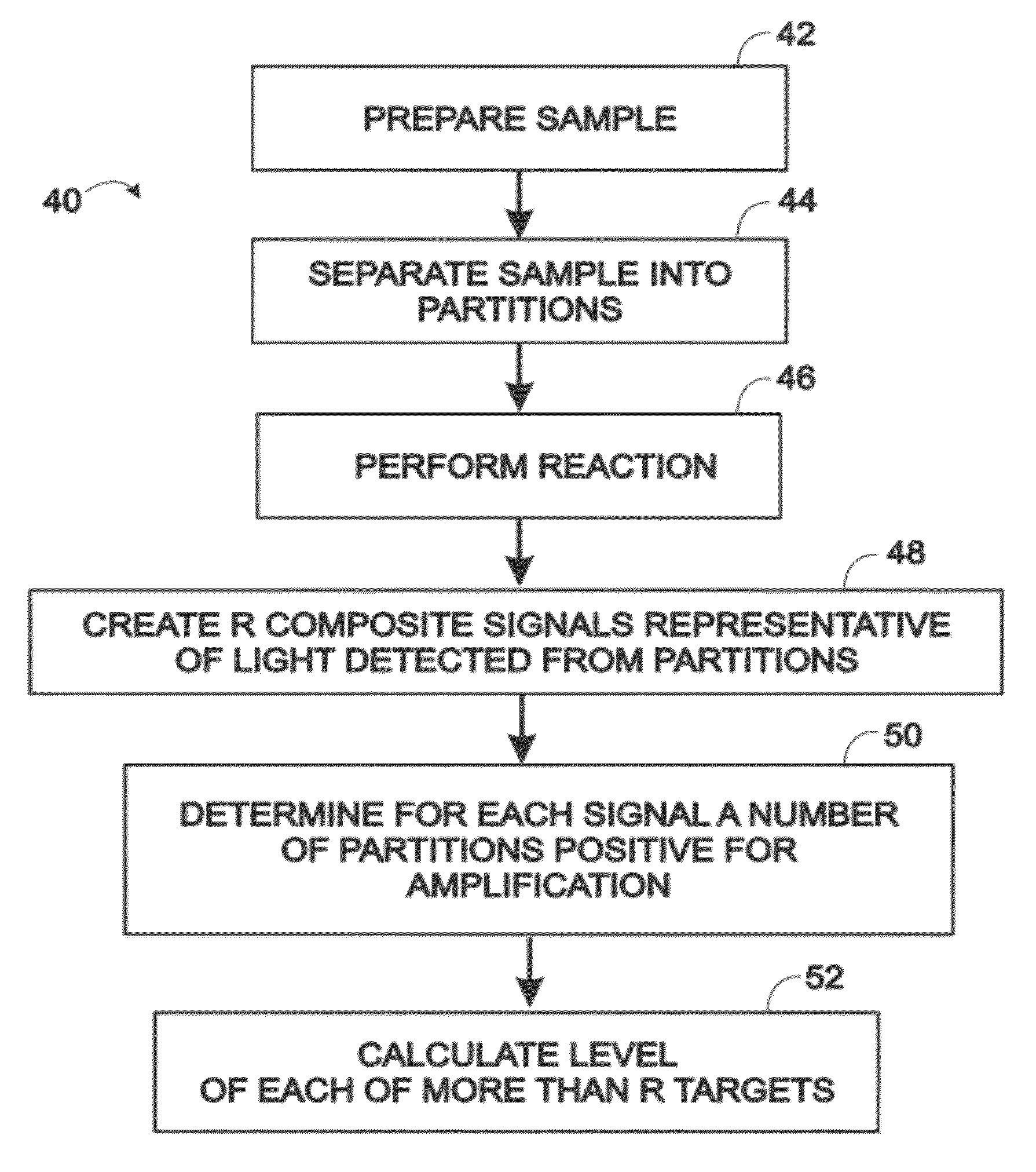
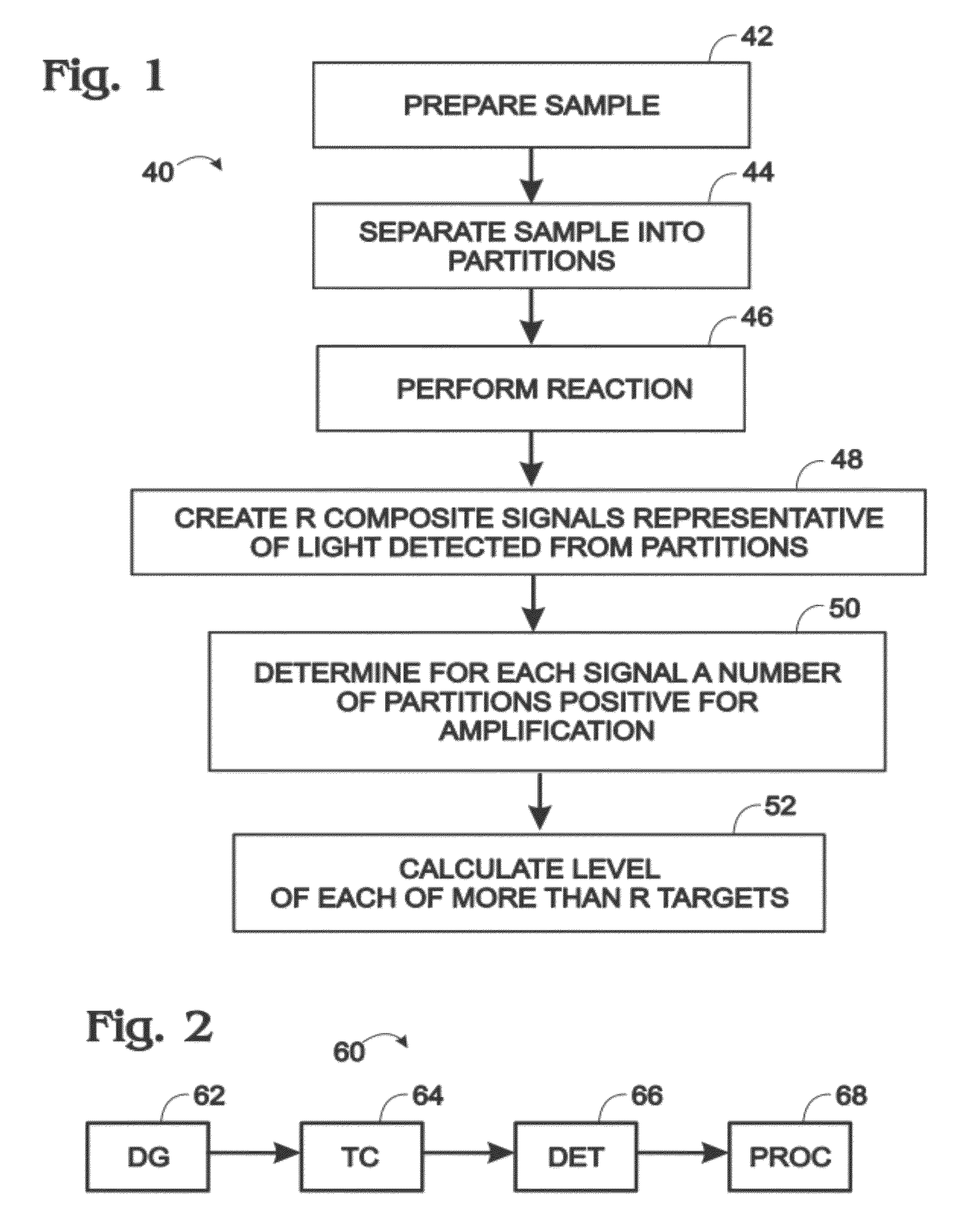
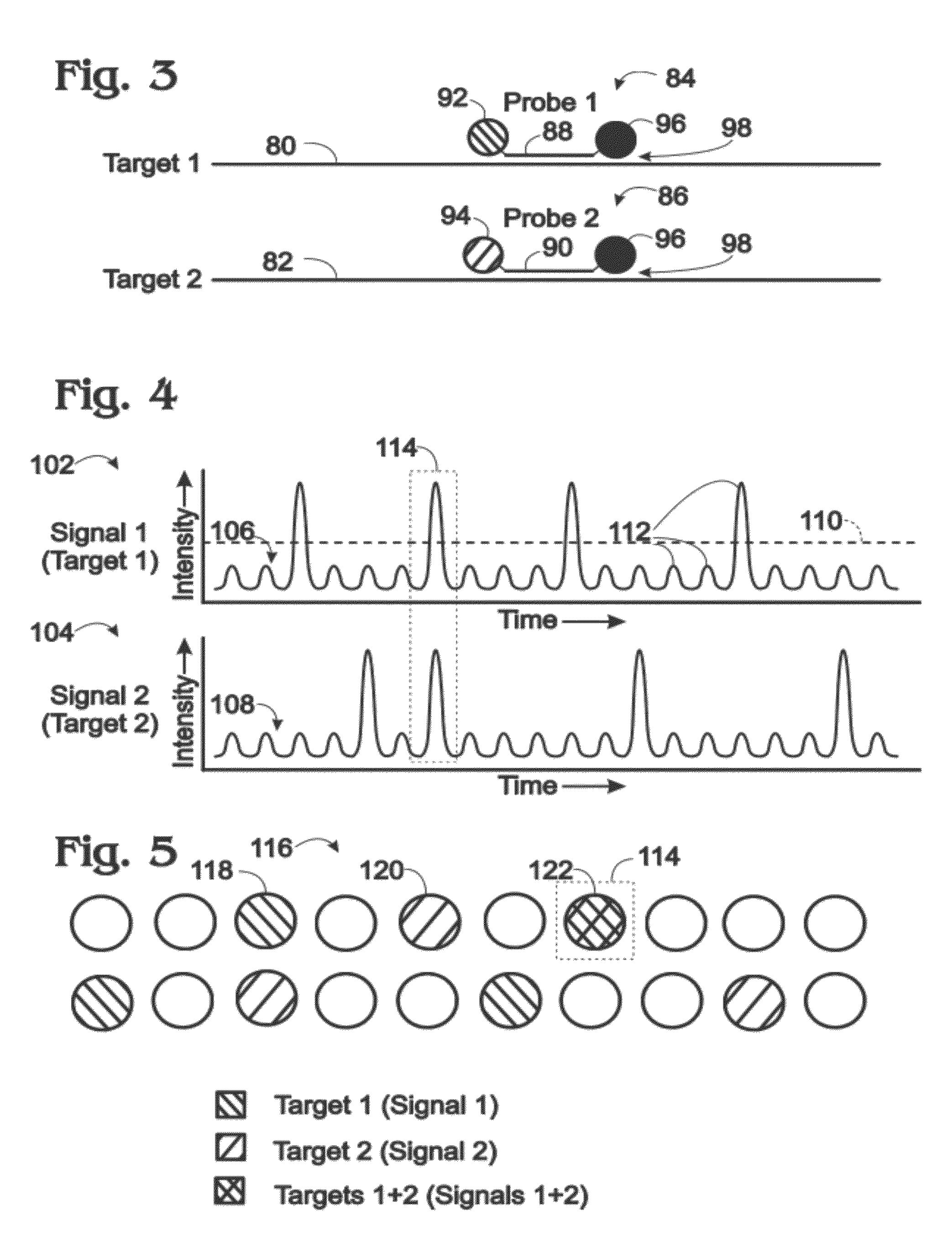
Multiplexed digital assays with combinatorial use of signals
ActiveUS20120329664A1Increase the number ofImprove reuseNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlgorithmSignaling system
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Operatively tuning implants for increased performance
ActiveUS8078440B2Physical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAnatomical structuresPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A method for preoperatively characterizing an individual patient's biomechanic function in preparation of implanting a prosthesis is provided. The method includes subjecting a patient to various activities, recording relative positions of anatomy during the various activities, measuring force environments responsive to the patient's anatomy and affected area during the various activities, characterizing the patient's biomechanic function from the relative positions and corresponding force environments, inputting the measured force environments, relative positions of knee anatomy, and patient's biomechanic function characterization into the one or more computer simulation models, inputting a computer model of the prosthesis into the one or more computer simulation models, and manipulating the placement of the prosthesis in the computer simulation using the patient's biomechanic function characterization and the computer model of the prosthesis to approximate a preferred biomechanical fit of the prosthesis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Method and system to create products
Systems and methods for creating fully custom products from scratch without exclusive use of off-the-shelf or pre-specified components. A system for creating custom products includes an image capture device for capturing image data and / or measurement data of a user. A computer is communicatively coupled with the image capture device and configured to construct an anatomic model of the user based on the captured image data and / or measurement data. The computer provides a configurable product model and enables preview and automatic or user-guided customization of the product model. A display is communicatively coupled with the computer and displays the custom product model superimposed on the anatomic model or image data of the user. The computer is further configured to provide the customized product model to a manufacturer for manufacturing eyewear for the user in accordance with the customized product model. The manufacturing system is configured to interpret the product model and prepare instructions and control equipment for the manufacturing of the customized product.
Owner:BIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com