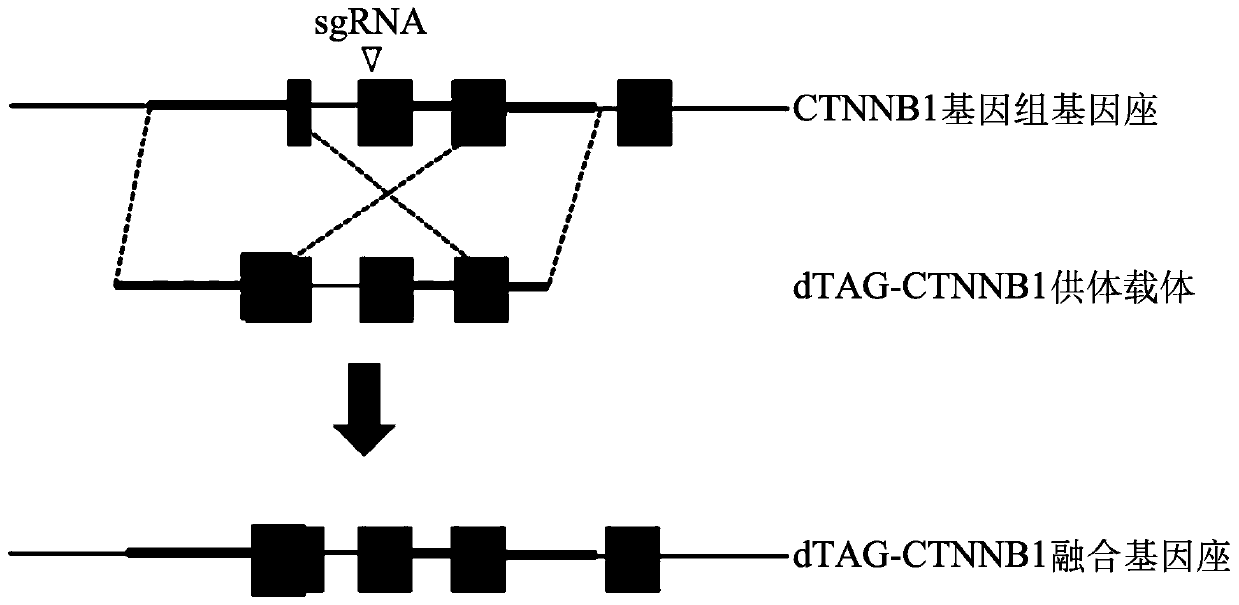
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
208results about "Fusion with degradation motif" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
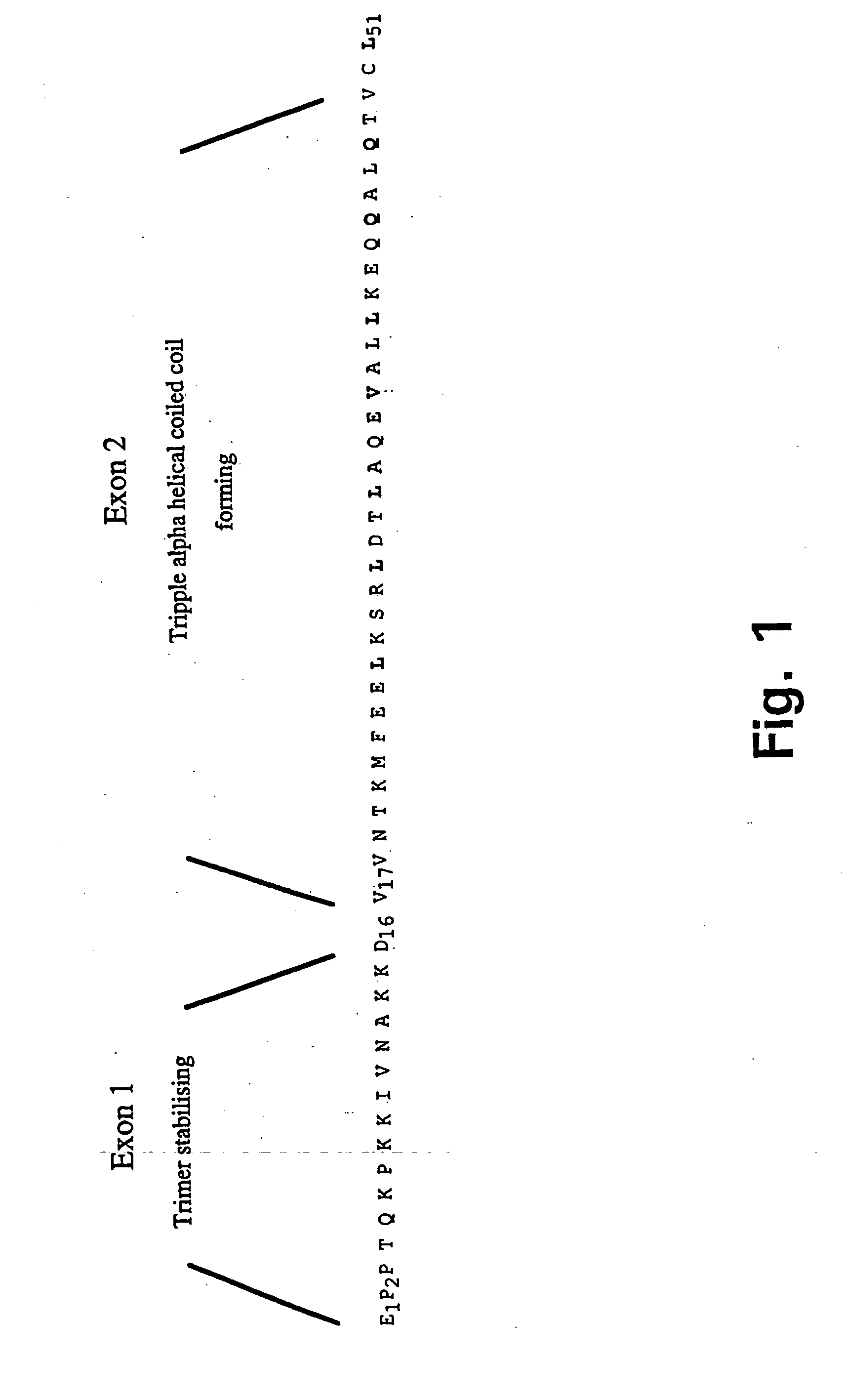
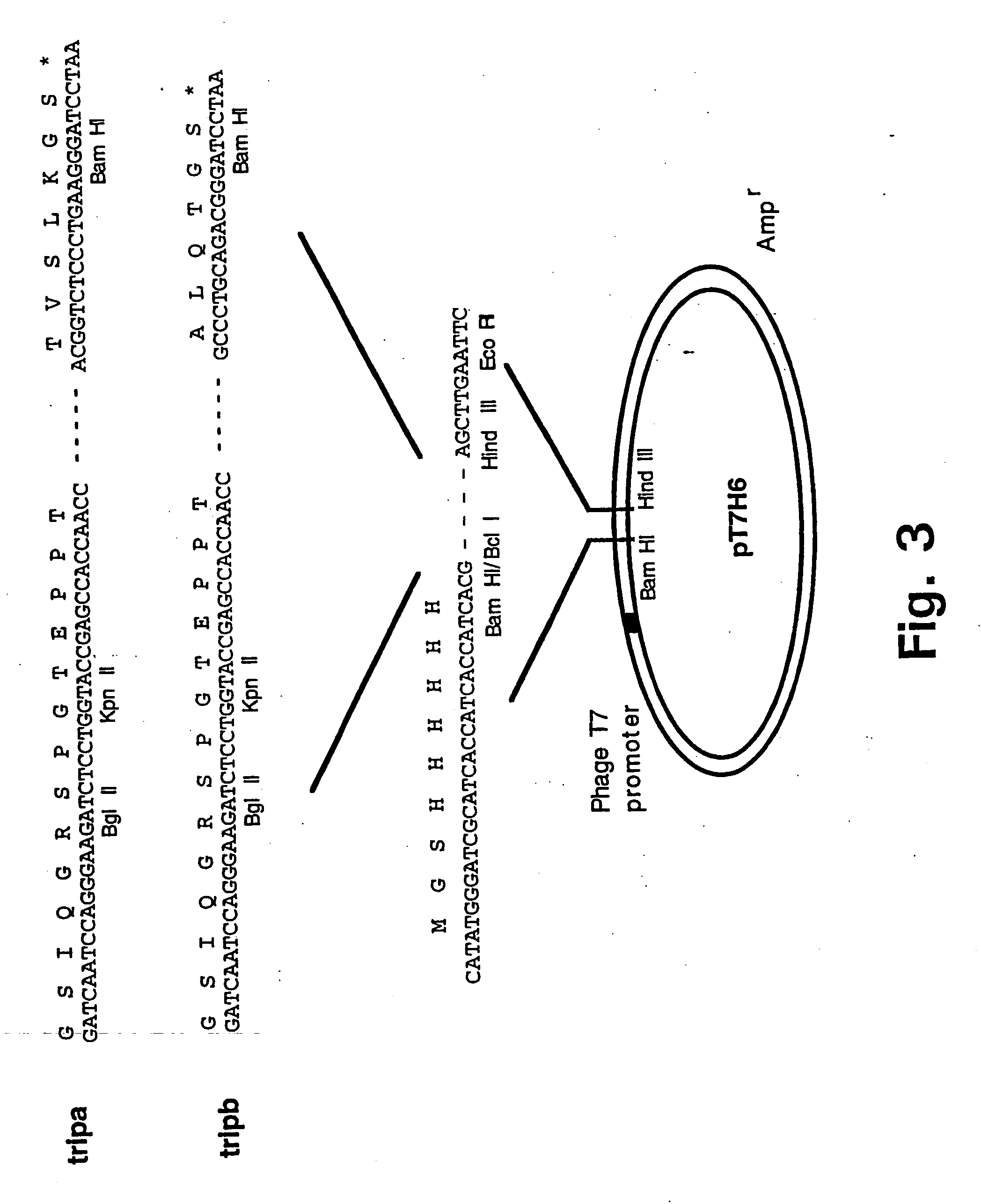
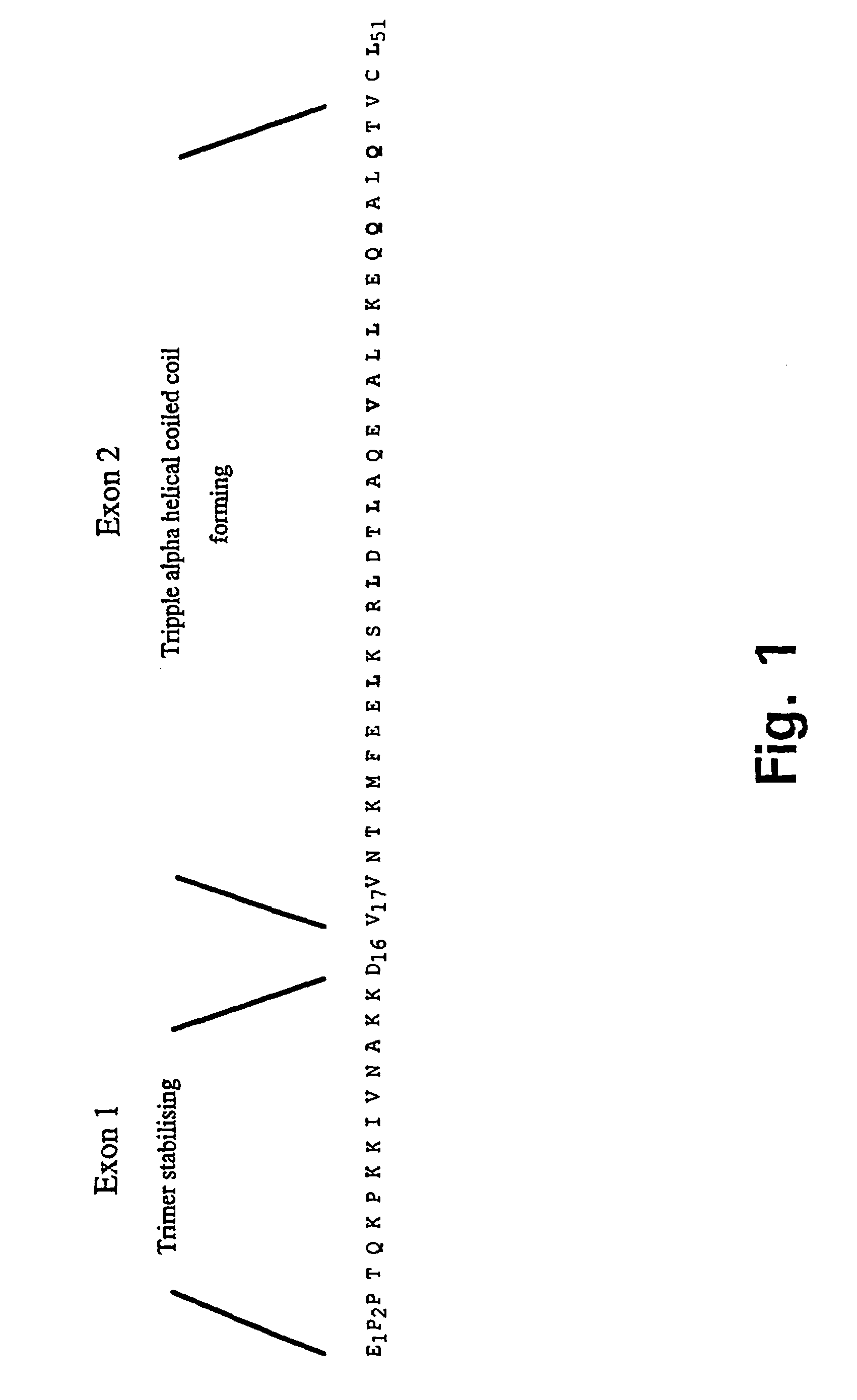
Trimerising module
The present invention relates to the design of trimeric polypeptides using polypeptide structural elements derived from the tetranectin protein family, and their use in rational de novo design and production of multi-functional molecules including the application of the multi-functional molecules in protein library technology, such as phage display technology, diagnostic and therapeutic systems, such as human gene therapy and imaging. The trimeric polypeptides being constructed as a monomer polypeptide construct comprising at least one tetranectin trimerising structural element (TTSE) which is covalently linked to at least one heterologous moiety, said TTSE being capable of forming a stable complex with two other TTSEs; or as an oligomer which is comprised of two monomer polypeptide constructs as mentioned above, and which comprises three TTSEs or a multiplum of three TTSEs, or which is comprised of three monomer polypeptide constructs.
Owner:ANAPHORE INC +1
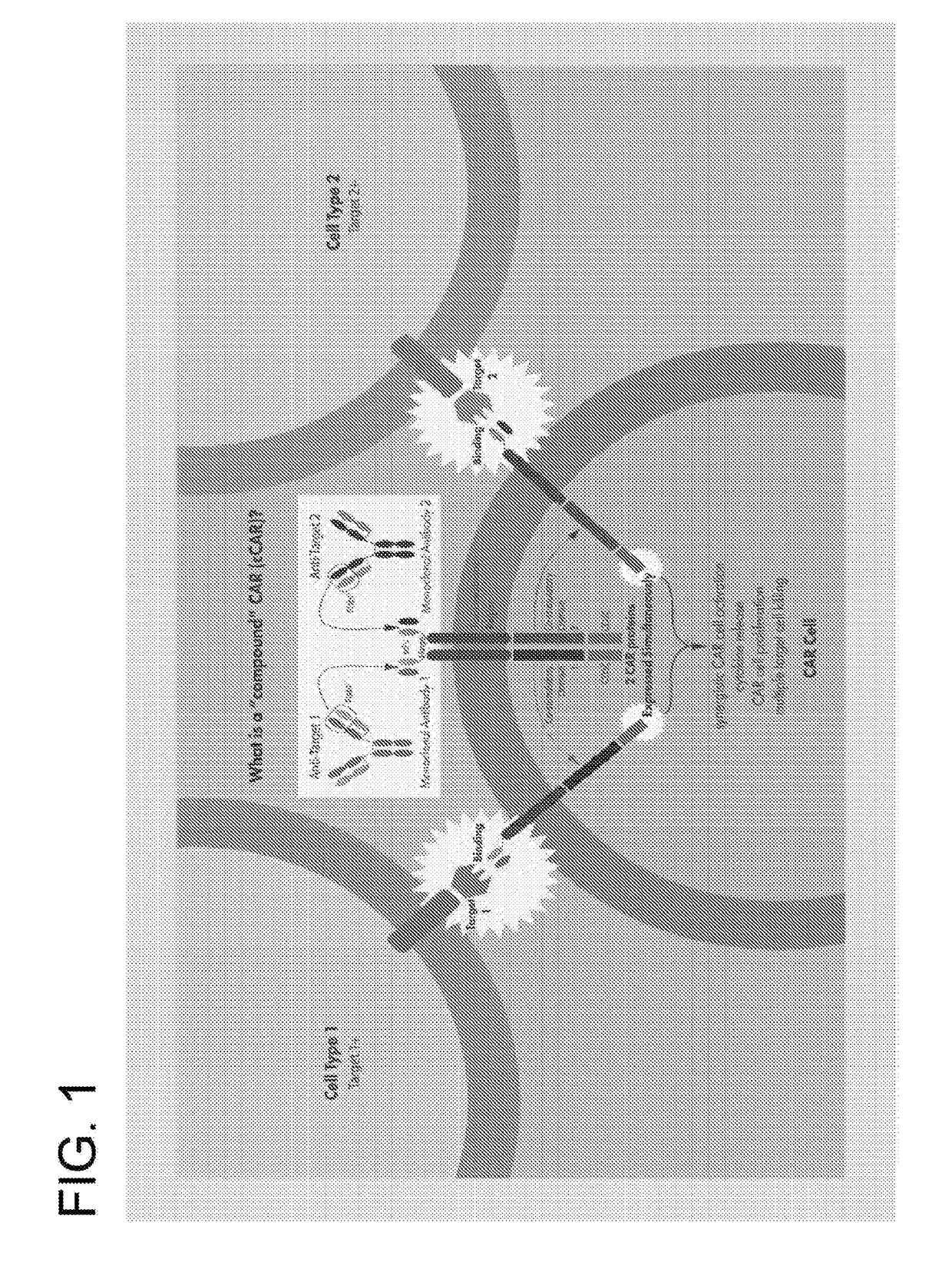
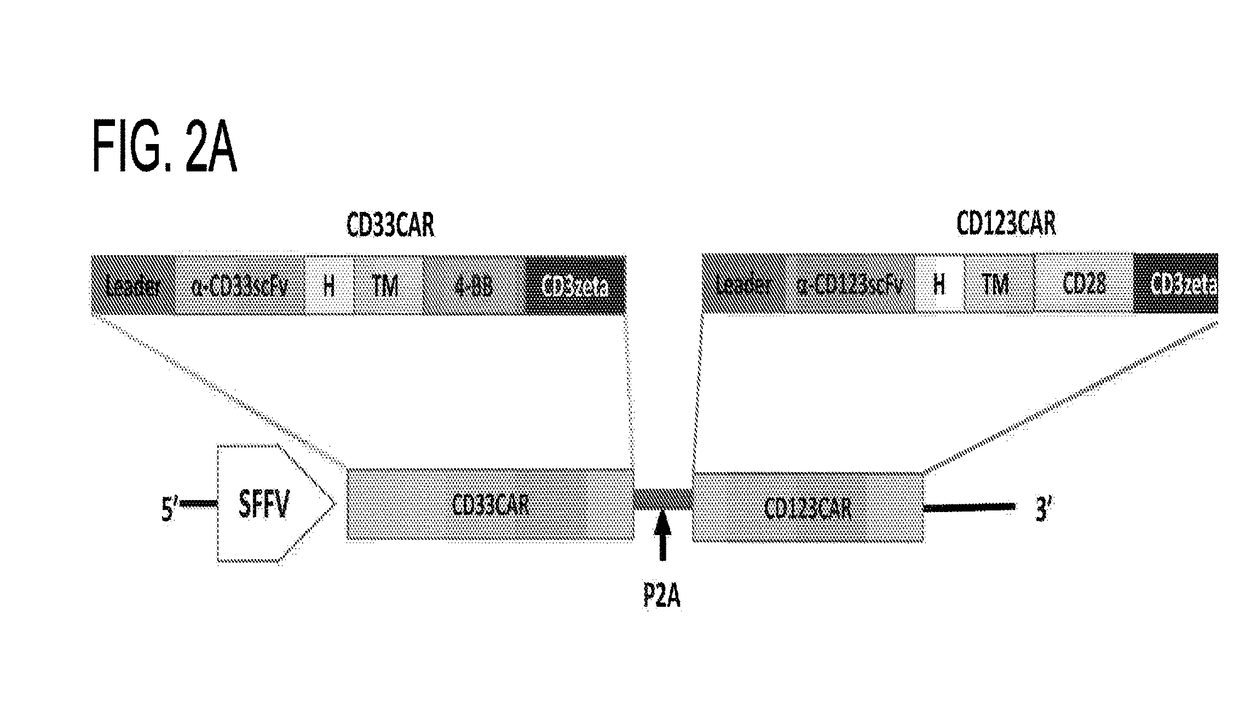
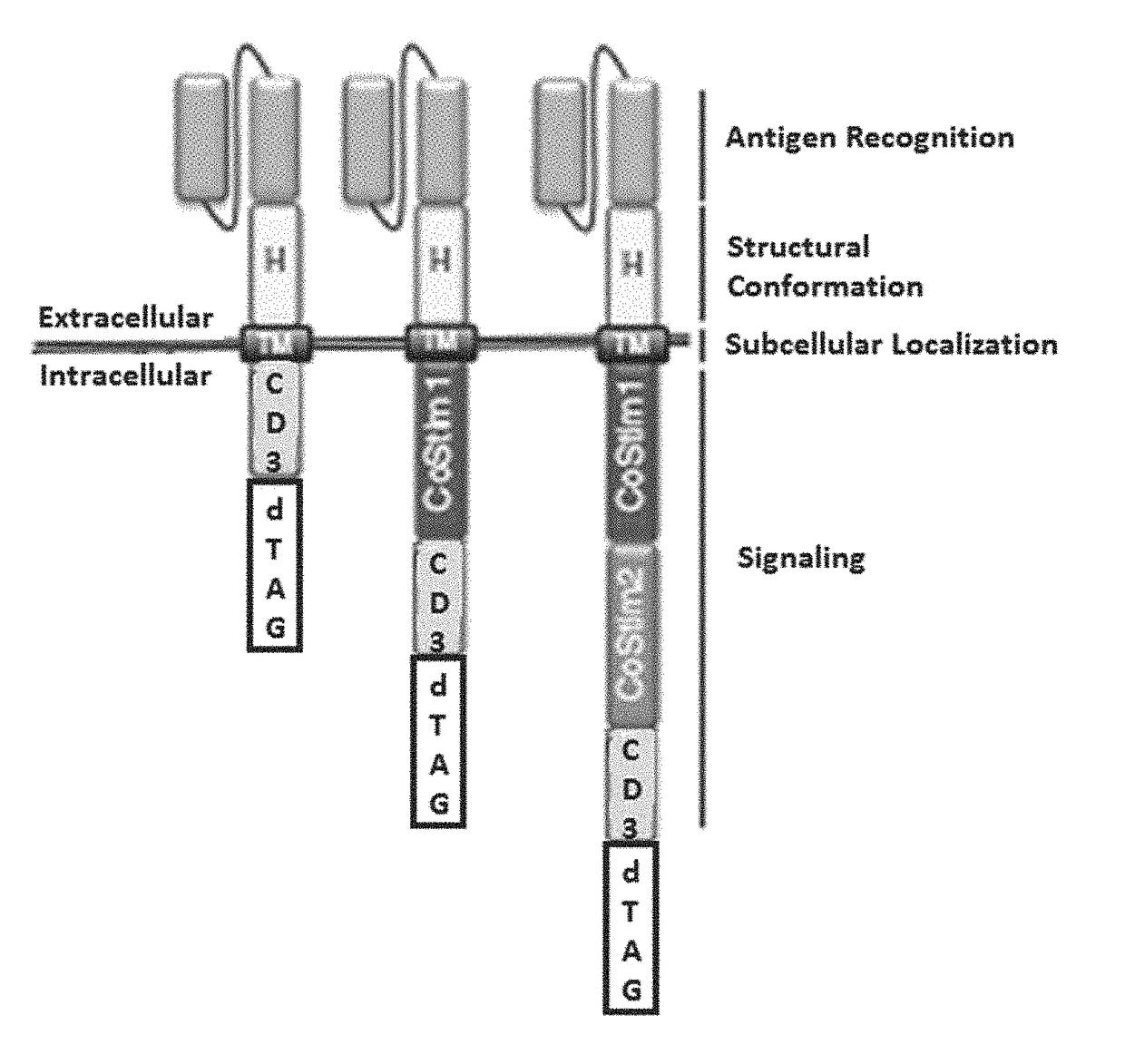
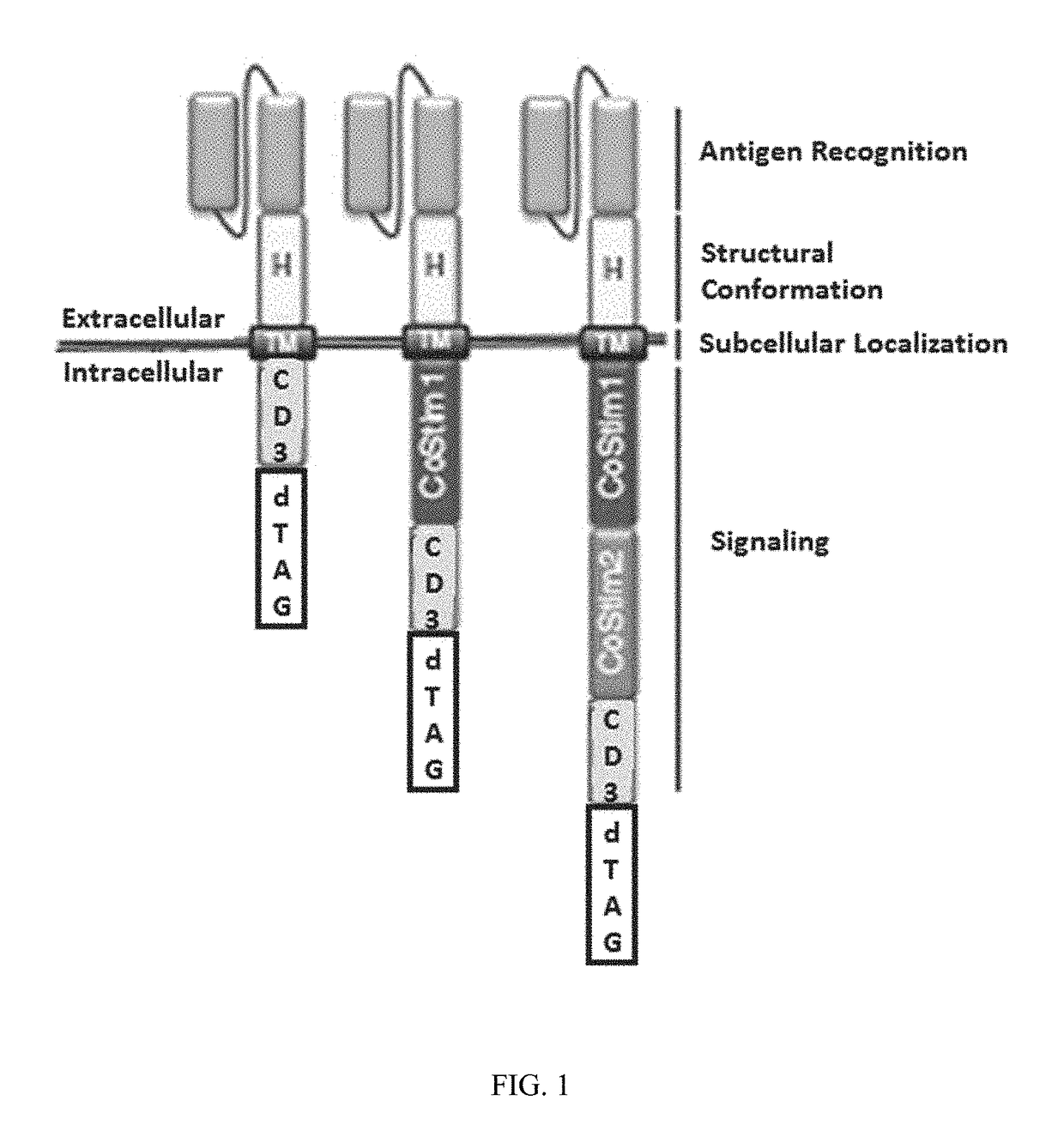
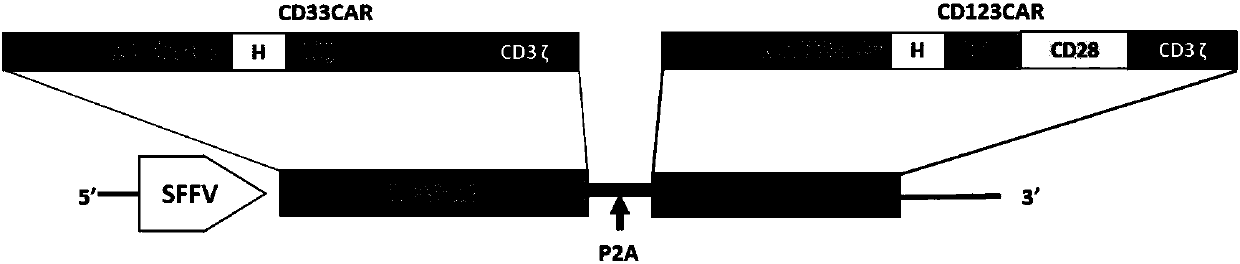
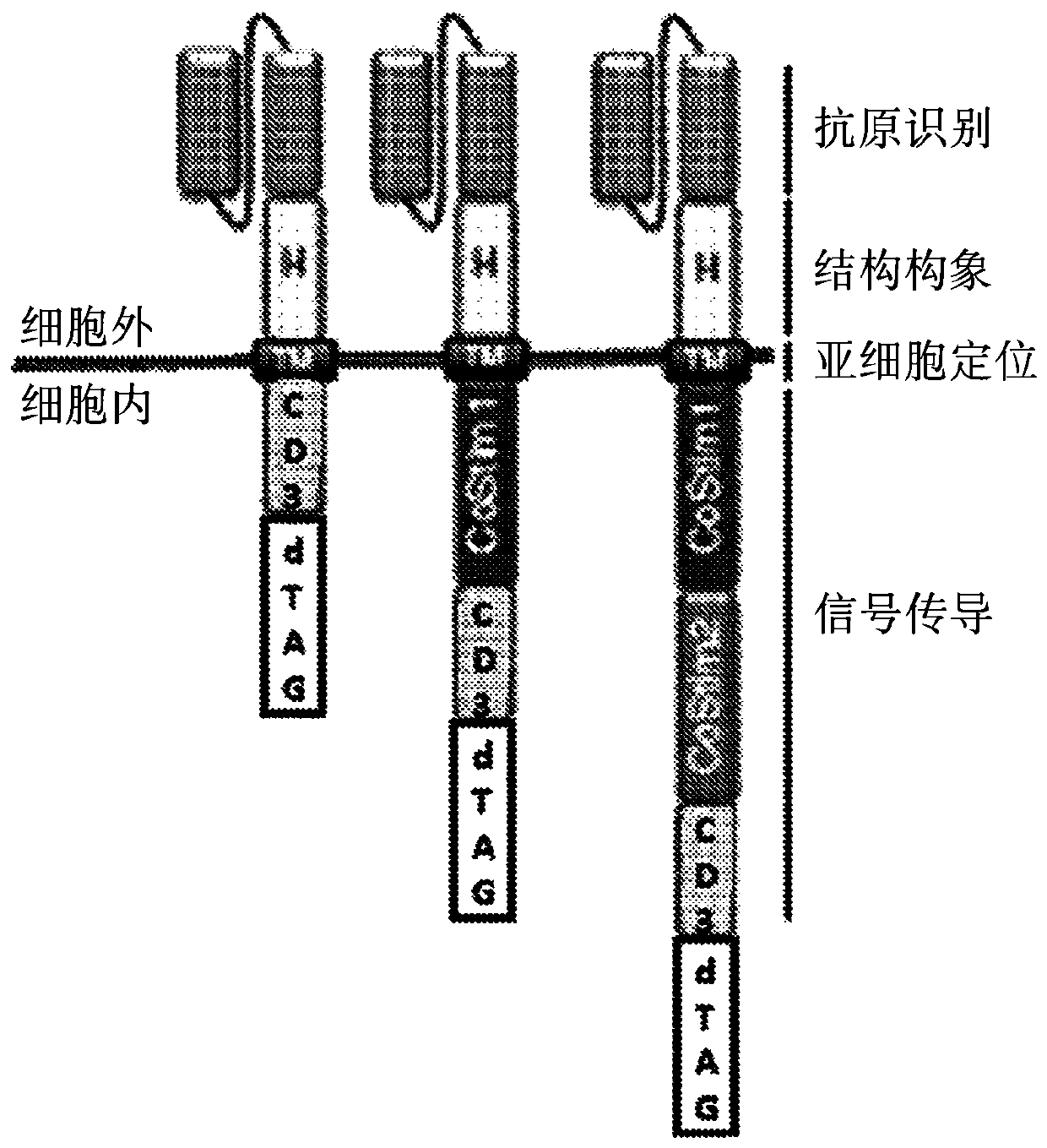
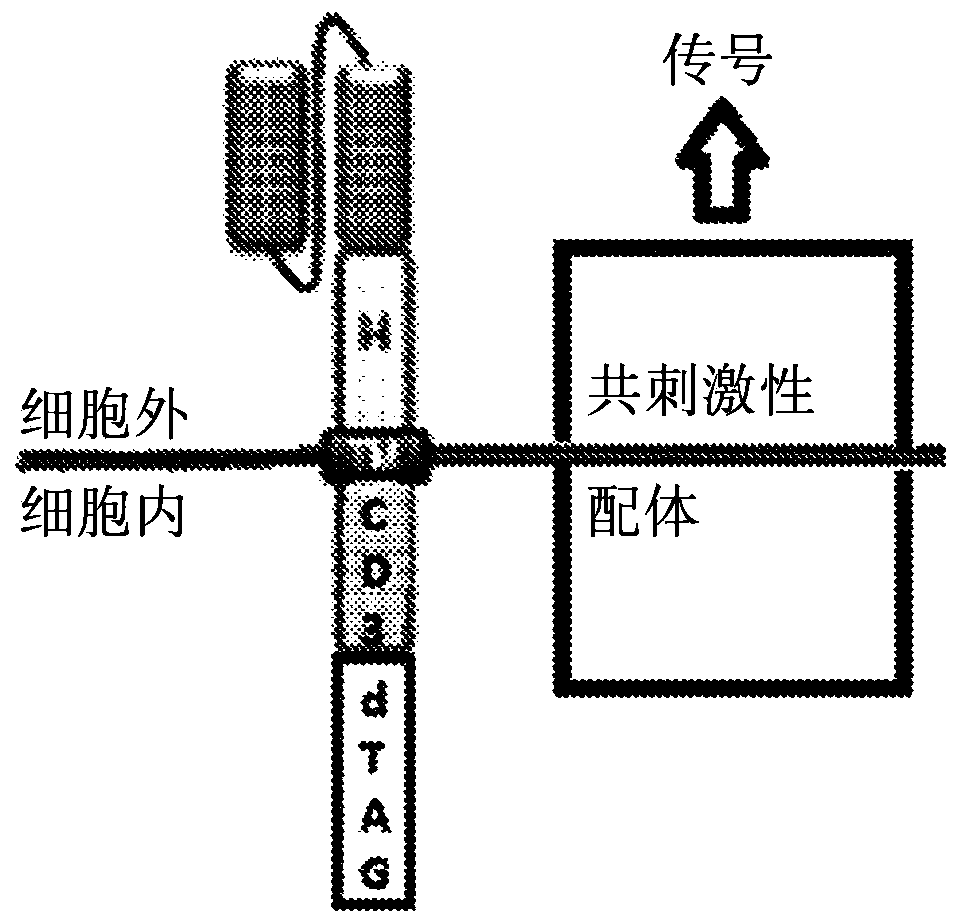
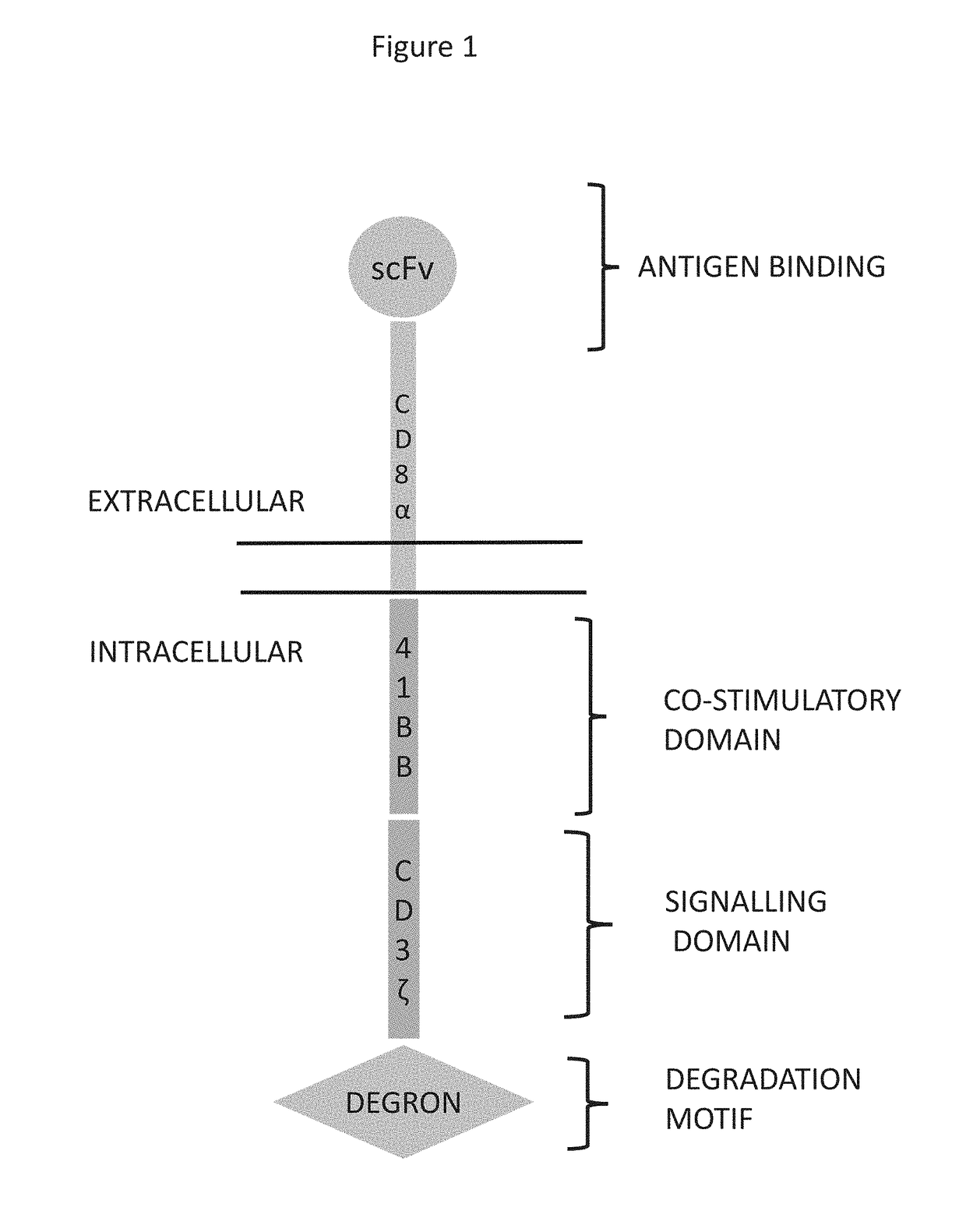
CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTORS (CARs), COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
ActiveUS20180187149A1Reduce in quantityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsCAR - Chimeric antigen receptor
The present invention relates to compositions and methods relating to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) polypeptides and methods relating thereto. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to engineered cells having chimeric antigen receptor polypeptides directed to at least two targets. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to engineered cells having chimeric antigen receptor polypeptides and an enhancer moiety.
Owner:ICELL GENE THERAPEUTICS LLC
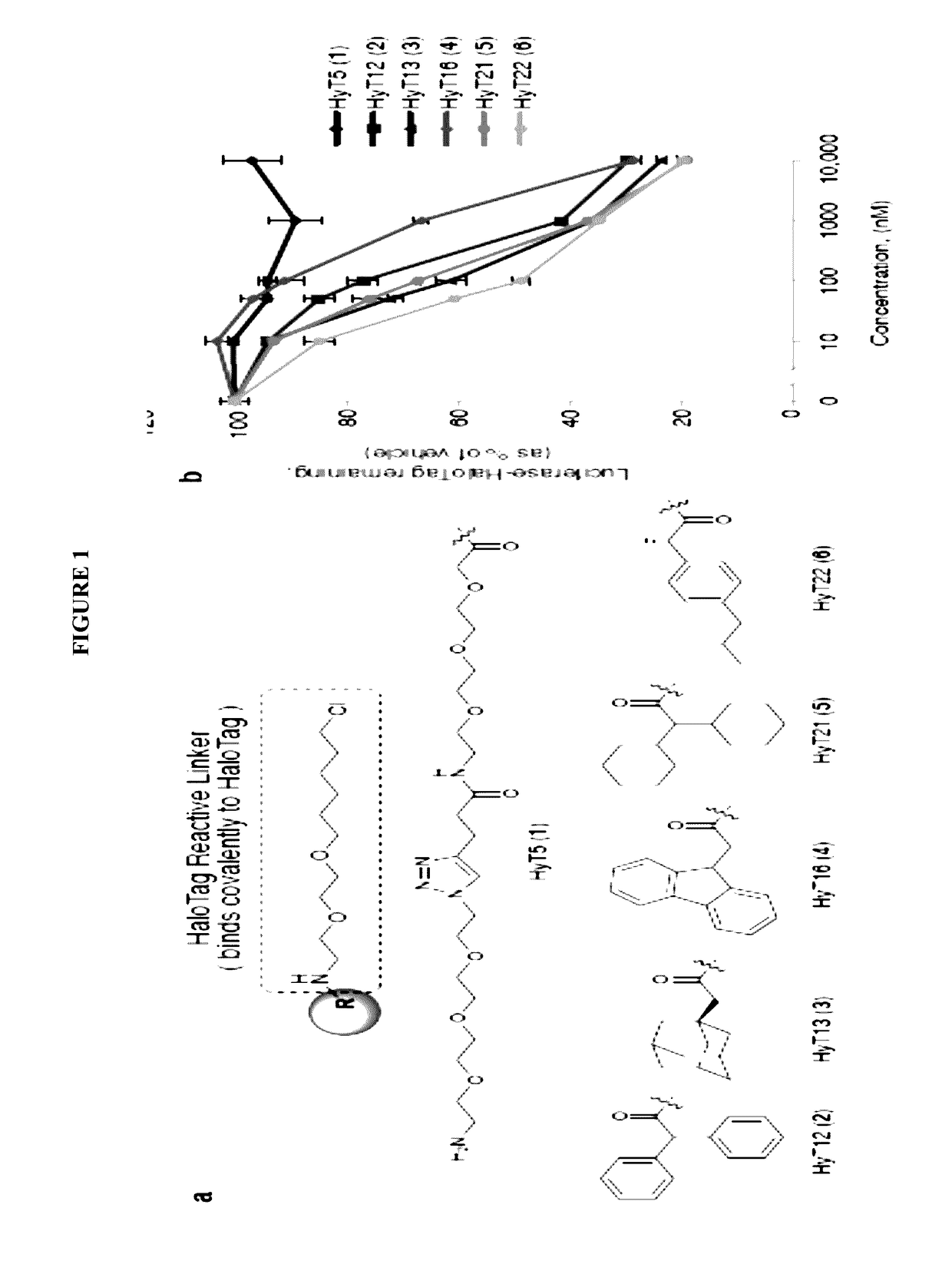
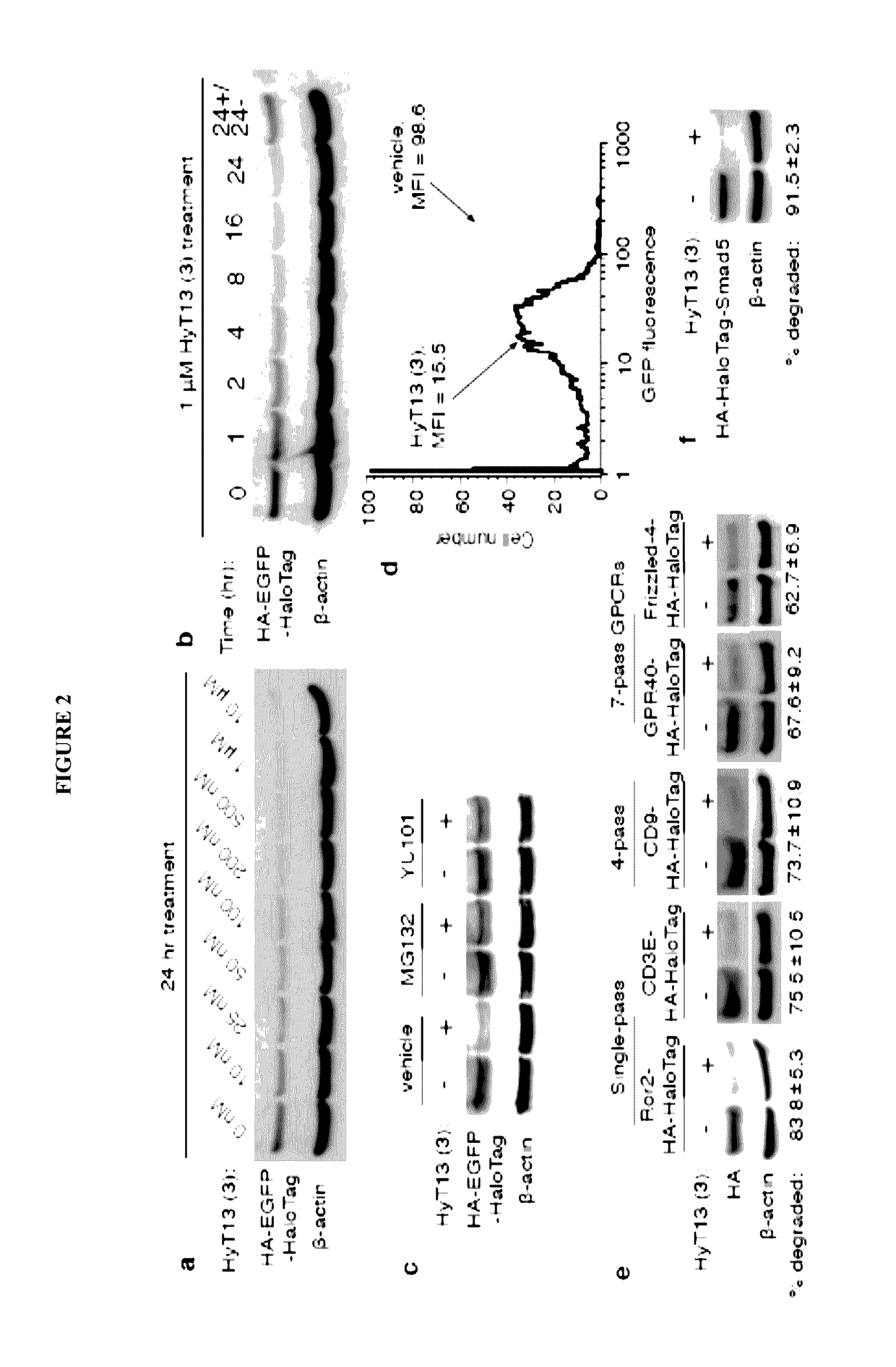
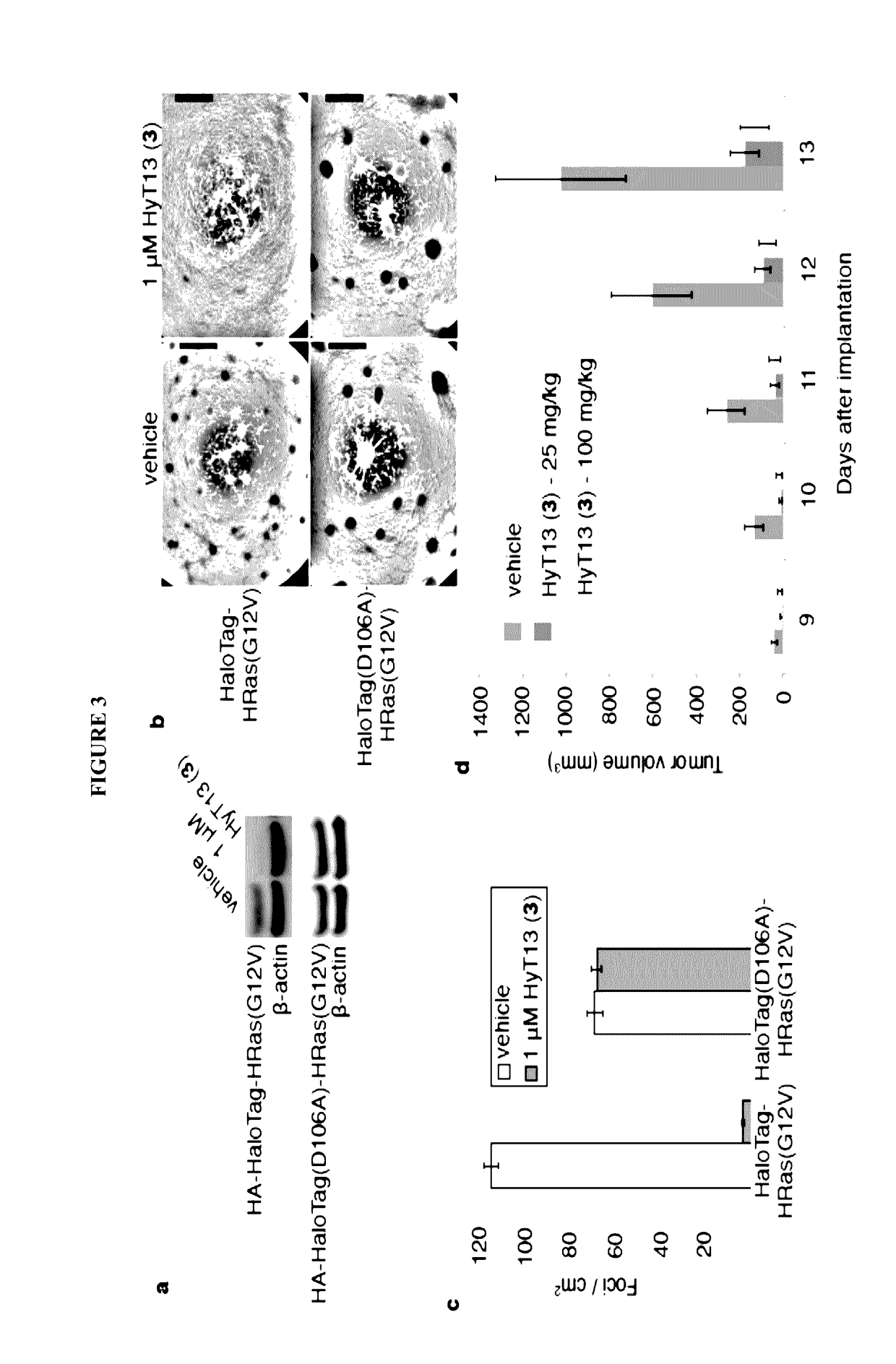
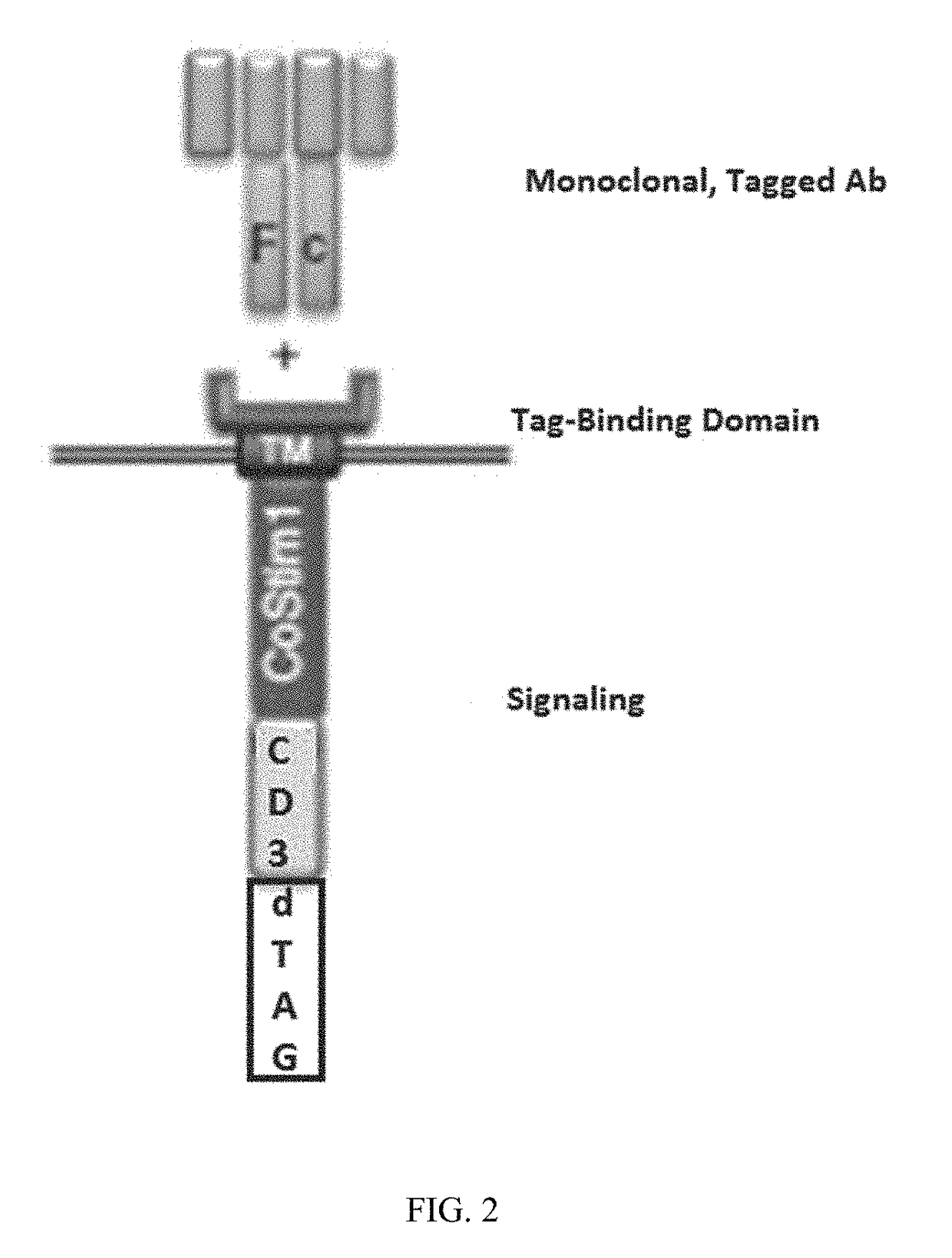
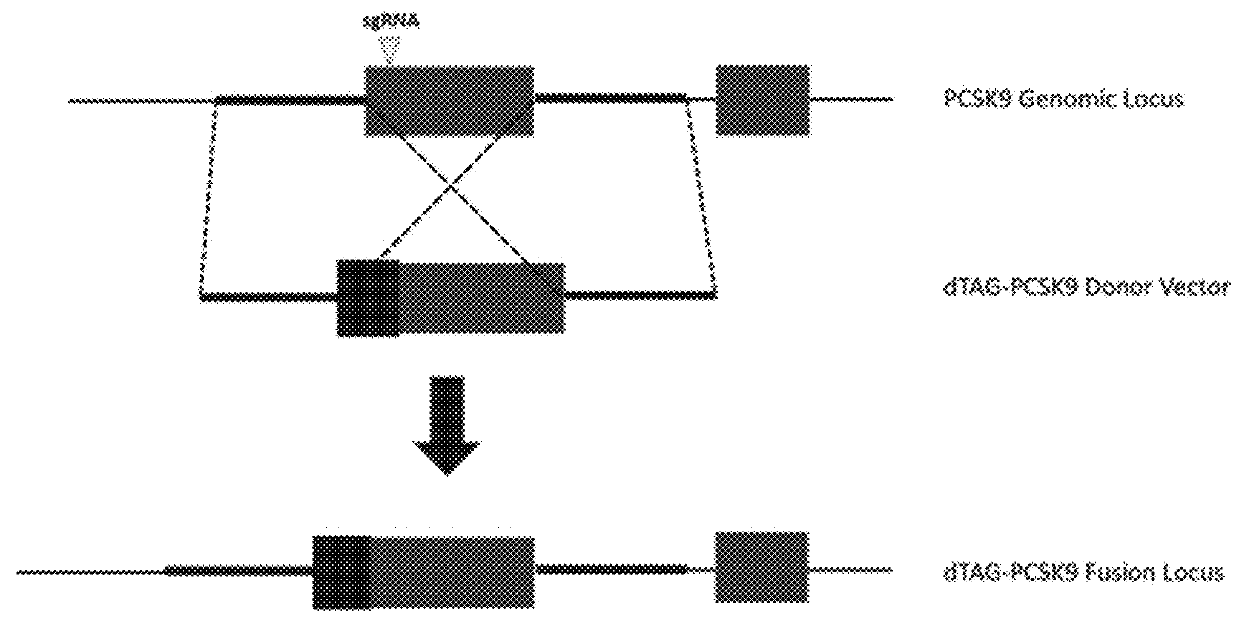
Small-molecule hydrophobic tagging of fusion proteins and induced degradation of same
The present invention includes compounds that are useful in perturbing or disrupting the function of a transmembrane or intracellular protein, whereby binding of the compounds to the transmembrane or intracellular protein induces proteasomal degradation of the transmembrane or intracellular protein. The present invention further includes a method of inducing proteasomal degradation of a transmembrane or intracellular protein. The present invention further includes a method of identifying or validating a protein of interest as a therapeutic target for treatment of a disease state or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
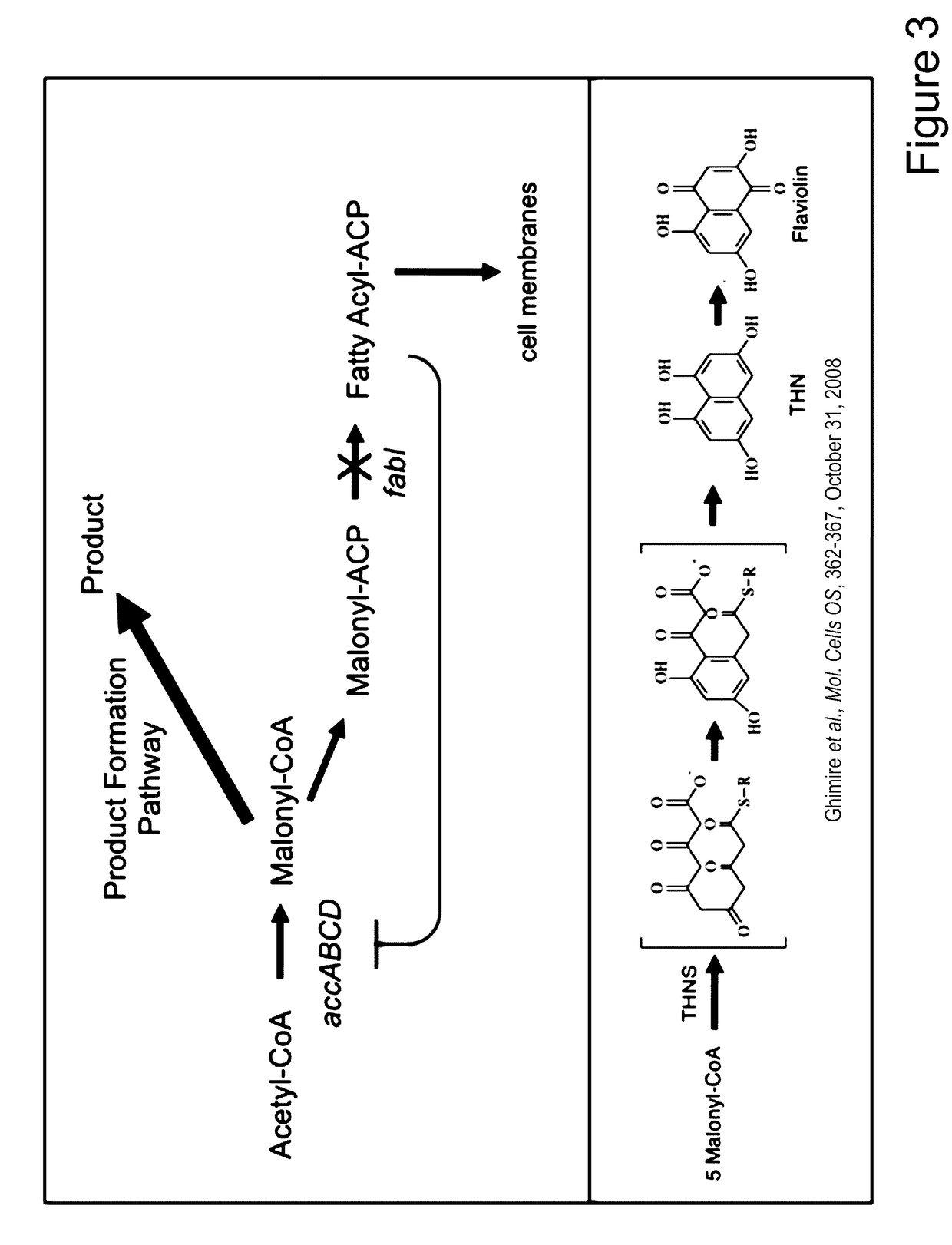
Methods and Molecules for Yield Improvement Involving Metabolic Engineering
ActiveUS20120070870A1Promote degradationPromote cell growthFusion with degradation motifTransferasesBiotechnologyBiology
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
Antibody/drug conjugates and methods of use
ActiveUS20140127241A1Reducing and inhibiting proliferationReducing and inhibiting and growthAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseDrug conjugation
The invention relates to conjugates that bind to targets, methods of using conjugates that bind to targets and methods of treating undesirable or aberrant cell proliferation or hyperproliferative disorders, such as tumors, cancers, neoplasia and malignancies that express a target.
Owner:A28 THERAPEUTICS INC
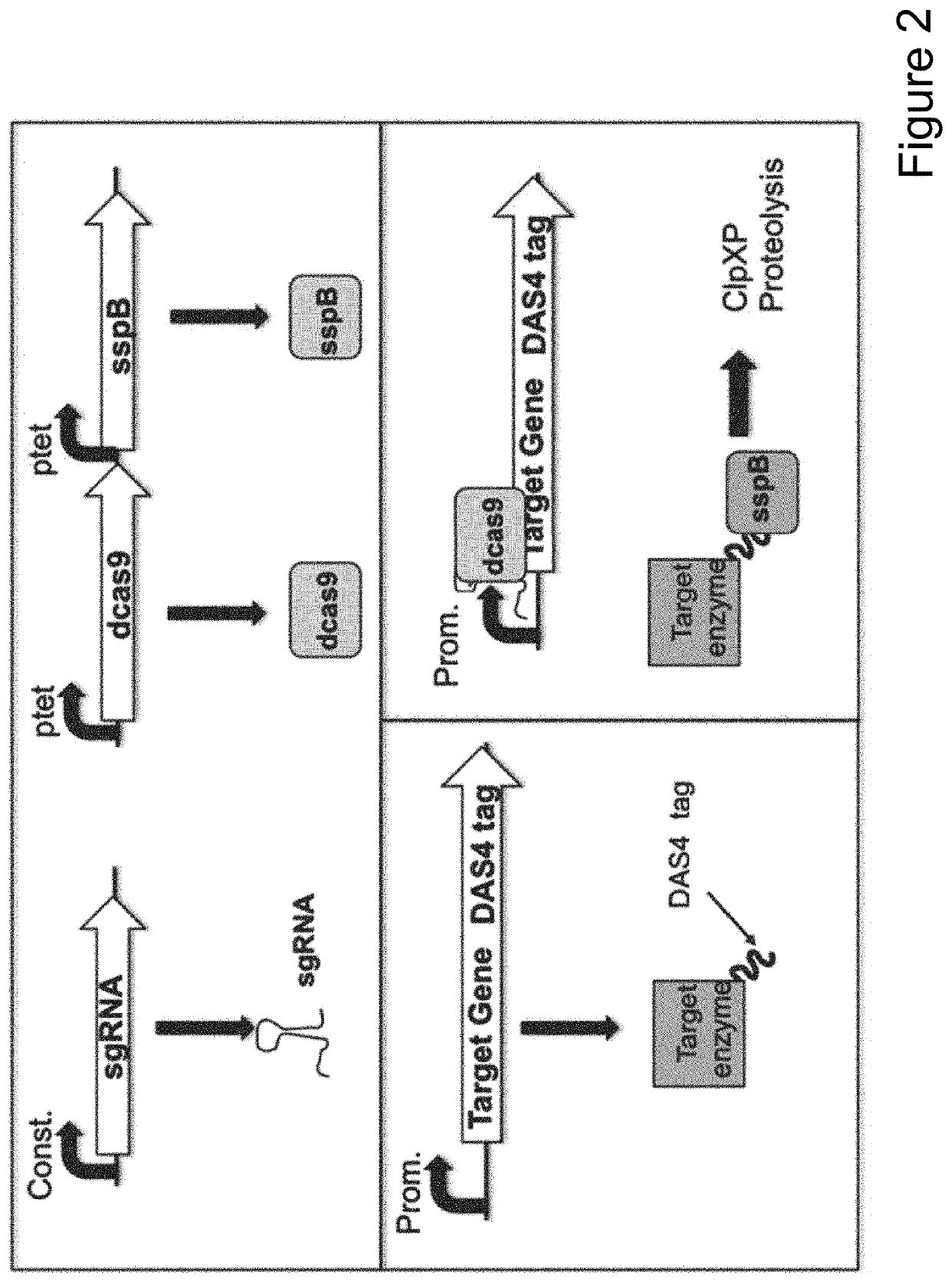
CRISPR-Mediated Genome Engineering for Protein Depletion
InactiveUS20170009242A1Efficient removalMinimal timeHydrolasesFusion with degradation motifCancer researchGenome engineering
The present invention provides compositions and methods for tagging a target gene with a degron (e.g., auxin-inducible degron) in a variety of eukaryotic cells using the CRISPR genome-editing technology. Also provided are cells that have been genetically modified using such compositions and methods.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Targeted protein degradation to attenuate adoptive t-cell therapy associated adverse inflammatory responses
ActiveUS20180169109A1Rapid cell deathOrganic active ingredientsFusion with degradation motifTumor lysis syndromeTumor Syndrome
This invention is in the area of compositions and methods for regulating chimeric antigen receptor immune effector cell, for example T-cell (CAR-T), therapy to modulate associated adverse inflammatory responses, for example, cytokine release syndrome and tumor lysis syndrome, using targeted protein degradation.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Tunable endogenous protein degradation
ActiveUS20180179522A1Negative consequencePermanently editing a gene can be avoidedOrganic active ingredientsFusion with degradation motifProtein targetNucleotide
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Trimerising module
The present invention relates to the design of trimeric polypeptides using polypeptide structural elements derived from the tetranectin protein family, and their use in rational de novo design and production of multi-functional molecules including the application of the multi-functional molecules in protein library technology, such as phage display technology, diagnostic and therapeutic systems, such as human gene therapy and imaging. The trimeric polypeptides being constructed as a monomer polypeptide construct comprising at least one tetranectin trimerising structural element (TTSE) which is covalently linked to at least one heterologous moiety, said TTSE being capable of forming a stable complex with two other TTSEs; or as an oligomer which is comprised of two monomer polypeptide constructs as mentioned above, and which comprises three TTSEs or a multiplum of three TTSEs, or which is comprised of three monomer polypeptide constructs.
Owner:ANAPHORE INC +1
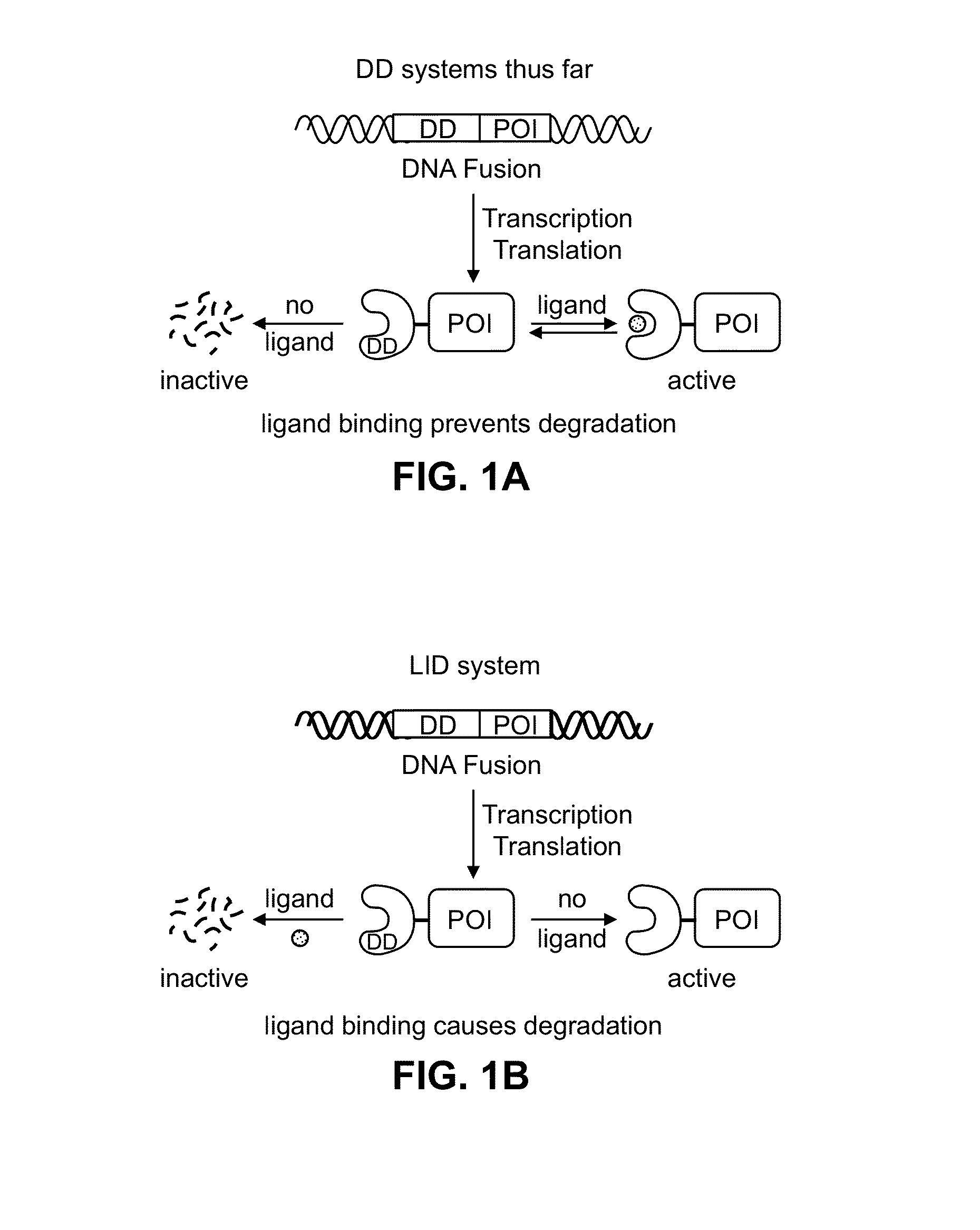
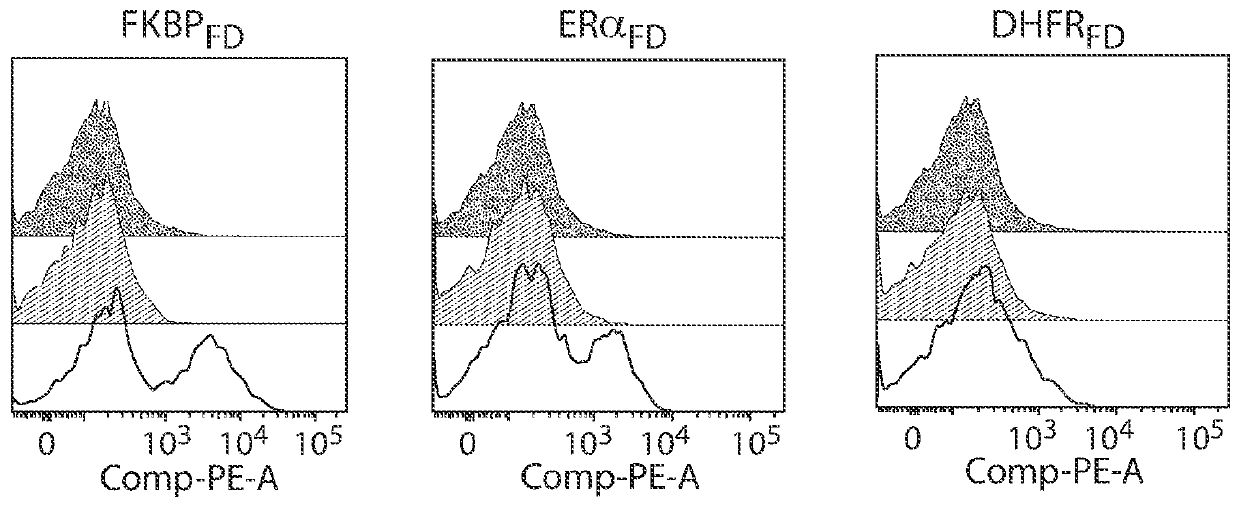
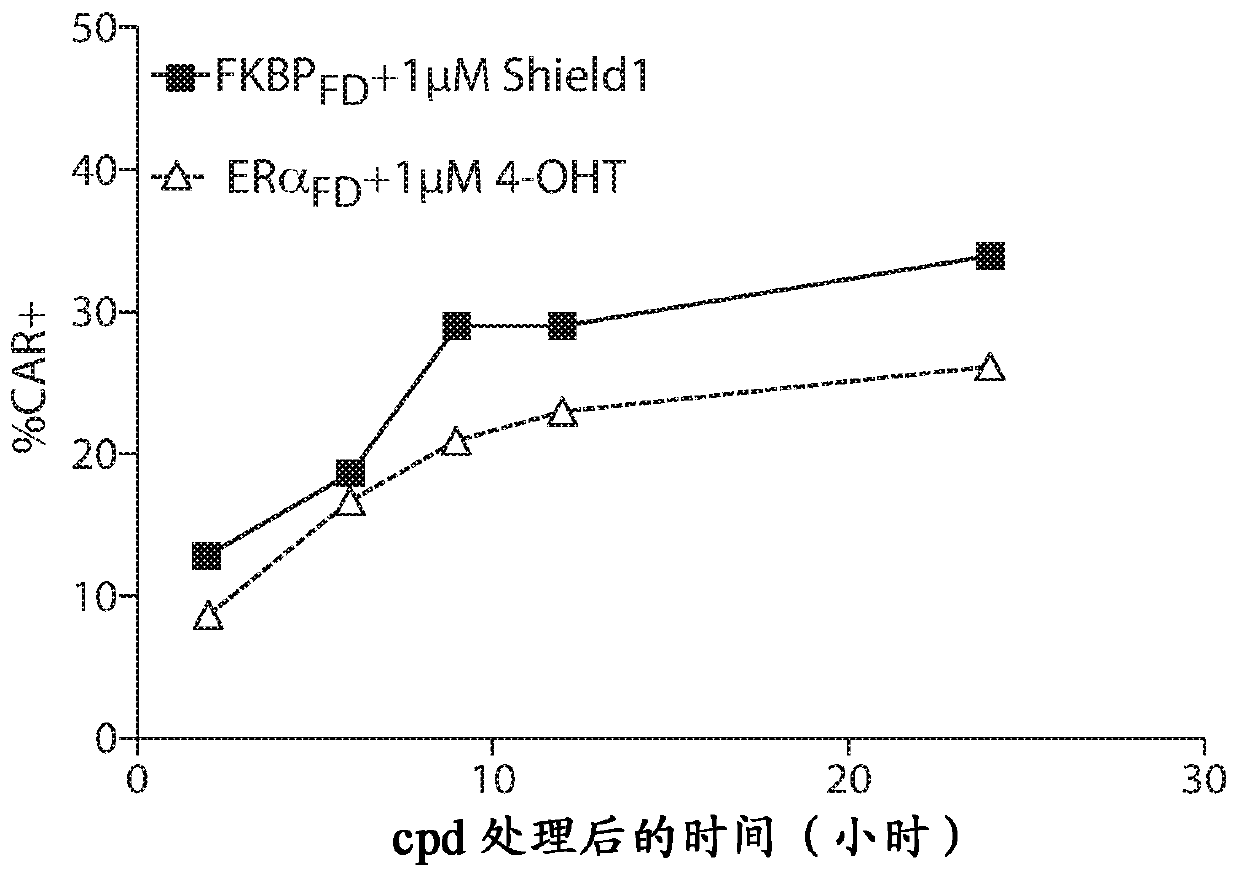
Estrogen-receptor based ligand system for regulating protein stability
Disclosed herein are systems, methods and compositions for rapidly and reversibly destabilizing a target protein in vitro or in vivo, in the presence or absence of a cell-permeable, synthetic molecule or ligand.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
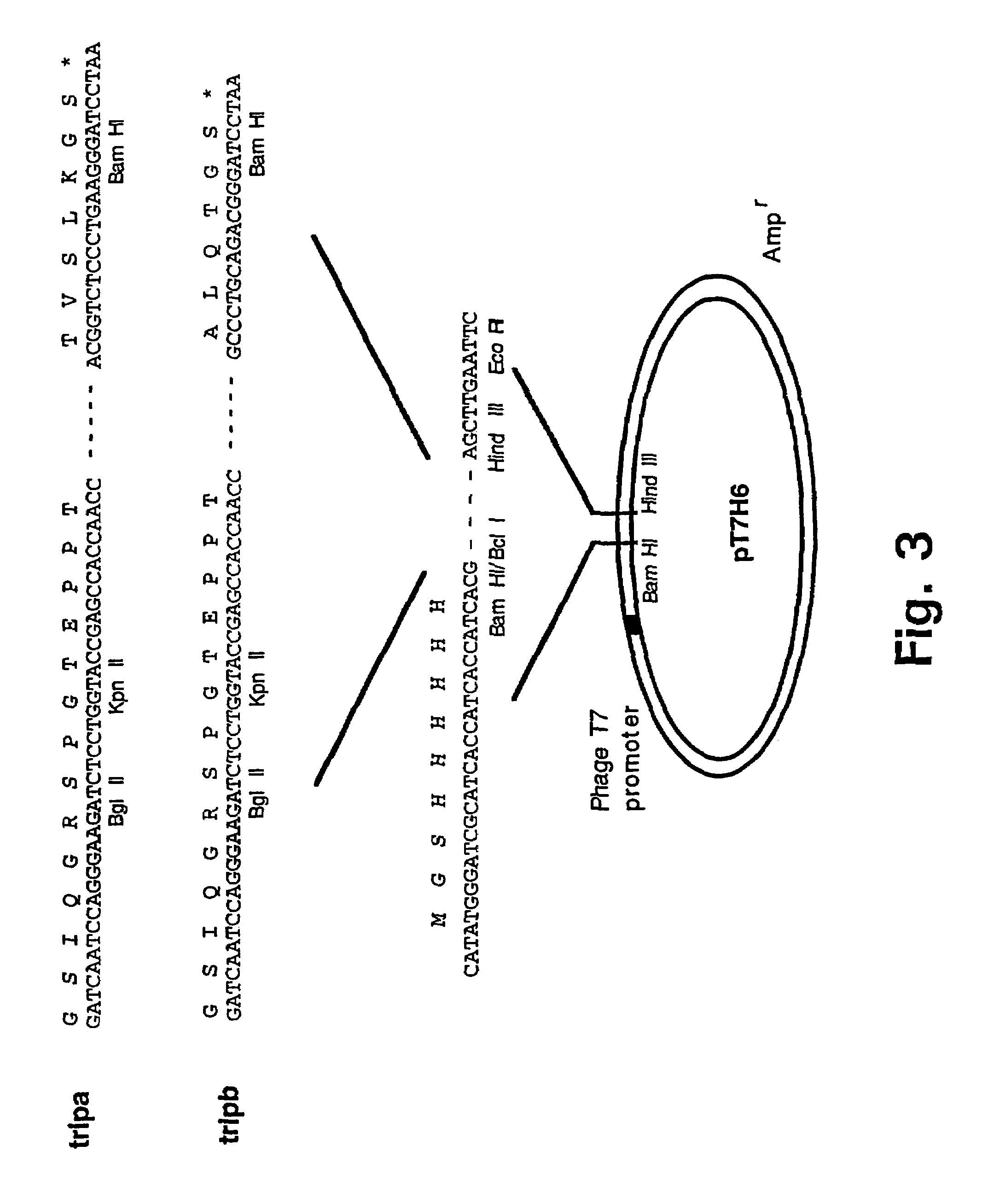
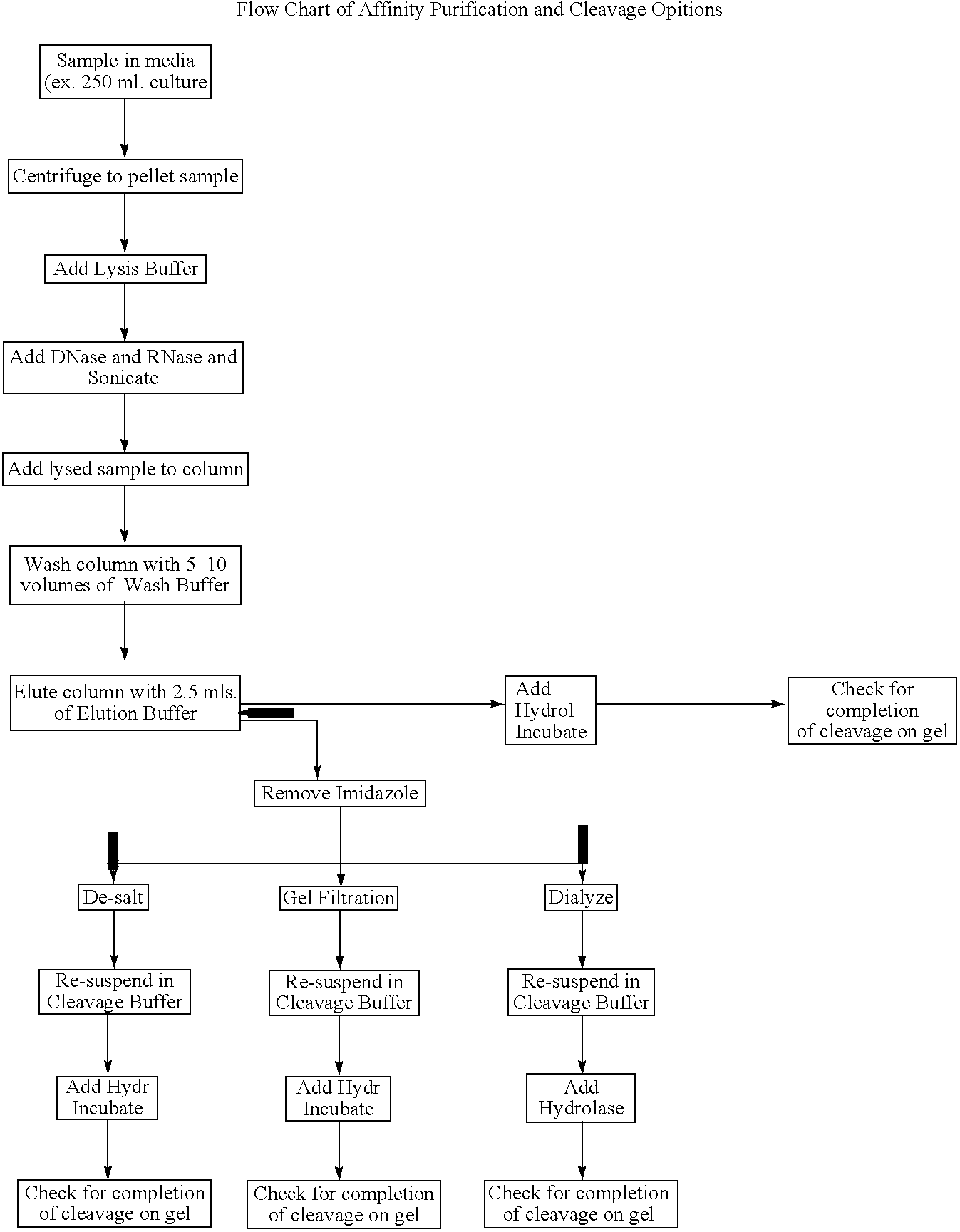
Methods and compositions for protein expression and purification
InactiveUS7060461B2Increase secretion levelIncrease secretionFungiBacteriaHeterologousPurification methods
Methods for enhancing expression levels and secretion of heterologous fusion proteins in a host cell are disclosed.
Owner:LIFESENSORS INC
CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTORS (CARs), COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
ActiveCN107849112APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to compositions and methods relating to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) polypeptides and methods relating thereto. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to engineered cells having chimeric antigen receptor polypeptides directed to at least two targets. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to engineered cells having chimeric antigen receptorpolypeptides and an enhancer moiety.
Owner:ICELL GENE THERAPEUTICS LLC +5
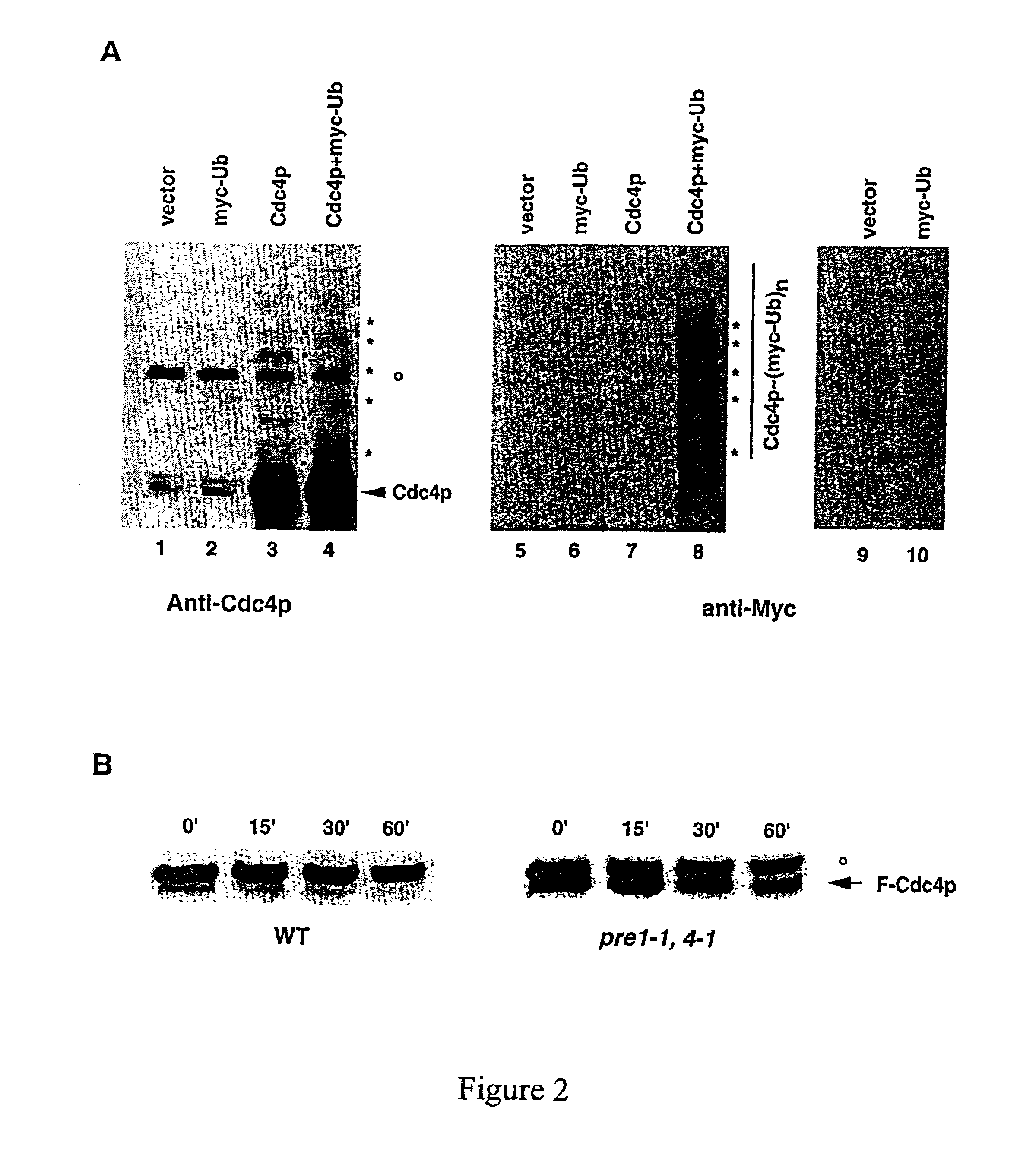
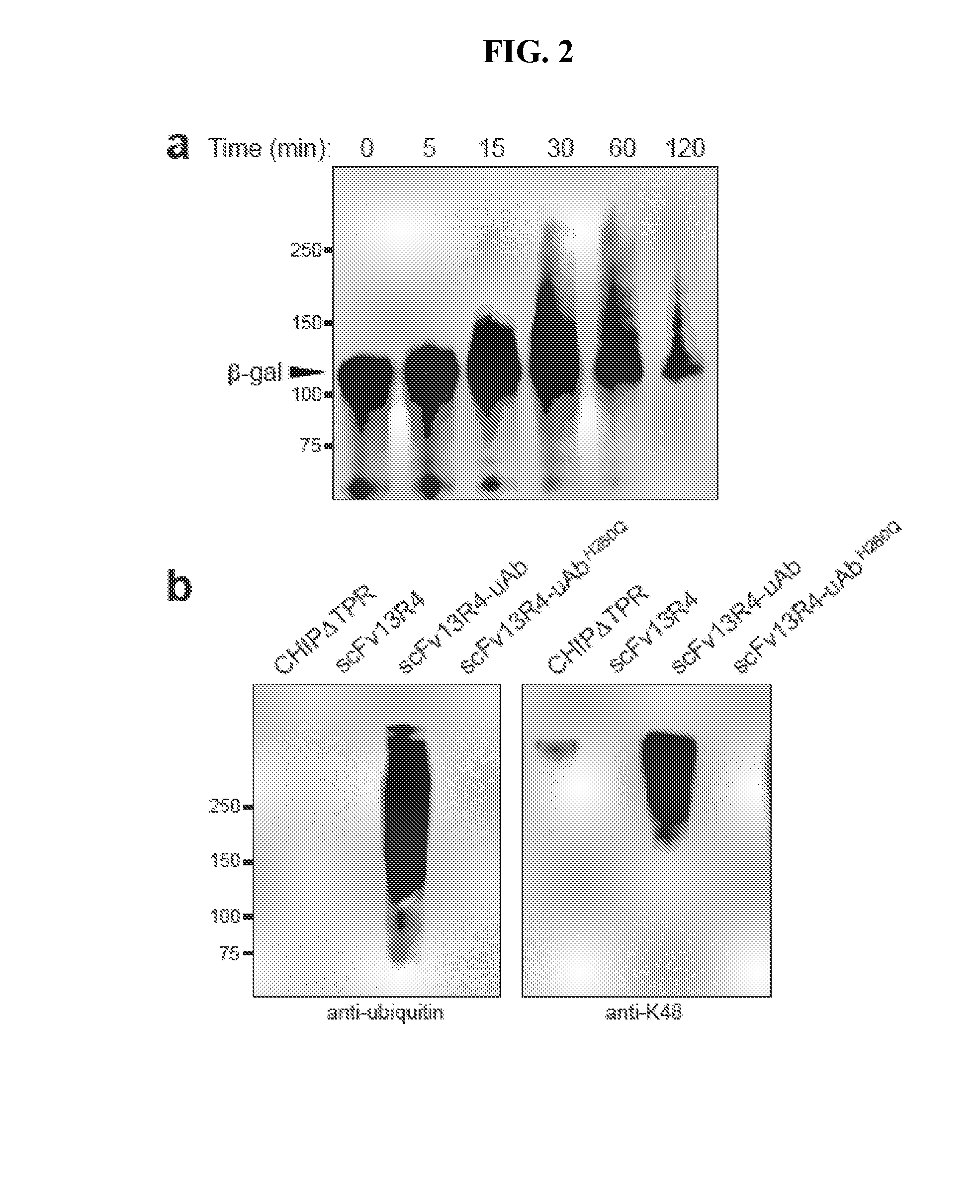
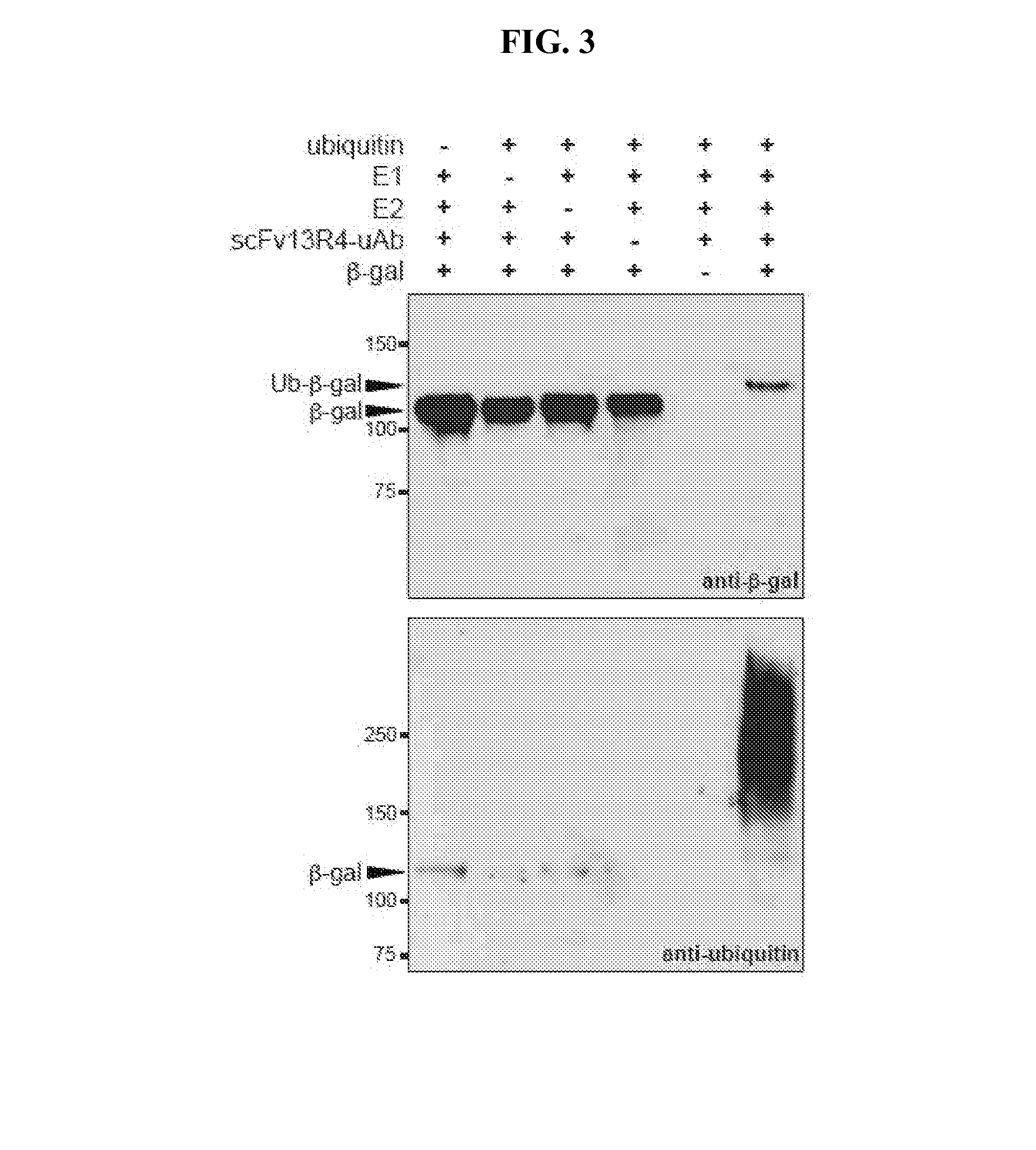
Targeted proteolysis by recruitment to ubiquitin protein ligases
InactiveUS7223556B1Decrease and increases activityReduce ubiquitinationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusion with degradation motifUbiquitin-Protein LigasesProteolysis
The present invention relates to methods and reagents for targeting proteolysis of a polypeptide by cis or trans association with a ubiquitin protein ligase, and further provides methods and reagents for inhibiting the ubiquitination and proteolysis of cellular proteins which are recognized by a ubiquitin protein ligase.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
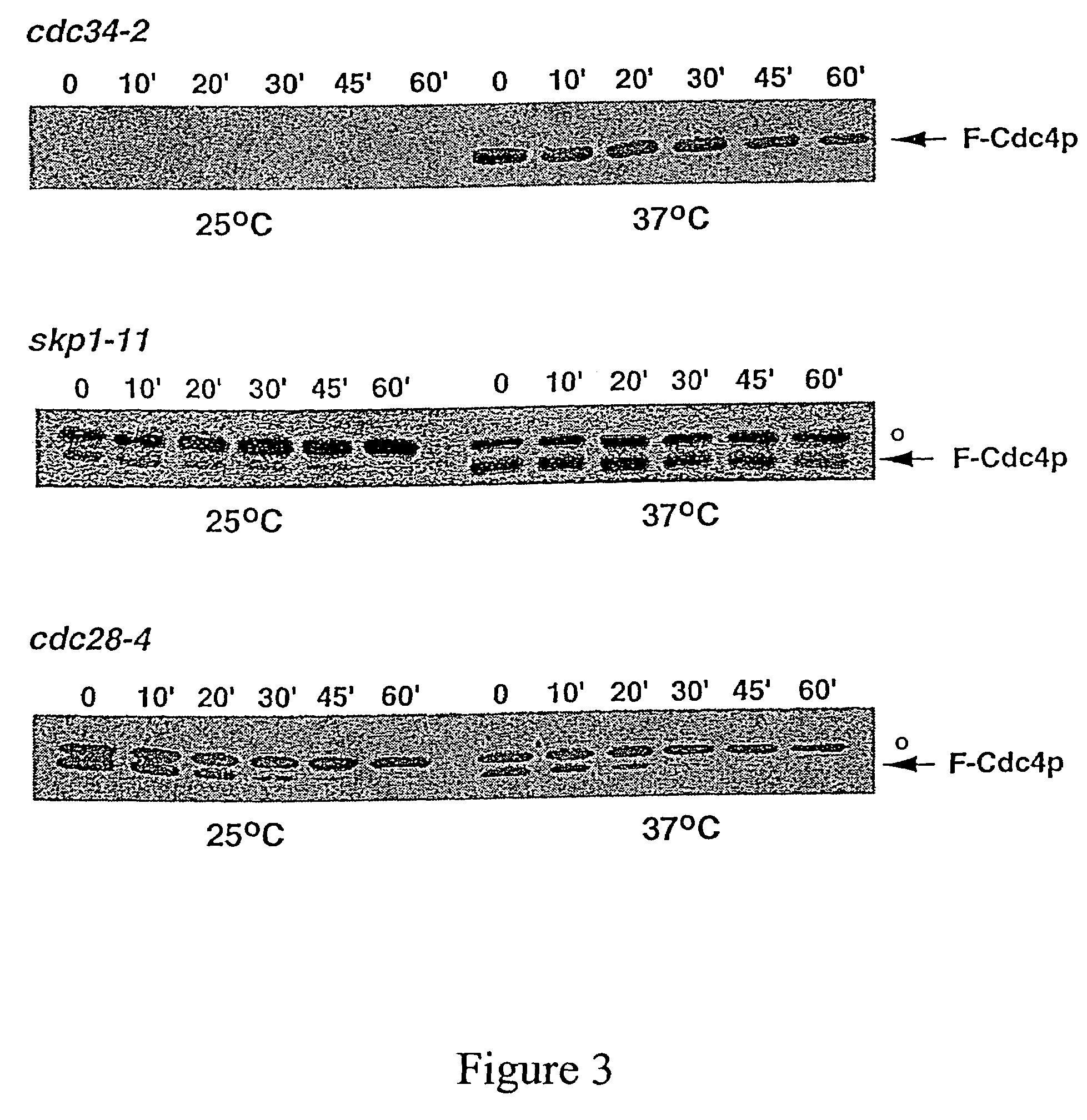
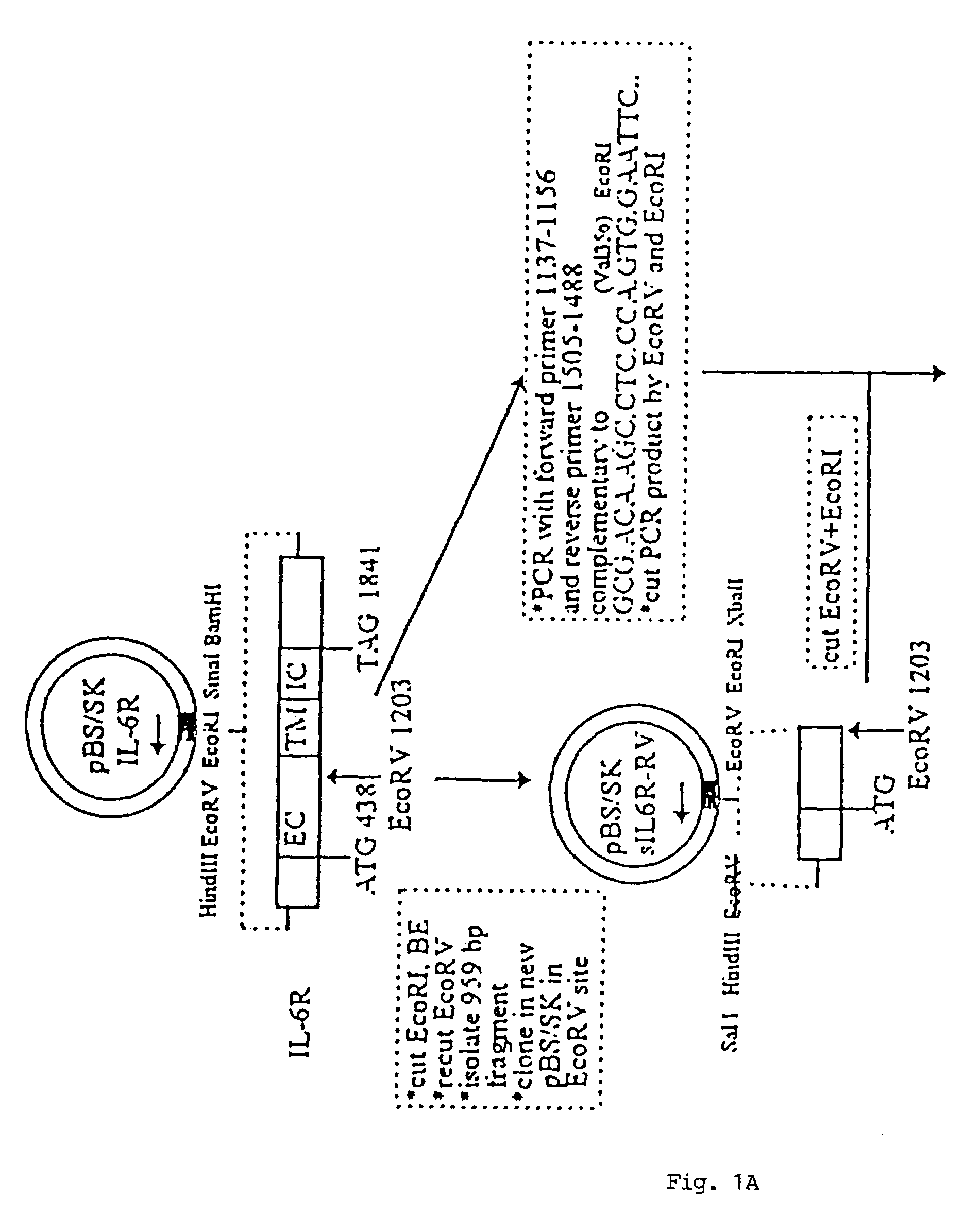
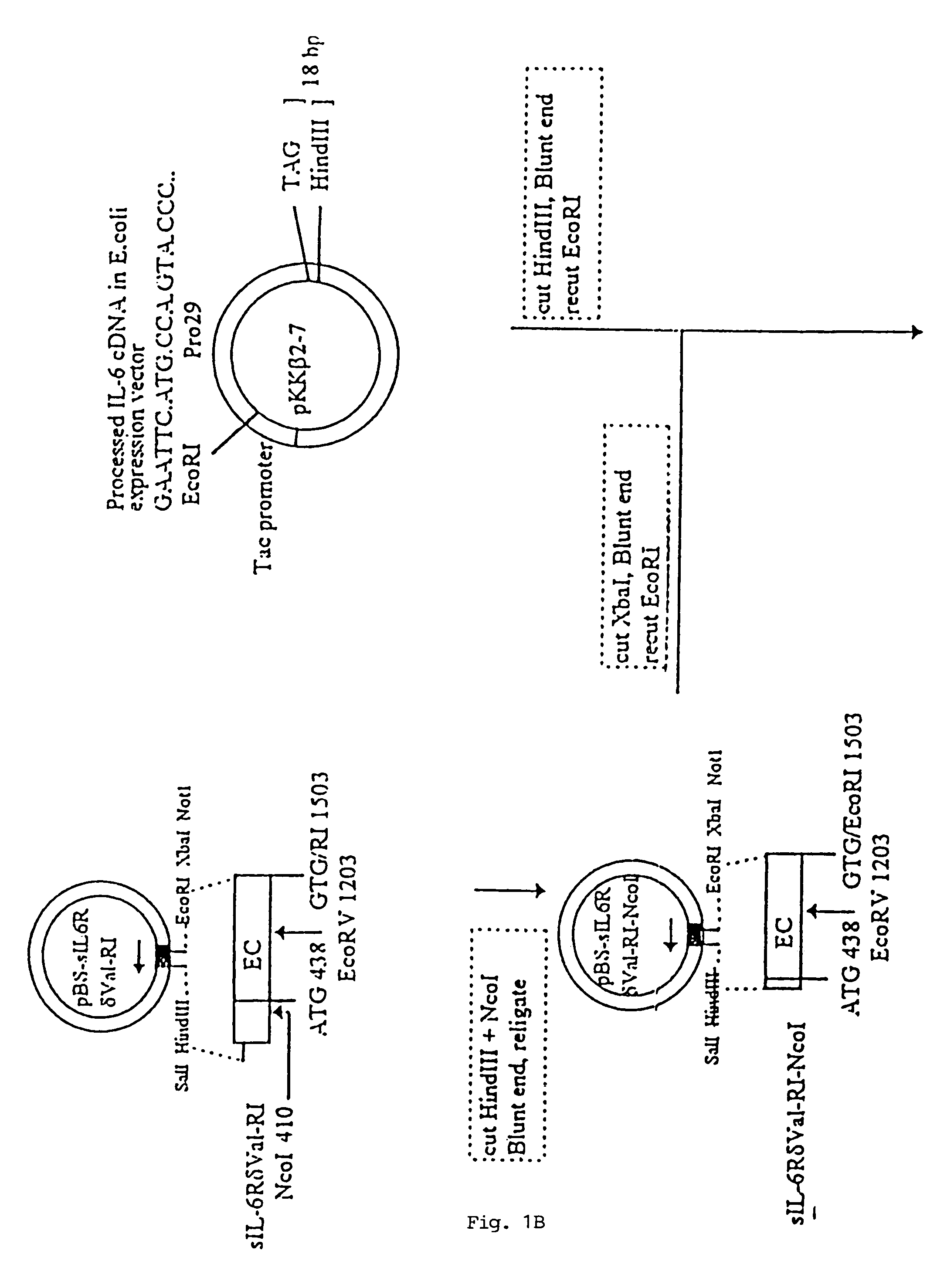
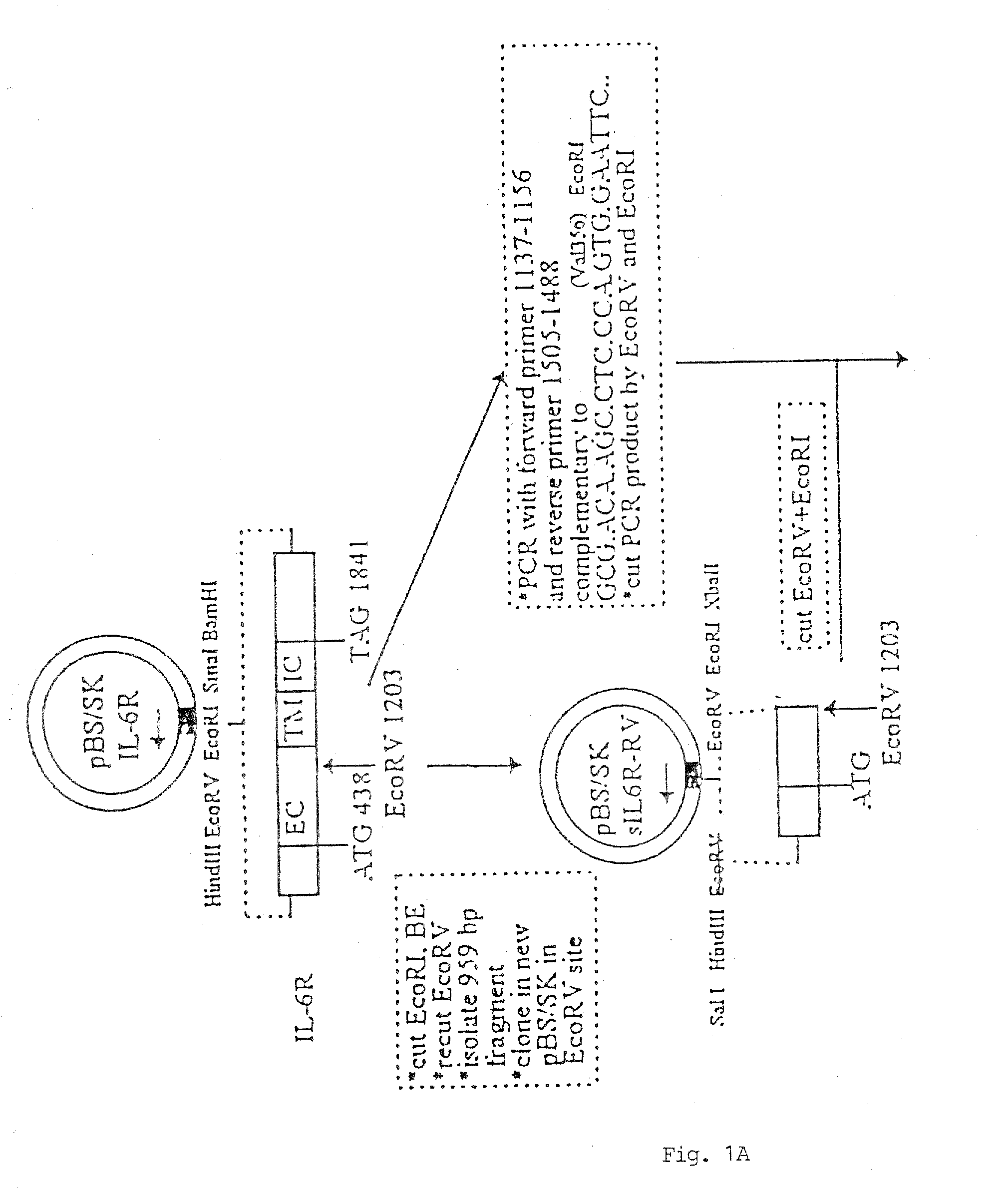
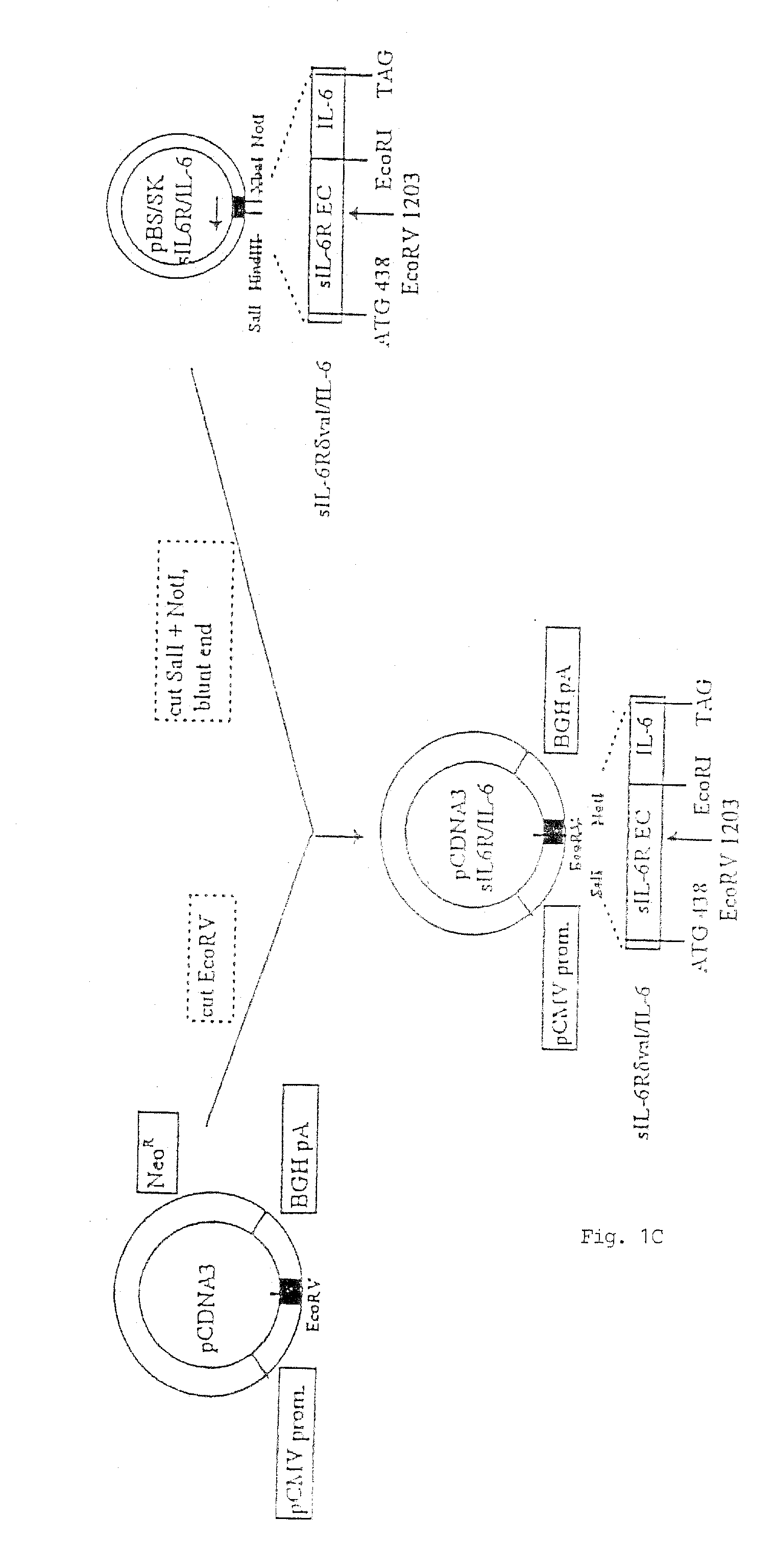
Chimeric interleukin-6 soluble receptor/ligand proteins
InactiveUS7198781B1Risk minimizationReduce potential immunogenicityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseInterleukin 6
Chimeric proteins constructed from the fusion of the naturally occurring form of the soluble IL-6 receptor and IL-6 which are useful for treatment of cancer and liver disorders, enhancement of bone marrow transplantation, and treatment of other IL-6 related conditions are provided.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Enhanced secretion of a polypeptide by a microorganism
InactiveUS6846653B2Increase productionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaMicroorganismSecreted substance
Described herein are methods for the enhanced production of secreted proteins. The secretion of a protein of interest having a substantially non-polar carboxy tail is enhanced by the placement of charged amino acid residues at the carboxy terminus either by adding to the native peptide or by replacing, i.e., substituting, the terminal residues of the native peptide.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Chimeric Interleukin-6 Soluble Receptor/Ligand Protein, Analogs Thereof and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070172455A1Risk minimizationReduce potential immunogenicityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseInterleukin 6
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Engineering of leader peptides for the secretion of recombinant proteins in bacteria
InactiveUS7419783B2Increased green fluorescent protein fluorescenceImproved protein exportBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides methods of isolating of leader peptides capable of directing export of heterologous proteins from the bacterial cytoplasm. The methods rely on the screening of libraries of putative leader peptides or of leader peptide mutants for sequences that allow rapid export and thus can rescue a short-lived reporter protein from degradation in the cytoplasm. The mutant leader peptides identified herein are shown to confer significantly higher steady state levels of export not only for short-lived reporter protein but also for other stable, long-lived proteins. These leader peptides can be used to direct or enhance protein secretion. The present invention further discloses methods for the export of cytoplasmically folded protein via the Tat pathway. Proteins having disulfide bonds are first folded within the cytoplasm in suitable oxidizing mutant strains. Such cytoplasmically pre-folded proteins containing disulfide bonds are then exported via the Tat pathway.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Peptide directed protein knockdown
ActiveUS20150266935A1Rapid and reversible knock-downReduced expression levelNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein target
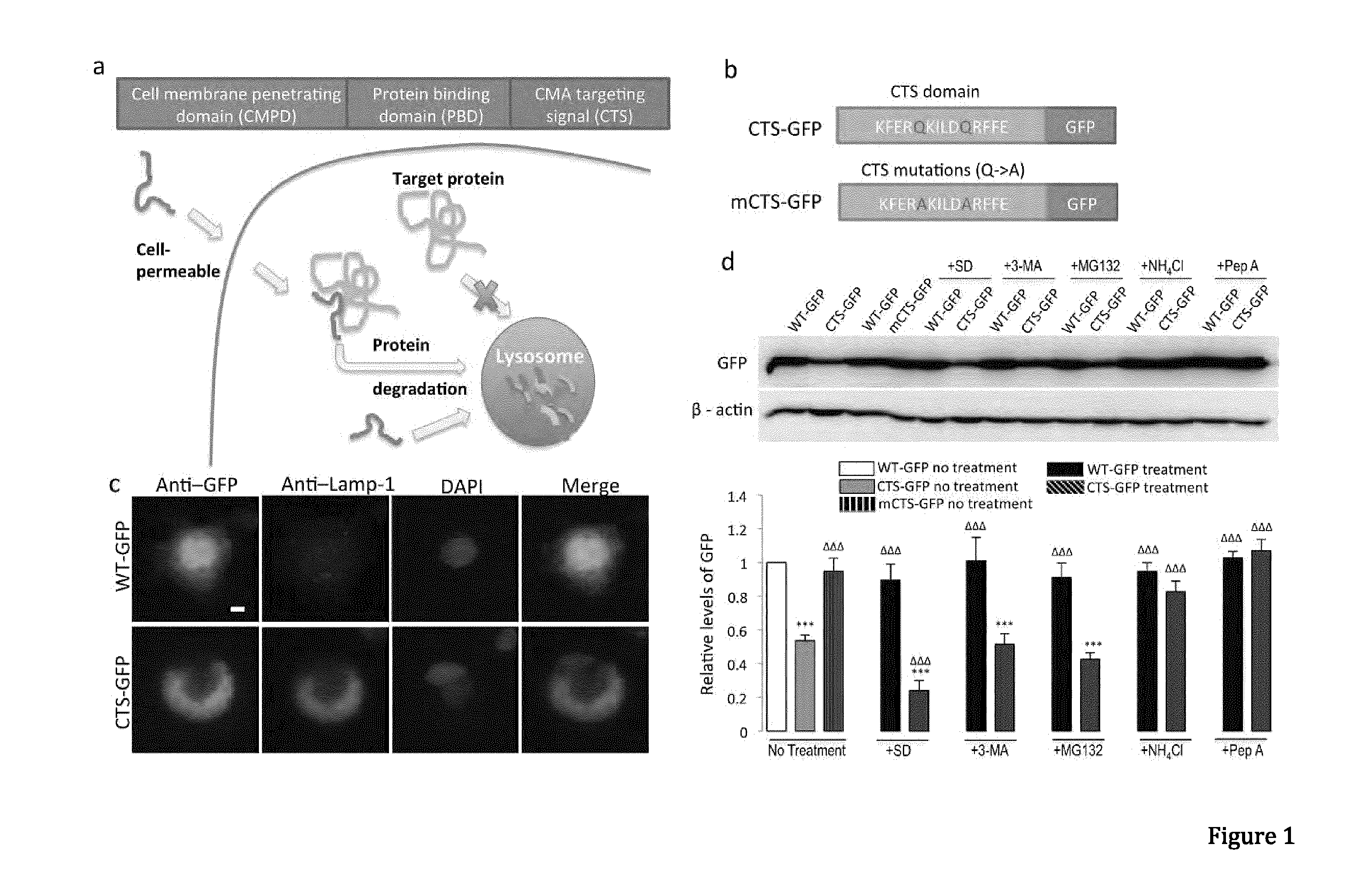
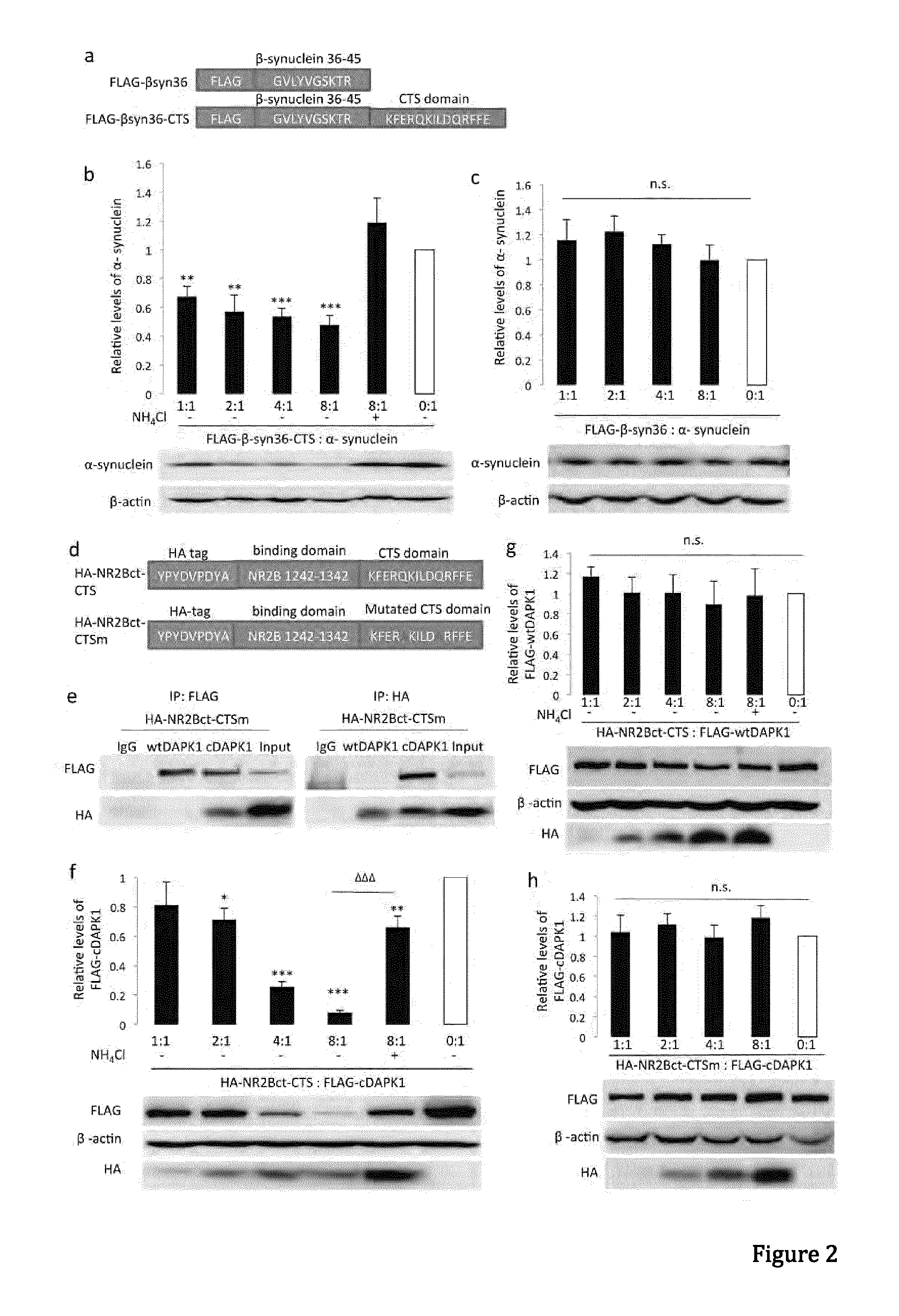
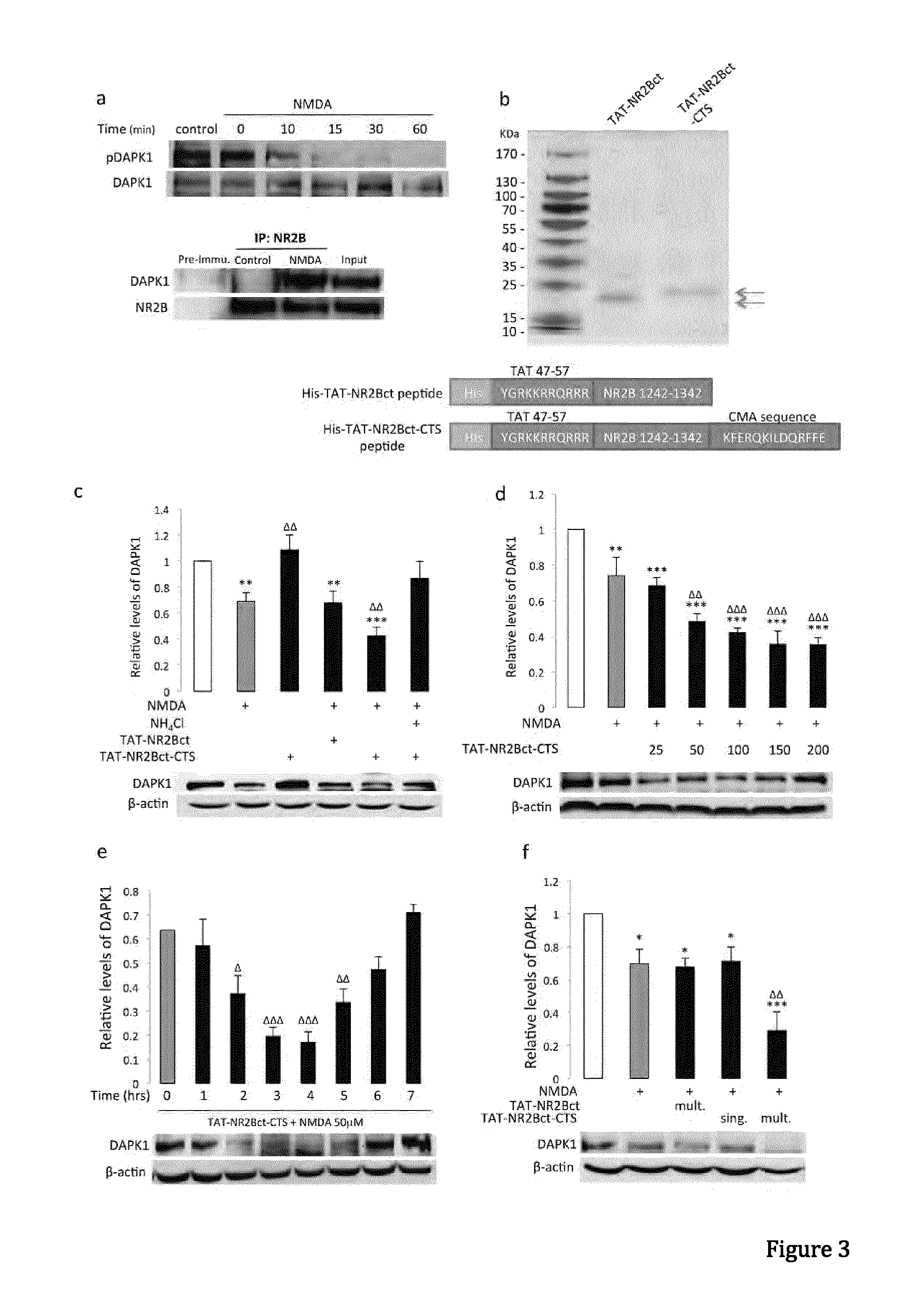
In one aspect, the invention provides a peptide comprising a chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA)-targeting signal domain; a protein-binding domain that selectively binds to a target cytosolic protein; and a cell membrane penetrating domain (CMPD). In another aspect, the invention provides methods for reducing the intracellular expression level of an endogenous target protein in vitro and in an animal, wherein the method involves administration of the peptide. Methods are also provided for treating a pathological condition in an animal, the methods comprising administering the peptide to the animal. In one embodiment, the pathological condition is a neurodegenerative disease. In another embodiment of the invention, the target cytosolic protein is death associated protein kinase 1 and the CMPD is protein transduction domain of the HIV-1 Tat protein.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Method of producing virus-like particles of picornavirus using a small-ubiquitin-related fusion protein expression system
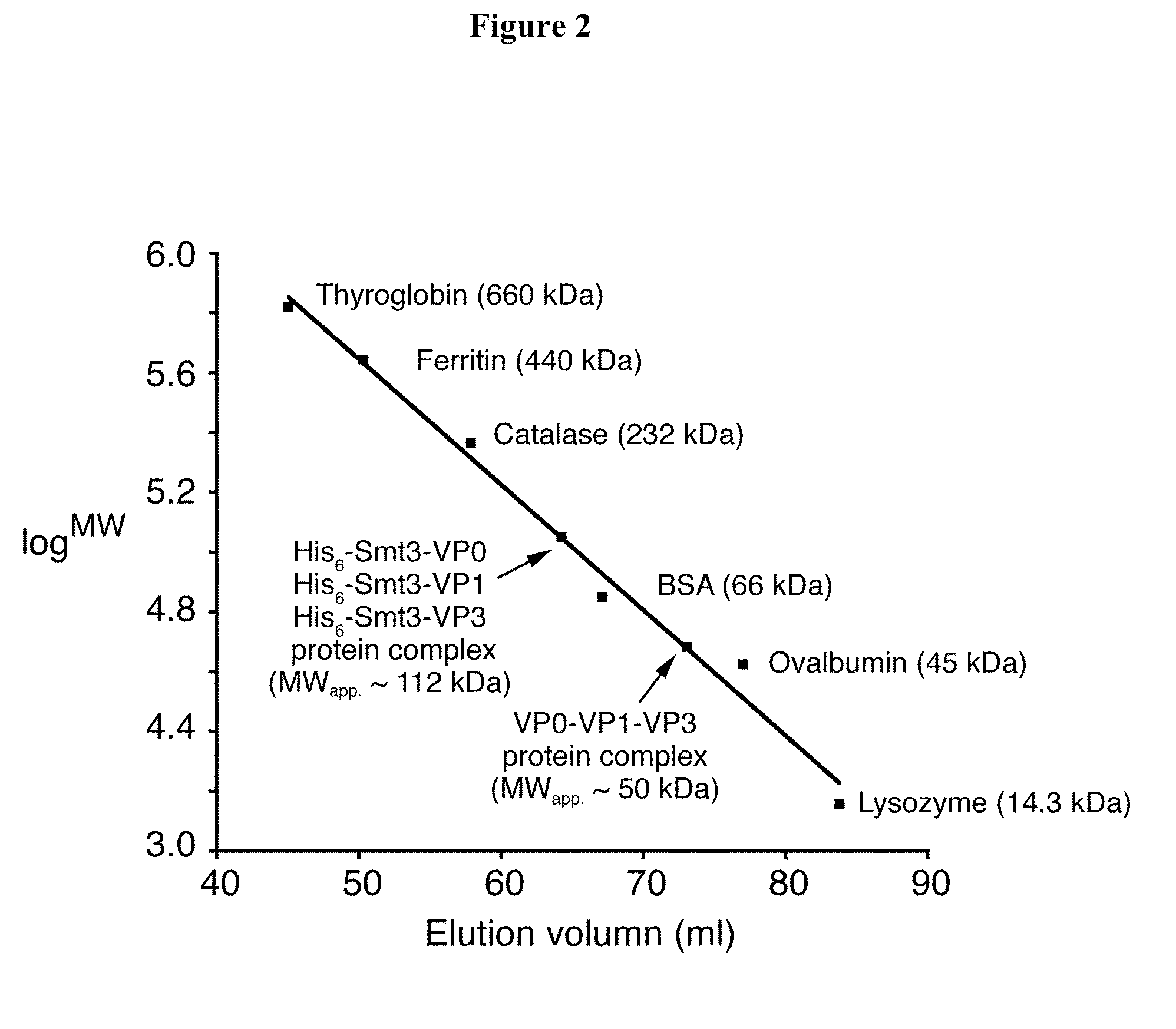
A method for producing picornaviral capsid protein complexes (e.g., picornavirus like particles) in E. coli using a small-ubiquitin-related fusion protein expression system and an E. coli strain used in practicing this method. Also disclosed is use of the picornaviral capsid protein complexes like thus prepared for eliciting immune responses.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Methods and compositions for protein expression and purification
InactiveUS7220576B2Increase secretion levelIncrease secretionBacteriaFusion with degradation motifHeterologousPurification methods
Methods for enhancing expression levels and secretion of heterologous fusion proteins in a host cell are disclosed.
Owner:LIFESENSORS INC
Rapidly cleavable SUMO fusion protein expression system for difficult to express proteins
A recombinant expression system for the expression of a poly amino acid, peptide or protein is provided. The poly amino acid of interest is expressed as a fusion protein that includes an amino acid sequence recognized and cleaved by a Ulp1 protease. The amino acid sequence joined to the poly amino acid of interest is preferably from a SUMO (small ubiquitin-like molecule) protein. This sequence imparts favorable solubility and refolding properties to the fusion protein. A purification tag may also be incorporated into the fusion protein for ease of isolation. The Ulp1 protease used to cleave the fusion protein may be the Ulp1 protease or the active Ulp1 protease fragment, Ulp1(403-621). The Ulp1 protease rapidly and specifically cleaves the fusion proteins of the invention at the Ulp1 cleavage site. The amino acid sequence recognized by a Ulp1 protease is cleaved asymetrically to leave only an N-terminal serine joined to the poly amino acid of interest. This recombinant expression system is particularly advantageous for expression and rapid and highly specific cleavage and purification of poly amino acids that have low solubilities or are difficult to express in other systems.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Regulating chimeric antigen receptors
PendingCN111386263APeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTumor lysis syndromeProtein target
This invention is in the area of compositions and methods for regulating chimeric antigen receptor immune effector cell, for example T-cell (CAR-T), therapy to modulate associated adverse inflammatoryresponses, for example, cytokine release syndrome and tumor lysis syndrome, using targeted protein degradation.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
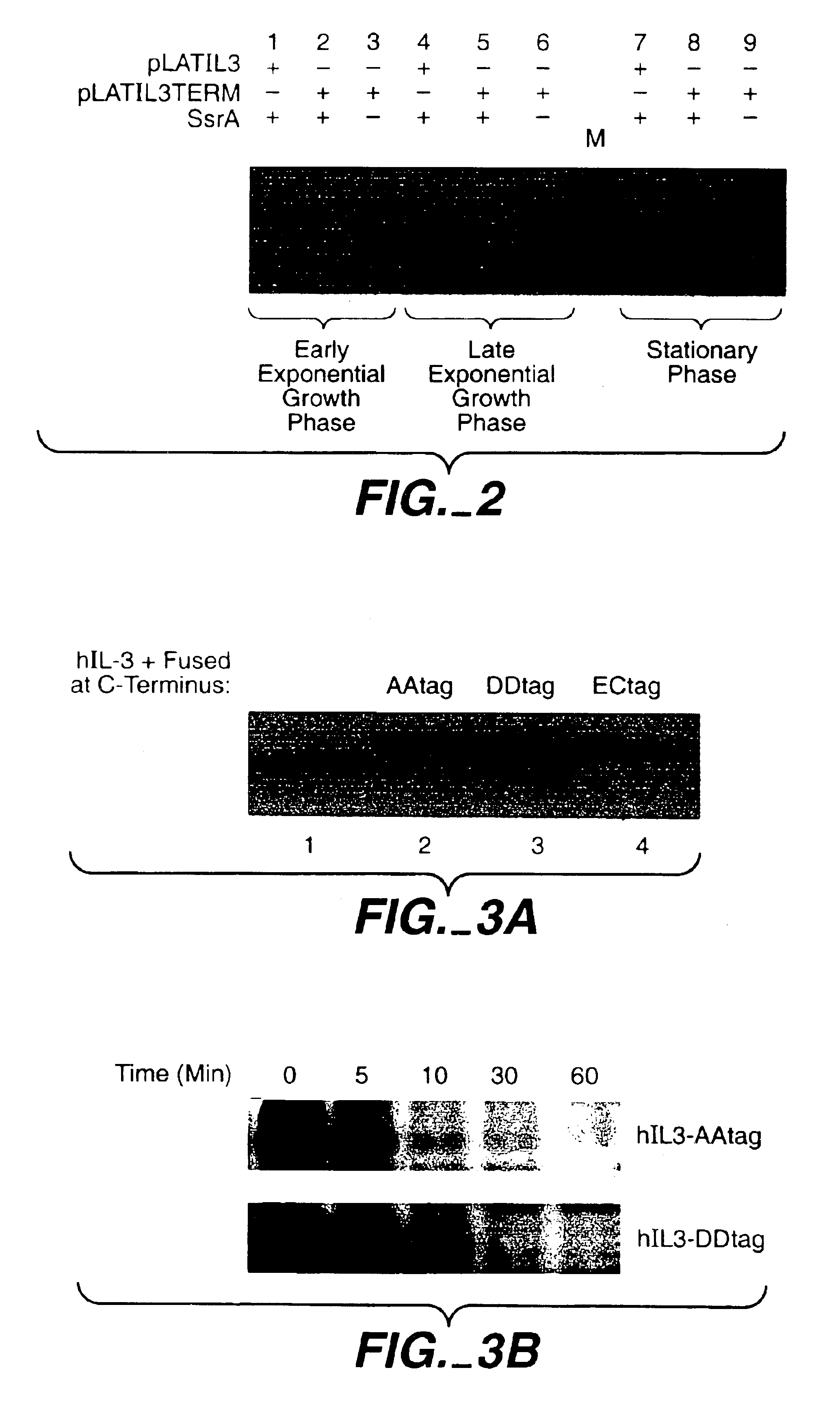
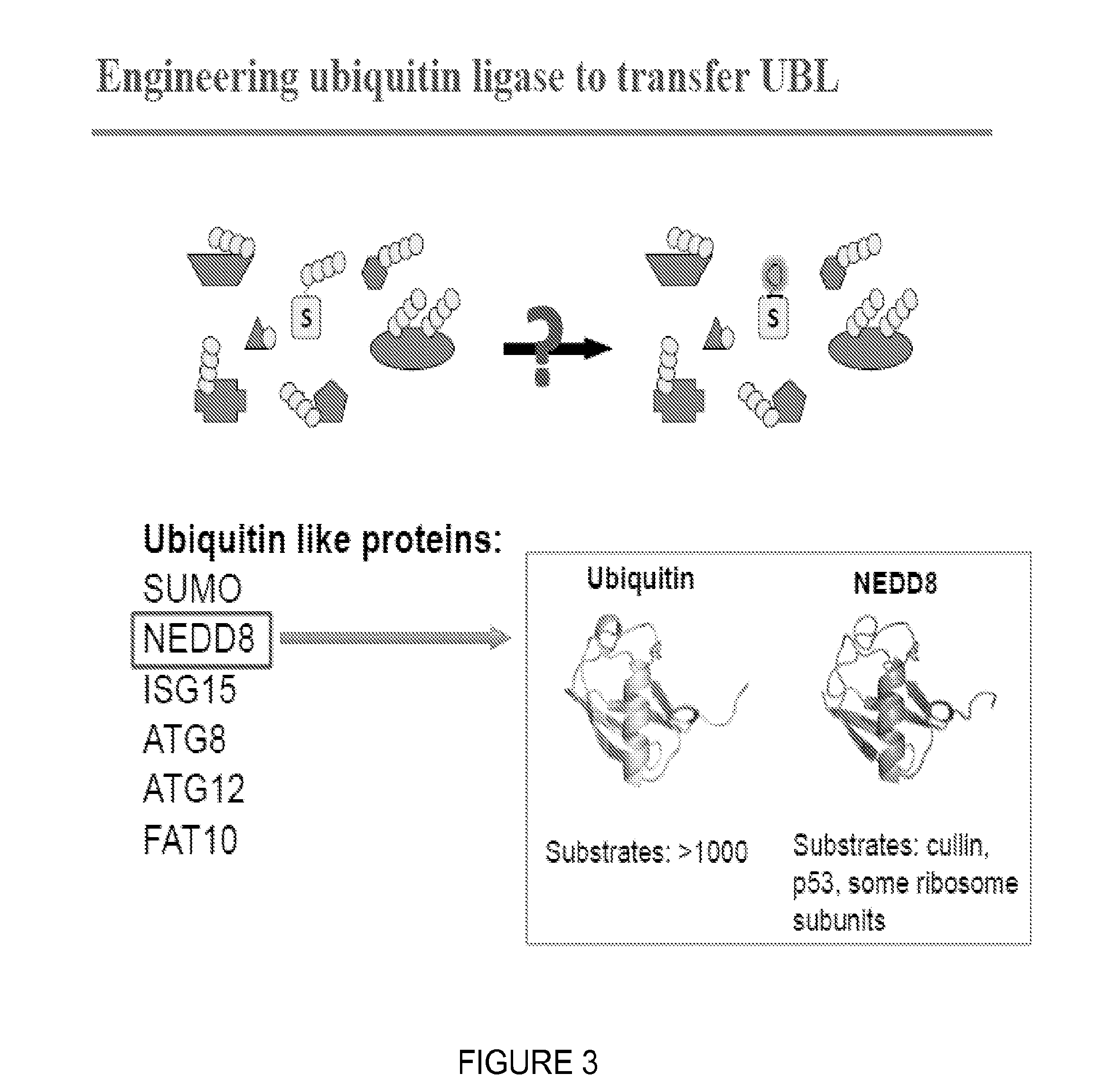
Catalytic Tagging System to Study Macro-Molecular Interactions Using Engineered Ubiquitin Ligase and Ubiquitin-Like Proteins to Facilitate Substrate Identification
The present invention describes an unbiased catalytic tagging system to search for target substrates. Identification of substrates for specific baits is accomplished by utilizing an orthogonal system consisting of an E1 activating enzyme, an E2 ubiquitin-like conjugating enzyme, and baits that are fused to the E2 ubiquitin-like conjugating enzyme. The present invention thus reveals important mutually antagonistic substrates of specific baits.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for rapid and dynamic flux control using synthetic metabolic valves
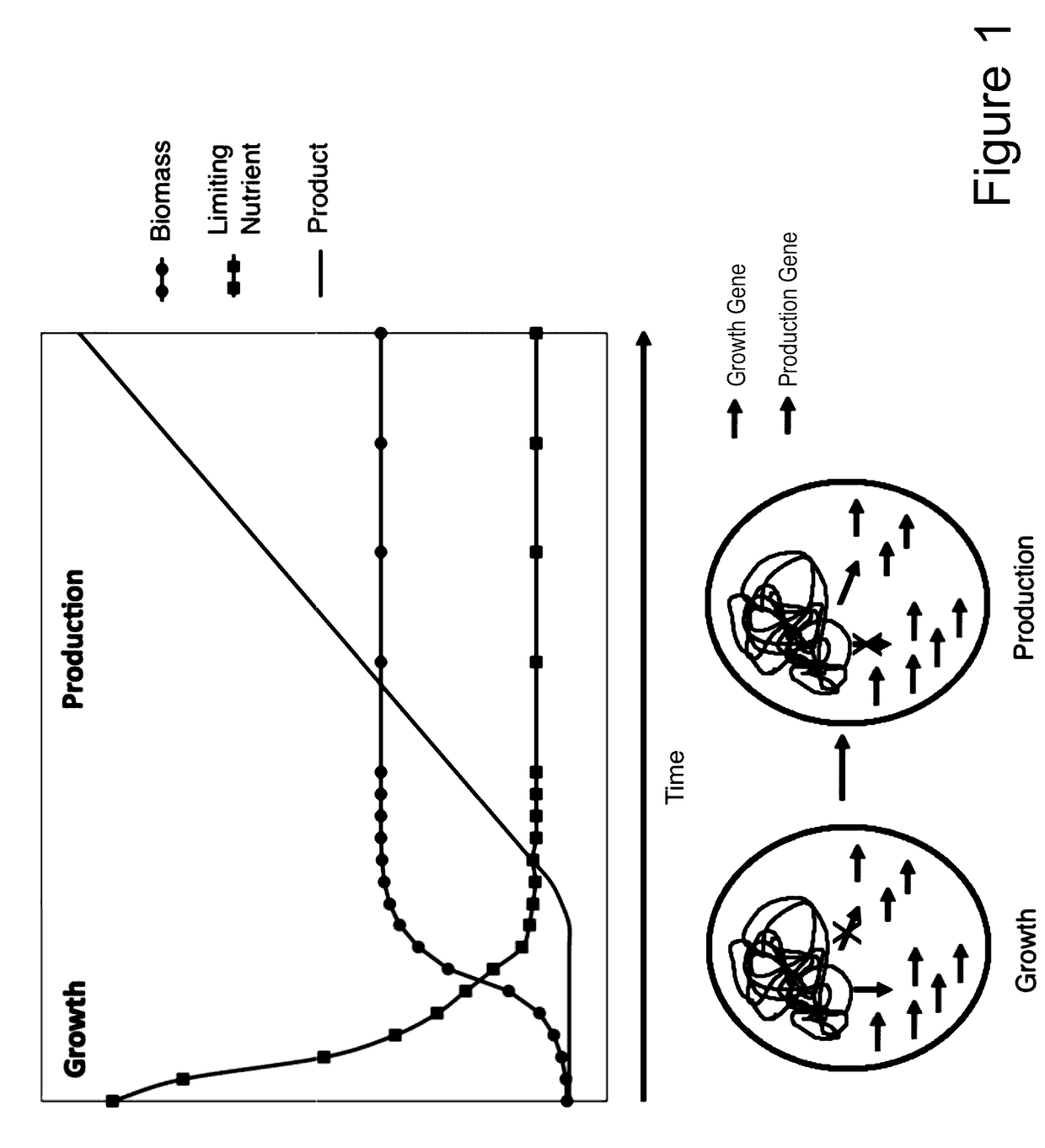
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganisms, such as bacterial and or fungal strains, and bioprocesses utilizing such strains. These strains enable the dynamic control of metabolic pathways, which can be used to optimize production. Dynamic control over metabolism is accomplished via a combination of methodologies including but not limited to transcriptional silencing and controlled enzyme proteolysis. These microbial strains are utilized in a multi-stage bioprocess encompassing at least two stages, the first stage in which microorganisms are grown and metabolism can be optimized for microbial growth and at least one other stage in which growth can be slowed or stopped, and dynamic changes can be made to metabolism to improve the production of desired product, such as a chemical or fuel.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Targeted Protein Degradation
ActiveUS20190002578A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyProtein targetChimeric antigen receptor
The invention relates to a method of controlling the level of a polypeptide sequence comprising administering a polypeptide sequence fused to a ubiquitin targeting protein which comprises a minimal degron structural motif. In particular, the polypeptide sequence comprises a chimeric antigen receptor therefore the present invention is useful in methods of cell and gene therapy where the activity of the chimeric antigen receptor needs to be controlled.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Compositions and methods for selective protein expression
Provided herein are fusion proteins including two protein domains separated by a heterologous protease cleavage site, wherein a first of the protein domains is a conditional expression domain. Thus, the fusion proteins comprise three essential elements: a conditional expression domain, a domain containing the protein of interest, and a protease cleavage domain separating the two. Also provided herein are methods for treating autoantibody and alloantibody-mediated diseases or conditions in a subject by targeting B cells with anti-B cell modified T cells. In one embodiment, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) modified T cell is selectively ablated in a subject after adoptive transfer. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the temporally regulated CAR modified T cell are also described herein.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Targeted protein silencing using chimeras between antibodies and ubiquitination enzymes
InactiveUS20140112922A1Simple and efficientEasy to implementPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention relates to an isolated chimeric molecule comprising a degradation domain including a eukaryotic U-box motif and a targeting domain capable of immuno specifically directing the degradation domain to a substrate where the targeting domain is heterologous to the degradation domain. A linker couples the degradation domain to the targeting domain. Also disclosed are compositions as well as methods of treating a disease, substrate silencing, screening agents for therapeutic efficacy against a disease, and methods of screening for disease biomarkers.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for rapid and dynamic flux control using synthetic metabolic valves
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Tunable endogenous protein degradation with heterobifunctional compounds
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Cross-Linked Peptides and Proteins, Methods of Making Same, and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20140057857A1Improve propertiesImprove enzyme stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusion with degradation motifCross-linkCrystallography
Cross-linked proteins and peptides, and methods of making and uses of such cross-linked proteins and peptides. The cross-linked proteins and peptides have rigid, distance-matching bismethylene aryl cross-linking moieties. Compositions comprising the cross-linked proteins and peptides can be used as pharmaceutical delivery formulations. The cross-linked proteins and peptides can have improved properties, such as cell permeability, as compared to the parent protein or peptide.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com