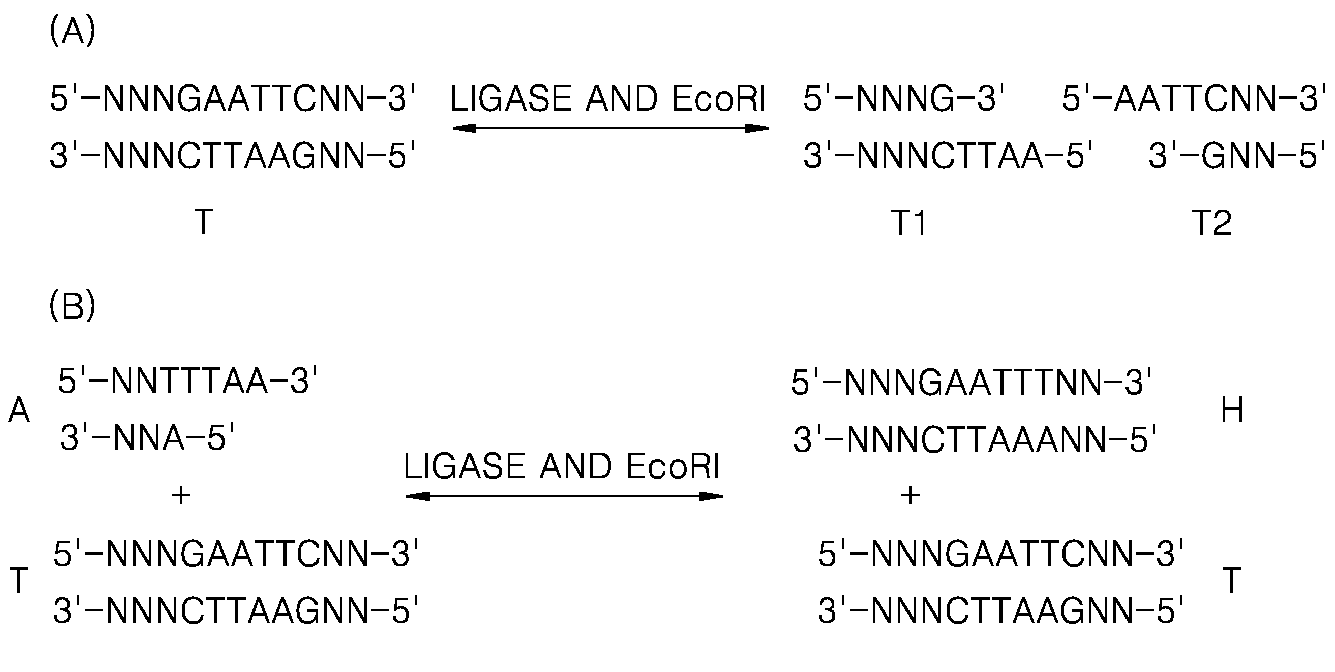Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
875 results about "Dna template" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
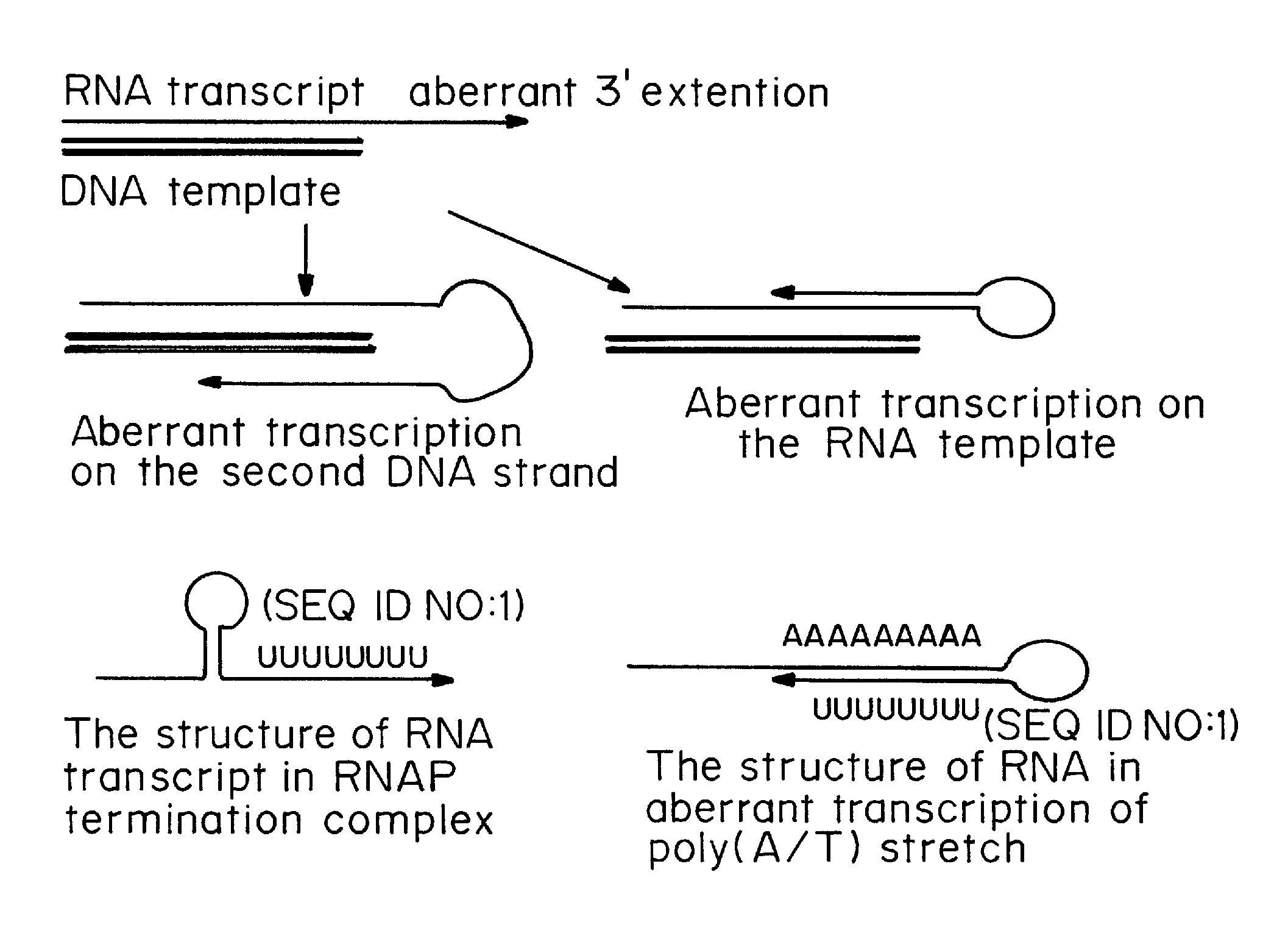
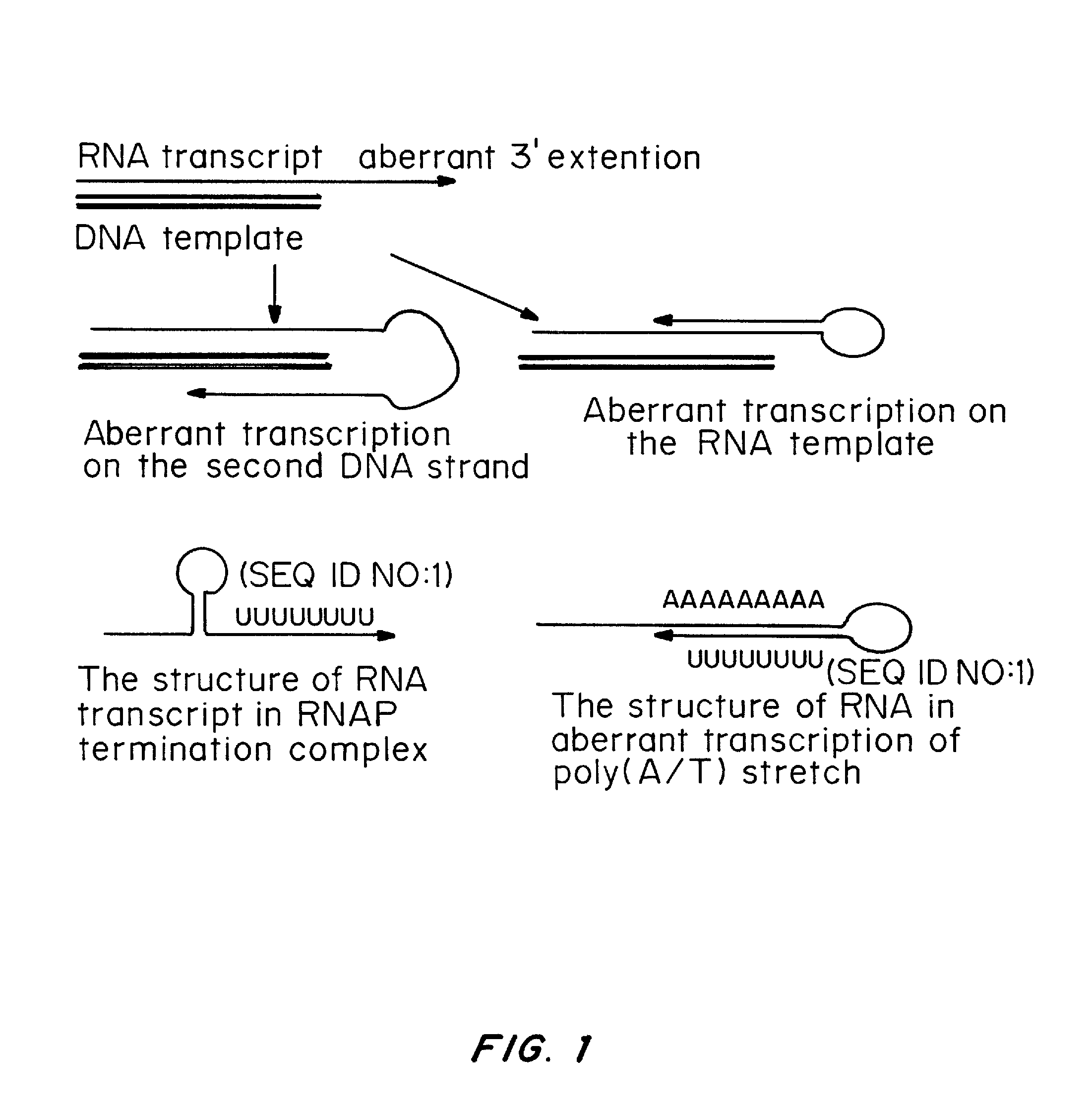
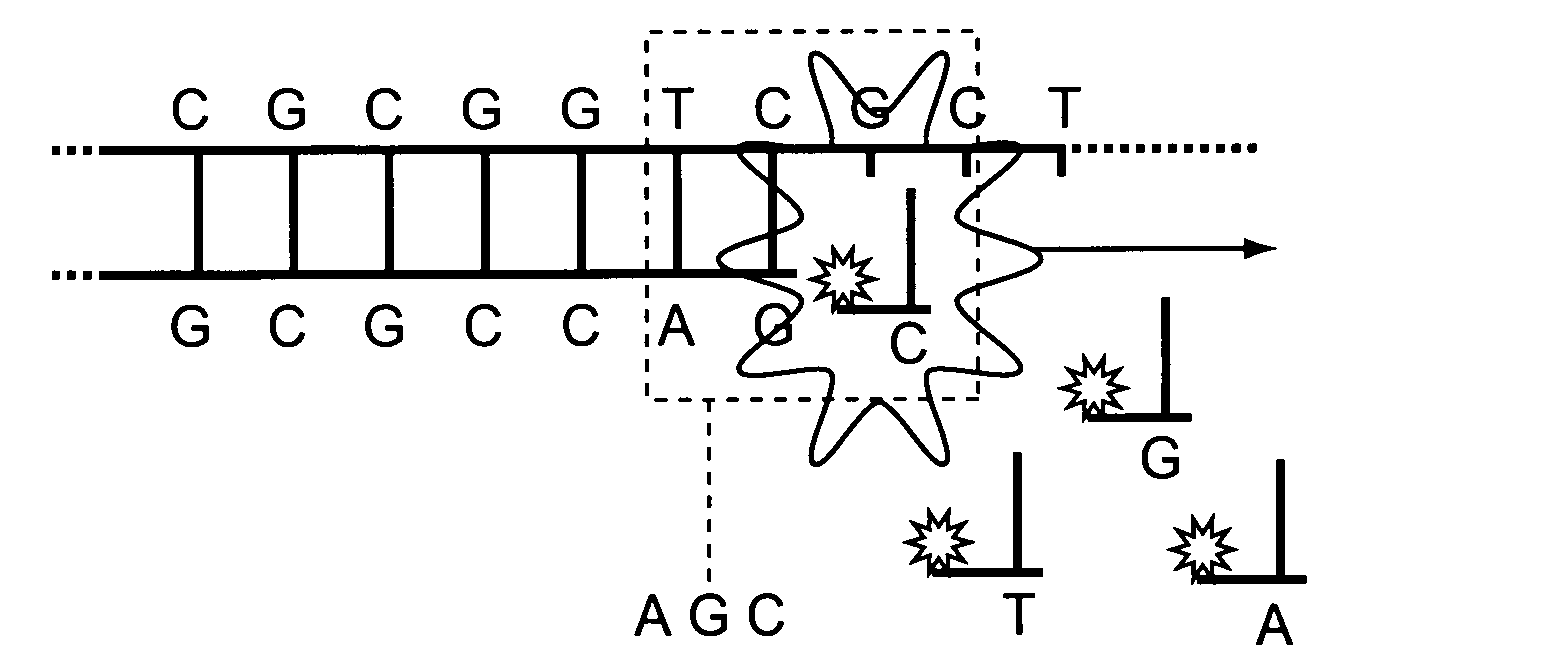
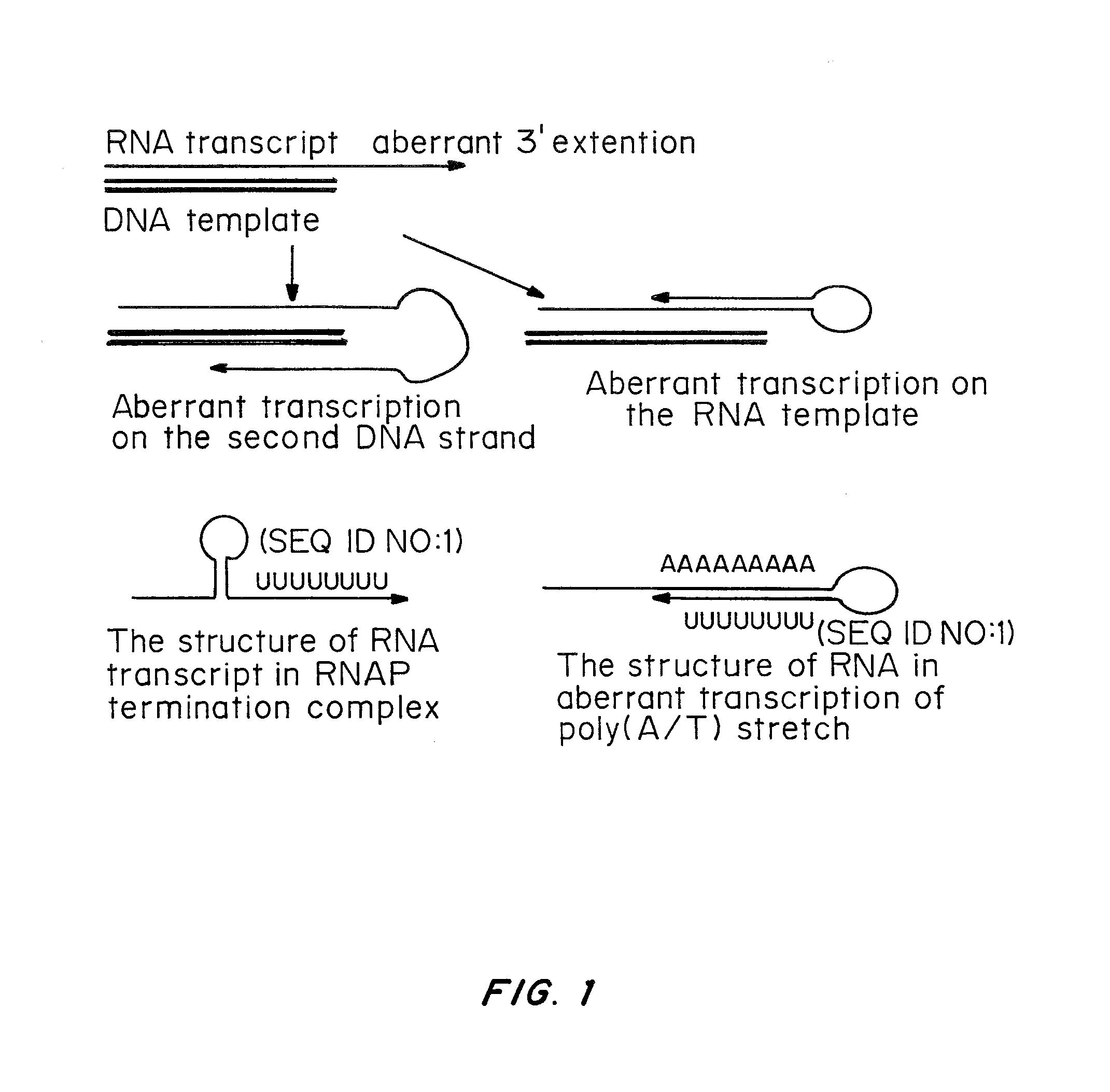
One strand of the DNA, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for RNA synthesis. As transcription proceeds, RNA polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create an RNA copy (which elongates during the traversal).
Polymerases
ActiveUS20060281109A1Improve the level ofProceed efficientlySugar derivativesHydrolasesModified dnaPolymerase L
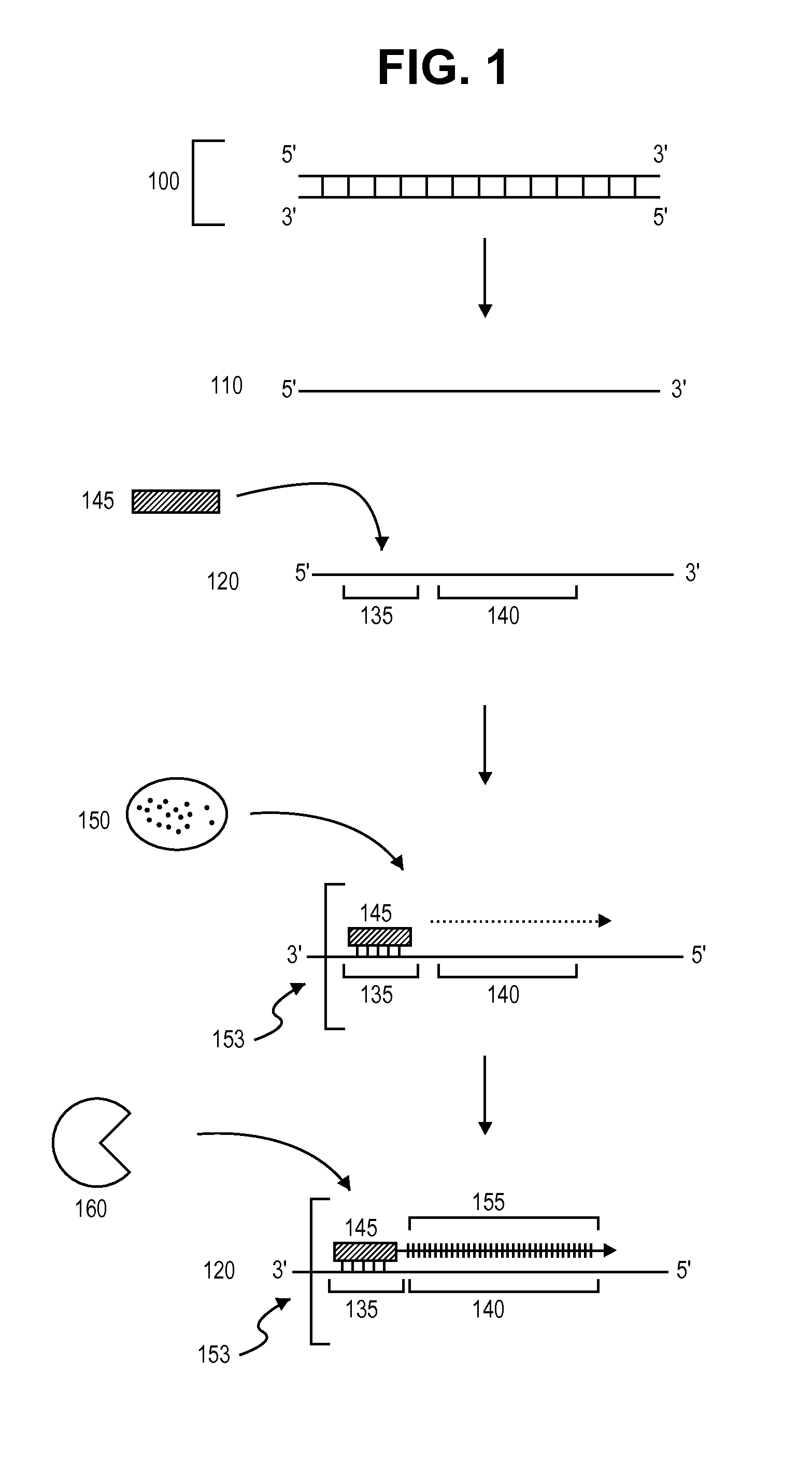
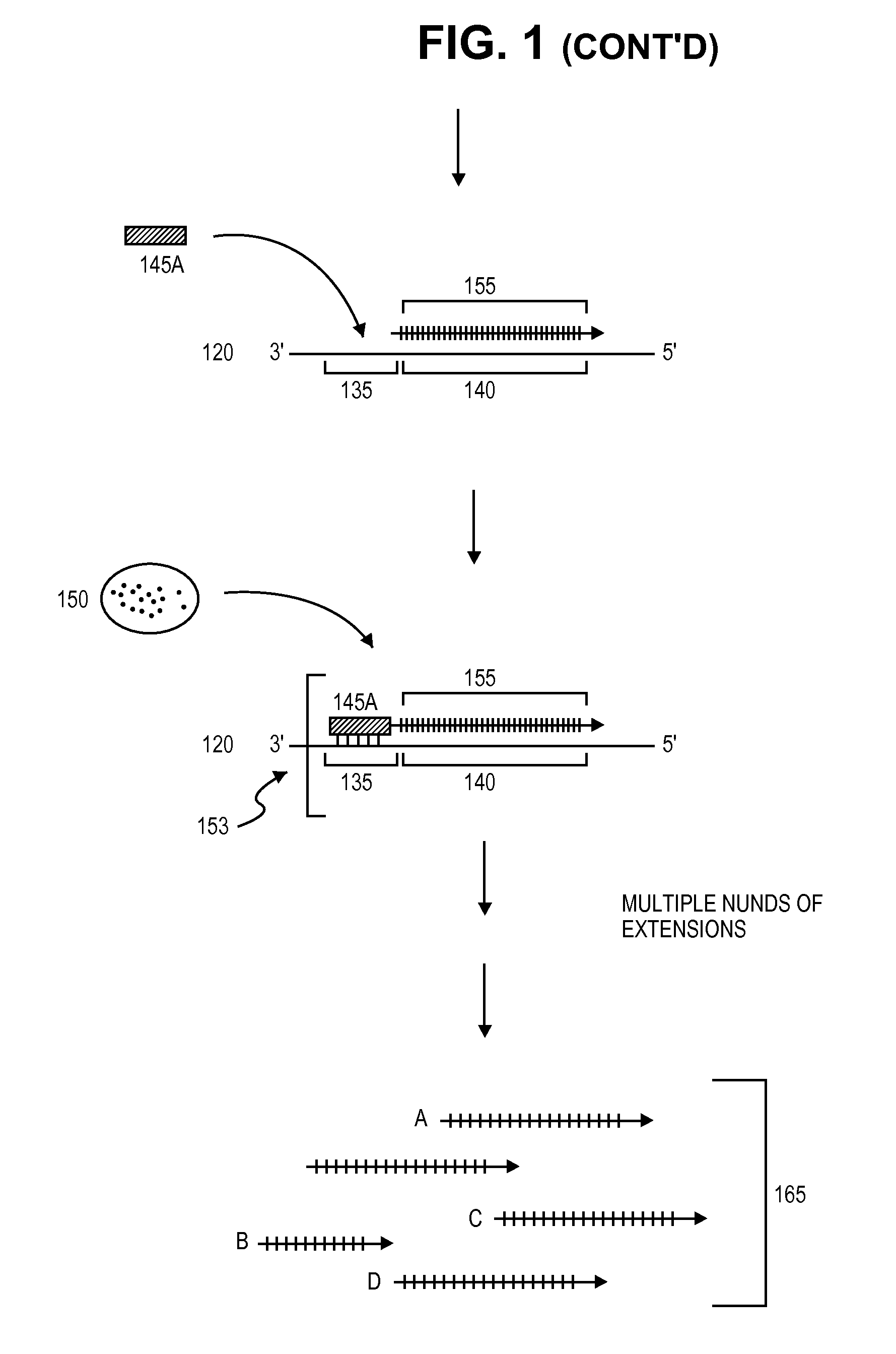
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Safe sequencing system
ActiveUS20140227705A1Sensitively accurately determiningMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideInstrumentation
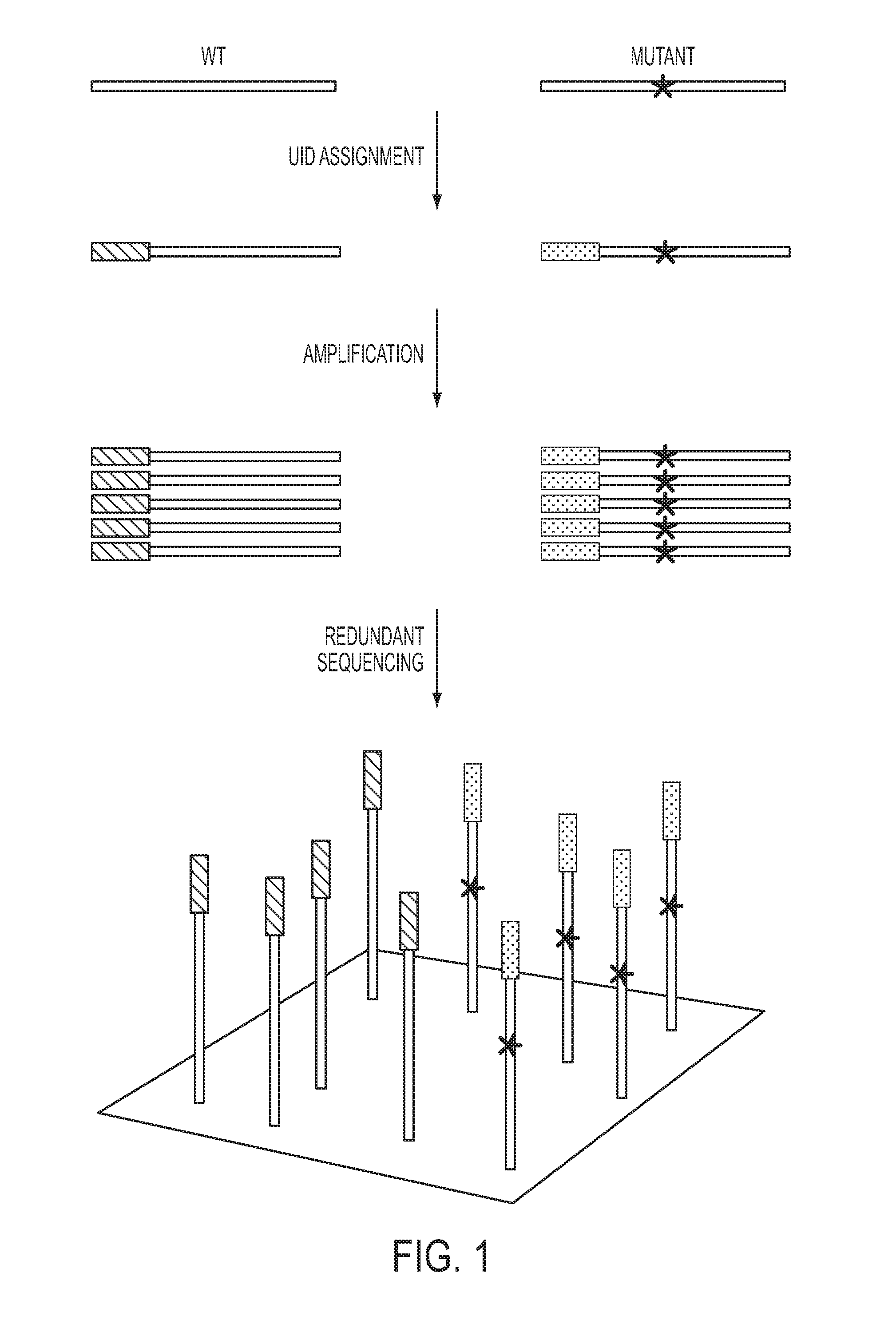
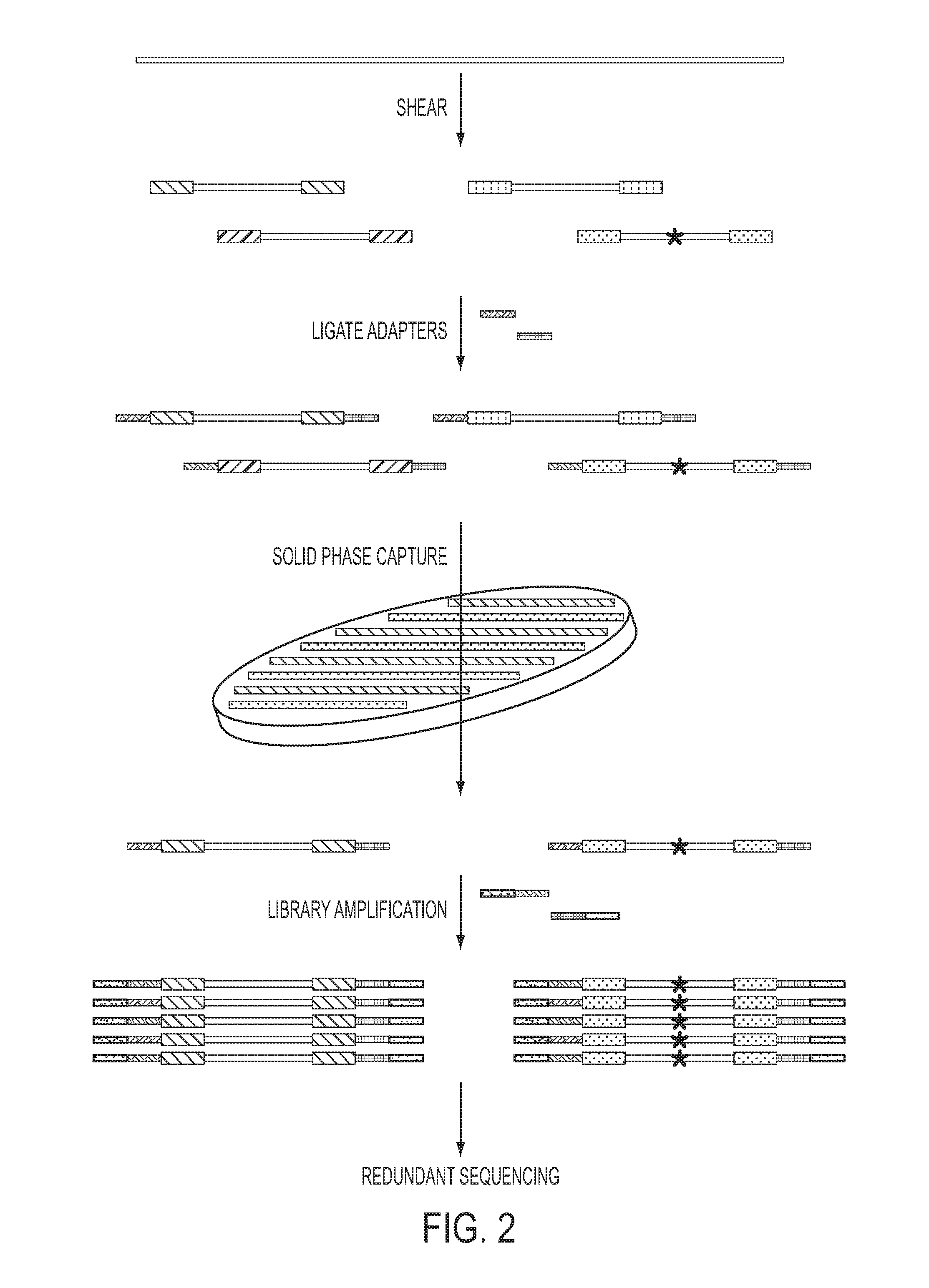
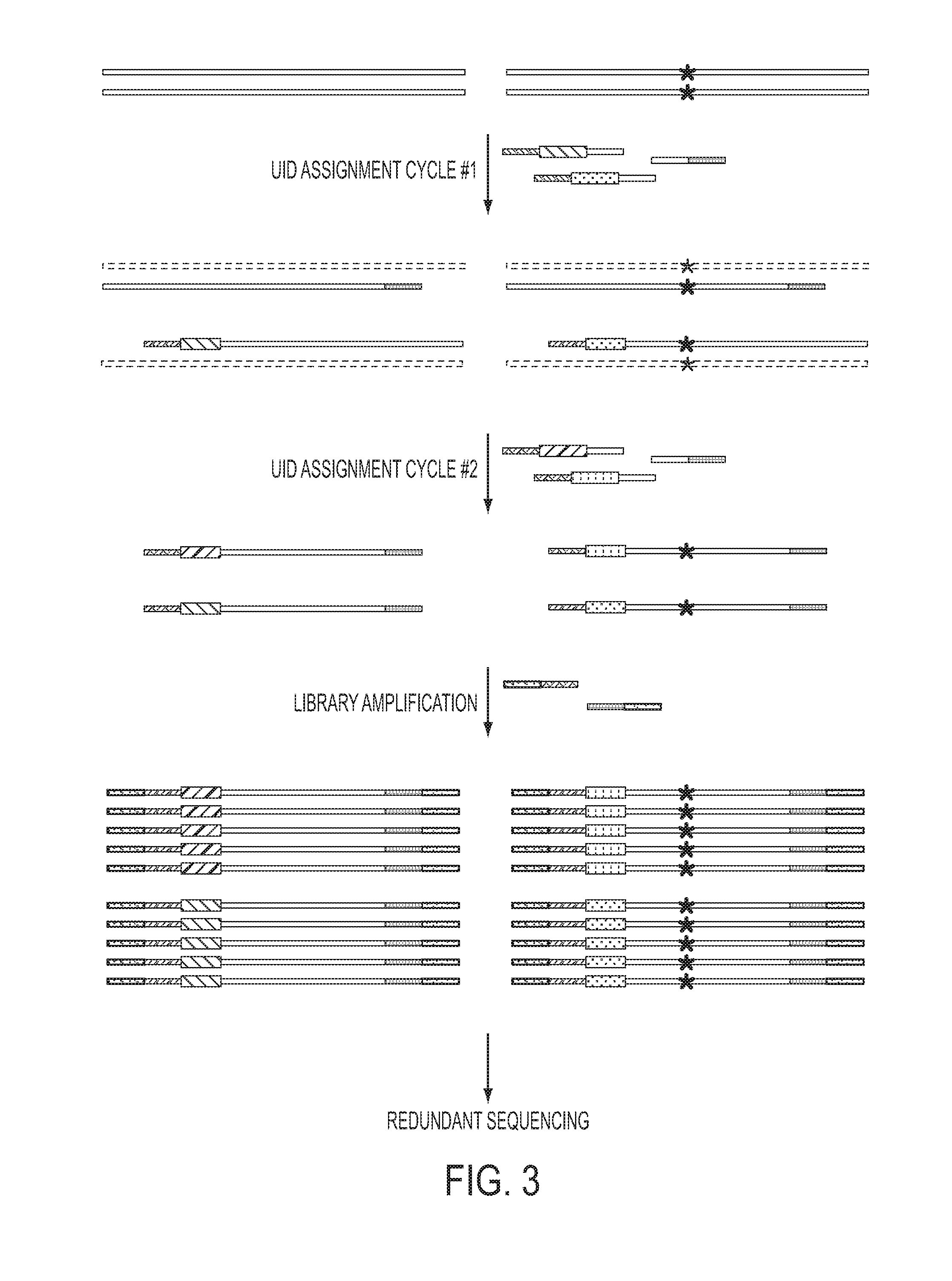
The identification of mutations that are present in a small fraction of DNA templates is essential for progress in several areas of biomedical research. Though massively parallel sequencing instruments are in principle well-suited to this task, the error rates in such instruments are generally too high to allow confident identification of rare variants. We here describe an approach that can substantially increase the sensitivity of massively parallel sequencing instruments for this purpose. One example of this approach, called “Safe-SeqS” for (Safe-Sequencing System) includes (i) assignment of a unique identifier (UID) to each template molecule; (ii) amplification of each uniquely tagged template molecule to create UID-families; and (iii) redundant sequencing of the amplification products. PCR fragments with the same UID are truly mutant (“super-mutants”) if ≧95% of them contain the identical mutation. We illustrate the utility of this approach for determining the fidelity of a polymerase, the accuracy of oligonucleotides synthesized in vitro, and the prevalence of mutations in the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of normal cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
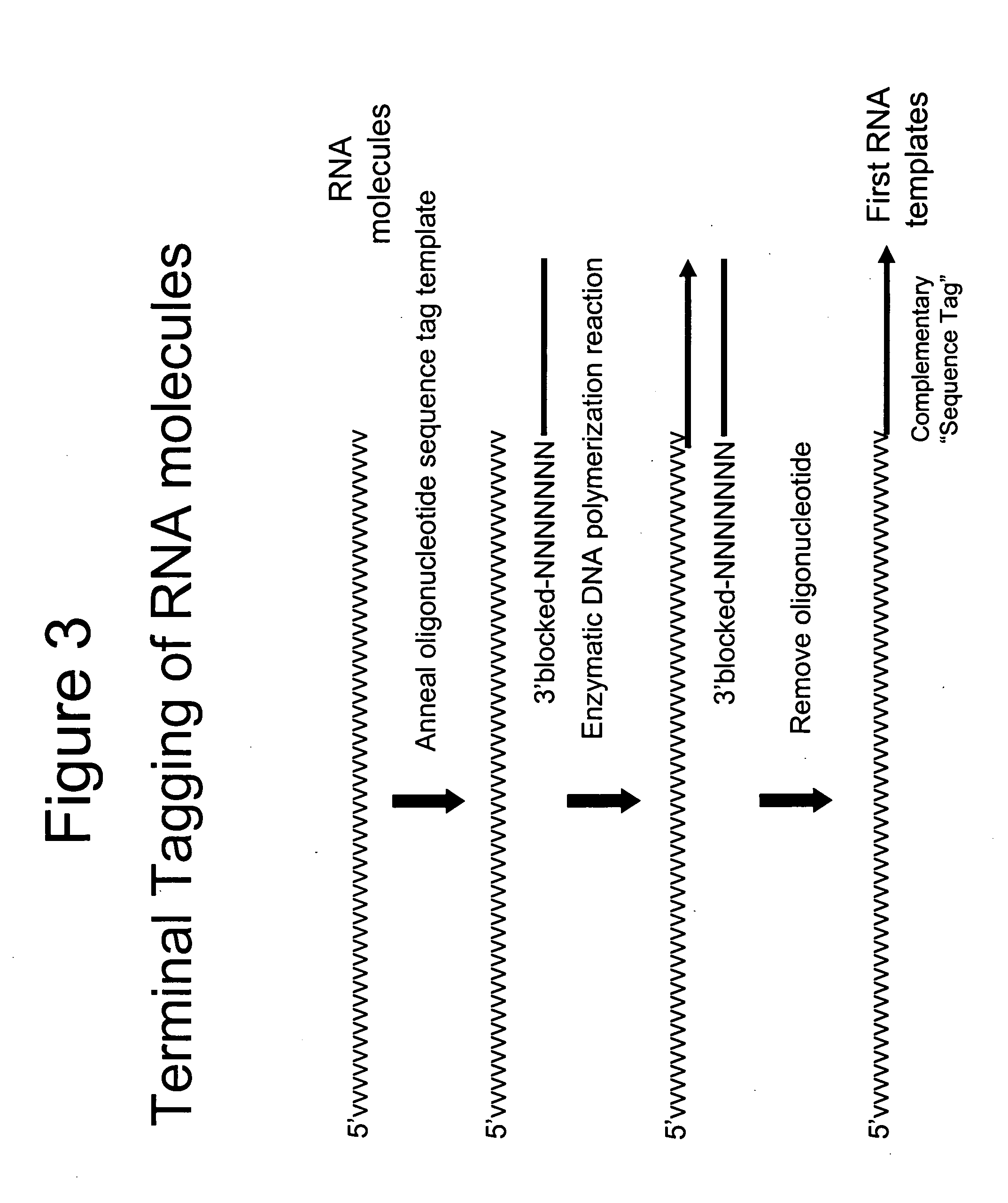
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050153333A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationDna amplificationDouble stranded
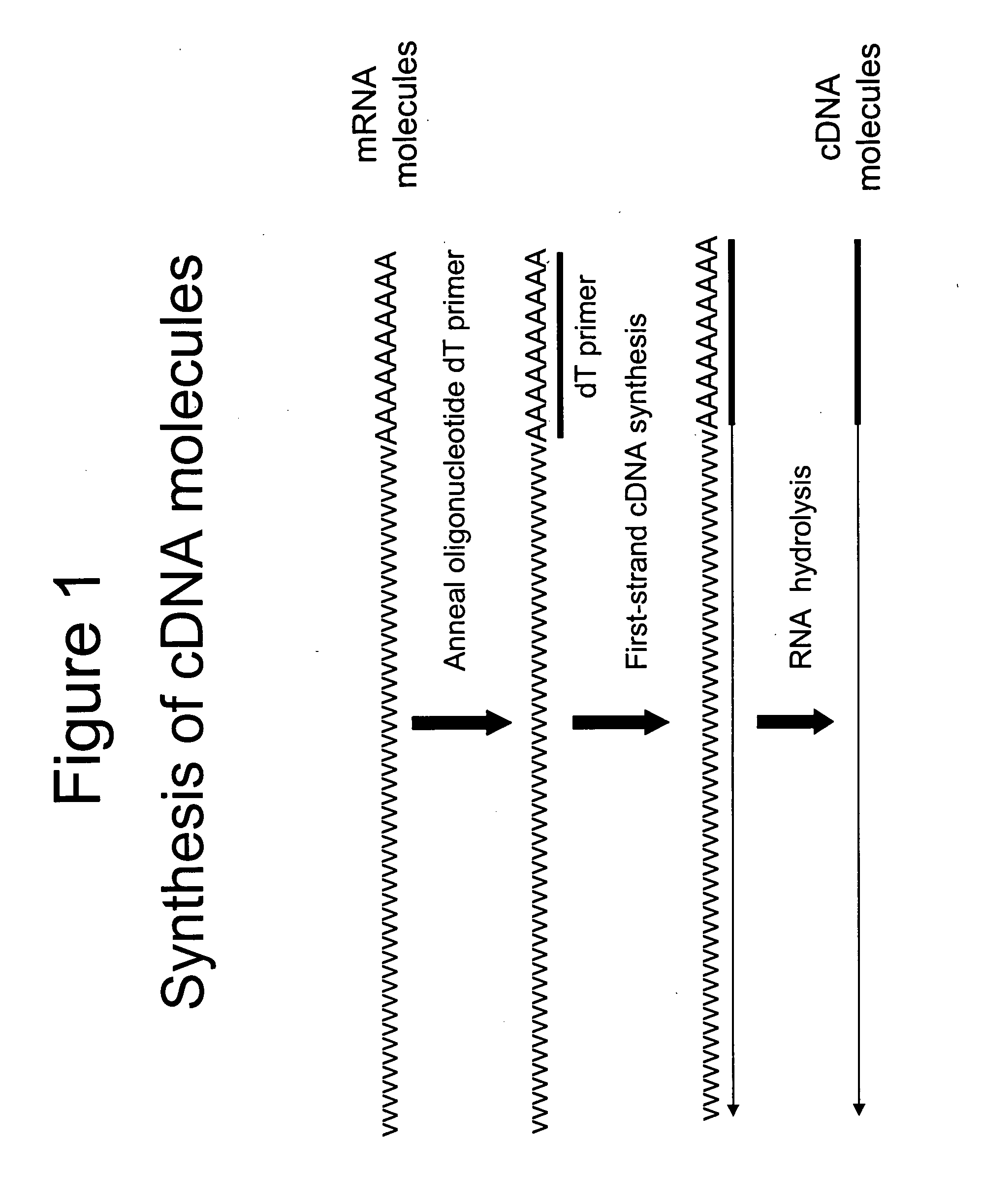
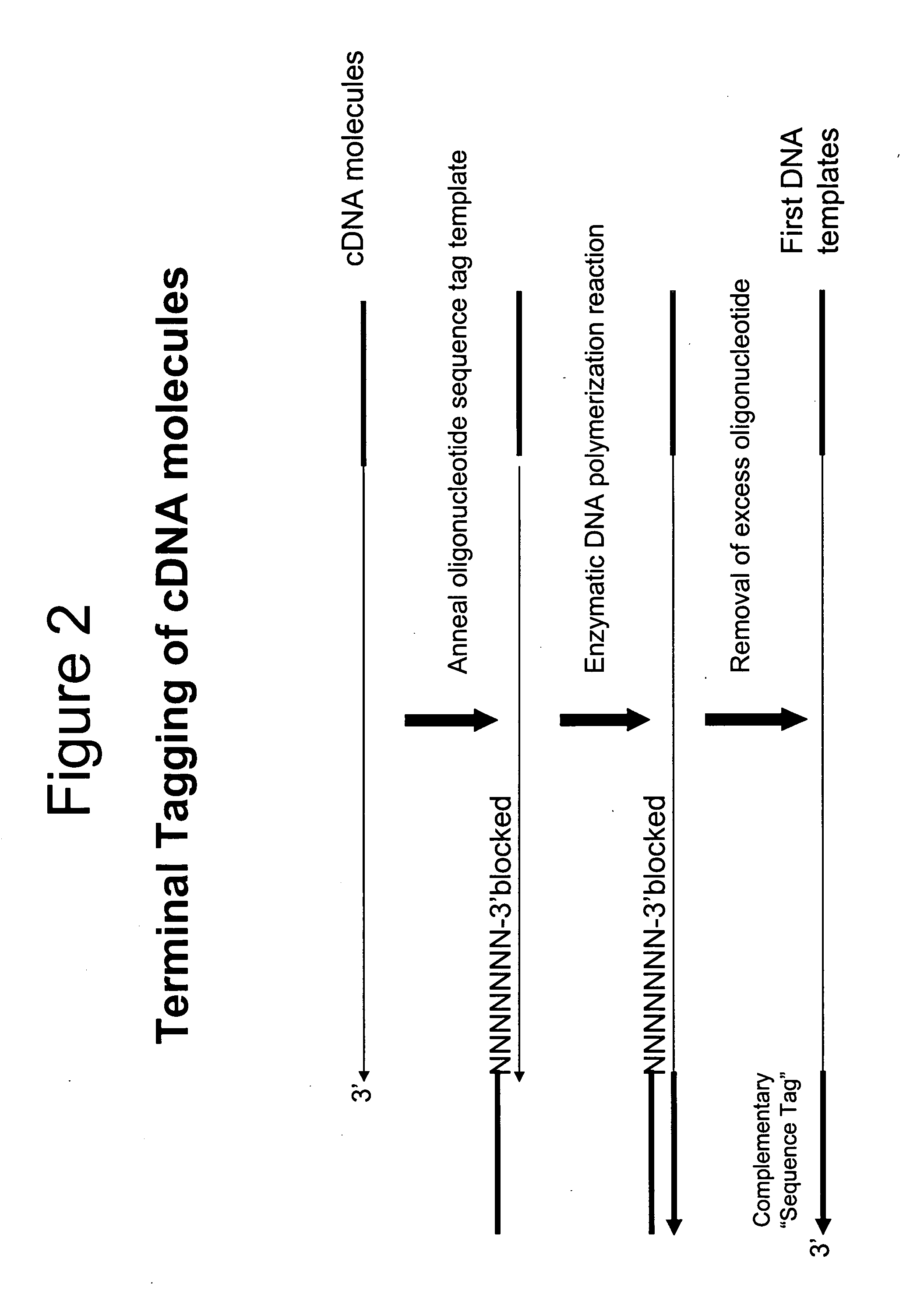
A method is provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The method involves contacting with a mixture of oligonucleotides, each having a sequence tag template, a random sequence and a blocked 3′ terminus, under conditions such that, the random sequence anneals with the nucleic acid molecules and the nucleic acid molecules are extended using the sequence tag template as template. For synthesis of RNA from DNA molecules having terminal sequence tags, the method includes forming DNA templates having a double stranded promoter sequence and synthesizing RNA from the DNA templates. For amplification of sequences from DNA molecules having terminal sequence tags, the method includes forming DNA templates by extension of one primer having a sequence that is complementary to the terminal sequence tag and another primer having a sequence that is derived form one of the DNA molecules.
Owner:EPICENT BIOTECH
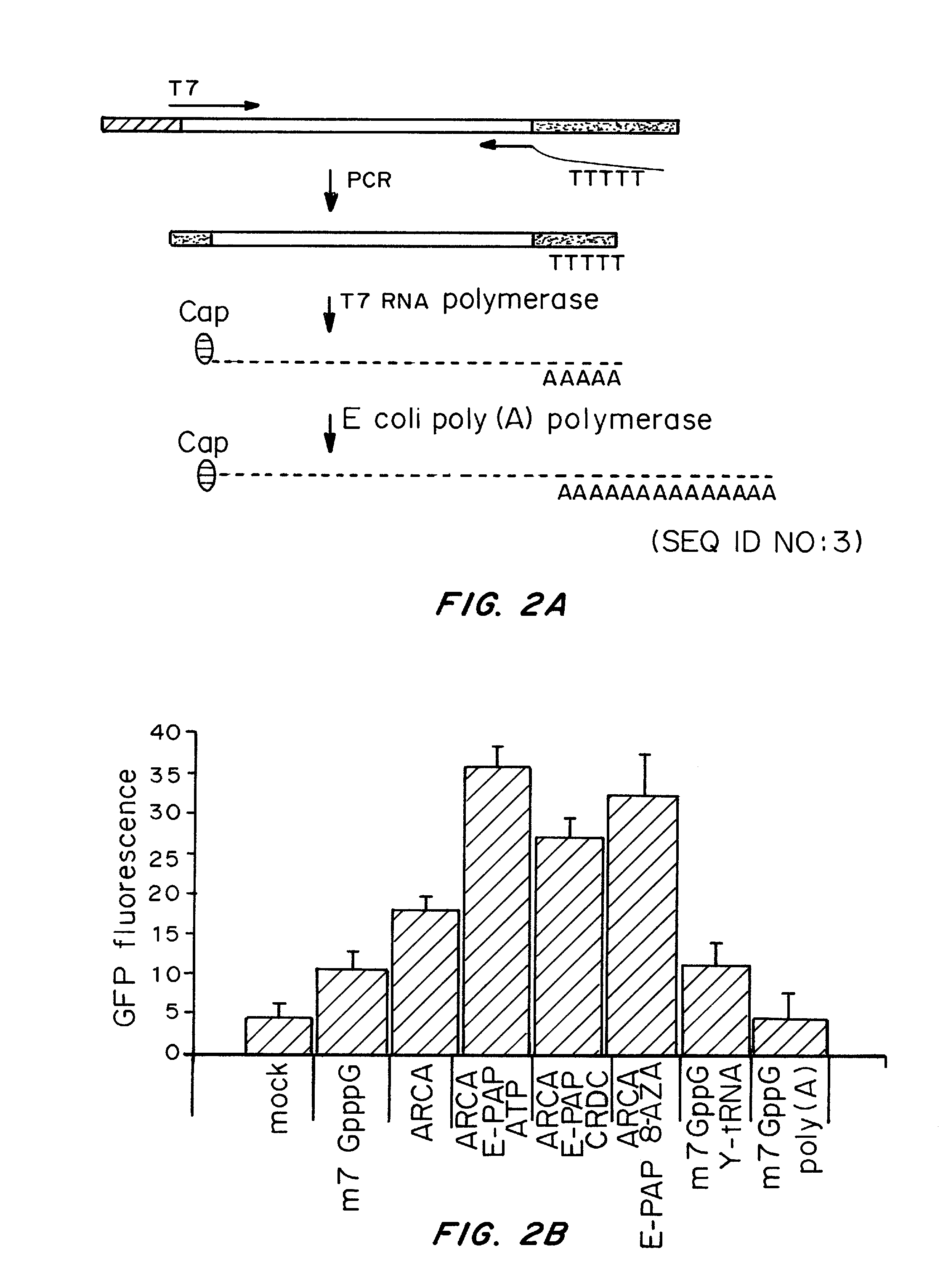
Transient Transfection with RNA
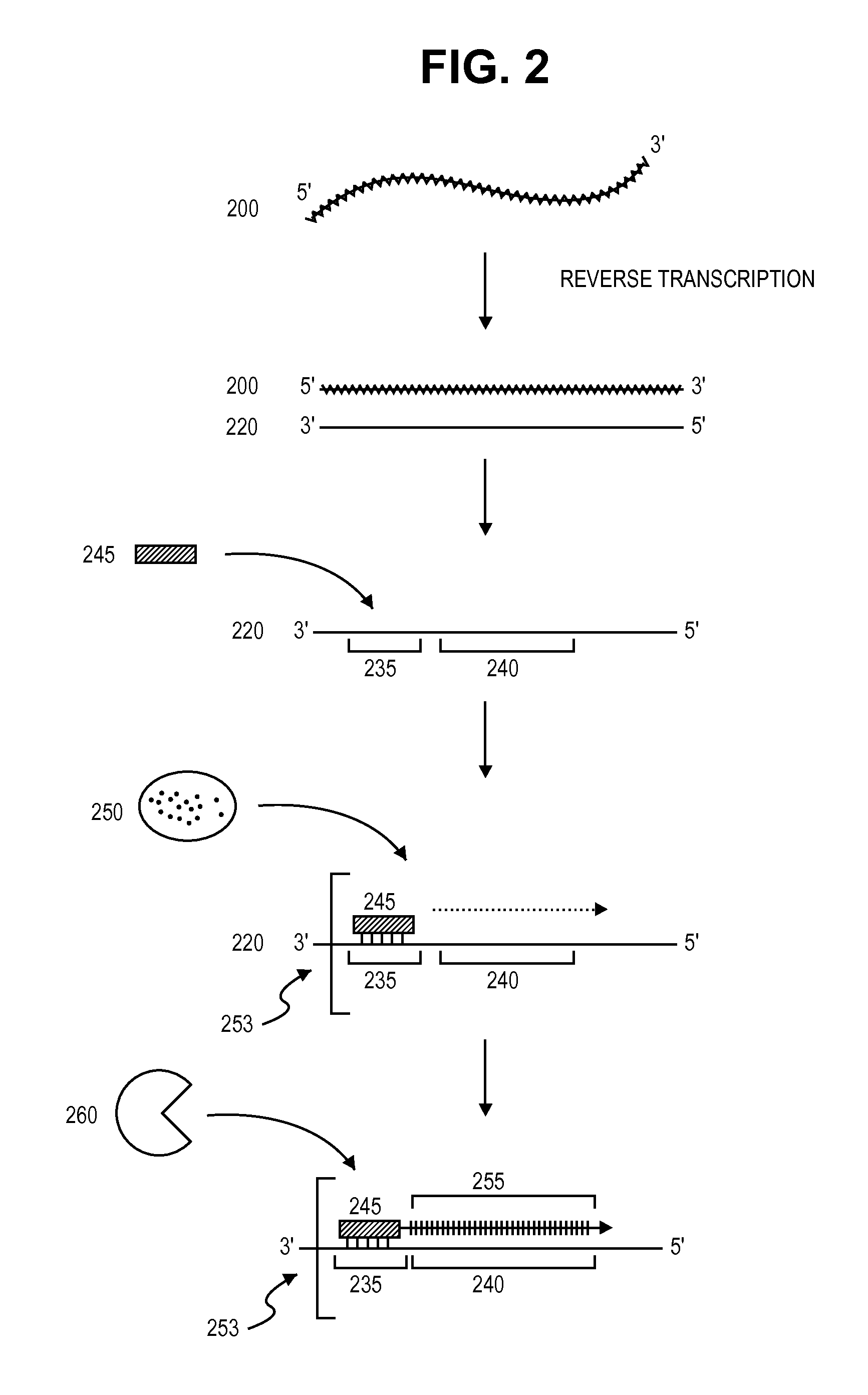
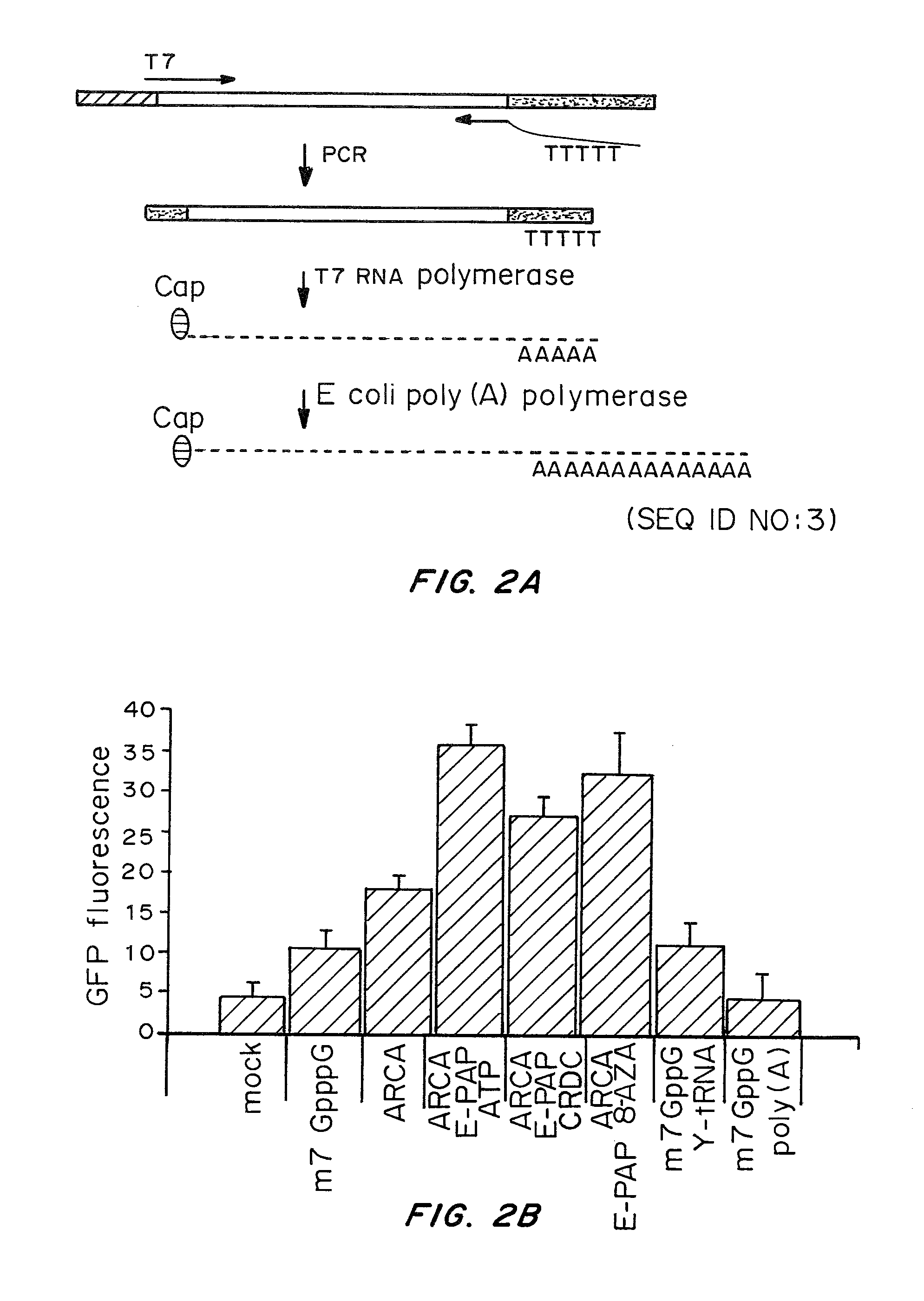
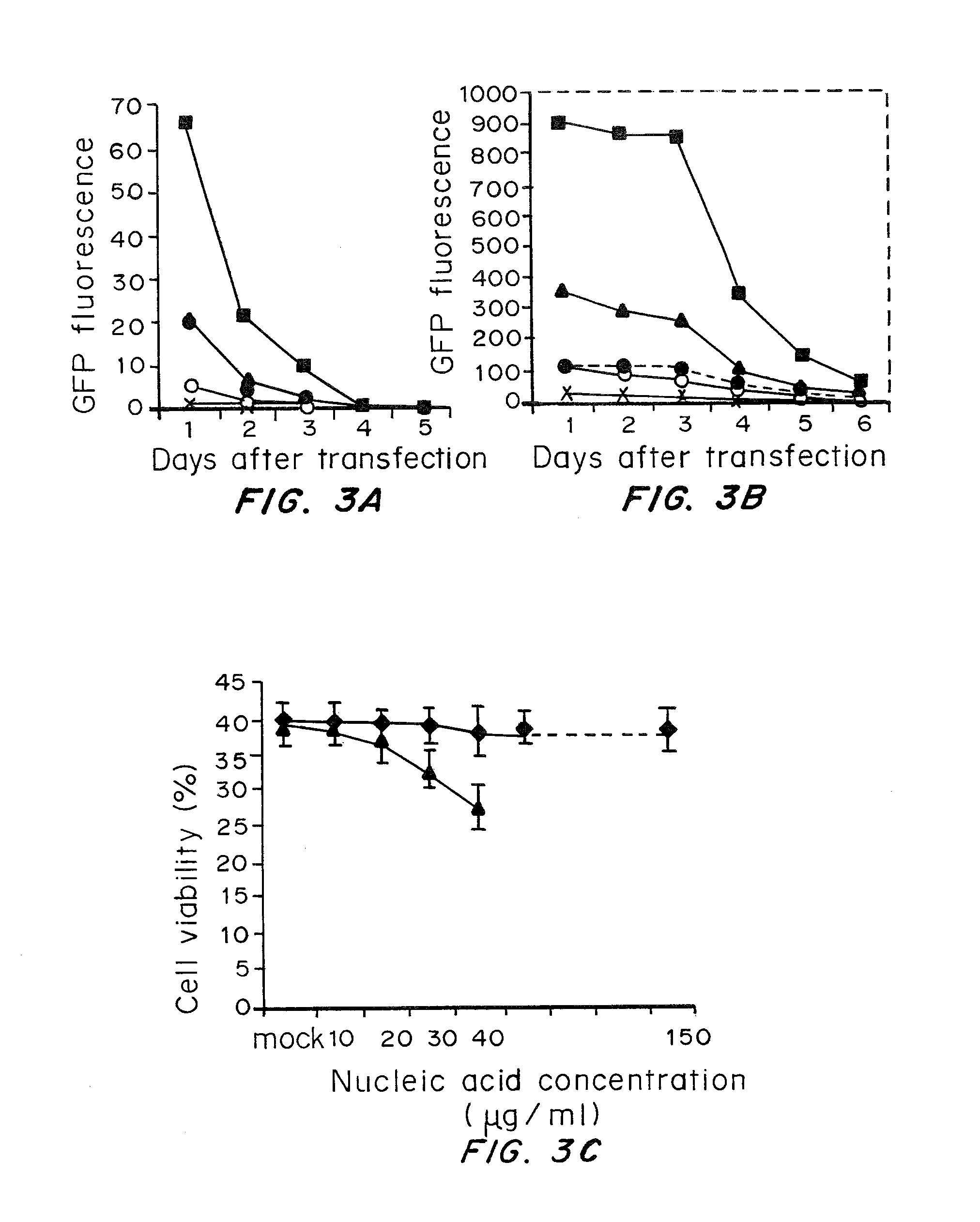
ActiveUS20080260706A1Lymphocyte transfectabilitySimilar efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDNA construct
A method of mRNA production for use in transfection is provided, that involves in vitro transcription of PCR generated templates with specially designed primers, followed by polyA addition, to produce a construct containing 3′ and 5′ untranslated sequence (“UTR”), a 5′ cap and / or Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES), the gene to be expressed, and a polyA tail, typically 50-2000 bases in length. This RNA can efficiently transfect different kinds of cells. This approach results in increased efficiency (fidelity and productivity) of mRNA synthesis and is less time consuming because it does not require cloning, and also consequently eliminates the unwanted errors and effects related to RNA made on DNA templates obtained with cloning techniques. The results of transfection of RNAs demonstrate that RNA transfection can be very effective in cells that are exceedingly difficult to transfect efficiently with DNA constructs. Further, the levels of gene expression following mRNA transfection are consistent from cell to cell in an experiment and these levels can be controlled over a wide range simply by changing the amount of mRNA that is transfected, and without obvious cytotoxic effects due to the levels of RNA per se. Due to high efficiency the cells can be simultaneously transfected with multiple genetic constructs. The method can be used to deliver genes into cells not- or only poorly transfectable for DNA, in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Enzymes resistant to photodamage
ActiveUS20100093555A1Reduce oxidationImprove the immunitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising modified DNA polymerases that exhibit improved photostability compared to the parental polymerases from which they were derived. Provided are methods for generating enzymes, such as DNA polymerases, with the aforementioned phenotype. Provided are methods of using polymerases with increased resistance to photodamage to make a DNA or to sequence a DNA template.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Engineering polymerases and reaction conditions for modified incorporation properties
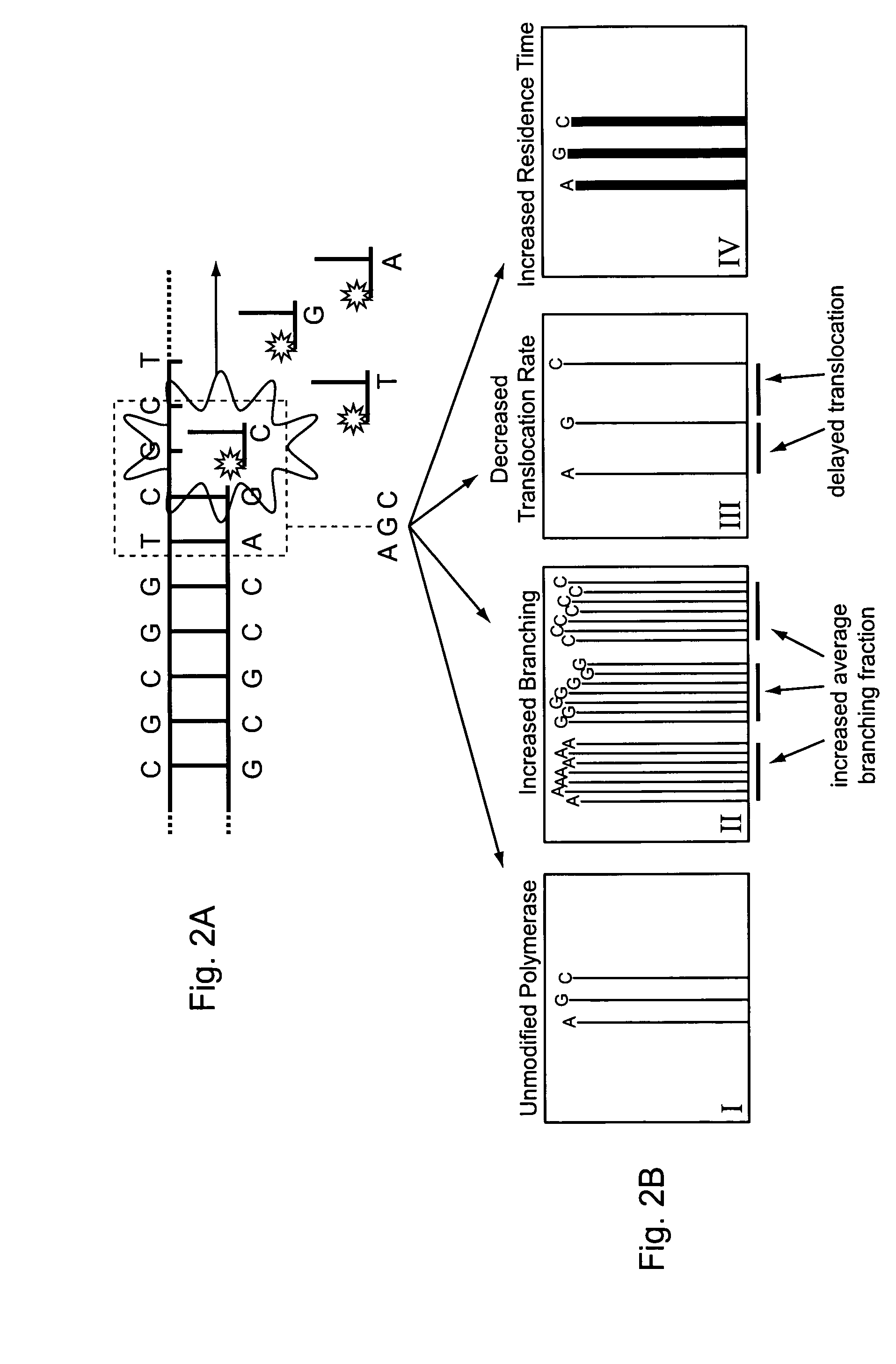
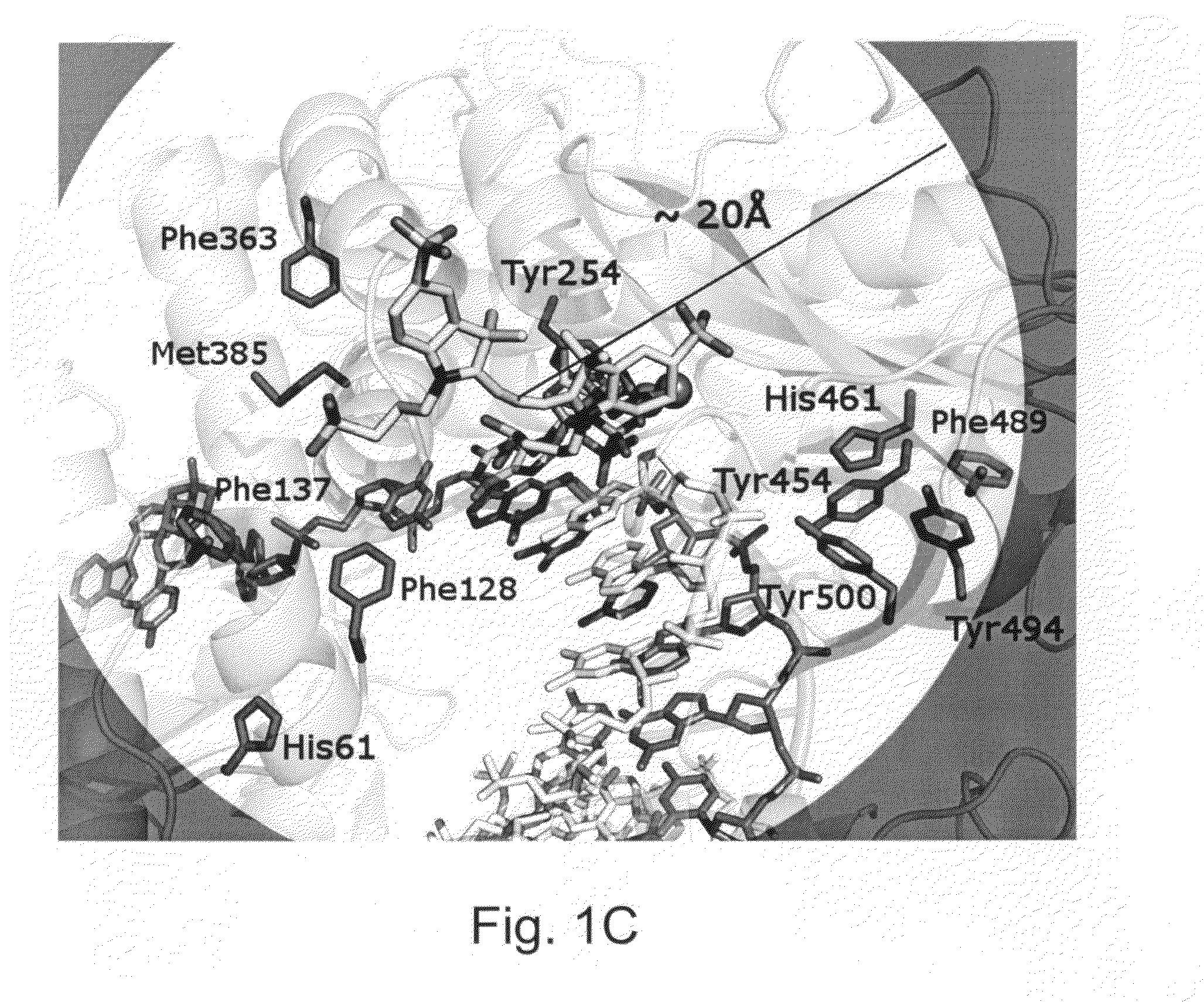
ActiveUS20100075332A1Easy to identifyDelayed translocationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LA-DNA
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Single-stranded polynucleotide amplification methods
The present invention provides amplification methods for producing a population of single stranded polynucleotides from a target polynucleotide, comprising (a) extending an RNA primer in a complex comprising (i) a DNA template comprising a sequence that is complementary to the target polynucleotide, and (ii) the RNA primer, wherein the RNA primer is hybridized to the DNA template, and (b) cleaving the RNA primer with an enzyme that cleaves RNA from an RNA / DNA hybrid such that another RNA primer hybridizes to the DNA template and repeats primer extension by strand displacement.
Owner:ELIM BIOPHARMLS
Methods and means for enhancing RNA production
ActiveUS20170114378A1Improved and economical meanImproved and economical and methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibonucleosideFiltration membrane
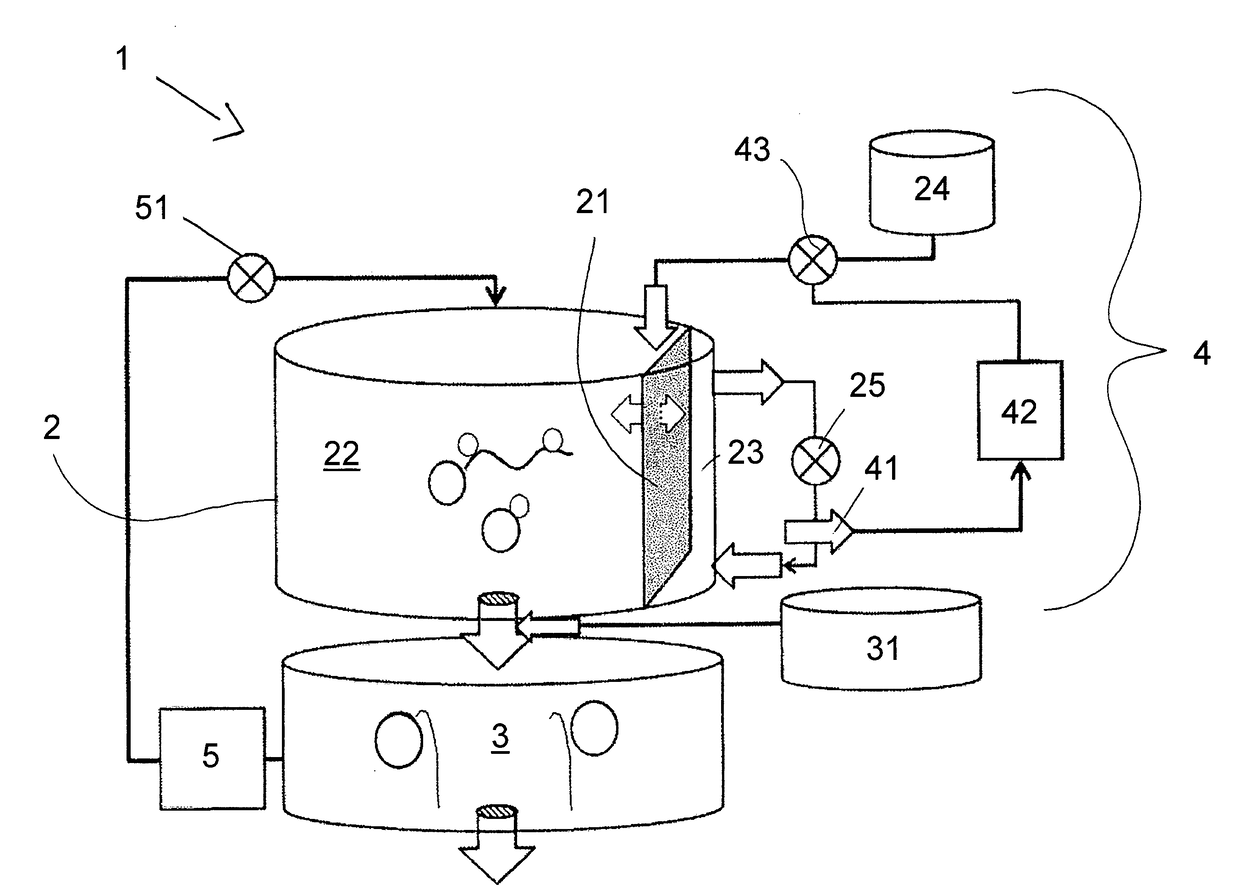
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing an RNA molecule of a given sequence, comprising the step of determining the fraction (1) for each of the four nucleotides G, A, C and U in said RNA molecule, and the step of synthesizing said RNA molecule by in vitro transcription in a sequence-optimized reaction mix, wherein said sequence-optimized reaction mix comprises the four ribonucleoside triphosphates GTP, ATP, CTP and UTP, wherein the fraction (2) of each of the four ribonucleoside triphosphates in the sequence-optimized reaction mix corresponds to the fraction (1) of the respective nucleotide in said RNA molecule, a buffer, a DNA template, and an RNA polymerase. Further, the present invention relates to a bioreactor (1) for synthesizing RNA molecules of a given sequence, the bioreactor (1) having a reaction module (2) for carrying out in vitro RNA transcription reactions in a sequence-optimized reaction mix, a capture module (3) for temporarily capturing the transcribed RNA molecules, and a control module (4) for controlling the infeed of components of the sequence-optimized reaction mix into the reaction module (2), wherein the reaction module (2) comprises a filtration membrane (21) for separating nucleotides from the reaction mix, and the control of the infeed of components of the sequence-optimized reaction mix by the control module (4) is based on a measured concentration of separated nucleotides.
Owner:CUREVAC REAL ESTATE GMBH
Construction and application of Zymomonas mobilis CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas (CRISPR-association proteins)9 system
InactiveCN104109687AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionGene expressionDna template
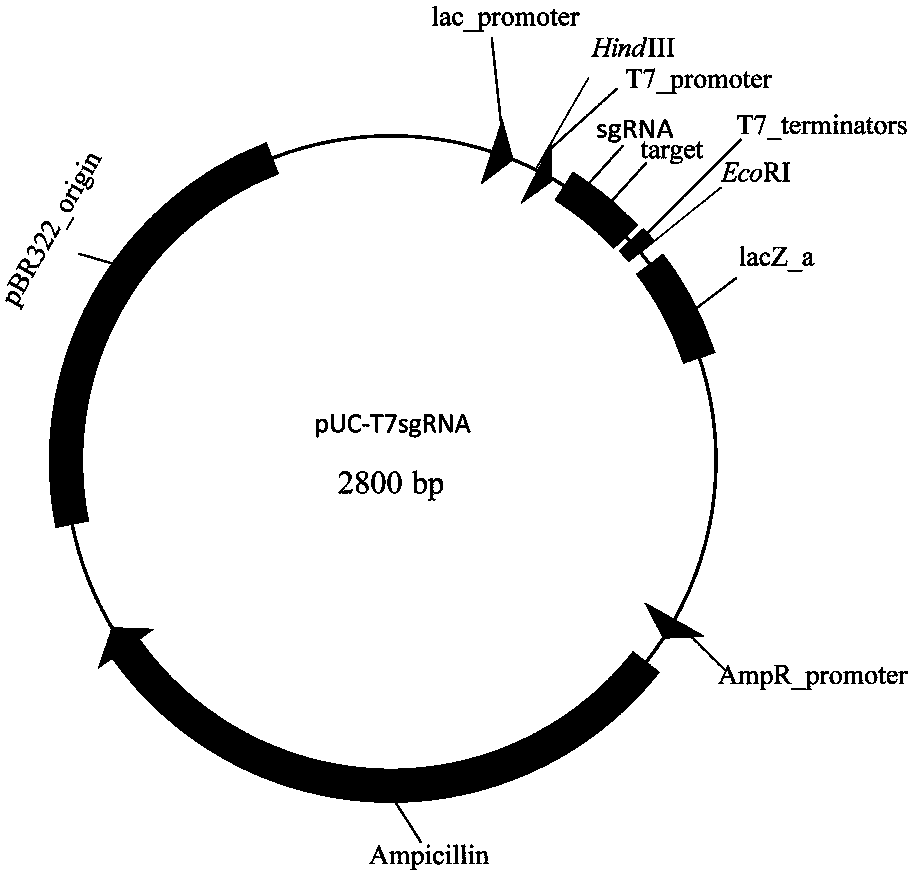
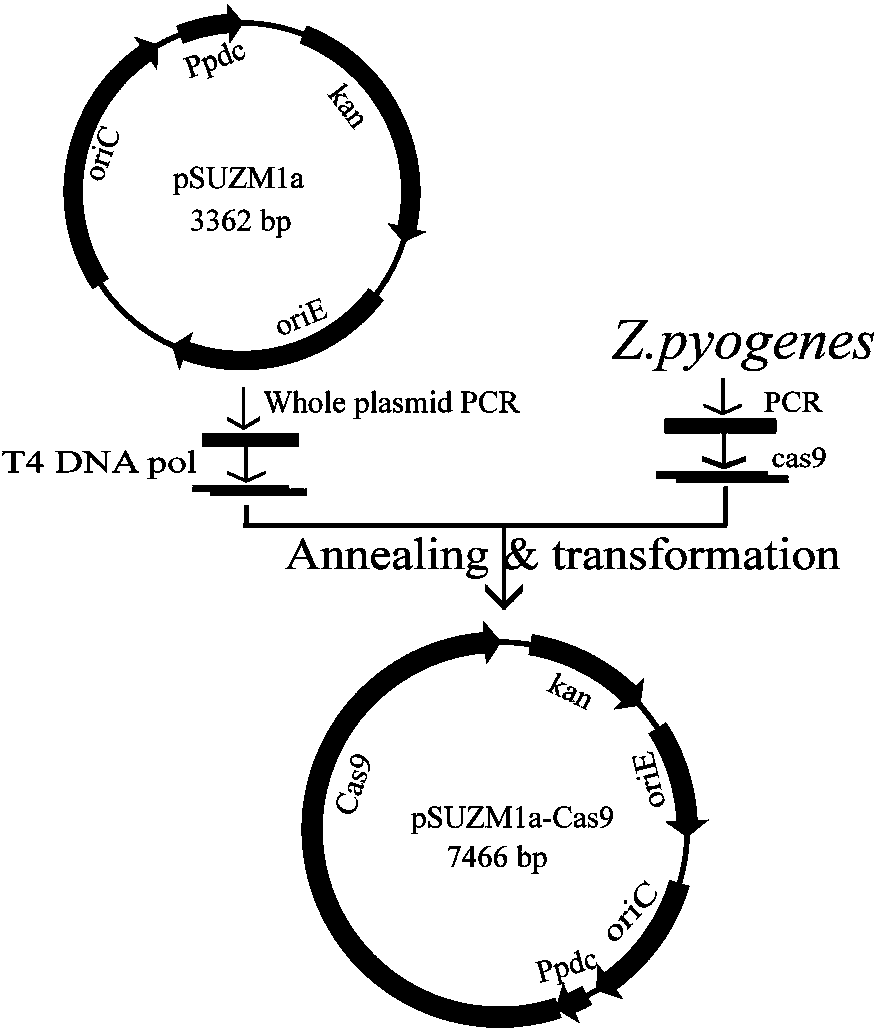
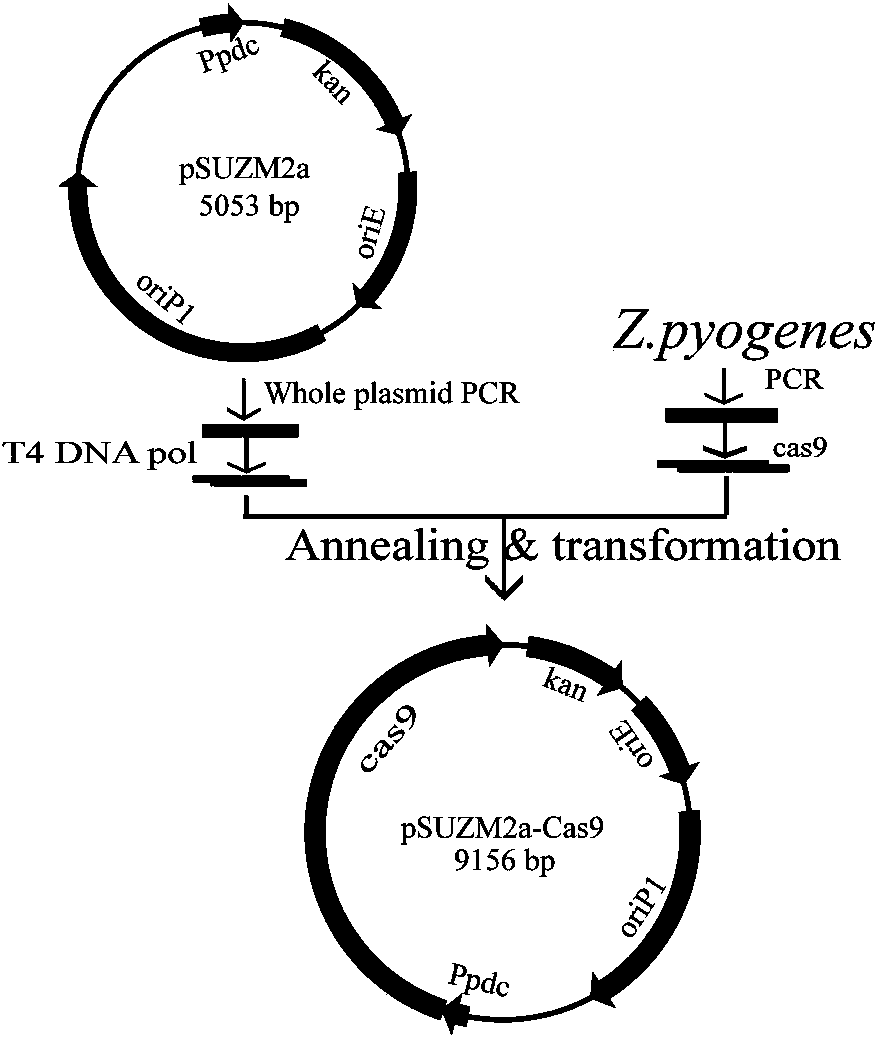
The invention discloses construction of CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas (CRISPR-association proteins) system expression plasmids pSUZM1a-Cas9, pSUZM2a-Cas9 and pSUZM3a-Cas9. The CRISPR-Cas system expression plasmids comprise a Zymomonas mobilis endogenous gene promoter, a selective marker gene and a Cas9 gene of a CRISPR system. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing an expression plasmid pUC-T7sgRNA (single-guide ribonucleic acid) comprising an origin of replication, the selective marker gene, a T7 gene promoter and terminator, a BbsI recognition sequence and a crRNA-tracrRNA sequence; designing a corresponding target sequence to ensure that a DNA template is subjected to in vitro transcription by virtue of T7RNA polymerase, and sgRNA and Cas9 gene expression plasmids obtained by purification are used for performing co-electrotransformation on escherichia coli and Z.mobilisZM4. Results show that an upp gene of escherichia coli DH5alpha can be successfully knocked out by adopting a CRISPR technology, and natural plasmids in Zymomonas mobilis can be effectively removed. The Cas9 gene expression plasmid, the sgRNA expression plasmid and a complete set of research methods established in the research process can be widely applied to the knockout of genes in a Zymomonas mobilis genome, thus the construction of a Zymomonas mobilis CRISPR-Cas9 system disclosed by the invention has good market application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Circular DNA vectors for synthesis of RNA and DNA
InactiveUS20080227160A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
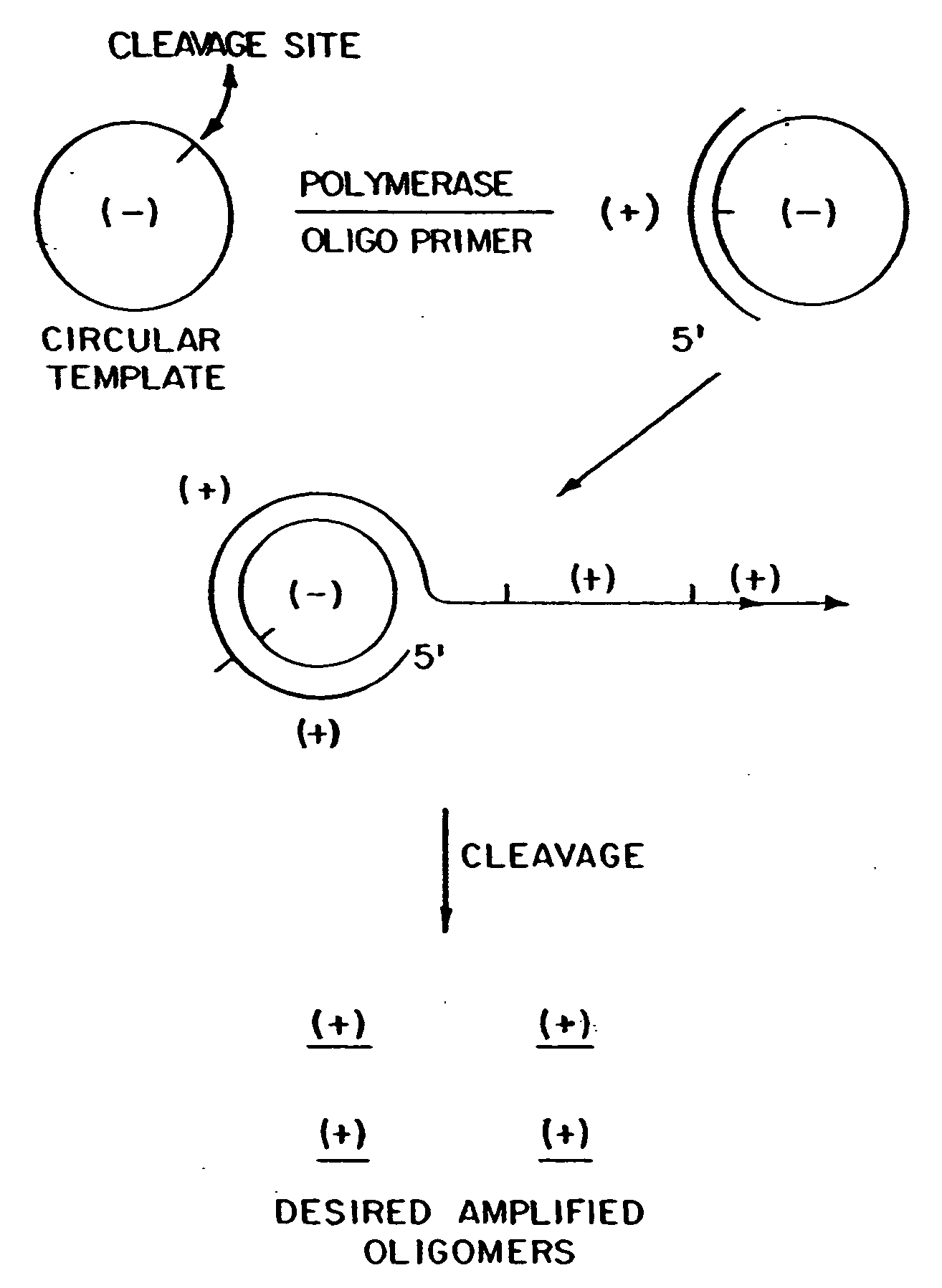
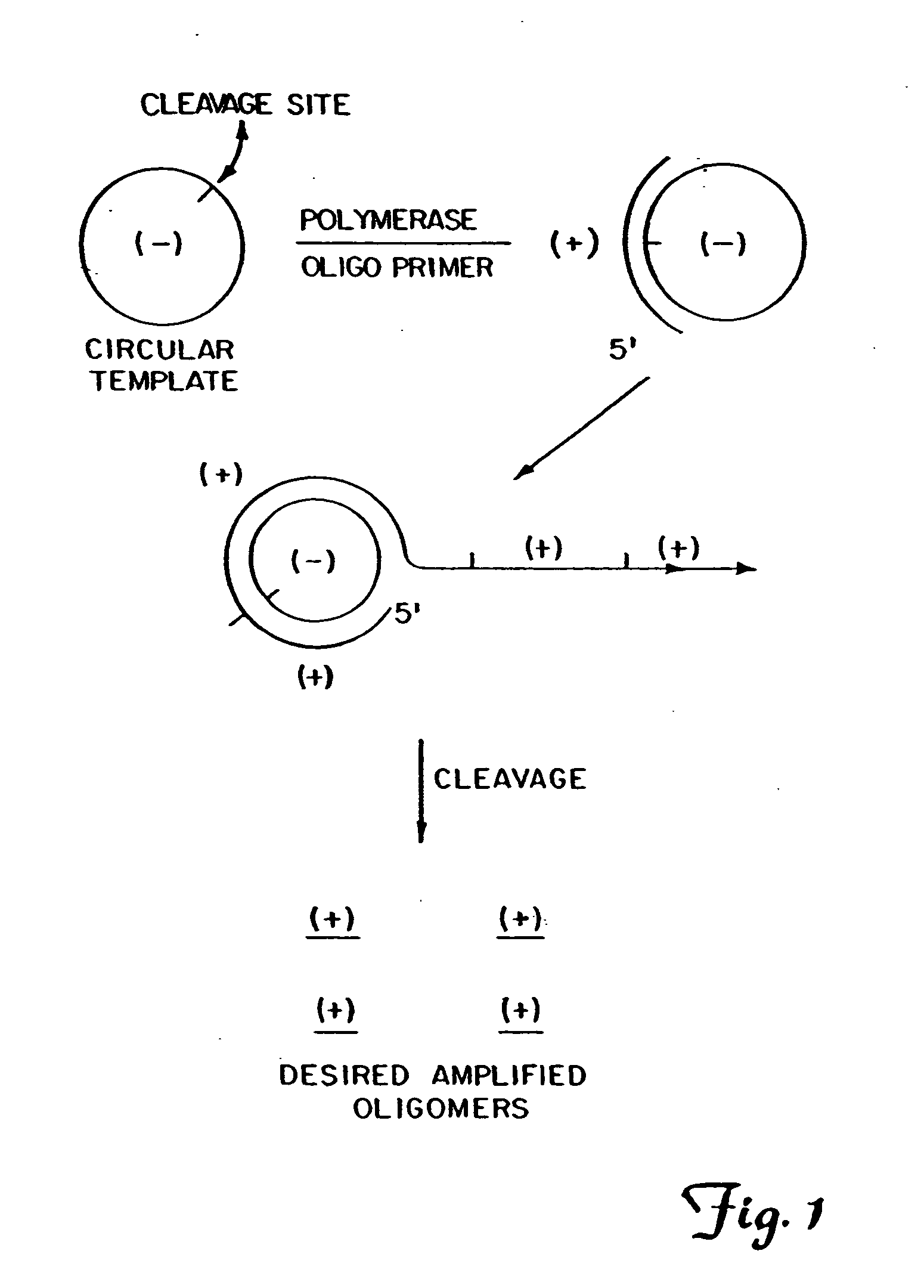
The present invention provides methods for synthesis and therapeutic use of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides and analogs. RNA oligonucleotides are synthesized using a small, circular DNA template which lacks an RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The RNA synthesis is performed by combining a circular single-stranded oligonucleotide template with an effective RNA polymerase and at least two types of ribonucleotide triphosphate to form an RNA oligonucleotide multimer comprising multiple copies of the desired RNA oligonucleotide sequence. Preferably, the RNA oligonucleotide multimer is cleaved to produce RNA oligonucleotides having well-defined ends. Preferred RNA oligonucleotide multimers contain ribozymes capable of both cis (autolytic) and trans cleavage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
DNA-templated combinatorial library chemistry
InactiveUS7479472B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundChemical library
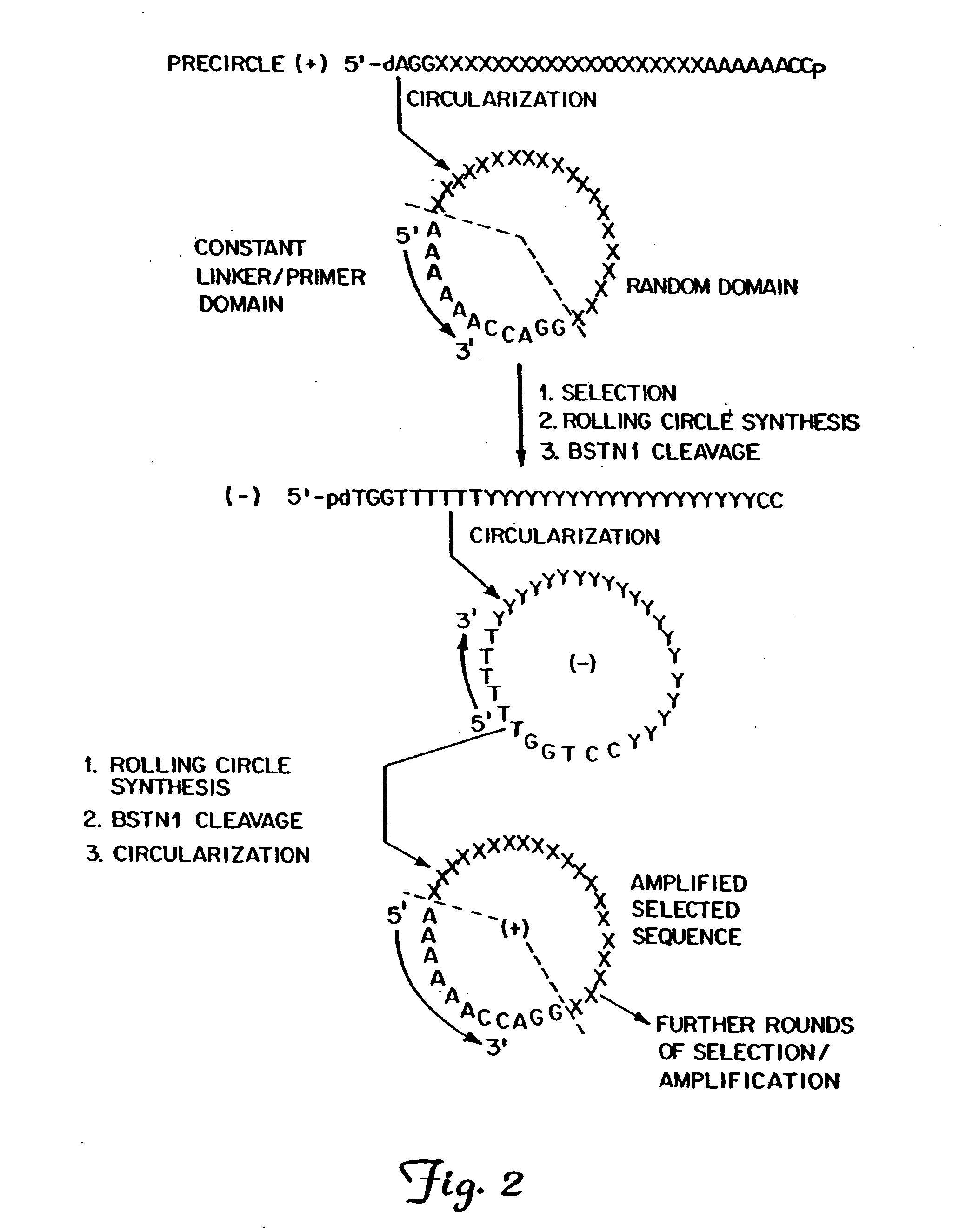
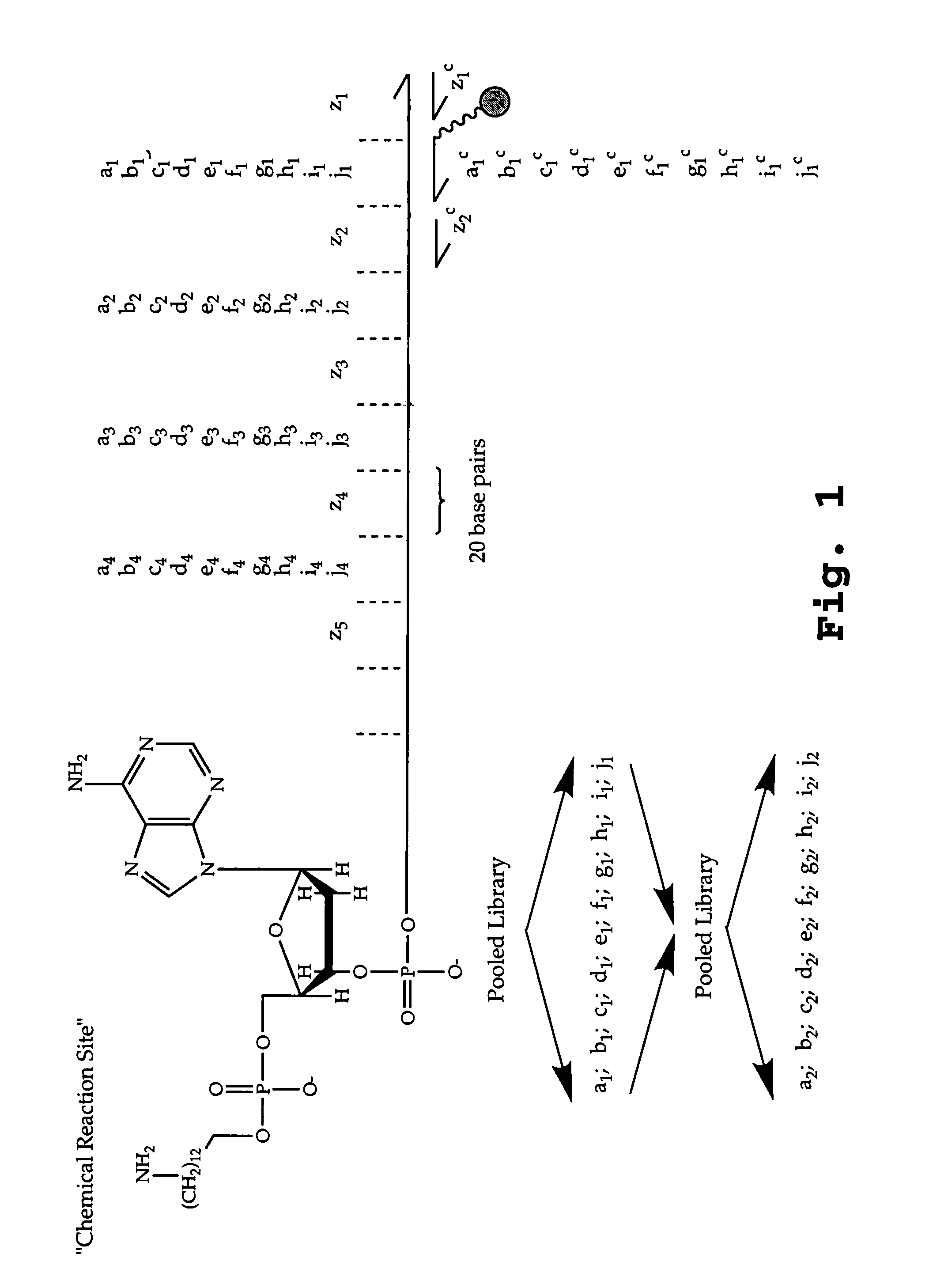
The present invention describes templated combinatorial chemical libraries comprised of a plurality of bifunctional molecules having both a chemical compound and a nucleic acid tag that defines the structure of the chemical compound and directs its synthesis. Also described are methods for producing, enriching and in vitro evolution of the bifunctional molecules of such libraries based on the nucleic acid tags and methods for selecting for library compounds having a desired activity.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Polymerases
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
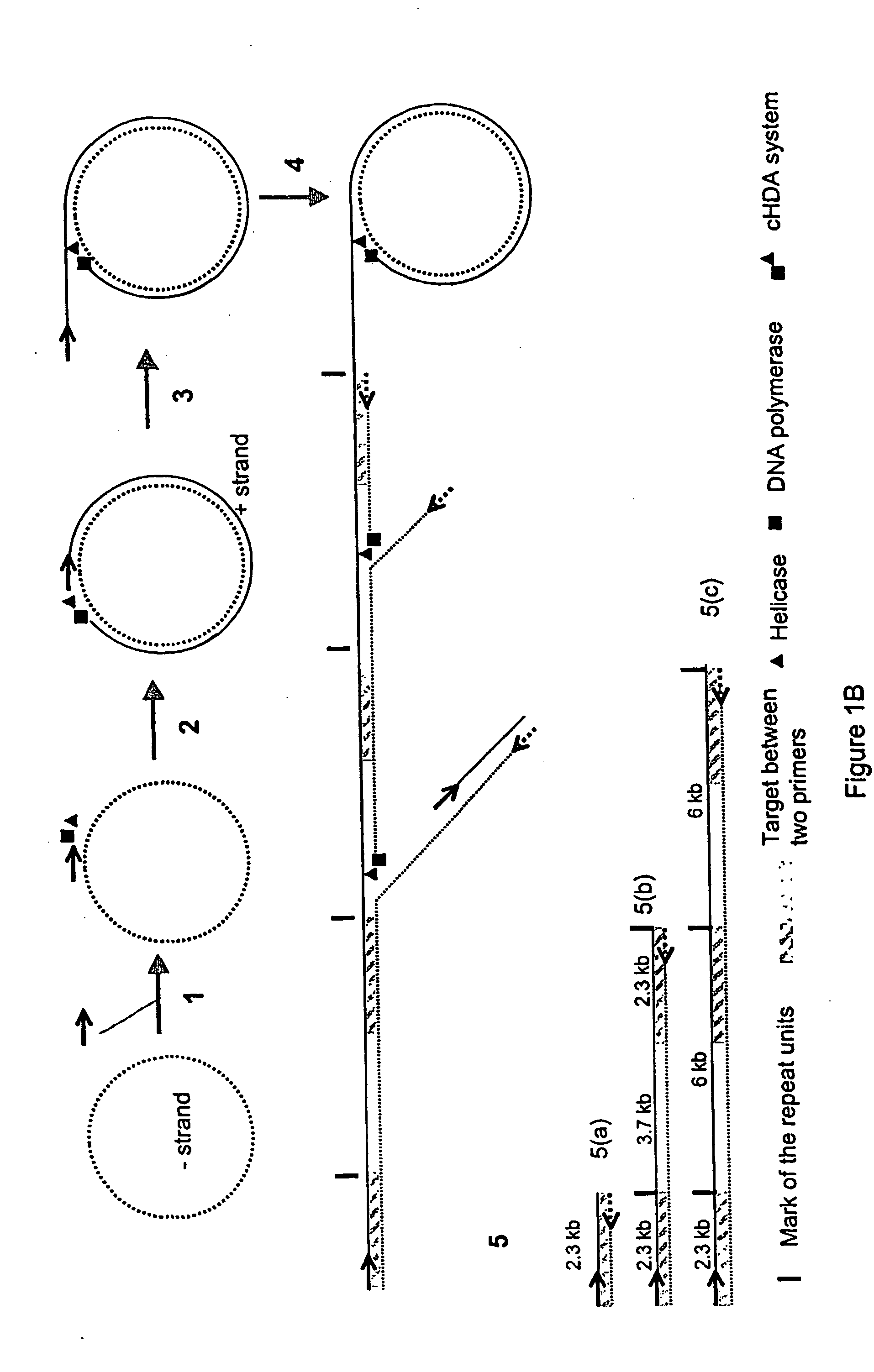
Helicase-dependent amplification of circular nucleic acids
InactiveUS20100075384A1Microbiological testing/measurementTransferasesDNA unwinding enzymePolymerase L
A helicase-mediated amplification method for circular DNA templates and target DNA sequences within the templates is provided. The method combines a DNA polymerase and a helicase preparation to amplify a target sequence as well as the entire circular DNA template.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Transient transfection with RNA
Owner:YALE UNIV
DNA polymerase blends and uses thereof
ActiveUS7960157B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementLong pcrGenomic DNA
The present invention discloses novel blends of chimeric and non-chimeric thermostable DNA polymerases for use in PCR, DNA sequencing and mutagenesis protocols. The invention allows for PCR reactions with shorter extension times that will facilitate PCR amplification of genomic DNA templates and improve the efficacy of long PCR.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Use of interfering RNA in the production of transgenic animals
ActiveUS20050266561A1Minimal effectSimple technologySugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsBiotechnologyTransgene
The invention provides cells and animals, as well as methods of producing cells and animals, that express at least one interfering RNA molecule to regulate the expression of a specific gene or family of genes. The invention further provides novel iRNA molecules, as well as DNA templates for producing iRNA molecules.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
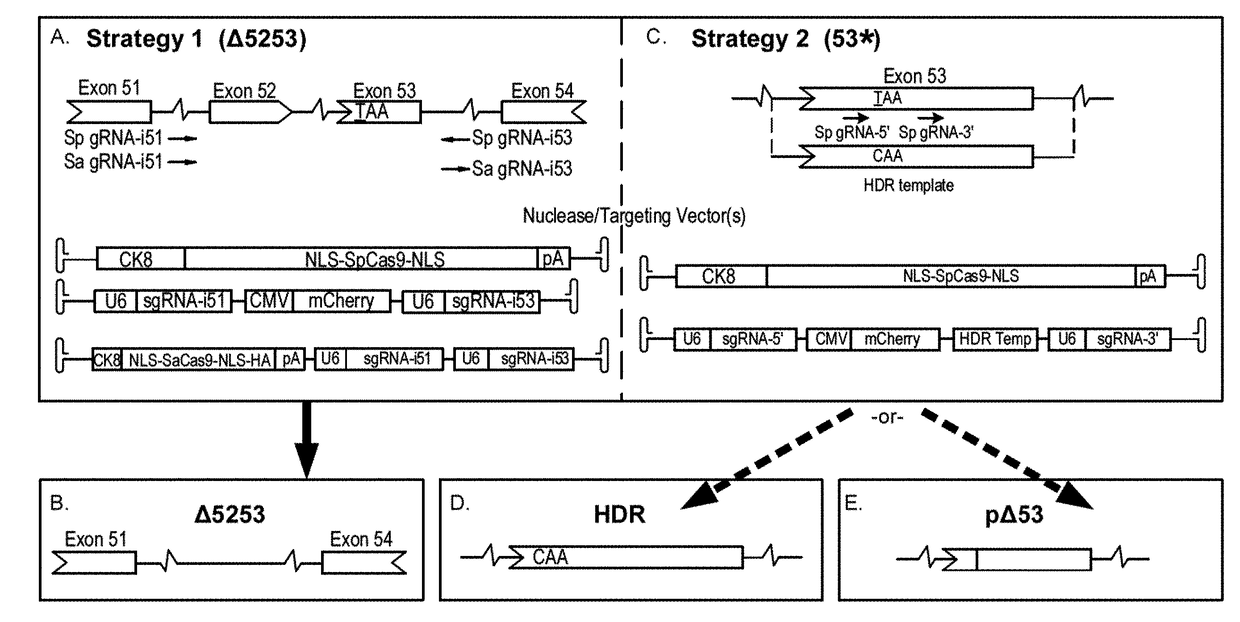
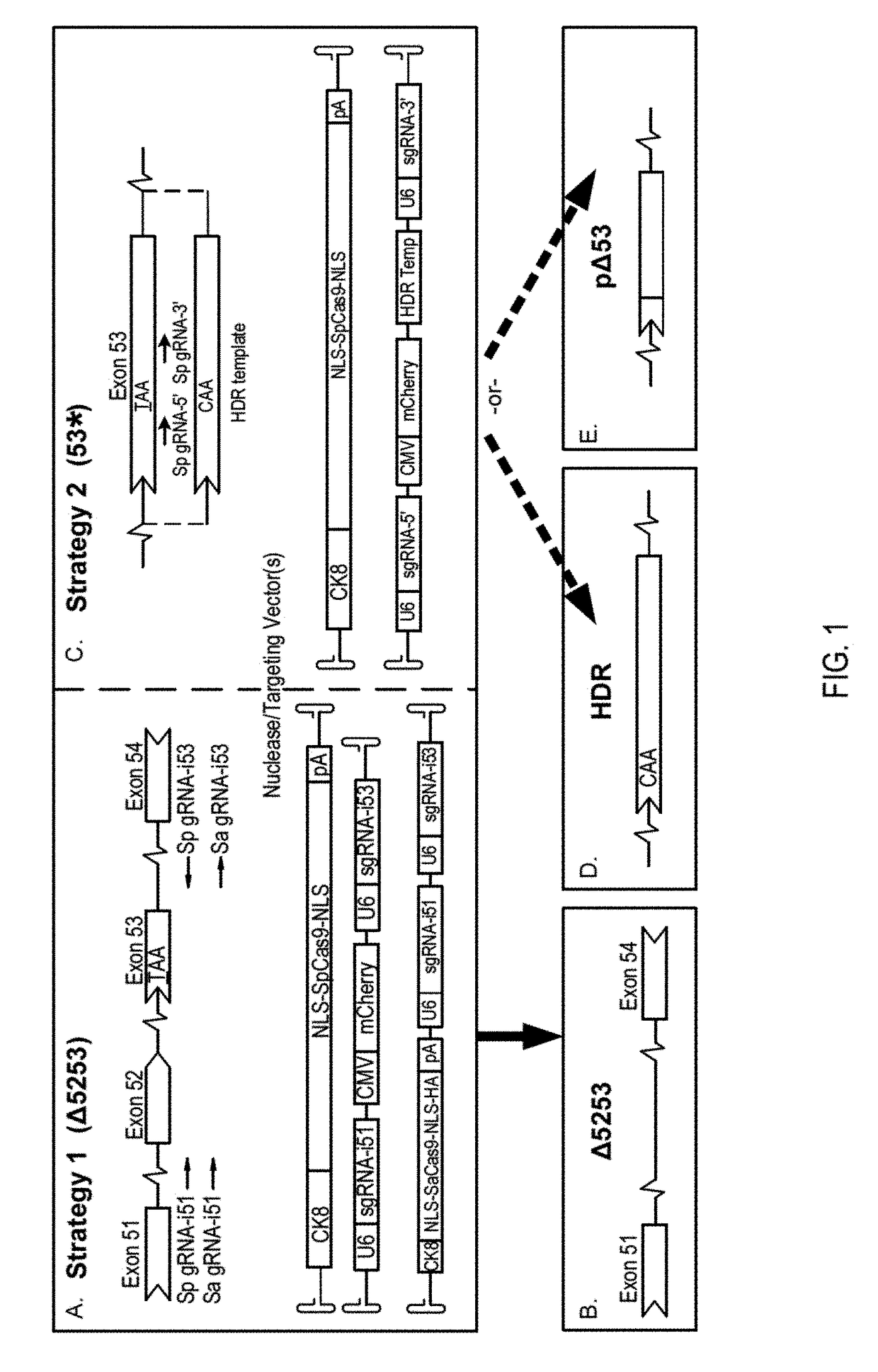
Muscle-specific crispr/cas9 editing of genes
Pharmaceutical compositions including a muscle-specific nuclease cassette, one or more guide RNA cassettes, and a delivery system for delivery of the muscle-specific nuclease cassette and the one or more gRNA cassettes are provided. The pharmaceutical composition may also include a mutation-corrected DNA template including a modification to be made in a target nucleic acid sequence. Methods for treating a subject having a muscular or neuromuscular disorder are also provided. The methods may include administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition. Methods of modifying or editing the sequence of a target nucleic acid sequence in a muscle cell are also provided. The methods may include contacting or transducing the muscle cell with a muscle-specific nuclease cassette and one or more gRNA cassettes.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Enzymes resistant to photodamage
ActiveUS9127259B2Improve the immunityReduce oxidationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPolymerase L
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
CRISPR/Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes
InactiveCN105400773AHigh infection efficiencyMeet the packaging ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationInfected cellCancer cell
The invention relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes. Firstly, an sgRNA library is established; then the sgRNA library is packaged by lentiviruses, and viruses are collected; the sgRNA library is screened in a cancer cell line, the obtained cells are extracted and screened, and genome DNAs of precancerous cells are screened; finally, enrichment of sgRNAs in the genome DNAs is carried out. When the provided method is compared with the prior art, the screening process of CRISPR / Cas9 cells is improved, the virus infection efficiency is determined and the virus MOI value is determined through a simple method and by utilization of puromycin resistance of infected cells, importantly, the restriction enzyme cutting method and a high flux method are combined, correct chromatin fragments can be obtained effectively, false positive caused by non-specific PCR amplification can be lowered, a DNA template of sgRNAs can be amplified efficiently, and a library establishment efficiency is raised.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
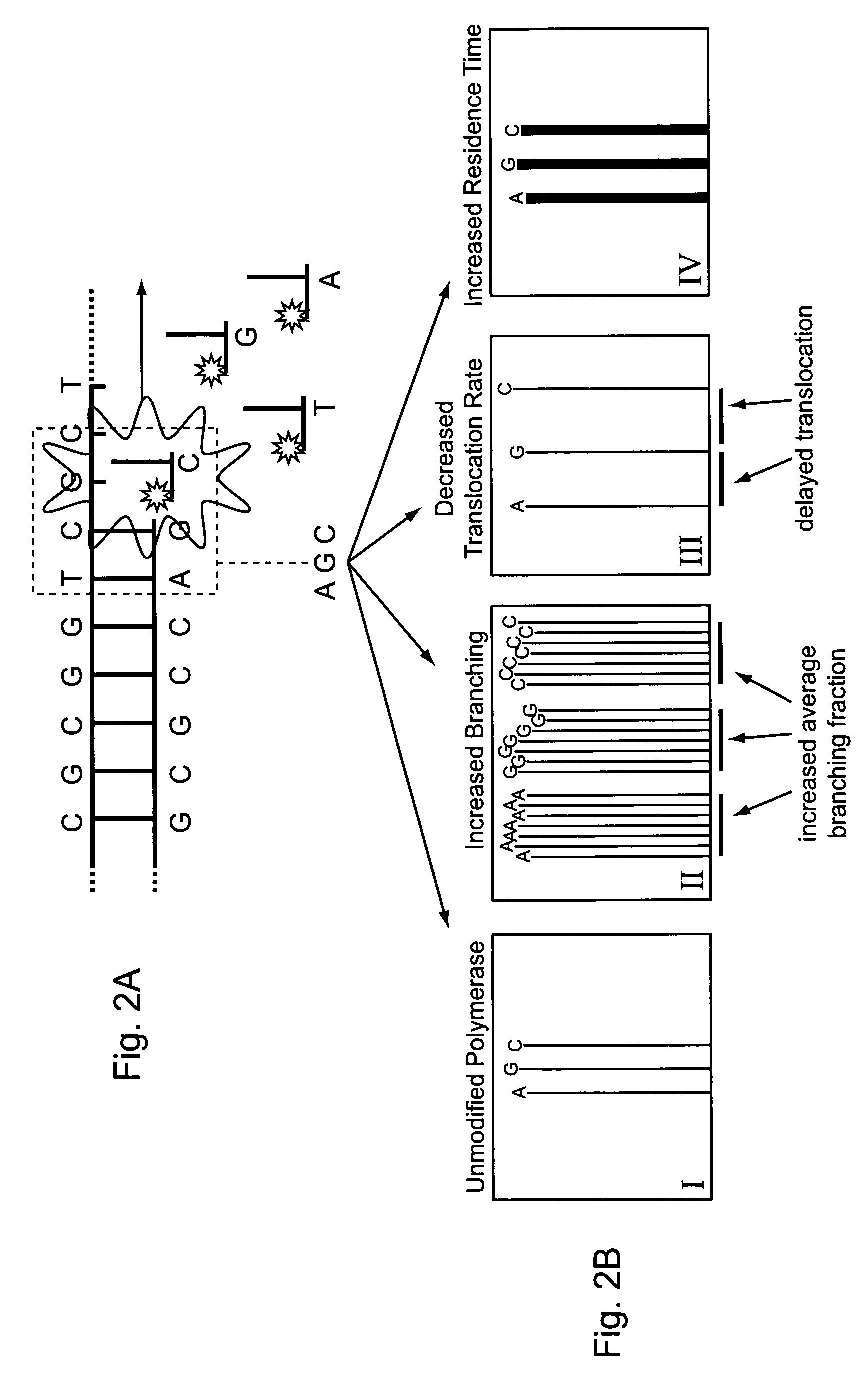
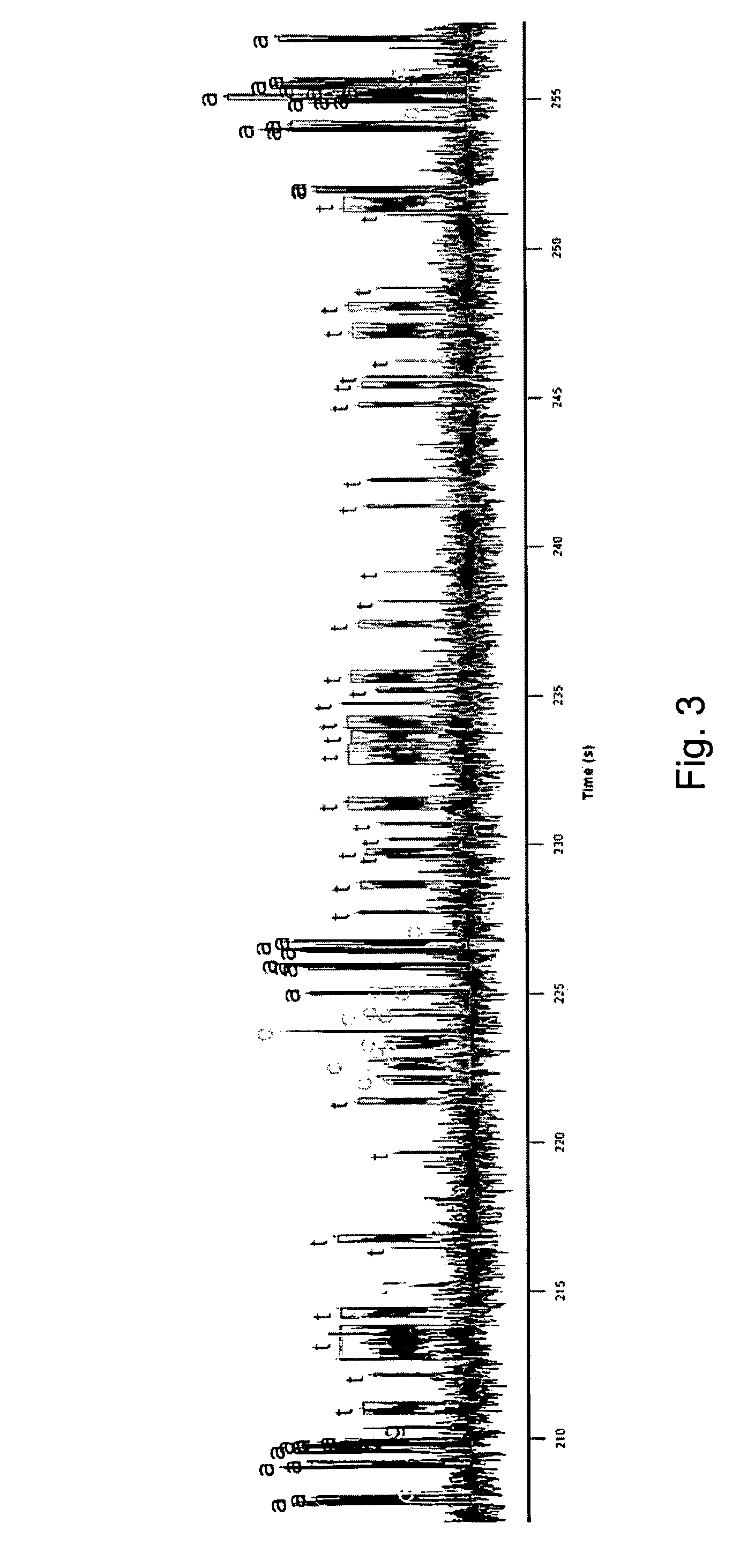
Method for sequencing using branching fraction of incorporatable nucleotides
ActiveUS8530164B2Easy to identifyIncrease) the branching rate of a polymerization reactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
Provided are methods for enhanced sequencing of nucleic acid templates. Also provided are reaction conditions that increase branching fractions during polymerization reactions. Also provided are compositions comprising modified recombinant polymerases that exhibit branching fractions that are higher than the branching fractions of the polymerases from which they were derived. Provided are compositions comprising modified recombinant polymerases that exhibit delayed translocation relative to the polymerases from which they were derived. Also provided are compositions comprising modified recombinant polymerases that exhibit increased nucleotide or nucleotide analog residence time at an active site of the polymerase. Provided are methods for generating polymerases with the aforementioned phenotypes and methods of using such polymerases to sequence a DNA template or make a DNA. Also provided are methods and nucleic acid sequencing systems for determining which labeled nucleotide is incorporated at a site during a template-dependent polymerization reaction.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Synthesis system, preparation, kit and preparation method of in-vitro DNA-to-Protein (D2P)
The invention provides a theoretical design and technical design of cell-free protein synthesis for DNA replication, transcription and translation coupling, a preparation, a kit and a preparation method. Specifically, with the application of the in-vitro cell-free synthesis system provided by the invention, complex protein can be synthesized, and moreover, DNA and mRNA can be synthesized; and effective, high-throughput and quite convenient protein synthesis can be completed with the use of a DNA template by a minute quantity (nanogram-microgram).
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Methods, systems, and reagents for direct RNA sequencing
ActiveUS20170159033A1Improve polymerase performanceDesirable propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAmino acid substitutionPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising recombinant polymerases that include amino acid substitutions, insertions, deletions, and / or exogenous features that confer modified properties upon the polymerase for sequencing RNA or RNA / DNA templates. Polymerases that topologically encircle the template nucleic acid are provided. Also provided are methods of using such polymerases to make a DNA or to sequence a template comprising RNA.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method of amplifying a target nucleic acid by rolling circle amplification
Provided is kit for and a method of amplifying a nucleic acid using rolling cyclic amplification (RCA), including amplifying a nucleic acid together with formation of a single-strand circular DNA template using RCA by reacting a reaction solution including: (a) two hairpin oligos, (b) a target nucleic acid, (c) a DNA ligase,(d) an endonuclease, (e) a DNA polymerase, and (f) a primer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
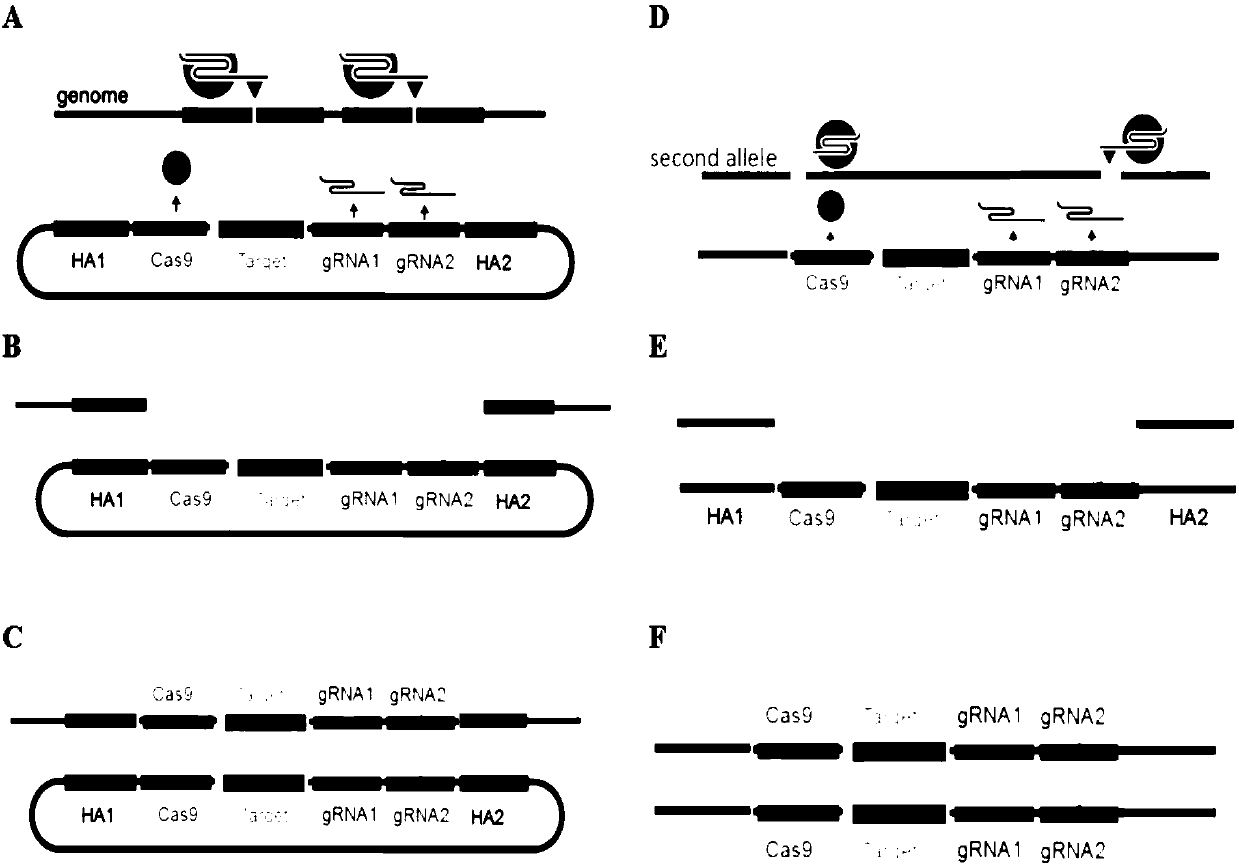
Precision and high-efficiency transgenic carrier as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107760715AReduce workloadReduce subsequent crossesStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNACatalytic effect
The invention discloses a precision and high-efficiency transgenic carrier as well as a construction method and application thereof. The transgenic carrier is obtained by completely assembling a genecoding CRISPR / Cas9 proteins, a DNA template of gRNAs, a homologous arm of a target gene side wing and a target gene to be transferred into a same plasmid vector. By adopting the precision and high-efficiency transgenic carrier as well as the construction method and application thereof, the workload and the subsequent hybridization for operating the gene in a laboratory can be significantly reduced, the homozygote generation time can be shortened, and the transgenic efficiency can be significantly increased. Based on an MCR method, the external target gene and the Cas9 gene are jointly transferred into silkworm genome in the process for precisely modifying the gene by virtue of the catalytic effect of the Cas9, the homozygote can be generated in a G0 generation, i.e. the mutation generatedon one copy can be automatically propagated onto an allele.
Owner:山东菌胜生物科技有限责任公司
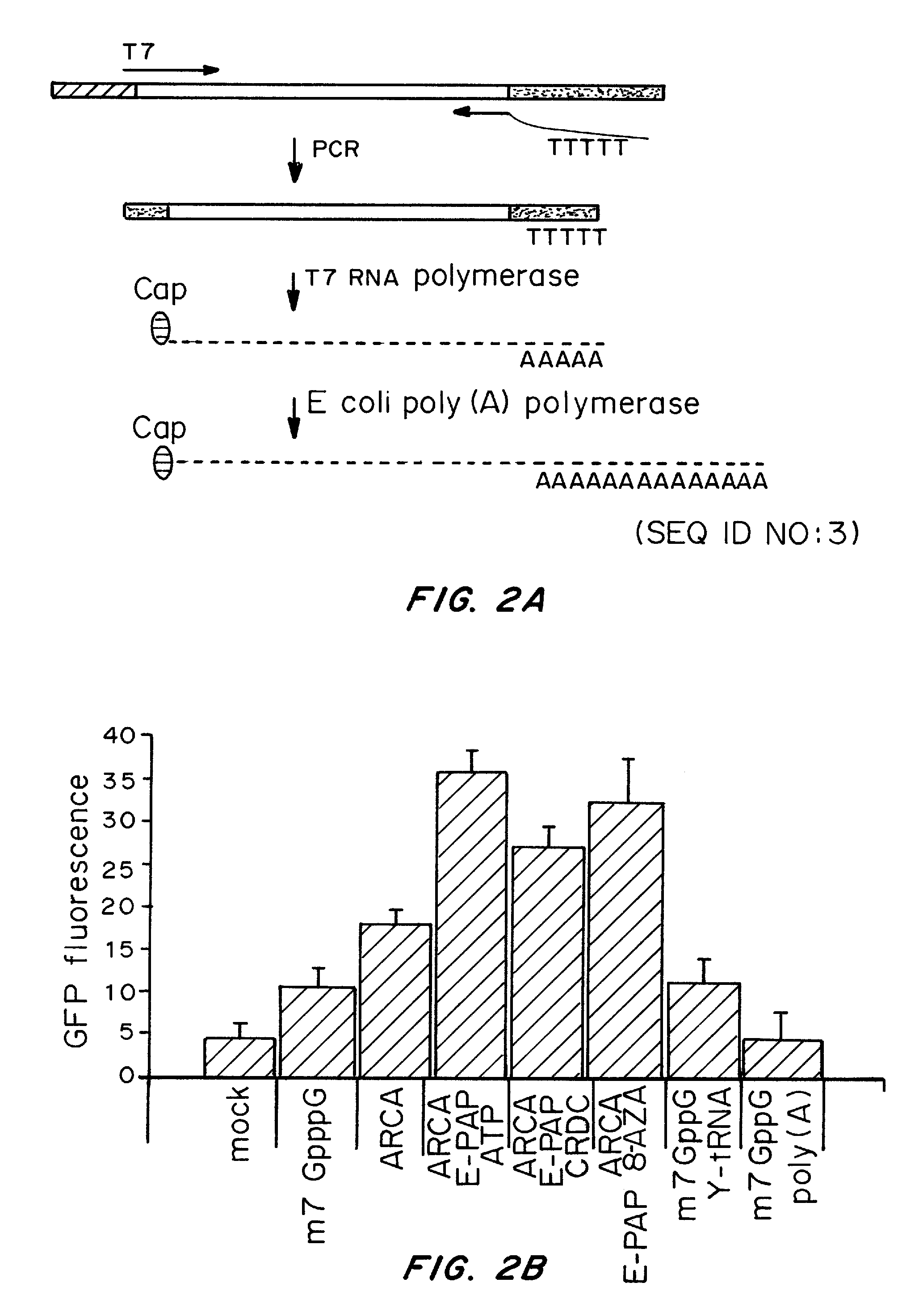
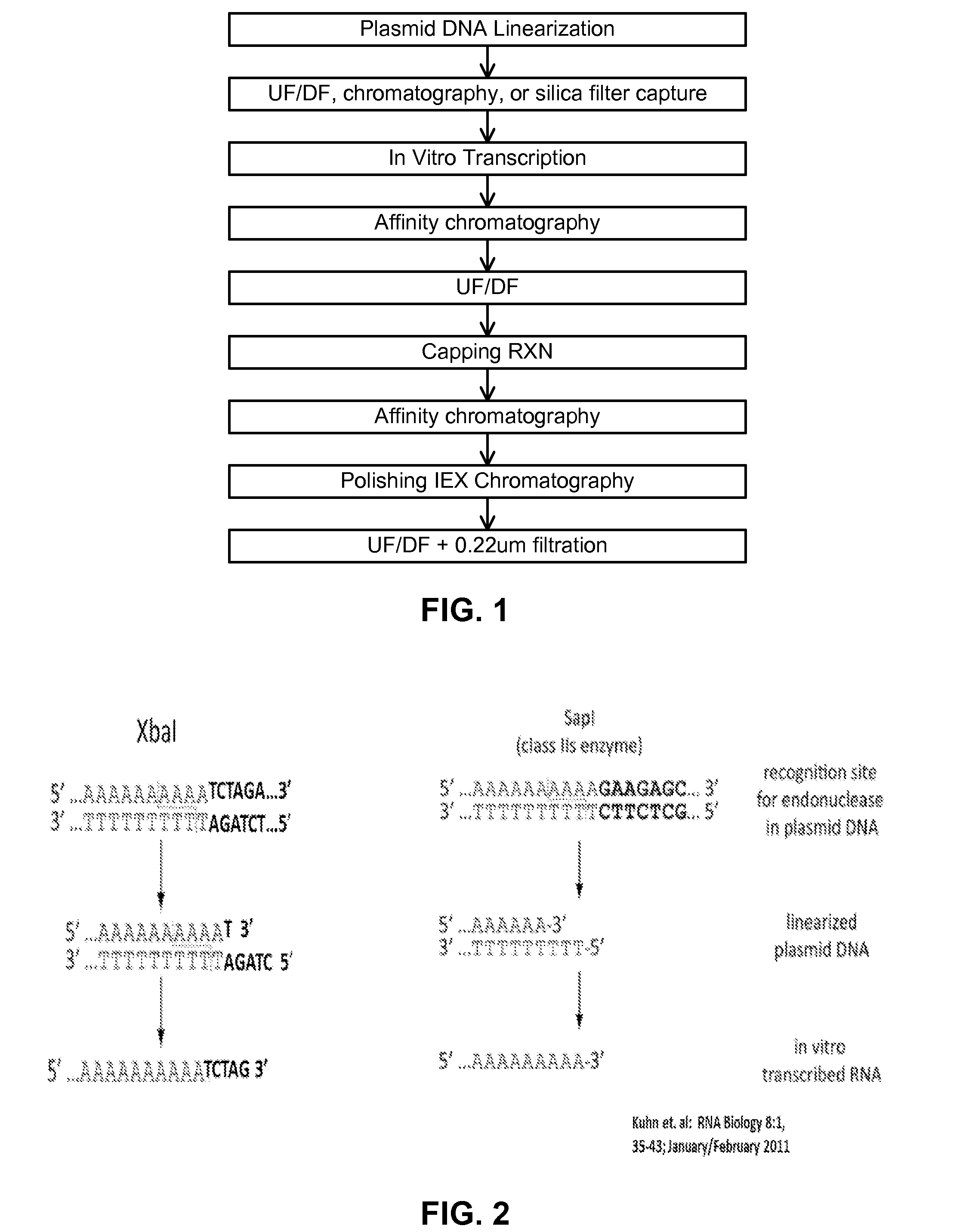
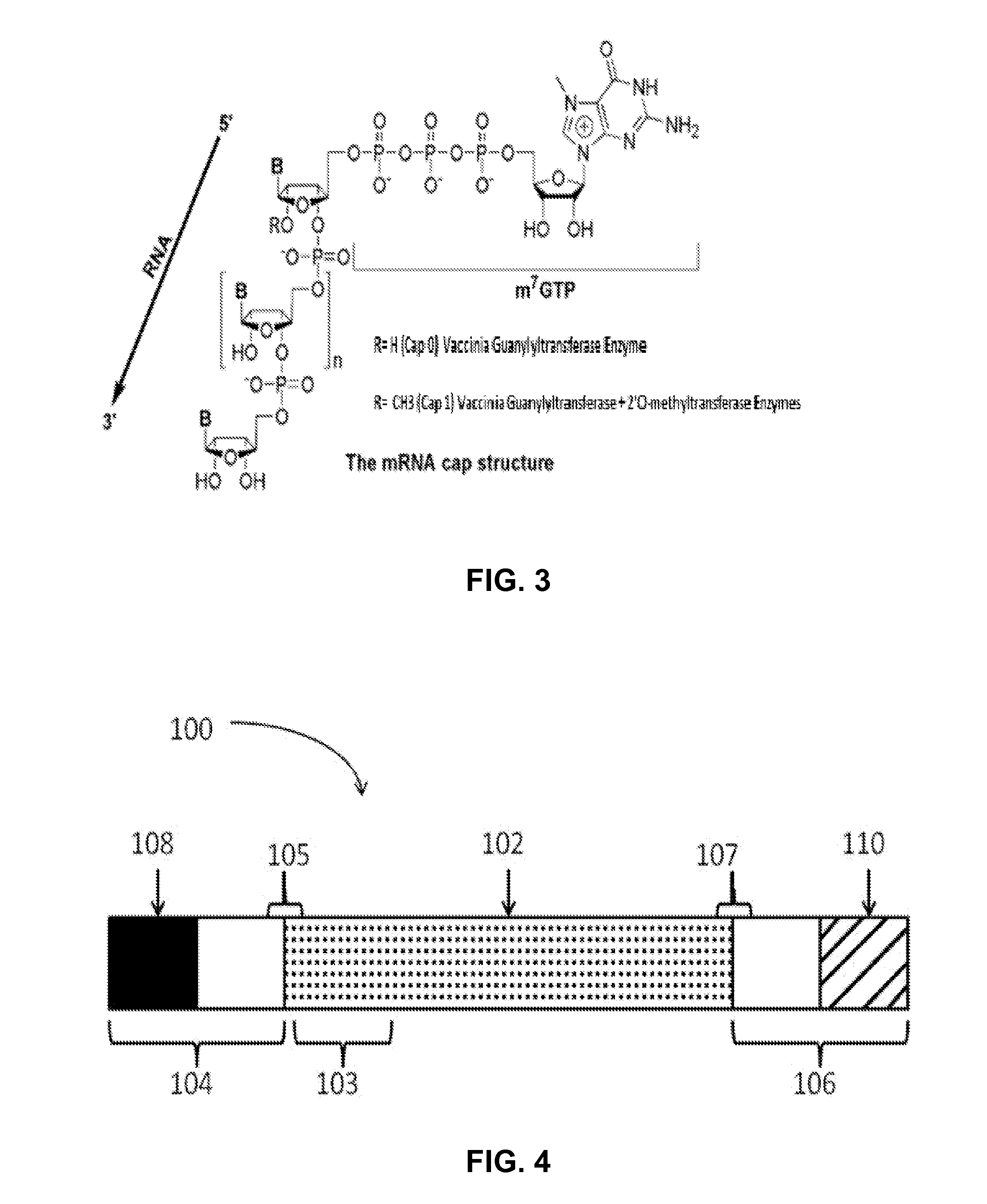
Manufacturing methods for production of RNA transcripts
ActiveUS20160024547A1High purityHigh potencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligo dtIn vitro transcription
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Detection Device And Methods Of Use
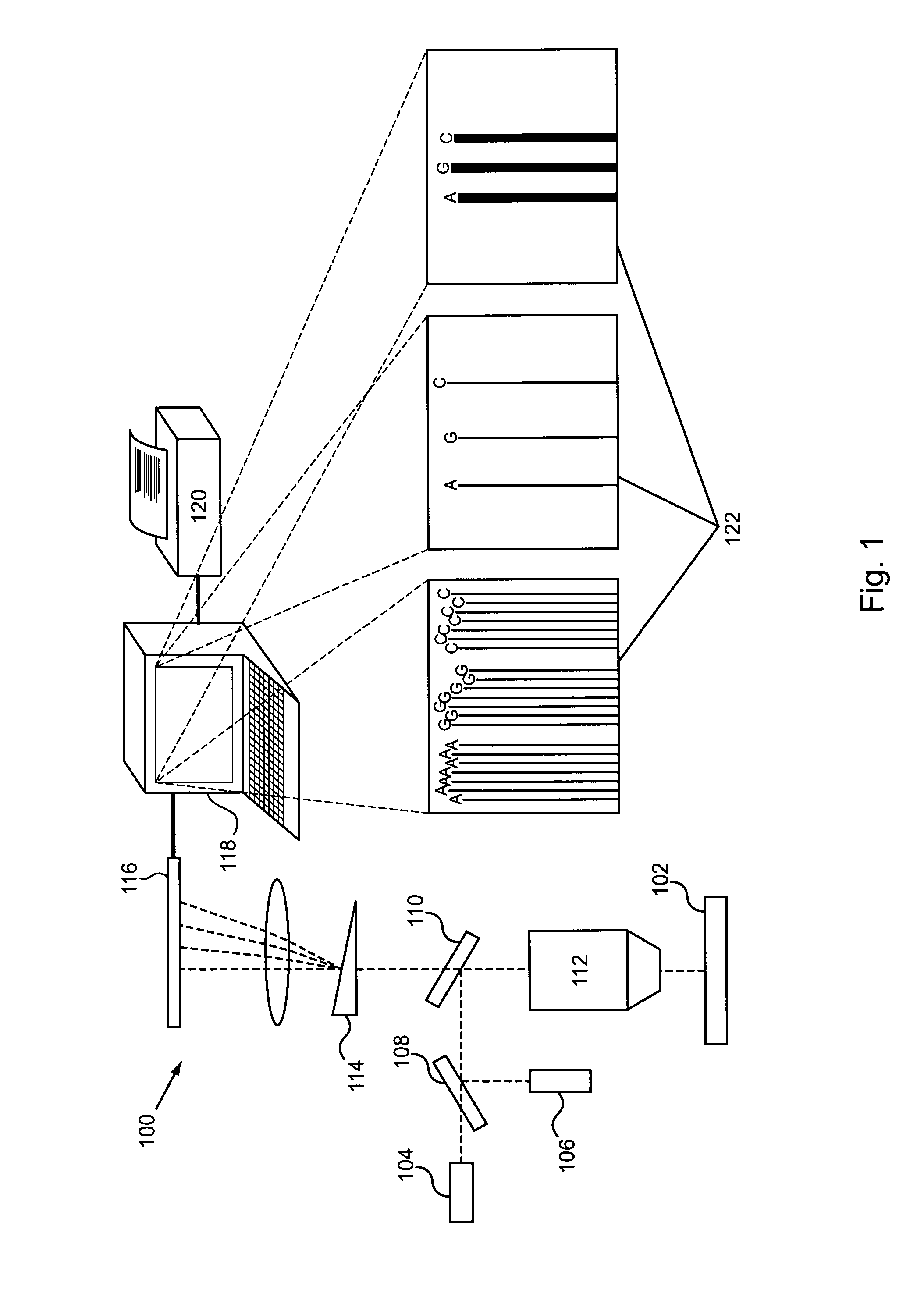
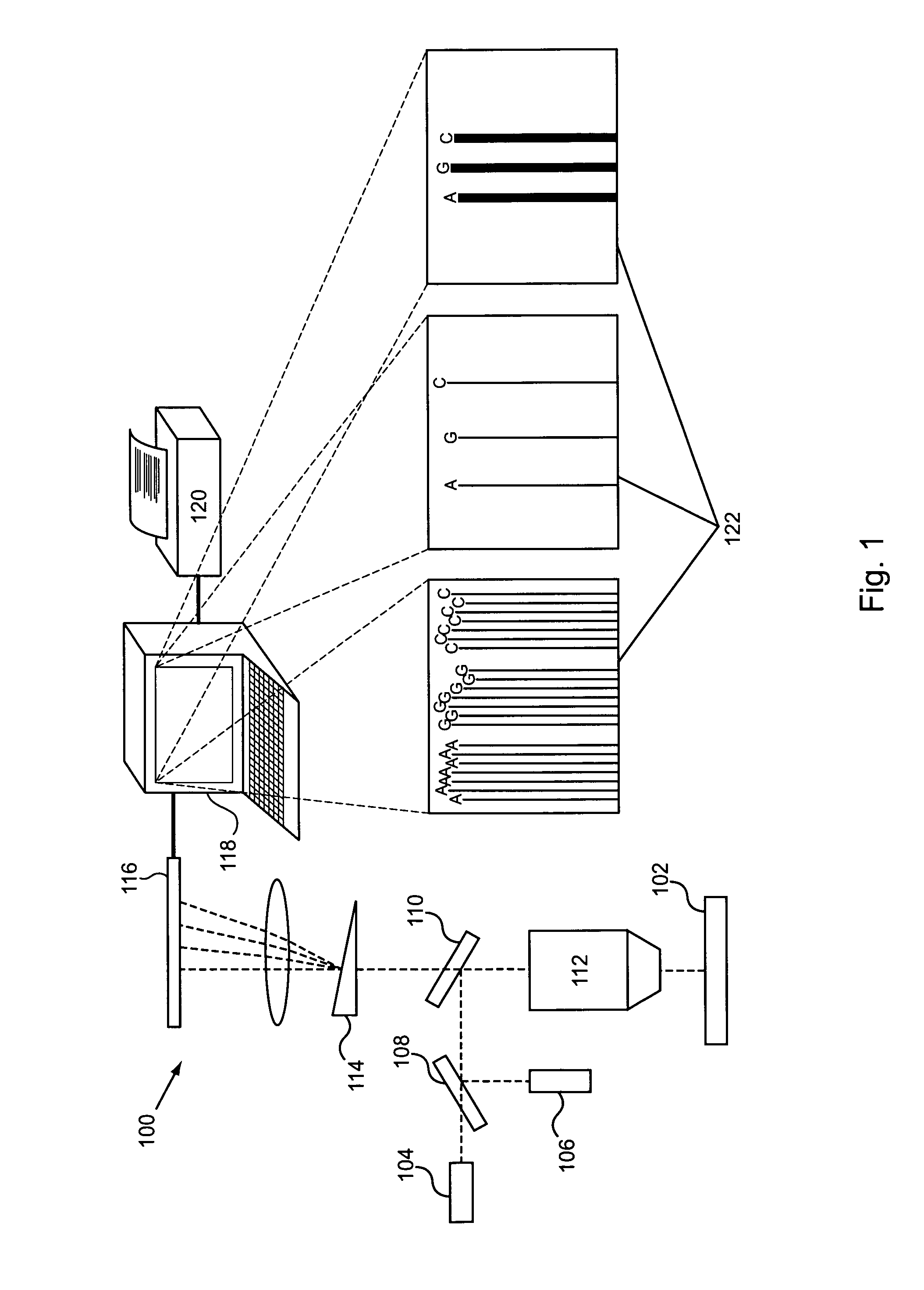
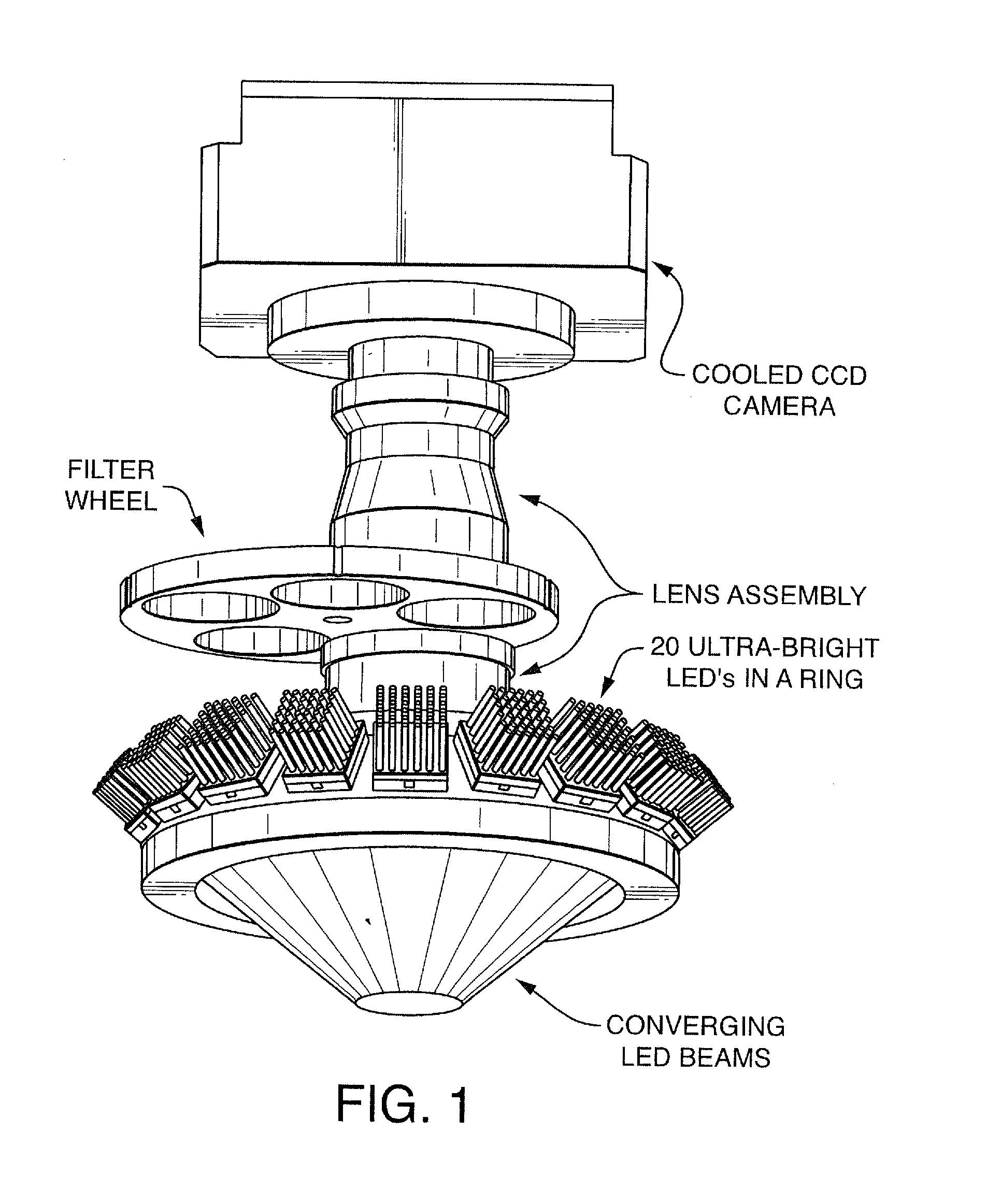
ActiveUS20100152050A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationDNAImage system
An imaging system for exciting and measuring fluorescence on or in samples comprising fluorescent materials (e.g. fluorescent labels, dyes or pigments). In one embodiment, a device is used to detect fluorescent labels on nucleic acid. In a preferred embodiment, the device is configured such that fluorescent labels in a plurality of different DNA templates are simultaneously detected.
Owner:ISOPLEXIS
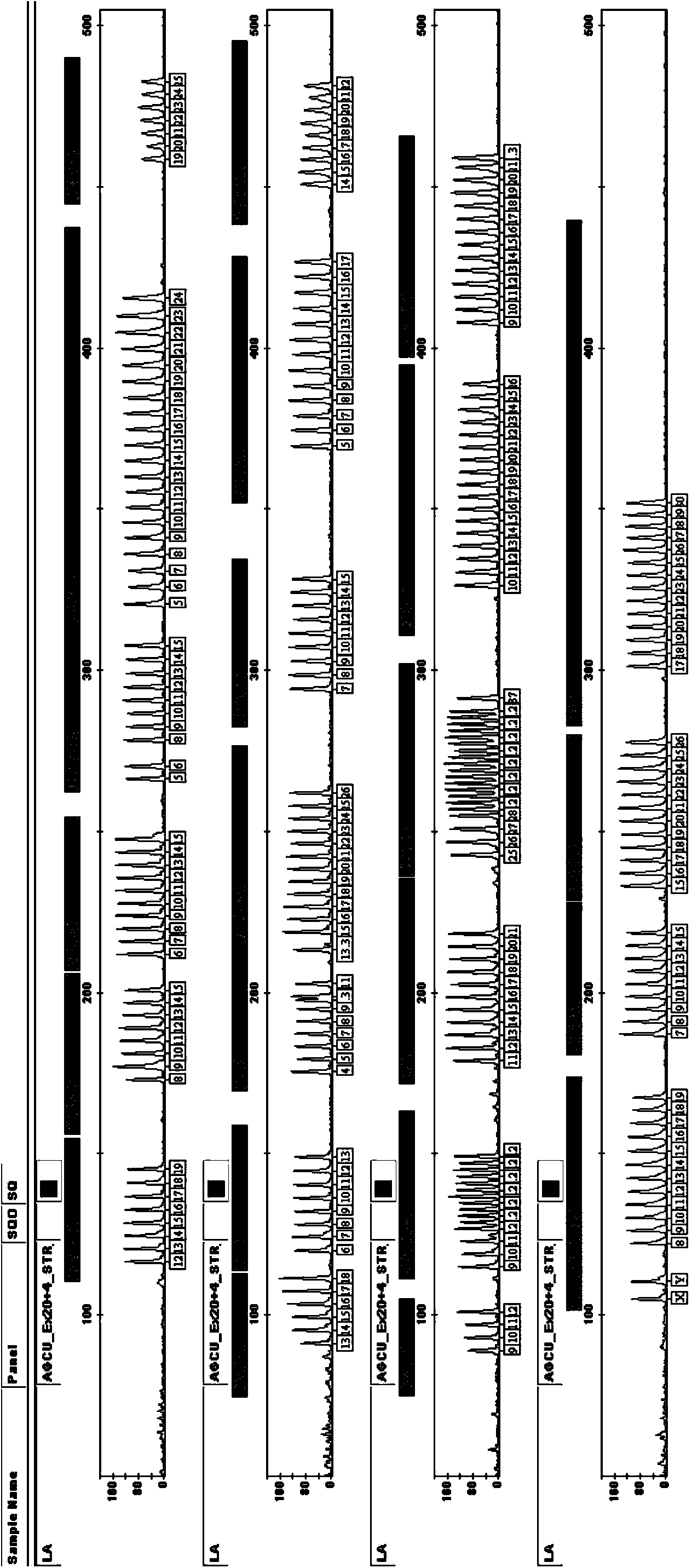
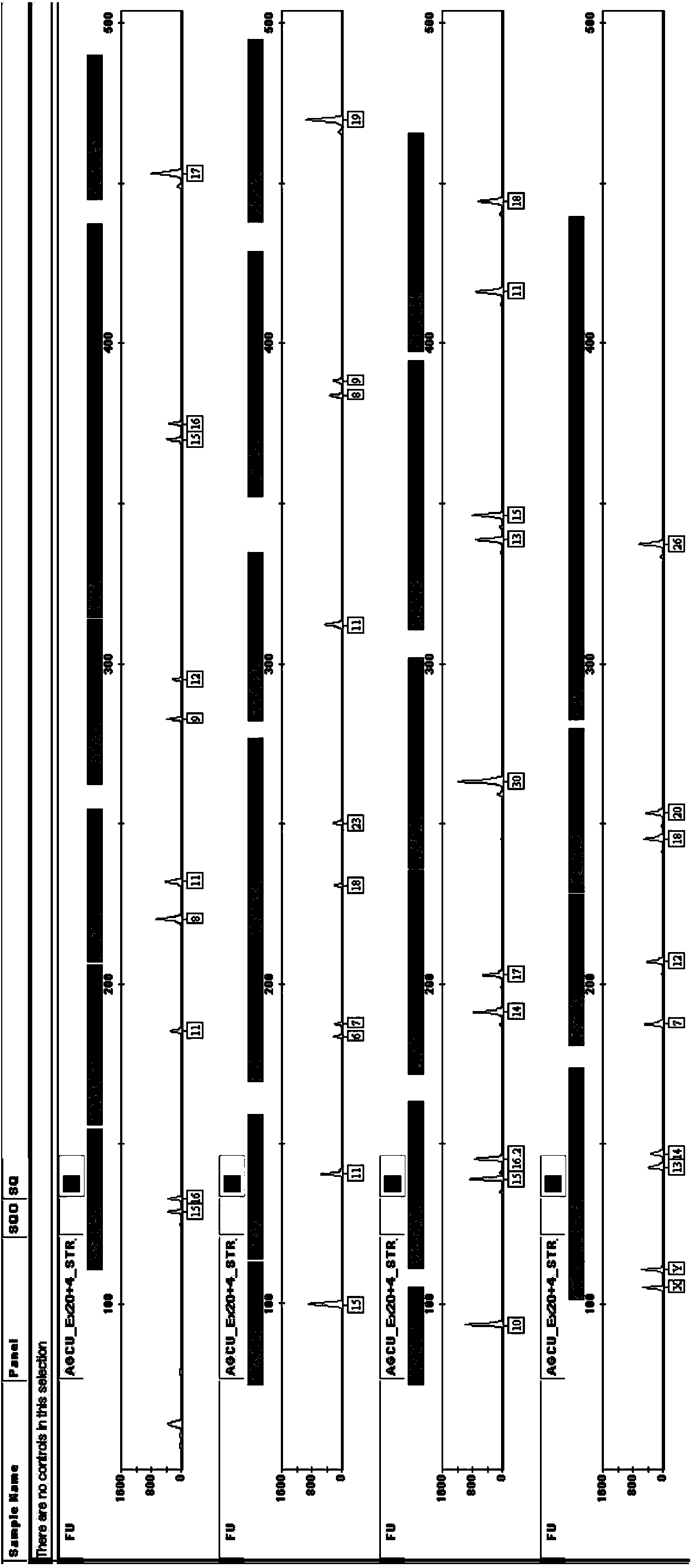
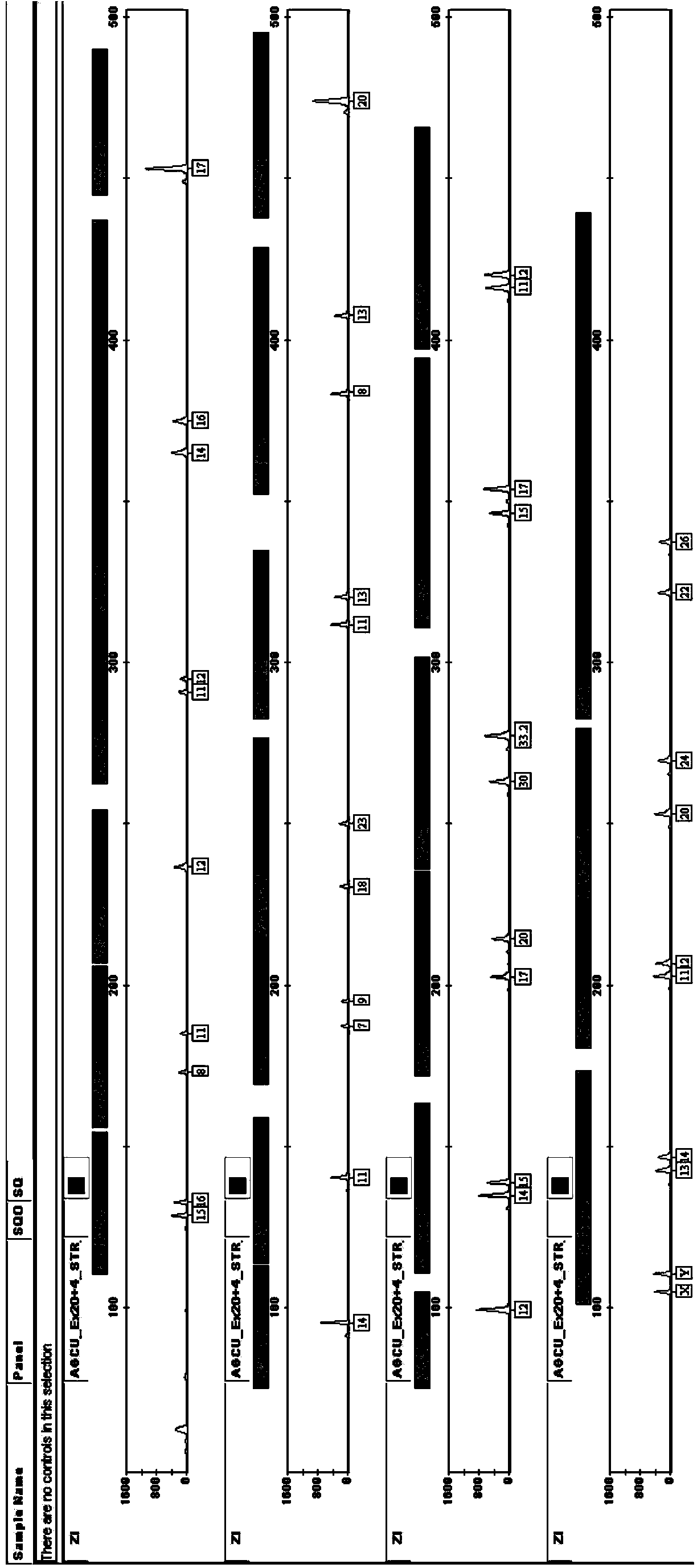
Kit for multiplex amplification of 24 loci of human genome DNA
ActiveCN103614361AQuick checkImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHuman DNA sequencingBlood filter paper
The invention relates to a five-color fluorescence labeling multiplex amplification system for analysis of 24 loci of human genome DNA at the same time. 19 autosome loci, 4 Y chromosome loci and 1 sex determination locus are detected at the same time. The system divides the 24 loci into 4 groups, and relates to fluorescence labeling of 5 colors. The fluorescence labeling multiplex amplification system has high sensitivity, under condition that the DNA template amount is 0.12ng, all the 24 loci can be detected, and the system is suitable for direct amplification of blood filter paper and FTA card collecting samples.
Owner:AGCU SCIENTECH +1
Kit for diagnosing gene of Leber optic neuropathy in heredity and detecting method
InactiveCN1661116ASolve difficult collection problemsShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseLesion
A reagent kit for the gene diagnosis of Leber's hereditary optical nerve (LHON) lesion which is caused by the mutations on 3 primary pathogenic sites (G11778A, G3460A and T14484C) is disclosed. Its detecting process includes such steps as designing and synthesizing the site specific PCR primer, using whole blood as DNA template, PCR amplification, and detecting said mutant sites of LHON patient.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Cells prepared by transient transfection and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20160151491A1Good metabolic stabilityConducive to survivalBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsDiseaseWhole body
Compositions and methods of making cells using RNA, and cells made using the disclosed compositions and methods are also provided. In exemplary embodiments, RNA is transfected into cells to effect a molecular, biological, physiological, or histological change in the cells. In preferred embodiments, the RNA is prepared in vitro, more preferably using a DNA template according to the provided compositions and methods. Methods for treating or inhibiting a disorder or disease such cancer are also provided. The methods can include, for example, locally or systemically administering to the host an effective amount of one or more RNAs; or an effective amount of population of cells isolated from the subject or a syngeneic or histocompatible subject, contacted ex vivo with one or RNAs, and optionally expanded. The cells can be, for example, immune cells or stem cells.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Sequencing joint and preparation method and application thereof in ultra-low frequency mutation detection
ActiveCN105861710AImprove detection accuracyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionDouble strand
The invention provides a sequencing joint and a preparation method and application thereof in ultra-low frequency mutation detection. The sequencing joint comprises a library amplification primer sequence, a target fragment amplification primer sequence and an error prompting sequence which are connected sequentially, the error prompting sequence is close to one side of a target fragment, the library amplification primer sequence is located on one side away from the target fragment, and the error prompting sequence is the sequence of a known base sequence. The error prompting sequence of the known base sequence is added on one side close to the target fragment, so that the error prompting sequence can add a specific foreign marker on each double-strand DNA template. Following sequencing data of the target fragment can be obtained conveniently, mutation introduced in the sequencing or library amplification step is screened or removed according to the fact whether the sequencing sequences have same error prompting sequences, then the sites with variation in the same positions of the two chains are determined to be real mutation, and the site with the mutation on one chain is identified as the amplification or sequencing error, so that the mutation detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING KEXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com