Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of prostatic acid phosphatase in prostate cancer
a prostate cancer and prostatic acid phosphatase technology, applied in the field of prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment, can solve the problems of uncureable disease relapse, hormone therapy, unrehabilitative, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing the growth rate of cancer cells, prolonging and/or restoring the effect and increasing the efficacy of androgen deprivation therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
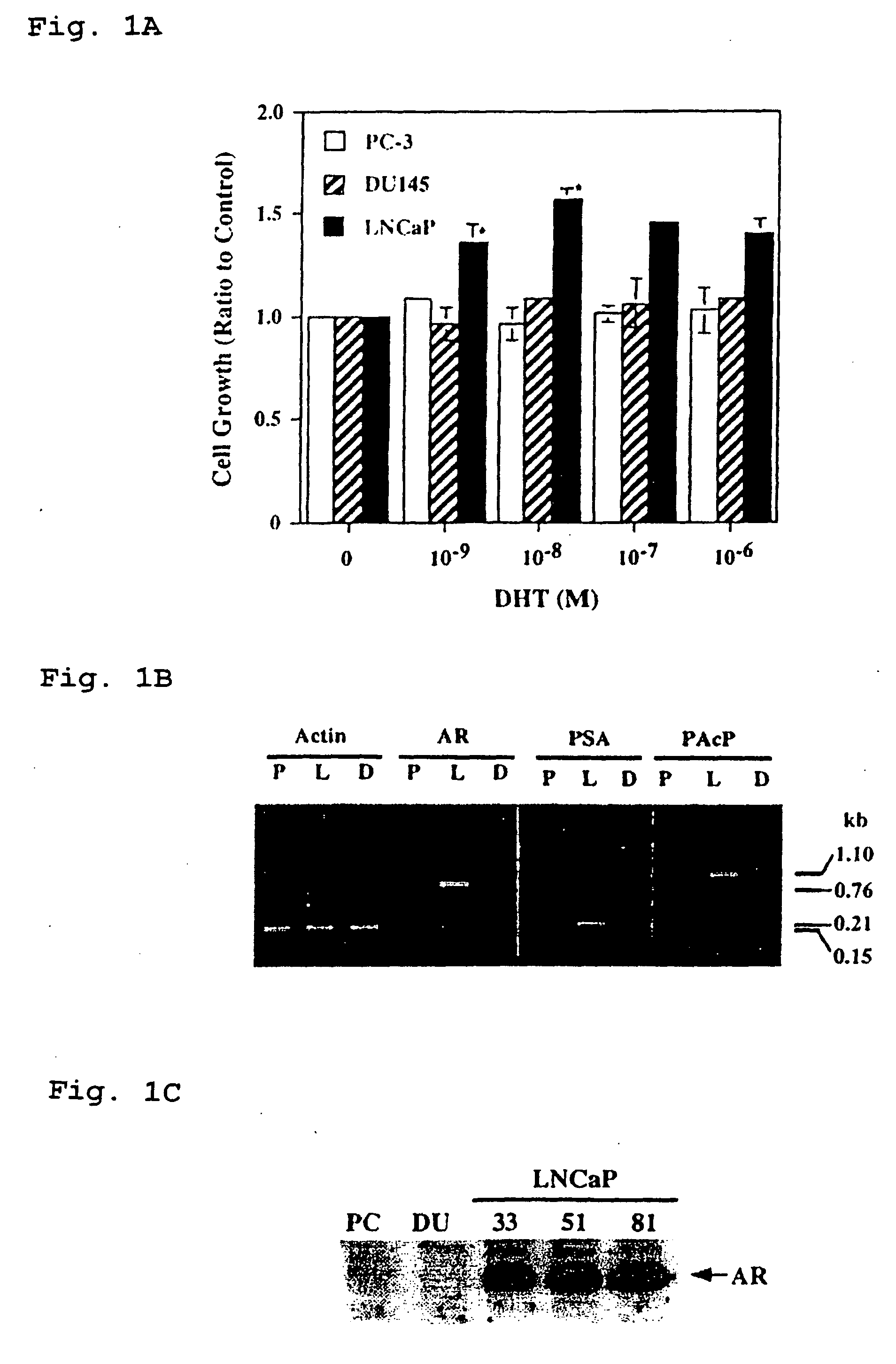
Human Prostatic Acid Phosphatase is a Marker for Androgen-Responsive Prostate Cancer Cell Lines
Experimental Procedures
[0090] Materials. FBS and RPMI 1640 medium were purchased from Life Technologies, Inc. The heat-inactivated dialyzed FBS that was a certified grade FBS containing less than 74 pM testosterone, was prepared as described previously (Lin et al., 1993, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 300:384-390). The steroid-reduced medium consisted of RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 2 or 5% (v / v) heat-inactivated dialyzed FBS. Thus, the final concentration of testosterone was less than 4 pM (Lin et al., 1993, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 300:384-390). Hepes, bovine serum albumin, Tris, p-nitrophenyl phosphate, DHT, L-(+)-tartaric acid, citric acid, formaldehyde, and EtBr were all purchased from Sigma. [[α]-32P]dCTP was from NEN Life Science Products. All other reagents were obtained as described in previous publications (Lin and Clinton, 1987, Adv. Prot. Phosphatases 4:199-228; Lin et al., 19...
example ii
Xenograft Animal Model System Mimics Clinical Human Prostate Cancers
Materials and Methods
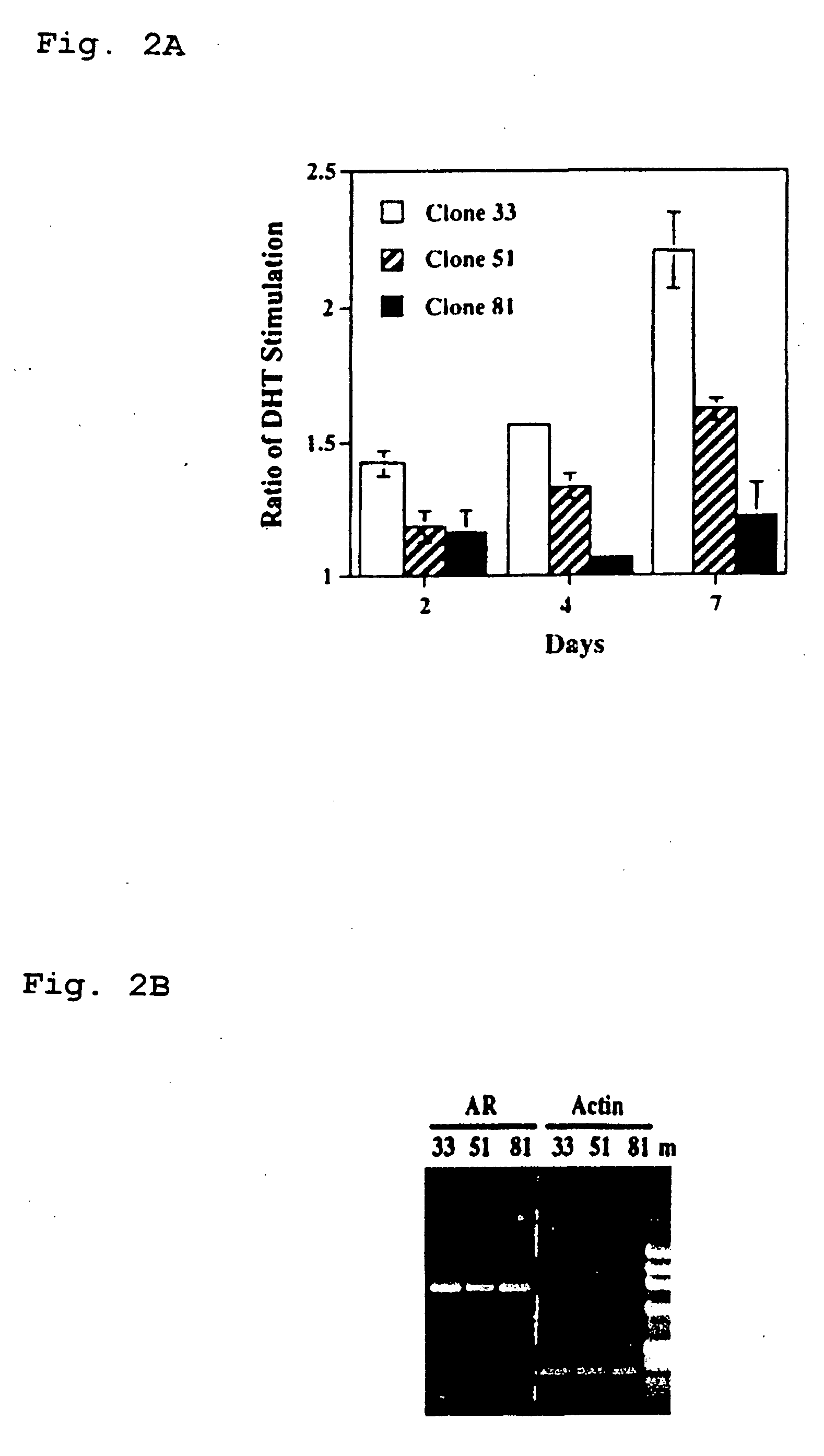
[0126] Cell cultures. Different LNCaP cells including clone-33 (i.e., passages 20-30), -51 (passages 45-60), and -81 (passages 85-120) were described previously (Lin et al., 1998, J. Biol. Chem. 273:5939-5947). Clone-33 LNCaP cells represented the LNCaP parental cells, and expressed a high level of endogenous PAcP (Lin et al., 1998, J. Biol. Chem. 273:5939-5947). The expression of PAcP was decreased in clone-51 cells, and further diminished in clone-81 cells. LNCaP-23, -28, -34, and -40 cells were subcloned cells from clone-81 LNCaP cells that transfected with a full length human PAcP cDNA driven by a pCMV-neo expression vector followed by G418 selection (Lin et al., 1998, J. Biol. Chem. 273:5939-5947). These PAcP cDNA transfected LNCaP cells expressed a low level of endogenous cellular PAcP as well as an exogenous cellular PAcP (Lin et al., 1998, J. Biol. Chem. 273:5939-5947). LNCaP-CMV cell...
example iii
Analysis of the Promoter of the Human Prostatic Acid Phoasphatase Gene
Materials and Methods
[0143] Materials. Cell culture medium, fetal bovine serum (FBS), gentamicin and Lipofectin reagent were obtained from Life Technologies, Inc. The MasterAmp PCR Optimization kit was from Epicentre Technologies Corp. Zero Blunt PCR cloning kit, and pCR-Blunt vector were obtained from Invitrogen Corp. pCATBasic, pCATEnchancer, pCATPromoter, pSV-, 6-galactosidase vectors and CAT assay kit were purchased from Promega Corp. DNA manipulations of plasmids were performed by conventional molecular biology techniques (Sambrook et al., 1989 Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.).
[0144] Cells culture. LNCaP cells were routinely maintained in RPMI1640 medium supplemented with 5% FBS, 1% glutamine, and 0.5% gentamicin. To examine androgen effect on PAcP expression, cells were maintained in a steroid-reduced medium, i.e., phenol red-free RPMI...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com