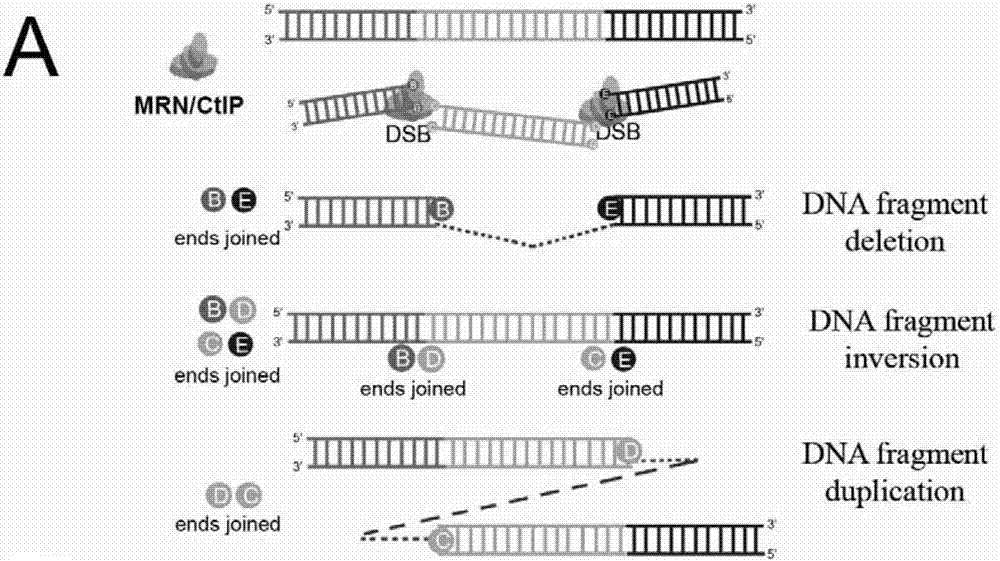
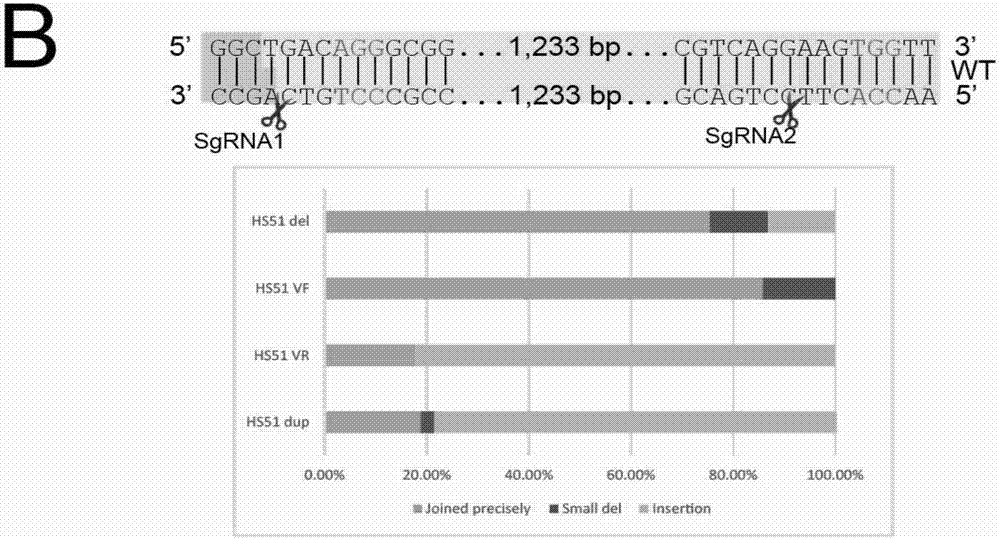
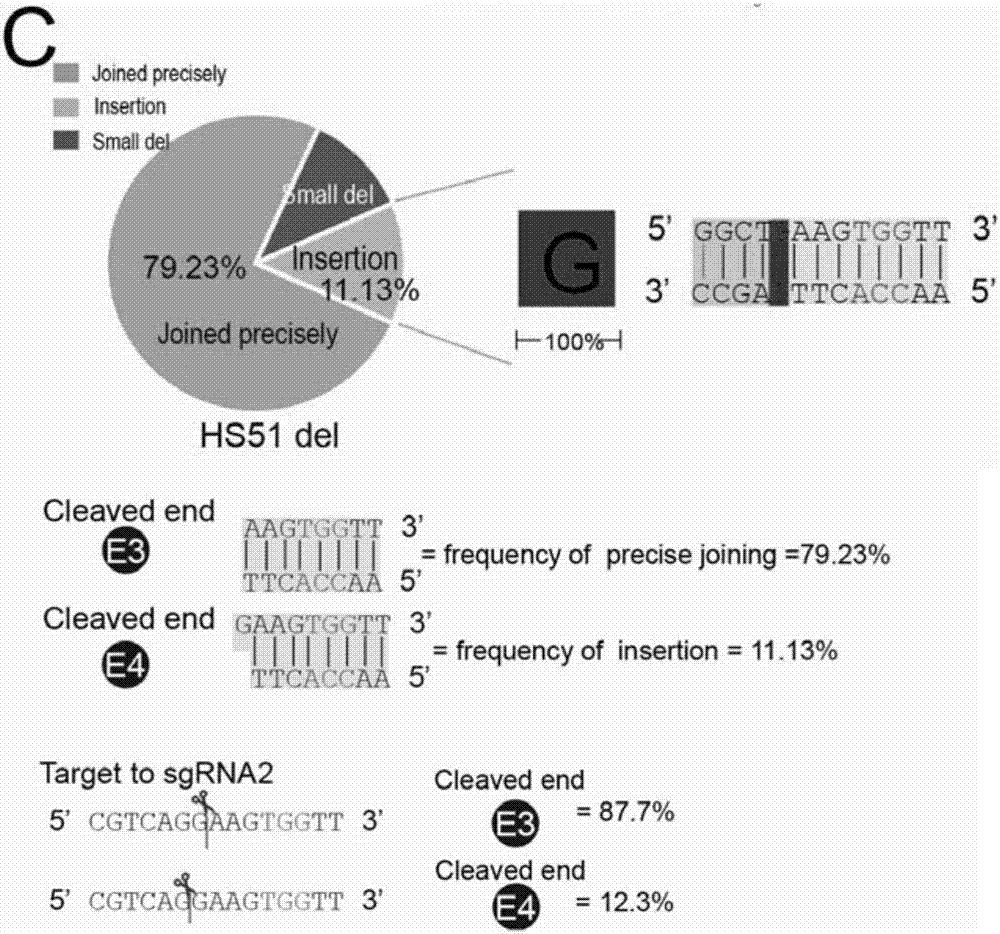
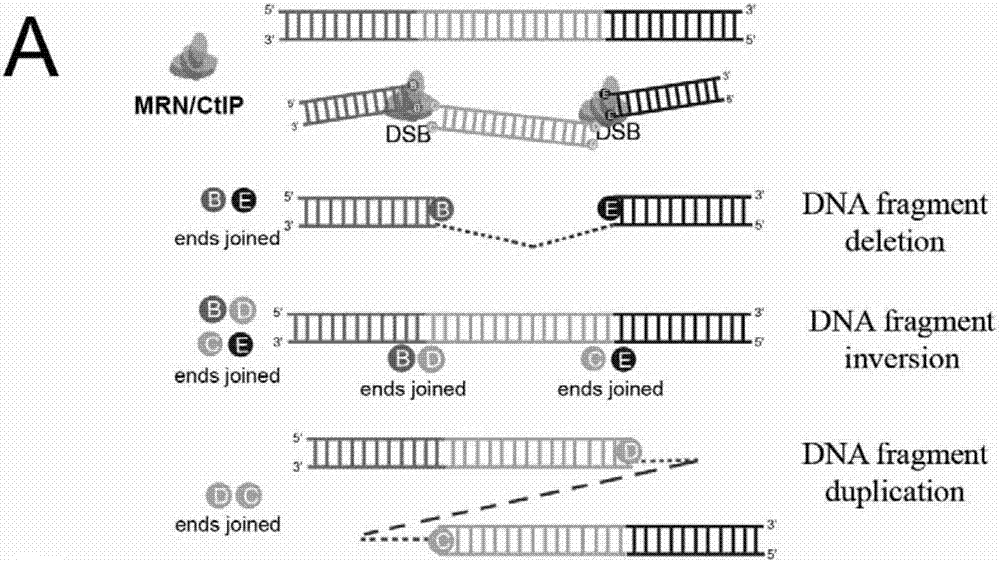
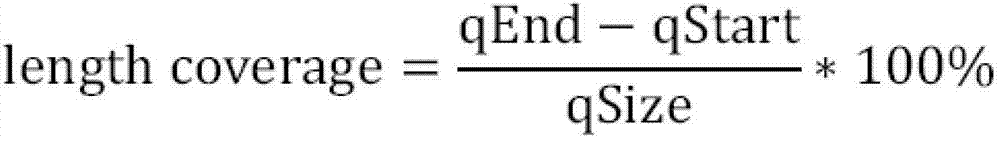Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
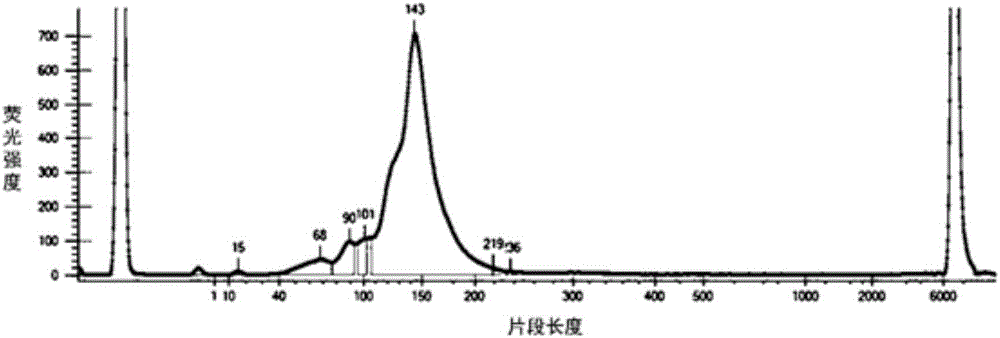
226 results about "Genomic Segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genomic segment extracted from a library e.g. BAC or YAC library to be used in the genetic manipulation of the animal model.
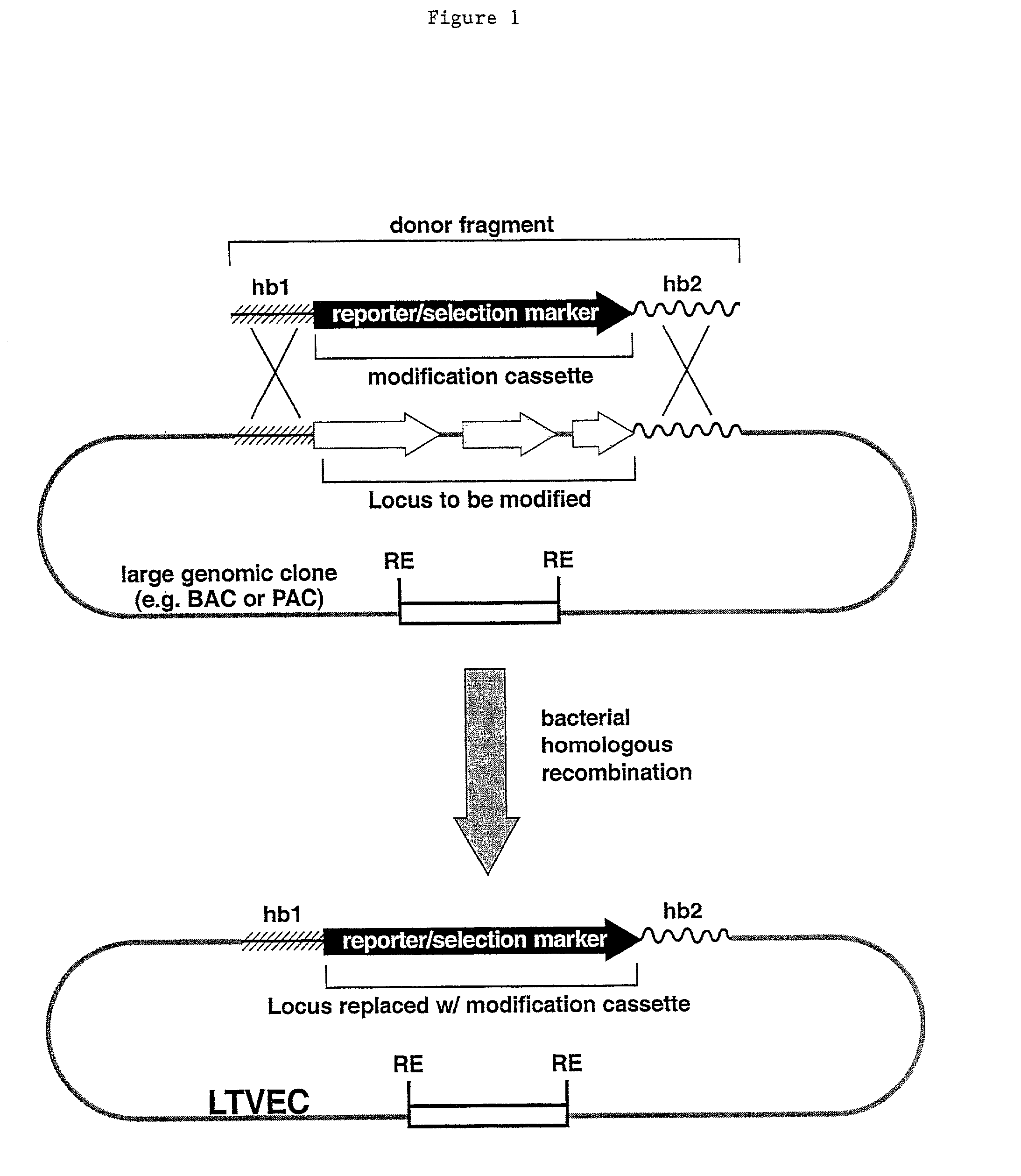
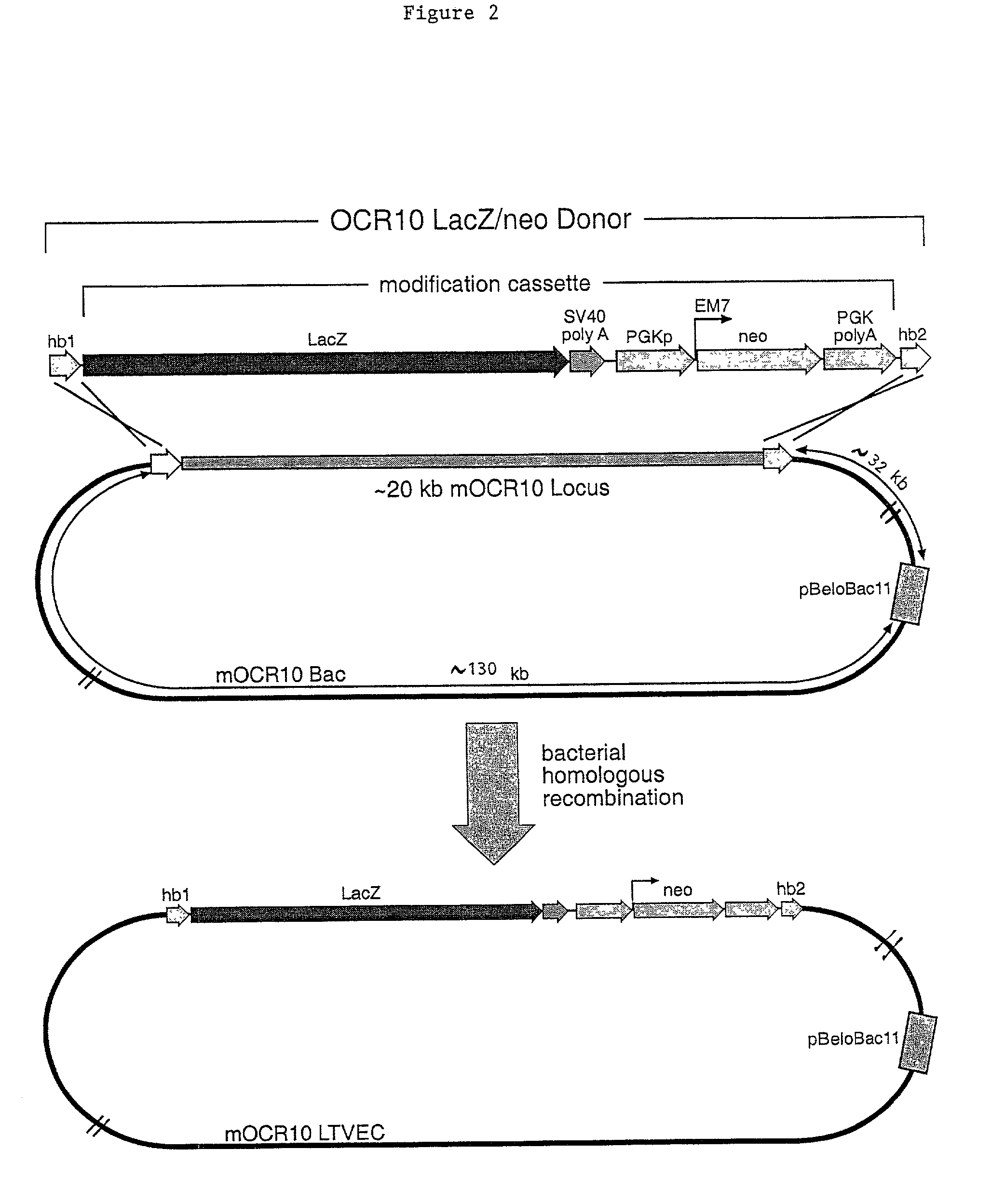
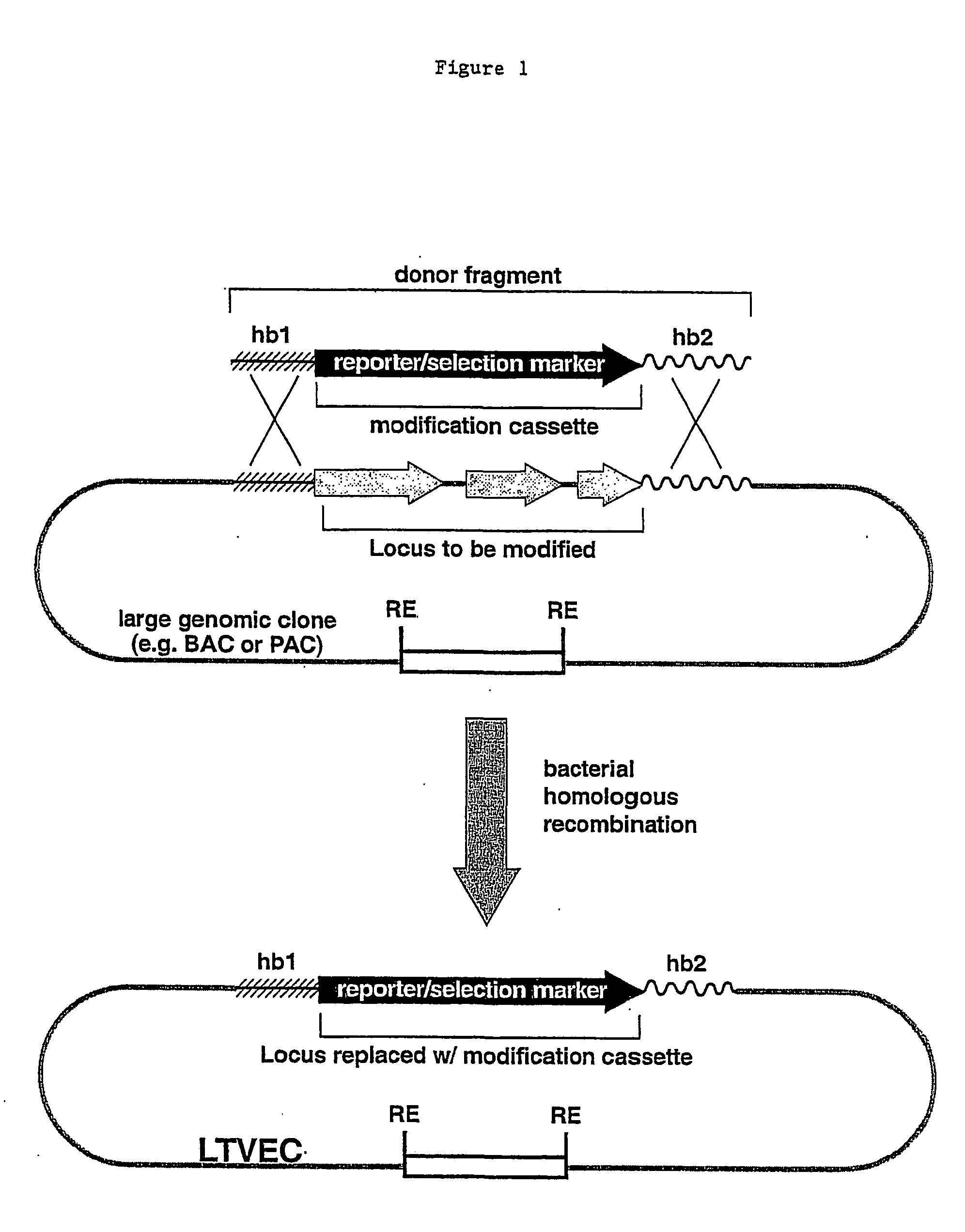
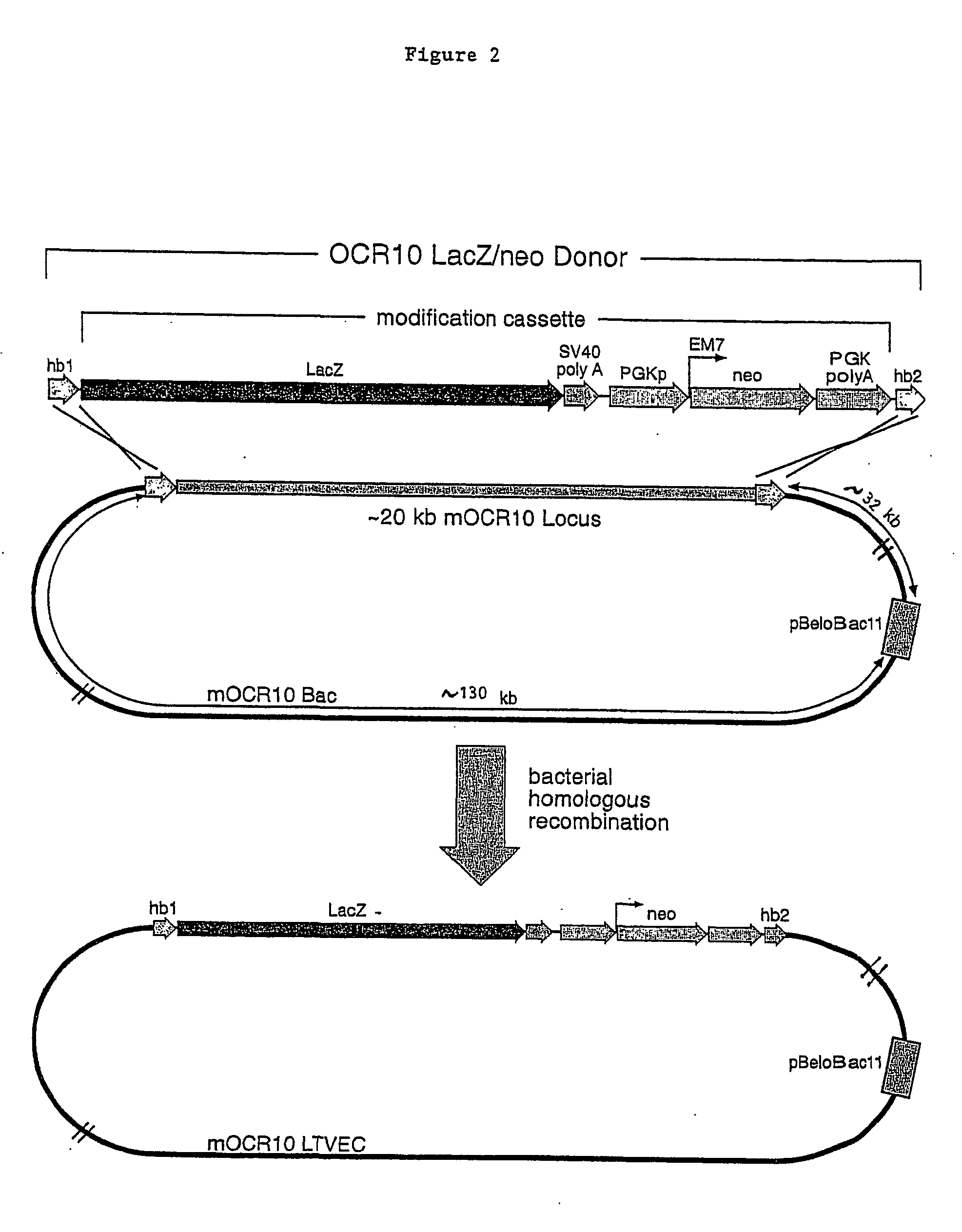
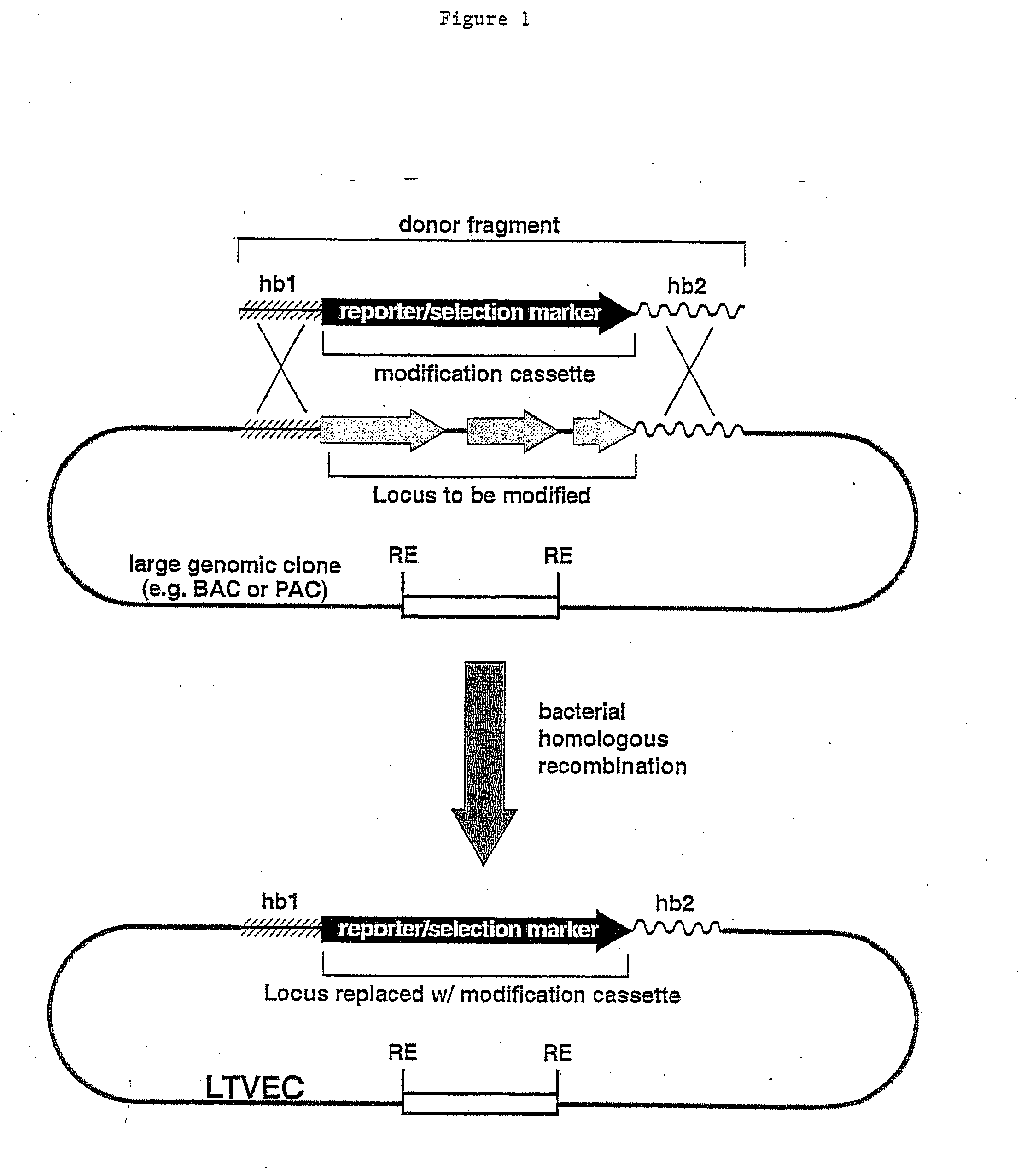
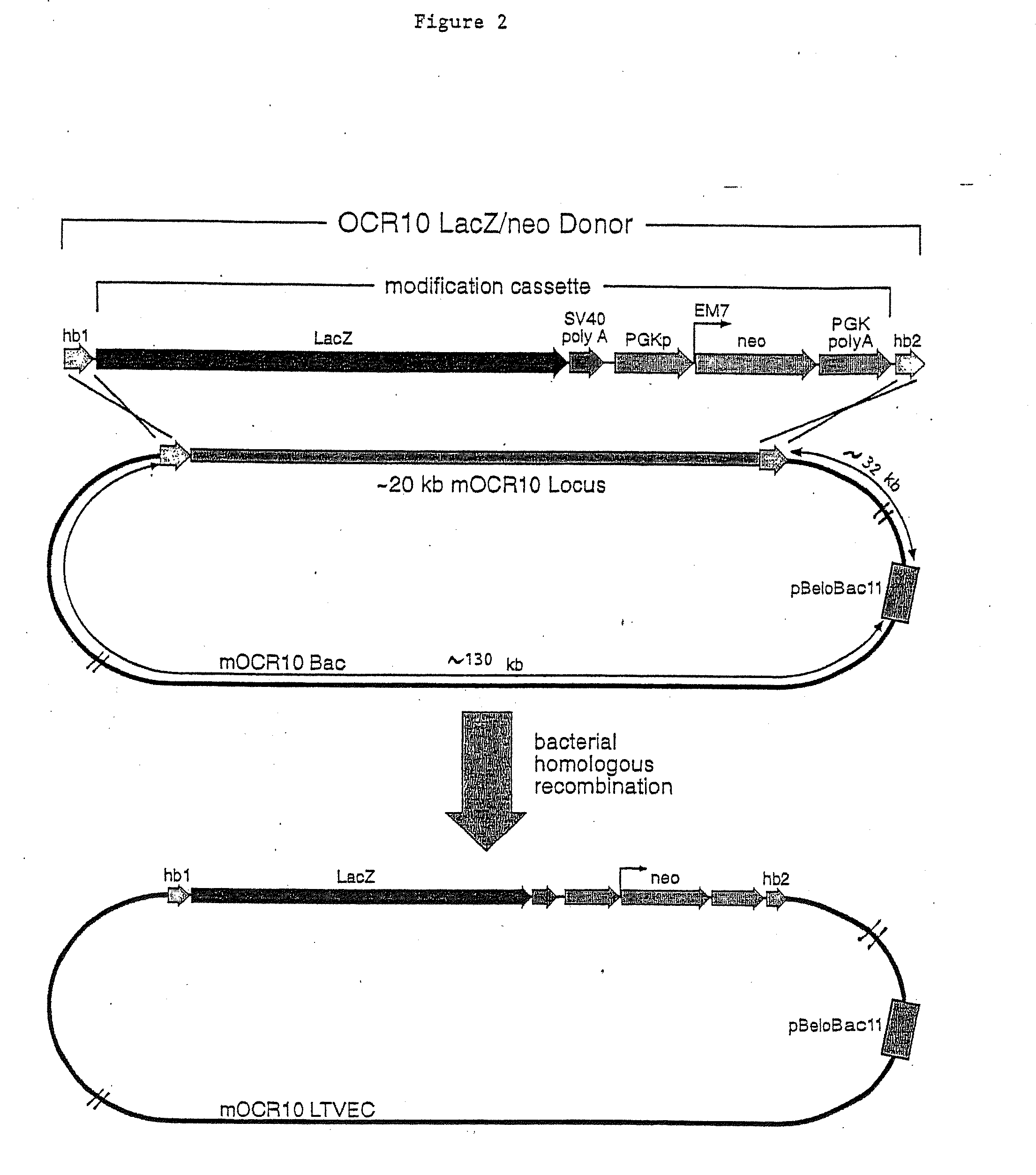
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
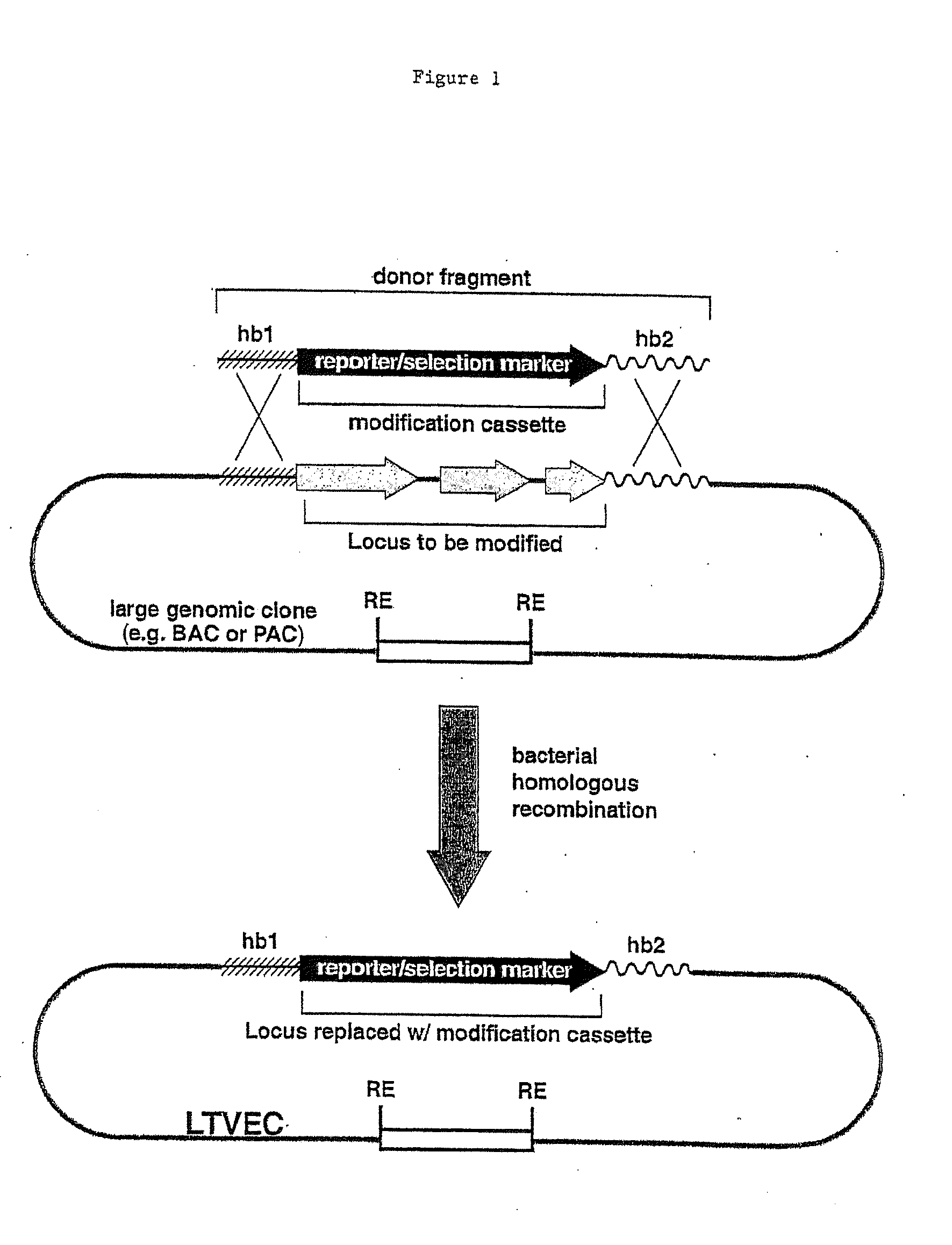
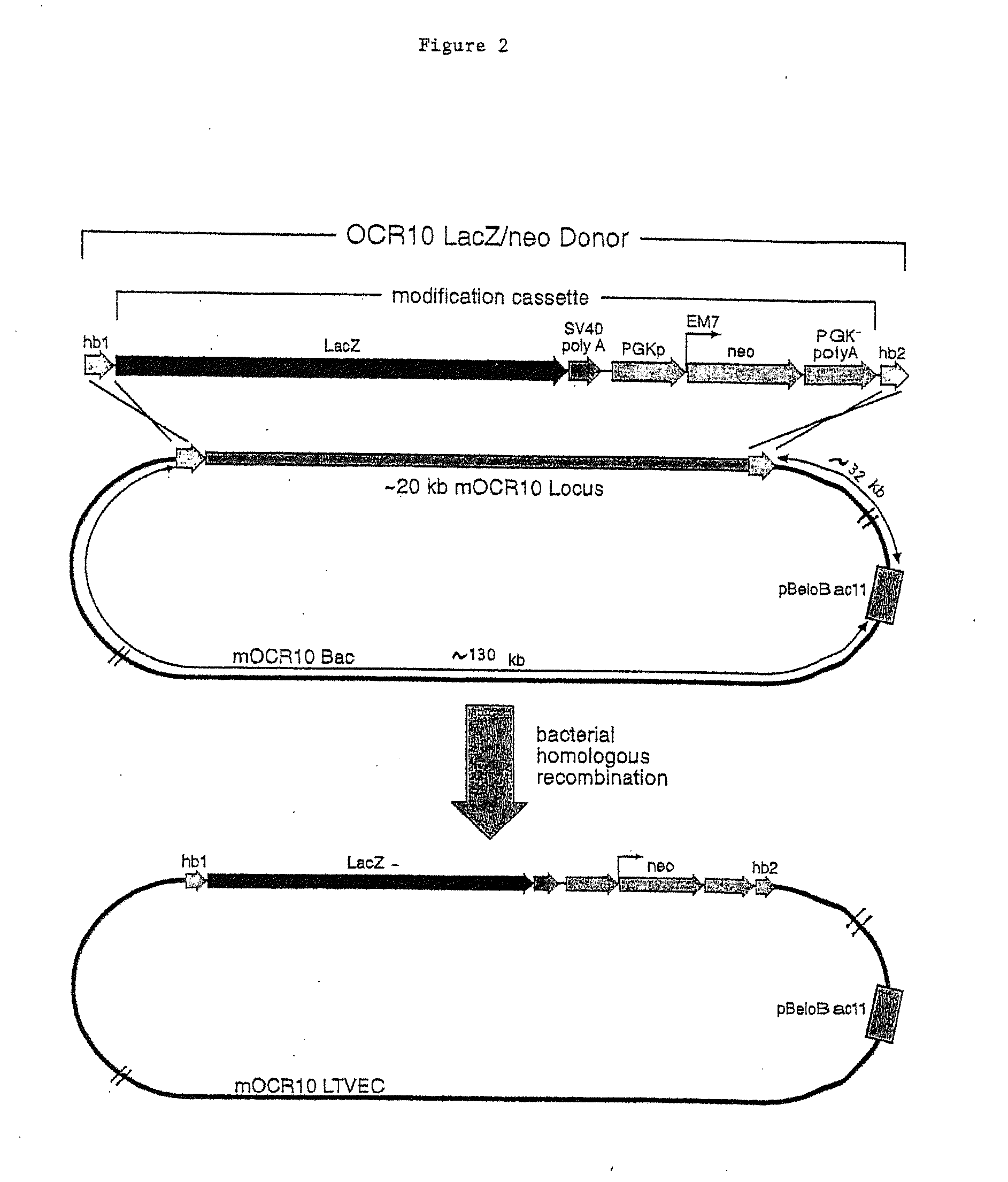
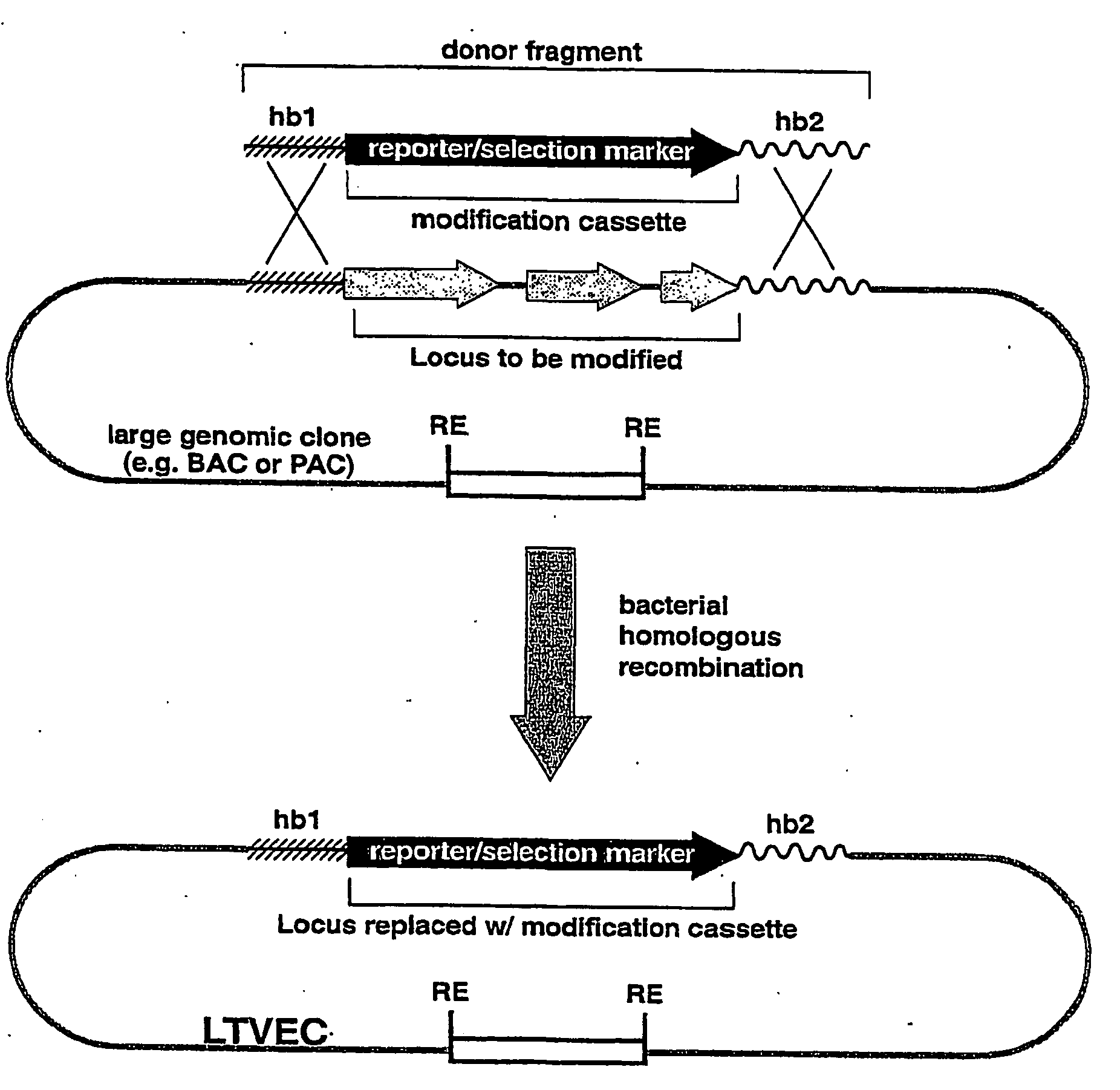
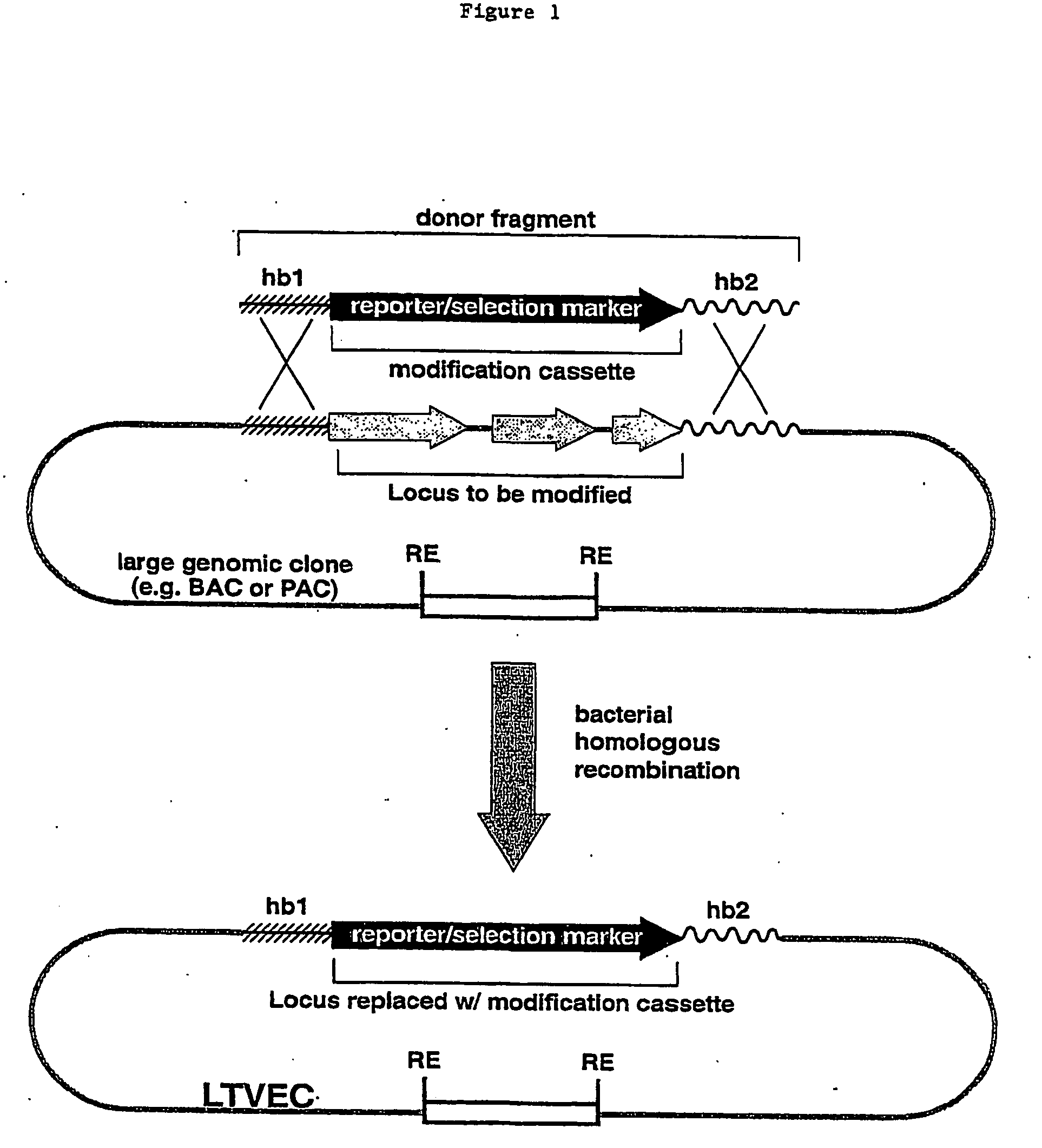
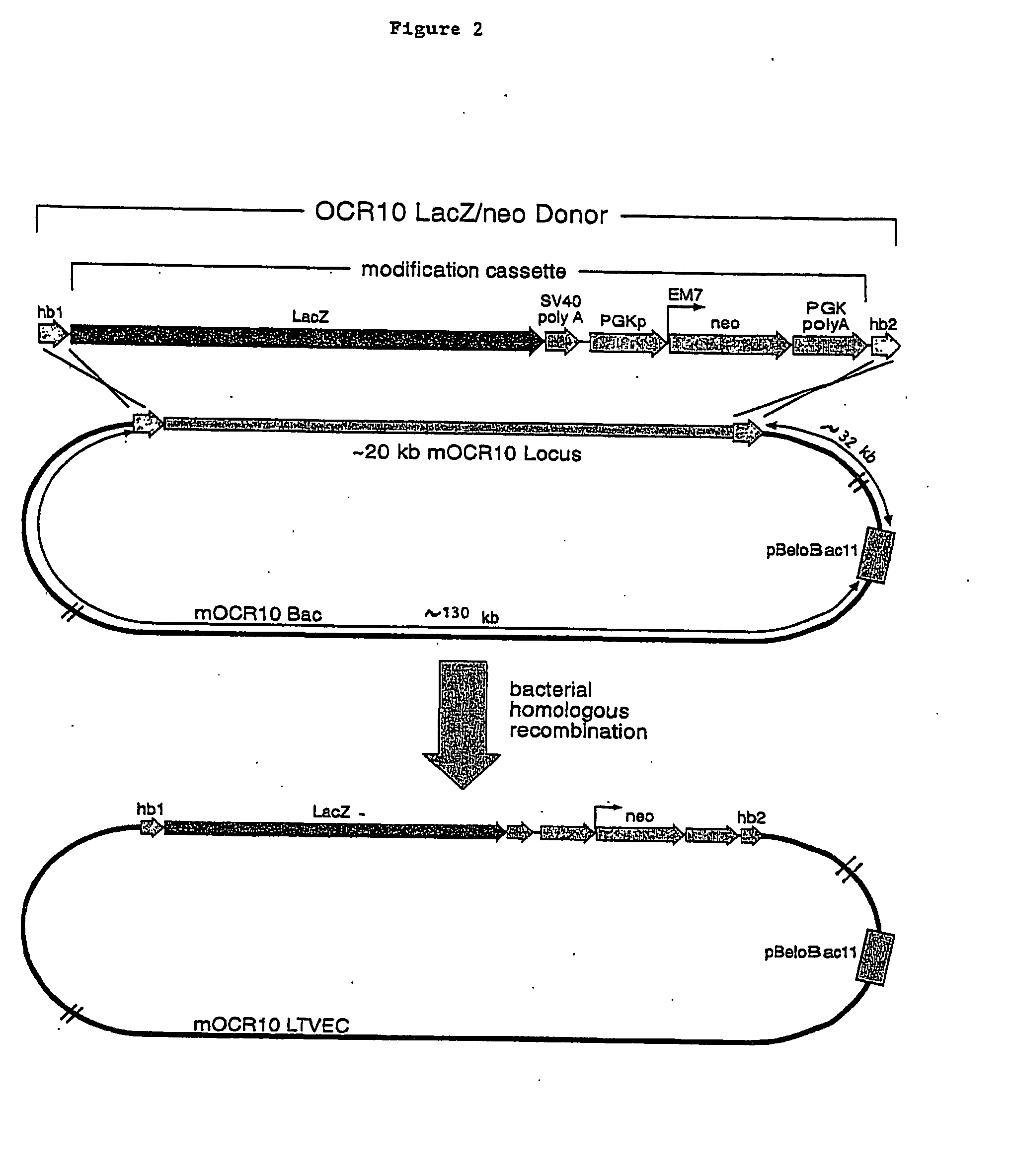
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
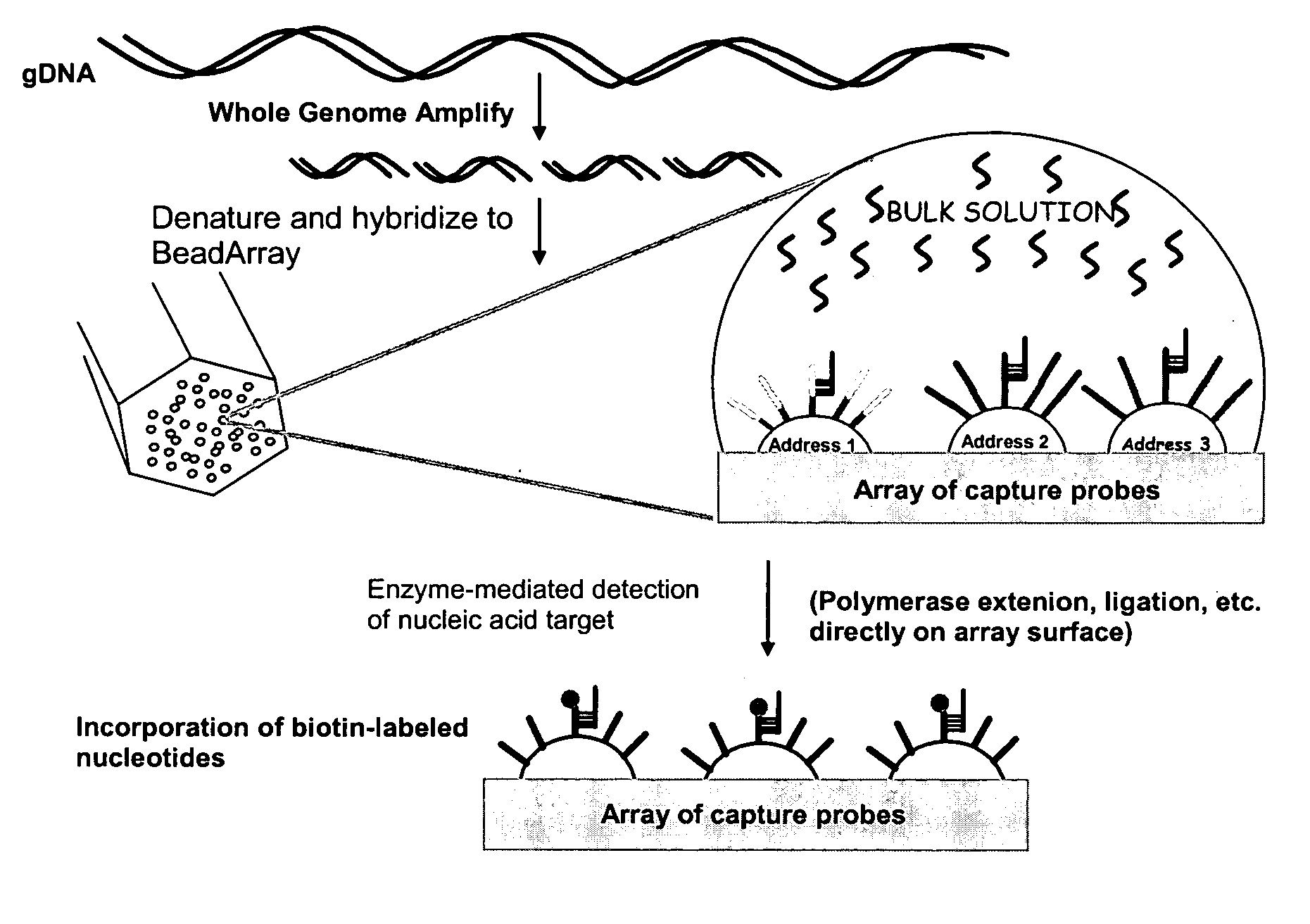
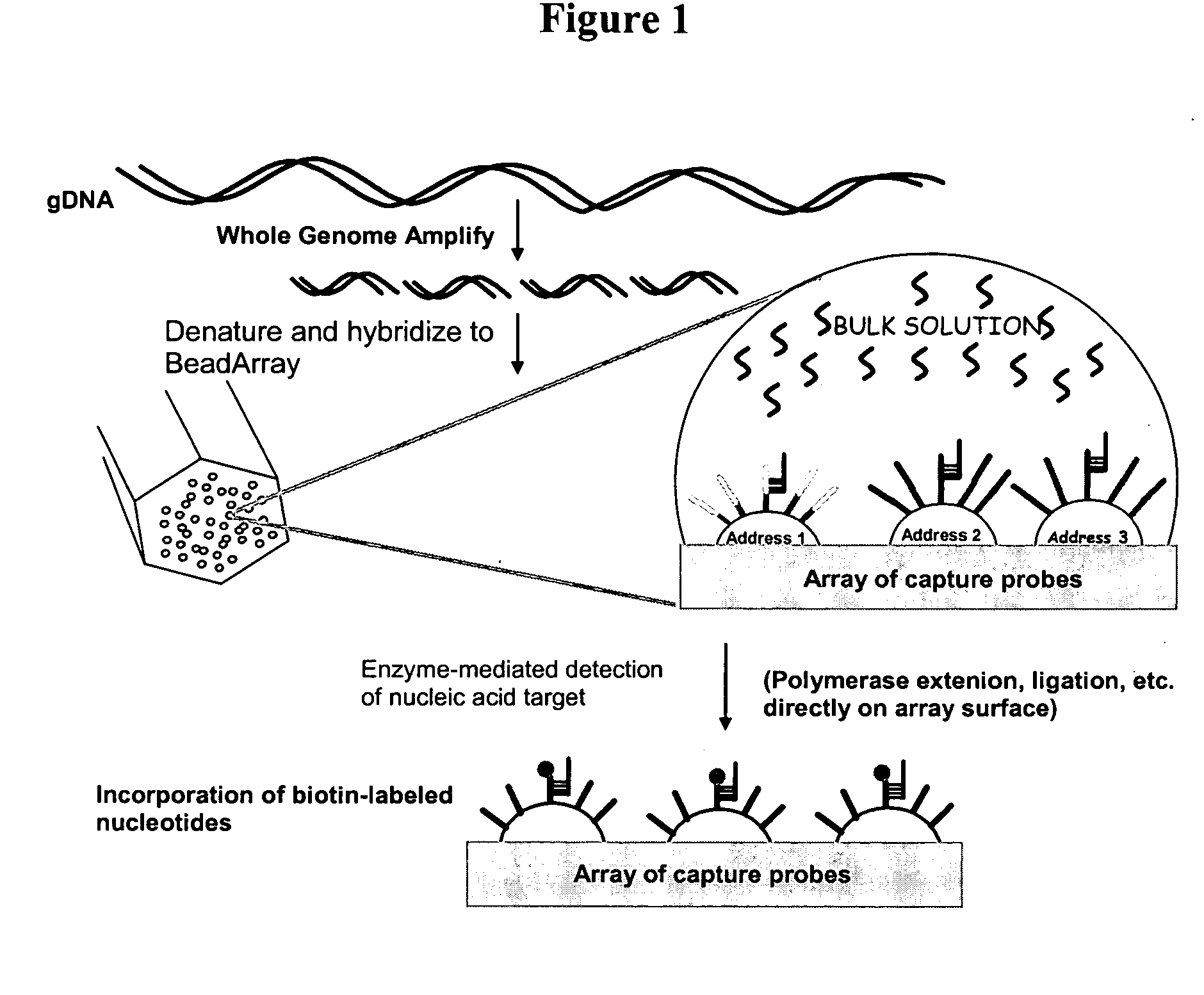
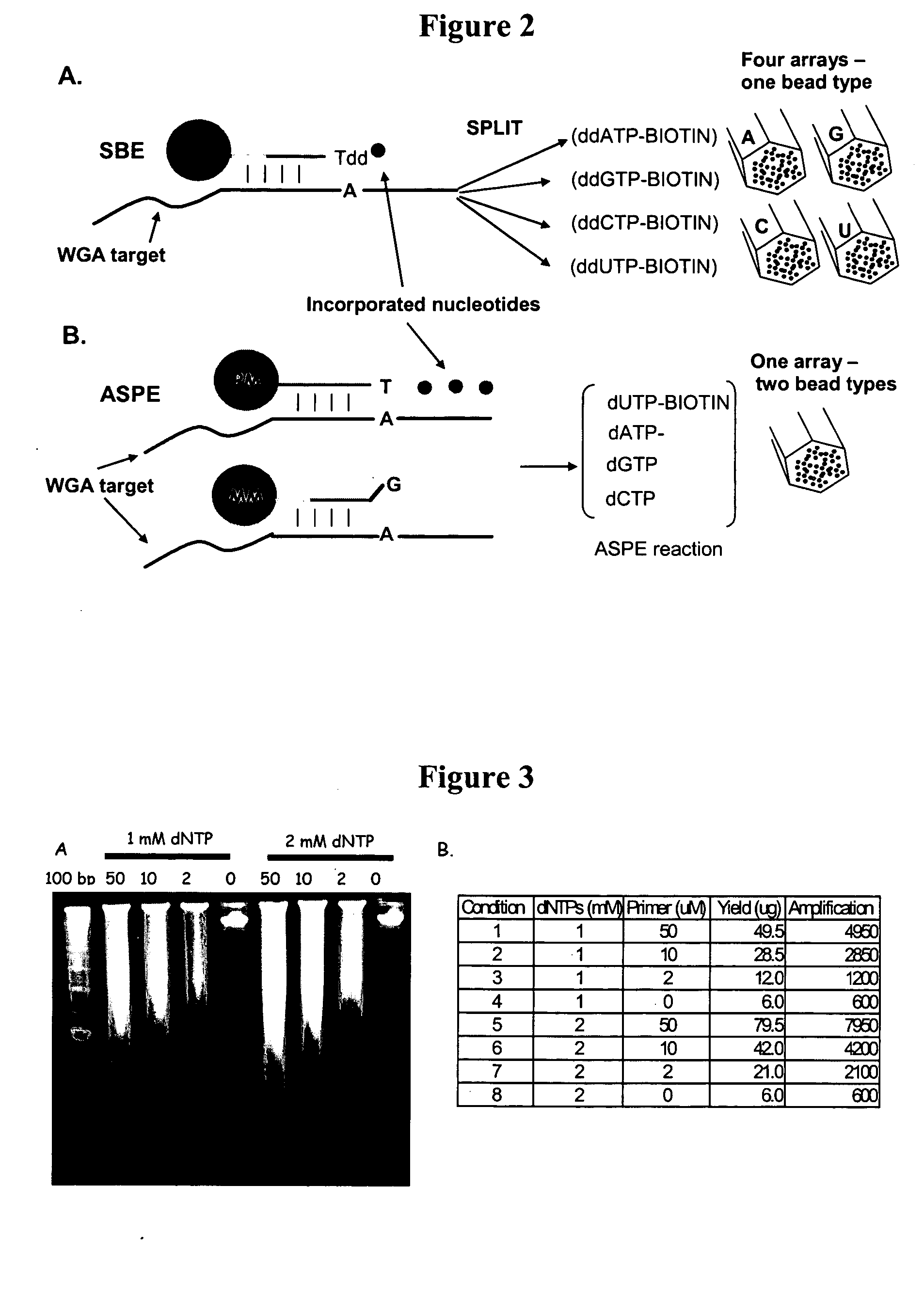
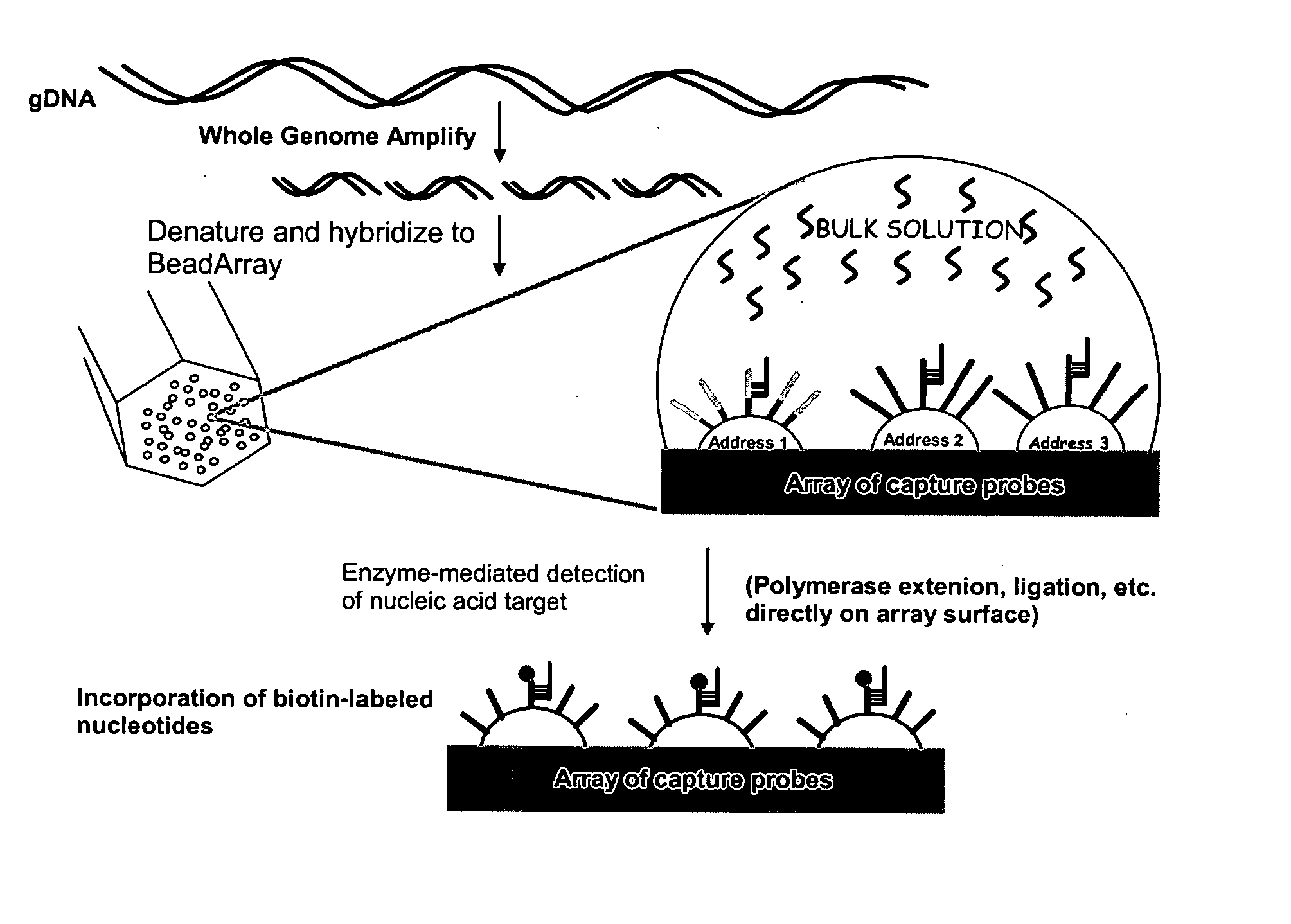
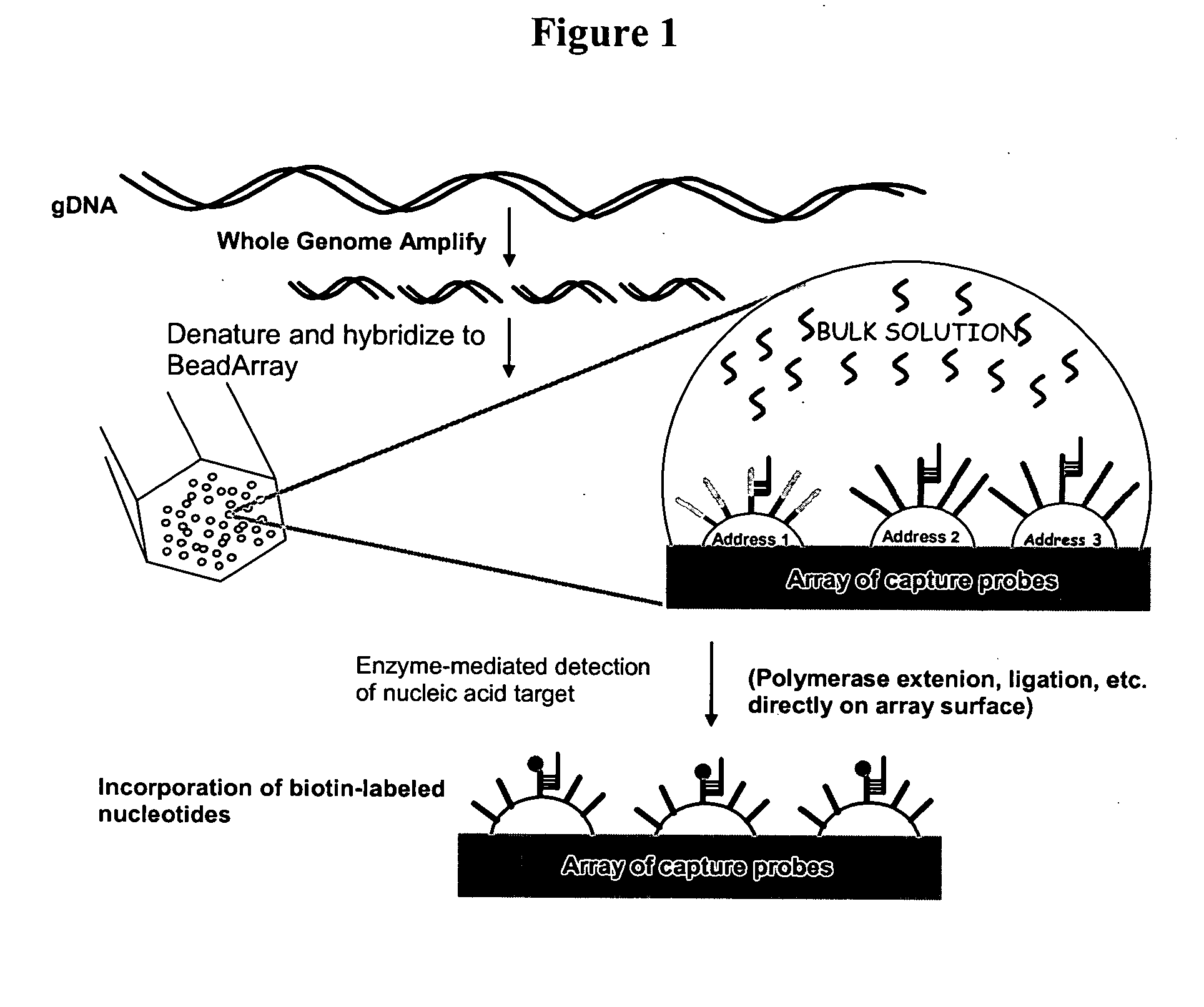
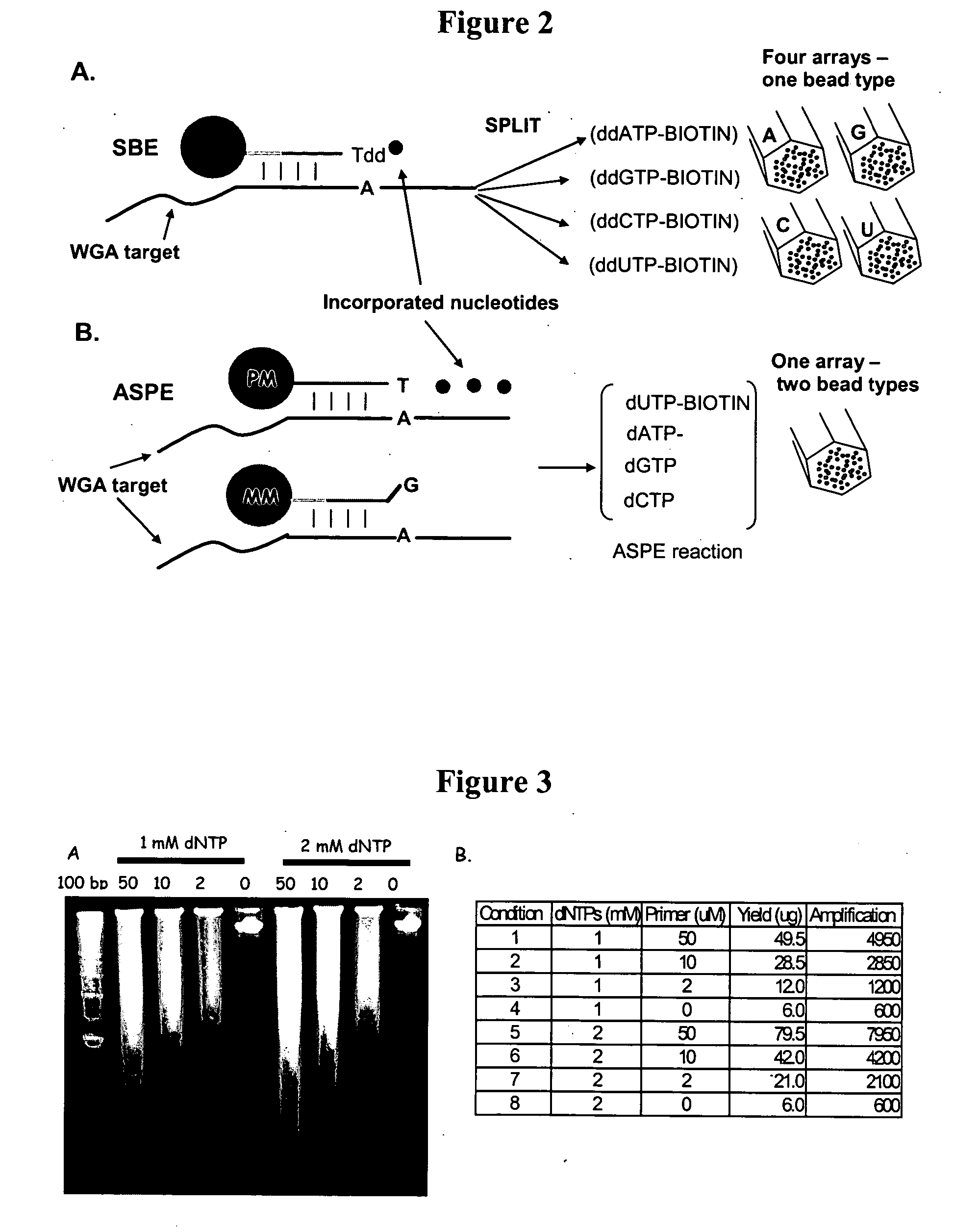
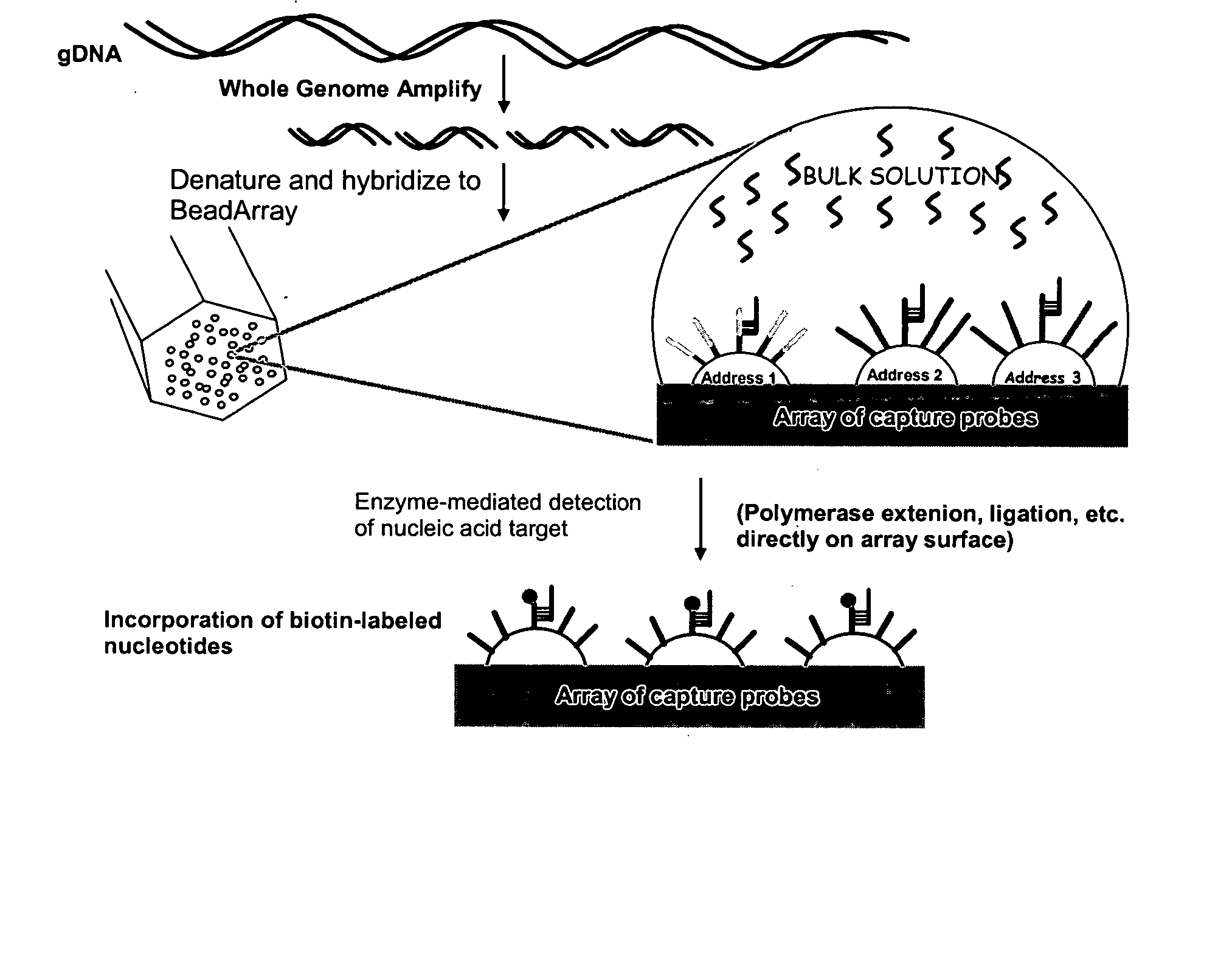
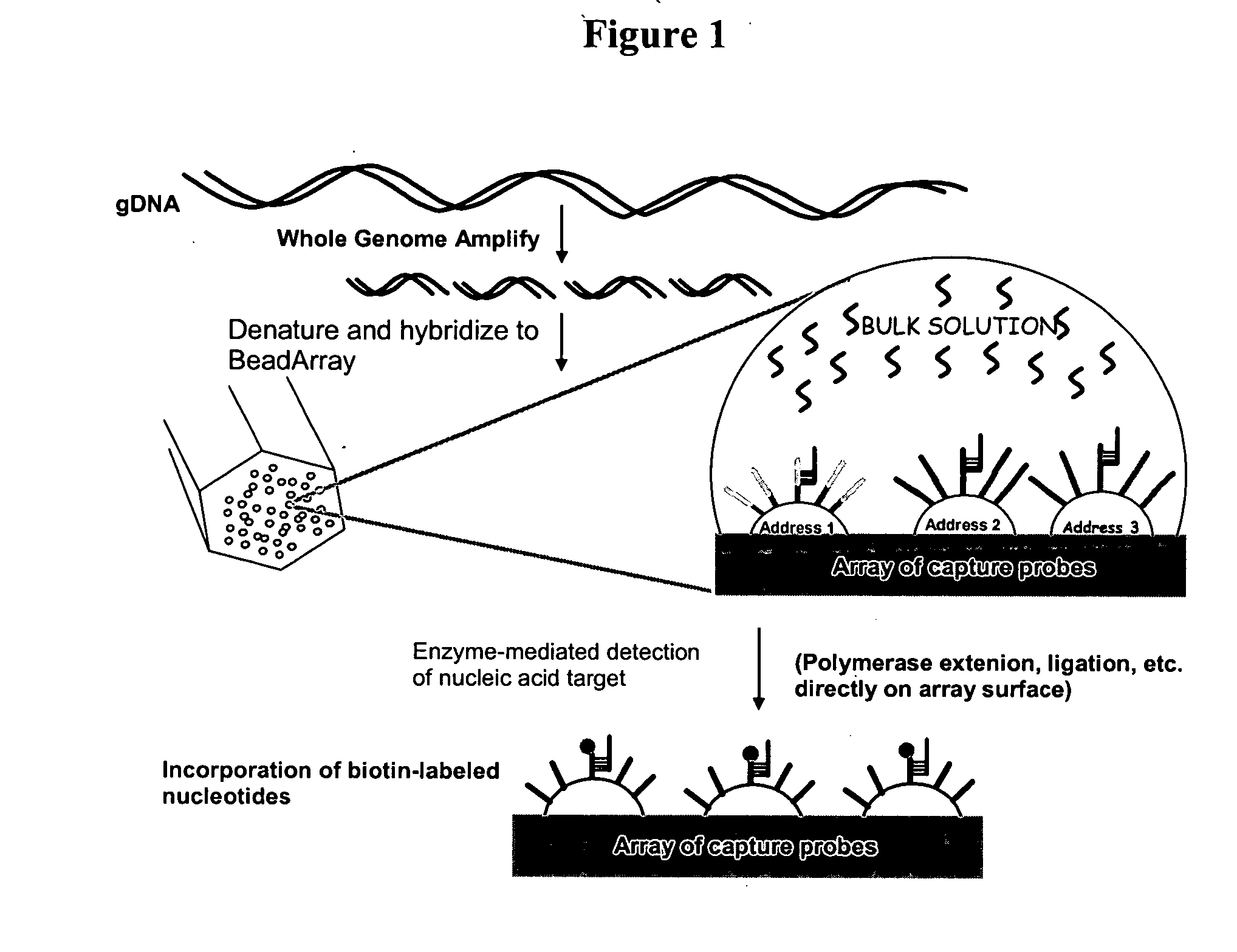
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
InactiveUS20050181394A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentGenotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Chromosome structural abnormality localization with single copy probes
InactiveUS7014997B2Eliminates spurious hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
Nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) hybridization probes are described which comprise a labeled, single copy nucleic acid which hybridizes to a deduced single copy sequence interval in target nucleic acid of known sequence. The probes, which are essentially free of repetitive sequences, can be used in hybridization analyses without adding repetitive sequence-blocking nucleic acids. This allows rapid and accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The probes are preferably designed by first determining the sequence of at least one single copy interval in a target nucleic acid sequence, and developing corresponding hybridization probes which hybridize to at least a part of the deduced single copy sequence. In practice, the sequences of the target and of known genomic repetitive sequence representatives are compared in order to deduce locations of the single copy sequence intervals. The single copy probes can be developed by any variety of methods, such as PCR amplification, restriction or exonuclease digestion of purified genomic fragments, or direct synthesis of DNA sequences. This is followed by labeling of the probes and hybridization to a target sequence.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Direct identification and measurement of relative populations of microorganisms with direct DNA sequencing and probabilistic methods
ActiveUS8478544B2Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic SegmentProbabilistic method
Owner:COSMOSID INC
Direct identification and measurement of relative populations of microorganisms with direct DNA sequencing and probabilistic methods
ActiveUS20120004111A1Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomic SegmentProbabilistic method
The present invention relates to systems and methods capable of characterizing populations of organisms within a sample. The characterization may utilize probabilistic matching of short strings of sequencing information to identify genomes from a reference genomic database to which the short strings belong. The characterization may include identification of the microbial community of the sample to the species and / or sub-species and / or strain level with their relative concentrations or abundance. In addition, the system and methods may enable rapid identification of organisms including both pathogens and commensals in clinical samples, and the identification may be achieved by a comparison of many (e.g., hundreds to millions) metagenomic fragments, which have been captured from a sample and sequenced, to many (e.g., millions or billions) of archived sequence information of genomes (i.e., reference genomic databases).
Owner:COSMOSID INC
Methods of Modifying Eukaryotic Cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
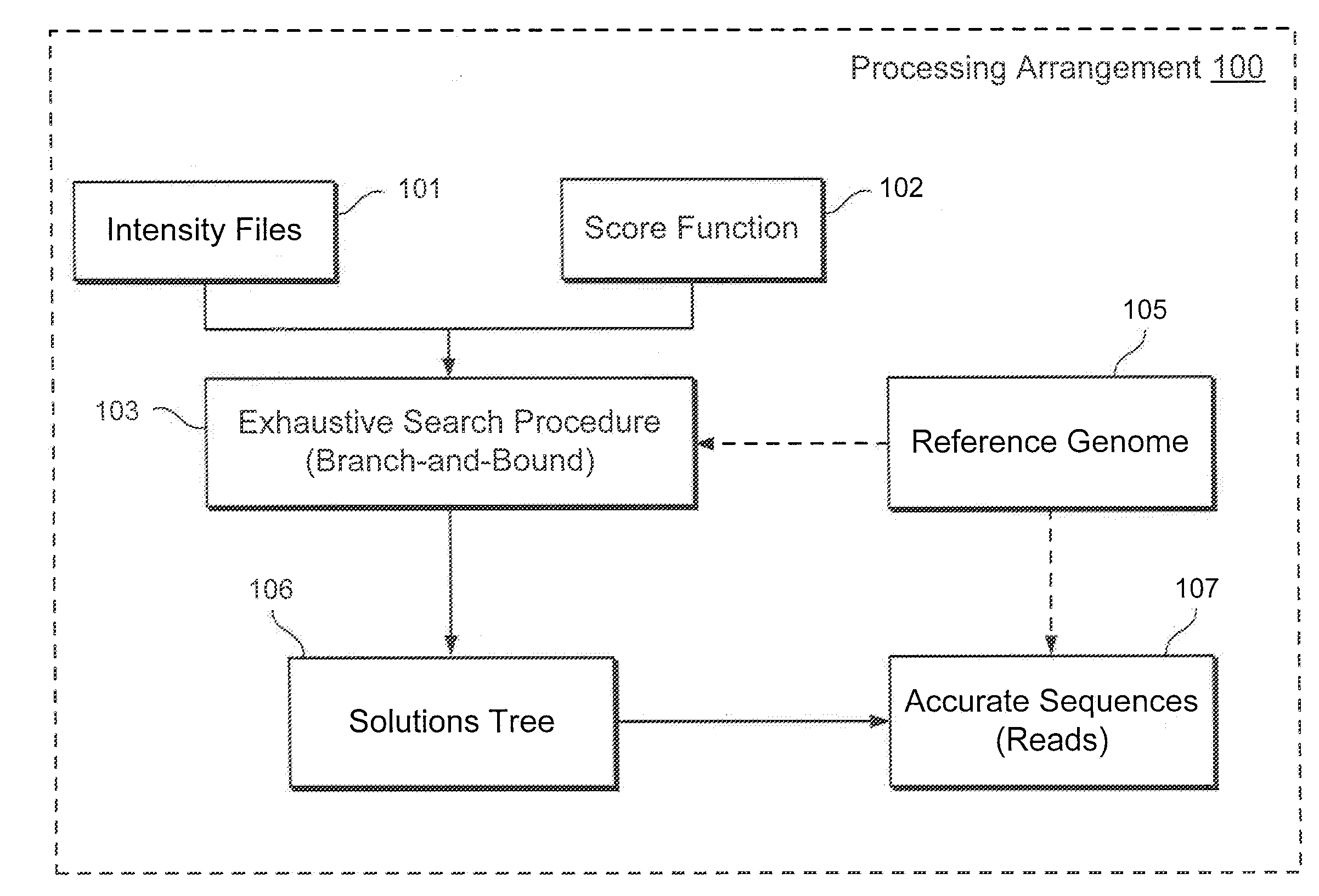
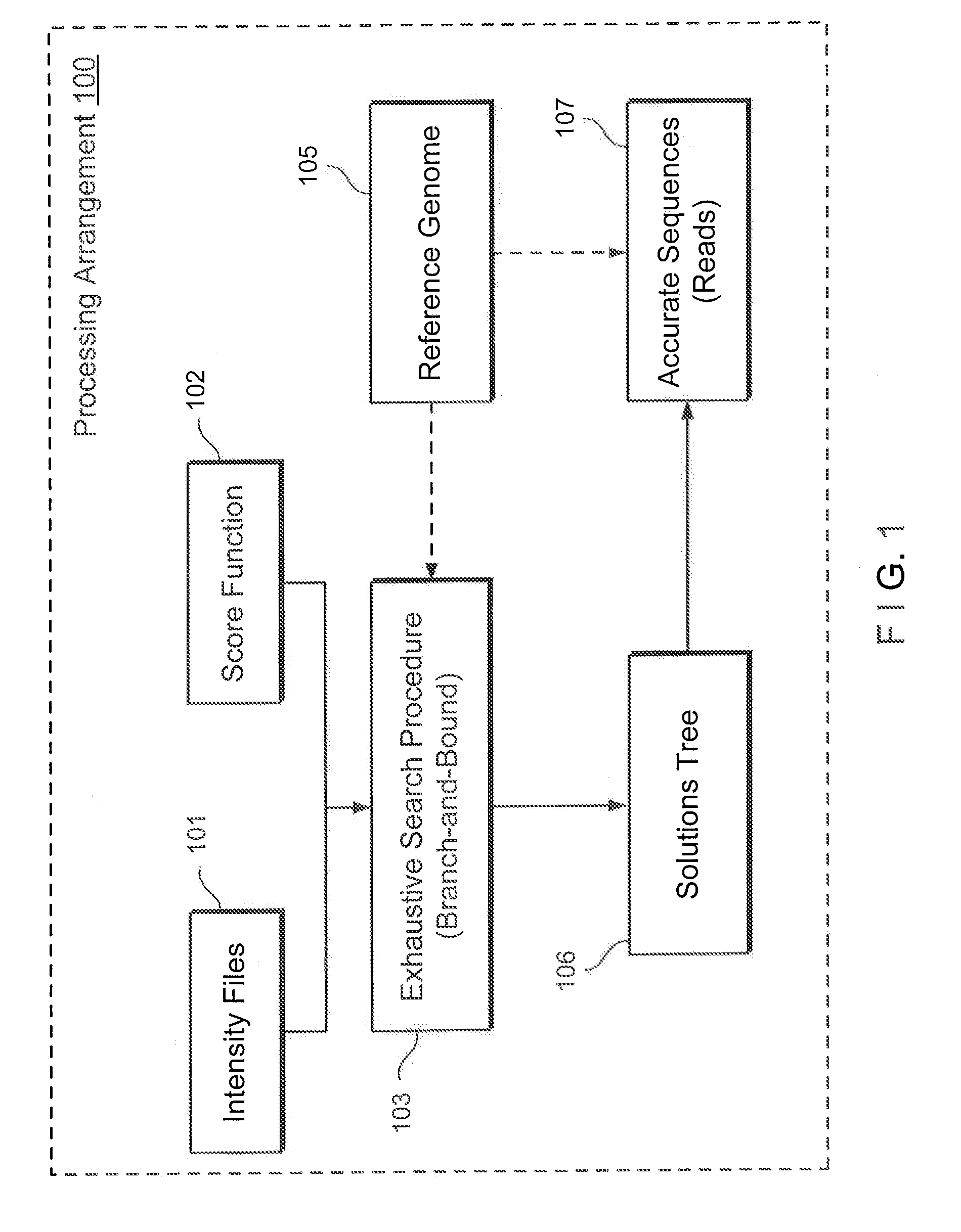
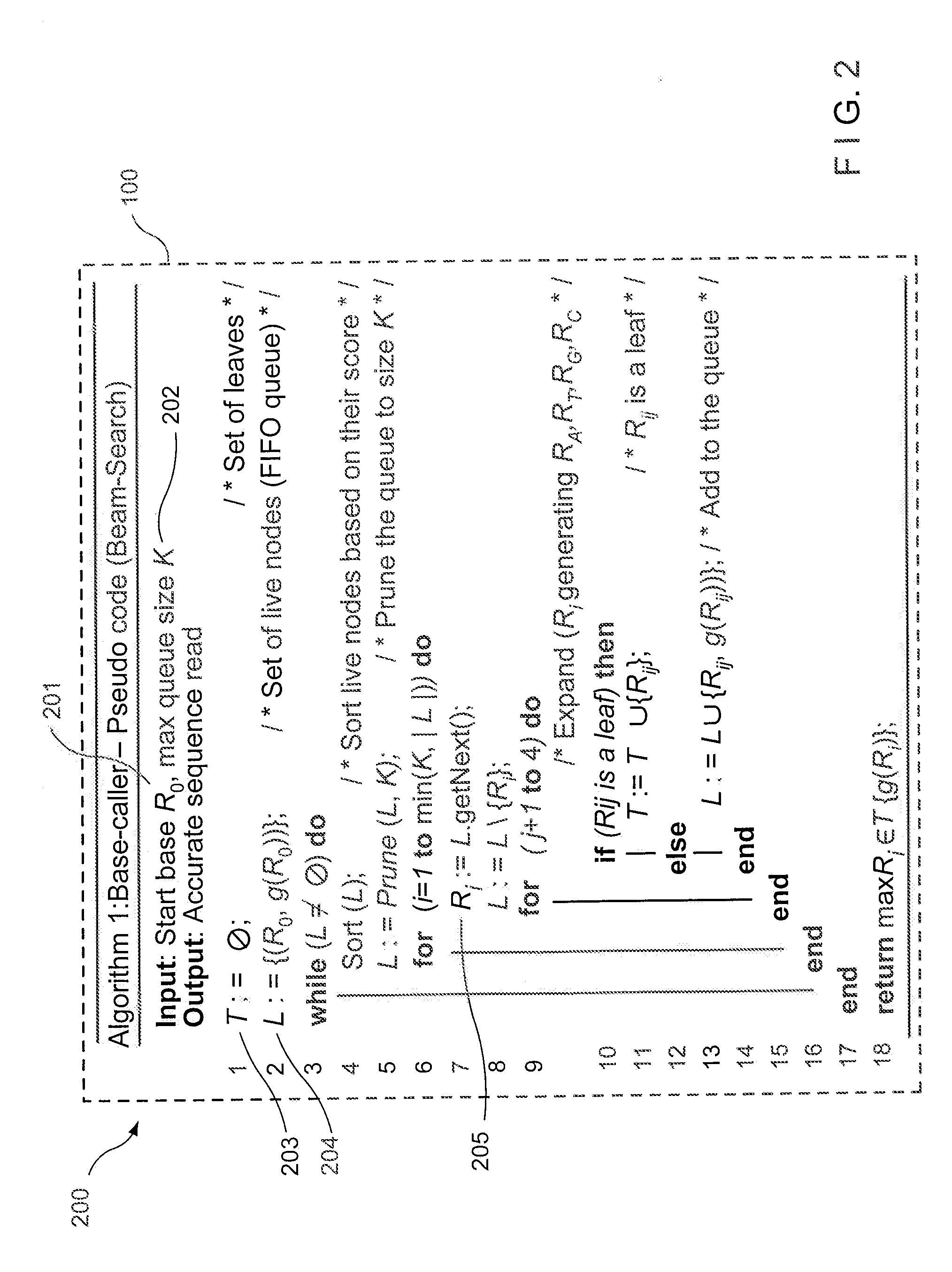
Method, computer-accessible medium and system for base-calling and alignment
Exemplary methods, procedures, computer-accessible medium, and systems for base-calling, aligning and polymorphism detection and analysis using raw output from a sequencing platform can be provided. A set of raw outputs can be used to detect polymorphisms in an individual by obtaining a plurality of sequence read data from one or more technologies (e.g., using sequencing-by-synthesis, sequencing-by-ligation, sequencing-by-hybridization, Sanger sequencing, etc.). For example, provided herein are exemplary methods, procedures, computer-accessible medium and systems, which can include and / or be configured for obtaining raw output from a sequencing platform configured to be used for reading fragment(s) of genomes, obtaining reference sequences for the genomes obtained independently from the raw output, and generating a base-call interpretation and / or alignment using the raw output and the reference sequences. For example, a score function can be determined based on information associated with the sequencing platform that can be used to analyze polymorphisms based on the base-call interpretation and / or alignment.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
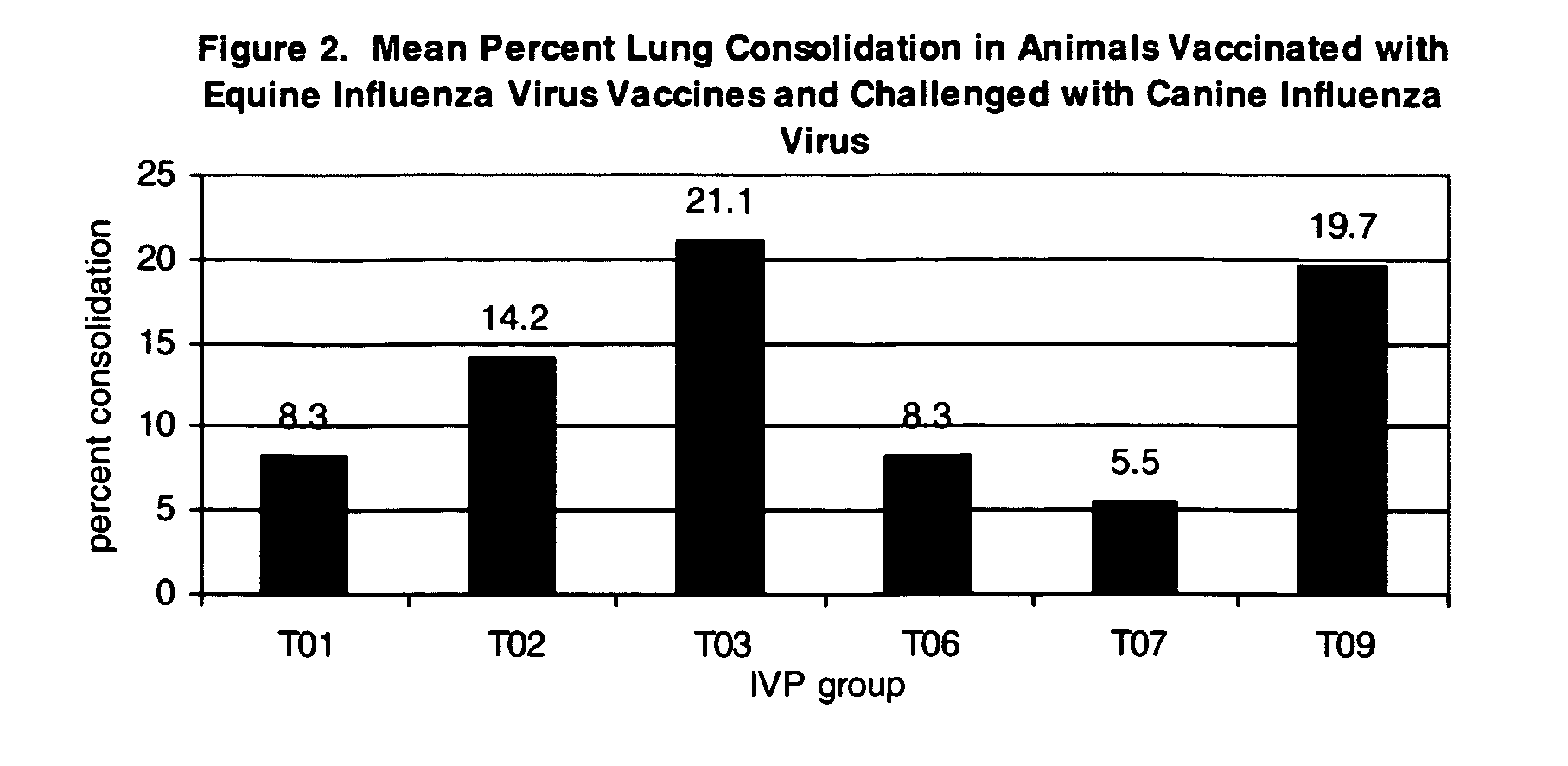
Vaccines and methods to treat canine influenza
The present invention relates to providing new vaccines and treatments for the diseases related to canine influenza virus. It discloses influenza viral antigens, and methods of presenting these antigens to canines, especially dogs. It relates to attenuated and killed vaccines. The present invention relates to experimentally generated canine and equine influenza viruses. The invention also includes influenza A, including H3, N8, H3N8, H7N7 and viruses which contain at least one genome segment from an canine or equine influenza virus. The present invention also relates to the use of these viruses in therapeutic compositions to protect canines, dogs in particular, from diseases caused by influenza viruses.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Cas9 nuclease G915F and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biologics, and particularly relates to a Cas9 nuclease G915F and application thereof. The Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-G915F) has activity of Cas9 nuclease and is applicable to a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system, and the Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-G915F) is prepared by mutating glycine at a 915th site of wild Cas9 nuclease into phenylalanine. When the Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-G915F) is adopted to cut double chains of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), protruding fractured tail ends can be generated, an alkali group complemented with the protruding fractured tail ends can be added in a filling connection mode, and precise edition on specific positions of genome DNA fragments can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cas9 nuclease K918A and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to Cas9 nuclease and application. The Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-K918A) disclosed by the invention has the activity of the Cas9 nuclease, is suitable for a CRISPR / Cas9 system and is obtained by mutating 918th lysine of wild type Cas9 nuclease into alanine. The Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-K918A) is adopted for cutting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) double strands to generate a predominantly-broken terminal; a basic group complemented with the predominantly-broken terminal can be added in a connection filling-in mode, so that accurate edition of a specific position of a genomic DNA fragment can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cas9 nuclease R919P and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and specifically relates to Cas9 nuclease and an application. The Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-R919P) has the activity as Cas9 nuclease, fits to a CRISPR / Cas9 system, and is made by mutating the 919 location arginine of wild Cas9 nuclease to proline. A protruding fracture terminal is generated by cutting a DNA double chain with the Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-R919P), and a basic group complementary to the protruding fracture terminal is added in a filling-in manner, so that accurate addition at a specific position of the genome DNA segment can be carried out.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods of Modifying Eukaryotic Cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Quantitative sequencing and library building method and quantitative sequencing and detecting method for fusion gene on basis of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application of quantitative sequencing and detecting method
ActiveCN107190329ALow backgroundStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic SegmentA-DNA
The invention discloses a quantitative sequencing and library building method for a fusion gene on the basis of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). The quantitative sequencing and library building method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a genome fragmentation DNA library and purifying the library; secondly, capturing a fusion gene generation region by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, purifying the captured gene and enriching a sequence containing a specific primer fragment; thirdly, capturing a target fragment containing the fusion gene by nested PCR amplification; fourthly, constructing a DNA sequencing library with high-throughput sequencing. The invention also discloses a quantitative sequencing and detecting method for the fusion gene by using the DNA sequencing library prepared by the quantitative sequencing and library building method, application of the quantitative sequencing and detecting method as well as a detection kit containing the DNA sequencing library. According to the quantitative sequencing and library building method disclosed by the invention, the downstream where a fusion breakpoint occurs is anchored by using a one-way specific primer; a target sequence is obtained by pairing specific primers with universal primers and using a PCR method; the background is further reduced label enriching and nested PCR, so that the specificity is improved, the time for building the library is shortened, and the cost for building the library is reduced; the quantitative sequencing and library building method is suitable for an FFPE (Formalin Fixed And Parafiin Embedded) sample or liquid biopsy.
Owner:CARRIER GENE TECH SUZHOU CO LTD +1
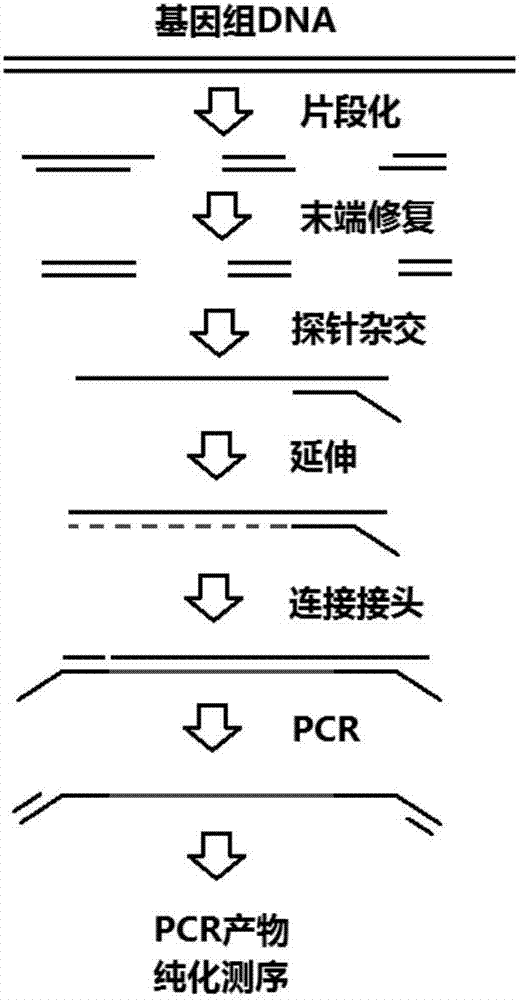
Method and kit for rapidly constructing target nucleic acidsequencing library on basis of probe capture and enrichment
PendingCN107236729AImprove data qualityHigh-precision detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic SegmentThermal denaturation
The invention discloses a method and a kit for rapidly constructing a target nucleic acidsequencing library on the basis of probe capture and enrichment. The method comprises following steps and adopts reagents required for the steps: genome DNA is subjected to fragmentation; DNA end repair is performed; a probe and a single-stranded DNA fragment formed through thermal denaturation are subjected to molecular hybridization; biotin-avidinmagnetic bead separation is executed; the probe is taken as a primer for primer extension, and a complementary strand is synthesized; one end of a double-stranded DNA fragment is connected with an linker, and the other end is not connected with the linker; PCR amplification is performed; DNA fragment lengthselection is executed; the reagents are used for completing the reactions of all the steps. Compared withconventionaltarget nucleic acid enrichment technologies, the method has the advantages of good fidelity, good reproducibility, high speed and high universality.
Owner:上海阅尔基因技术有限公司
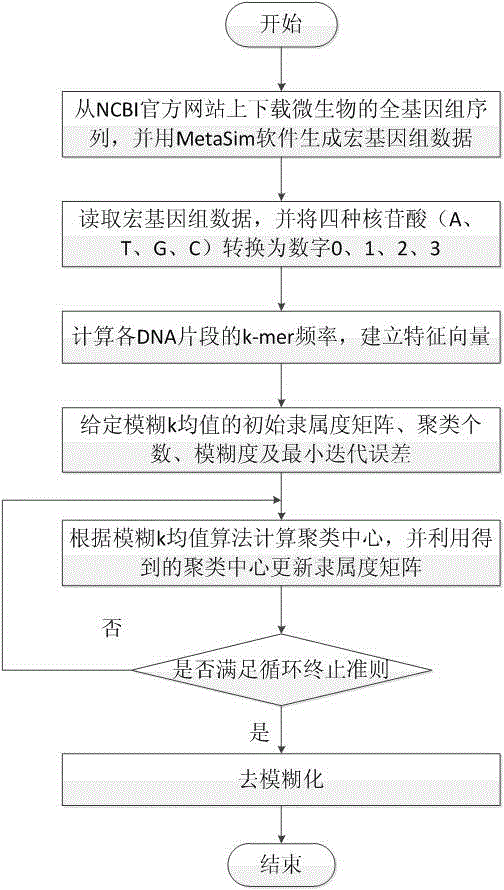
Micro genome segment clustering method based on fuzzy k-mean
The invention relates to a micro genome segment clustering method based on fuzzy k-mean, and belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics analysis. The micro genome segment clustering method based on the fuzzy k-mean aims at utilizing the self features of micro genome segments under the condition of no assembly of the micro genome segments, and then the micro genome segments are clustered, so the number of contained species and the abundance ratio of species are obtained. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining the micro genome segments, establishing the feature vectors, utilizing the fuzzy k-mean method to cluster, and calculating the number of the contained species and the abundance ratio of the species according to the clustering results. The method has the advantages of directness and convenience.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods for selectively capturing and amplifying exons or targeted genomic regions from biological samples
InactiveUS20090318305A1Easy to storeEasy amplificationLibrary screeningDNA preparationGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
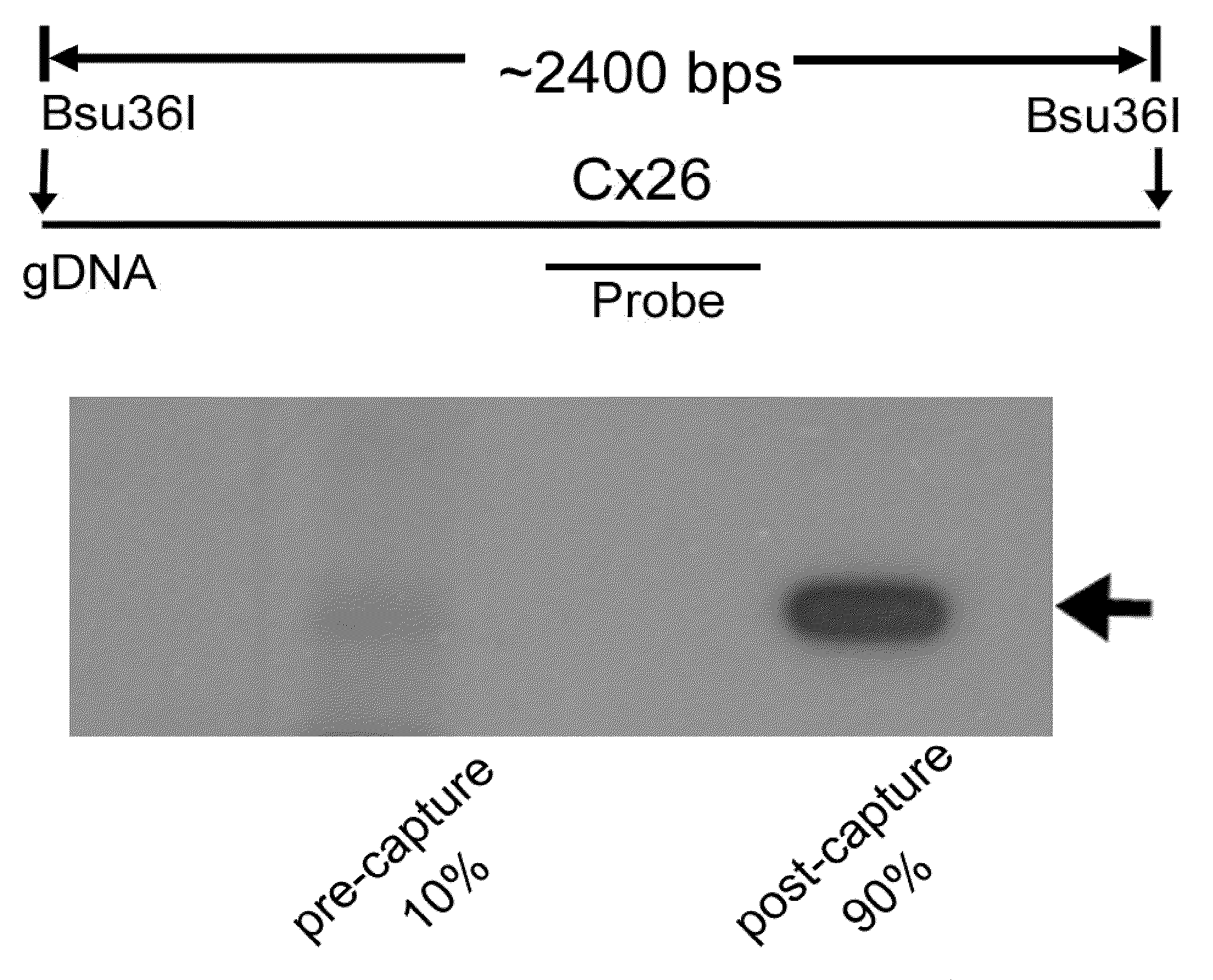
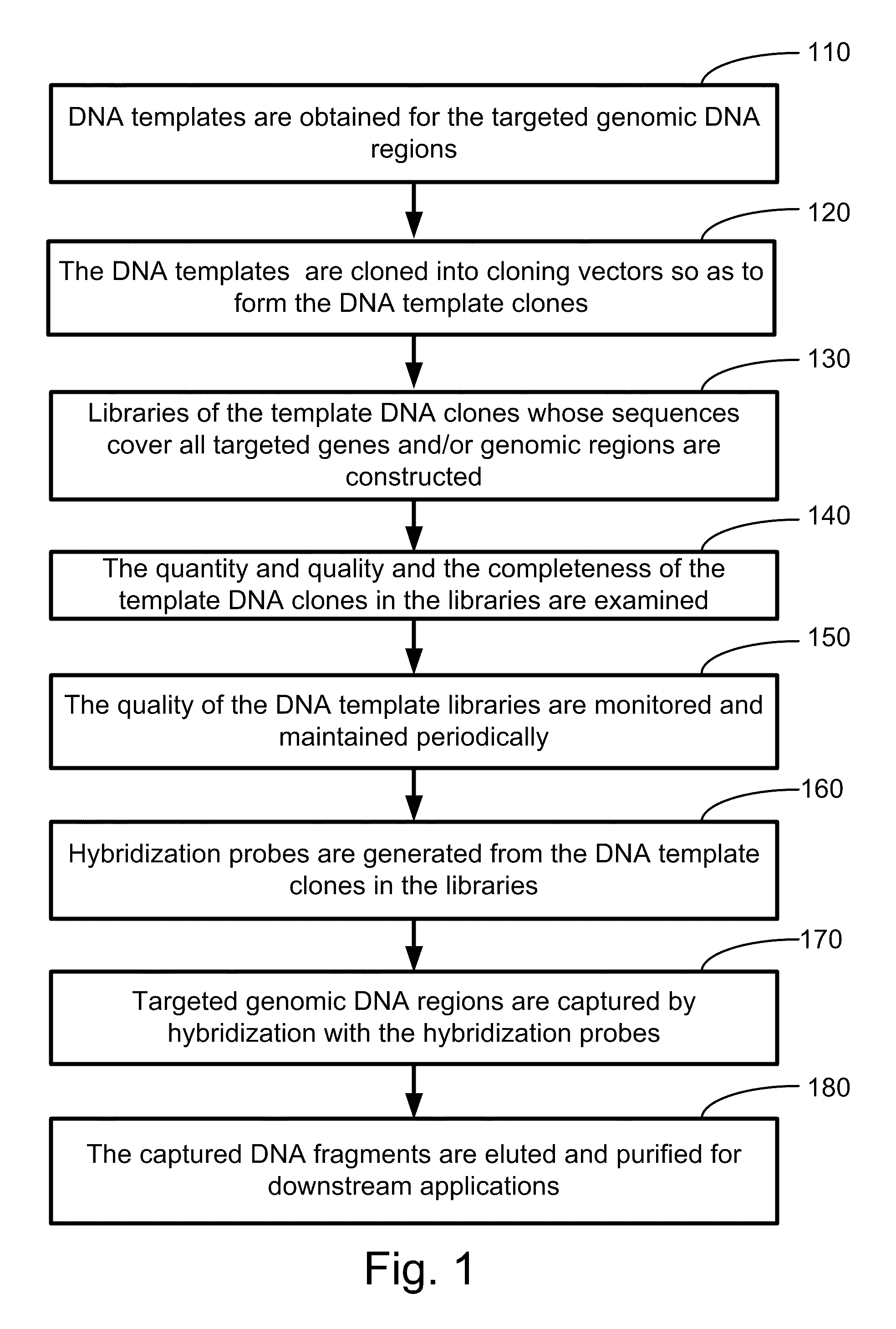
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for selectively capturing and / or amplifying exons or targeted genomic regions from biological samples. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of obtaining DNA templates for the targeted genomic region, cloning the DNA templates into cloning vectors to form template DNA clones, constructing libraries of the template DNA clones that cover at least the targeted genomic regions, generating hybridization probes from the DNA template clones in the libraries, capturing the targeted genomic DNA regions by hybridizing the targeted genomic DNA samples (fragmented either mechanically or enzymatically) with the generated hybridization probes, and eluting the captured genomic fragments by using conditions for releasing and separating the bound DNA from the hybridization probes.
Owner:LIN XI ERICK +1
Virulence of streptococci
InactiveUS7670835B2Increase virulenceMinimal effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsGenomic SegmentVaccination
The invention relates to the field of diagnosis of and vaccination against Streptococcal infections and to the detection of virulence markers of Streptococci. The invention discloses a method for modulating virulence of a Streptococcus, the method comprising modifying a genomic fragment of Streptococcus wherein the genomic fragment comprises at least a functional part of a fragment identifiable by hybridization in Streptococcus suis to a nucleic acid or fragment thereof as shown in FIG. 5.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
Tri-segmented arenaviruses as vaccine vectors
ActiveUS20170319673A1High genetic stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenomic SegmentDisease
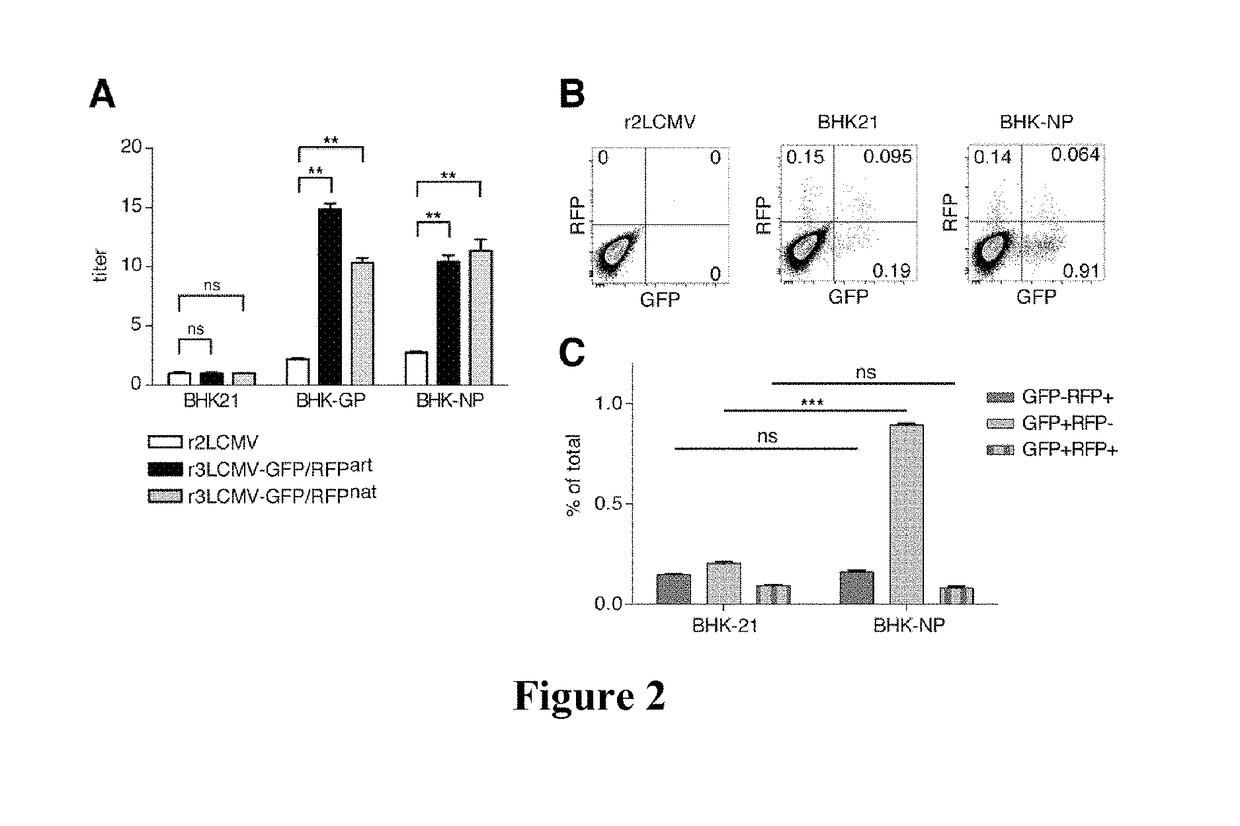
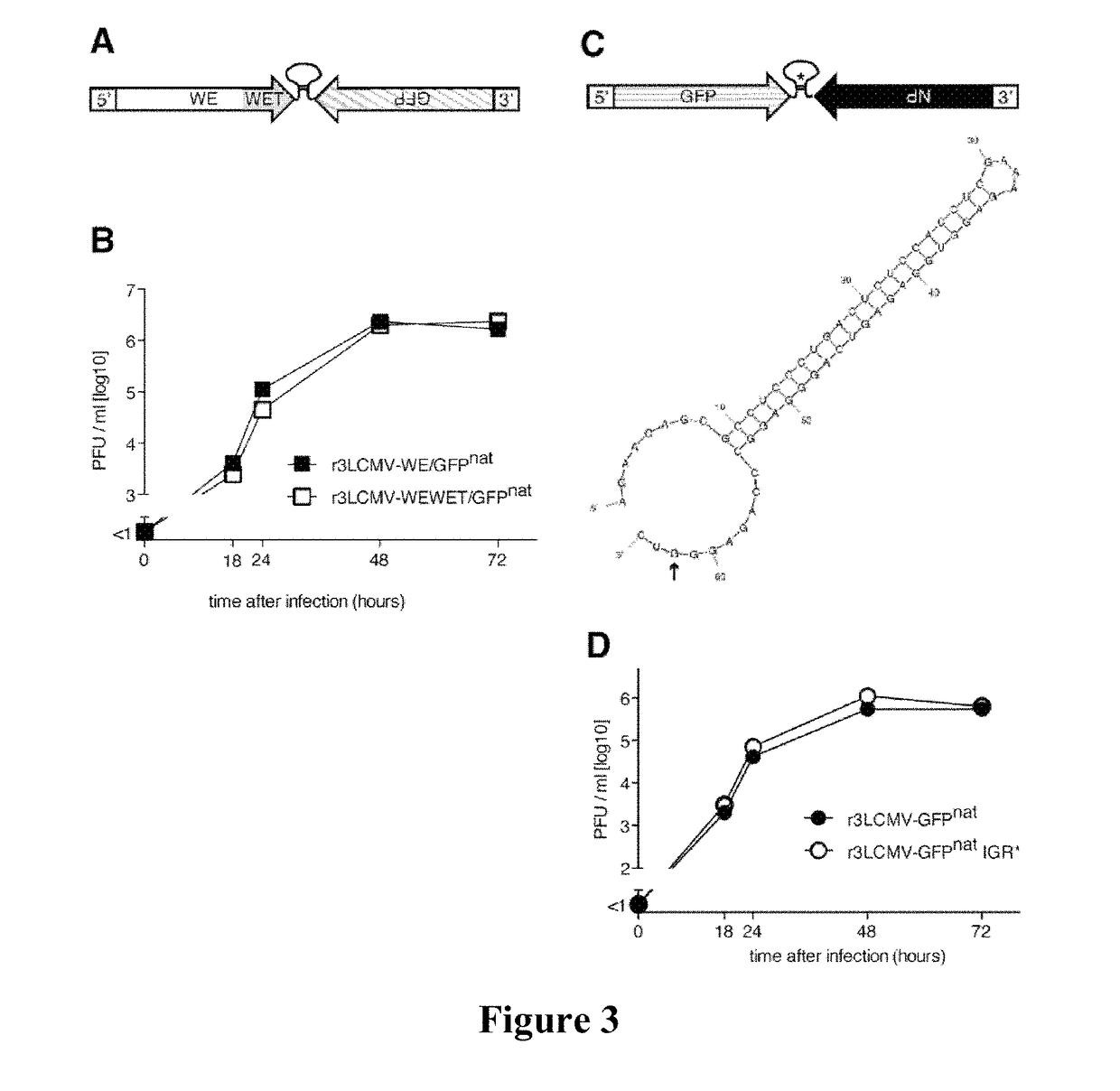
The present application relates to arenaviruses with rearrangements of their open reading frames (“ORF”) in their genomes. In particular, described herein is a modified arenavirus genomic segment, wherein the arenavirus genomic segment is engineered to carry a viral ORF in a position other than the wild-type position of the ORF. Also described herein are trisegmented arenavirus particles comprising one L segment and two S segments or two L segments and one S segment. The arenavirus, described herein may be suitable for vaccines and / or treatment of diseases and / or for the use in immunotherapies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
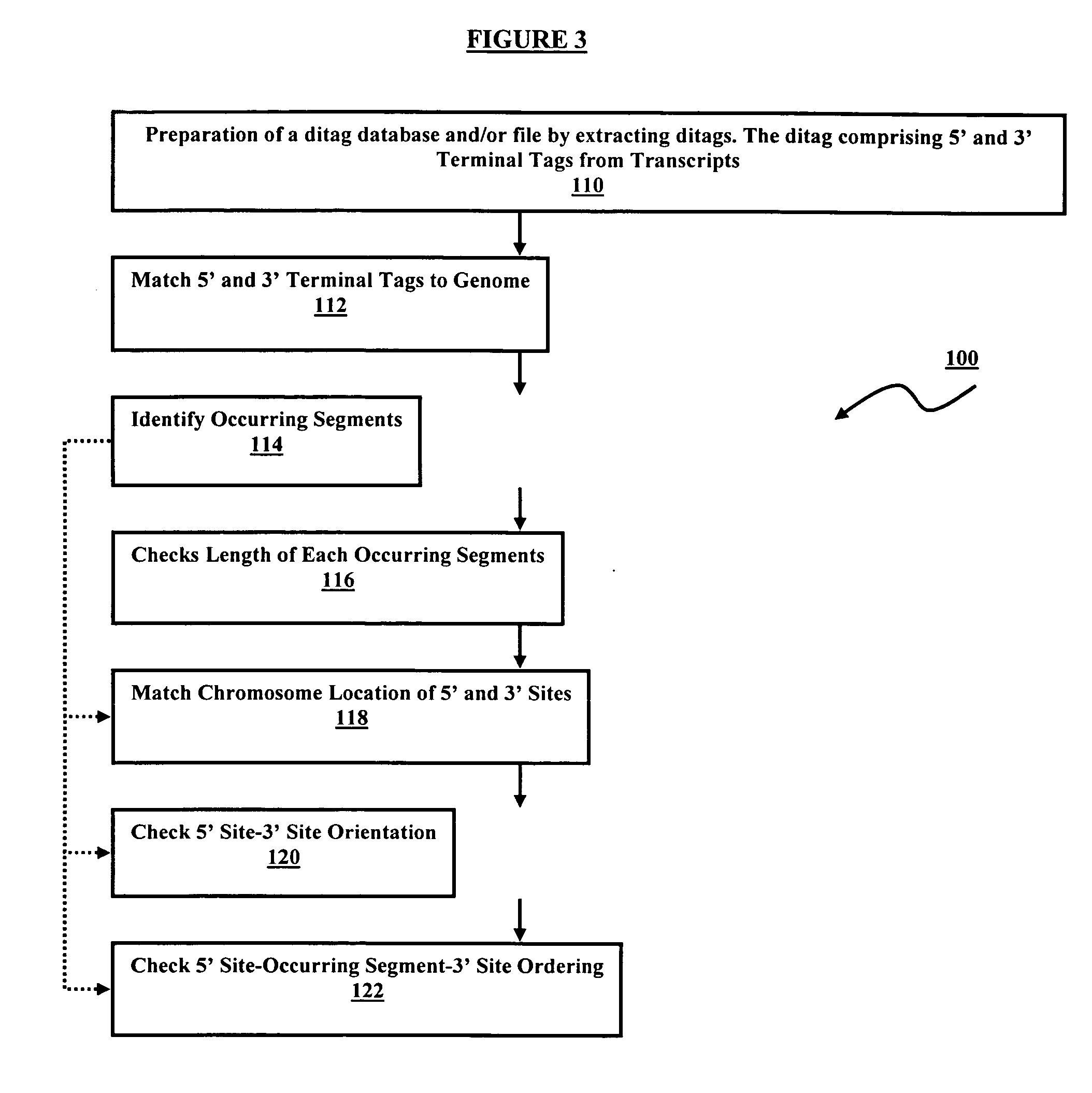
Method of processing and/or genome mapping of ditag sequences
InactiveUS20060281097A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomic SegmentNucleotide sequencing
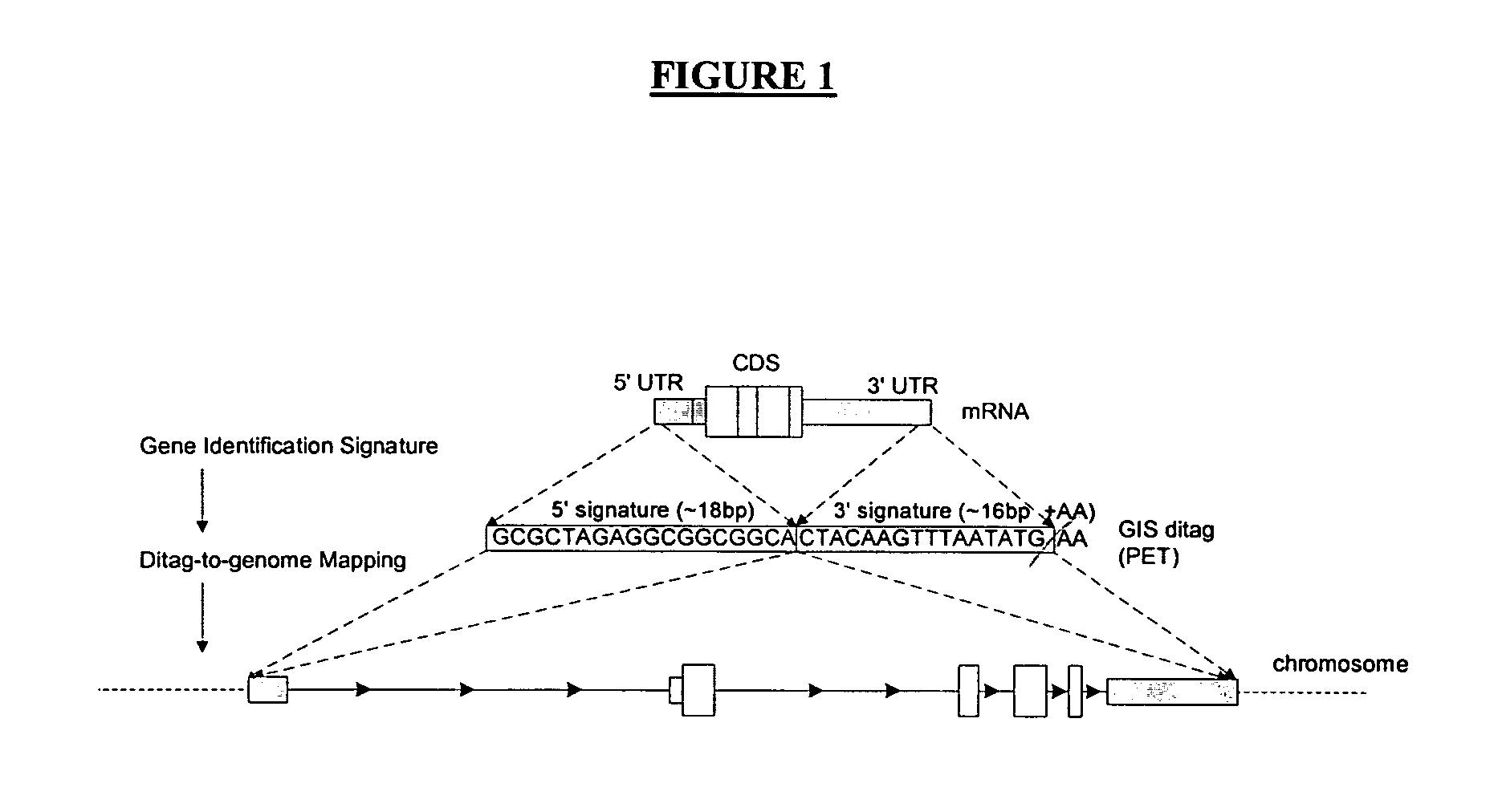
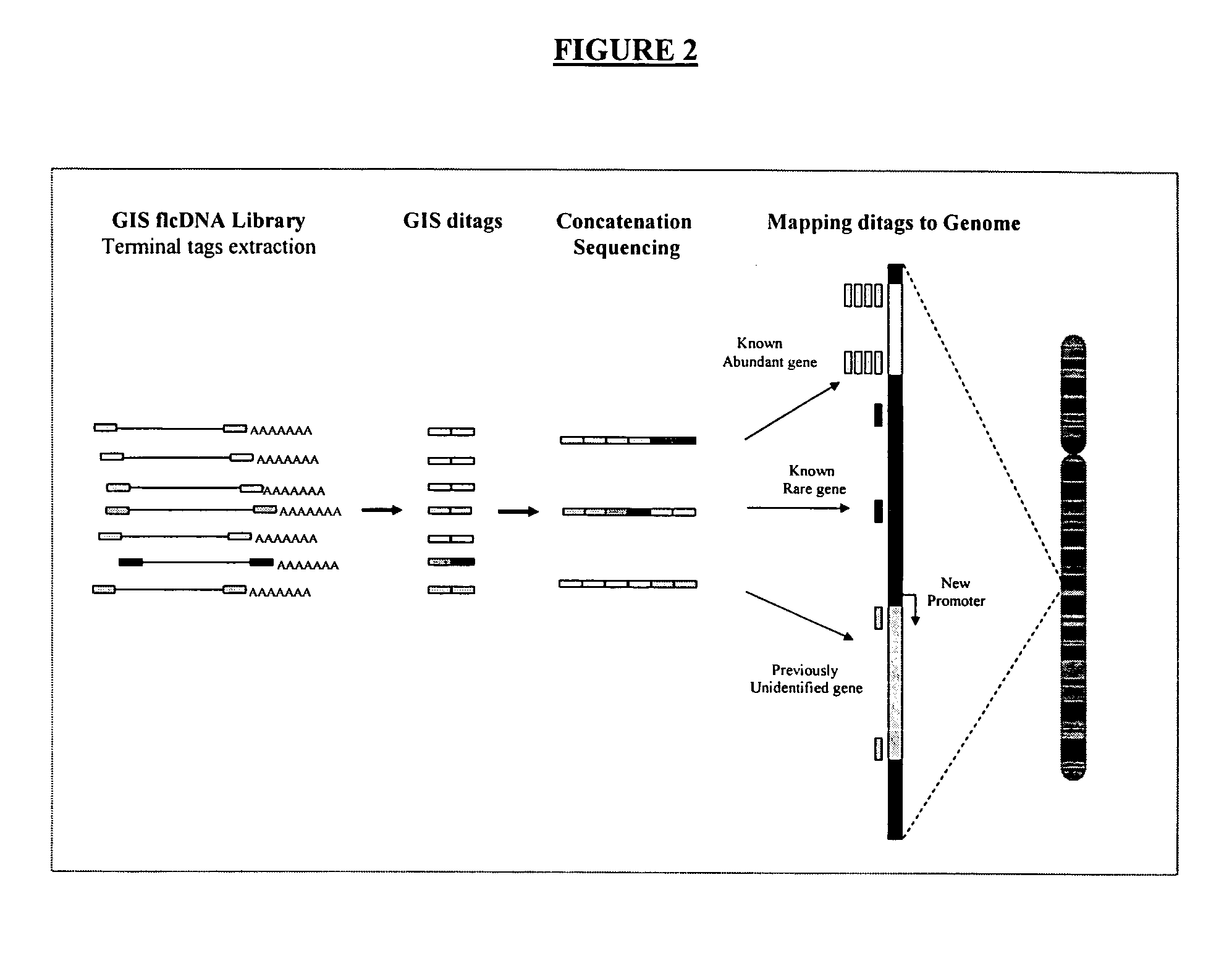
Method of processing and / or genome mapping of ditag sequences There is provided a method and system for processing and / or mapping ditag nucleotide sequence(s) to a genome, the ditag sequence comprising the 5′ terminal tag and the 3′ terminal tag of a nucleic acid molecule or fragment thereof or genomic fragment. The method of processing comprises preparing a database or file comprising at least one ditag sequence. The method of mapping comprises preparing a database or file of ditag(s), and mapping the ditag sequence(s) to the genome, comprising matching the 5′ and the 3′ terminal tags of the ditag sequence to at least a portion of the genome.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and device for assembling genomes by utilizing long transcriptome sequencing result
InactiveCN102789553AIncrease the lengthSpecial data processing applicationsSequencing dataGenomic Segment
The invention relates to a method and a device for assembling genomes by utilizing a long transcriptome sequencing result. The method adopts the scheme that transcriptome sequencing reading segments and genome segments of the same species are compared; only one transcriptome sequencing reading segment from a comparison to one genome segment is removed, query blocks of reserved transcriptome sequencing reading segments are filtered under specified conditions; block connection relative to the reserved query blocks are obtained according to the specified conditions; and the genome segments are connected on the basis of the block connection, thereby completing assembling of the genome sequences. According to the method for assembling the genomes by utilizing the long transcription sequence result, long segment sequencing data including a large amount of existing and published Sanger data can be utilized, so that the genome sequences can be assembled by utilizing the long transcriptome sequencing reading sequence.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
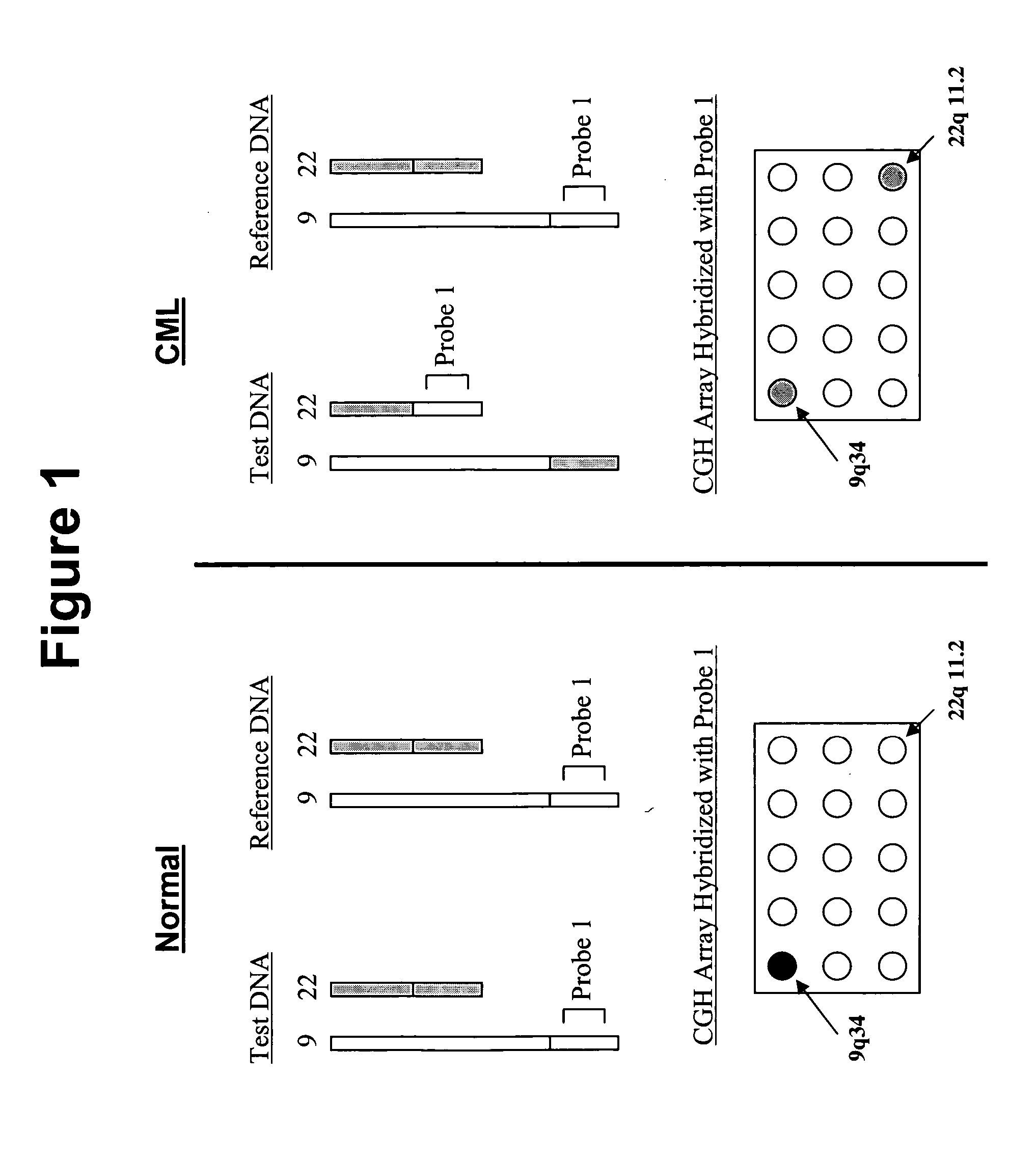
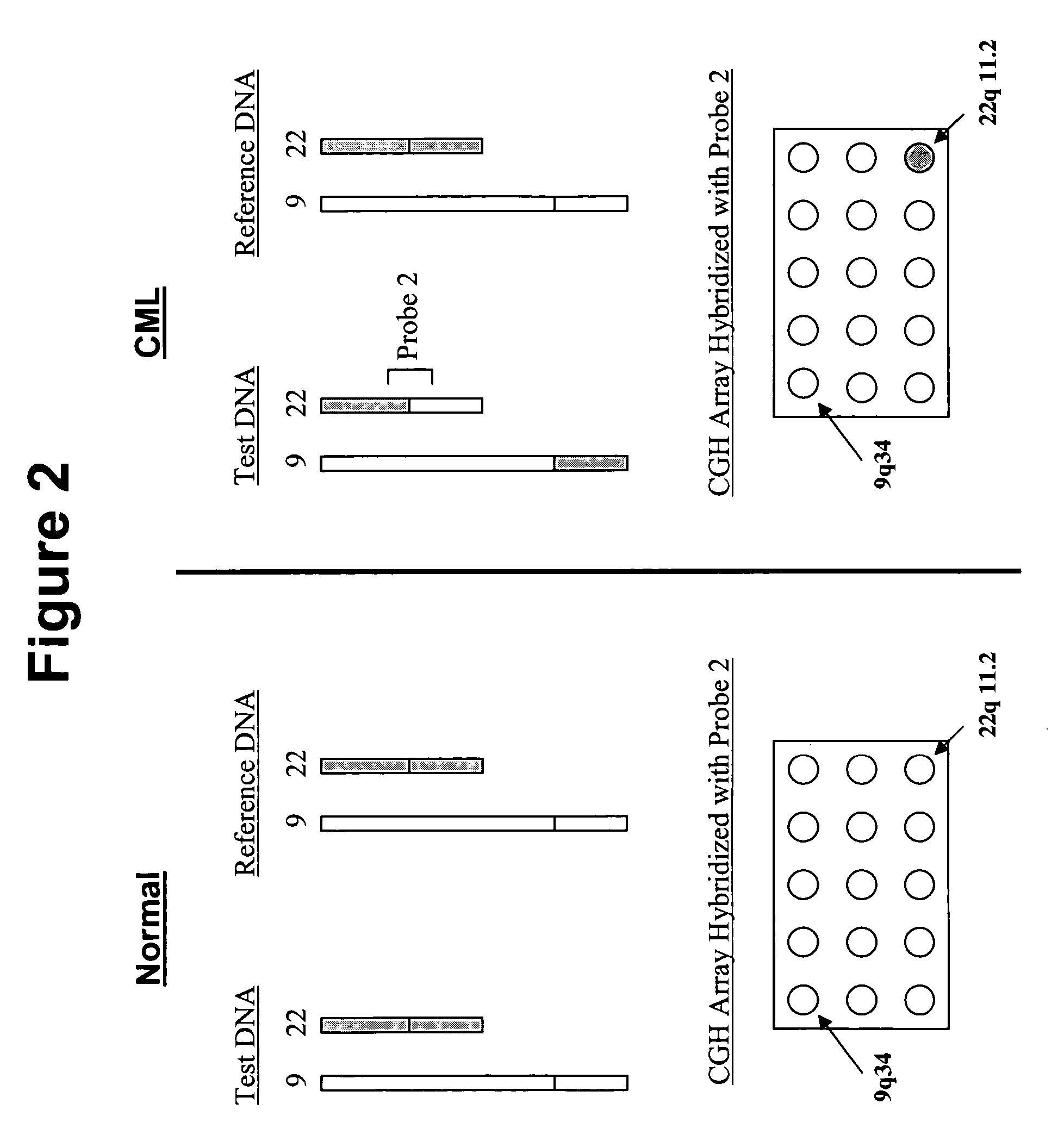
Balanced translocation in comparative hybridization
InactiveUS20070122820A1Quicker and more methodIncrease profitSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention provides comparative genomic hybridization methods for detecting and mapping chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases, or to detecting the phenomena of large scale copy number variants. The method includes hybridization with one or more probes for detecting balanced translocations. Such probes may be complementary to the moving genomic segment which is translocated or may be complementary to the translocation break point.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
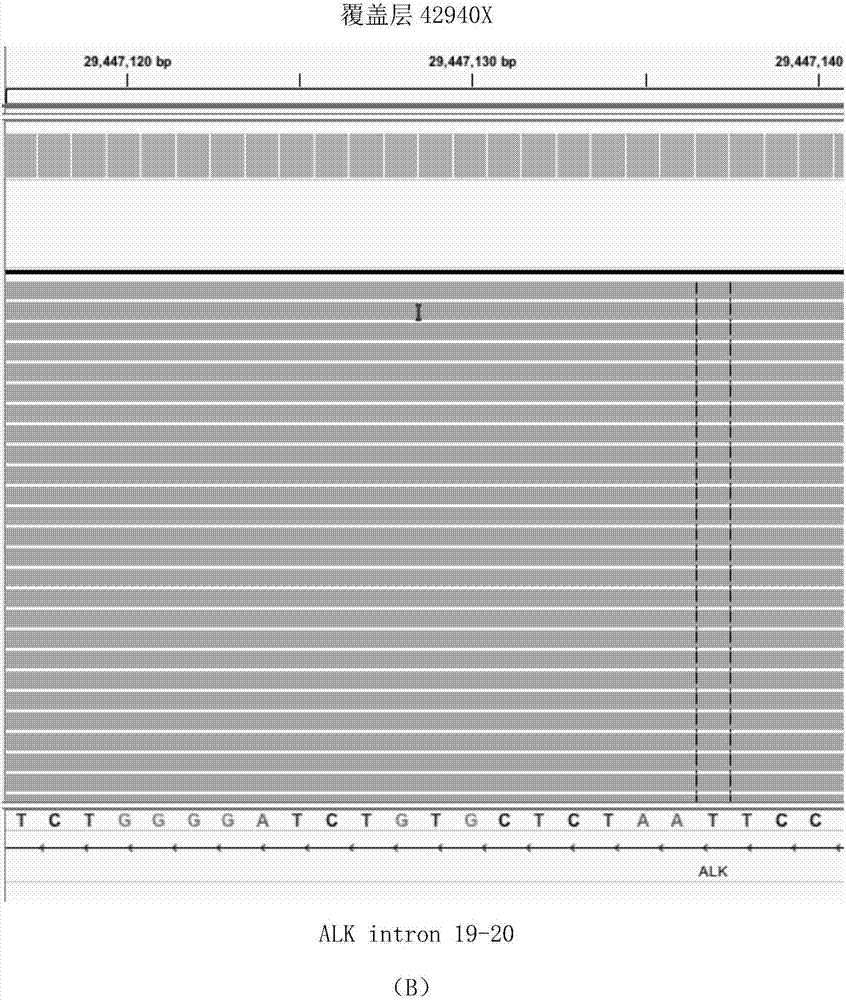
Quality control method for detecting human EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) gene variation based on high-throughput sequencing and kit
InactiveCN106636404AImprove efficiencyReduce testing quality control costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSanger sequencingPositive control
The invention discloses a quality control method for detecting human EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) gene variation based on high-throughput sequencing and a kit, and applications thereof. The quality control method comprises the following steps: extracting a plurality of genome DNAs of an EGFR gene variation-positive human tumor cell line; measuring variation positive sites as positive control sites through a Sanger sequencing method; fragmenting the genome DNAs and mixing according to a certain proportion to obtain a quality control product which can be applied high-throughput sequencing detection of human EGFR gene variation. The kit comprises the human EGFR gene variation detection quality control product.
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting methylated CpG islands
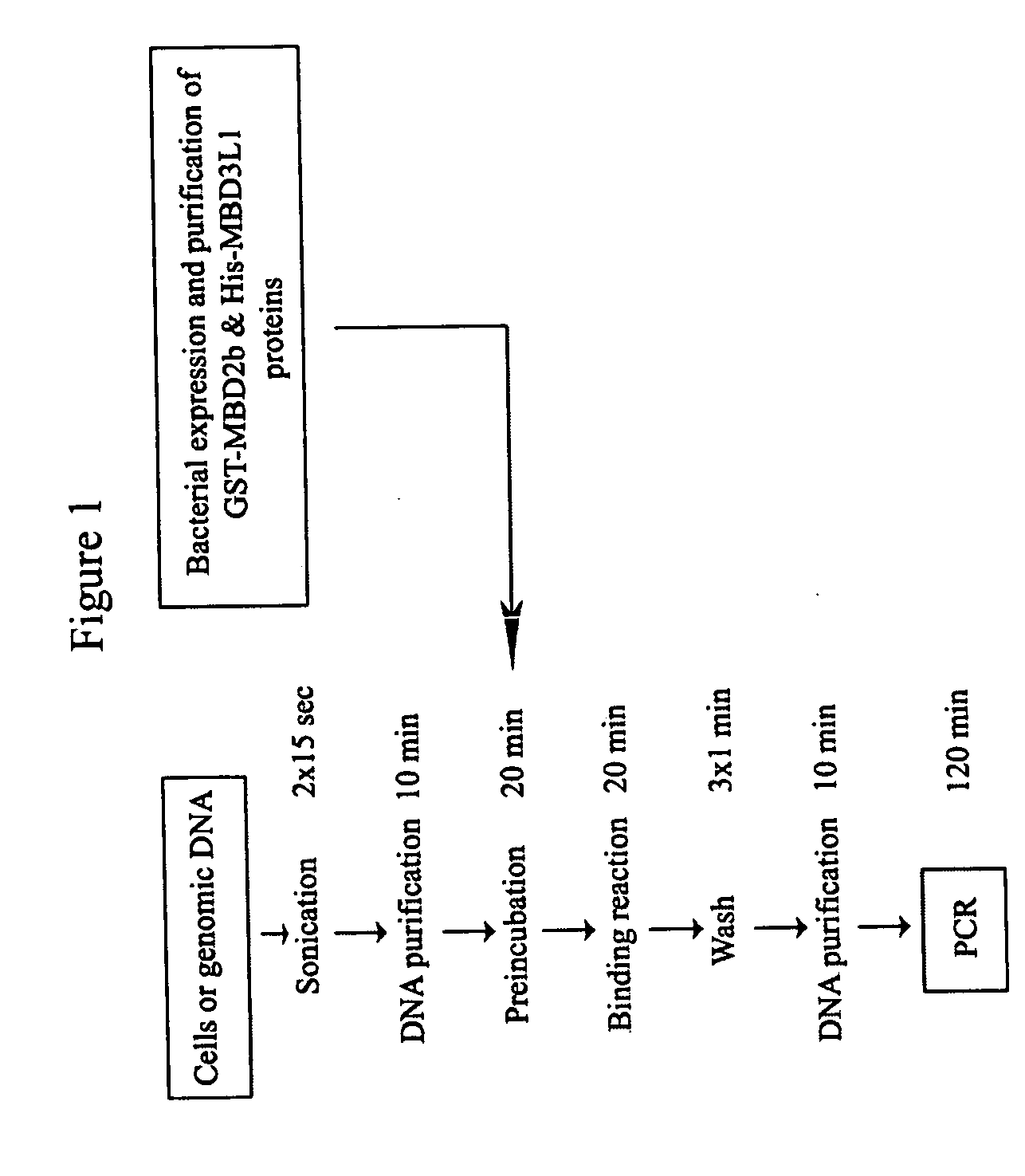
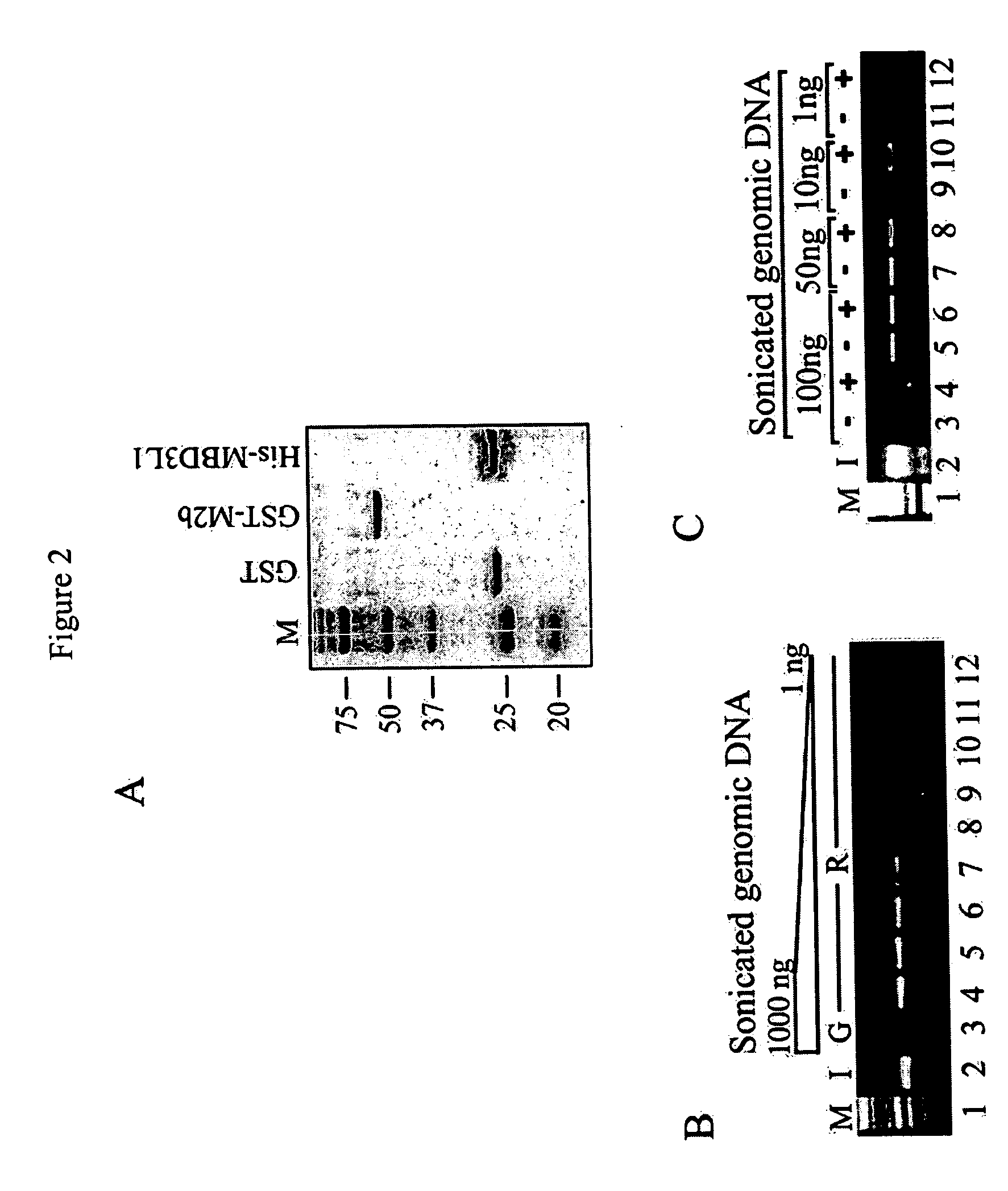
The present invention provides new and improved assay for detection of genomic methylated CpG islands. This new method is termed the methylated-CpG island recovery assay (MIRA). In accordance with one embodiment, MIRA comprises the steps of: (a) incubating genomic DNA fragments with a methylated CpG island binding protein in the presence of a binding partner for the binding protein to produce bound DNA containing methylated CpG islands, (b) isolating the bound DNA, and (c) detecting CpG island methylation by gene-specific amplification reactions. In accordance with a preferred embodiment, MIRA comprises the steps of: (a) incubating sonicated genomic DNA with a matrix containing a fusion protein of glutathione S-transferase (GST) and MBD2b (GST-MBD2b) in the presence of MBD3L1 to produce bound DNA containing methylated CpG islands, (b) eluting bound DNA from the matrix, and (c) detecting CpG island methylation by gene-specific amplification reactions.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
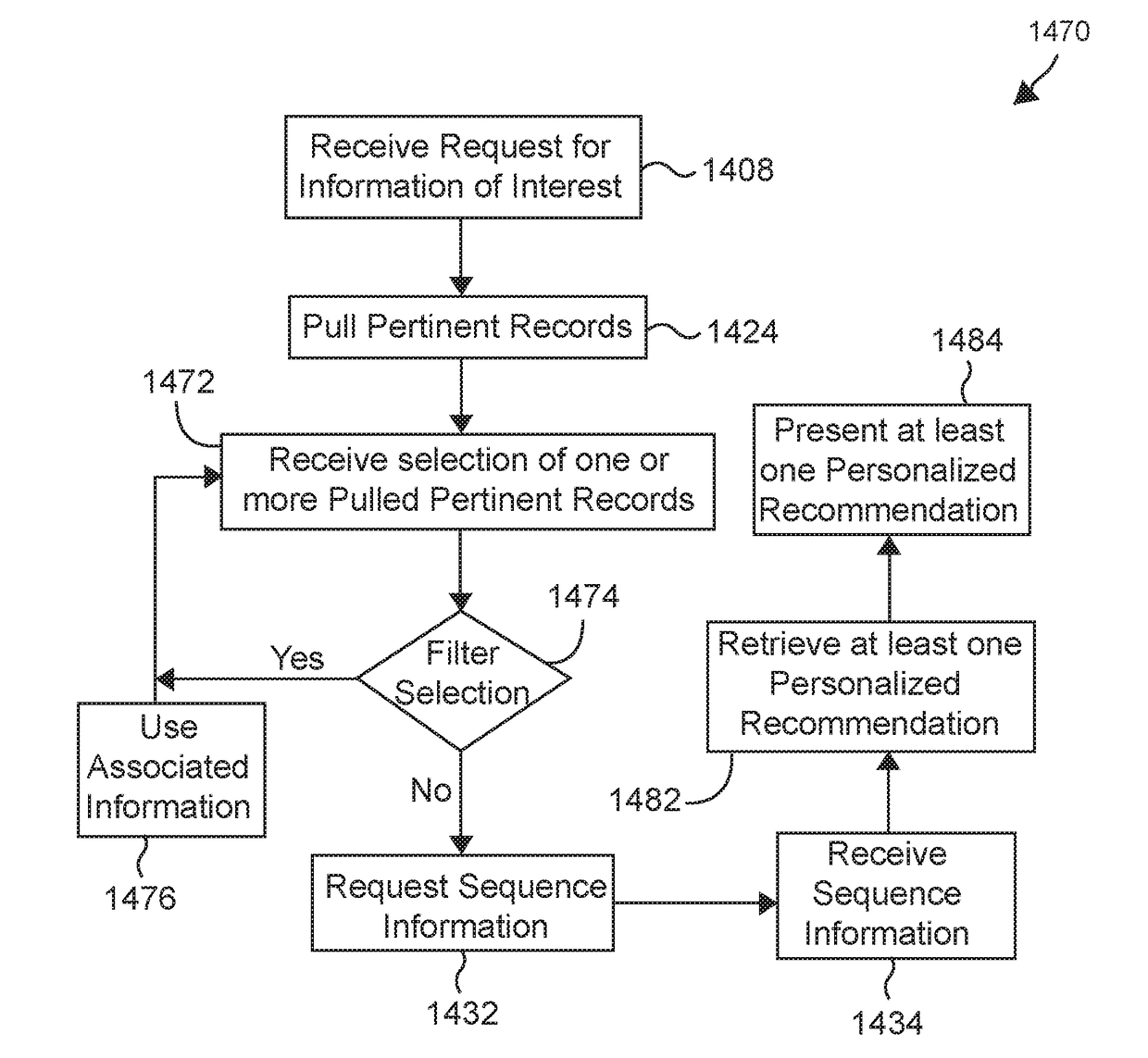
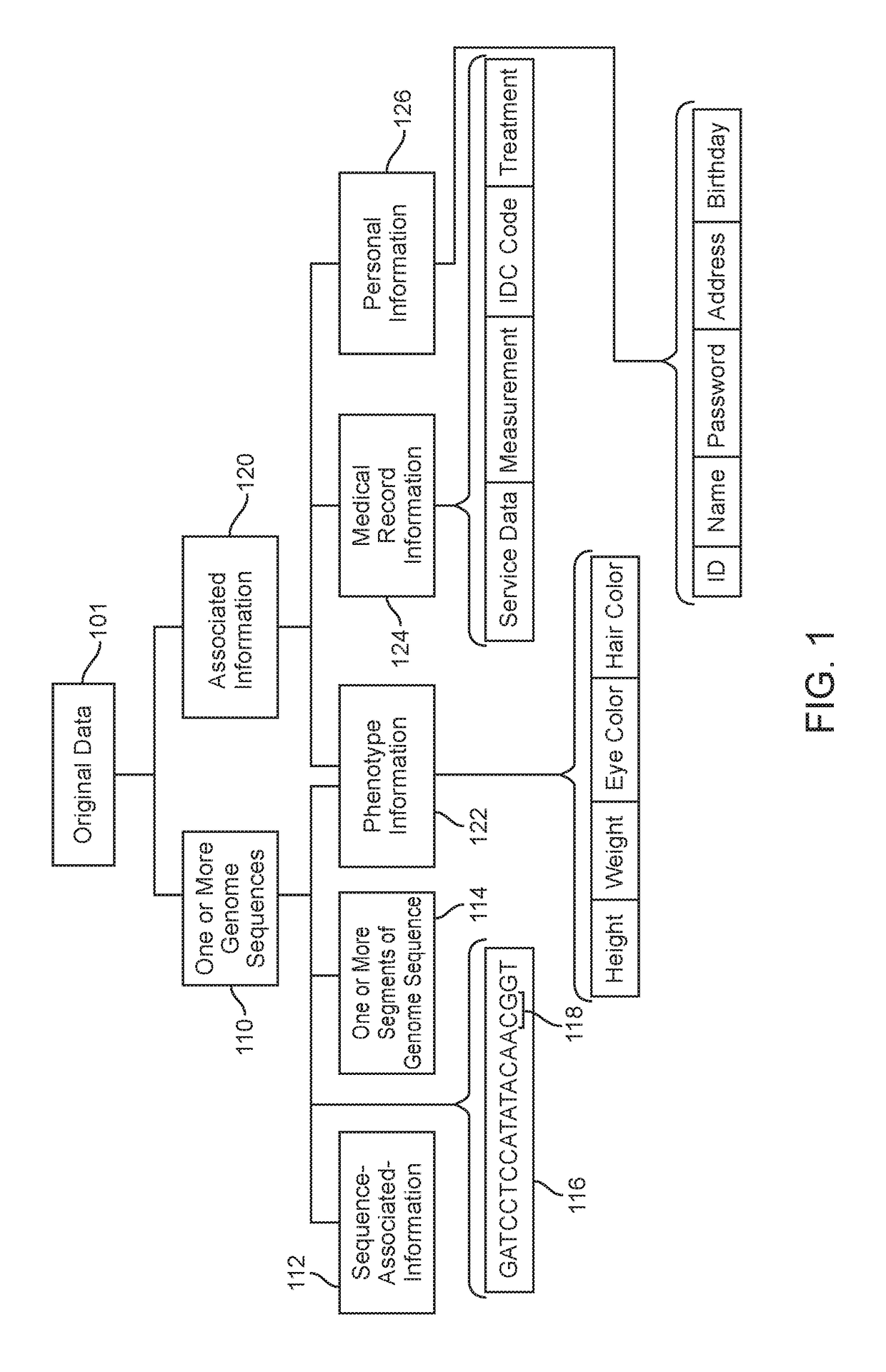
Methods and systems for anonymizing genome segments and sequences and associated information
ActiveUS20170308717A1Prevent and minimize and mitigate identificationMinimize storage spaceDigital data protectionBioinformaticsGenomic SegmentRelevant information
Various methods and systems for processing at least some of genome sequences and at least some of associated information, for an individual, may be described and disclosed herein. A purpose of such processing may be to prevent, minimize, and / or mitigate against (1) identification of the individual from such genome sequence information and / or from associated information; and / or (2) using such genome sequence information and / or associated information as a basis for discriminating against the individual. In some embodiments, such processing may comprise one or more of: segmenting genome sequences for at least a purpose of anonymizing genome information; using anchor segments for a purpose of minimizing storage space in storing of genetic sequence information; generating at least one linkage record; generating at least one anonymized linkage record; processing a request for genetic study results; processing genetic study results received; and / or generating personalized information of interest pertaining to the individual.
Owner:HUANG ETHAN
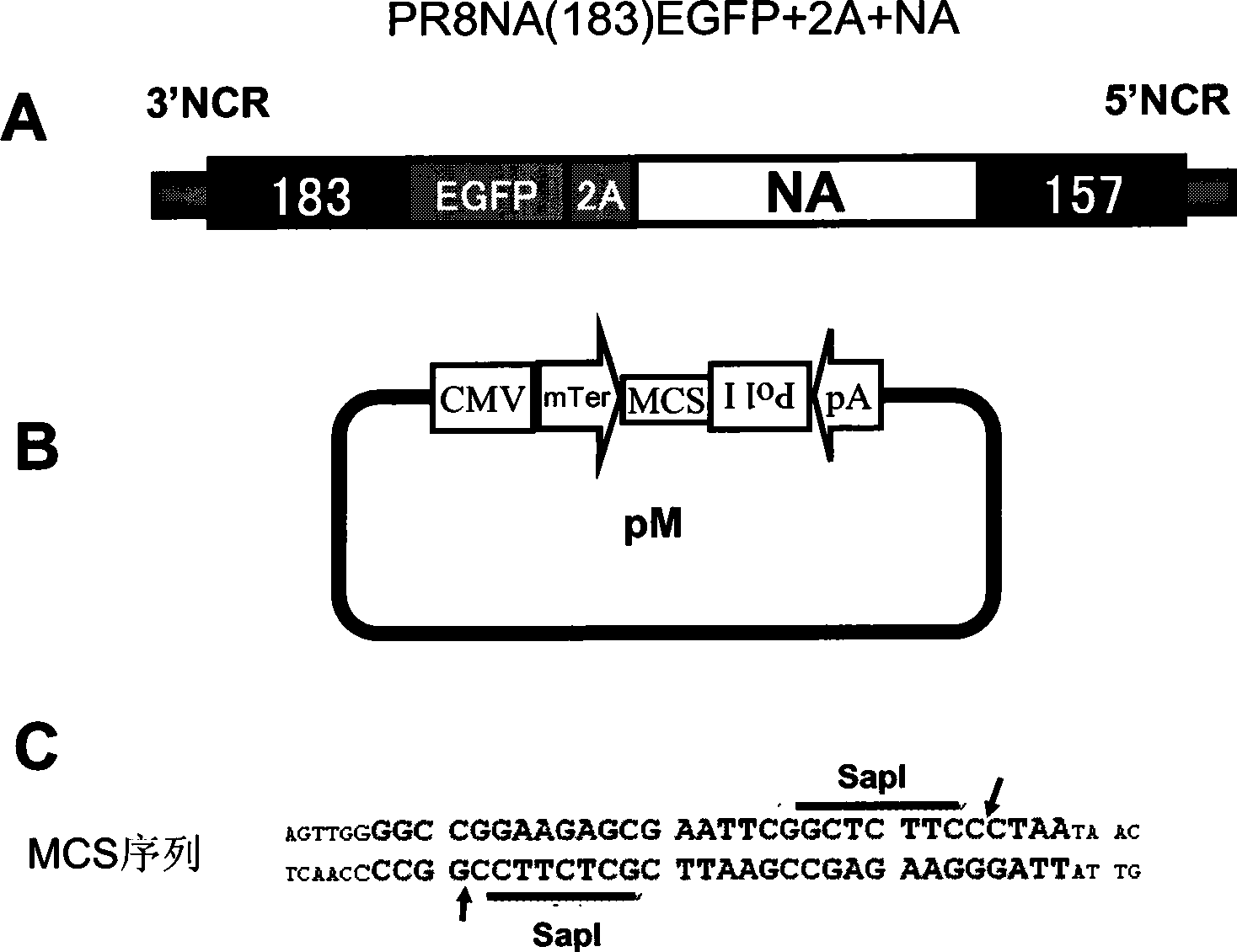
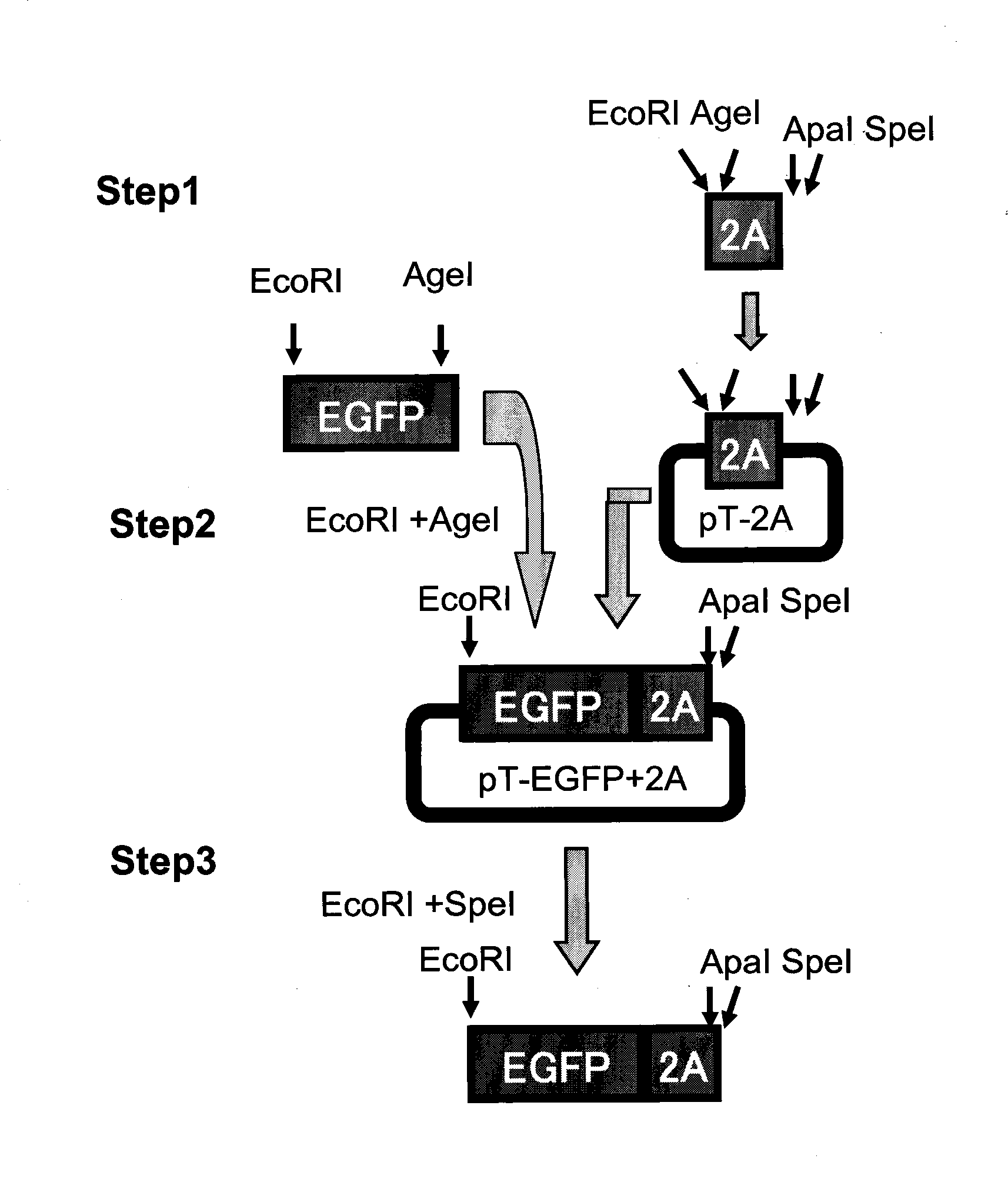
Recombinant influenza virus vector carrying foreign genes in NA segment and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101532030AIncrease the lengthWork around capacity constraintsGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementViral vectorBioreactor
The invention discloses a recombinant influenza virus vector carrying foreign genes in an NA segment, which can be rescued in cells by a virus rescue method and can be amplified in chick embryos in large quantities. The invention also discloses a preparation method thereof, comprising the following steps: firstly constructing plasmids used for rescuing influenza viruses and introduced with the foreign genes on the NA genome segment of the influenza virus and carrying out rescue on host cells. The foreign gene is connected with the NA genome segment by a 2A segment. The foreign gene comprises EGFP reporter genes and adopts a CMV / huPolI bidirectional influenza virus rescue system. The recombinant influenza virus vector overcomes capacity limit of the foreign genes in the influenza virus genome, enjoys stable passage in chick embryos, can be applied to vaccine and drug development and tumor treatment and can produce recombinant cell factor drugs in cheap chick embryo bioreactors.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com