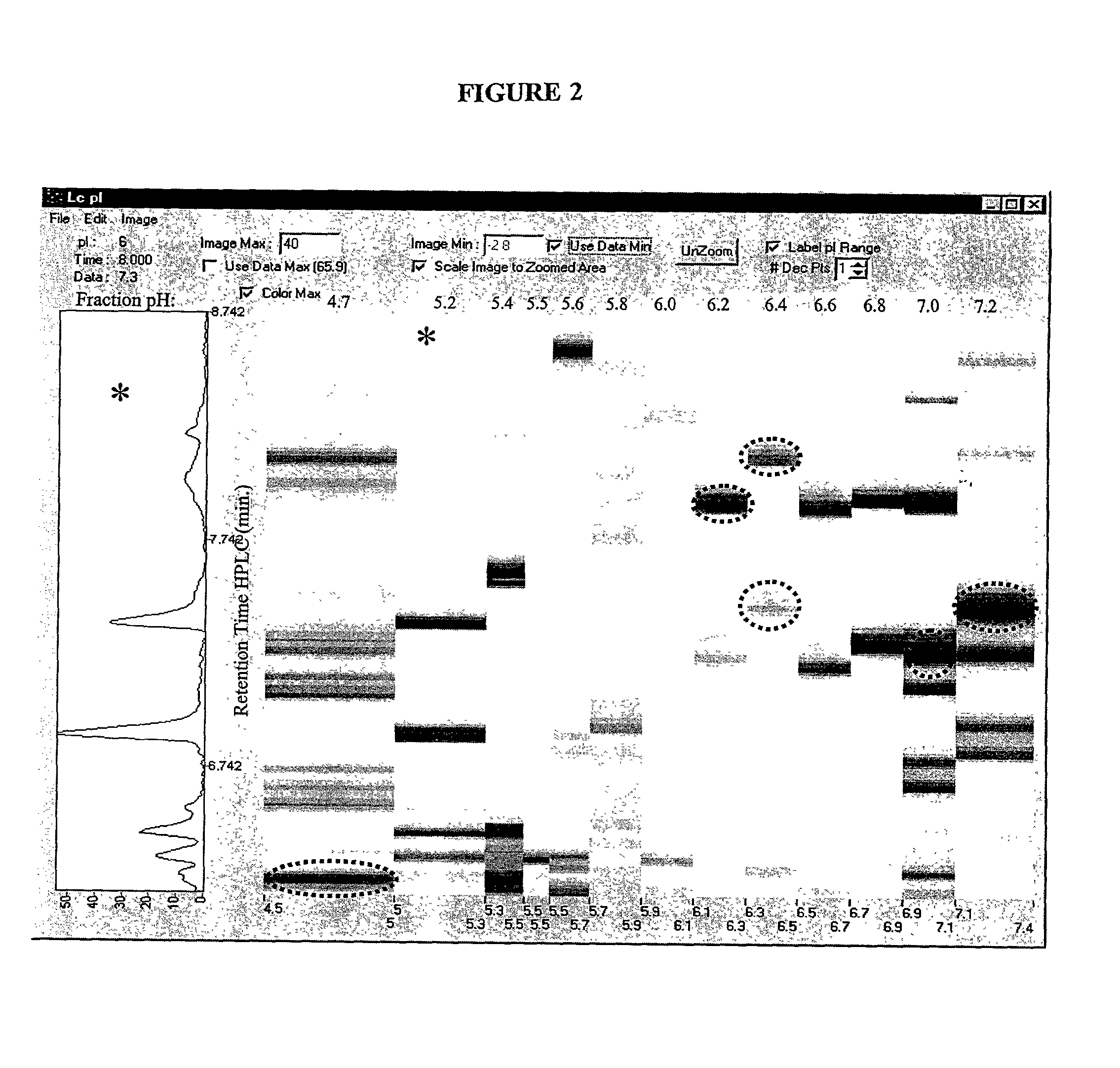
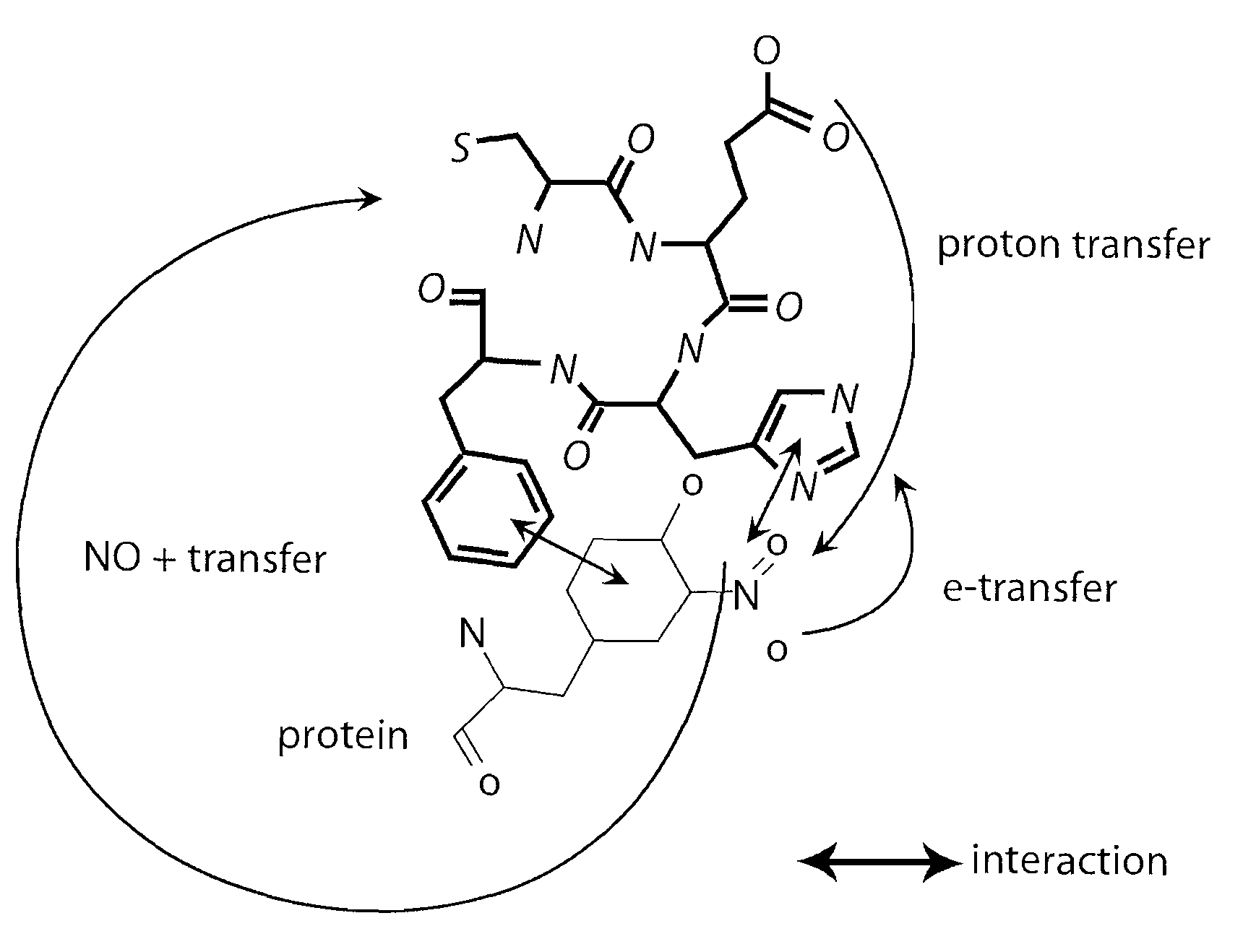
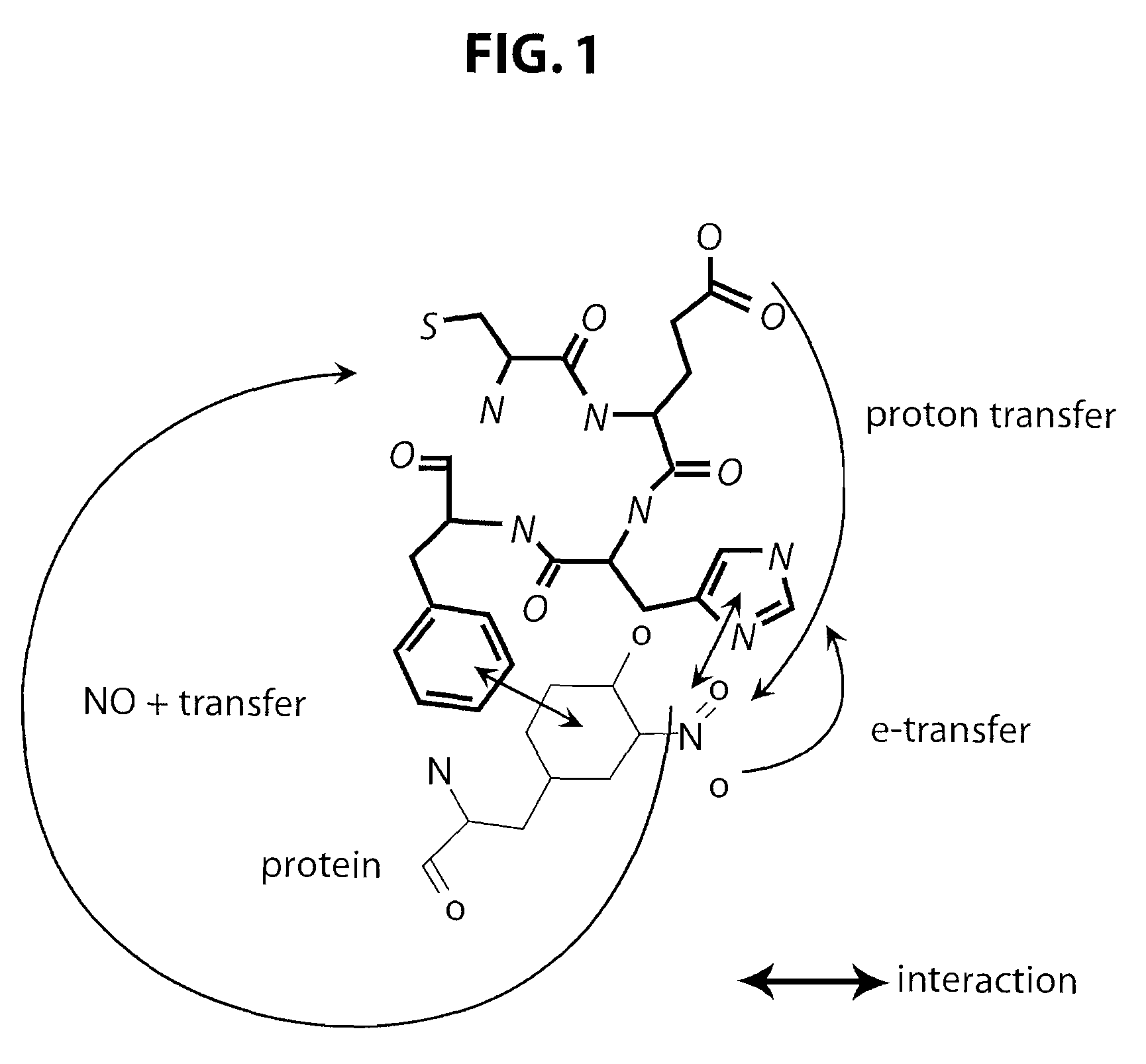
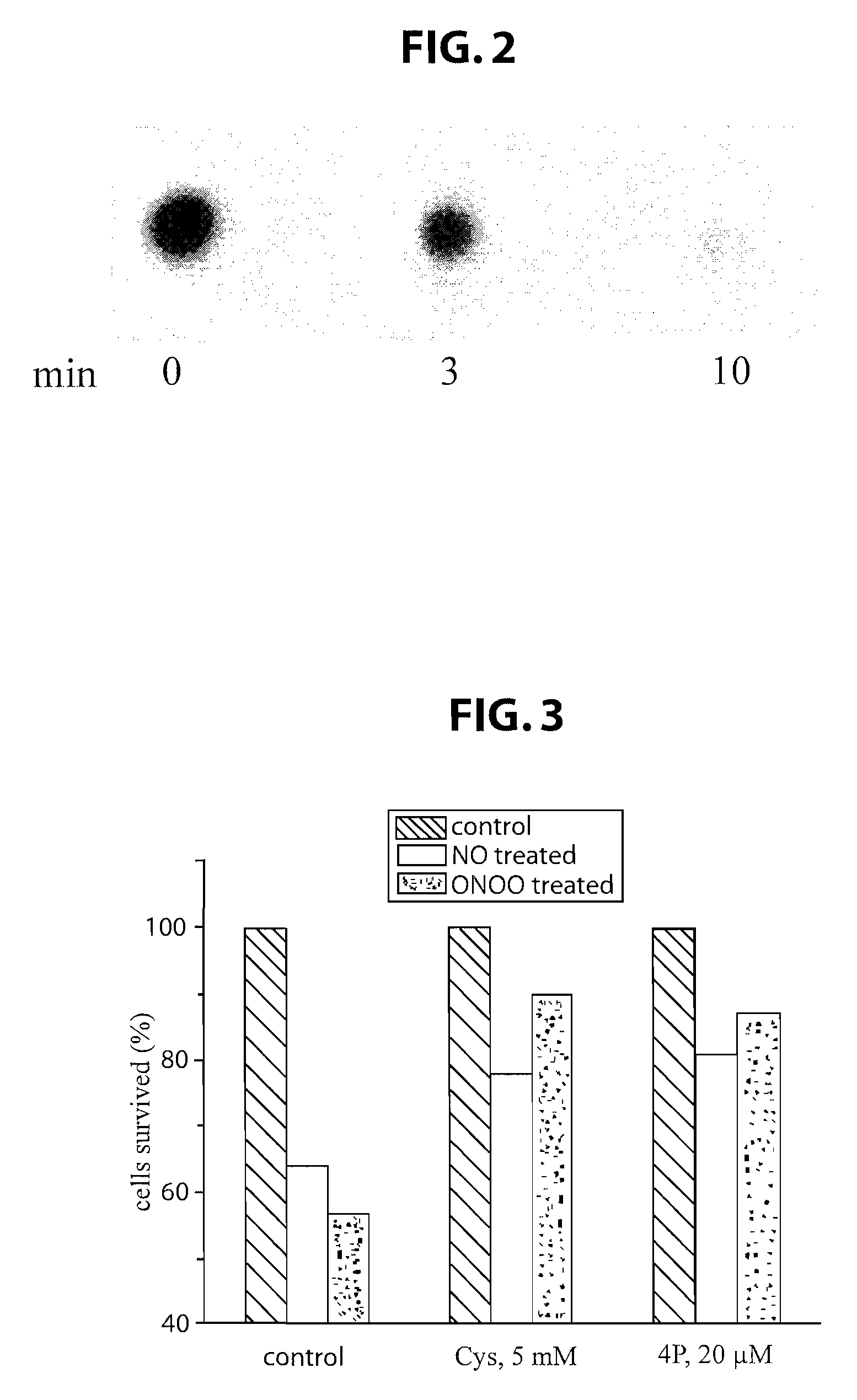
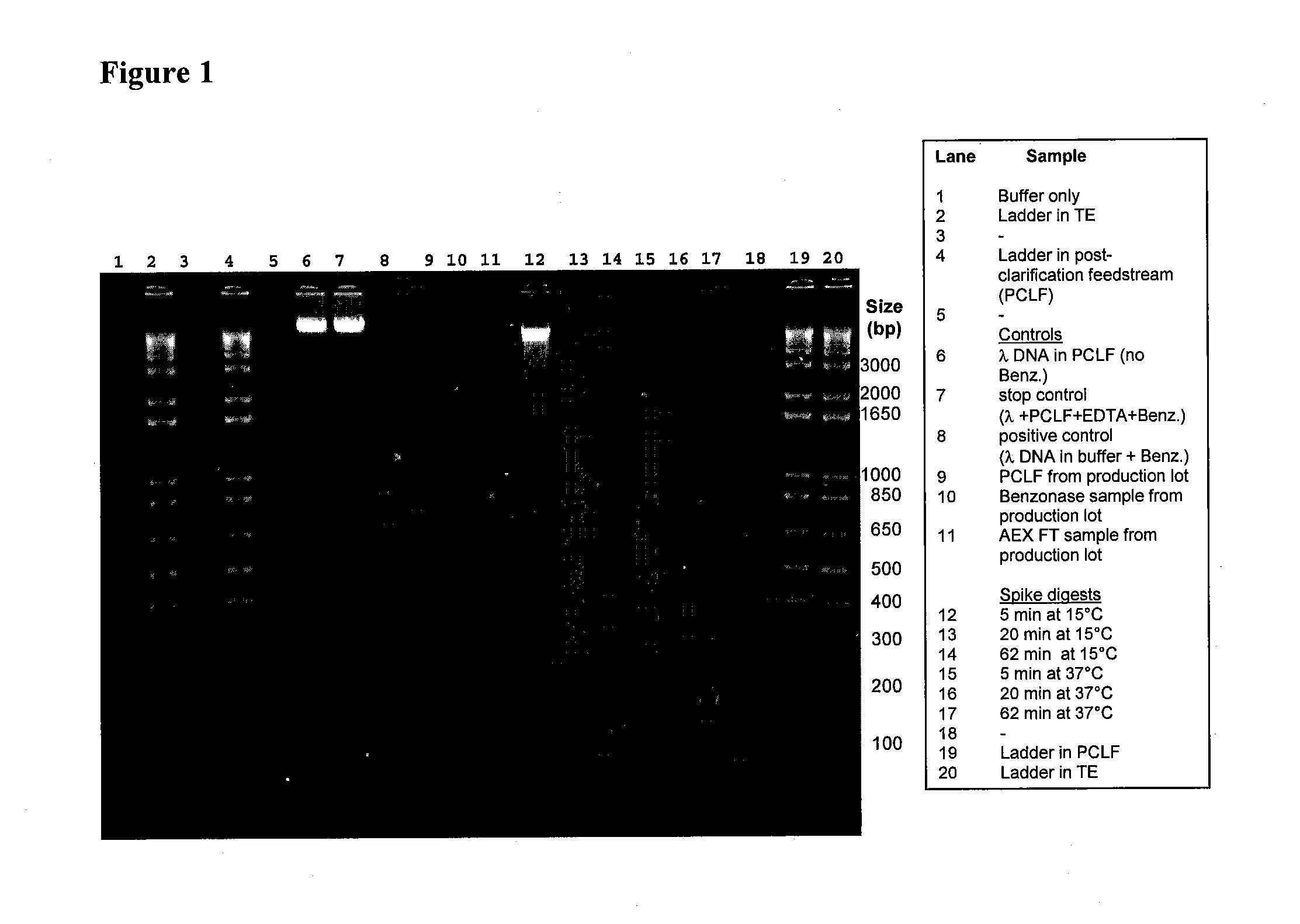
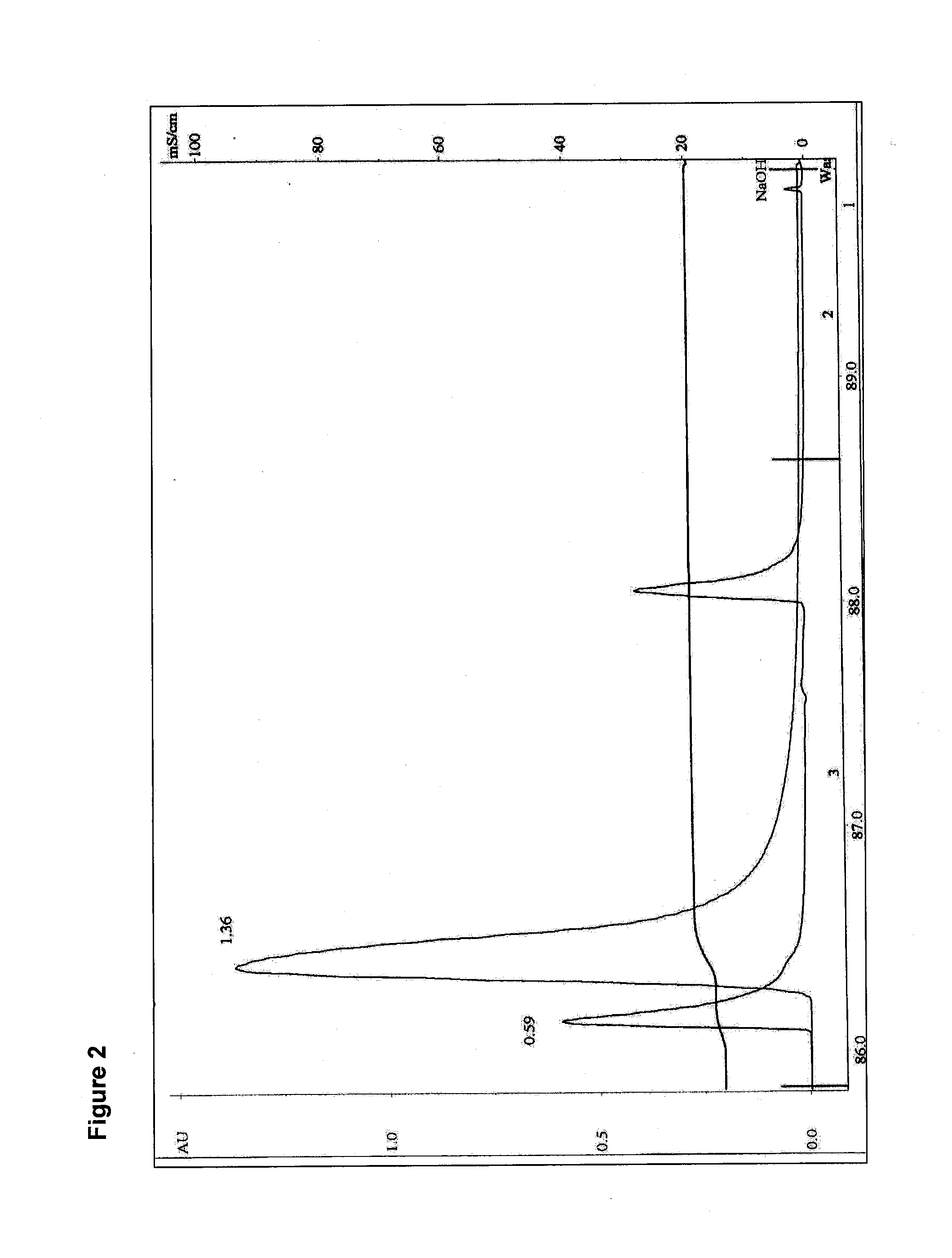
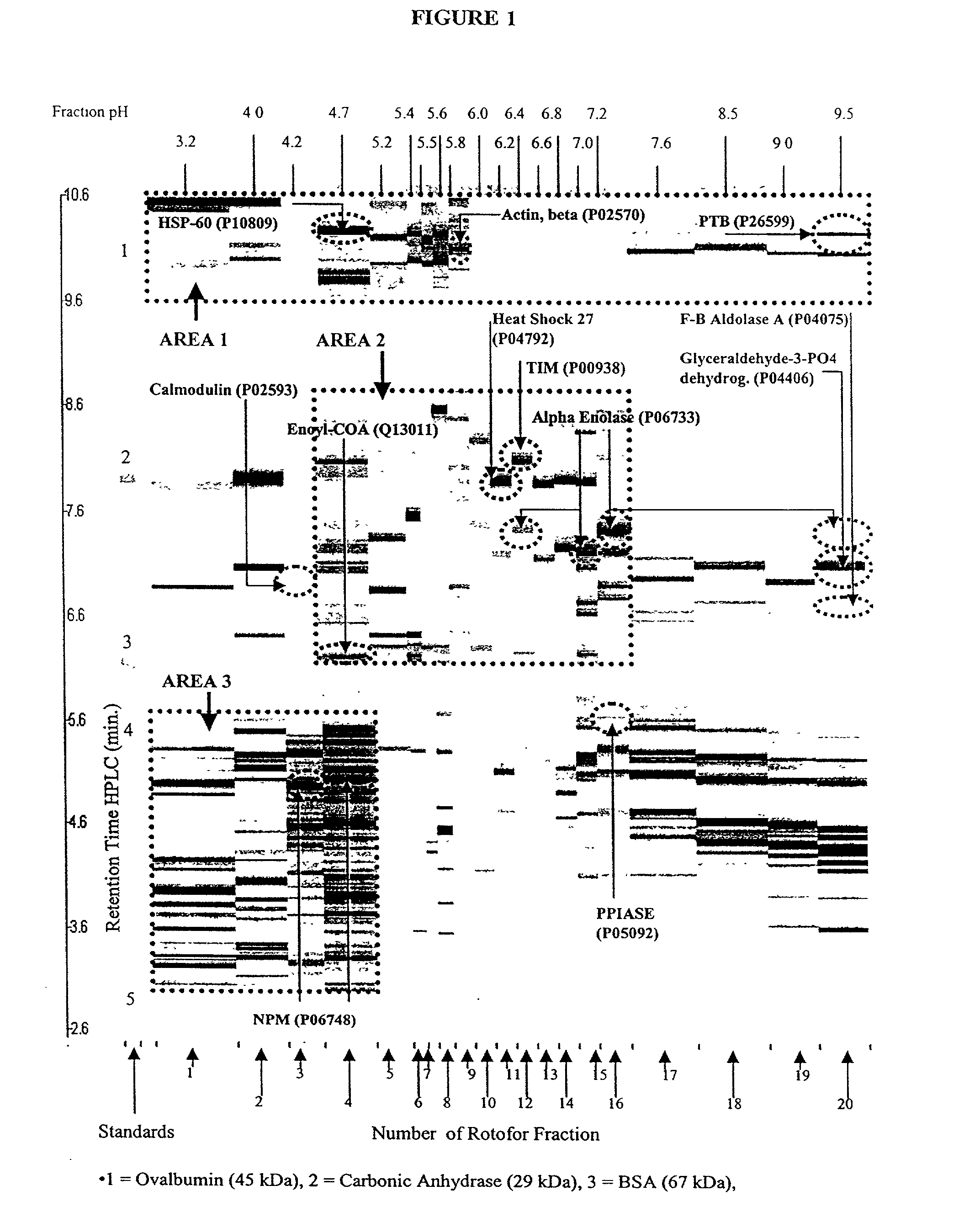
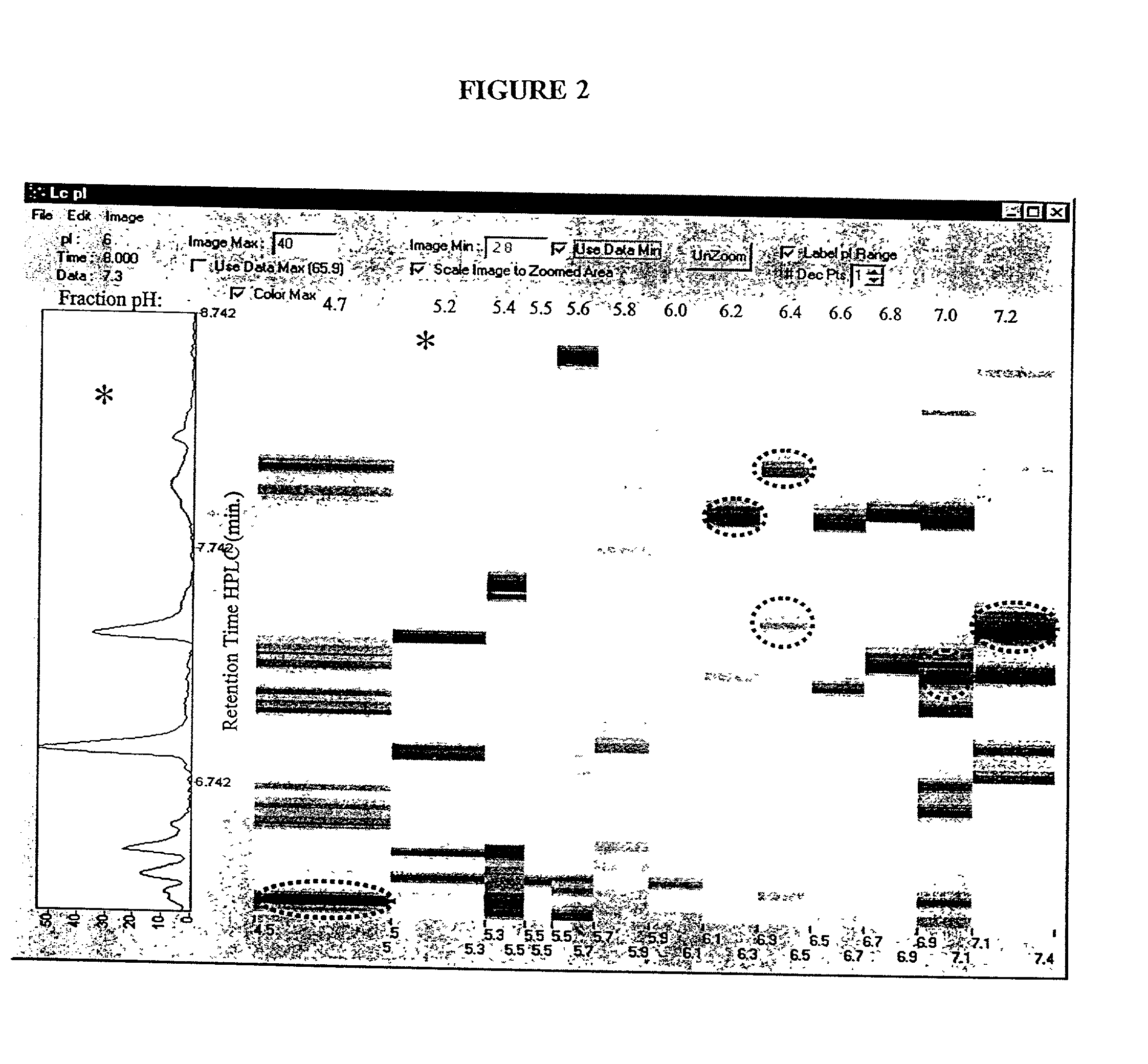
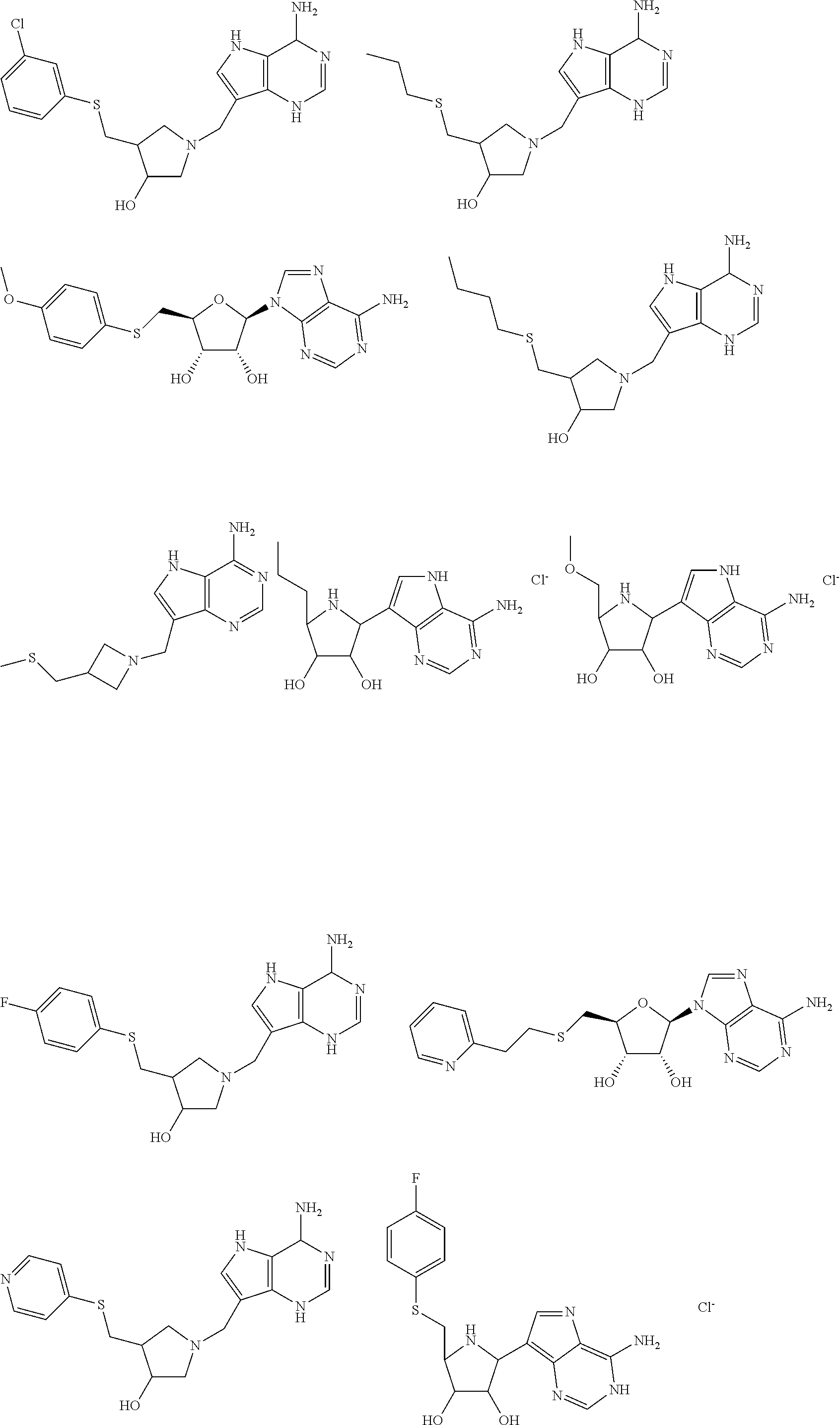
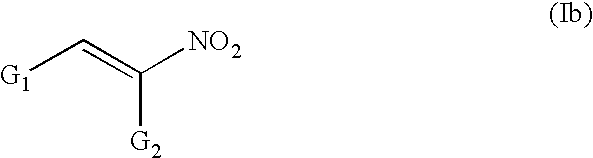Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Cellular protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular Protein Chemistry. Maintaining the natural shape of proteins is essential for life. Failure to do so is origin of lethal, incurable diseases such as Cystic Fibrosis, Alzheimer, Parkinson, ALS, or cancer. Common to those diseases are fatal distortions in protein shape.
Protein separation and display
InactiveUS20020098595A1Easy transferSuitable for automationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementProtein insertionImproved method
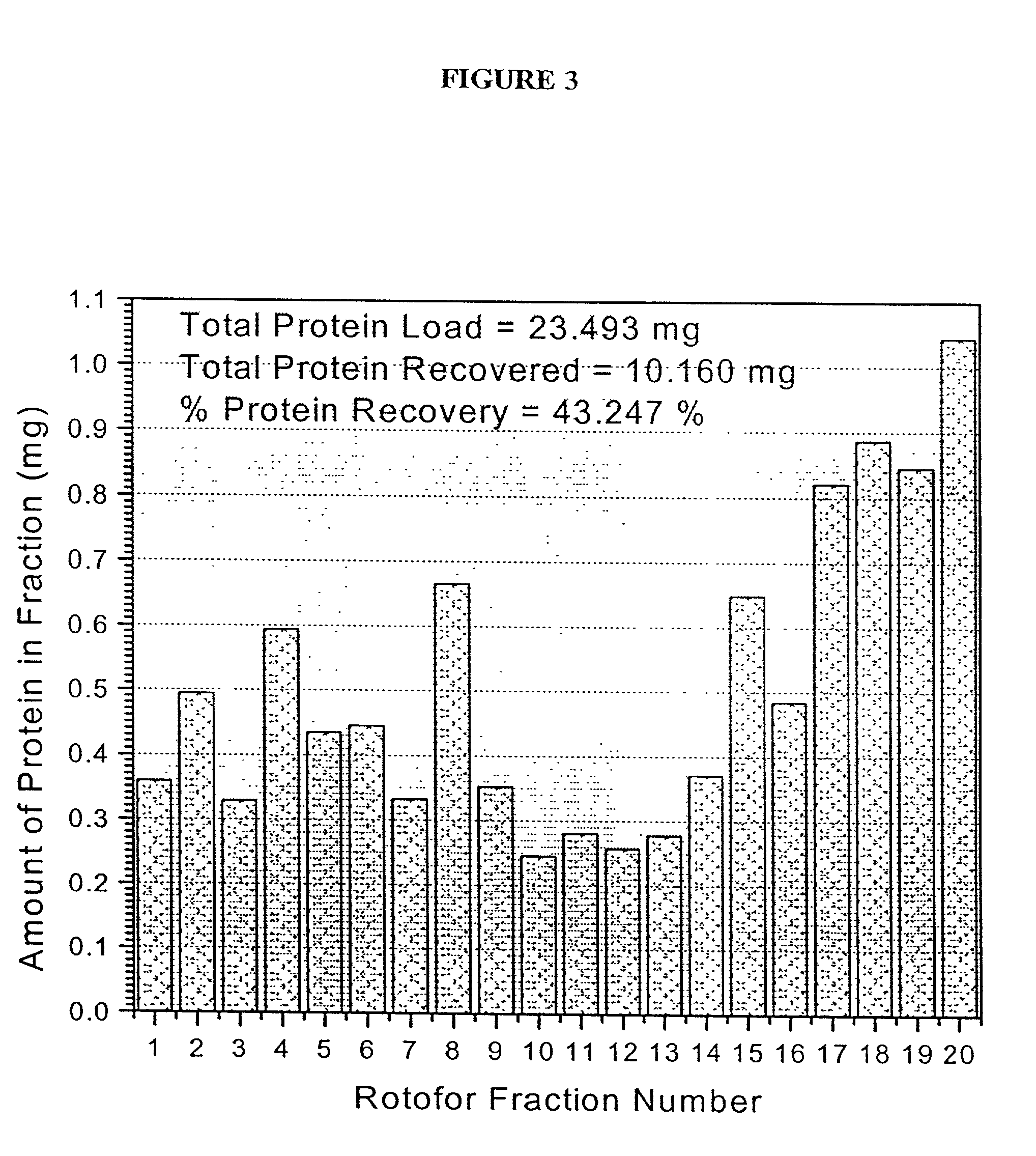
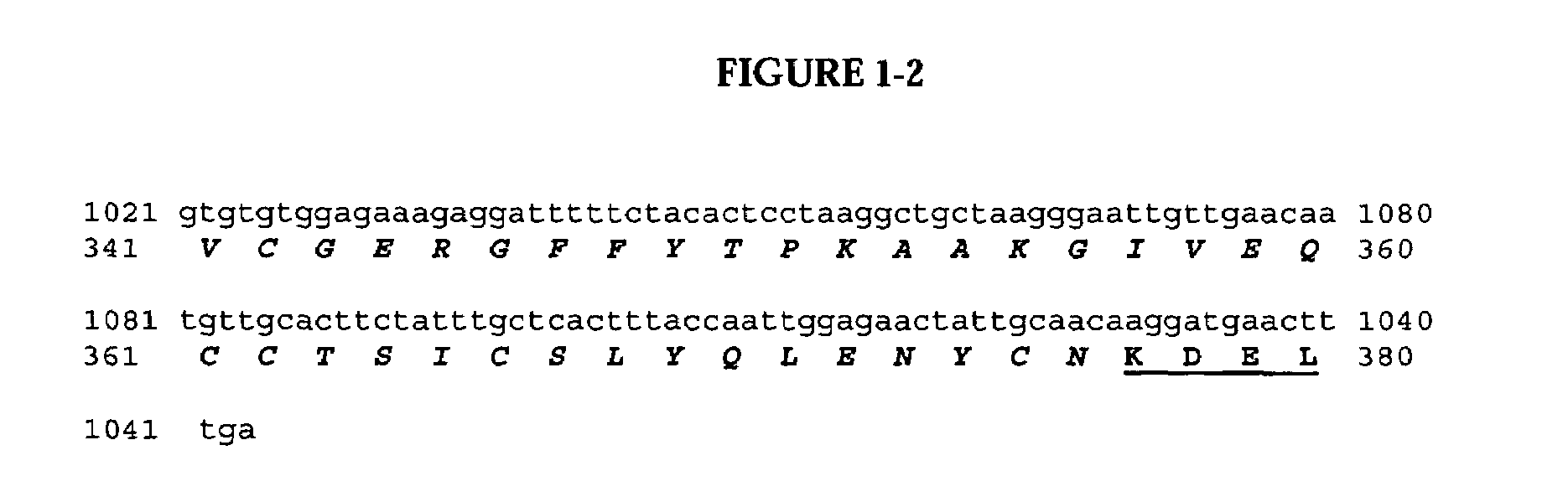
The present invention relates to multi-phase protein separation methods capable of resolving and characterizing large numbers of cellular proteins, including methods for efficiently facilitating the transfer of protein samples between separation phases. In particular, the present invention provides an automated system for the separation, identification, and characterization of protein samples. The present invention thus provides improved methods for the analysis of samples containing large numbers of proteins.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Short peptides useful for treatment of ischemia/reperfusion injury and other tissue damage conditions associated with nitric oxide and its reactive species
ActiveUS20080182797A1Avoid tissue damageLevel of protectionNervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsPregnancyAllograft rejection
This invention discloses isolated short peptides comprising the amino acid sequence Cys-Glu-Phe-His (CEFH) and analogs thereof as well as compositions comprising CEFH peptides and analogs thereof. The CEFH peptides disclosed herein are effective in mediating the denitration of 3-nitrotyrosines (3-NT) in cellular proteins thereby preventing tissue damage associated with excess nitric oxide (NO) and its reactive species. The CEFH peptides disclosed herein are useful in the treatment of ischemia / reperfusion (I / R) injury of various tissues (e.g., I / R injury of heart muscle associated with heart attack or cardiac surgery, I / R injury of brain tissue associated with stroke, I / R injury of liver tissue, skeletal muscles, etc.), septic shock, anaphylactic shock, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases), neuronal injury, atherosclerosis, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune uveitis, pulmonary fibrosis, oobliterative bronchiolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), sepsis, inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, allograft rejection, autoimmune myocarditis, myocardial inflammation, pulmonary granulomatous inflammation, influenza- or HSV-induced pneumonia, chronic cerebral vasospasm, allergic encephalomyelitis, central nervous system (CNS) inflammation, Heliobacterium pylori gastritis, necrotizing entrerocolitis, celliac disease, peritonitis, early prosthesis failure, inclusion body myositis, preeclamptic pregnancies, skin lesions with anaphylactoid purpura, nephrosclerosis, ileitis, leishmaniasis, cancer, and related disorders.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Methods for the isolation and analysis of cellular protein content
InactiveUS6969614B1Rapid and reliable to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesLymphatic SpreadPresent method
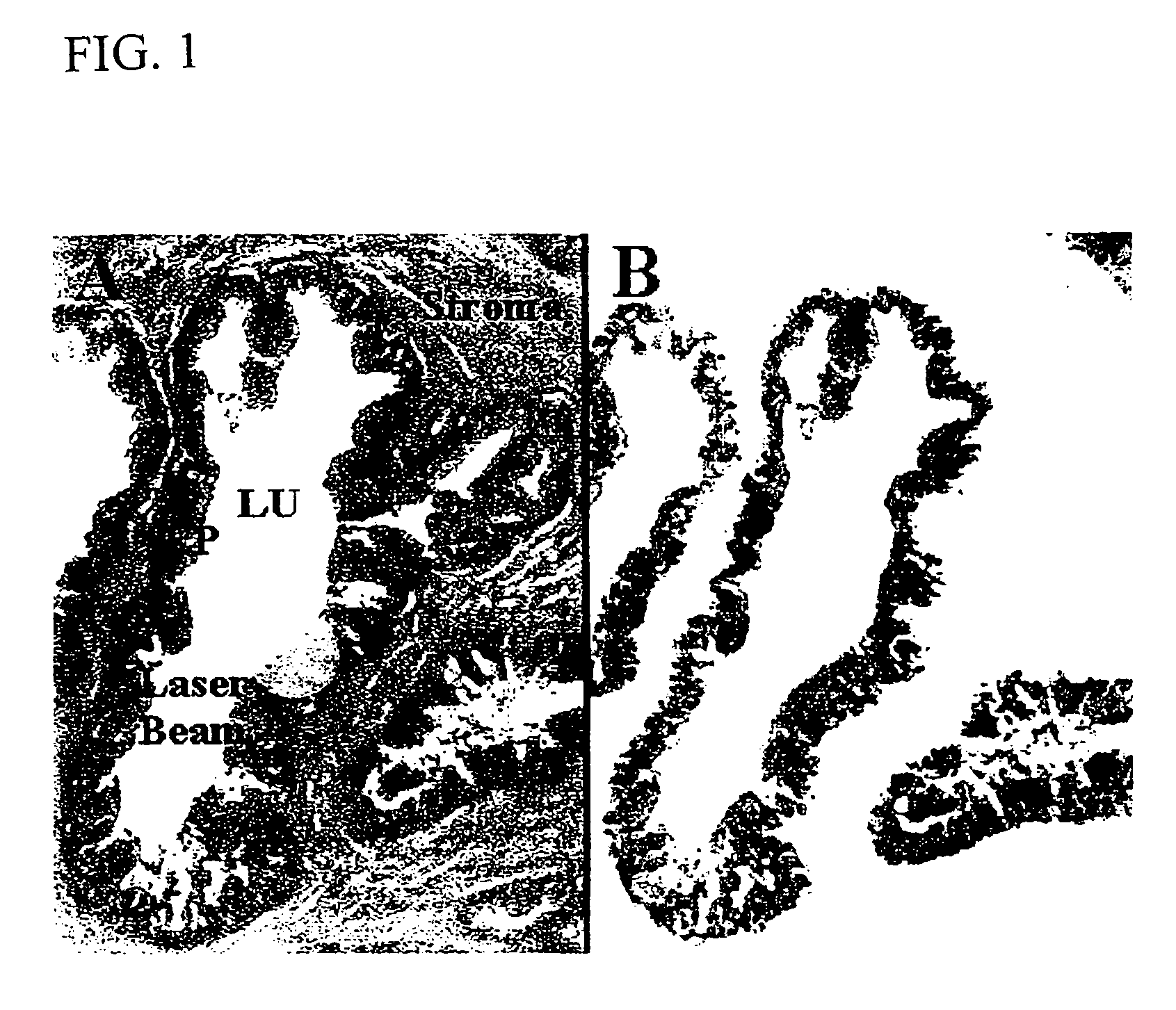
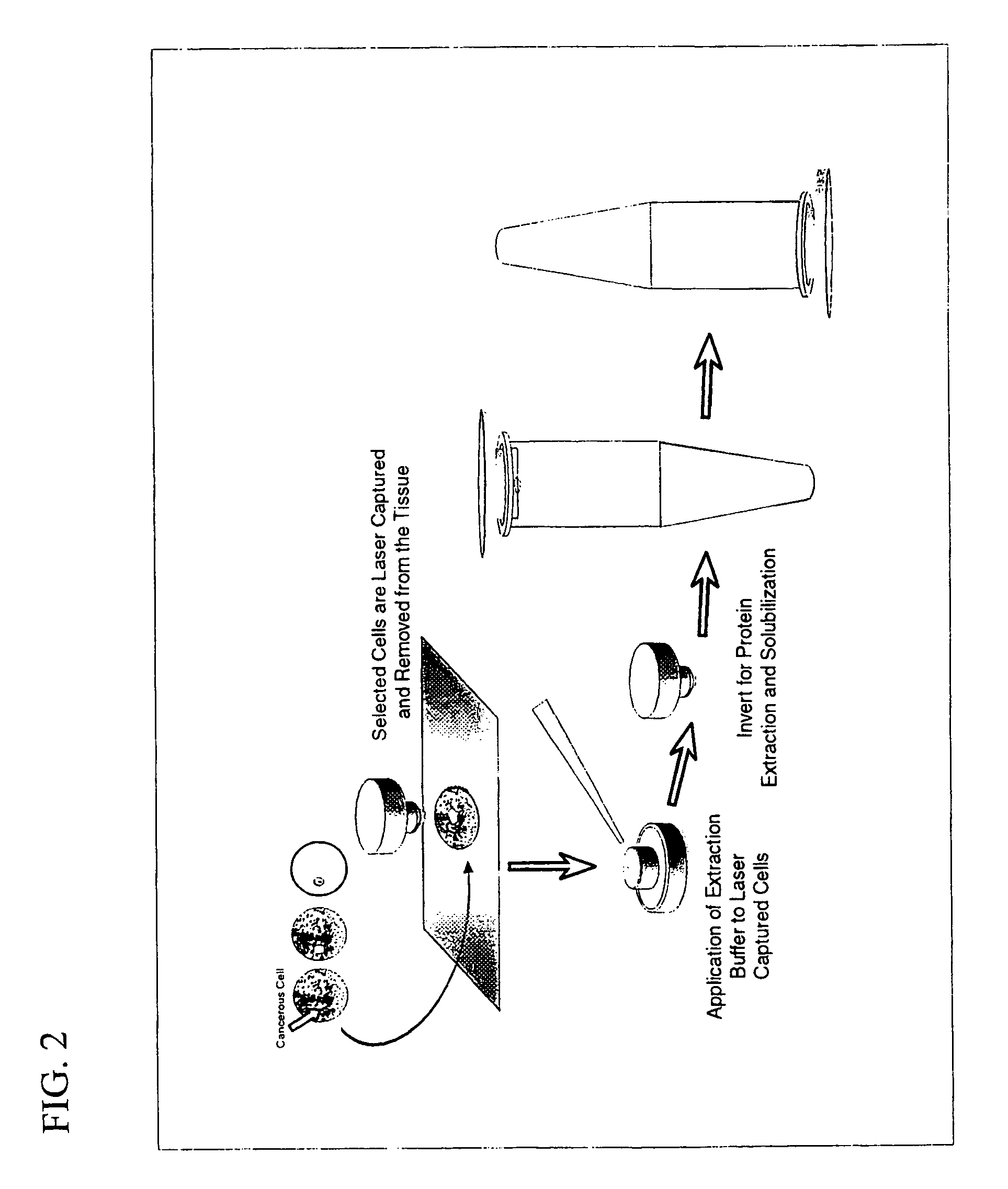
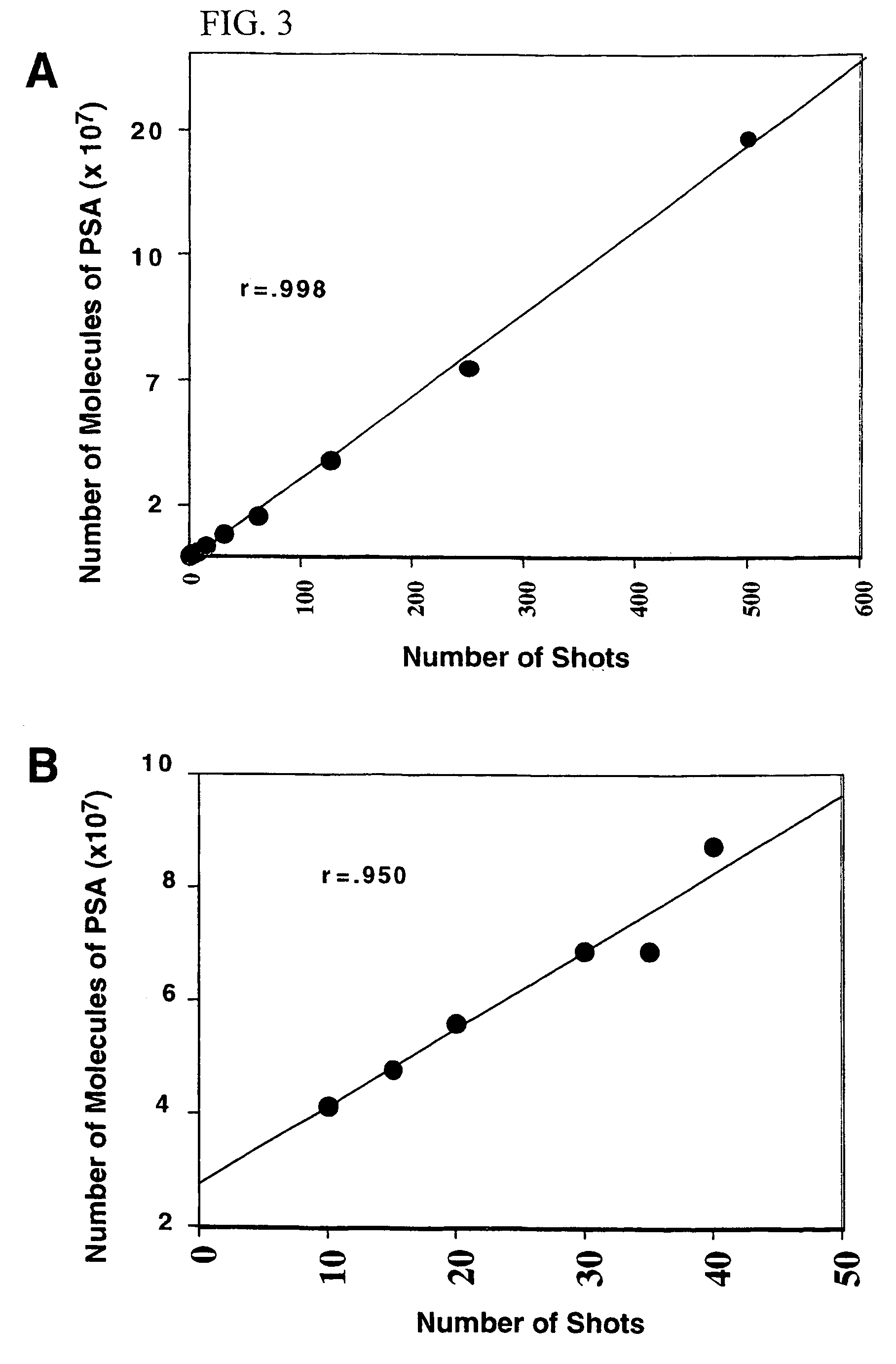
The present invention describes devices and methods for performing protein analysis on laser capture microdissected cells, which permits proteomic analysis on cells of different populations. Particular disclosed examples are analysis of normal versus malignant cells, or a comparison of differential protein expression in cells that are progressing from normal to malignant. The protein content of the microdissected cells may be analyzed using techniques such as immunoassays, 1D and 2D gel electrophoresis characterization, Western blotting, liquid chromatography quadrapole ion trap electrospray (LCQ-MS), Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization / Time of Flight (MALDI / TOF), and Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization Spectroscopy (SELDI). In addition to permitting direct comparison of qualitative and quantitative protein content of tumor cells and normal cells from the same tissue sample, the methods also allow for investigation of protein characteristics of tumor cells, such as binding ability and amino acid sequence, and differential expression of proteins in particular cell populations in response to drug treatment. The present methods also provide, through the use of protein fingerprinting, a rapid and reliable way to identify the source tissue of a tumor metastasis.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
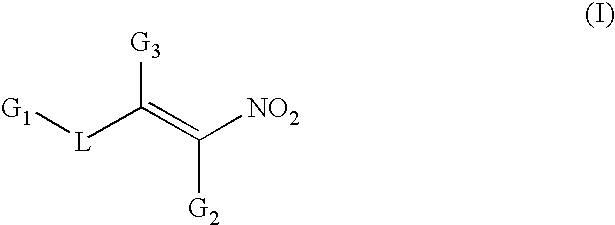
Conjugated nitro alkene anticancer agents based on isoprenoid metabolism
InactiveUS7312191B2Minimize abilityEliminate side effectsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellRHOB
Conjugated nitro alkene compounds hamper or prevent proliferation of cancer cells in cell culture and in cancer patients, which can result in a decrease in tumor size and / or disappearance of the cancer. The compounds may act by interference with cancer cell biochemistry, in which isoprenoid groups such as farnesyl and geranylgeranyl become bonded to various oncogenic proteins such as Ras, RhoA, RhoB, or some other growth-related cellular protein(s).
Owner:ARIZONA BIOMEDICAL RES COMMISSION
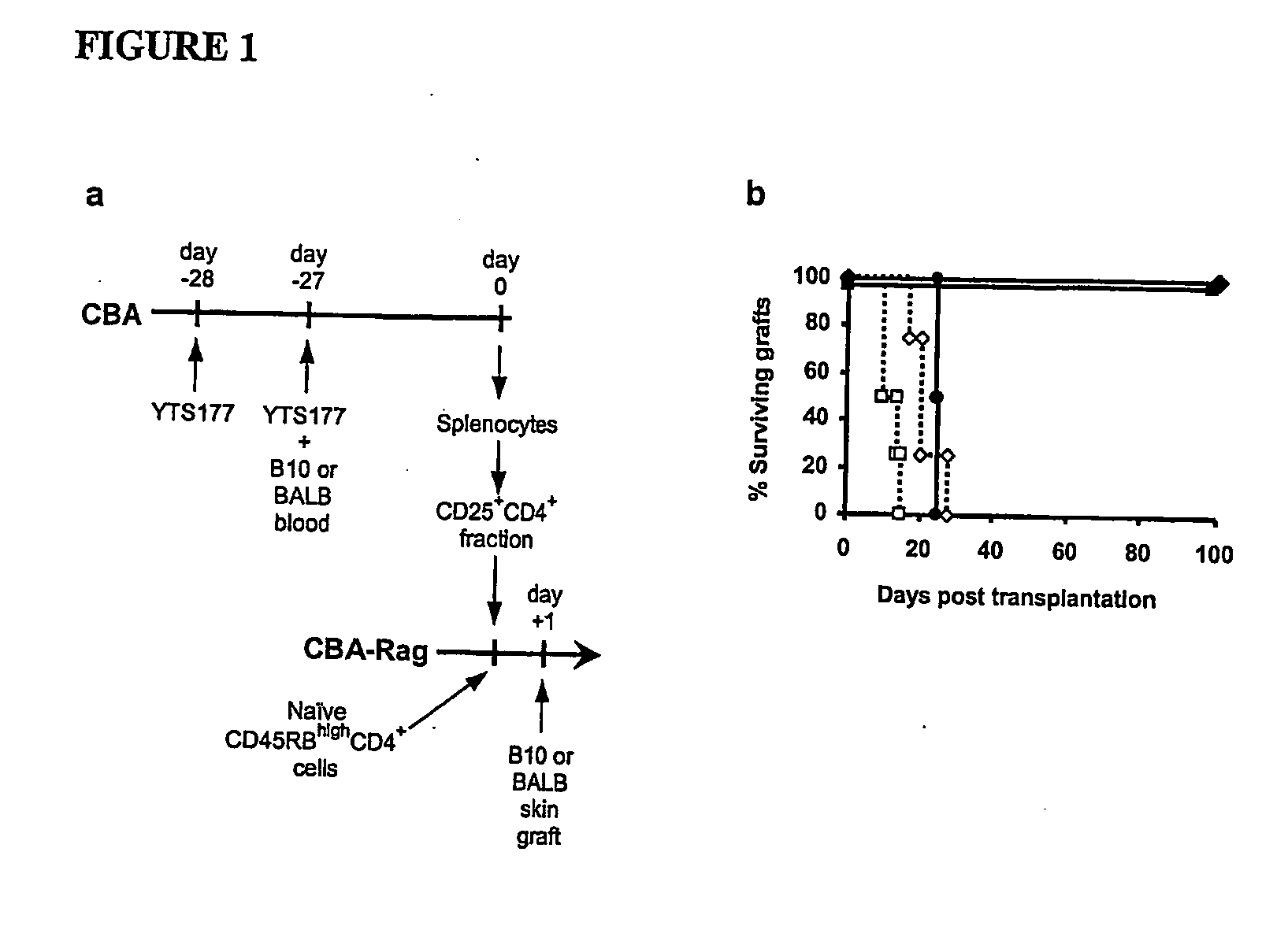
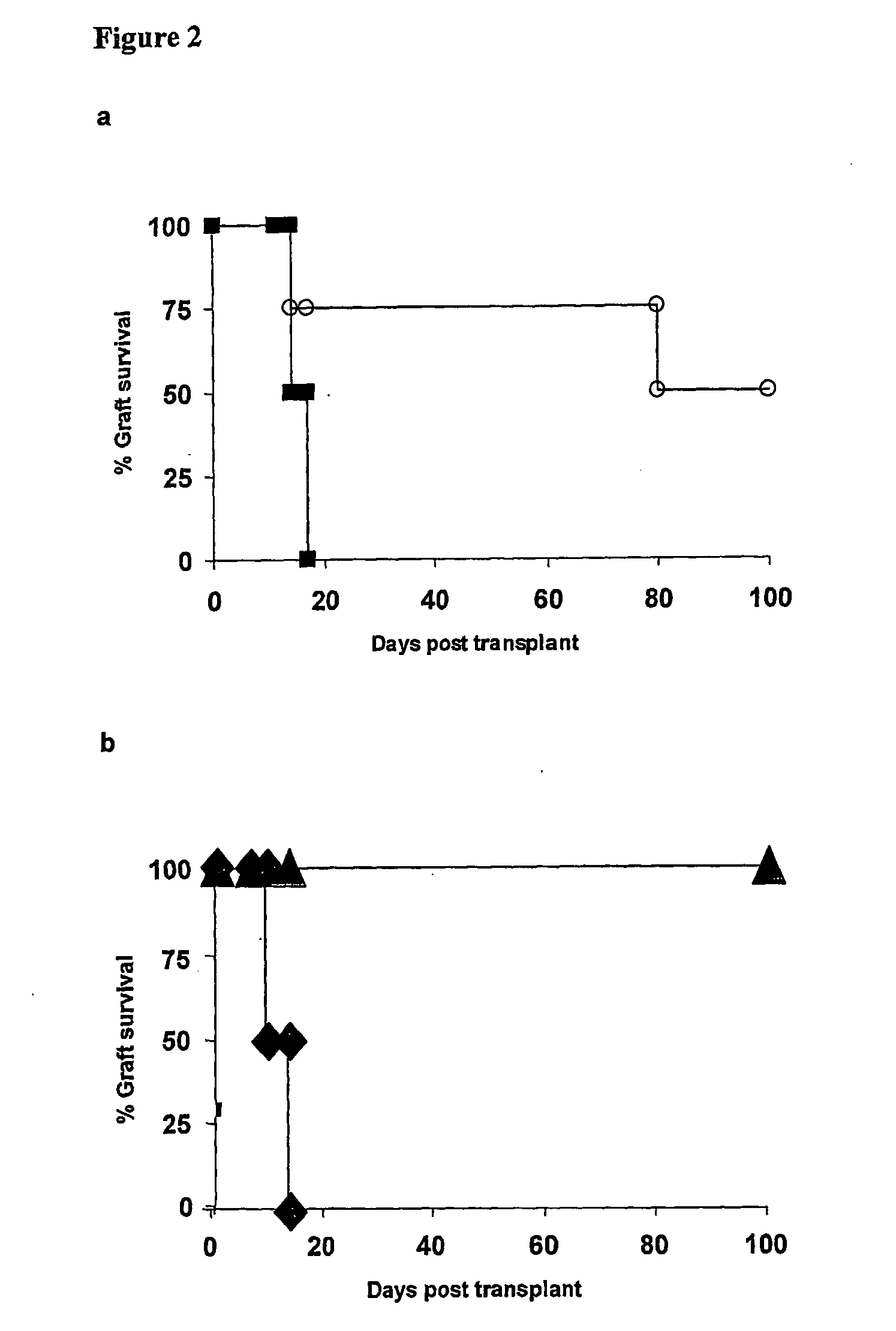
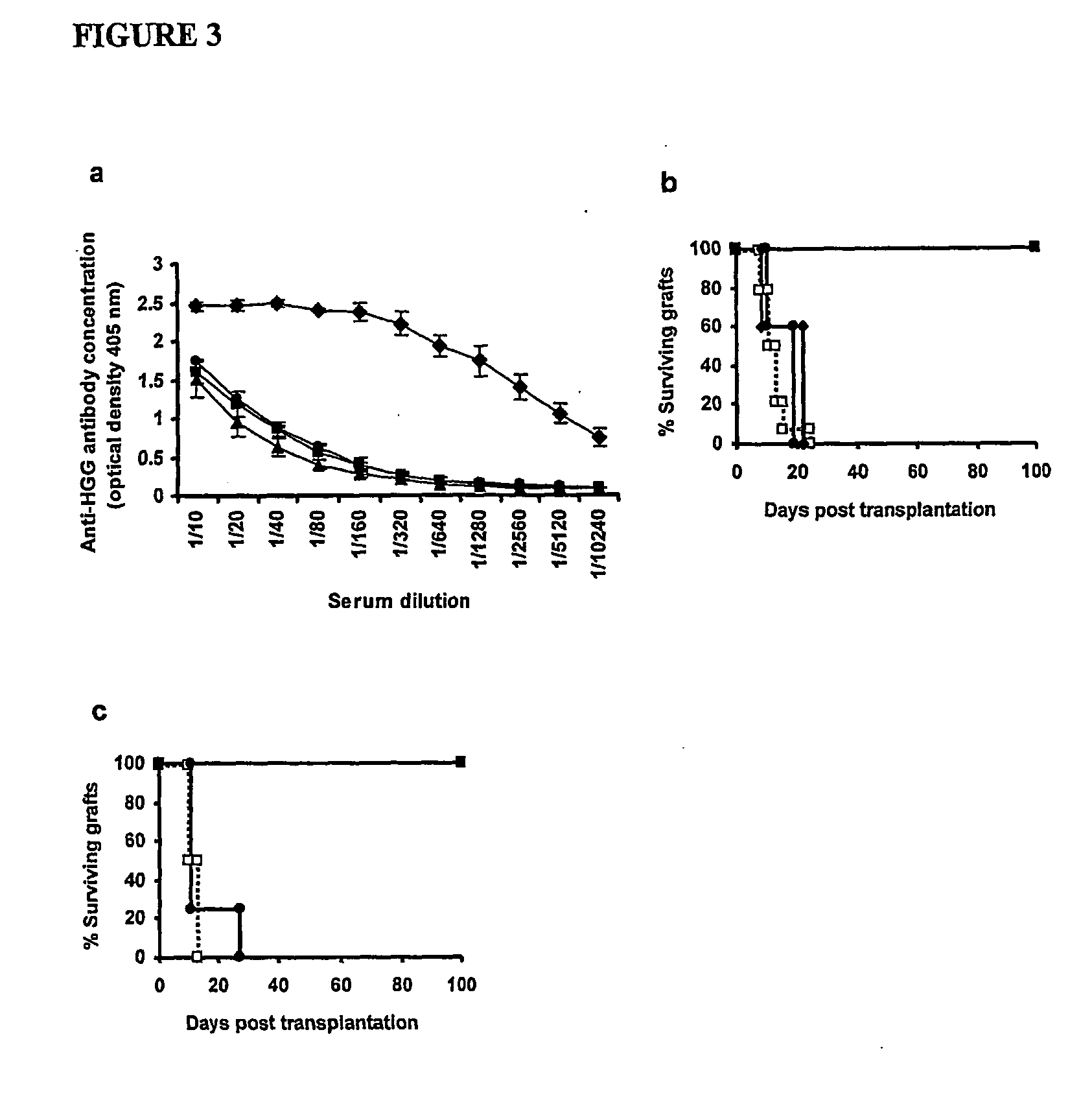
Suppression of transplant rejection
InactiveUS20070166307A1Vertebrate cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionRegulatory T cell
The present invention relates to a transplant rejection in an animal suppressed by administration of an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, preferably an anti-CD4 antibody, together with a non-cellular protein antigen to generate in the animal a population of regulatory T-lymphocytes; reactivating said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes by further administration to the animal of the non-cellular protein antigen; and transplanting said organ or tissue whilst said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes is activated. Regulatory T cells can be generated ex vivo by culturing T cells with an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, in the presence of cells that present either alloantigen or a non-cellular protein antigen. Ex vivo generated T-lymphocytes can be used as an alternative method of overcoming transplant rejection or in combination with the in vivo method. A similar approach can be adopted for the treatment of autoimmune conditions.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Methods for purification of recombinant aav vectors
Provided herein are methods for the purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors that can be used for gene transfer and specifically for gene therapy or vaccination. Recombinant AAV vectors of the invention are substantially free of in-process impurities, including production components such as cellular nucleic acids, cellular proteins, helper virus, and media components.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Protein mapping
InactiveUS20040010126A1Easy to separateShorten analysis timeComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein profilingProtein insertion
The present invention relates to multiphase protein separation methods capable of resolving large numbers of cellular proteins. The methods of the present invention provide protein profile maps for imaging and comparing protein expression patterns. The present invention provides alternatives to traditional 2-D gel separation methods for the screening of protein profiles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods for the production of insulin in plants
InactiveUS7547821B2Simple methodReadily apparentSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSingle-Chain AntibodiesPlanting seed
Commercial production of human insulin can be affected via transgenic expression in plant seeds. Thus, levels of insulin accumulation exceeding 0.1% of total cellular protein can be achieved recombinantly, through expression of the insulin with a single-chain antibody as a fusion partner. Production in seeds offers flexibility in storage and shipment of insulin as a raw material, and insulin retains its activity upon extraction from stored seed. Further, the amount of biomass subjected to extraction is limited, due to the relatively low water content of plant seeds.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC
Mammalian Genes Involved in Infection
InactiveUS20130323835A1Reduce infectionReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsMammalNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequences and cellular proteins encoded by these sequences that are involved in infection or are otherwise associated with the life cycle of one or more pathogens.
Owner:ZIRUS
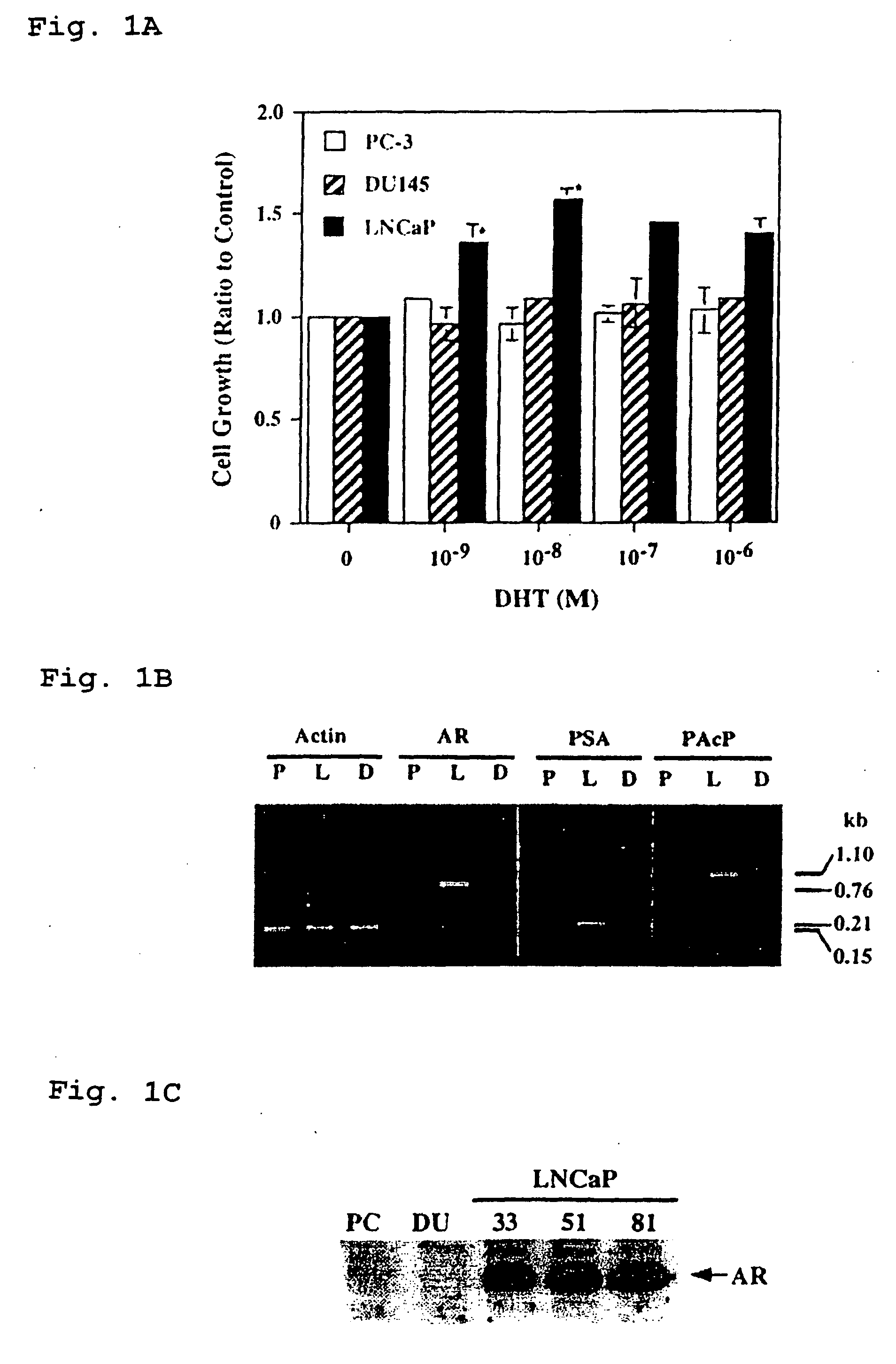
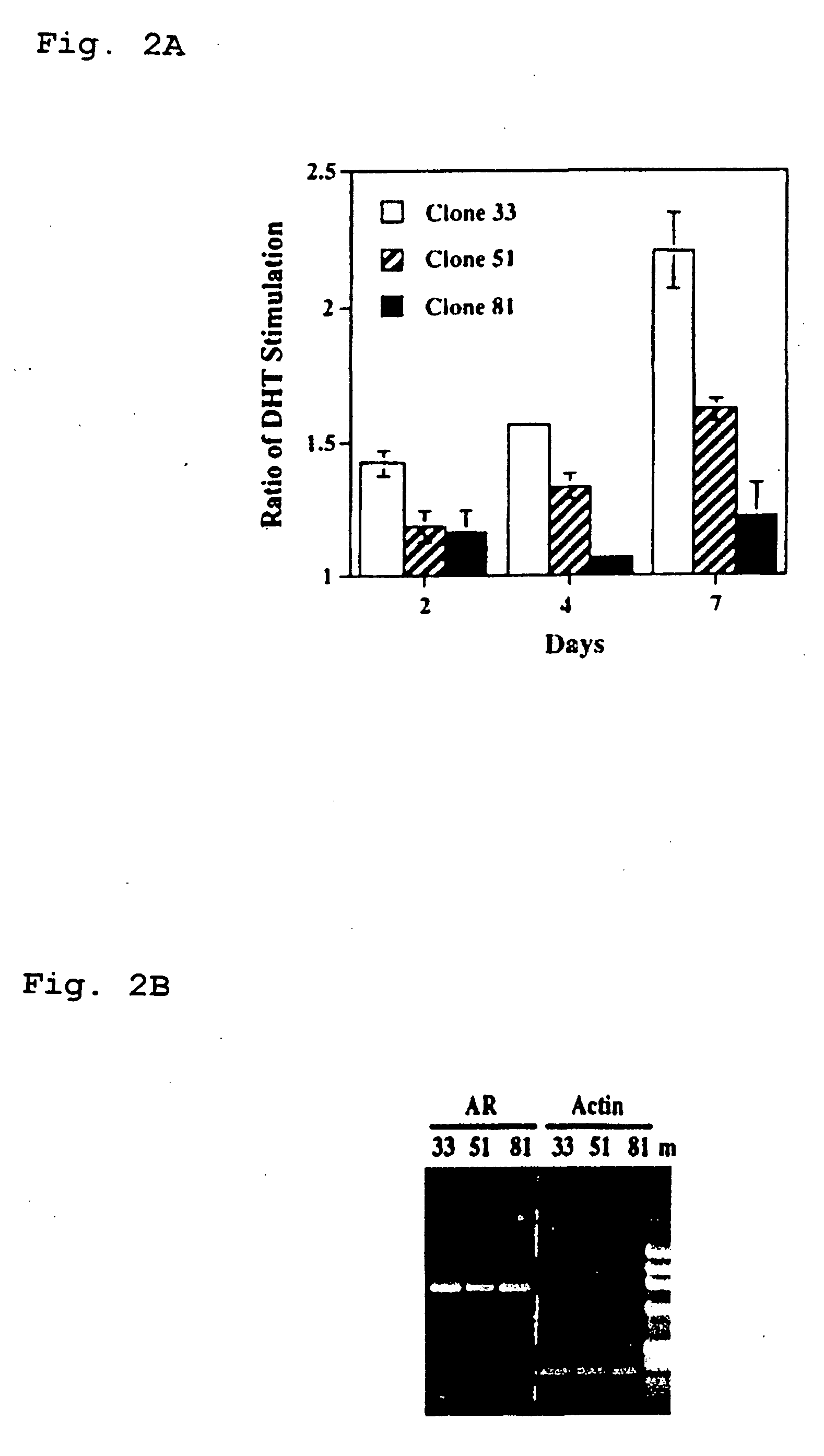
Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of prostatic acid phosphatase in prostate cancer
InactiveUS20060294615A1Good curative effectGood effectBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAndrogenMammal
Presented is a therapeutic method to treat prostate carcinomas in mammals comprising the administration of cellular PAcP protein. Also presented is a method to diagnose androgen-insensitive prostate carcinomas by determining the expression level of cellular PAcP in the prostate carcinomas, a decrease in expression being indicative of androgen-insensitivity. A promoter region that is specifically expressed in prostate tissue is presented, as is a xenograft animal model that mimics human prostate carcinomas in the expression of cellular PAcP.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
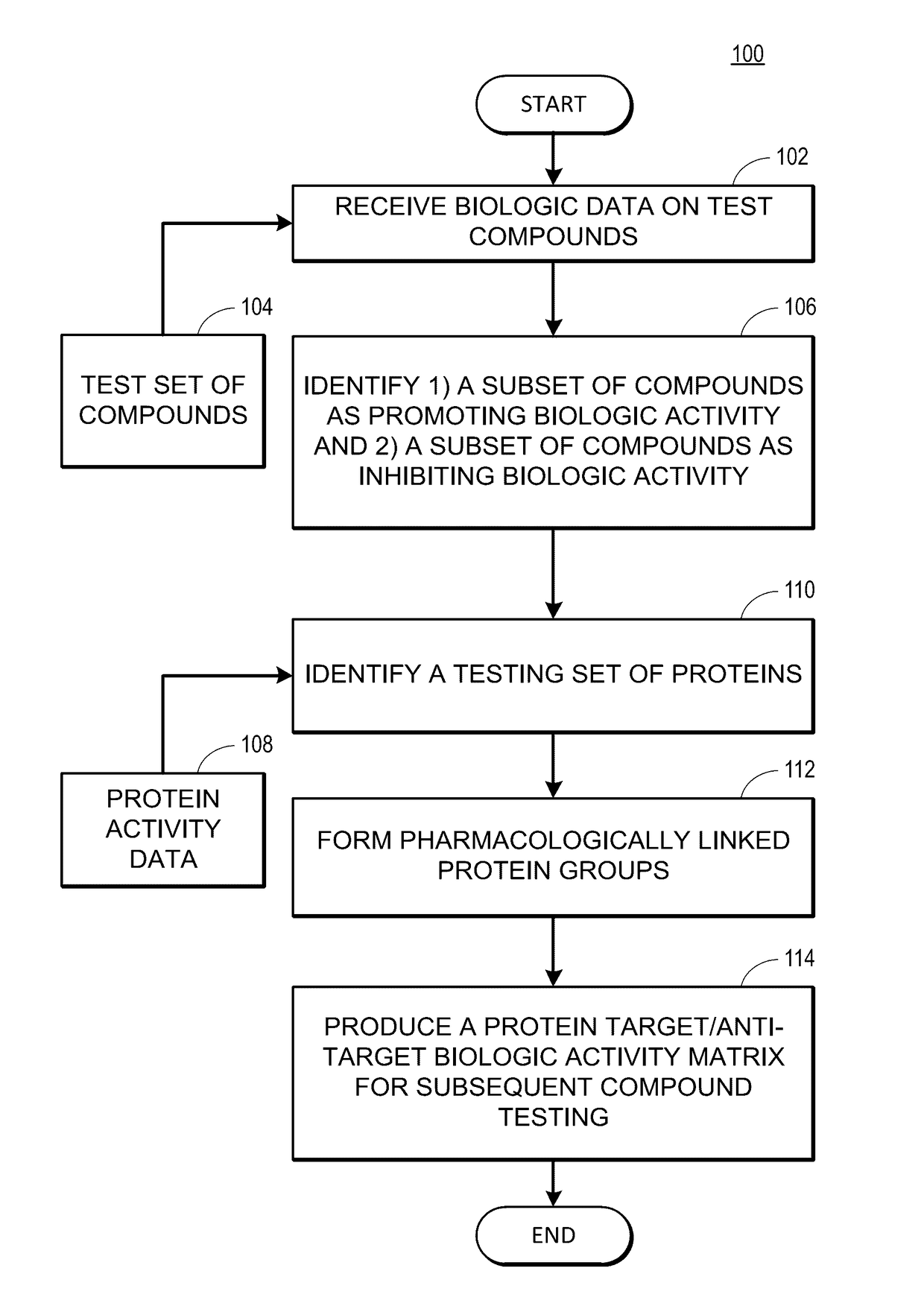
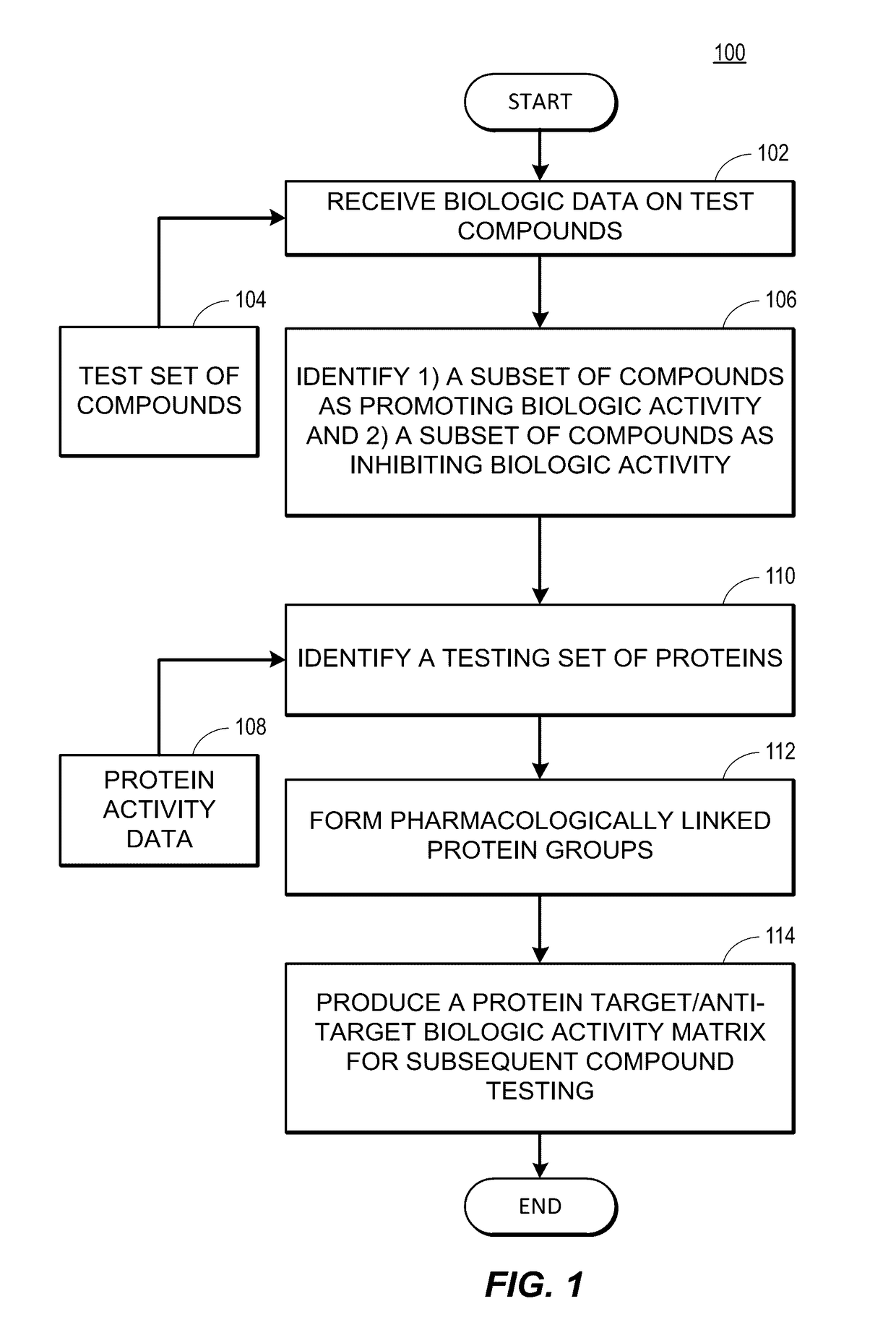
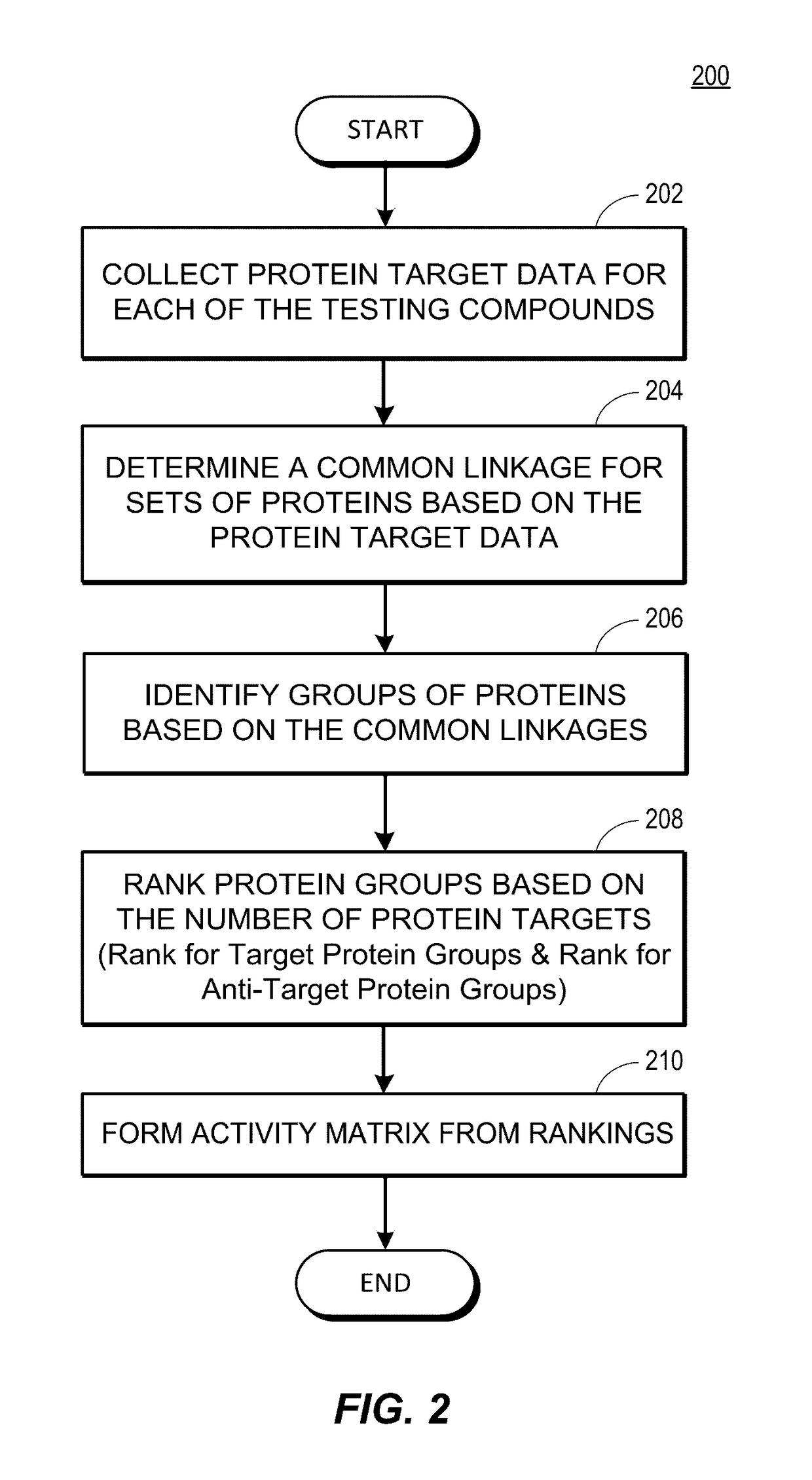
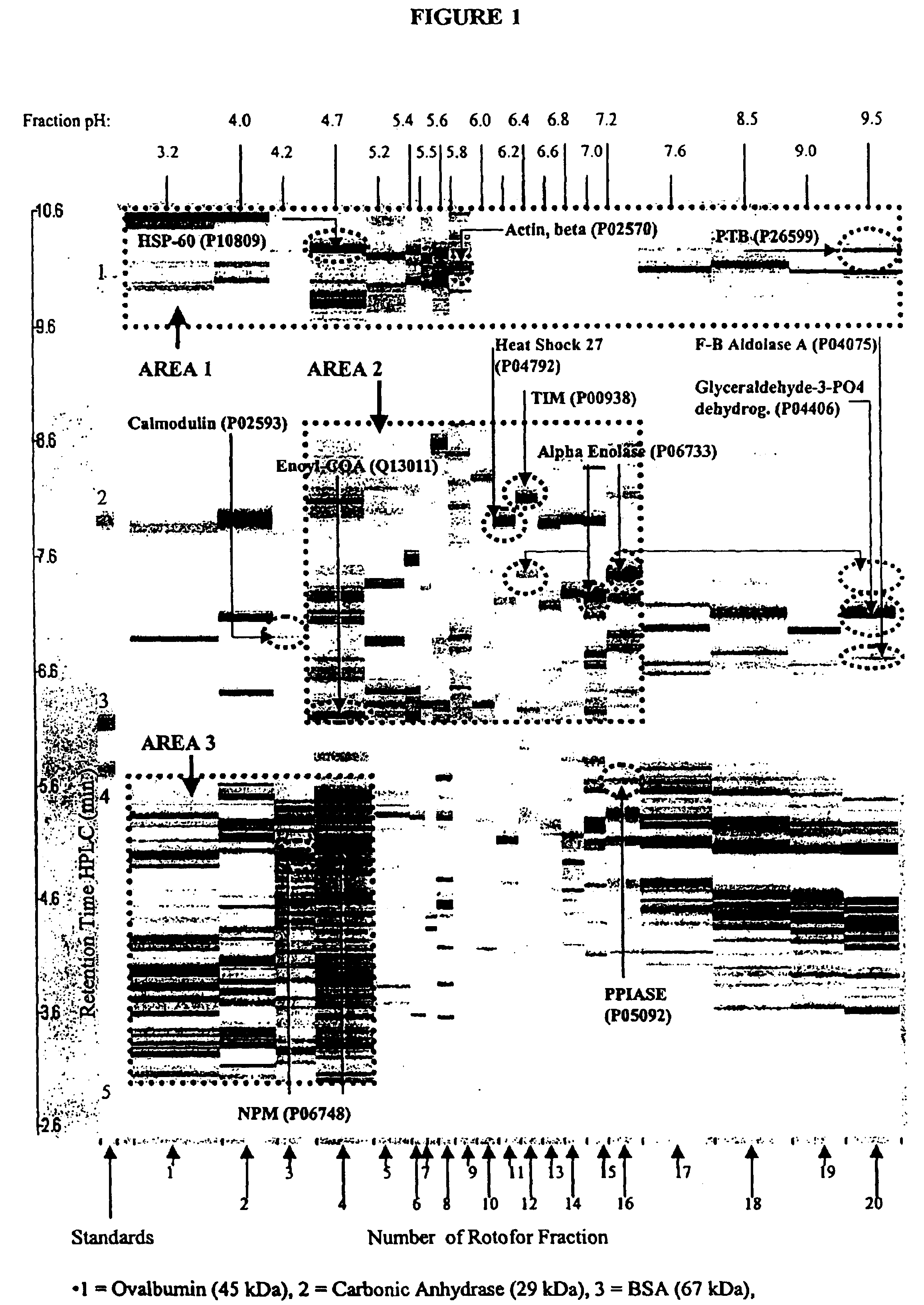
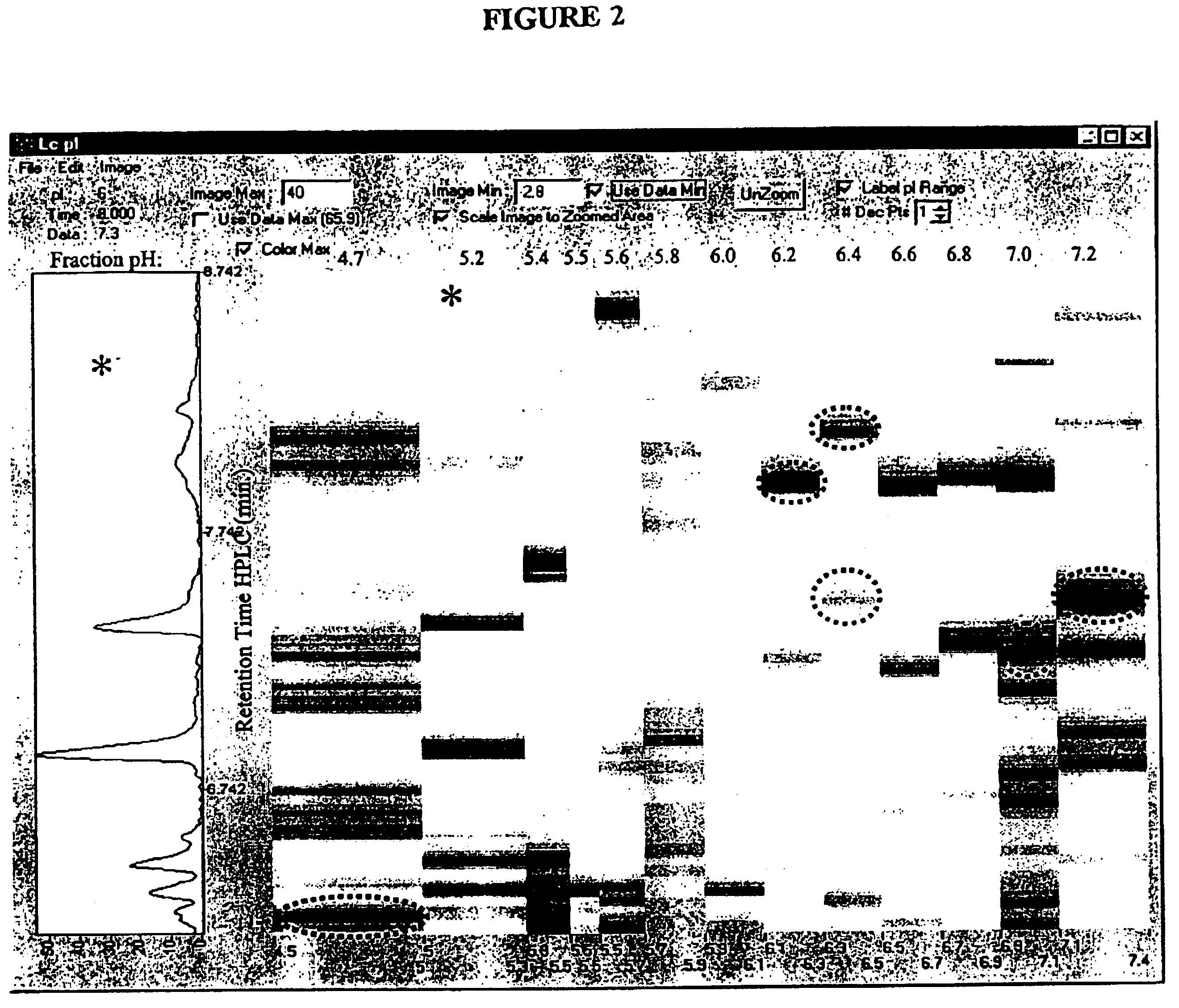
Rapid identification of pharmacological targets and Anti-targets for drug discovery and repurposing
InactiveUS20170147743A1Efficient identificationImprove biological activityMolecular designBiostatisticsRankingRapid identification
A computing system automatically analyzes various drug or other compound targets using biologic activity data for cellular proteins, and develops a target / anti-target matrix identifying pharmacologically responsive targets intended for drug engagement, and pharmacologically responsive anti-targets intended for avoidance of drug engagement. The system separates compounds into subsets based on biological threshold data and groups proteins through pharmacological similarity. The system ranks protein groupings in generating the matrix and uses the rankings to recommend compounds and compound groupings for testing to treat a pathology. The system compares new compounds against the matrix to recommend new compounds for testing.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Three dimensional protein mapping
InactiveUS6931325B2Easy transferComponent separationData visualisationImproved methodMulti dimensional
The present invention relates to multi-phase protein separation methods capable of resolving and characterizing large numbers of cellular proteins, including methods for efficiently facilitating the transfer of protein samples between separation phases. In particular, the present invention provides systems and methods for the generation of multi-dimensional protein maps. The present invention thus provides improved methods for the analysis of samples containing large numbers of proteins.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Targeted proteolysis by recruitment to ubiquitin protein ligases
InactiveUS7223556B1Decrease and increases activityReduce ubiquitinationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusion with degradation motifUbiquitin-Protein LigasesProteolysis
The present invention relates to methods and reagents for targeting proteolysis of a polypeptide by cis or trans association with a ubiquitin protein ligase, and further provides methods and reagents for inhibiting the ubiquitination and proteolysis of cellular proteins which are recognized by a ubiquitin protein ligase.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for treating genetically- defined proliferative disorders with hsp90 inhibitors
The invention relates generally to methods of treating cell proliferative diseases with HSP90 inhibitors and, depending on the specific aspect and embodiment(s) claimed, to the treatment of proliferative diseases that are associated with fusion proteins, e.g., bcrabl, or mutant proteins or cellular protein isoforms, e.g., mutant forms of p53.
Owner:CONFORMAL THERAPEUTICS CORP (US)
Biomolecule arrays
InactiveUS7244598B2Facilitate simultaneous monitoringImprove throughputMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesBiomoleculeCellular protein
Array systems that facilitate the simultaneous monitoring of many interactions between biological molecules and the analysis of cellular protein interactions with high throughput. The present invention provides methods and arrays for analyzing biochemical pathways by forming an array of immobilized biomolecules; exposing the array to biomolecules in solution; and detecting modification of the immobilized biomolecules, modification of the biomolecules in solution, and / or binding of biomolecules in solution to immobilized biomolecules.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
Host Cell Kinases as Targets for Antiviral Therapies Against HCV Infection
InactiveUS20110229484A1Preventing HCV infectionPrevent relapseAnimal cellsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseKinase inhibition
The present invention provides several networks of cellular protein kinases as potential targets for medical intervention against hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and HCV-related diseases and disorders in mammals, including humans. The invention relates to therapeutic protocols and pharmaceutical compositions designed to inhibit the activity of one or more of these protein kinases for the prevention and / or treatment of infections and diseases caused by HCV. The invention also relates to methods for the identification of kinase inhibitors that may be used to treat and / or prevent HCV infections and HCV-related diseases.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
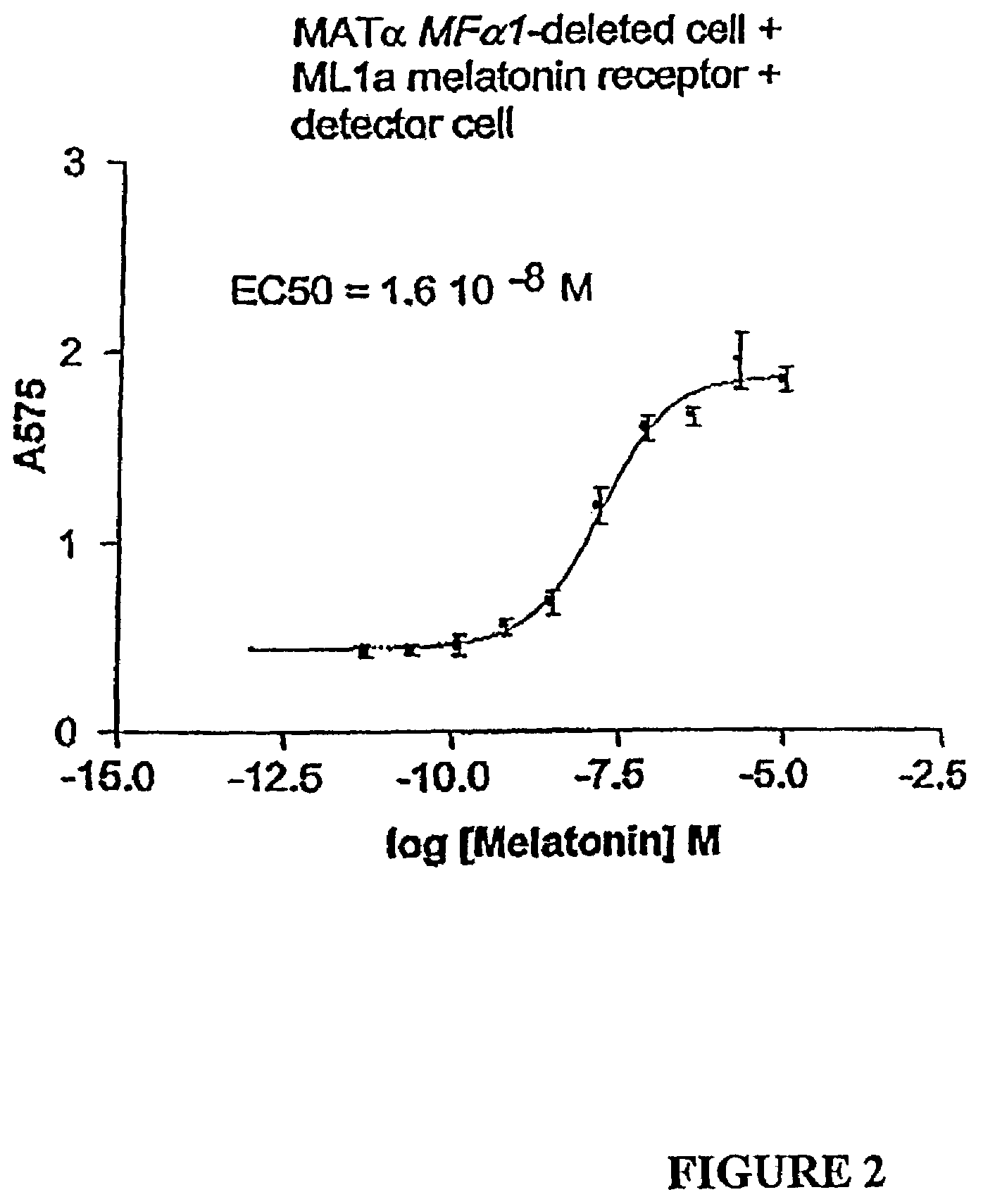
Cell surface proteins and use thereof as indicators of activation of cellular signal transduction pathways
InactiveUS20050196743A1Sensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHeterologousCell Surface Proteins
The present invention makes available a rapid, reproducible, robust assay system for screening and identifying pharmaceutically effective compounds that specifically interact with and modulate the activity of a cellular protein, e.g., a receptor or ion channel. The subject assay enables rapid screening of large numbers of compounds to identify those which act as an agonist or antagonist to the bioactivity of the cellular protein. In this system, the cell is treated with a compound, and functional interaction of this compound with a cellular receptor yields a detectable signal, which can be specifically measured. The subject assays include methods of identifying compounds which specifically modulate, for example, heterologous receptors coupled to the pheromone response pathway in yeast. The subject assays are particularly amenable to the identification of specific agonists and antagonists of G protein-coupled receptors.
Owner:CADUS TECH
Mammalian genes involved in toxicity and infection
InactiveUS20140242692A1Low toxicityReduced activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMammalToxicology
The present invention relates to cellular proteins that are involved in toxicity and infection or are otherwise associated with the life cycle of one or more pathogens.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method and composition for treating sarcopenia
PendingUS20180326026A1Reduce the total massDecline in muscle functionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansVertebrate antigen ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
A method of treating sarcopenia comprises immunizing a subject in need thereof against AGE-modified proteins or peptides of a cell. Immunizing a subject includes administering a vaccine that comprises an AGE antigen. Vaccines against AGE-modified proteins or peptides contain an AGE antigen, an adjuvant, optional preservatives and optional excipients.
Owner:SIWA CORP (US)
DNA (desoxyribonucleic acid) fluorescent hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107596436AGood biocompatibilityHas antibacterial propertiesFermentationBandagesCytotoxicityEngineering
The invention discloses DNA (desoxyribonucleic acid) fluorescent hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: (1) DNA hydrogel is prepared; (2) the DNAhydrogel is put in sterile water, water is changed once every 15-30 min, and water is changed 3-5 times in total; (3) the DNA hydrogel obtained in the step (2) is added to a phosphate buffer and an AgNO3 water solution for a reaction; a NaBH4 water solution is added, the mixture reacts, and the DNA fluorescent hydrogel is obtained. The DNA fluorescent hydrogel has good biocompatibility and material softness, can effectively avoid secondary injury of wound as medical dressing and can relieve pain of the wound; the hydrogel has fluorescence and has certain antibacterial property and no cytotoxicity. The hydrogel preparation process is simple and convenient. The hydrogel can be applied to the field of medical dressing, immunotherapy, tissue engineering, monocellular culture, drug sustained release, protein synthesis, biosensors and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Methods for identifying cell surface receptor protein modulators
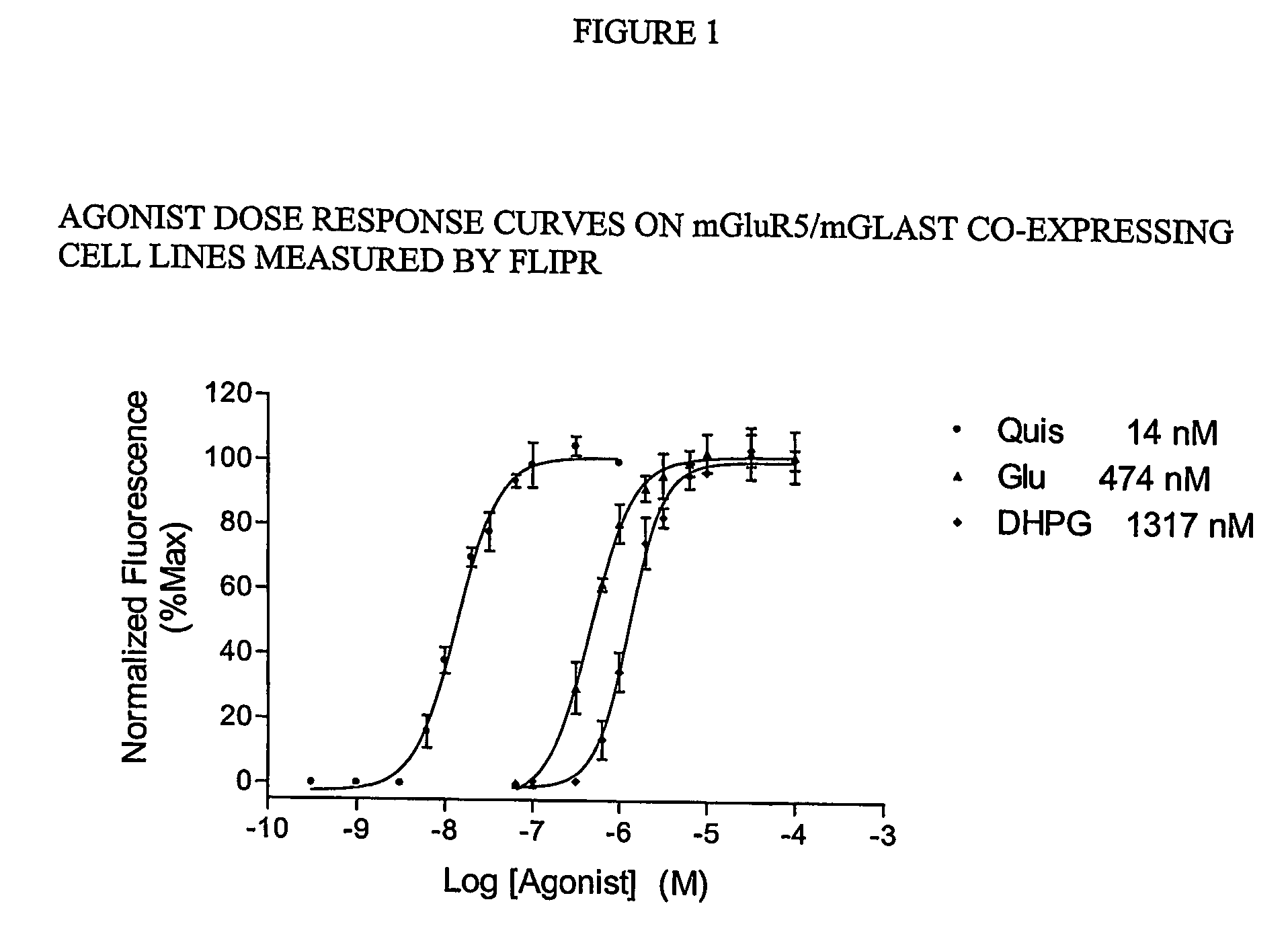
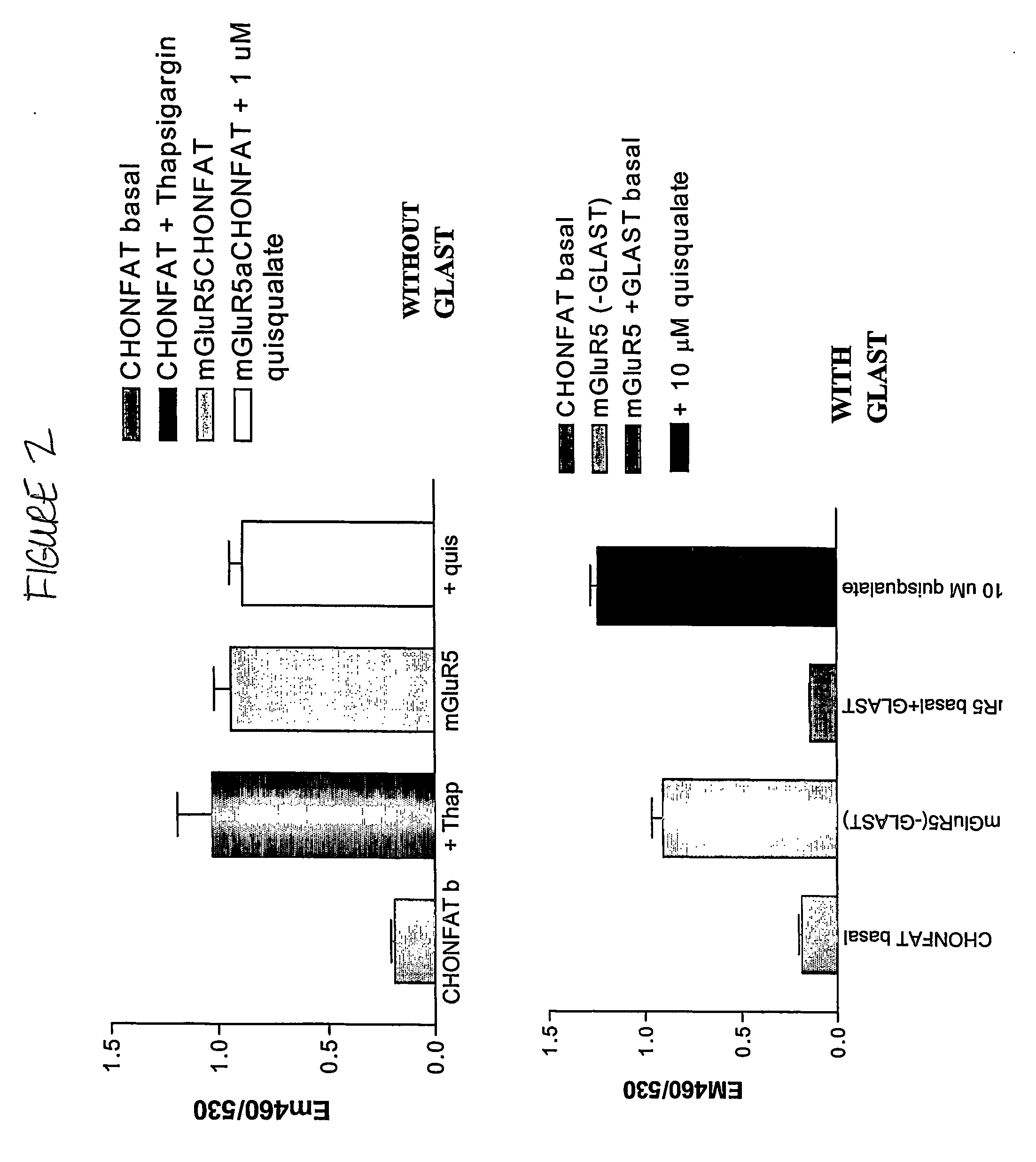
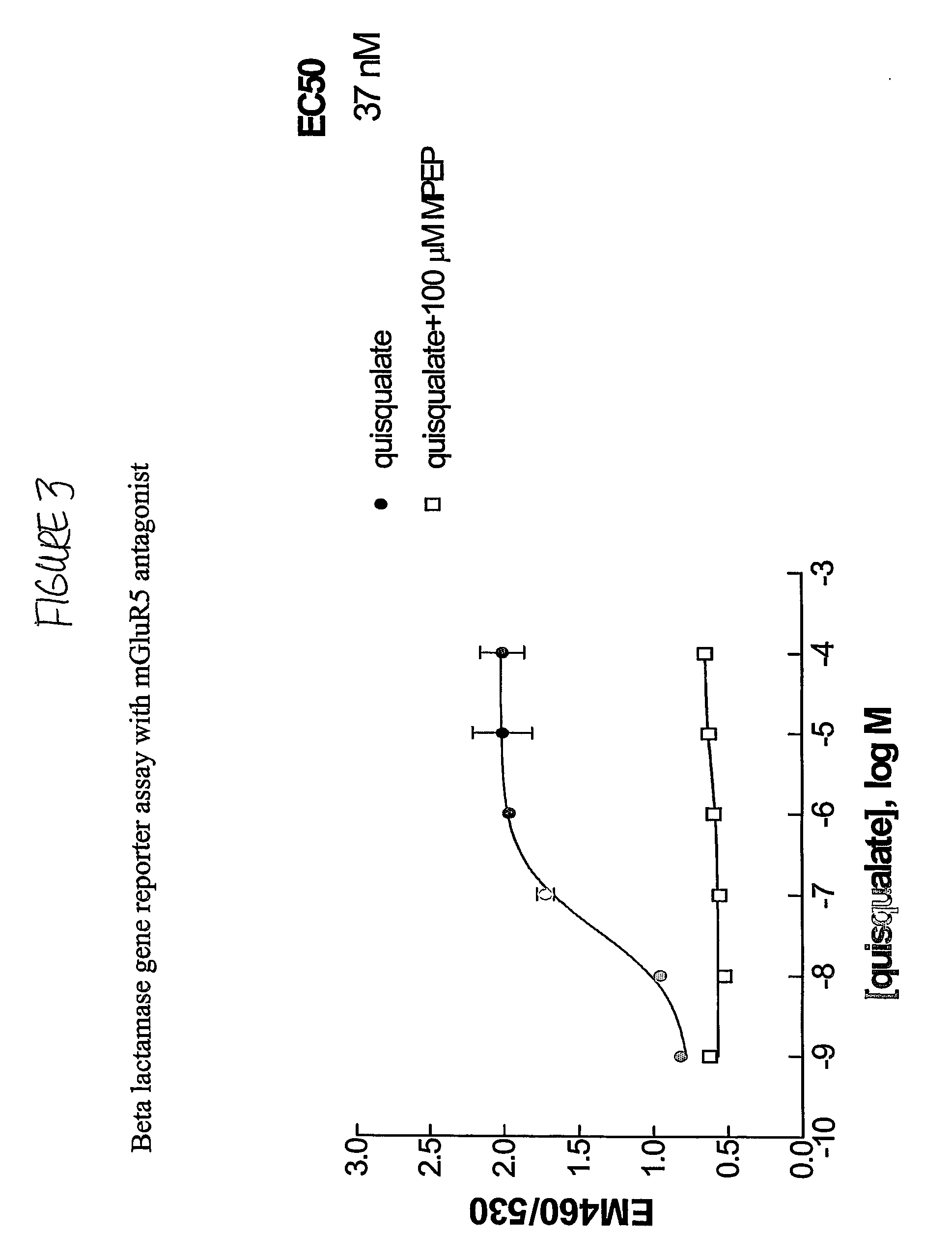
InactiveUS20060275835A1Quick filterImprove isolationBiological material analysisBiological testingCell Surface ProteinsMetabotropic glutamate receptor
The present invention makes available a rapid, effective assay for screening and identifying pharmaceutically effective compounds that specifically interact with and modulate the activity of a target cell surface protein, e.g., a receptor or ion channel. The subject assay enables rapid screening of large numbers of compounds to identify those which modulate the bioactivity of the cellular proteins. The subject assays are particularly amenable for high throughput formats and are particular useful in identifying modulators of a mammalian metabotropic glutamate receptor protein.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Method for inducing migration of adult stem cells derived from adipose tissue
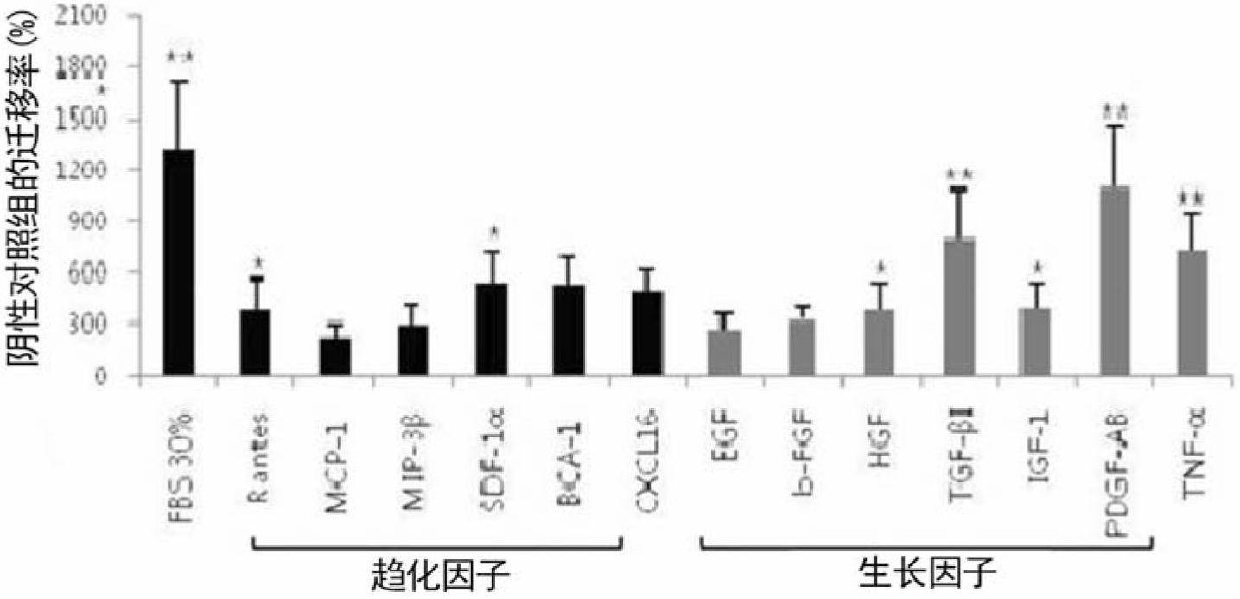
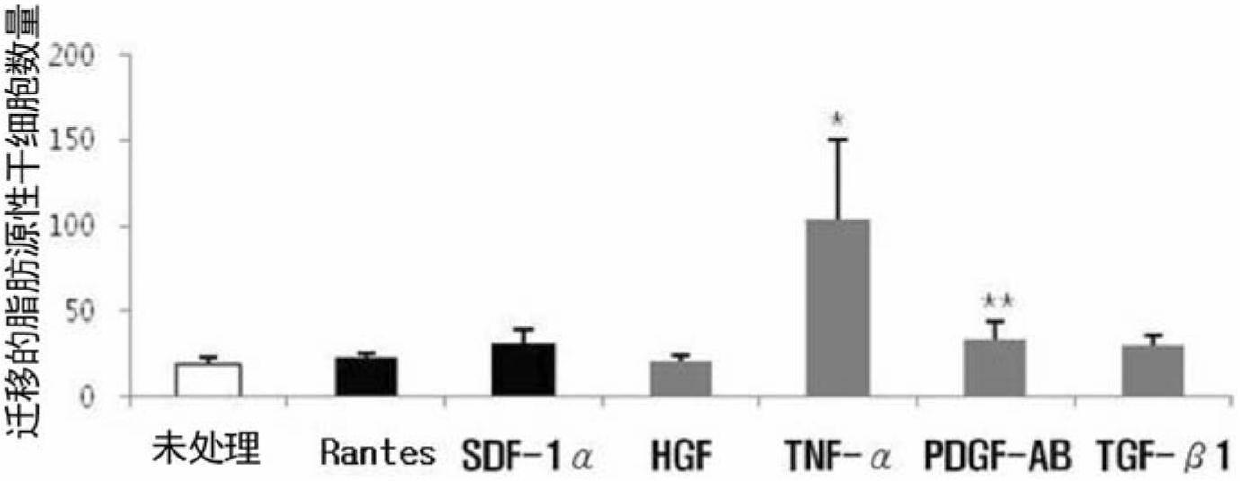
The present invention relates to cell migration capacity of adult stem cells derived from adipose tissue, and more specifically, to treatment of adipose-derived, adult stem cells with cellular protein secretions. In particular, the present invention is a new use for adipose stem cells, whereby pretreatment of adipose-derived, adult stem cells with a specific chemokine or growth factor induces a more effective migration to diseased parts of the body. Adipose-derived adult stem cells, pretreated with specific chemokine or growth factor may be intravenously administered as a simple way to target stem cells (targetting) to the site of the disease and represents potential for cell therapy.
Owner:RNL BIO
Methods for the Detection of Colorectal Cancer
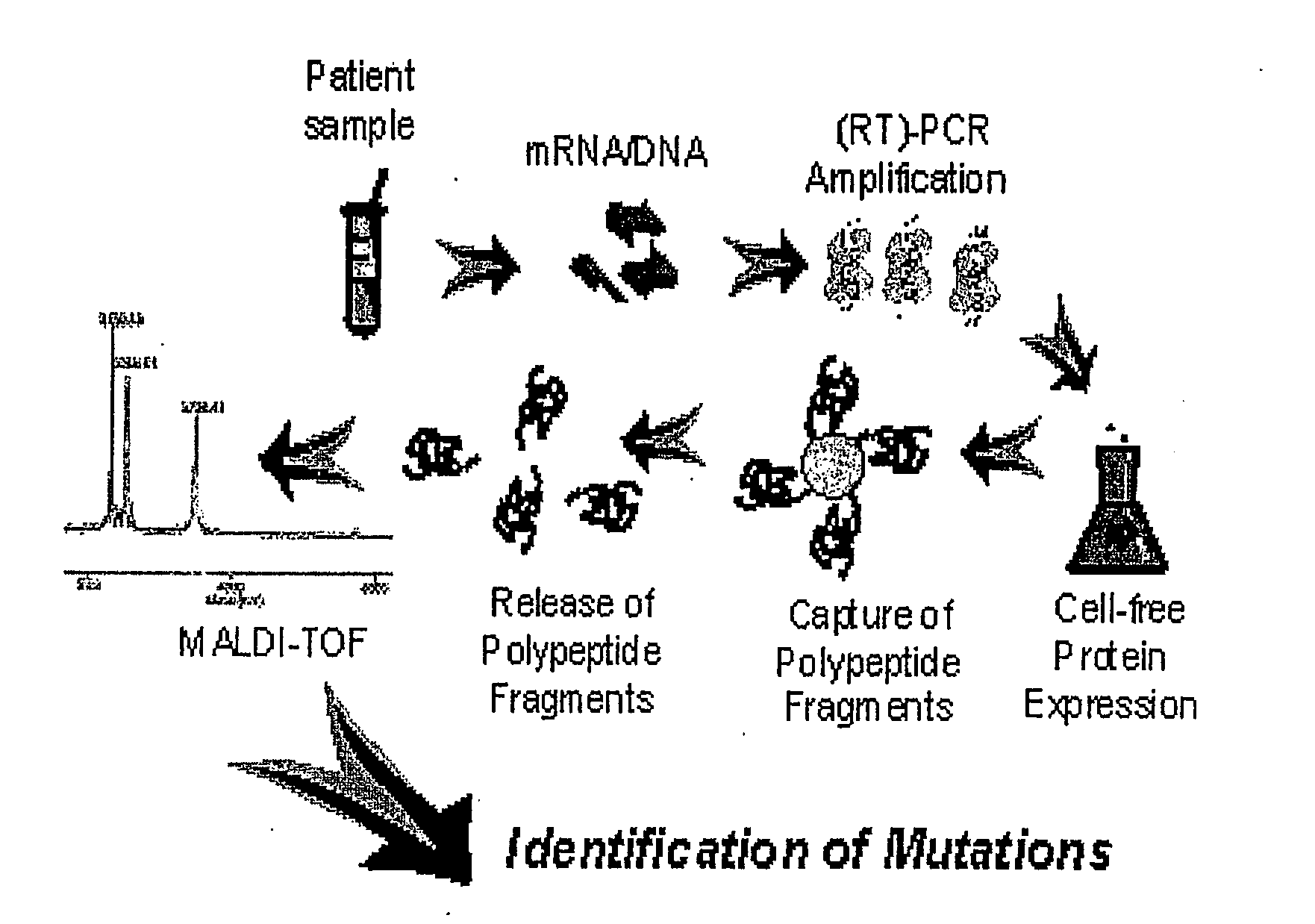
InactiveUS20110045991A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell-free protein synthesisAmino acid
This invention relates to an approach for detection of chain truncating mutations based on the utilization of existing sample collection methods such as FOBT platforms, together with advanced methods for cell-free protein expression. “When further combined with mass spectrometry, the invention provides the ability to simultaneously detect changes in the amino acid sequence of multiple peptides. In some embodiments, DNA is isolated from a patient fecal sample and specific regions of a gene (i.e., for example, a K-ras gene or an APC gene) are PCR amplified using specifically designed primers that allow translation of encoded peptide fragments in a cell-free protein synthesis system. Nascent proteins are affinity purified and their mass is detected by MALDI-TOF which allows identifying low levels of mutations.
Owner:AMBERGEN INC
Synthetic gene coding for human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for the expression in E. coli
InactiveUS7655437B2Improved expression level (accumulation)Antibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliColony-stimulating factor
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
Methods for treating genetically-defined proliferative disorders with HSP90 inhibitors
The invention relates generally to methods of treating cell proliferative diseases with HSP90 inhibitors and, depending on the specific aspect and embodiment(s) claimed, to the treatment of proliferative diseases that are associated with fusion proteins, e.g., berab1, or mutant proteins or cellular protein isoforms, e.g., mutant forms of p53.
Owner:CONFORMAL THERAPEUTICS CORP (US)
Assay system for simultaneous detection and measurement of multiple modified cellular proteins
InactiveUS7049151B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorEnzymologySulfateCellular material
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Model Taste Cells and Methods of Use for Identifying Modulators of Taste Sensation
InactiveUS20080026416A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTaste receptor ligandEnteroendocrine cell
The present invention provides model taste cells that naturally or recombinantly express taste receptors and relevant cellular proteins and / or molecules useful for taste signal transduction. The present invention further provides methods of use for these model taste cells for screening for compounds that modulate sweet and / or other taste signal transduction. Compositions comprising the compounds / modulators identified using the model taste cells are also provided. In preferred embodiments, the model taste cells are derived from human HuTu-80 enteroendocrine cells, and derivative cells thereof.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
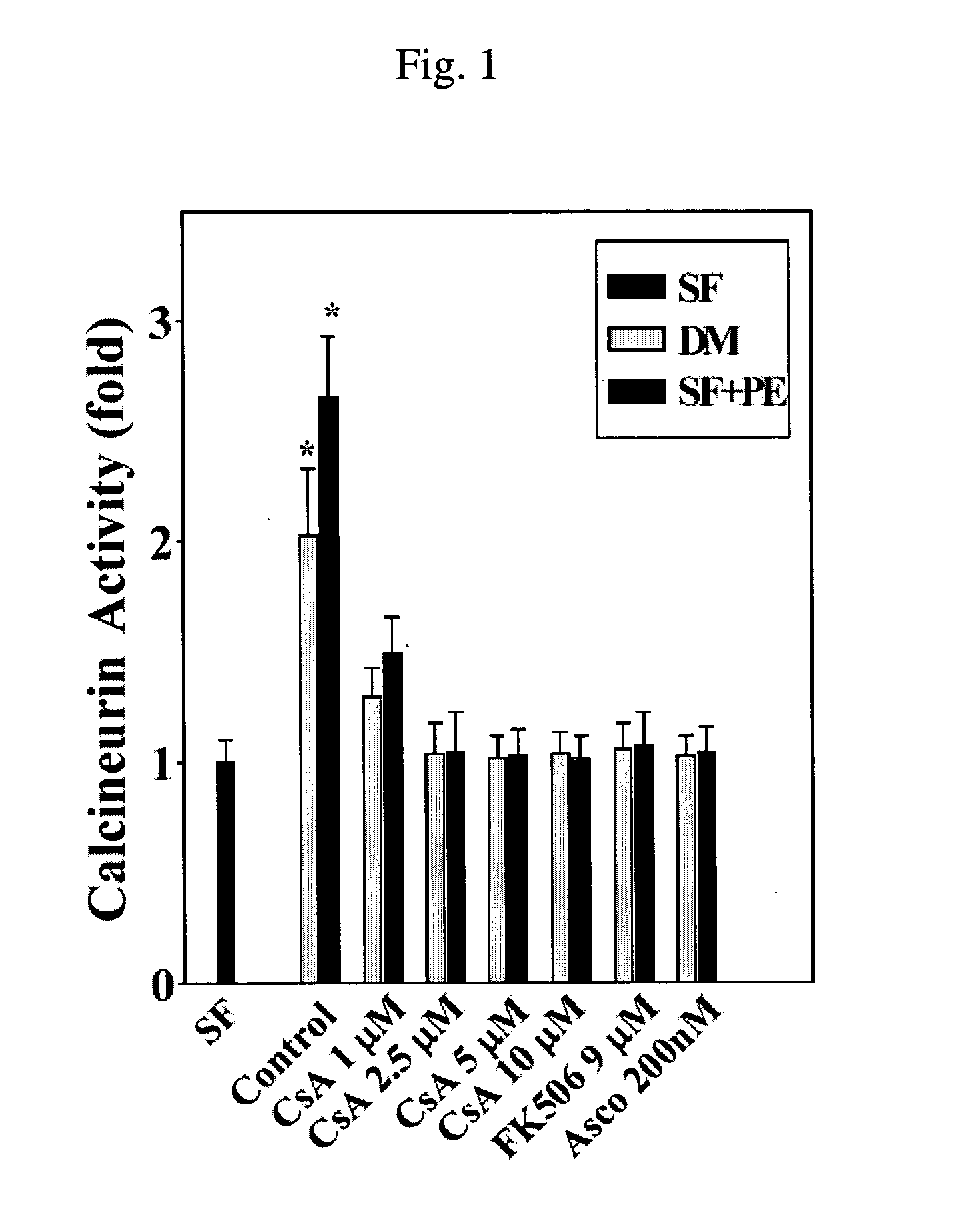
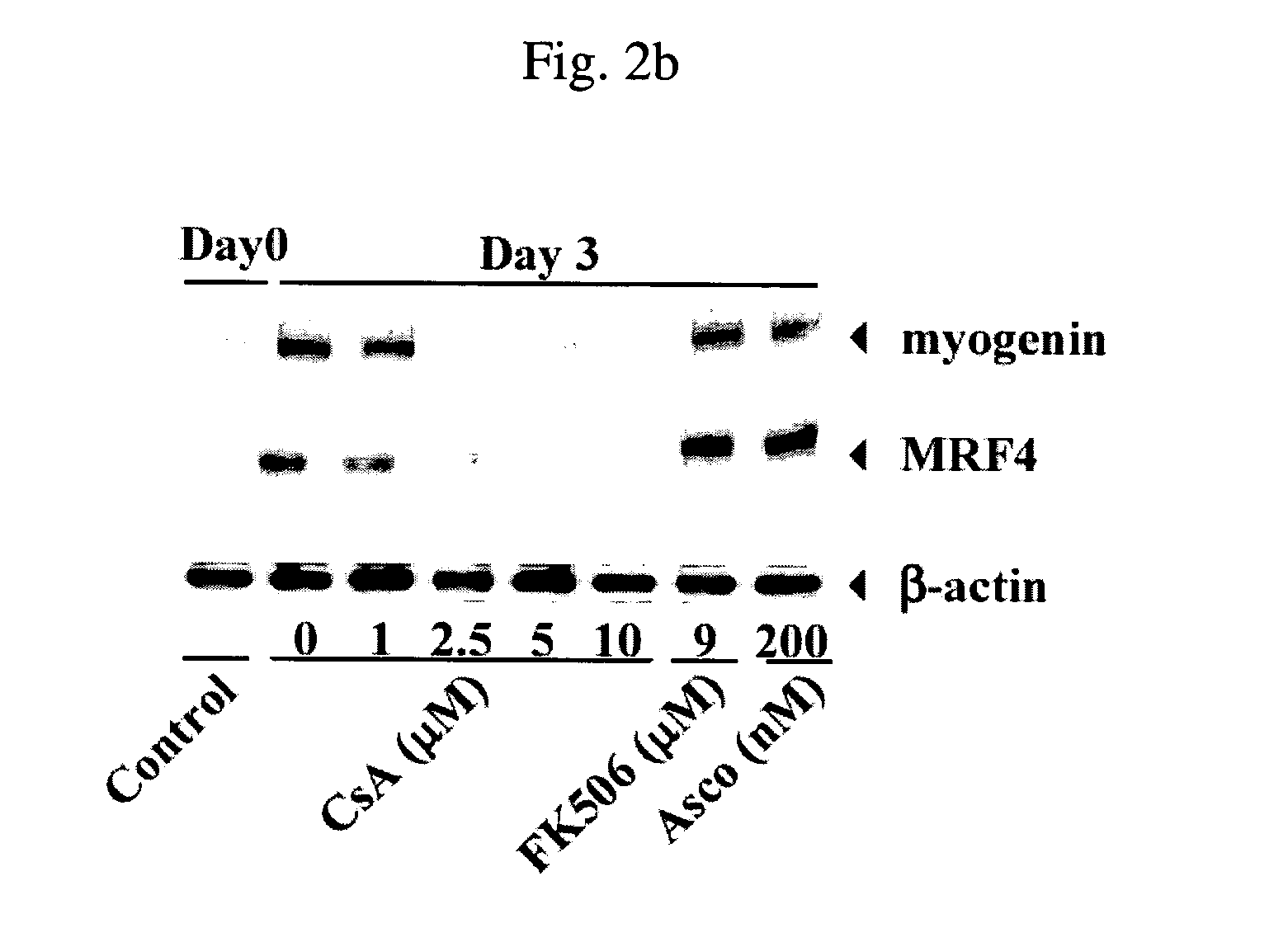
Use of cyclophilin as antioxidant and prevention of cyclosporin a-induced toxicity in cell transplantation by overexpression of cyclophilin
InactiveUS20050074438A1Reduce the impactLow toxicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntioxidantTransplant rejection
Disclosed is a cyclophilin protein with PPIase activity functioning as an antioxidant. When being overexpressed in transplanted cells, the cyclophilin protein remarkably reduces the cytotoxicity induced by cyclosporin A or its analogues so that it can greatly improve the success rate in transplantation. Also, disclosed is a composition useful to prevent transplant rejection, comprising a recombinant expression vector which can over-express a cyclophilin protein with PPIase activity. The recombinant expression vector is introduced into cells which are thus transformed to be resistant to cyclosporin A and its analogues. A method of preparing such cells is also disclosed.
Owner:KIM SUNG SOO
System for detection of a functional interaction between a compound and a cellular signal transduction component
InactiveUS7090991B2Sensitive highHigh expressionFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHeteroreceptor
The present invention makes available a rapid, reproducible, robust assay system for screening and identifying pharmaceutically effective compounds that specifically interact with and modulate the activity of a cellular protein, e.g., a receptor. or ion channel. The subject assay enables rapid screening of large numbers of compounds to identify those which act as an agonist or antagonist to the bioactivity of the cellular protein. In this system, the first cell is treated with a compound, and functional interaction of this compound with a cellular receptor yields a secreted signal. A second cell, bearing a receptor for this secreted signal, makes use of an indicator gene in a signaling pathway coupled to this second receptor. The subject assays include methods of identifying compounds which specifically modulate, for example, heterologous receptors coupled to the pheromone response pathway in yeast. The subject assays are particularly amenable to the identification of specific agonists and antagonists of G protein-coupled receptors.
Owner:CADUS TECH
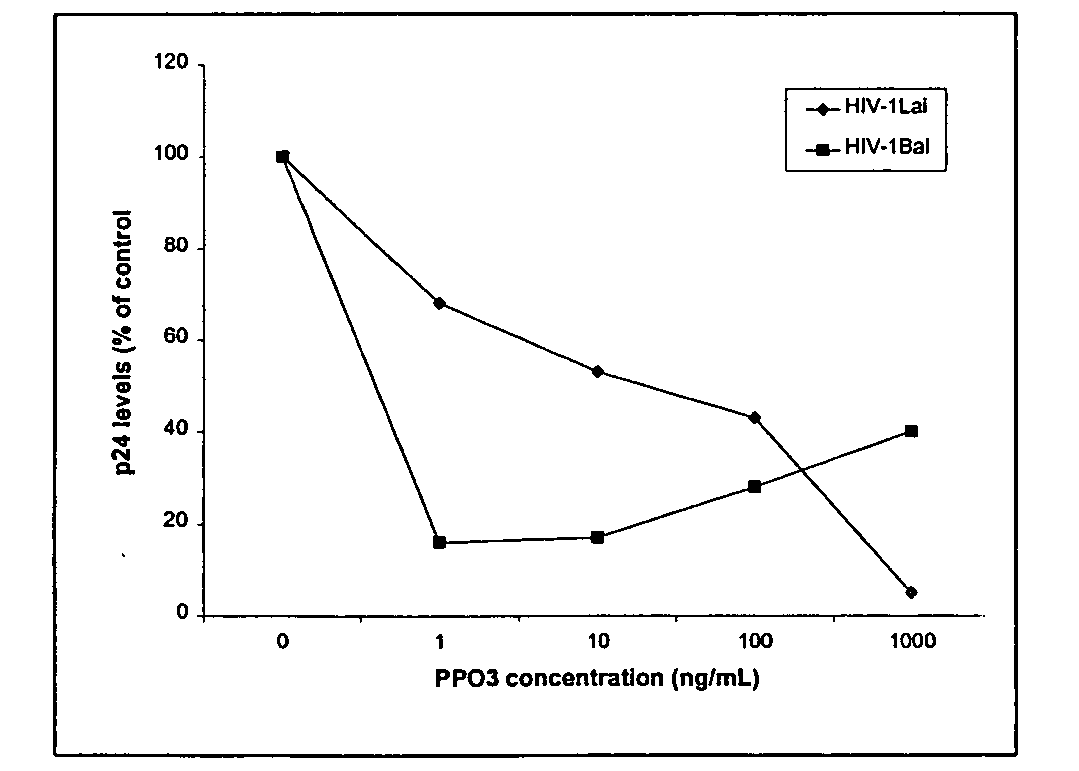
Immunokine composition and method
InactiveUS20080248992A1Avoid infectionControl spreadPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsImmunodeficiency virusOrganism
A composition and method for preventing HIV infection of mammalian cells. One aspect of the invention relates to an anti-immunodeficiency virus immunokine capable of binding to a cellular protein in a manner that prevents HIV infection of that cell. The compositions can include either an active bioactive polypeptide, such as native cobratoxin, and / or an inactivated bioactive polypeptide, such as cobratoxin in which one or more of the native disulfide bridges have been prevented from forming. The term “immunokine” is used to refer to an inactivated bioactive polypeptide, whether inactivated by chemical, genetic, and / or synthetic means as described herein, with the proviso that a corresponding active bioactive polypeptides can be included where applicable (e.g., for in vitro use).
Owner:PHYLOMED CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com