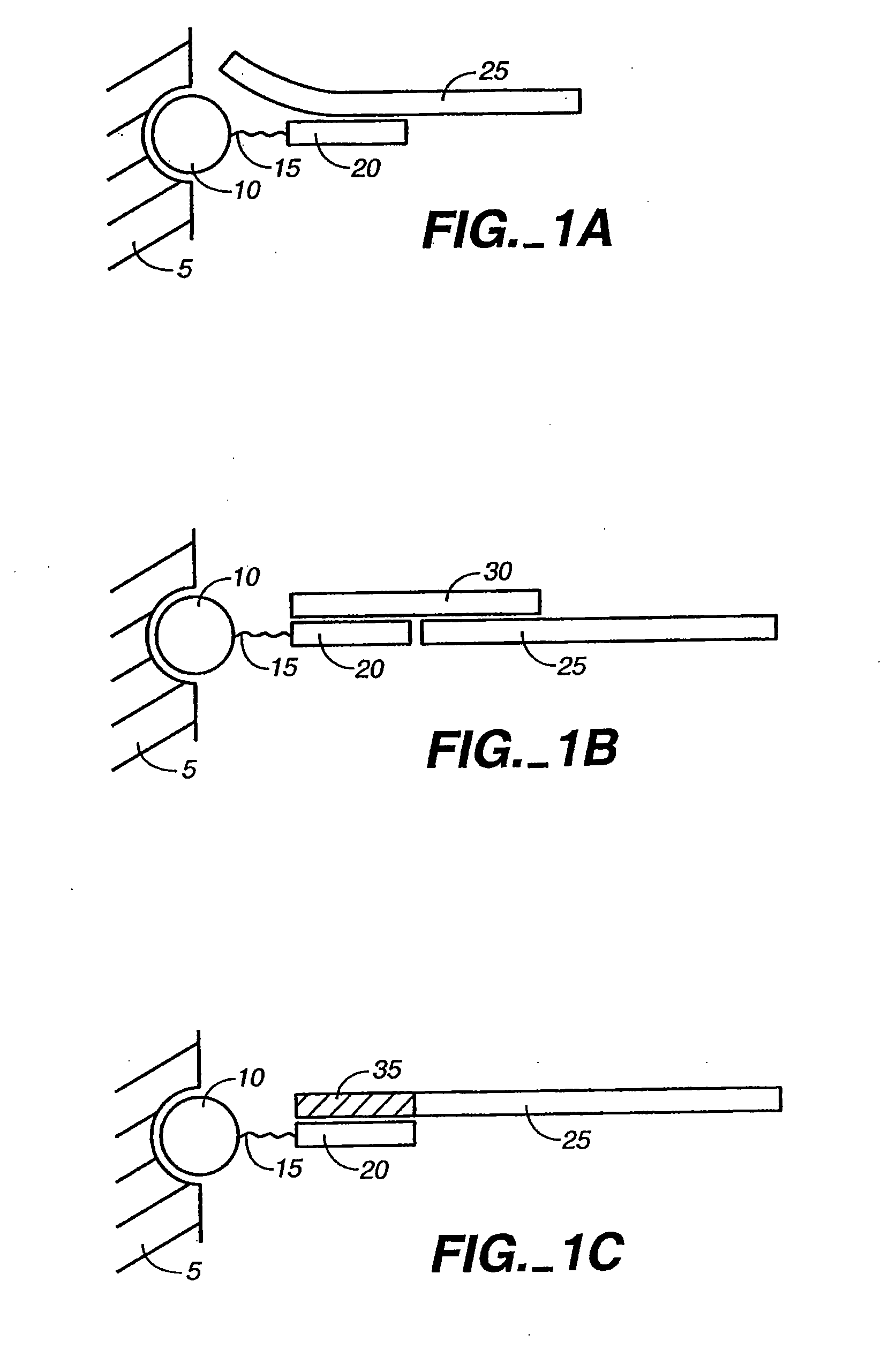
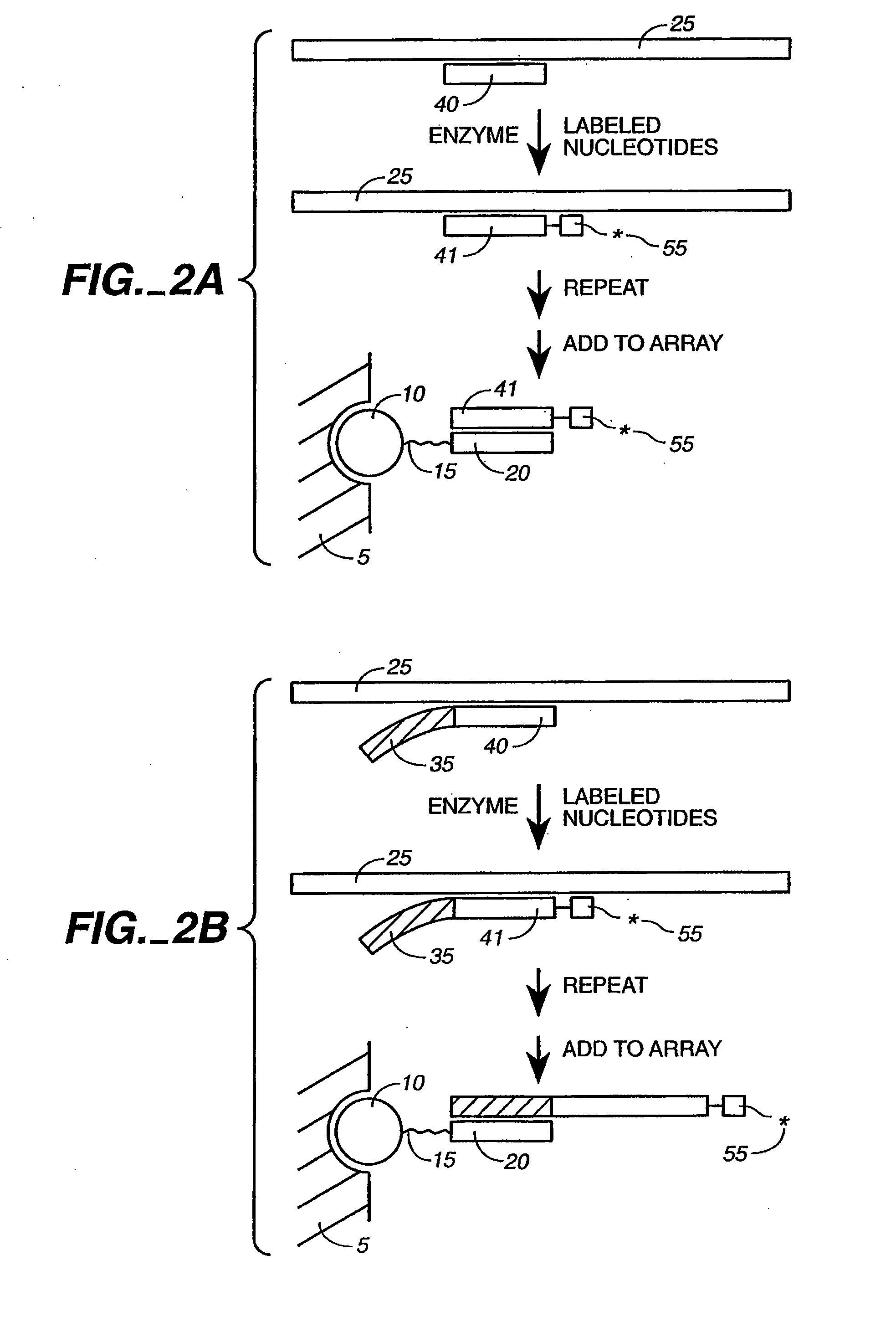
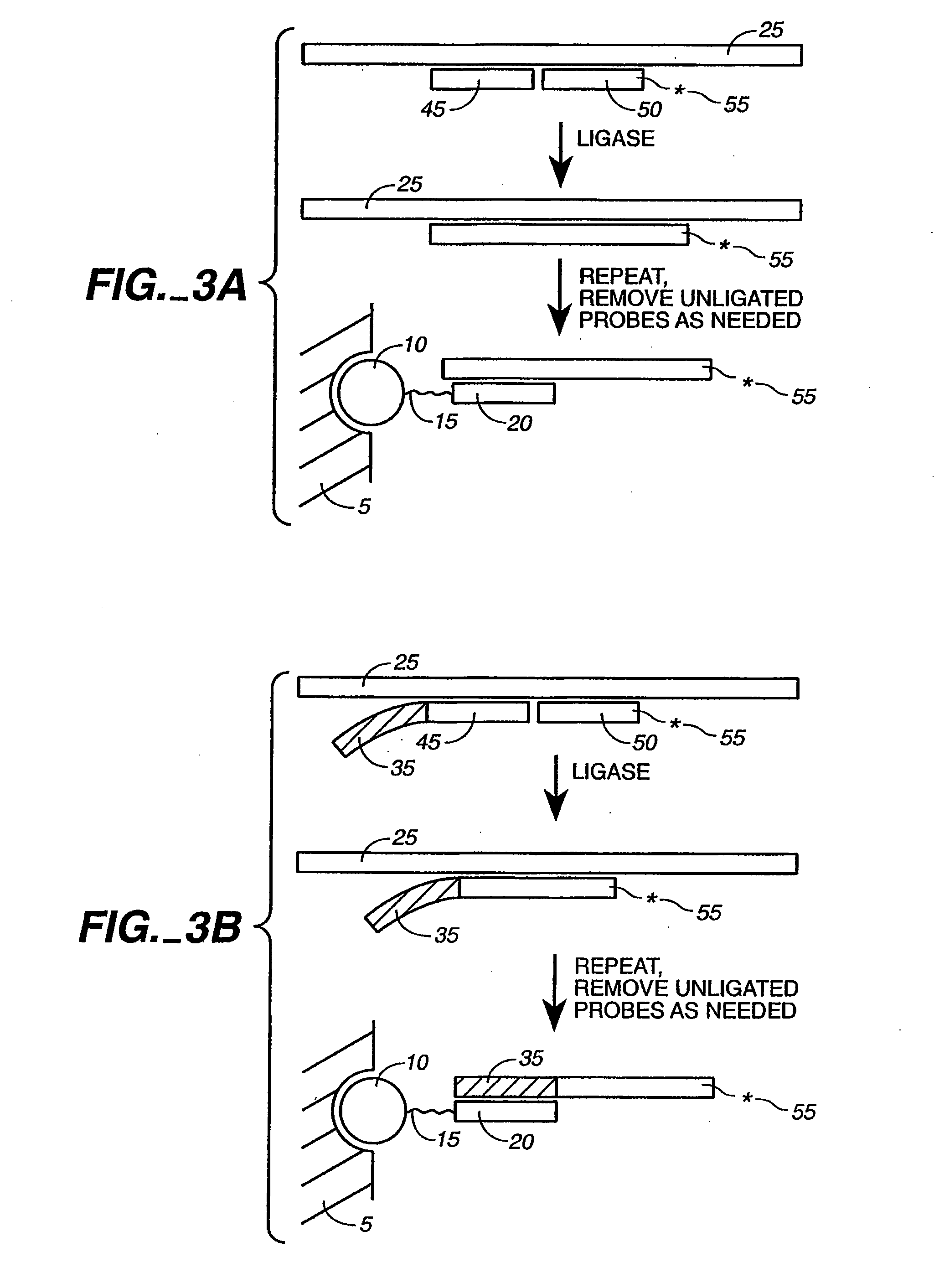
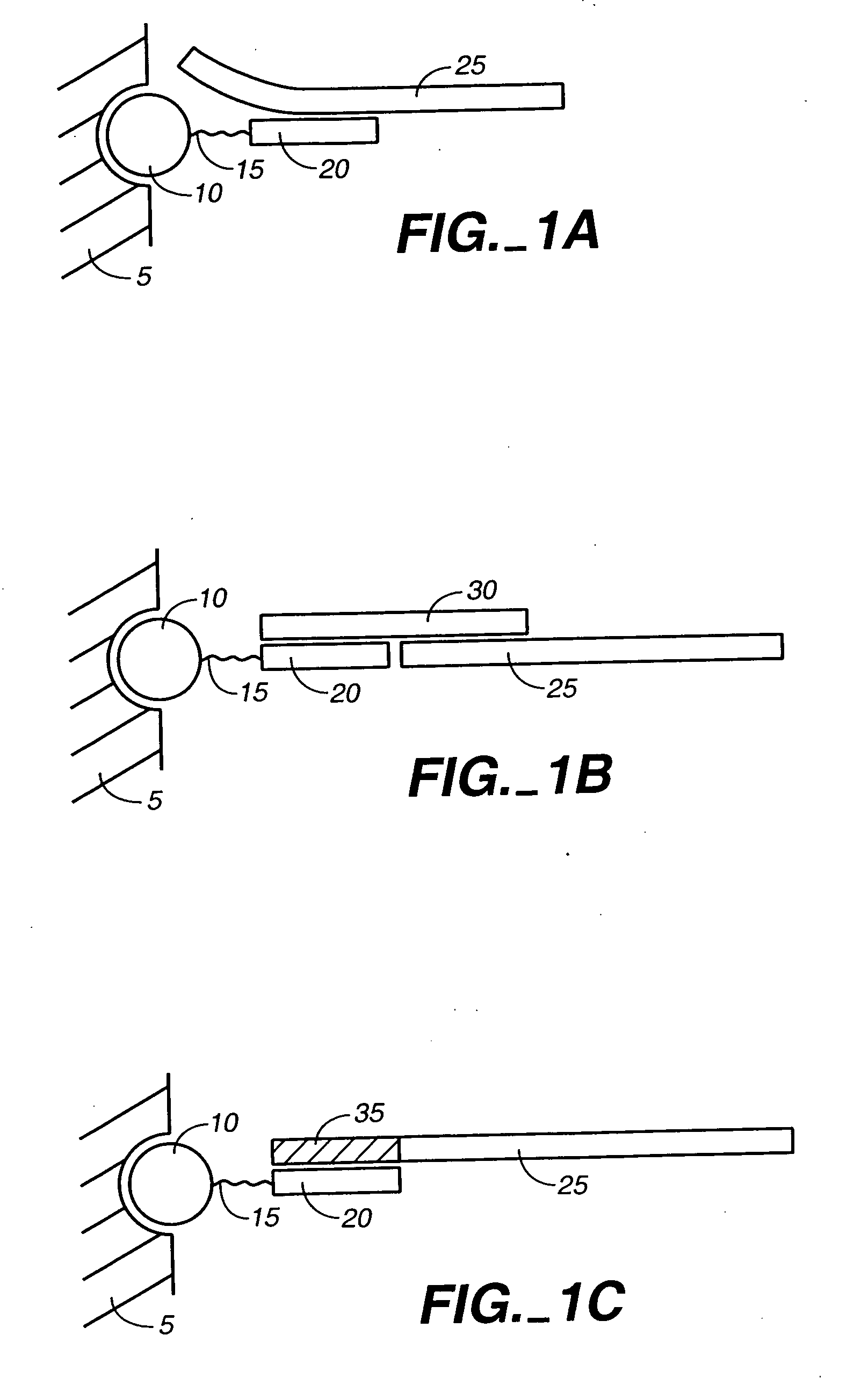
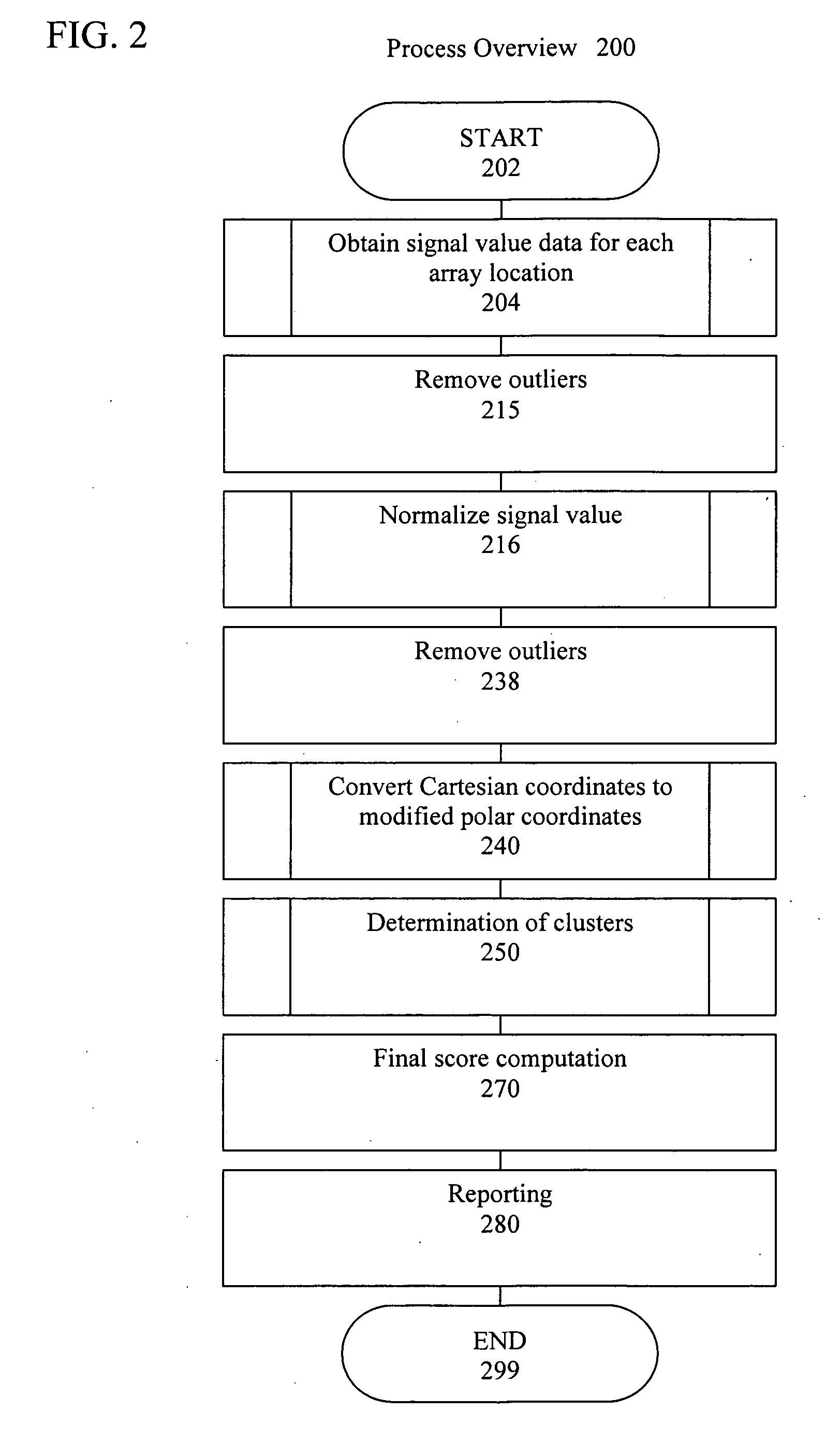
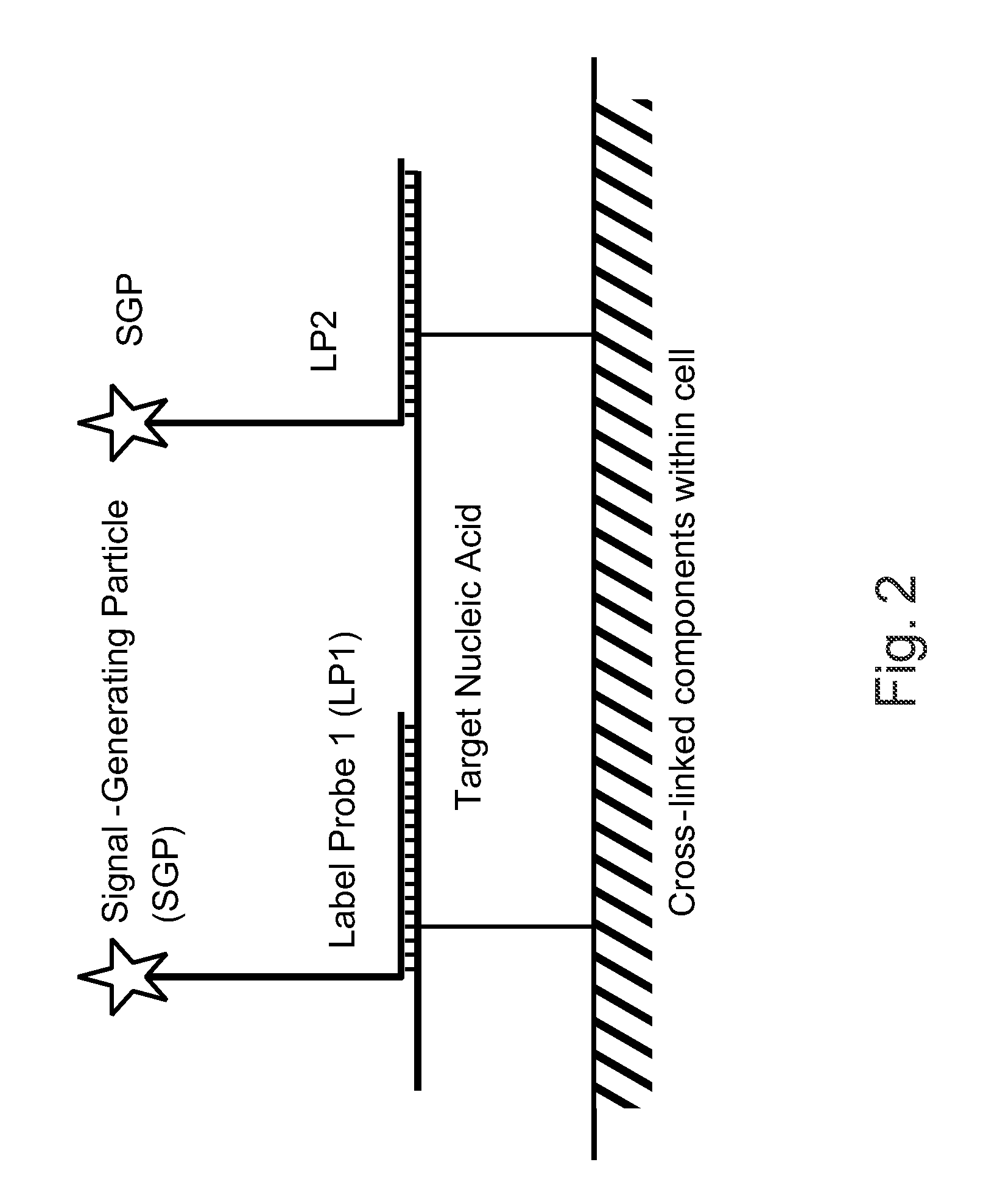
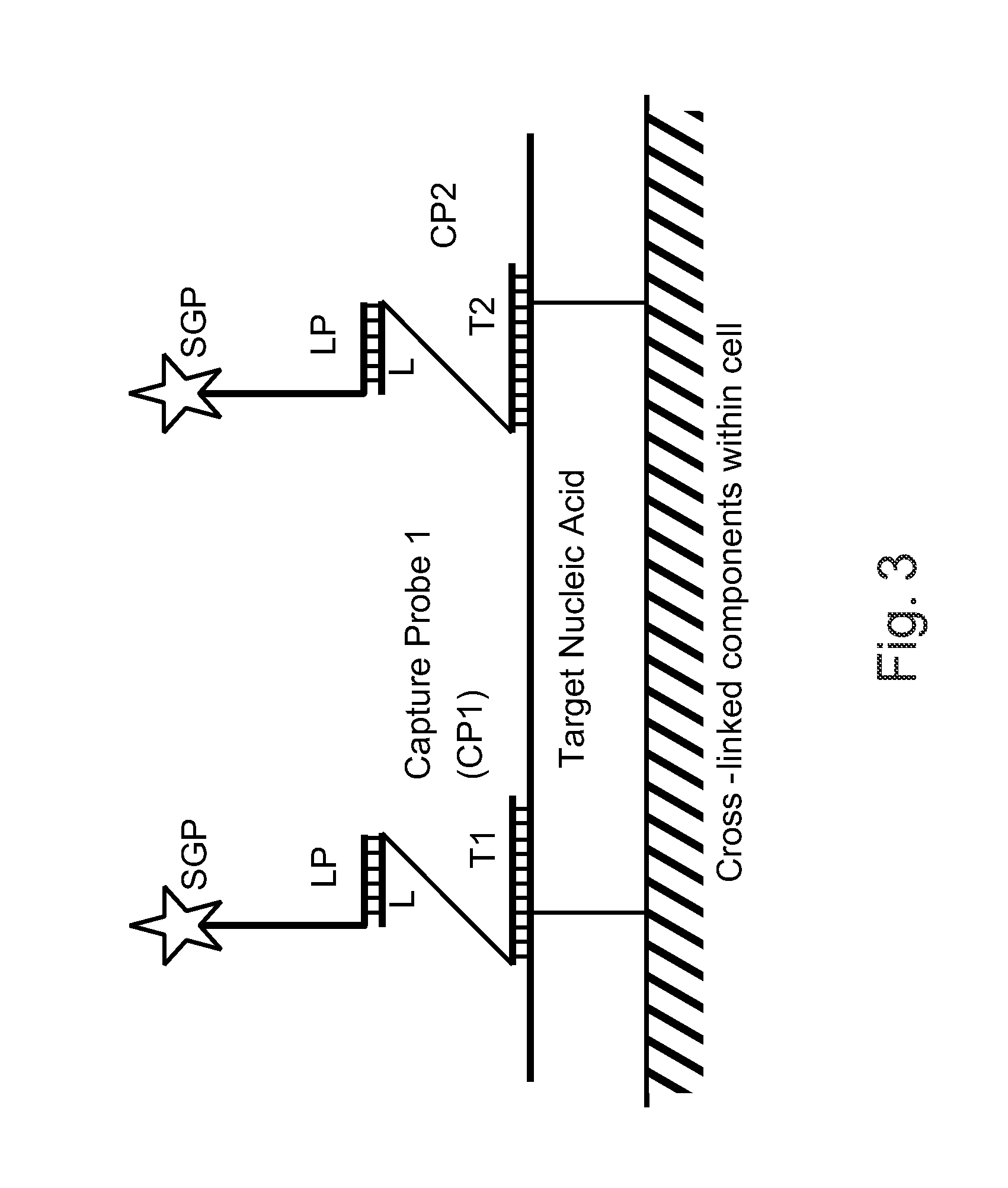
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
982 results about "Genotyping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
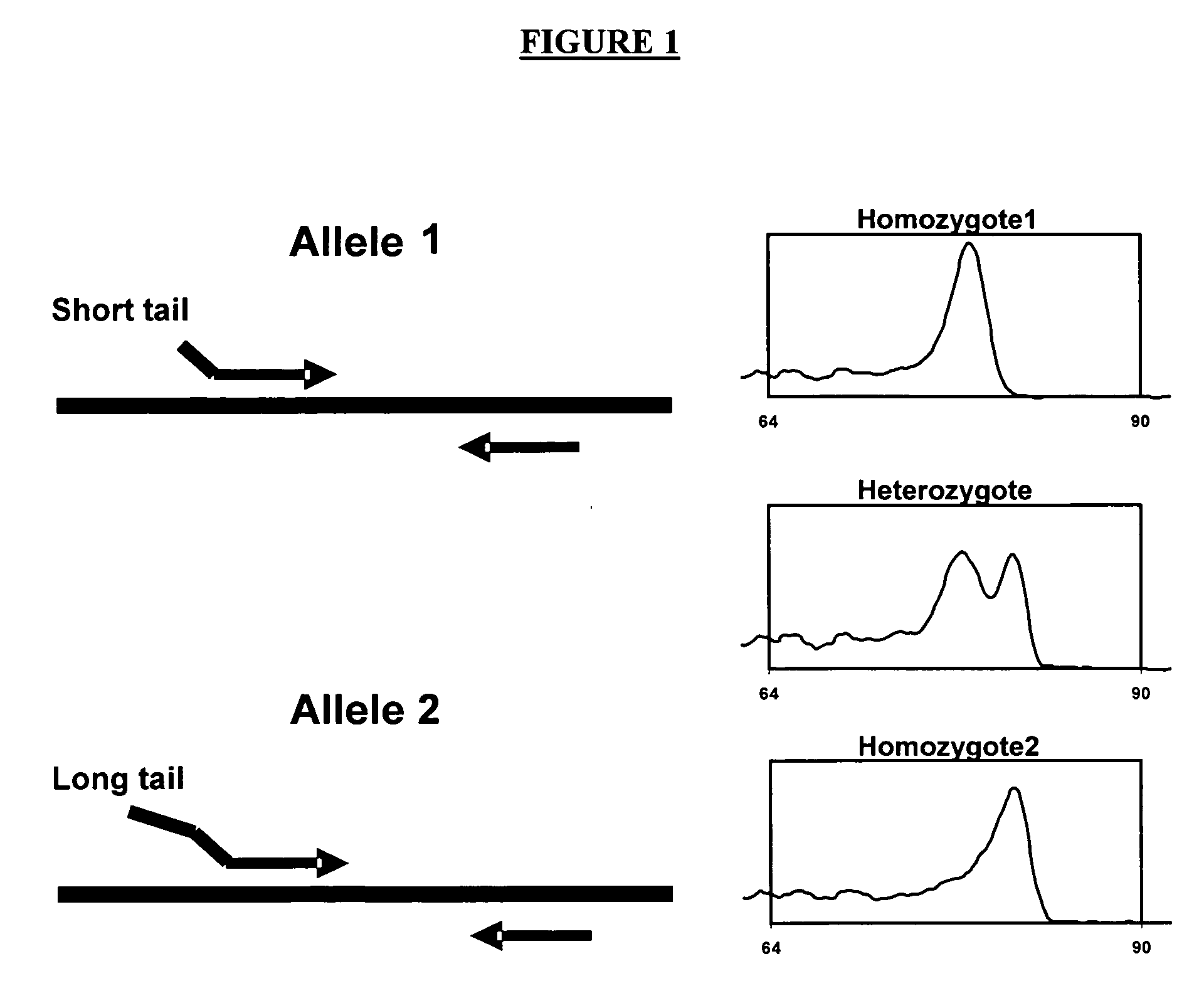
Genotyping is the process of determining differences in the genetic make-up (genotype) of an individual by examining the individual's DNA sequence using biological assays and comparing it to another individual's sequence or a reference sequence. It reveals the alleles an individual has inherited from their parents. Traditionally genotyping is the use of DNA sequences to define biological populations by use of molecular tools. It does not usually involve defining the genes of an individual.
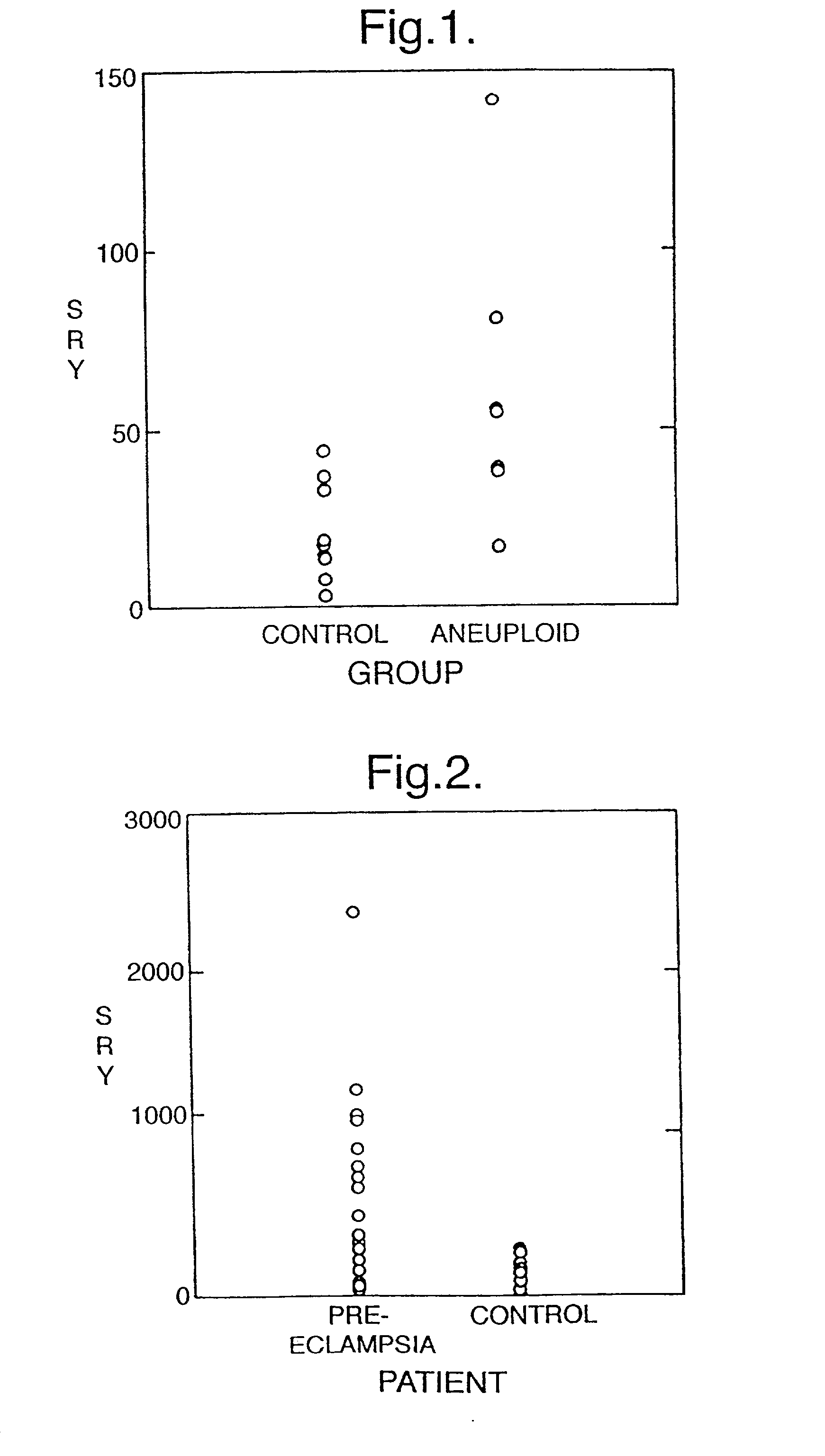
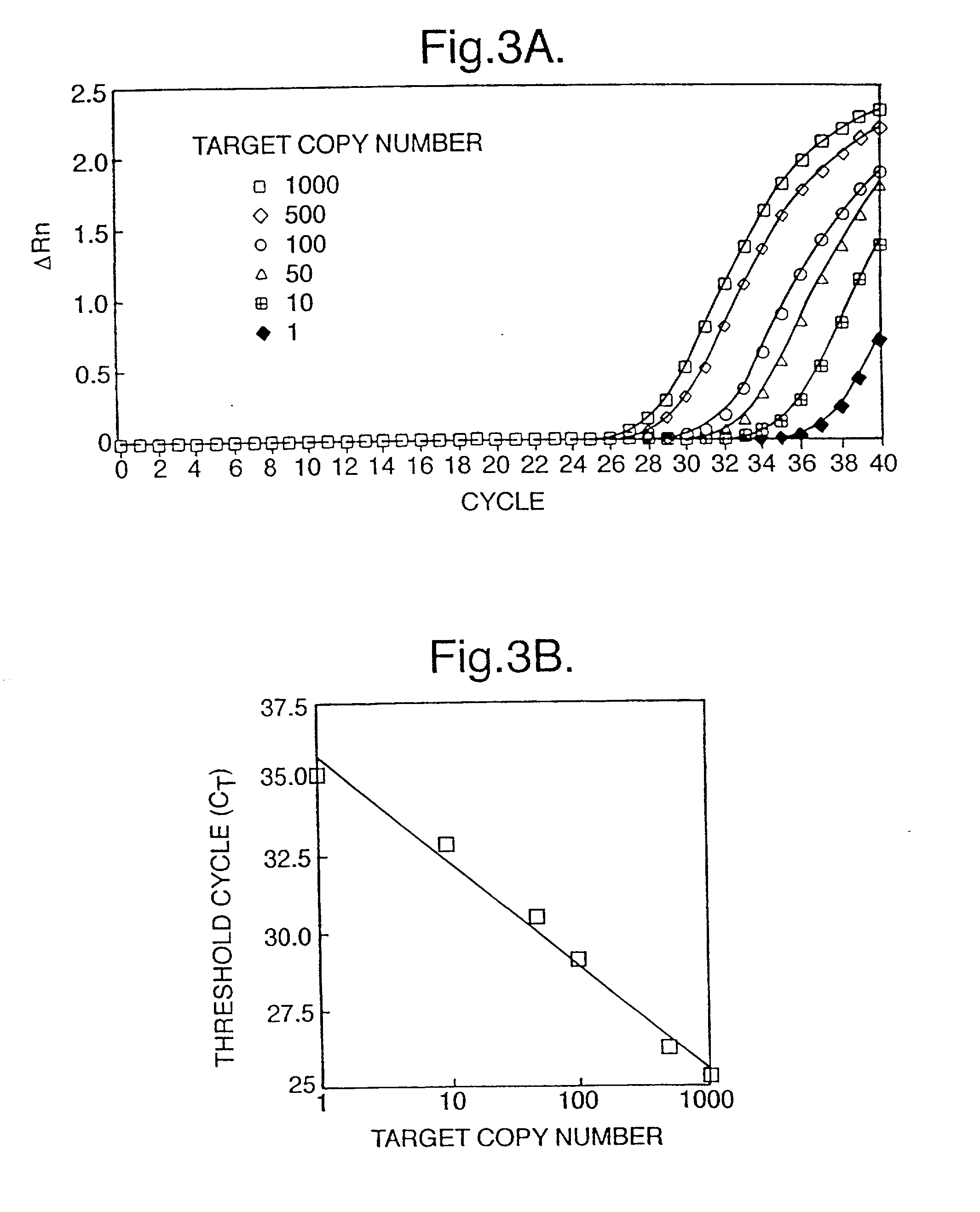
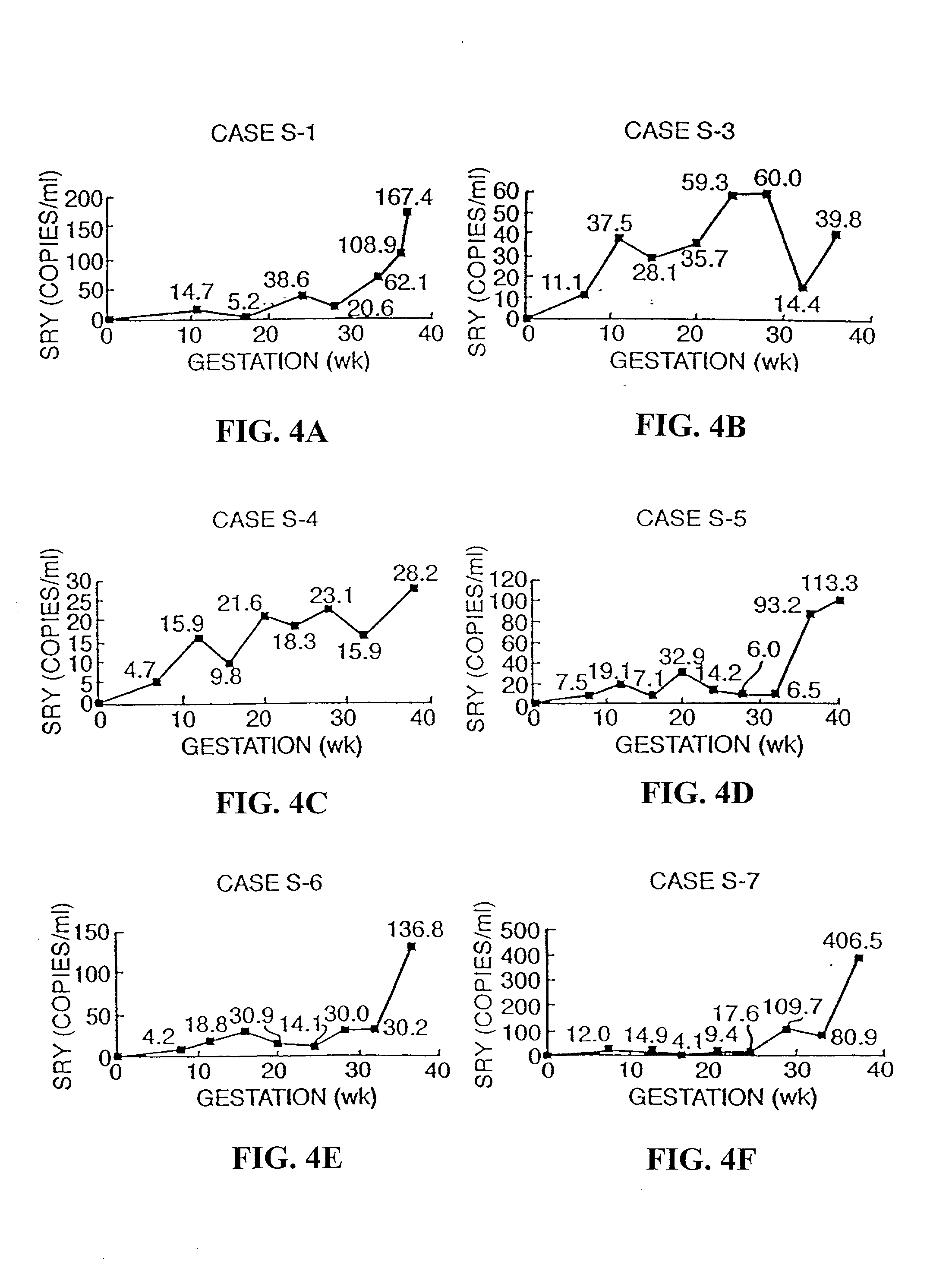
Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis
InactiveUS6258540B1% accurate detection rateIncrease the amount of foetal nucleic acid materialMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPrenatal diagnosisBlood typing
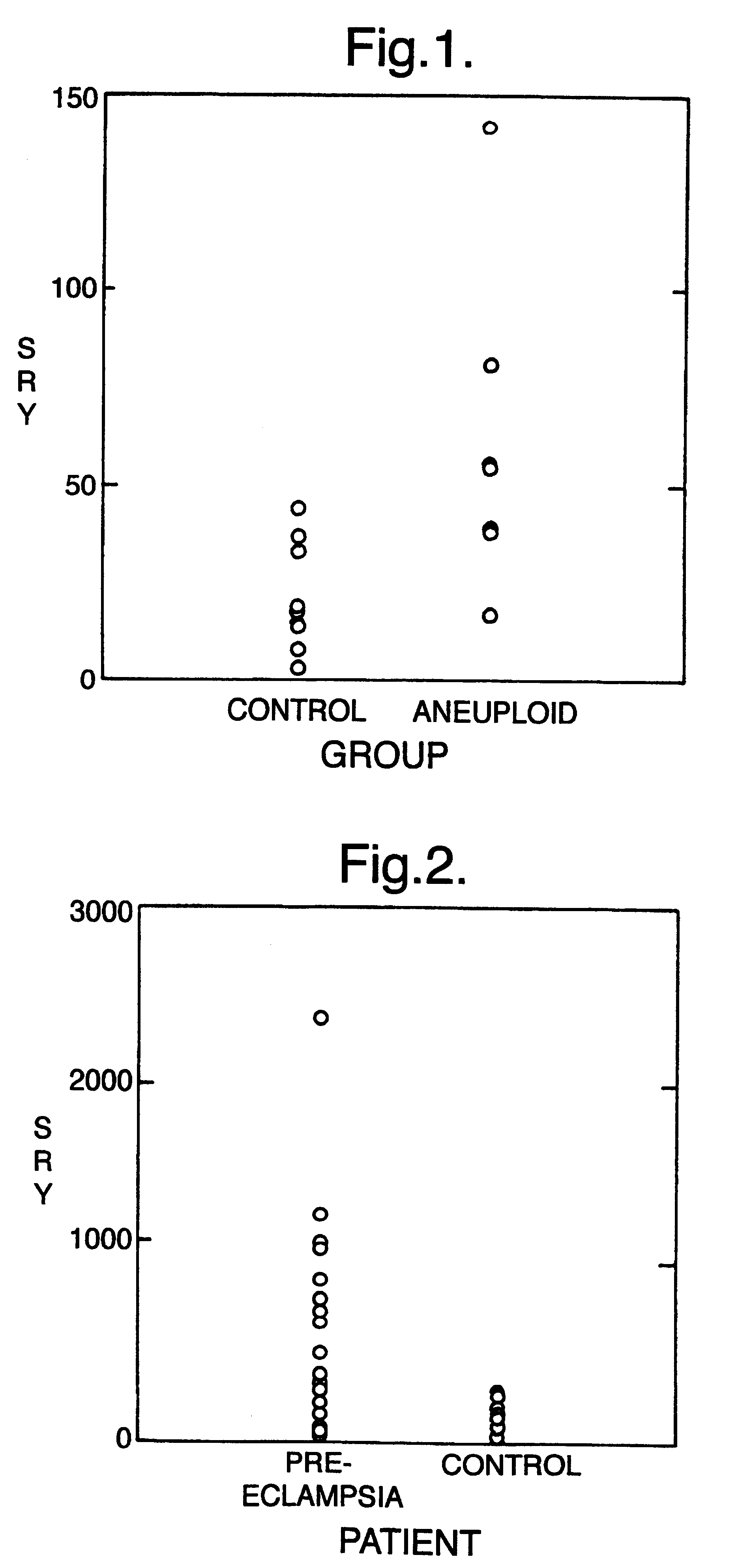
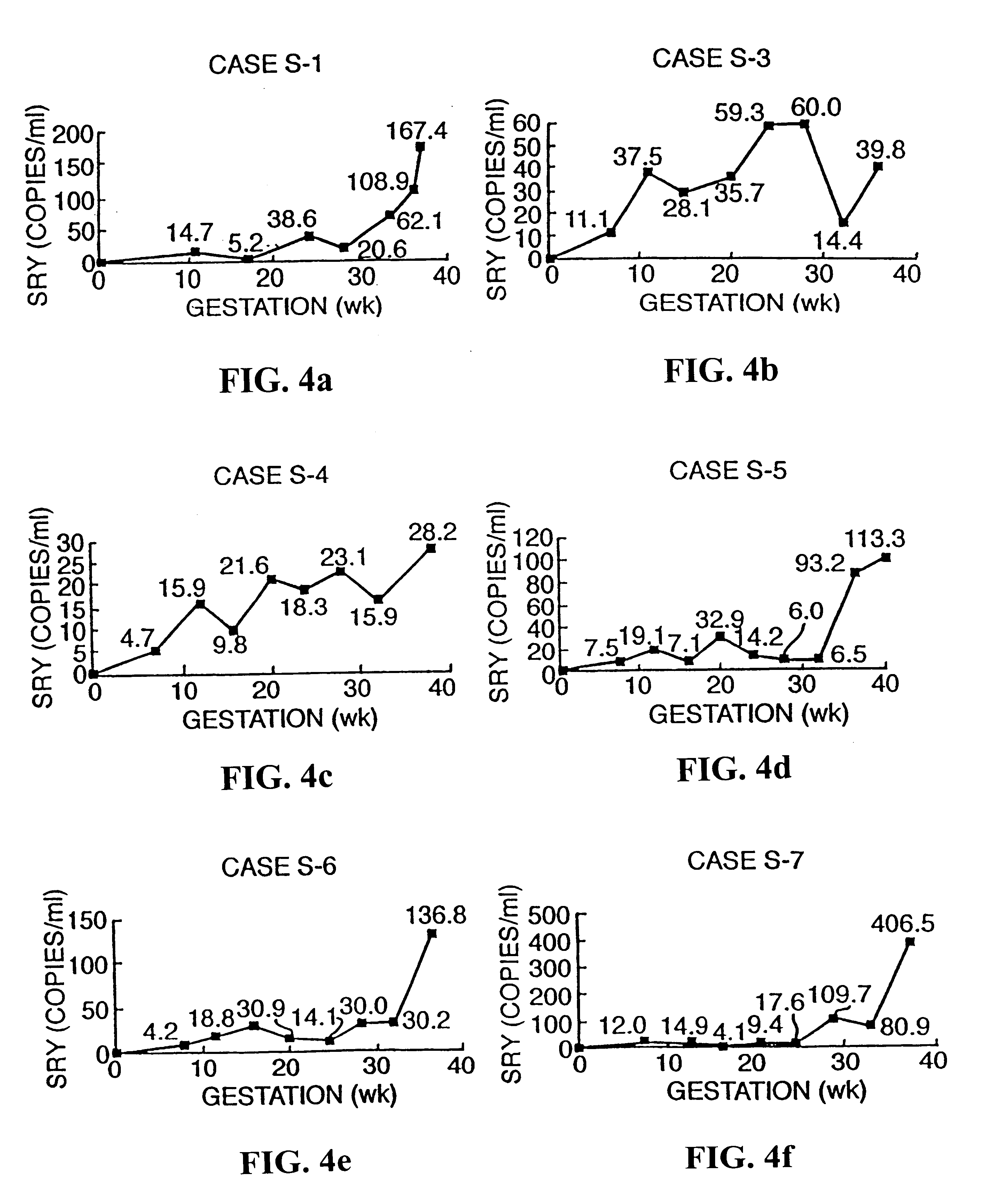
The invention relates to a detection method performed on a maternal serum or plasma sample from a pregnant female, which method comprises detecting the presence of a nucleic acid of foetal origin in the sample. The invention enables non-invasive prenatal diagnosis including for example sex determination, blood typing and other genotyping, and detection of pre-eclampsia in the mother.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
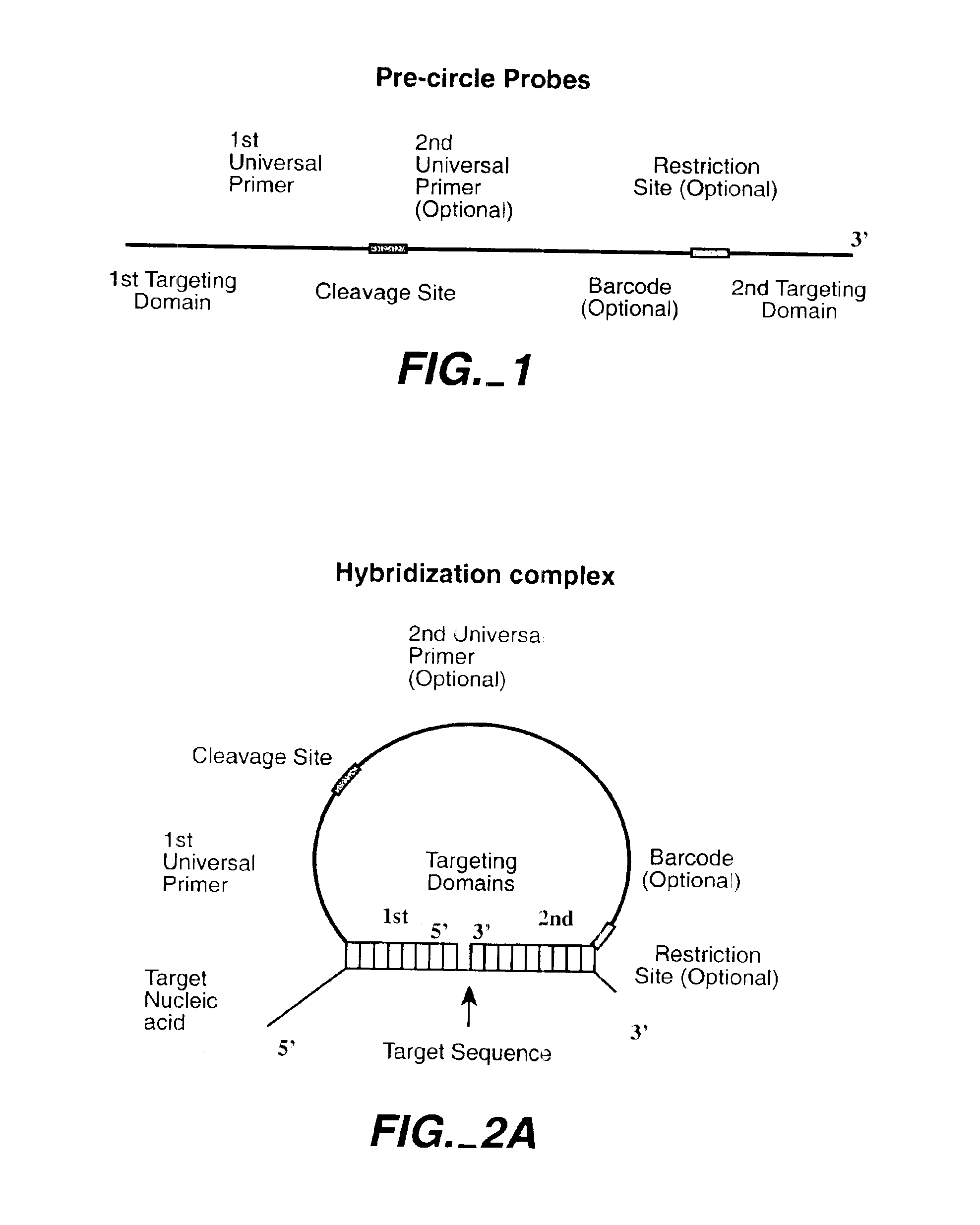
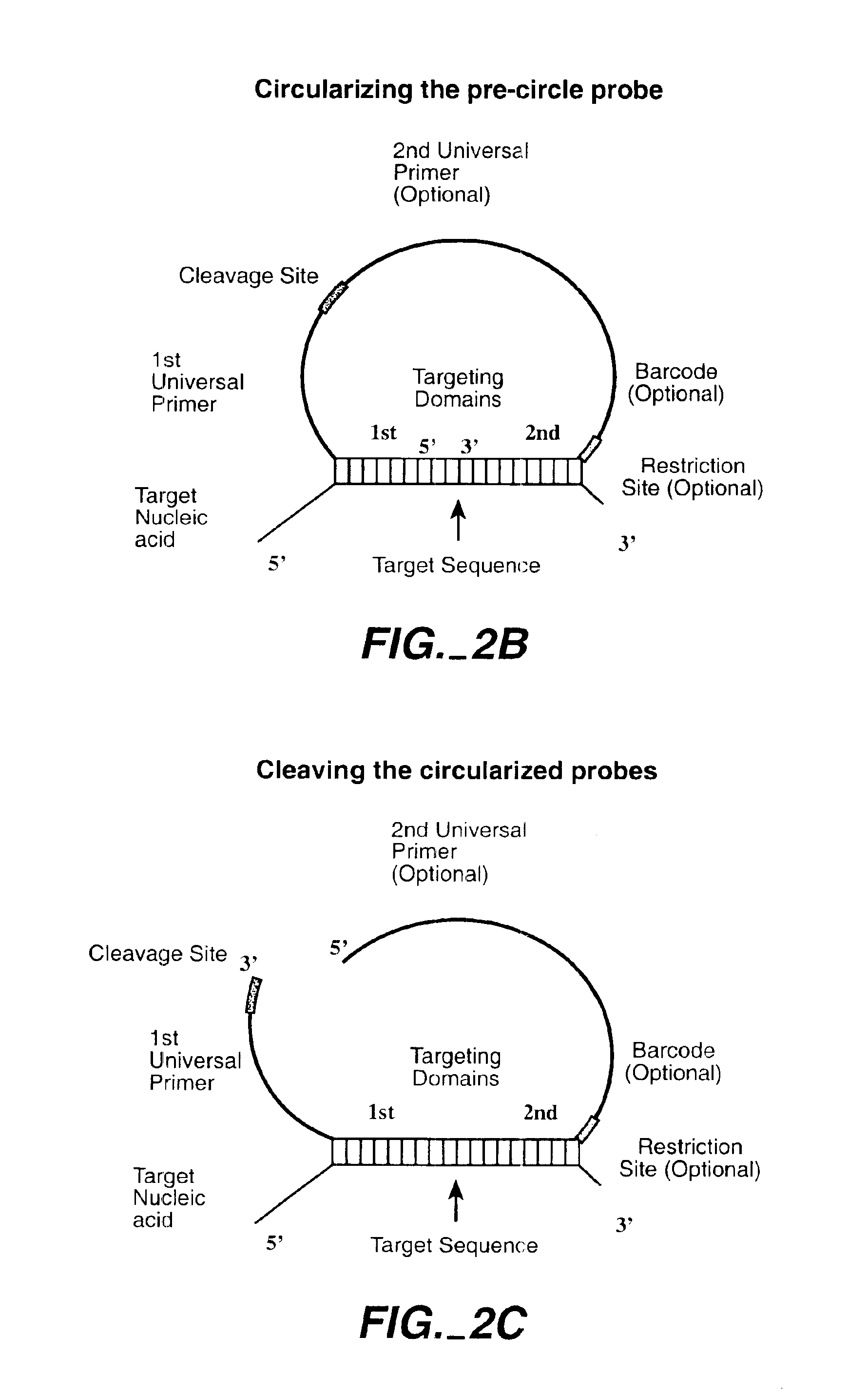
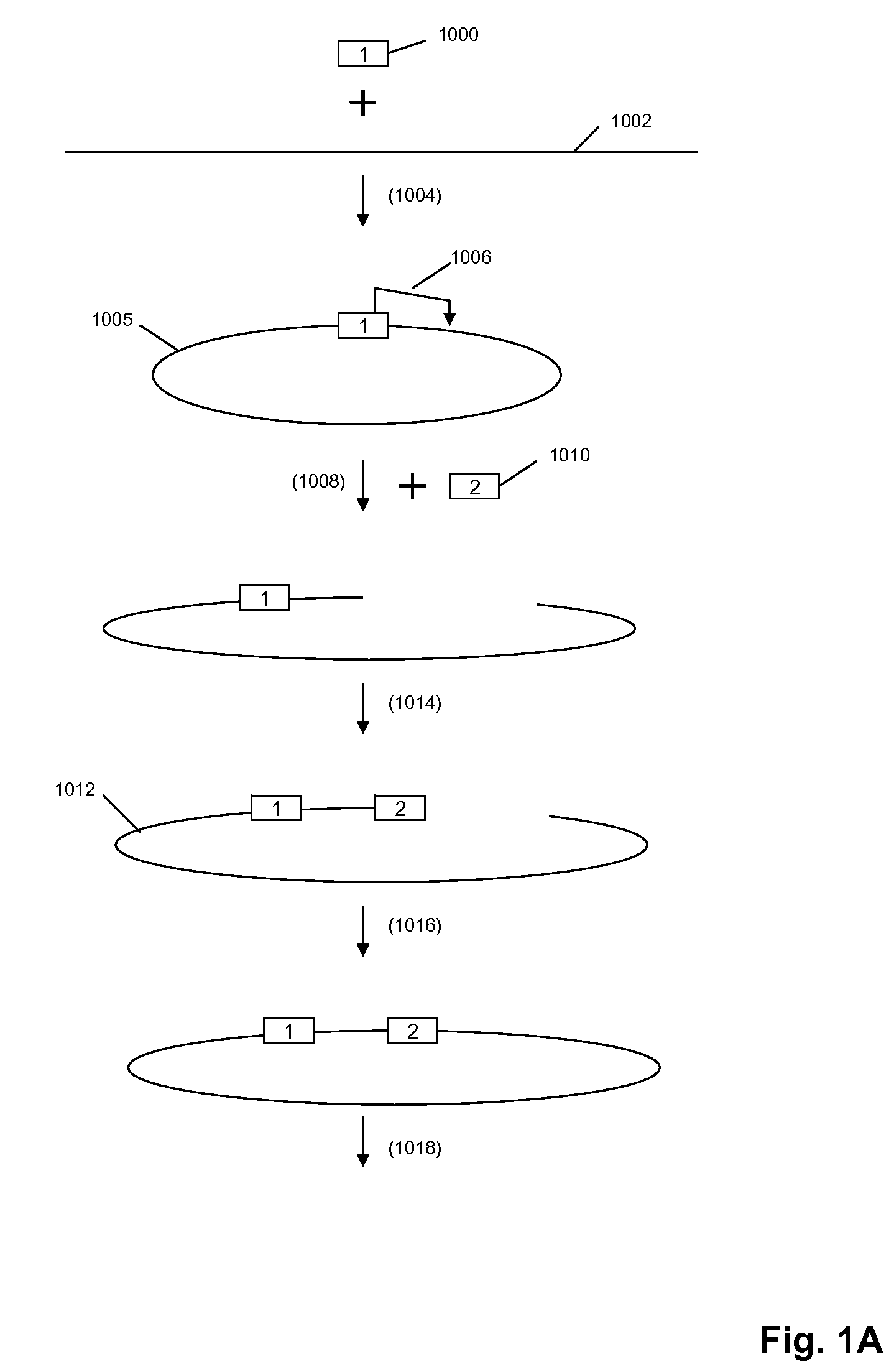
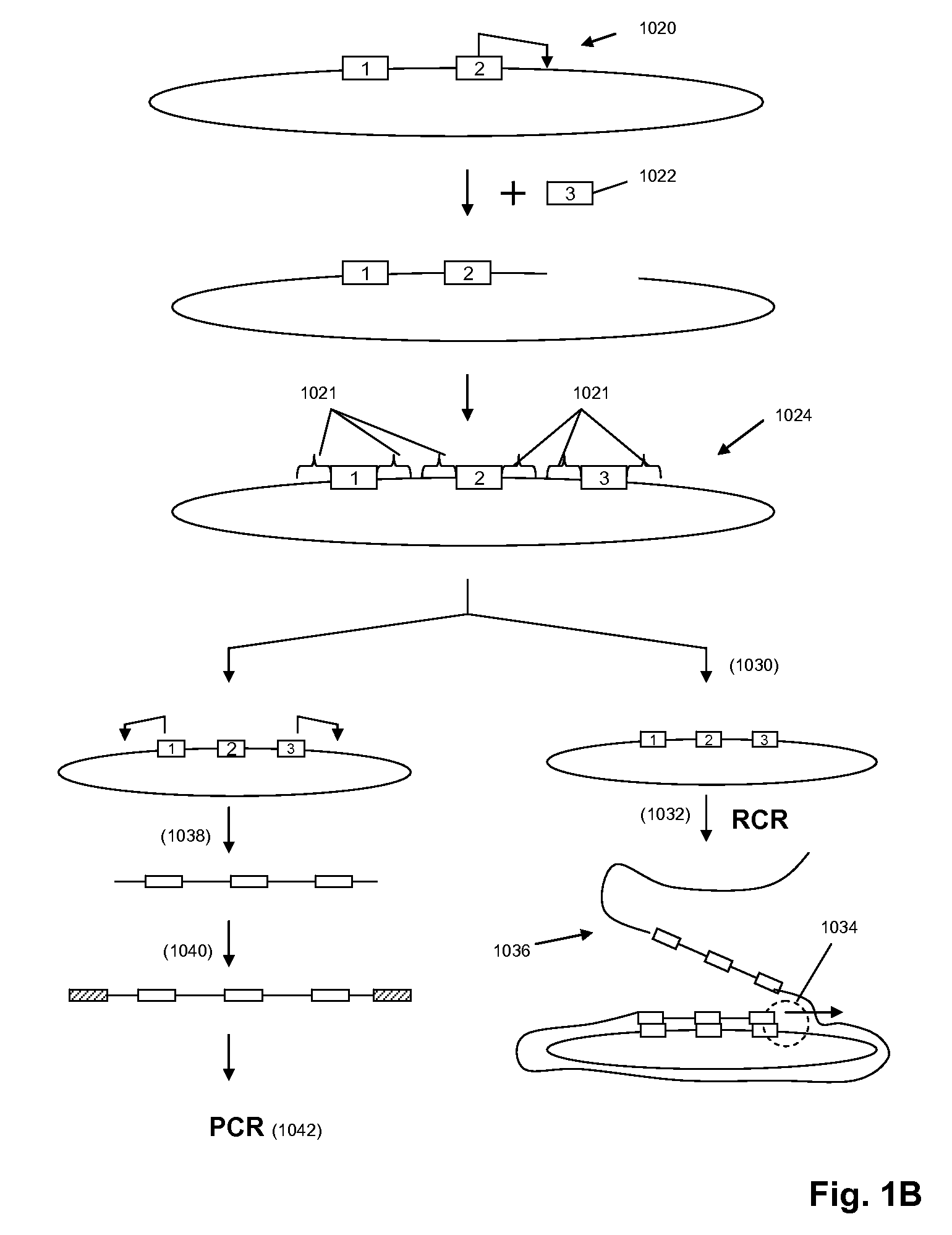
Direct multiplex characterization of genomic DNA
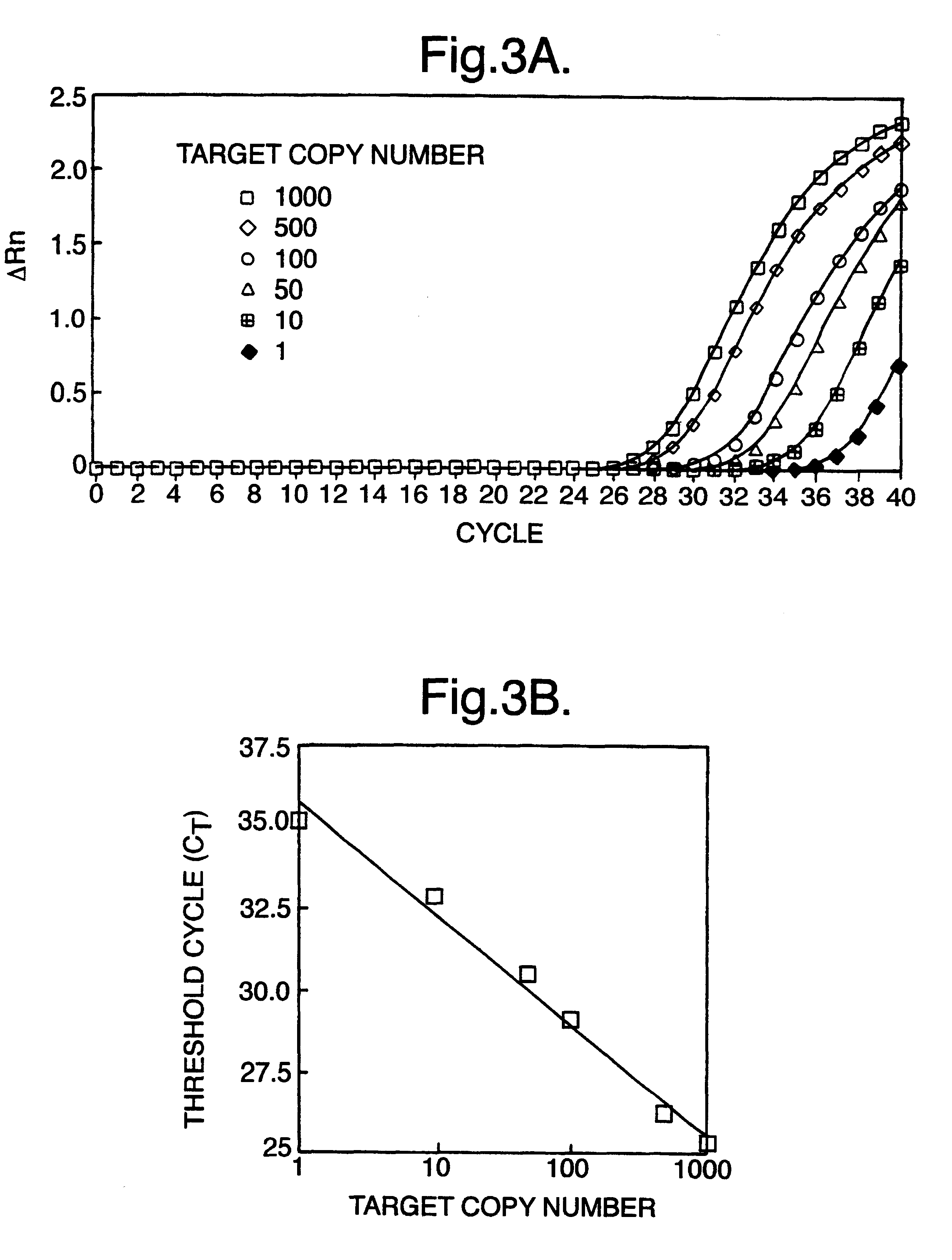
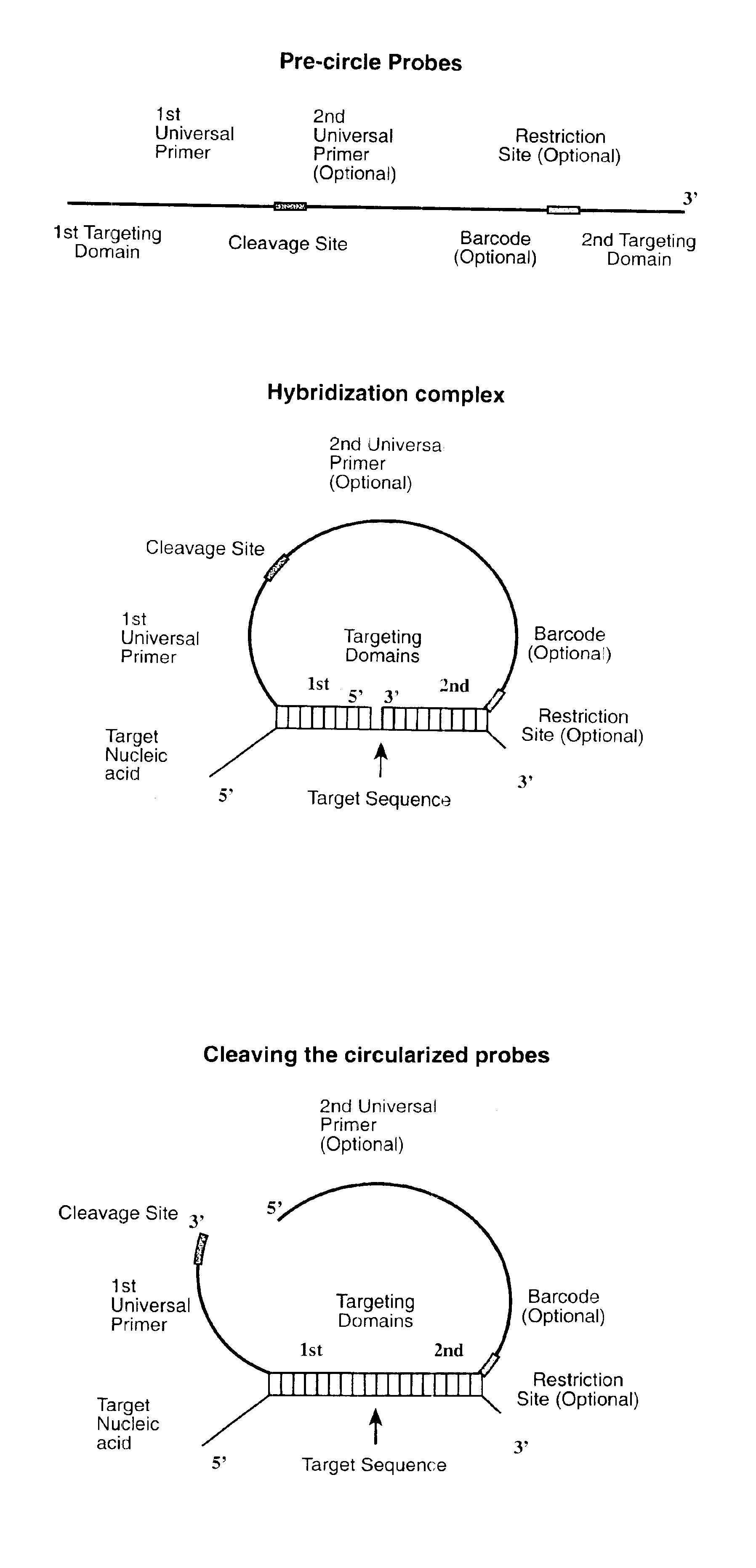
The invention is directed to novel methods of multiplexing nucleic acid reactions, including amplification, detection and genotyping. The invention relies on the use of precircle probes that are circularized in the presence of the corresponding target nucleic acids, cleaved, and then amplified.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
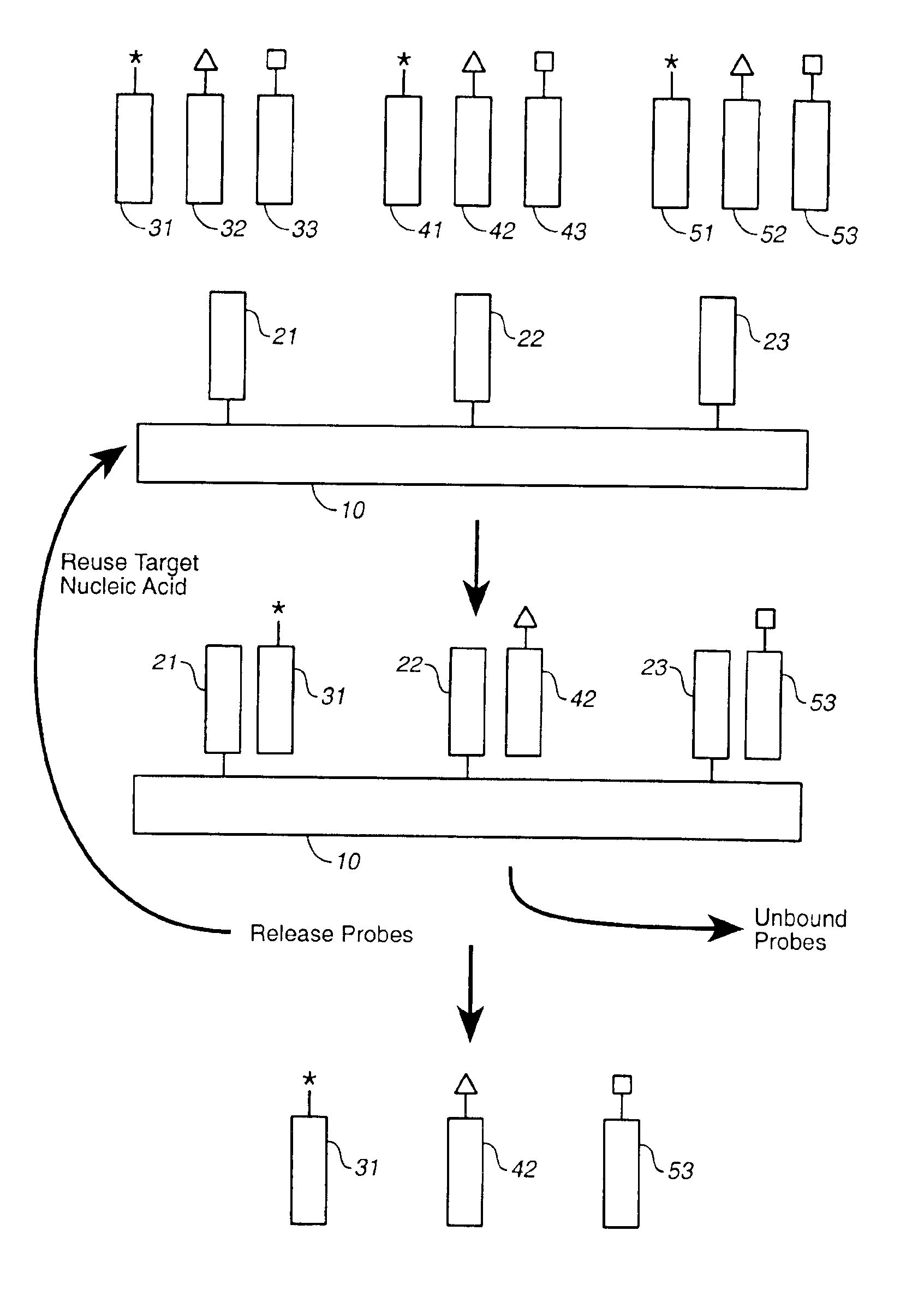
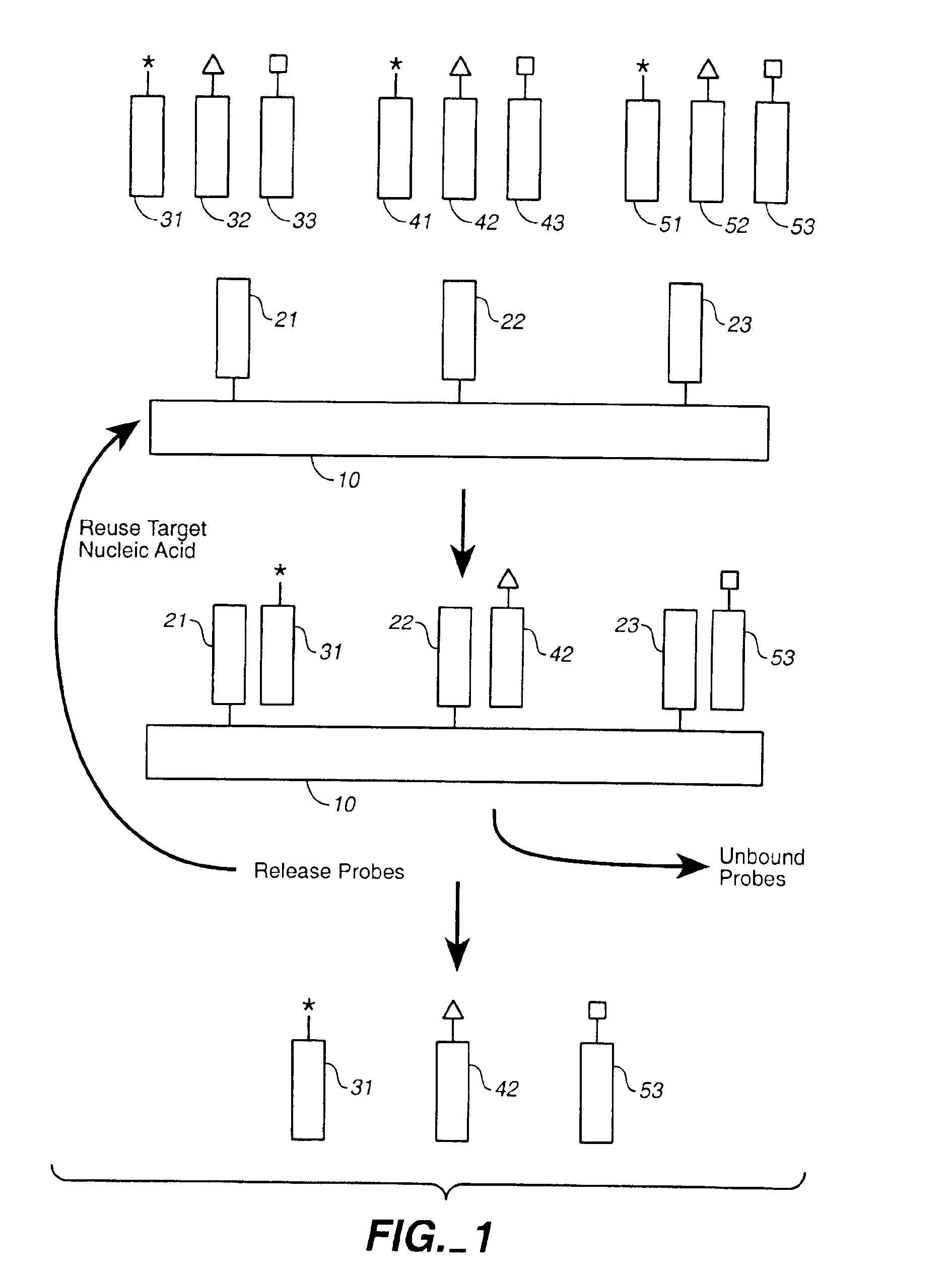
Compositions and methods for repetitive use of genomic DNA
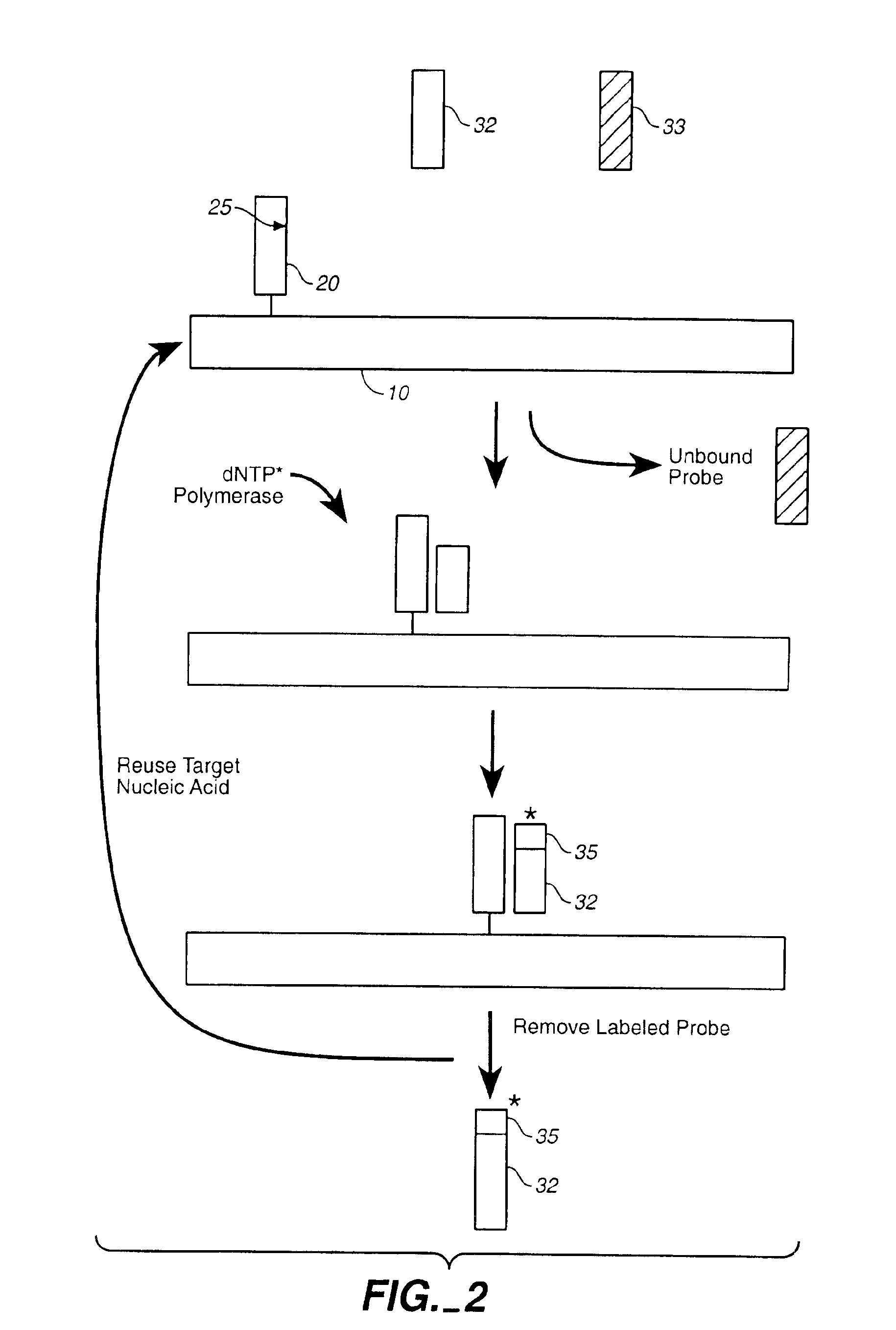
The present invention relates to detection or genotyping (or other sample analysis) of target nucleic acids following immobilization of the target nucleic acids onto a surface. The target nucleic acids can be re-used multiple times, thus conserving sample materials and simplifying sample preparation.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Universal selective genome amplification and universal genotyping system
InactiveUS20050019776A1Enriches SNPsImprove reuseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSmall fragmentGenomic DNA
The invention relates to methods for isolating and amplifying small fragments of genomic DNA for genotyping polymorphisms in human populations.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
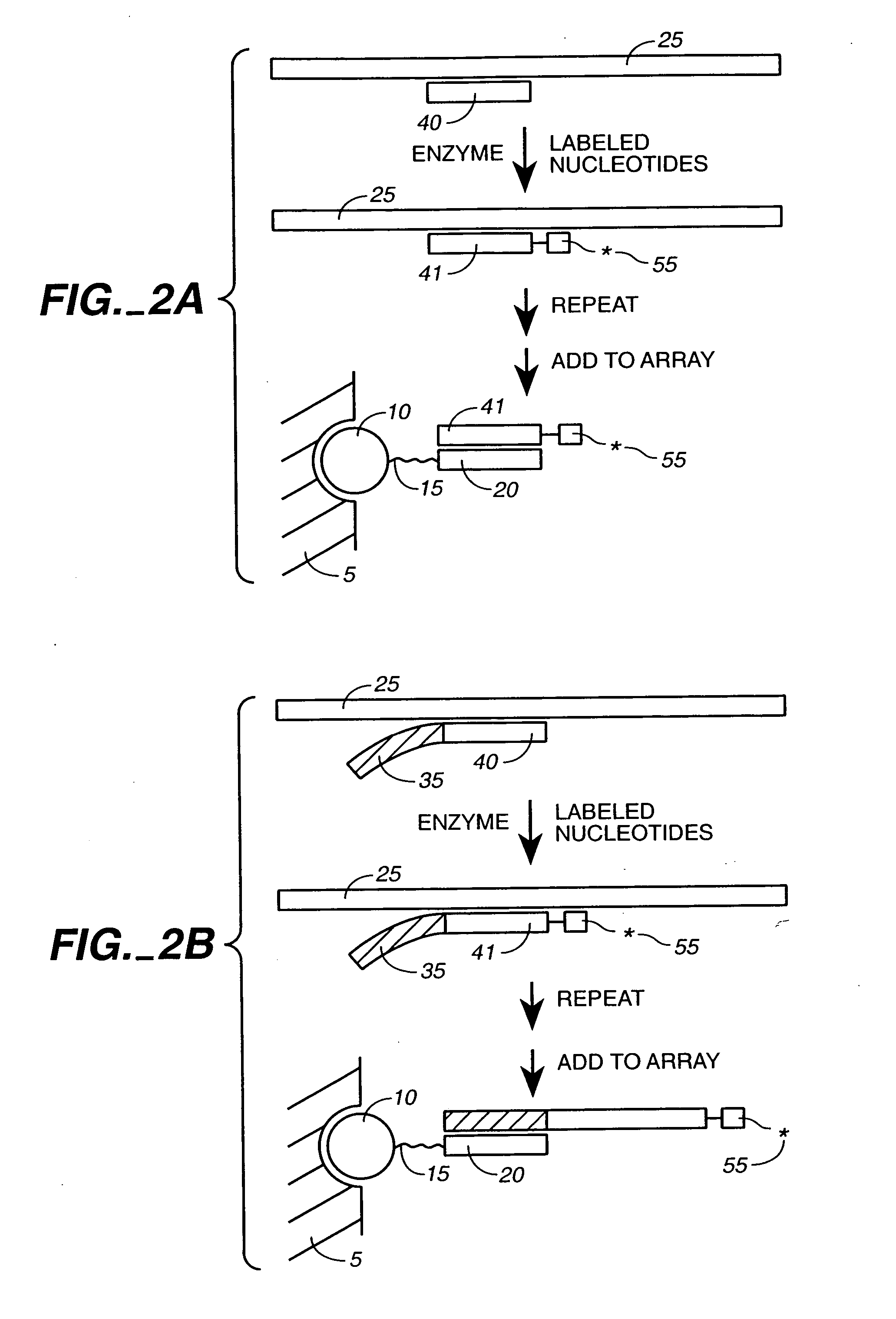
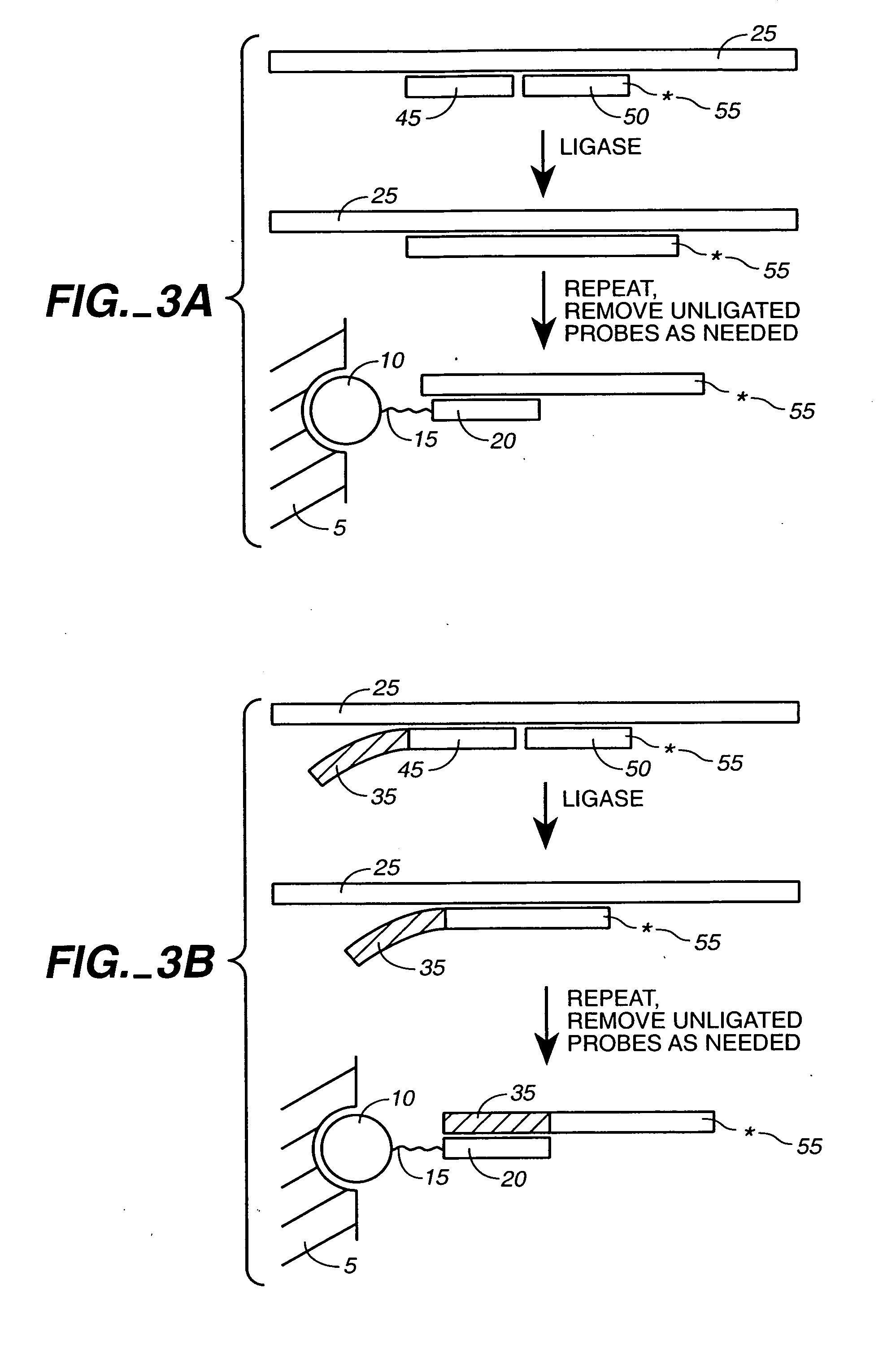
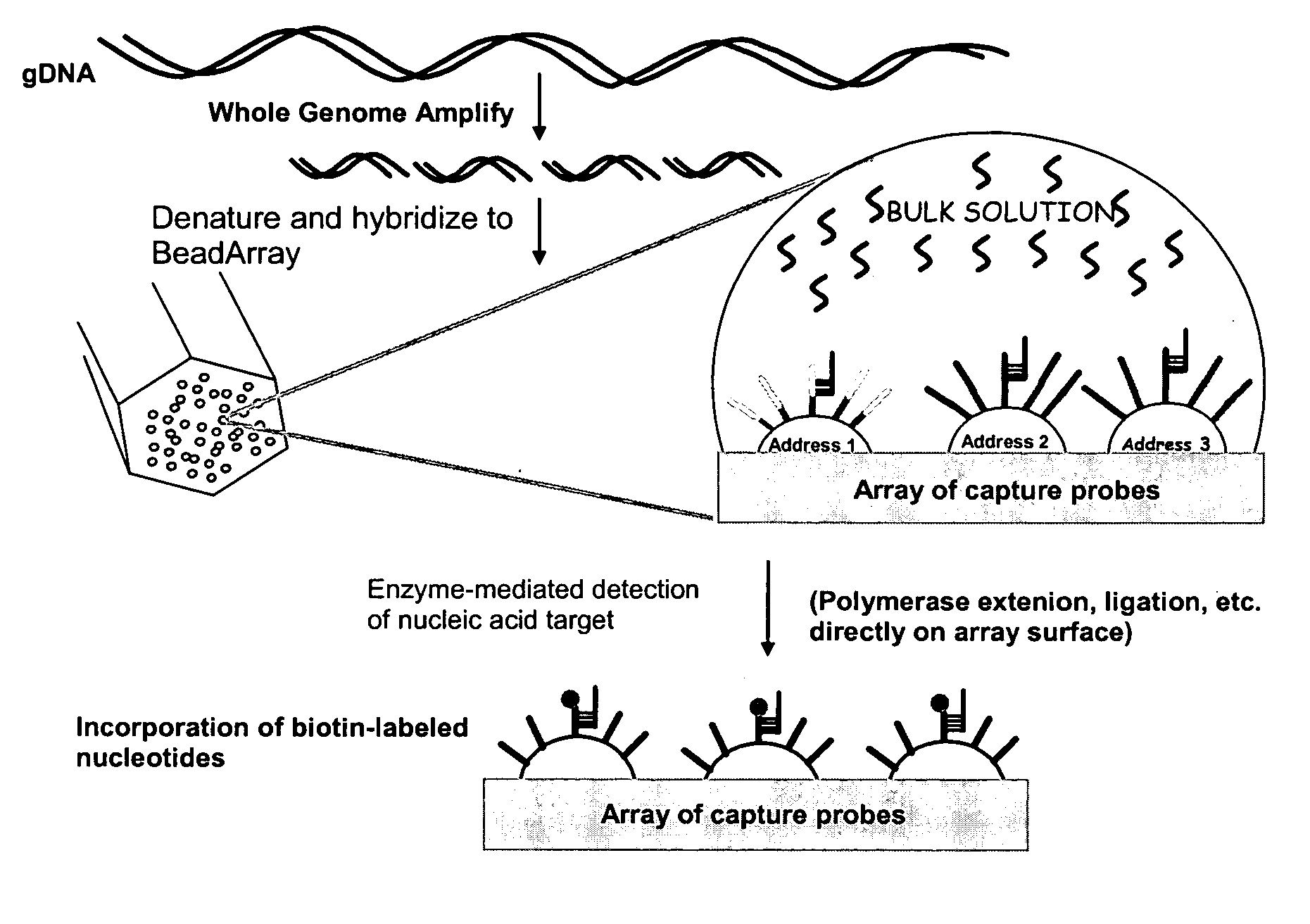
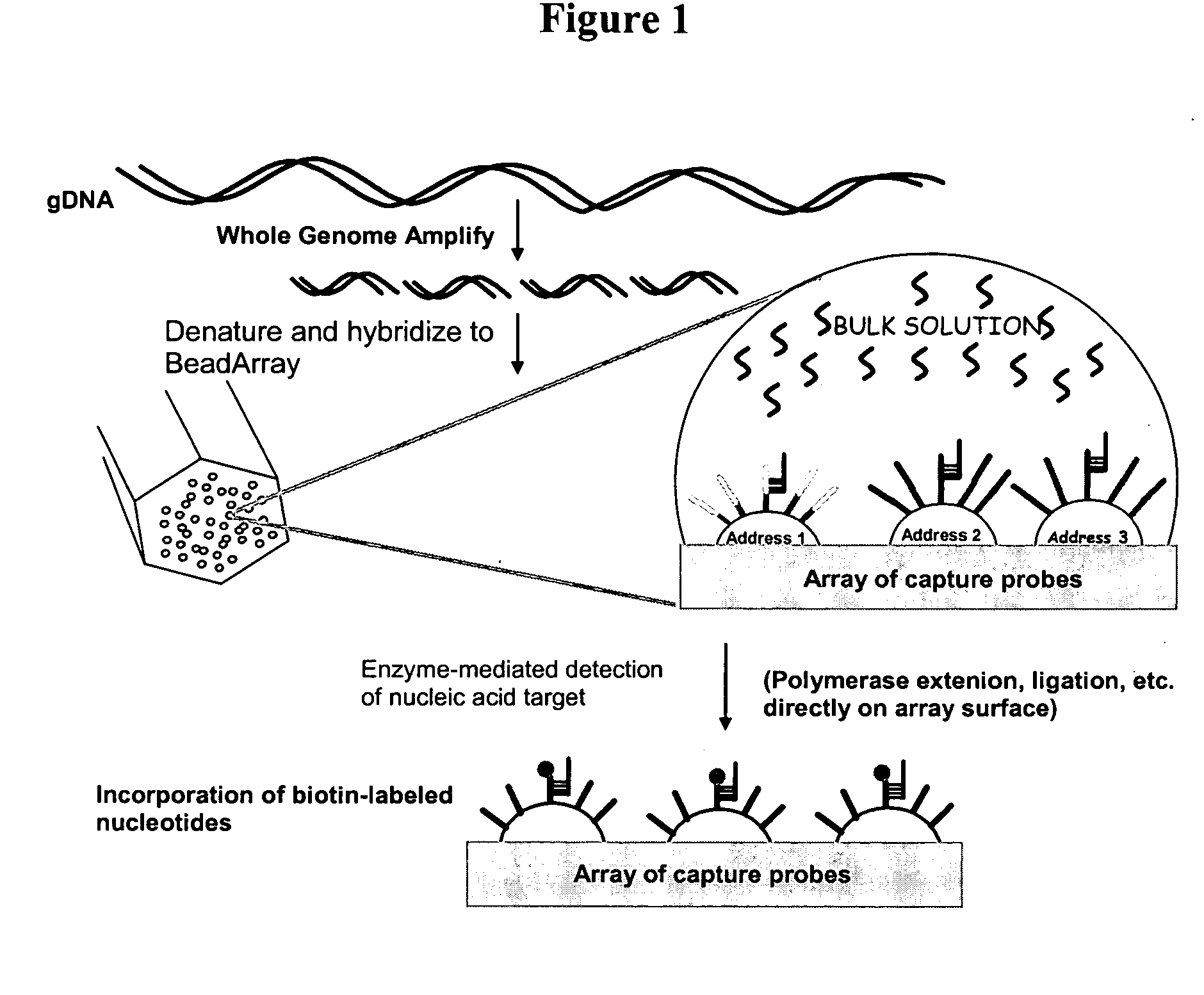
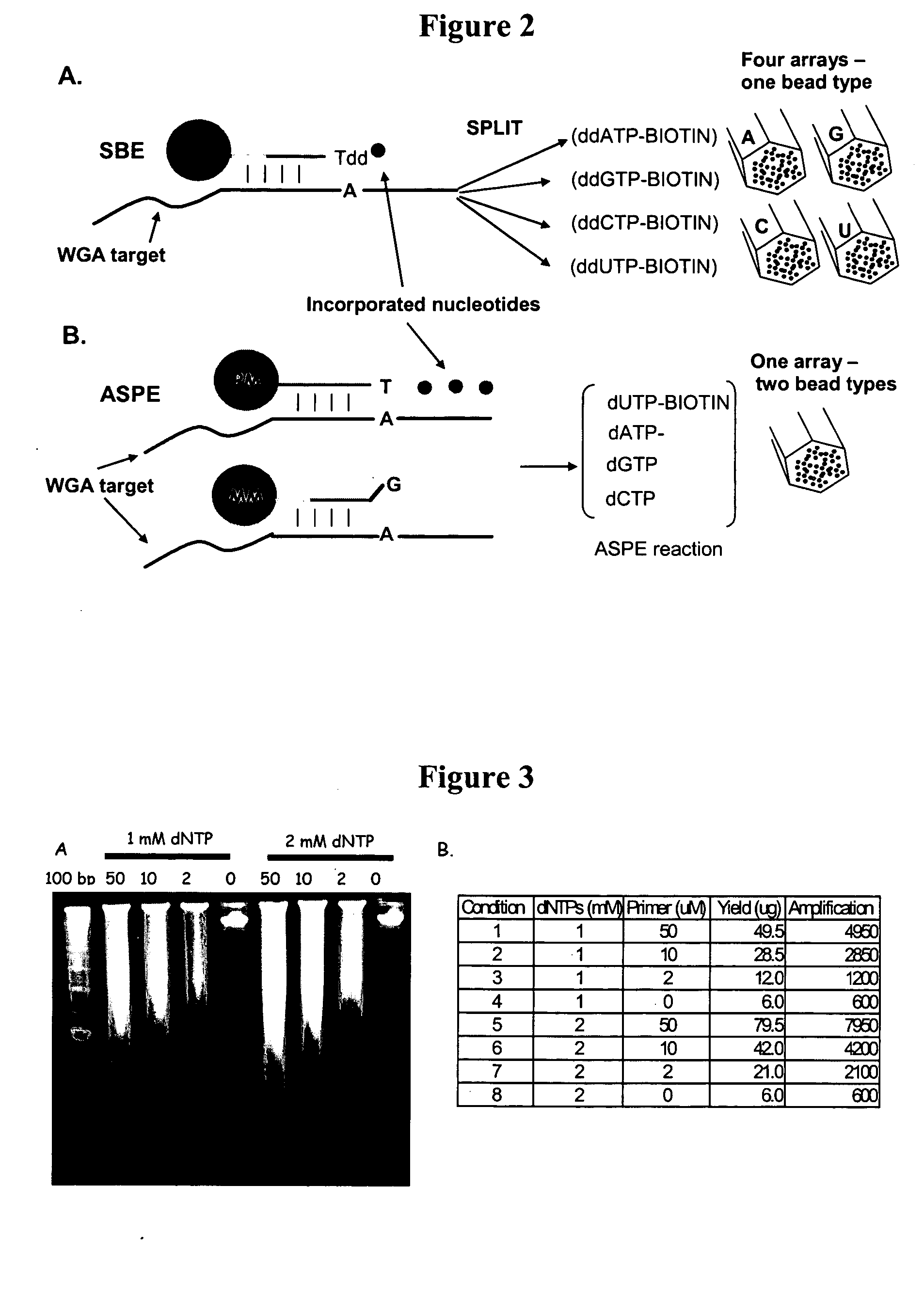
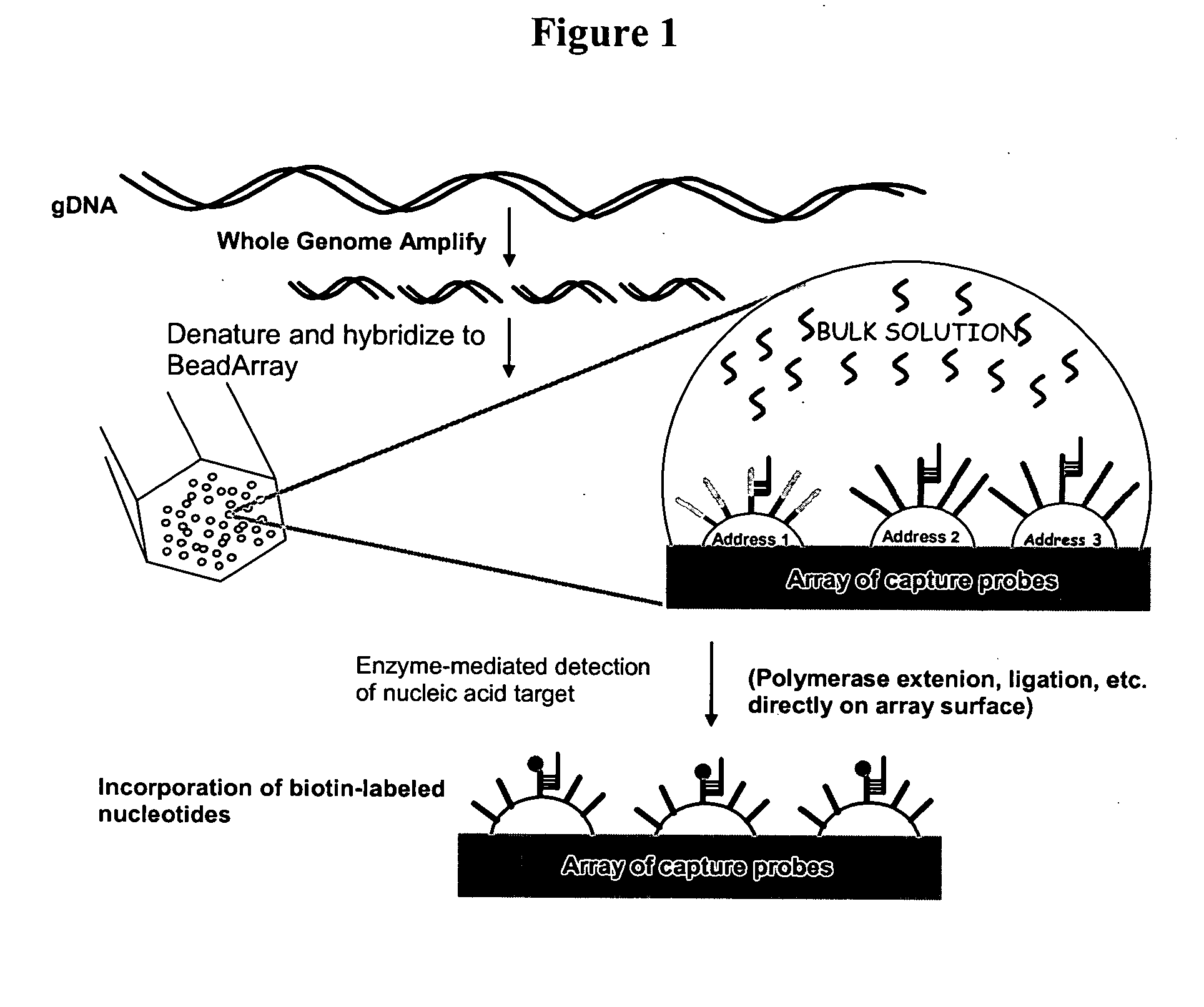
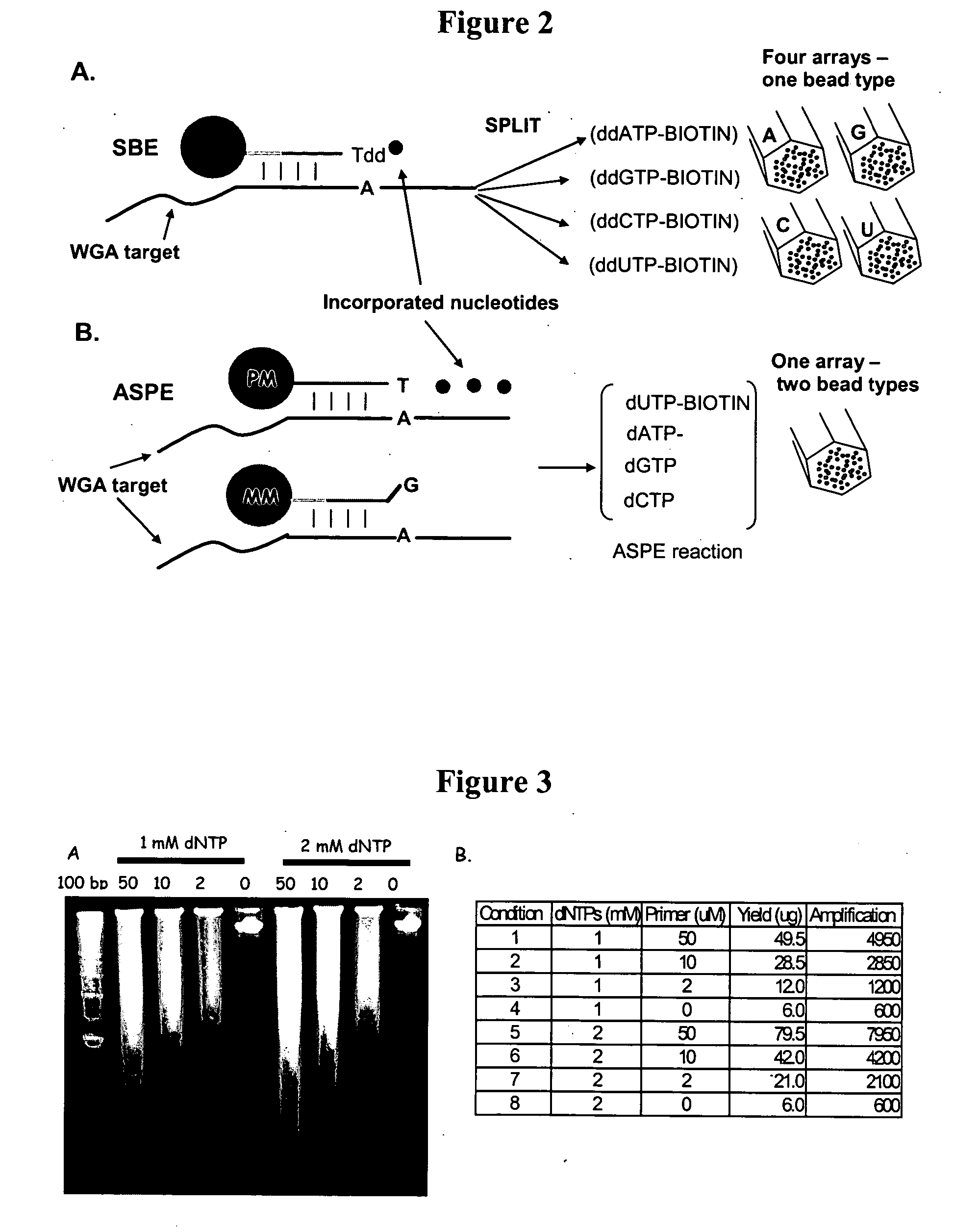
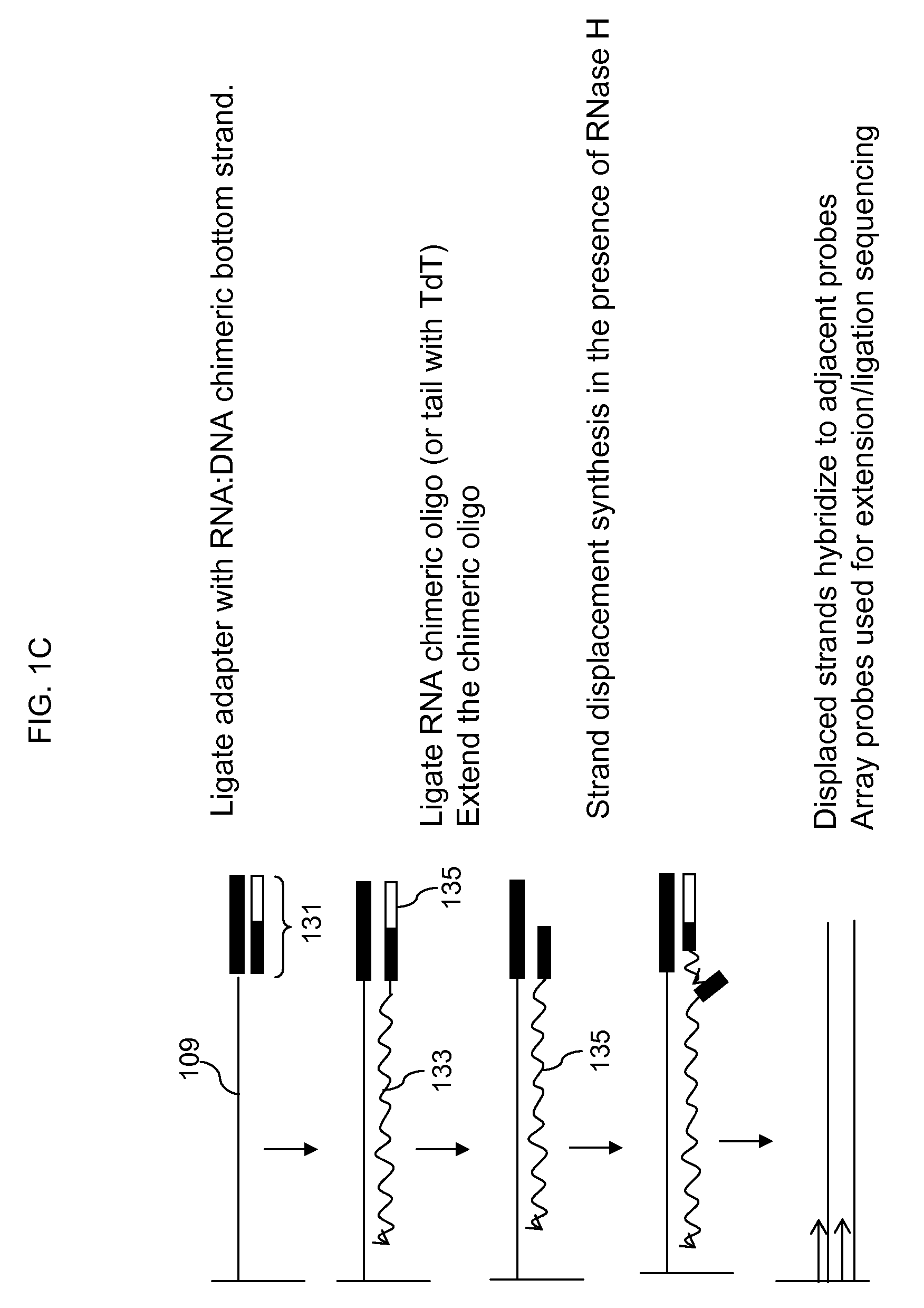
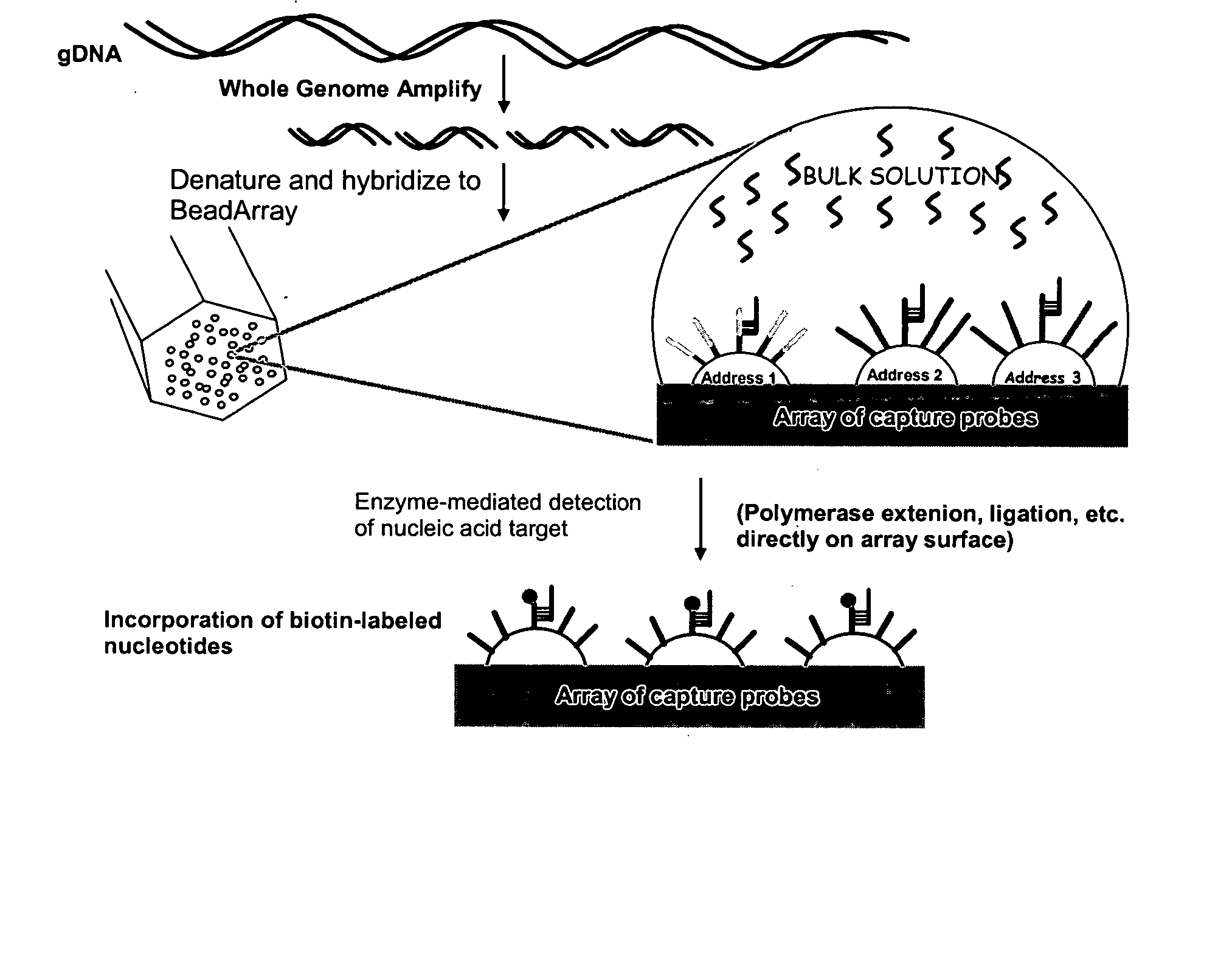
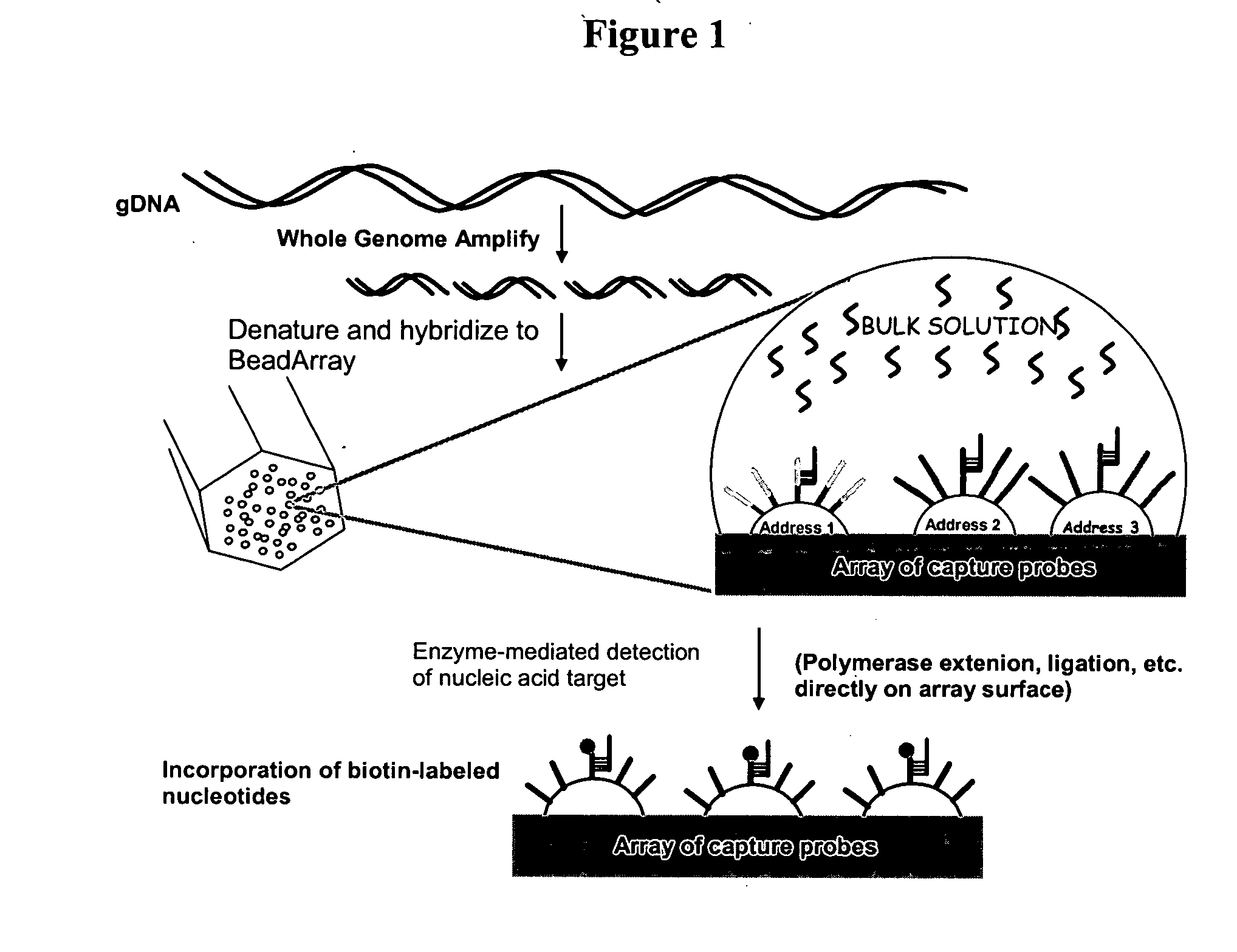
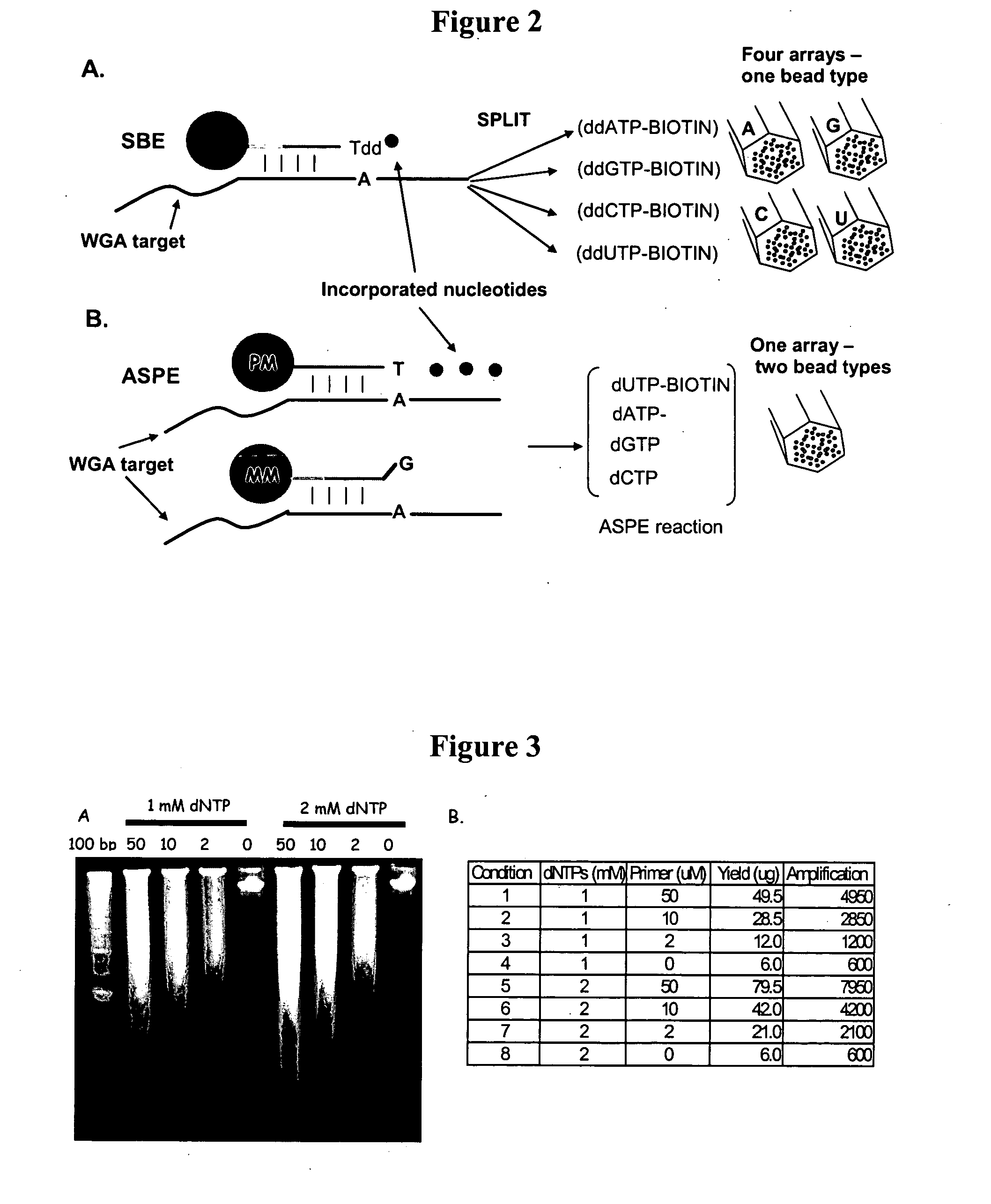
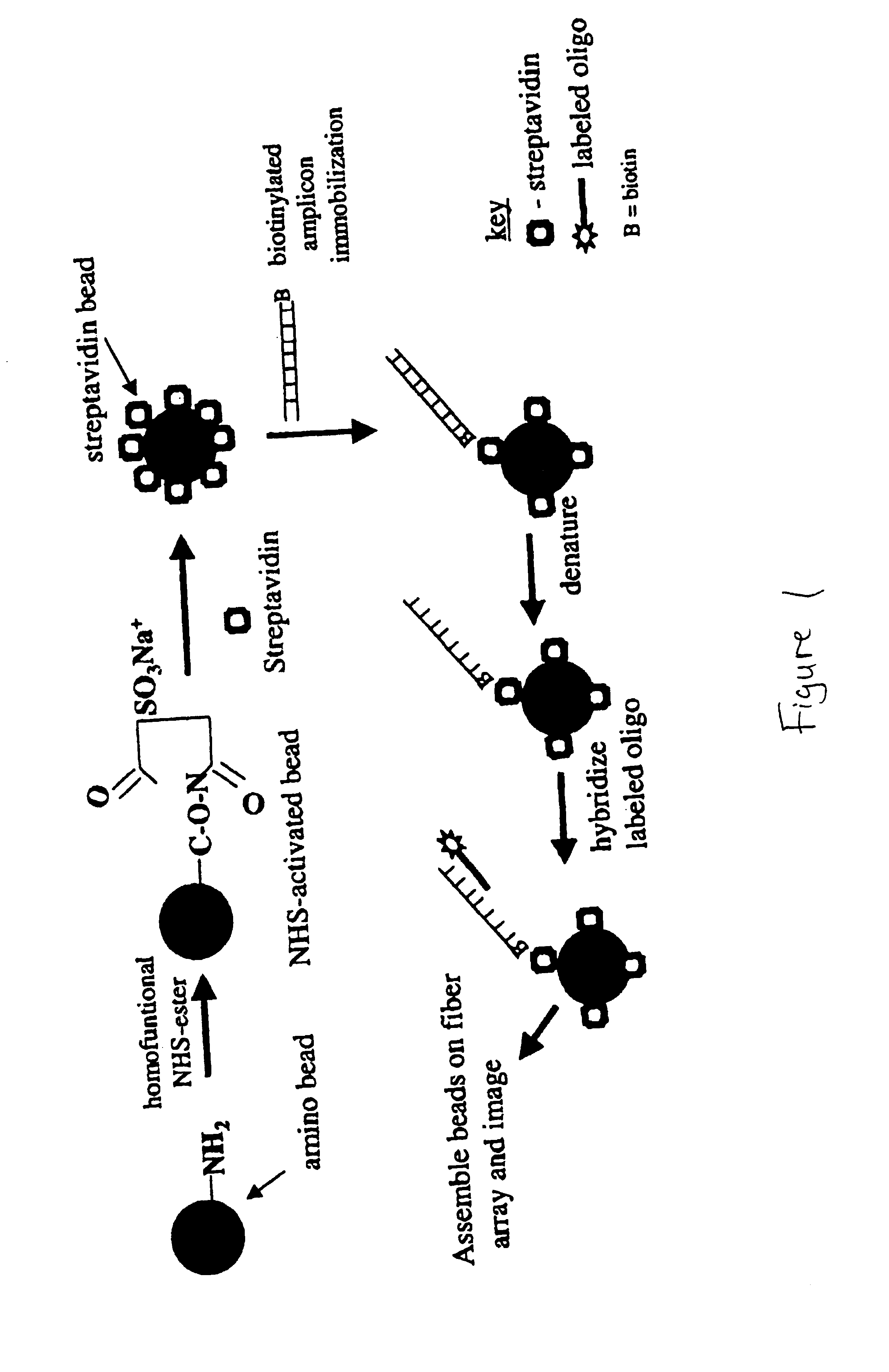
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
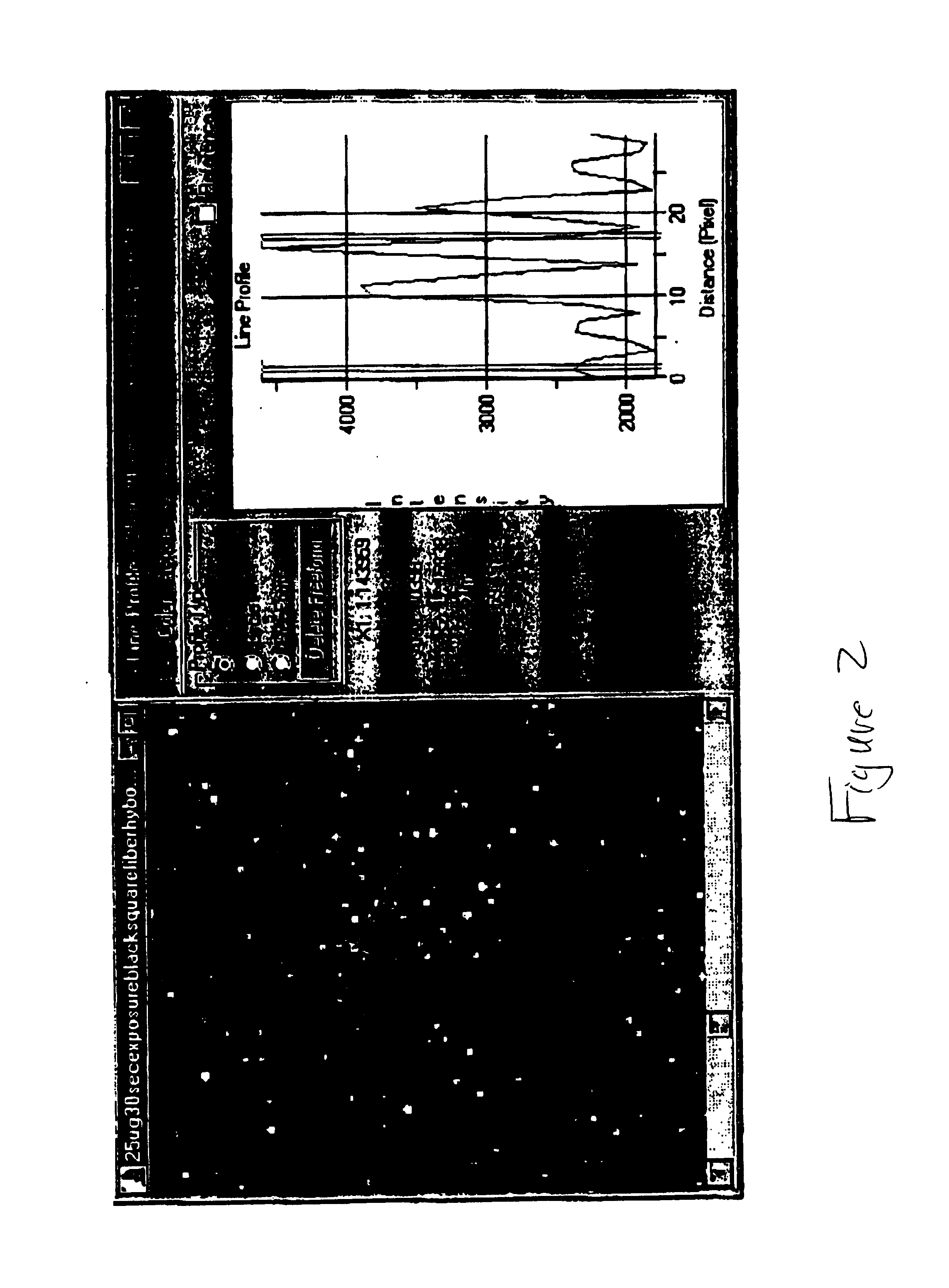
InactiveUS20090186349A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideMicrosphere
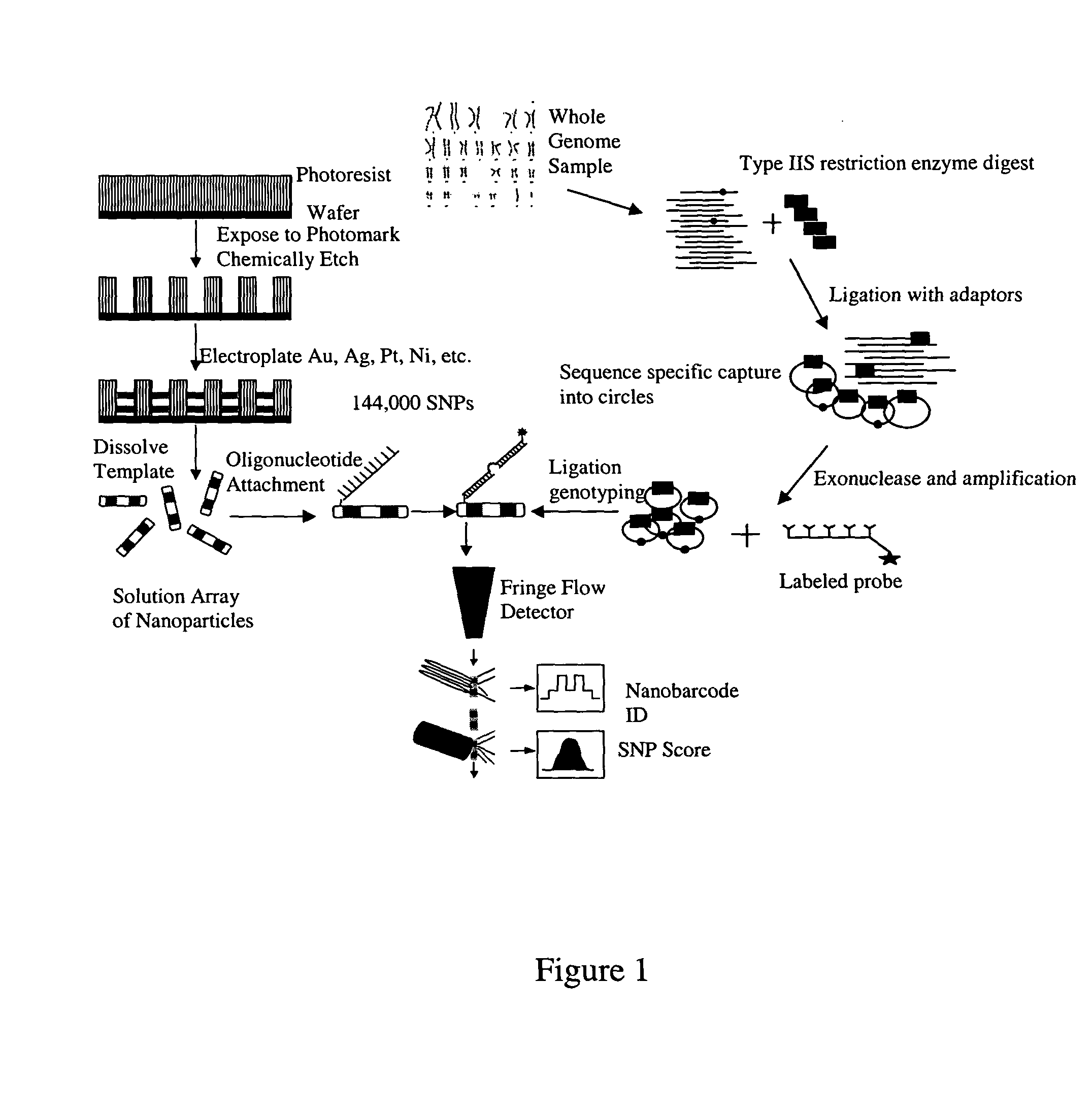
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
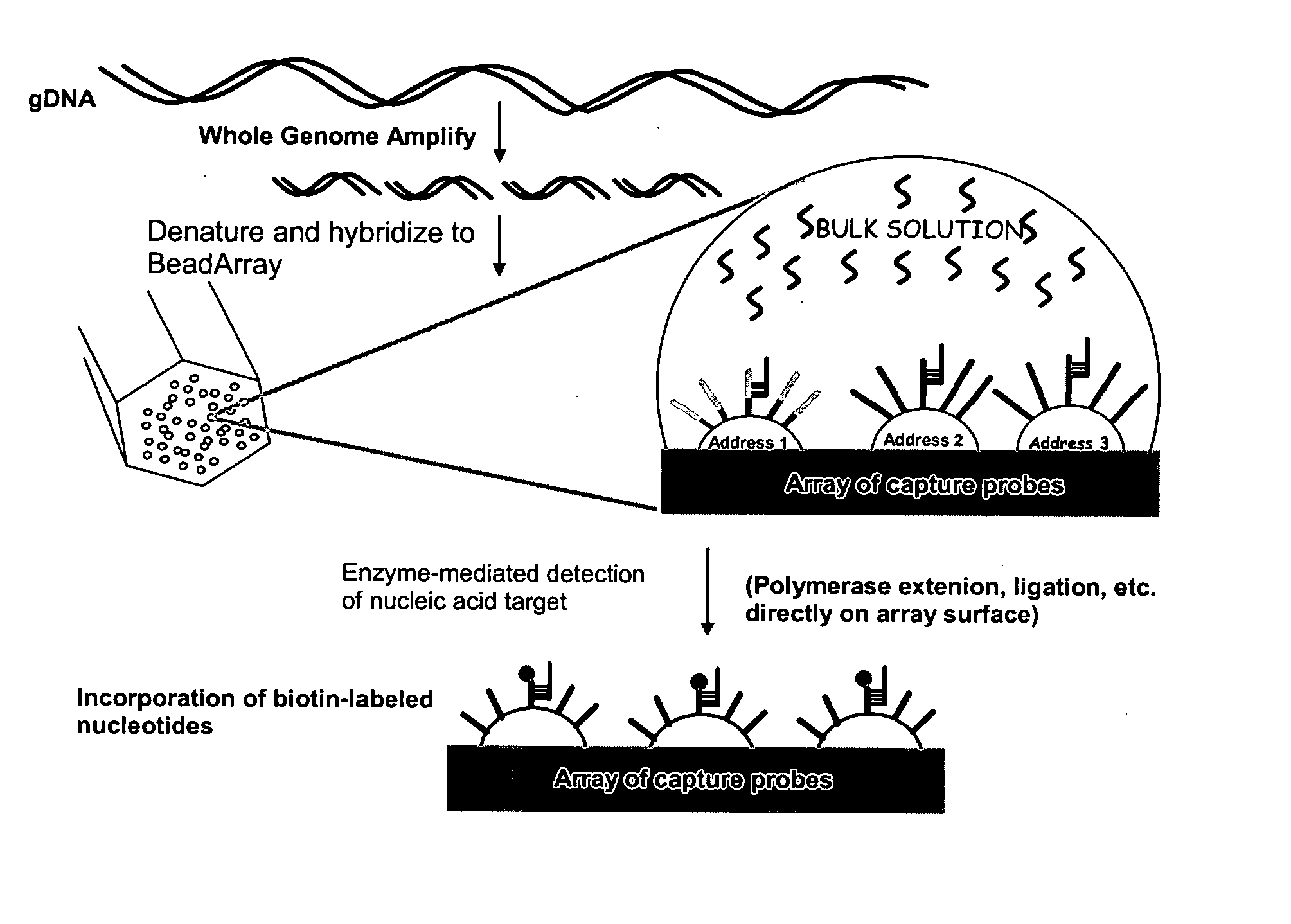
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
InactiveUS20050181394A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentGenotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Oligonucleotides for genotyping thymidylate synthase gene
ActiveUS20070031829A1Sensitive and convenient detectionEasy to aimSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenomic DNA
Oligonucleotides for genotyping the thymidylate synthase gene are provided. The number of tandem repeats in the promoter region of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the hybridization of an oligonucleotide of the invention to the genomic DNA of a subject. Therefore, the genotype of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the number of tandem repeats. The genotype relates to the responsiveness of a subject towards an antitumor agent.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis
InactiveUS20010051341A1Improve accuracy100% accurate detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPrenatal diagnosisBlood typing
The invention relates to a detection method performed on a maternal serum or plasma from a pregnant female, which method comprises the presence of a nucleic acid of fetal origin in the sample. The invention enables non-invasive prenatal diagnosis including, for example, sex determination, blood typing and other genotyping, and detection of pre-eclampsia in the mother.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
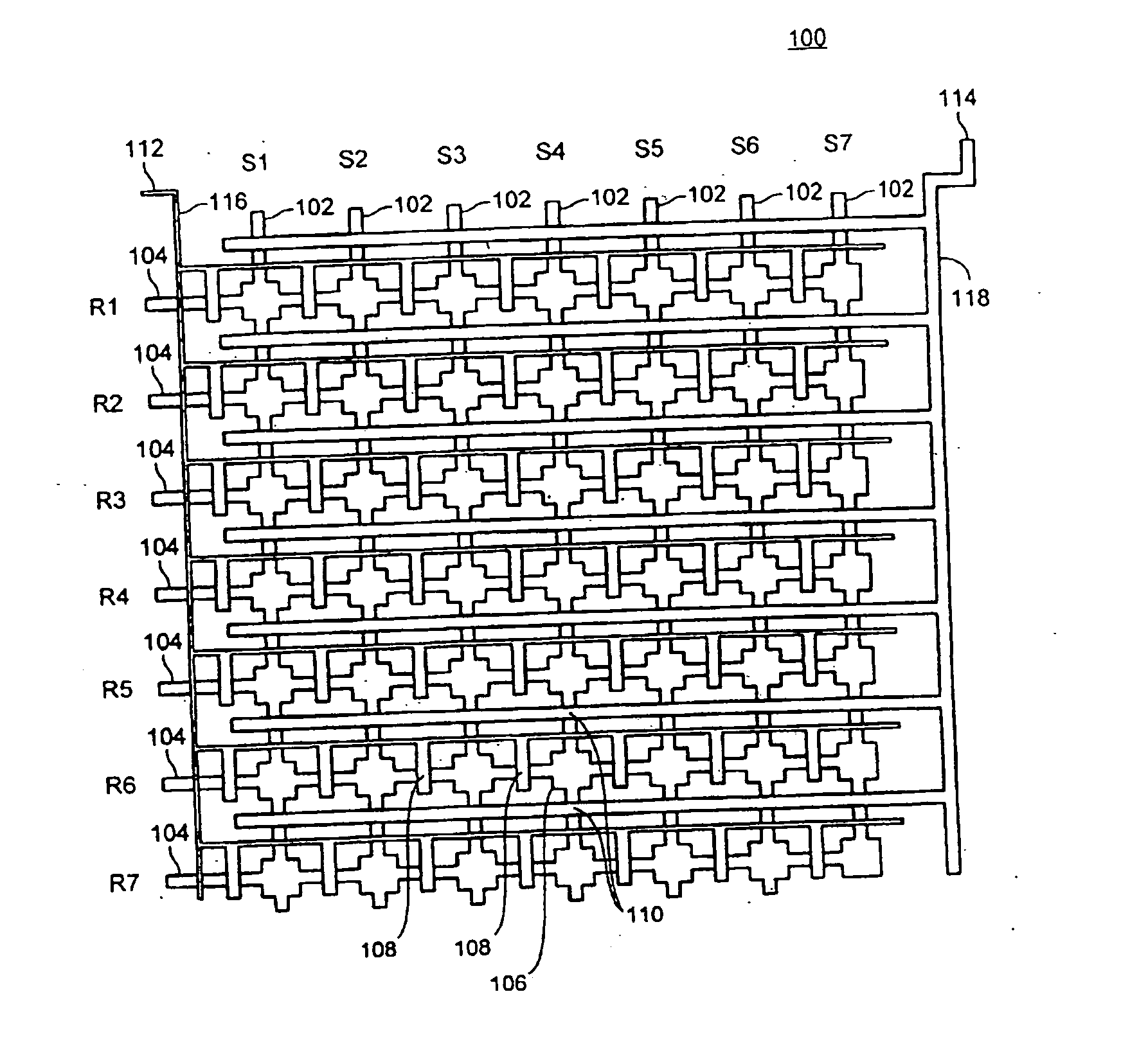
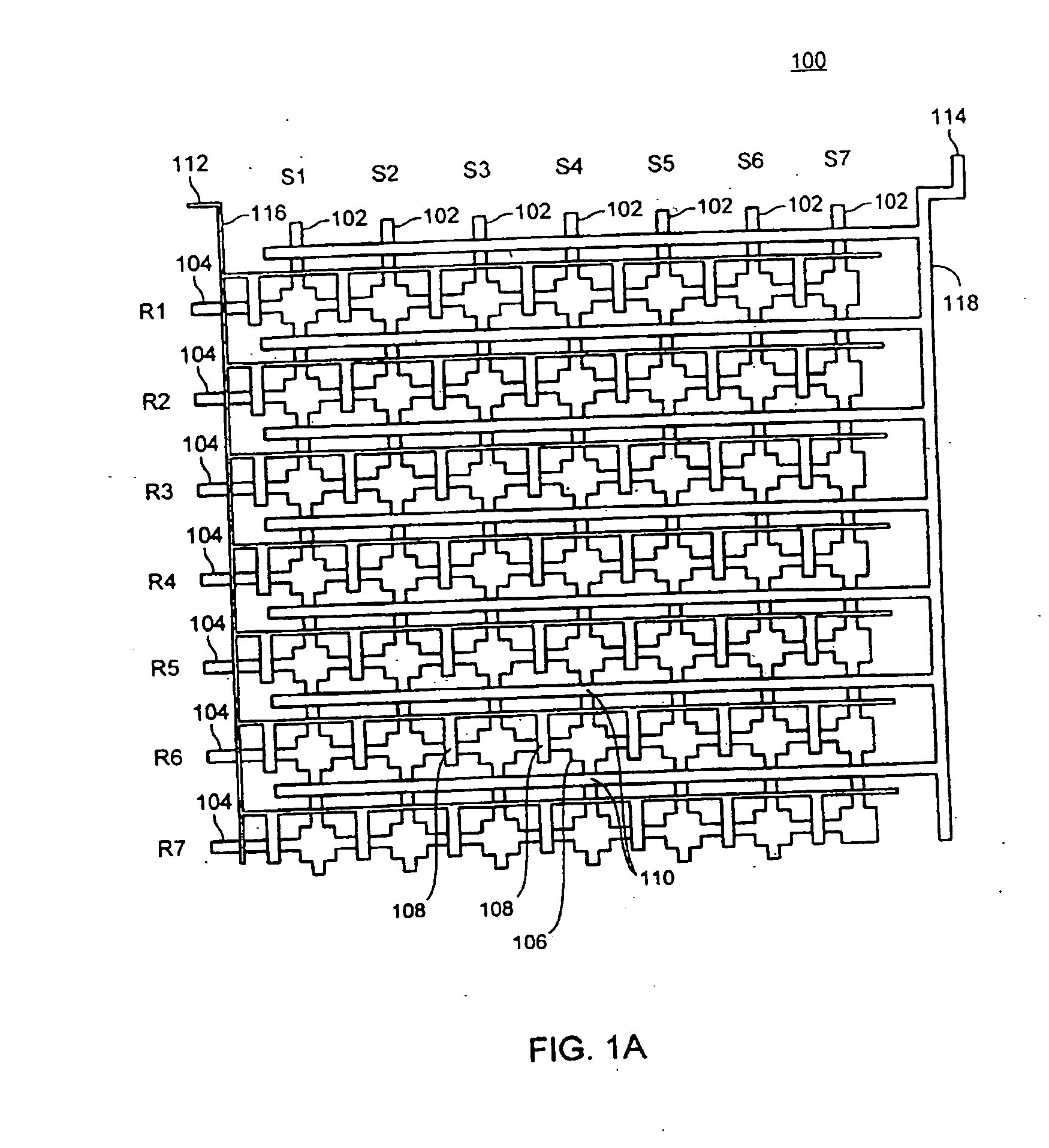
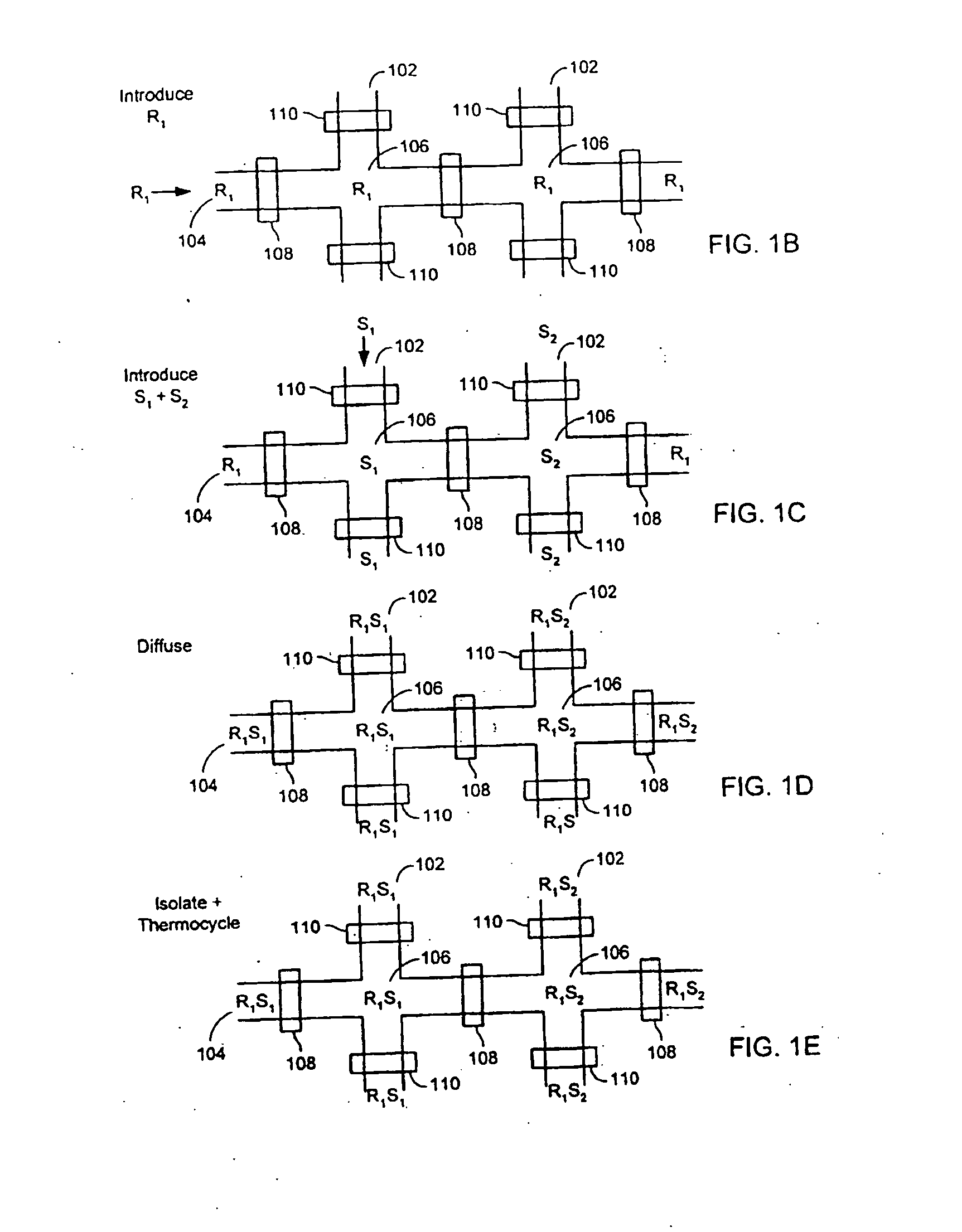
Microfluidic device and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050019792A1Prevent evaporationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlGenotyping
A variety of elastomeric-based microfluidic devices and methods for using and manufacturing such devices are provided. Certain of the devices have arrays of reaction sites to facilitate high throughput analyses. Some devices also include reaction sites located at the end of blind channels at which reagents have been previously deposited during manufacture. The reagents become suspended once sample is introduced into the reaction site. The devices can be utilized with a variety of heating devices and thus can be used in a variety of analyses requiring temperature control, including thermocycling applications such as nucleic acid amplification reactions, genotyping and gene expression analyses.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
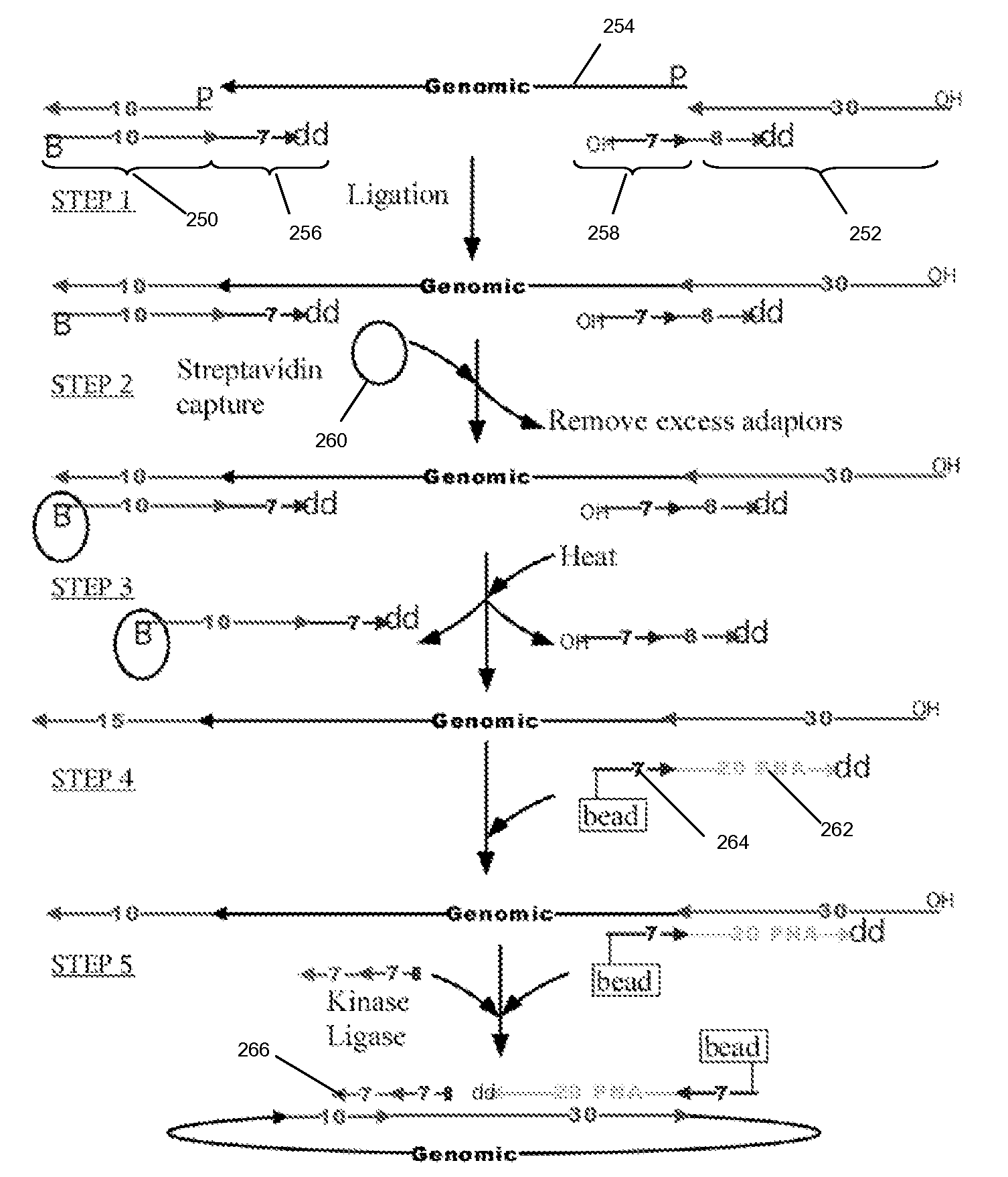
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Locus specific amplification using array probes
Methods are provided for multiplexed amplification of selected targets and analysis of the amplified targets. In preferred aspects the amplification and analysis take place on the same solid support and preferably in a localized area such as a bead or a feature of an array. In preferred aspects the analysis is a determination of sequence at one or more locations in the amplified target. The methods may be used for genotyping, sequencing and analysis of copy number.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Rice whole genome SNP chip and application thereof
ActiveCN102747138AImprove throughputGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementManufacturing technologyGermplasm
The present invention discloses a rice whole genome SNP chip and an application thereof. A method for preparing the chip comprises: (1) obtaining a first class of probes on a chip, wherein sequencing is performed to obtain a parental genome sequence, resequencing data of other rice varieties in a public database are combined, a Nipponbare genome is adopted as a reference sequence, a MAQ software is adopted to match and analyze all the sequencing data, and finally a SNP marker is screened; (2) obtaining a second class of probes on the chip, wherein a rice function gene is obtained from the public database, sequence difference reflecting gene function is searched, and a SNP / INDEL probe is designed according to the sequence difference; (3) adopting an infinium chip manufacturing technology to produce a SNP chip; and (4) testing accuracy and application efficiency of the chip. The chip of the present invention can be applicable for rice germplasm resource molecule marker fingerprint analysis, seed authenticity detection, filial generation genotyping, and other related researches.
Owner:先正达集团股份有限公司
Microfluidic devices and methods of using same
ActiveUS7666361B2Prevent evaporationHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementTemperature controlElastomer
A variety of elastomeric-based microfluidic devices and methods for using and manufacturing such devices are provided. Certain of the devices have arrays of reaction sites to facilitate high throughput analyses. Some devices also include reaction sites located at the end of blind channels at which reagents have been previously deposited during manufacture. The reagents become suspended once sample is introduced into the reaction site. The devices can be utilized with a variety of heating devices and thus can be used in a variety of analyses requiring temperature control, including thermocycling applications such as nucleic acid amplification reactions, genotyping and gene expression analyses.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Pyrophosphorolysis and incorporation of nucleotide method for nucleic acid detection
InactiveUS7090975B2Useful in detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDepolymerizationNucleic acid detection
Processes are disclosed using the depolymerization of a nucleic acid hybrid and incorporation of a suitable nucleotide to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze for the presence of predetermined nucleic acid target sequences. Applications of those processes include the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms, identification of single base changes, genotyping, medical marker diagnostics, mirosequencing, and.
Owner:PROMEGA
Genetic Variants as Markers for Use in Urinary Bladder Cancer Risk Assessment, Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment
InactiveUS20130296175A1Easy to analyzeNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBladder cancerGenotyping
Polymorphic variants that have been found to be associated with risk of urinary bladder cancer are provided herein. Such polymorphic markers are useful for diagnostic purposes, such as in methods of determining a susceptibility, and for prognostic purposes, including methods of predicting prognosis and methods of assessing an individual for probability of a response to therapeutic 5 agents, as further described herein. Further applications utilize the polymorphic markers of the invention include screening and genotyping methods. The invention furthermore provides related kits, and computer-readable media and apparatus.
Owner:DECODE GENETICS EHF +1
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Parallel genotyping of multiple patient samples
InactiveUS7285384B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMicrosphere
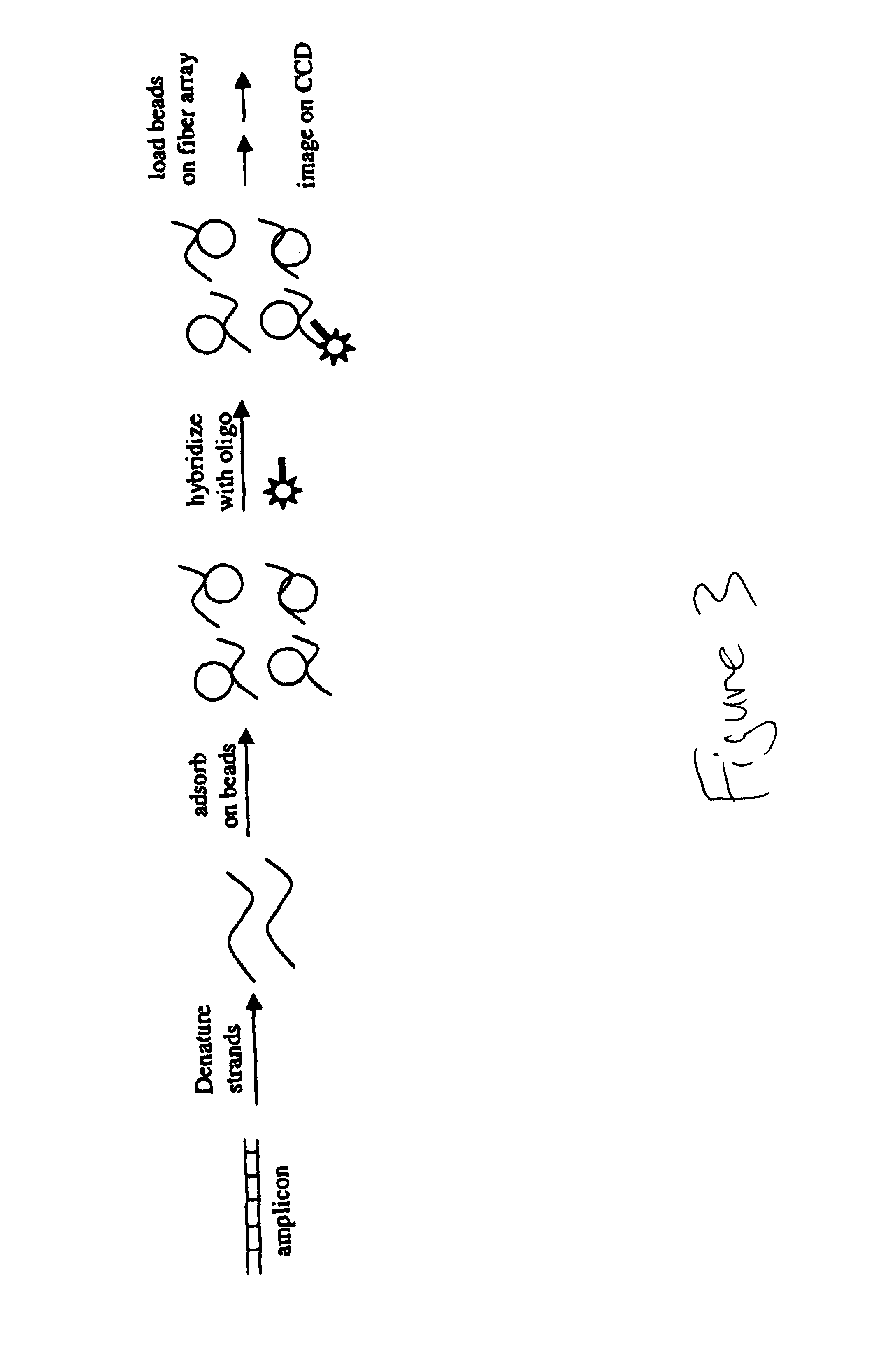
The present invention relates to parallel genotyping (or other sample analysis) of multiple patients by direct sample immobilization onto microspheres of an array. The patient beads can then be used in a variety of target analyte analyses.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Artificial intelligence and global normalization methods for genotyping
Described herein are systems and methods for normalizing data without the use of external controls. Also described herein are systems and methods for analyzing cluster data, such as genotyping data, using an artificial neural network.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
High throughput correlation of polymorphic forms with multiple phenotypes within clinical populations
A computer-assisted method of looking for pharmacologic targets, in which large numbers of persons are enrolled in drugh clinical trials, they are medically examined and documented, tissue samples are taken, the tissue samples are genotyped, and an examination is made of the genotypes to try to ascertain associations between the genotypes and the documented disease phenotypes of the patients.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Methods of detecting nucleic acid sequences with high specificity
InactiveUS20130023433A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
The invention relates to methods of detecting nucleic acids, including methods of detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences in multiplex branched-chain DNA assays, are provided. Nucleic acids captured on a solid support or suspending cells are detected, for example, through cooperative hybridization events that result in specific association of a label with the nucleic acids. The invention further relates to methods to improve probe hybridization specificity and their application in genotyping. The invention also relates to in situ detection of mis-joined nucleic acid sequences. The invention relates to reducing false positive signals and improve signal-to-background ratio in hybridization-based nucleic acid detection assay. The invention further relates to method to improve specificity in hybridization based nucleic acid using co-location probes. Compositions, tissue slides, sample of suspended cells, kits, and systems related to the methods are also described.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Methods for rapid detection and identification of biogents in epidemiological and forensic investigations
InactiveUS20070048735A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenotypingEpidemiologic survey
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic investigations by identification of bioagents associated with biowarfare and acts of terrorism or crime. The methods are also useful for epidemiological investigations by genotyping of bioagents.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Methods of genotyping using differences in melting temperature
InactiveUS20060172324A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide primersGenotyping
The present invention relates to the identification of a particular nucleotide polymorphism in a nucleic acid sample in a single reaction utilizing oligonucleotide primers with different melting temperature characteristics.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Detection of nucleic acid reactions on bead arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the use of microsphere arrays to detect and quantify a number of nucleic acid reactions. The invention finds use in genotyping, i.e. the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids, particularly alterations such as nucleotide substitutions (mismatches) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Similarly, the invention finds use in the detection and quantification of a nucleic acid target using a variety of amplification techniques, including both signal amplification and target amplification. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used in nucleic acid sequencing reactions as well. All applications can include the use of adapter sequences to allow for universal arrays.
Owner:GUNDERSON KEVIN +2
Method for genotyping polymorphisms in humans
ActiveUS7300788B2Easy to analyze and useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides nucleic acid sequences that are complementary, in one embodiment, to a wide variety of human polymorphisms. The invention provides the sequences in such a way as to make them available for a variety of analyses including genotyping a large number of SNPs in parallel. The invention also provides a collection of human SNPs that is useful for genetic analysis within and across populations. As such, the invention relatesd to diverse fields impacted by the nature of genetics, including biology, medicine, and medical diagnostics.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nucleic acid probes and methods to detect and/or quantify nucleic acid analytes
InactiveUS6902900B2Enhance binding affinityLow fluorescenceMonoazo dyesSugar derivativesDouble strandedFluorescence
The invention comprises novel methods and strategies to detect and / or quantify nucleic acid analytes. The methods involve nucleic acid probes with covalently conjugated dyes, which are attached either at adjacent nucleotides or at the same nucleotide of the probe and novel linker molecules to attach the dyes to the probes. The nucleic acid probes generate a fluorescent signal upon hybridization to complementary nucleic acids based on the interaction of one of the attached dyes, which is either an intercalator or a DNA groove binder, with the formed double stranded DNA. The methods can be applied to a variety of applications including homogeneous assays, real-time PCR monitoring, transcription assays, expression analysis on nucleic acid microarrays and other microarray applications such as genotyping (SNP analysis). The methods further include pH-sensitive nucleic acid probes that provide switchable fluorescence signals that are triggered by a change in the pH of the medium.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Hppd-inhibitor herbicide tolerance
ActiveUS20110185445A1Negatively impactingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePlant cell
This invention relates generally to the detection of genetic differences among soybeans. More particularly, the invention relates to soybean quantitative trait loci (QTL) for tolerance or sensitivity to HPPD-inhibitor herbicides, such as mesotrione and isoxazole herbicides, to soybean plants possessing these QTLs, which map to a novel chromosomal region, and to genetic markers that are indicative of phenotypes associated with tolerance, improved tolerance, susceptibility, or increased susceptibility. Methods and compositions for use of these markers in genotyping of soybean and selection are also disclosed, as are methods and compositions for use of these markers in selection and use of herbicides for weed control. Also disclosed are isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides relating to such tolerance or sensitivity and methods of introgressing such tolerance into a plant by breeding or transgenically or by a combination thereof. Plant cells, plants, and seeds produced are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for fabricating a biochip using the high density carbon nanotube film or pattern
InactiveUS20050019791A1Improve defectsUtility and advantageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical conductorFluorescence
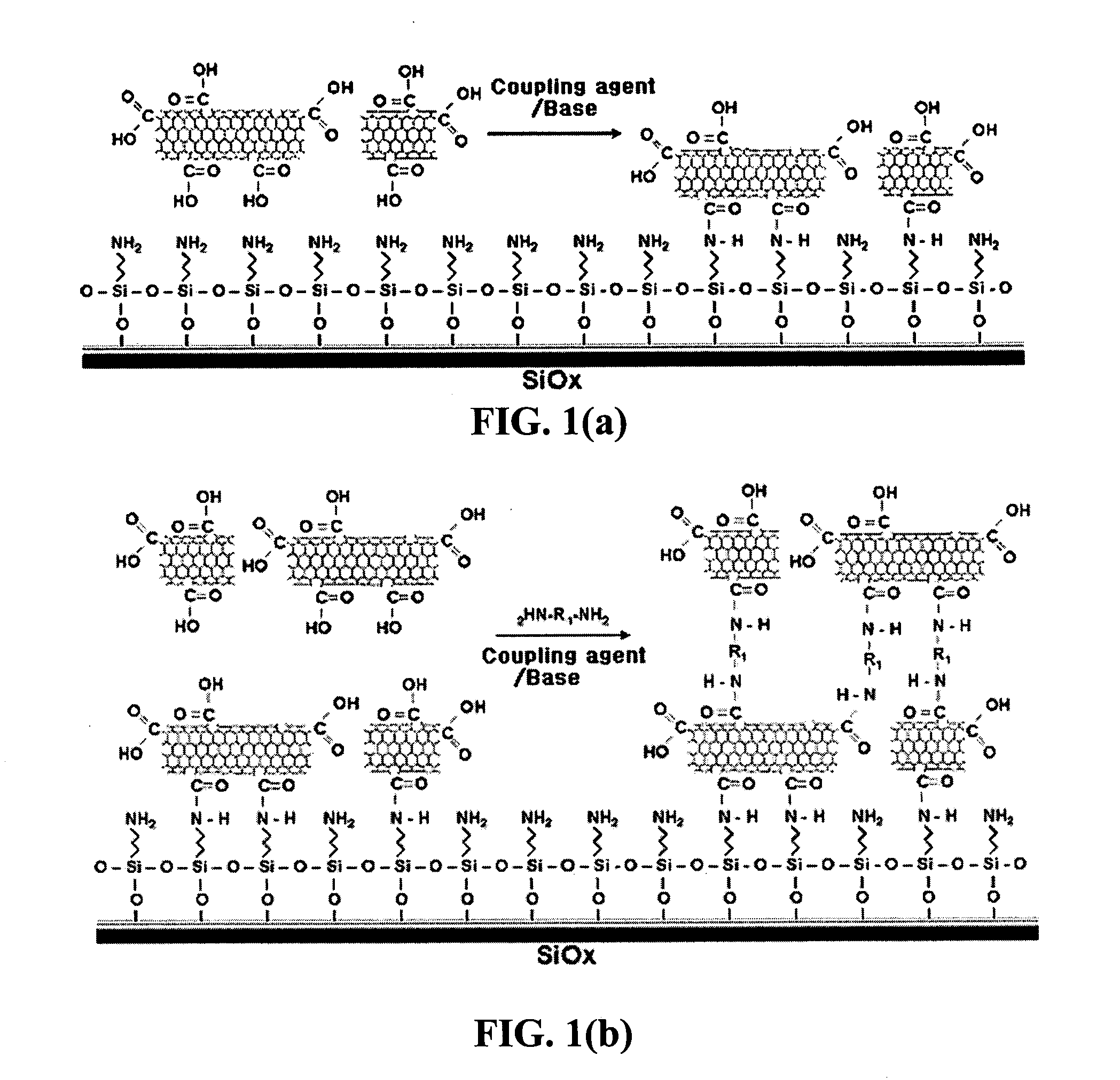
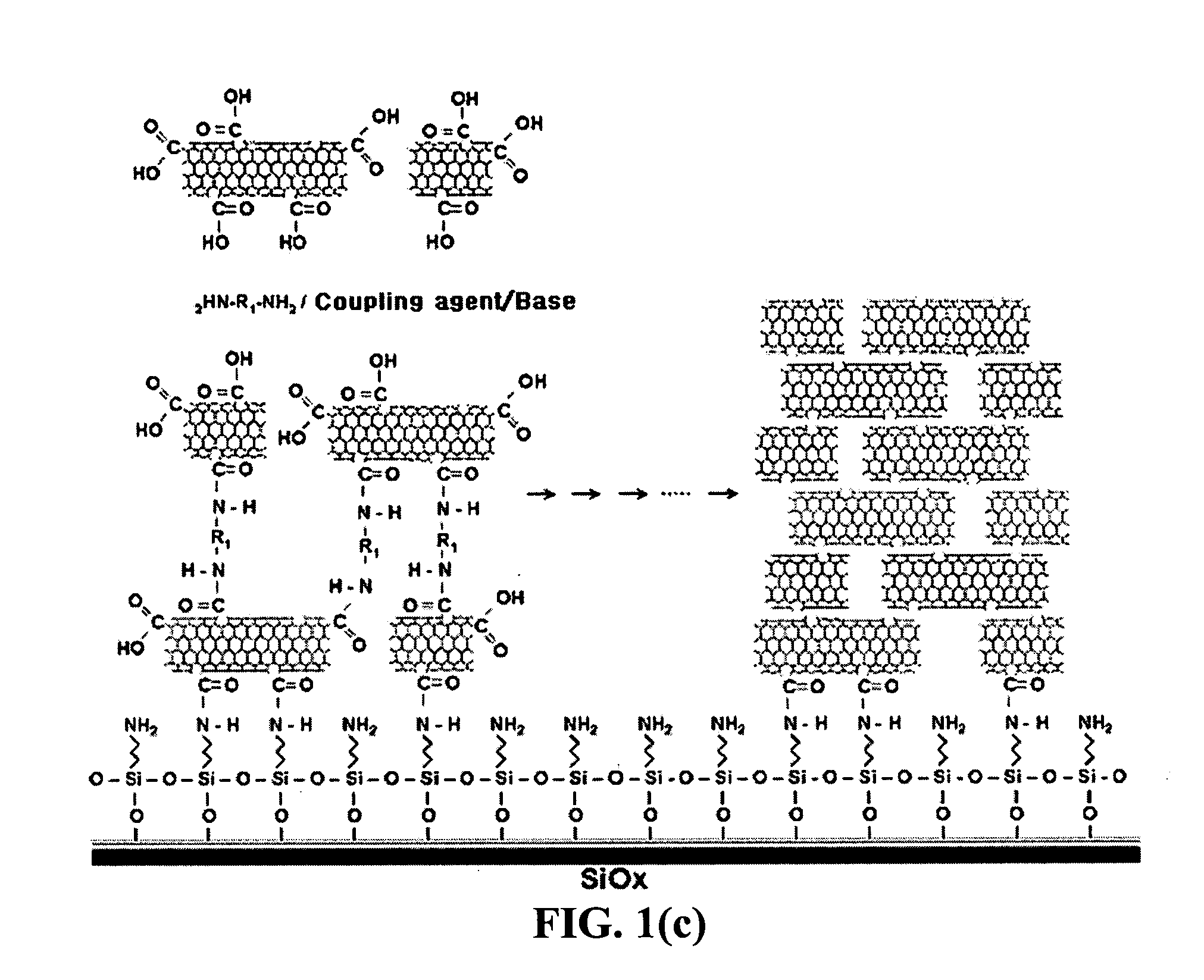
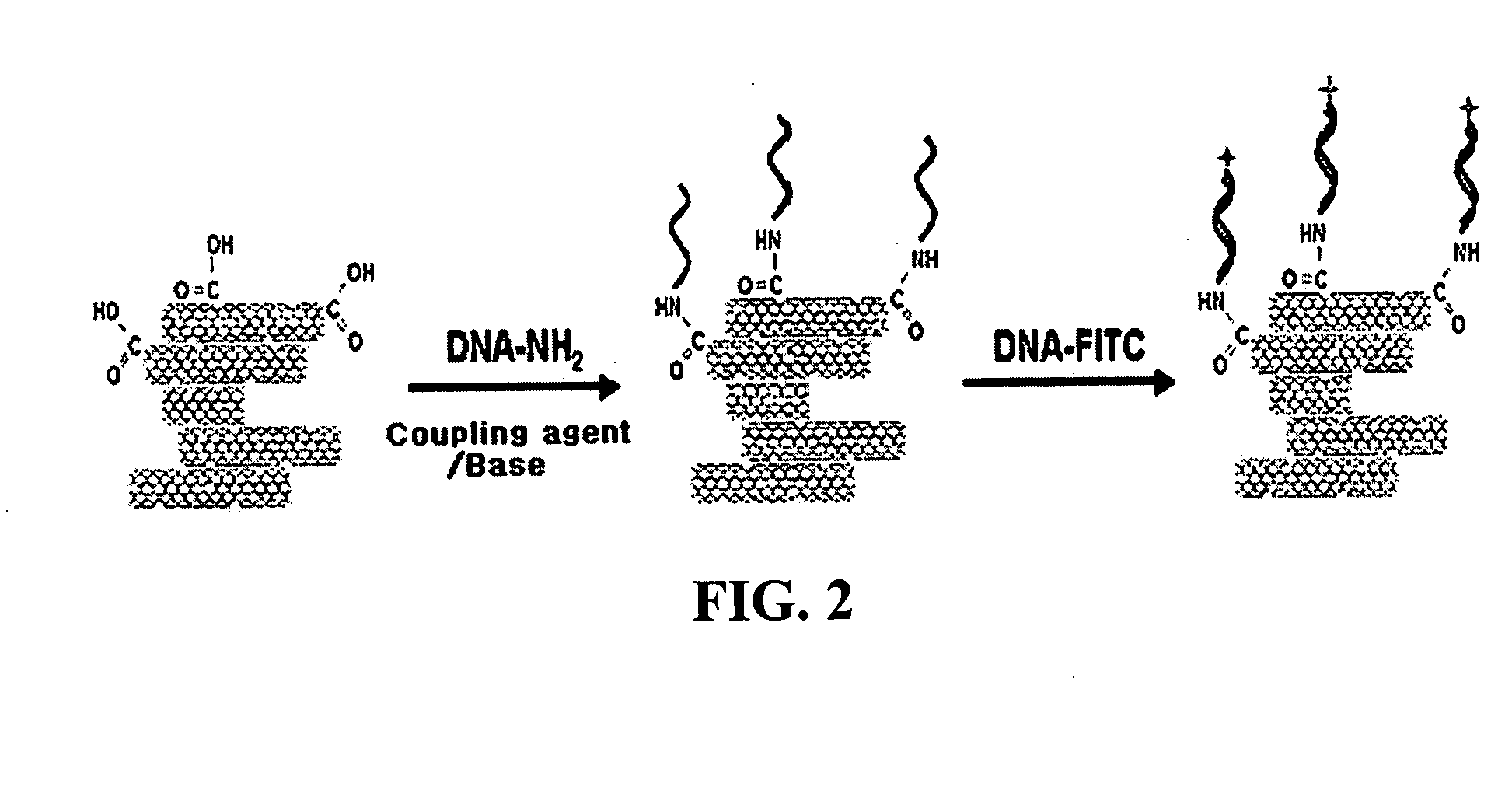
The present invention relates to a CNT-biochip comprising a bio-receptor which is attached by means of an exposed chemical functional group on a surface of a high density CNT film or pattern which is produced by laminating repeatedly carbon nanotubes (CNT) by chemical bond on the substrate modified with amine groups, and a method for fabricating the same. According to the present invention, it is possible to fabricate various types of CNT-biochips by chemical or physicochemical bonding of various bio-receptors to a CNT pattern (or film) containing exposed carboxyl groups or a CNT pattern (or film) modified by various chemical functional groups. Also, it is possible to fabricate a CNT-biochip comprising bio-receptors attached evenly with high density on a surface of a CNT film where chemical functional groups are abundant and present evenly. Further, the CNT-biochip is applicable to next generation biochips which measure an electrical or electrochemical signal using both conductor and semiconductor properties of the CNT, thereby not needing labeling. Particularly, upon fluorescent measurement of DNA hybridization using the CNT-DNA chip according to the present invention, it is possible to show more distinct signals, thereby producing excellent results. The CNT-DNA chip is useful for genotyping, mutation detection, pathogen identification and the like.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
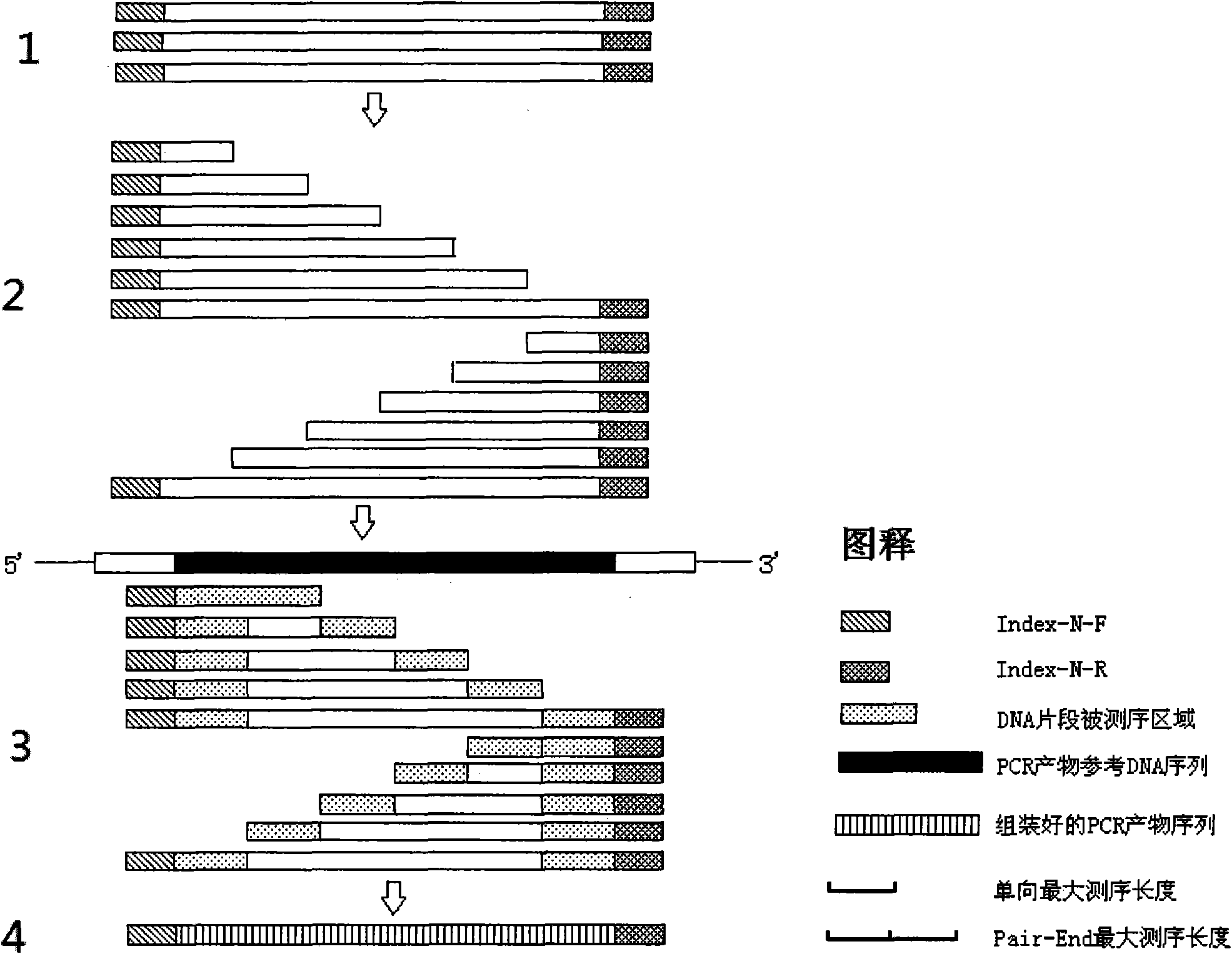
DNA molecular label technology and DNA incomplete interrupt policy-based PCR sequencing method
The invention provides a PCR sequencing method. The length of a PCR product which can be completely measured by a sequencer exceeds the measuring length of the sequencer through the combination of a primer label, a DNA incomplete interrupt policy and second-generation sequencing technology (Pair-End sequencing technology) and by taking full advantage of the characteristics of high flux and low cost of a second-generation sequencer at the same time, so that the application range of the method is greatly widened. At the same time, the invention also provides the primer label for the PCR sequencing method and the application of the method to gene typing, particularly to HLA analysis.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com