Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70results about "Hydrocarbon oils refining control/regulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
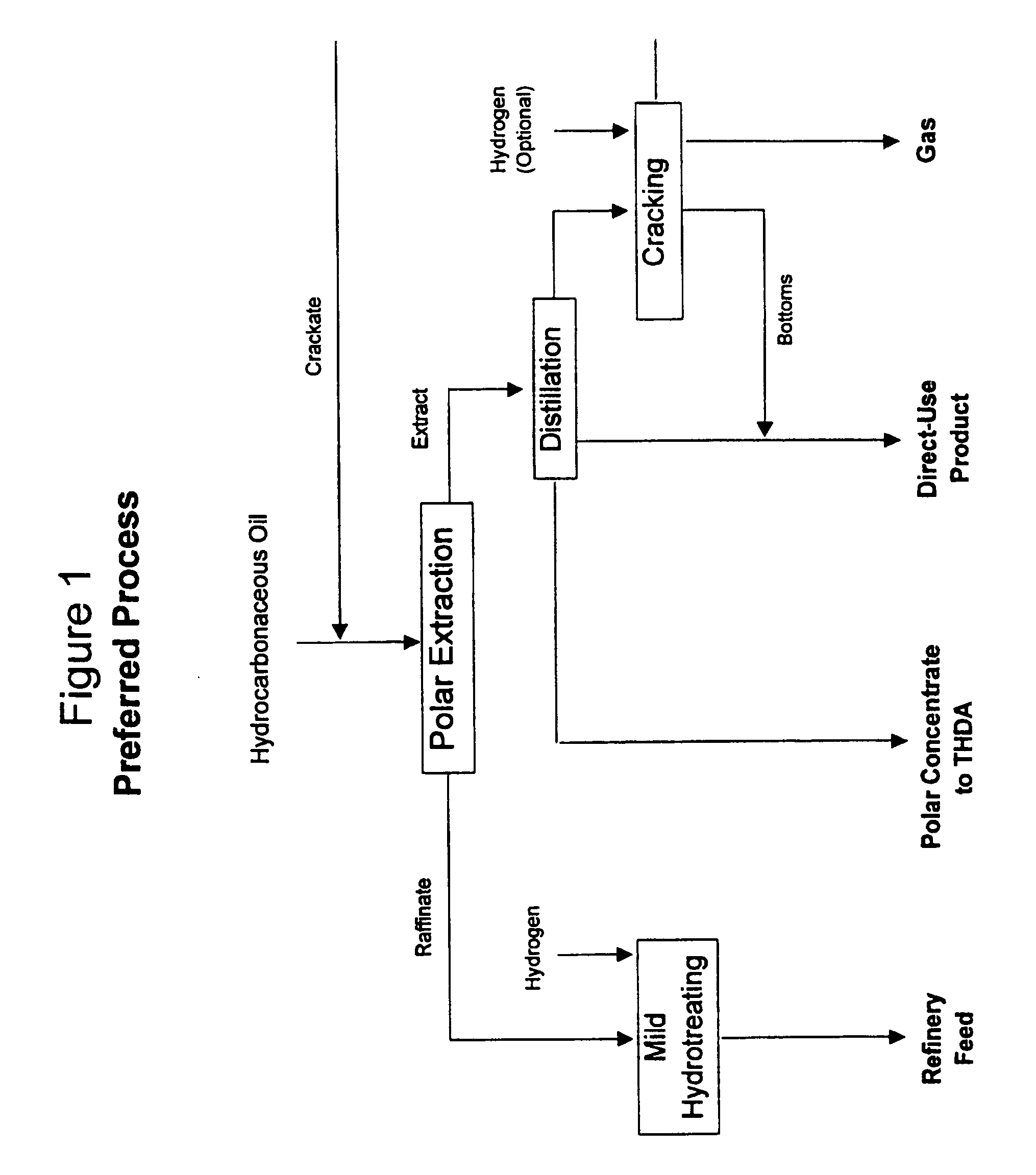
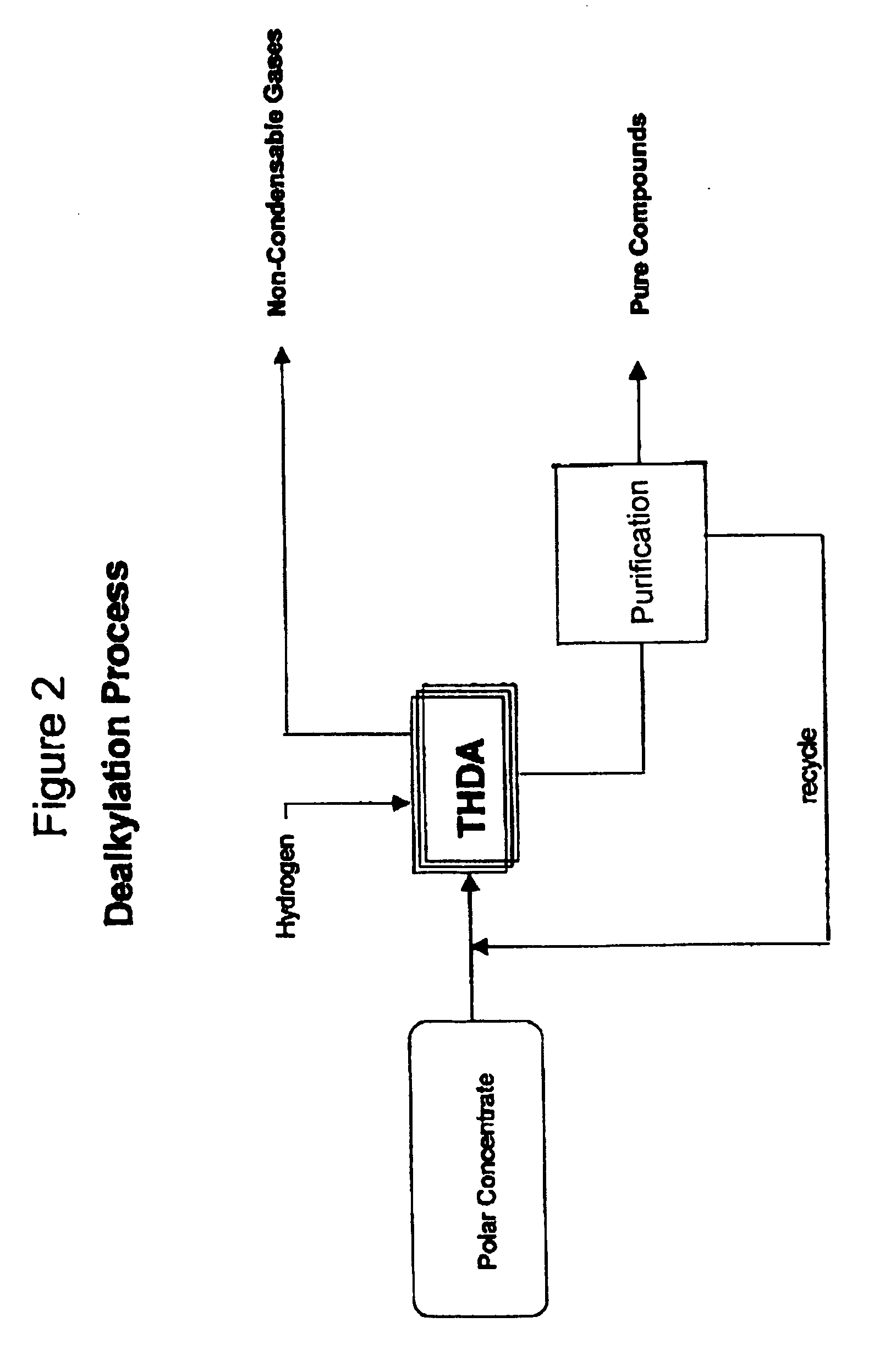
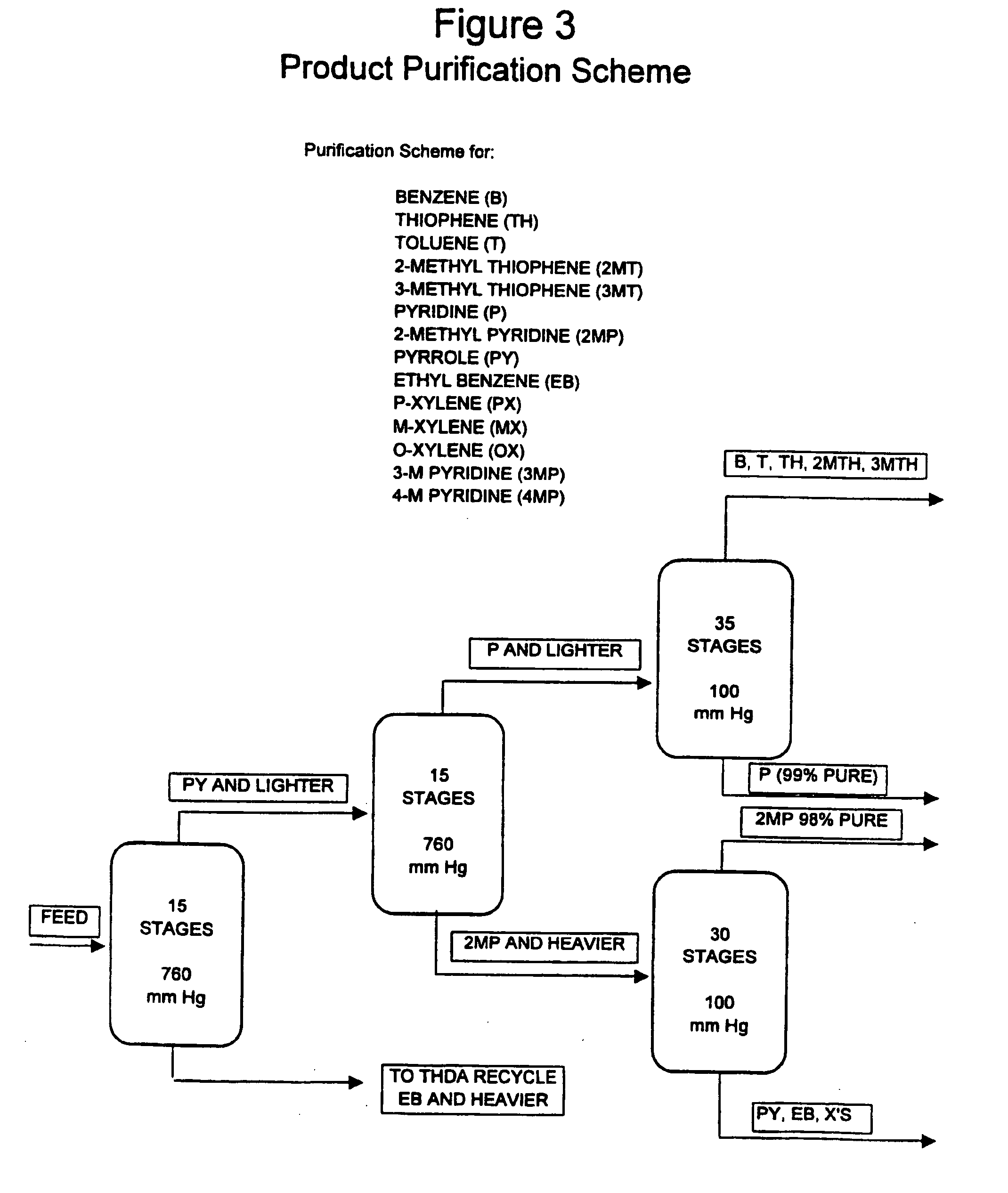
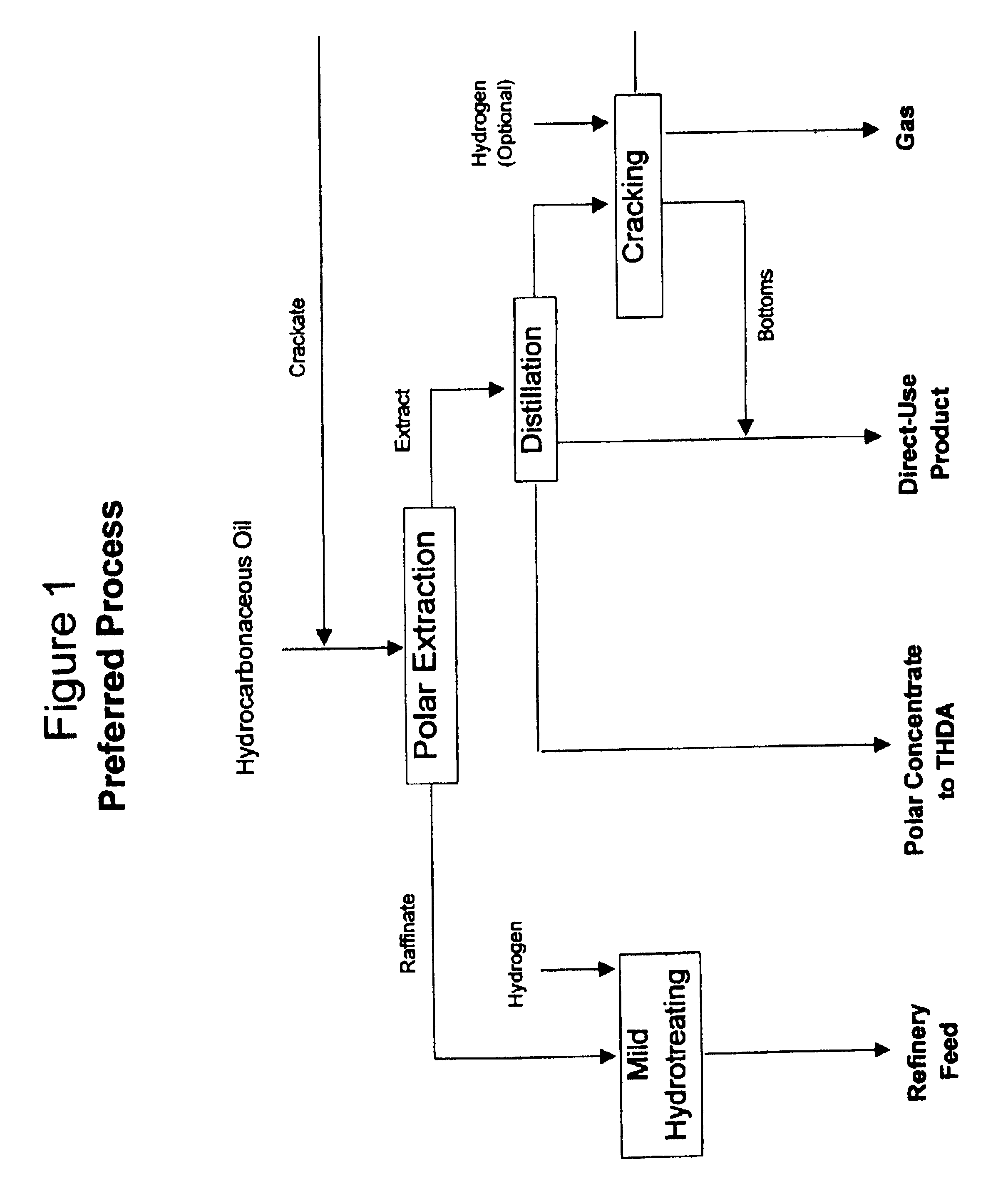
Process for enhancing the value of hydrocarbonaceous natural resources
InactiveUS20050167337A1Little and wasteLittle and valueHydrocarbon distillationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesSolubilityNatural resource
A process for upgrading hydrocarbonaceous oil containing heteroatom-containing compounds where the hydrocarbonaceous oil is contacted with a solvent system that is a mixture of a major portion of a polar solvent having a dipole moment greater than about 1 debye and a minor portion of water to selectively separate the constituents of the carbonaceous oil into a heteroatom-depleted raffinate fraction and heteroatom-enriched extract fraction. The polar solvent and the water-in-solvent system are formulated at a ratio where the water is an antisolvent in an amount to inhibit solubility of heteroatom-containing compounds and the polar solvent in the raffinate, and to inhibit solubility of non-heteroatom-containing compounds in the extract. The ratio of the hydrocarbonaceous oil to the solvent system is such that a coefficient of separation is at least 50%. The coefficient of separation is the mole percent of heteroatom-containing compounds from the carbonaceous oil that are recovered in the extract fraction minus the mole percent of non-heteroatom-containing compounds from the carbonaceous oil that are recovered in the extract fraction. The solvent-free extract and the raffinate concentrates may be used directly or processed to make valuable petroleum, chemical or industrial products.
Owner:JAMES W BUNGER & ASSOC
Process for enhancing the value of hydrocabonaceous natural recources
InactiveUS6875341B1Little and valueReduce total process throughputRefining with acid-containing liquidsHydrocarbonsSolubilitySolvent free
Owner:JWBA
Process for upgrading of Fischer-Tropsch products
A process for treating nitrogen-containing, substantially paraffinic product derived from a Fischer-Tropsch process. The substantially paraffinic product is purified in a purification process to lower the concentration of oxygen, nitrogen, and other impurities. The nitrogen content of the purified product is monitored, and the conditions of the purification step are adjusted to increase nitrogen removal if the nitrogen content of the purified product exceeds a preselected value.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Coalescer For Co-Current Contactors
ActiveUS20160263516A1Increase droplet sizeIncrease in sizeGas treatmentDispersed particle separationSolventDroplet size
The disclosure includes a method, comprising passing a fluid into a co-current contactor, passing a solvent into the co-current contactor, dividing the solvent into solvent droplets having a first average droplet size, placing the fluid in contact with the solvent droplets to create a combined stream, coalescing at least a portion of the solvent droplets to create solvent droplets having a second average droplet size, wherein the second average droplet size is greater than the first average droplet size, and separating the fluid and the solvent.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
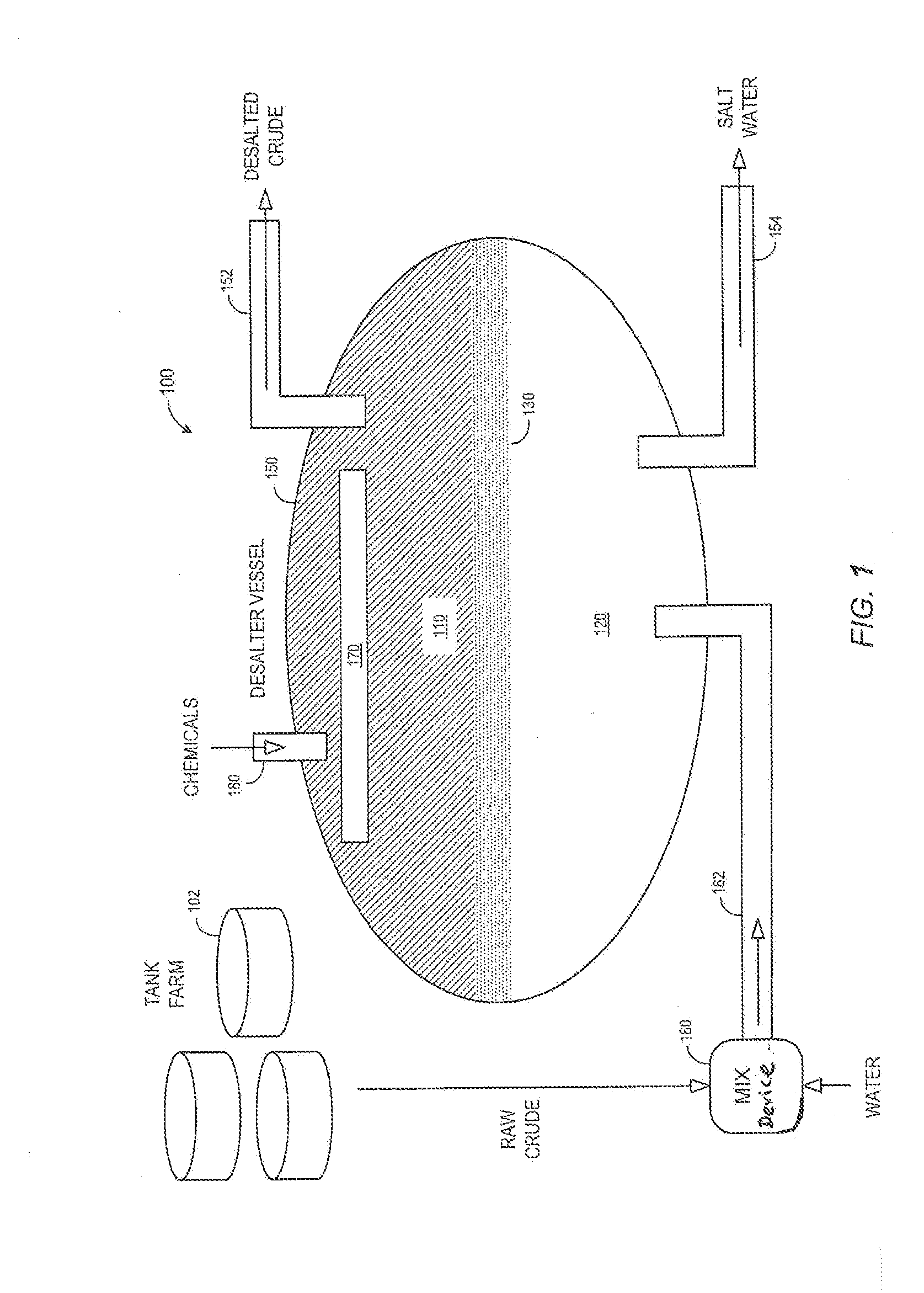
Separator for desalting petroleum crude oils having rag layer withdrawal
ActiveUS20140251874A1Minimal downtimeDewatering/demulsification with electric/magnetic meansRefining by water treatmentEmulsionAutomatic control
An improved separator for desalting petroleum crude oils which may be operated in a continuous manner under automatic control; the improved desalter is therefore well suited to modern refinery operation with minimal downtime. A portion of the emulsion layer is withdrawn from the desalter through external withdrawal ports according to the thickness and position of the emulsion layer with the selected withdrawal header(s) being controlled by sensors monitoring the position and thickness of the emulsion layer. The withdrawn emulsion layer can be routed as such or with the desalter water effluent to a settling tank or directly to another unit for separation and reprocessing.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Method for using native bitumen markers to improve solvent-assisted bitumen extraction
ActiveUS8449764B2Quality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementSulfurManganese
In solvent-assisted bitumen extraction, a native marker, for example: sulfur, nickel, vanadium, iron copper, or manganese, is used to control the solvent to bitumen ratio in a process stream such as a stream from a froth separation unit (FSU) and / or to measure hydrocarbon loss in a tailings solvent recovery unit (TSRU).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
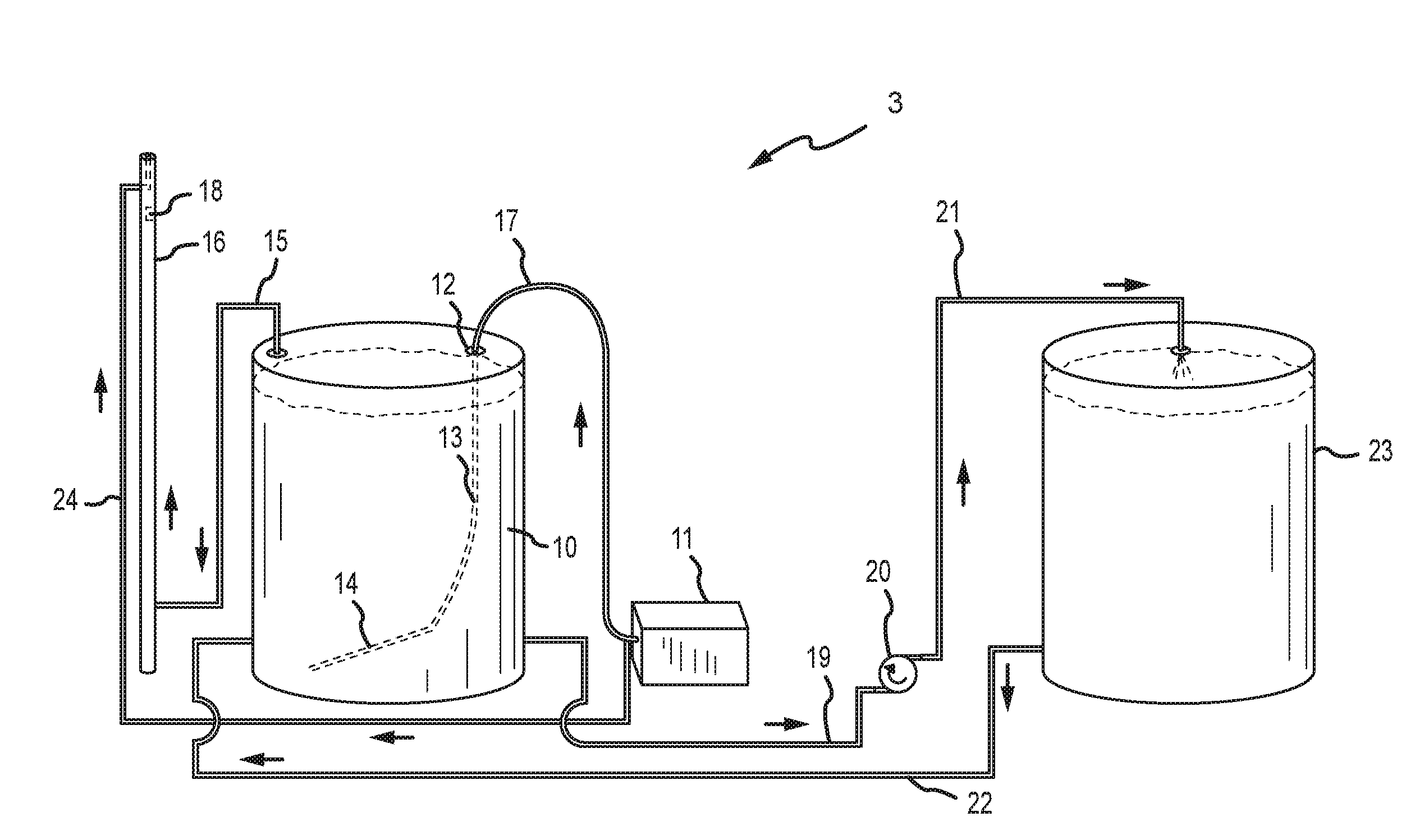
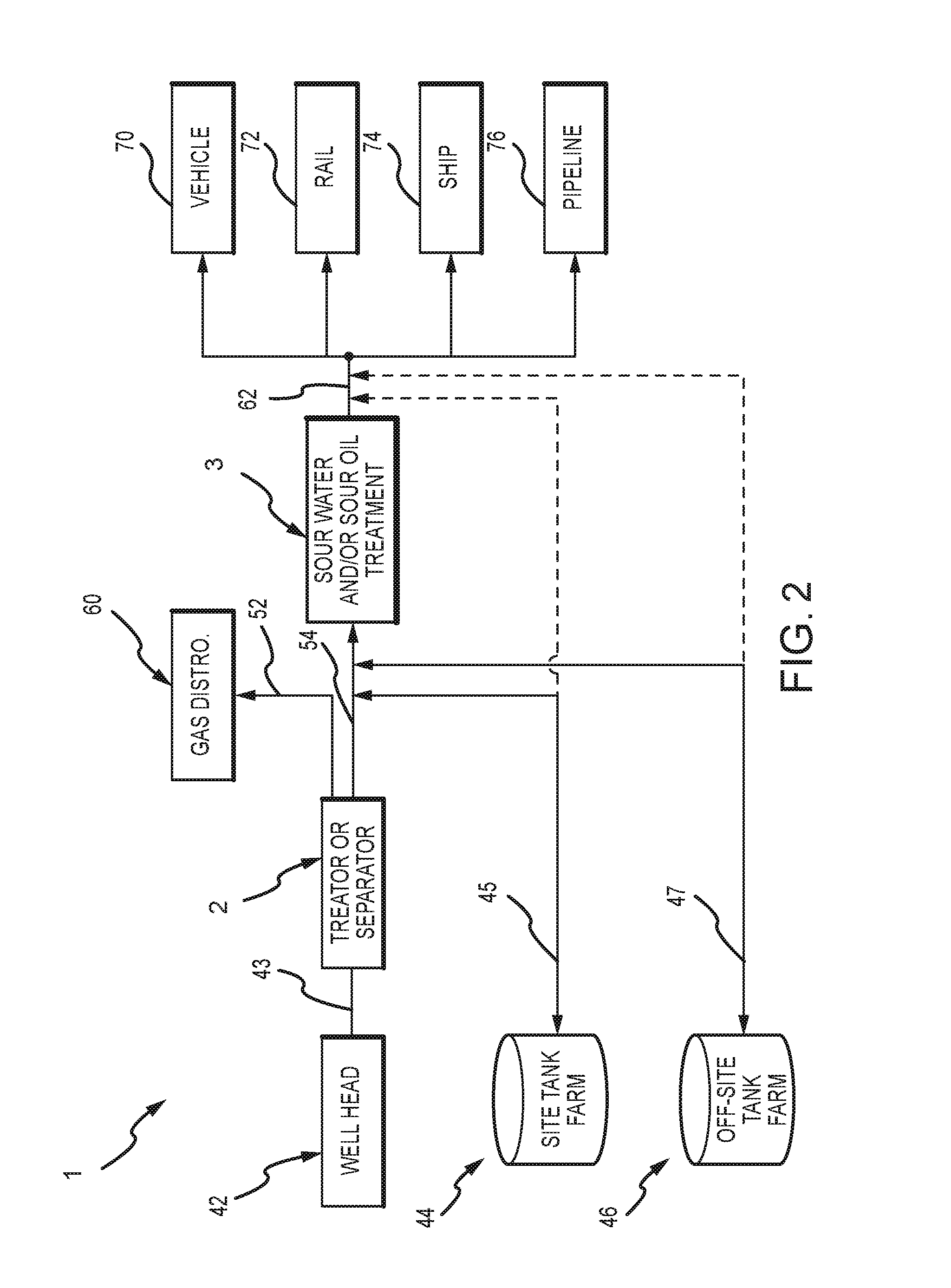
Method and system for removing hydrogen sulfide from sour oil and sour water
ActiveUS9028679B2Reduce contentHigh levelWater treatment parameter controlLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesScavengerHydrocarbon
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to a system and method to remove hydrogen sulfide from sour water and sour oil. In particular, hydrogen sulfide is removed from sour water and sour oil without the need for special chemicals, such as catalyst chemicals, scavenger chemicals, hydrocarbon sources, or a large scale facility. The system and method in the present invention is particularly useful in exploratory oil and gas fields, where large facilities to remove hydrogen sulfide may be inaccessible. The present invention addresses the need for safe and cost effective transport of the deadly neurotoxin. Particular embodiments involve a system and method that can be executed both on a small and large scale to sweeten sour water and sour oil.
Owner:ANSCHUTZ EXPLORATION
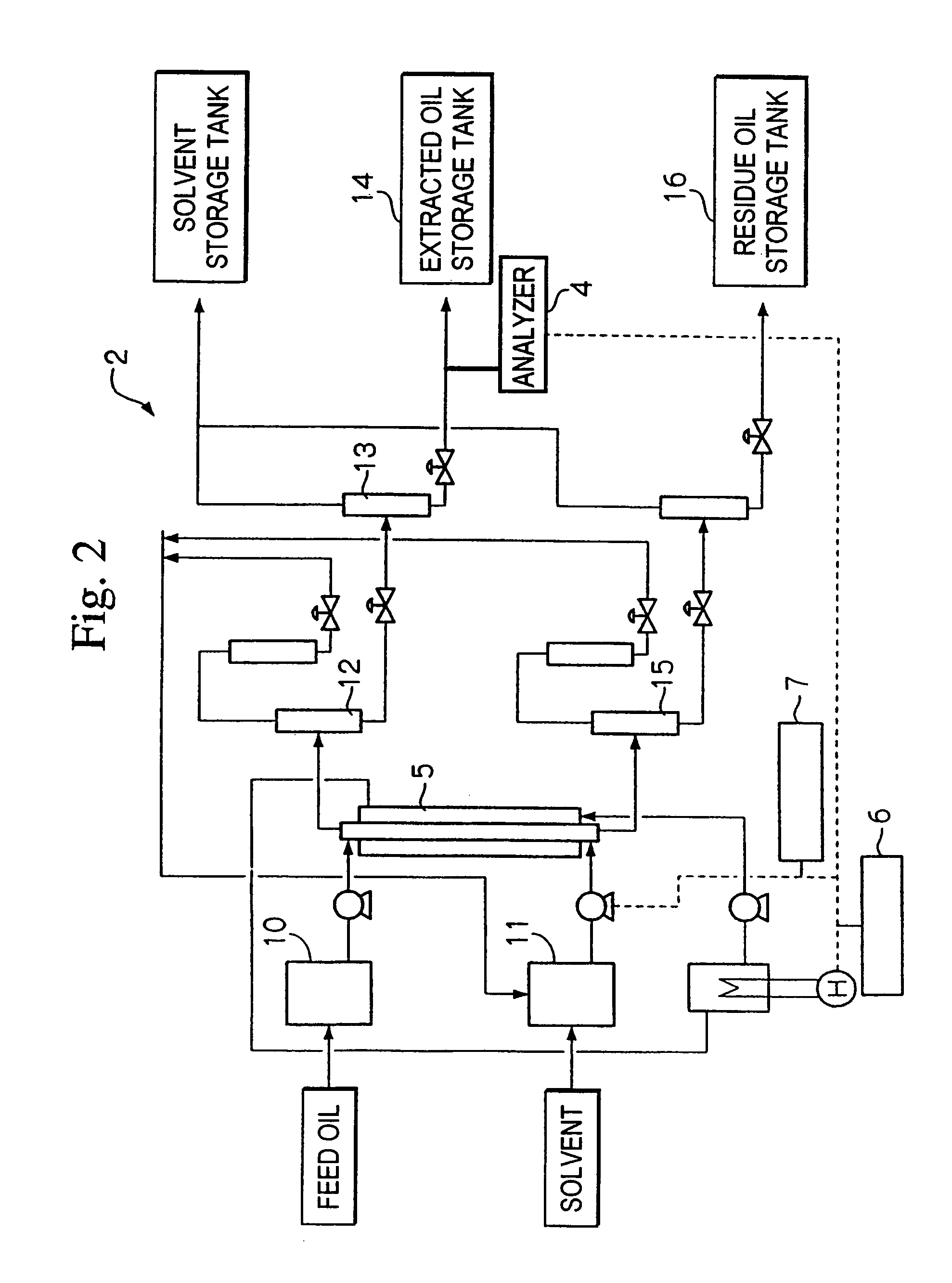
Method of refining heavy oil and refining apparatus
InactiveUS7857964B2Increase the number ofHigh yieldRadiation pyrometryWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionHydrogenation processSolvent
The present invention relates to a method in which grades of oil are refined according to their object from a feed oil. This method has a solvent extraction process that obtains an extracted oil, and a hydrogenation process that subjects the obtained extracted oil to hydrogenation process in the presence of hydrogen and a catalyst to obtain a hydrorefined oil. The solvent extraction conditions are selected by using the poly-aromatic concentration as an index for calculating the concentration of heptane insoluble components in the residue of the extracted oil obtained by the solvent extraction process that cannot be fractionally distilled.
Owner:JGC CORP
Method and system for removing hydrogen sulfide from sour oil and sour water
ActiveUS9364773B2Reduce contentHigh levelWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment parameter controlScavengerHydrocarbon
Owner:ANSCHUTZ EXPLORATION
Advisory controls of desalter system
ActiveUS20150361350A1Dewatering/demulsification with chemical meansLiquid separation auxillary apparatusDemulsifierFirst principle
The present invention concerns a method of providing advisory controls for a desalter system. The method allows a user to continuously monitor performance of the desalter system, to continuously monitor position of the emulsion band (or rag layer), to control the emulsion band using demulsifiers, and to recommend to users how to maintain optimal pressure drop at the mixing device of the desalter system. This is achieved by using a first principles based model combined with a sensor to measure the position, quality and size of the emulsion band. The first principles based model takes into account the geometry of the desalter system, physical properties of the crude oil and water, as well as the operating conditions. Thus, the method provides users with sensing of an emulsion layer through direct measurements and also gives recommendations on appropriate corrective actions to be initiated during upsets.
Owner:BL TECH INC
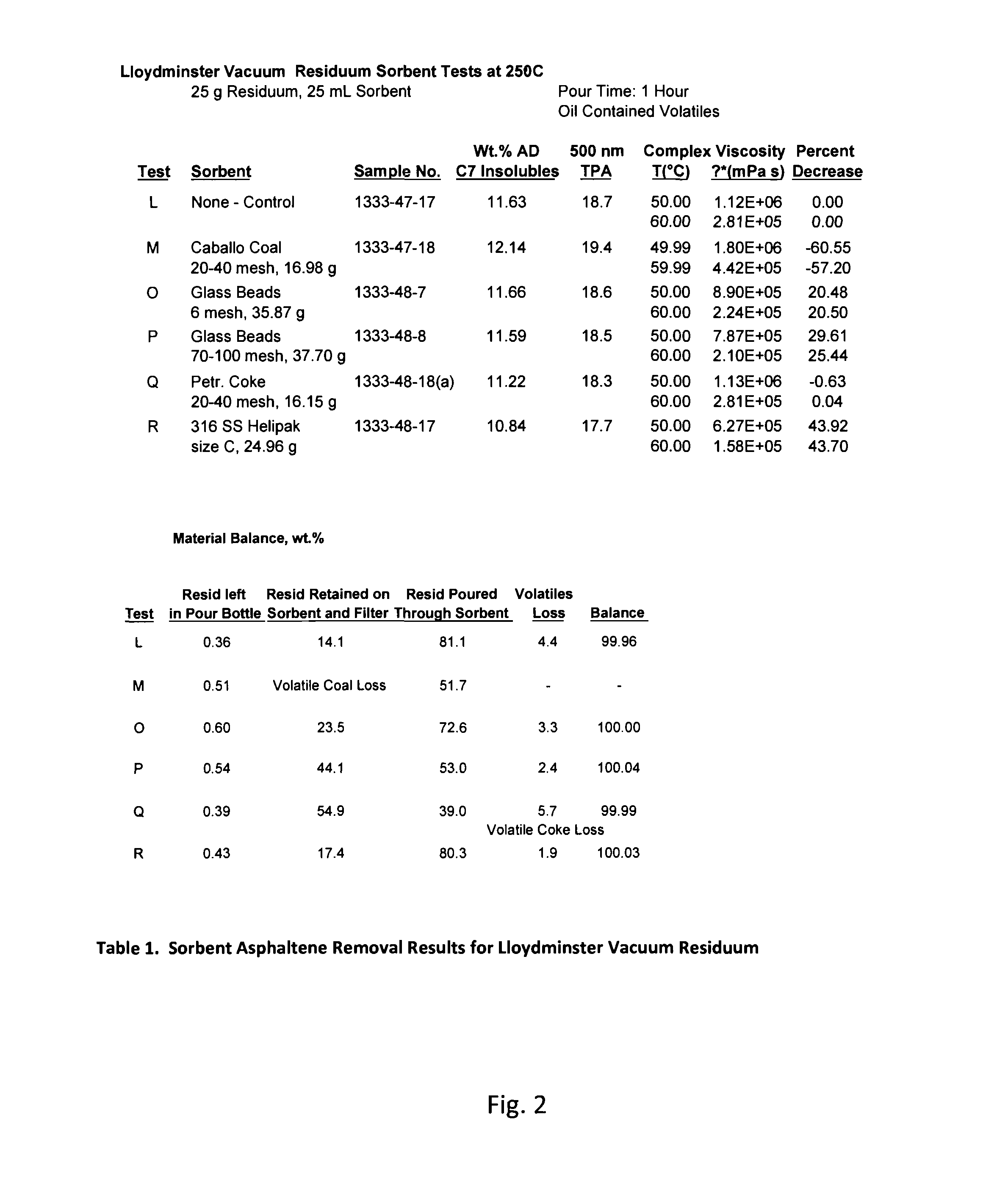
Hydrocarbon Viscosity Reduction Method
InactiveUS20140021101A1Reduce in quantityImprove energy efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationSorbentViscosity
In accordance with particular descriptions provided herein, certain embodiments of the inventive technology may be described as a hydrocarbon viscosity reduction method that comprises the steps of: treating a hydrocarbon having asphaltenes therein to generate a treated hydrocarbon, wherein said hydrocarbon has a first viscosity; contacting said treated hydrocarbon with a sorbent (whether as a result of pouring or other means); and adsorbing at least a portion of said asphaltenes onto said sorbent, thereby removing said at least a portion of said asphaltenes from said hydrocarbon so as to generate a viscosity reduced hydrocarbon having a second viscosity that is lower than said first viscosity.
Owner:WESTERN RES INST INC
Method and system for removing hydrogen sulfide from sour oil and sour water
ActiveUS9708196B2Transportation safetyWater treatment parameter controlElectrostatic separatorsScavengerHydrocarbon
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to a system and method to remove hydrogen sulfide from sour water and sour oil. In particular, hydrogen sulfide is removed from sour water and sour oil without the need for special chemicals, such as catalyst chemicals, scavenger chemicals, hydrocarbon sources, or a large scale facility. The system and method in the present invention is particularly useful in exploratory oil and gas fields, where large facilities to remove hydrogen sulfide may be inaccessible. The present invention addresses the need for safe and cost effective transport of the deadly neurotoxin. Particular embodiments involve a system and method that can be executed both on a small and large scale to sweeten sour water and sour oil.
Owner:ANSCHUTZ EXPLORATION
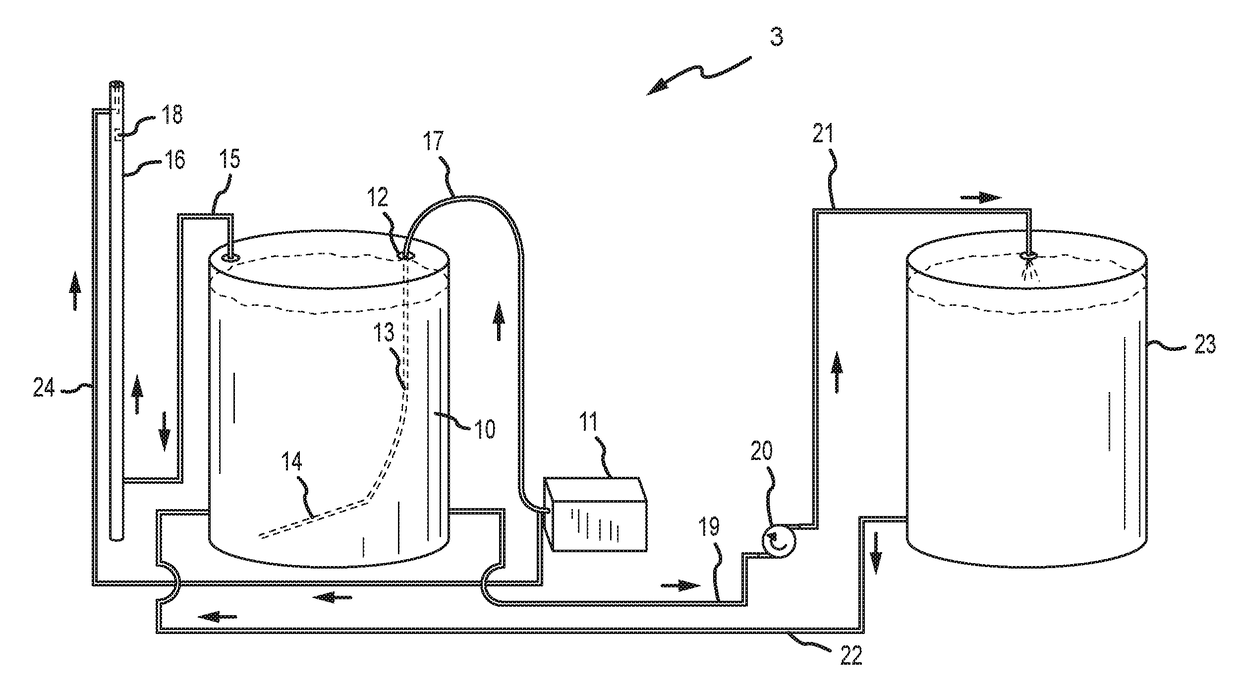
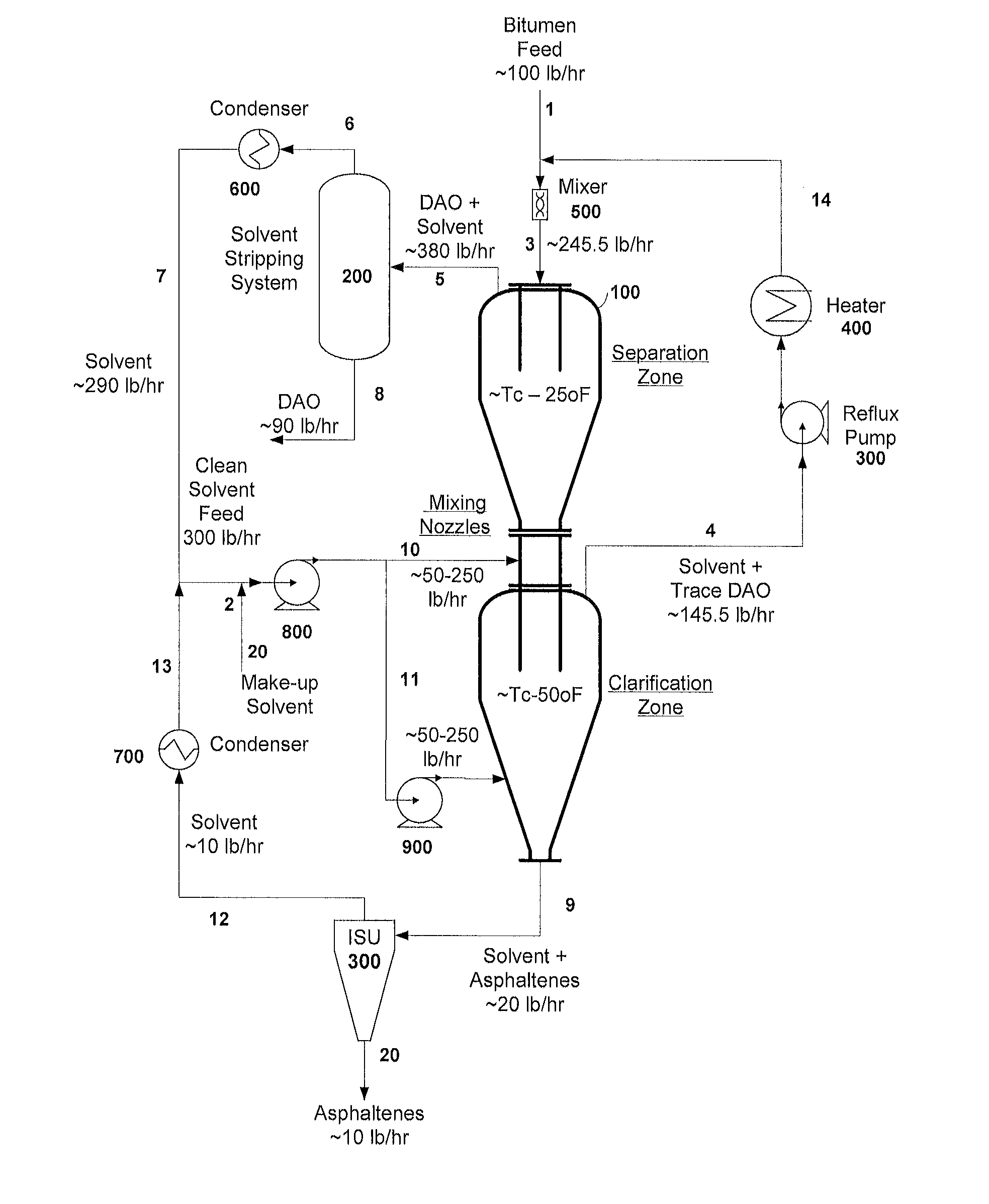
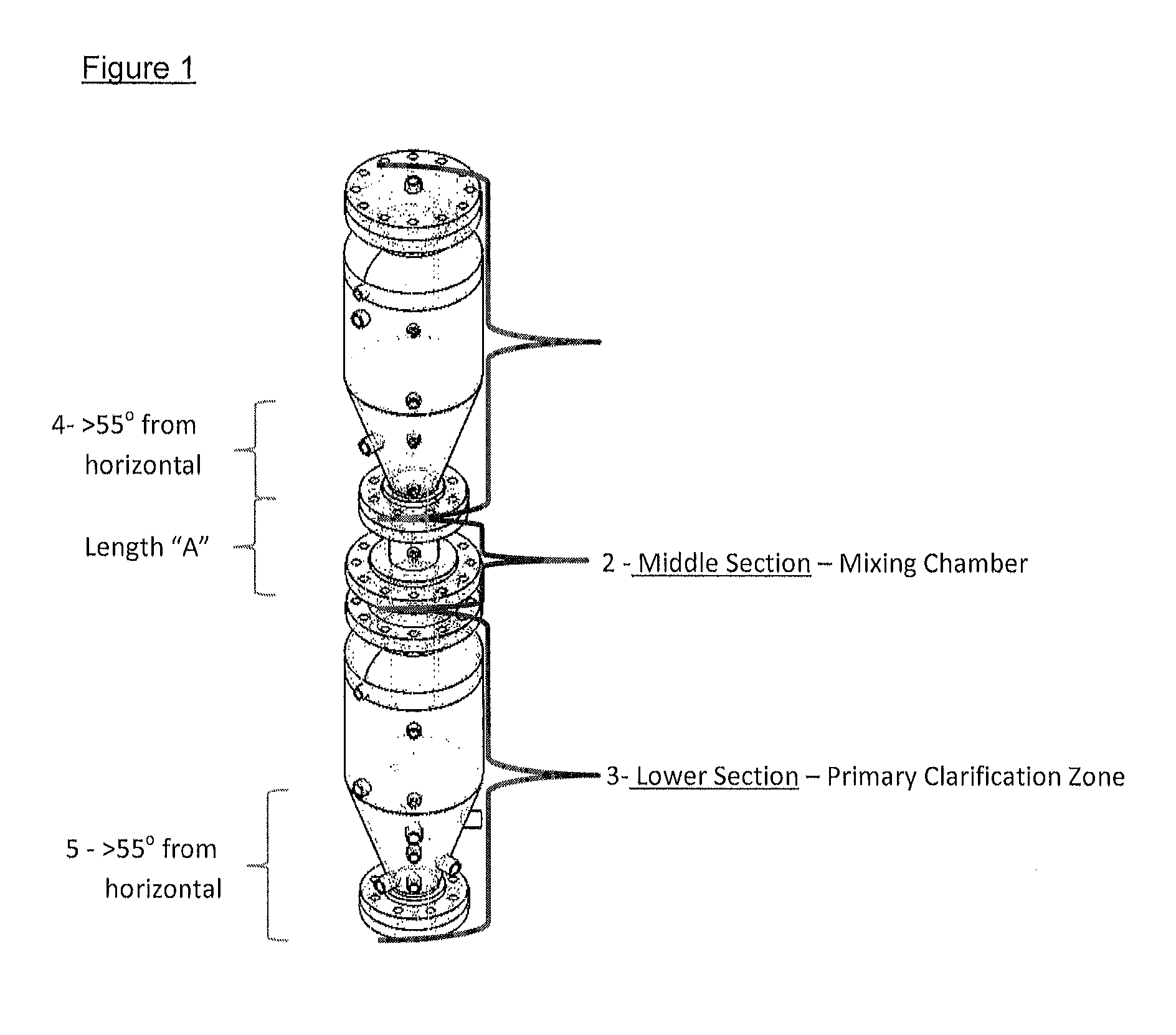
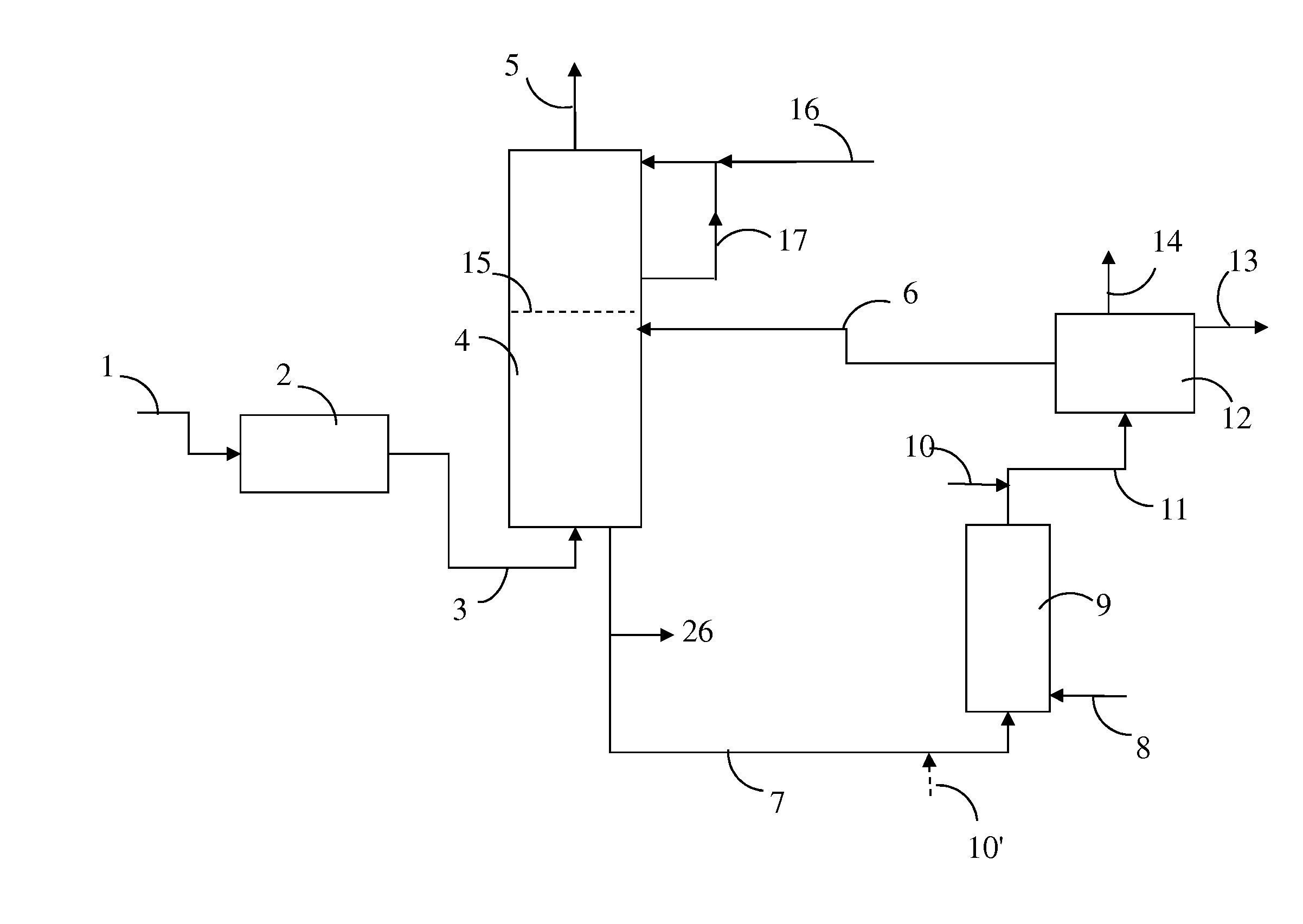
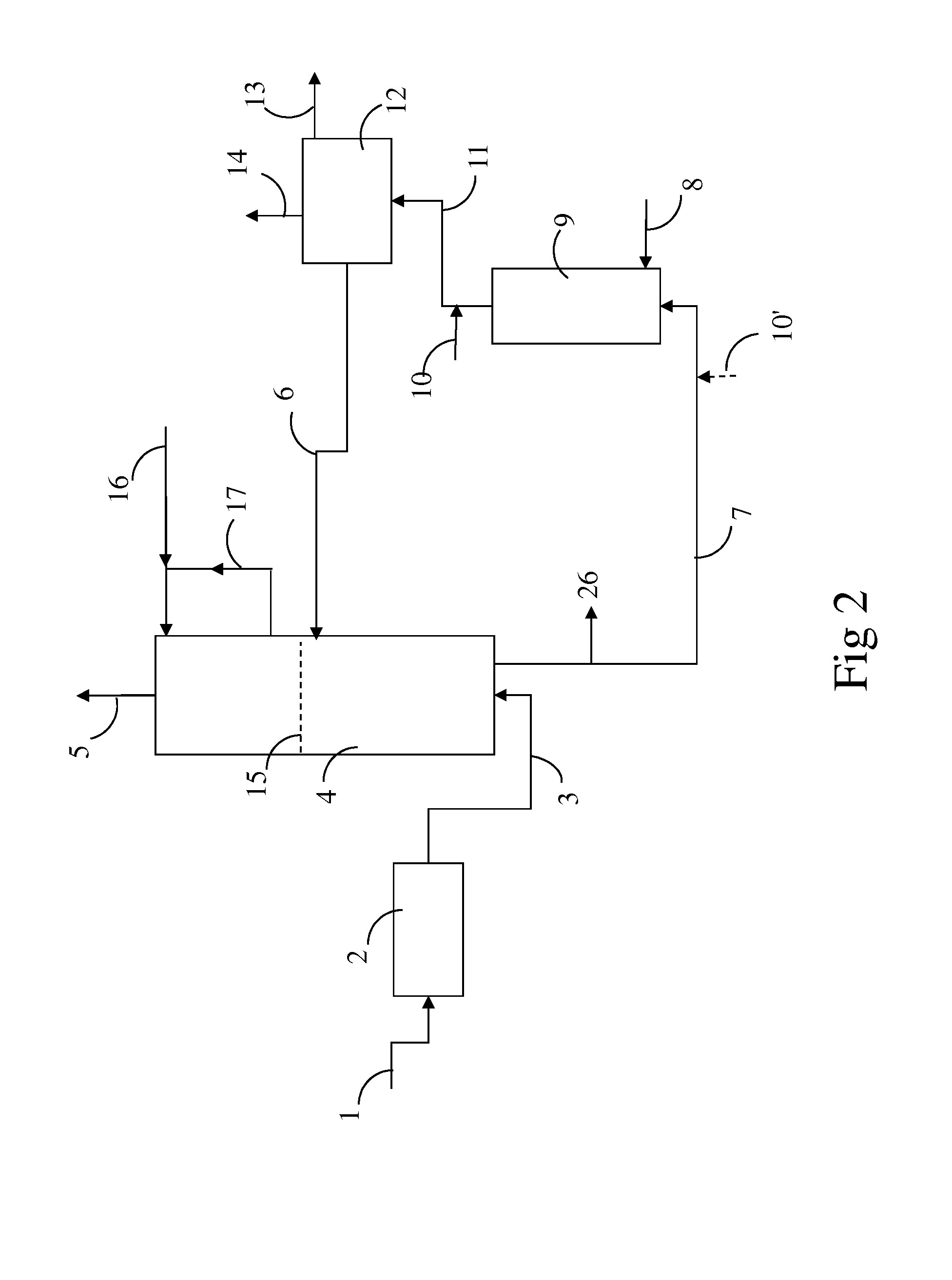
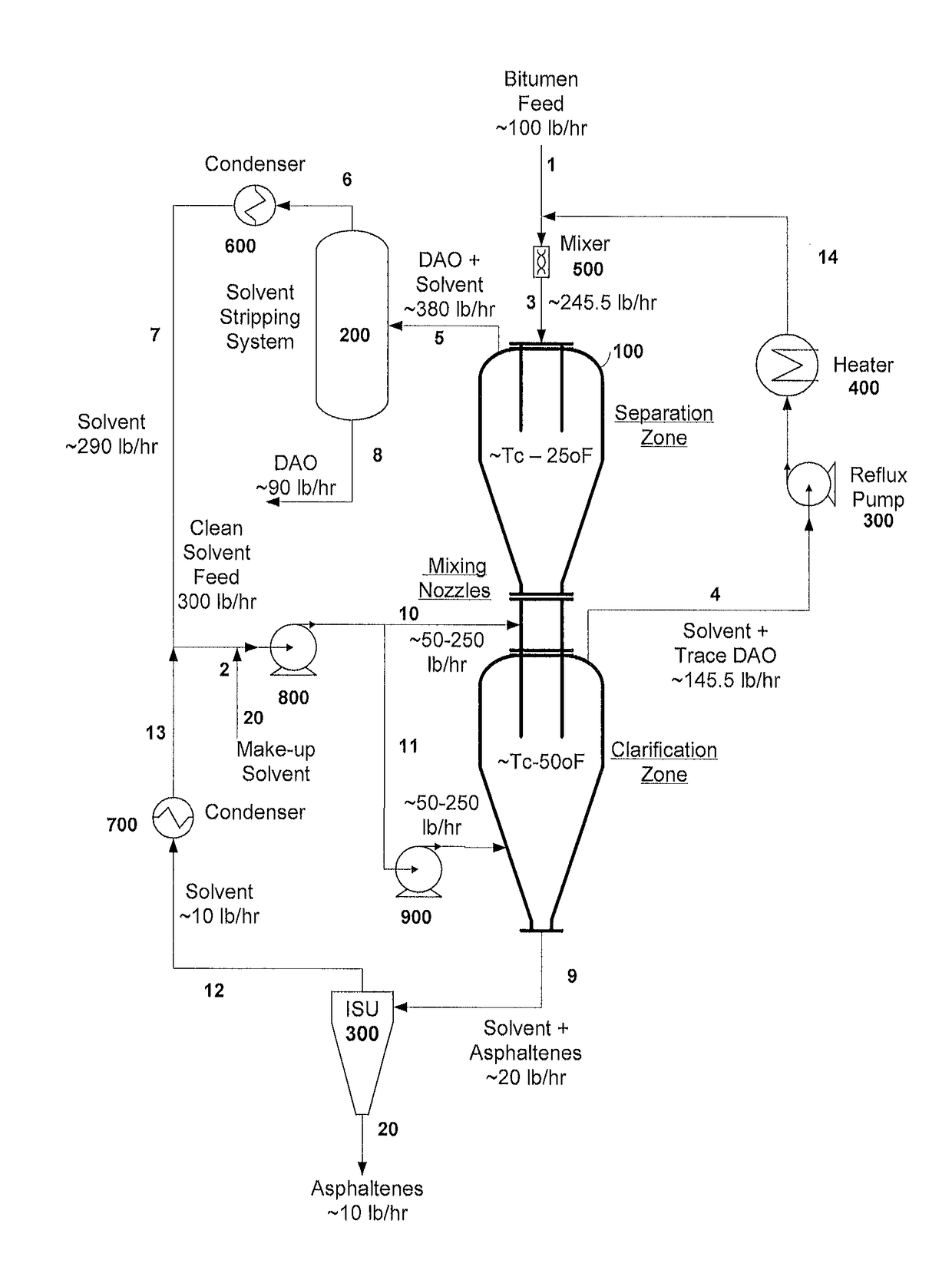
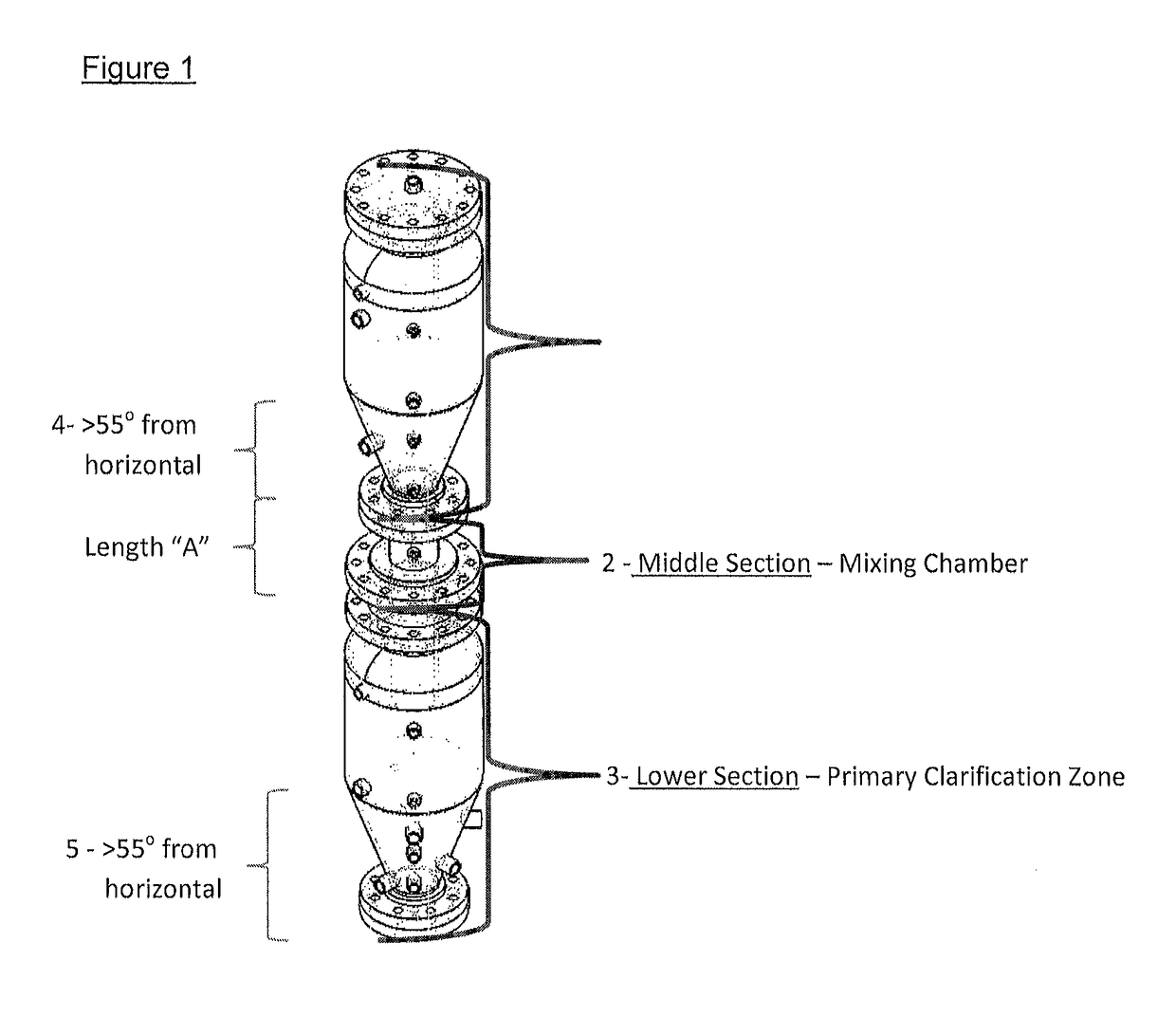
Separation of solid asphaltenes from heavy liquid hydrocarbons using novel apparatus and process ("ias")
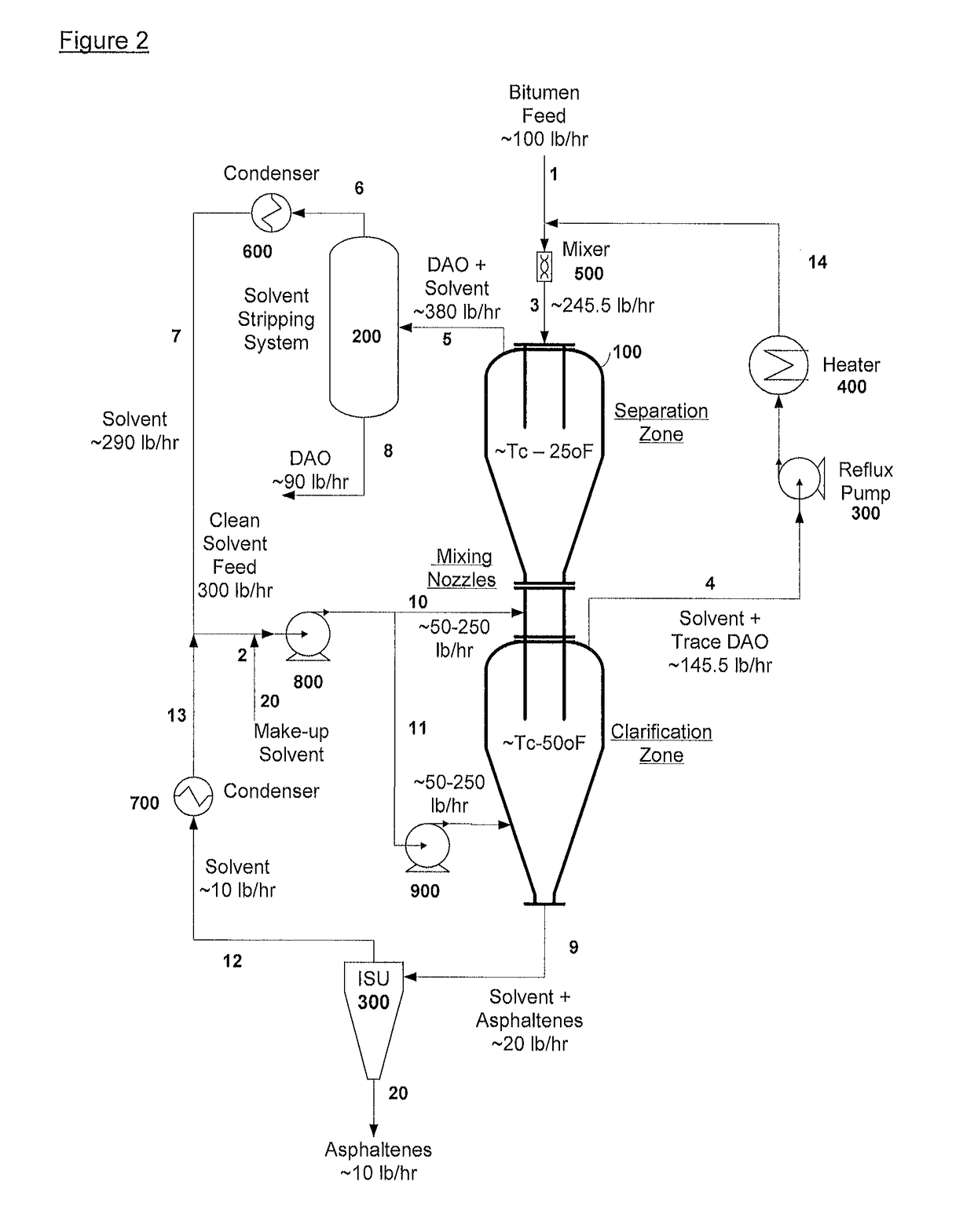
ActiveUS20140246357A1Reduce pluggingMitigate settlingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolvent extractionLiquid hydrocarbonsEngineering
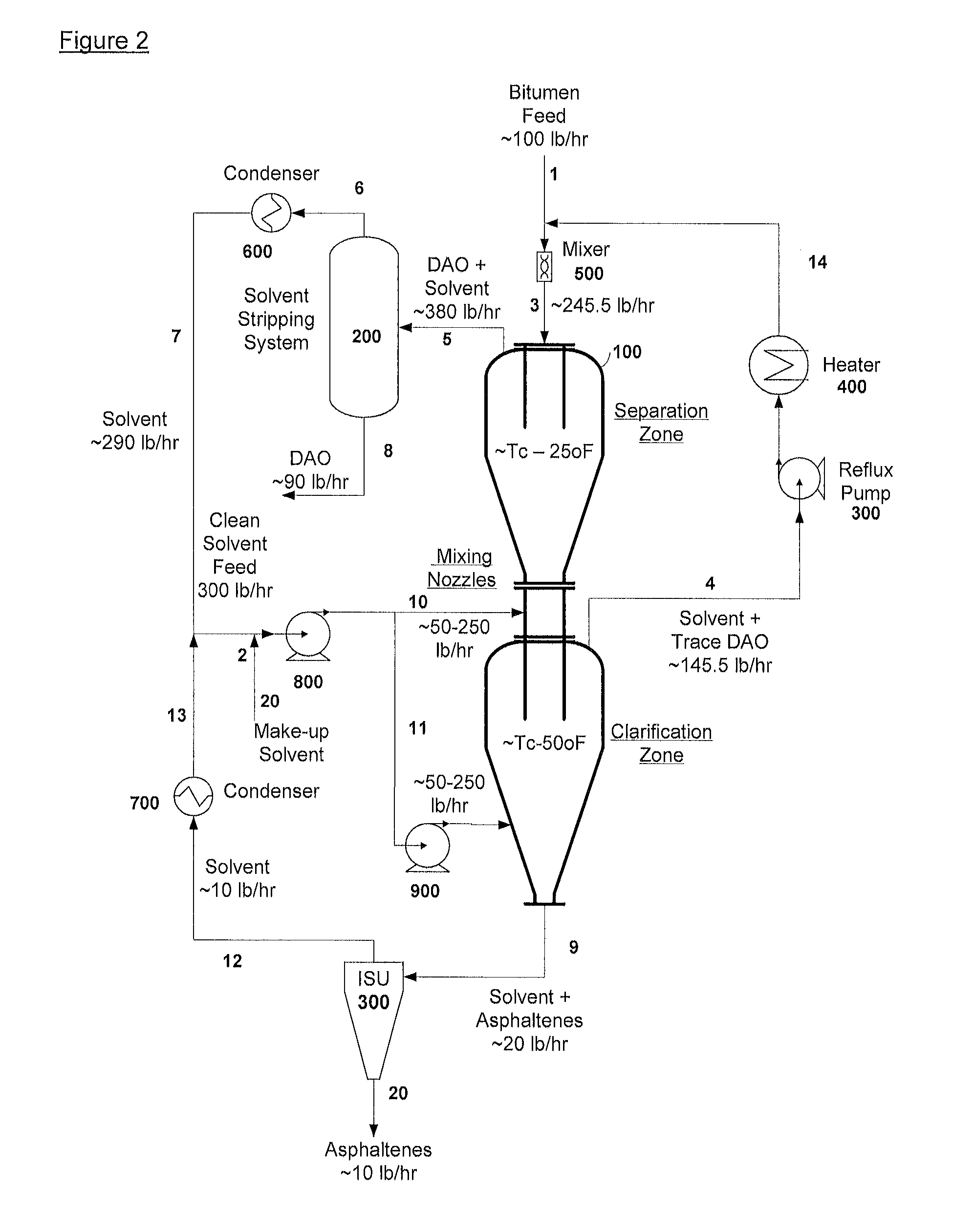
An apparatus and process is provided for improved asphaltene separation from heavy hydrocarbon or bitumen with low process complexity through mass transfer using solvent and counter-current flows, with three sections: an upper DAO / solid-asphaltene separation zone, a middle solvent mixing and segregation zone, and a bottom clarification zone. Solvent mixed with heavy hydrocarbon forms a process feed introduced to the process vessel's upper zone and exposed to counter-current solvent removing DAO from solid asphaltene particles in the feed, the particles fall through the middle zone and are mixed with introduced solvent, which introduced solvent segregates DAO-rich solution in the upper zone (for extraction from that zone) from solvent-rich mixtures in the middle mixing and lower clarification zones. Solvent flows and precipitate movement are controlled to optimize mass transfer in process, resulting in high DAO recovery and dry, solid asphaltene product.
Owner:SUNCOR ENERGY INC
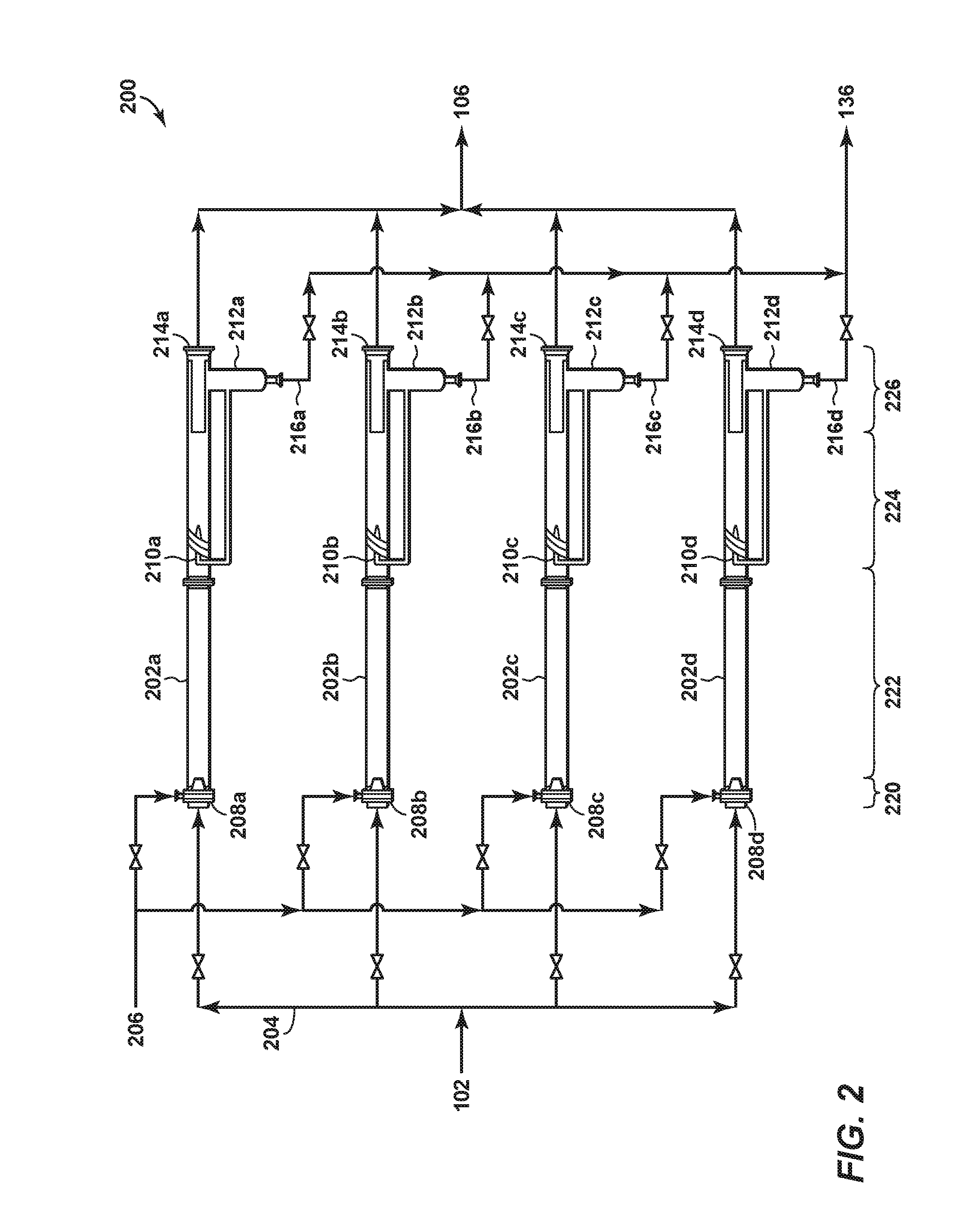
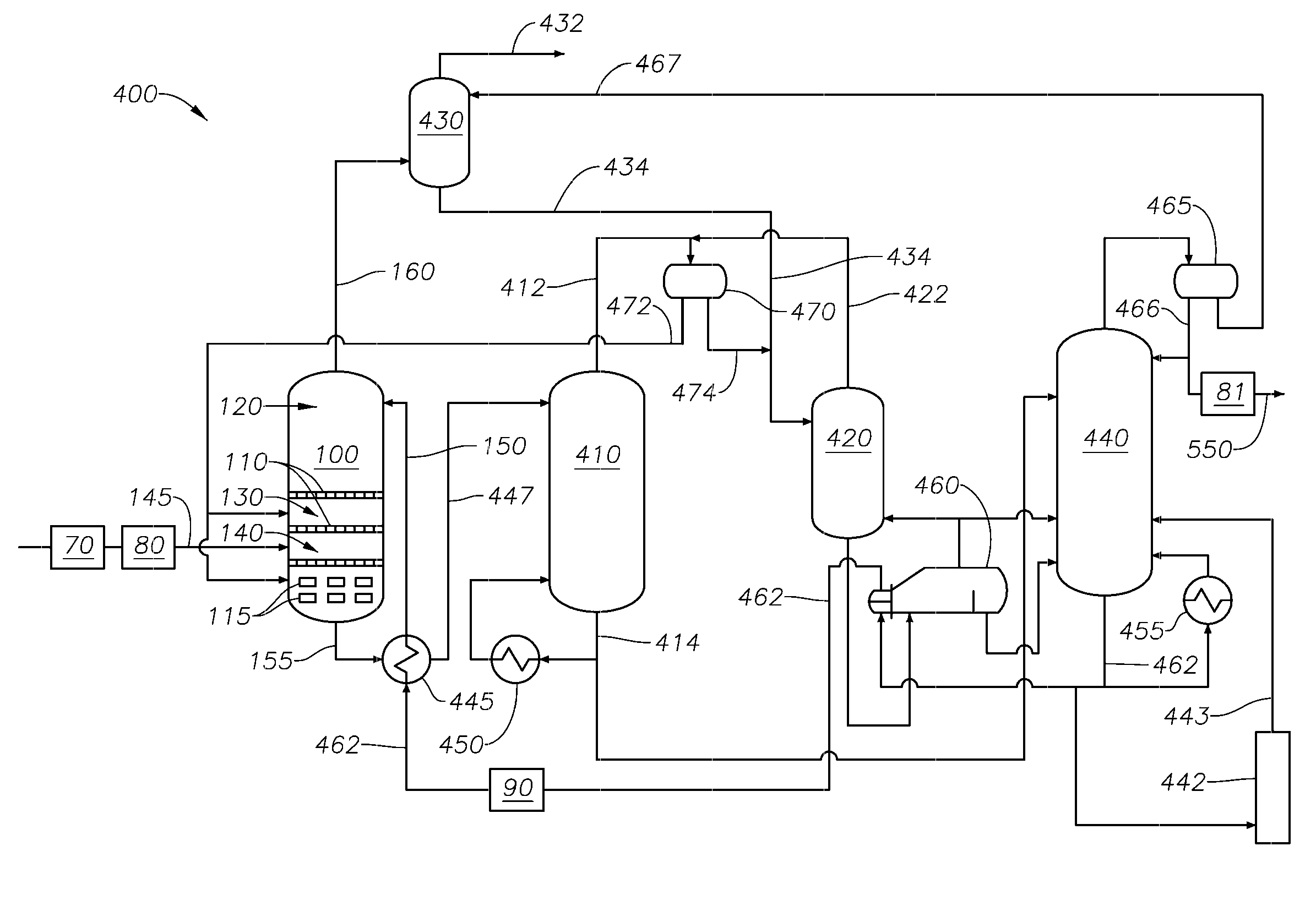
Process for controlling operations of a residue process unit
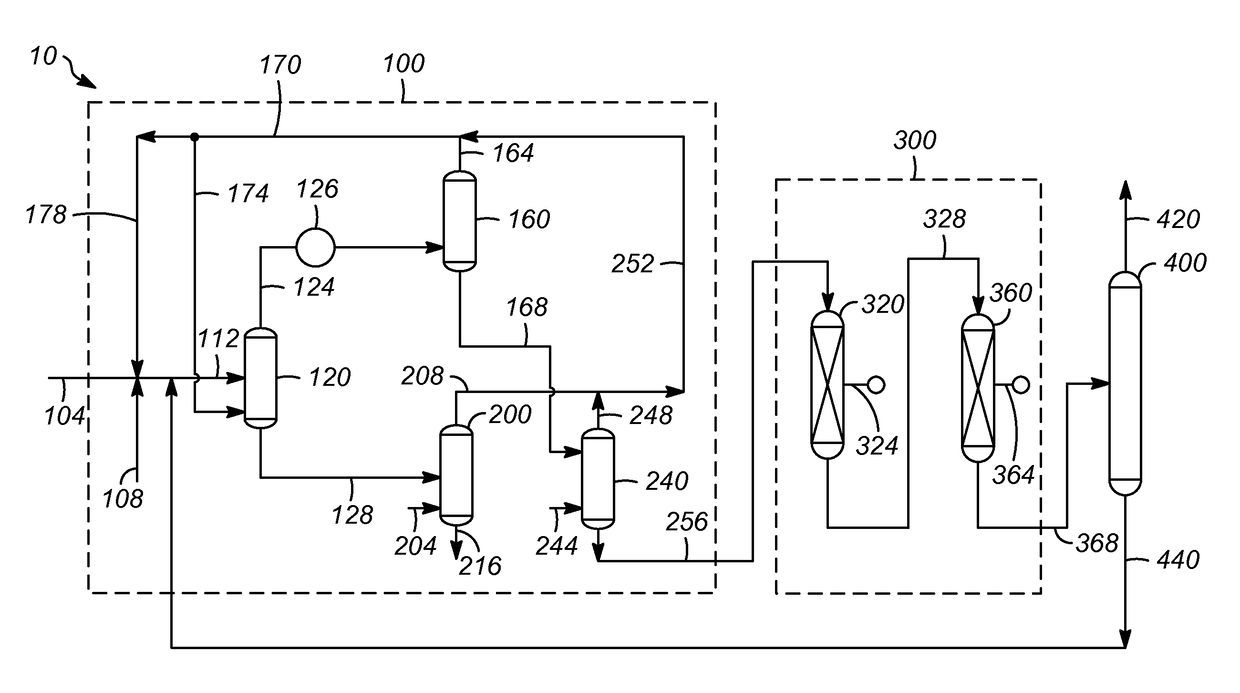
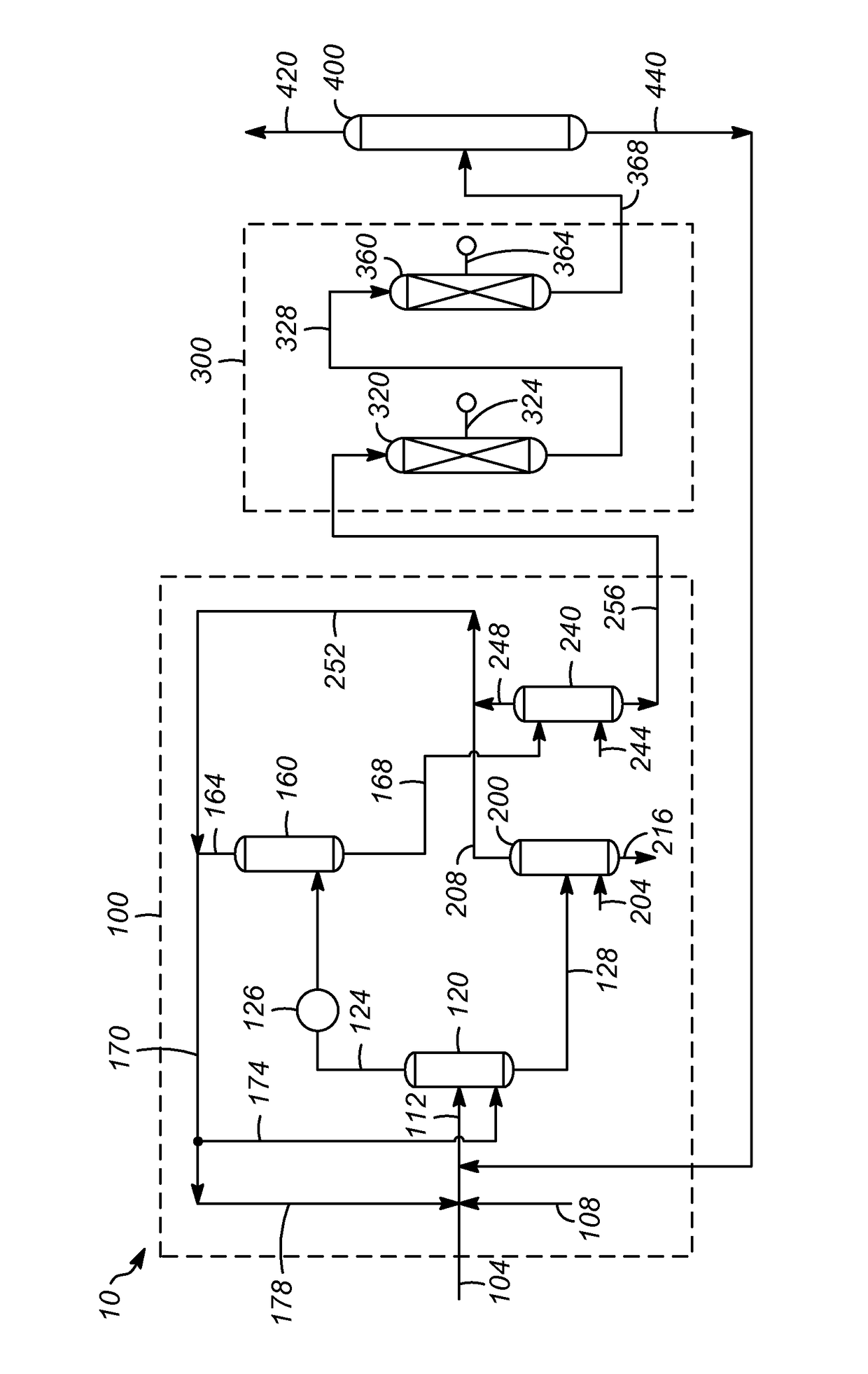
ActiveUS9663732B2Improve extraction efficiencyTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationSolventChemistry
One exemplary embodiment can be a process for controlling operations of a residue process unit. The process may include analyzing an overhead stream from an extraction column in a solvent deasphalting zone to determine a density of the overhead stream, and adjusting conditions of the extraction column in response to the density determined for the overhead stream depending on the operating constraints of one or more downstream hydroprocessing zones.
Owner:UOP LLC
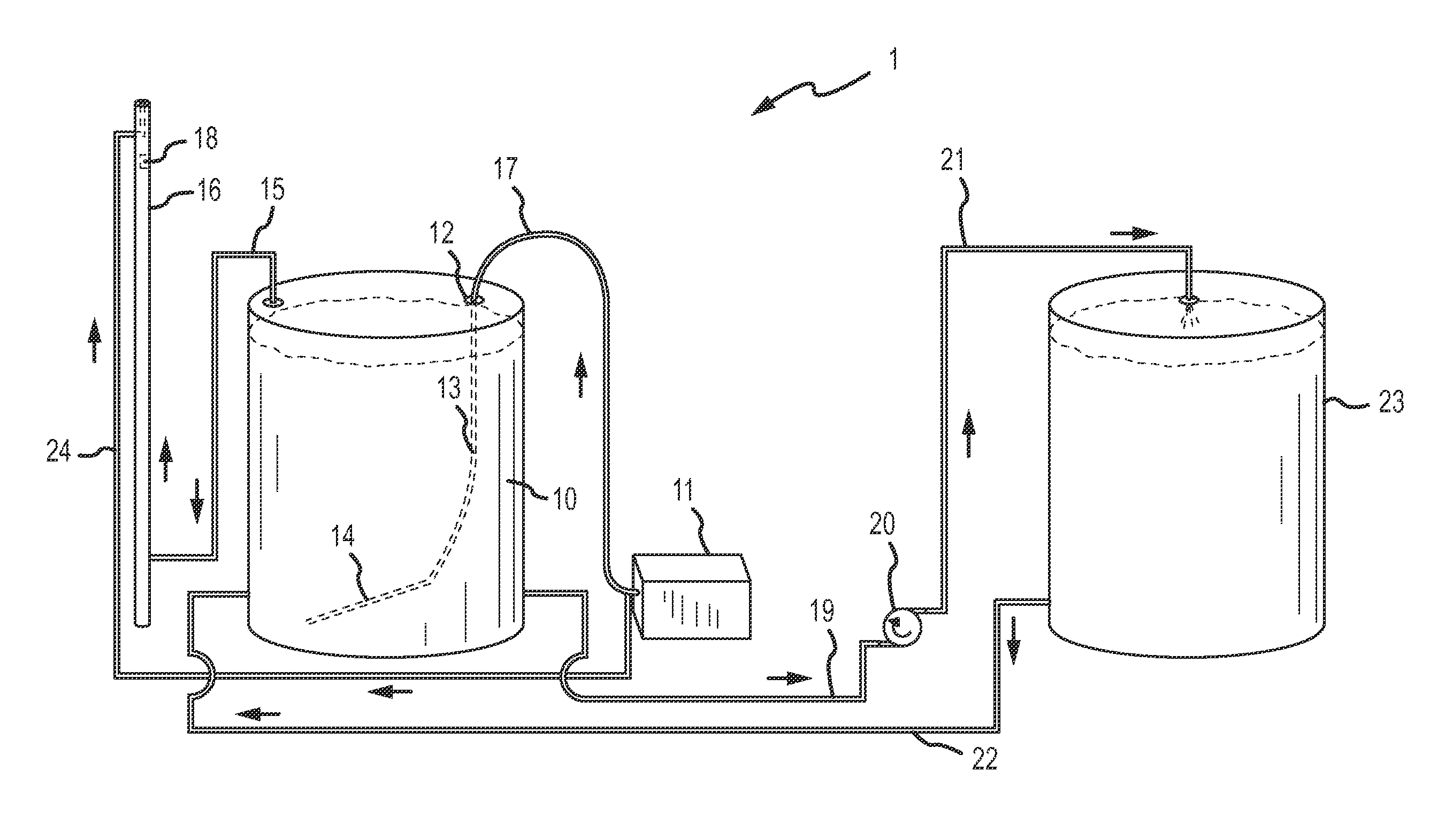
System and method of delivering dilution water droplets within an oil-and-water stream
InactiveUS20150299581A1Improve performanceImprove contact efficiencyFlow mixersTransportation and packagingWash waterWater flow
A system for desalting a crude oil stream includes an elongated, vertically oriented vessel that has an interior piping structure arranged concentric to the vessel. The piping structure, which may have more than one level, has a plurality of spray nozzles oriented at a downward angle for atomizing wash water into a downward flowing crude oil stream. The spray nozzles may be located on a same side or opposite sides of the piping structure. Where multiple levels are used, the number of spray nozzles on each level may be the same as or different than the number of spray nozzles on other levels. The pressure drop through each spray nozzle is preferably no greater than 300 psi and the nozzles preferably deliver a dilution water droplet preferably no larger than 300 microns in diameter. A mixing valve, static mixer, or both can be placed downstream of the vessel.
Owner:CAMERON SOLUTIONS
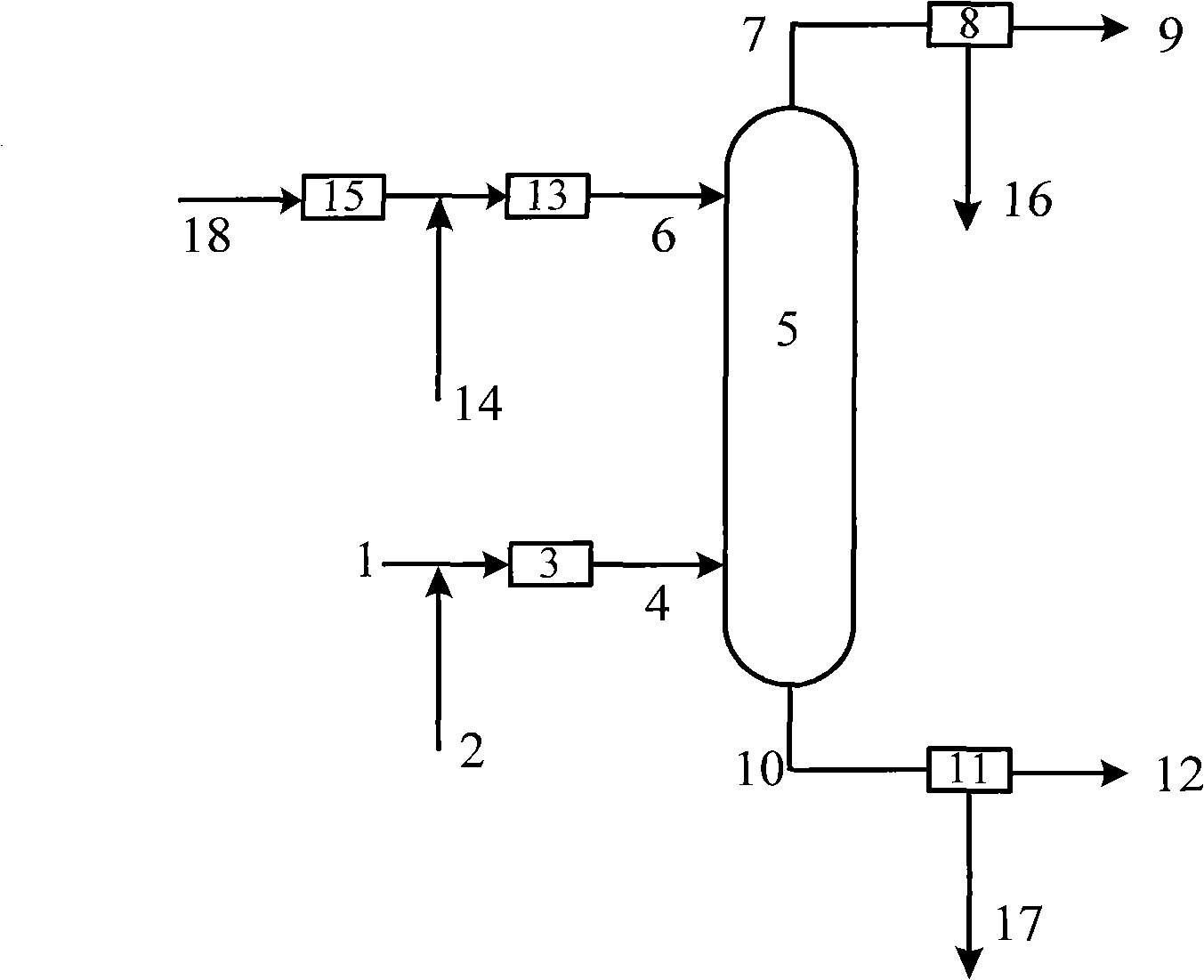
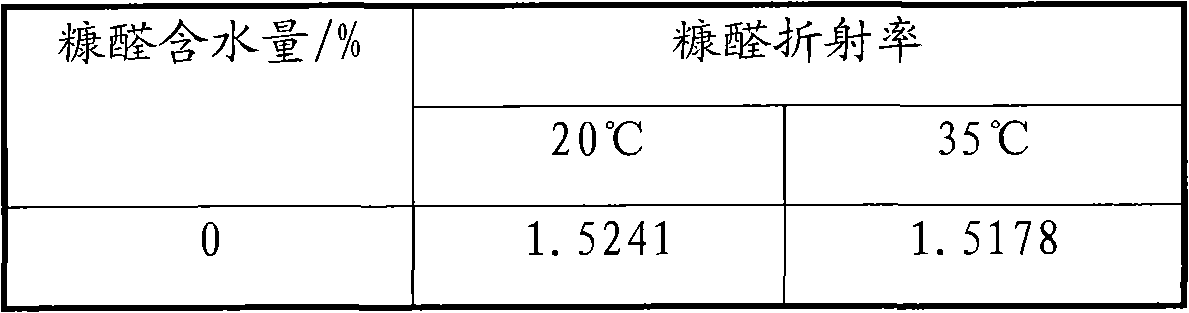
Control method and control device for moisture content of furfural in extraction of furfural and method for preparing aromatic rubber oil
ActiveCN102585886ARegulatory selectivityIncrease water contentHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationCounter currentSolvent refining
The invention relates to a control method and a control device for the moisture content of furfural in the extraction of the furfural and a method for preparing aromatic rubber oil. The method for preparing the aromatic rubber oil comprises the following steps of: mixing a part of furfural from a furfural drying tower with raw oil and enabling the mixture to enter the lower part of an extracting tower; mixing the other part of furfural from the furfural drying tower with water and enabling the mixture to enter the upper part of the extracting tower; carrying out counter-current contact on the two parts of materials in the extracting tower; and separating raffinate from overhead raffinate. By adopting the control method provided by the invention, the moisture content of the furfural entering the upper part of the extracting tower is controlled between more than 0.5 weight percent and 10 weight percent; and the raw oil is solvent refining extract oil or dewaxed oil of the solvent refining extract oil. The aromatic rubber oil prepared by adopting the method has high yield, the prepared aromatic rubber oil satisfies the directive requirements of European Union 2005 / 69 / EC, and the mass percent of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is less than 3 percent.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for controlling operations of a residue process unit
ActiveUS20160068768A1Improve extraction efficiencyComputer controlWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenSolventTreatment unit
One exemplary embodiment can be a process for controlling operations of a residue process unit. The process may include analyzing an overhead stream from an extraction column in a solvent deasphalting zone to determine a density of the overhead stream, and adjusting conditions of the extraction column in response to the density determined for the overhead stream depending on the operating constraints of one or more downstream hydroprocessing zones.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method and System for Removing Hydrogen Sulfide from Sour Oil and Sour Water
ActiveUS20140238902A1Reduces sulfur-by-weight contentHigh level of hydrogenWater treatment parameter controlLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesScavengerHydrocarbon
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to a system and method to remove hydrogen sulfide from sour water and sour oil. In particular, hydrogen sulfide is removed from sour water and sour oil without the need for special chemicals, such as catalyst chemicals, scavenger chemicals, hydrocarbon sources, or a large scale facility. The system and method in the present invention is particularly useful in exploratory oil and gas fields, where large facilities to remove hydrogen sulfide may be inaccessible. The present invention addresses the need for safe and cost effective transport of the deadly neurotoxin. Particular embodiments involve a system and method that can be executed both on a small and large scale to sweeten sour water and sour oil.
Owner:ANSCHUTZ EXPLORATION
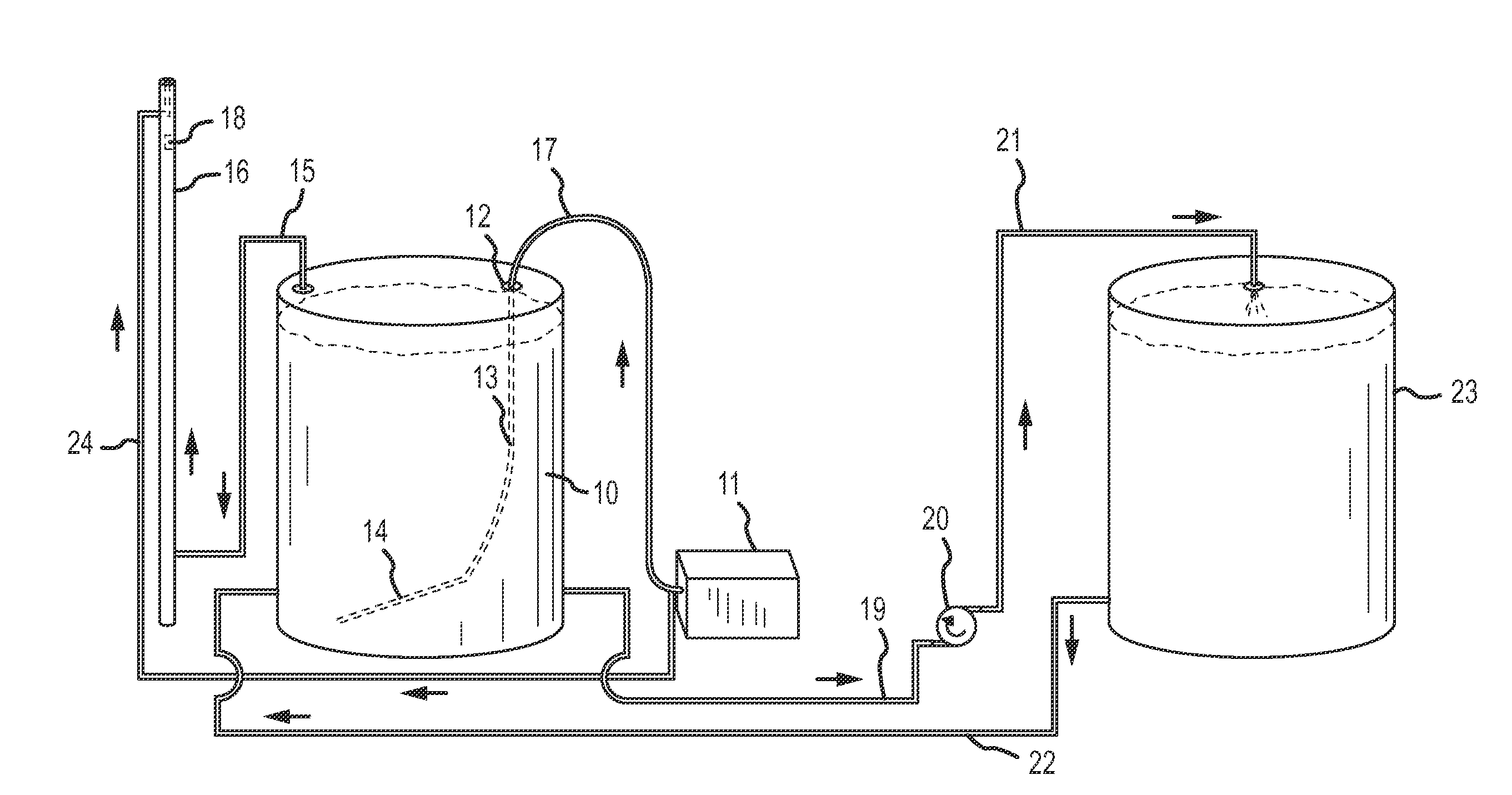
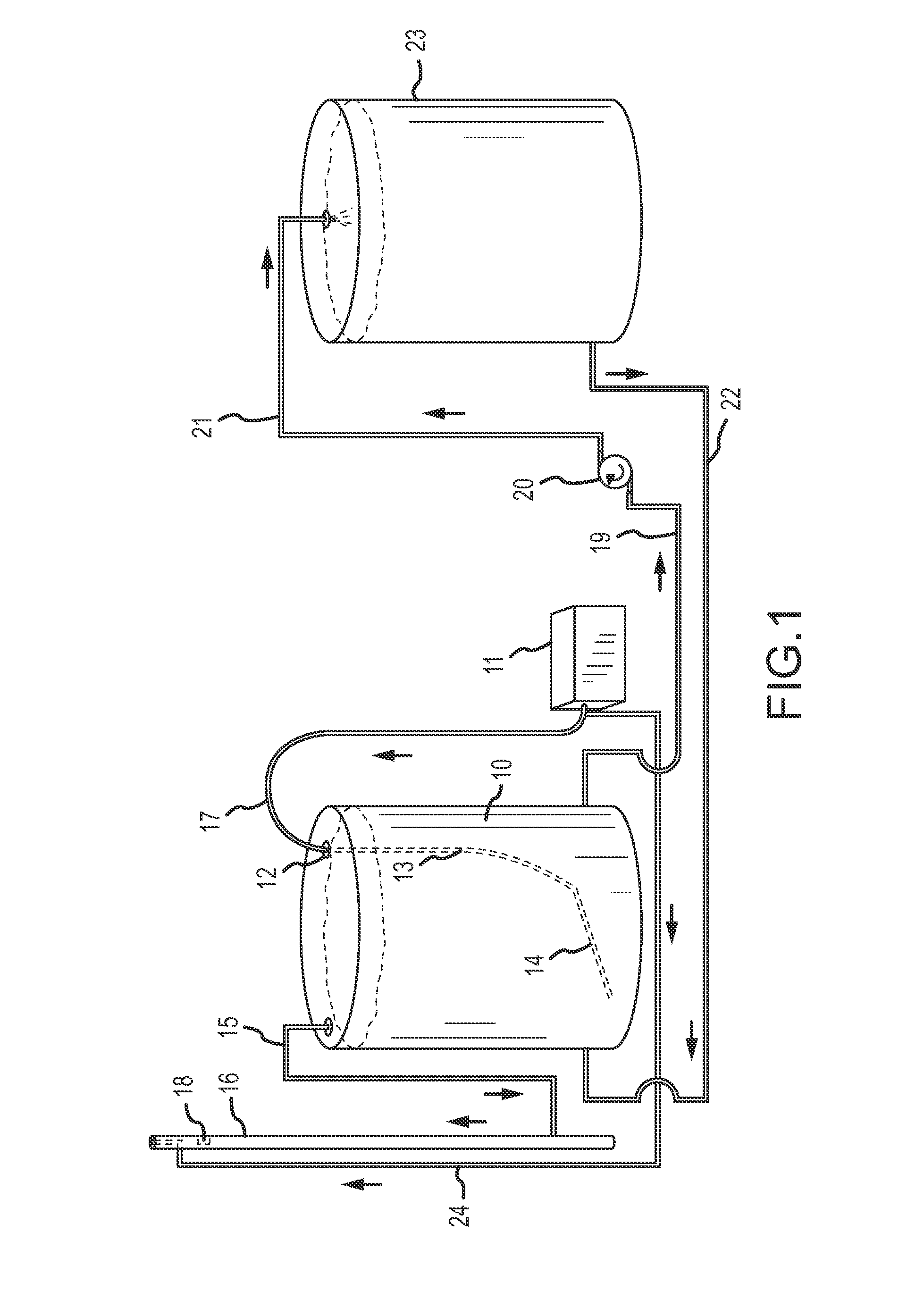
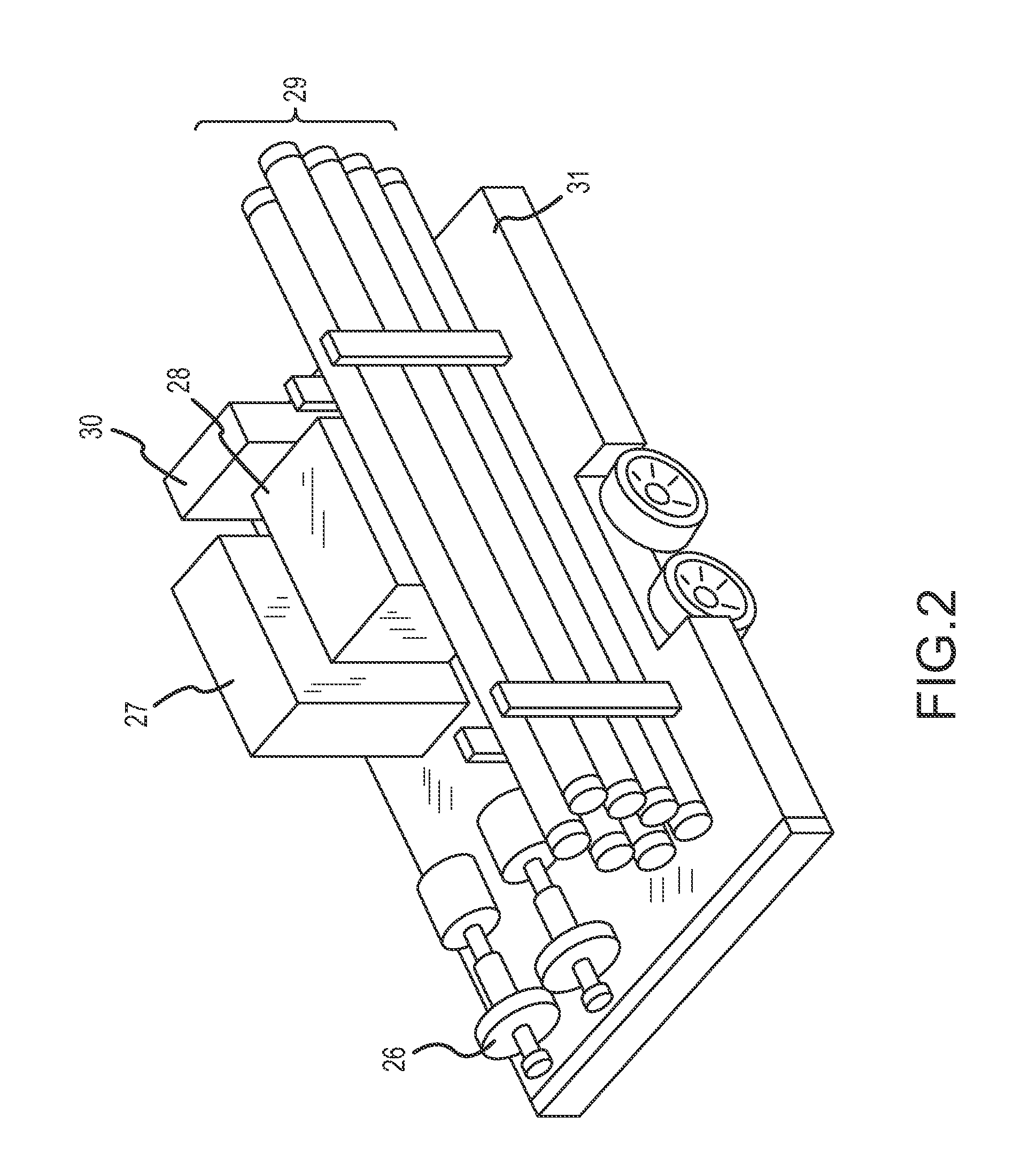
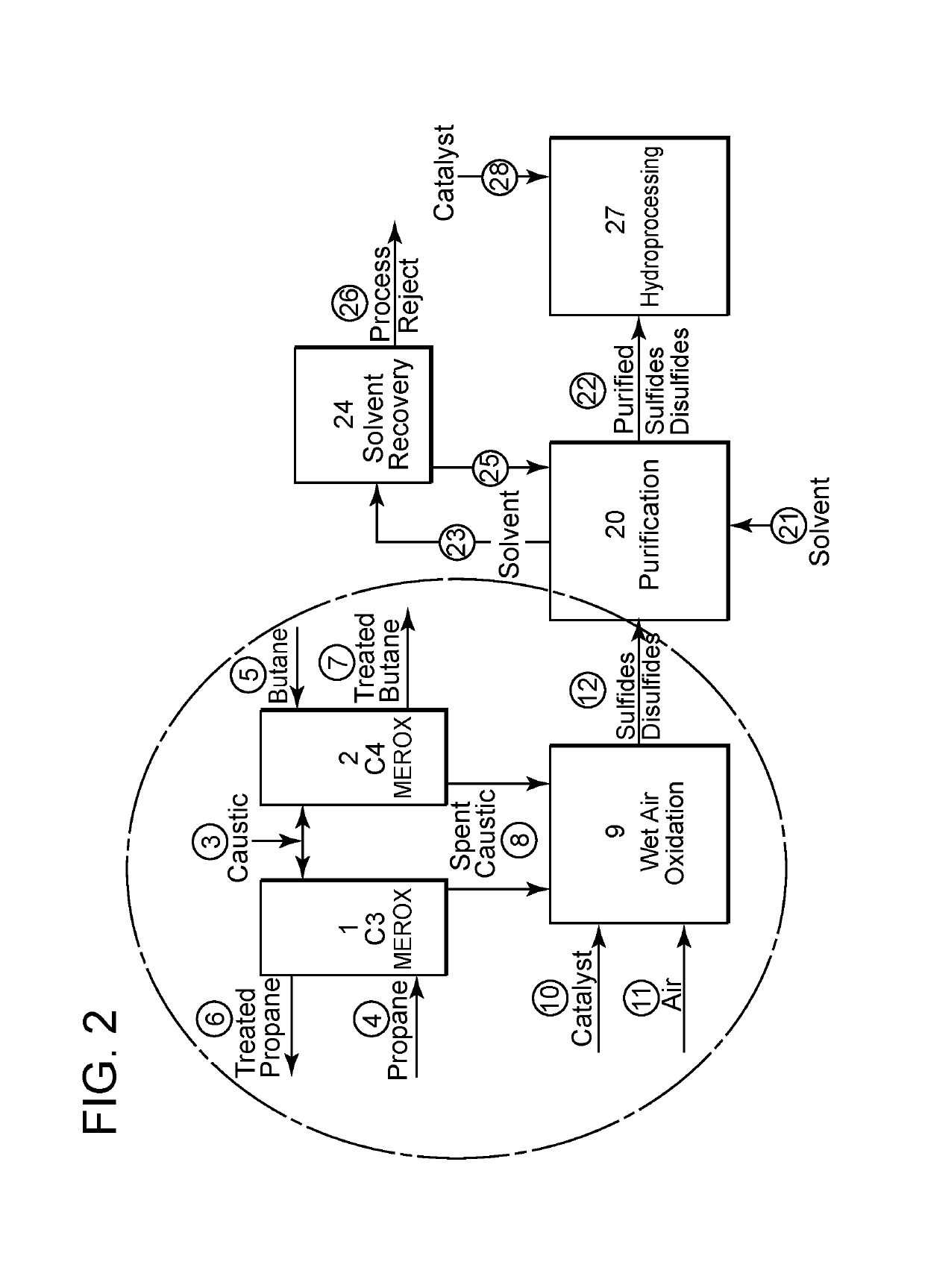
Integrated process for activating hydroprocessing catalysts with in-situ produced sulfides and disulphides
The invention involves an integrated process in which a hydrocarbon feedstock is treated with a caustic (alkaline) extraction to remove sulfides, disulfides, and mercaptans. These extracted materials are further treated, and are then used to activate hydrotreating catalysts.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
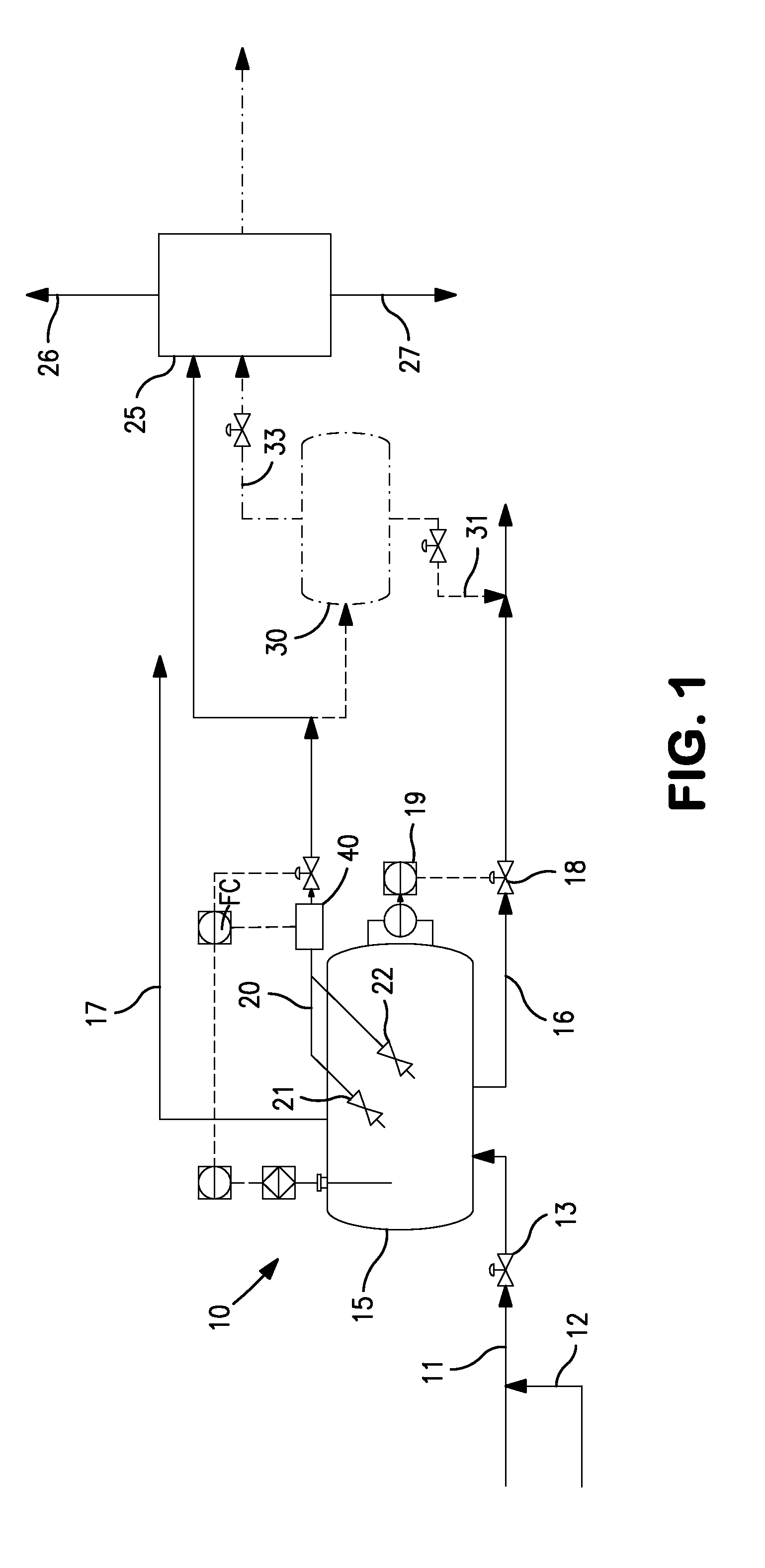
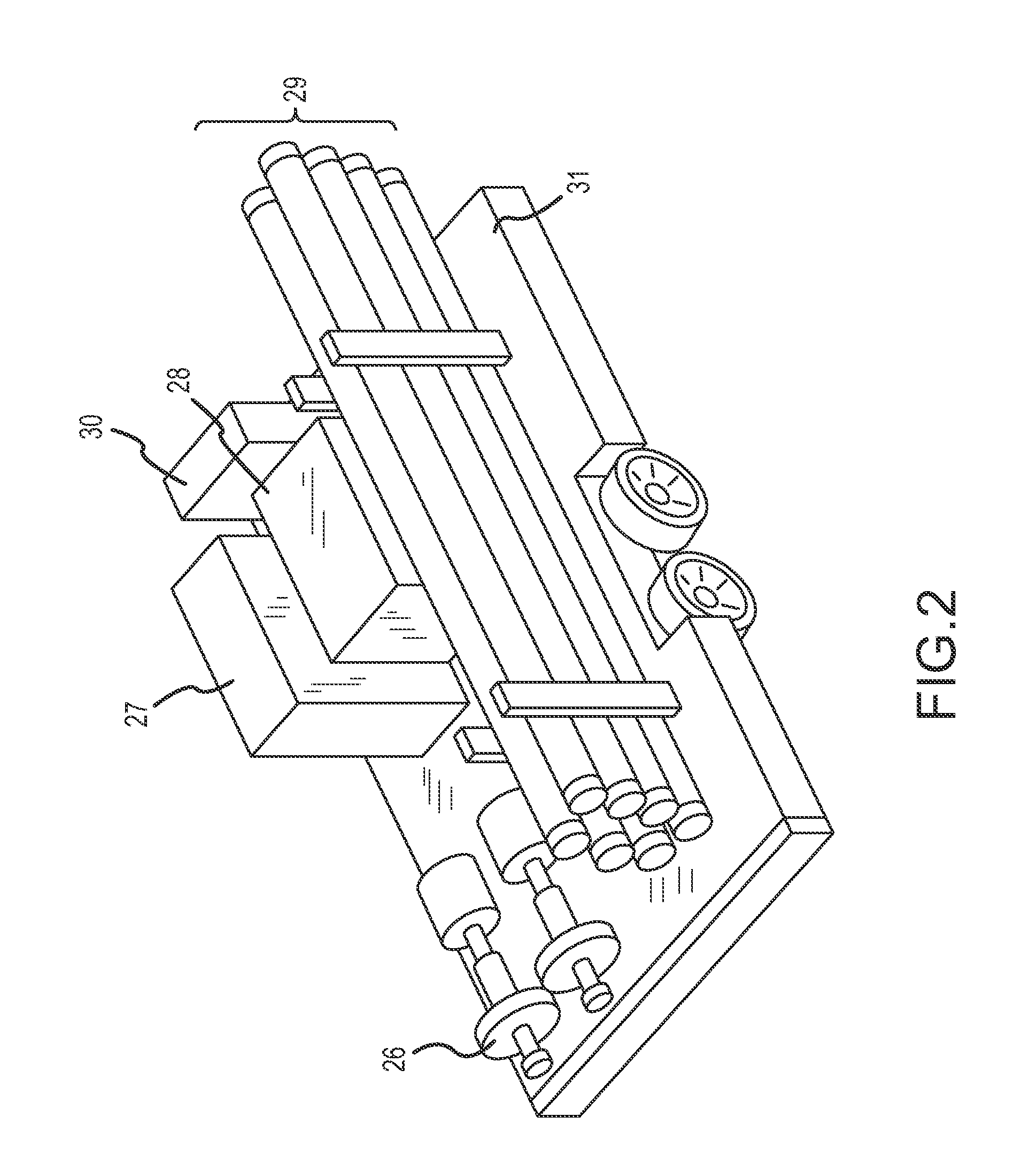
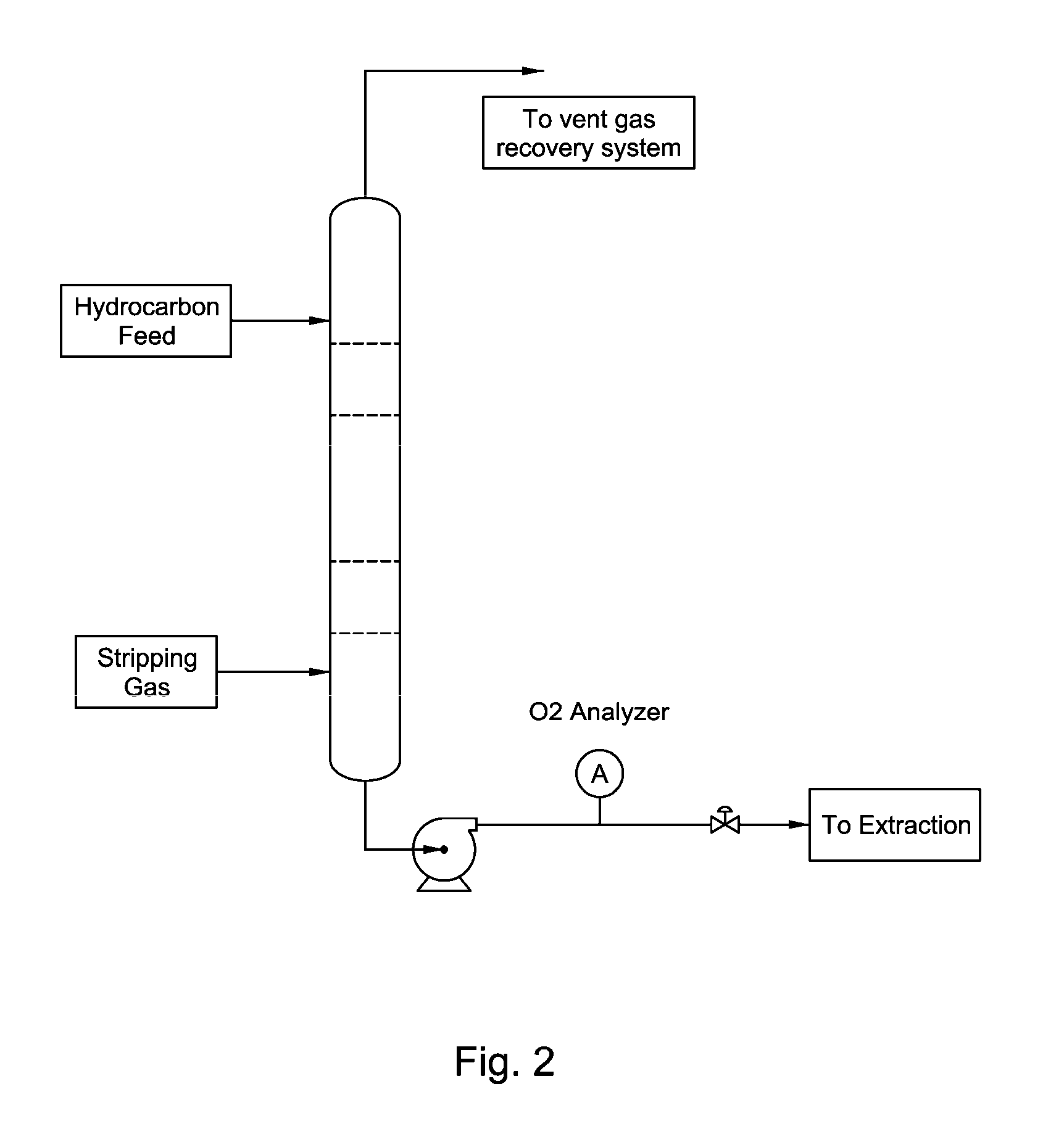
Solvent Quality Control in Extraction Processes
InactiveUS20120197057A1Improvement in quality and long-term reliabilityMaintain stabilityHydrocarbon distillation control/regulationDistillation purification/separationExtractive distillationQuality control
The invention concerns the control of solvent systems in processes and apparatus for the separation of aromatic hydrocarbons from non-aromatic hydrocarbons in liquid-liquid extraction, extractive distillation, and the combination thereof.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Intergration of residue hydrocracking and solvent deasphalting
ActiveCN105008494AHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesReactor systemHydrogen
A process for upgrading residuum hydrocarbons is disclosed. The process may include: contacting a residuum hydrocarbon fraction and hydrogen with a first hydroconversion catalyst in a first ebullated bed hydroconversion reactor system; recovering a first effluent from the first ebullated bed hydroconversion reactor system; solvent deasphalting a vacuum residuum fraction to produce a deasphalted oil fraction and an asphalt fraction; contacting the deasphalted oil fraction and hydrogen with a second hydroconversion catalyst in a second hydroconversion reactor system; recovering a second effluent from the second hydroconversion reactor system; and fractionating the first effluent from the first ebullated bed hydroconversion reactor system and the second effluent from the second hydroconversion reactor system to recover one or more hydrocarbon fractions and the vacuum residuum fraction in a common fractionation system.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH INC
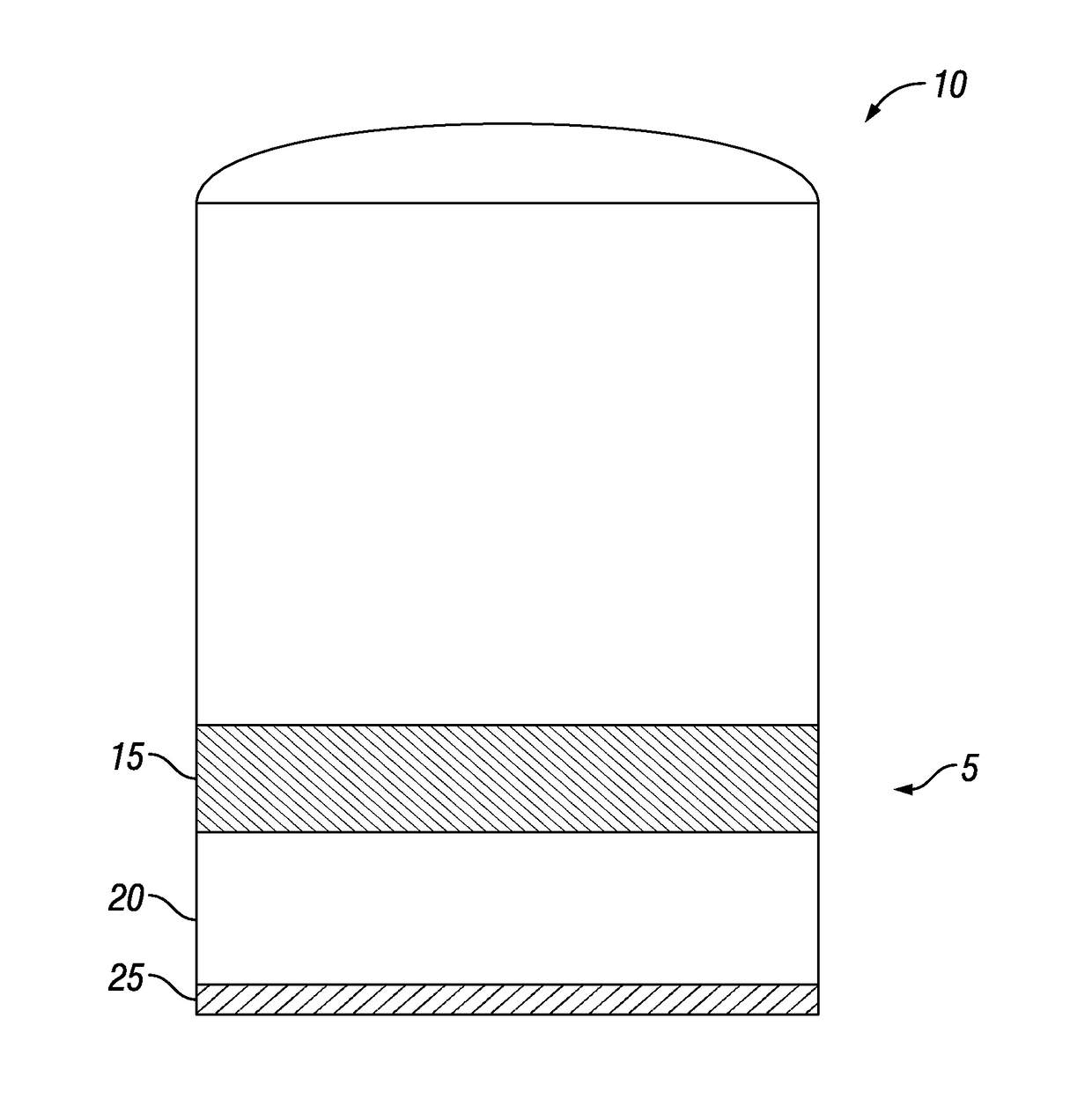
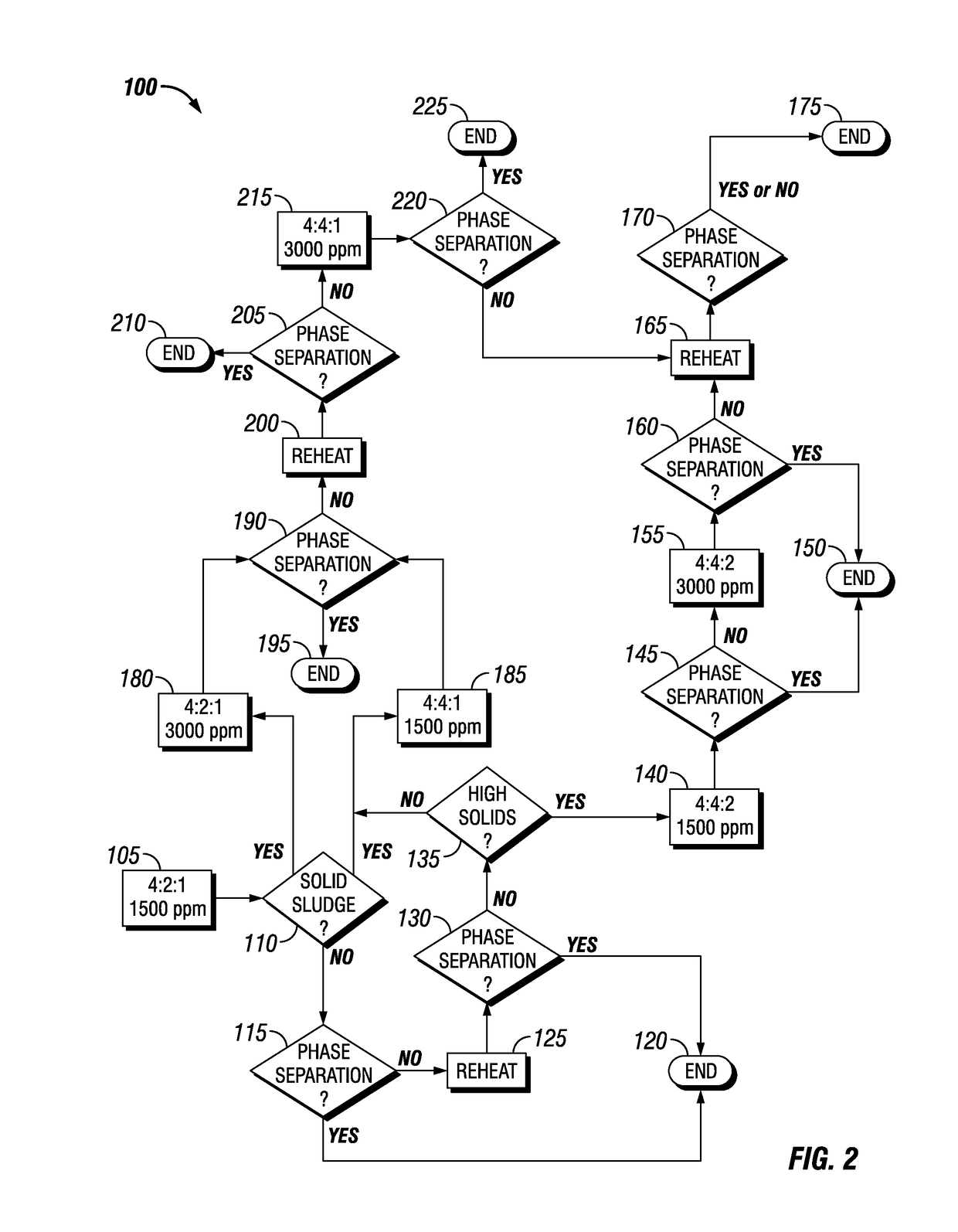
Optimization of a Method for Isolation of Paraffinic Hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20170190986A1Dewatering/demulsification with chemical meansDewatering/demulsification regulation/controlSludgeThree-phase
A method and composition for isolating a paraffinic hydrocarbon layer from a sludge comprising paraffinic hydrocarbons, water, and solids. The method includes contacting the sludge with isopropylamine dodecylbenzene sulfonate, a cutter stock, and water. The isopropylamine dodecylbenzene sulfonate comprises a concentration of at least 1500 ppm. The ratio of sludge:cutter:water is at least 4:2:1. The method also includes determining if the sludge has separated into a three phase separation comprising a paraffinic hydrocarbon layer, a water layer, and a layer of settled solids.
Owner:HPC PETROSERV INC
Deasphalting process for production of feedstocks for dual applications
ActiveUS20140238903A1Increase profitSignificant energy savingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationSolventOperating temperature
The invention concerns with improved and more flexible deasphalting process for production of lube oil base stock as well as feed stock for secondary processes depending on requirement from heavy residual hydrocarbon oil containing saturates, aromatics, resins and asphaltenes etc by contacting the oil with a solvent comprising of hydrocarbon containing two to six carbon atoms, preferably LPG having C3-C4 hydrocarbons and mixture thereof at predetermined deasphalting conditions wherein the yield of deasphalted oil including its quality is controlled by varying the deasphalting conditions including the operating temperature. The yield variations of 15 to 60 wt % is achieved by swinging the temperature by about 10-20° C. within the operative temperature range of 70-130° C. keeping the rest of the operating conditions including solvent to feed ratio same. The LPG solvent can be recovered using supercritical mode of operation using technology known in the art and recycled.
Owner:INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
Device for extracting sulphur-containing compounds by liquid-liquid extraction by means of a soda solution with an optimized final washing step
ActiveUS20140284250A1Refining with aqueous alkaline solutionsHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationChemical compoundGasoline
Process of extracting sulphur-containing compounds from a hydrocarbon cut of the gasoline or LPG type by liquid-liquid extraction with a soda solution employing a unit (2) for pretreatment of the feedstock to be treated placed upstream of the extraction unit (4), the soda being introduced into the extraction column (4) in the form of two circuits operating either in parallel, or in series.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Separation of solid asphaltenes from heavy liquid hydrocarbons using novel apparatus and process (“IAS”)
ActiveUS9976093B2Reduce pluggingMitigate settlingLiquid solutions solvent extractionHydrocarbon oils refining control/regulationLiquid hydrocarbonsAsphaltene
An apparatus and process is provided for improved asphaltene separation from heavy hydrocarbon or bitumen with low process complexity through mass transfer using solvent and counter-current flows, with three sections: an upper DAO / solid-asphaltene separation zone, a middle solvent mixing and segregation zone, and a bottom clarification zone. Solvent mixed with heavy hydrocarbon forms a process feed introduced to the process vessel's upper zone and exposed to counter-current solvent removing DAO from solid asphaltene particles in the feed, the particles fall through the middle zone and are mixed with introduced solvent, which introduced solvent segregates DAO-rich solution in the upper zone (for extraction from that zone) from solvent-rich mixtures in the middle mixing and lower clarification zones. Solvent flows and precipitate movement are controlled to optimize mass transfer in process, resulting in high DAO recovery and dry, solid asphaltene product.
Owner:SUNCOR ENERGY INC
Solvent quality control in extraction processes
InactiveUS8471088B2Improvement in quality and long-term reliabilityMaintain stabilitySolvent extractionHydrocarbon distillation control/regulationExtractive distillationQuality control
The invention concerns the control of solvent systems in processes and apparatus for the separation of aromatic hydrocarbons from non-aromatic hydrocarbons in liquid-liquid extraction, extractive distillation, and the combination thereof.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for separating particles containing alkali metal salts from liquid hydrocarbons
ActiveUS10435631B2Refining with non-metalsPhotography auxillary processesOrganosulfur compoundsLiquid hydrocarbons
The present technology provides a process that includes heating a first mixture of elemental sulfur and particles comprising an alkali metal sulfide in a liquid hydrocarbon to a temperature of at least 150° C., to provide a sulfur-treated mixture comprising agglomerated particles; and separating the agglomerated particles from the sulfur-treated mixture to provide a desulfurized liquid hydrocarbon and separated solids. This process may be used as part of a suite of processes for desulfurizing liquid hydrocarbons contaminated with organosulfur compounds and other heteroatom-based contaminants. The present technology further provides processes for converting carbon-rich solids (e.g., petroleum coke) into fuels.
Owner:ENLIGHTEN INNOVATIONS INC
Separator for desalting petroleum crude oils having rag layer withdrawal
ActiveUS9493712B2Minimal downtimeDewatering/demulsification with electric/magnetic meansRefining by water treatmentAutomatic controlThermodynamics
An improved separator for desalting petroleum crude oils which may be operated in a continuous manner under automatic control; the improved desalter is therefore well suited to modern refinery operation with minimal downtime. A portion of the emulsion layer is withdrawn from the desalter through external withdrawal ports according to the thickness and position of the emulsion layer with the selected withdrawal header(s) being controlled by sensors monitoring the position and thickness of the emulsion layer. The withdrawn emulsion layer can be routed as such or with the desalter water effluent to a settling tank or directly to another unit for separation and reprocessing.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Coalescer for co-current contractors
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method and System for Removing Hydrogen Sulfide from Sour Oil and Sour Water
ActiveUS20160289575A1Transportation safetyWaste water treatment from quariesLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesScavengerHydrocarbon
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to a system and method to remove hydrogen sulfide from sour water and sour oil. In particular, hydrogen sulfide is removed from sour water and sour oil without the need for special chemicals, such as catalyst chemicals, scavenger chemicals, hydrocarbon sources, or a large scale facility. The system and method in the present invention is particularly useful in exploratory oil and gas fields, where large facilities to remove hydrogen sulfide may be inaccessible. The present invention addresses the need for safe and cost effective transport of the deadly neurotoxin. Particular embodiments involve a system and method that can be executed both on a small and large scale to sweeten sour water and sour oil.
Owner:ANSCHUTZ EXPLORATION
Popular searches
Extraction purification/separation Refining with two or more solvents Oxygen compounds preparation by reduction Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production Adsorption purification/separation Chemical modification purification/separation Naphtha reforming Refining to eliminate hetero atoms Co-current extraction Gaseous mixture working up
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com