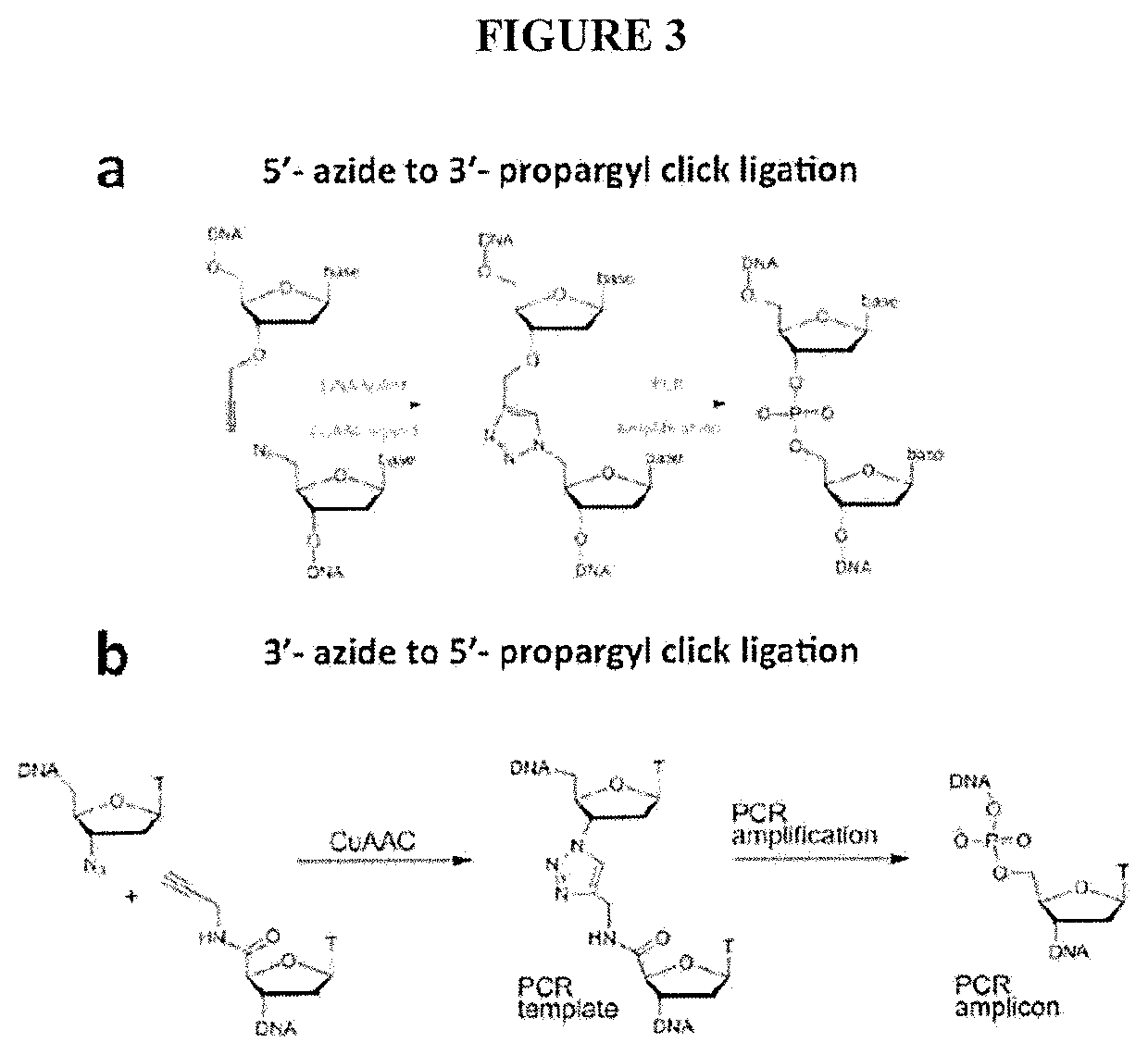
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Dna complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
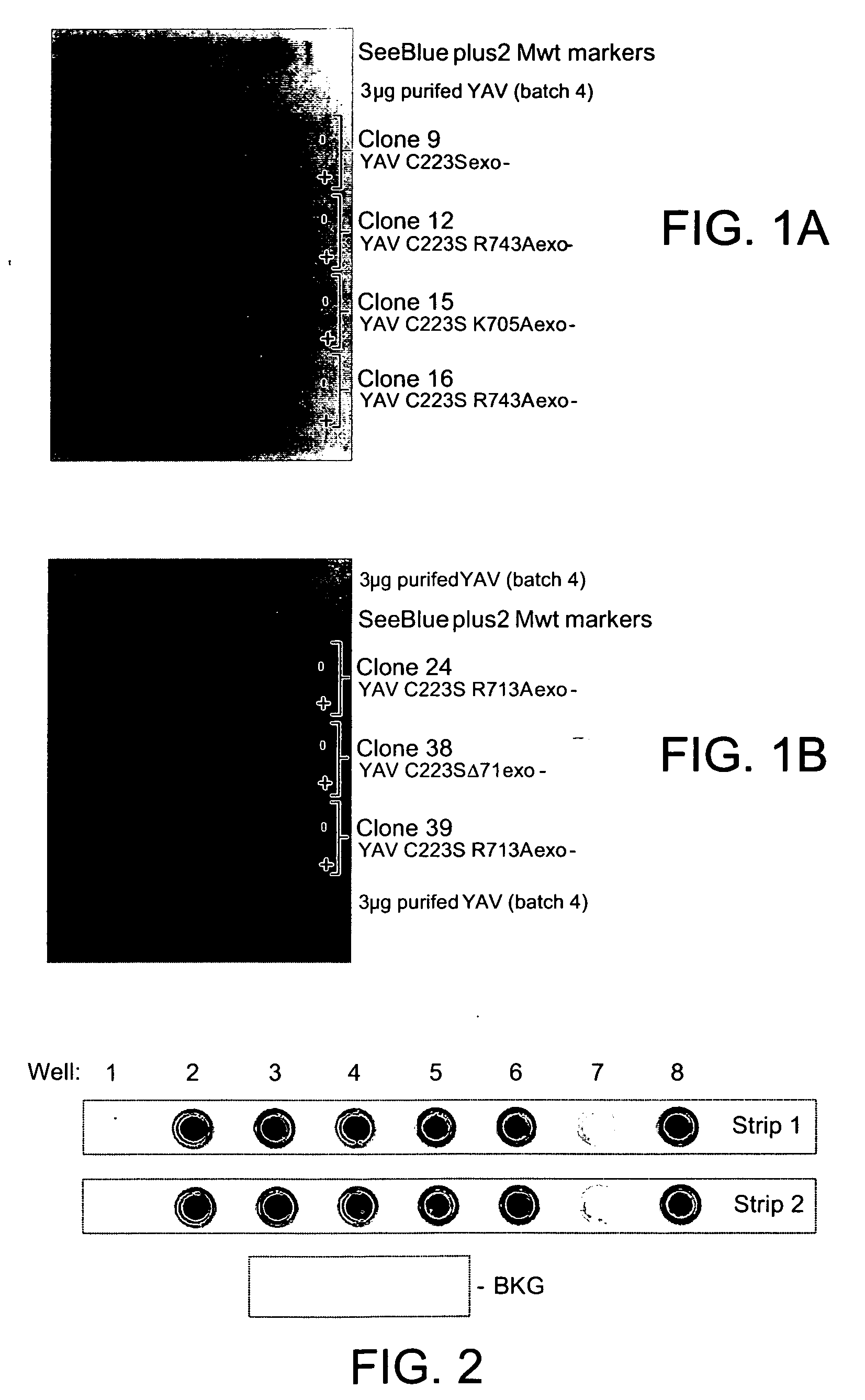
Polymerases
ActiveUS20060281109A1Improve the level ofProceed efficientlySugar derivativesHydrolasesModified dnaPolymerase L
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Cationic lipid compositions targeting angiogenic endothelial cells
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polymerases
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
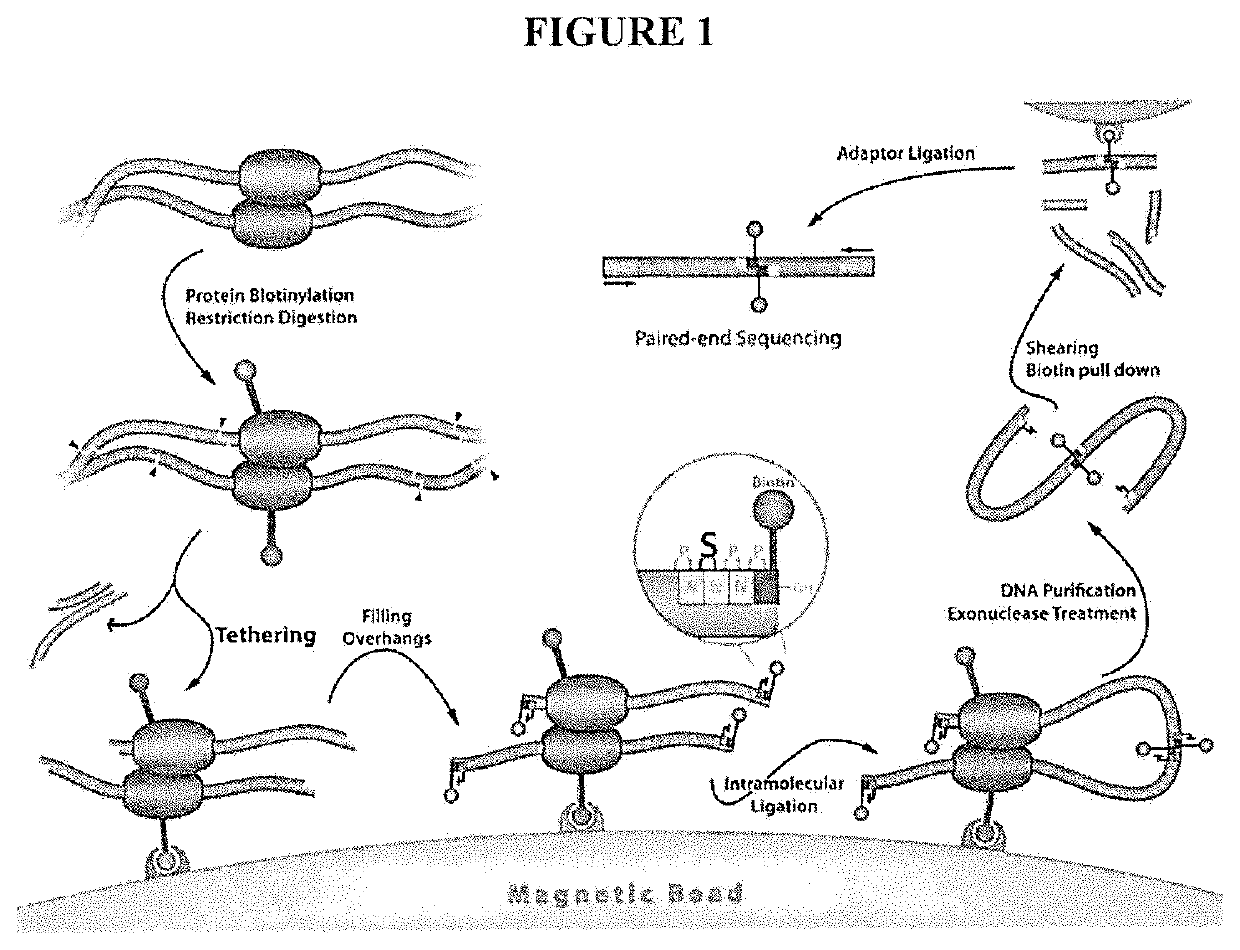
Tethered Conformation Capture
InactiveUS20110287947A1High resolutionReduce noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCross-linkEnzyme
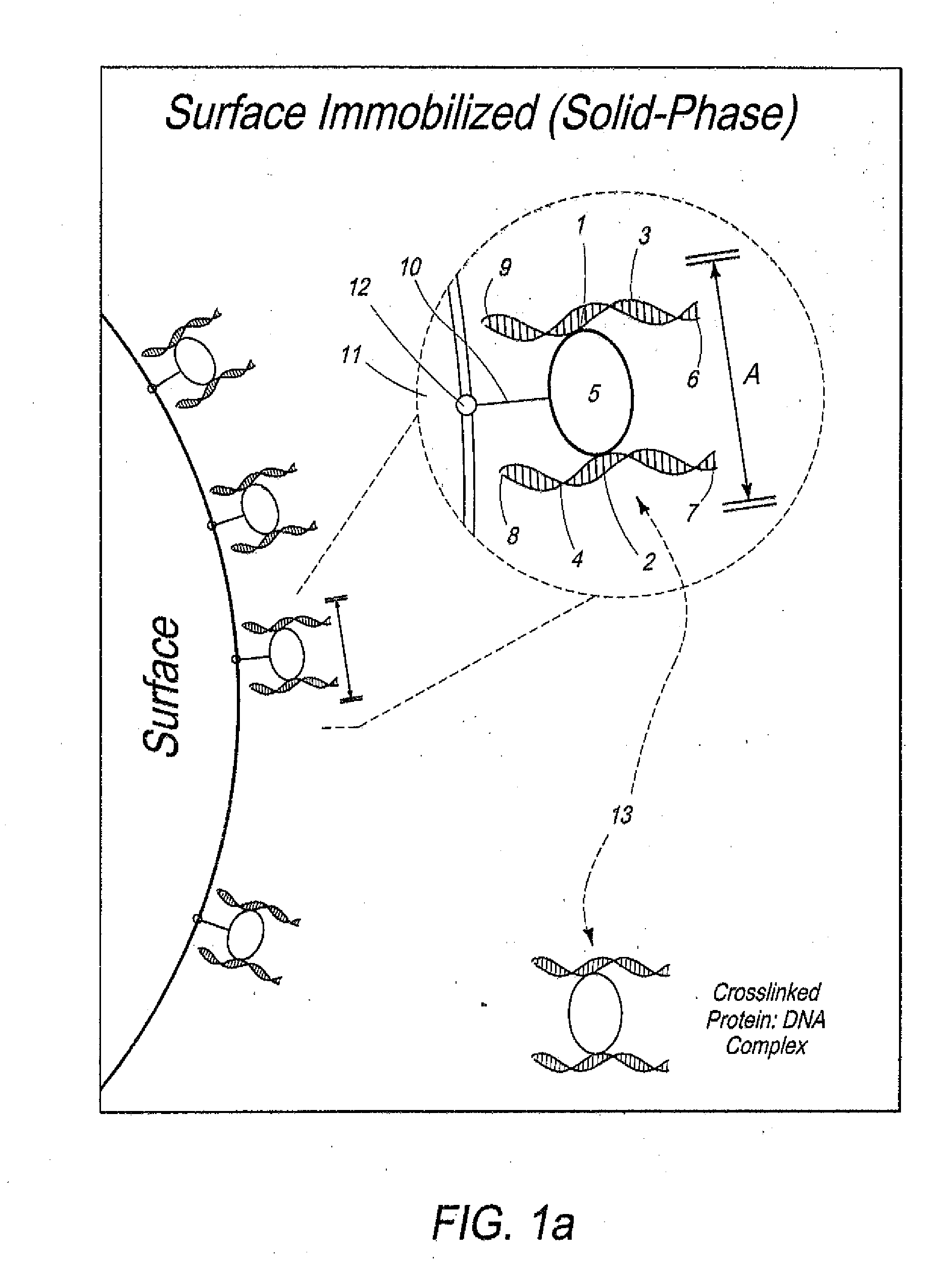
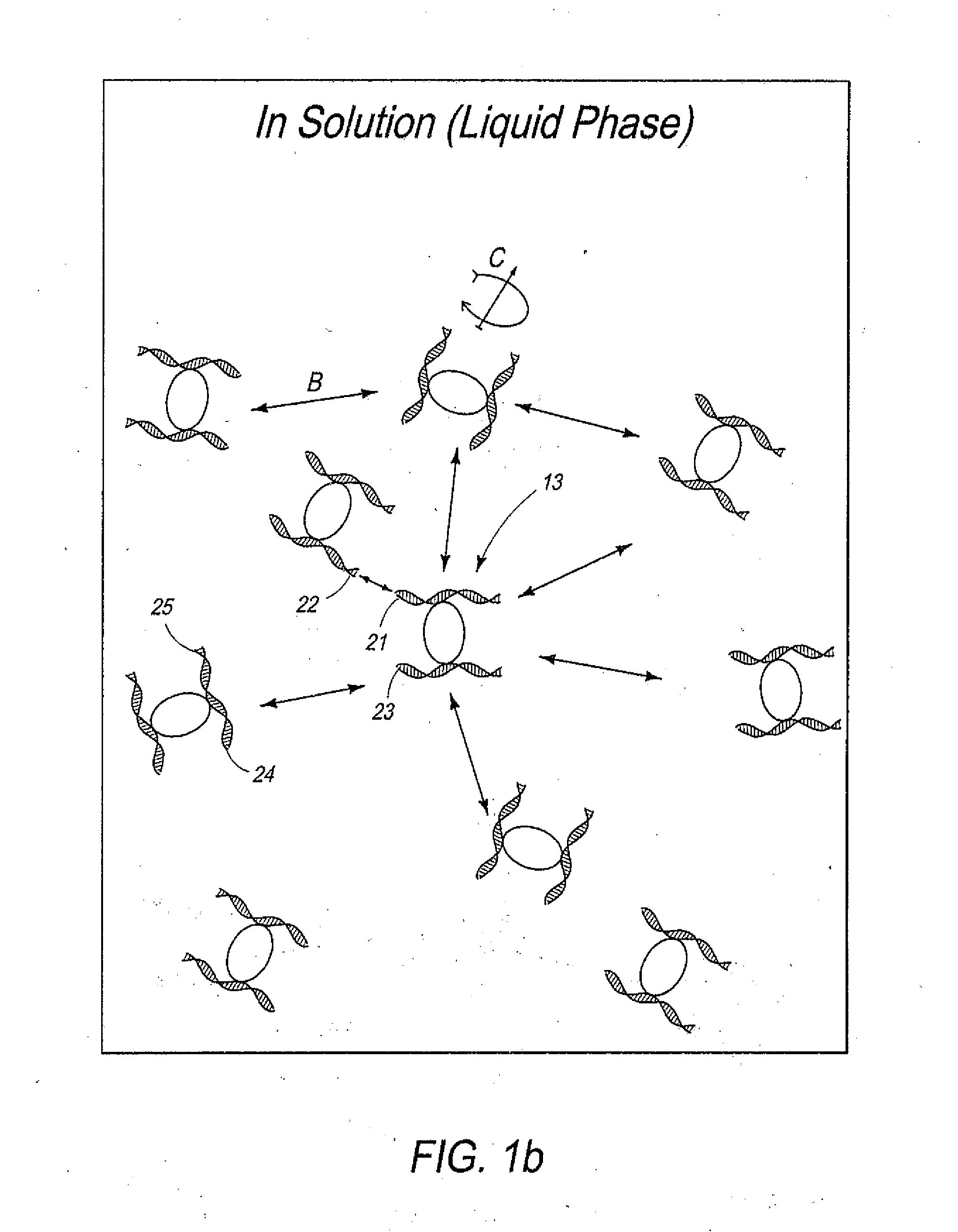
Disclosed are methods and systems for determining the three-dimensional structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. More specifically, disclosed are methods and systems for obtaining chromatin structural information by surface immobilization, i.e tethering crosslinked protein:DNA complexes and / or ligated DNA complexes to media such as beads, gels, and or matrices during the conformation capture assay. In general, the method includes contacting a cell with a cross-linking reagent to cross-link DNA and protein in the cell; lysing the cell, producing cross-linked protein:DNA complexes by cutting the chromatin using a chemical, physical or enzymatic method, substantially immobilizing the cross-linked protein:DNA complexes, ligating the cross-linked protein:DNA complexes intramolecularly such that the ligated protein:DNA complexes represent structural organization of the chromatin; characterizing the ligated DNA by sequencing or other methods; and identifying any structural organization of the chromatin. The structural organization preferably includes information relating to interacting loci of the chromatin.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Cationic liposome delivery of taxanes to angiogenic blood vessels
InactiveUS7112338B2Precise deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationCell selectivity
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
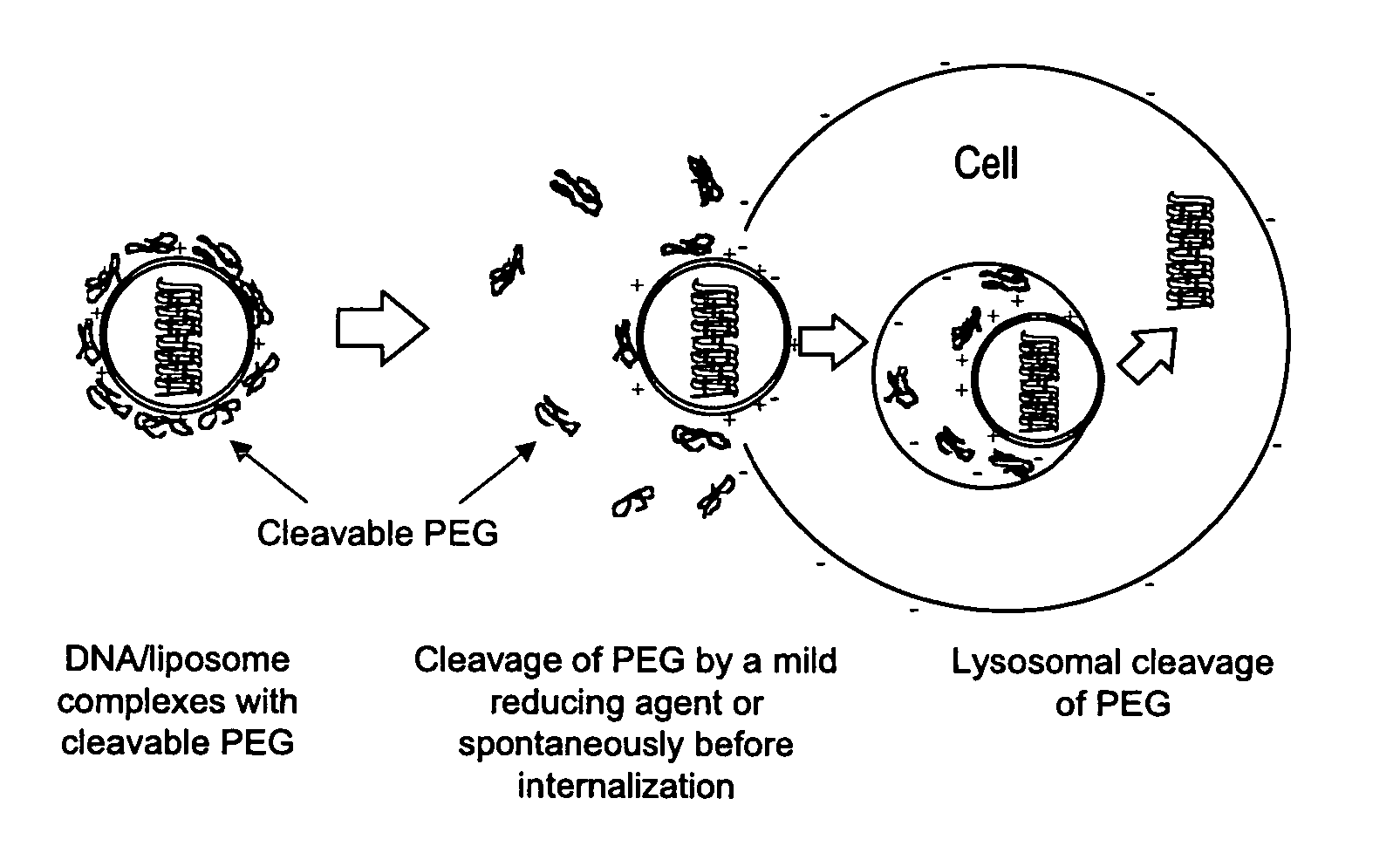
Gene delivery mediated by liposome-DNA complex with cleavable peg surface modification
A liposome composition and method for delivery of a nucleic acid in vivo or ex vivo is described. The liposomes in the composition are comprised of (i) a cationic lipid and (ii) a lipid joined to a hydrophilic polymer by a releasable linkage. The liposomes are associated with a nucleic acid for delivery to a cell.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Synthesis of quinobenzoxazine analogues with topoisomerase II and quadruplex interactions for use as antineoplastic agents
InactiveUS6528517B1Potentiated antibiotic activityPotentiated anticancer activityBiocideOrganic chemistryDNA underwindingType II topoisomerase
The present invention discloses a novel quinobenzoxazine self-assembly complex on DNA and on the topoisomerase II-DNA complex. The related model is used to design a new series of quinobenzoxazines, pyridobenzophenoxazines, pyrridonaphthophenoxazines, and other related compounds that may exhibit anticancer or antibiotic activity. The anticancer activity of these compounds is thought to operate via stabilization of the topoisomerase II-DNA complex and / or interaction with G-quadruplexes, while the antibiotic activity of these compounds derives from their ability to inhibit gyrase, the bacterial type II topoisomerase.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Improved polymerases
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
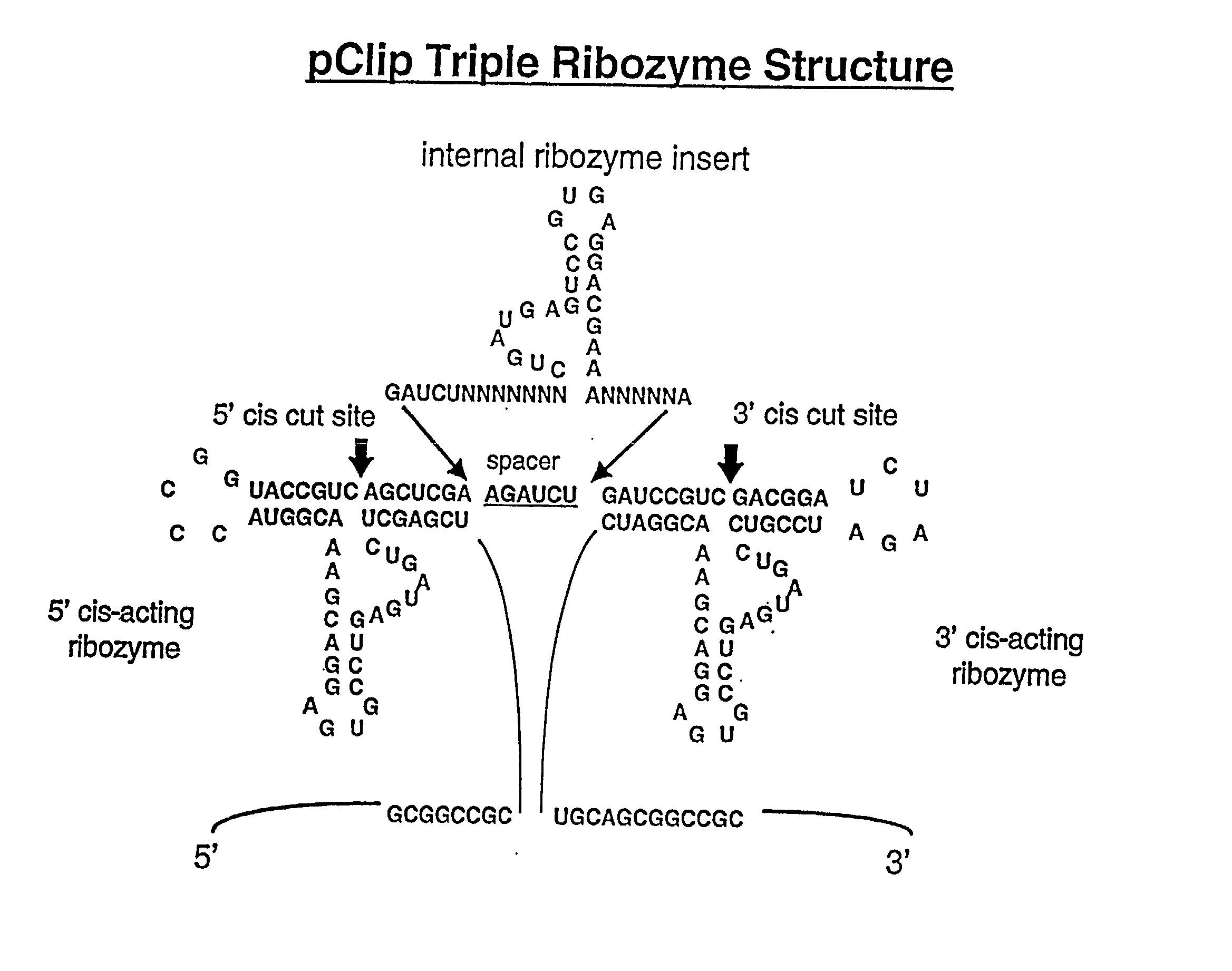
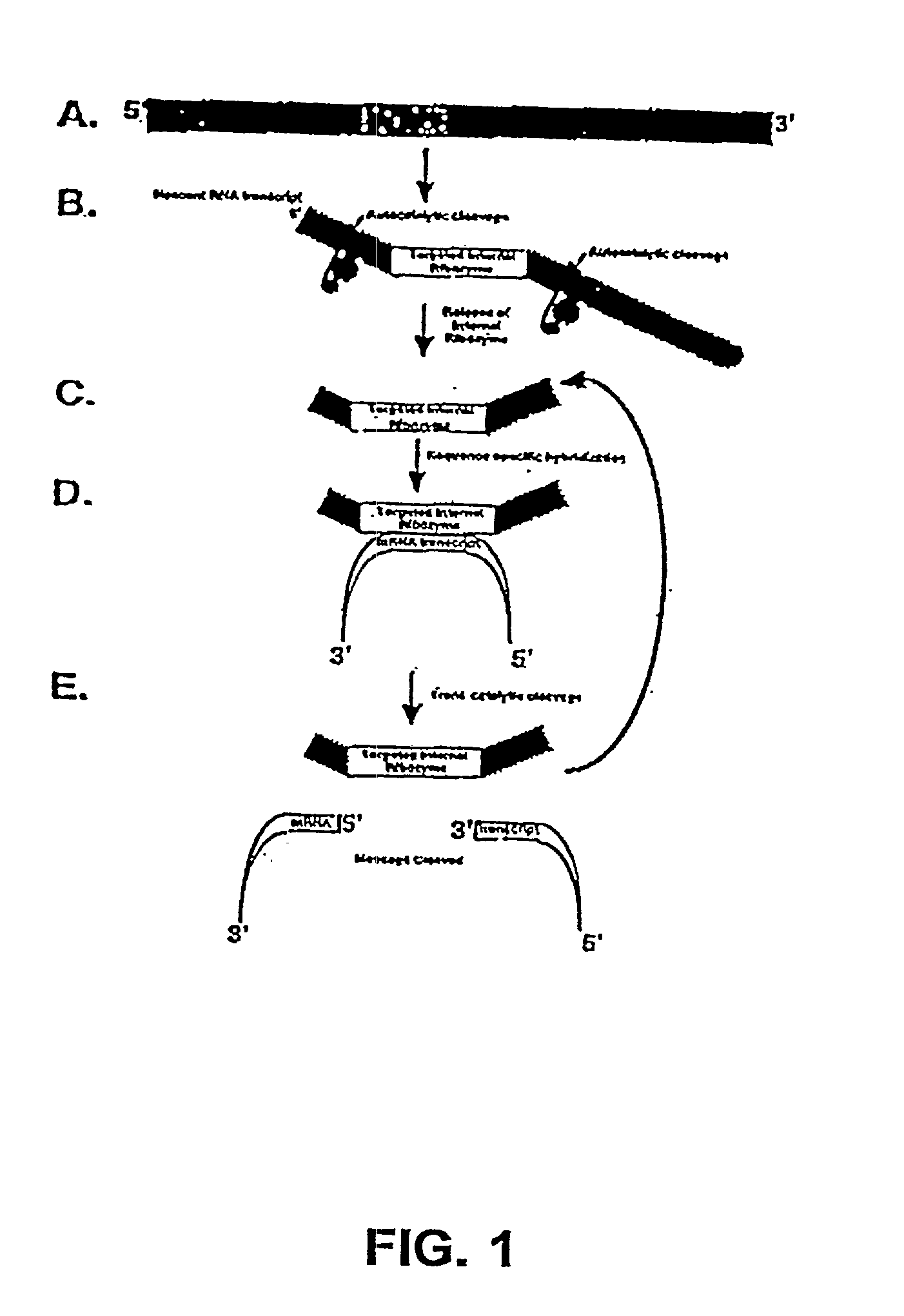
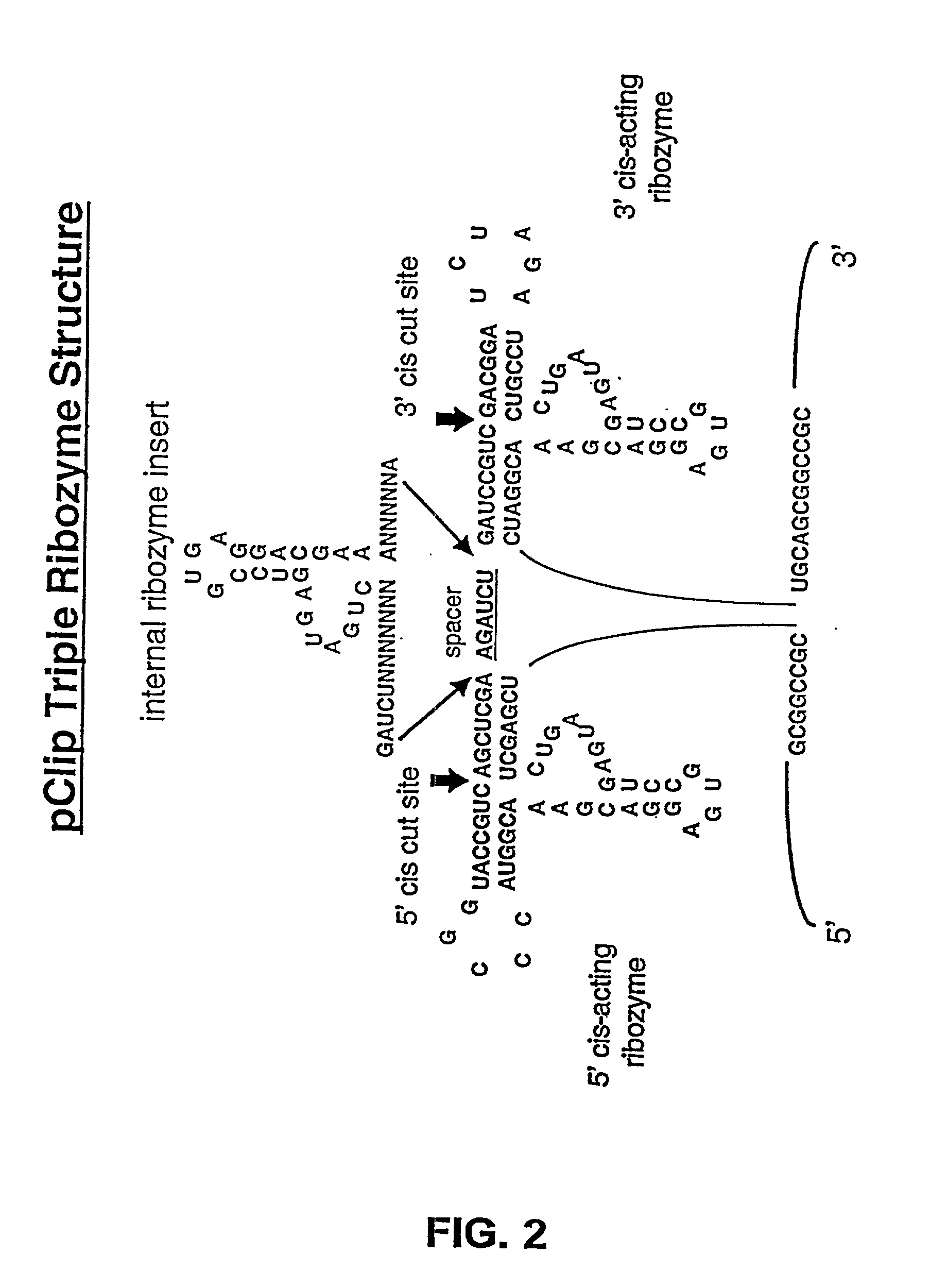
Tissue-specific and target RNA-specific ribozymes
InactiveUS20030092651A1Improve stabilityHigh activityVirusesSugar derivativesLipid formationMultinucleate
The present invention relates to multi-ribozymes and their use to target RNA in a tissue-specific, target RNA-specific, or pathogen-specific manner for the treatment of cancers, proliferative disease, and bacterial, parasitic and viral infections. More specifically, the present invention relates to the use of virions and viral vectors to package and deliver DNA encoding the multi-ribozymes to a host. The present invention relates to the use of liposomes and lipid-DNA complexes to deliver DNA encoding ribozymes to a host. Most specifically, the invention relates to the use of target specific virions to package and deliver DNA comprising a target specific promoter and encoding a ribozyme(s) directed to the target organism nucleic acids. The present invention further relates to a novel vectors encoding a multi-ribozyme structure with enhanced 5' and / or 3' autocatalytically cleaving ribozymes. The invention further relates to nucleotides encoding a multi-ribozyme comprising one or more ribozyme cassettes which contain one or more trans-acting ribozymes and one or more autocatalytically cleaving ribozyme sequences.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
Polymeric formulations for drug delivery
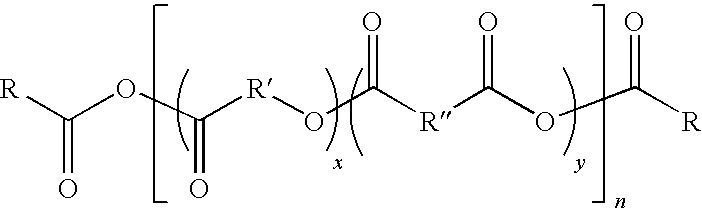
Poly(ester-anhydrides) or polyesters formed from ricinoleic acid and natural fatty diacids and their method of preparation and its use for delivering bioactive agents including small drug molecules, peptides and proteins, DNA and DNA complexes with cationic lipids or polymers or nano and microparticles loaded with bioactive agents are disclosed herein. The drug delivery compositions are administered to a patient in a liquid form, increase in viscosity in vivo to form a drug depot or implant, and are able to release the incorporated bioactive agent for weeks. In the preferred embodiment, the drug delivery formulations are administered by injection. In one embodiment, the compositions are suitable for local or regional delivery of drugs to diseased sites, such as treating solid tumors and bone infections. In a preferred embodiment, the drug delivery compositions are suitable for site-specific chemotherapy for the treatment of solid tumors including: squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck, prostate cancer, and sarcomas for intratumoral injection or insertion.
Owner:EFRAT BIOPOLYMERS LTD
Label-free sensing of pna-dna complexes using nanopores
InactiveUS20120276530A1Improve bindingImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanomedicineDiseaseVirus
Embodiments disclosed herein relate to a method of detecting specific DNA sequences and the application of this method in the detection of pathogens, viruses, drug-resistant pathogens, genomic variations associated with disease / disorder susceptibility etc. based on specific signature sequences unique to the pathogens, viruses, drug-resistant pathogens or genomic variations. The method can also be used to distinguish a pool of same-sized dsDNA on the basis of sequence differences. The method uses non-optically labeled bis-PNA and / or gamma-PNA probes to tag specific target sequences for identification by solid-state nanopores.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Subunit Vaccines for Herpes Viruses and Methods of Use
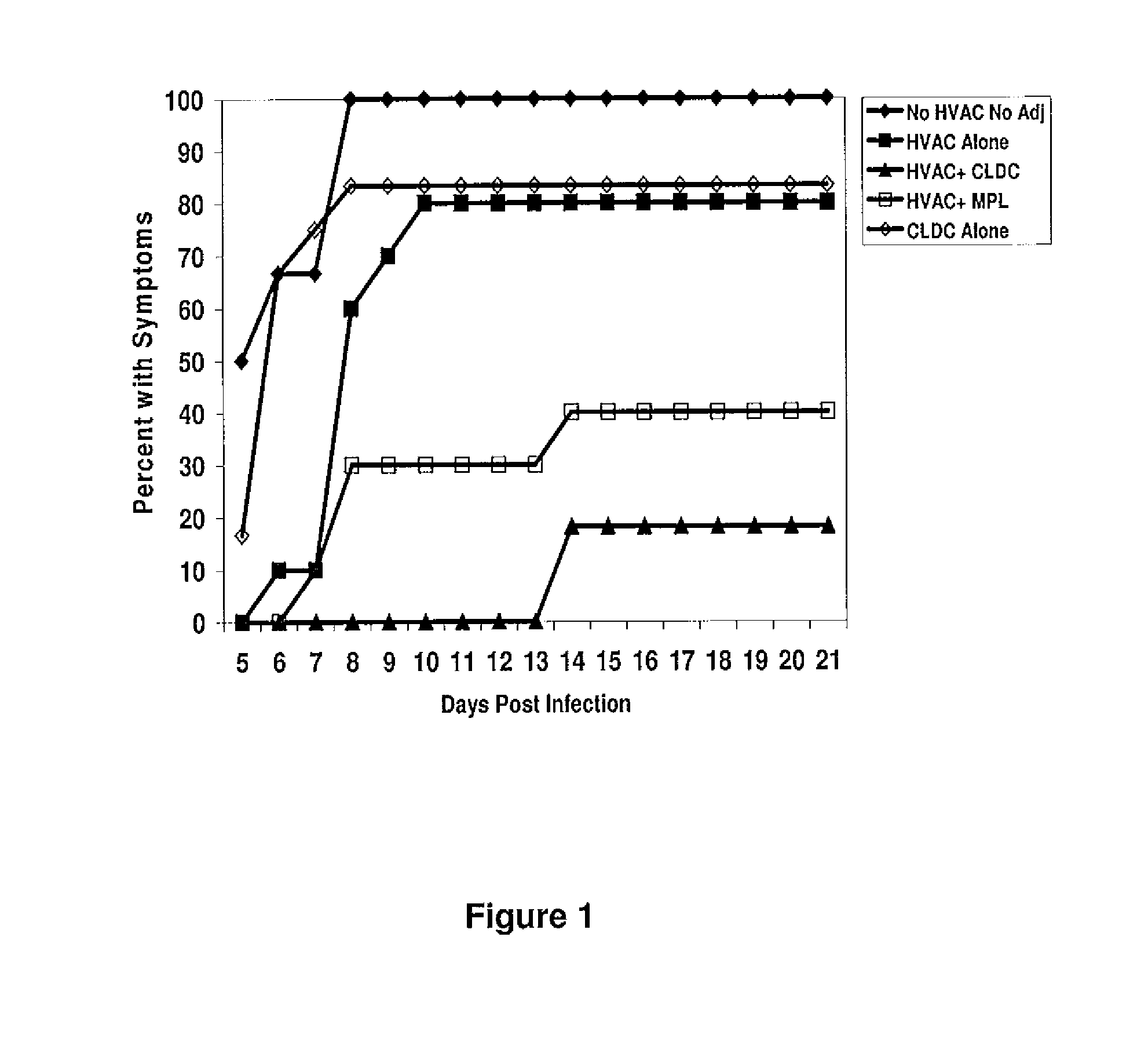
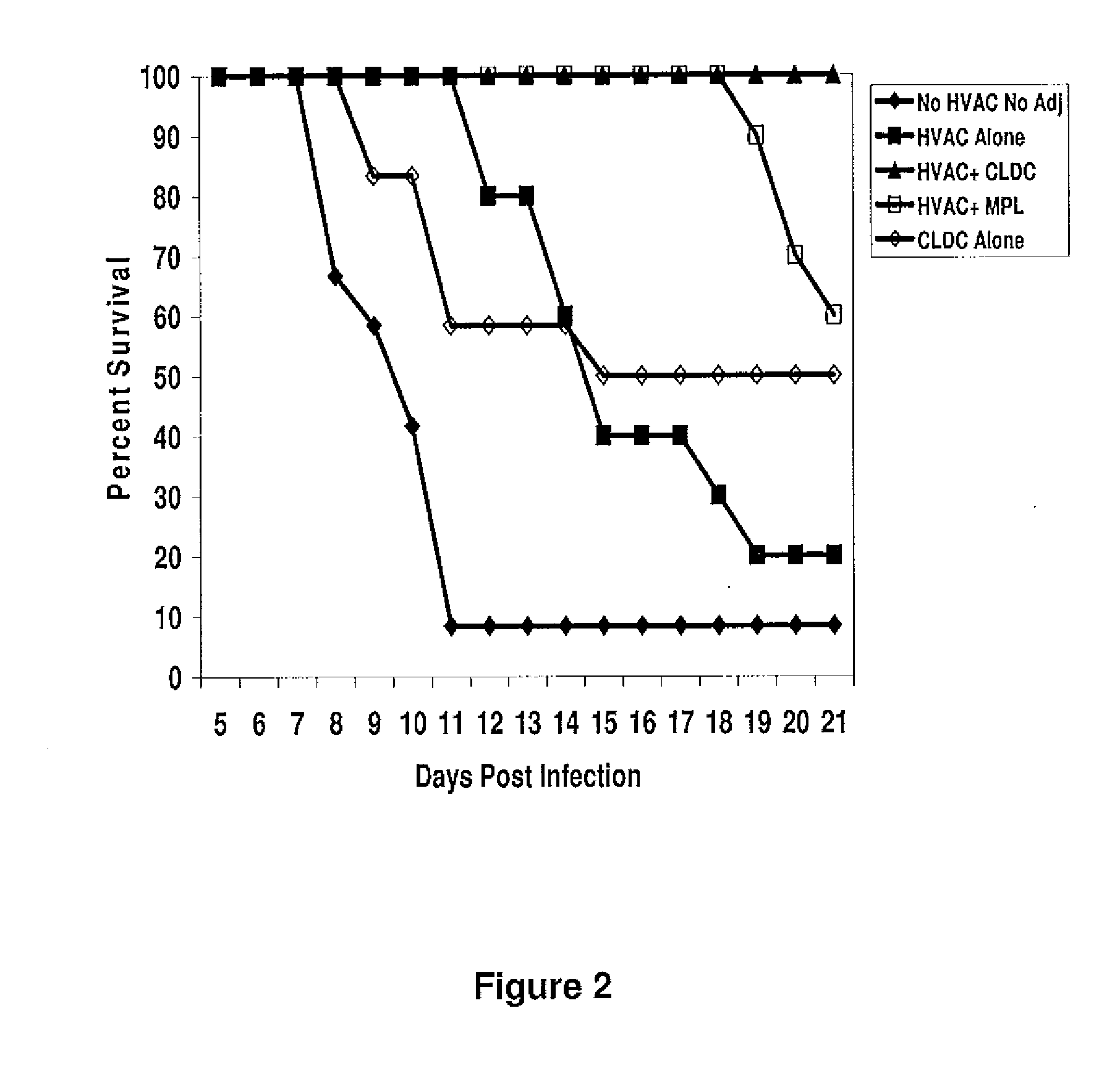
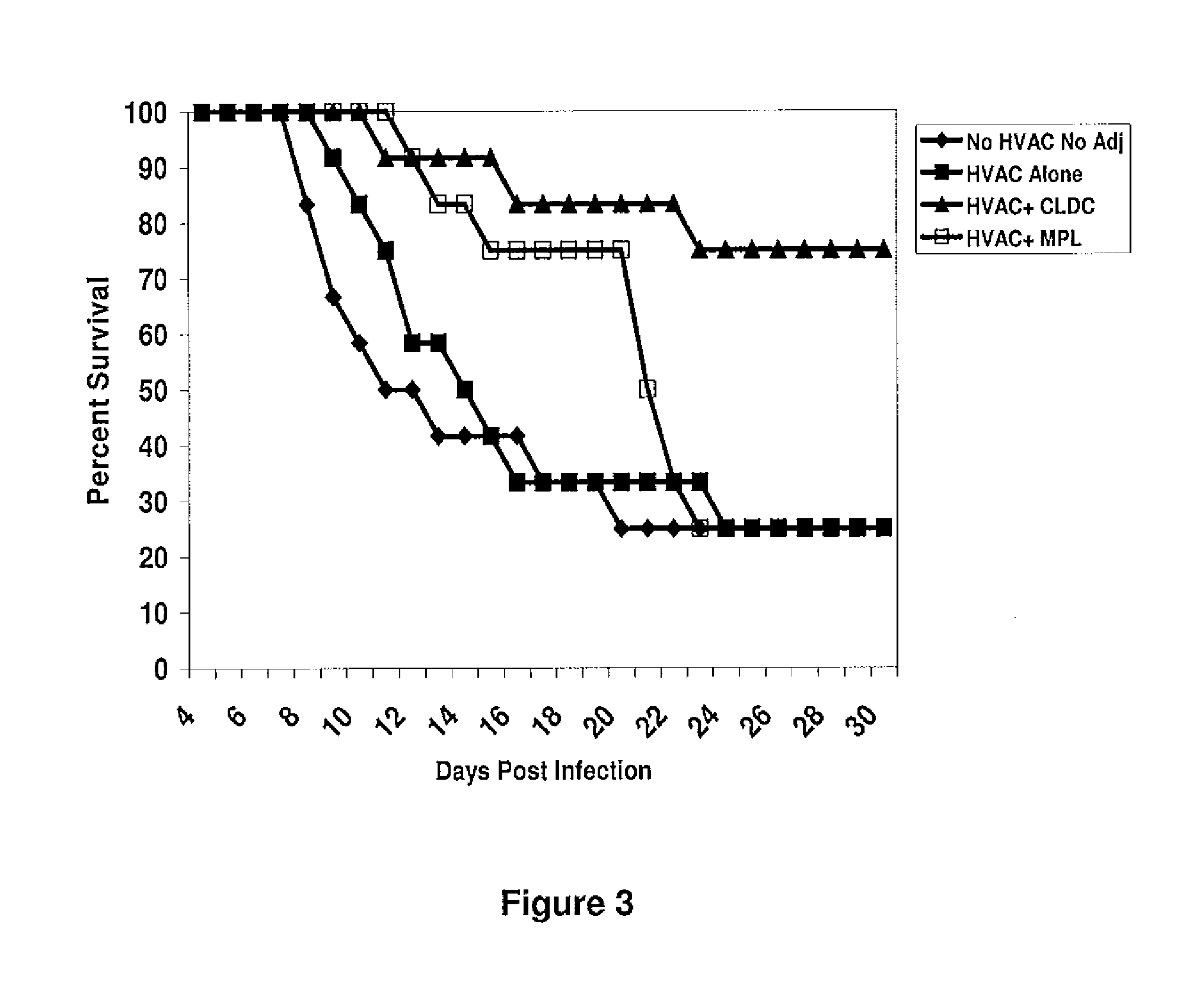
The present disclosure generally relates to vaccine compositions for Herpes Simplex Viruses (HSV) types 1 and / or 2. The vaccines comprise isolated antigens or glycoprotein subunits of the viruses, optionally with an adjuvant, such as a cationic liposome DNA complex (CLDC). Also the present disclosure contains methods of vaccinating a subject utilizing these compositions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
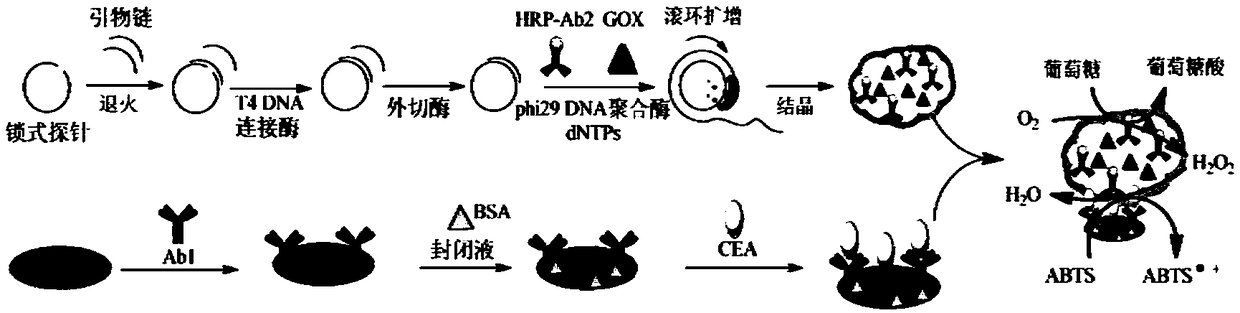
Novel protein-DNA complex for detecting carcino-embryonic antigen as well as synthetic method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and particularly relates to a novel protein-DNA complex for detecting a carcino-embryonic antigen as well as a synthetic method and application thereof. The novel protein-DNA complex comprises a horseradish peroxidase-marked carcino-embryonic antigen secondary antibody, glucose oxidase and a DNA structure. The novel protein-DNAcomplex structure encapsulated with a great amount of enzyme-labeled secondary antibodies and glucose oxidase is established on the basis of a rolling circle replication technology and is used as enzyme cascade signal amplification probe. A 96-pore plate is used for fixing carcino-embryonic antigen monoclonal antibody molecules, after the to-be-detected carcino-embryonic antigen is added, a sandwiched structure is formed. The encapsulated glucose oxidase is used for catalyzing the glucose to be oxidized to generate H2O2, then the H2O2 is catalyzed by virtue of the horseradish peroxidase to oxidize ABTS, so that the high-sensitivity and high-specificity colorimetry detection of the carcino-embryonic antigen can be realized, and the novel protein-DNA complex has important significance for the early diagnosis and clinical research of cancers.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
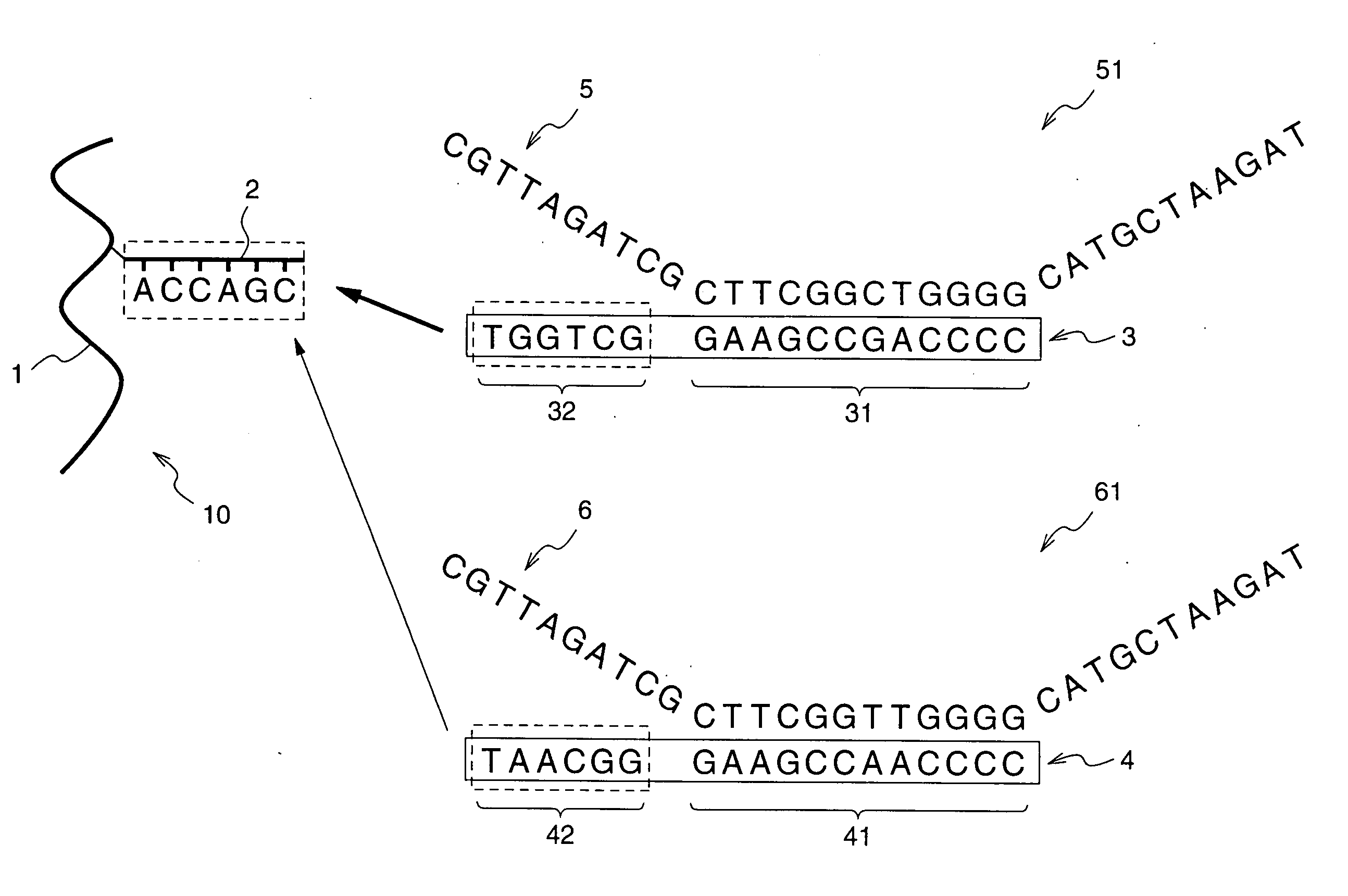
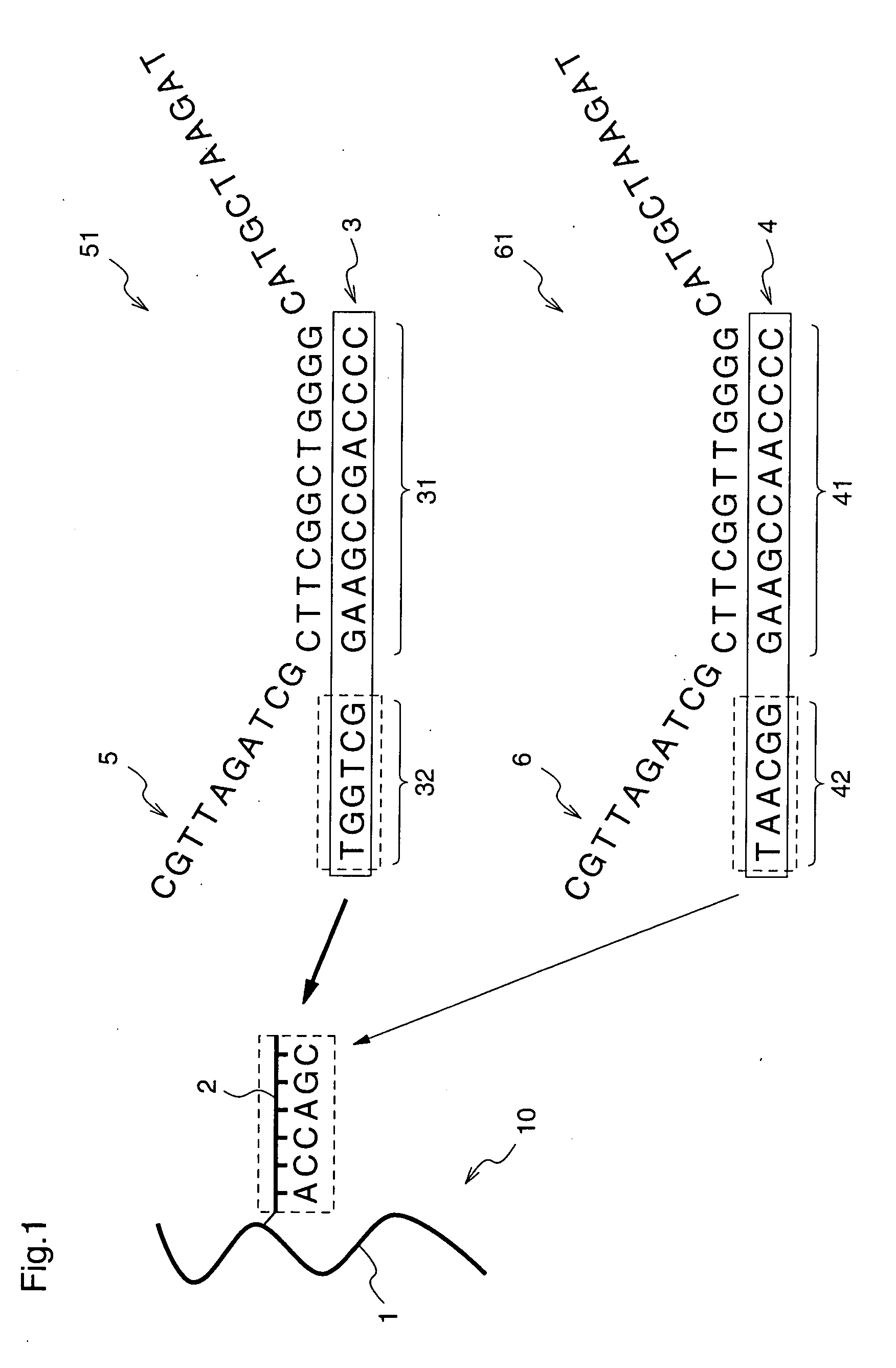
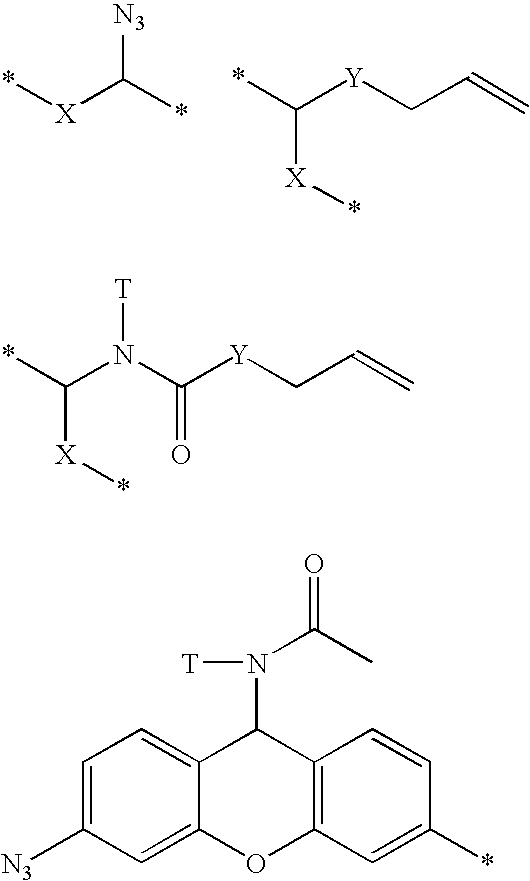
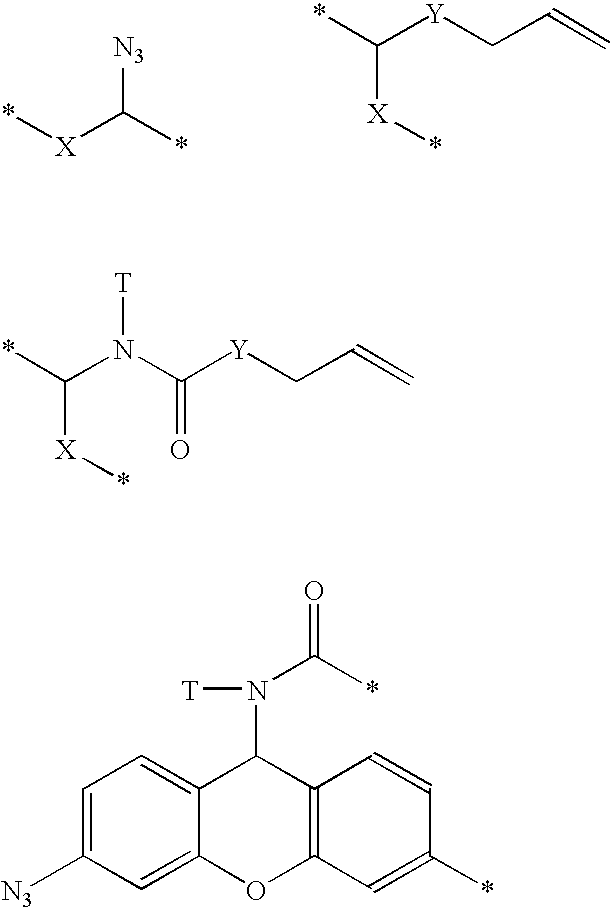
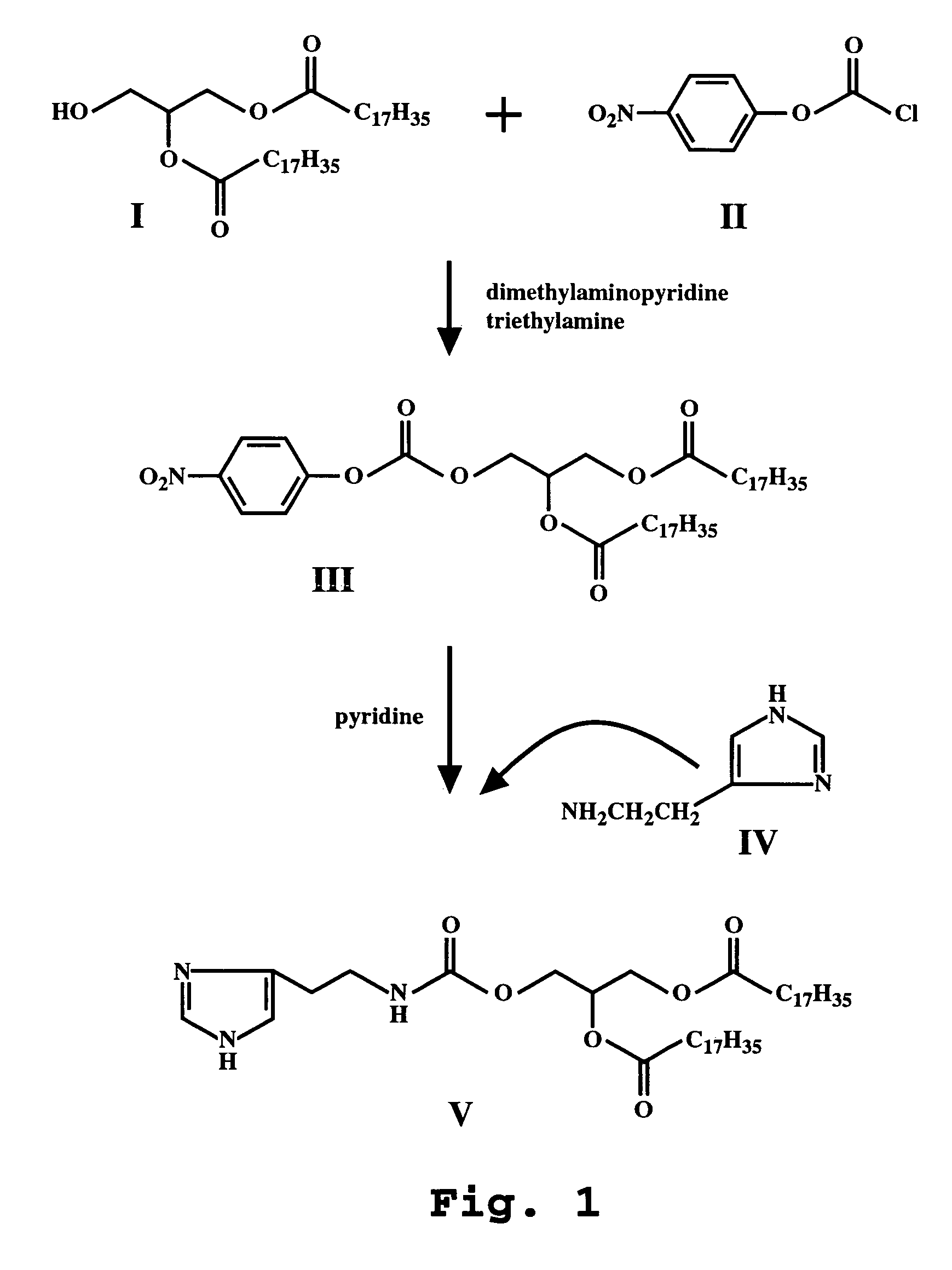
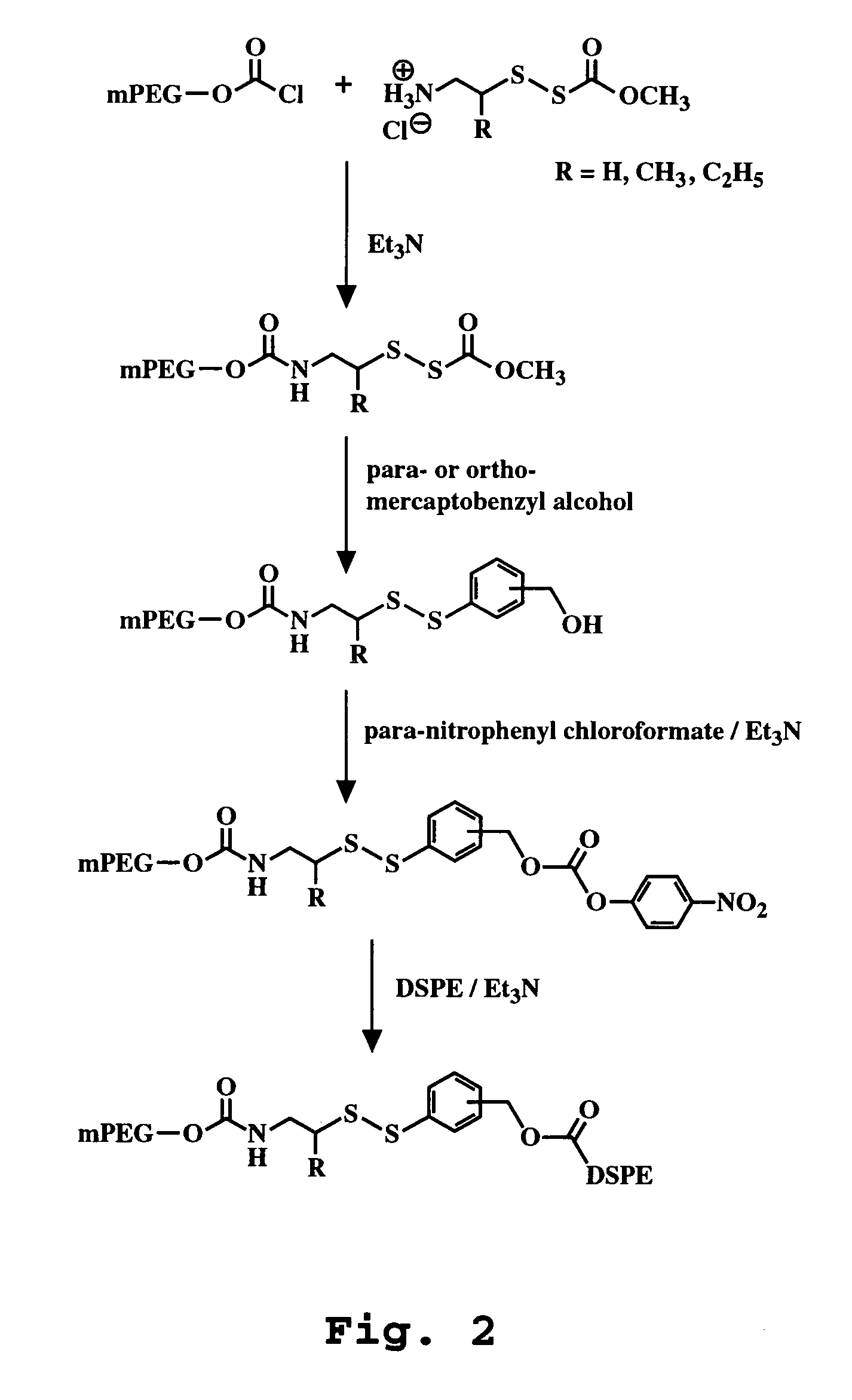
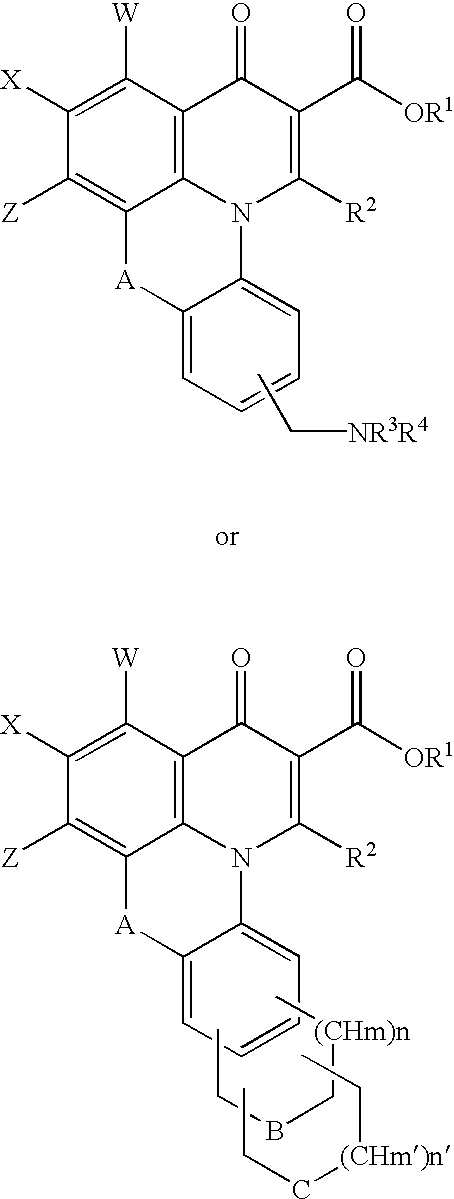
[12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector
ActiveCN105541799AImprove targetingImprove monitoring tracking performanceOrganic chemistryGenetic material ingredientsCholic acidFluorescence
The invention provides a [12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing a targeted group and a fluorescent group and a transgenic vector containing the same. The invention also discloses preparation methods of the cationic lipid and the transgenic vector. The cationic lipid provided by the invention contains the targeted group cholic acid and the fluorescent group naphthalimide simultaneously; the transgenic vector formed by the cationic lipid has lower cytotoxicity, has a certain targeting property on hepatoma cells, not only can monitor intracellular transport and release of vector / DNA complexes in a same cell but also has a certain selectivity on the hepatoma cells to promote the development of gene therapy, and also has higher transfection efficiency; the preparation methods of the cationic lipid and the transgenic vector are simple, mature, and easy to control.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Cationic liposome delivery of taxanes to angiogenic blood vessels
InactiveUS20100226970A1Precise deliveryInhibit angiogenesisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideCell selectivity
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Carbocyanines for G-Quadruplex DNA Stabilization and Telomerase Inhibition
Cyanines which selectively bind to G-quadruplex DNA complexes, particularly quadruplexes expressed in cancer cells, and methods of making and using thereof are described herein. The cyanine can be a symmetrical or unsymmetrical streptocyanine, hemicyanine, closed chain cyanine, or combinations thereof. The cyanine is preferably substituted with one or more groups that minimize or prevent aggregation of the cyanine and / or inhibit binding of the cyanine to duplex DNA. One or more of the cyanines can be formulated with one or more pharmaceutical excipients and / or carrier to prepare pharmaceutical compositions suitable for administration to a patient, particular a human patient. The compounds and compositions described herein can be used to treat diseases or disorders characterized by the expression of G-quadruplex DNA, such as cancer.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Method for enhancing proliferation and post-transplantation survival ability of adipose derived stem cells
InactiveCN106434542APromote proliferationImprove proliferative abilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsA-DNASerine
The invention discloses a method for enhancing proliferation and post-transplantation survival ability of adipose derived stem cells. TGF-[beta]1 at a special concentration is added to culture of the adipose derived stem cells, and the TGF-[beta]1, after binding with a TGF-[beta]II type receptor (TGF-[beta]RII), activates and recruits TGF-[beta]I receptor (TGF-[beta]RI) composition so as to form a receptor complex in the form of a dimer. The TGF-[beta]RII can phosphorylate a glycine-serine enriched region (GS sequence) of the TGF-[beta]RI and activate serine / threonine activity of the TGF-[beta]RI. The activated TGF-[beta]RI can phosphorylate receptor related smad2 and smad3 proteins, and then the smad2 / smad3 form a complex and further bind with smad4; the formed complex is transferred into cell nucleus; the smad3 and the smad4 are bound to a DNA sequence called SBE, while the smad2 reacts with the DNA complex through an interaction with the smad4, so that the expression of an ECM synthetic gene is activated. The proliferation of the adipose derived stem cells, which are processed by virtue of the method provided by the invention, is accelerated and the post-transplantation survival ability is enhanced.
Owner:山东海斯福生物科技有限公司
High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism detecting method based on magnetic nano-particles and universal label technique
InactiveCN101205560ALow costNo additional typing stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementMulti siteHigh flux
The invention discloses a multi-sample multi-site typing method against single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in a genome by using magnetic nano particles as carriers and combining with the technology of universal label probe. The invention is characterized in that: a labeled PCR product is directly fixed on the magnetic nano particles through covalent unions between labels, or a labeled primer is fixed on the magnetic nano particles to directly execute solid-phase PCR amplification, thereby forming magnetic nano particles-DNA complex (MNP-ssDNA). Then, the MNPs-ssDNA is hybridized with a detecting probe of corresponding site and a labeled universal label probe, thereby achieving multi-sample multi-site high flux SNP detection. The advantages of the invention are that: only a pair of labeled probes are required by using the universal label technology to achieve the multi-site typing, and the typing cost is greatly reduced; meanwhile, the invention overcomes the defects of high cost, time consuming, taking trouble, etc. caused by purifying and concentrating a target sequence waiting for detecting in the prior art by using the advantages that the magnetic nano particles are easily separated, etc. Therefore, the method has the advantages of typing mass samples simply, efficiently and accurately.
Owner:李松 +1
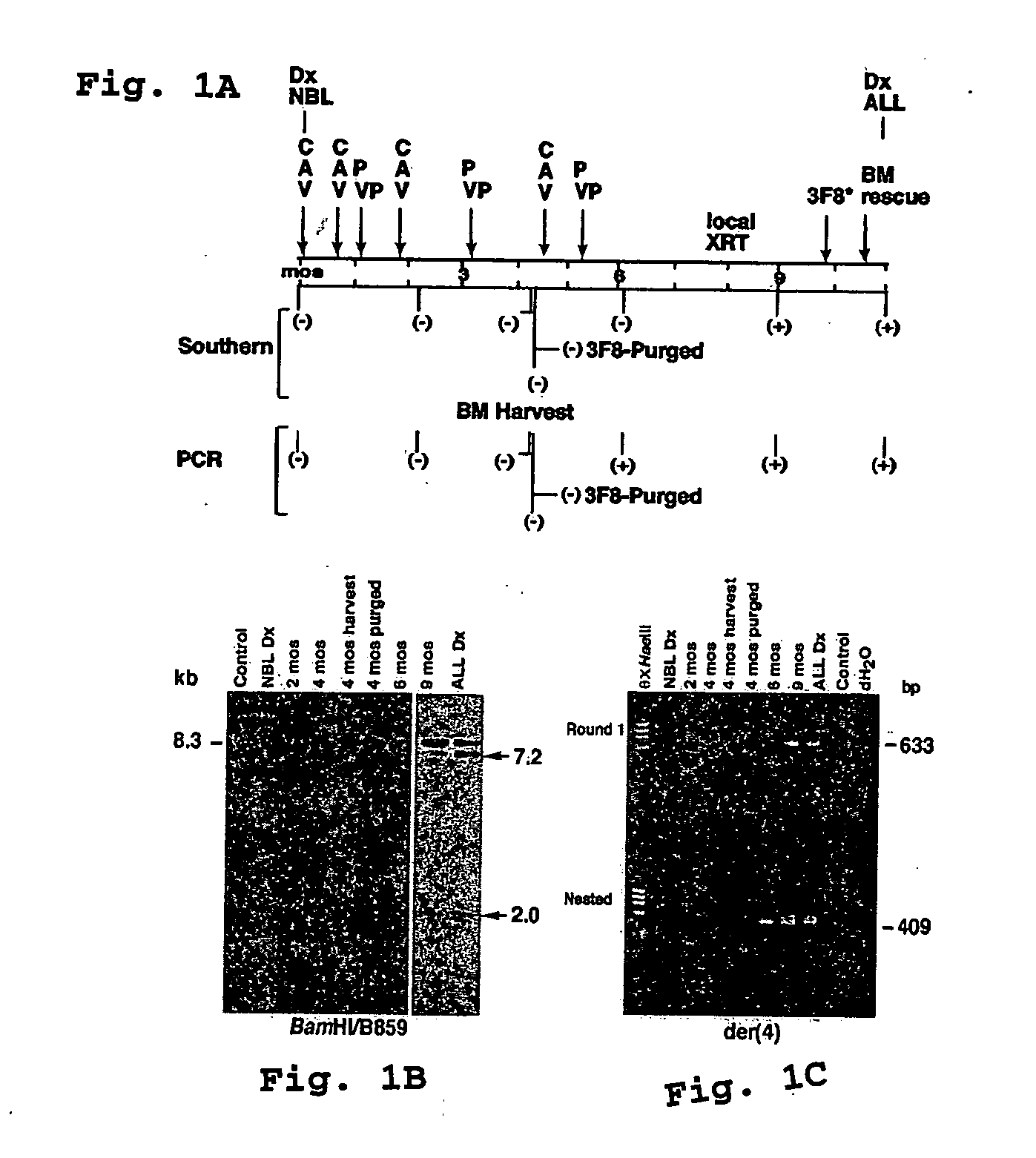
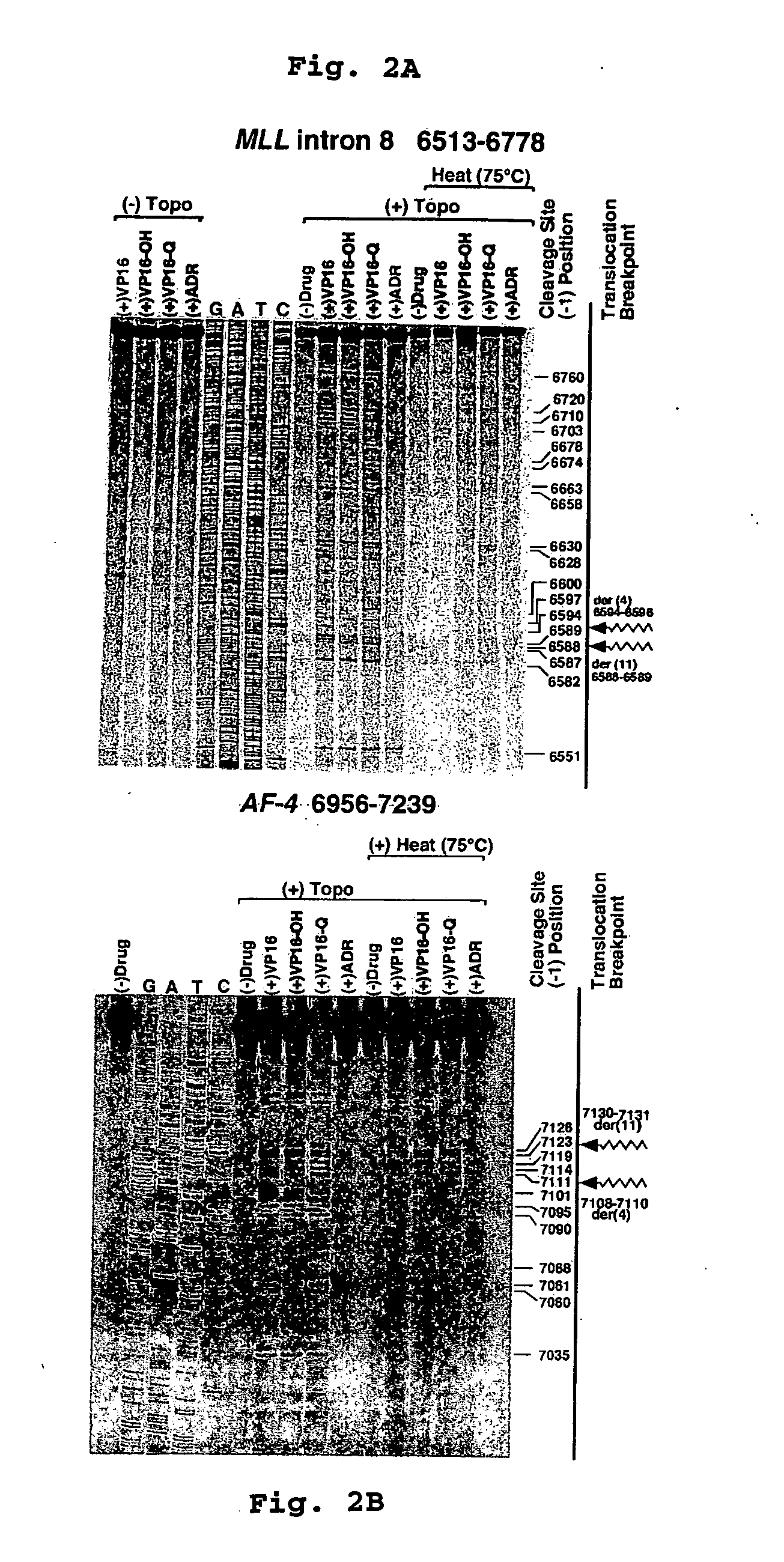
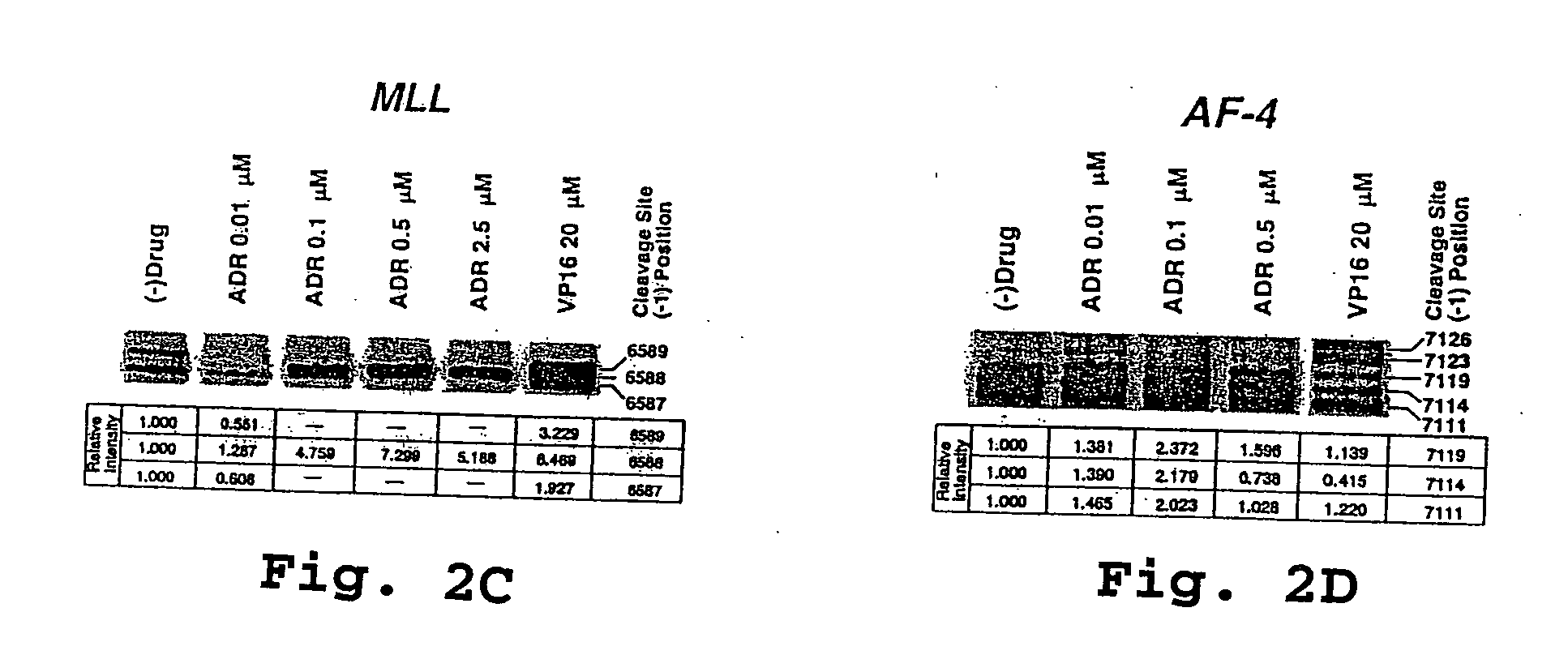
Compositions and methods for the detection of DNA topoisomerase II complexes with DNA
InactiveUS20060063184A1Prevent leukemogenic eventHigh expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNA Topoisomerase IIDna complex
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Three-dimensional structures of HDAC9 and Cabin1 and compound structures and methods related thereto
Disclosed are the three-dimensional structures of two complexes: a Cabin1 / MEF2B / DNA complex and a MITR / MEF2B / DNA complex. Also disclosed are methods of using such structures and models derived therefrom in structure-based design methods to identify regulators of the interaction of MEF2 with its cognate ligands / corepressors, to compounds that can be designed or identified based on the knowledge of such structures and models, and to methods of using such compounds in therapeutic methods. Also disclosed are peptide and non-peptide regulatory compounds that regulate, and preferably inhibit, MEF2.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
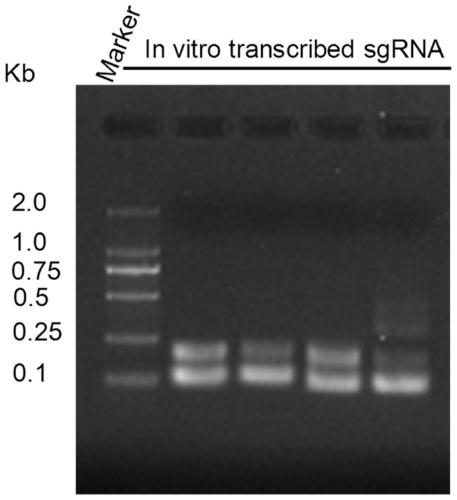
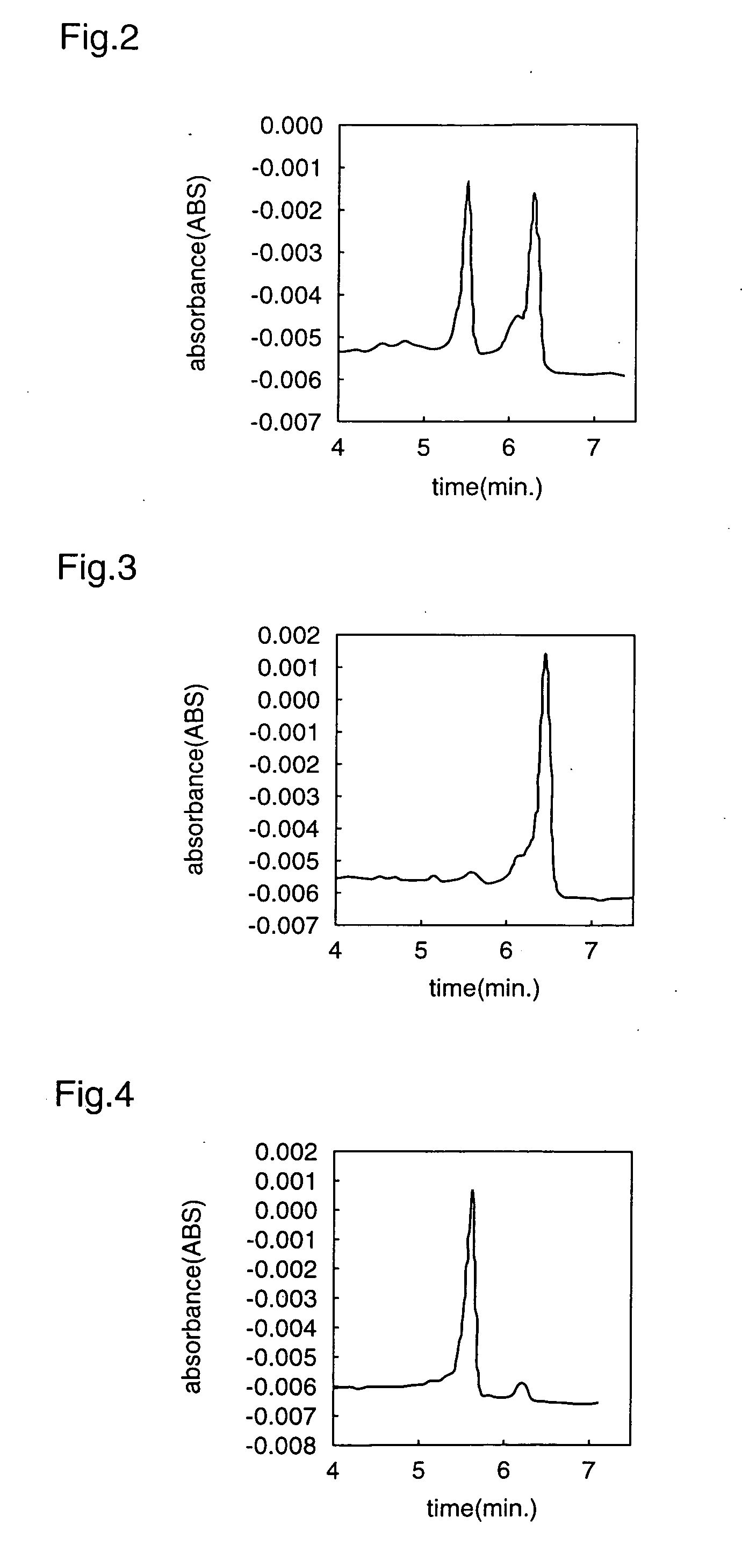
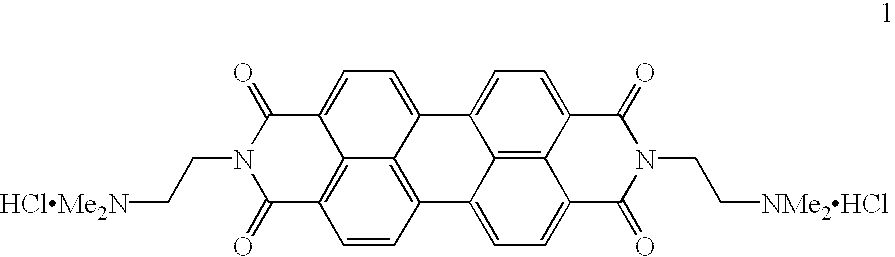
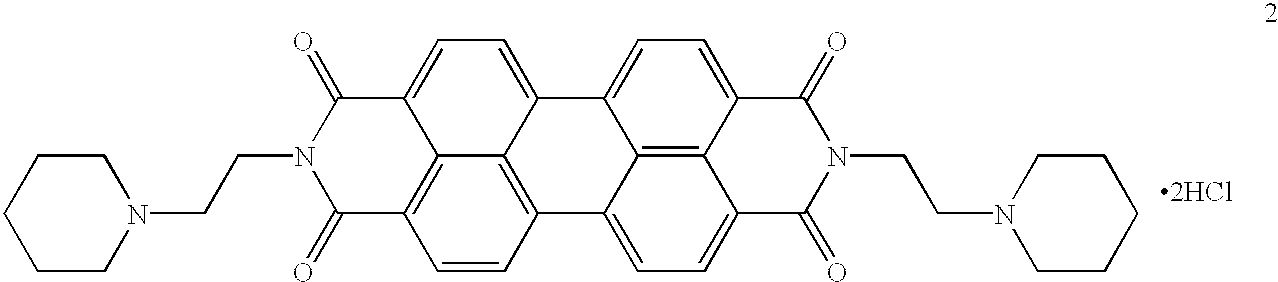
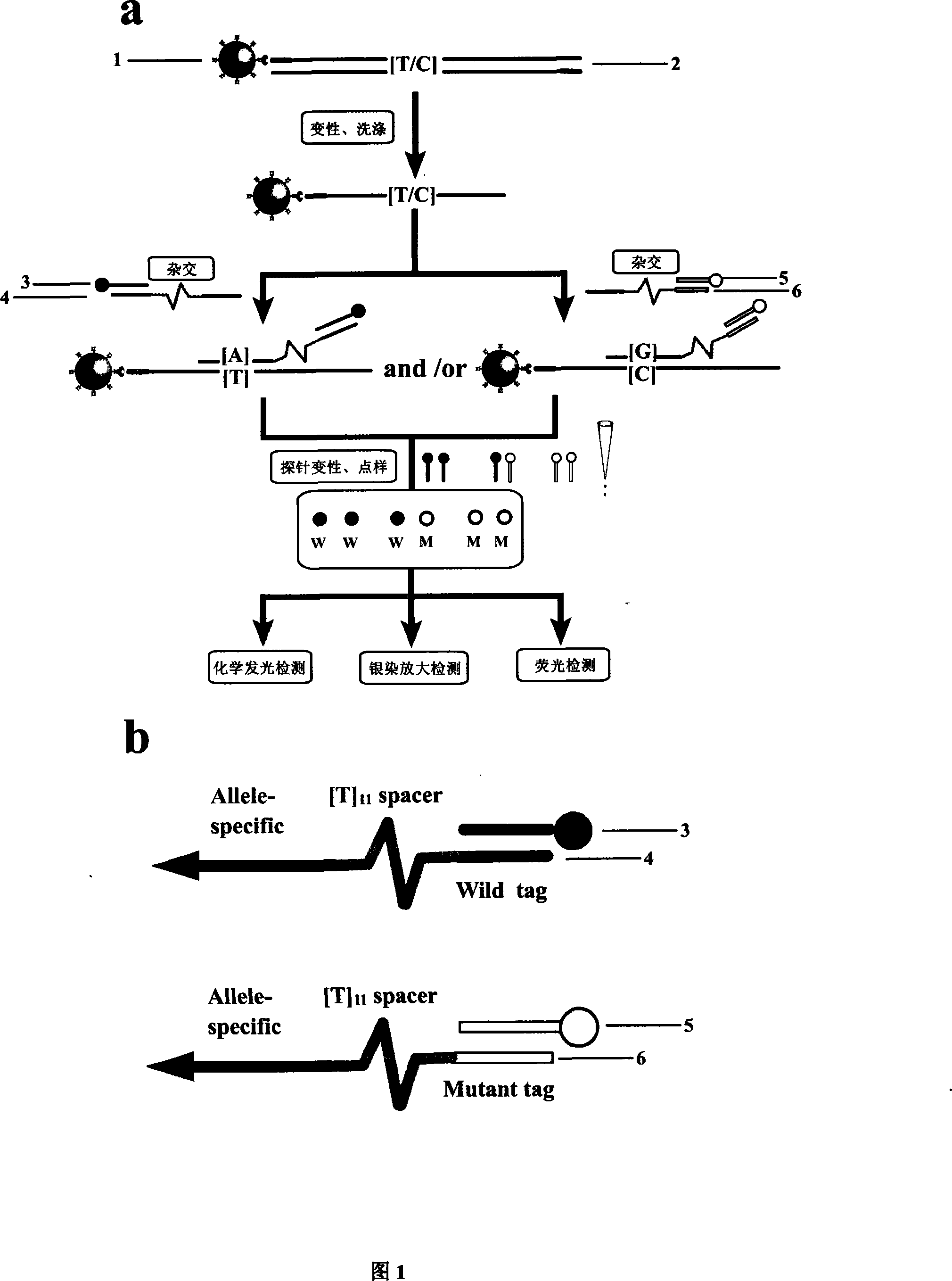
Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)]
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
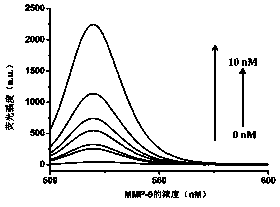
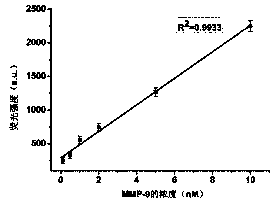
Method for detecting MMP-9 through graphene oxide fluorescent sensor
The invention relates to a method for detecting MMP-9 through a graphene oxide fluorescent sensor and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The method comprises carrying out hybridization on a dipeptide DNA complex containing a middle MMP-9 cleavage site and complementary molecules at two ends of a template DNA to obtain a DNA double-strand containing a middle neck loop structure, wherein the MMP-9 can be used for digestion at the dipeptide site and the neck loop DNA extends to form a single-stranded DNA fragment, mixing the fluorescently labeled single-stranded DNA and graphene oxide to cause DNA fluorescence quenching, and mixing the fluorescence quenching system and the DNA compound system subjected to digestion so that the fluorescently labeled DNA and the extending single-stranded DNA are complementary and hybridized to form a double-stranded DNA structure and the quenched fluorescence is recovered. According to a corresponding relationship of the MMP-9 concentration and the fluorescence intensity, MMP-9 can be detected. The method is easy to operate, has high sensitivity and good specificity and provides a feasible method for actual sample detection.
Owner:浙江金果知识产权有限公司
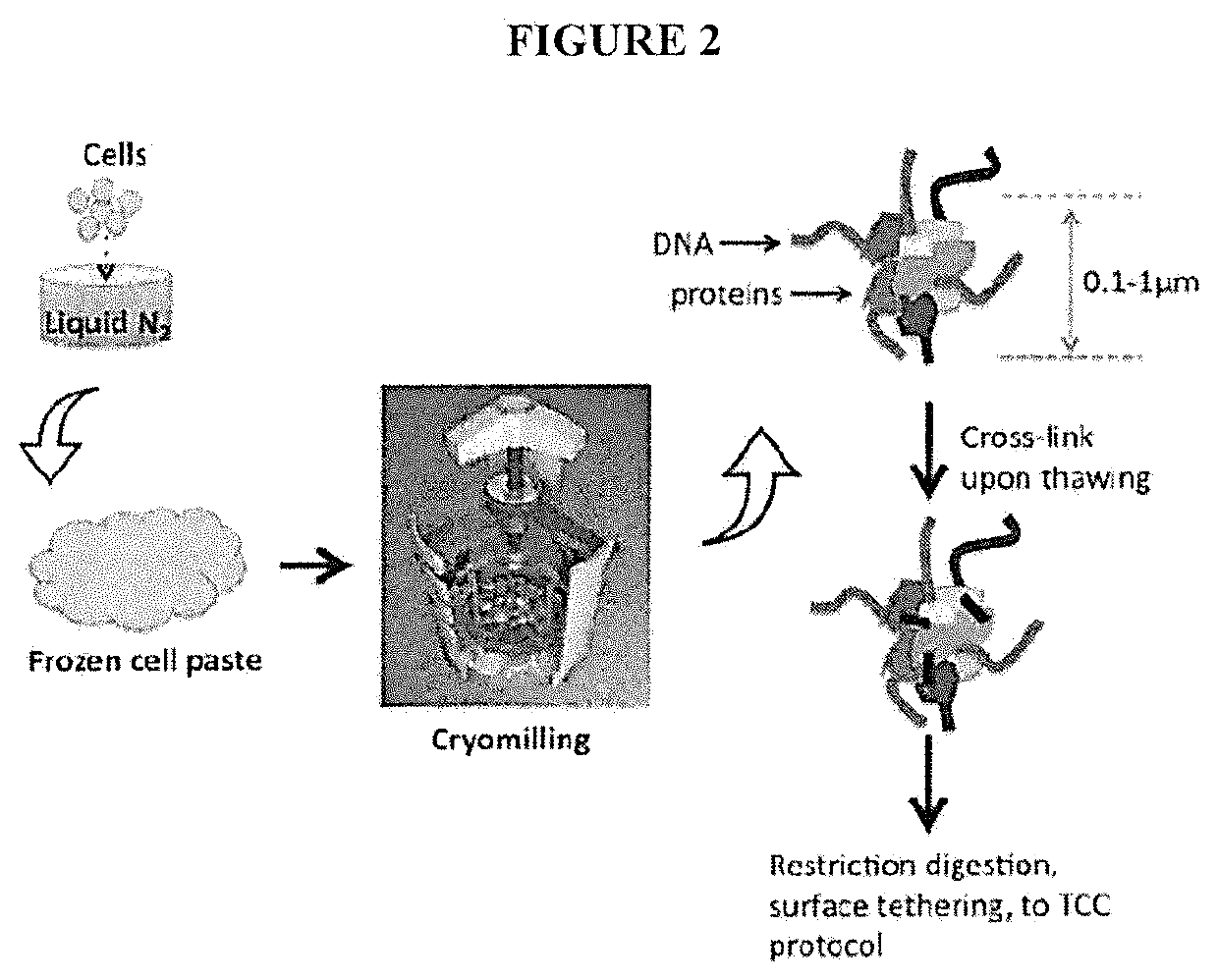
Genome-wide mapping of dna-dna proximities in the nucleus
ActiveUS20200071746A1High resolutionReduce noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationAssayProtein-protein complex
Disclosed are methods and systems for determining the three-dimensional structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. More specifically, disclosed are methods and systems for obtaining chromatin structural information by surface immobilization that includes tethering crosslinked protein:DNA complexes and / or ligated DNA complexes to media such as beads, gels, and or matrices during the conformation capture assay. In general, the method includes flash freezing a cell such that the structural organization of the chromatin or other protein:DNA complexes is preserved, cryomilling the cell, producing cross-linked protein:DNA complexes by cutting the chromatin using a chemical, physical or enzymatic method, substantially immobilizing the cross-linked protein:DNA complexes, ligating the cross-linked protein:DNA complexes intramolecularly such that the ligated protein:DNA complexes represent structural organization of the chromatin; characterizing the ligated DNA by sequencing or other methods; and identifying any structural organization of the chromatin. The structural organization preferably includes information relating to interacting loci of the chromatin.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Glass carbon electrode decorated by carbon nano tube-DNA complex and its production method and application
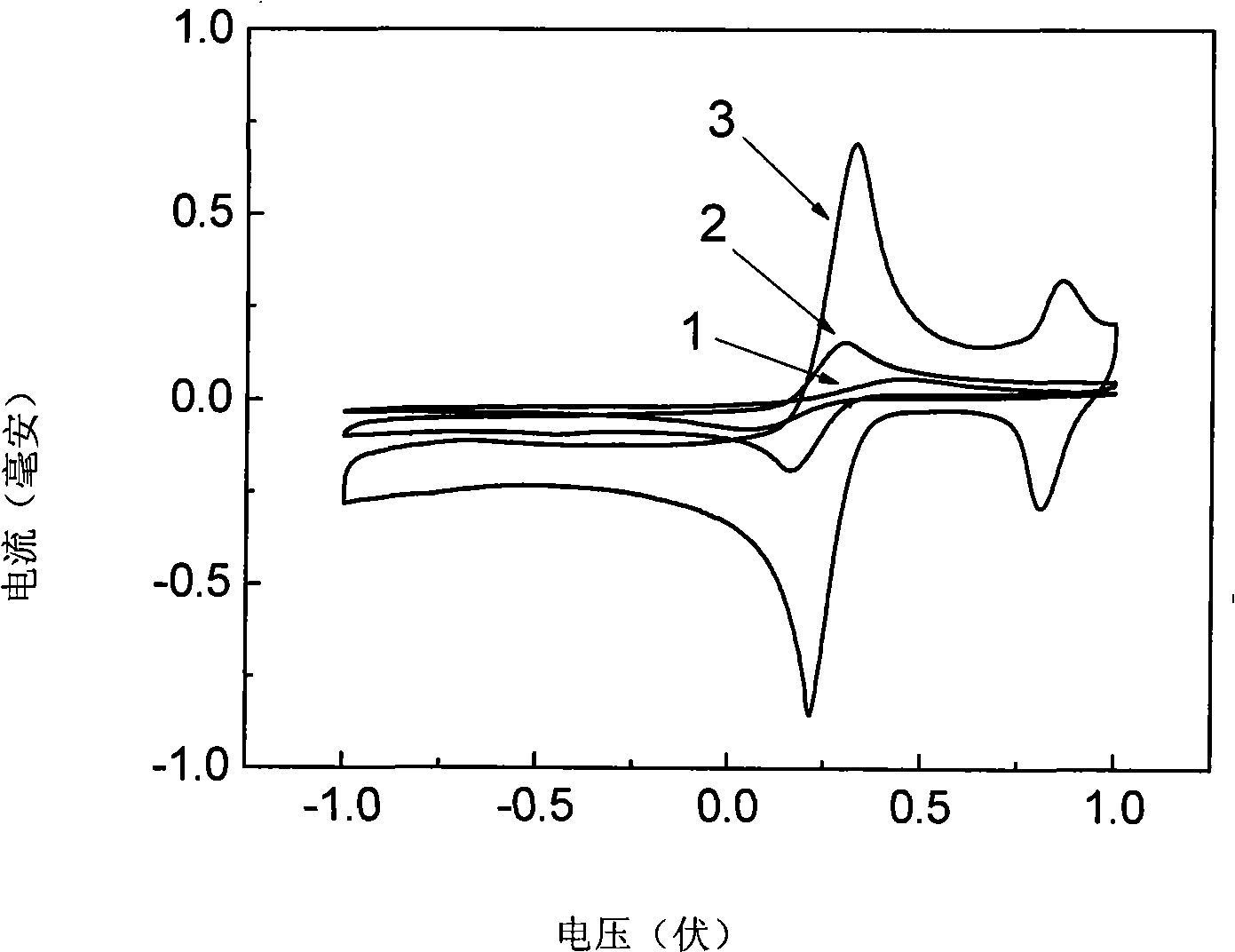
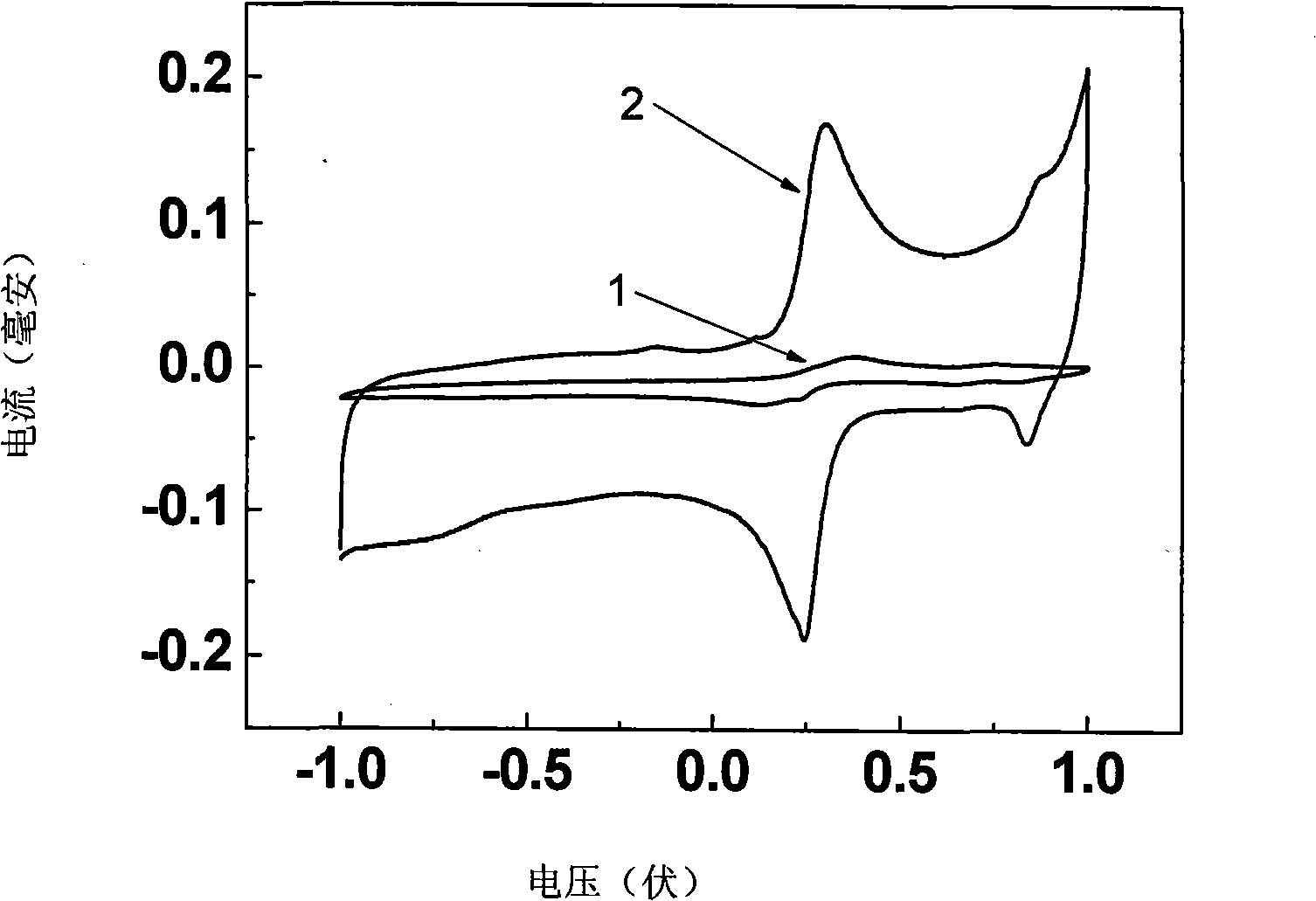
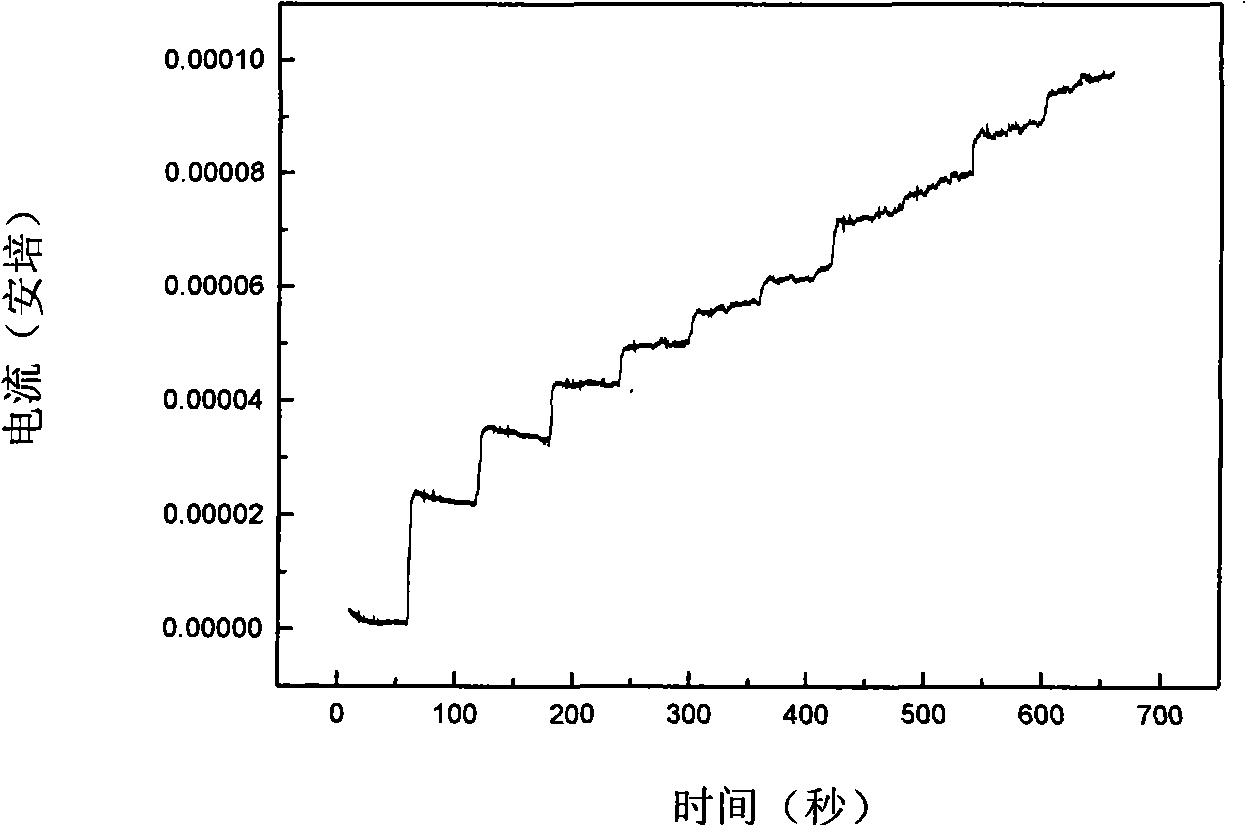
InactiveCN101271079AEasy to detectHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesDNA SolutionsBiological body
The invention discloses a modifying glassy carbon electrode with a carbon nanotube-DNA complex, a preparation method and an application thereof. The modifying glassy carbon electrode with the carbon nanotube-DNA complex is formed by coating a carbon nanotube-DNA complex film at the outside of a glassy carbon electrode substrate. The process of the preparation method is that a carbon nanotube and water solution of single stranded DNA which only contains G and T are mixed to prepare carbon nanotube-DNA mixed liquid, the carbon nanotube-DNA solution is prepared by the ultrasonic breaking mixed treatment and the centrifugal separation, the powder carbon nanotube-DNA complex is obtained by freeze drying, and the modifying glassy carbon electrode with the carbon nanotube-DNA is prepared by coating the carbon nanotube-DNA complex film formation on the glassy carbon electrode. The prepared modifying glassy carbon electrode with the carbon nanotube-DNA has application in the detection of the concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution. The preparation method has the advantage that the preparation process is simple, which is particularly easy to realize the detection of the concentration of the hydrogen peroxide solution in a biological body.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cationic liposome delivery of taxanes to angiogenic blood vessels
InactiveUS20050271714A1Precise deliveryInhibit angiogenesisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationAngiogenesis growth factor
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
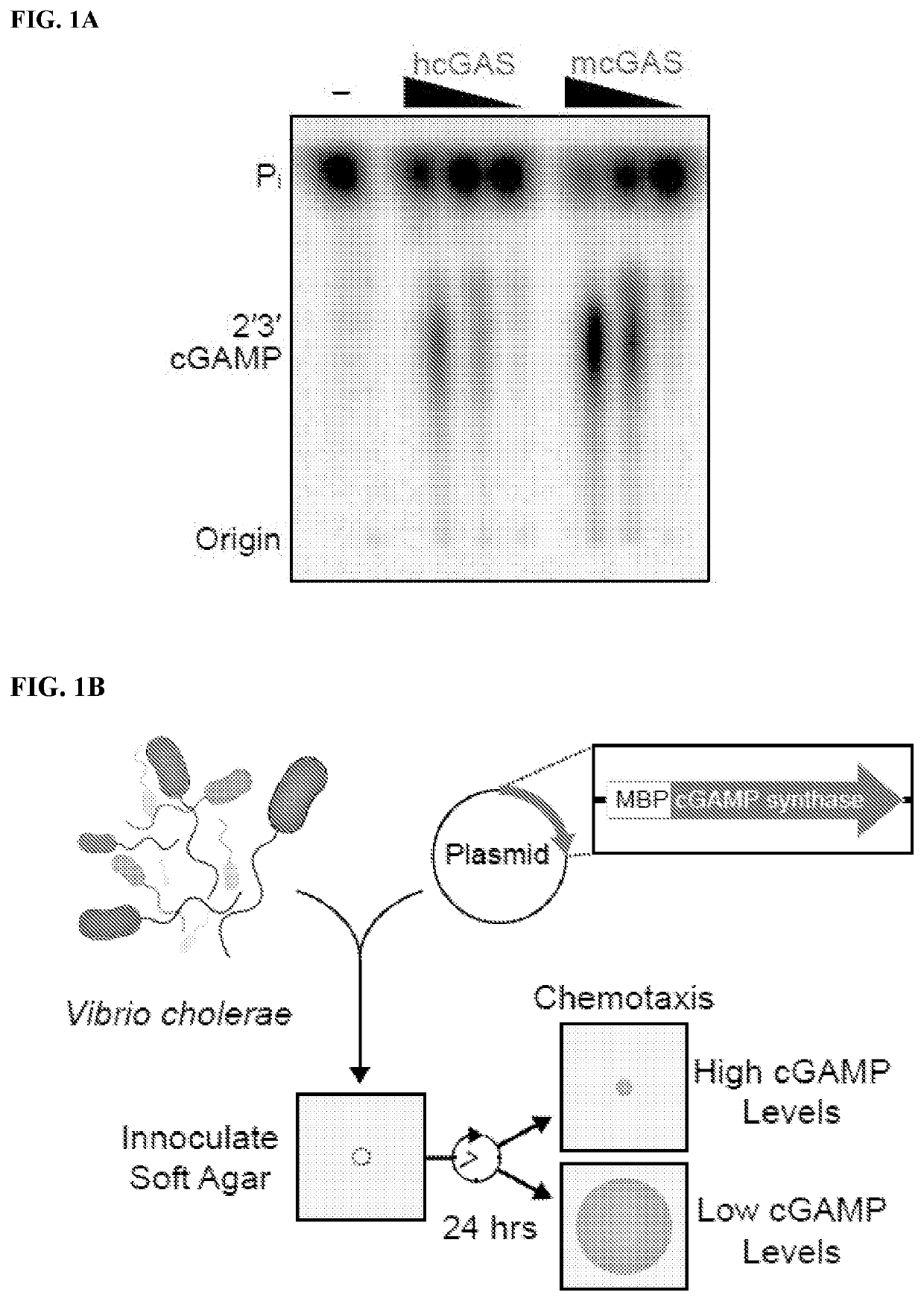
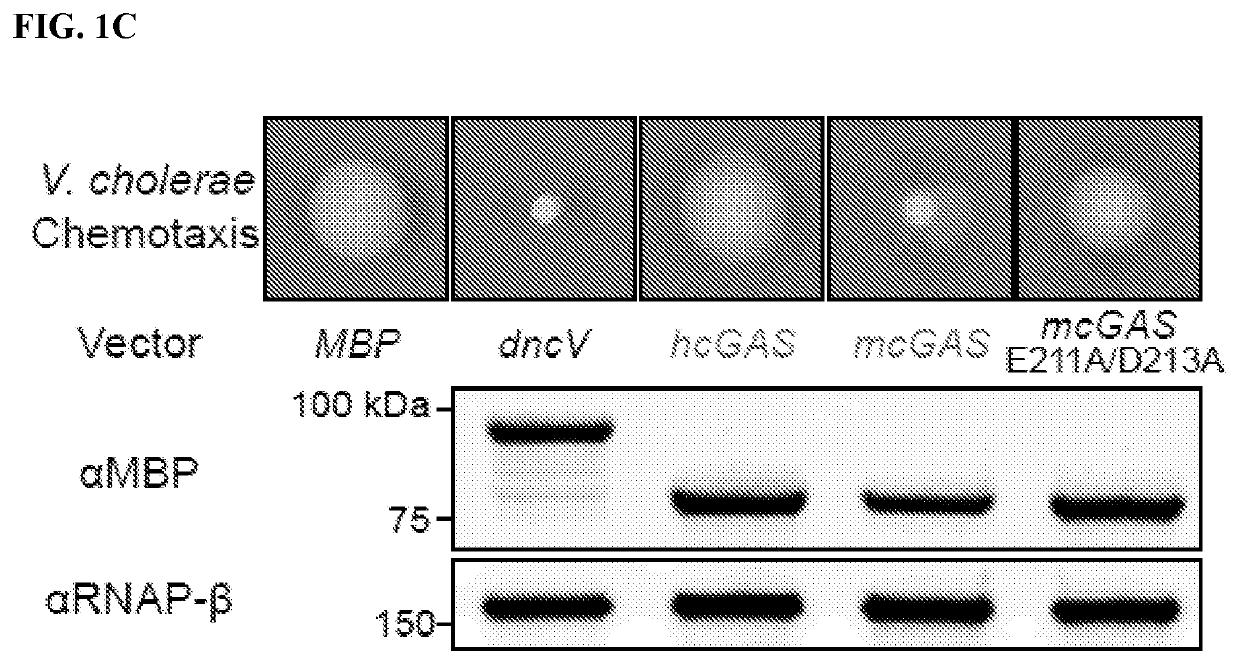
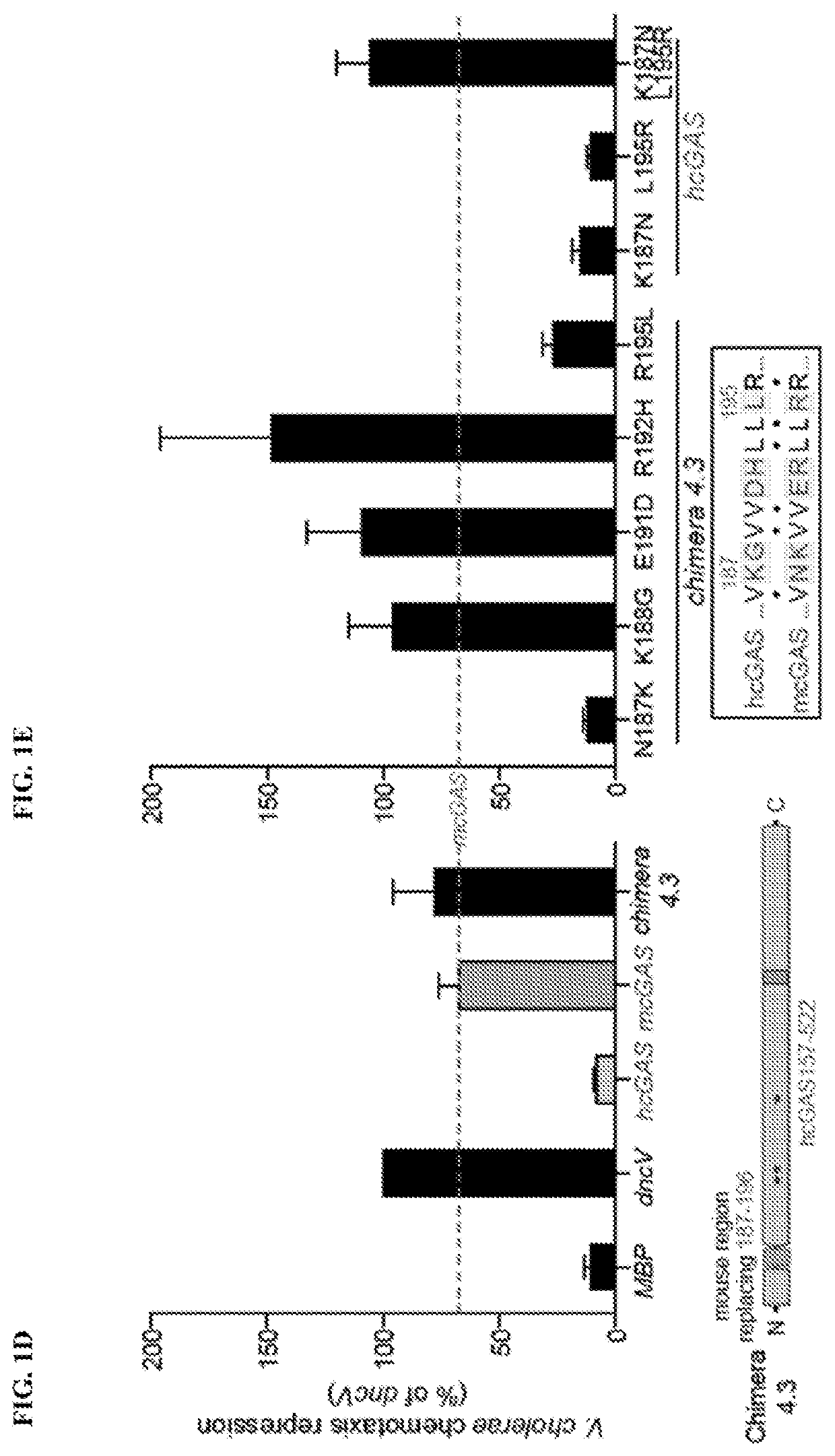
Structure of the human cgas-dna complex and uses thereof
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery of the human-specific regulatory control of cGAS and the structure of the active human cGAS-DNA complex, as well as compositions comprising the modified hcGAS polypeptide, hcGAS-DNA complex, hcGAS-DNA-ATP complex, and methods of screening for modulators of the structure, expression, and / or activity of such polypeptides and complexes.
Owner:PRESODENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
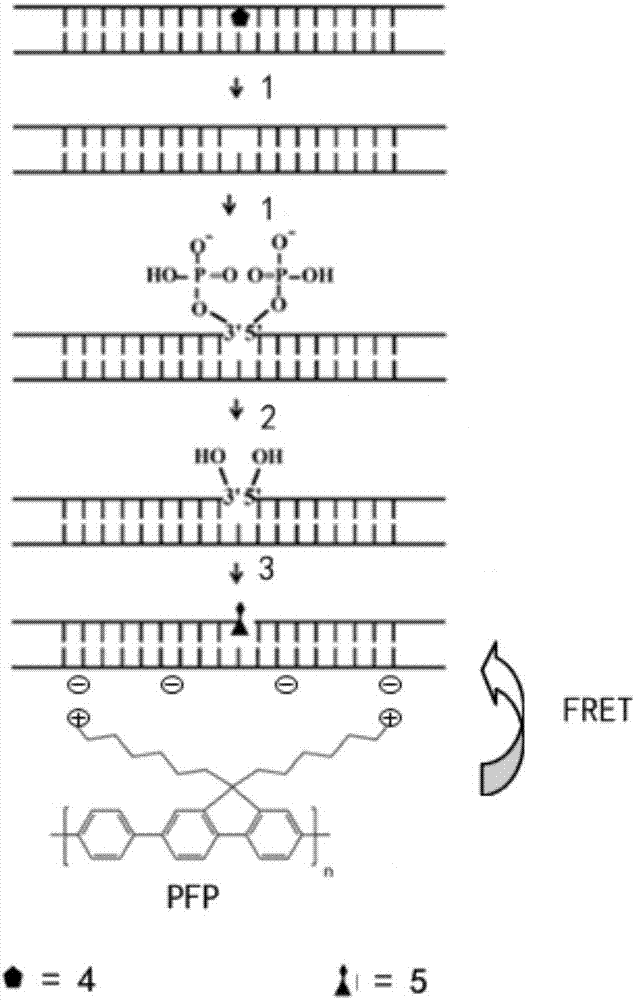
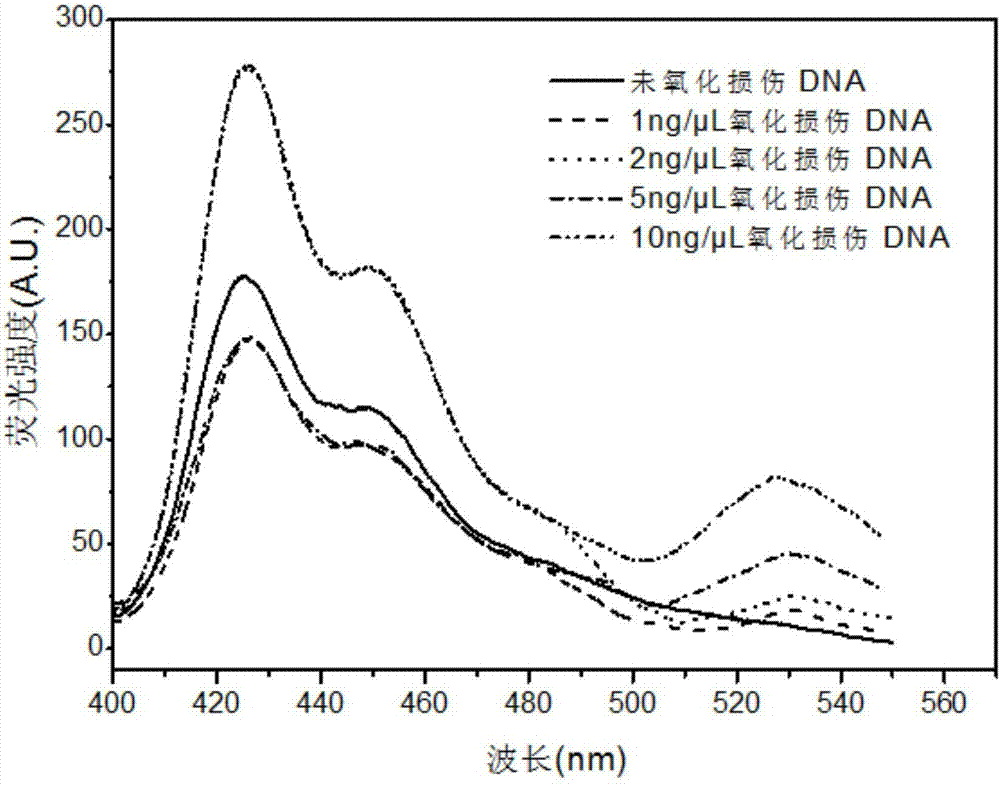
Oxidative damage DNA detection method
InactiveCN106939336AInjury mitigation steps are cumbersomeEase sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
The invention discloses an oxidative damage DNA detection method, and relates to the technical field of DNA oxidative damage detection. The method comprises (a) obtaining of DNA containing 3 ', 5'-phosphate group nucleotide voi, to be more specific, adding a DNA repair enzyme for recognition and cutting of oxidized DNA bases; (b) introduction of hydroxyl into 3 ', 5' site, to be more specific, adding alkaline phosphatase for dephosphorylation to obtain the DNA containing 3 ', 5'-hydroxyl group nucleotide voids; (c) introduction of a fluorescent marker, to be more specific, adding DNA polymerase I and the fluorescent marker to obtain fluorescence-labeled DNA; (d) formation of a PFP-DNA complex, to be more specific, adding PFP to obtain the PFP-DNA complex; and (e) oxidative damage DNA detection, to be more specific, detecting damage DNA by FRET. The method alleviates the disadvantages of tedious steps, low sensitivity and low selectivity of DNA damage detection in the prior art. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity and high accuracy.
Owner:CHINA INST OF SPORT SCI
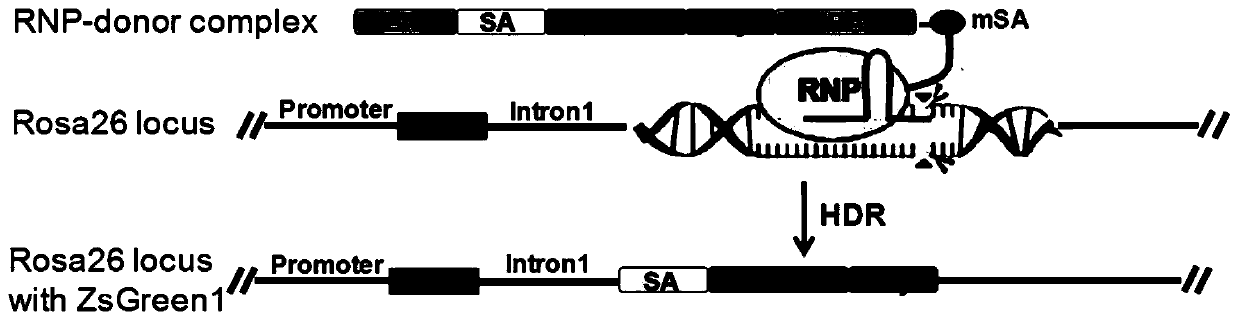
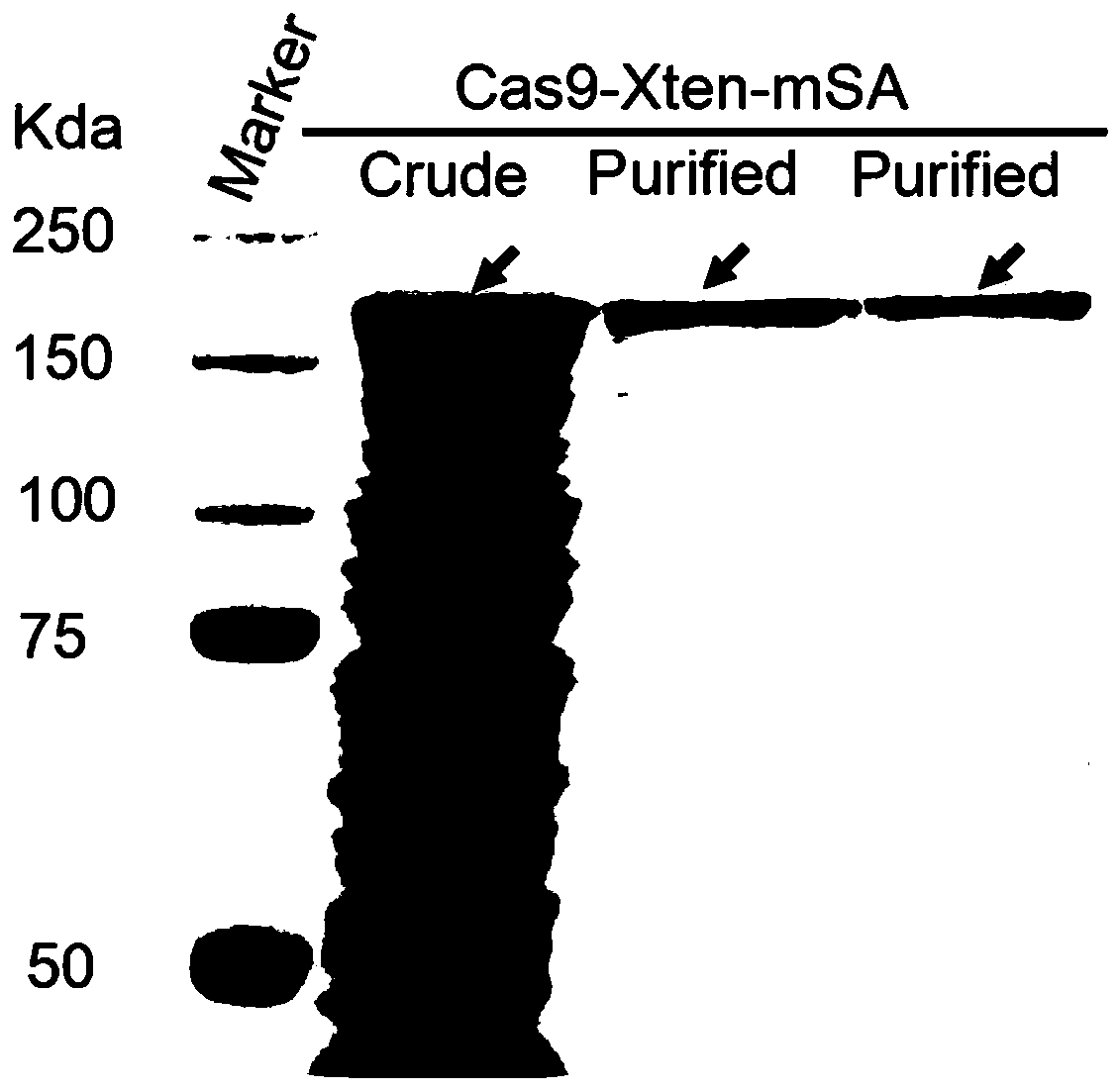
Efficient clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats ribonucleoprotein (CRISPR RNP) and donor DNA co-location mediated gene insertion or replacement method and application thereof
ActiveCN111575319AAccurate replacementHigh homologous recombination efficiencyHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyLivestock breeding
The invention discloses an efficient clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats ribonucleoprotein (CRISPR RNP) and donor DNA co-location mediated gene insertion or replacement method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) biotin labeling is performed on donor DNA to obtain biotin-labeled donor DNA; (2) fusion protein of Cas9 protein and monovalent streptavidin, sgRNA and the biotin-labeled donor DNA are evenly mixed and undergo standing to obtain a CRISPR RNP-donor DNA complex; and (3) cell nucleus transformation is performed on the CRISPR RNP-donor DNA complex to realize gene insertion or replacement. According to the method, by utilizing the characteristic that the fusion protein can be combined with the biotin-labeled donor DNA, the CRISPRRNP and the donor DNA appear at a target locus together, and precise insertion of the donor DNA at the target locus or accurate replacement of a gene at the target locus is realized; and the method issuitable for the aspect of crop and livestock breeding.
Owner:AGRO BIOLOGICAL GENE RES CENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
DNA separation device, DNA separation method, and ligand DNA
InactiveUS20070138013A1Short timeSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisViscosity
A ligand DNA including a probe portion having a sequence that is complementary to a target DNA to be detected in a sample DNA, and a probe portion having a base sequence that is complementary to a base sequence of a marker DNA 2 in a conjugate DNA 10 is formed, and the sample DNA and the ligand DNA are combined to form a DNA complex, and further, the DNA complex is made to perform electrophoresis in the conjugate DNA. Therefore, it is possible to provide a DNA separation detection method which can appropriately separate the sample DNA and deal with various kinds of target sample DNAs in short time, without the necessity of searching for an optimum electrophoresis condition by complicatedly combining the amount of a bonding control agent to be contained in the conjugate DNA, the viscosity of linear polymer, the amount of the sample DNA, the amount of the conjugate DNA, and the like, for each DNA sequence as a detection target, when separating the sample DNA by electrophoresis.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Method for preparing nanometer particles of galactose hydroxyapatite-polylysine
InactiveCN1736365AEfficient combinationImprove the effect of liver cancer treatmentPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsCentrifugationVacuum drying
Disclosed is a process for preparing nanometer particles of galactose hydroxyapatite-polylysine which comprises, rinshing hydroxyapatite nano granules with water, centrifuging and collecting deposition, vacuum drying, grinding, suspending hydroxyapatite nano particle powder deposition into water, carrying out ultrasonic oscillation, charging cerebrose polylysine solution, mixing and stirring, centrifuging to remove the supernatant fluid, suspending the deposition into deionized water.
Owner:张阳德
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![[12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector [12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a9418184-cd97-49fc-be12-62b9c4d99c2b/HDA0000874188930000011.PNG)
![[12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector [12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a9418184-cd97-49fc-be12-62b9c4d99c2b/HDA0000874188930000012.PNG)
![[12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector [12] aneN3 cationic lipid containing targeted group and fluorescent group, transgenic vector, and preparation methods of cationic lipid and transgenic vector](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a9418184-cd97-49fc-be12-62b9c4d99c2b/HDA0000874188930000013.PNG)






![Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a89e95e4-cadd-413a-9c94-c5855ba078a6/HDA0001245086610000011.png)
![Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a89e95e4-cadd-413a-9c94-c5855ba078a6/HDA0001245086610000012.png)
![Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] Reagent kit and method for bidirectional signal amplification detection on miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a89e95e4-cadd-413a-9c94-c5855ba078a6/HDA0001245086610000021.png)