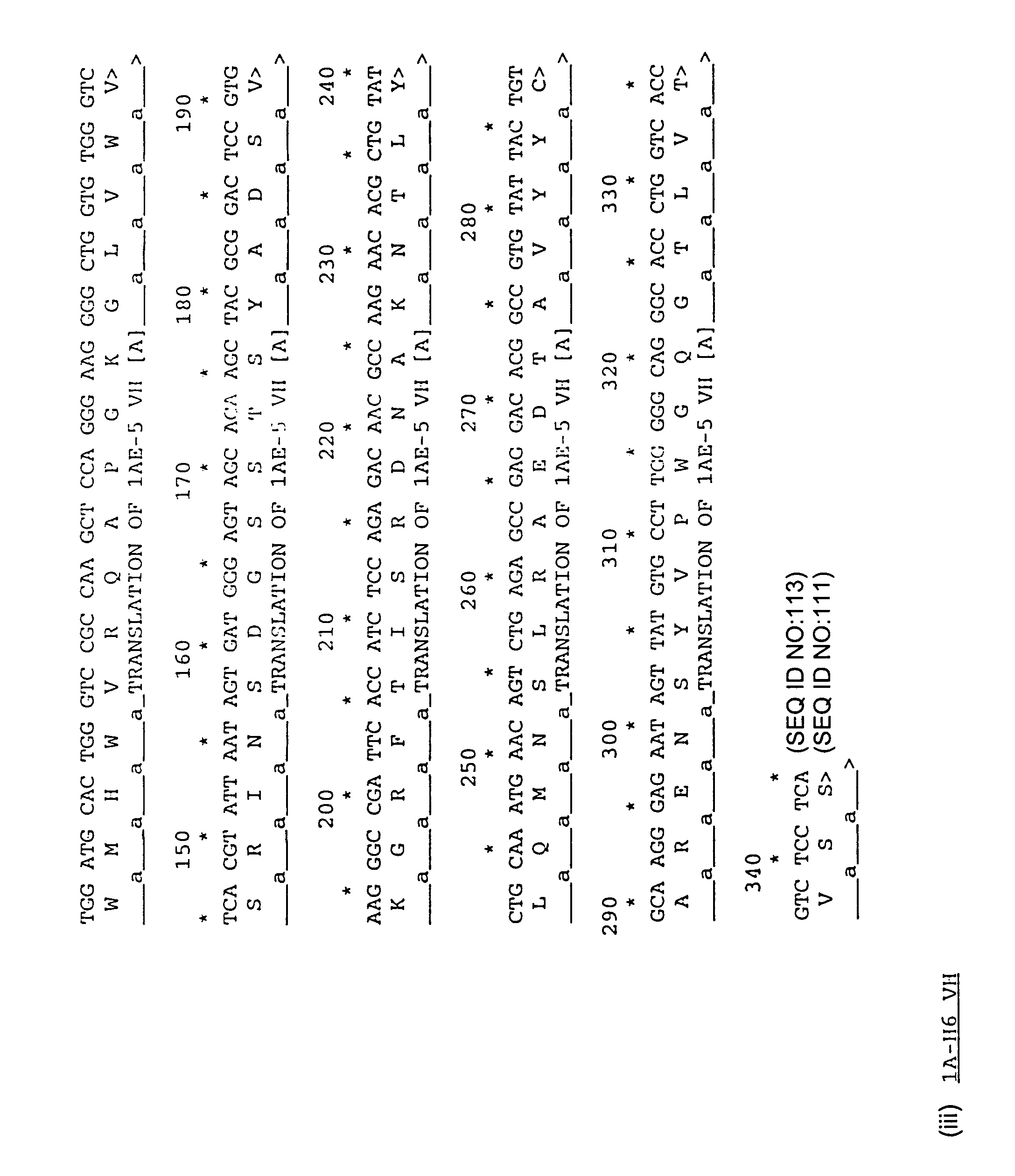
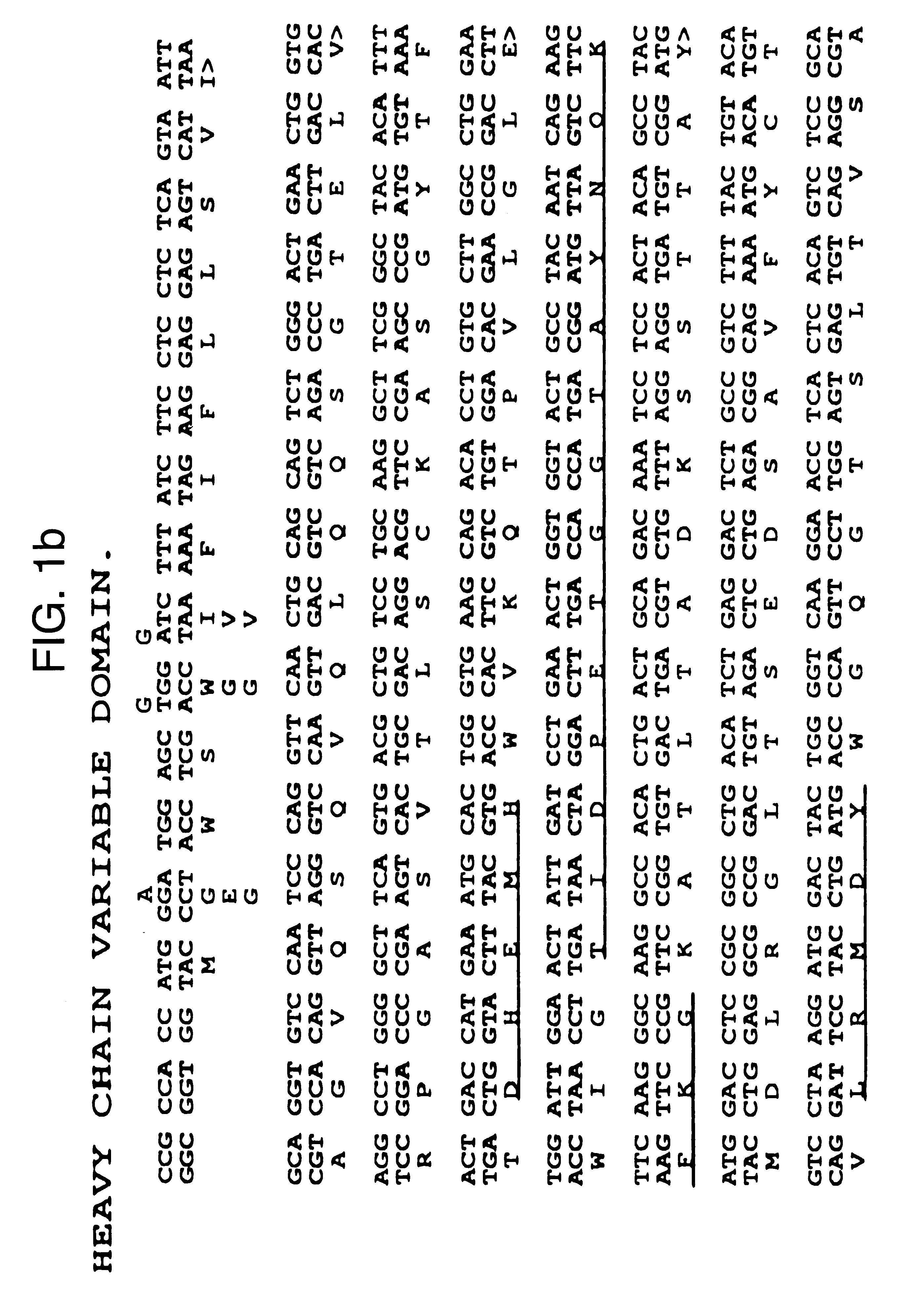
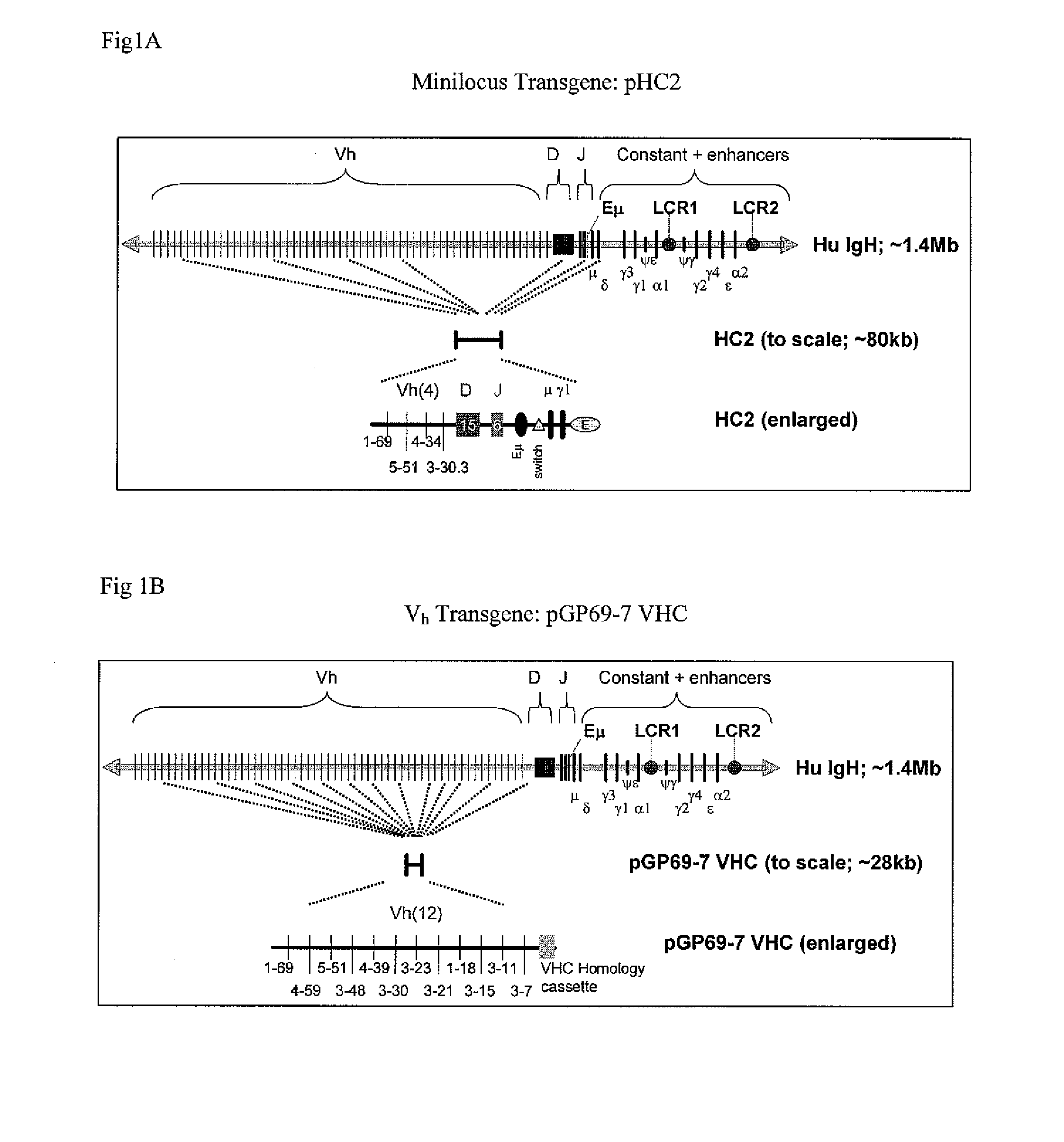
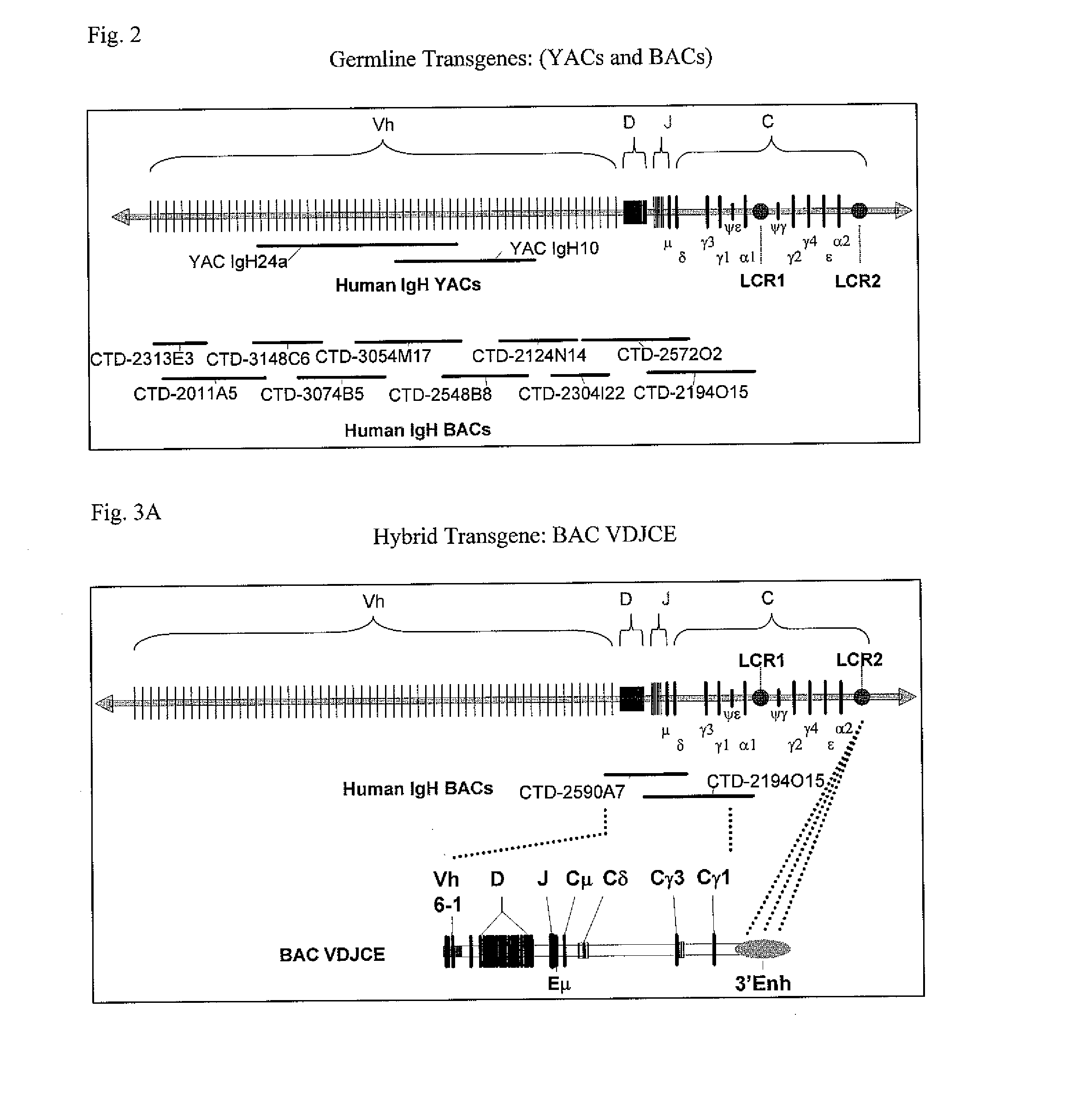
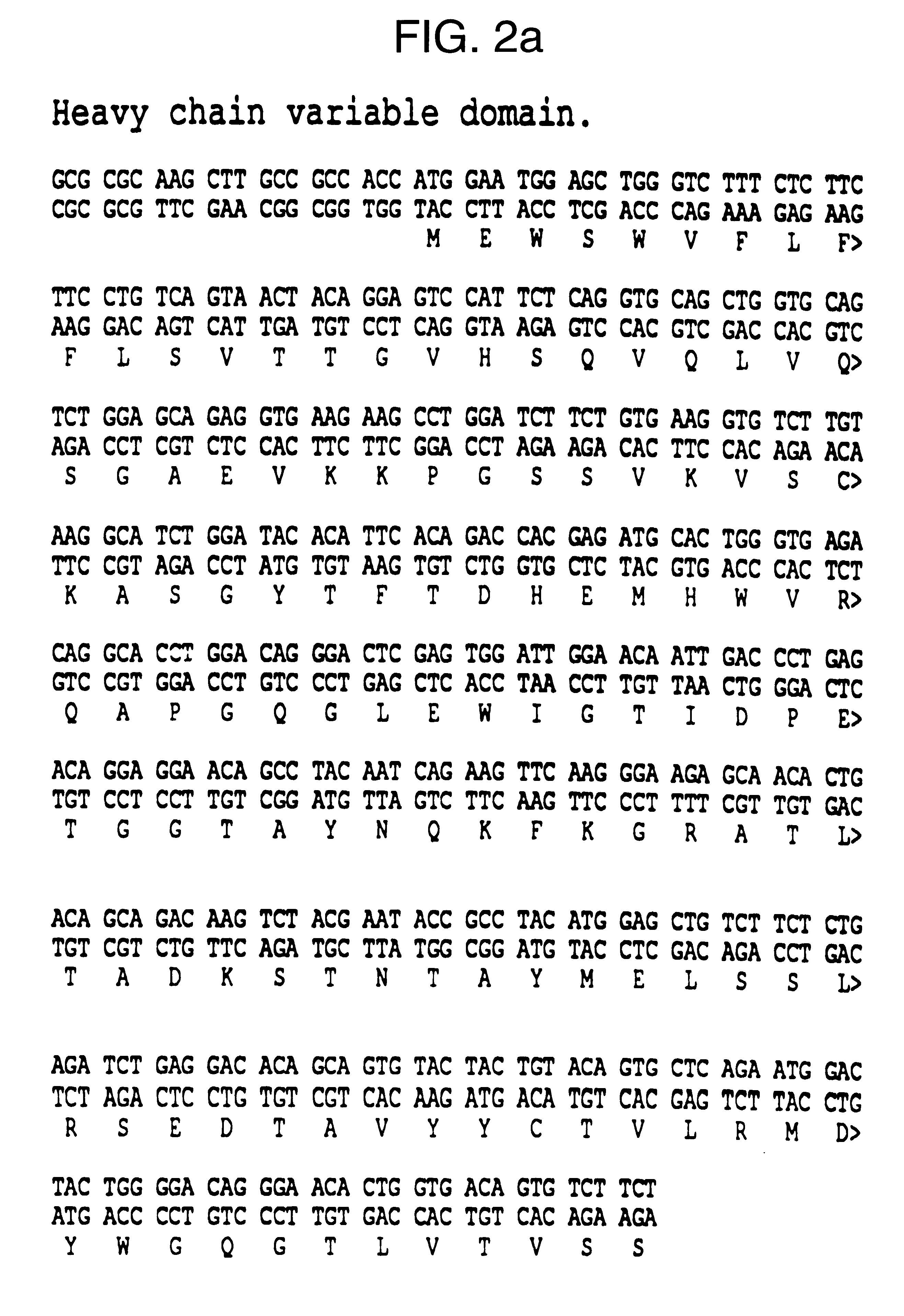Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
128 results about "Isotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In immunology, the immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype (class) is encoded by the constant region segments of the immunoglobulin gene which form the Fc (Fragment crystallizable region) portion and the lower segment of the Fab (Fragment antigen-binding) portion of an antibody. The expression of a specific isotype determines the function of an antibody via the specific binding to Fc receptor molecules on different immune effector cells. Isotype expression reflects the maturation stage of a B cell. Naive B cells express IgM and IgD isotypes with unmutated variable genes, which are produced from the same initial transcript following alternative splicing. Expression of other antibody isotypes (IgD, IgM IgG1-4, IgA1-2, IgE) occurs via a process of class-switch recombination (CSR) after antigen exposure. Class-switching is mediated by the AID (activation-induced cytidine deaminase) enzyme and only occurs after the B cell binds an antigen through its B cell receptor, and is further activated through interaction with a T helper cell.
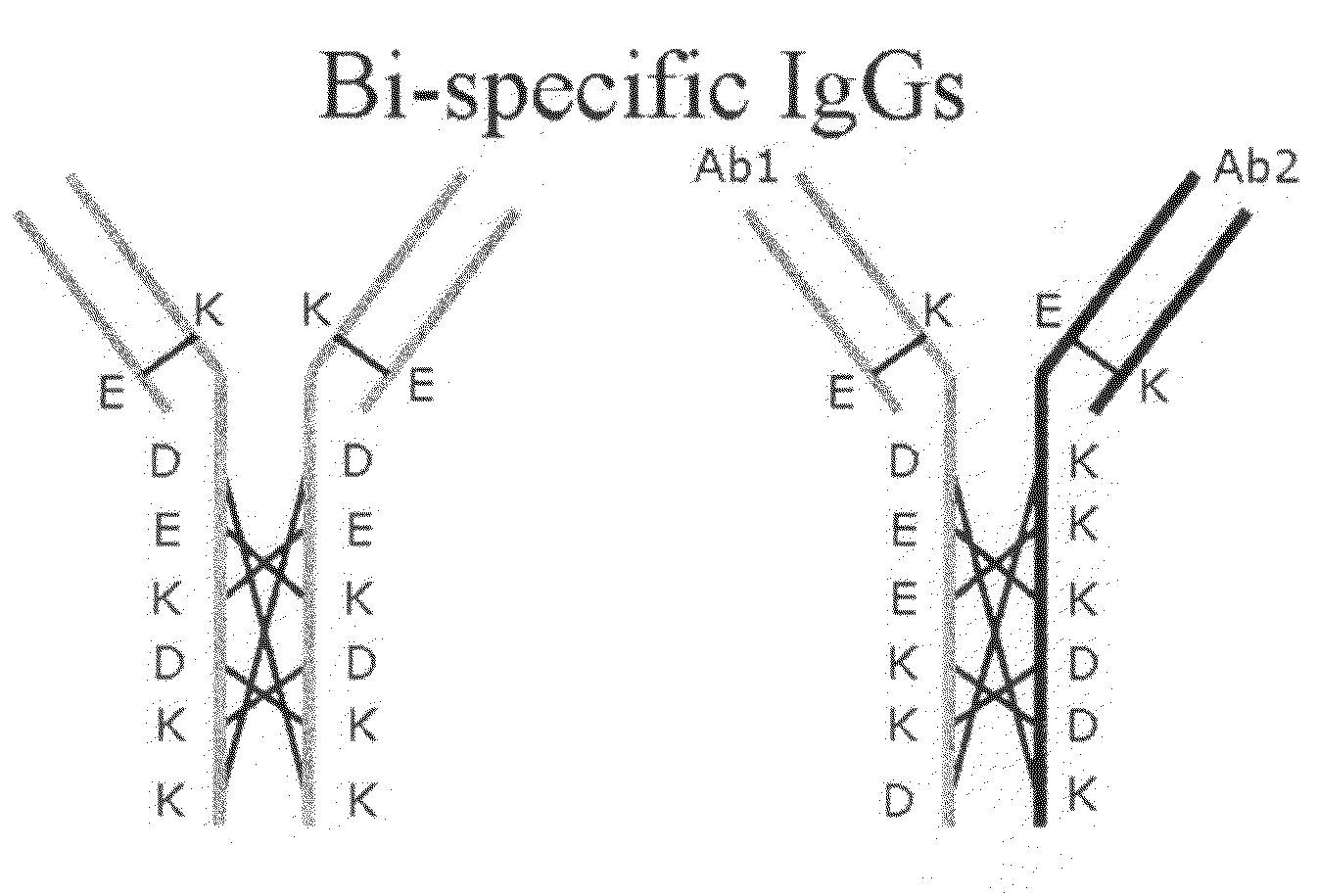
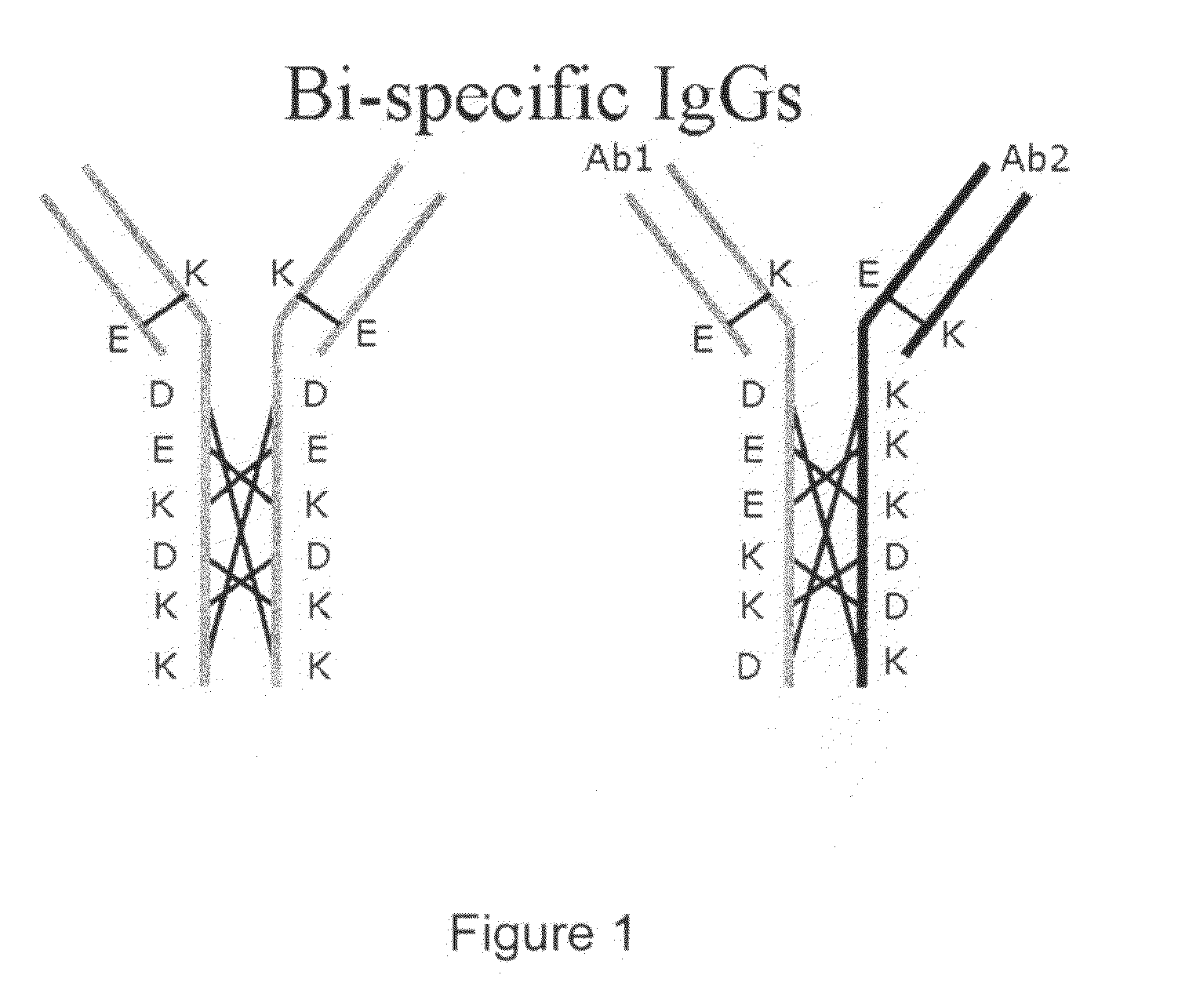
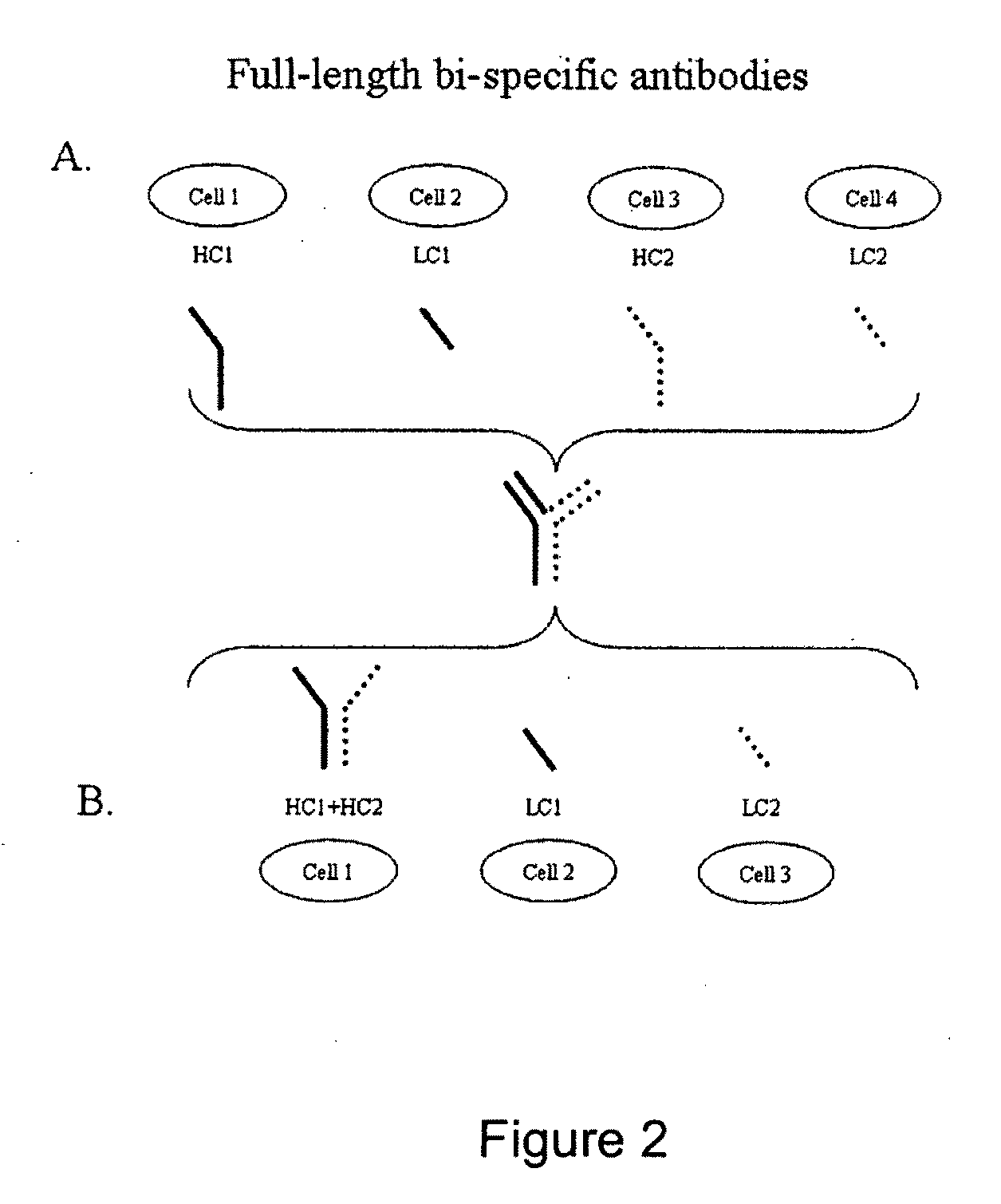
Production of Bispecific Antibodies
InactiveUS20090182127A1Reduce interactionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsConstant domainHeavy chain
Bispecific antibodies comprising (a) a first light-heavy chain pair having specificity for a first target and a sufficient number of substitutions in its heavy chain constant domain with respect to a corresponding wild-type antibody of the same isotype to significantly reduce the formation of first heavy chain-first heavy chain dimers and (b) a second light-heavy chain pair comprising a heavy chain having a sequence that is complementary to the sequence of the first pair heavy chain sequence with respect to the formation of intramolecular ionic interactions, wherein the first pair or second pair comprises a substitution in the light chain and complementary substitution in the heavy chain that reduces the ability of the light chain to interact with the heavy chain of the other light chain-heavy chain pair are provided. Methods of producing such antibodies in one or more cells also are provided.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
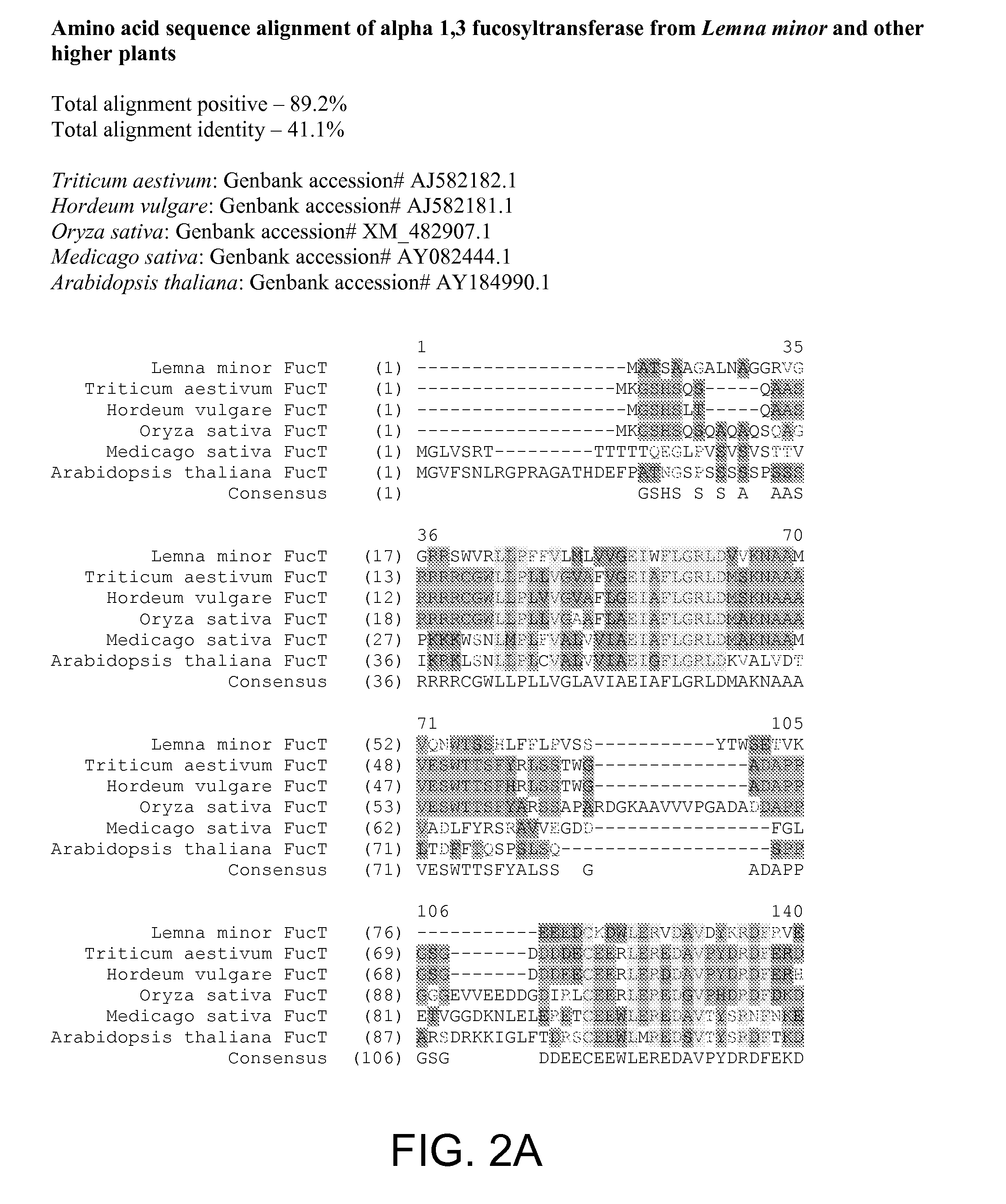
Compositions and methods for humanization and optimization of n-glycans in plants
InactiveUS20080060092A1Enhanced effector functionHigh antibody activityAntipyreticAnalgesicsGrowth plantGlycan
Methods for altering the N-glycosylation pattern of proteins in higher plants are provided. The methods comprise introducing into the plant a recombinant construct that provides for the inhibition of expression of α1,3-fucosyltransferase (FucT) and β1,2-xylosyltransferase (XylT) in a plant. Use of these constructs to inhibit or suppress expression of both of these enzymes, and isoforms thereof, advantageously provides for the production of endogenous and heterologous proteins having a “humanized” N-glycosylation pattern without impacting plant growth and development. Stably transformed higher plants having this protein N-glycosylation pattern are provided. Glycoprotein compositions, including monoclonal antibody compositions, having substantially homogeneous glycosylation profiles, and which are substantially homogeneous for the G0 glycoform, are also provided.
Owner:BIOLEX INC +1
Polynucleotides Encoding Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
PendingUS20190298658A1Minimize unwanted immune activationImprove translation efficiencyPowder deliveryCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMetaboliteNanoparticle
The invention relates to mRNA therapy for the treatment of cystic fibrosis. mRNAs for use in the invention, when administered in vivo, encode cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), isoforms thereof, functional fragments thereof, and fusion proteins comprising CFTR. mRNAs of the invention are preferably encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to effect efficient delivery to cells and / or tissues in subjects, when administered thereto. mRNA therapies of the invention increase and / or restore deficient levels of CFTR expression and / or activity in subjects. mRNA therapies of the invention further decrease levels of toxic metabolites associated with deficient CFTR activity in subjects.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
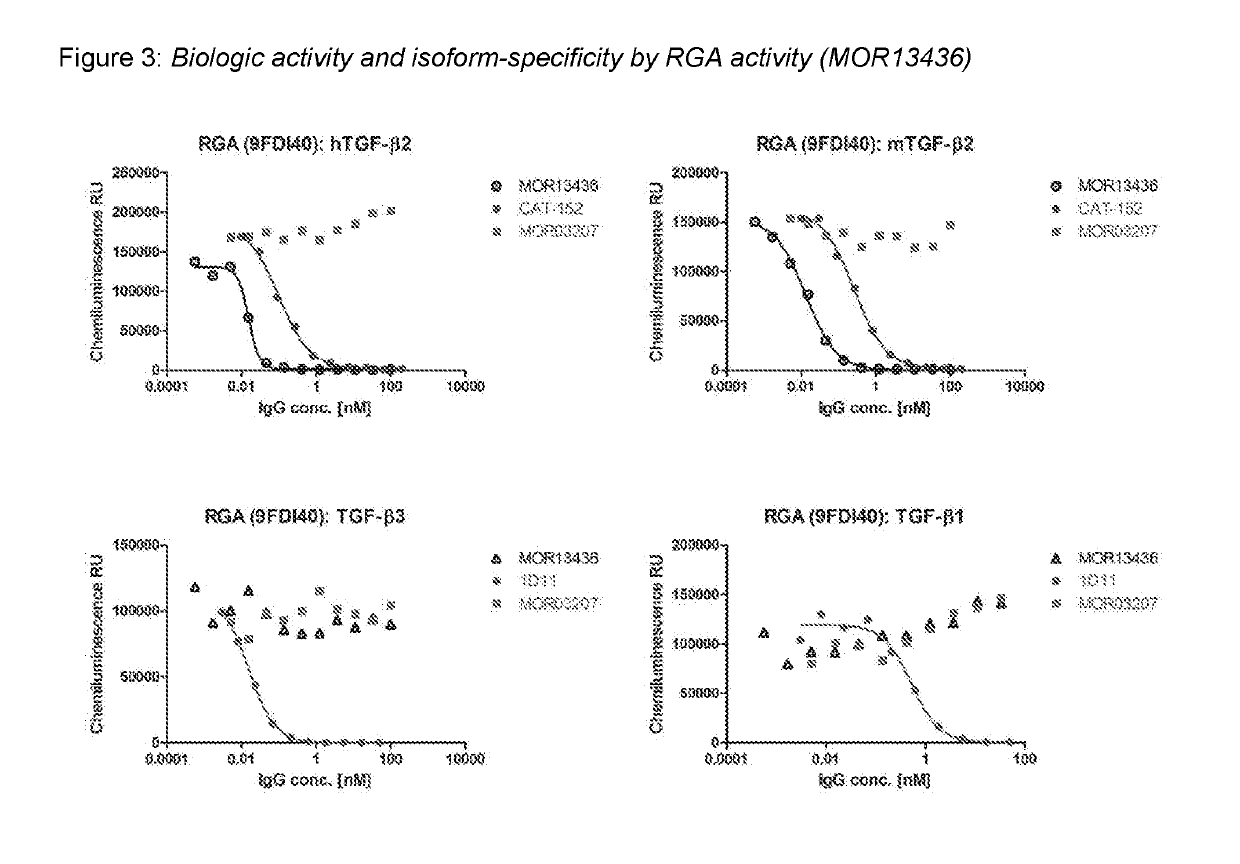
Human antibodies specific for TGFbeta2
InactiveUS7368111B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDiseaseEpitope
Specific binding members comprising human antibody antigen binding domains specific for human transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) bind specifically isoforms TGFβ2 and TGFβ1 or both, preferentially compared with TGFβ3. Specific binding members may be isolated and utilized in the treatment of disease, particularly fibrotic disease and also immune / inflammatory diseases. Therapeutic utility is demonstrated using in vitro and in vivo models. Full sequence and binding information is provided, including epitope sequence information for particularly advantageous specific binding member which binds the active form of TGFβ2, neutralizing its activity, but does not bind the latent member.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
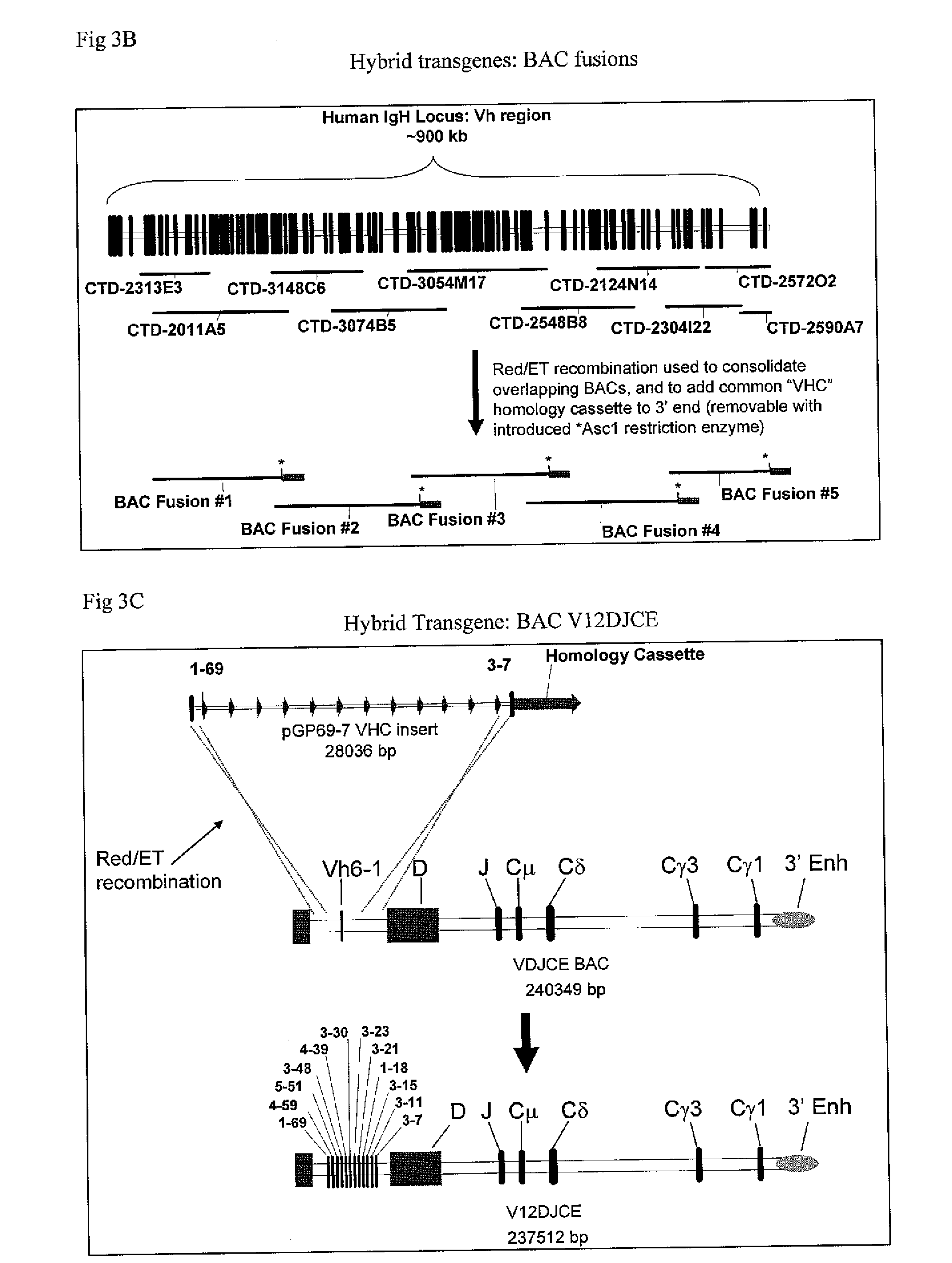
Transgenic animals for producing specific isotypes of human antibodies via non-cognate switch regions
InactiveUS20060134780A1Immunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenBeta globulins
The present invention provides fully human antibodies in a transgenic animal of a desired isotype in response to immunization with any virtually any desired antigen. The human immunoglobulin heavy chain transgene in the foregoing animals comprises a human constant region gene segment comprising exons encoding the desired heavy chain isotype, operably linked to switch segments from a constant region of a different heavy chain isotype, i.e., a non-cognate switch region. Said additional constant region segment comprises a switch region and human constant region coding segment, wherein the constant region coding segment is operably linked to a switch region that it is not normally associated with, i.e., a non-cognate switch region. In the transgenes of the invention, the non-cognate switch region may be a switch region from a different species than the constant region coding segment. The switch region and membrane exons of the invention may comprise a human gamma-2 constant region and the secreted constant region exons are from a human gamma-1 or a human gamma-4 constant region.
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC
Antibodies against E-selectin
InactiveUS6204007B1Avoid consumptionAlteration of antibody side chain interactionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticNatural antibodyFc(alpha) receptor
This invention relates to whole antibodies of neutral isotype having specificity for E-selectin, process for their preparation (using vectors), pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and their use in therapy and diagnosis. Said antibodies are variants of natural antibodies altered in the Fc region, especially in the CH2 domain, so that the interactions with antibodies Fc receptors and complement are very low.
Owner:CELLTECH R & D LTD
Hco32 and hco27 and related examples
The instant invention relates to transgenic non-human animals capable of producing heterologous antibodies, transgenes used to produce such transgenic animals, transgenes capable of functionally rearranging a heterologous D gene in V-D-J recombination, immortalized B-cells capable of producing heterologous antibodies, methods and transgenes for producing heterologous antibodies of multiple isotypes, methods and transgenes for producing heterologous antibodies wherein a variable region sequence comprises somatic mutation as compared to germline rearranged variable region sequences, transgenic nonhuman animals which produce antibodies having a human primary sequence and which bind to human antigens, hybridomas made from B cells of such transgenic animals, and monoclonal antibodies expressed by such hybridomas.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
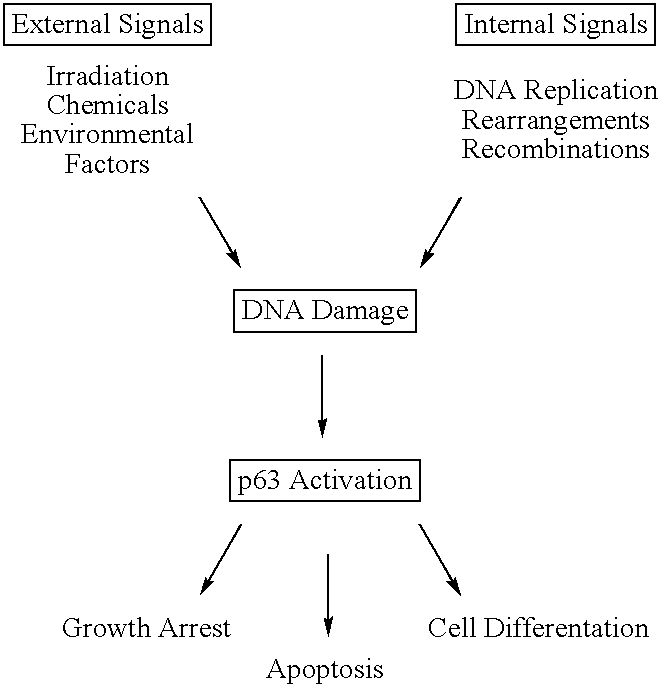
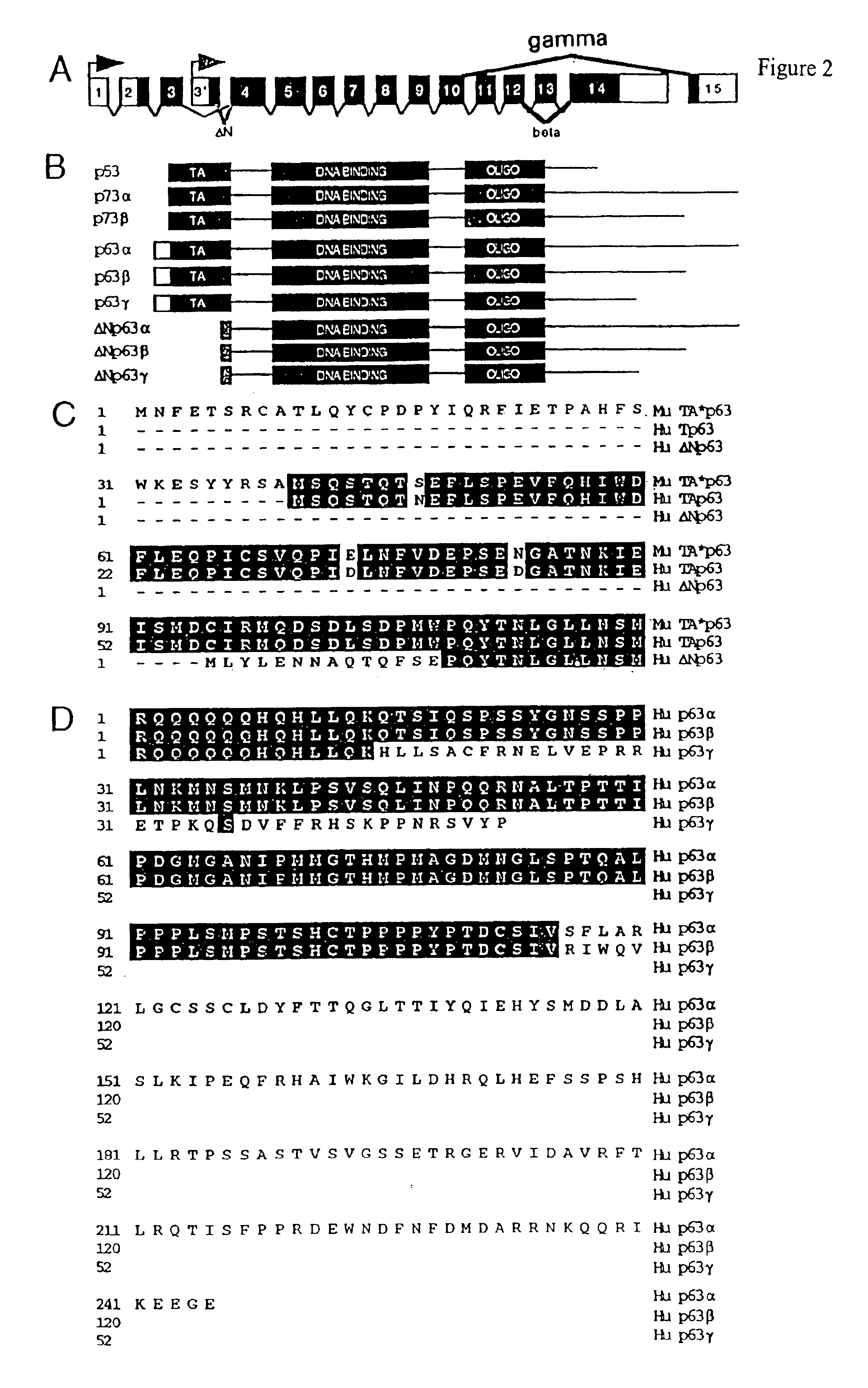
Cell regulatory genes, encoded products, and uses related thereto
InactiveUS6946256B1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSuppressorApoptosis
This application describes the cloning of p63, a gene at chromosome 3q27-29, that bears homology to the tumor suppressor p53. The p63 gene encodes at least six different isotypes. p63 was detected in a variety of human and mouse tissue and demonstrates remarkably divergent activities, such as the ability to transactivate p53 reporter genes and induce apoptosis. Isotopes of p63 lacking a transactivation domain act as dominant negatives towards the transactivation by p53 and p63.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +2
Tubulin isotype screening in cancer therapy using halichondrin B analogs
Chemotherapeutic agents that interfere with microtubule assembly or disassembly in the cell are potent inhibitors of cell replication. Examples of such agents include halichondrin B analogs. It has been shown that the susceptibility of certain cancers to analogs of halichondrin B correlates with the expression of particular tubulin isotypes or other microtubule-associated proteins such as MAP-4 and stathmin. Correlations such as these may be used in identifying patients suitable for treatment using a particular chemotherapeutic agent. Such a system avoids treating patients with cytotoxic compounds where there is a minimal or no effect on the cancer. The invention also provides a system of establishing these correlations for different compounds and cancer types. The system will be particularly useful in establishing correlations between anti-microtubule agents and cancers such as lung, breast, and ovarian cancer. Kits and reagents useful in practicing the invention are also provided.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
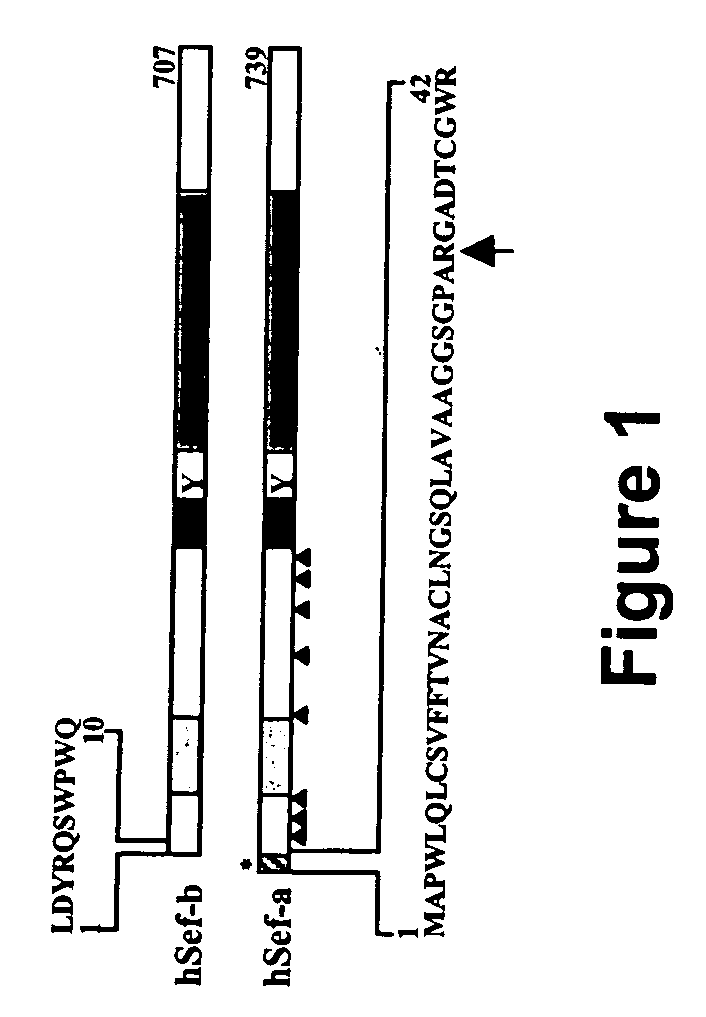
Human Sef isoforms and methods of using same for cancer diagnosis and gene therapy
InactiveUS20060293240A1Reduce expressionIncrease in tumor malignancyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCancers diagnosisTissue sample
A method and pharmaceutical compositions useful for inhibiting the growth of solid tumors are provided. Specifically, the method is effected by administering to a subject in need thereof an agent capable of upregulating the expression level and / or activity of at least a functional portion of Sef, wherein the functional portion being capable of inhibiting RTK-mediated cell proliferation. Also provided are methods and kits for diagnosing and staging of cancer by detecting the expression level of hSef in a tissue sample, wherein a decrease in hSef expression level is indicative of cancer.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Human Monoclonal Antibodies Against CD20
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies which bind to and inhibit human CD20, and related antibody-based compositions and molecules, are disclosed. The human antibodies can be produced by a transfectoma or in a non-human transgenic animal, e.g., a transgenic mouse, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals and hybridomas which produce the human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the human antibodies.
Owner:GENMAB AS
Antibody specific to central nervous system tau protein
InactiveUS20050181460A1Reliable analysisSamplingImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeripherinEpitope
The present invention provides an antibody which specifically recognizes a CNS tau protein but not a peripheral tau protein. More specifically, the present invention provides an antibody obtainable by using a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence of a connective portion between the amino acid sequence encoded by Exon 4 of a gene encoding a tau protein and the amino acid sequence encoded by Exon 5 thereof as an epitope specific to the isoform of tau protein predominantly existing in central nervous tissues. The present invention further provides a method of detecting Alzheimer's disease and a reagent kit using the antibody.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM MEDIENCE
Hybrid constant regions
ActiveUS20140294825A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenHexamerins
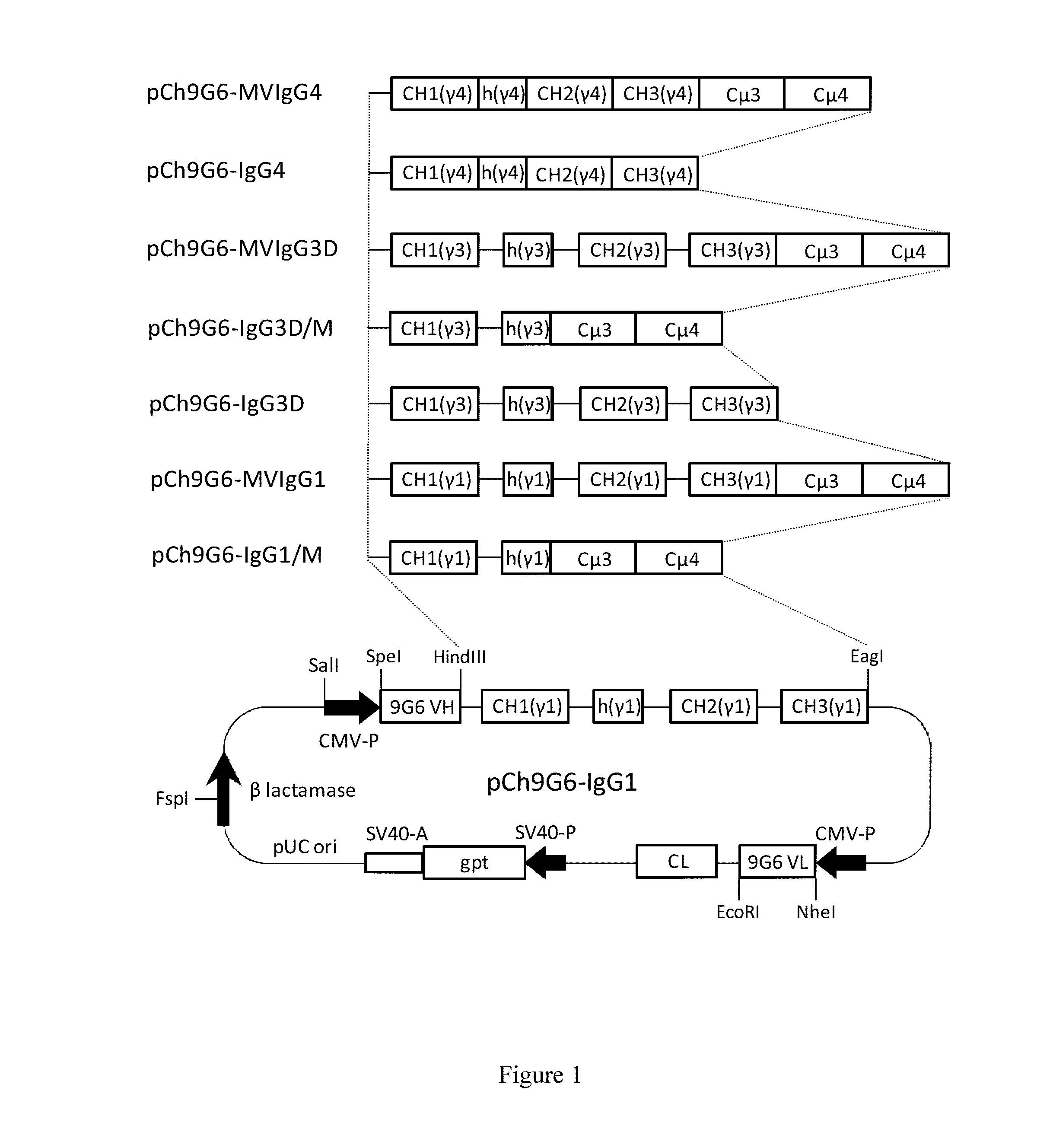
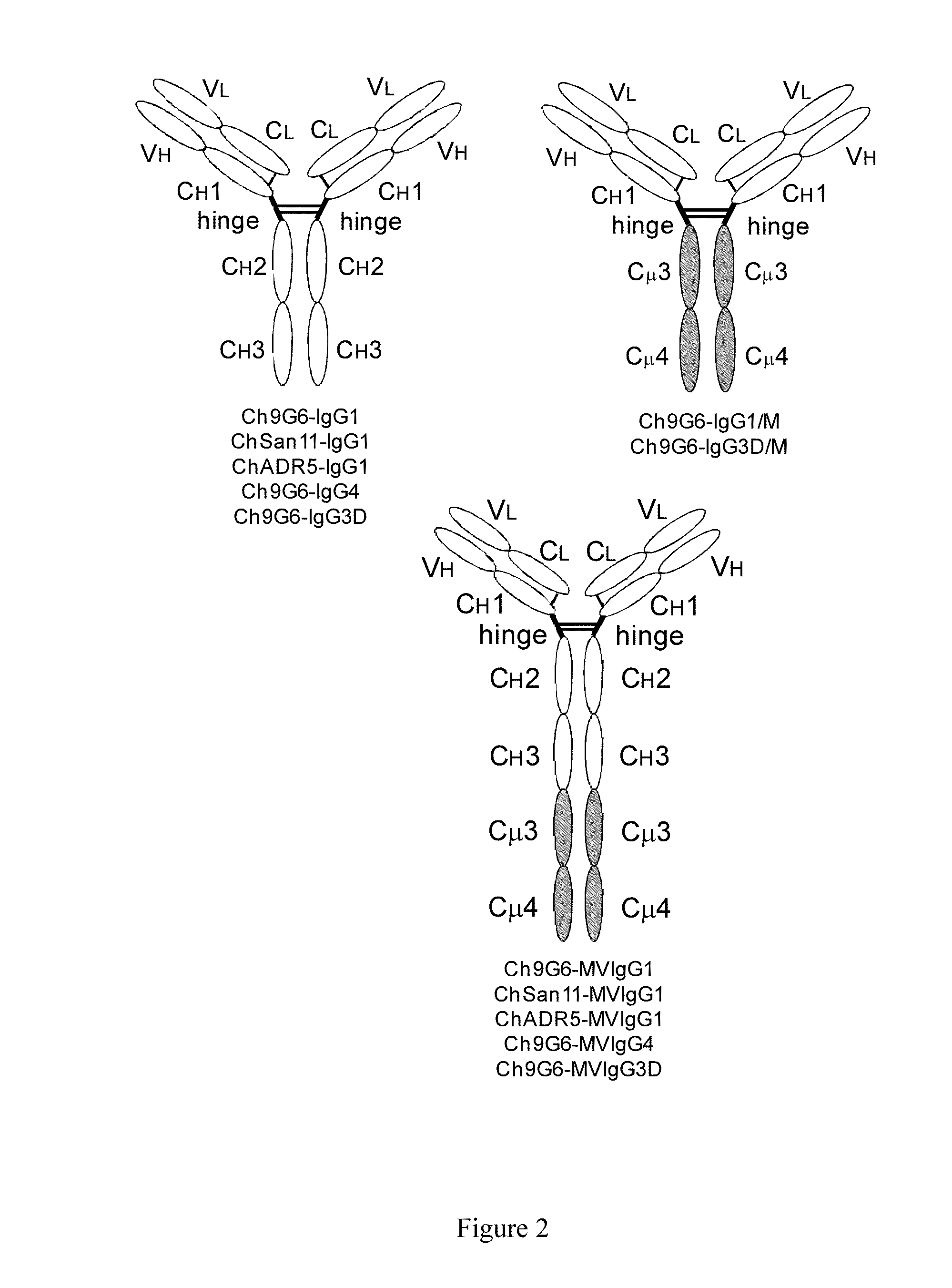
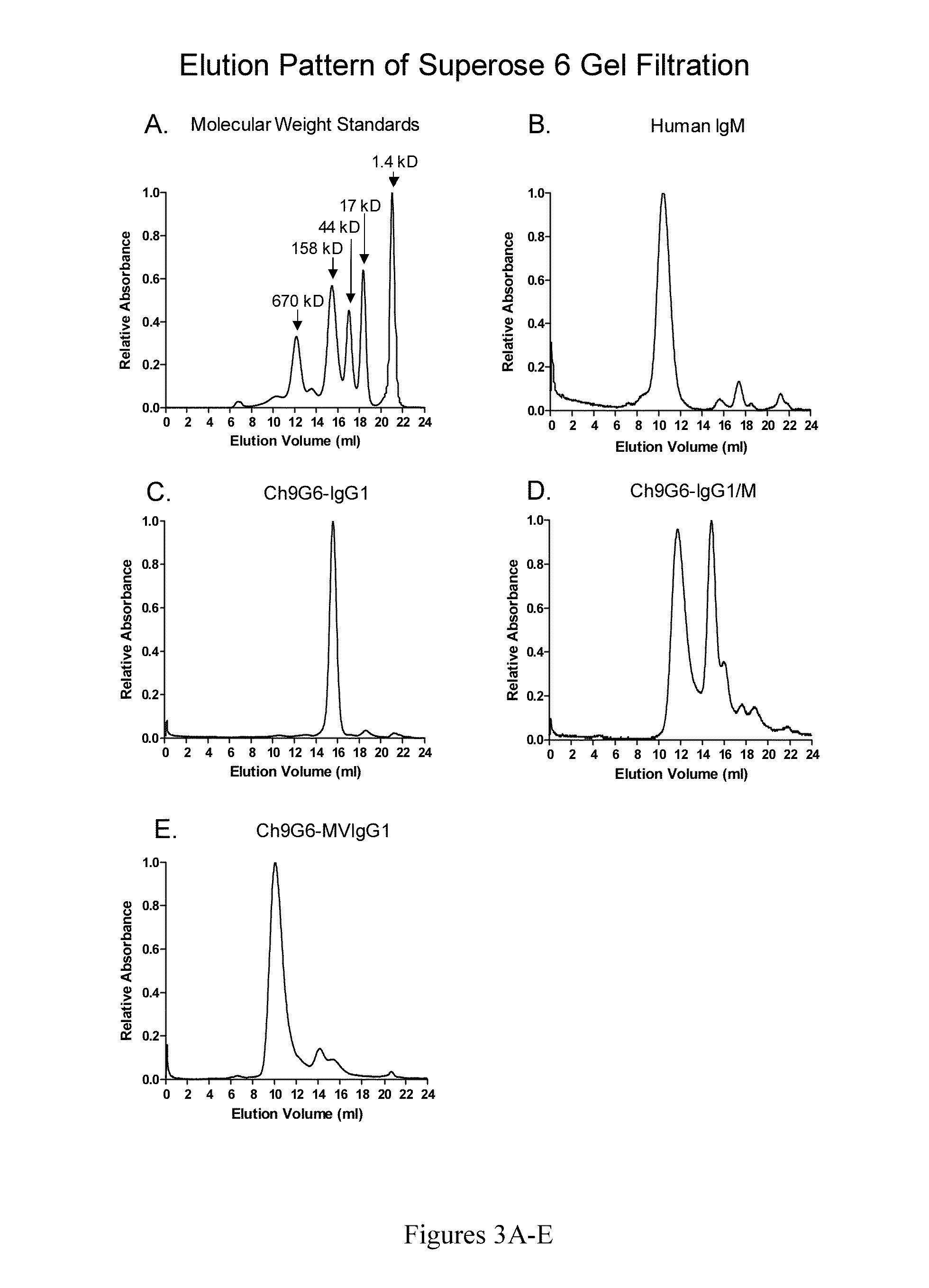
The invention provides hybrid constant regions and antibodies or fusion proteins incorporating the same. The hybrid constant regions include at least CH2 and CH3 regions of an IgG or IgA constant region and Cμ3 and Cμ4 regions of a Cμ constant region. The hybrids retain properties of both component constant regions. The hybrids retain the ability of a Cμ constant region to form multivalent complexes, e.g., pentameric or hexameric structures. IgG hybrids also retain IgG properties including pH-dependent FcRn binding, which is associated with a relatively long in vivo half-life, and specific binding to protein G, which facilitates purification. Depending on the isotype and subtype, the nature of the antigen and presence of additional IgG CH1 and hinge domains, IgG hybrids may also retain properties of specific binding to protein A, and effector functions ADCC, CDC and opsonization. IgA hybrids retain the property of IgA of binding to an Fc-alpha receptor CD89.
Owner:JN BIOSCI
Antibody of anti human CD20 from human resources functionally, and application
ActiveCN1958615ALow immunogenicityMaintain propertiesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseCD20
This invention discloses functional humanized antibody against CD20 molecules and its application. The functional humanized antibody specifies human CD20 molecules, and is composed of a light chain and a heavy chain, each of which comprises a constant region and a variable region. The constant region of the heavy chain is isotypic human IgG1 constant region, and that of the light chain is isotypic human kappa constant region. The variable region of the heavy chain is shown in SEQ ID No.2, and that of the light chain is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The functional humanized antibody has low immunogenicity. Experiments show that the functional humanized antibody has the same specificity and affinity as the original murine antibody. Drugs containing the functional humanized antibody and its derivatives can be used for treating cancers or immune system diseases with the high-expression of CD20, such as rheumatic arthritis and lupus erythematosus.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
Monoclonal antibodies reactive with defined regions of the T cell antigen receptor
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies which recognize defined regions of the T-cell receptor (TCR). In a specific embodiment, the invention provides monoclonal antibodies which are reactive with a constant region of the alpha chain of the TCR. In particular embodiments, the invention relates to two monoclonal antibodies, termed alpha F1 and alpha F2, which react with two different epitopes on the framework region of the alpha monomer of the TCR molecule. In another specific embodiment, the invention is directed to monoclonal antibodies reactive with a variable region of the beta chain of the TCR. In particular, the invention provides two monoclonal antibodies, termed W112 and 2D1, which react with beta chain variable regions V beta 5.3 and V beta 8.1, respectively. In another specific embodiment, the invention is directed to monoclonal antibodies reactive with a variable region of the delta chain of the TCR. In particular, the invention provides monoclonal antibody delta TCS1, isotype IgG2a. The monoclonal antibodies of the invention have value in diagnosis and therapy and are useful tools for study of the immune system.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Antibody of anti human CD20 from human resources functionally, and application
ActiveCN100455598CImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsRadioactive preparation carriersCD20Disease
This invention discloses functional humanized antibody against CD20 molecules and its application. The functional humanized antibody specifies human CD20 molecules, and is composed of a light chain and a heavy chain, each of which comprises a constant region and a variable region. The constant region of the heavy chain is isotypic human IgG1 constant region, and that of the light chain is isotypic human kappa constant region. The variable region of the heavy chain is shown in SEQ ID No.2, and that of the light chain is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The functional humanized antibody has low immunogenicity. Experiments show that the functional humanized antibody has the same specificity and affinity as the original murine antibody. Drugs containing the functional humanized antibody and its derivatives can be used for treating cancers or immune system diseases with the high-expression of CD20, such as rheumatic arthritis and lupus erythematosus.
Owner:SINOMAB BIOSCI
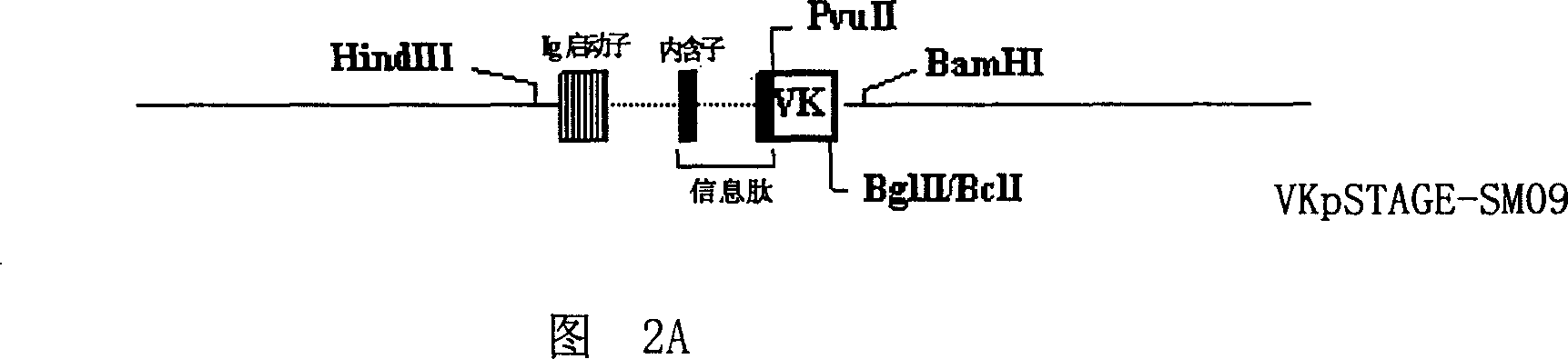
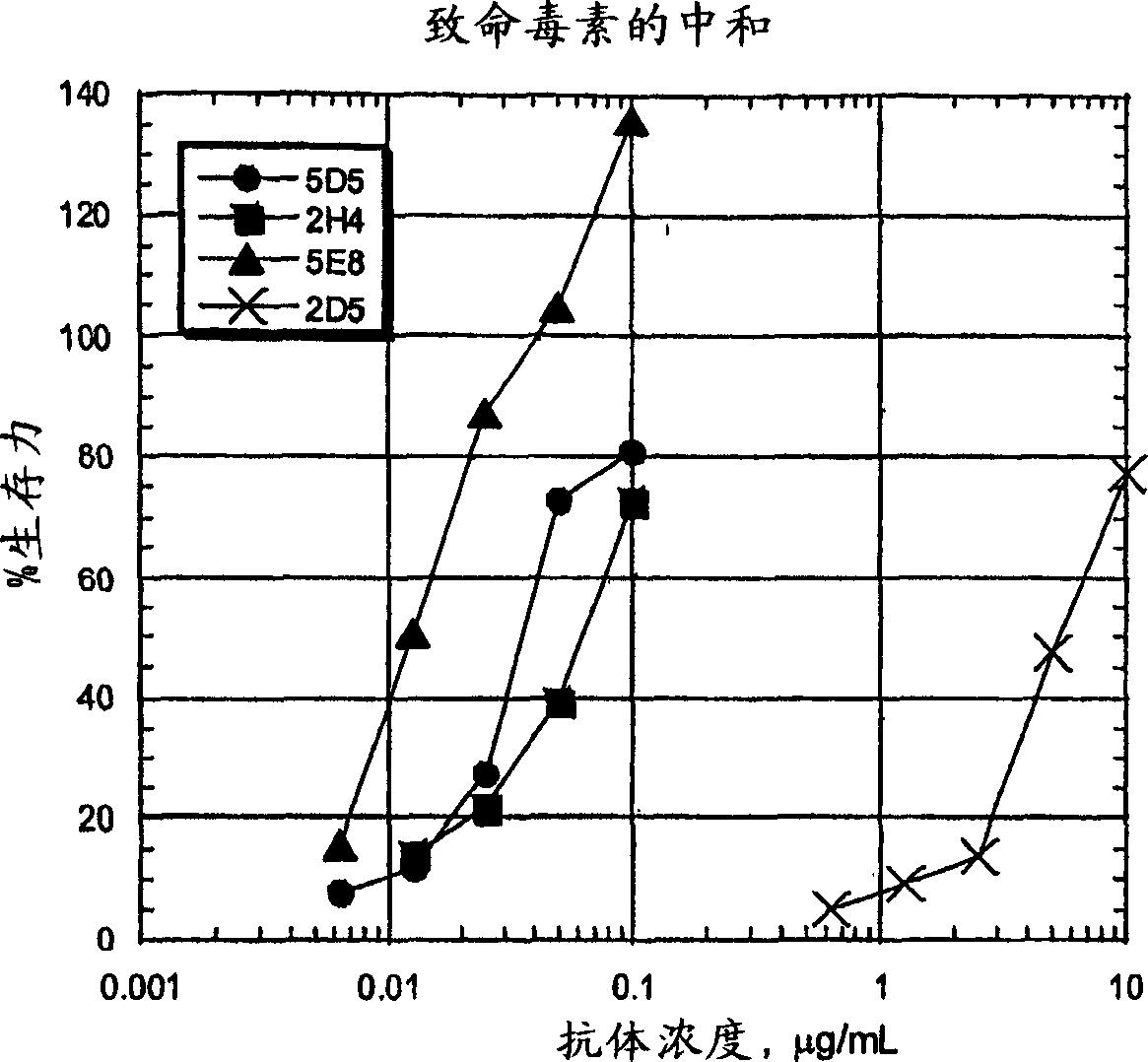
Human monoclonal antibodies against bacillus anthracis protective antigen
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies that bind anthrax protective antigens are disclosed. Human antibodies can be produced in non-human transgenic animals, such as transgenic mice, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are derivatives of human antibodies (e.g., bispecific antibodies and immunoconjugates), pharmaceutical compositions containing human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals and hybridomas producing human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic uses of human antibodies method.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
TGFbeta 2 Antibodies
ActiveUS20190092846A1Muscular disorderSkeletal disorderMonoclonal antibodyTransforming growth factor beta
This invention is in the field of anti-transforming growth factor beta 2 (TGF-β2) antibodies. In particular, the invention provides human monoclonal antibodies that bind the human TGF-β2 isoform preferentially over the human TGF-β1 or TGF-β3 isoforms.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Assays for detecting antibodies specific to therapeutic Anti-ige antibodies and their use in anaphylaxis
ActiveUS20110183363A1Low affinityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisAnaphylactic reactionAntibody
The invention provides methods and reagents useful for detecting anti-drug antibodies of IgE isotype to therapeutic anti-IgE antibodies, and methods for assessing risk of anaphylaxis to administration of a therapeutic anti-IgE antibody.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for generating high affinity antibodies
InactiveUS20060234296A1High affinityImprove efficiencyAnimal cellsPeptide librariesDiseaseAs Directed
The invention relates to high affinity human monoclonal antibodies, particularly those directed against isotypic determinants of immunoglobulin E (IgE), as well as direct equivalents and derivatives of these antibodies. These antibodies bind to their respective target with an affinity at least 100 fold greater than the original parent antibody. These antibodies are useful for diagnostics, prophylaxis and treatment of disease.
Owner:TANOX
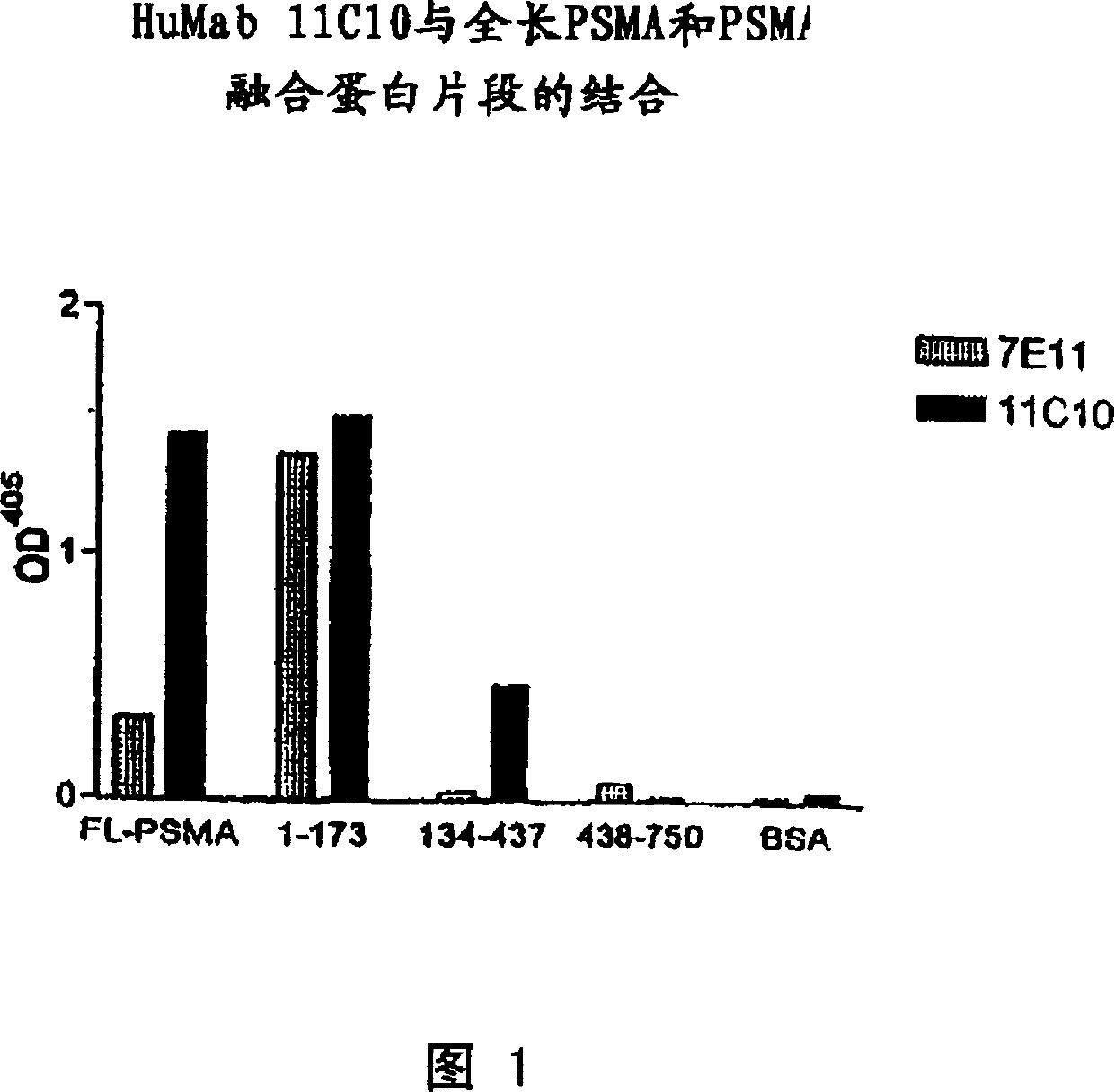
Human monoclonal antibodies to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA)
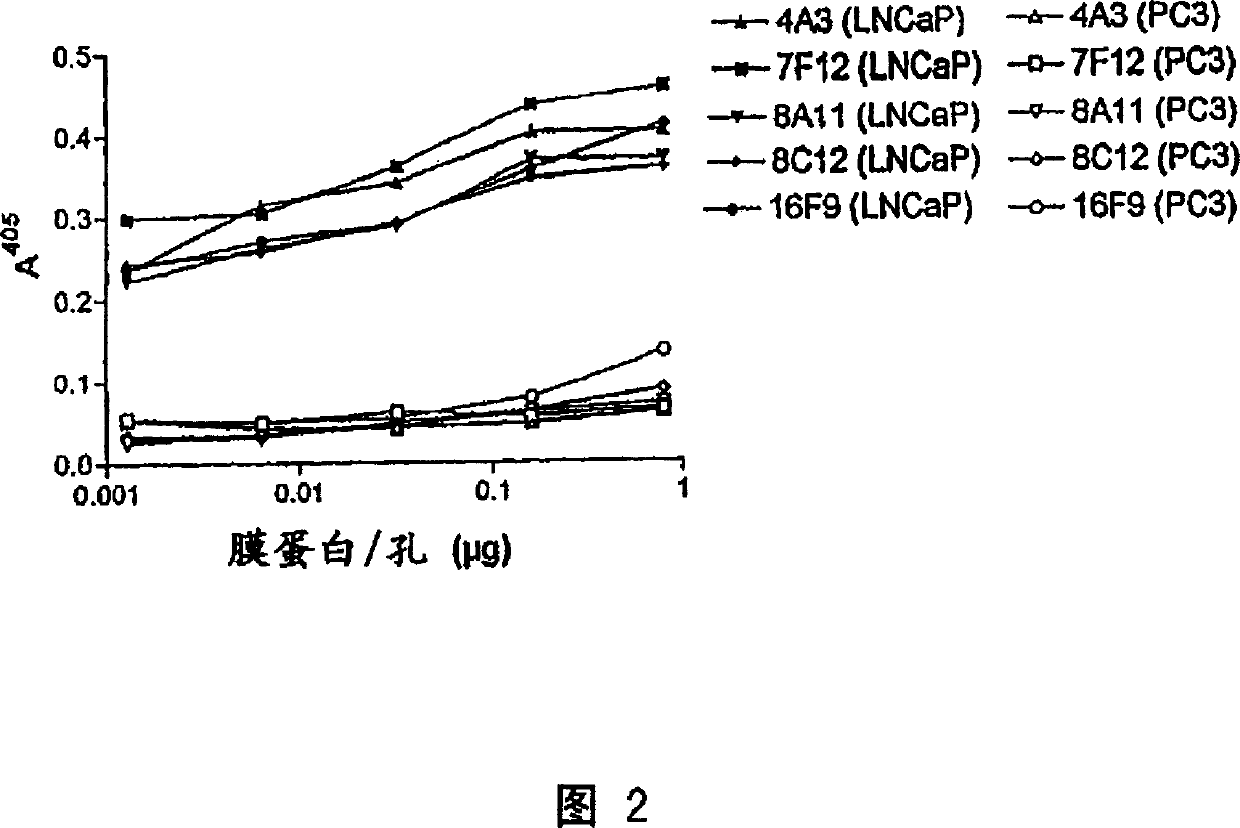
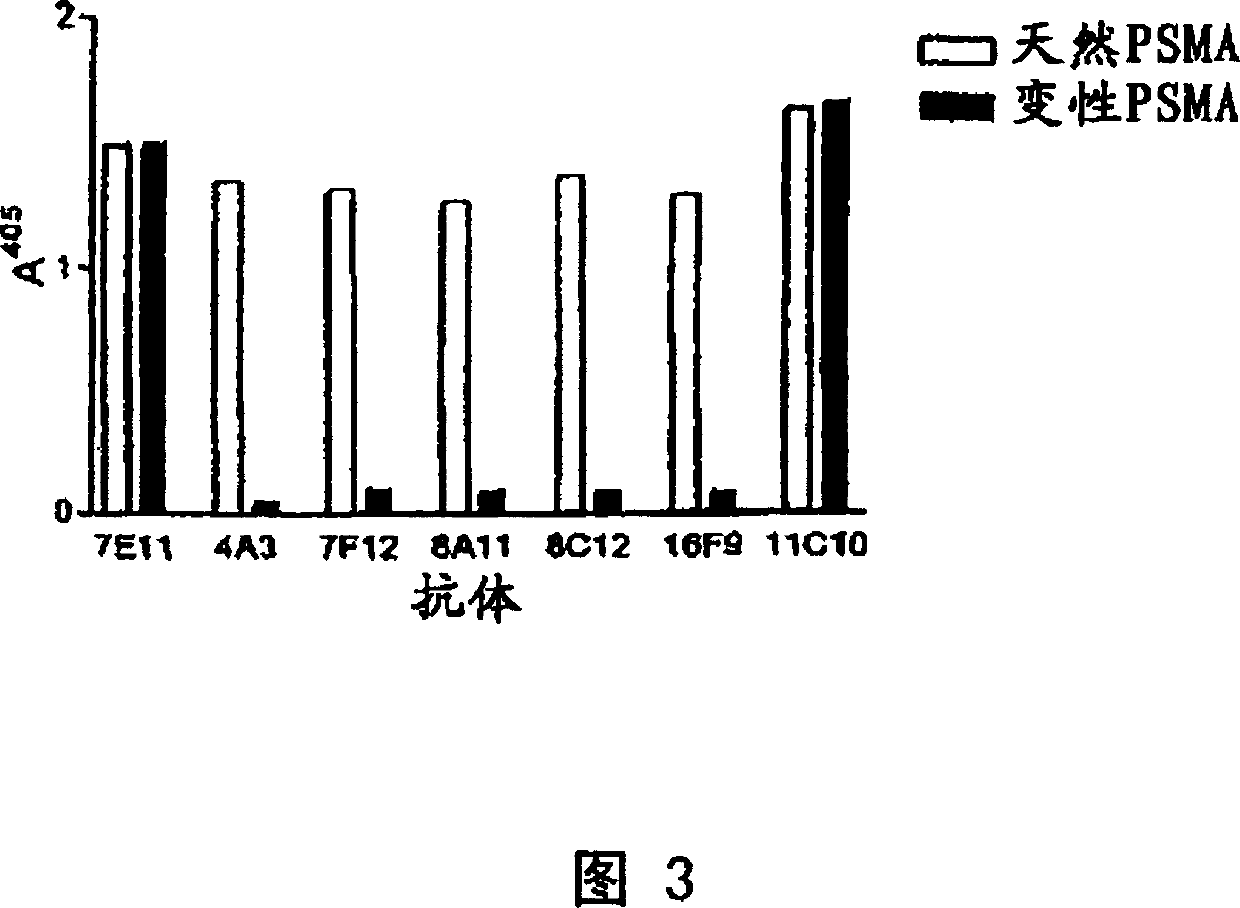
InactiveCN1652821AHybrid cell preparationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenV(D)J recombination
The present invention discloses isolated human monoclonal antibodies that bind to PSMA and relates to related antibody-based compositions and molecules. Such human antibodies can be produced by V-D-J recombination and isotype switching in non-human transgenic animals, such as transgenic mice, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions containing the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals, and hybridomas producing the human antibodies, as well as therapeutic and diagnostic methods using the human antibodies.
Owner:MEDAREX LLC
Immunologically discernible cell surface variants for use in cell therapy
PendingCN110191948ALow antigenicityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAAntigen receptorsCell therapy
The invention relates to a mammalian cell, particularly a human cell, expressing a first isoform of a surface protein, wherein the first isoform is functionally indistinguishable, but immunologicallydistinguishable from a second isoform, for use in a medical treatment of a patient having cells expressing the second isoform form of the surface protein. The invention further relates to an agent selected from 1) a compound comprising, or consisting of, an antibody or antibody-like molecule and 2) an immune effector cell bearing an antibody-like molecule or an immune effector cell bearing a chimeric antigen receptor, for use in a method of treatment of a medical condition, wherein the agent is specifically reactive to either a first or a second isoform of a surface protein, wherein the firstisoform is functionally indistinguishable, but immunologically distinguishable from the second isoform, and wherein the agent is administered to ablate a cell bearing the isoform that the agent is reactive to.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
Method for identification of cellular protein antigens and presence of antibodies to specific cellular protein antigens in serum
InactiveUS20040191841A1Facilitating tumor cell killingInhibit tumor cell growthMaterial analysisDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for identification of cellular protein antigens to which patients with cancer, or patients at risk for cancer, may develop autoantibodies. The method of the invention involves the use of patient derived sera for the identification of the cellular protein antigens using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis followed by Western Blot analysis. The identification of such protein antigens provides novel markers that can be utilized for screening, for diagnostics and prognosis of disease. The invention also provides for the use of the identified protein antigens in immunoassays designed to detect the presence of serum antibodies to the specific protein antigens in sera from individuals that may harbor such antibodies. The invention further relates to the use of the identified antigens as immunogens for stimulation of an immune response in patients expressing such protein antigens. The invention is demonstrated by way of example in which elevated levels of circulating autoantibodies reactive against a tumor specific antigen were identified in sera derived from a lung cancer patient. In addition, elevated levels of circulating autoantibodies reactive against several specific beta-tubulin isoforms were detected in the sera of neuroblastoma patients.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
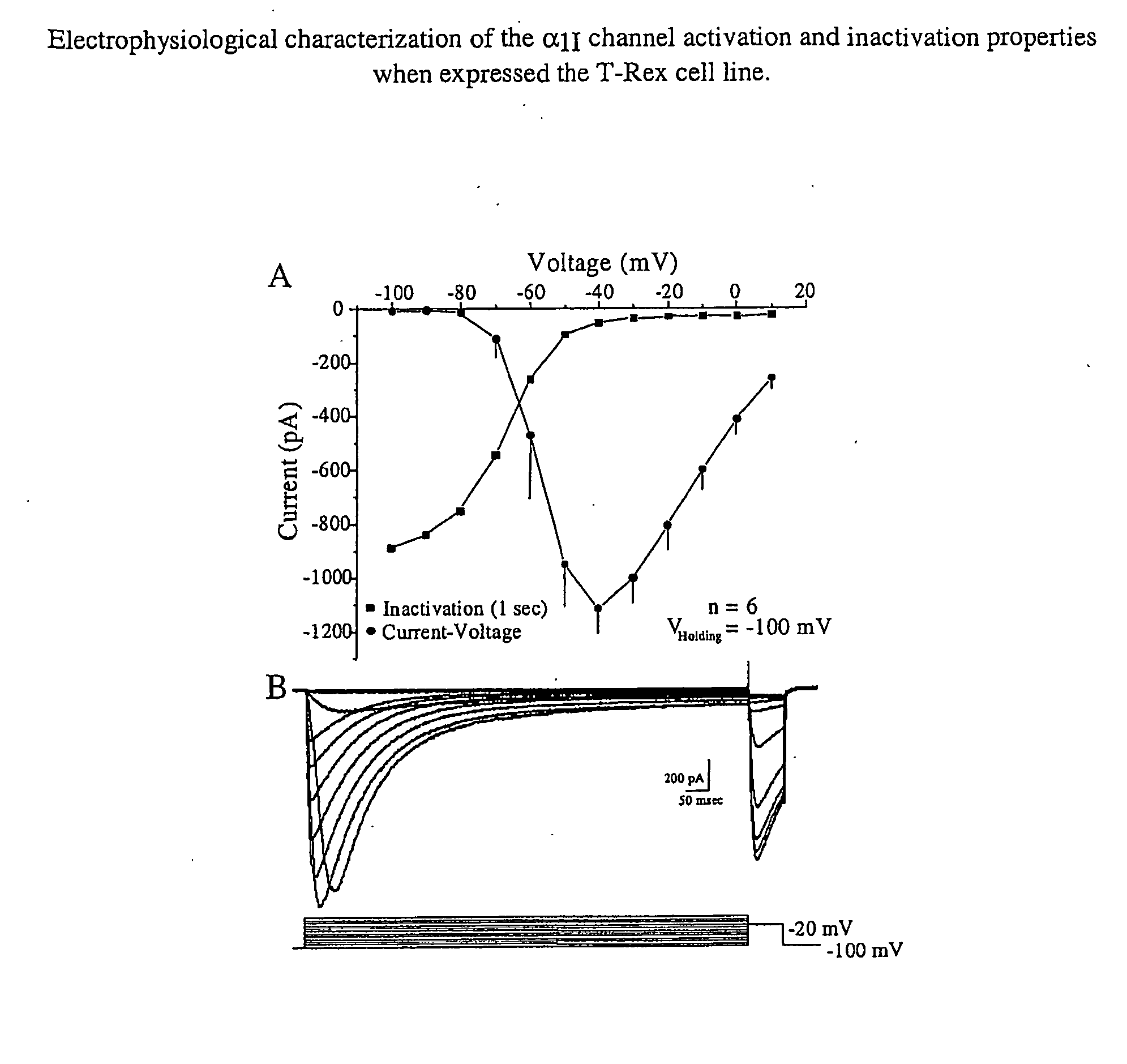
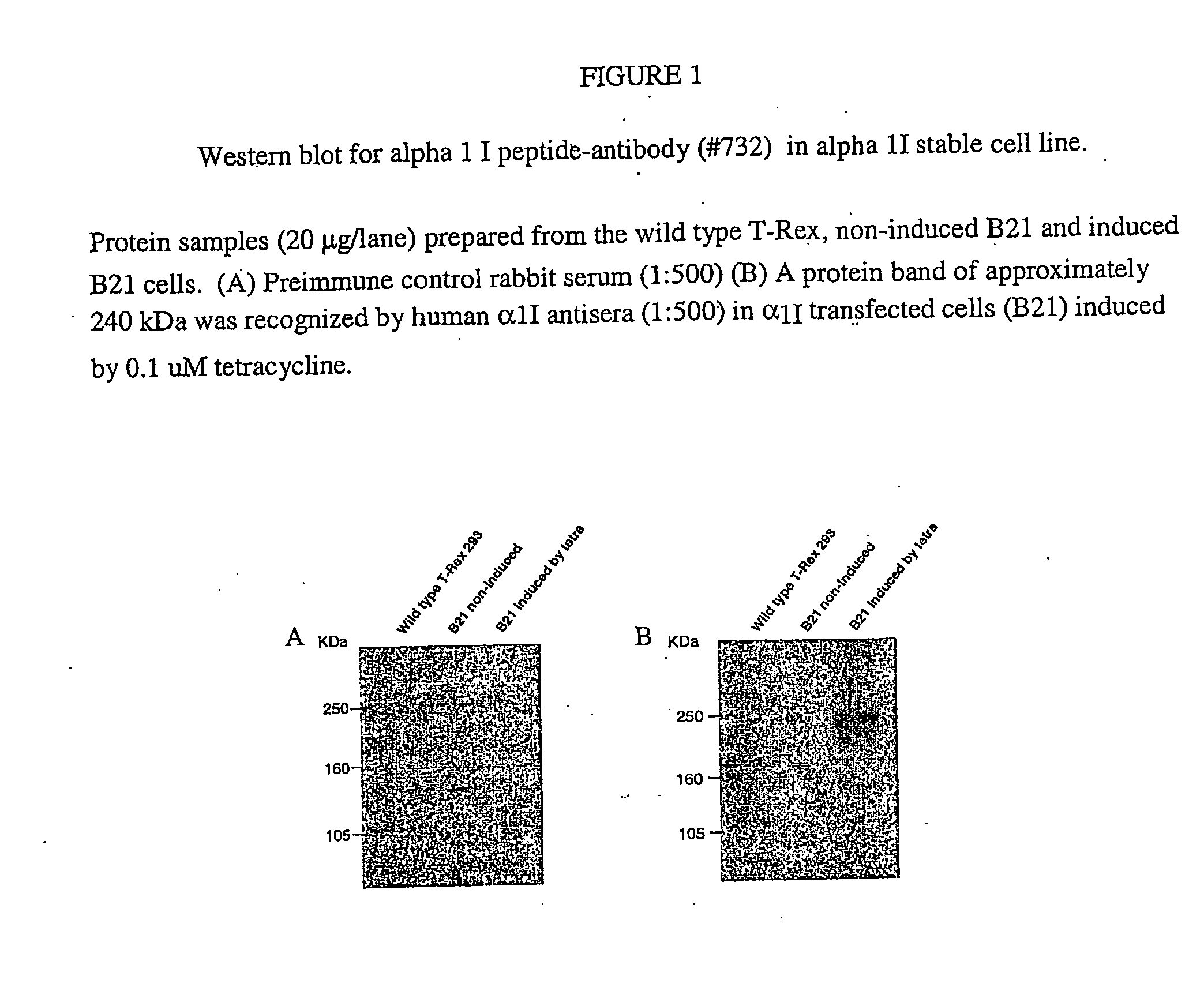
Nucleic Acid Molecules Encoding Novel Human Low-Voltage Activated Calcium Channel Proteins, Designed-Alpha 1I-1 and Alpha 1I-2, Encoded Proteins and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080248040A1Nervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
Disclosed are mammalian nucleic acid sequences encoding α1I subunit isoforms of a voltage-gated calcium channel. Specifically disclosed are novel variants of the α1I subunit designated herein as α1I-1 and α1I-2. In other aspects, the disclosure relates to expression vectors which encode the novel subunits of the invention, as well as cells containing such vectors. Antibodies specific for each of the variant subunits are also provided. The nucleic acid sequences of the invention find application, for example, in screening for compounds which modulate the activity of voltage-gated calcium channels and also in diagnostic methods for diagnosing various T-type channel mediated disorders, e.g., epilepsy, cancer, pain, sleep disorders and the autoimmune disease Lambert-Eaton Syndrome. Diagnosing defects in α1I subunit genes of a patient with a neuronal disease such as epilepsy are also included. An additional application of the nucleic acid sequences of the invention is in therapeutic methods of treatment for α1I subunit mediated disorders.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Isoform-specific, context-permissive tgfb1 inhibitors and use thereof
InactiveUS20180207267A1Slow tumor growthRaise the possibilityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsMedicineDisease cause
Disclosed herein are therapeutic use of isoform-specific, context-permissive inhibitors of TGFβ1 in the treatment of disease that involve TGFβ1 dysregulation.
Owner:SCHOLAR ROCK INC
Combined assay for the differential diagnosis of the alzheimer's disease
PendingUS20190285651A1Material analysis by optical meansDisease diagnosisPatient stratificationAmyloid beta
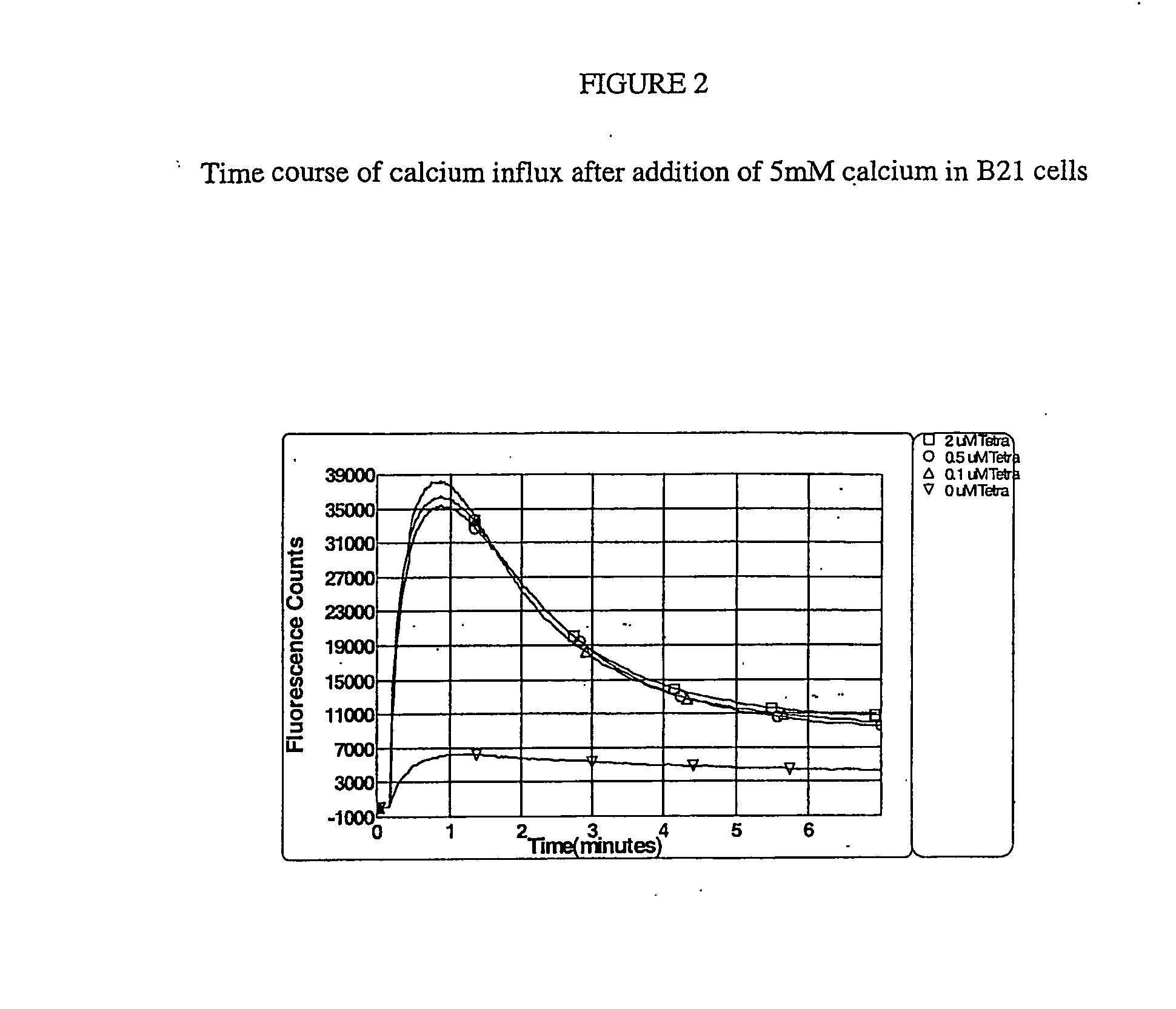
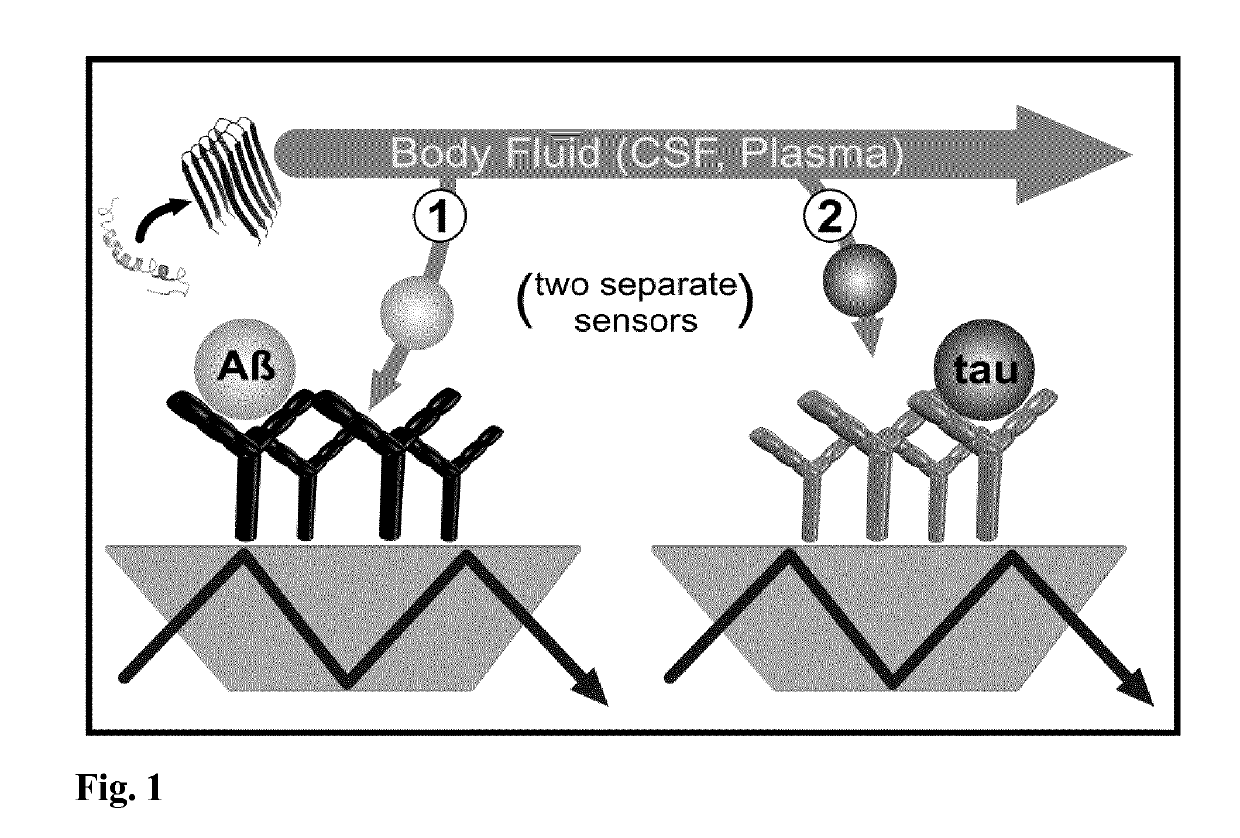
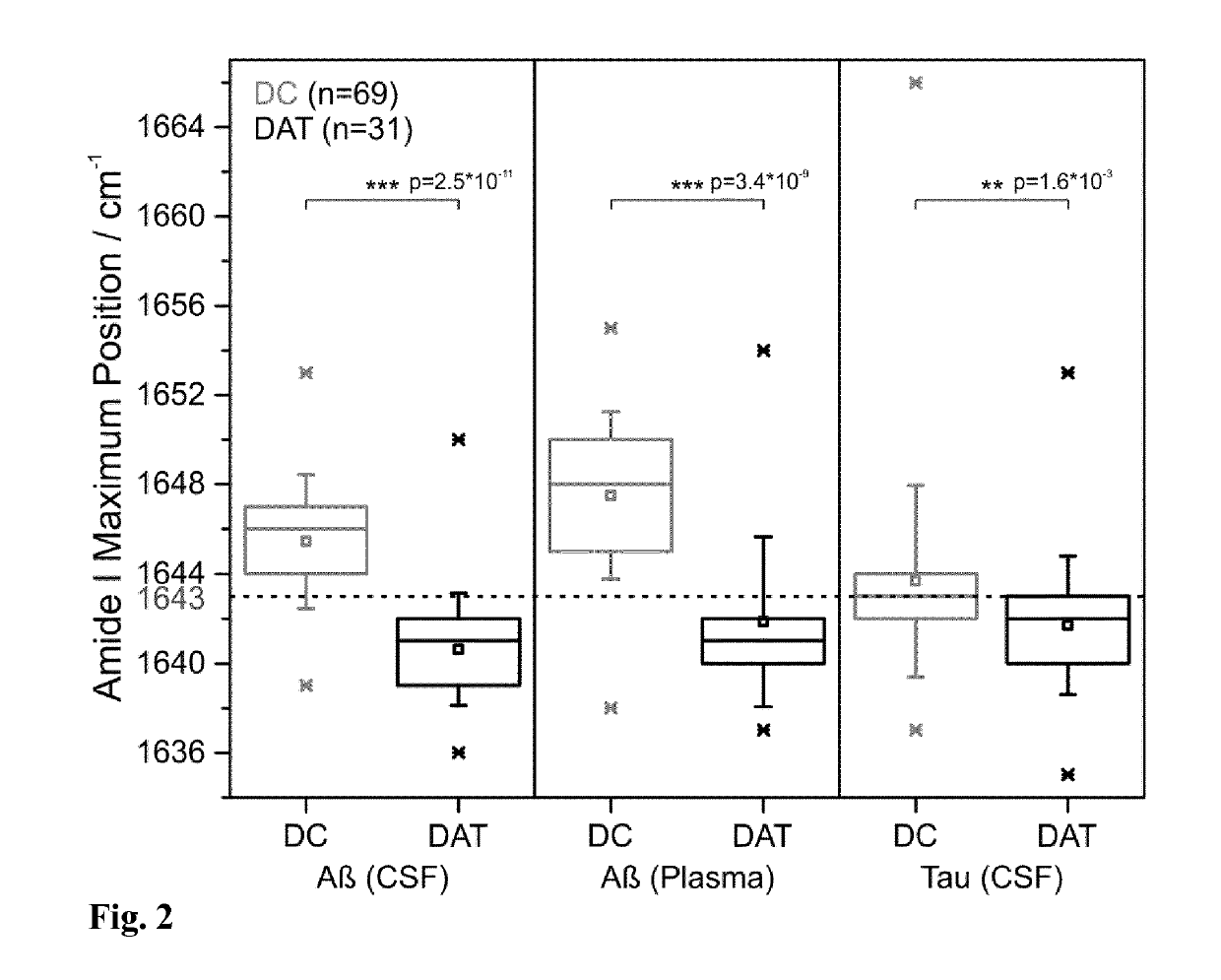
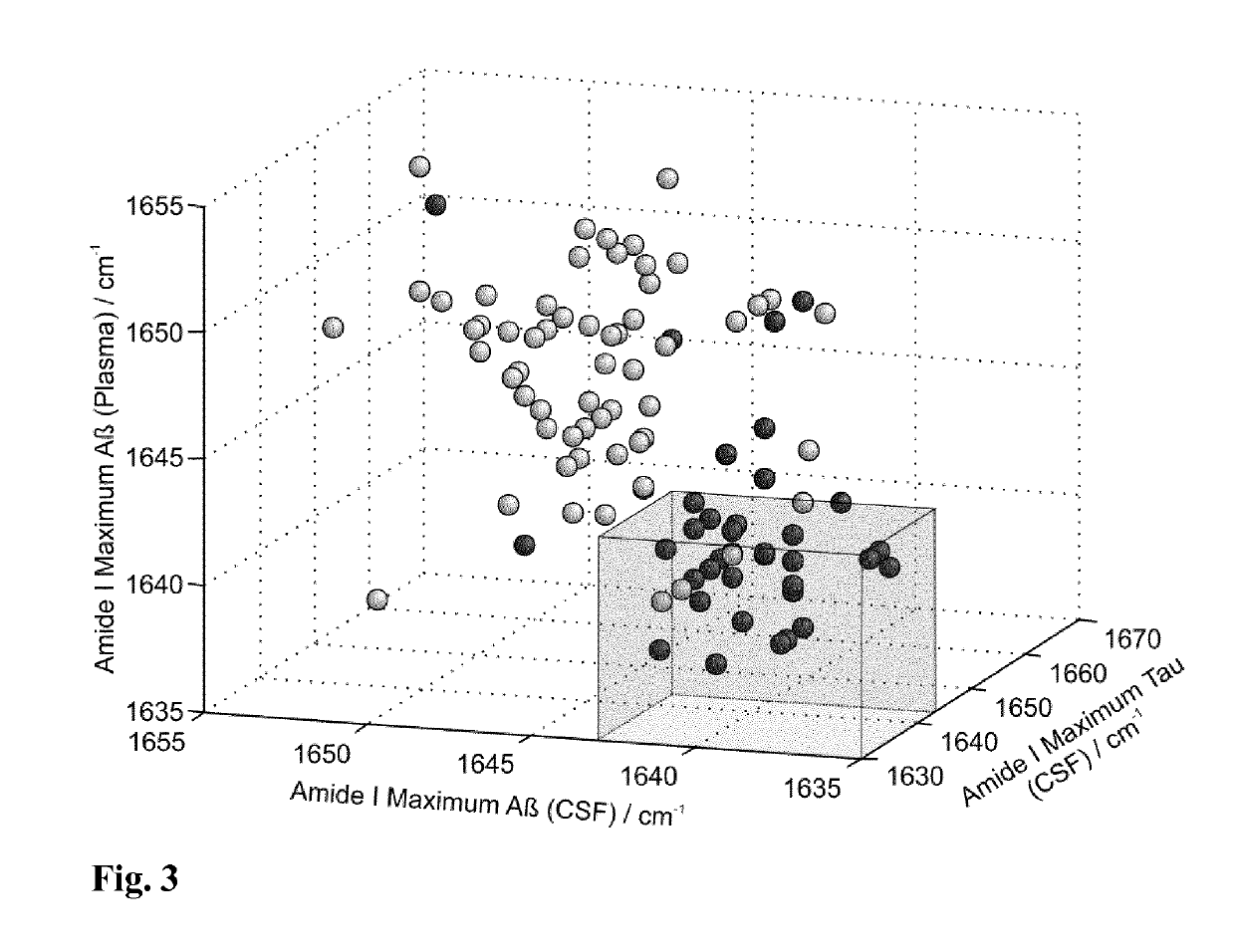
The invention provides a combined immuno-infrared assay for the differential diagnosis and sub classification of Alzheimer's disease into different disease stages. The method can be applied for assured disease diagnostics and patient stratification. The assay considers the label-free detection of the change within the Amyloid-beta peptide and Tauprotein secondary structure distribution in bodily fluids. This secondary structure change from native to β-sheet enriched isoforms appears years before clinical disease manifestation. Now, the combined method utilizes this shift for diagnostics based on liquid biopsies.
Owner:BETASENSE GMBH
Human Sef isoforms and methods of using same for cancer gene therapy
InactiveUS20060079444A1High expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesCancer geneSolid tumor
A method and pharmaceutical compositions useful for inhibiting the growth of solid tumors are provided. Specifically, the method is effected by administering to a subject in need thereof an agent capable of upregulating the expression level and / or activity of at least a functional portion of Sef, wherein the functional portion being capable of inhibiting RTK-mediated cell proliferation.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method for the detection of apolipoprotein e4
The present invention provides a method for the detection of Apolipoprotein E isotype 4 (ApoE4) or fragments thereof in a blood sample of a subject, whereby said method comprises the steps of contacting said sample with a solid phase, contacting said sample with at least one binder binding specifically to ApoE4 or a fragment thereof, thereby forming an ApoE4-binder-complex, and detecting the ApoE4-binder-complex.
Owner:SPHINGOTEC
Hla-g transcripts and isoforms and their uses
PendingCN110799530APeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisAntiendomysial antibodiesPharmaceutical drug
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Isoform specific soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (SFLT) binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160347843A1Low riskSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigen bindingTyrosine kinase
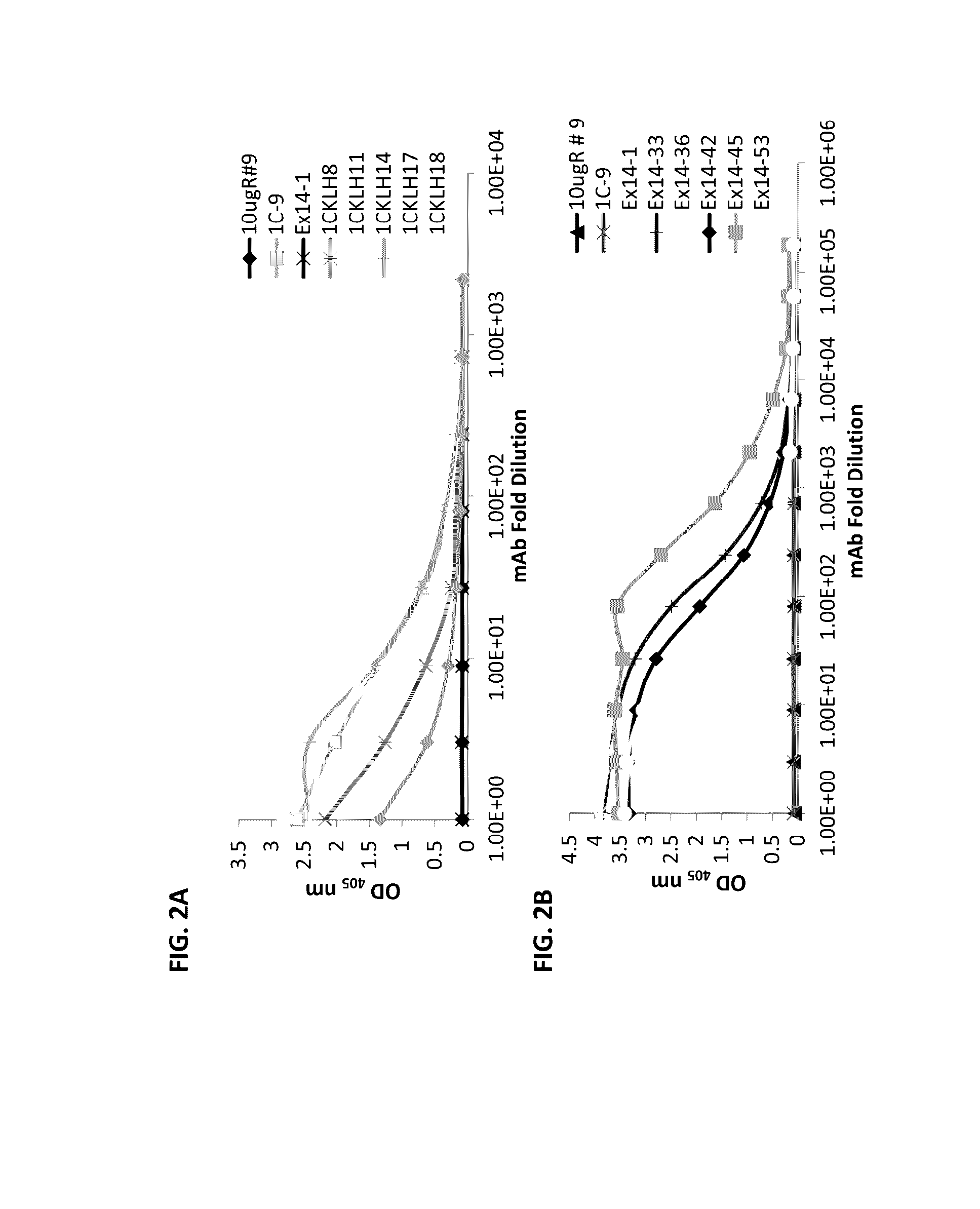
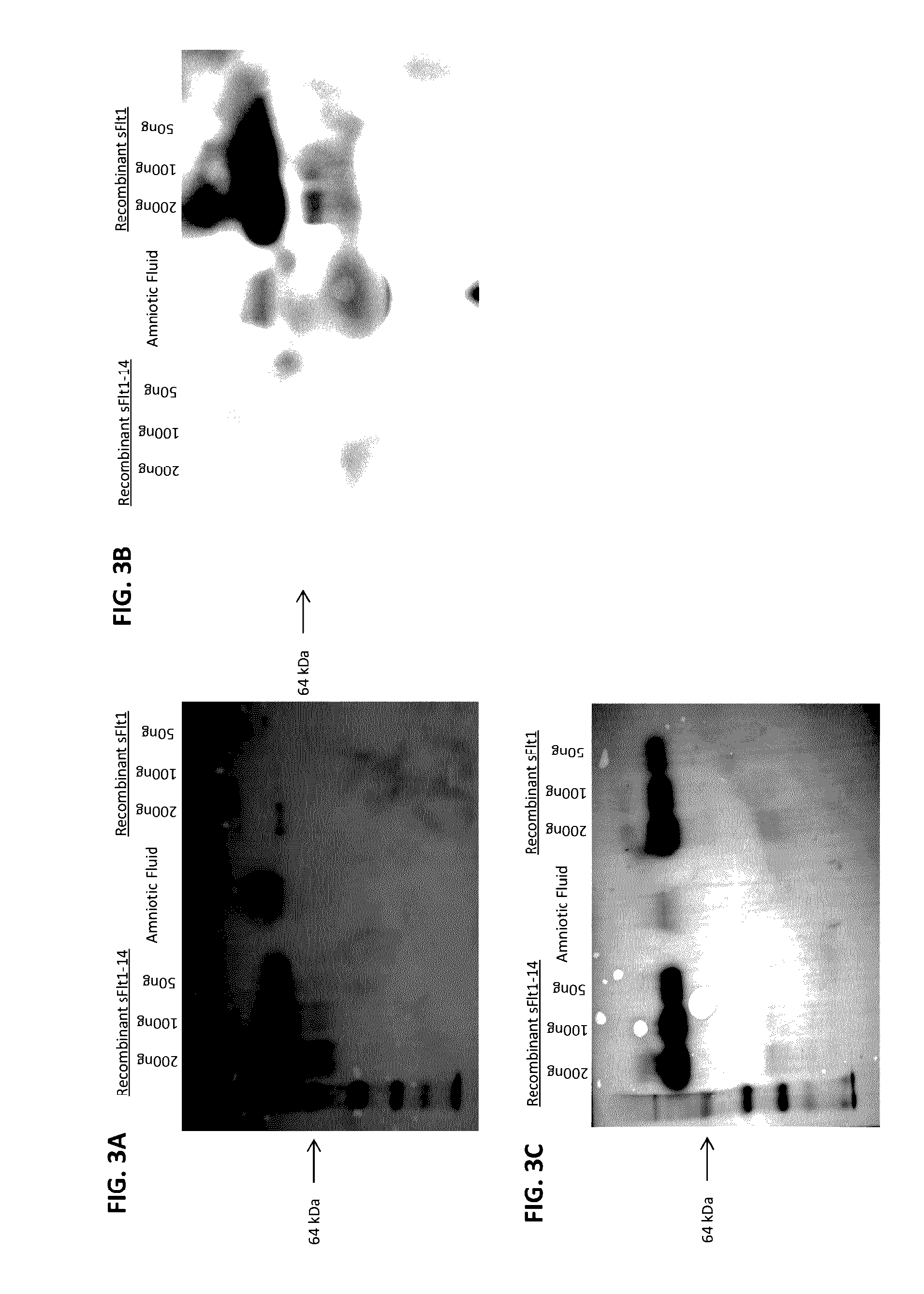
Aspects of the present disclosure relate to binding agents (e.g., antibodies and antigen binding fragments) that bind soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt1) in an isoform specific manner. In some embodiments, immunological assay methods utilizing isoform-specific antibodies or antigen binding fragments that bind sFlt1 isoforms are provided for assessing biological samples obtained from pregnant subjects, e.g., for purposes of evaluating preeclampsia status in the subject.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com