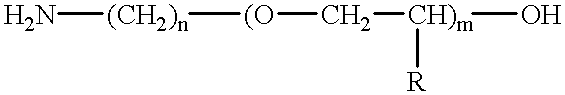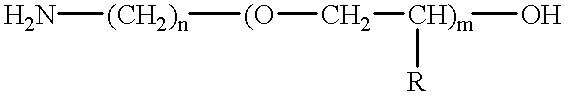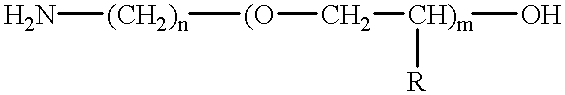Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60results about How to "Degrade solvent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermostable pigments, films and effect coatings, and mixtures for their production
InactiveUS6423246B1Reduce interactionDegrade solventLiquid crystal compositionsBoltsLiquid crystallineColor shift
A mixture of crosslinkable liquid-crystalline substances having a chiral phase (LC mixture), containing polymerizable groups, where at least 90% of the polymerizable groups are part of molecules containing at least two polymerizable groups (crosslinker molecules), wherein from 3.2 to 15 mmol of polymerizable groups are present per g of LC mixture. The crosslinked pigments show little color shift in the presence of solvents or upon application to substrate different temperatures.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
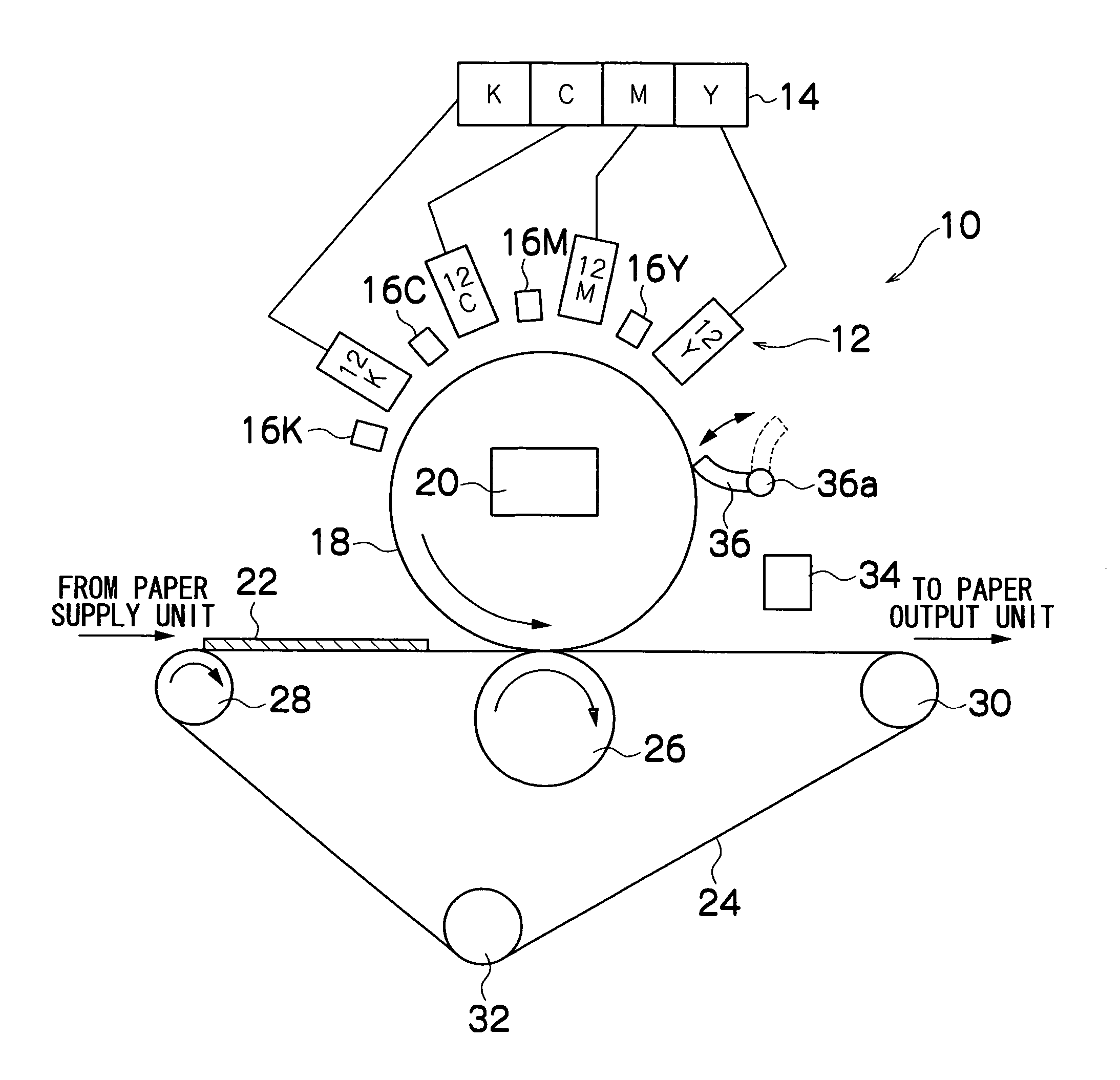
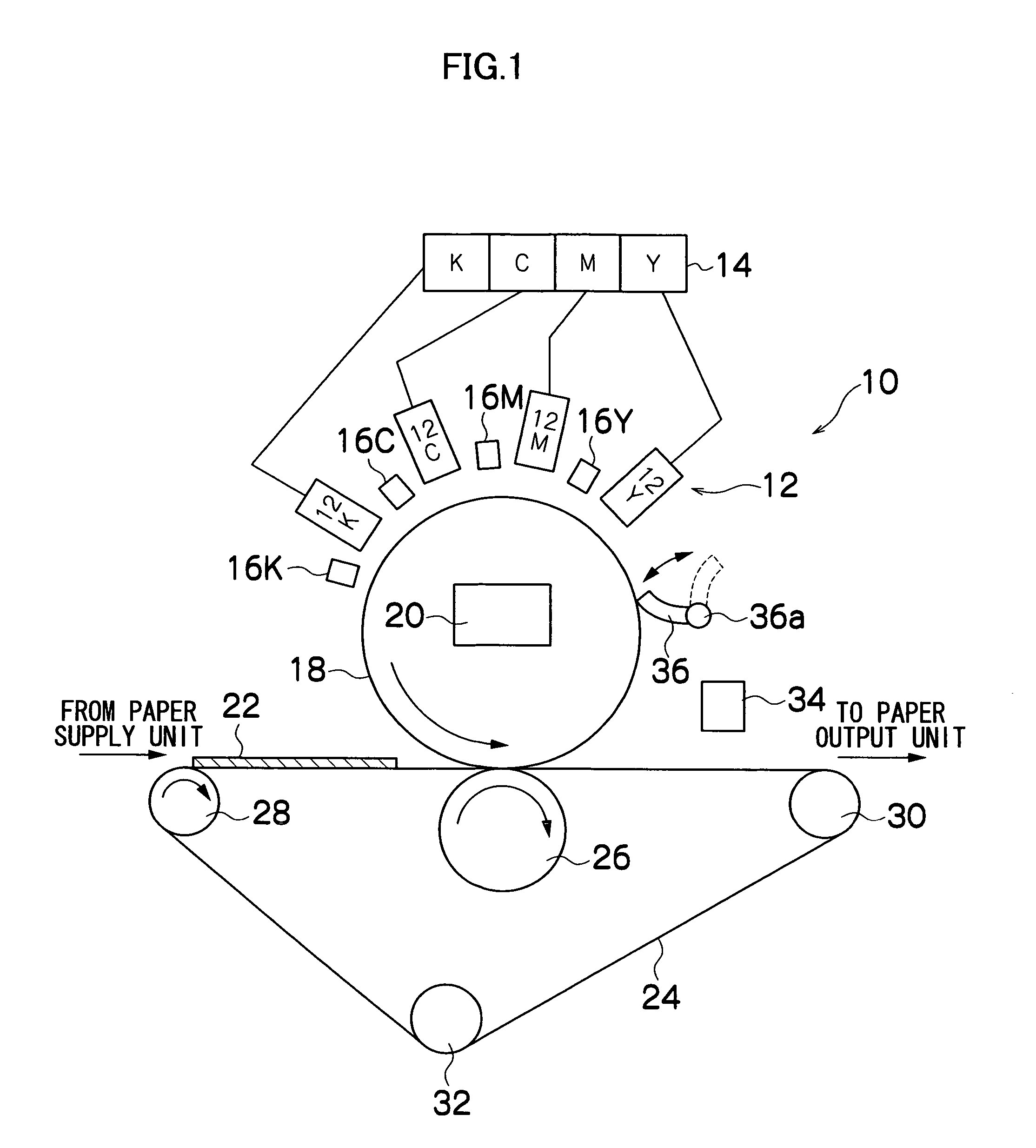
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060066704A1Improve image qualityReduce the amount requiredInking apparatusEvaporationImage formation
The image forming apparatus comprises: an ejection head which ejects droplets of a radiation curing liquid; an intermediate transfer medium on which an image is formed by the droplets ejected from the ejection head; an evaporation device which evaporates the droplets deposited on the intermediate transfer medium; a preliminary curing device which emits radiation onto the droplets deposited on the intermediate transfer medium in order to semi-cure the droplets so that the droplets do not blend with each other; and a transfer device which presses a recording medium against the intermediate transfer medium so that the image formed on the intermediate transfer medium is transferred onto the recording medium, wherein: the droplets deposited on the intermediate transfer medium are evaporated by the evaporation device; and the evaporated droplets are semi-cured by the radiation emitted from the preliminary curing device, and then the image formed on the intermediate transfer medium is transferred onto the recording medium by the transfer device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
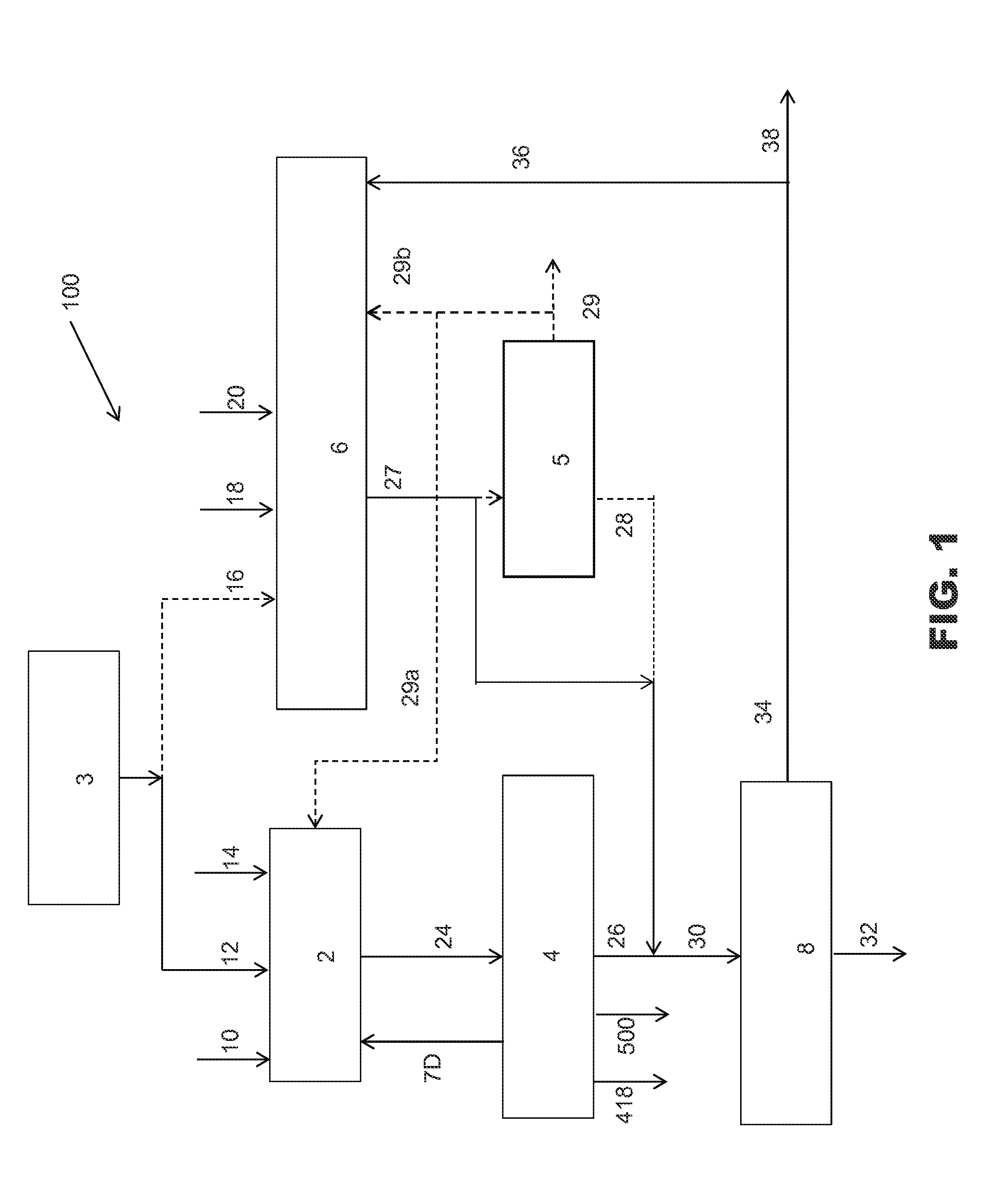
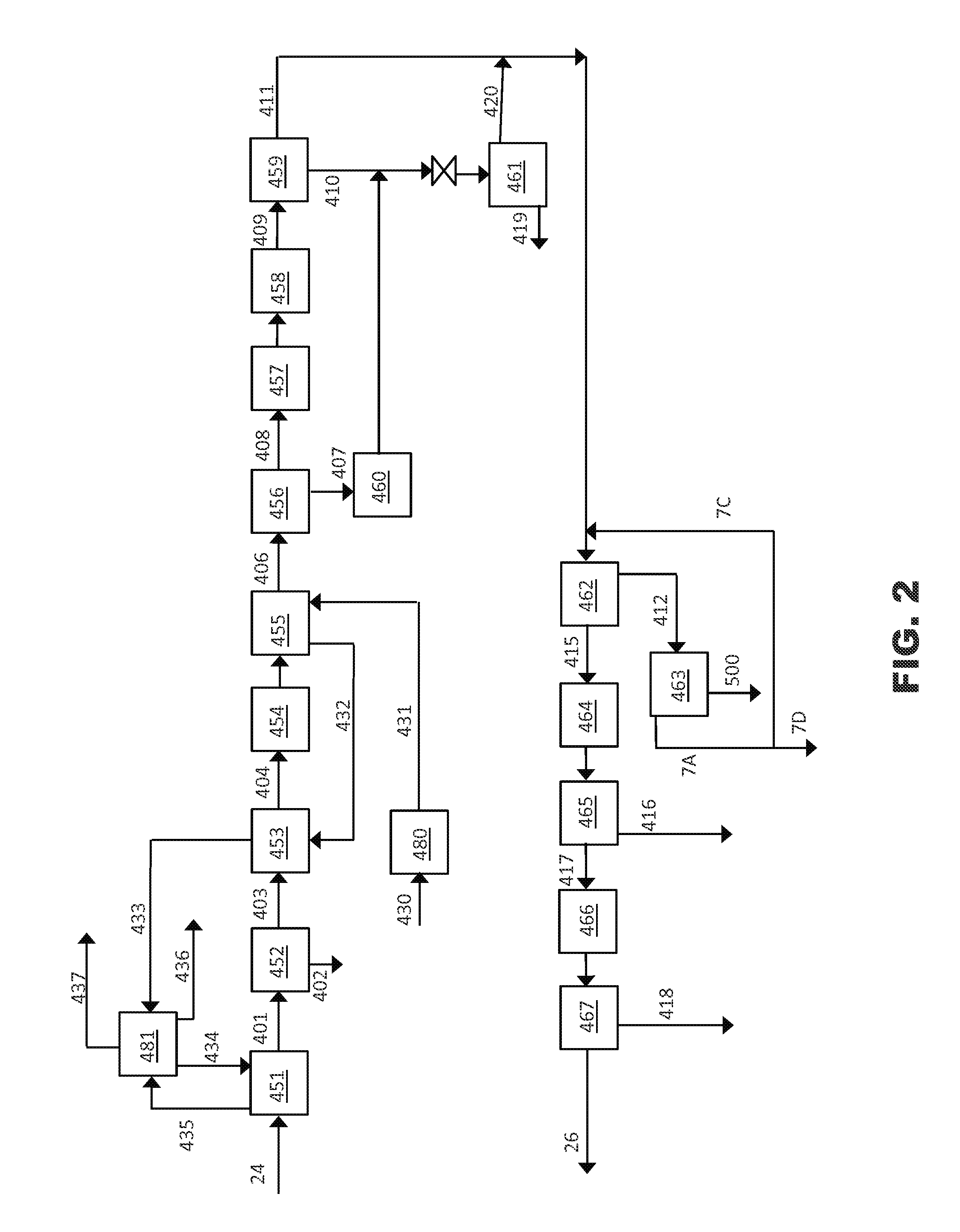
Acid gas management in liquid fuel production process
ActiveUS20150005398A1Promote formationLow costGas modification by gas mixingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionSyngasSteam reforming
A process and method for producing liquid fuel product from hydrogen and carbon monoxide containing streams produced by gasifying solid carbonaceous feedstock and steam reforming of light fossil fuels. The gasifier syngas is treated to preferentially remove at least 99% of sulfur containing impurities and less than 50% of the CO2 to produce a treated gasifier syngas and a CO2 enriched gas. The treated gasifier syngas and the light fossil fuel conversion unit product gas are combined to form a mixed syngas that is converted into a liquid fuel product. The CO2 enriched gas is used in the gasification unit.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
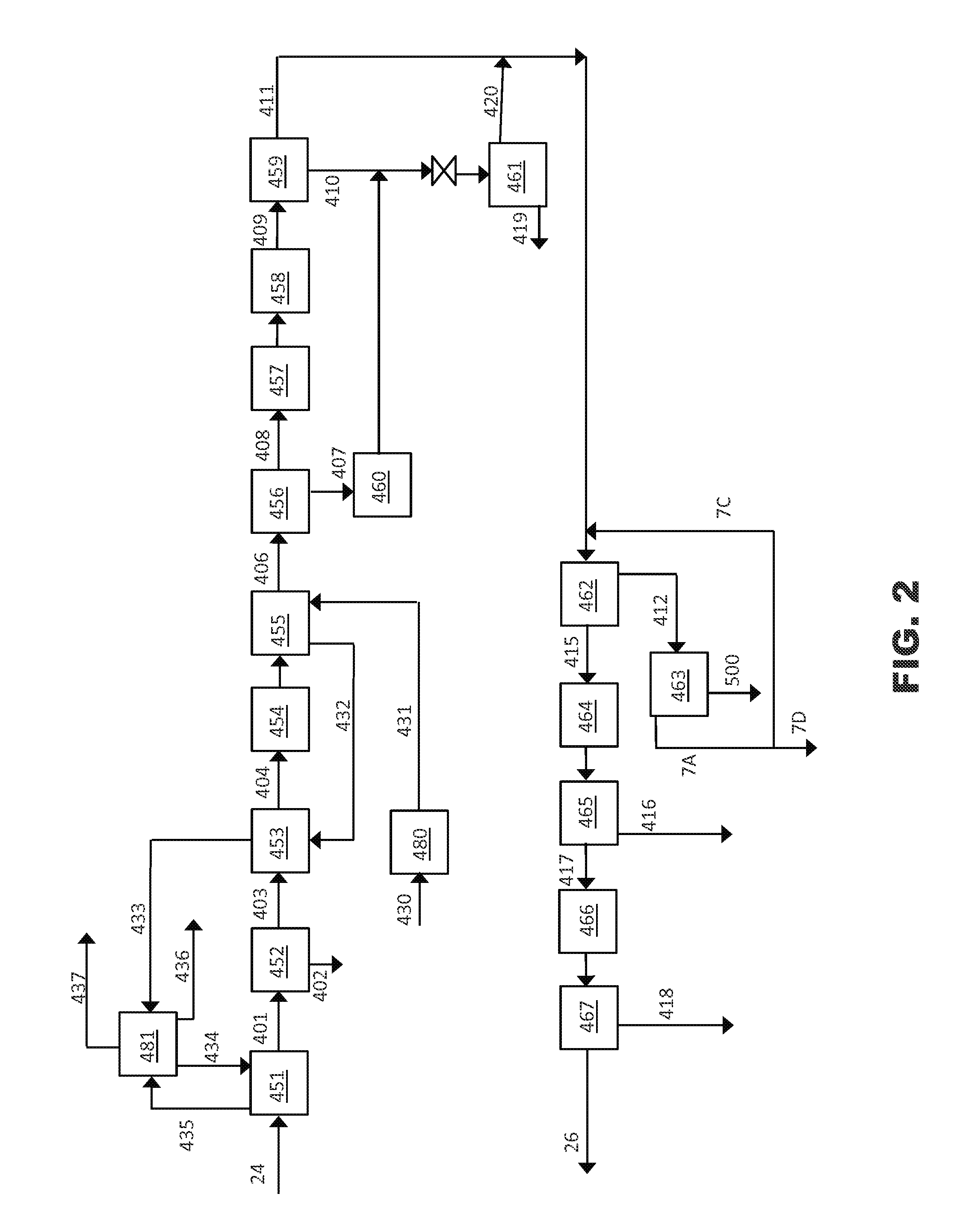
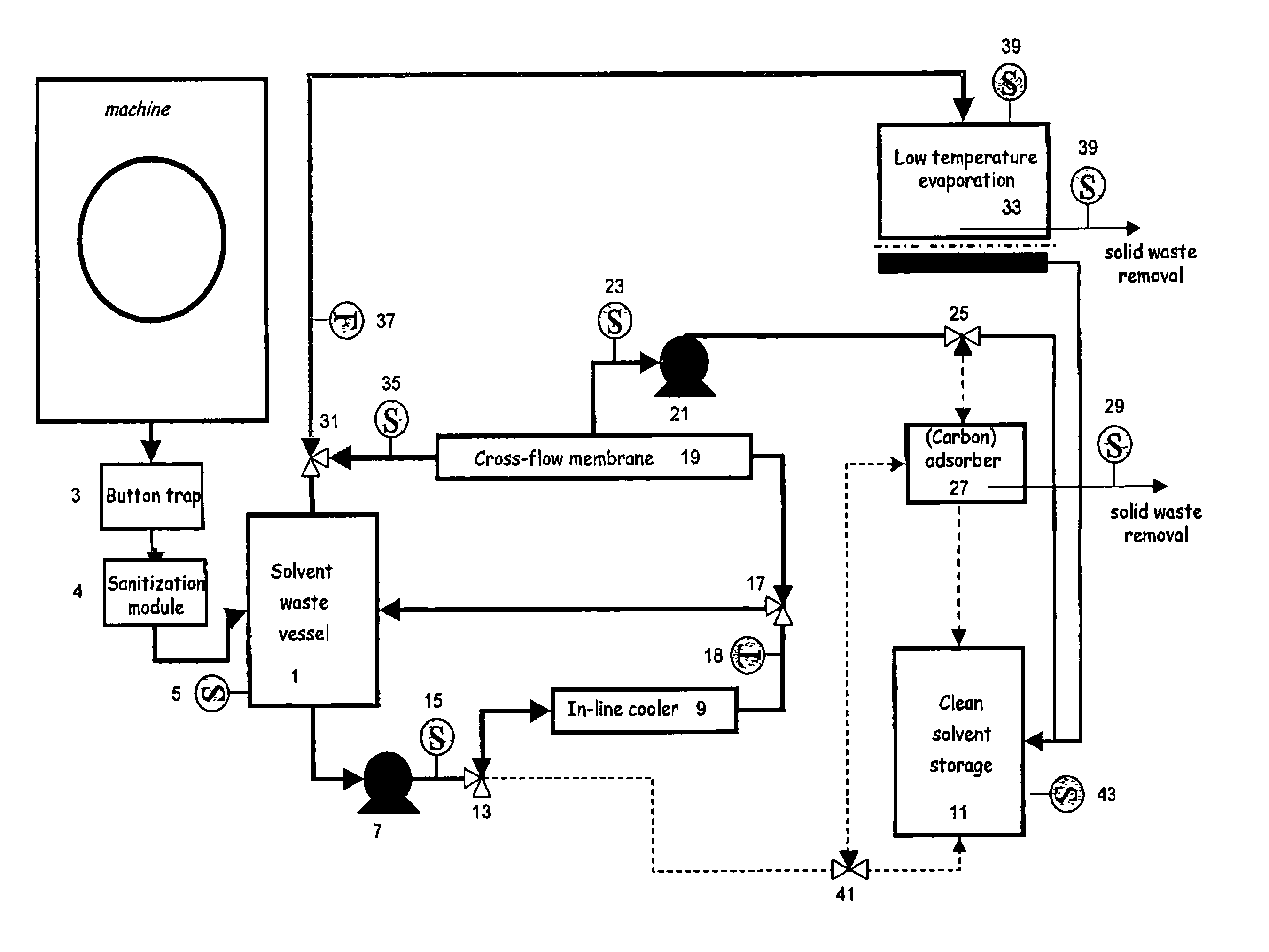
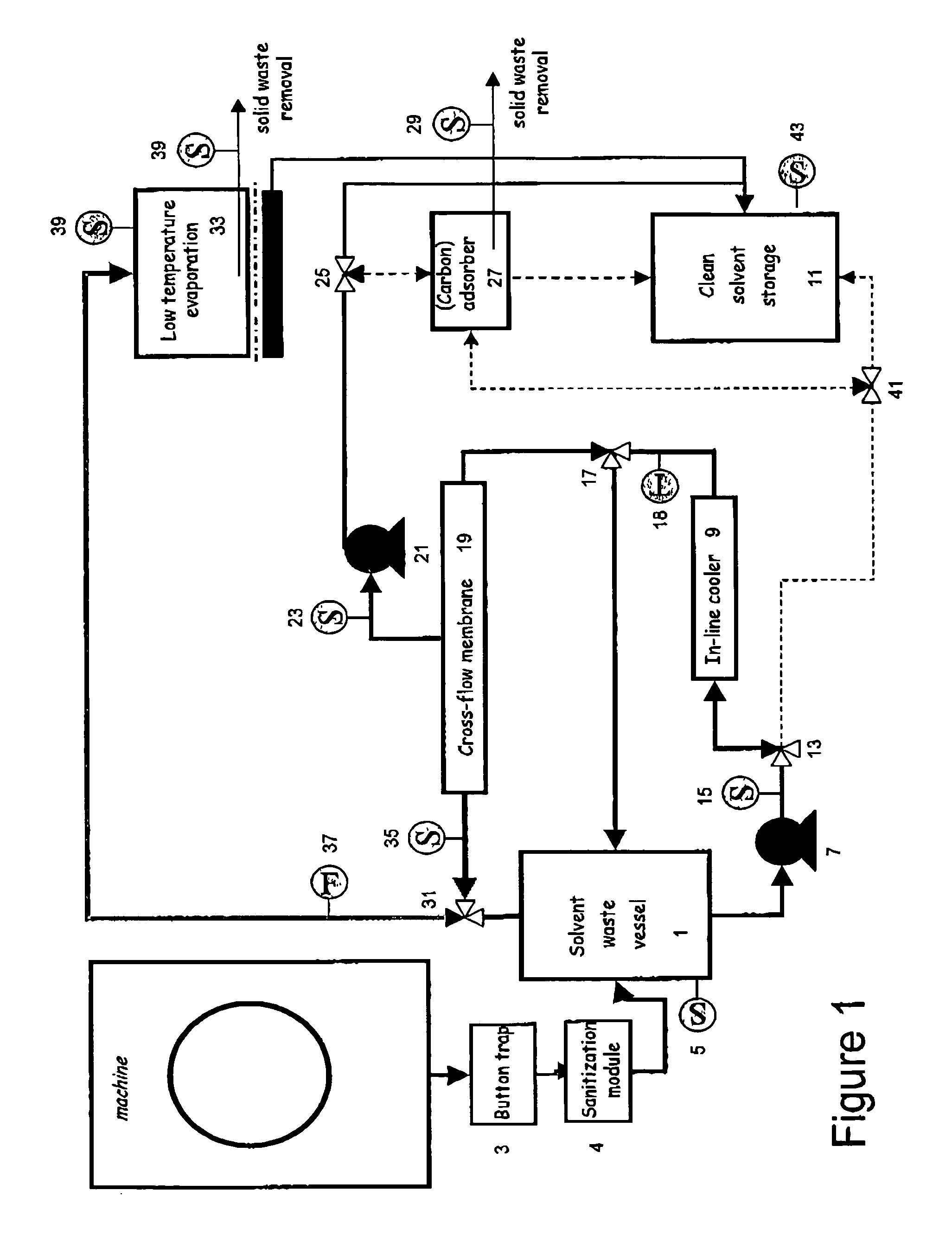
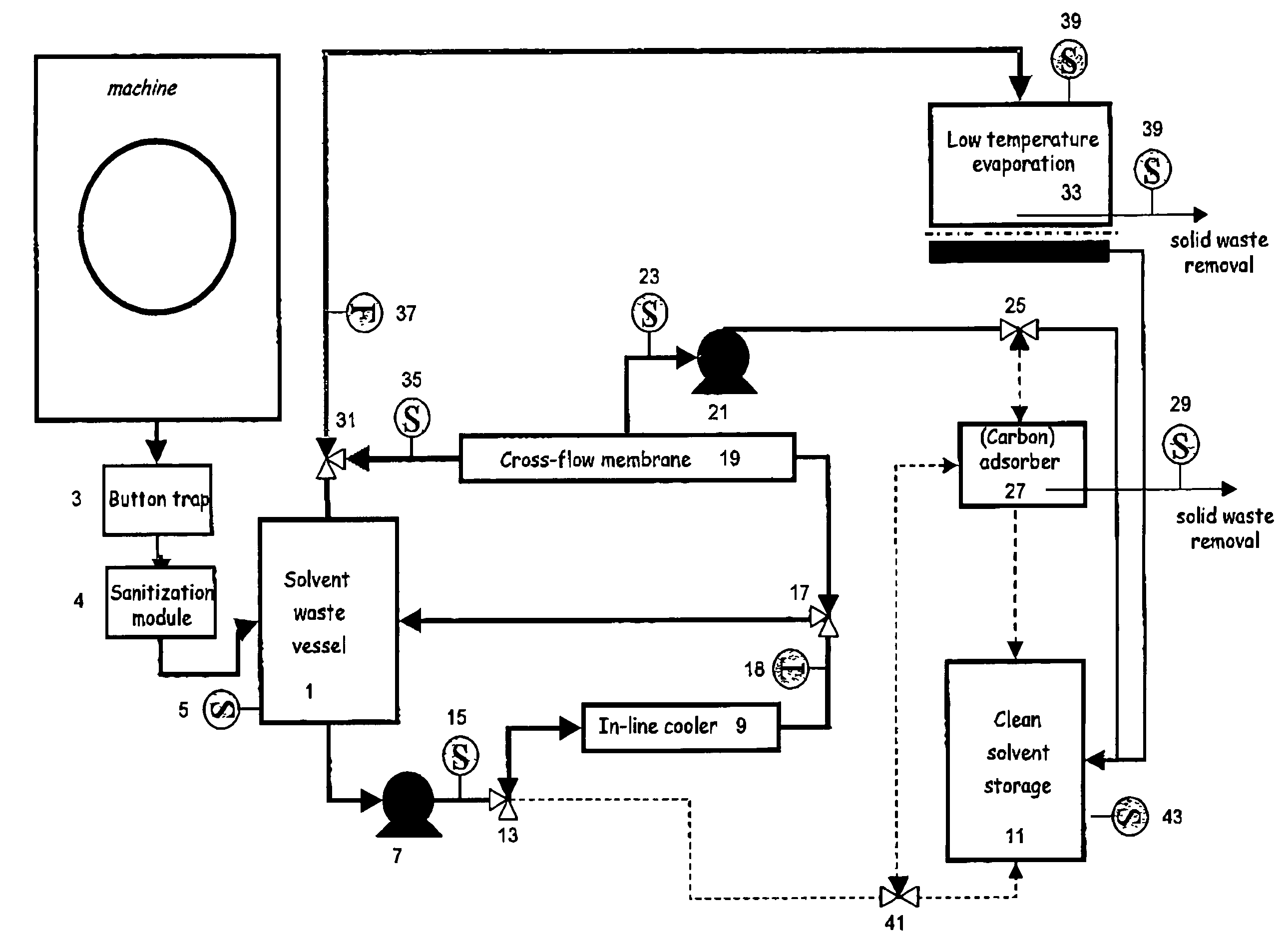
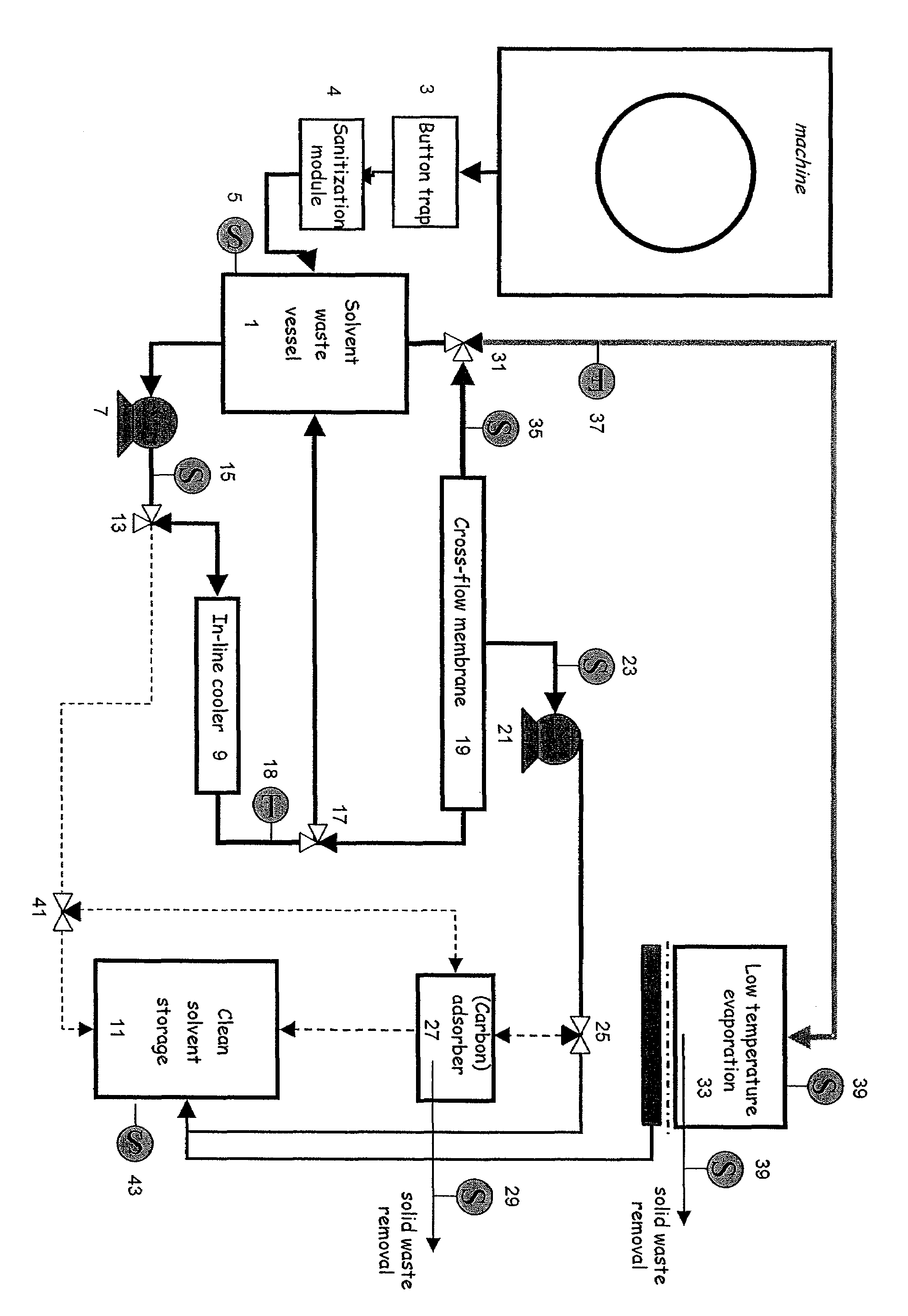
Solvent cleaning process
InactiveUS20050126606A1Small apertureDegrade solventDry-cleaning apparatusSolid sorbent liquid separationSolventDry cleaning
An improved solvent recovery process for use in a dry cleaning method uses selective cleaning of a predetermined solvent fraction.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Non-aqueous electrolyte and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell
InactiveUS20040091786A1Reduce gas volumeExcellent characteristicsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsPhysical chemistryDiphenyl disulfide
A non-aqueous electrolyte containing propylene carbonate and 1,3-propanesultone as additives can reduce the amount of a gas evolved during storage at a high temperature of a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell comprising the electrolyte, a non-aqueous electrolyte containing at least one compound selected from the group consisting of vinylene carbonate, diphenyl disulfide, di-p-tolyldisulfide and bis(4-methoxyphenyl)disulfide as an additive can improve cycle characteristics of a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell comprising the electrolyte, and a non-aqueous electrolyte containing a combination of the above two types of additives can provide a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell exhibiting excellent retention of capacity and storage stability.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
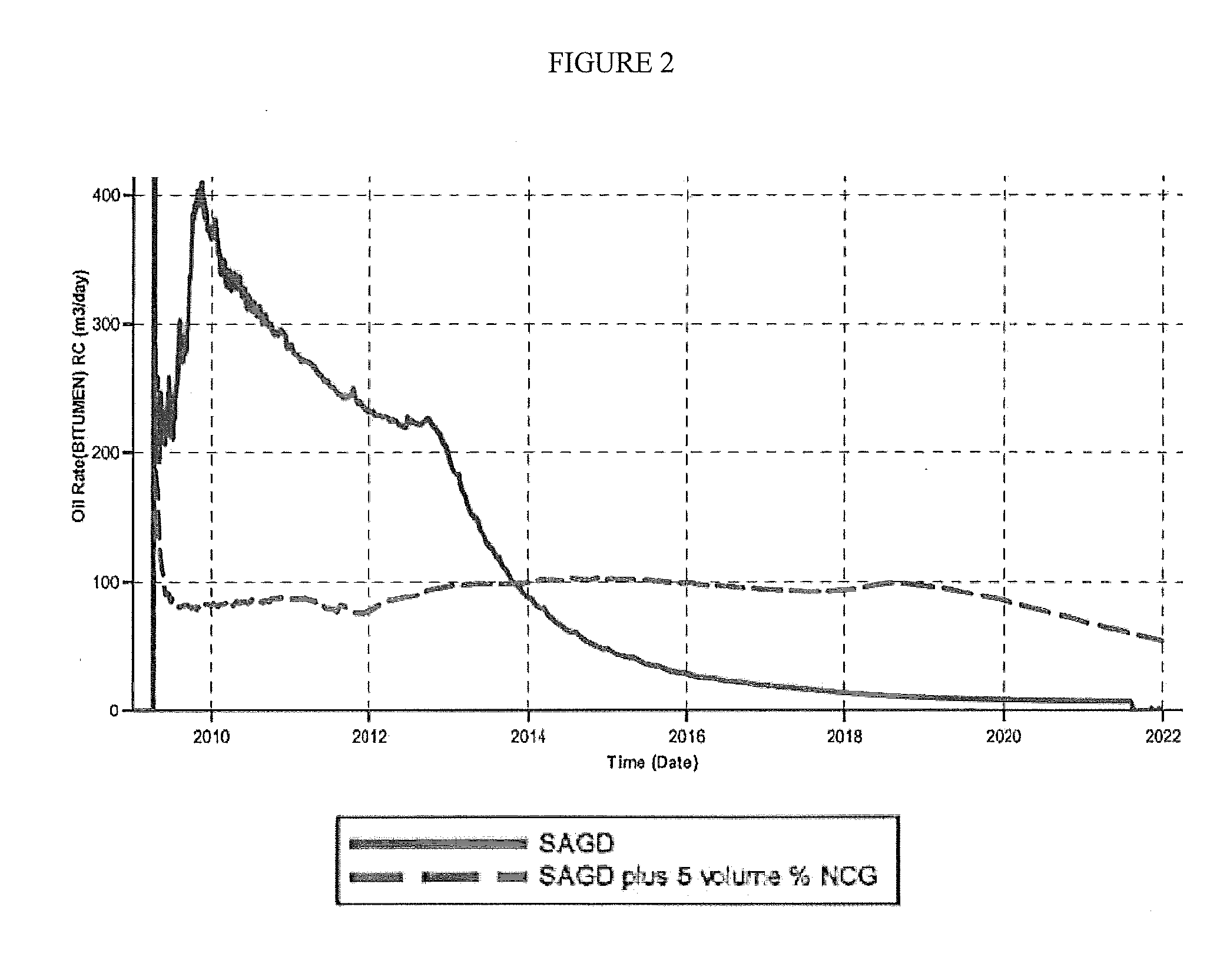
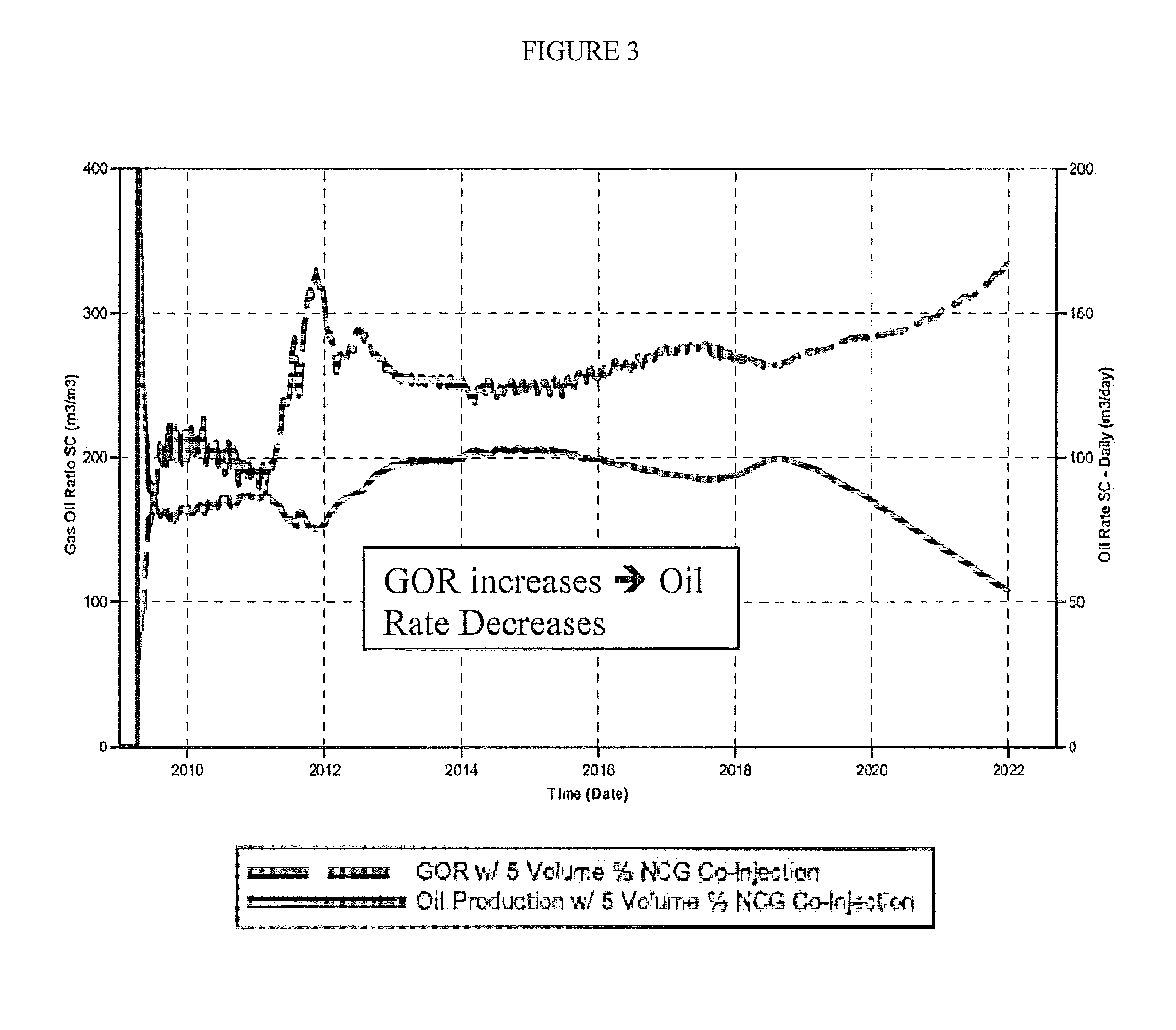
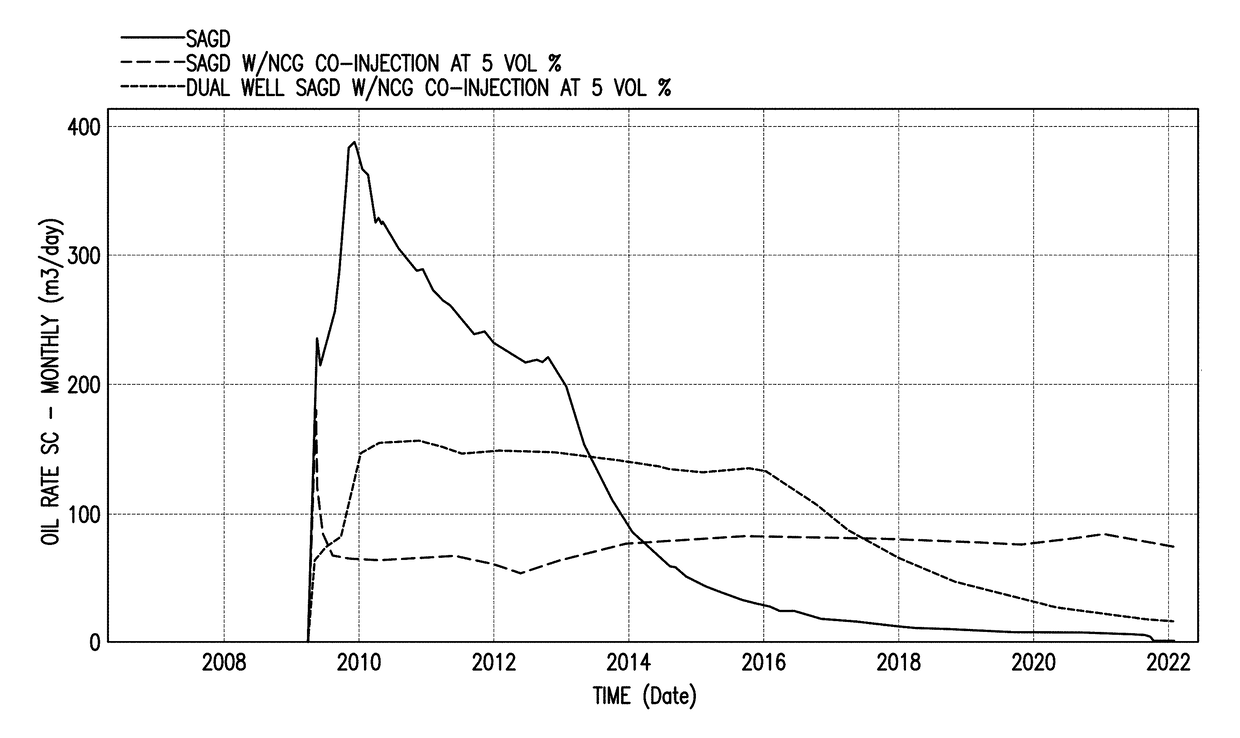
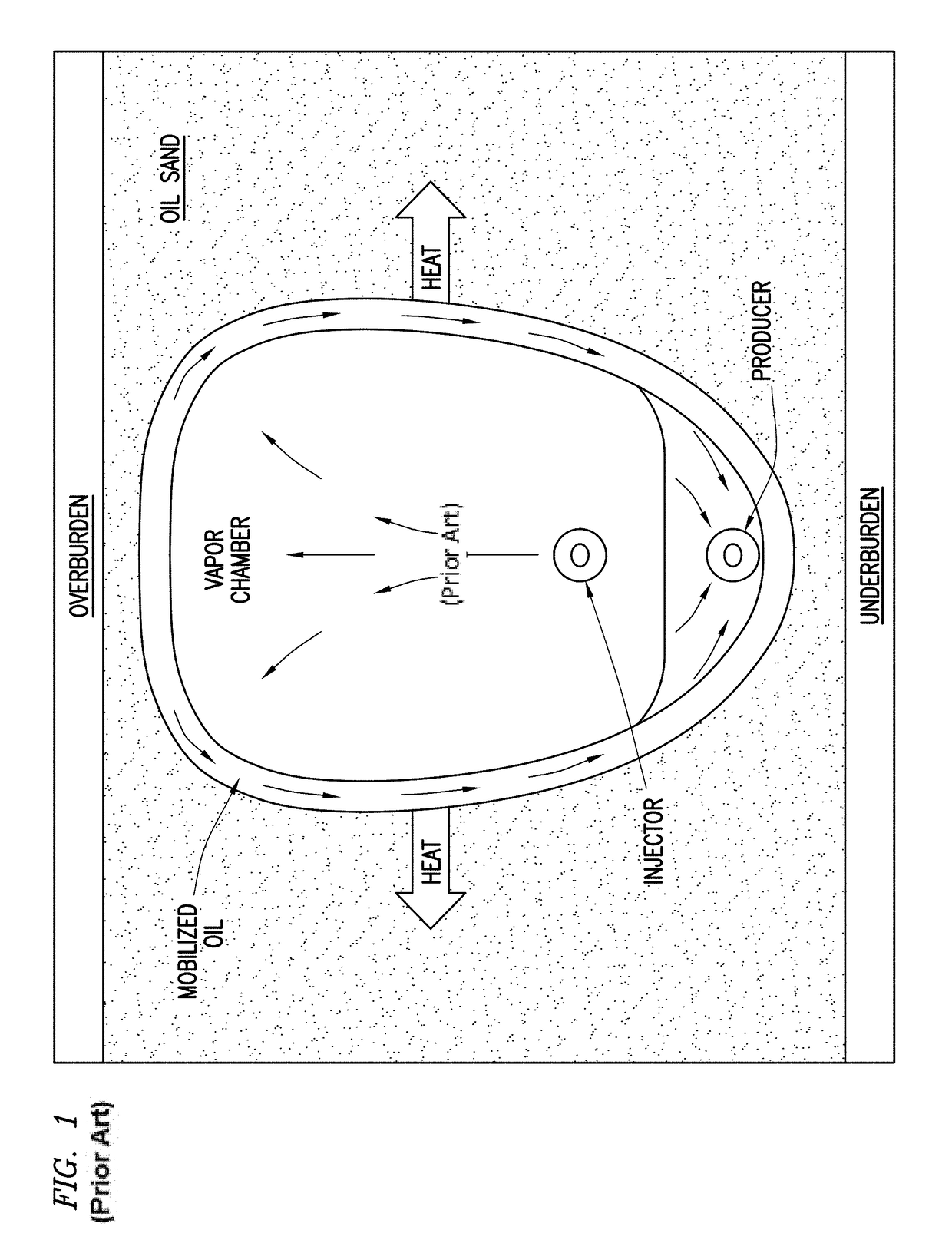
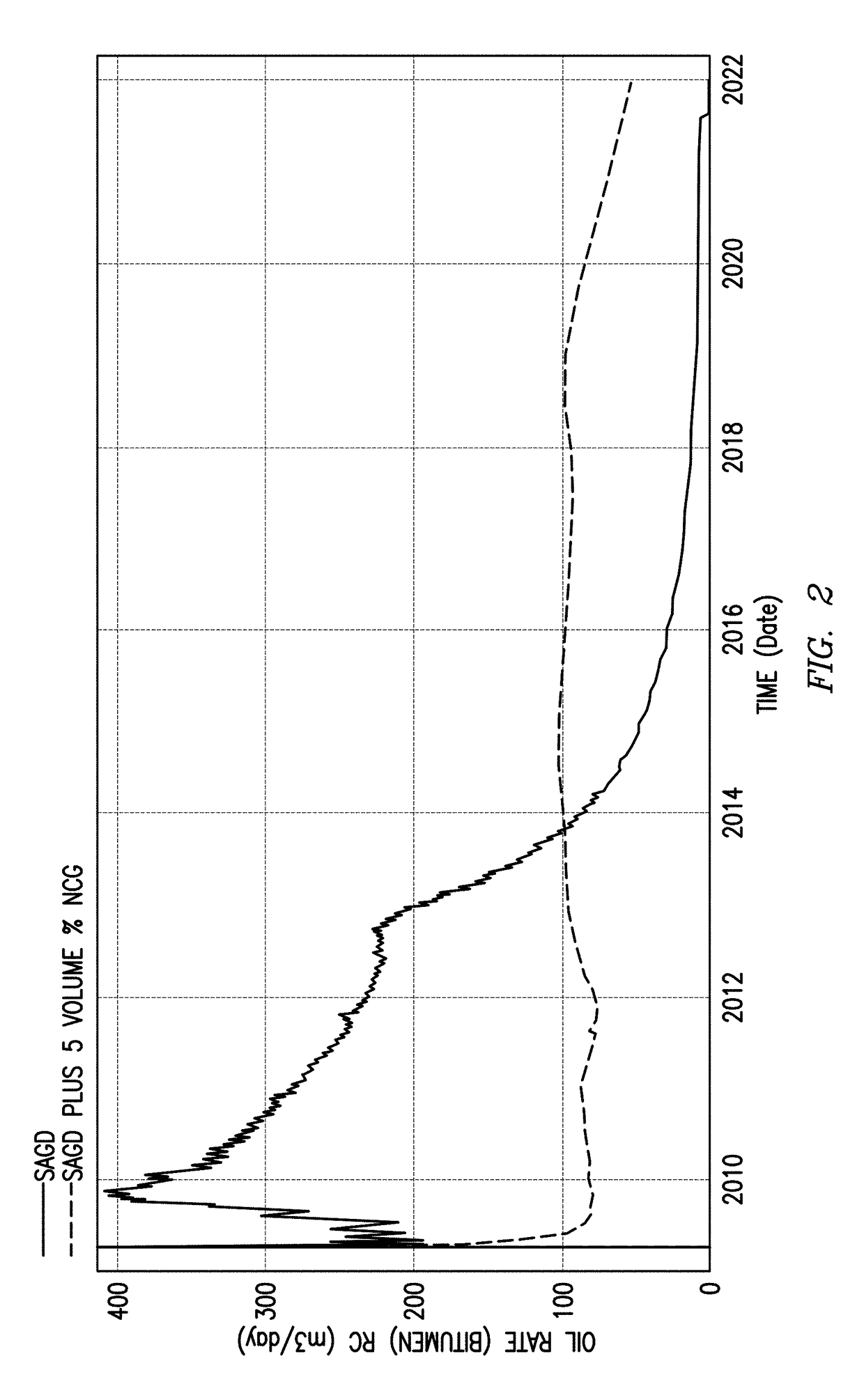
Dual injection points in sagd
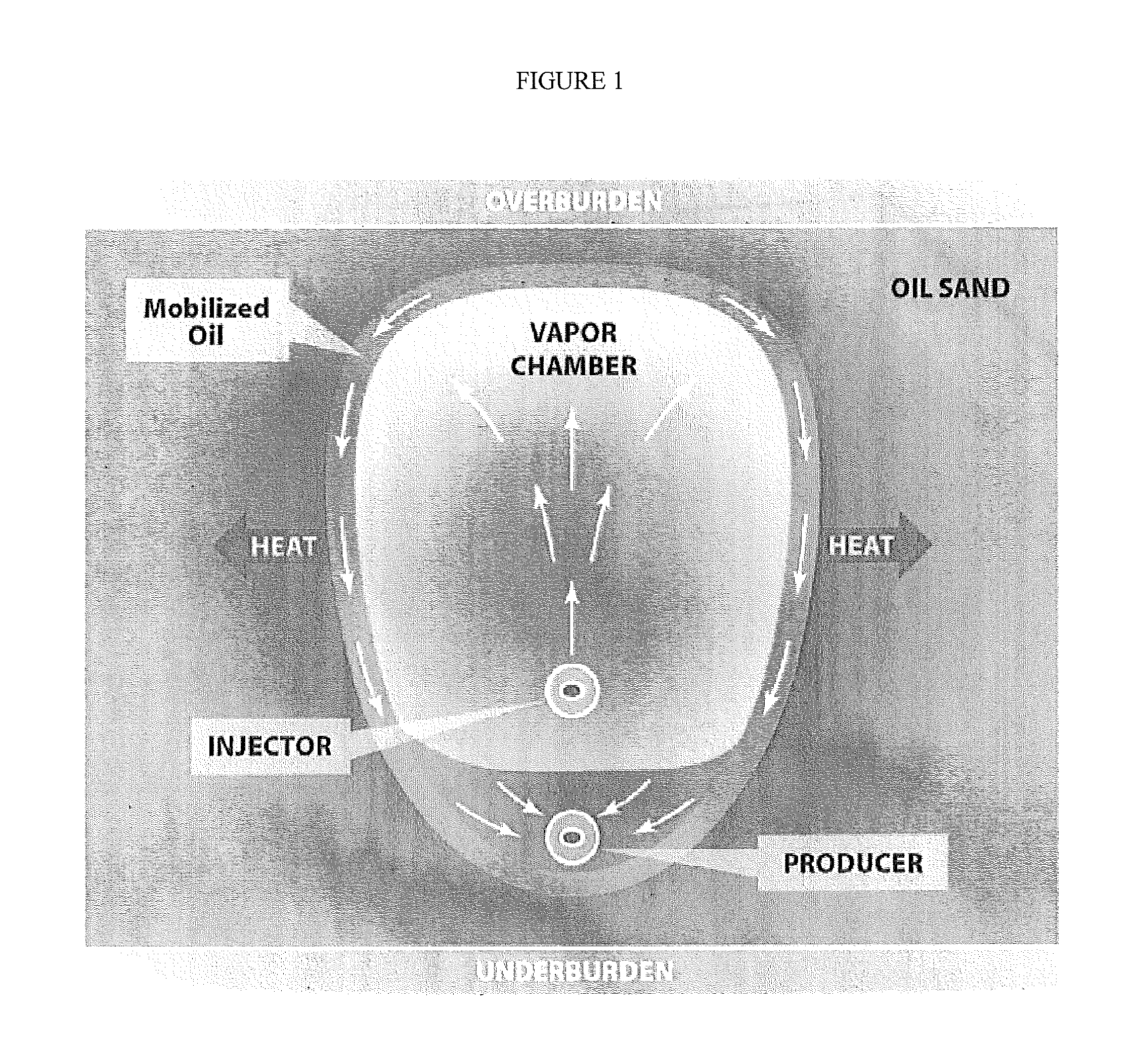
ActiveUS20120247760A1Improve efficiencyReducing solvent refluxFluid removalDual injectionHorizontal wells
A method for recovering petroleum from a formation, wherein at least two injection wells and at least one production well are in fluid communication with said formation, comprising: introducing a gaseous mixture into a first and a second injection well at a temperature and a pressure, wherein said gaseous mixture comprises steam and non-condensable gas (NCG); and recovering a fluid comprising petroleum from said production well, wherein said injection wells and a production well are horizontal wells, and wherein said first injection well is disposed 1-10 meters above said production well, and said second injection well is disposed at least 5 meters above said first injection well.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
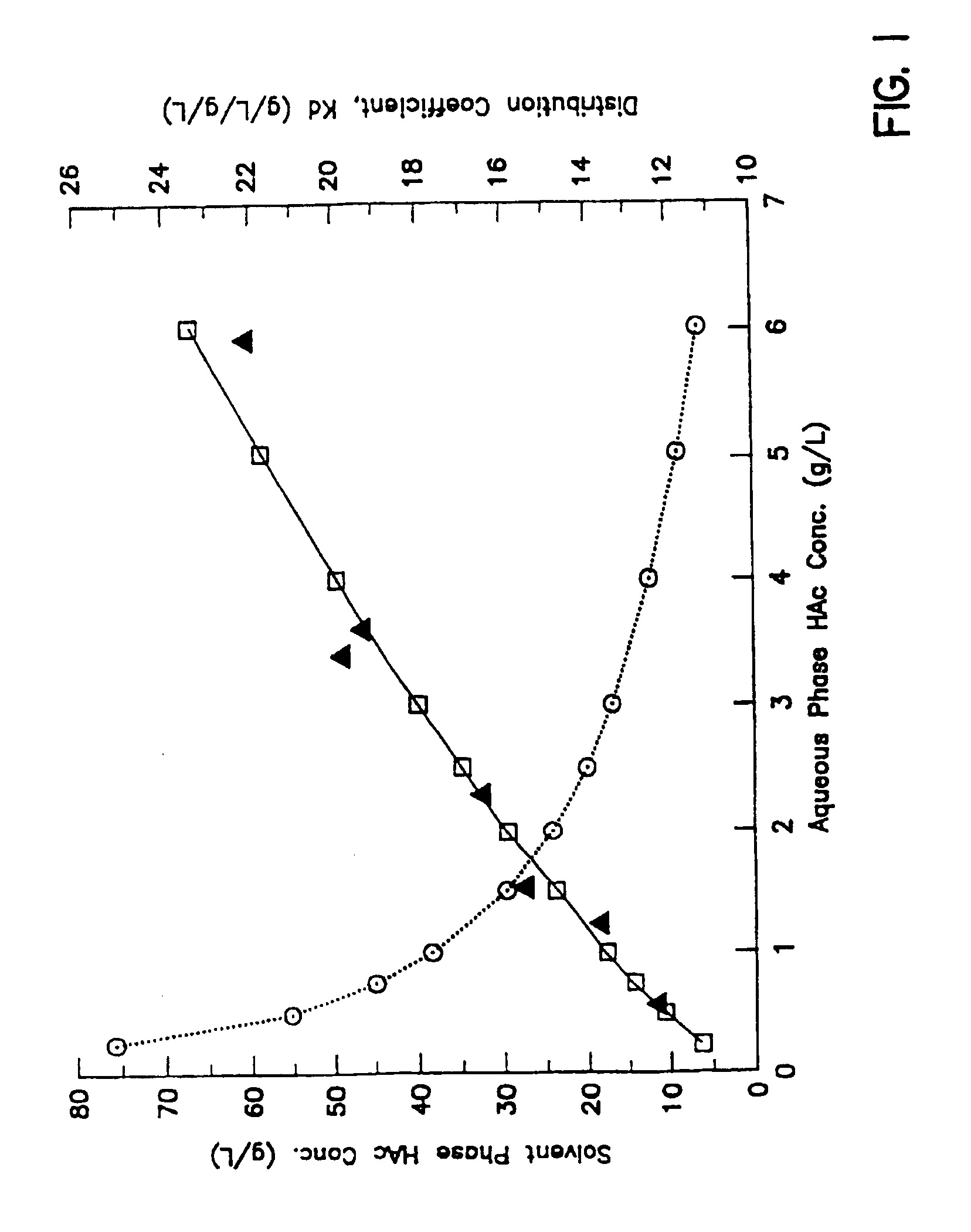
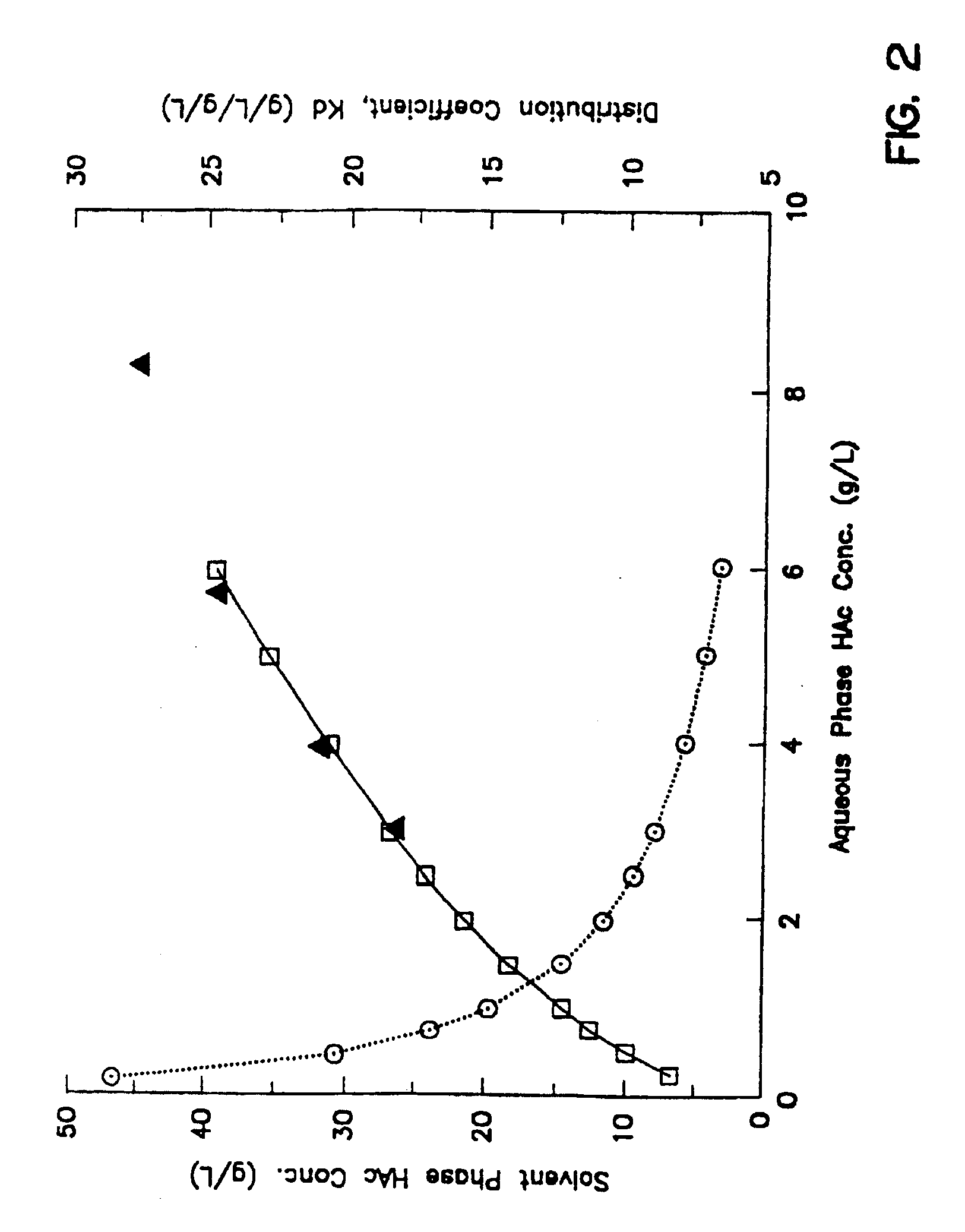
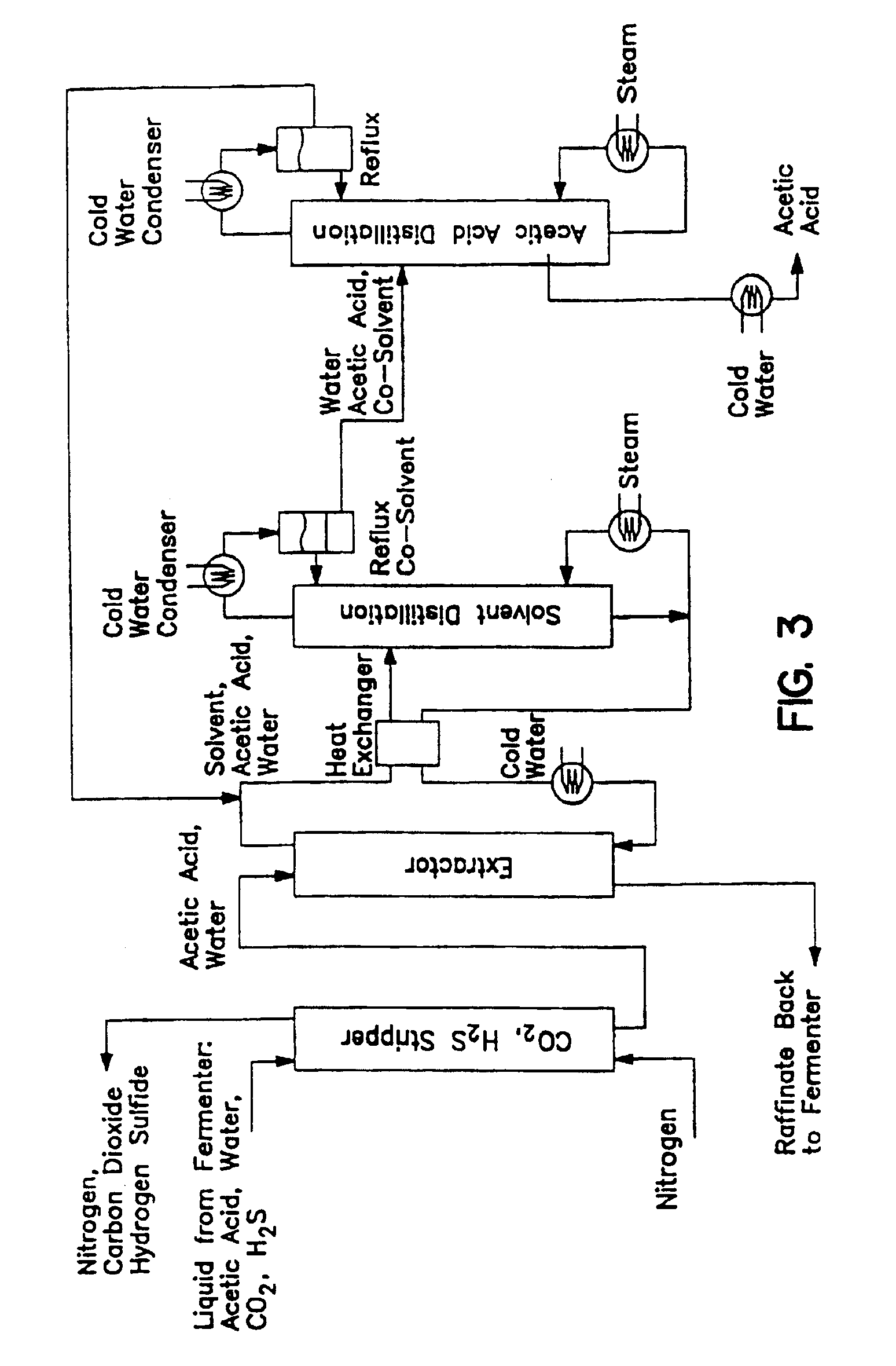
Microbial process for the preparation of acetic acid as well as solvent for its extraction from the fermentation broth
InactiveUSRE39175E1Easy to operateReduce the temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAcetic acid
A modified water-immiscible solvent useful in the extraction of acetic acid from aqueous streams is a substantially pure mixture of isomers of highly branched di-alkyl amines. This solvent is substantially devoid of mono-alkyl amines and alcohols. Solvent mixtures formed of such a modified solvent with a desired cosolvent, preferably a low boiling hydrocarbon which forms an azeotrope with water are useful in the extraction of acetic acid from aqueous gaseous streams. An anaerobic microbial fermentation process for the production of acetic acid employs such solvents, under conditions which limit amide formation by the solvent and thus increase the efficiency of acetic acid recovery. Methods for the direct extraction of acetic acid and the extractive fermentation of acetic acid also employ the modified solvents and increase efficiency of acetic acid production. Such increases in efficiency are also obtained where the energy source for the microbial fermentation contains carbon dioxide and the method includes a carbon dioxide stripping step prior to extraction of acetic acid in solvent.
Owner:INEOS BIO SA
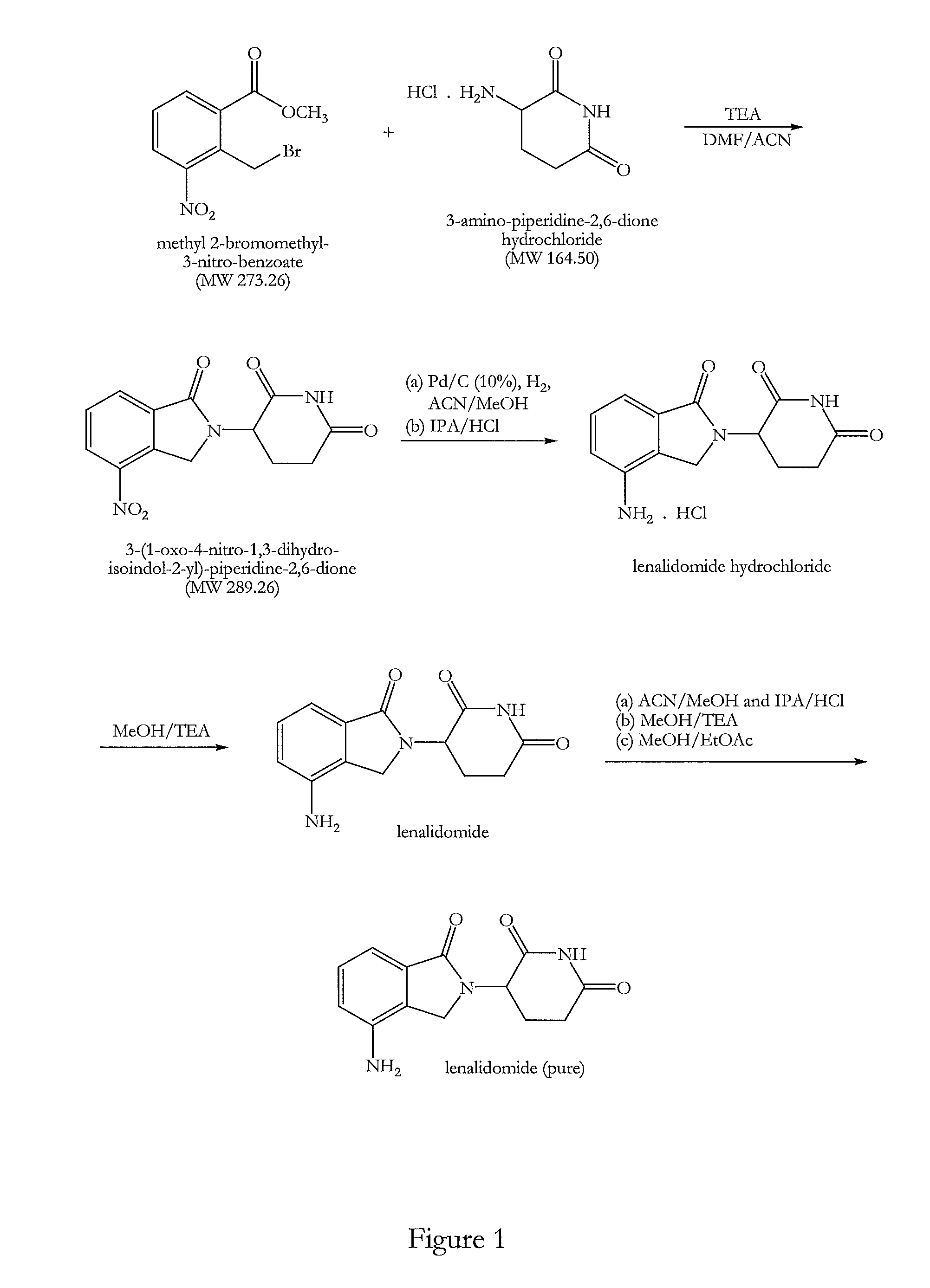
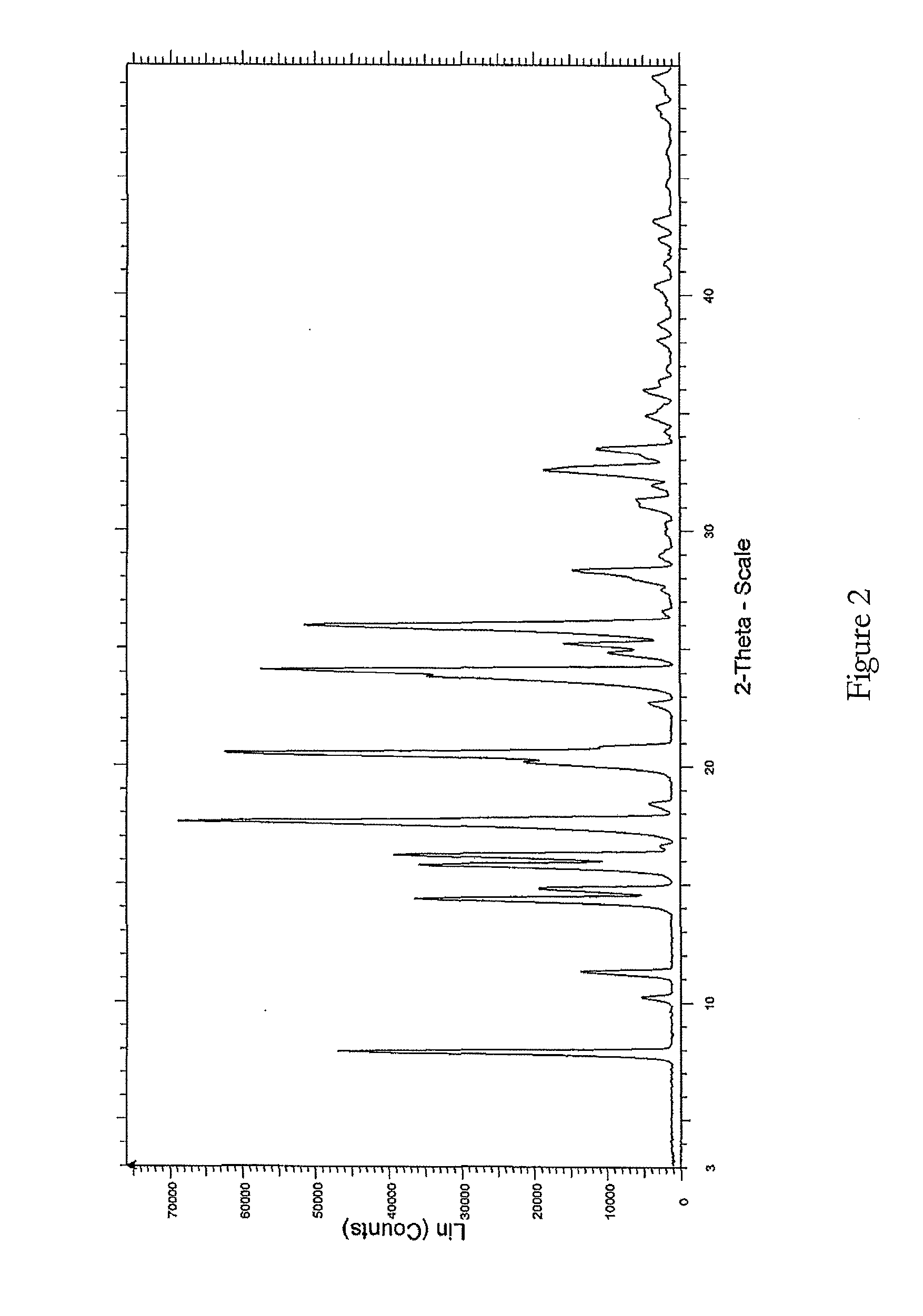
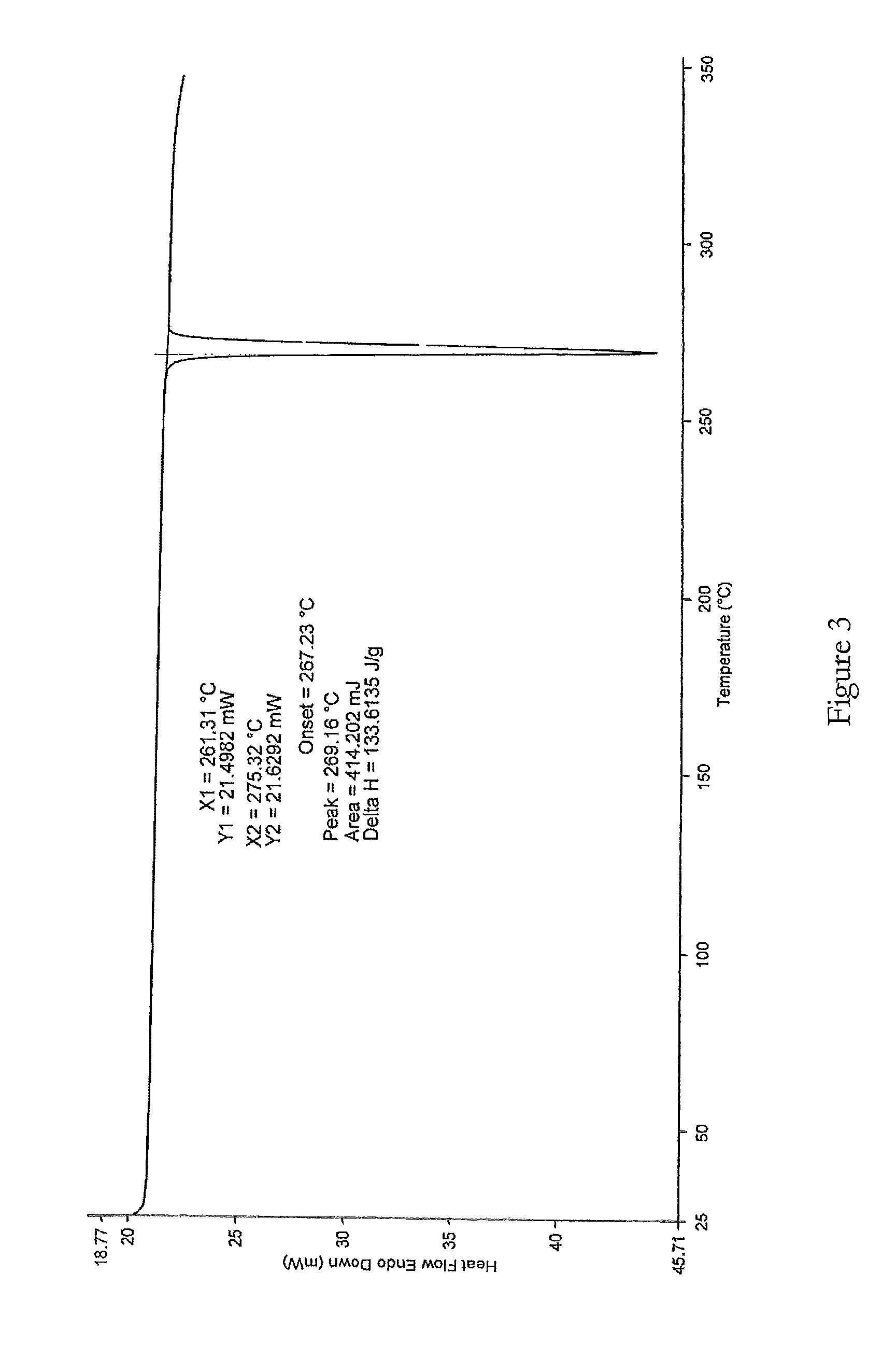
Process
The present invention relates to improved processes for preparing 3-(4-amino-1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-isoindol-2-yl)-piperidine-2,6-dione (I) (lenalidomide) and its intermediate 3-(1-oxo-4-nitro-1,3-dihydro-isoindol-2-yl)-piperidine-2,6-dione. The present invention further relates to improved processes for preparing lenalidomide crystalline form A, use of said crystalline form A as an active pharmaceutical ingredient or as an intermediate in the preparation of further crystalline or amorphous forms of lenalidomide, compositions comprising lenalidomide crystalline form A and their use in the treatment of disease.
Owner:GENERICS UK LTD
Solvent cleaning process
InactiveUS7497877B2Small apertureDegrade solventDry-cleaning apparatusSolid sorbent liquid separationSolvent refiningDry cleaning
An improved solvent cleaning process of cleaning a non-aqueous solvent used in a dry cleaning process for fabrics including consecutive wash cycles for washing respective fabrics batches, including a basic solvent refining cycle and a first advanced solvent refining cycle, the basic solvent refining cycle including a step of separating solvent into a first solvent fraction and a second solvent fraction which is less clean than the first fraction, wherein the basic and first advanced solvent refining cycles are independently effected when solvent to be cleaned fulfils a respective predetermined condition.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Amino-polyether-modified epoxy and cationic electrodeposition paint composition containing the same
InactiveUS6462106B2Give flexibilityDegrade solventPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPaints for electrolytic applicationsEpoxyEthyl group
Disclosed is a novel amino-polyether-modified epoxy for an electrodeposition paint. The amin-polyether-modified epoxy compound is obtained by reacting amino polyether represented by a formula as follow:wherein m is an integer of 5 or more, R is hydrogen, methyl group or ethyl group, and n is 2 or 3, with polyglycidyl ether having a molecular weight of 1,000 to 7,000 and an epoxy equivalent of 500 to 3,500, wherein an equivalent ratio of a primary amino group of the amino polyether to an epoxy group of the polyglycidyl ether is controlled within the range of 0.52 to 1.0.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT AUTOMOTIVE COATINGS
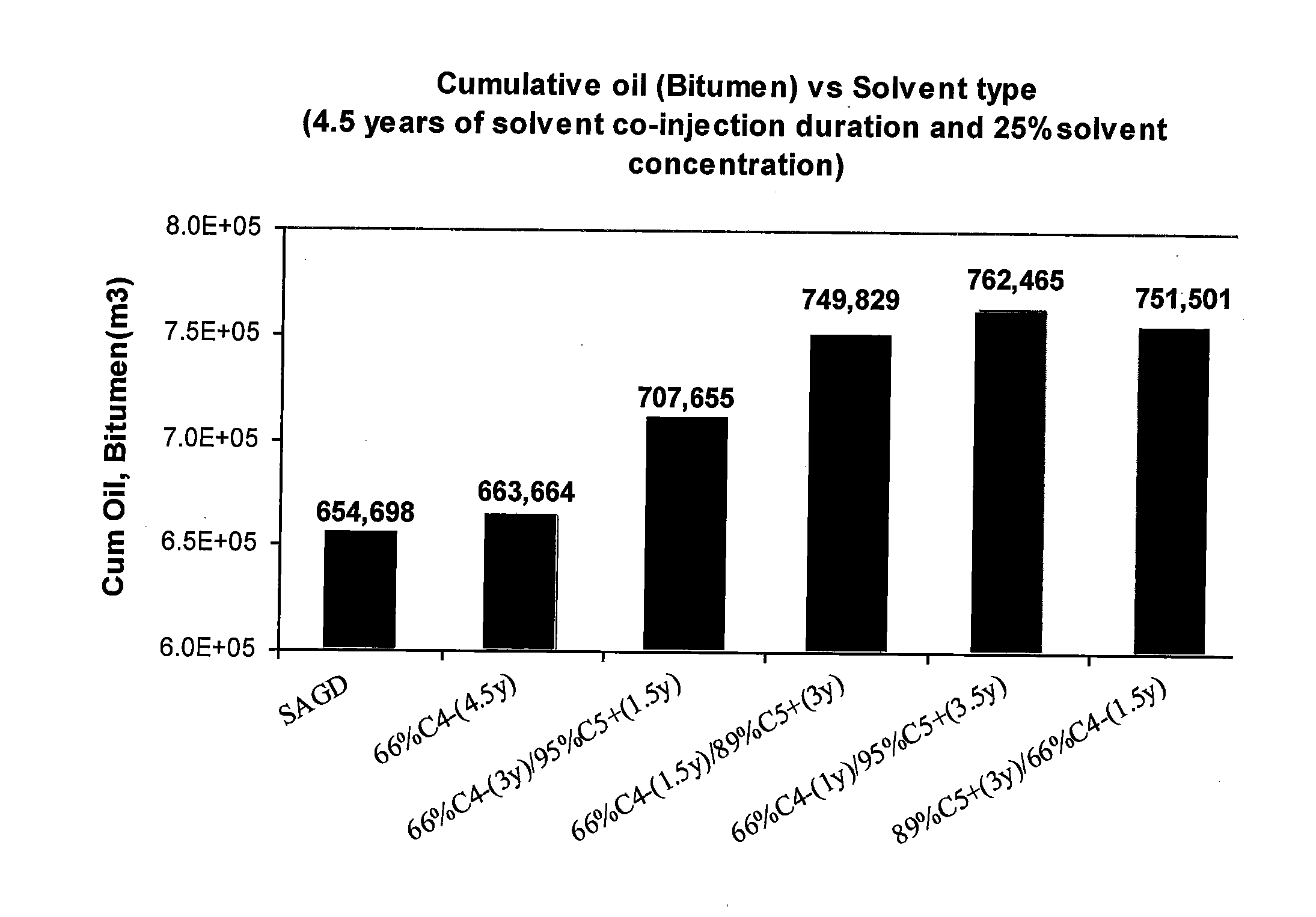
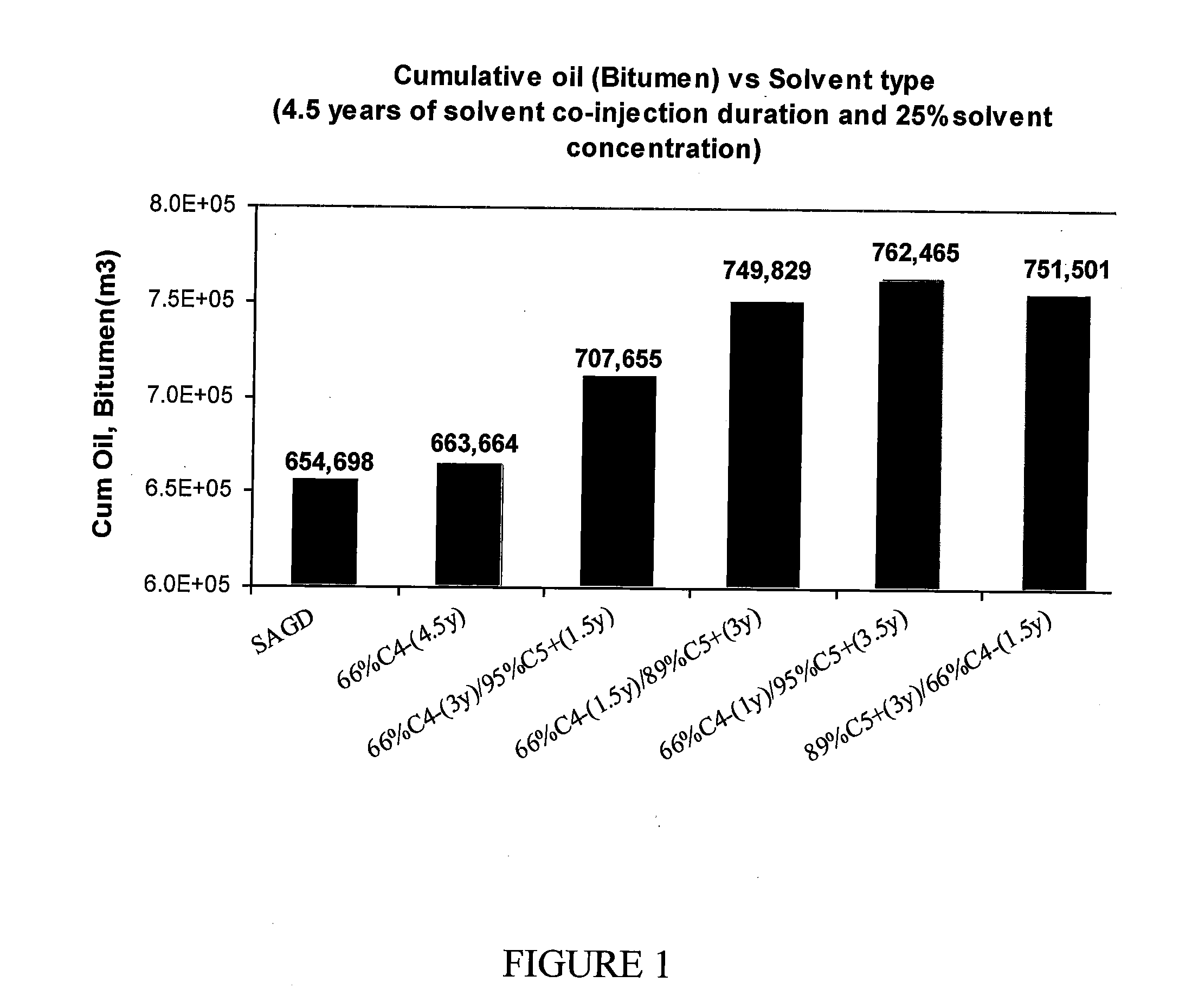
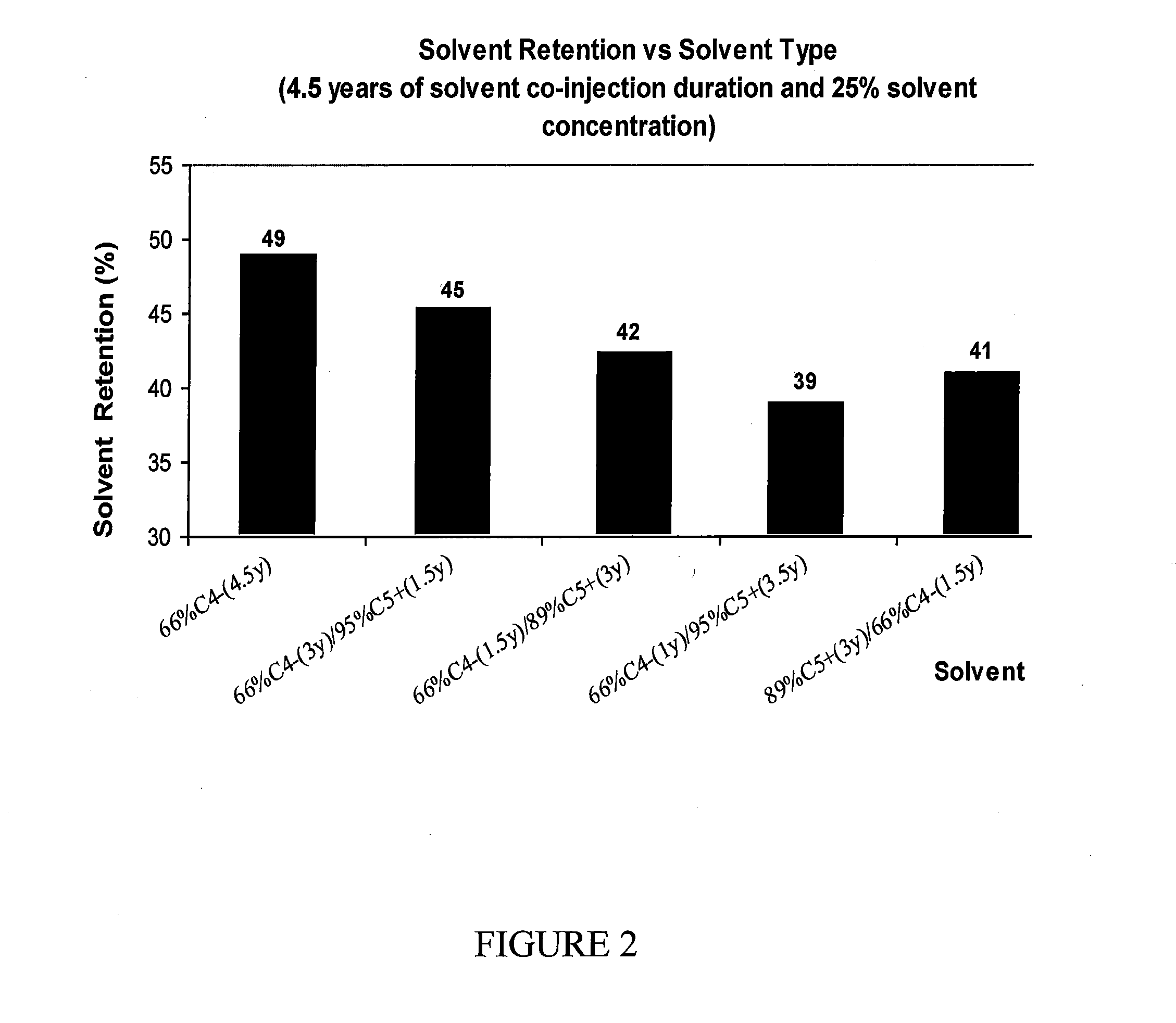
Hydrocarbon recovery with steam and solvent stages
ActiveUS20140144627A1Reduces viscosity of oilLow viscosityFluid removalDrilling compositionFuel oilSteam-assisted gravity drainage
A steam-assisted gravity drainage method includes a two stage solvent injection scheme, wherein steam plus solvent injection is followed by steam plus heavier-solvent injection. The two solvent injections improve recoveries of both the heavy oil and the injected solvent while limiting steam requirements, thus improving the economics of the method.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Flexible electroconductive foam, and method of preparation thereof
InactiveUS7008565B2Degrade solventReduce swellingSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialDopantLiquid medium
A method of preparing an electroconductive foam, and the foam so prepared. An electroconductive polymer such as polyaniline is dispersed in a liquid medium that includes an aromatic solvent such as xylene and an organic dopant / dispersant such as an aromatic sulfonic acid. The electroconductive polymer together with the organic dopant / dispersant constitute between 10% and 25% of the resulting dispersion. The dispersion is introduced to the pores of an electrically insulating foam matrix such as polyurethane. Excess dispersion is expelled and the foam is dried actively, to line the pores with an electroconductive lining.
Owner:MORE ENERGY
Polymer composites having highly dispersed carbon nanotubes and methods for forming same
ActiveUS20090001325A1Increase relative volatilityDegrade solventNon-metal conductorsNanotechOrganic solventBoiling point
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
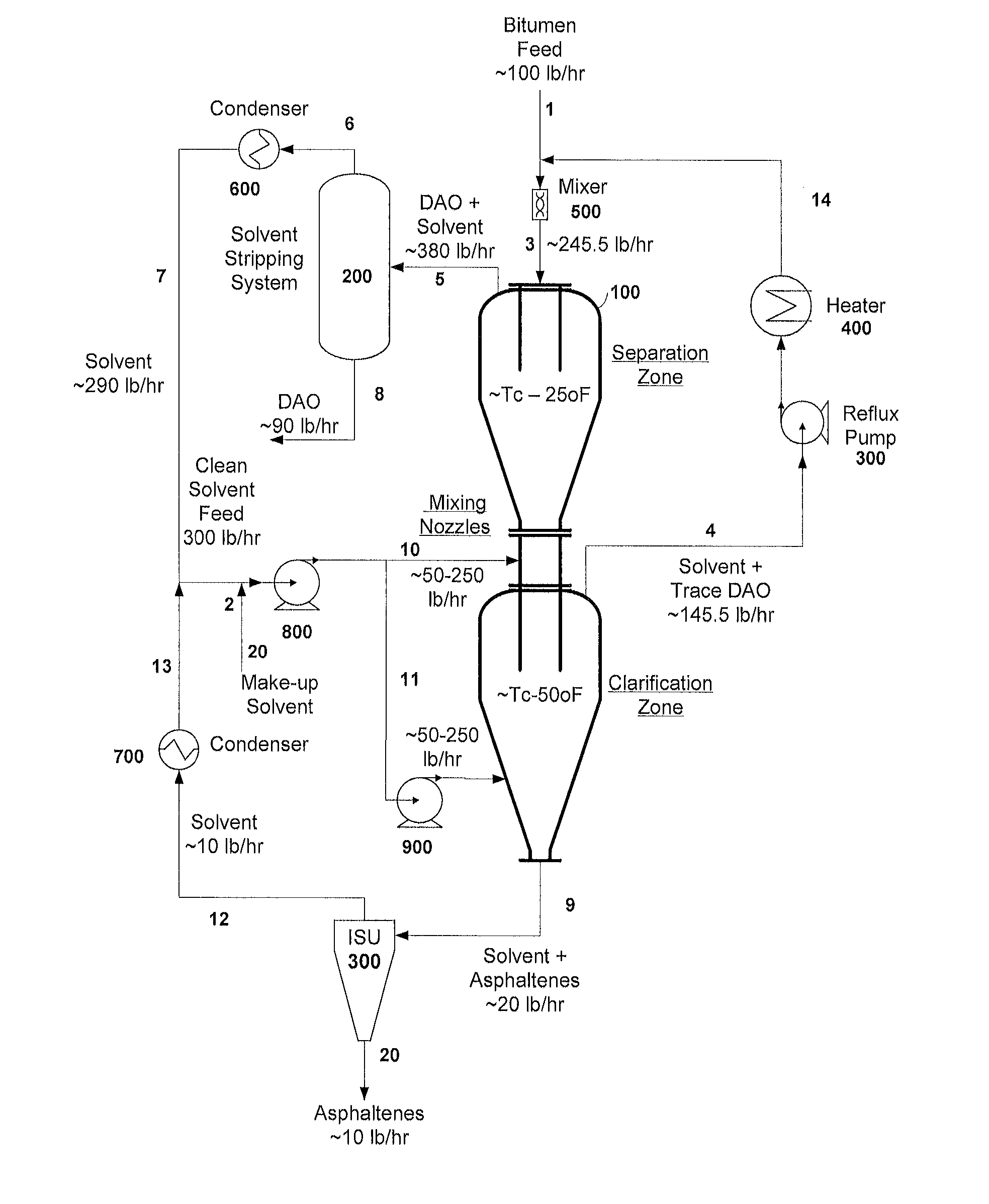
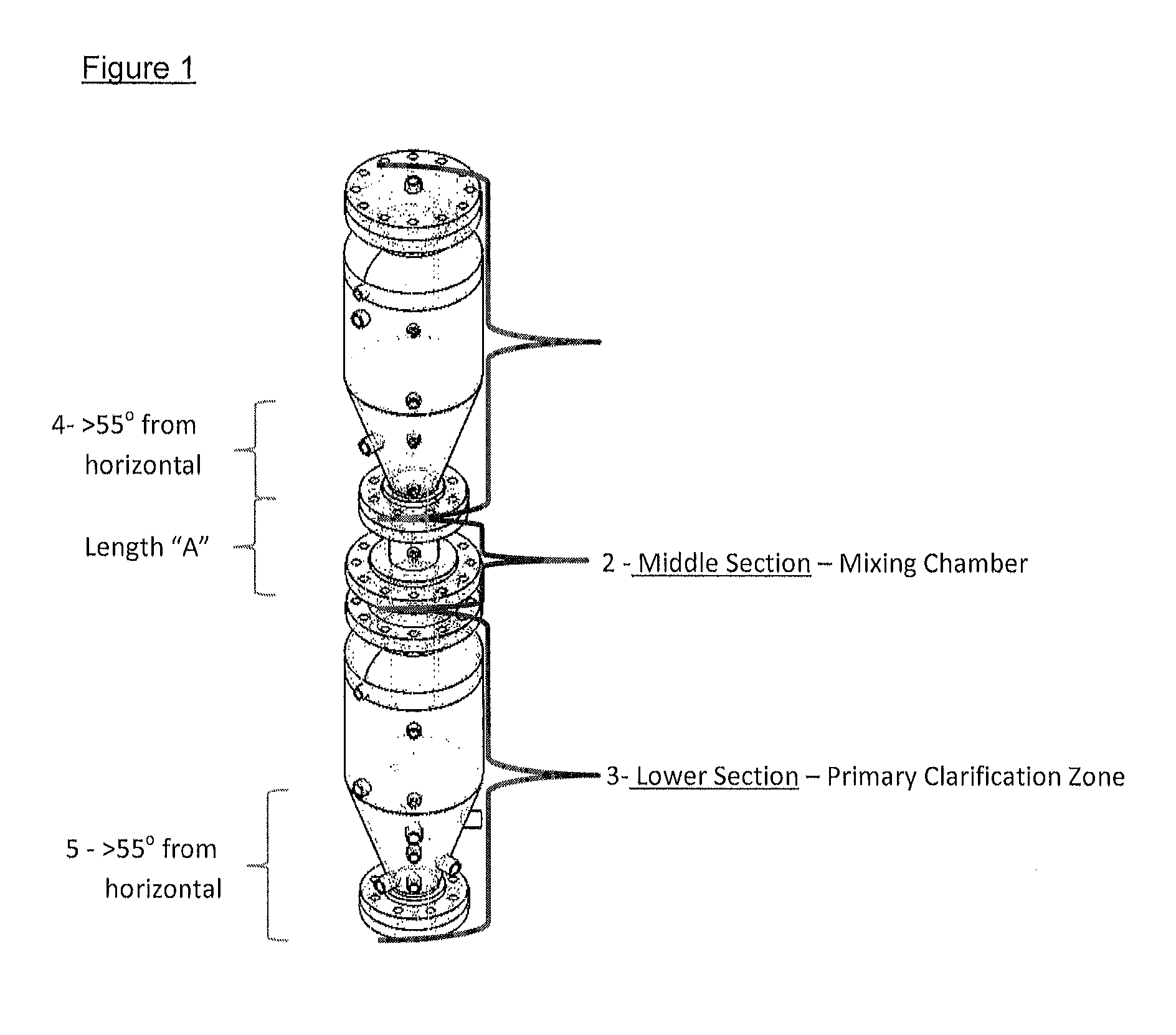
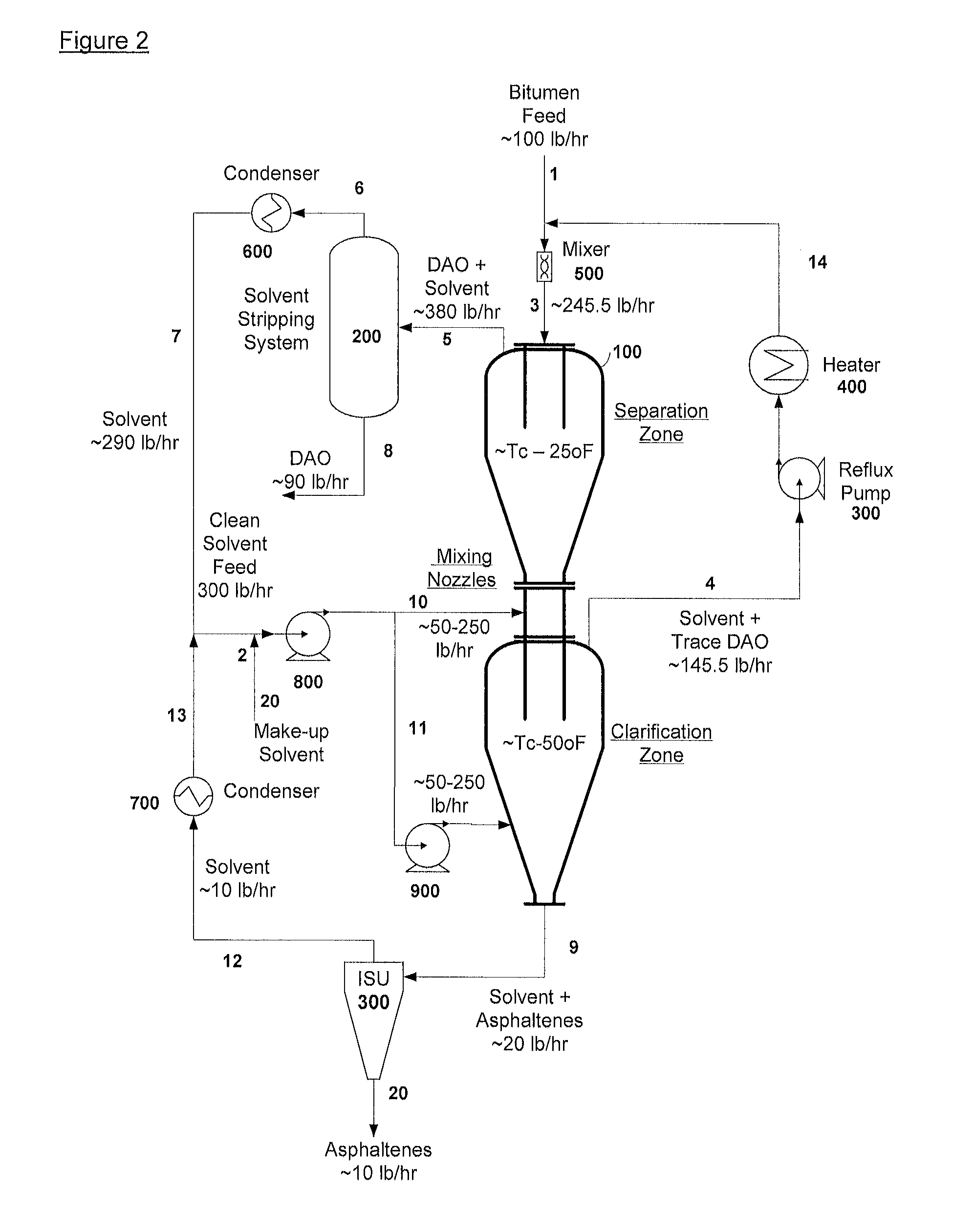
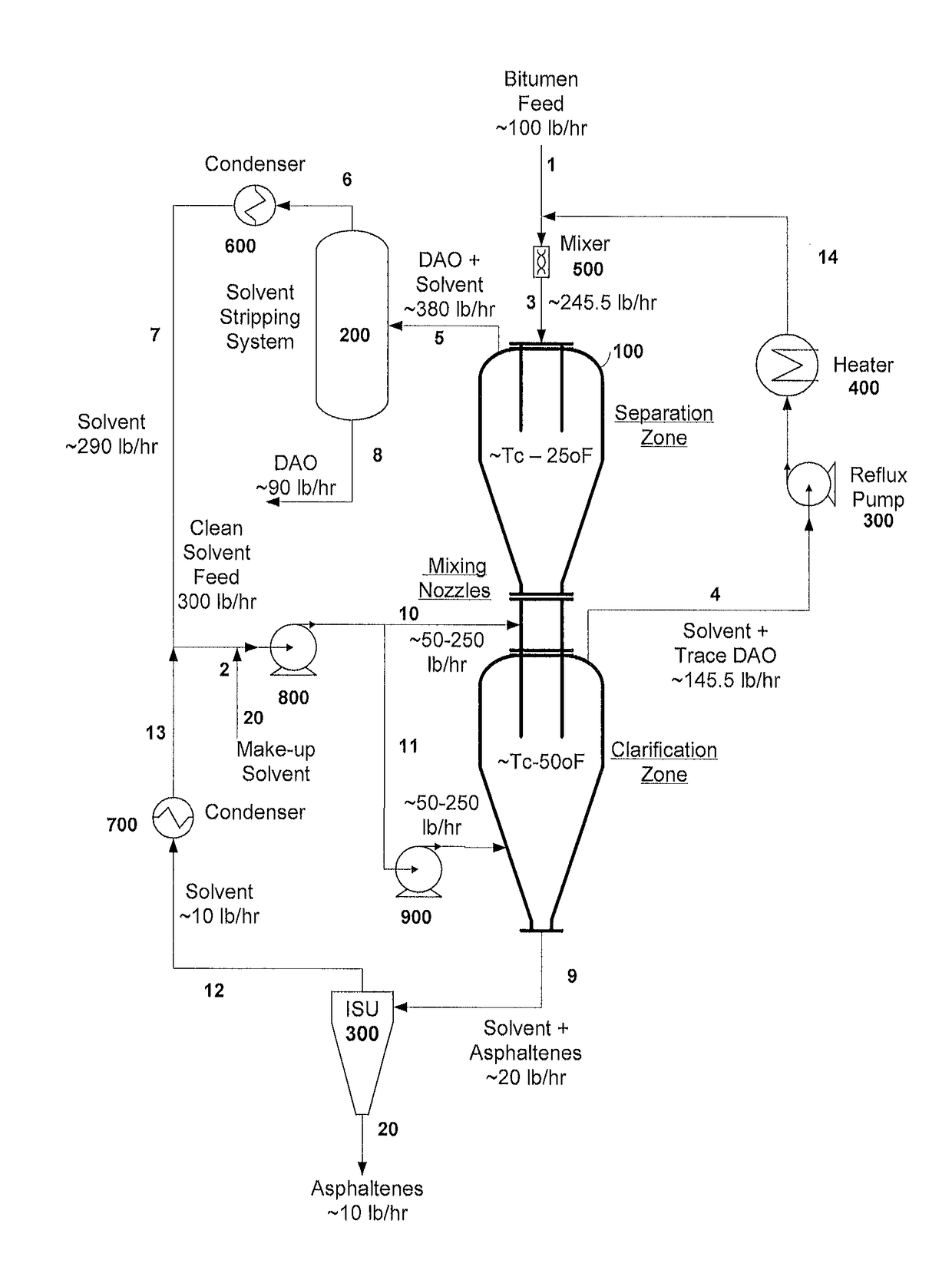
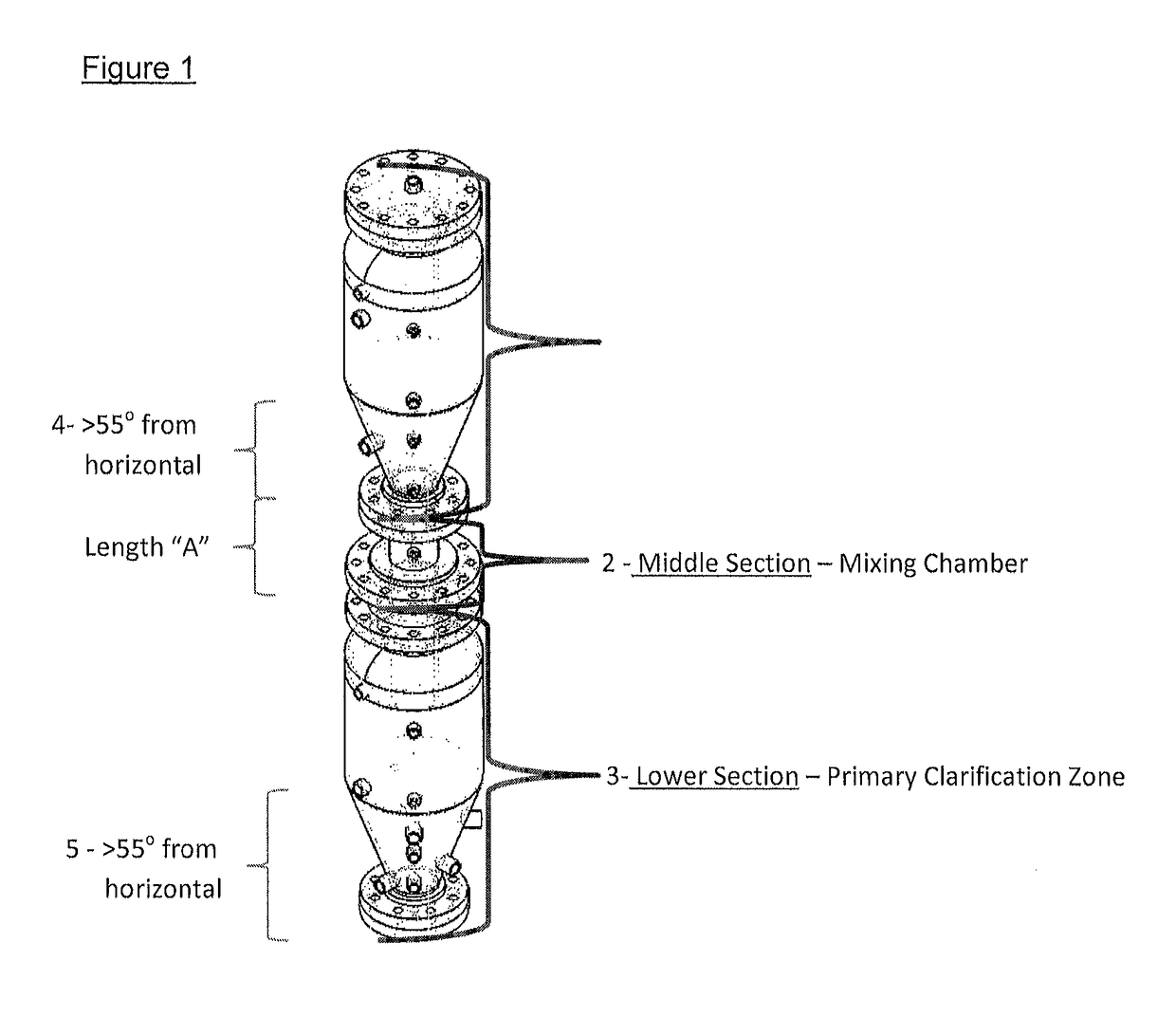
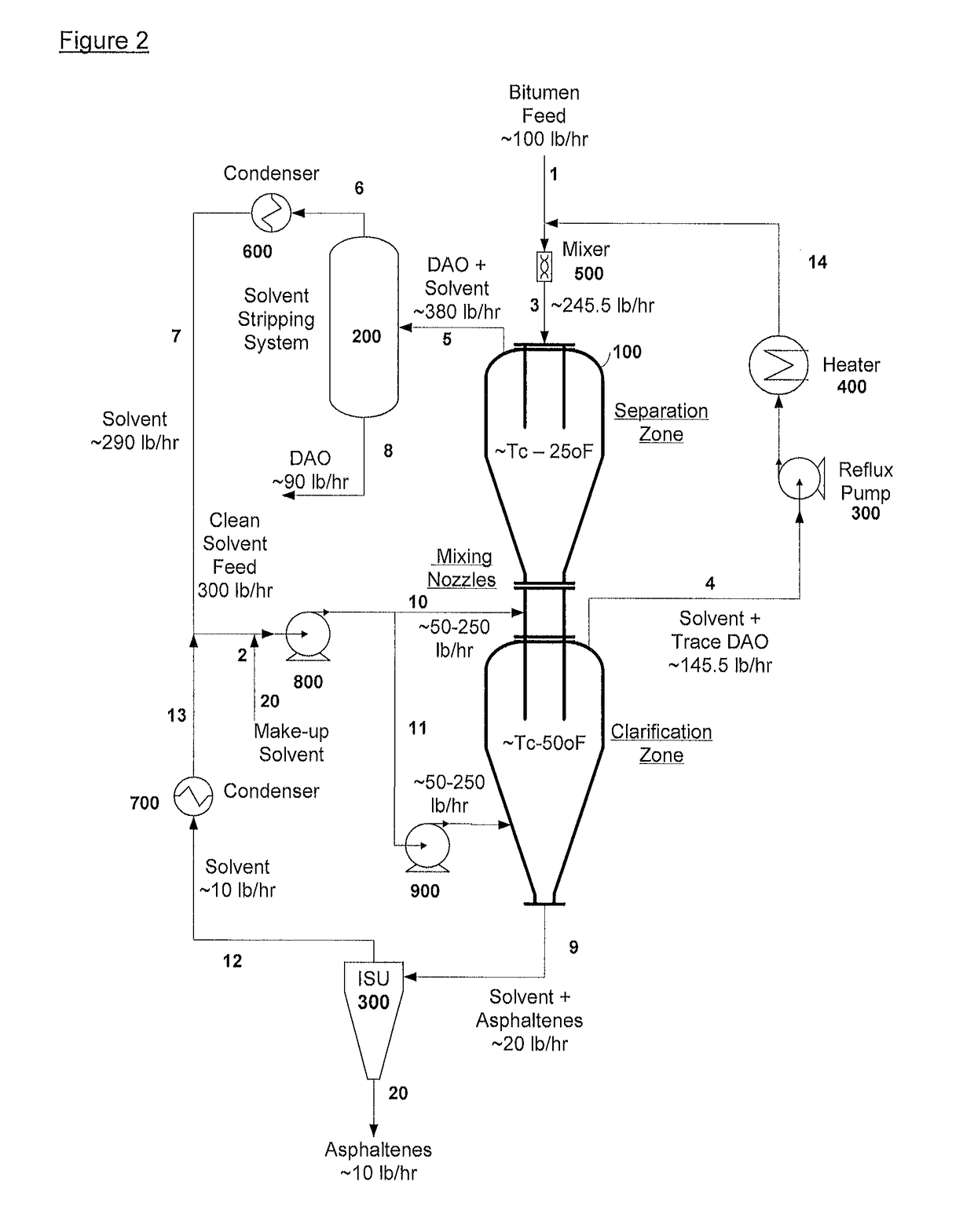
Separation of solid asphaltenes from heavy liquid hydrocarbons using novel apparatus and process ("ias")
ActiveUS20140246357A1Reduce pluggingMitigate settlingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolvent extractionLiquid hydrocarbonsEngineering
An apparatus and process is provided for improved asphaltene separation from heavy hydrocarbon or bitumen with low process complexity through mass transfer using solvent and counter-current flows, with three sections: an upper DAO / solid-asphaltene separation zone, a middle solvent mixing and segregation zone, and a bottom clarification zone. Solvent mixed with heavy hydrocarbon forms a process feed introduced to the process vessel's upper zone and exposed to counter-current solvent removing DAO from solid asphaltene particles in the feed, the particles fall through the middle zone and are mixed with introduced solvent, which introduced solvent segregates DAO-rich solution in the upper zone (for extraction from that zone) from solvent-rich mixtures in the middle mixing and lower clarification zones. Solvent flows and precipitate movement are controlled to optimize mass transfer in process, resulting in high DAO recovery and dry, solid asphaltene product.
Owner:SUNCOR ENERGY INC
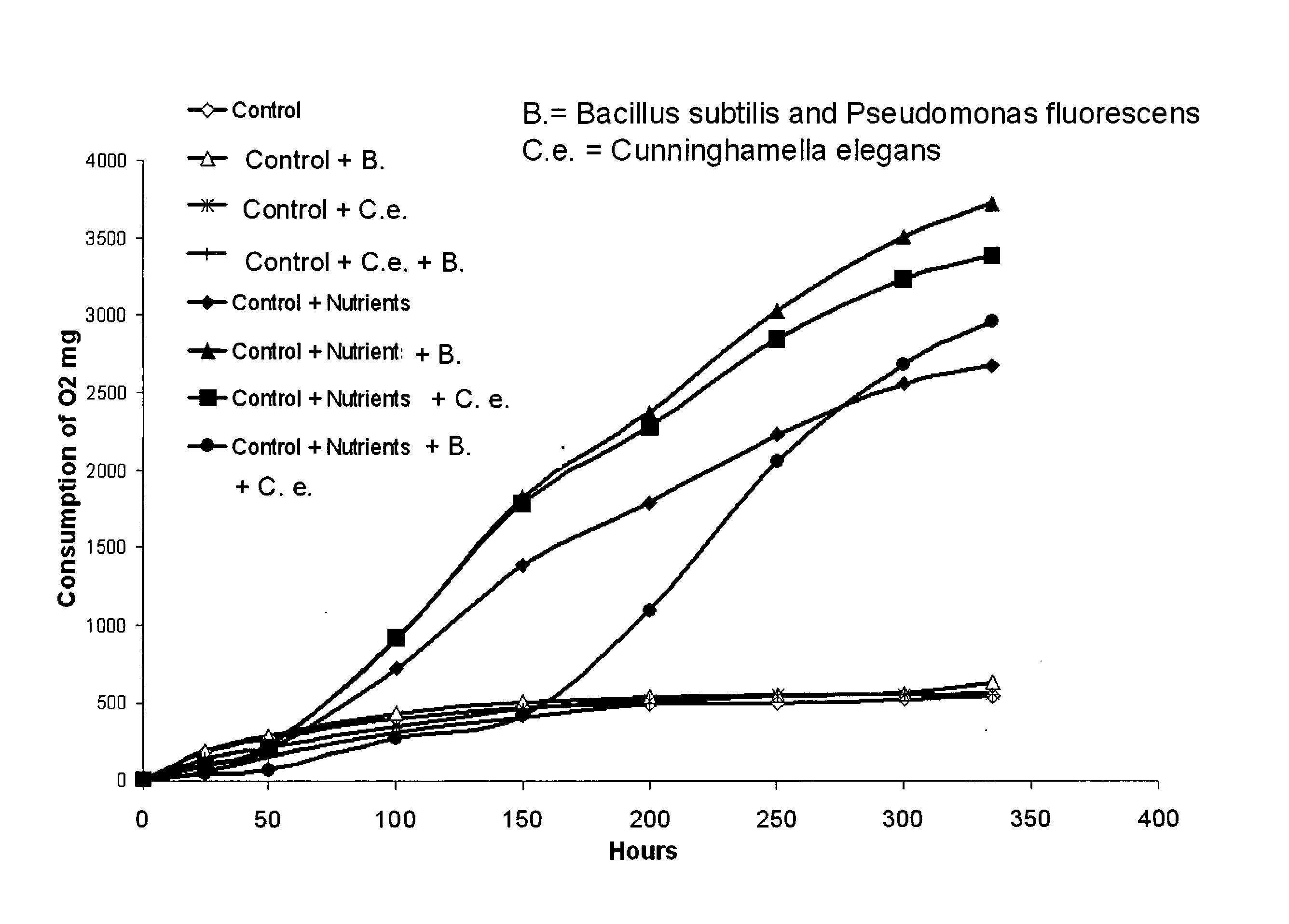
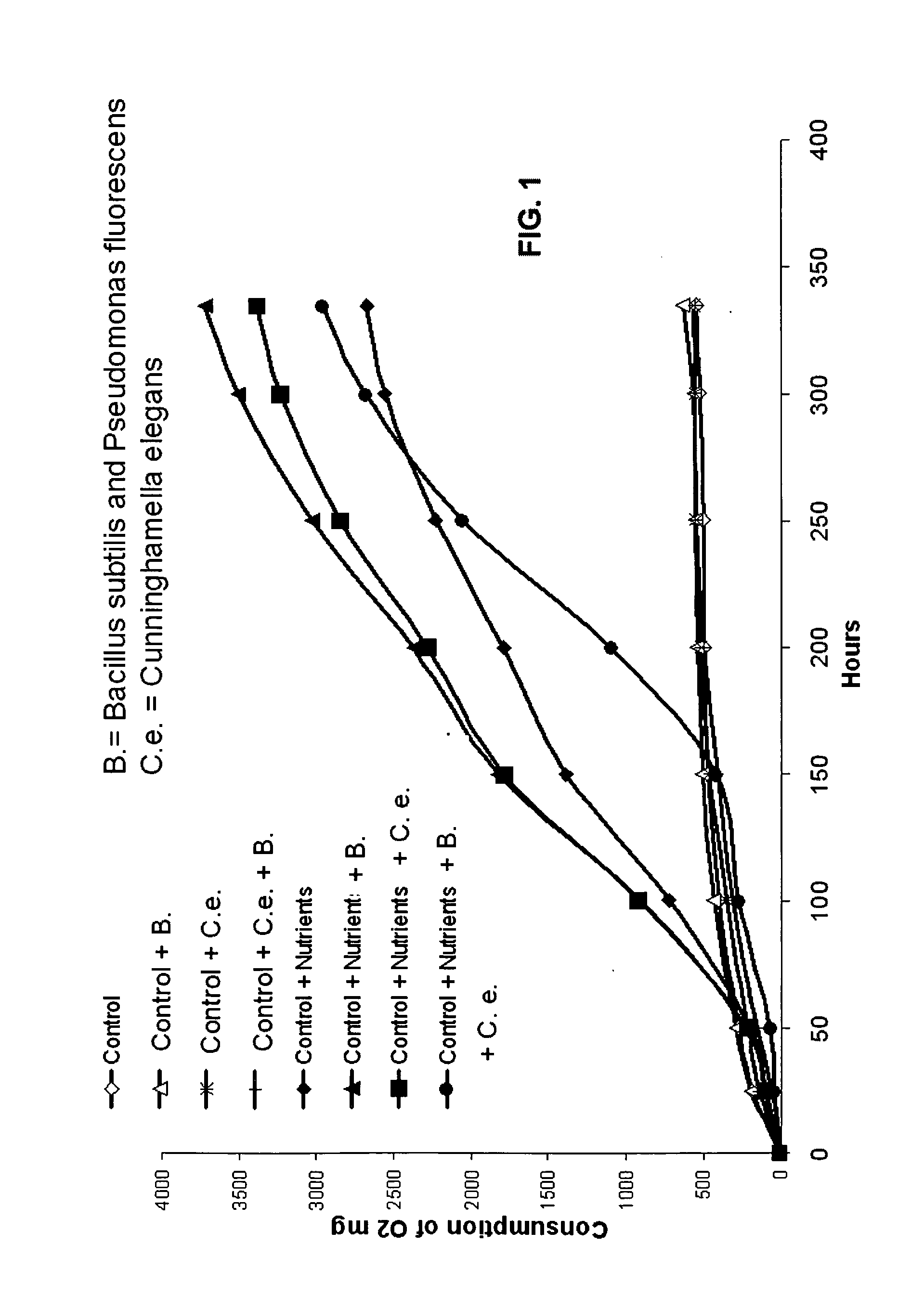
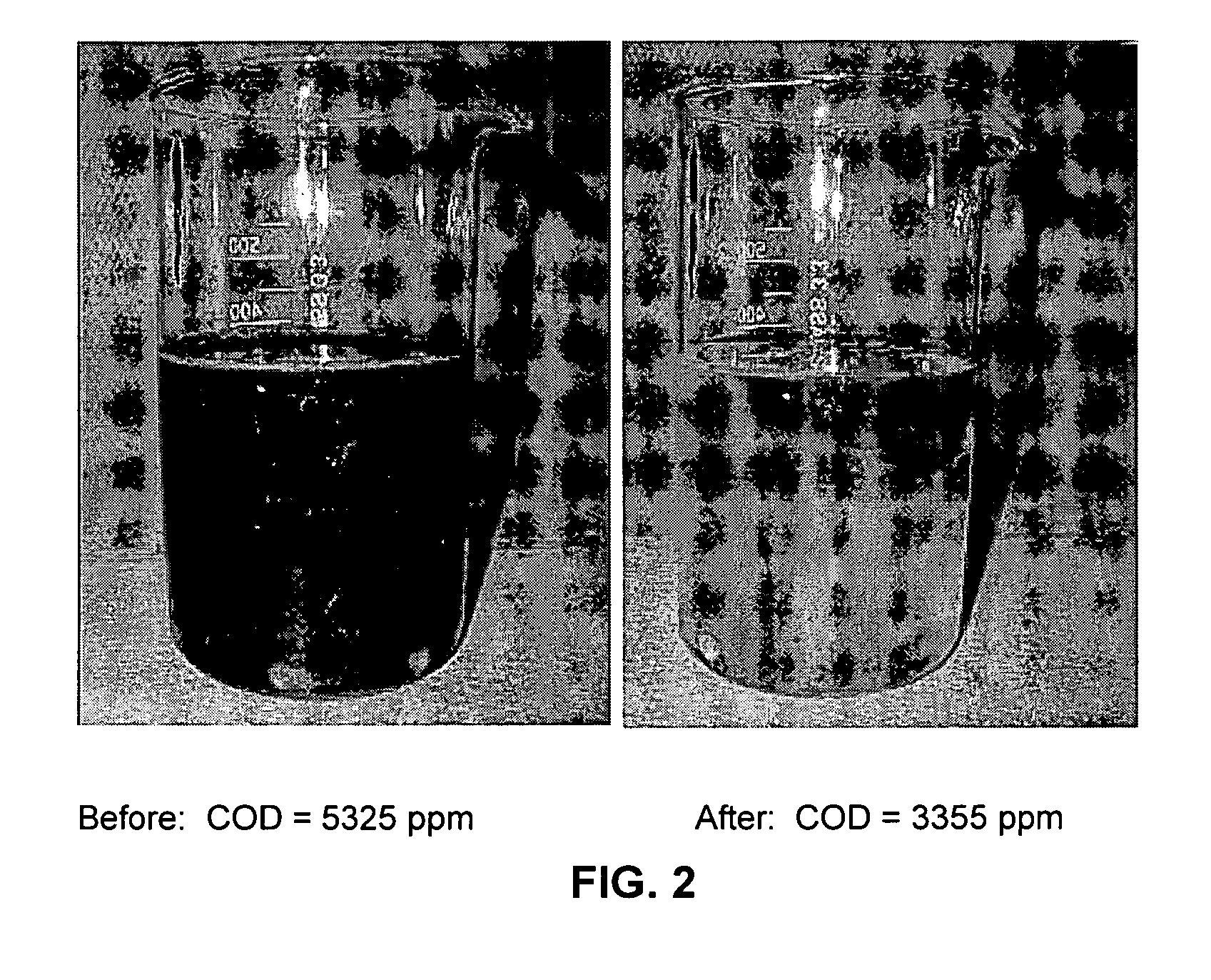
Microbial degradation of water-borne paint containing high levels of organic solvent
InactiveUS20080185337A1Reduce decreaseReduce additionalPaint waste treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandOrganic solvent
A method for degrading, detackifying and reducing solvent in water comprising organic solvent-laden water-borne paint that comprises adding to the water an effective degrading, detackifying and / or solvent-reducing amount of at least one microorganism culture and sufficient micronutrients to sustain the growth of the at least one microorgansim culture and to reduce solvent content of the water. A method of reducing chemical oxygen demand in water comprising organic solvent-laden water-borne paint, wherein the water contains an excess amount of organic solvent from one or both of paint spray operations and paint spray nozzle cleaning operations, the method comprising adding to the water an effective degrading and detackifying amount of at least one microorganism culture and micronutrients to sustain the growth of the at least one microorgansim culture, whereby chemical oxygen demand in the water is reduced by at least 50% relative to the same system without adding the micronutrients.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
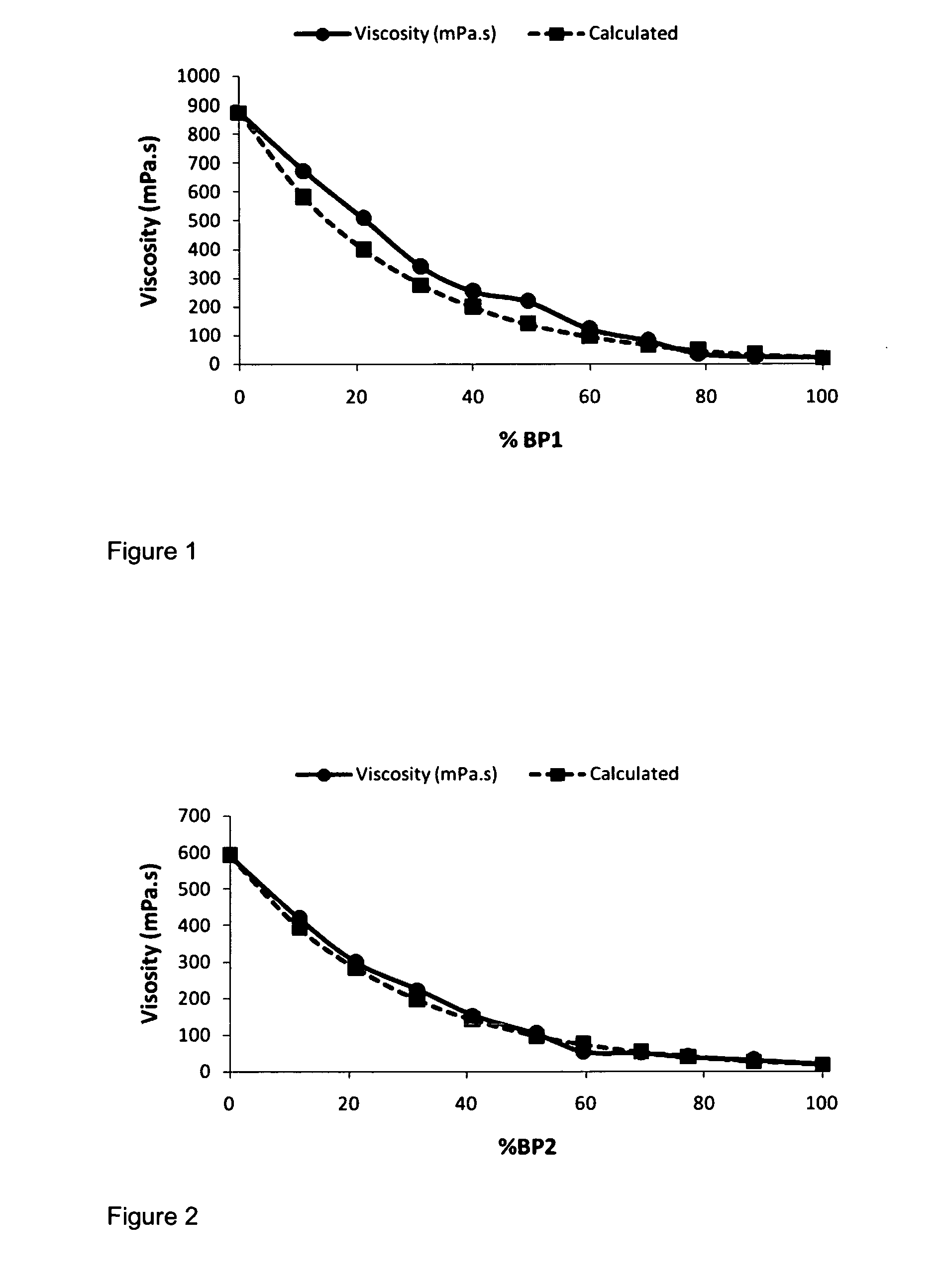
Use of Branched Copolymers in Polymer Blends
InactiveUS20120157318A1High viscosityLow viscosityCosmetic preparationsBiocideViscosityPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to the use of a branched addition copolymer in combination with a polymer in a solution or melt formulation to reduce the viscosity of the solution formulation and / or melt formulation compared to the viscosity of a solution and / or melt comprising the polymer alone wherein the branched addition copolymer is obtainable by an addition polymerisation process, methods for the preparation of the formulations, and novel branched addition copolymers for use as same.
Owner:UNILEVER PLC
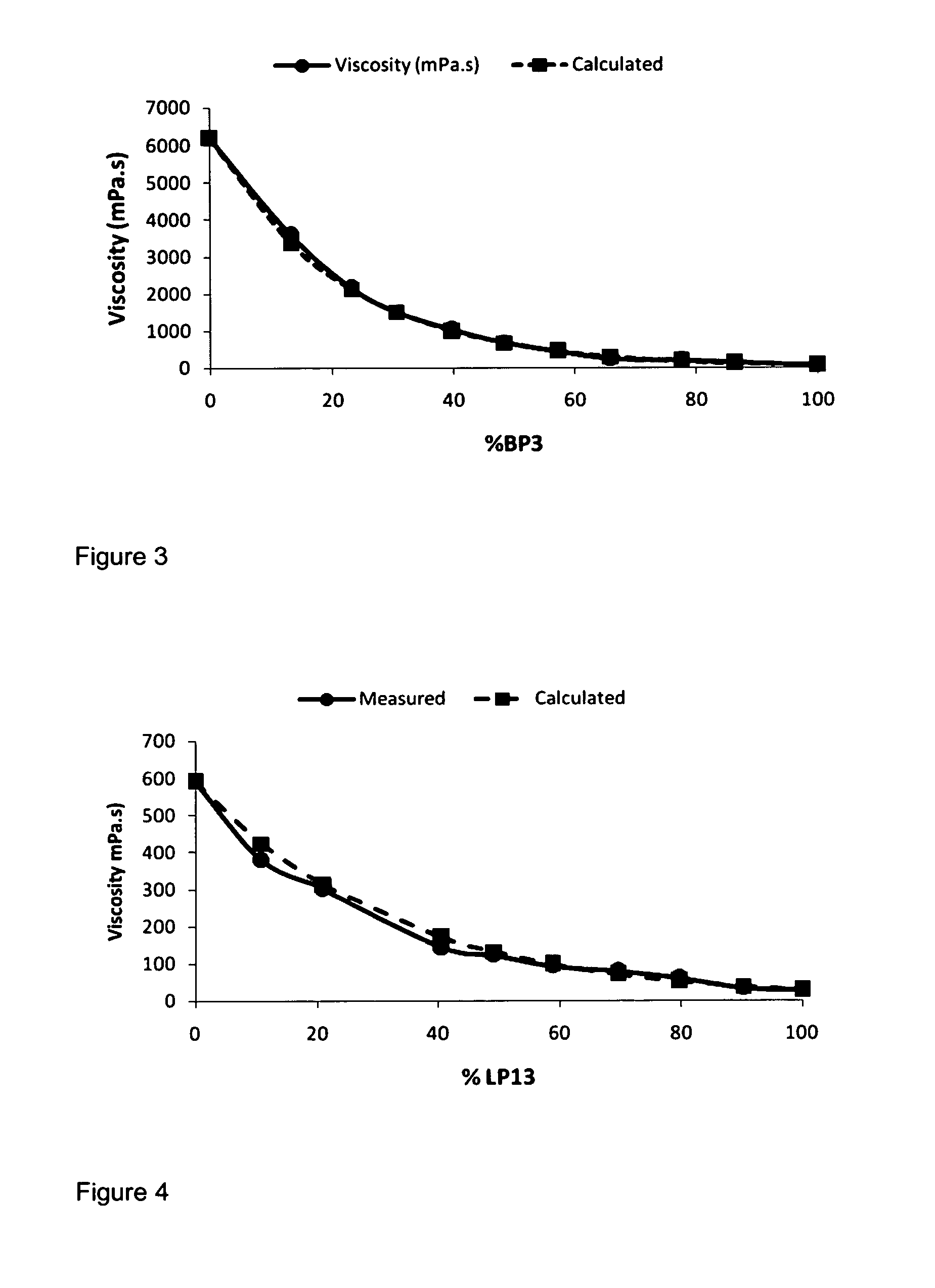
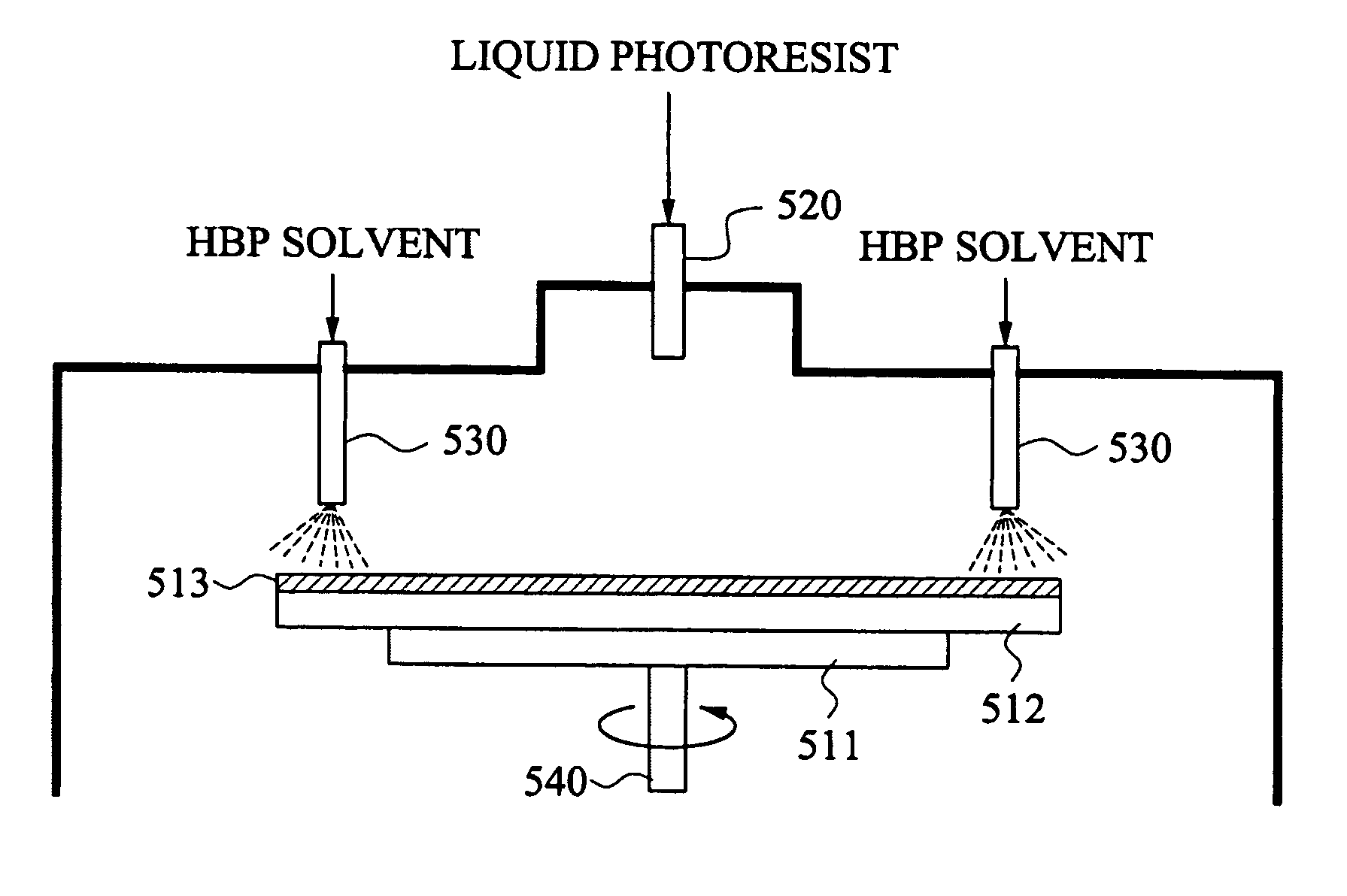
Photoresist coating system and method
InactiveUS20070077352A1Spread evenlyCoated evenlyPretreated surfacesPhotomechanical coating apparatusResistBoiling point
A photoresist coating system and method solving an edge bead problem that occurs in photoresist coating by adding at least one of high boiling point solvent, which may generate a film on the surface of a solvent having a higher boiling point than a solvent contained in a liquid photoresist or the surface of the liquid photoresist, or by supplying a surfactant to an edge of the wafer, with the surfactant being combinable with the solvent or capable of forming a film on the solvent.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
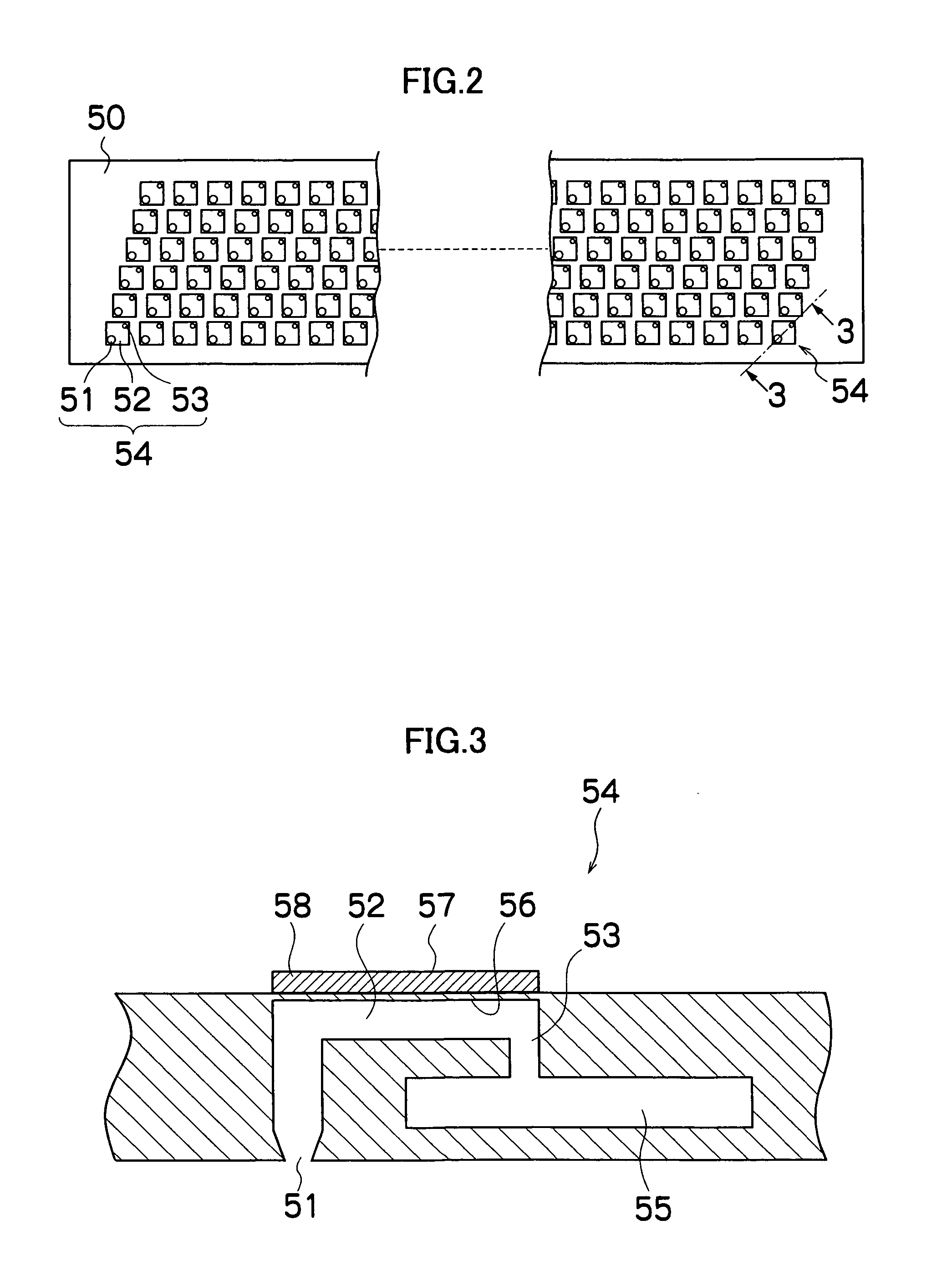
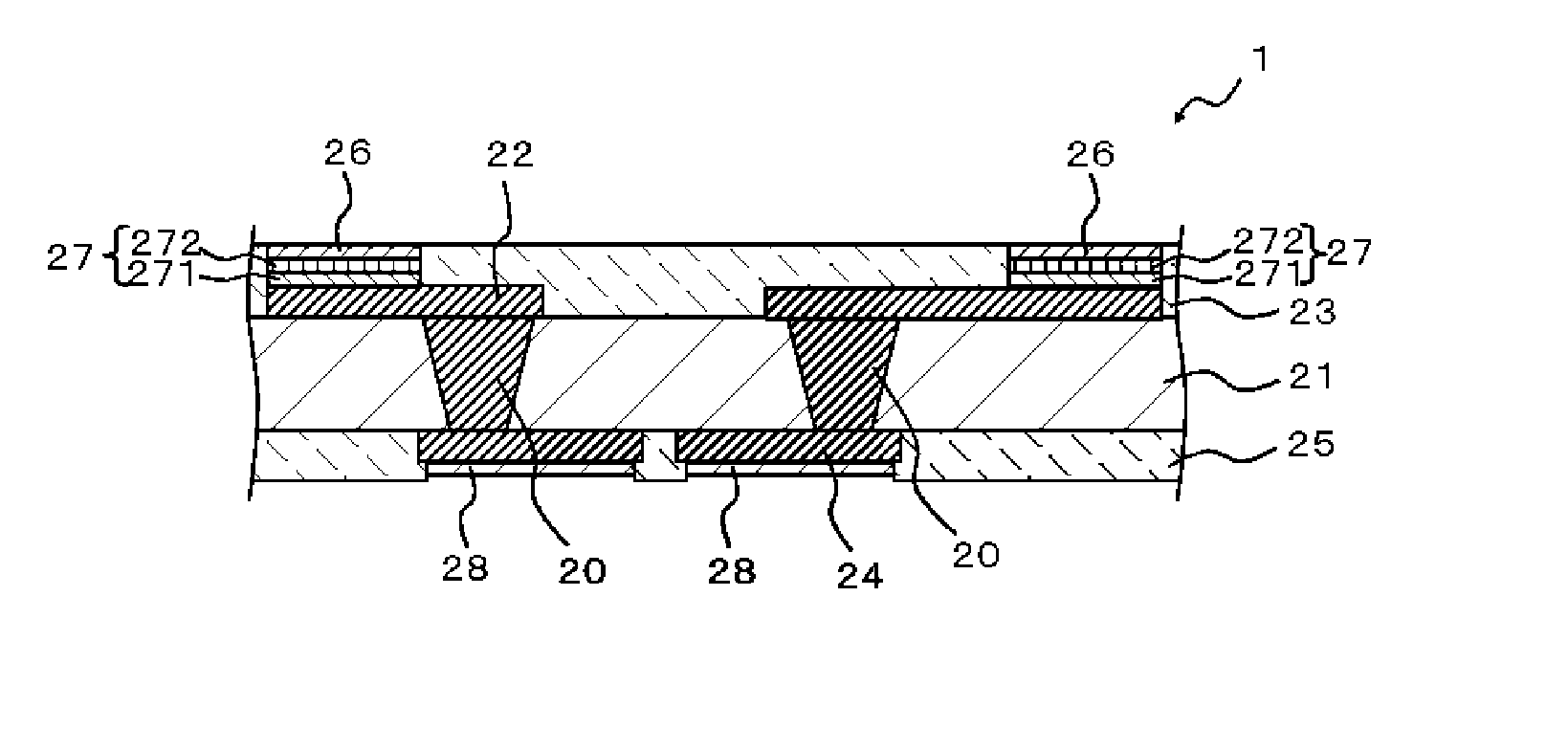
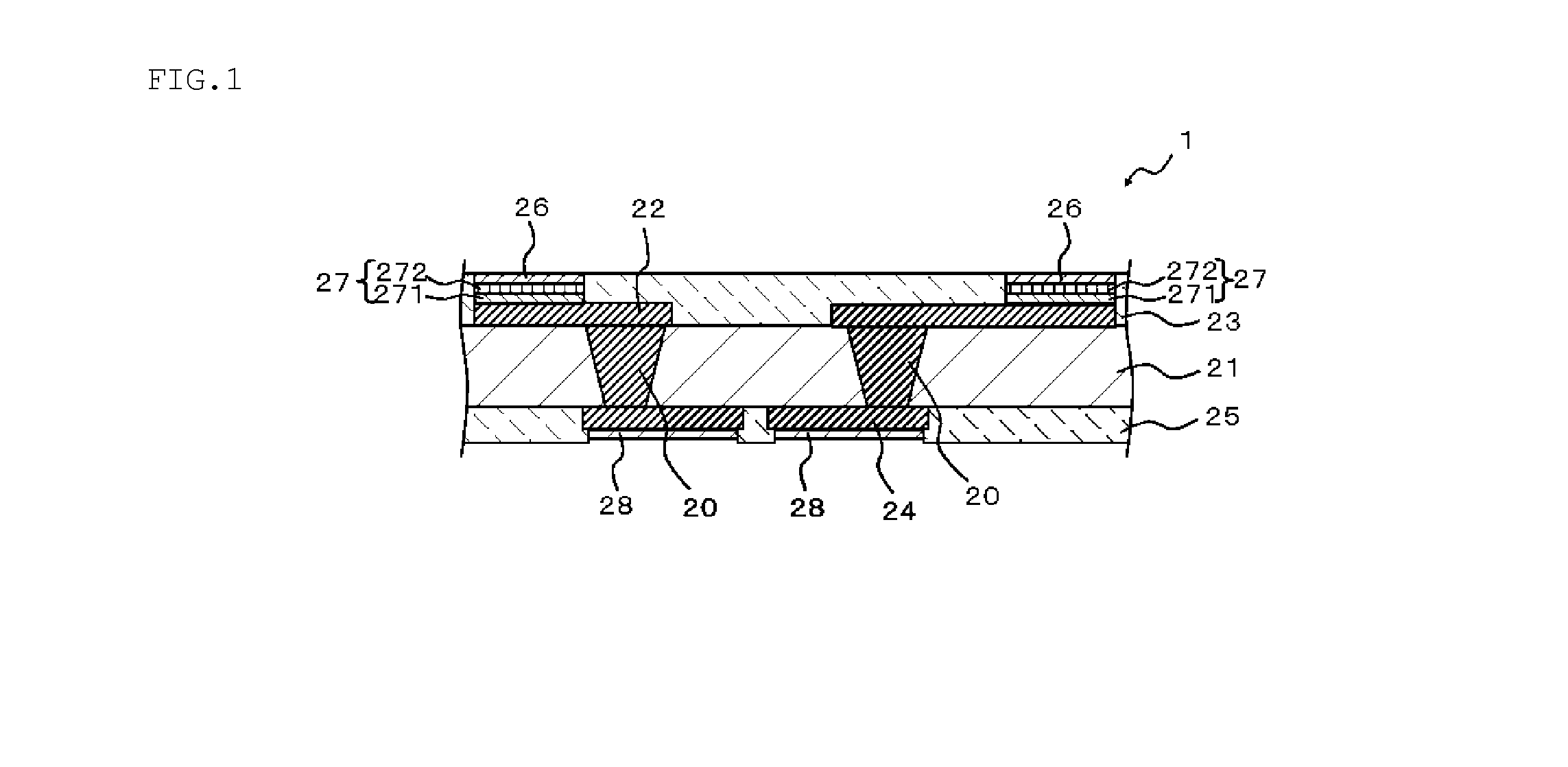
Circuit board, semiconductor device, process for manufacturing circuit board and process for manufacturing semiconductor device
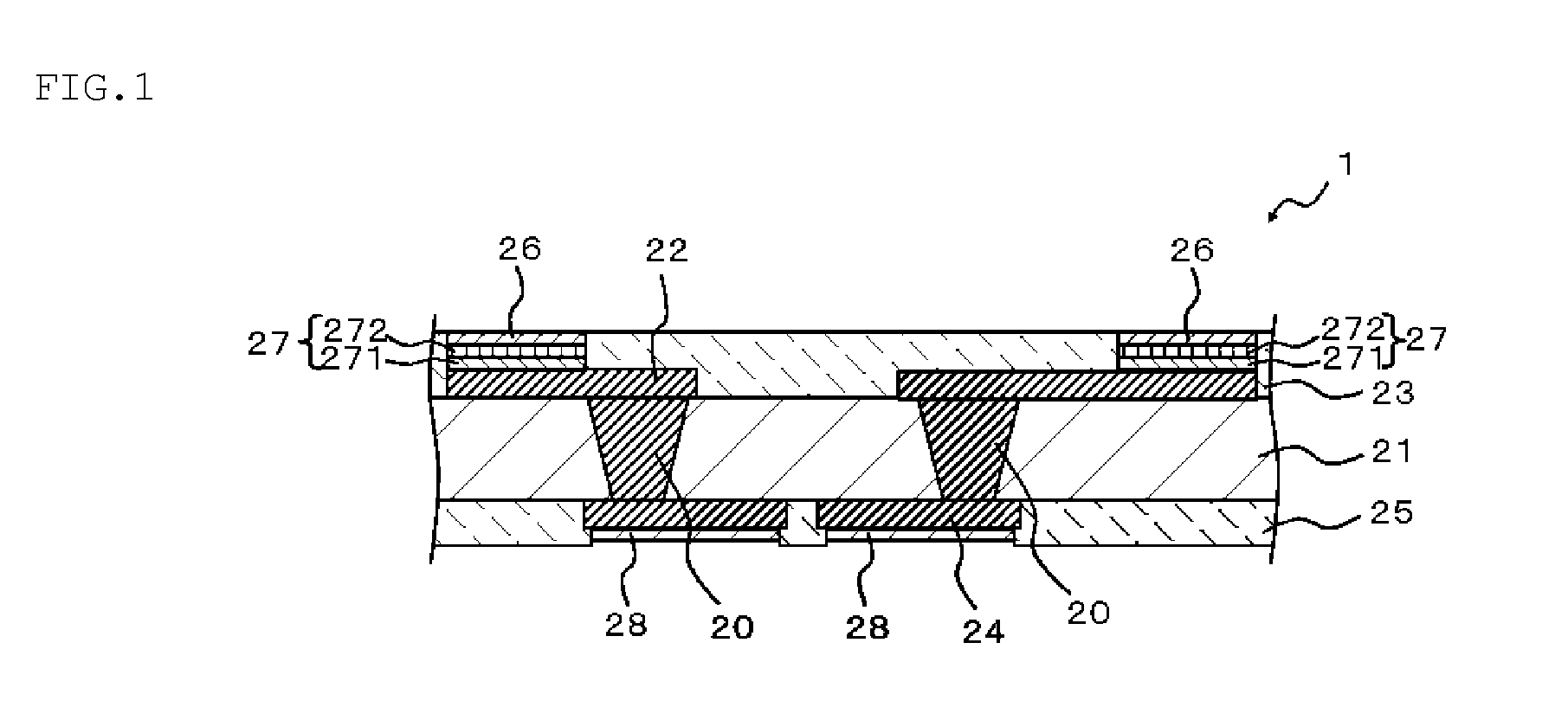
InactiveUS20130015582A1Solubility to solvent is deterioratedDeteriorating film-forming abilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsPower semiconductor deviceGlass transition point
A circuit board (1) exhibits an average coefficient of thermal expansion (A) of the first insulating layer (21) in the direction along the substrate surface in a temperature range from 25 degrees C. to its glass transition point of equal to or higher than 3 ppm / degrees C. and equal to or lower than 30 ppm / degrees C. Further, an average coefficient of thermal expansion (B) of the second insulating layer (23) in the direction along the substrate surface in a temperature range from 25 degrees C. to its glass transition point is equivalent to an average coefficient of thermal expansion (C) of the third insulating layer (25) in the direction along the substrate surface in a temperature range from 25 degrees C. to its glass transition point. (B) and (C) are larger than (A), and a difference between (A) and (B) and a difference between (A) and (C) are equal to or higher than 5 ppm / degrees C. and equal to or lower than 35 ppm / degrees C.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Production of Delta 9 Tetrahydrocannabinol
InactiveUS20110046213A1Promote resultsReduce stepsBiocideNervous disorderDelta-9-tetrahydrocannabinolCarboxylic acid
Δ9 THC is obtained by extracting Δ9 THC and Δ9 THC carboxylic acid from plant material using a non-polar solvent and decarboxylating the Δ9 THC acid into Δ9 THC in the same solvent, without a solvent swap, in the presence of aqueous base. The Δ9 THC is then washed to remove inorganic impurities, still in the same original solvent.
Owner:RESOLUTION CHEM
Acid gas management in liquid fuel production process
InactiveUS9145525B2Low costReduce the overall heightOxygen-containing compound preparationGas modification by gas mixingSteam reformingSyngas
A process and method for producing liquid fuel product from hydrogen and carbon monoxide containing streams produced by gasifying solid carbonaceous feedstock and steam reforming of light fossil fuels. The gasifier syngas is treated to preferentially remove at least 99% of sulfur containing impurities and less than 50% of the CO2 to produce a treated gasifier syngas and a CO2 enriched gas. The treated gasifier syngas and the light fossil fuel conversion unit product gas are combined to form a mixed syngas that is converted into a liquid fuel product. The CO2 enriched gas is used in the gasification unit.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Dual injection points in SAGD
A method for recovering petroleum from a formation, wherein at least two injection wells and at least one production well are in fluid communication with said formation, comprising: introducing a gaseous mixture into a first and a second injection well at a temperature and a pressure, wherein said gaseous mixture comprises steam and non-condens able gas (NCG); and recovering a fluid comprising petroleum from said production well, wherein said injection wells and a production well are horizontal wells, and wherein said first injection well is disposed 1-10 meters above said production well, and said second injection well is disposed at least 5 meters above said first injection well.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Separation of solid asphaltenes from heavy liquid hydrocarbons using novel apparatus and process (“IAS”)
ActiveUS9976093B2Reduce pluggingMitigate settlingLiquid solutions solvent extractionHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationLiquid hydrocarbonsAsphaltene
An apparatus and process is provided for improved asphaltene separation from heavy hydrocarbon or bitumen with low process complexity through mass transfer using solvent and counter-current flows, with three sections: an upper DAO / solid-asphaltene separation zone, a middle solvent mixing and segregation zone, and a bottom clarification zone. Solvent mixed with heavy hydrocarbon forms a process feed introduced to the process vessel's upper zone and exposed to counter-current solvent removing DAO from solid asphaltene particles in the feed, the particles fall through the middle zone and are mixed with introduced solvent, which introduced solvent segregates DAO-rich solution in the upper zone (for extraction from that zone) from solvent-rich mixtures in the middle mixing and lower clarification zones. Solvent flows and precipitate movement are controlled to optimize mass transfer in process, resulting in high DAO recovery and dry, solid asphaltene product.
Owner:SUNCOR ENERGY INC
Hydrazide chelate complex compound, optical recording medium using the compound and recording method thereof
InactiveUS20090252013A1Improve solubilityLow light fastnessHydrazone dyesLayered productsSolubilityRecording layer
Provided are a novel hydrazide chelate complex compound which is excellent in terms of both solubility in a coating solvent and light fastness, which can be used for blue laser recording, and which is useful as a dye for forming a recording layer of an optical recording medium, the hydrazide chelate complex compound being represented by general formula (1) below; and a dye for forming a recording layer of an optical recording medium, the dye containing the compound.In general formula (1), ring A represents an aromatic ring; R1 and R6 each represent an aromatic ring group or a monovalent nonaromatic ring substituent having 20 or less carbon atoms; R2 to R5 each represent a hydrogen atom, an aromatic ring group, or a monovalent nonaromatic ring substituent having 20 or less carbon atoms; n represents 0 or 1; a represents an integer of 1 to 3; M represents a transition metal atom; and X represents an atom of Groups 14 to 16 of the periodic table.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
Circuit board, semiconductor device, process for manufacturing circuit board and process for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS8742568B2Increase thermal resistanceDegrade solventSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsVitrificationThermal expansion
A circuit board (1) exhibits an average coefficient of thermal expansion (A) of the first insulating layer (21) in the direction along the substrate surface in a temperature range from 25 degrees C. to its glass transition point of equal to or higher than 3 ppm / degrees C. and equal to or lower than 30 ppm / degrees C. Further, an average coefficient of thermal expansion (B) of the second insulating layer (23) in the direction along the substrate surface in a temperature range from 25 degrees C. to its glass transition point is equivalent to an average coefficient of thermal expansion (C) of the third insulating layer (25) in the direction along the substrate surface in a temperature range from 25 degrees C. to its glass transition point. (B) and (C) are larger than (A), and a difference between (A) and (B) and a difference between (A) and (C) are equal to or higher than 5 ppm / degrees C. and equal to or lower than 35 ppm / degrees C.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
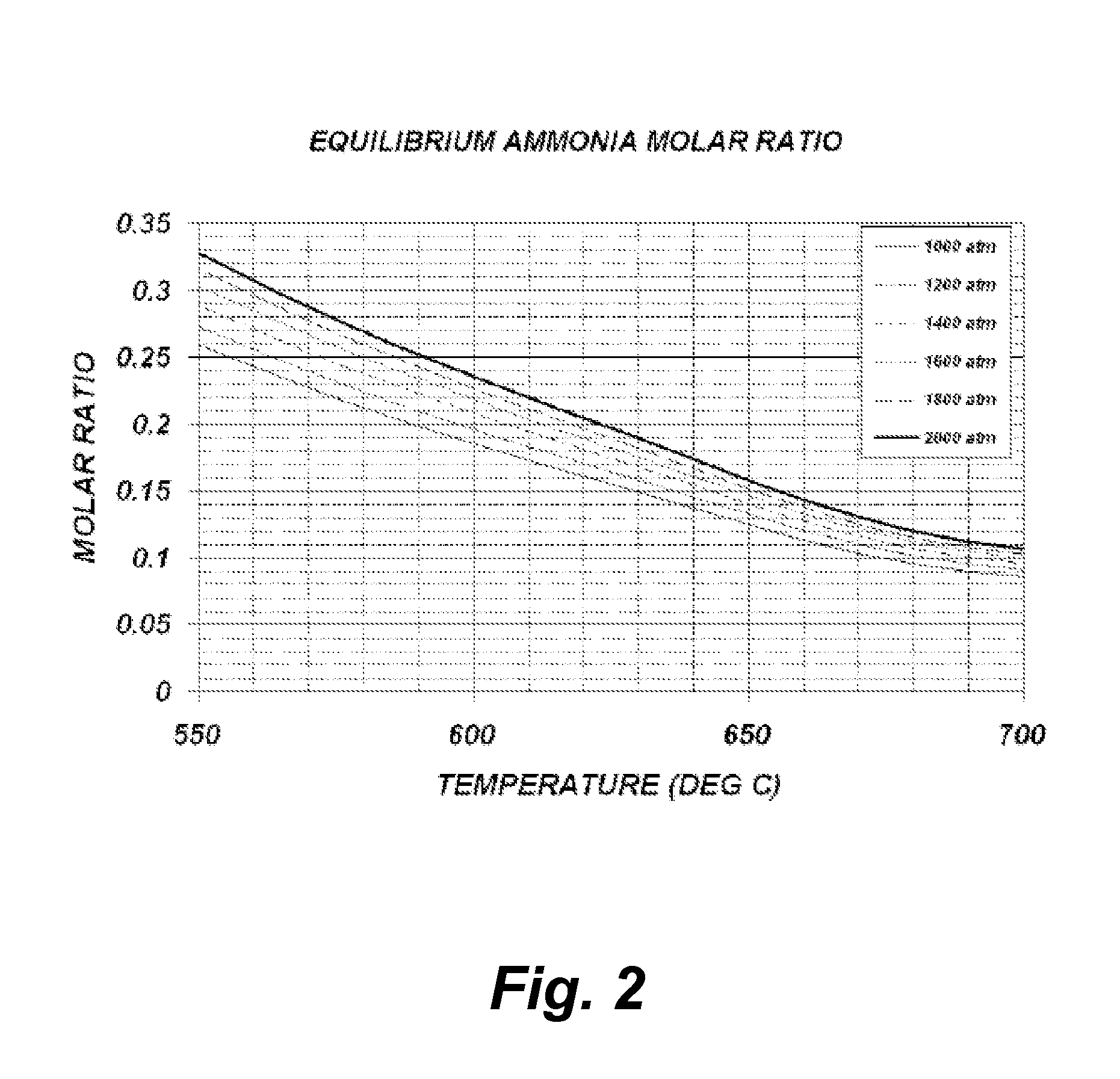
Addition of hydrogen and/or nitrogen containing compounds to the nitrogen-containing solvent used during the ammonothermal growth of group-iii nitride crystals
InactiveUS20110212013A1Increase productionReduce decompositionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSolventDecomposition
A method for adding hydrogen-containing and / or nitrogen-containing compounds to a nitrogen-containing solvent used during ammonothermal growth of group-Ill nitride crystals to offset decomposition products formed from the nitrogen-containing solvent, in order to shift the balance between the reactants, i.e. the nitrogen-containing solvent and the decomposition products, towards the reactant side.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Utilization of Ferric Ammonium Citrate for In Situ Remediation of Chlorinated Solvents
InactiveUS20140030797A1Promote degradationAccelerated dechlorinationSolid waste disposalWater contaminantsUltrasound attenuationIn situ remediation
Accelerated dechlorination of soil and water contaminated with chlorinated solvents in situ is achieved by delivering ferric ammonium citrate into the soils and / or water. The induction of ferric ammonium citrate into sulfate-rich reducing conditions initiates a combined abiotic and biotic mechanism for the dechlorination of subsurface contaminants. Initial and rapid removal of chlorinated solvents is achieved by way of reductive transformation, a mechanism utilizing the creation of an iron-bound soil mineral (pyrite) followed by stimulating conditions for enhanced biological natural attenuation.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Enrichment Method of Ergosterol Peroxide from Sporoderm-Broken Ganoderma Lucidum Spore Powder
ActiveUS20170360802A1Good and safe for environmentIncrease contentOrganic active ingredientsChewing gumSporeEnrichment methods
The invention provides an enrichment method of Ergosterol peroxide from sporoderm-broken Ganoderma lucidum spore powder, comprising the steps of preparing crude extract containing Ergosterol peroxide, purification by medium pressure preparative chromatography, purification by simulated moving-bed, and recrystallization. The operation of this invention is simple and stable, with higher yield and low cost, suiting for industrial continuous production.
Owner:GUANGDONG YUEWEI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Device and method for fixing a toner image by solvent vapor while reducing the solvent drag-out
InactiveUS7006783B2Degrade solventElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternSolvent vaporEngineering
Owner:OCE PRINTING SYST
Sulfonic acid ester compound and use therefor
ActiveUS10513491B2Improve solubilityImprove flatnessOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSulfonateCarbon number
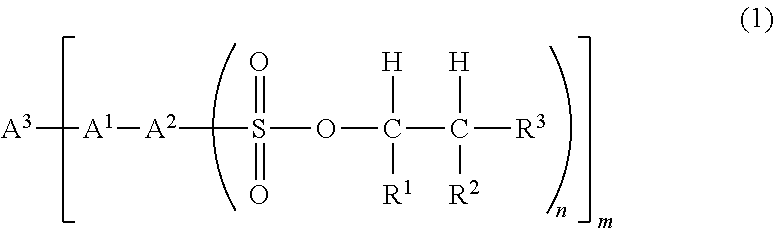
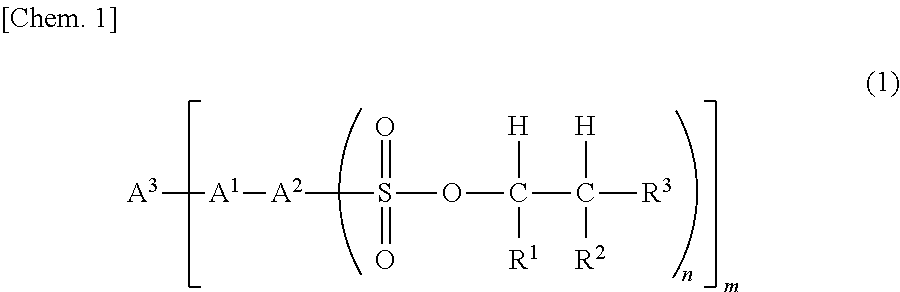
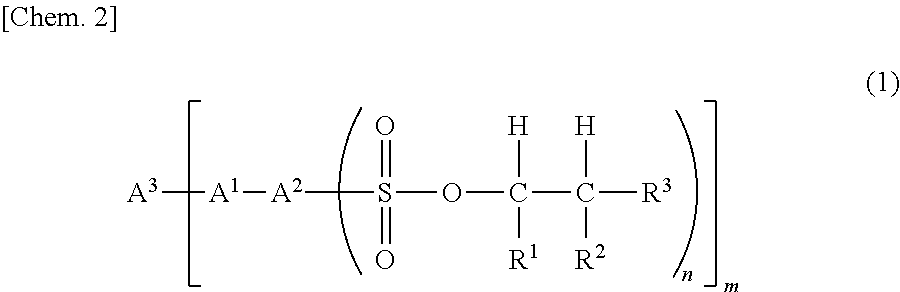
Provided is a sulfonic acid ester compound represented by formula (1).(In the formula, R1 and R2 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, or a straight-chain or branched monovalent aliphatic hydrocarbon group. R3 represents a straight-chain or branched monovalent aliphatic hydrocarbon group. The sum of the carbon numbers of R1, R2 and R3 is 6 or greater. A1 represents —O— or —S—. A2 represents an aromatic group having a valence of (n+1). A3 represents a hydrocarbon group which has a valence of m, and is unsubstituted or has a substituent that contains one or more aromatic rings. m represents an integer satisfying 2≤m≤4. n represents an integer satisfying 1≤n≤4).
Owner:NISSAN CHEM CORP
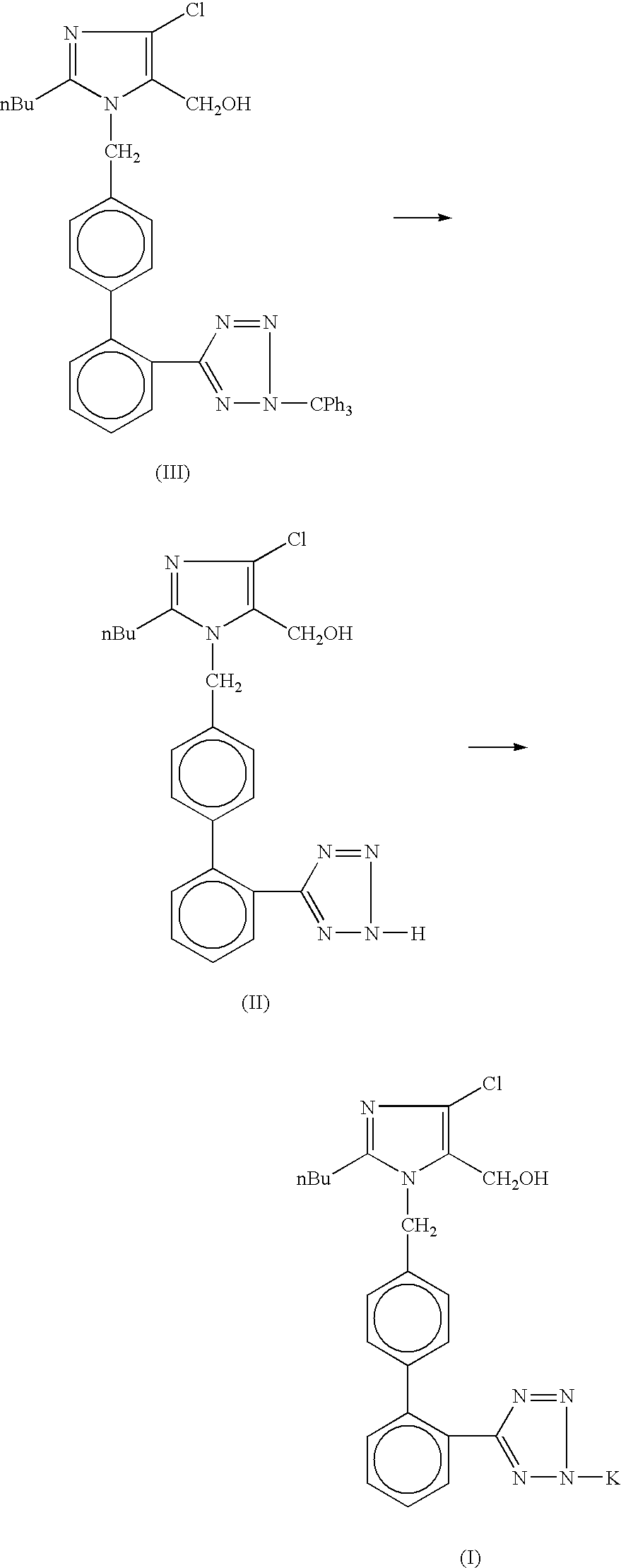
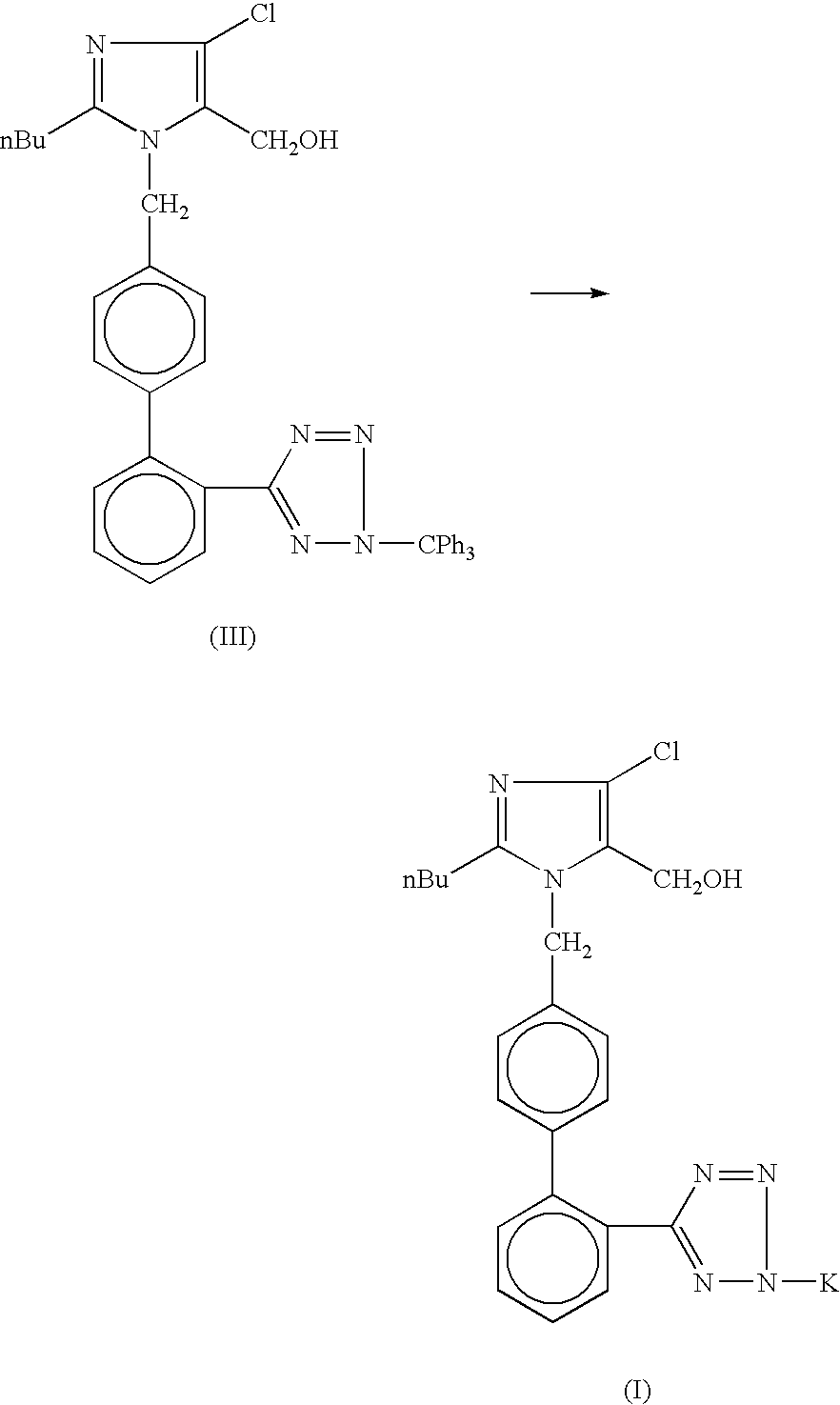
Losartan potassium synthesis
InactiveUS20040224998A1High purityReduction of solvent usageBiocideOrganic chemistryPotassiumPrimary alcohol
Owner:IPCA LAB LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com