Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4040results about How to "Reduce interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymerases
ActiveUS20060281109A1Improve the level ofProceed efficientlySugar derivativesHydrolasesModified dnaPolymerase L
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
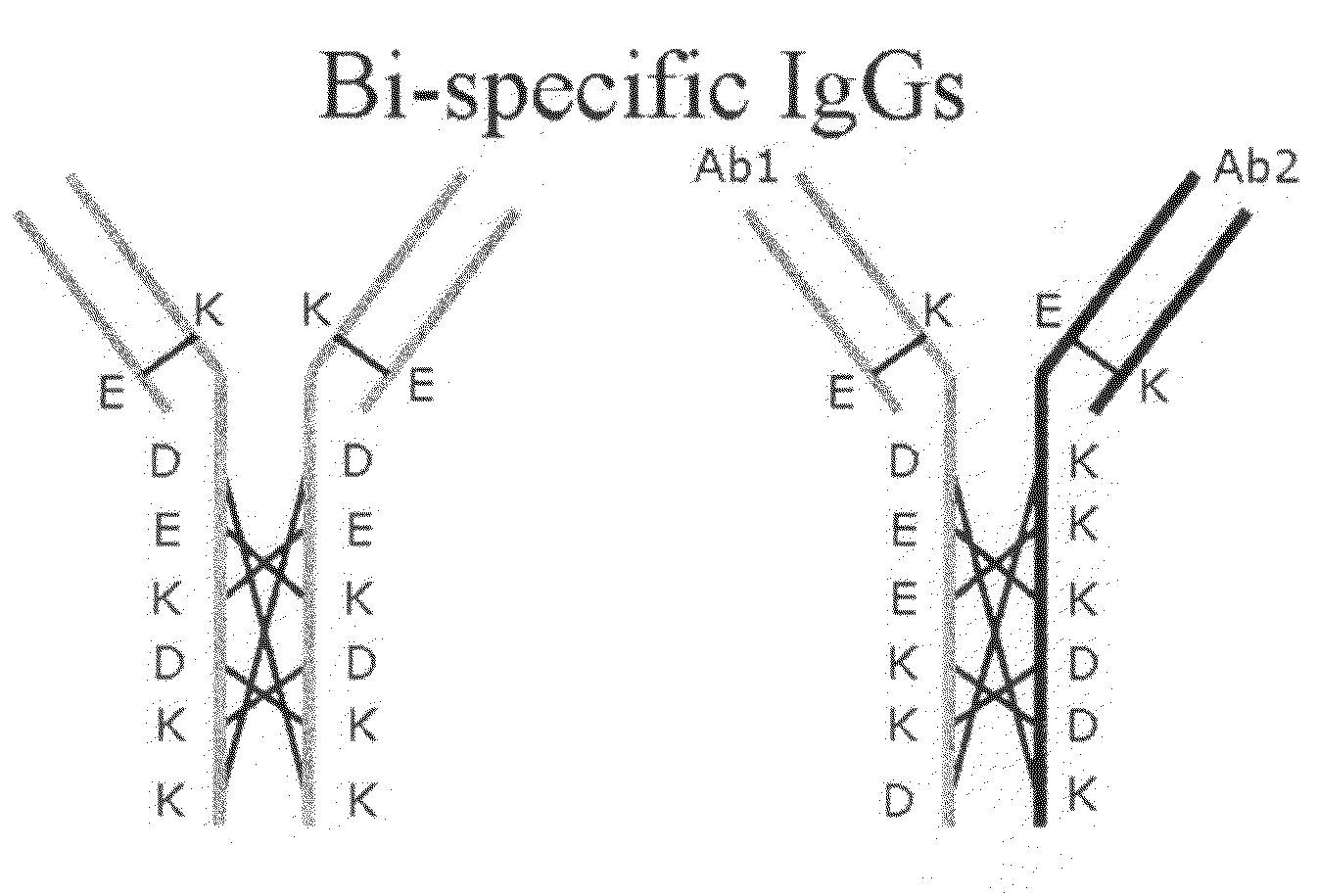
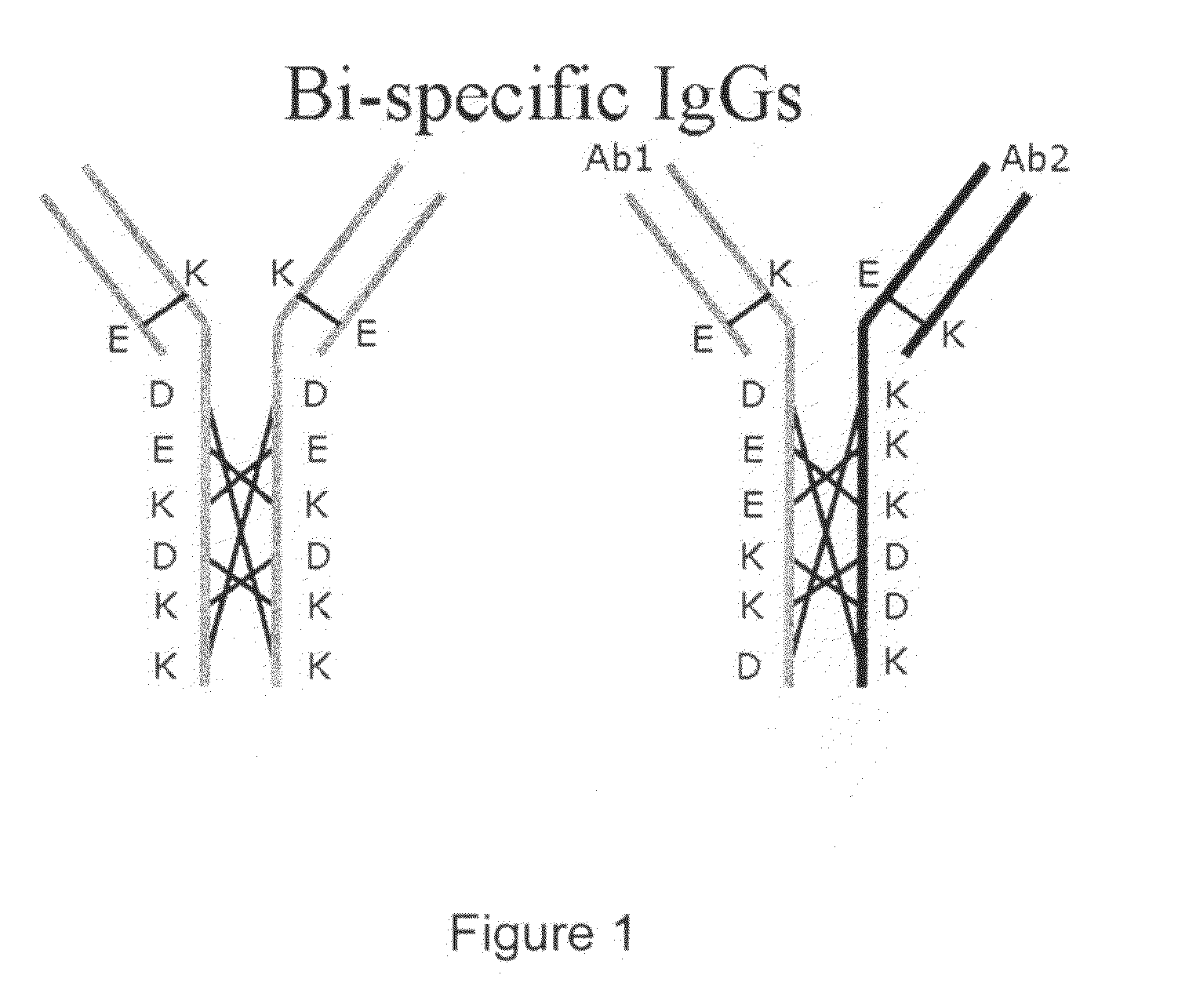
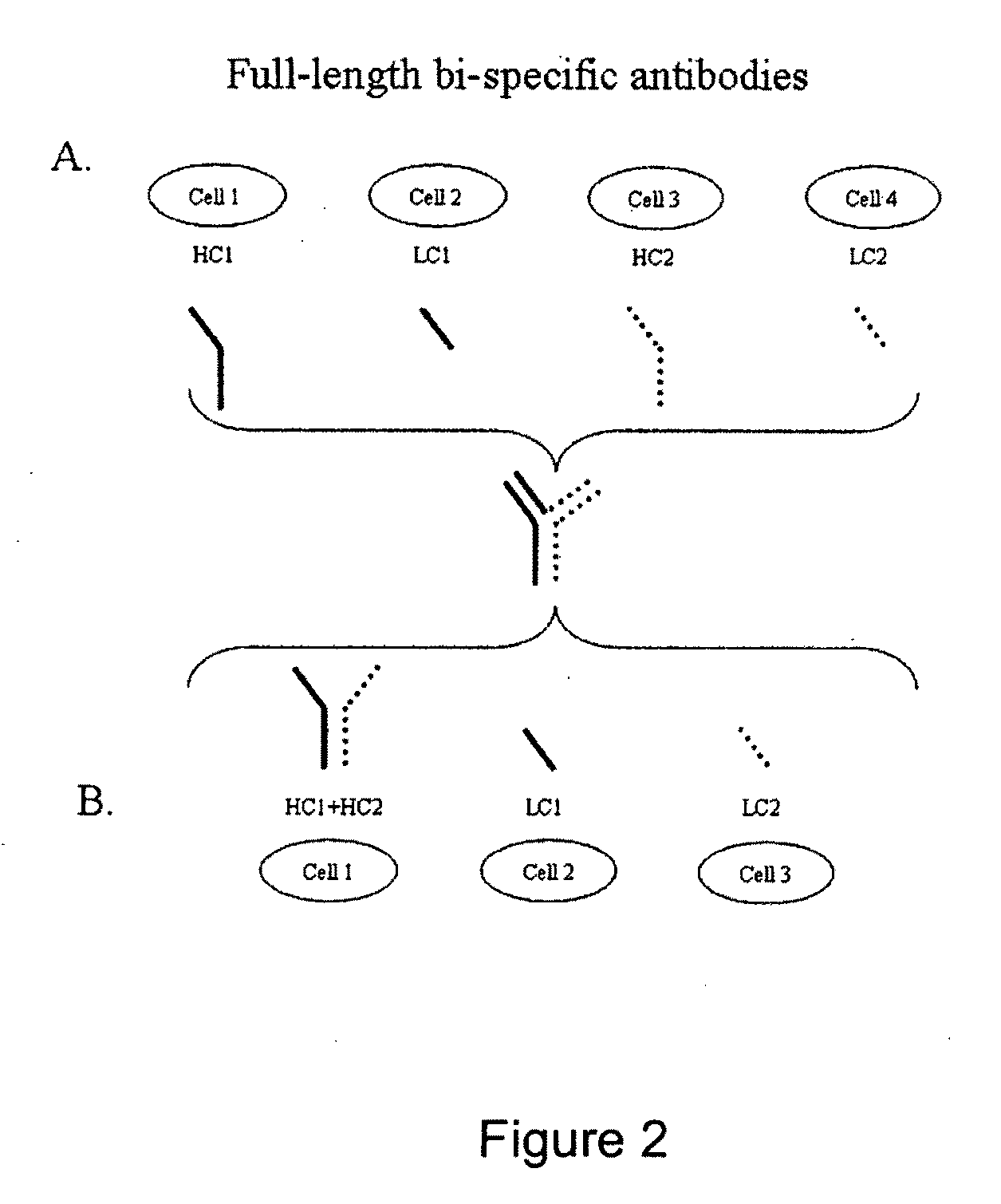
Production of Bispecific Antibodies
InactiveUS20090182127A1Reduce interactionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsConstant domainHeavy chain
Bispecific antibodies comprising (a) a first light-heavy chain pair having specificity for a first target and a sufficient number of substitutions in its heavy chain constant domain with respect to a corresponding wild-type antibody of the same isotype to significantly reduce the formation of first heavy chain-first heavy chain dimers and (b) a second light-heavy chain pair comprising a heavy chain having a sequence that is complementary to the sequence of the first pair heavy chain sequence with respect to the formation of intramolecular ionic interactions, wherein the first pair or second pair comprises a substitution in the light chain and complementary substitution in the heavy chain that reduces the ability of the light chain to interact with the heavy chain of the other light chain-heavy chain pair are provided. Methods of producing such antibodies in one or more cells also are provided.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
LOW TEMPERATURE ALD SiO2
InactiveUS20080113097A1Reduce interactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPyridineSilicon dioxide
The present invention generally comprises a silicon dioxide atomic layer deposition method. By providing pyridine as a catalyst, water may be utilized as the oxidization source while depositing at a low temperature. Prior to exposing the substrate to the water, the substrate may be exposed to a pyridine soak process. Additionally, the water may be co-flowed to the chamber with the pyridine through separate conduits to reduce interaction prior to entering the chamber. Alternatively, the pyridine may be co-flowed with a silicon precursor that does not react with pyridine.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Wireless energy transfer for person worn peripherals
InactiveUS20130007949A1Reduce interactionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemHand heldEngineering
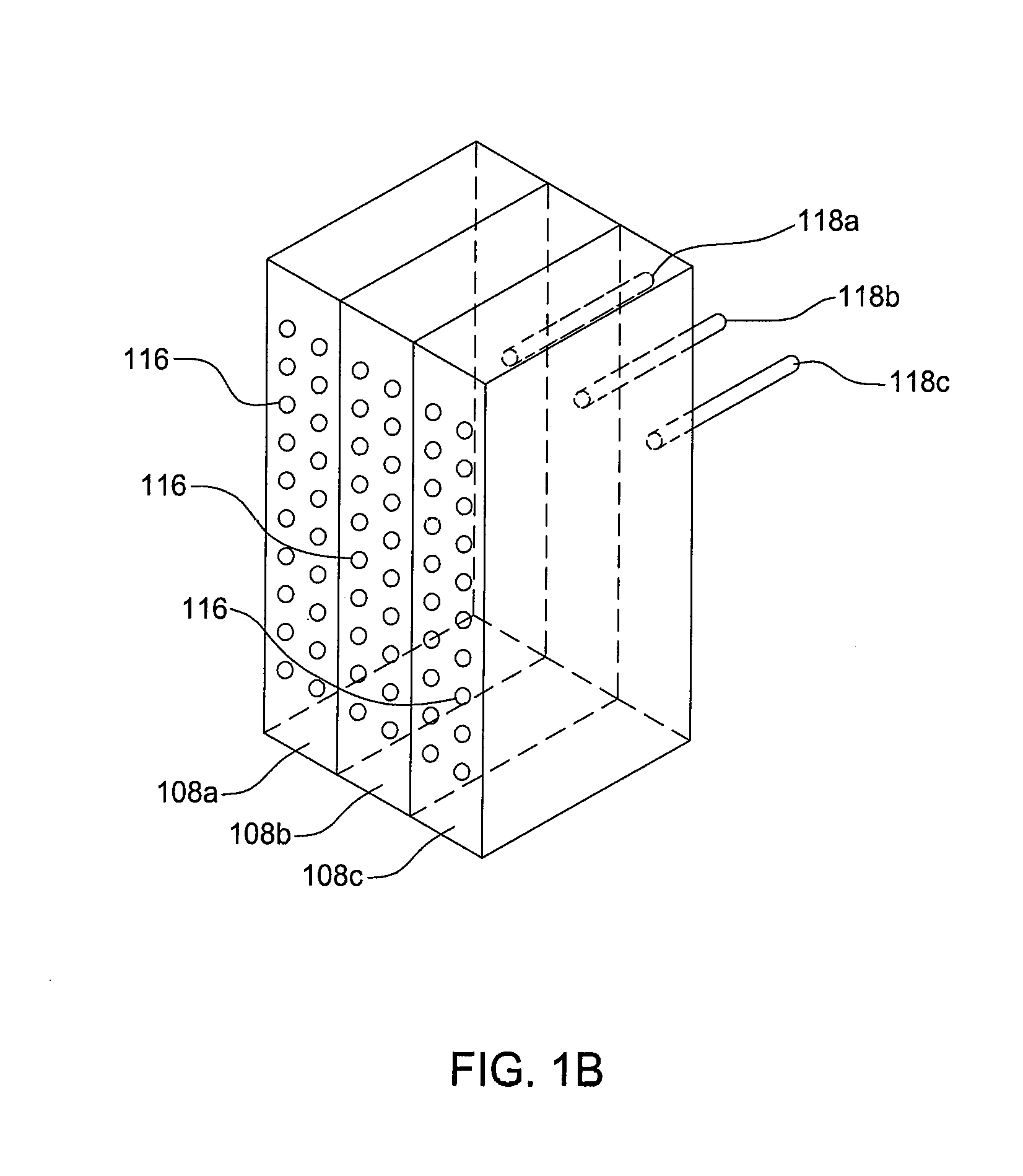
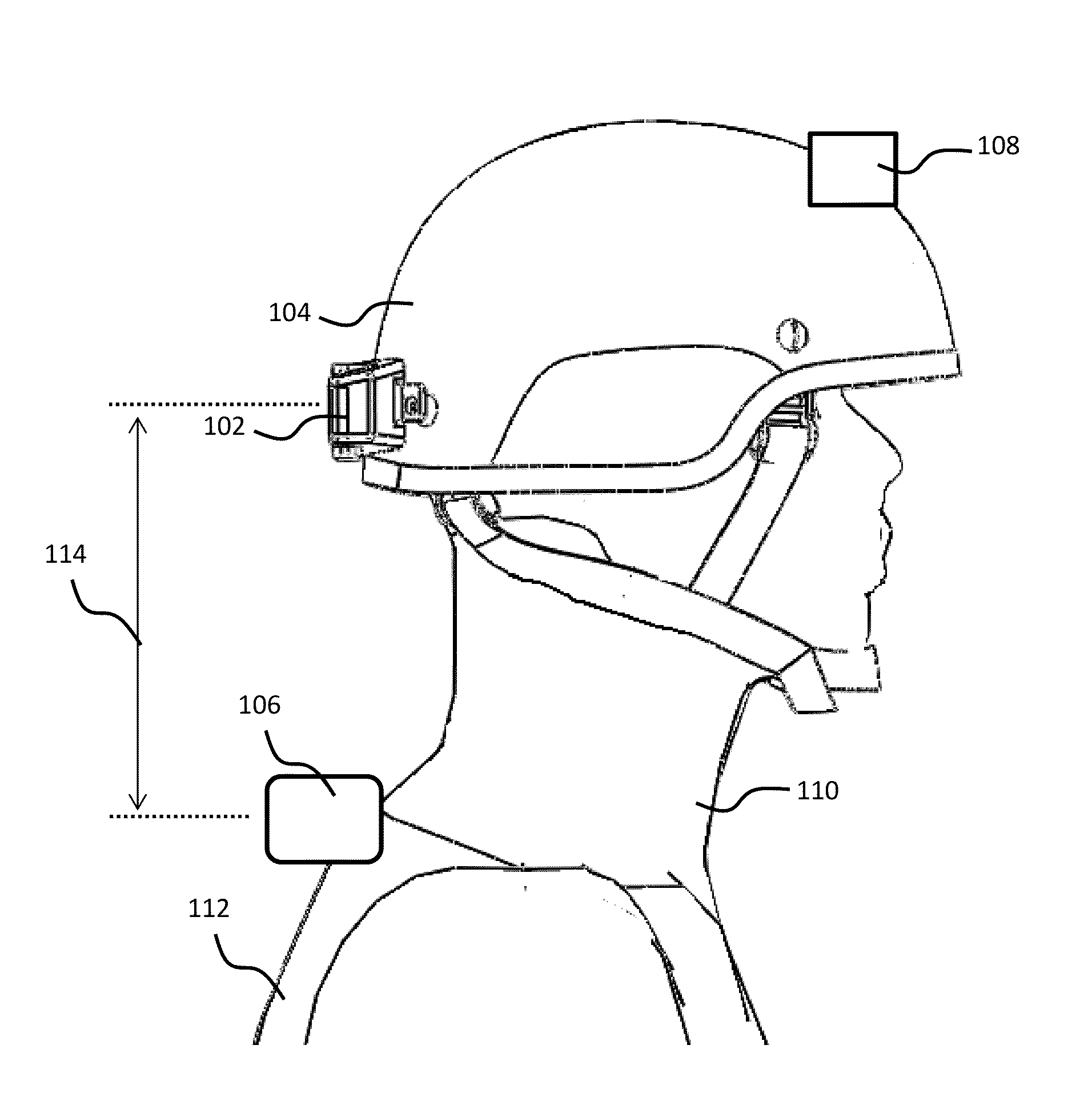
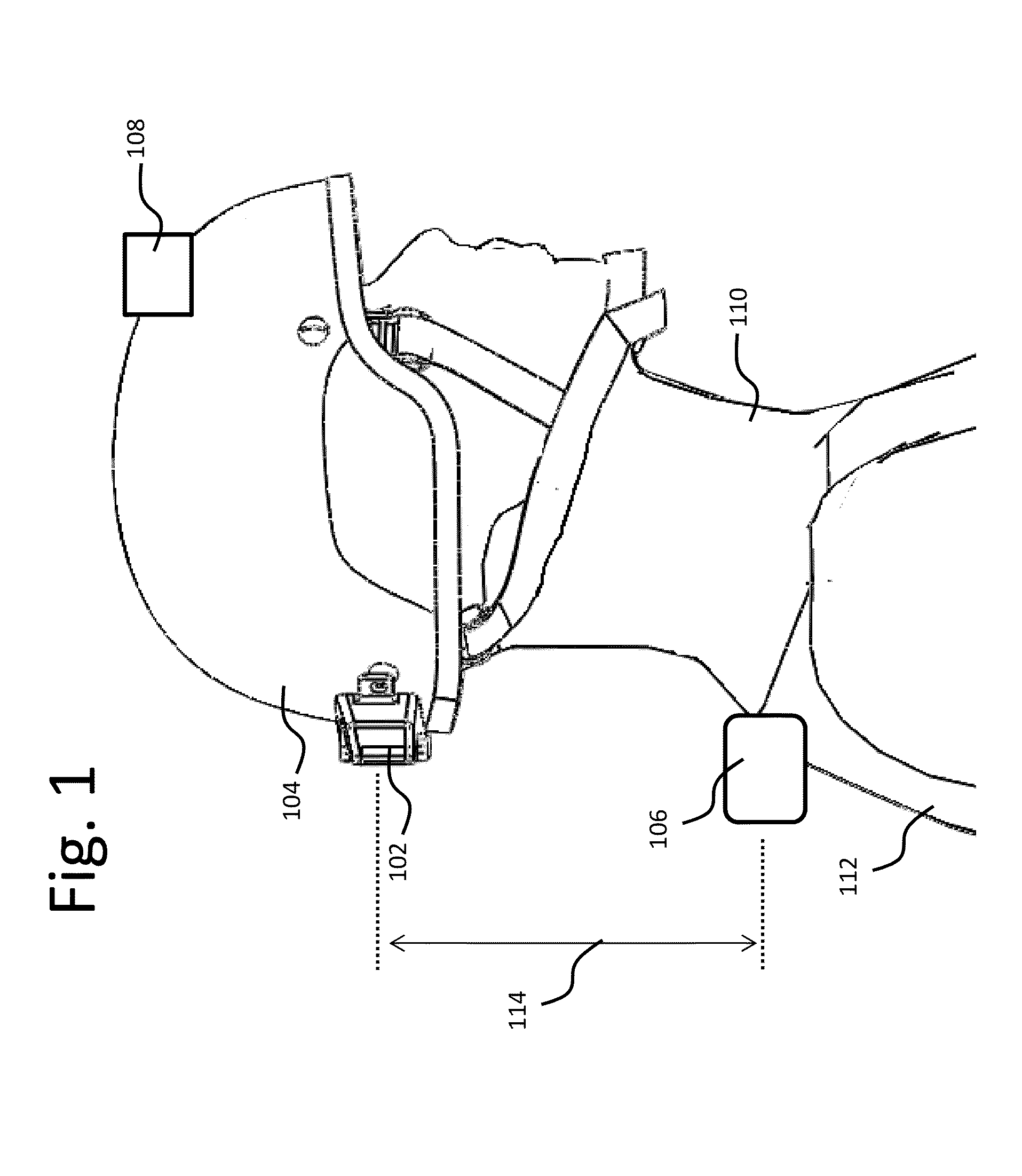
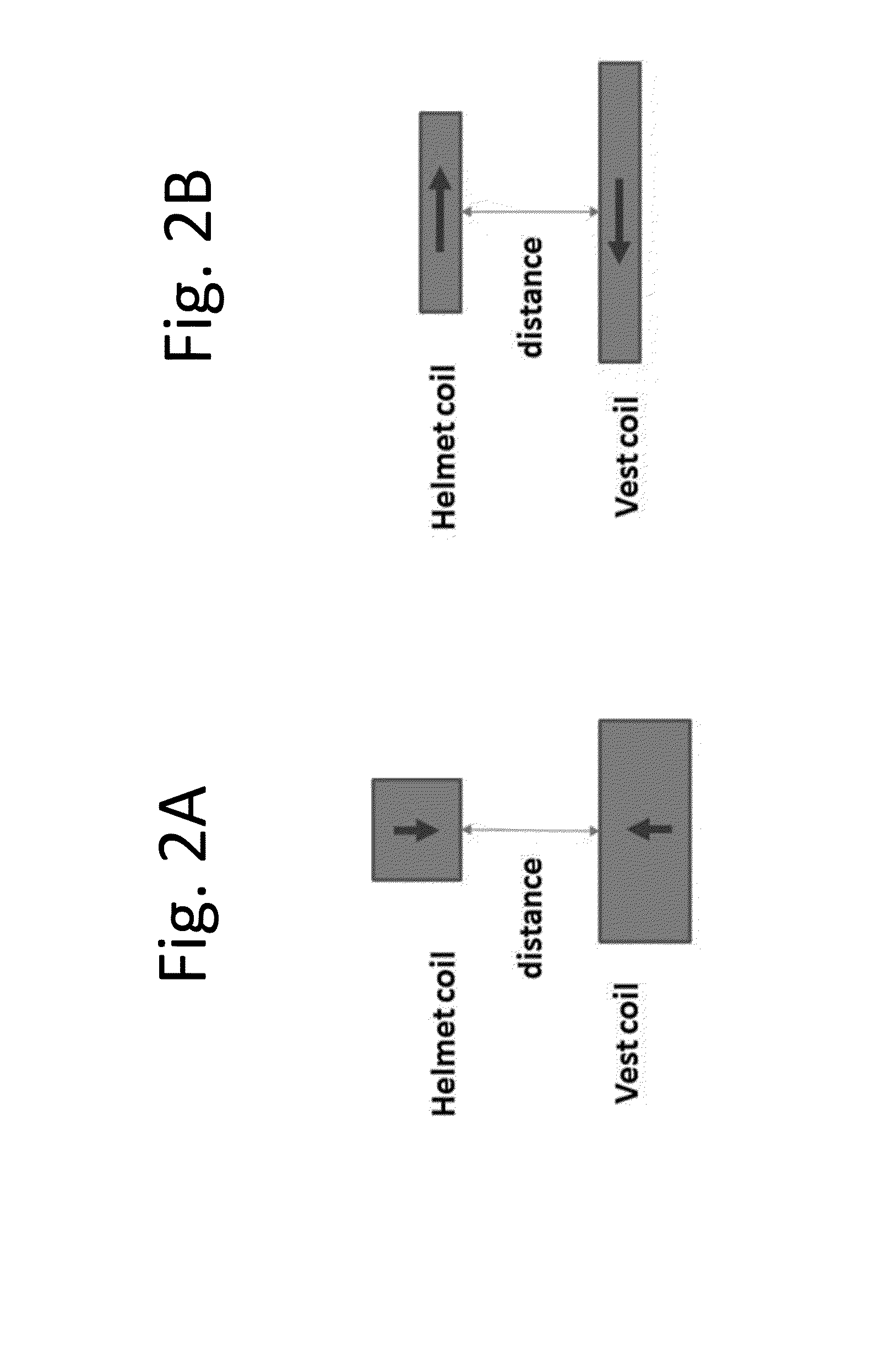
Described is a system for wireless energy transfer for person worn peripherals. The system makes use of a technique referred to as strongly-coupled magnetic resonance to transfer energy across a distance without wires and enables efficient transfer of energy over distances of 10 to 18 cm or more. The system comprises a resonant power source, which could be embedded in a person's equipment vest or backpack receiving power from a central battery pack or micro fuel cell, and a resonant power capture unit which could be integrated with the helmet or hand held weapon, electronic device, and the like that may be carried or handled by a person.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Leveraging Collaborative Cloud Services to Build and Share Apps
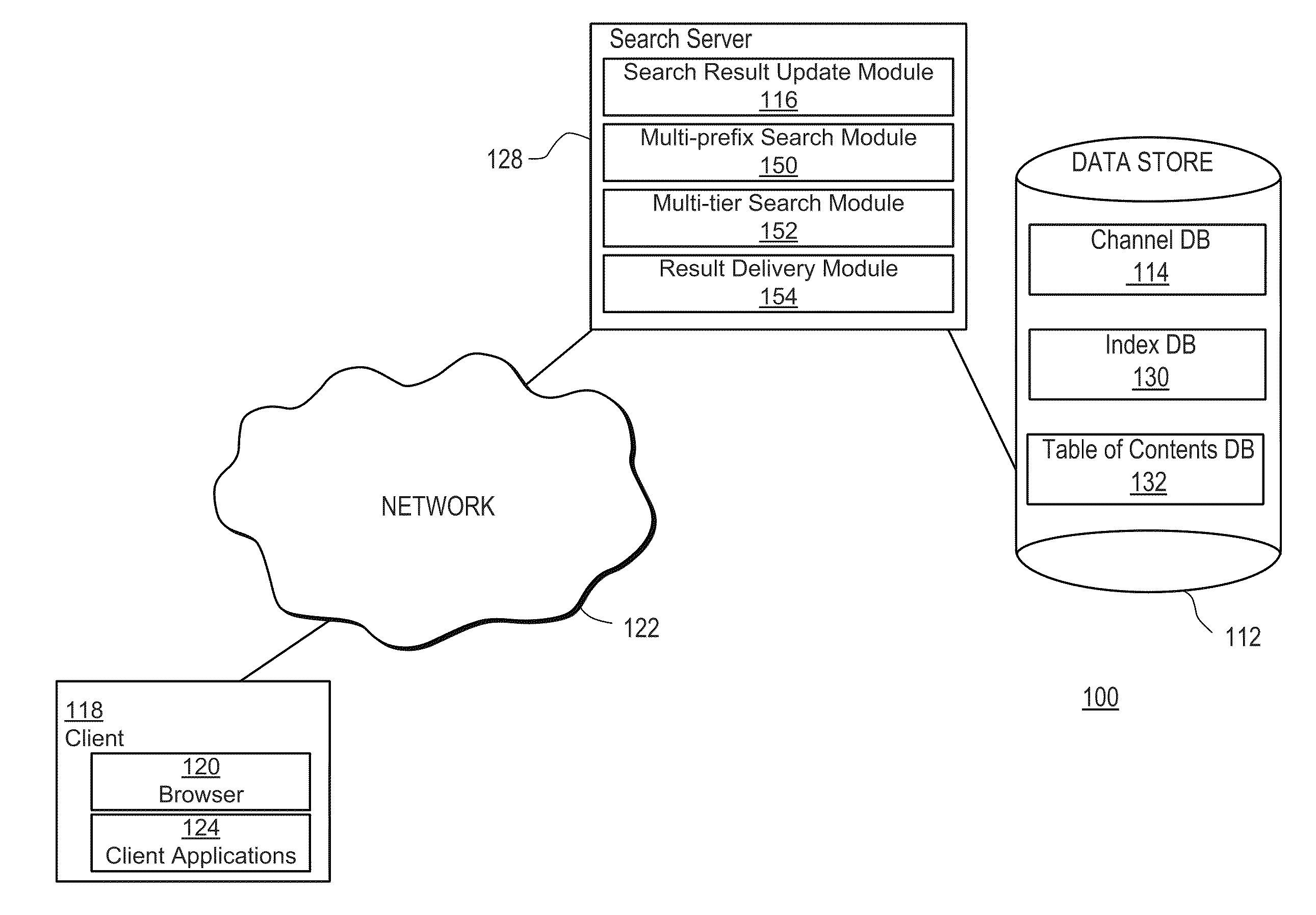
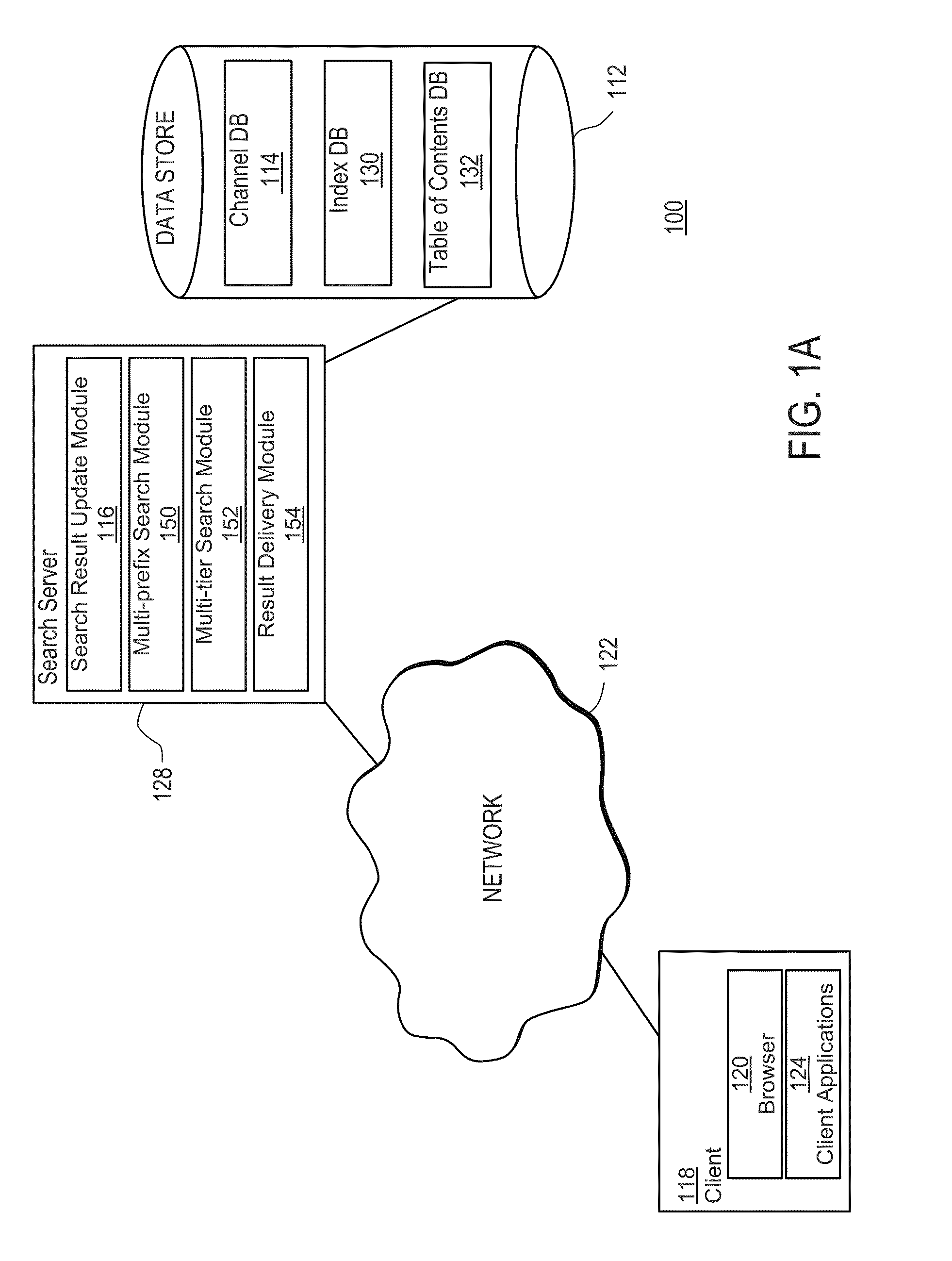
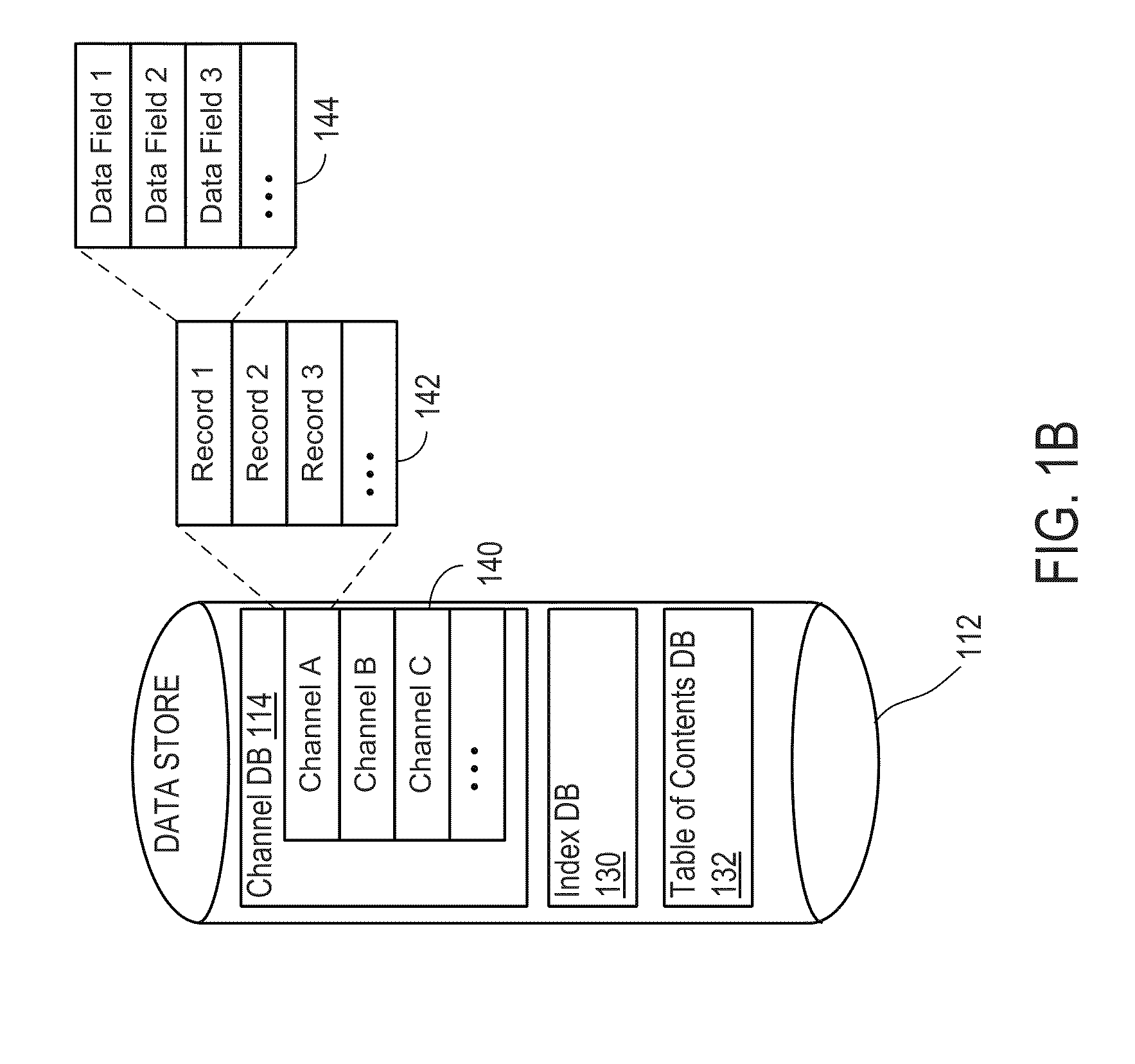
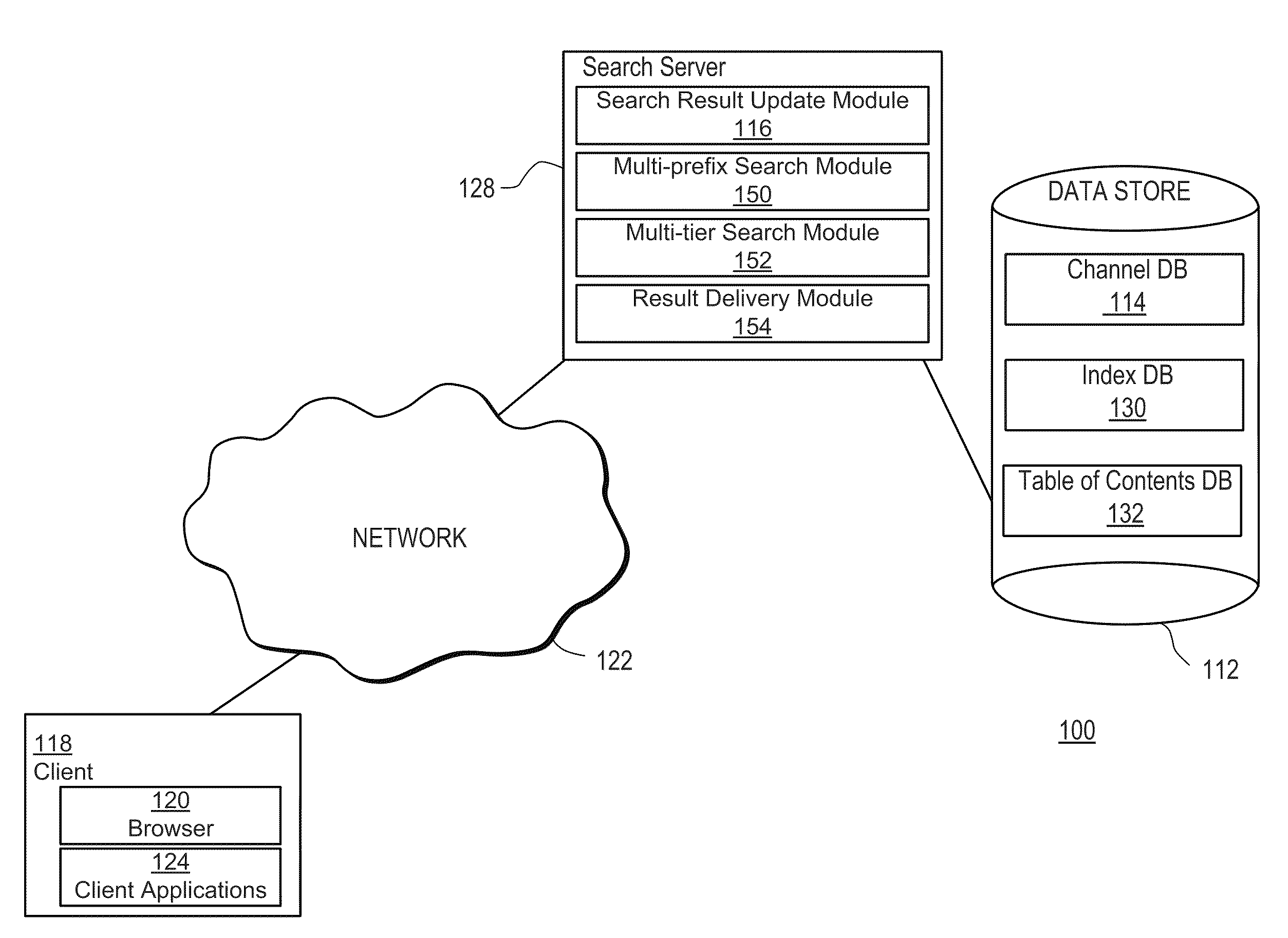
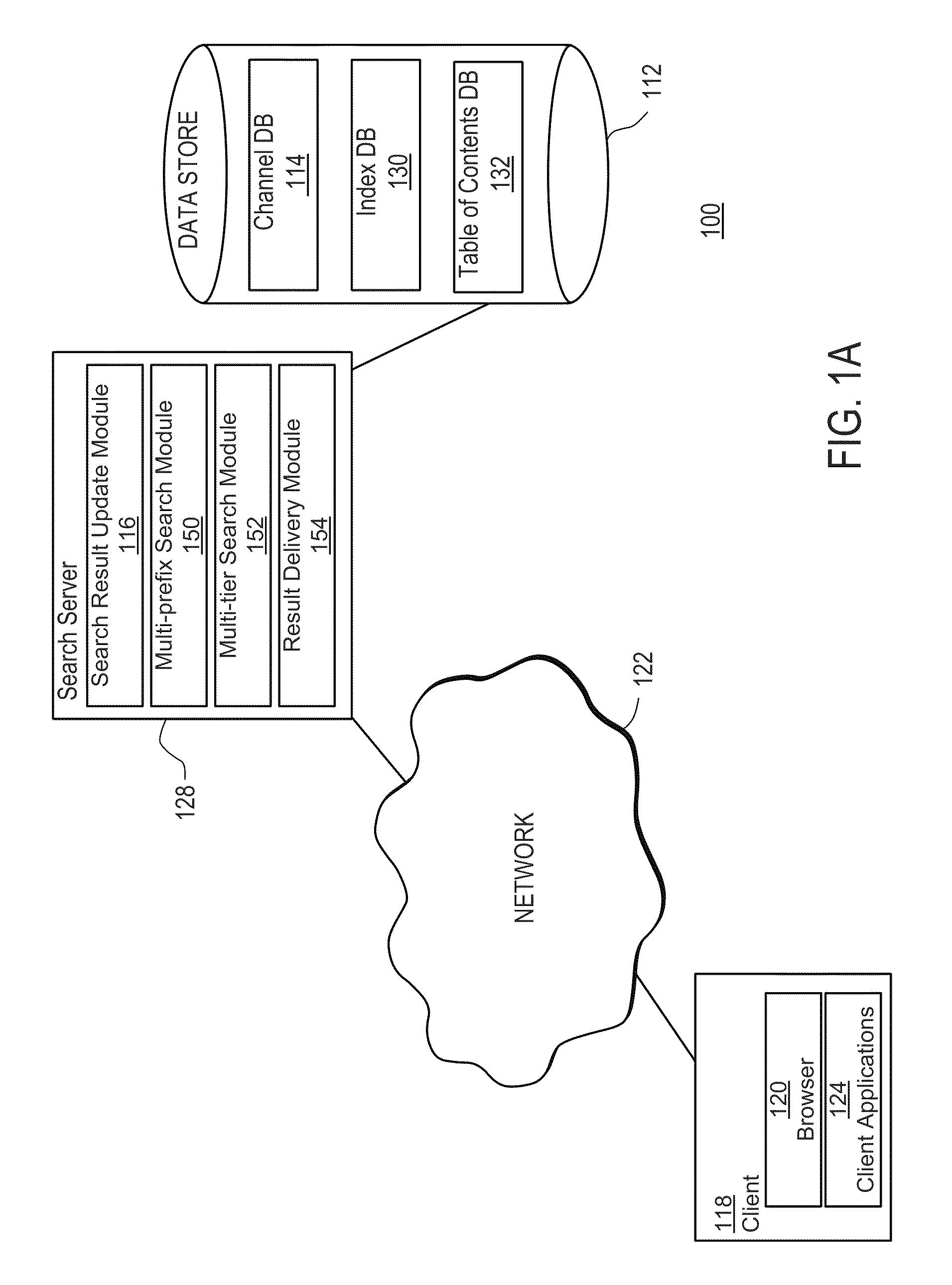
ActiveUS20110083167A1Facilitate targeted searchFacilitates targeted mobile searchesDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsApplication softwareContext specific
The present invention includes systems and methods for retrieving information via a flexible and consistent targeted search model that employs interactive multi-prefix, multi-tier and dynamic menu information retrieval techniques (including predictive text techniques to facilitate the generation of targeted ads) that provide context-specific functionality tailored to particular information channels, as well as to records within or across such channels, and other known state information. Users are presented with a consistent search interface among multiple tiers across and within a large domain of information sources, and need not learn different or special search syntax. A thin-client server-controlled architecture enables users of resource-constrained mobile communications devices to locate targeted information more quickly by entering fewer keystrokes and performing fewer query iterations and web page refreshes, which in turn reduces required network bandwidth. Applications are built by leveraging existing collaborative cloud services that enable the maintenance and sharing of user content.
Owner:BOOPSIE INC
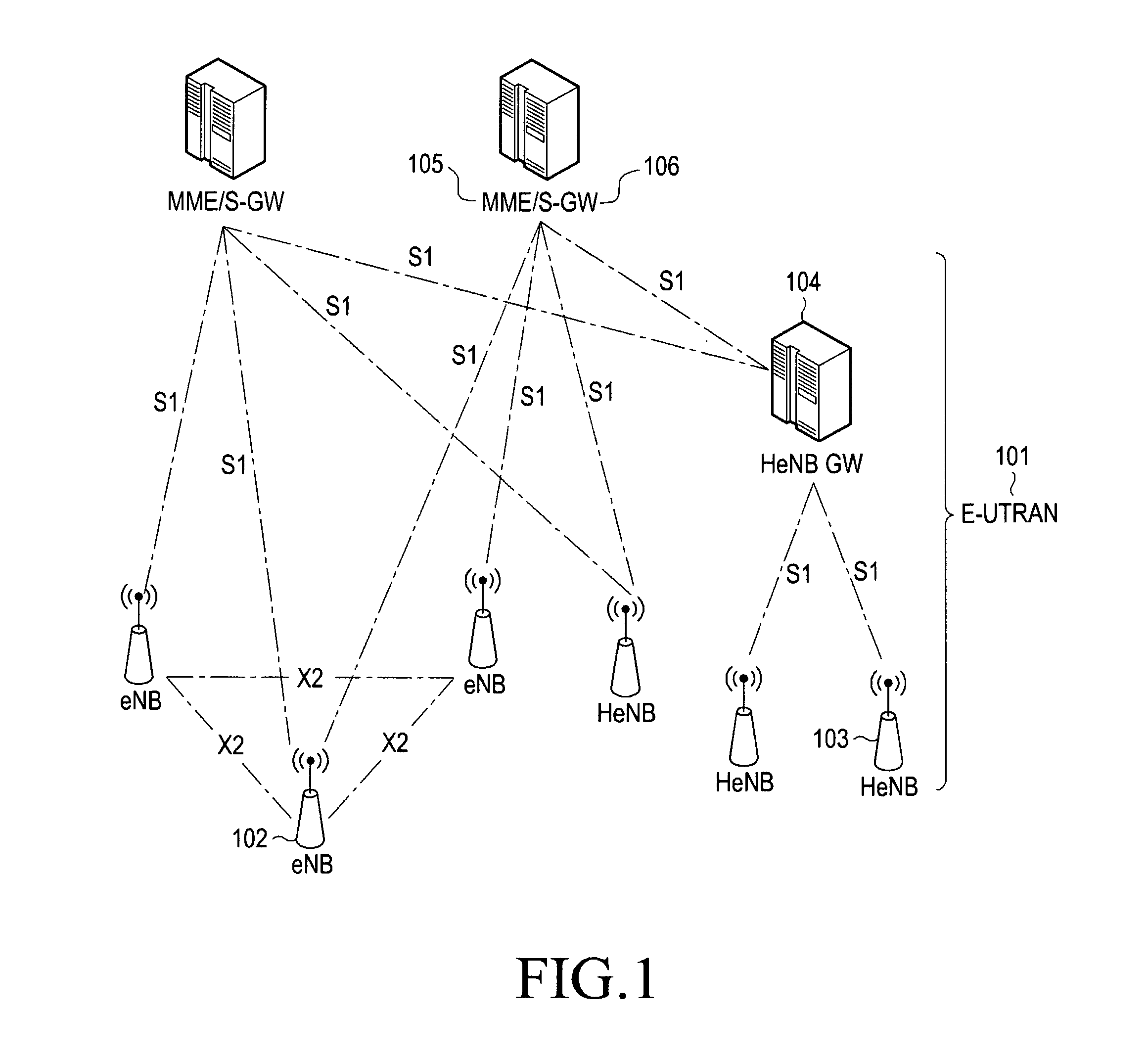
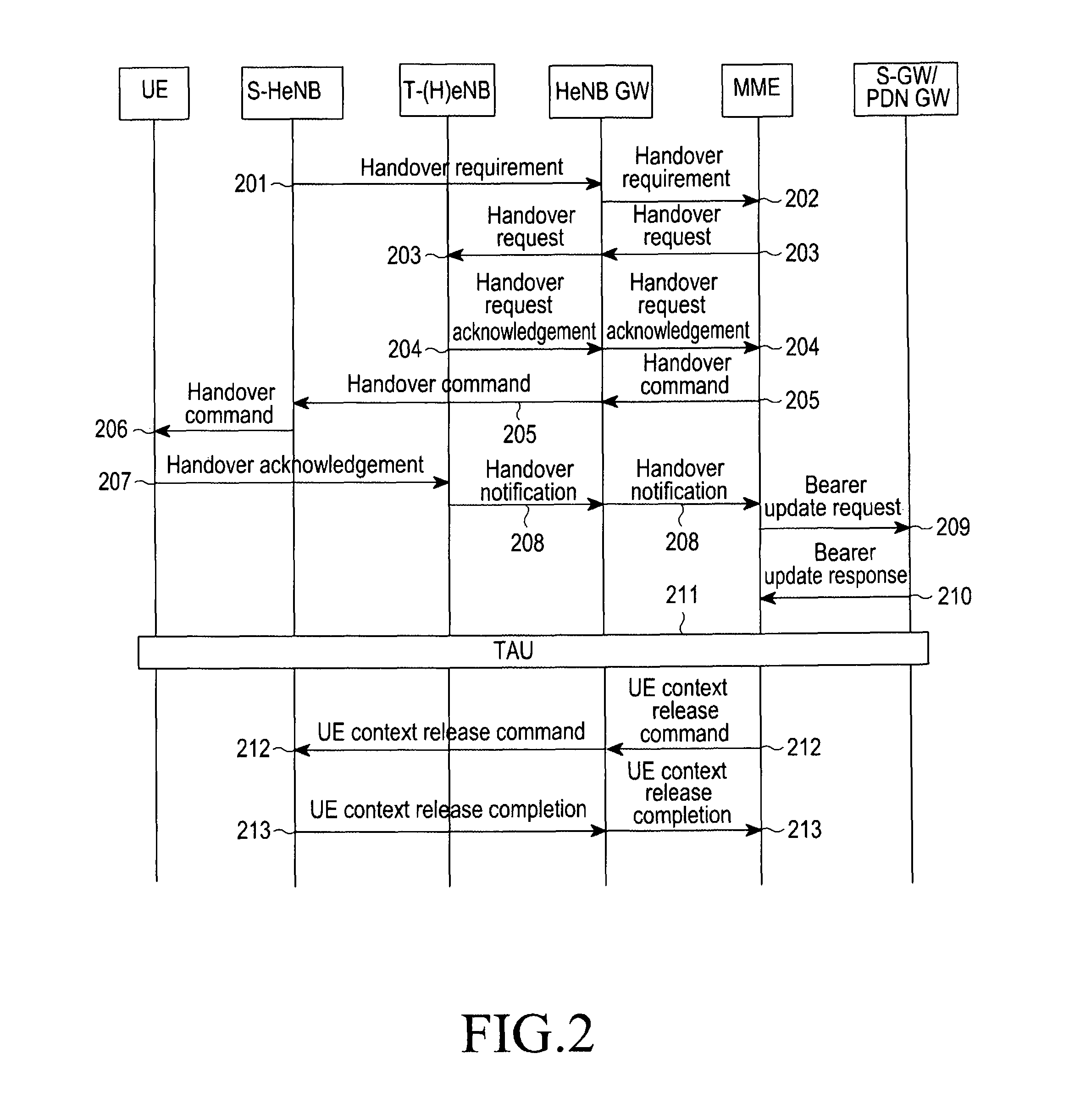
Method and apparatus for performing handover
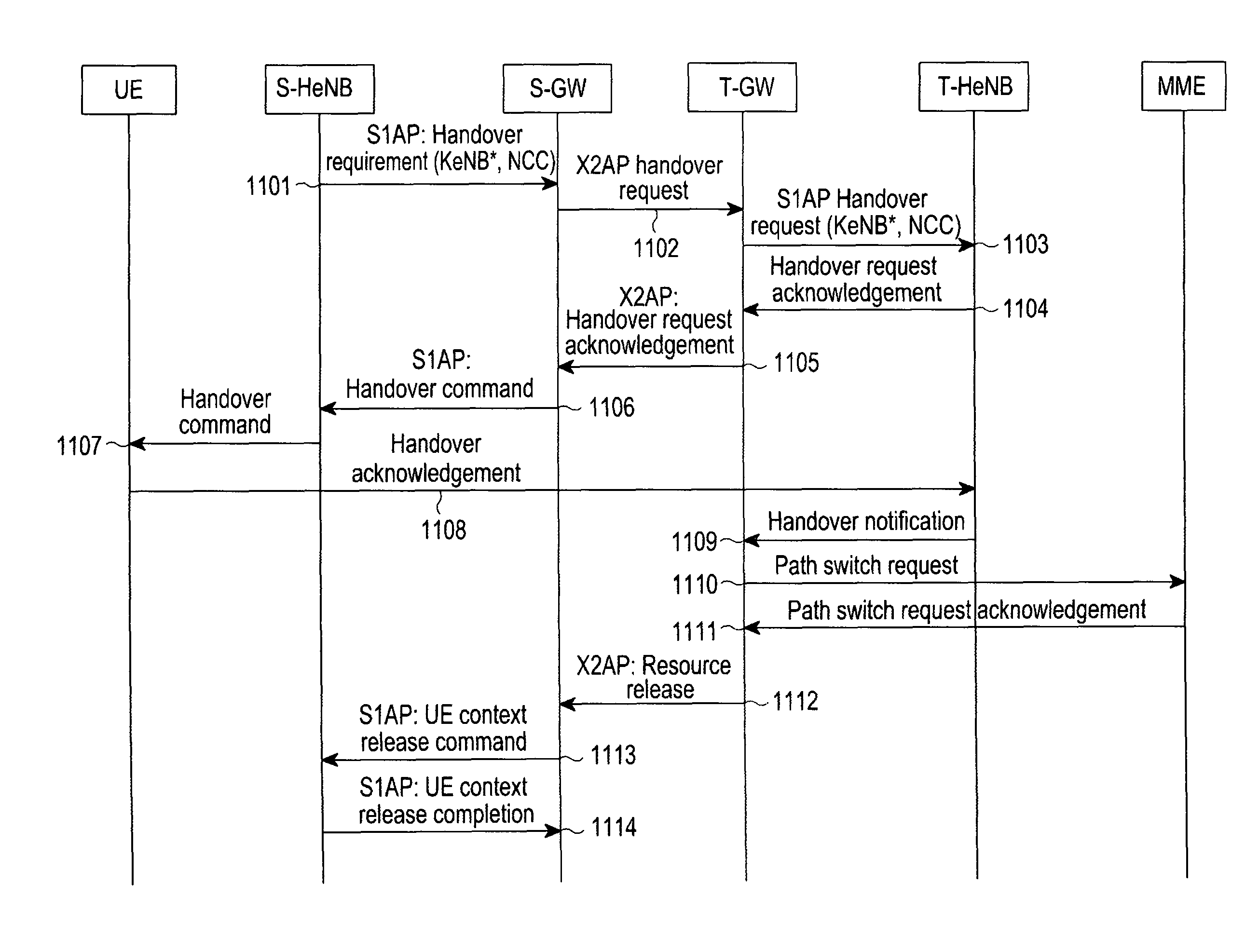
ActiveUS8520636B2Network degradationLow costNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesUser equipmentHandover
A method and an apparatus perform a handover using the X2 interface. A source base station transmits a handover requirement message, for a handover to a destination base station of a user equipment (UE), to a source base station gateway. When a handover command message indicating performing of the handover to a destination base station of the UE is received from the source base station gateway, the handover command message is transmitted to the UE. When a UE context release command message is received from the source base station gateway, a context of the UE is released. And a UE context release completion message, representing that the context of the UE is released, is transmitted to the source base station gateway. The handover requirement message includes a Next-hop Chaining Counter (NCC) and an encryption key for a communication between the UE and the destination base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
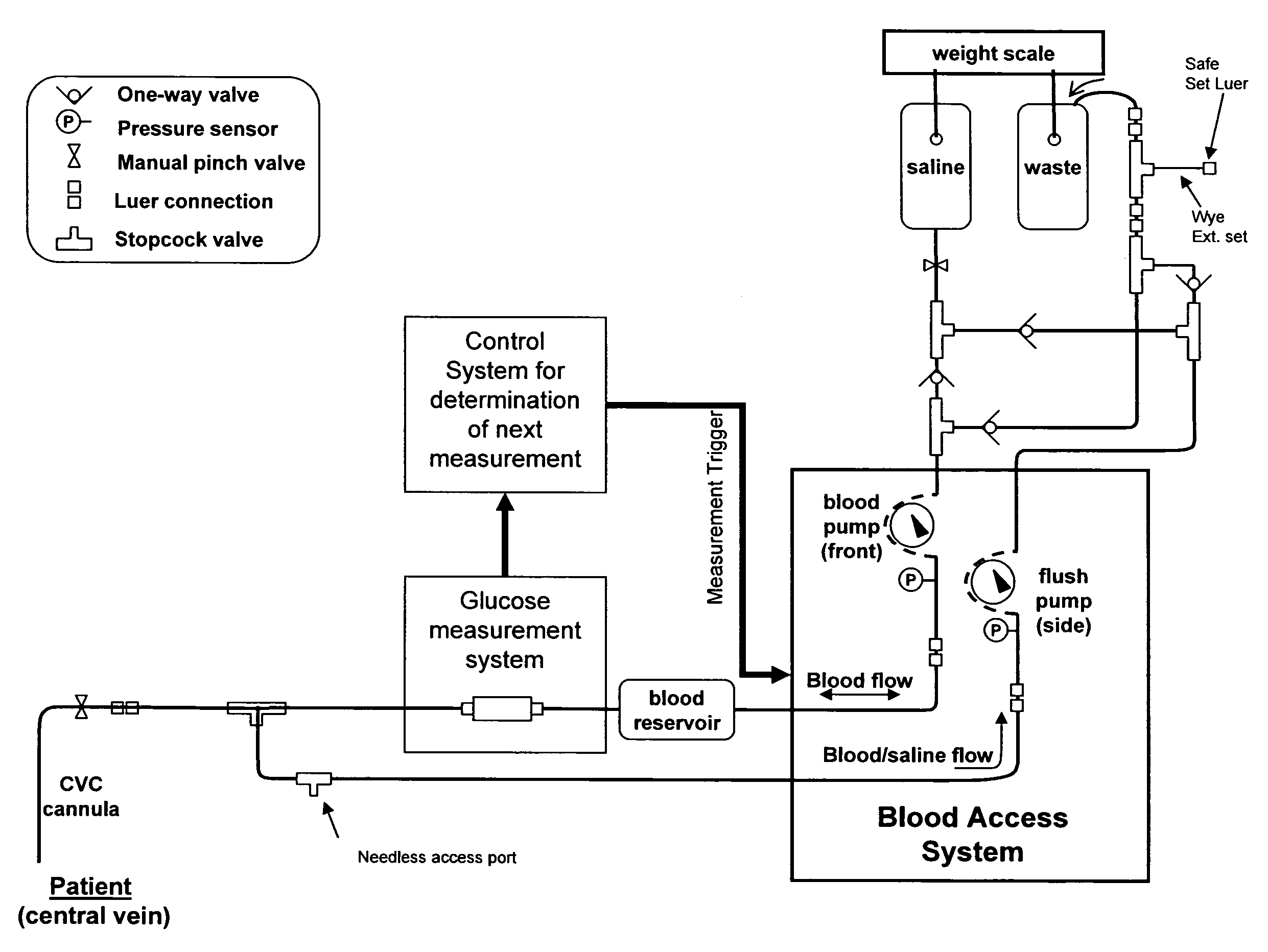
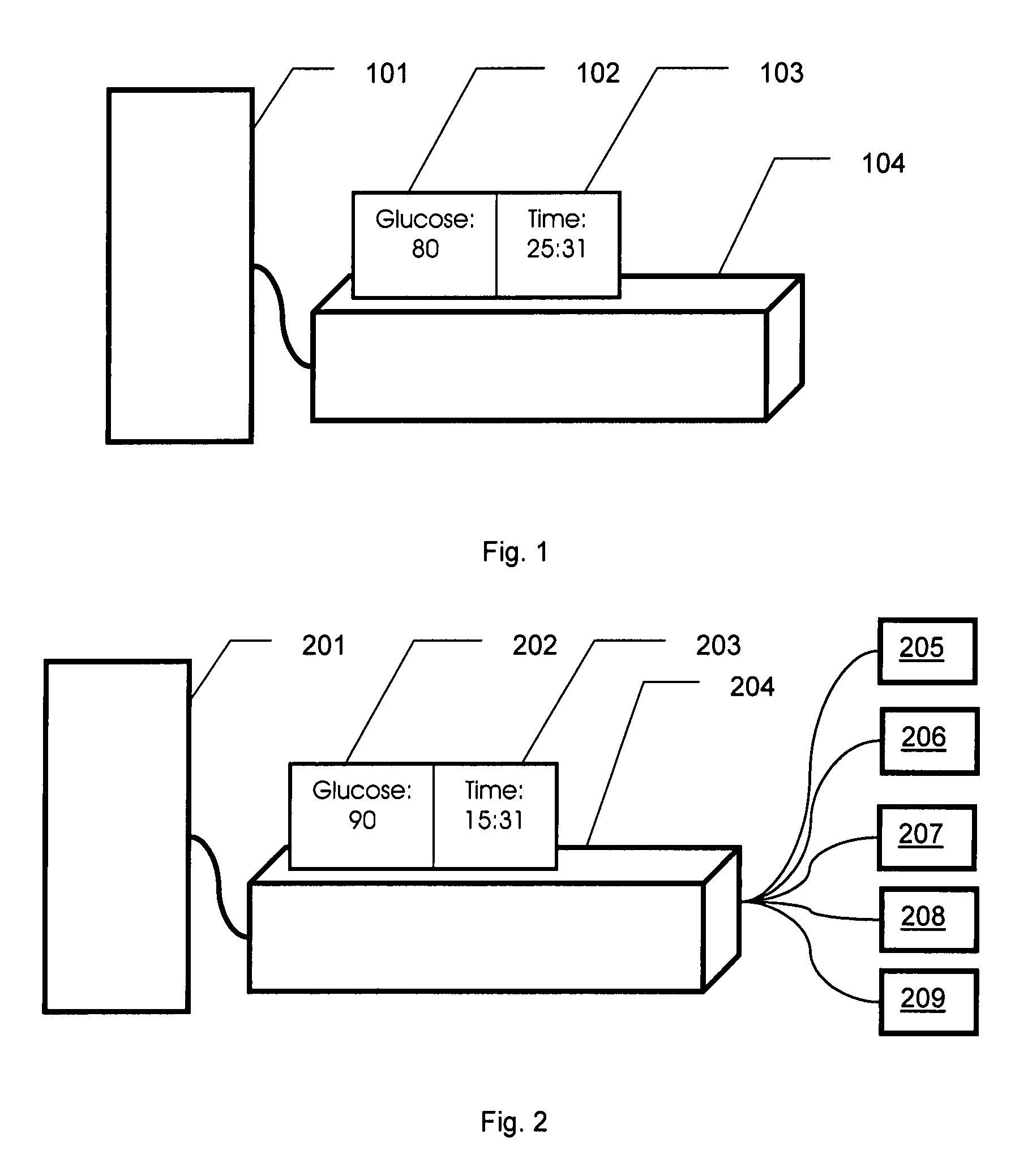
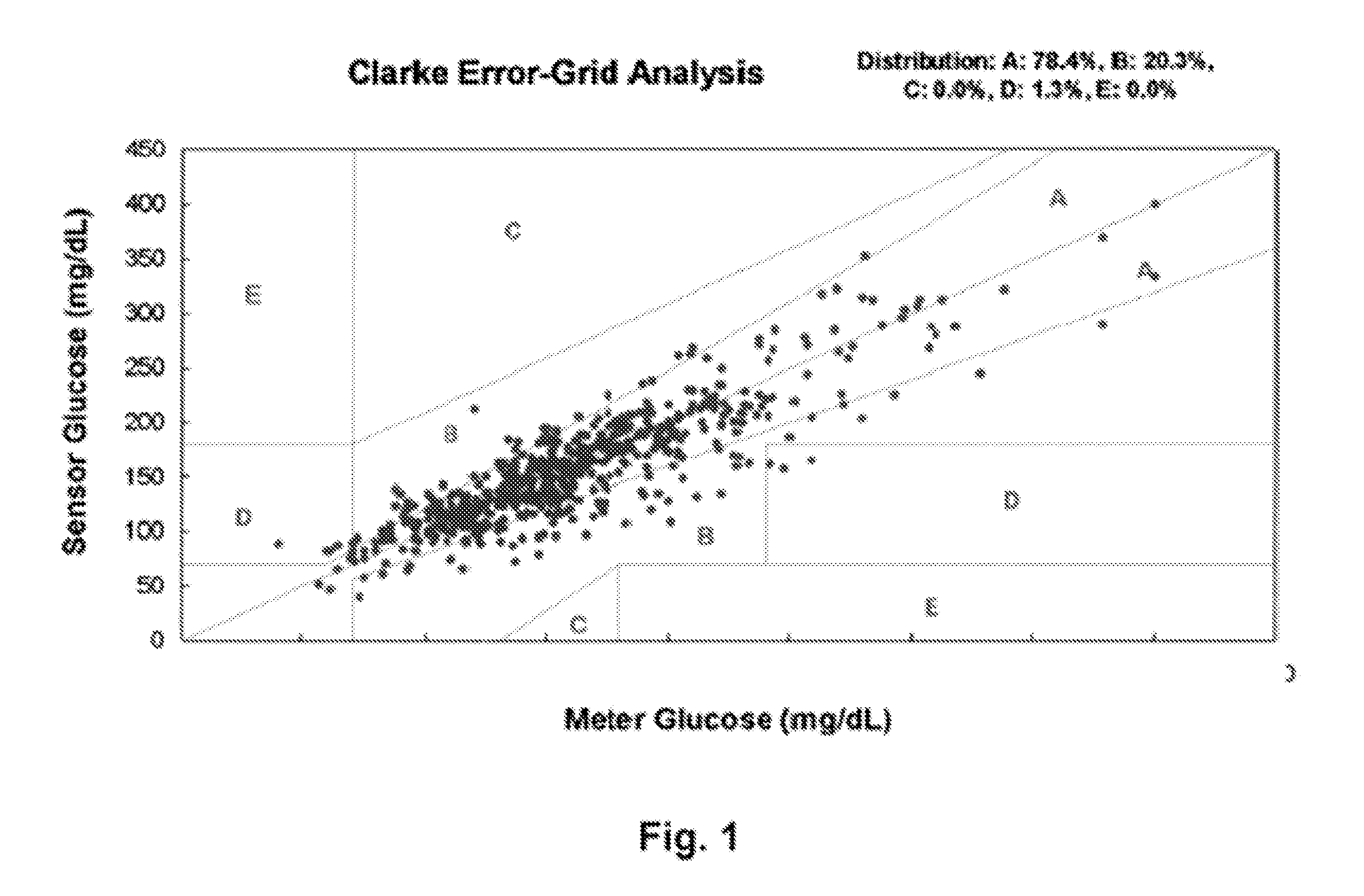
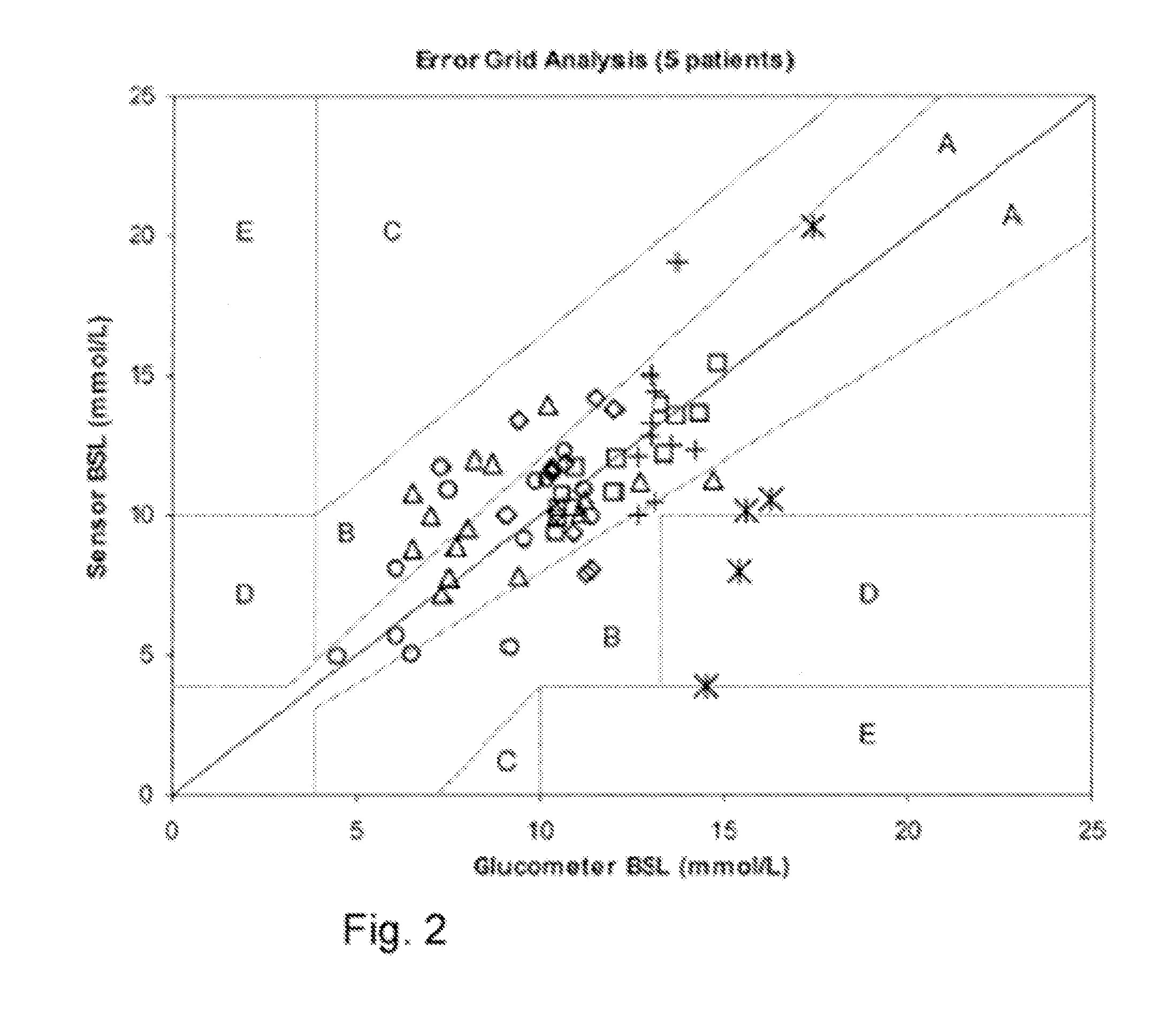
Variable Sampling Interval for Blood Analyte Determinations
InactiveUS20090054753A1Efficient measurementGreat patient safetyMedical simulationLocal control/monitoringAnalyteMedicine
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses that can provide measurement of glucose with variable intervals between measurements, allowing more efficient measurement with greater patient safety. A method according to the present invention can comprise measuring the value of an analyte such as glucose at a first time; determining a second time from a patient condition, an environmental condition, or a combination thereof; then measuring the value of the analyte at the second time (where the second time can be expressed as an interval after the first time, an absolute time, or a time indicated when certain patient or environmental conditions, or both, are reached or detected). The second time can be determined, as an example, from a comparison of the analyte value at the first time with a threshold. The interval between the first time and the second time can be related to the difference between the analyte value at the first time and the threshold; e.g., the closer to the threshold, the closer the two measurement times. The invention can be used with automated measurement systems, allowing the system to determine measurement times and automatically make measurements at the determined times, reducing operator interaction and operator error.
Owner:ROBINSON MARK RIES +2
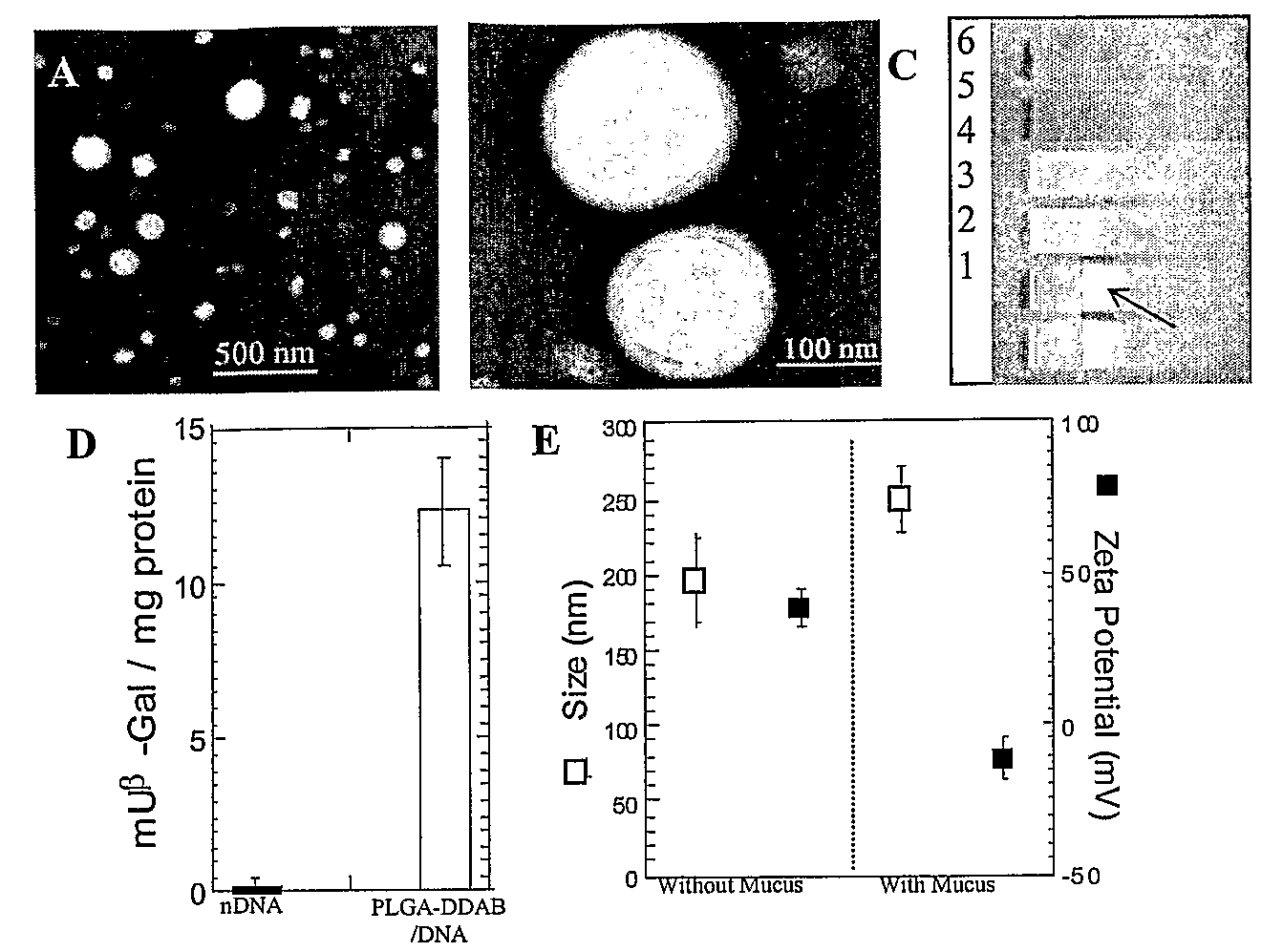
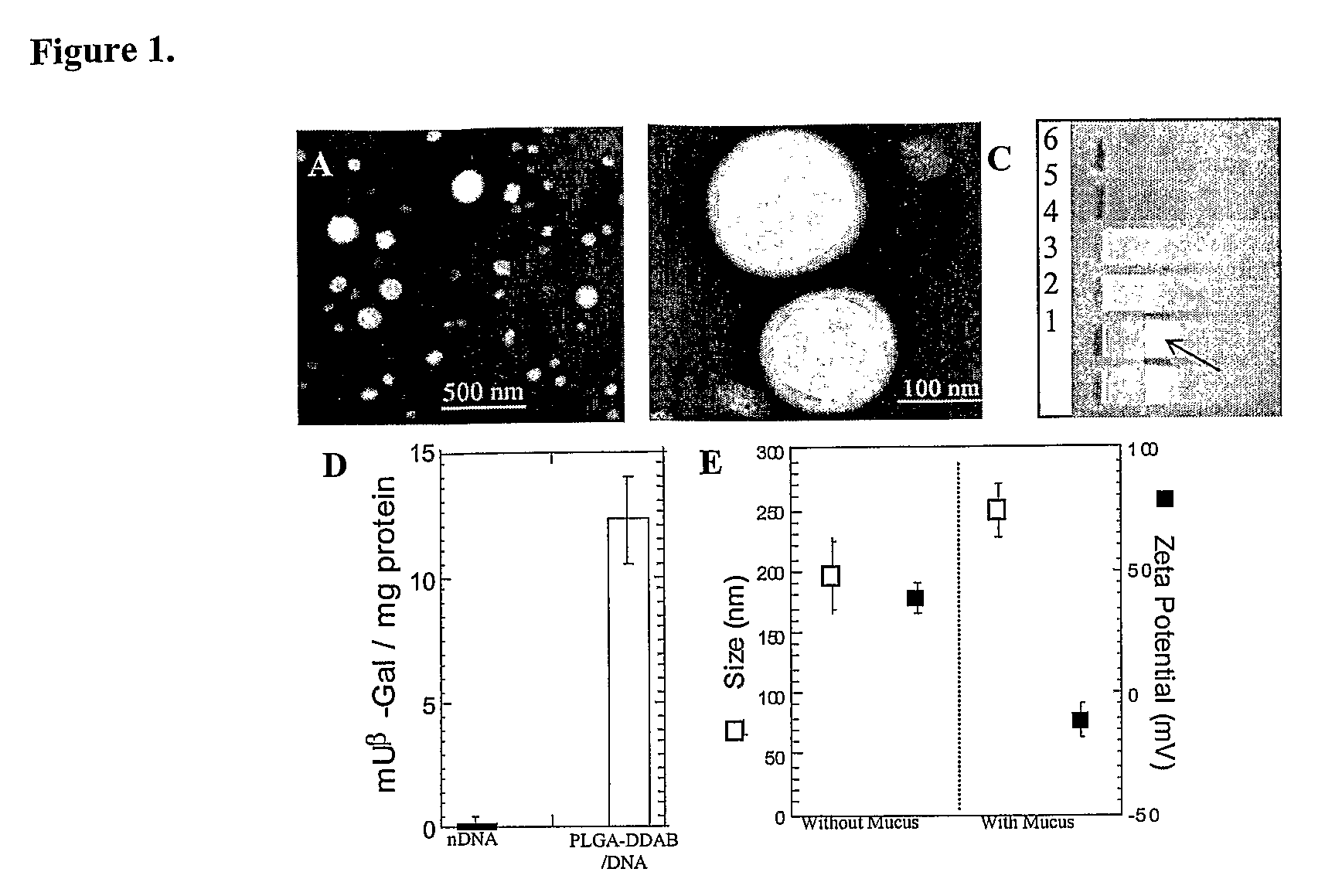
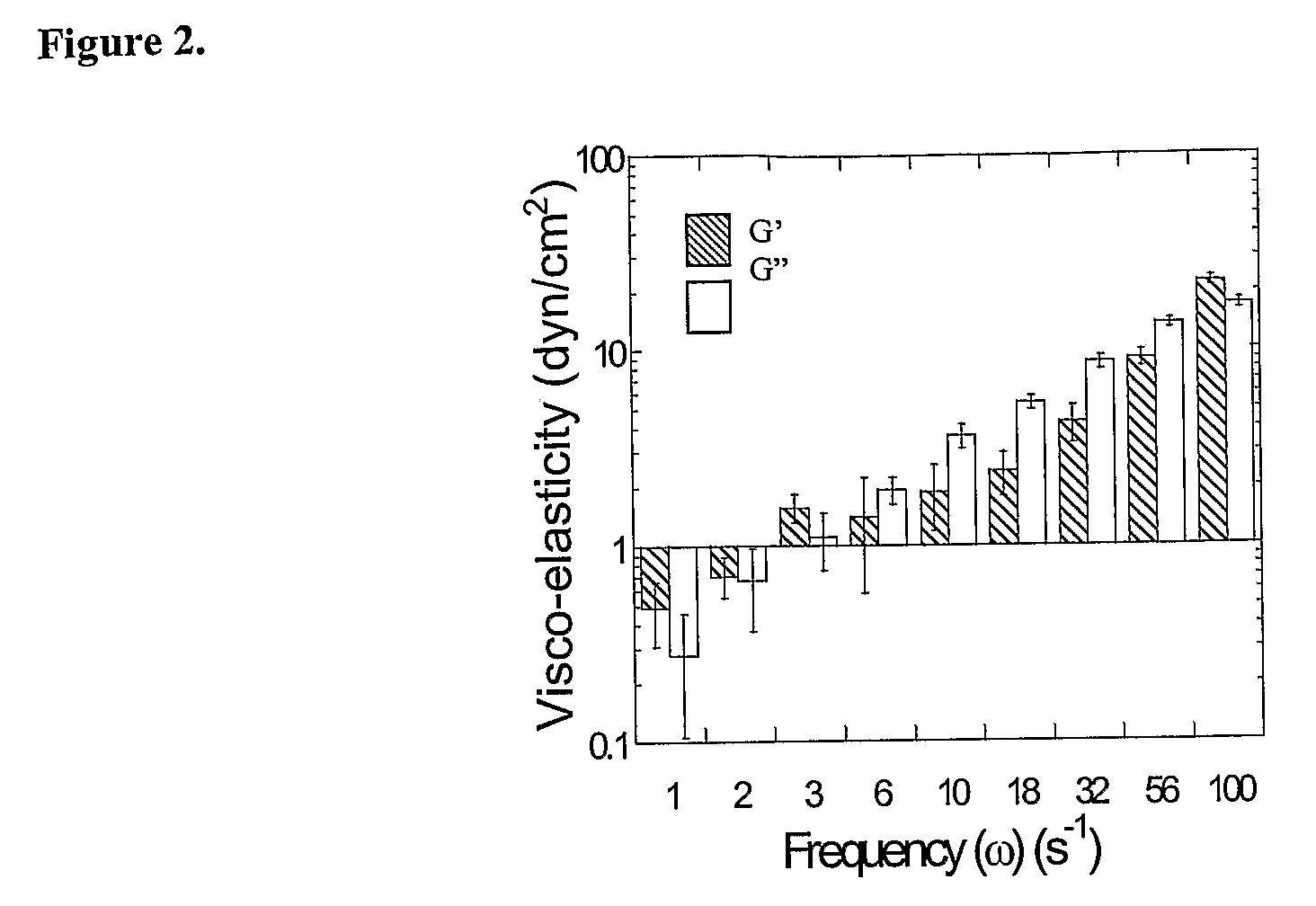
Drugs And Gene Carrier Particles That Rapidly Move Through Mucous Barriers
ActiveUS20080166414A1Easy adhesionPromote complexationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCrystallographyMucus
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and compositions for the treatment of persistent infections
ActiveUS20070122378A1Reduced activityReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiologyPathology
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the treatment, prevention, or reduction of persistent infections, such as chronic infections, latent infections, and slow infections and cancer. The methods and compositions of the invention are also useful for the alleviation of one or more symptoms associated with such infections and cancer.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +3
Precision inductive devices and methods
ActiveUS20060145800A1Mitigation of flux leakage effectImprove balanceTransformers/inductances casingsPrinted inductancesEngineeringInductor
A low cost, low profile, small size and high performance inductive device for use in, e.g., electronic circuits. In one exemplary embodiment, the device includes a ferrite core comprising multiple inductors and optimized for electrical and magnetic performance. Improvements in performance are obtained by, inter alia, control of the properties of the gap region(s) as well as placement of the windings relative to the gap. The magnetic path properties of the inductors at the ends of the device are also optionally controllable so as to provide precise matching of inductances. Optionally, the device is also self-leaded, thereby simplifying its installation and mating to a parent device (e.g., PCB). Methods for manufacturing and utilizing the device are also disclosed.
Owner:PULSE ELECTRONICS
Object tracking system with automated system control and user identification
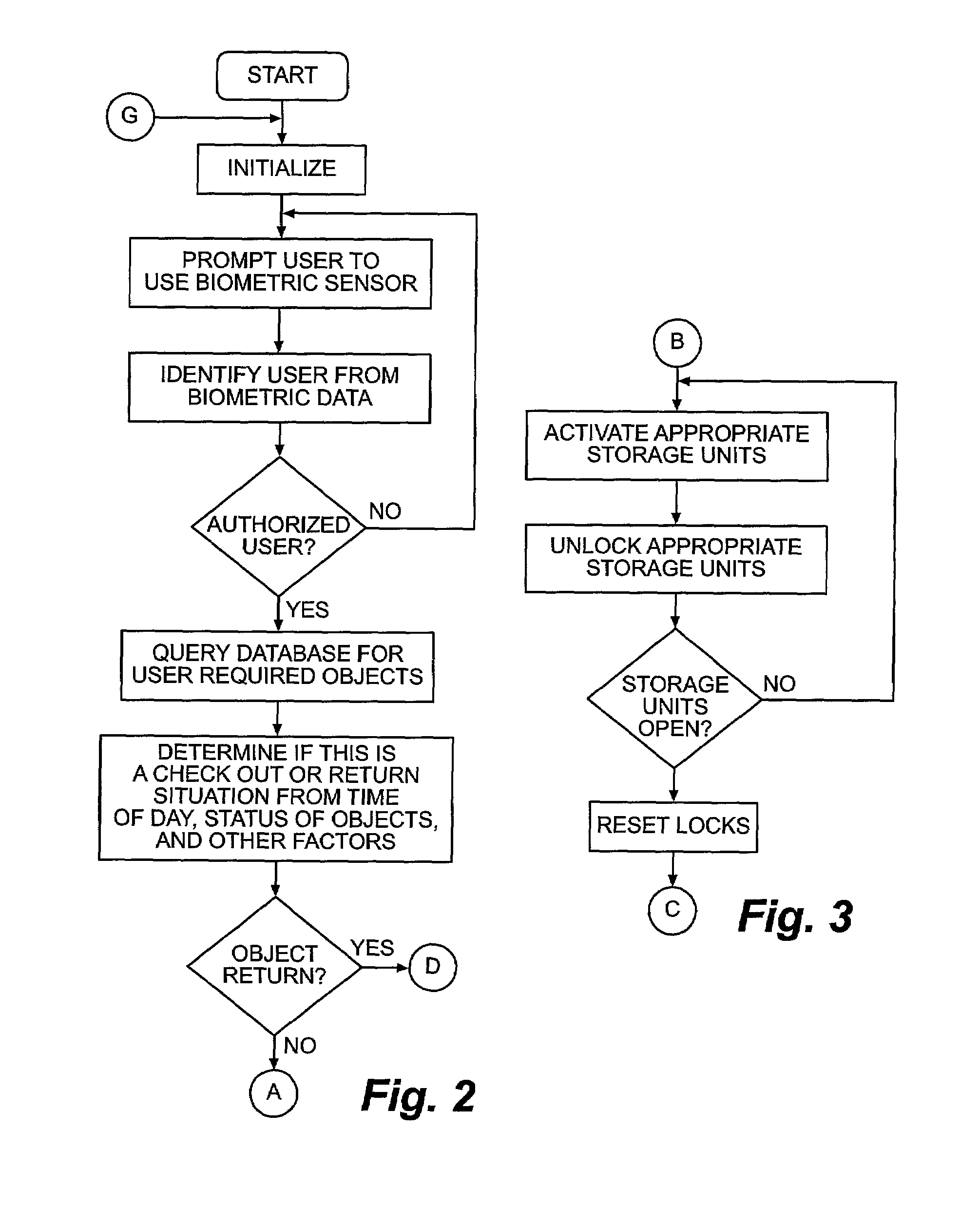
ActiveUS7336174B1Reduce significantly and eliminate completely levelReduces user interactionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingWork tools storagePattern recognitionAutomatic control
An enhanced object tracking system for tracking and controlling access to a plurality of objects such as keys is disclosed. The object tracking system implements many improvements including automated user identification using biometric data extracted from the user with a minimum of user interaction, tracking of objects both inside and outside their storage units, the locking of objects within slots of their storage unit to guard against illicit removal and return of keys and to insure random slot rotation, image and visual based inventory verification methodologies, and tracking of objects during times when they are checked out of the system. The result is an intelligent object tracking system with automated control functions and high reliability.
Owner:KEY CONTROL HLDG
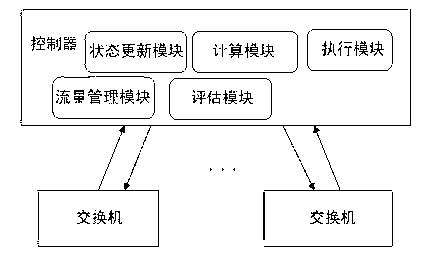
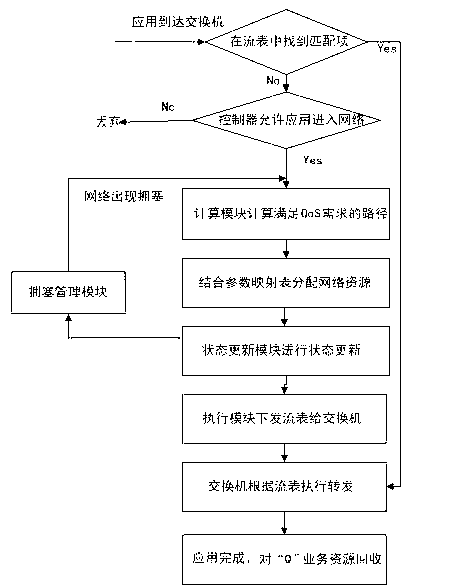
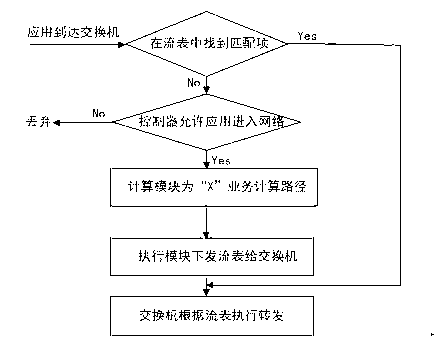
Controller for determining network state based on SDN (Software Defined Networking) and determination method thereof
The invention discloses a controller for determining a network state based on an SDN (Software Defined Networking) and a determination method thereof. The controller comprises a state updating module, a calculation module, an execution module, a flow management module and an evaluation module, wherein the state updating module is used for updating through a state and a path calculated by the calculation module; the calculation module is used for calculating a current network resource state N; the execution module is used for setting rules according to the path calculated by the calculation module and writing the path into a flow meter; the flow management module is used for carrying out congestion avoidance, flow supervision and shaping; and the evaluation module is used for carrying out synthetic judgment according to the current network resource state N calculated by the calculation module and QoS (Quality of Service) requirements of an application when receiving the application transmitted by a switch. According to the controller, the network state can be accurately controlled, a forwarding plane is precisely controlled, a 'Q+X' resource distribution mode is proposed, and the network resource is scheduled, so that the flexibility, the high efficiency, the intelligence and the optimization of a network can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
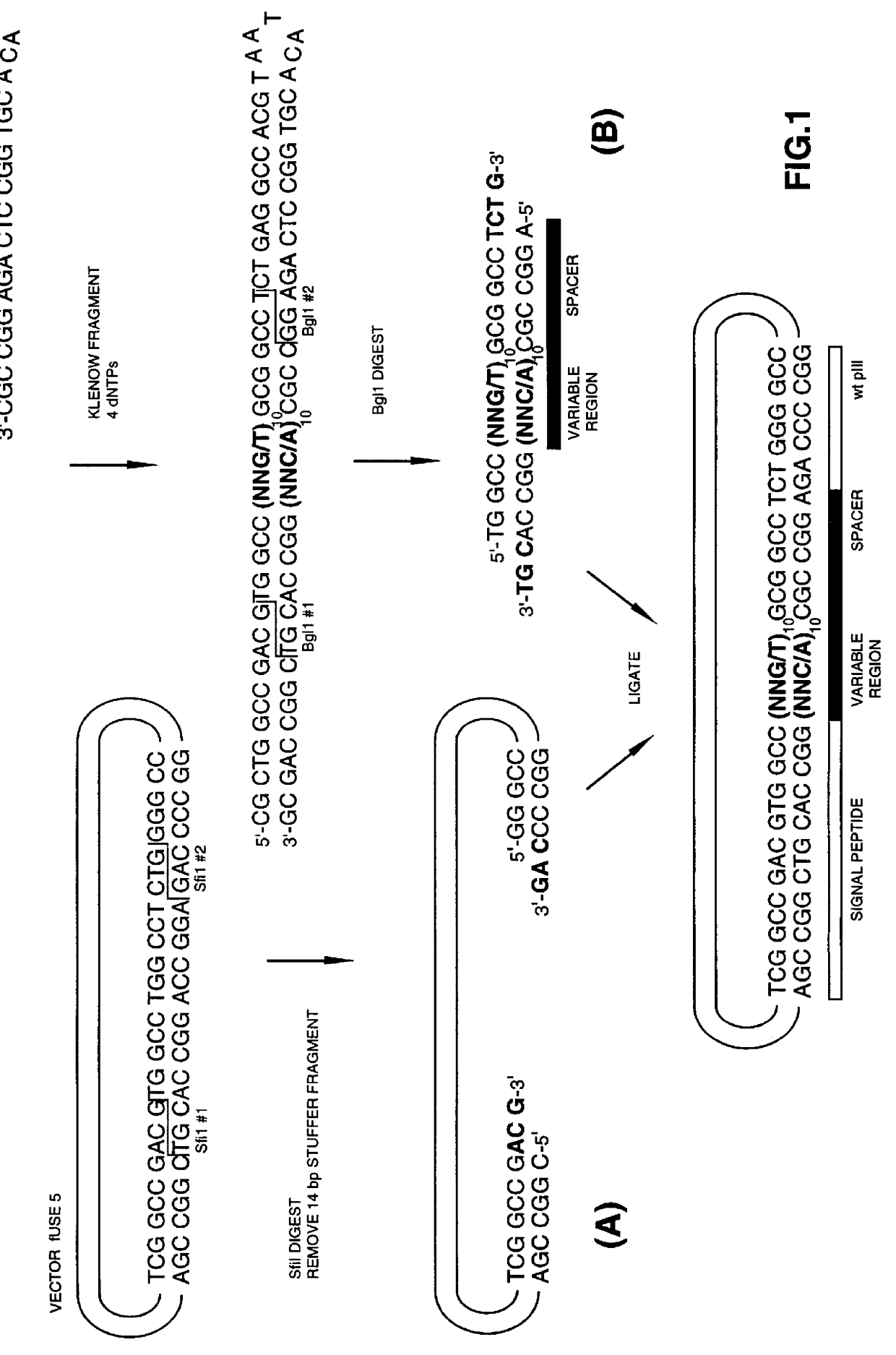
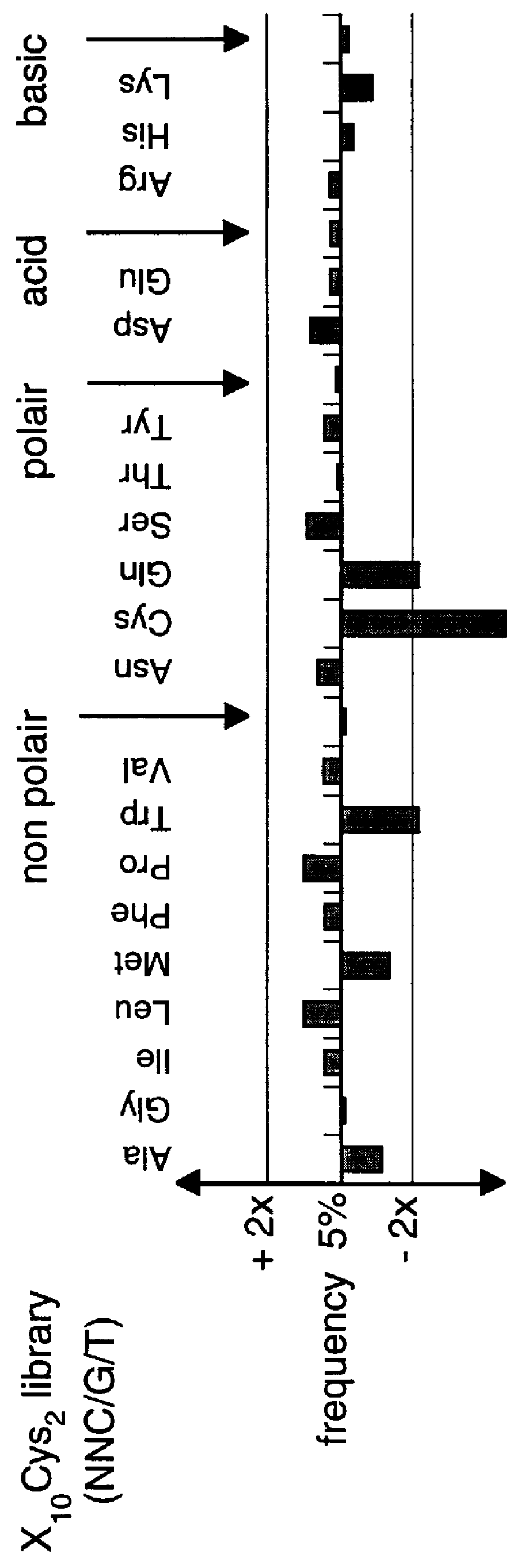
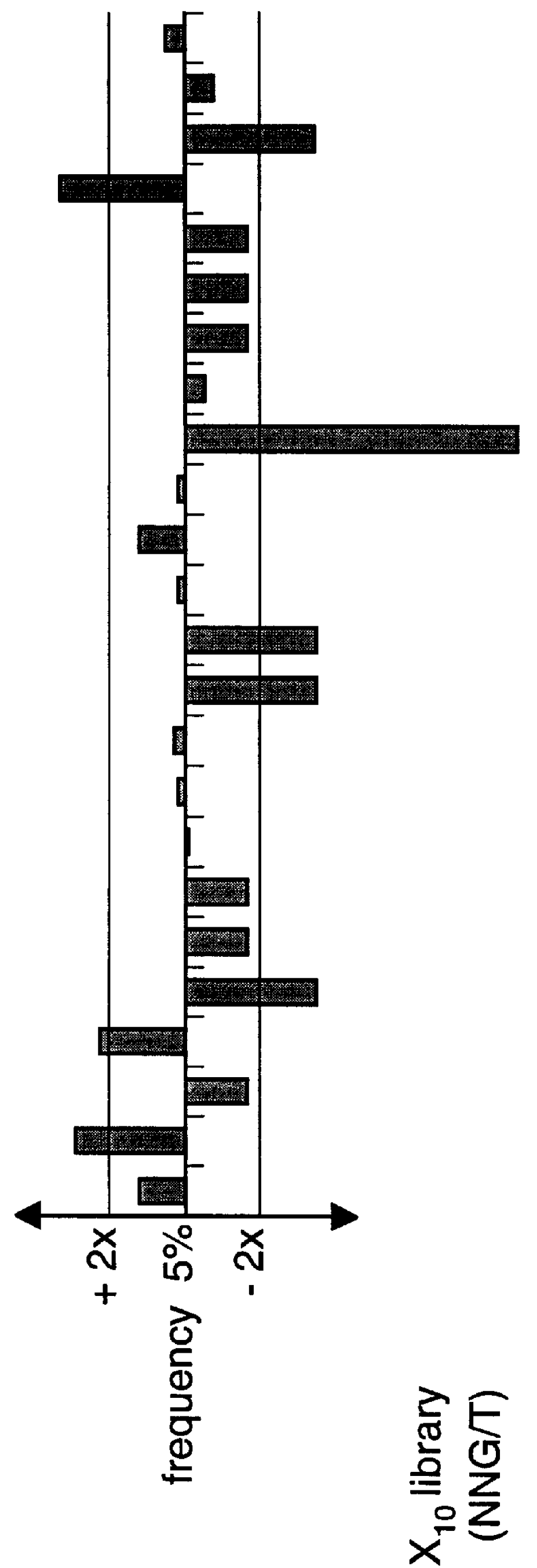
Methods of generating novel peptides
The present invention describes peptides capable of specifically binding to preselected micromolecules or to their natural receptor. The preselected molecules include but are not limited to drugs, vitamins, neuromediators and steroid hormones. Methods of using the phage display libraries to identify peptide compositions in preselected binding interactions are also disclosed. The retrieved peptides mimicking a natural receptor binding site to preselected molecules are used as is or as ligands to re-screen the same or different libraries to find and / or derive new receptor ligands, or are used to elicit the production of antibodies capable of binding to the natural receptor. The two categories of effector molecules (peptides or antibodies) may find diagnostic, therapeutic or prophylactic uses. The peptides directly derived from the phage display libraries may be used as drug detectors or antidotes. The others may be used to identify, target, activate or neutralize the receptor for the preselected micromolecules, the receptor being known or unknown.
Owner:BIOPHAGE
Abuse resistant melt extruded formulation having reduced alcohol interaction
InactiveUS20090317355A1Reduced and limited dose-dumping effectReduce interactionBiocideNervous disorderVerapamilOral medication
The present invention relates to compositions for oral administration. The invention preferably comprises at least one abuse-resistant drug delivery composition for delivering a drug having potential for dose dumping in alcohol, related methods of preparing these dosage forms, and methods of treating a patient in need thereof comprising administering the inventive compositions to the patient. Most preferably, the dosage form includes verapamil. These formulations have reduced potential for abuse. In another formulation, preferably the abuse relevant drug is an opioid and the non-abuse relevant drug is acetaminophen or ibuprofen. More preferably, the opioid is hydrocodone, and the non-abuse relevant analgesic is acetaminophen. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosage forms are characterized by resistance to solvent extraction; tampering, crushing or grinding. Certain embodiments of the inventions provide dosage forms that provide an initial burst of release of drug followed by a prolonged period of controllable drug release.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
Screening and therapeutic methods for promoting wakefulness and sleep
InactiveUS6884596B2Reduce the binding forceEnhanced interactionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMammalPhysiology
The invention provides methods of screening for a compound for promoting wakefulness in a mammal. The method is practiced by providing a compound that is a PrRP receptor agonist and determining the ability of the compound to promote wakefulness. Also provided by the invention are methods of screening for a compound for promoting sleep in a mammal. The methods are practiced by providing a compound that is a PrRP receptor antagonist and determining the ability of the compound to promote sleep. In addition, the invention provides a method of promoting wakefulness in a mammal. The method is practiced by administering to a mammal an effective amount of a PrRP receptor agonist. The invention further provides a method of promoting sleep in a mammal. The method is practiced by administering to a mammal an effective amount of a PrRP receptor antagonist.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for improved stent retention
InactiveUS6979346B1Increased frictional contactImprove interferenceStentsSurgeryBalloon catheterGuide tube
An implantable medical device, such as a stent, having roughened areas on an inner surface of the device for enhancing frictional contact between the medical device and a delivery system, such as a balloon catheter to secure the medical device to the delivery system during delivery of the medical device to a body lumen of a patient. Various methods for forming the roughened areas are also provided. The roughened areas may be coated with a material, such as a non-thrombogenic material, to enhance the compatibility of the inner surface of the medical device with fluid flowing through the vessel lumen of the patient.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
System and method for parallel execution of data generation tasks
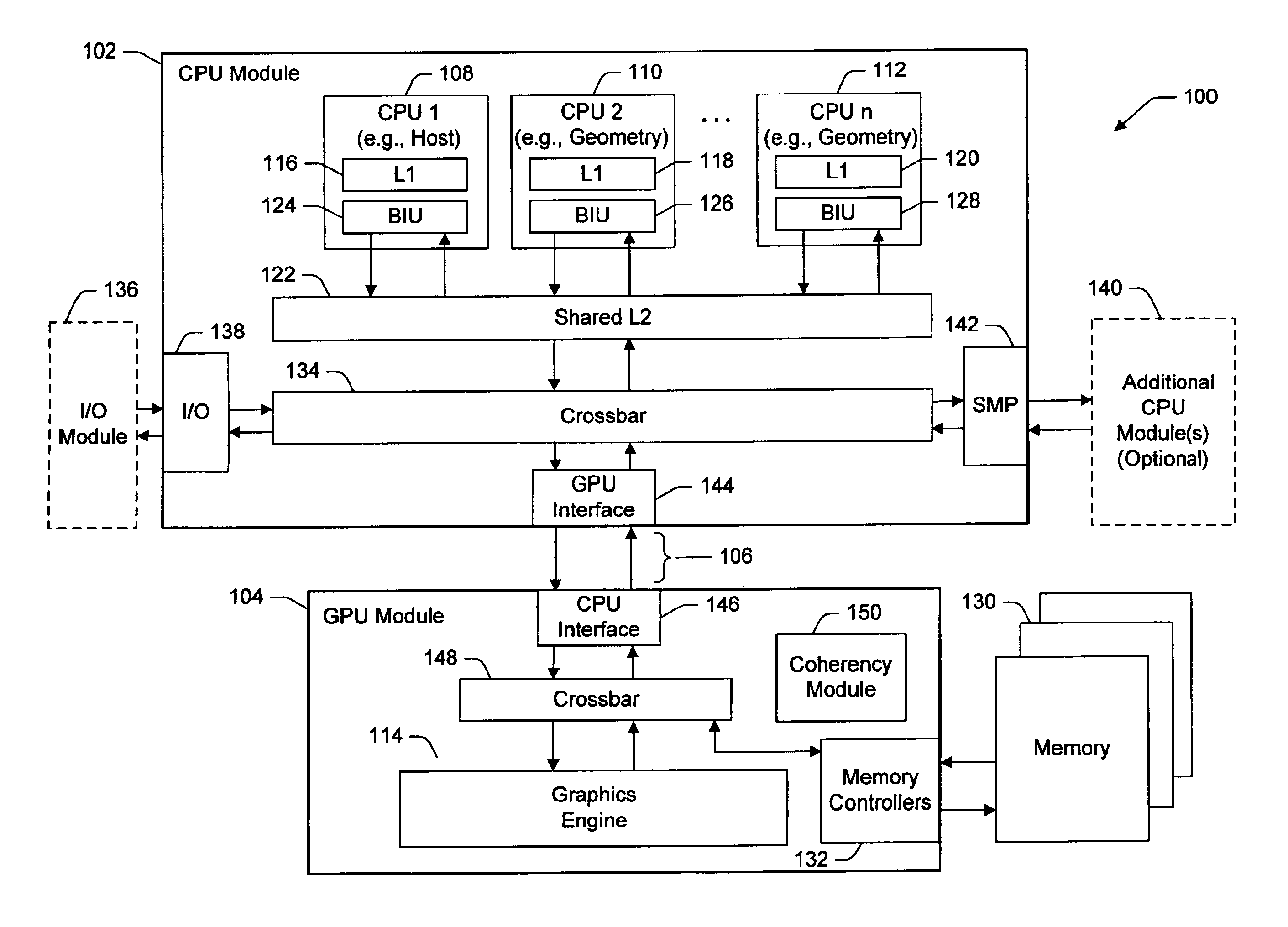
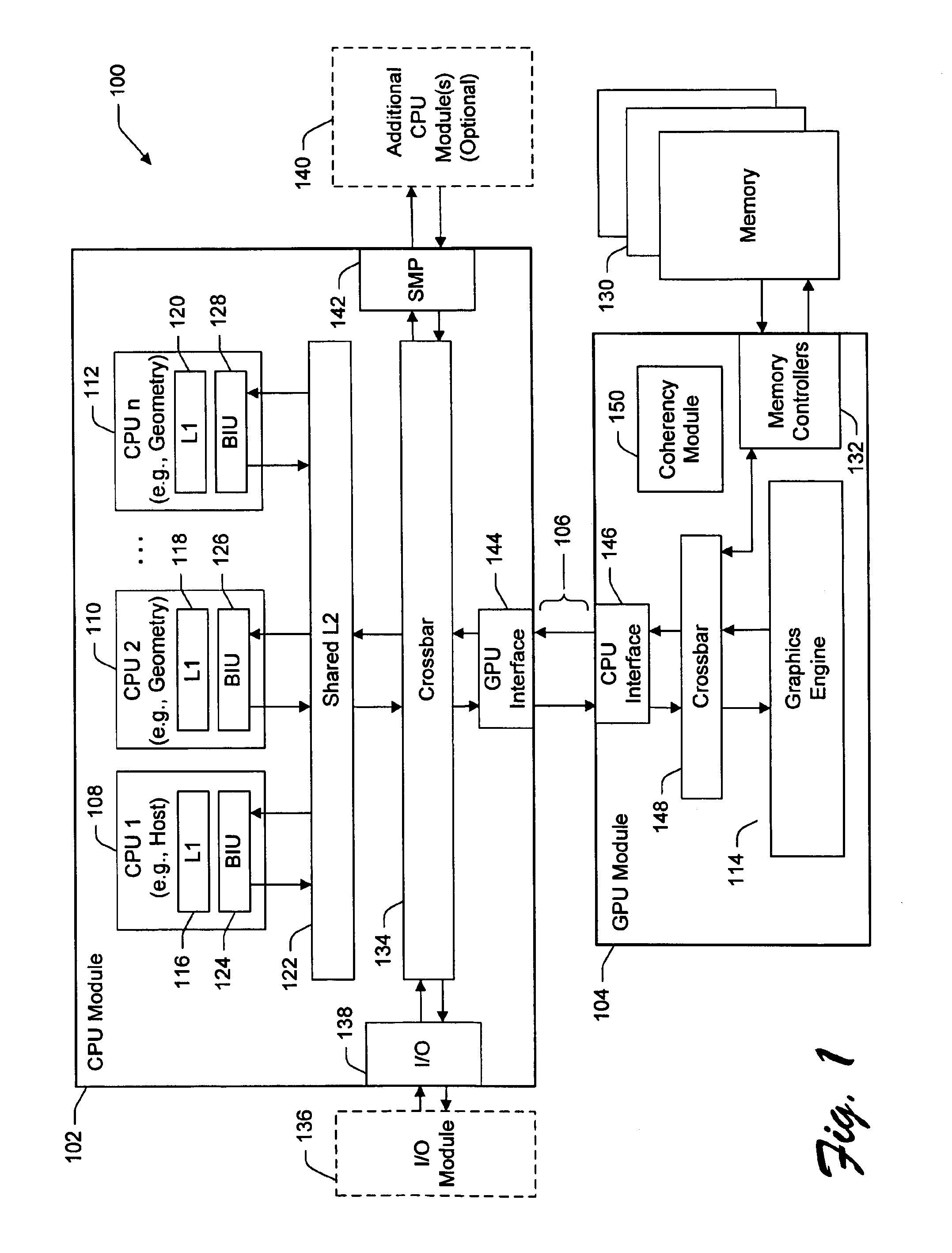
InactiveUS6862027B2Reduce storage requirementsReduces deleterious bandwidth restrictionResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsParallel computing
A CPU module includes a host element configured to perform a high-level host-related task, and one or more data-generating processing elements configured to perform a data-generating task associated with the high-level host-related task. Each data-generating processing element includes logic configured to receive input data, and logic configured to process the input data to produce output data. The amount of output data is greater than an amount of input data, and the ratio of the amount of input data to the amount of output data defines a decompression ratio. In one implementation, the high-level host-related task performed by the host element pertains to a high-level graphics processing task, and the data-generating task pertains to the generation of geometry data (such as triangle vertices) for use within the high-level graphics processing task. The CPU module can transfer the output data to a GPU module via at least one locked set of a cache memory. The GPU retrieves the output data from the locked set, and periodically forwards a tail pointer to a cacheable location within the data-generating elements that informs the data-generating elements of its progress in retrieving the output data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
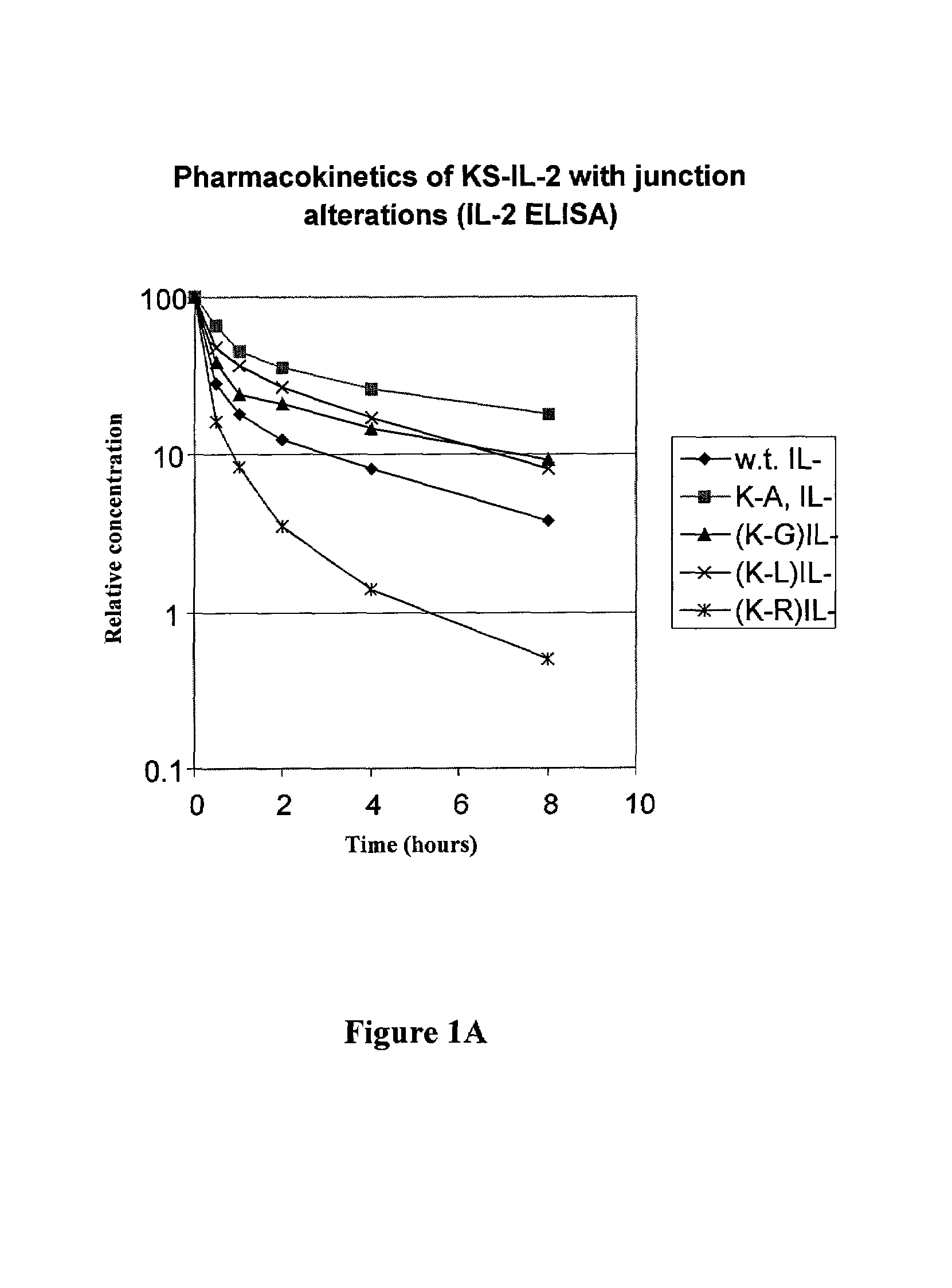
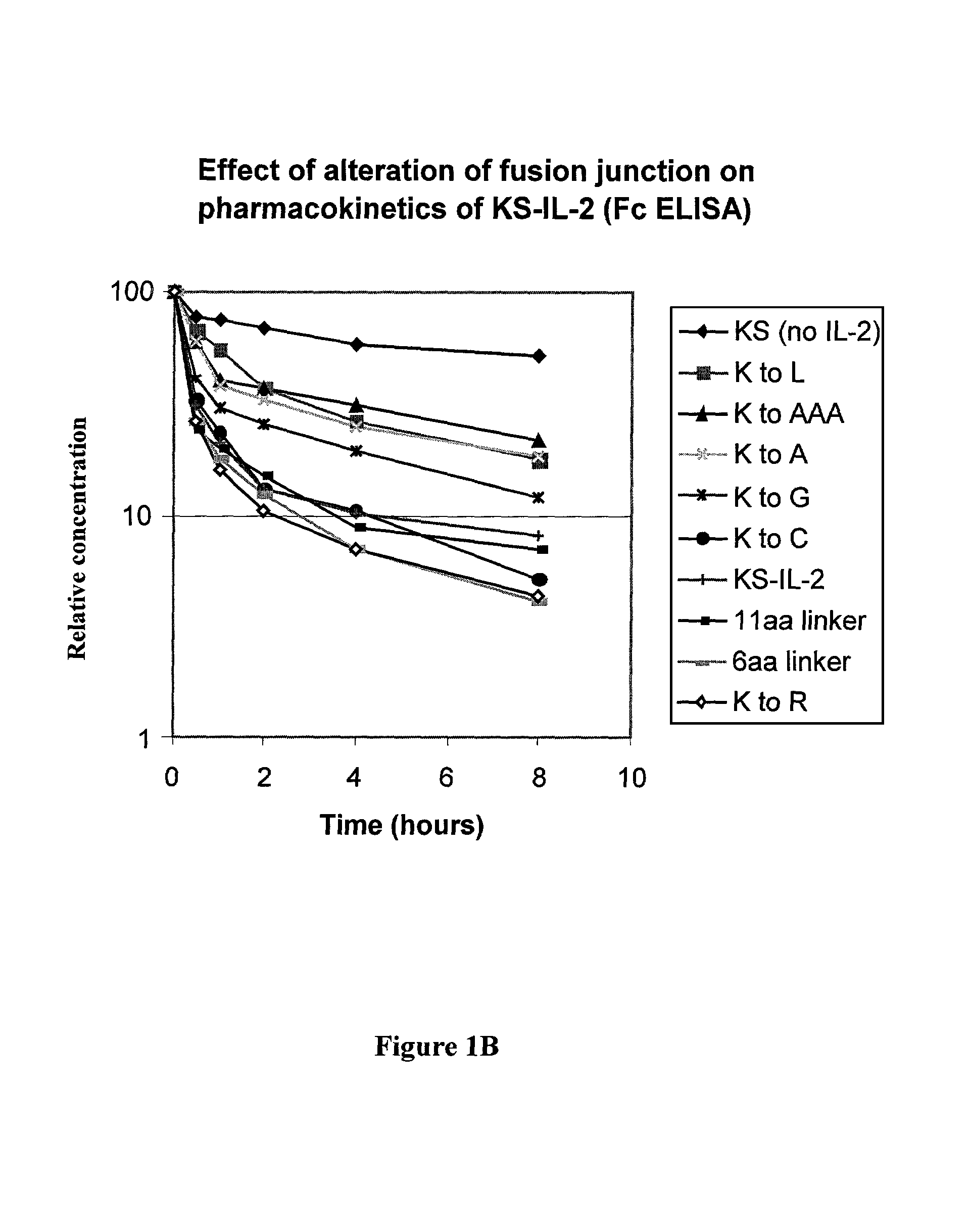
Enhancing the circulating half-life of antibody-based fusion proteins
InactiveUS7091321B2Increased serum half-lifeHigh affinityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLymphatic SpreadHalf-life
Disclosed are compositions and methods for enhancing the circulating half-life of antibody-based fusion proteins. Disclosed methods and compositions rely on altering the amino acid sequence of the junction region between the antibody moiety and the fused protein moiety in an antibody-based fusion protein. An antibody-based fusion protein with an altered amino acid sequence in the junction region has a greater circulating half-life when administered to a mammal. Disclosed methods and compositions are particularly useful for reducing tumor size and metastasis in a mammal.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Thermostable pigments, films and effect coatings, and mixtures for their production
InactiveUS6423246B1Reduce interactionDegrade solventLiquid crystal compositionsBoltsLiquid crystallineColor shift
A mixture of crosslinkable liquid-crystalline substances having a chiral phase (LC mixture), containing polymerizable groups, where at least 90% of the polymerizable groups are part of molecules containing at least two polymerizable groups (crosslinker molecules), wherein from 3.2 to 15 mmol of polymerizable groups are present per g of LC mixture. The crosslinked pigments show little color shift in the presence of solvents or upon application to substrate different temperatures.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
Determination of blood pump system performance and sample dilution using a property of fluid being transported
InactiveUS20120065482A1Avoids large swing in level of blood glucoseEven and predictable control systemMedical devicesCatheterAnalyteMedicine
Owner:ROBINSON MARK RIES +14
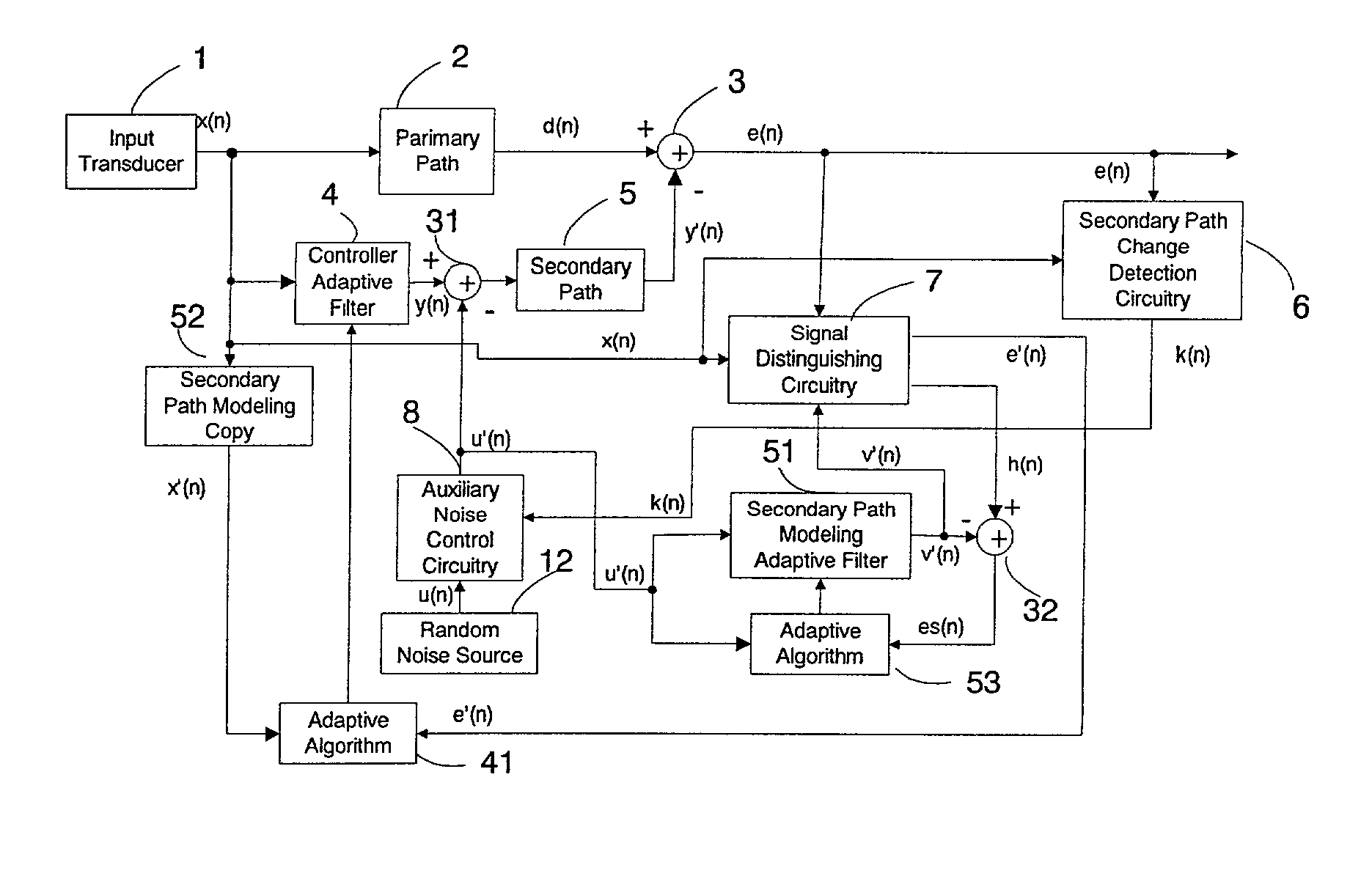
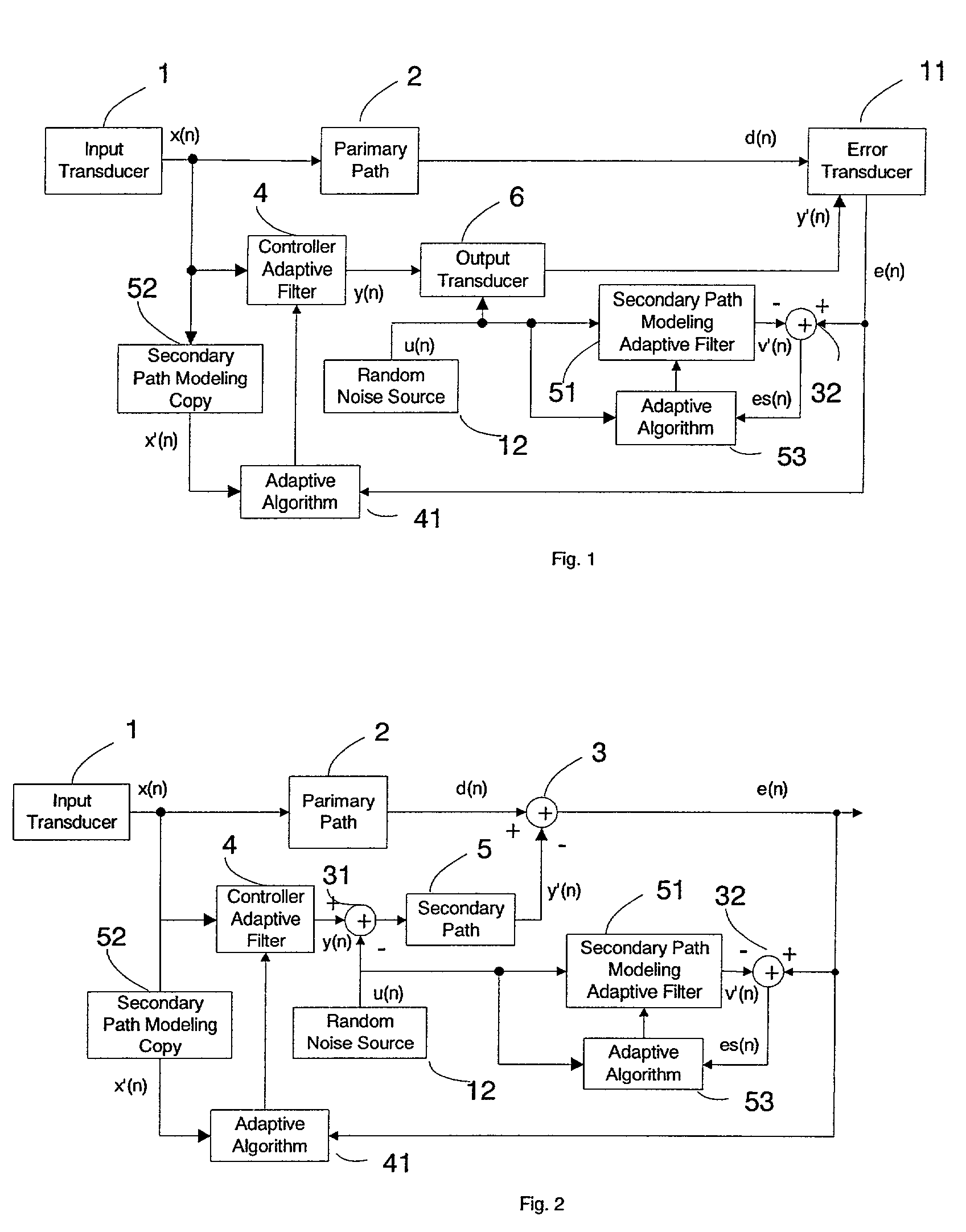
Active noise control system with on-line secondary path modeling
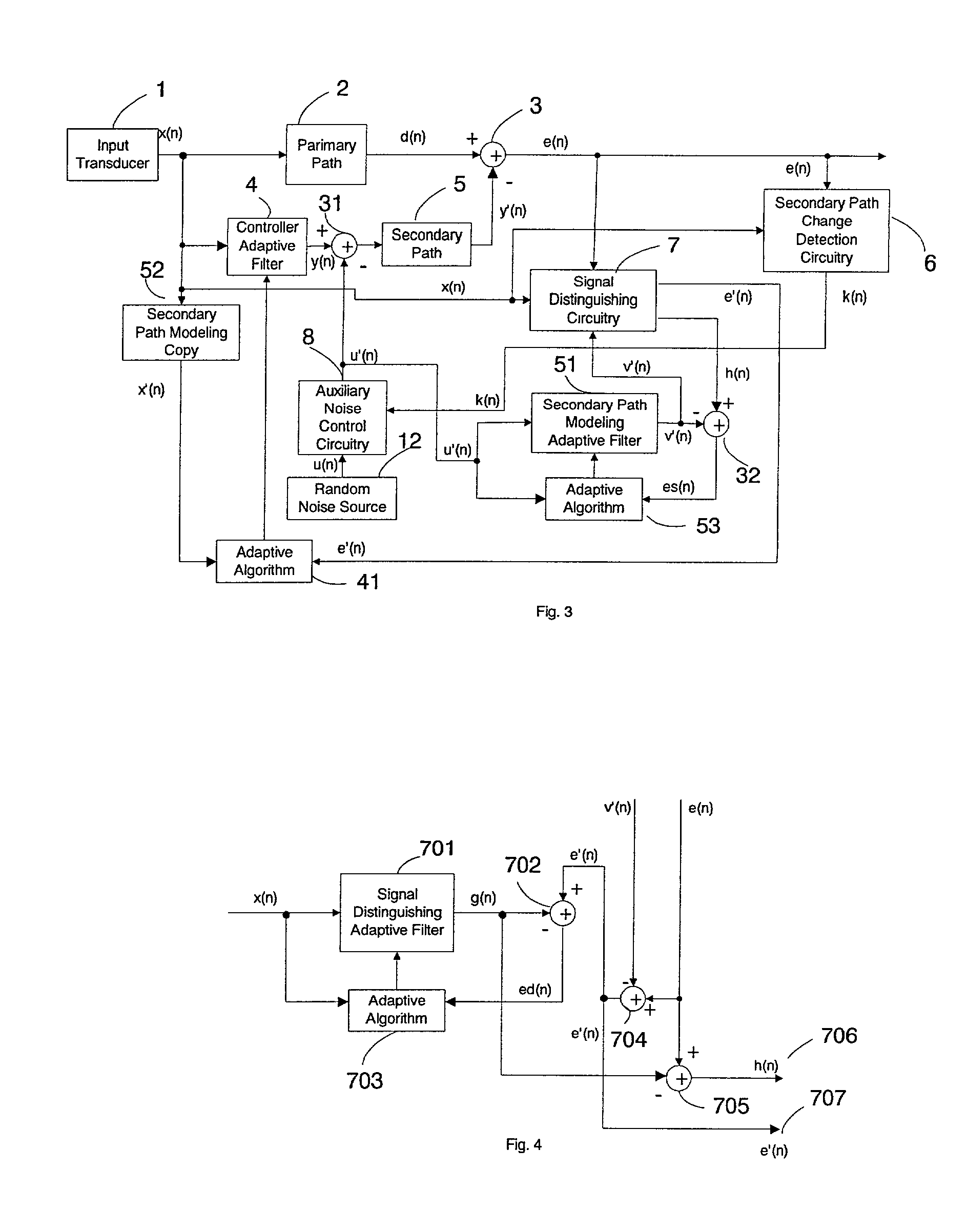
An active noise control system is provided to specify an input transducer, an error transducer, an output transducer and an active noise controller for generating an anti-phase canceling acoustic signal to attenuate an input noise and to output a reduced noise. The active noise control system also performs on-line secondary path modeling. For this purpose the active noise control system comprises, in addition to known systems, a secondary path change detection circuitry (6), a signal distinguishing circuitry (7) and an auxiliary noise control circuitry (8), all of them being used to model said secondary path. FIG. 3
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
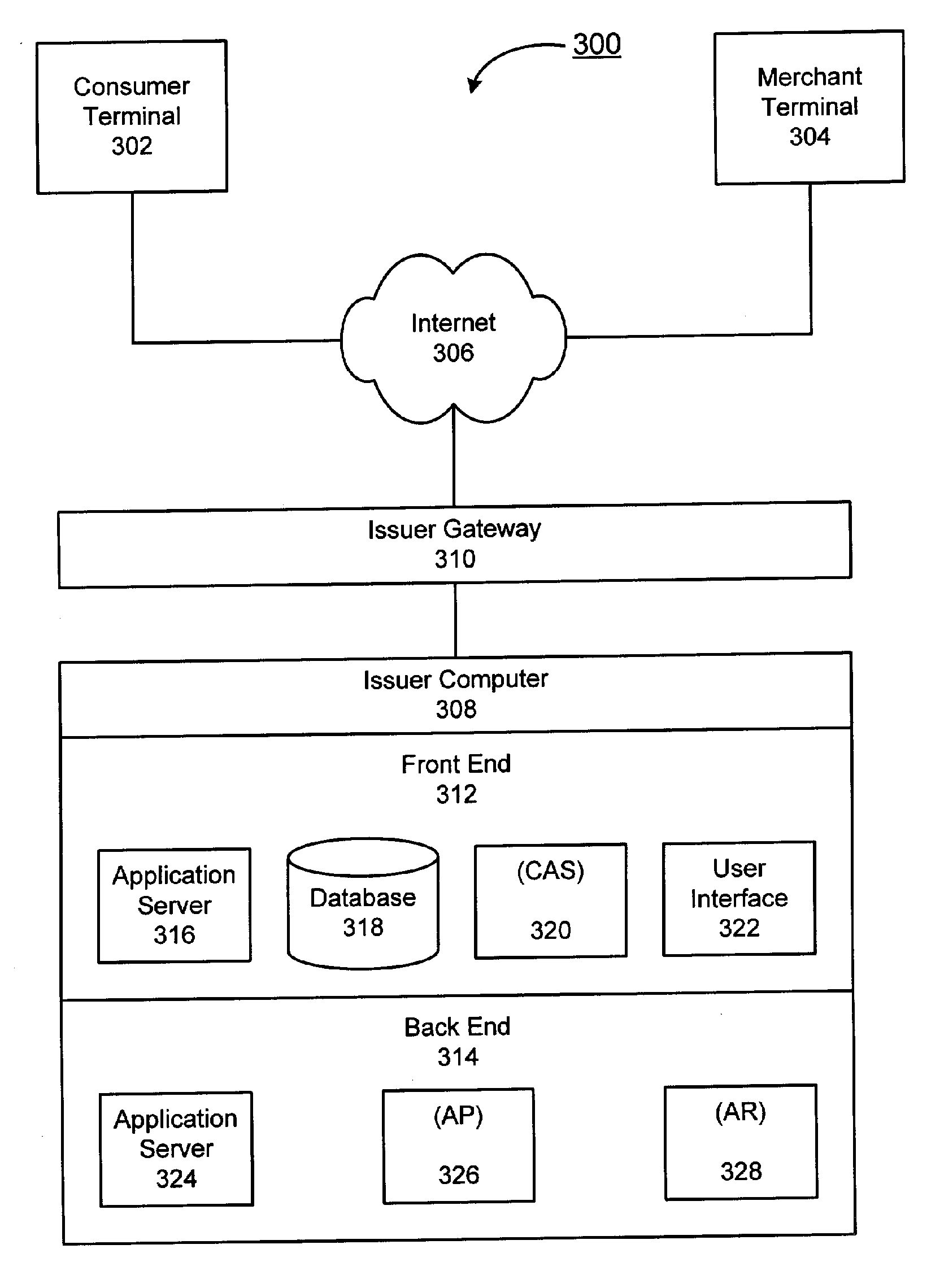
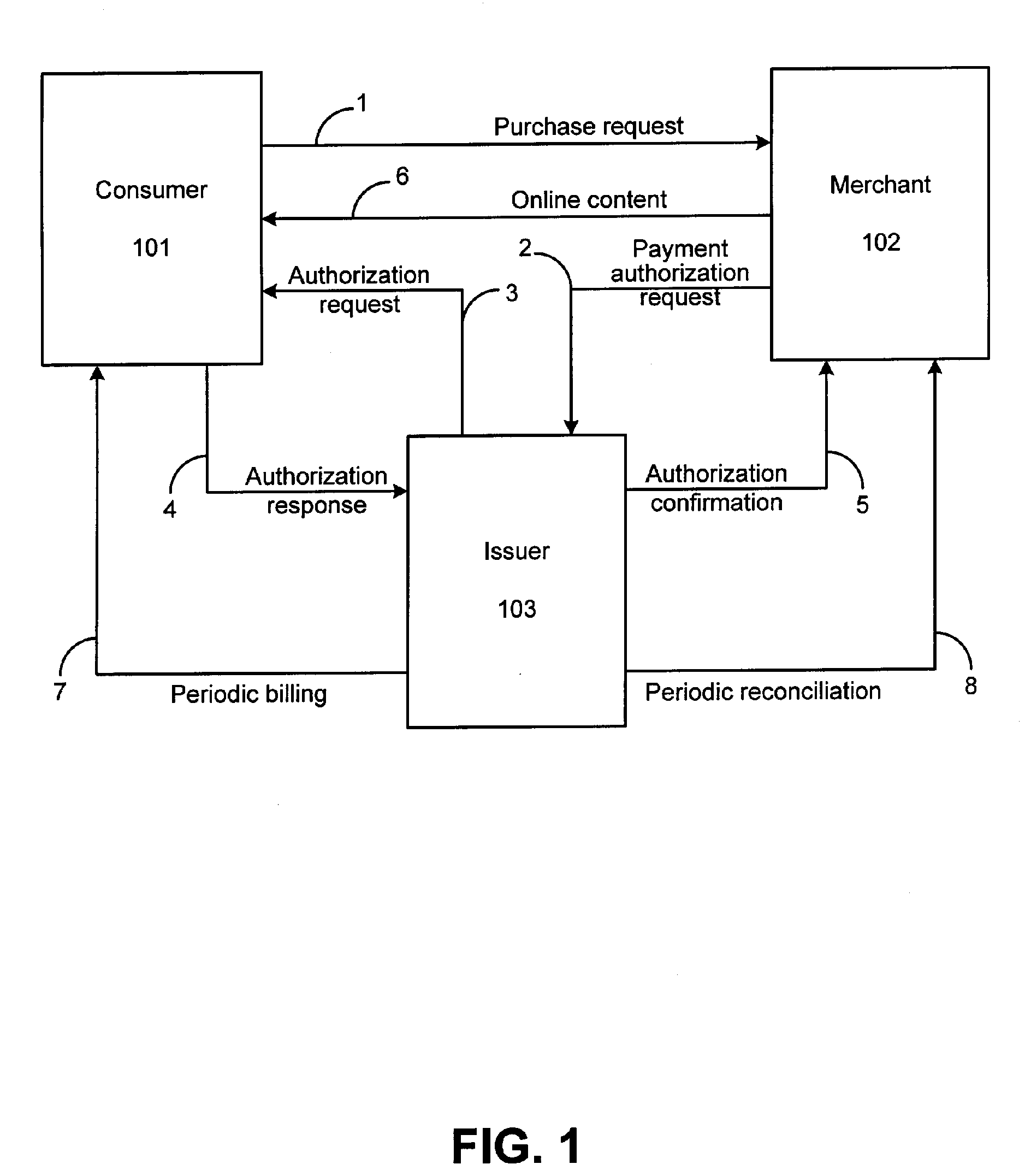
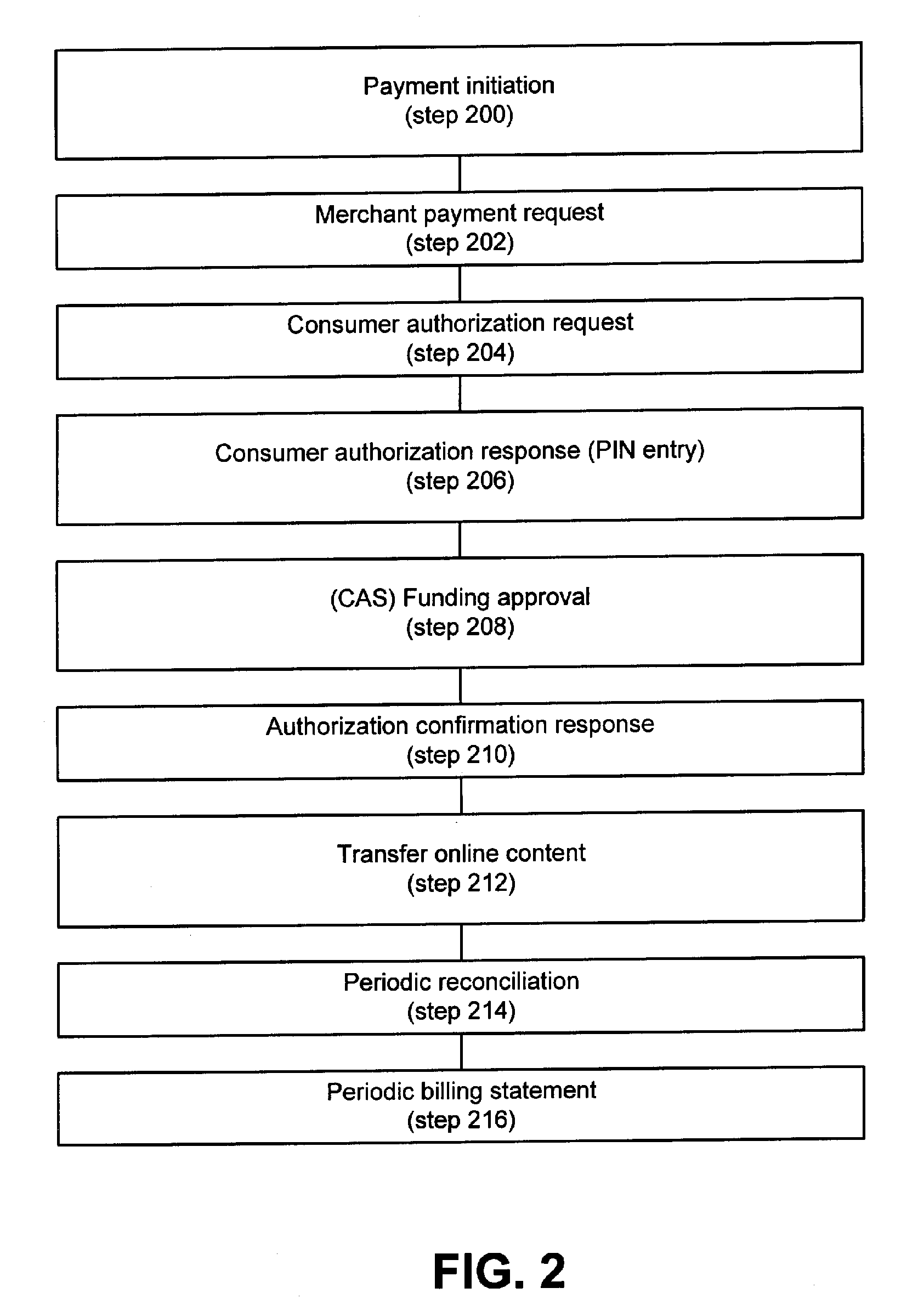
System for facilitating online electronic transactions
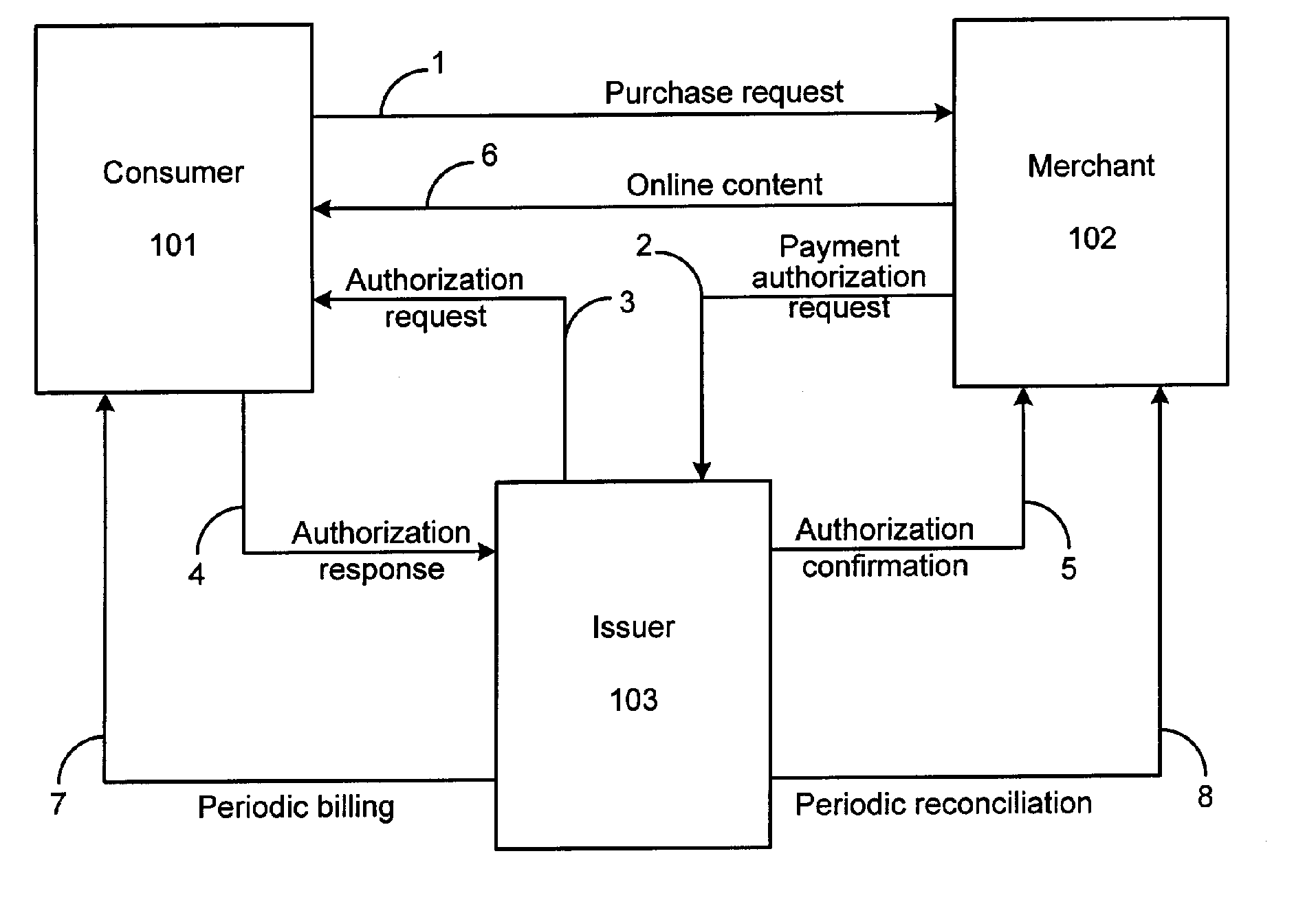
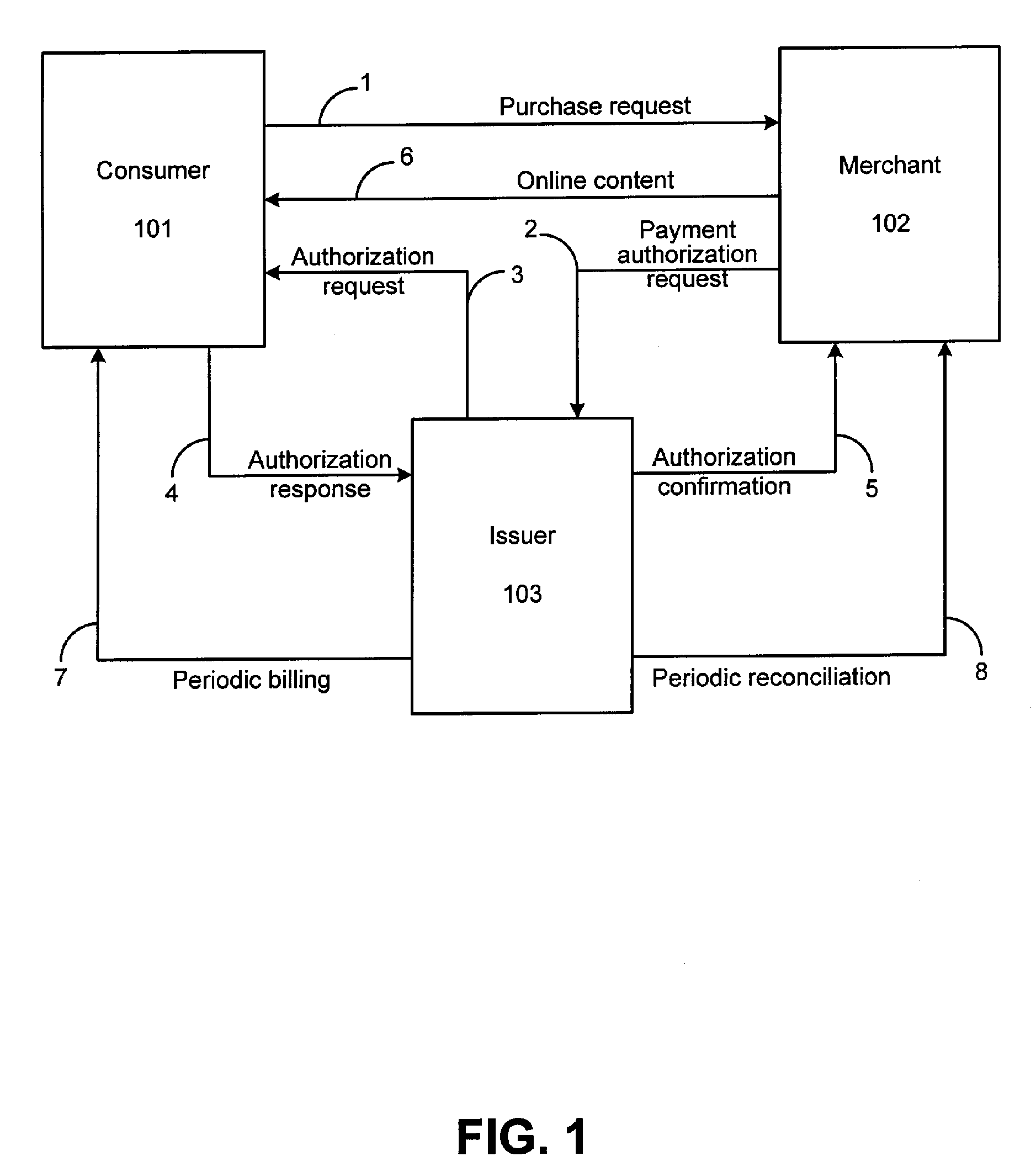
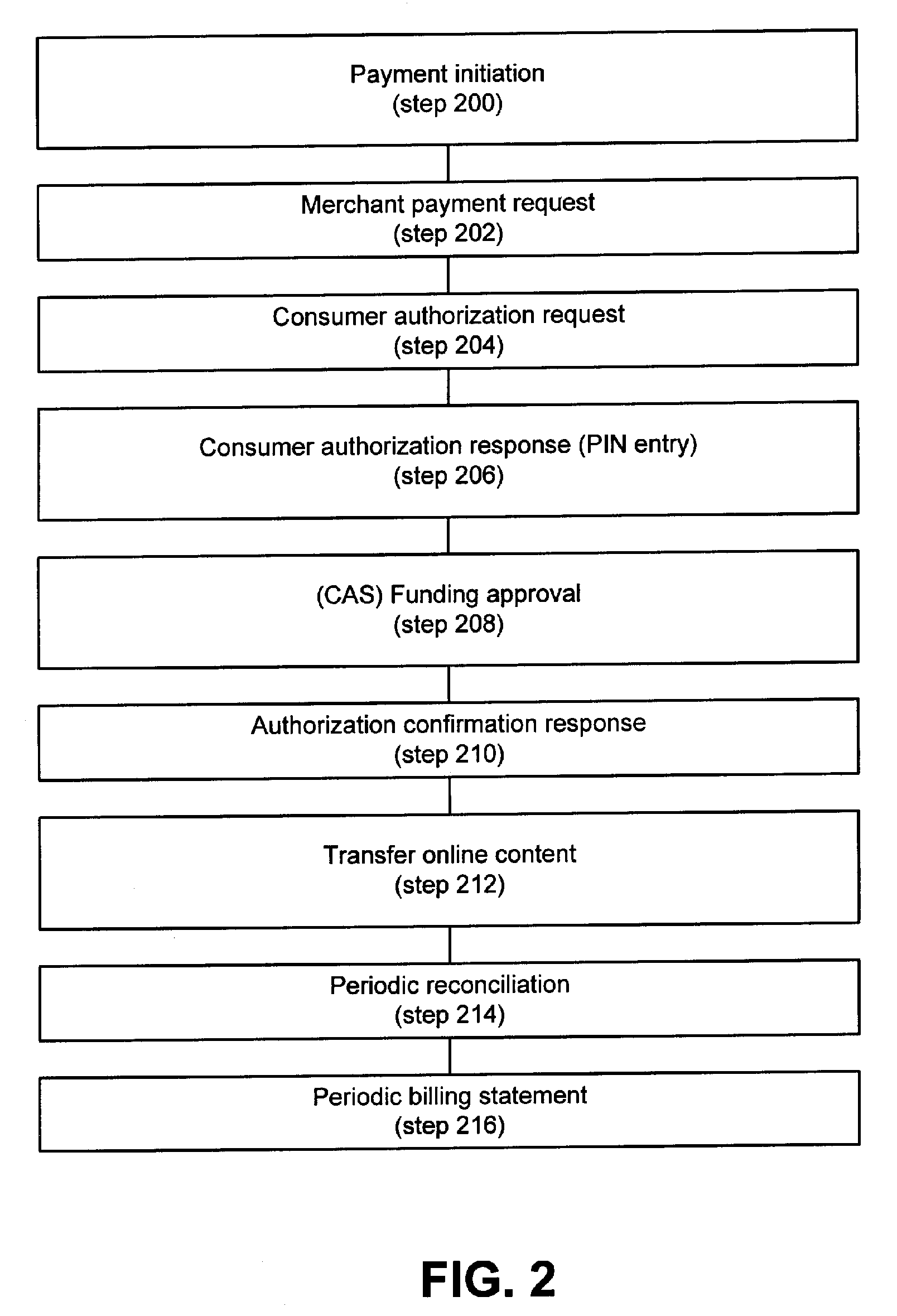
ActiveUS7210620B2Facilitates secure online content micropaymentsWell formedComplete banking machinesFinancePaymentWeb service
The invention provides systems and methods within existing business and technology infrastructures and processes for facilitating an electronic transaction including payment by an account issuer to a merchant for online purchases by a consumer. The invention uses a web services model including request and response messages to provide simplified authentication and authorization through entry of the consumer's PIN, without the release of the consumer's account or billing information to the merchant. The invention reduces authorization processing, and reduces the transaction fees for online transactions, increasing the viability of lower value transactions.
Owner:AMERIPRISE FINANCIAL
Leveraging Collaborative Cloud Services to Build and Share Apps
InactiveUS20110078243A1Facilitate targeted searchFacilitates targeted mobile searchesDigital data information retrievalText processingClient-sideContext specific
The present invention includes systems and methods for retrieving information via a flexible and consistent targeted search model that employs interactive multi-prefix, multi-tier and dynamic menu information retrieval techniques (including predictive text techniques to facilitate the generation of targeted ads) that provide context-specific functionality tailored to particular information channels, as well as to records within or across such channels, and other known state information. Users are presented with a consistent search interface among multiple tiers across and within a large domain of information sources, and need not learn different or special search syntax. A thin-client server-controlled architecture enables users of resource-constrained mobile communications devices to locate targeted information more quickly by entering fewer keystrokes and performing fewer query iterations and web page refreshes, which in turn reduces required network bandwidth. Applications are built by leveraging existing collaborative cloud services that enable the maintenance and sharing of user content.
Owner:BOOPSIE INC
Method and apparatus for developing and checking technical configurations of a product
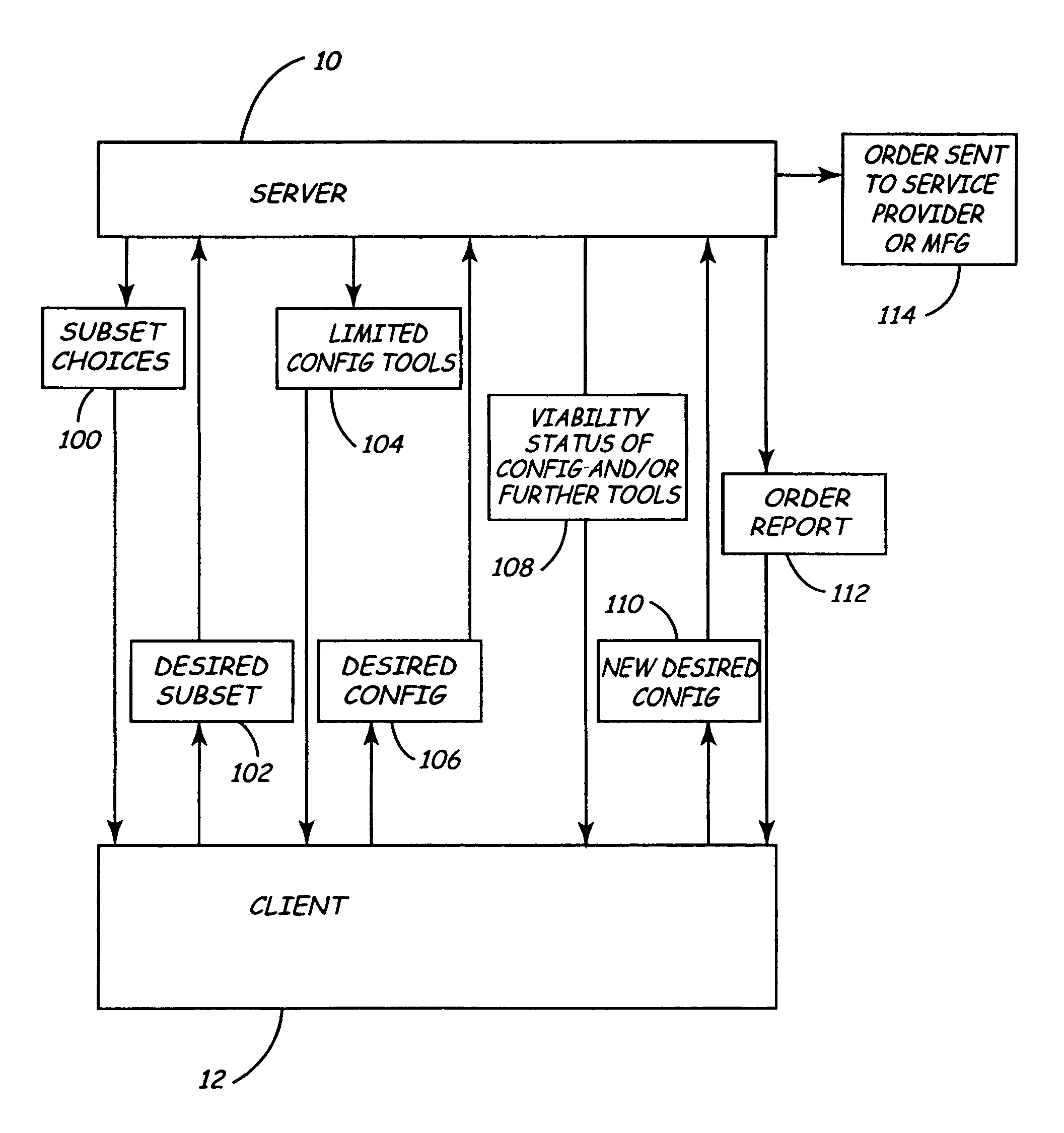
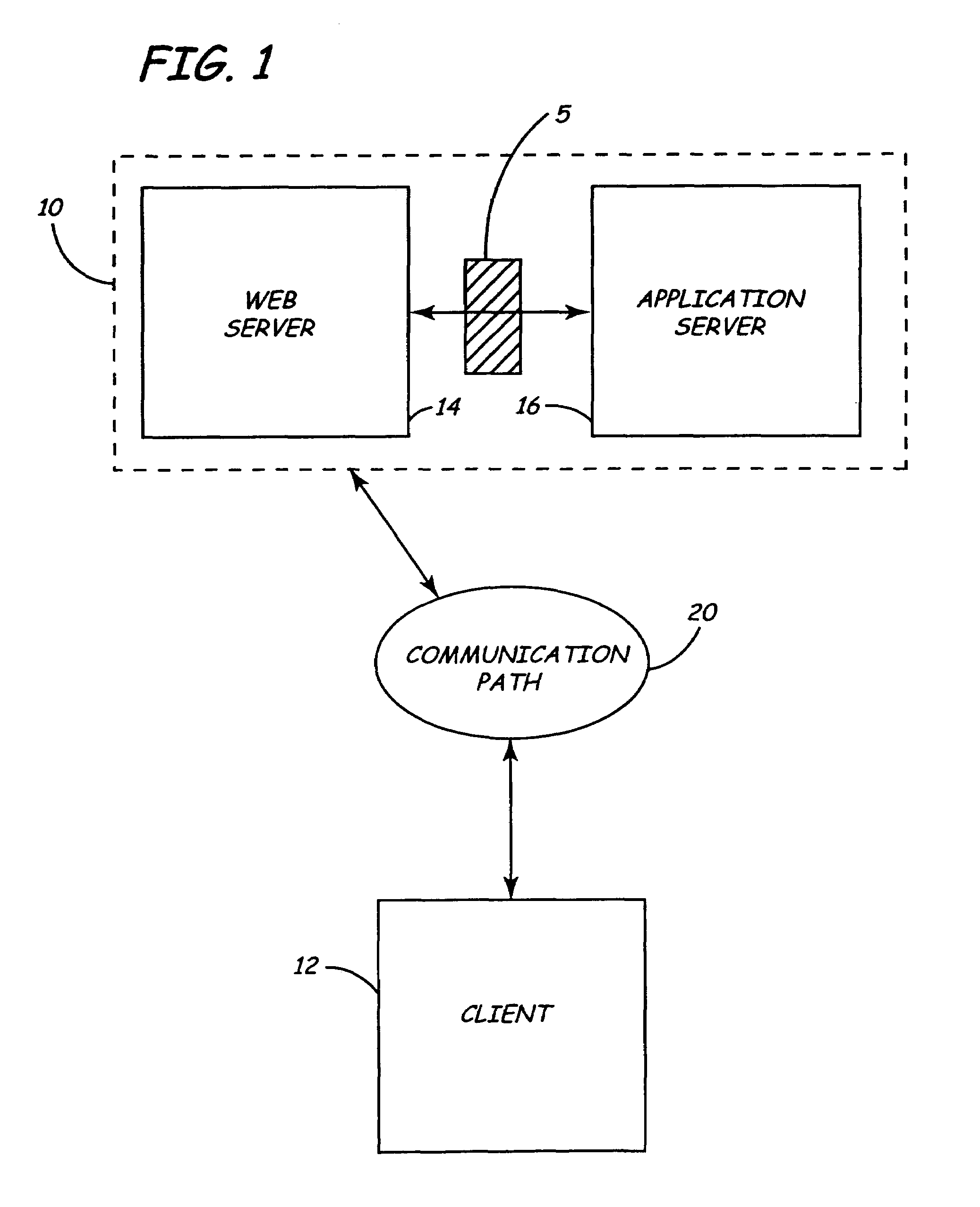
InactiveUS7003548B1Reduce interactionMinimal data transferMultiple digital computer combinationsCAD network environmentTechnical communicationClient-side
A method for developing a technical configuration and electronically delivering to a client from a server an order report for the technical configuration. The method comprises interactively eliciting and electronically receiving from a user on the client a desired technical configuration, wherein the act of interactively eliciting and electronically receiving comprises providing to the client from the server a limited configuration engine and performing a first, limited check on the viability of the desired technical configuration on the client using the limited configuration engine; performing a second, final check on the viability of the desired technical configuration using a full configuration engine on the server; and, in response to the final check, preparing and outputting on the client an electronic order report.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Large-mode-area optical fibers with reduced bend distortion
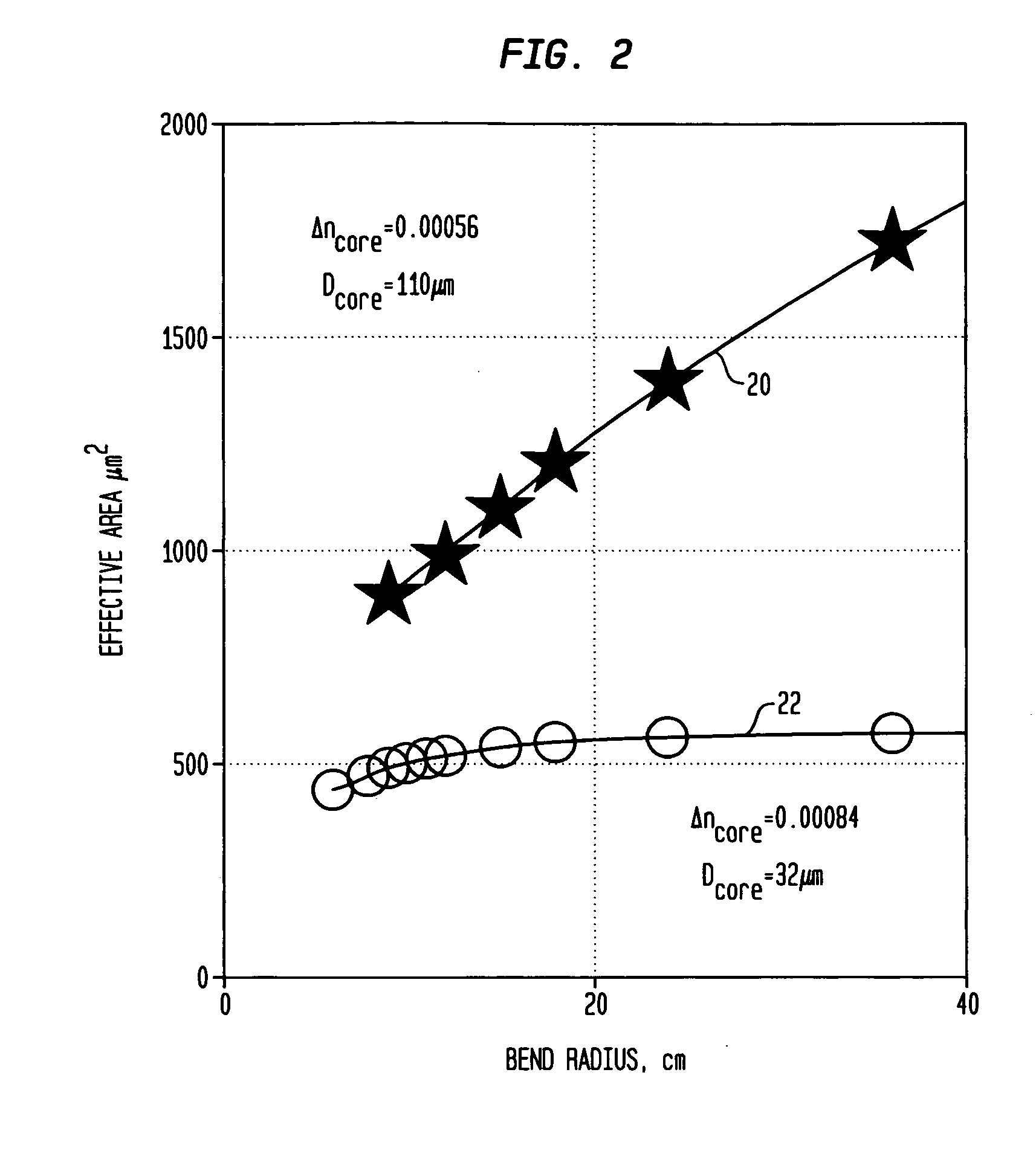
ActiveUS20090059353A1Reduces effective transverse mode areaReduce interactionGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsEngineeringBend radius
In a LMA optical fiber the index of the core region is graded (i.e., as viewed in a radial cross-section) and has a grading depth of Δng, as measured from a central maximum at or near the axis to a lower level that is not greater than the central maximum and not less than the index of the cladding region. When the fiber is to be bent at a bend radius, the grading depth, the radius of the core region, and the difference between the central maximum index and the cladding region index are configured to reduce bend distortion. They may also advantageously be configured to maximize the effective mode-field area of the fundamental mode, suppress higher order modes, and reduce bend loss. In a preferred embodiment, the core region includes a centralized gain region, which in turn includes a dark region that is no more than 30% of the area of the gain region. Also described is a method of making such LMA fibers.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Device for preparing a hot beverage
InactiveUS7412921B2Improve foaming qualityReduce riskReady-for-oven doughsBeverage vesselsInternal pressureWater flow
The invention relates to a capsule for the preparation of a beverage obtained by supplying hot water within the capsule under pressure and releasing the beverage from the capsule. The capsule includes a food substance therein, a first surface adapted to be traversed by a flow of water entering the capsule, and a second surface adapted to be traversed by a flow of beverage exiting the capsule. The second surface is adapted to deform outwardly upon action of the inside water pressure thereon. Also, that surface includes at least one opening member capable of deforming inwards the capsule upon a mechanical reaction force applied from outside onto the closure member as a result of the deformation of the second surface due to the build-up of the inside pressure.
Owner:NESTEC SA
System for facilitating online electronic transactions
ActiveUS20060144925A1Increase contentReduced consumer-merchant-issuer interactionComplete banking machinesFinancePaymentWeb service
The invention provides systems and methods within existing business and technology infrastructures and processes for facilitating an electronic transaction including payment by an account issuer to a merchant for online purchases by a consumer. The invention uses a web services model including request and response messages to provide simplified authentication and authorization through entry of the consumer's PIN, without the release of the consumer's account or billing information to the merchant. The invention reduces authorization processing, and reduces the transaction fees for online transactions, increasing the viability of lower value transactions.
Owner:AMERIPRISE FINANCIAL
Ionizer and method for gas-cluster ion-beam formation
ActiveUS7173252B2Improve efficiencyImprove throughputParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansPlasma electronElectron source
An ionizer for forming a gas-cluster ion beam is disclosed including inlet and outlet ends partially defining an ionization region traversed by a gas-cluster jet and one or more plasma electron source(s) for providing electrons to the ionizing region for ionizing at least a portion of the gas-clusters to form a gas-cluster ion beam. One or more sets of substantially linear rod electrodes may be disposed substantially parallel to and in one or more corresponding partial, substantially cylindrical pattern(s) about the gas-cluster jet axis, wherein some sets are arranged in substantially concentric patterns with differing radii. In certain embodiments, the ionizer includes one or more substantially linear thermionic filaments disposed substantially parallel to the gas-cluster jet axis, heating means, electrical biasing means to judiciously bias sets of the linear rod electrodes with respect to the thermionic filaments to achieve electron repulsion.
Owner:TEL EPION
Coke-oven gas methanation catalyst and preparation method thereof
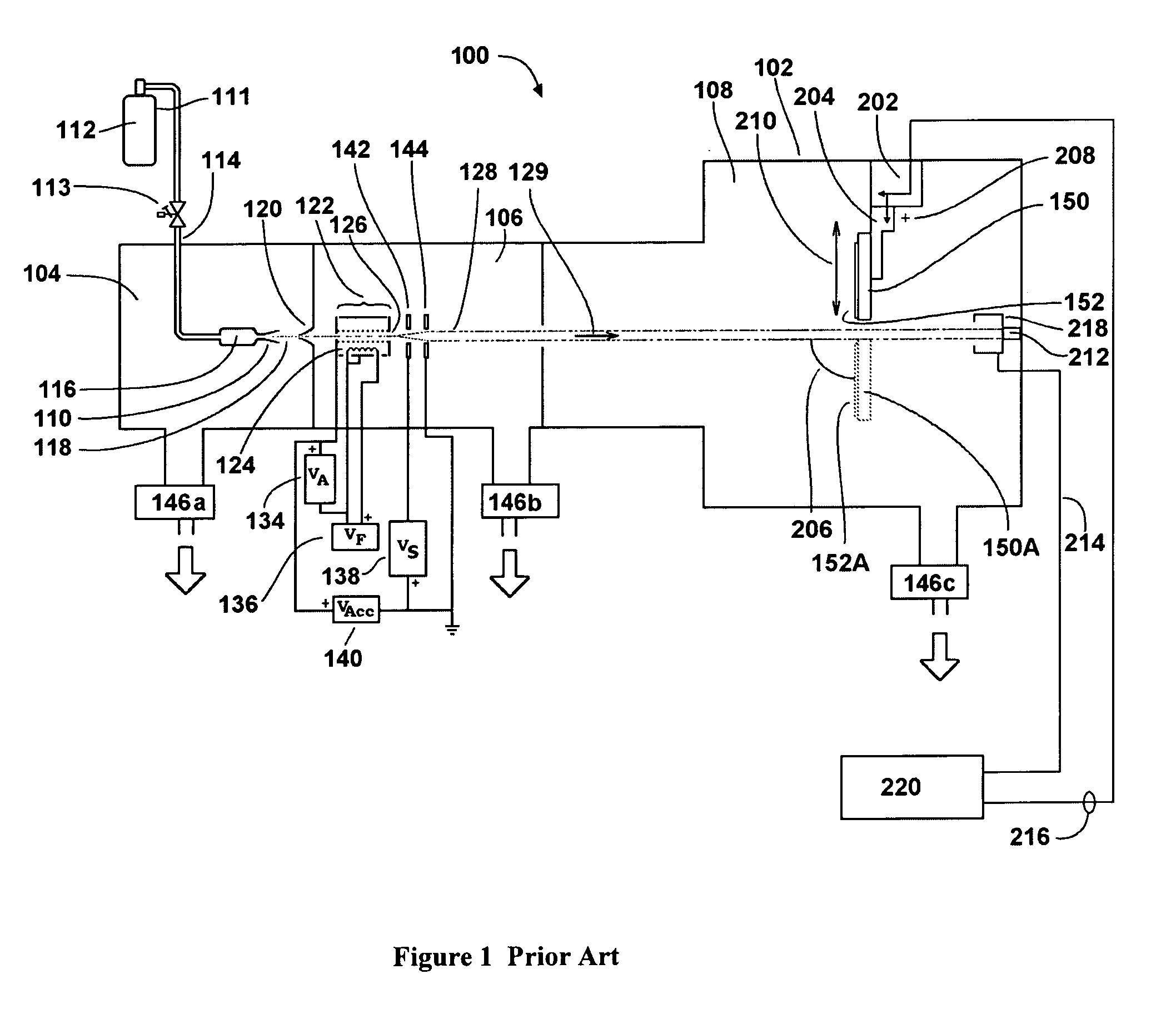
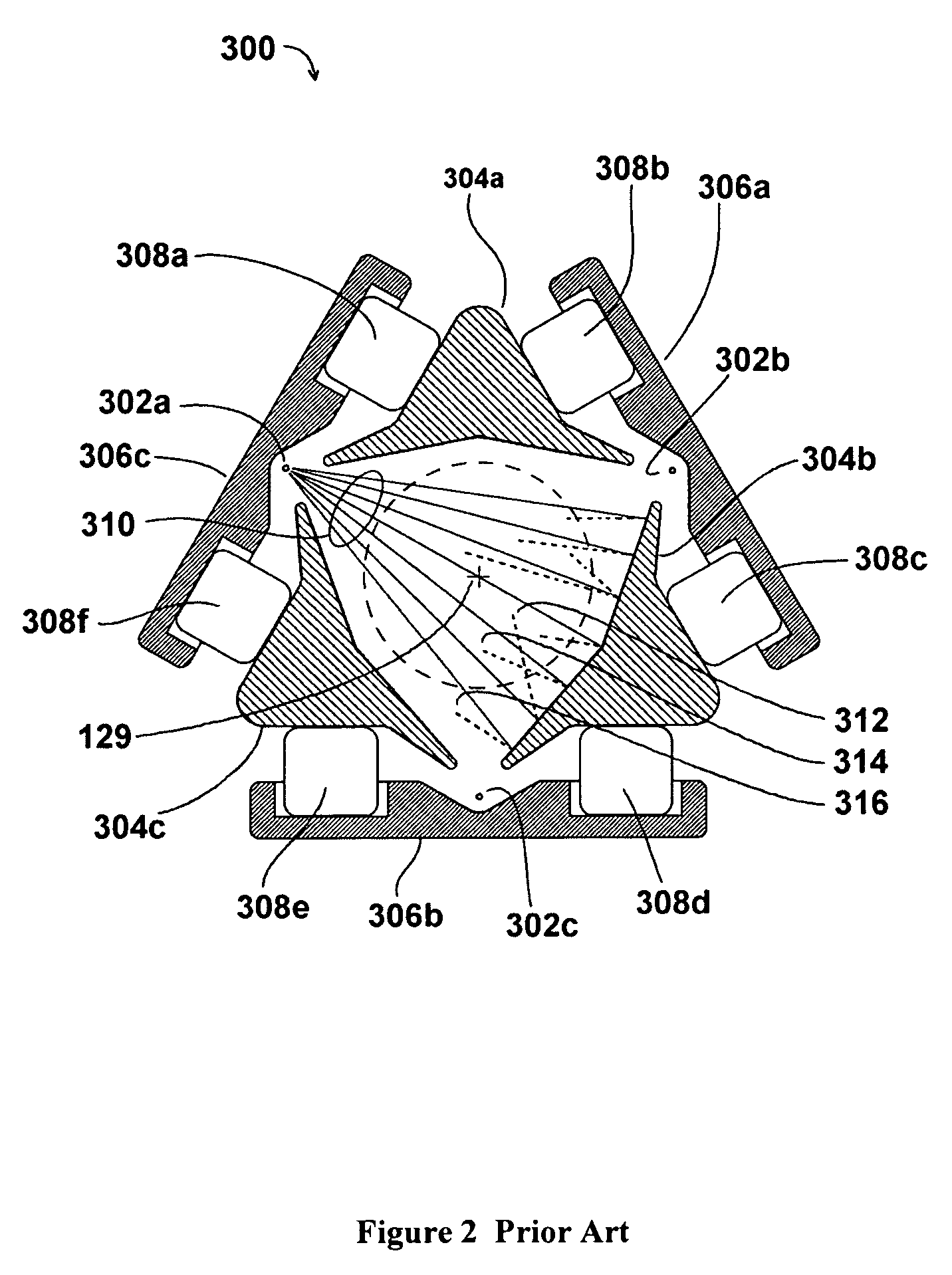
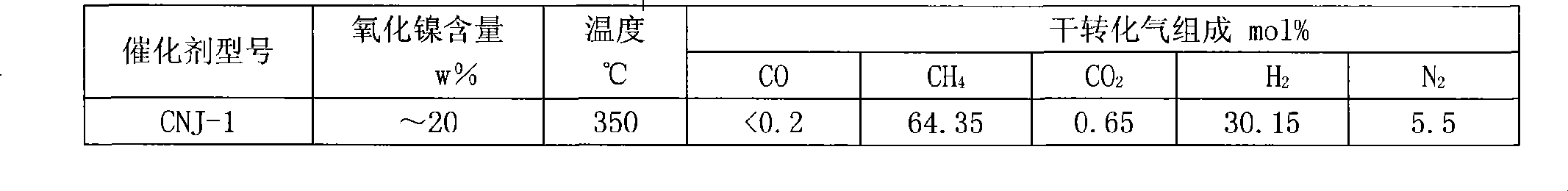
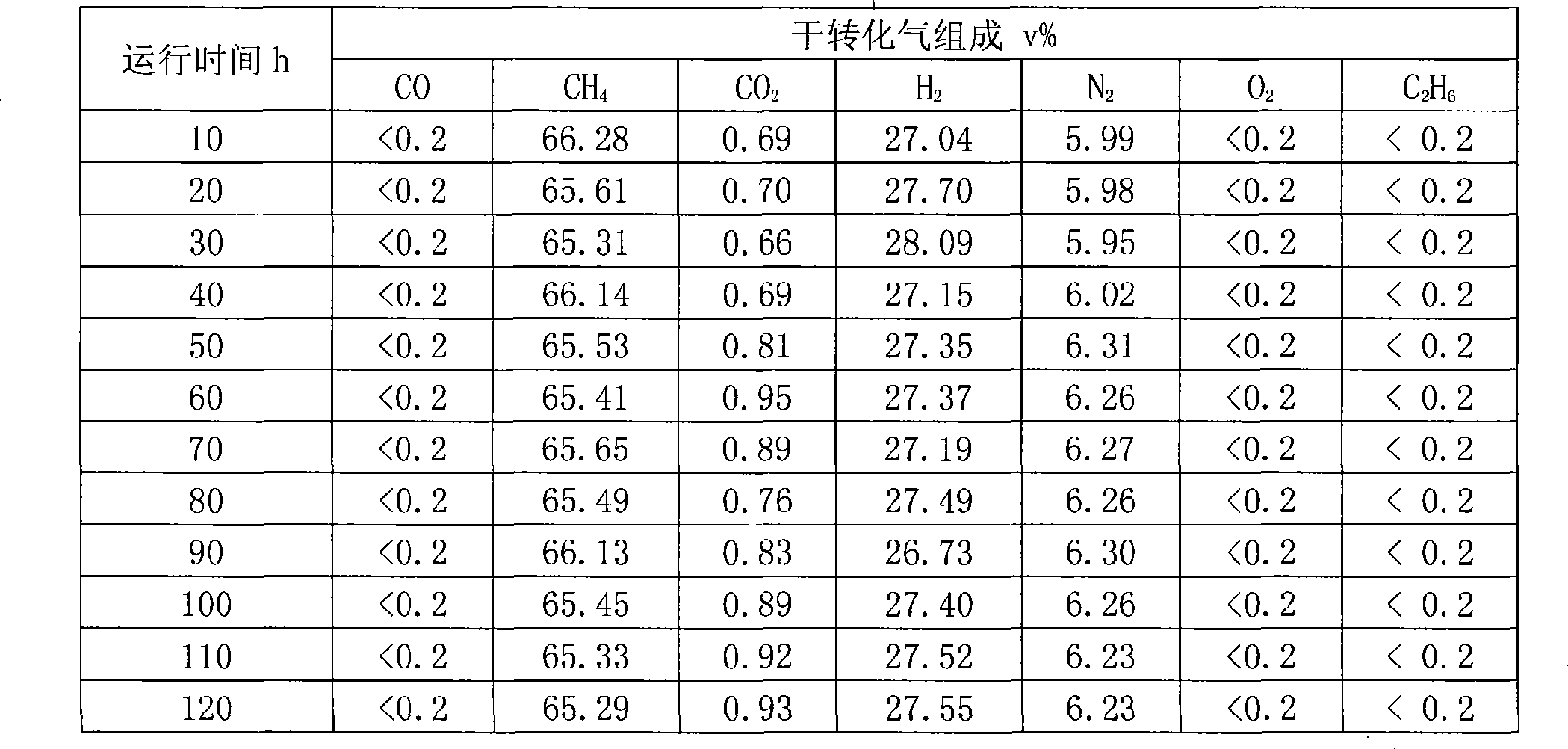
ActiveCN101391218AHigh activityImprove carbon resistanceHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMethanationActive component
The invention discloses a coke oven gas methanation catalyst, which takes Al2O3 as a carrier, nickel as a main active component, and MgO as an auxiliary agent; wherein: the active component nickel exists in the catalyst in the form of NiO, and the carrier Al2O3 and the auxiliary agent MgO form a carrier structure of magnesia-alumina spinel; the main components respectively include, by weight percentage: 5 percent to 20 percent of NiO, 30 percent to 80 percent of Al2O3, and 1 percent to 50 percent of MgO. The catalyst has the advantages of high strength, good activity, good thermal stability, excellent anti-coking performance and good low temperature activity, and also has the properties of transforming high hydrocarbon and good anti-oxidation. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the coke oven gas methanation catalyst.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Methods for the optical transmission of polarization multiplex signals
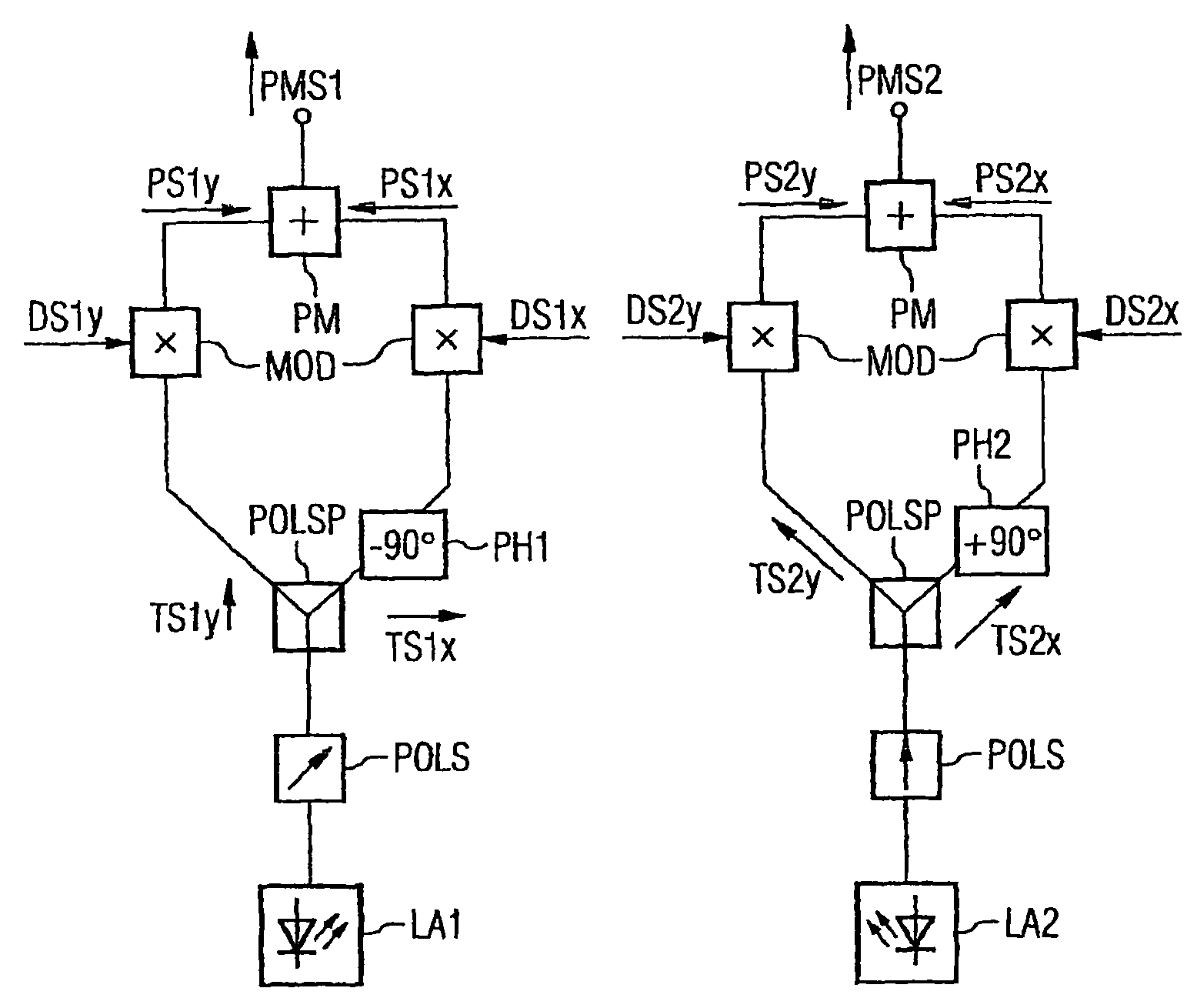
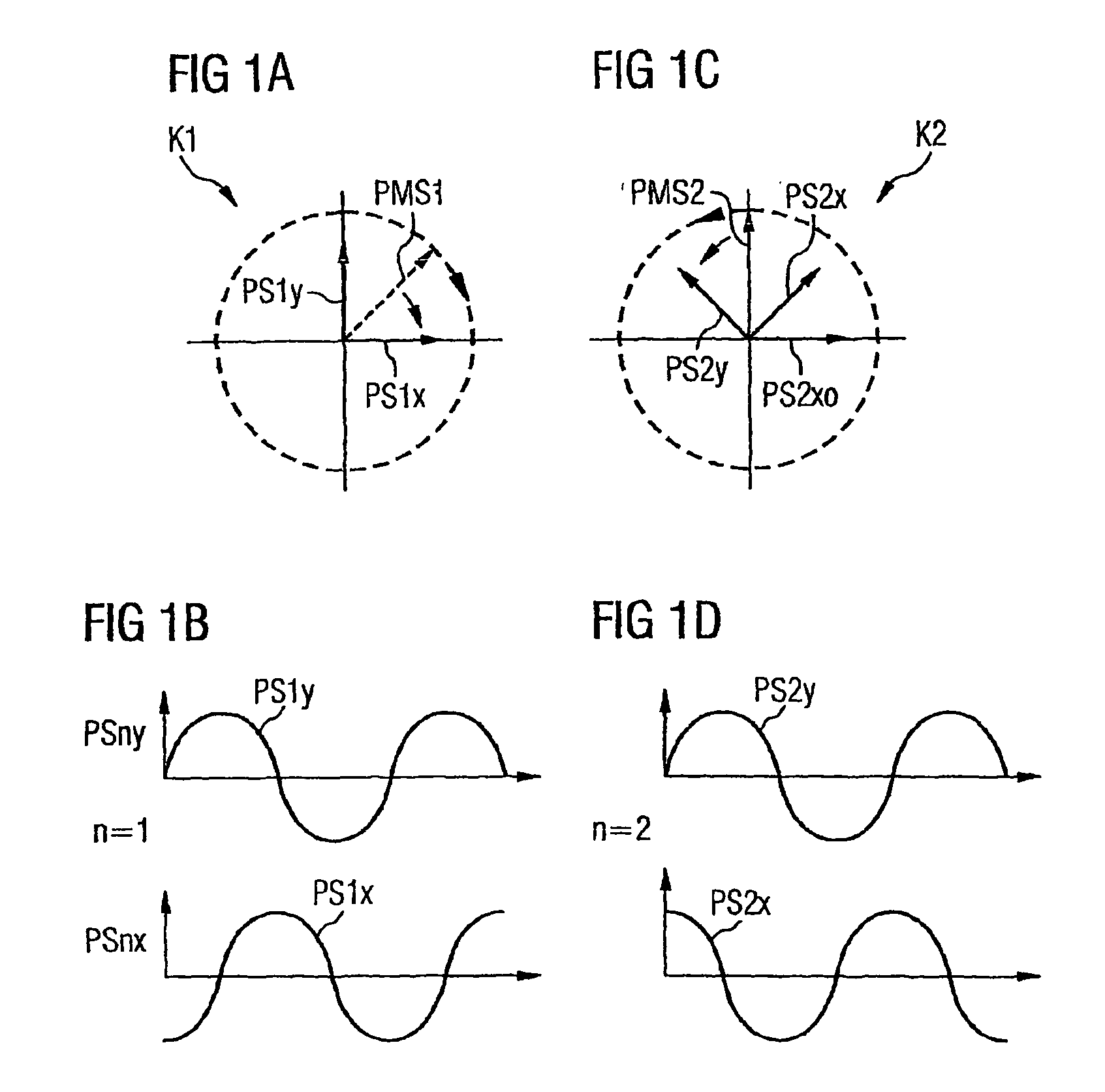
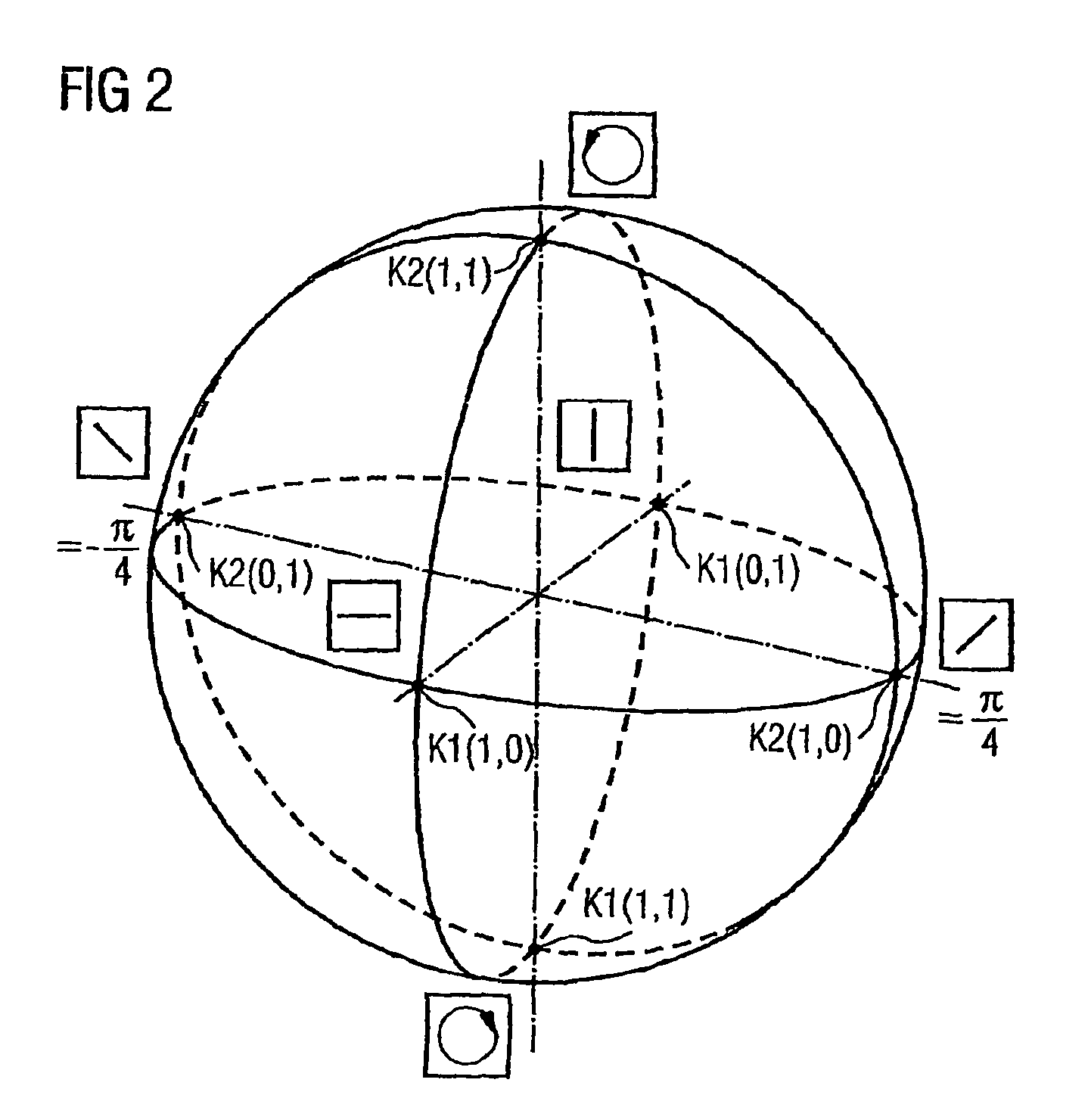
InactiveUS7865080B2Reduce interactionStrong mutual interferencePolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhysicsPolarization plane
In order to reduce mutual interferences between POLMUX and signals, the signals are transmitted with differed to each other carrying signals, thereby making it possible to obtain the circular polarization of each resulting POLMUX signal. Each second POLMUX signal is transmissible with an opposite circular polarization. In order to reduce also interferences when only one modulated data signal is transmitted through a POLMUX channel, a polarization plane of modulated data signals of each second POLMUX channel is turned at 45°. In a variant, polarization multiplex signals are produces and the resulting polarizations thereof in adjacent channels are perpendicular to each other.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com