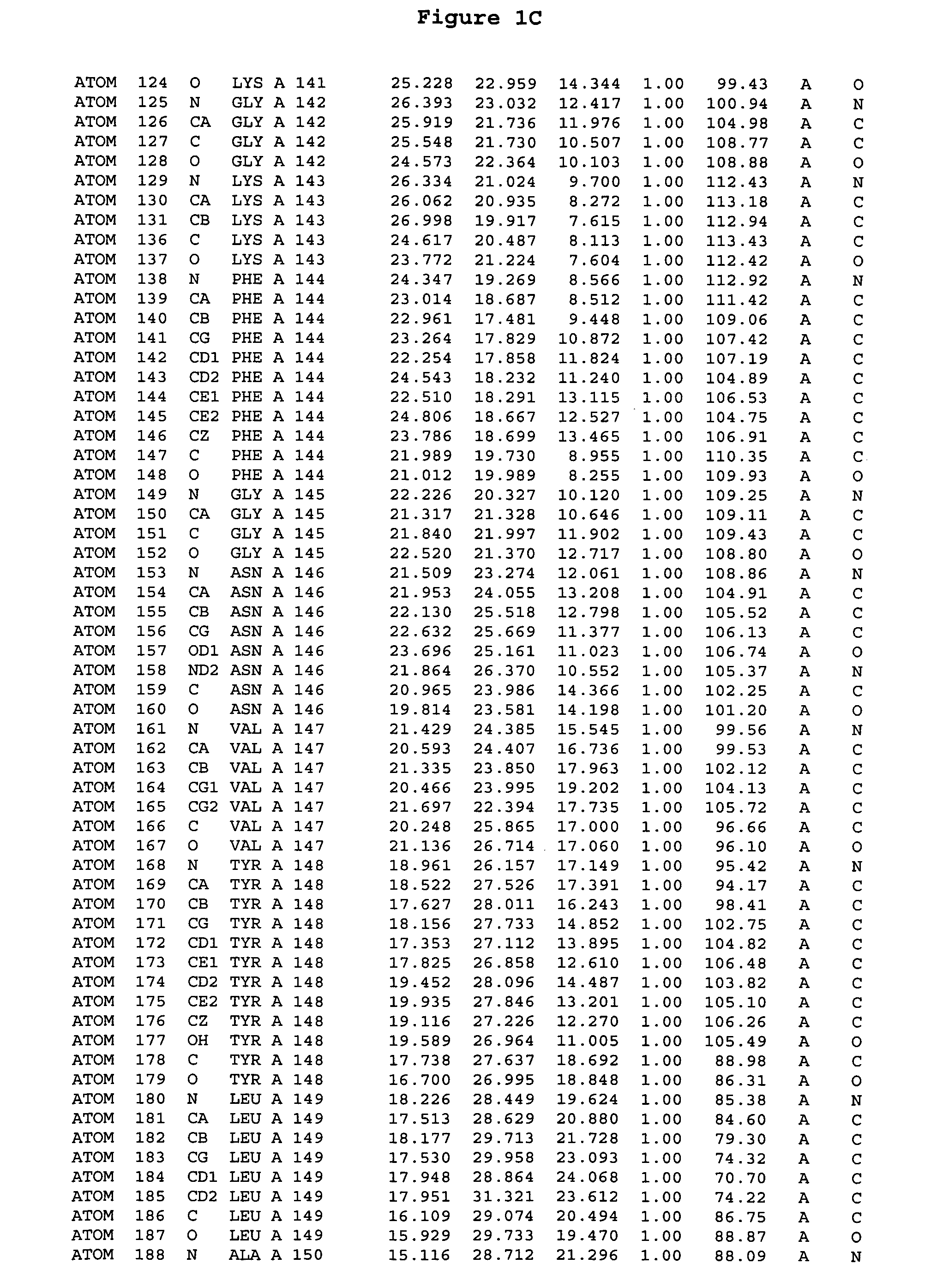
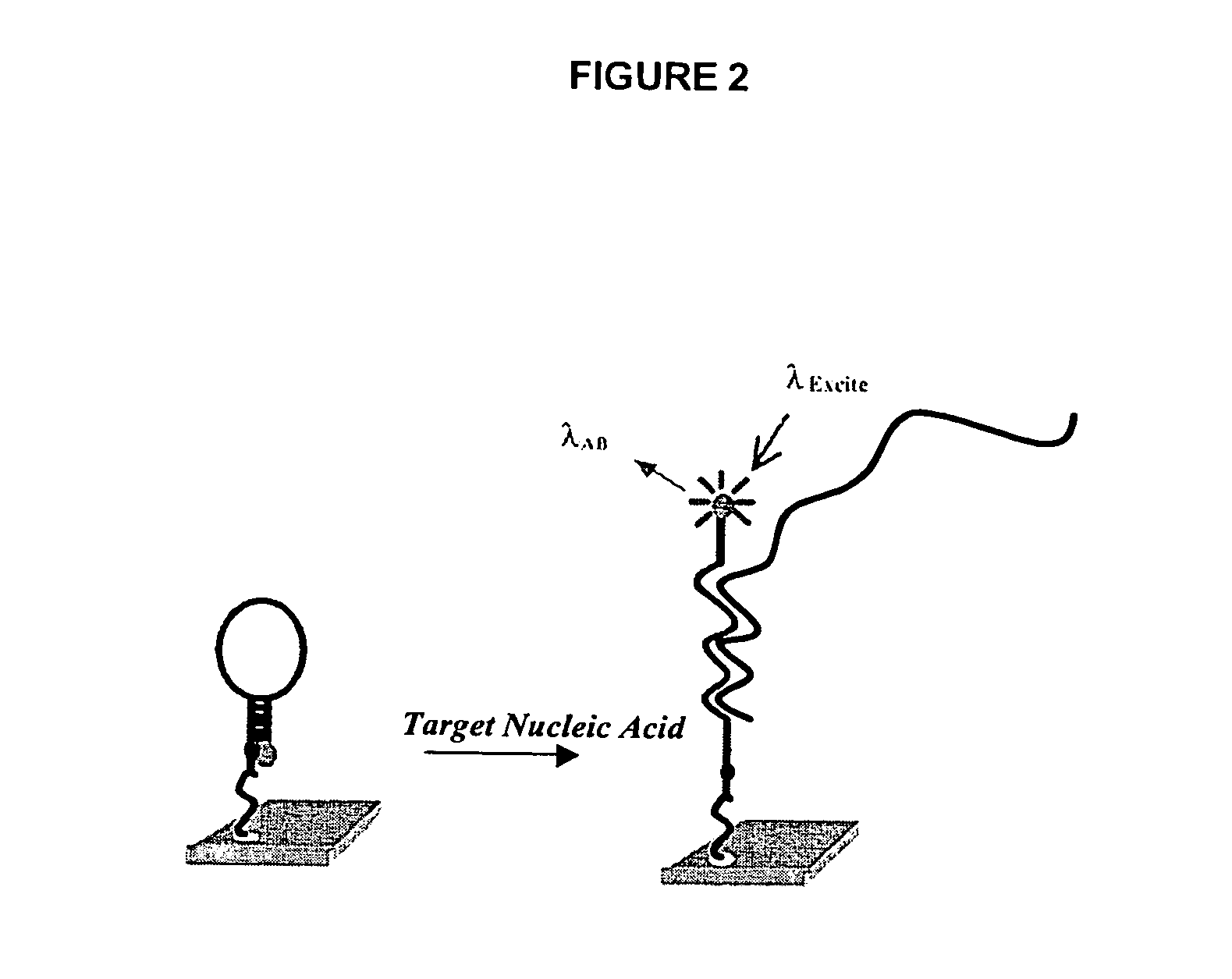
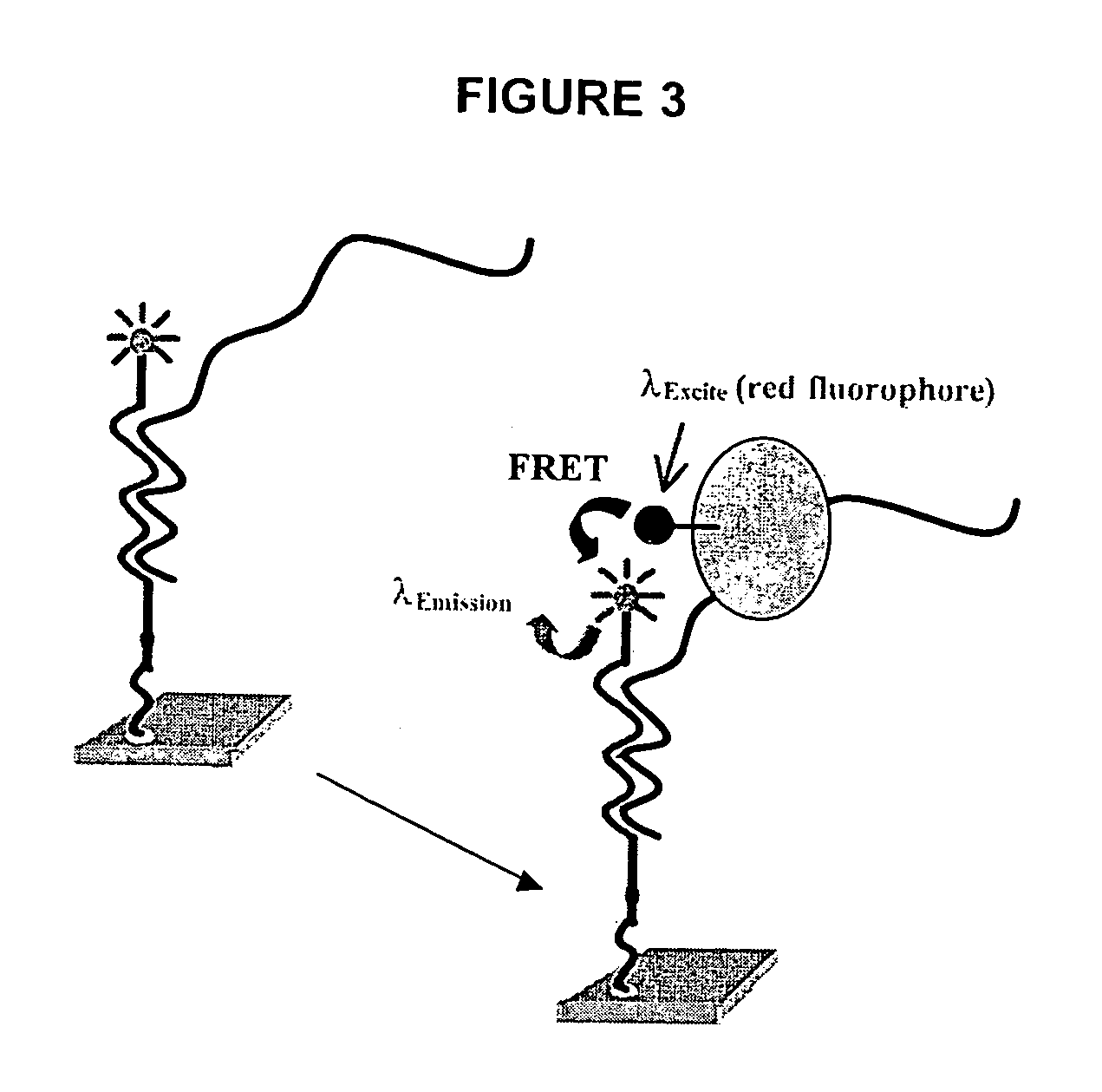
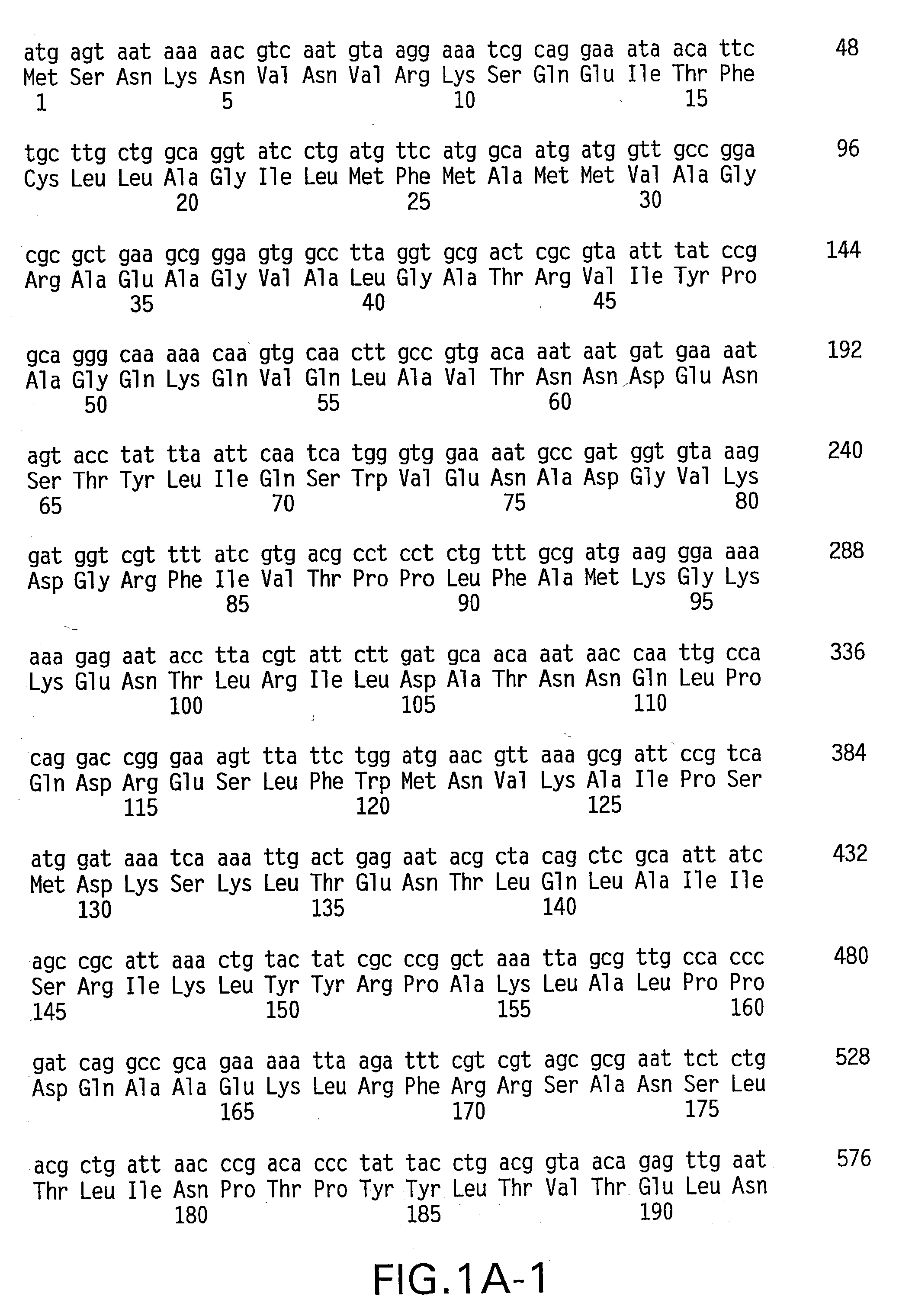
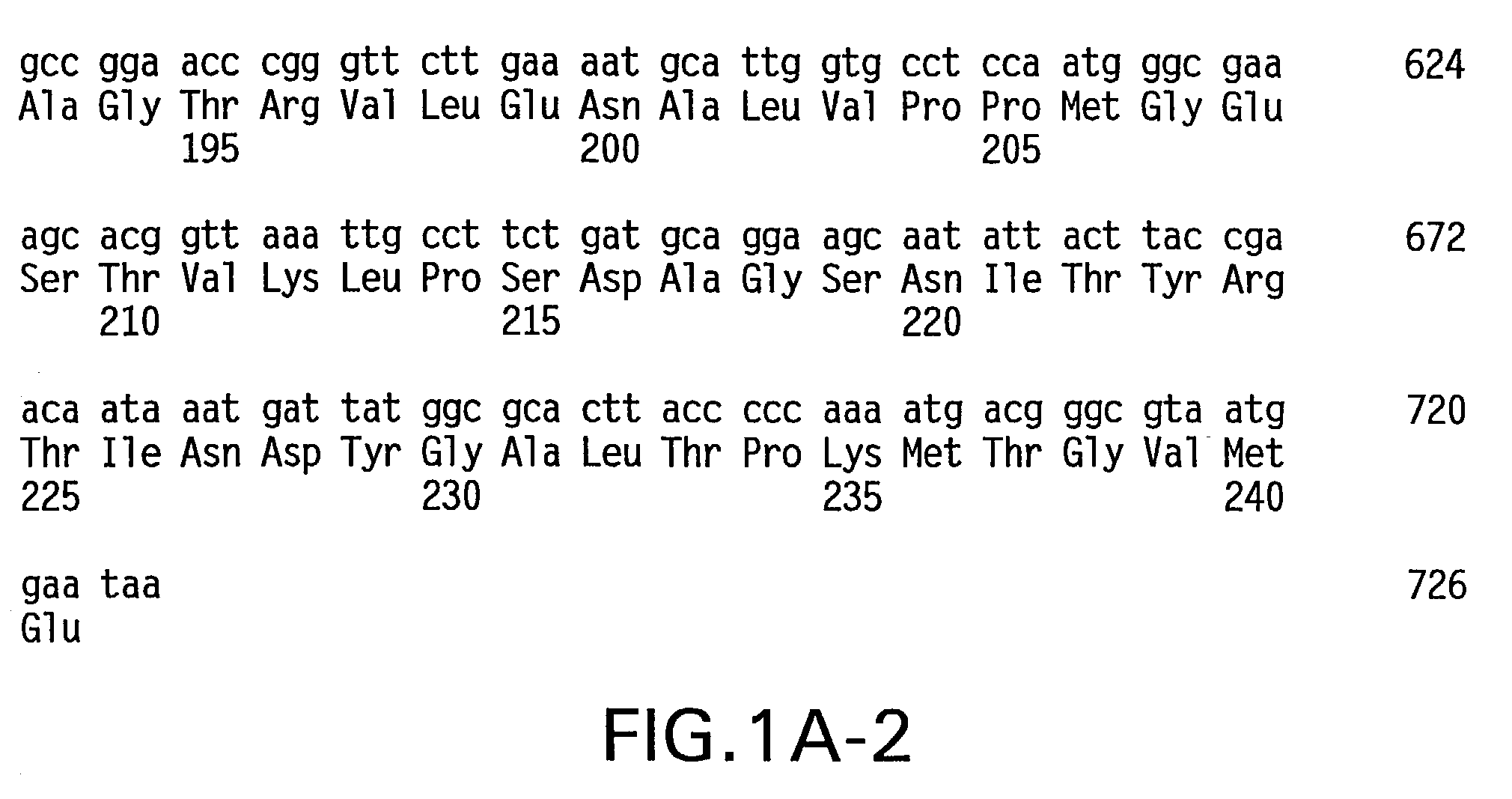
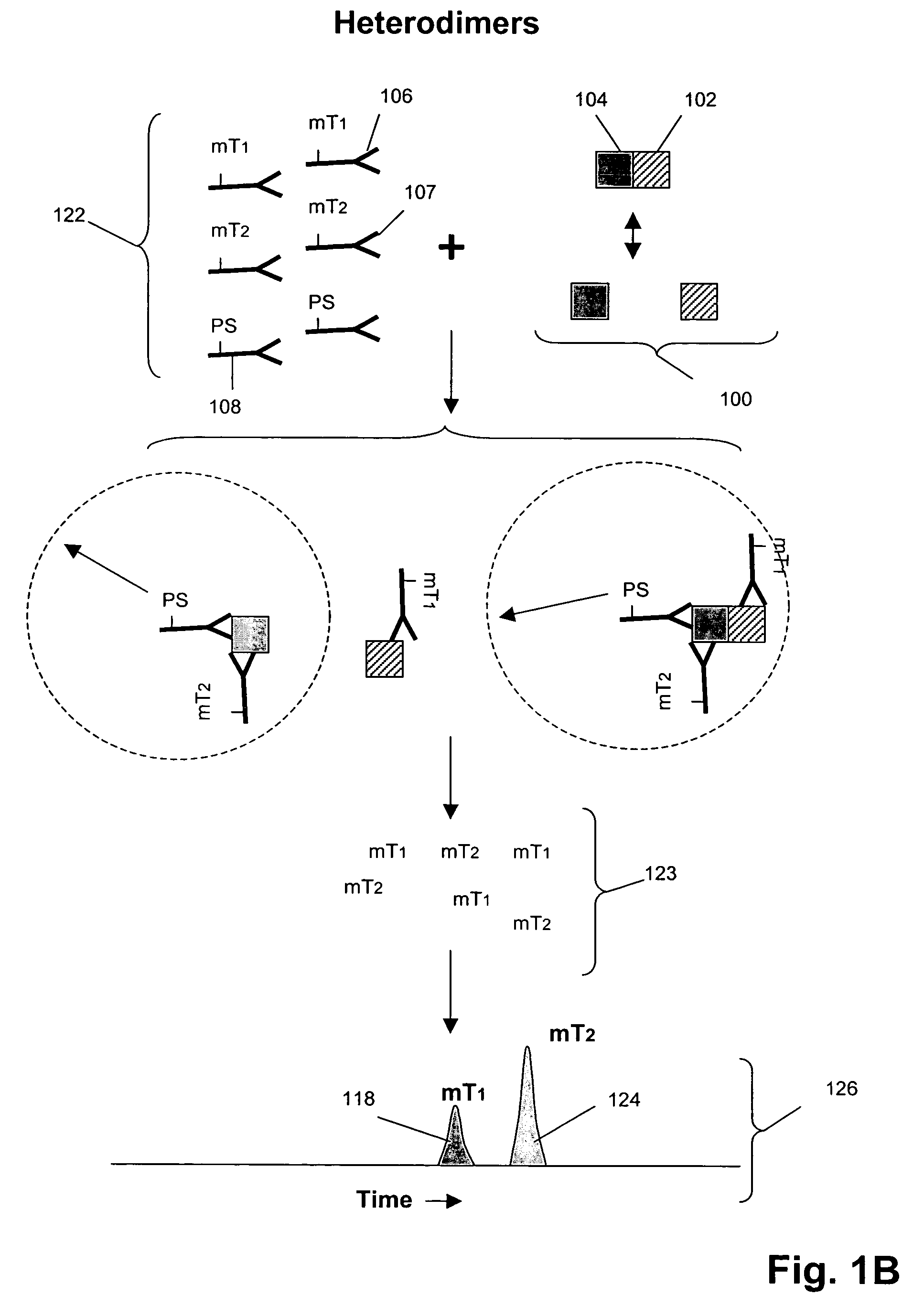
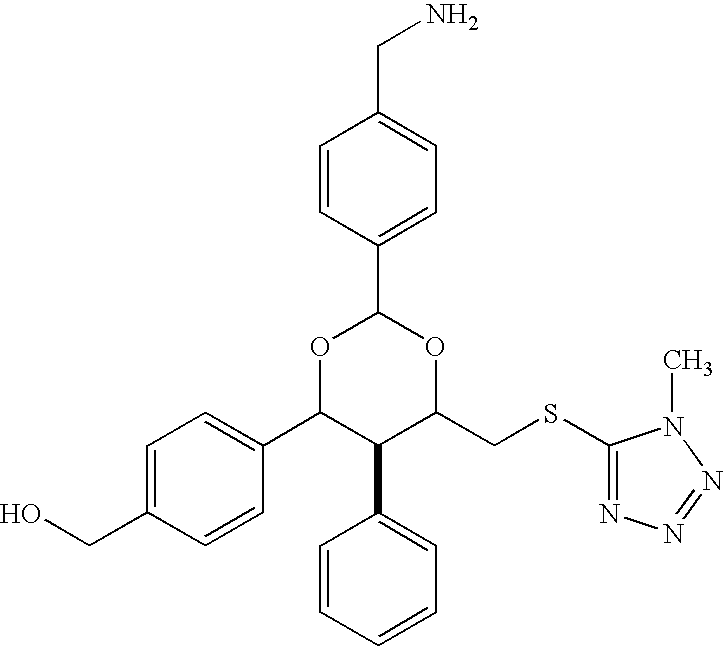
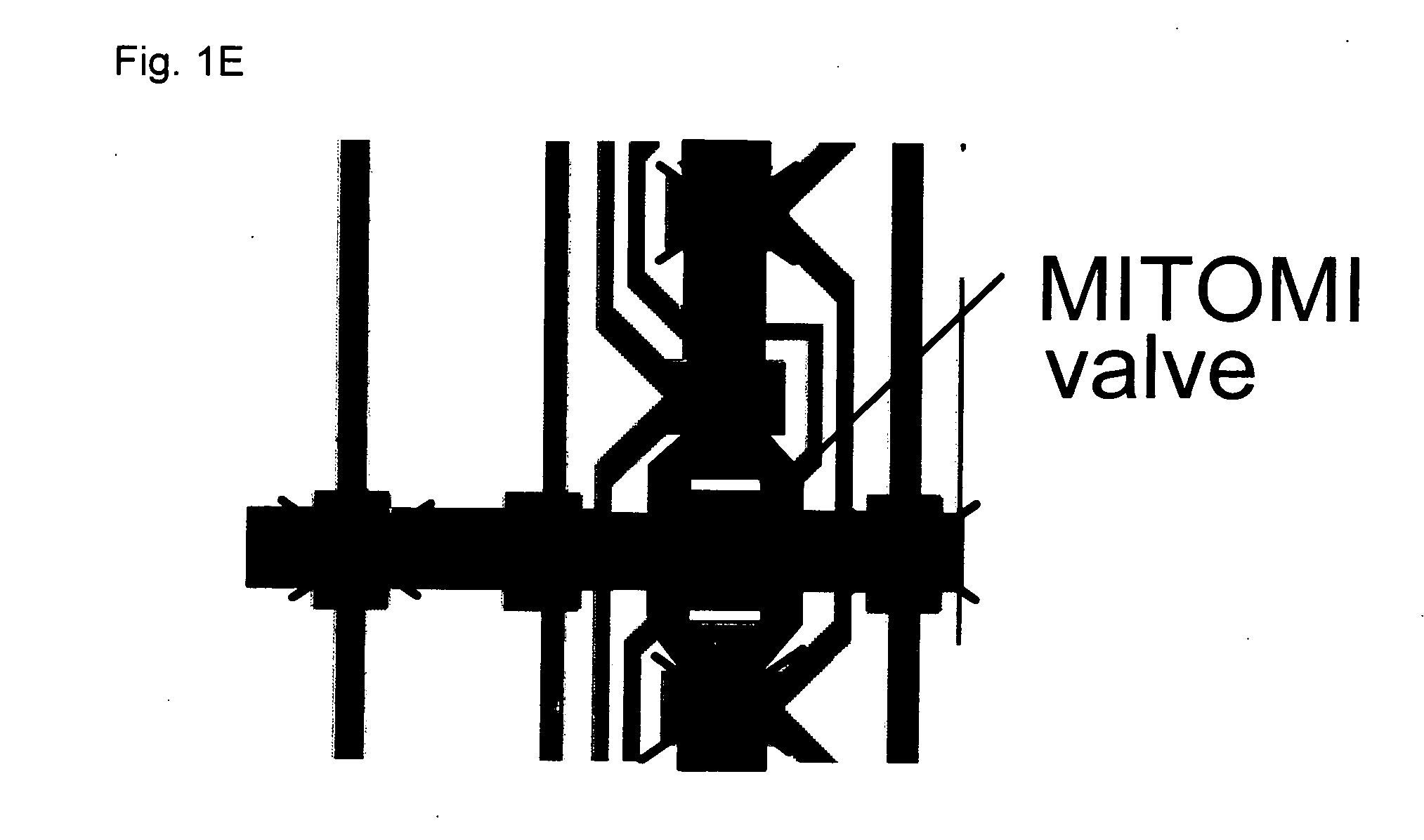Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
466 results about "Protein-protein complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
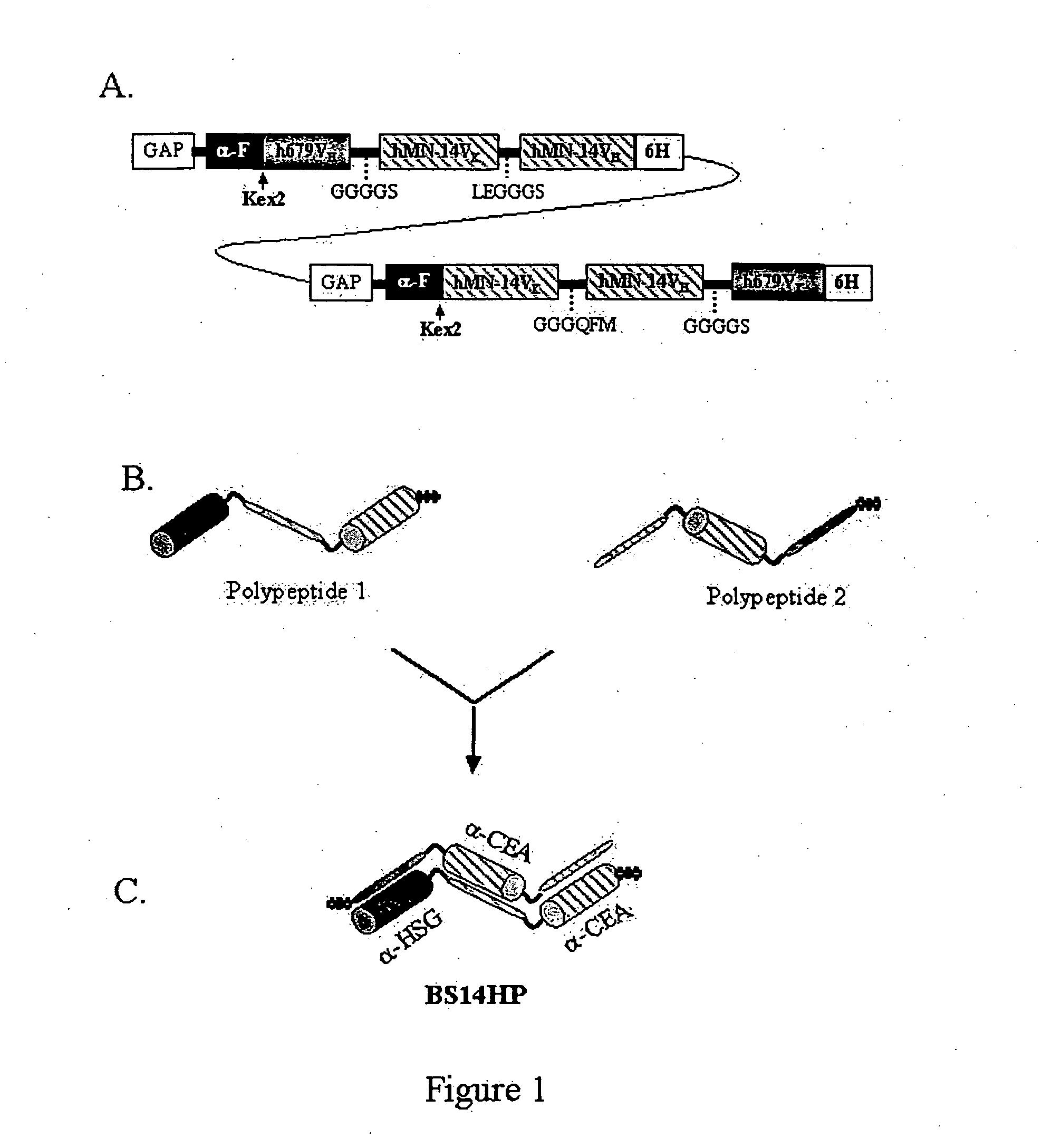
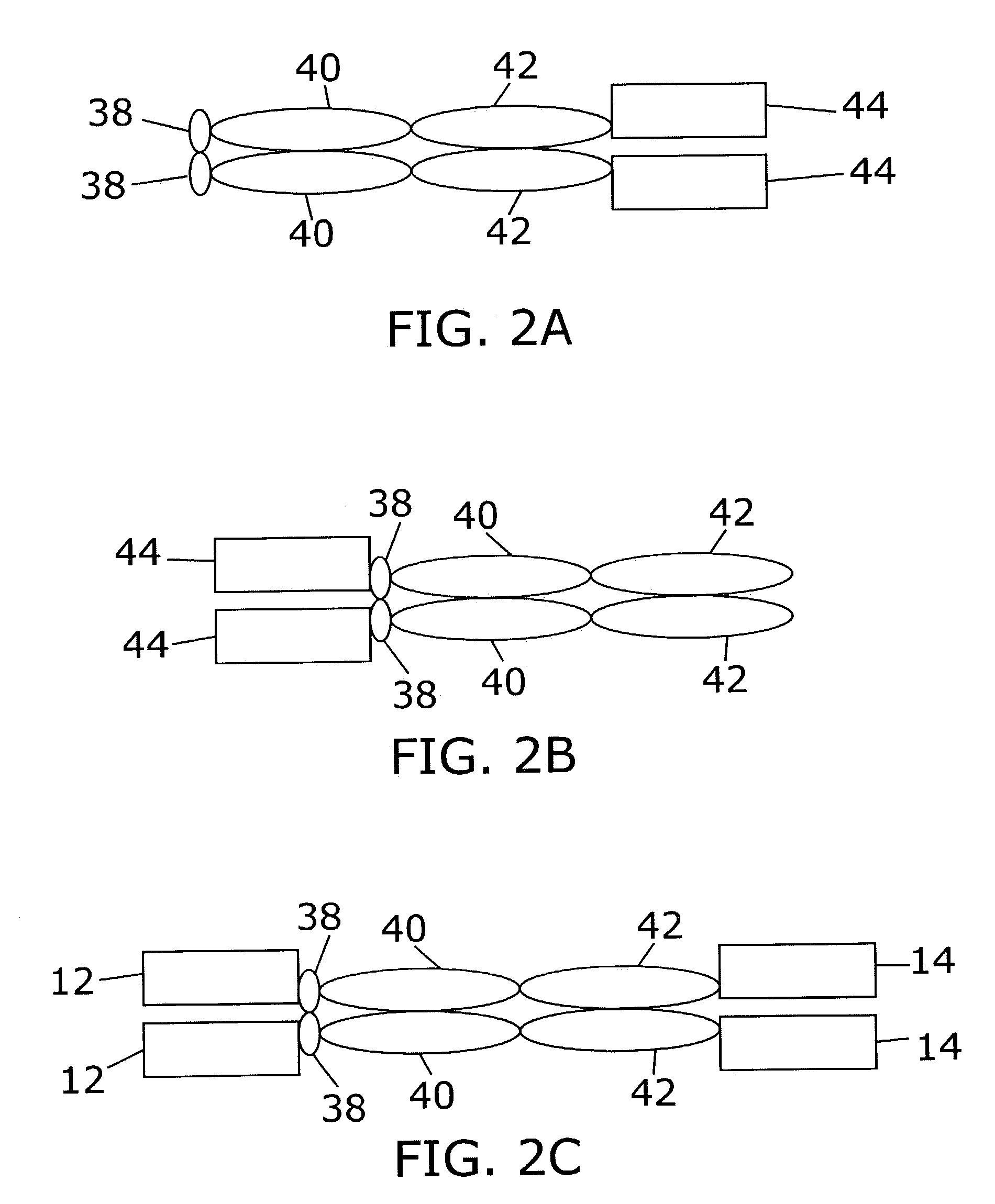
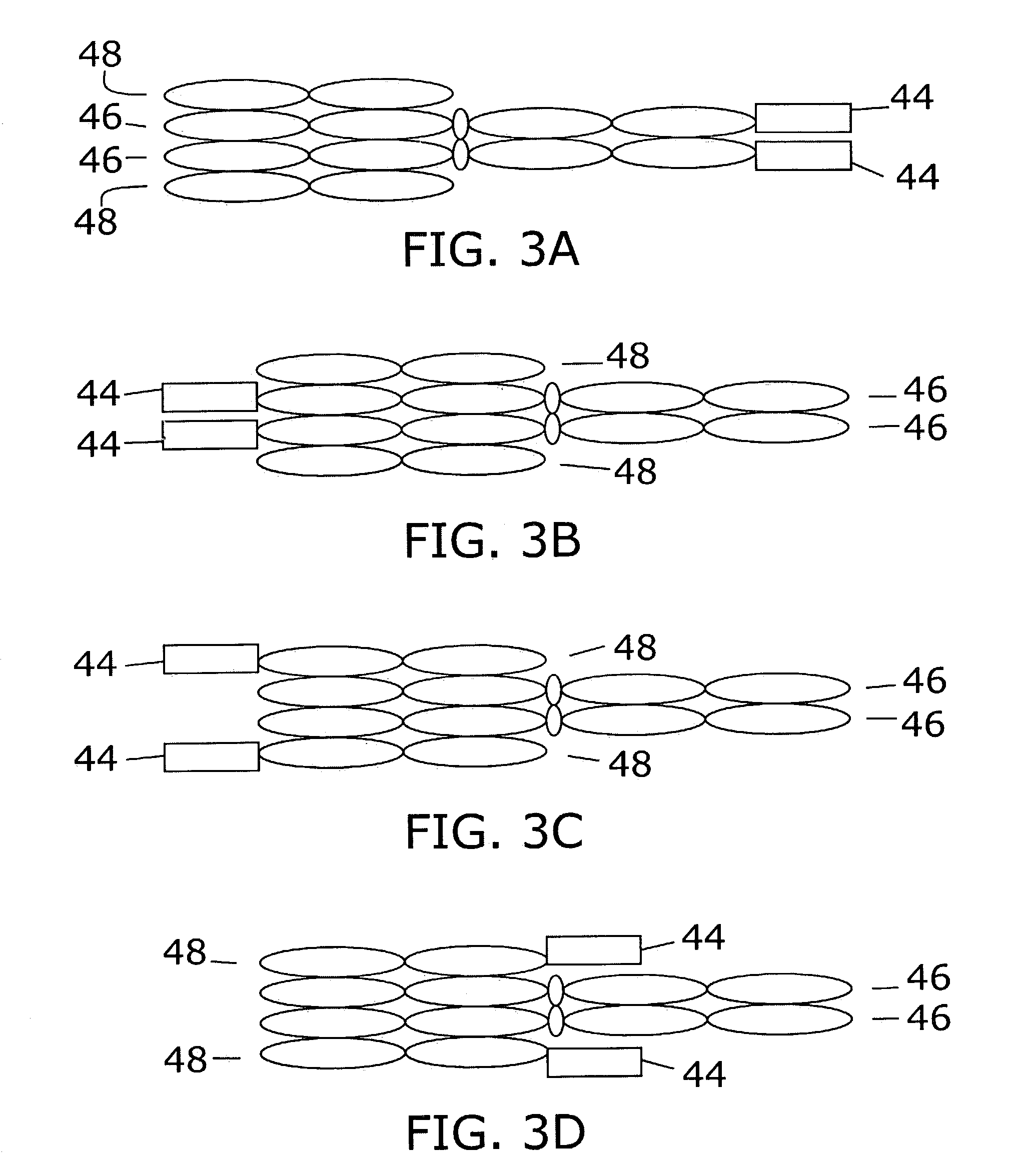
Polyvalent protein complex
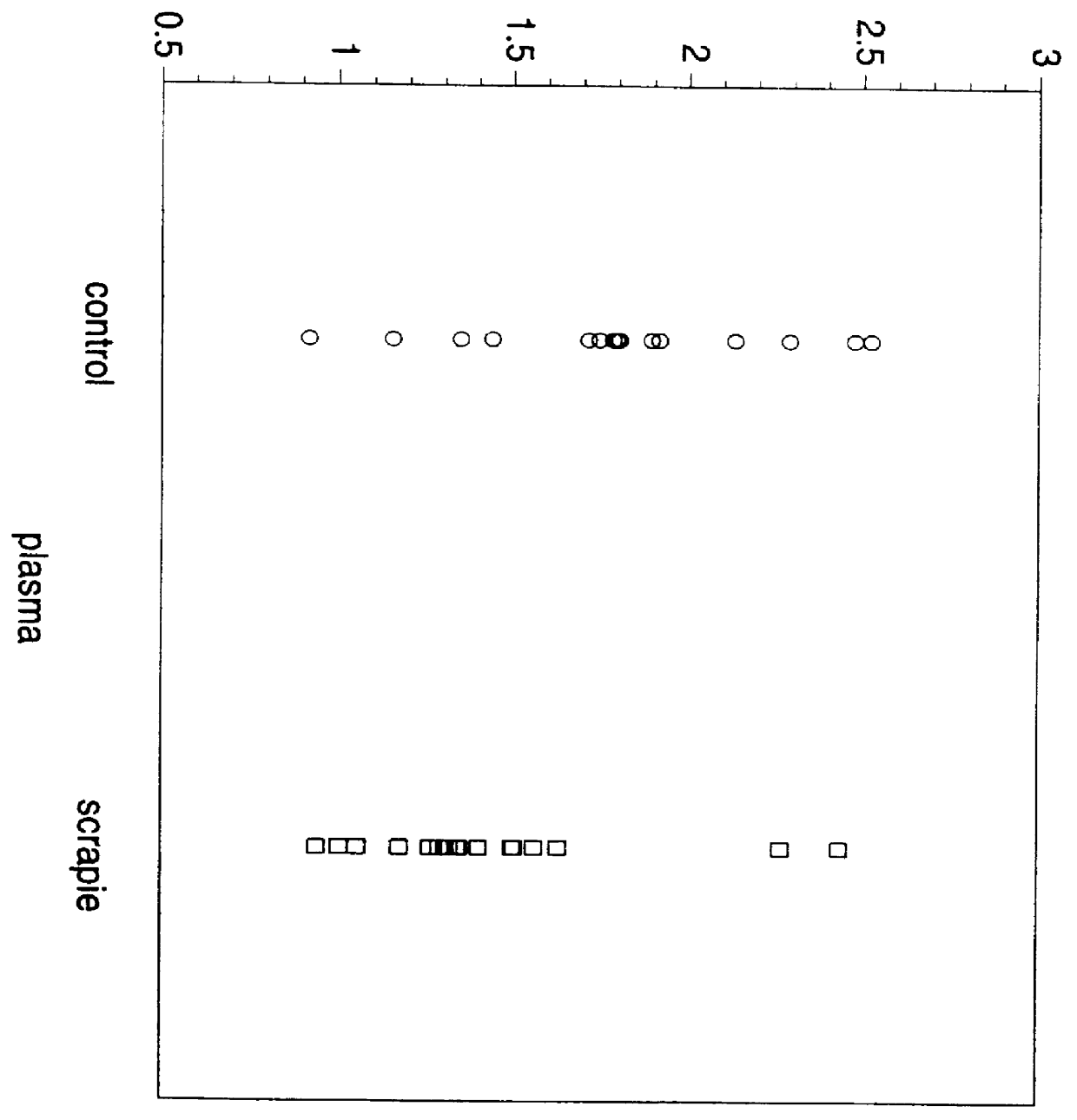
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
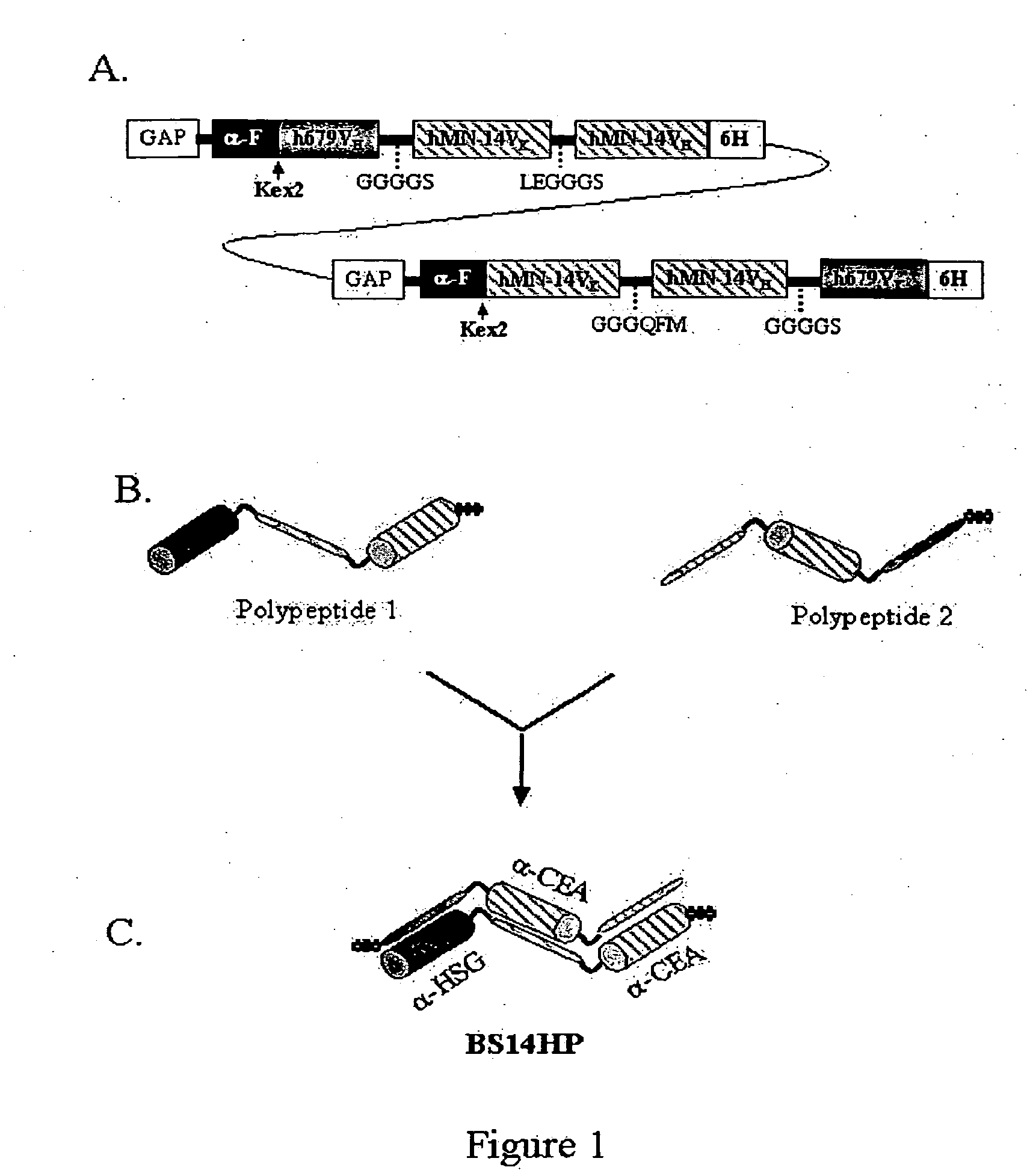
Polyvalent protein complex
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Protein complexes having Factor VIII:C activity and production thereof
InactiveUS6060447AImprove stabilityHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFactor iiADAMTS Proteins
Recombinant protein complexes having human Factor VIII:C activity are expressed in a eukaryotic host cell by transforming the host cell with first and second expression cassettes encoding a first polypeptide substantially homologous to human Factor VIII:C A domain and a second polypeptide substantially homologous to human Factor VIII:C C domain, respectively. In the present invention, the first polypeptide may be extended having at its C-terminal a human Factor VIII:C B domain N-terminal peptide, a polypeptide spacer of 3-40 amino acids, and a human Factor VIII:C B domain C-terminal peptide. Expression of the second polypeptide is improved by employing an .alpha..sub.1 -antitrypsin signal sequence.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Compositions and methods for treating diseases
InactiveUS20050222029A1Preventing and ameliorating diseaseEfficient modulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein-protein complexDisease cause
Protein complexes are provided comprising at least one interacting pair of proteins. The protein complexes are useful in screening assays for identifying compounds effective in modulating the protein complexes, and in treating and / or preventing diseases and disorders associated with the protein complexes and / or their constituent interacting members.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
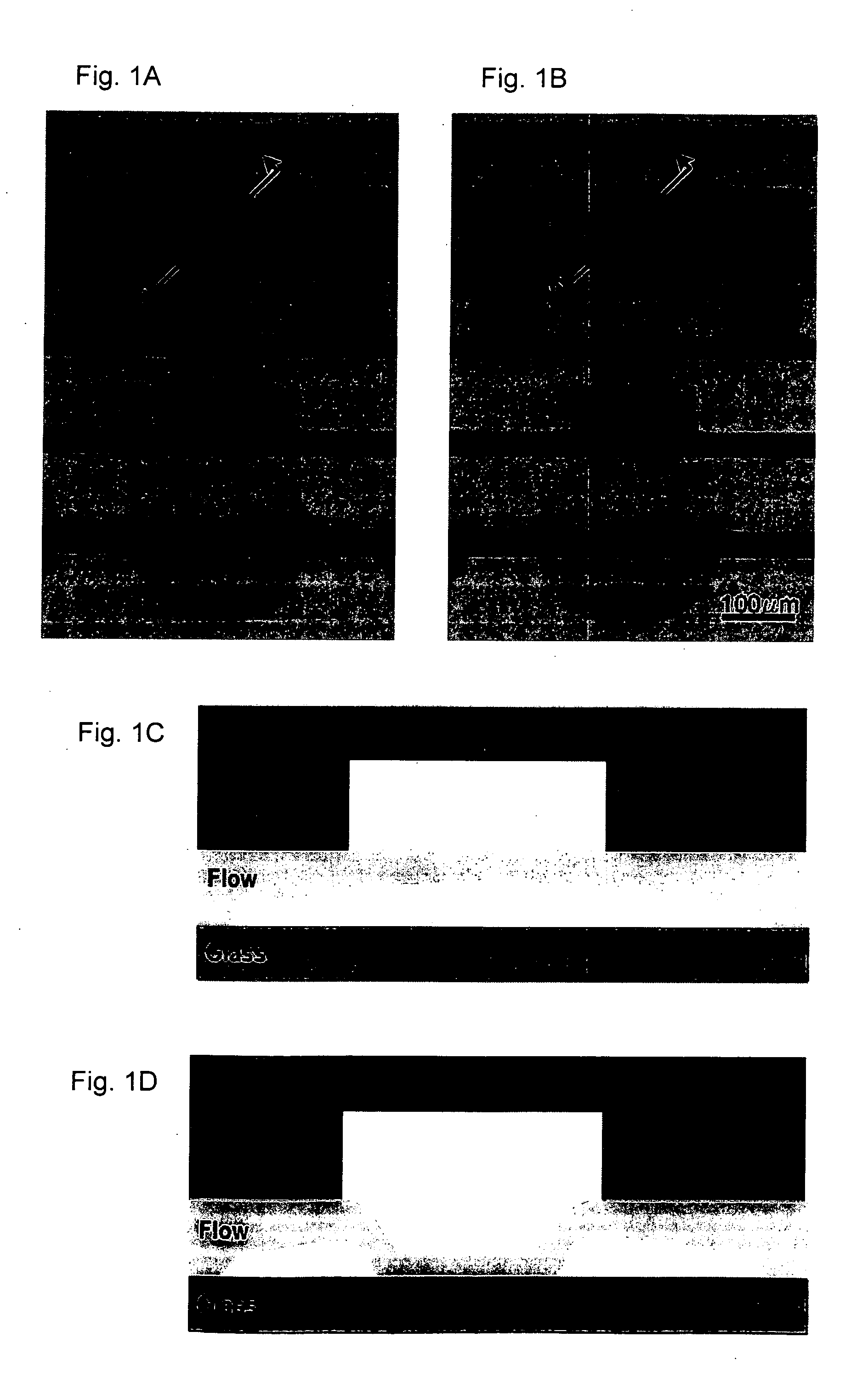
Mechanically induced trapping of molecular interactions
InactiveUS20070224617A1Reduce pressureRapid lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurface patternChemical physics
The invention provides devices and methods for surface patterning the substrate of a microfluidic device, and for detection and analysis of interactions between molecules by mechanically trapping a molecular complex while substantially expelling solvent and unbound solute molecules. Examples of molecular complexes include protein-protein complexes and protein-nucleic acid complexes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Inhibitors of GSK-3 and crystal structures of GSK-3beta protein and protein complexes
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Processes for removing cells and cell debris from tissue and tissue constructs used in transplantation and tissue reconstruction
InactiveUS20070123700A1Improve inflammatory responseImprove responseHeart valvesDead animal preservationPresent methodFresh Tissue
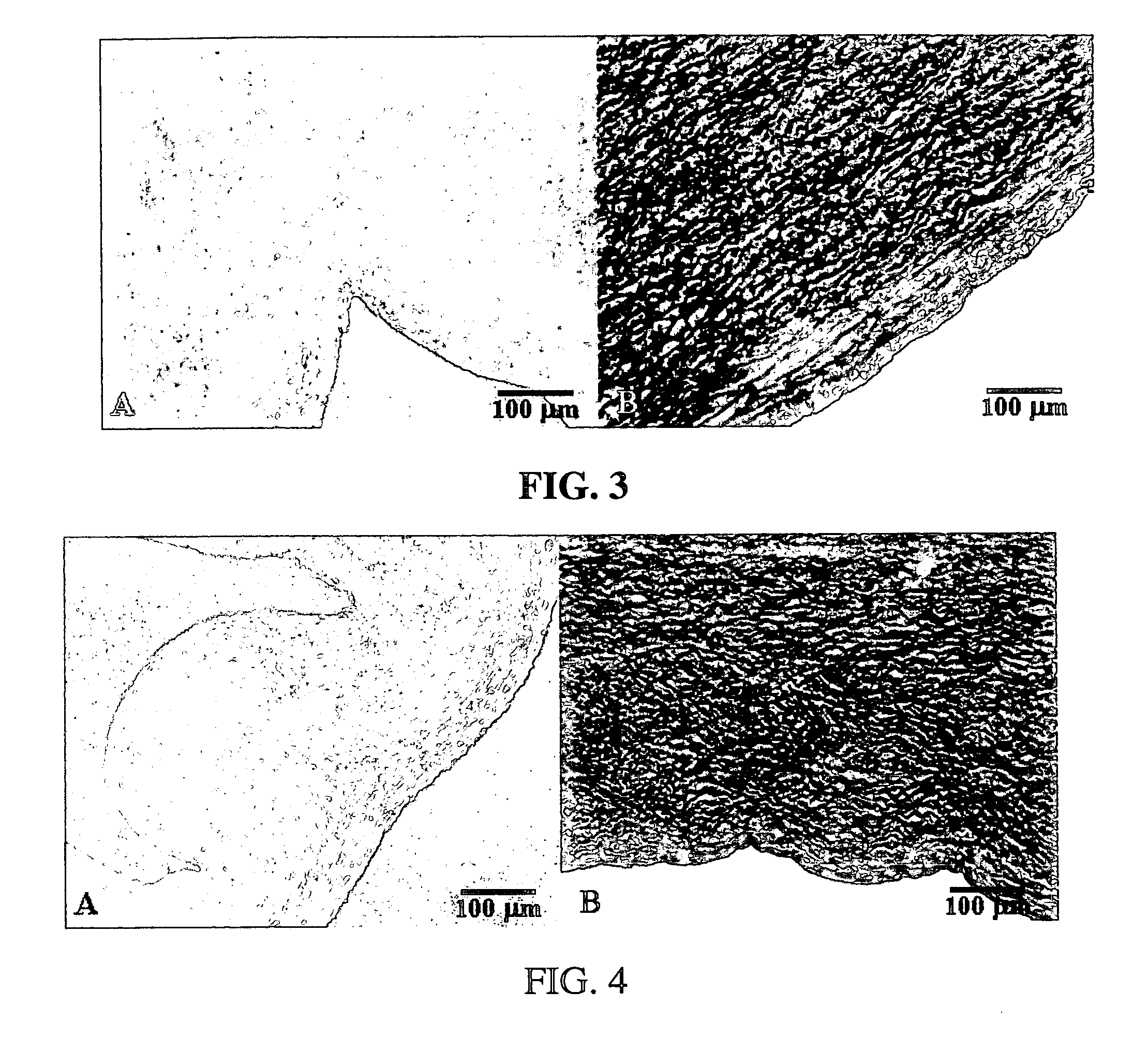
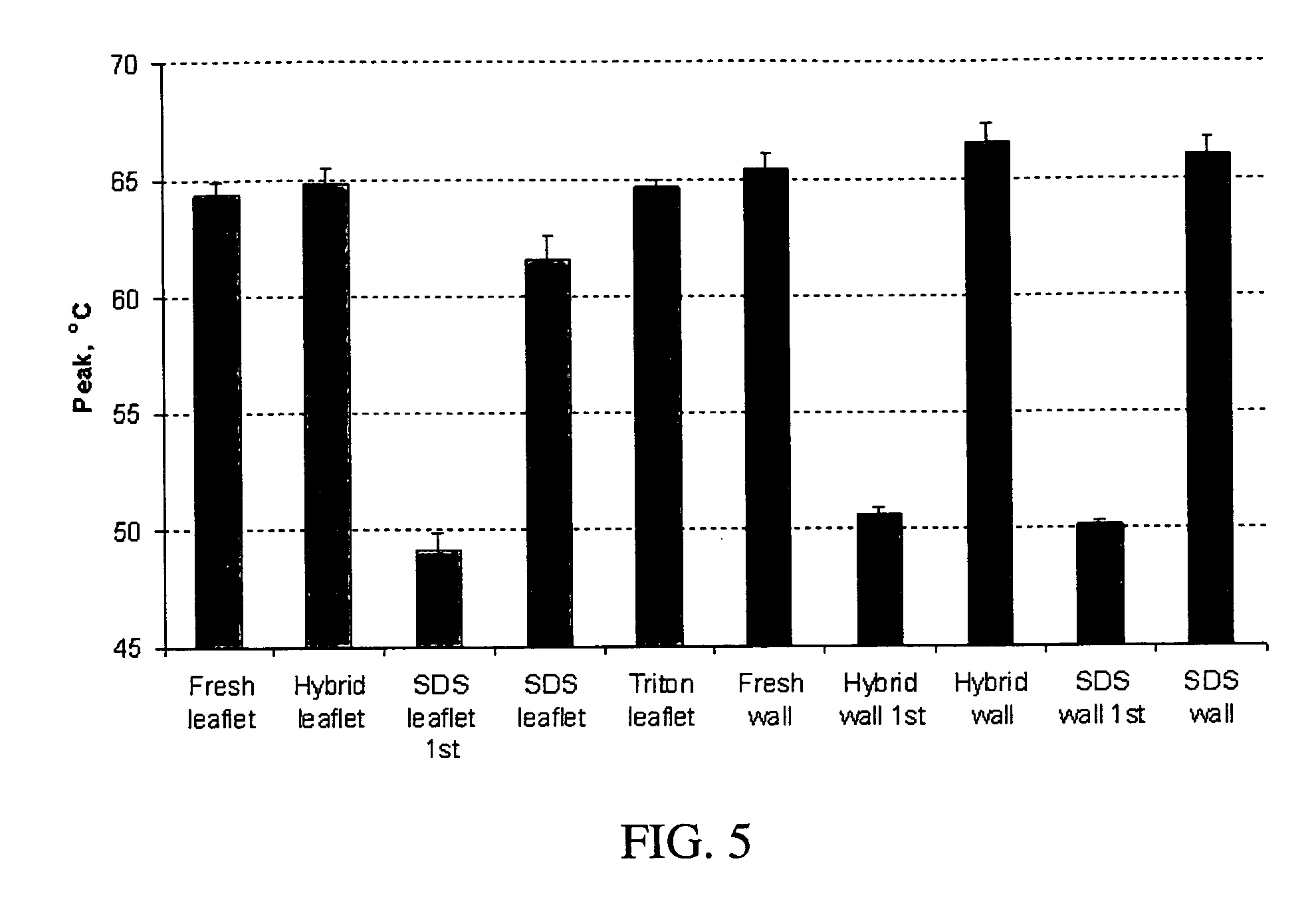
Methods for decellularizing mammalian tissue for use in transplantation and tissue engineering. The invention includes methods for simultaneous application of an ionic detergent and a nonionic detergent for a long time period, which may exceed five days. One method utilizes SDS as the ionic detergent and Triton-X 100 as the nonionic detergent. A long rinse step follows, which may also exceed five days in length. This long duration, simultaneous extraction with two detergents produced tissue showing stress-strain curves and DSC data similar to that of fresh, unprocessed tissue. The processed tissue is largely devoid of cells, has the underlying structure essentially intact, and also shows a significantly improved inflammatory response relative to fresh tissue, even without glutaraldehyde fixation. Significantly reduced in situ calcification has also been demonstrated relative to glutaraldehyde fixed tissue. Applicants believe the ionic and non-ionic detergents may act synergistically to bind protein to the ionic detergent and may remove an ionic detergent-protein complex from the tissue using the non-ionic detergent. The present methods find one exemplary use in decellularizing porcine heart valve leaflet and wall tissue for use in transplantation.
Owner:UEDA YUICHIRO +1
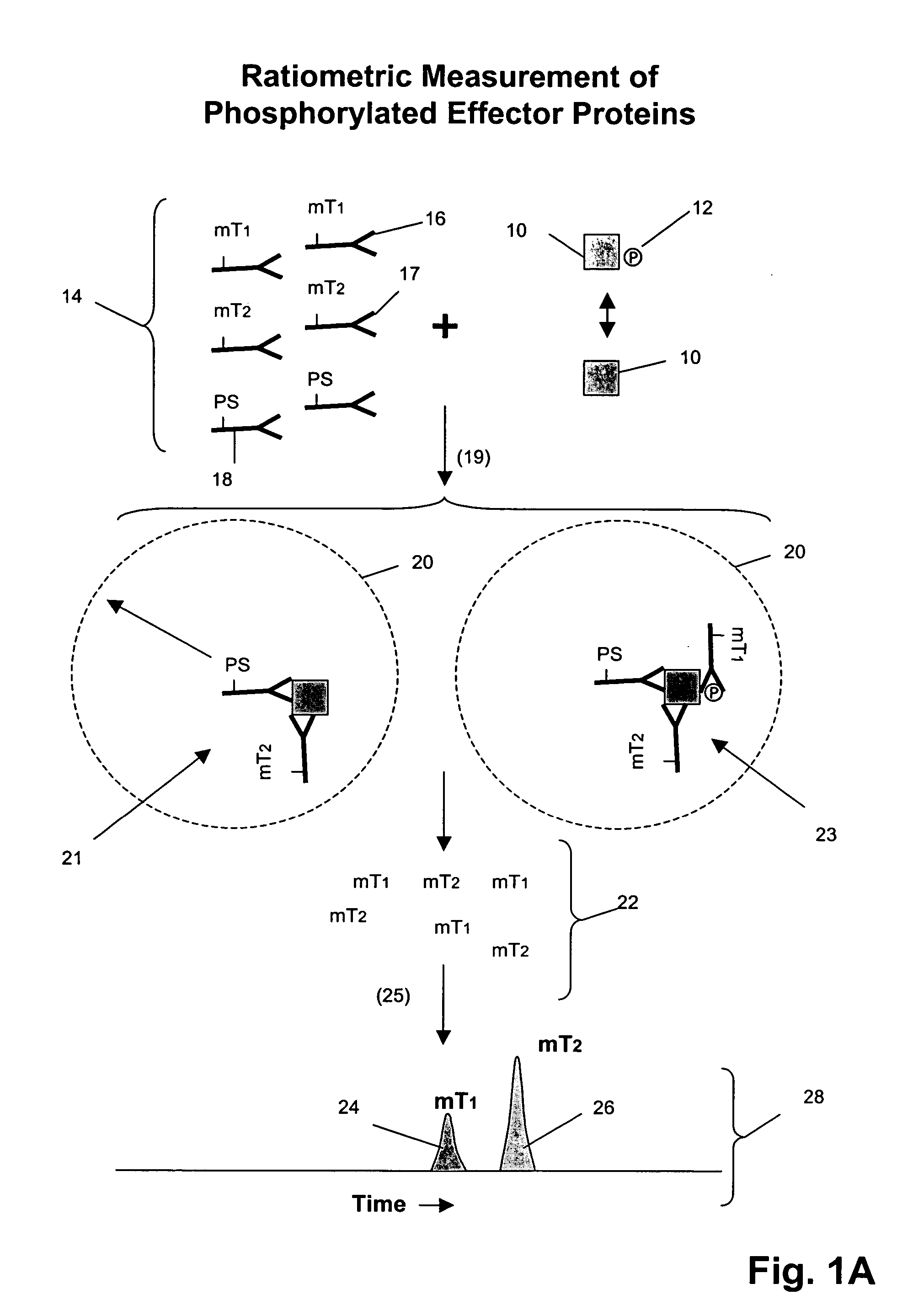
Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathway analysis for diagnosis and therapy
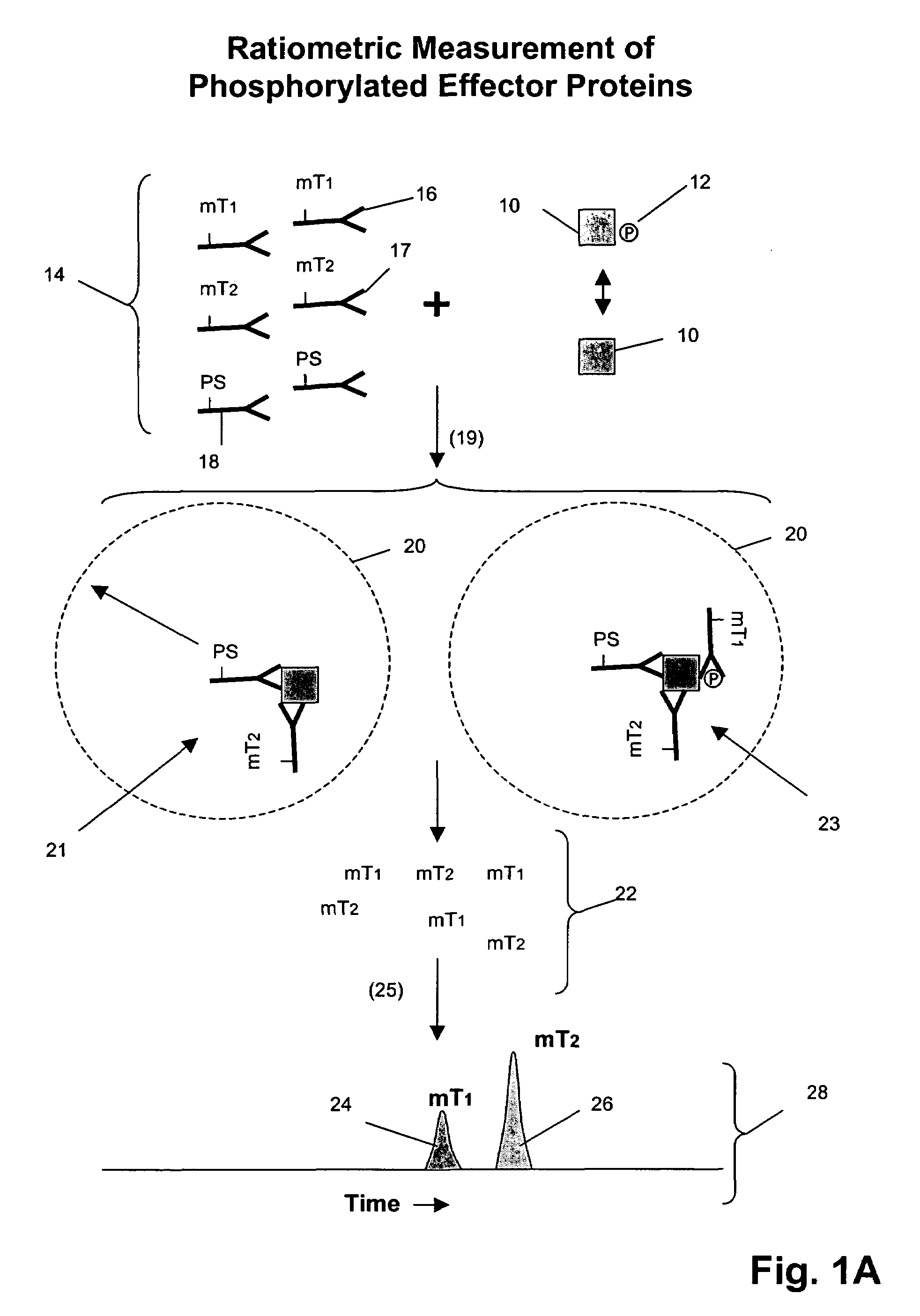
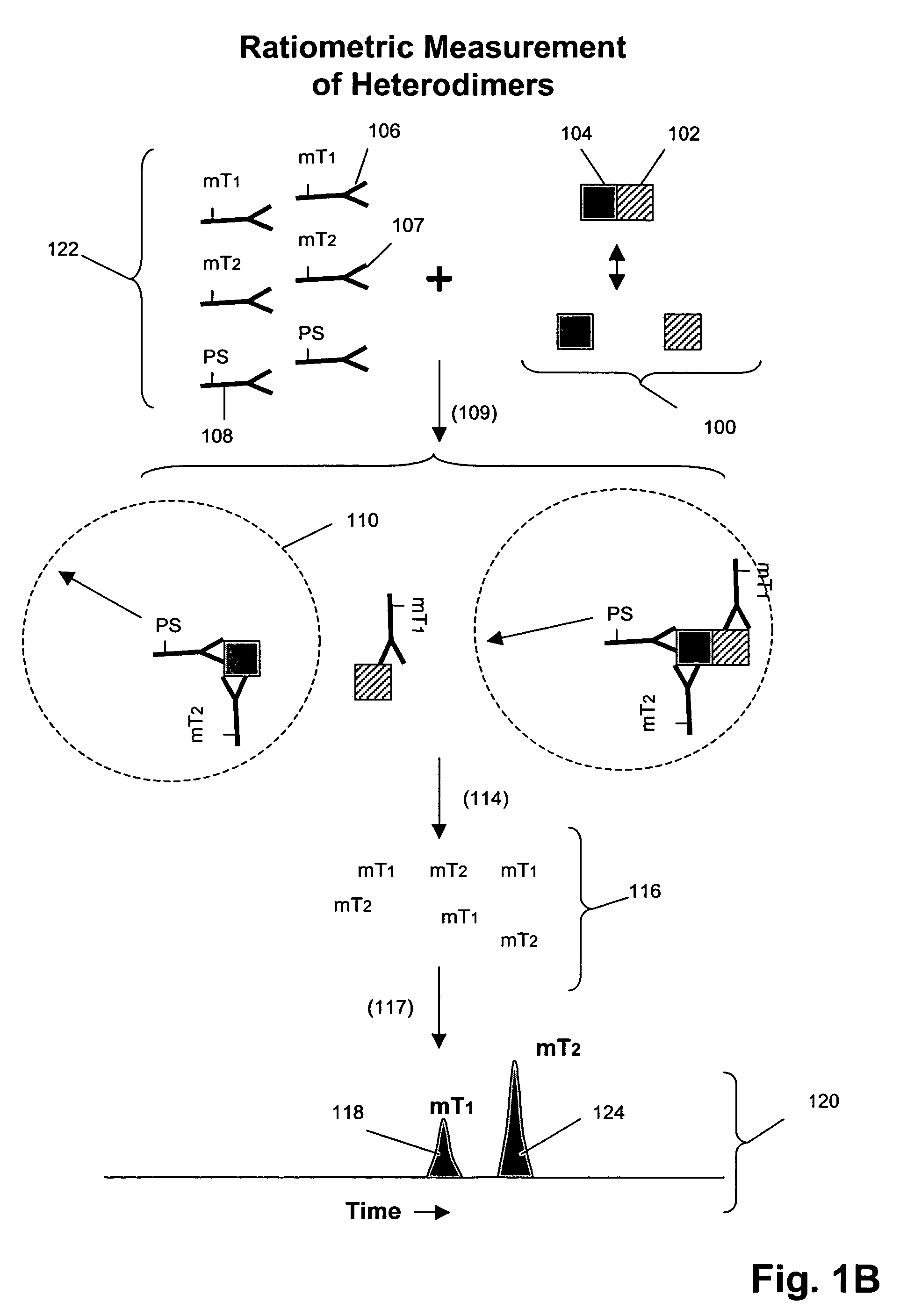
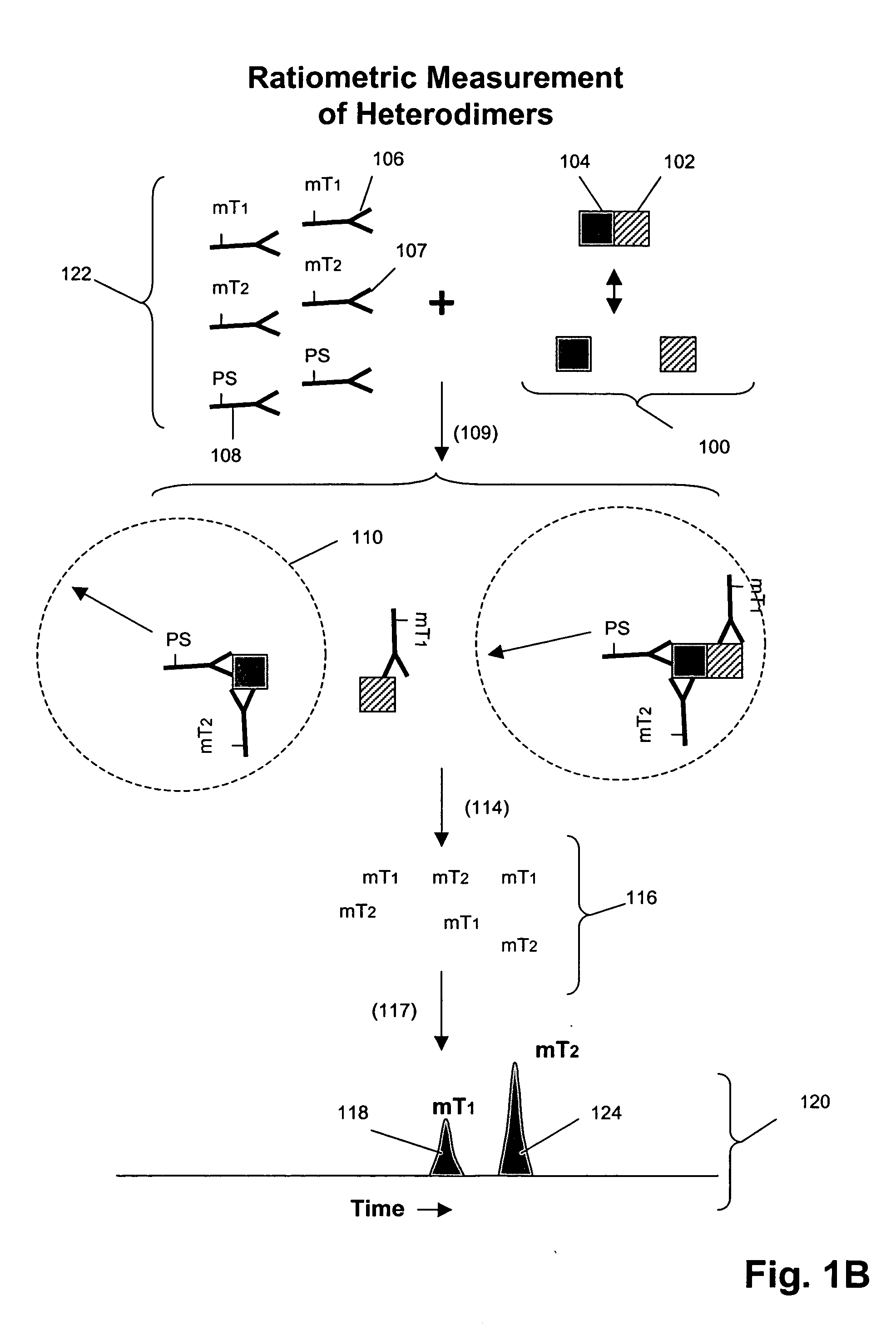
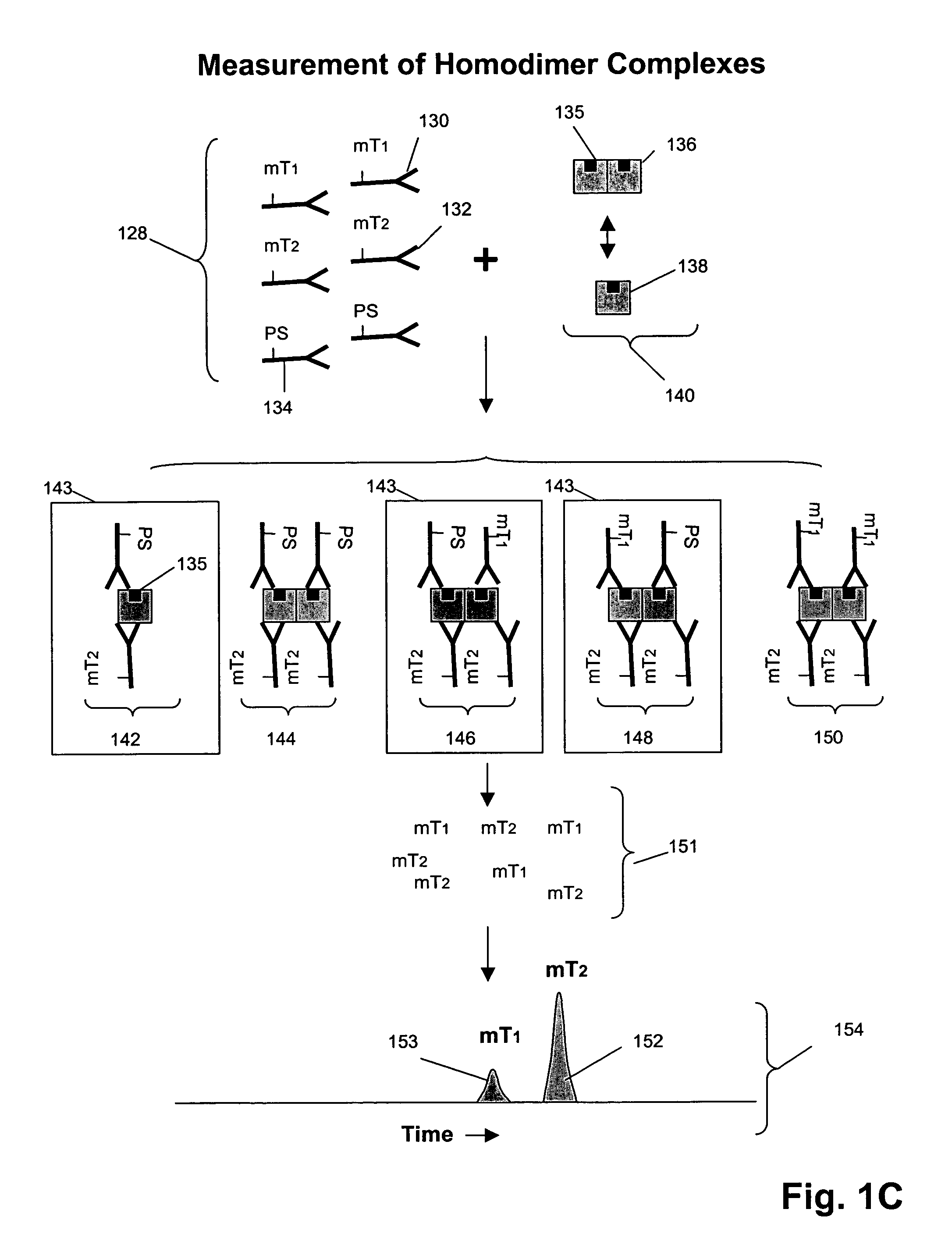
The invention provides a method for determining the activation status of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) pathways in either cell samples or patient samples by measuring receptor dimerization and relative amounts of protein-protein complexes or activated effector proteins that are characteristic of an RTK pathway. The invention also provides a method of using such status information to select patients responsive to pathway-specific drugs, and more particularly, to methods for measuring ErbB receptors and receptor complexes and using such information to select patients responsive to ErbB pathway-specific drugs. Preferably, methods of the invention are implemented by using sets of binding compounds having releasable molecular tags that are specific for multiple components of one or more complexes formed in RTK activation. After binding, molecular tags are released and separated from the assay mixture for analysis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Assembly and screening of highly complex and fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6610472B1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleotide
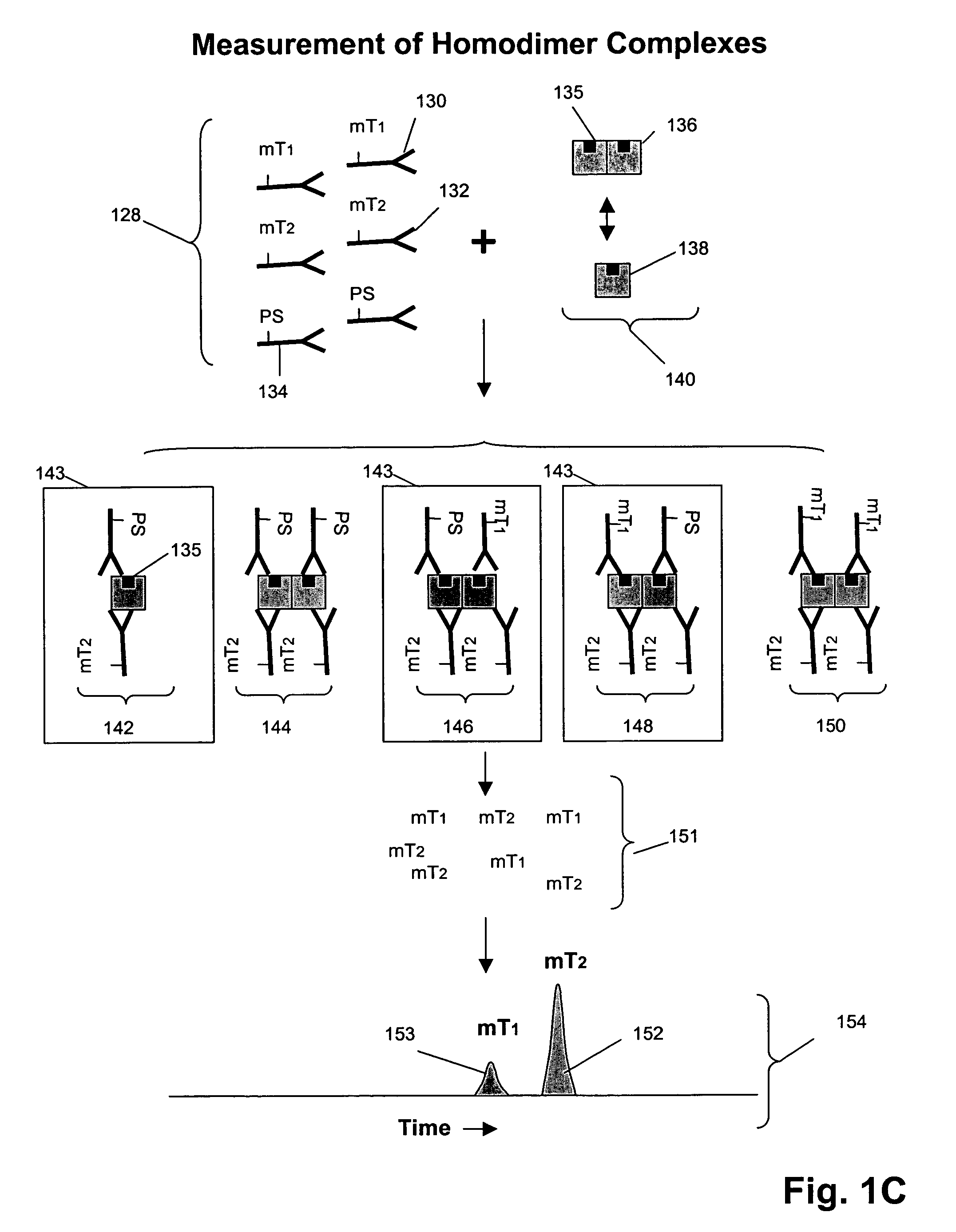
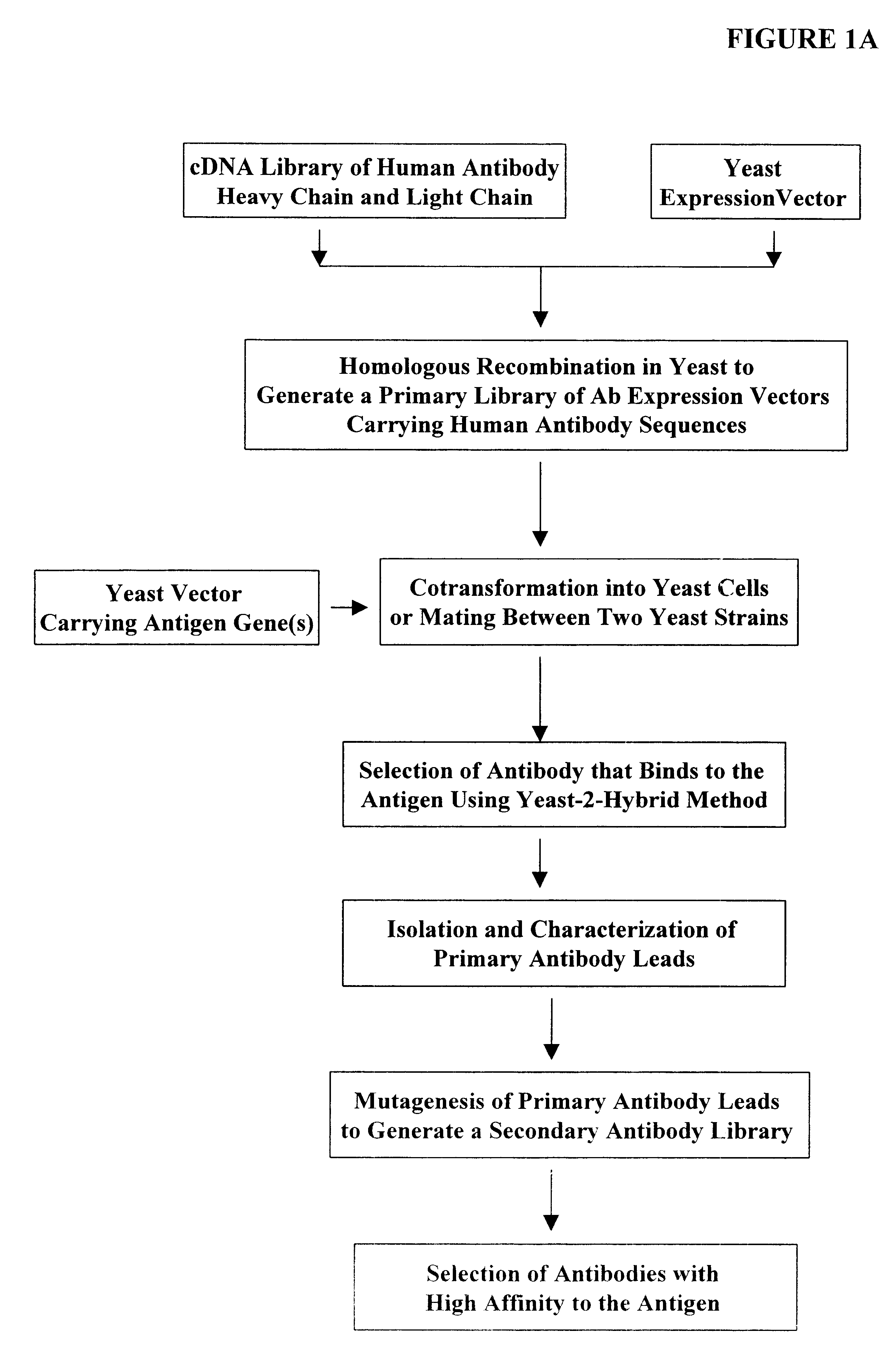
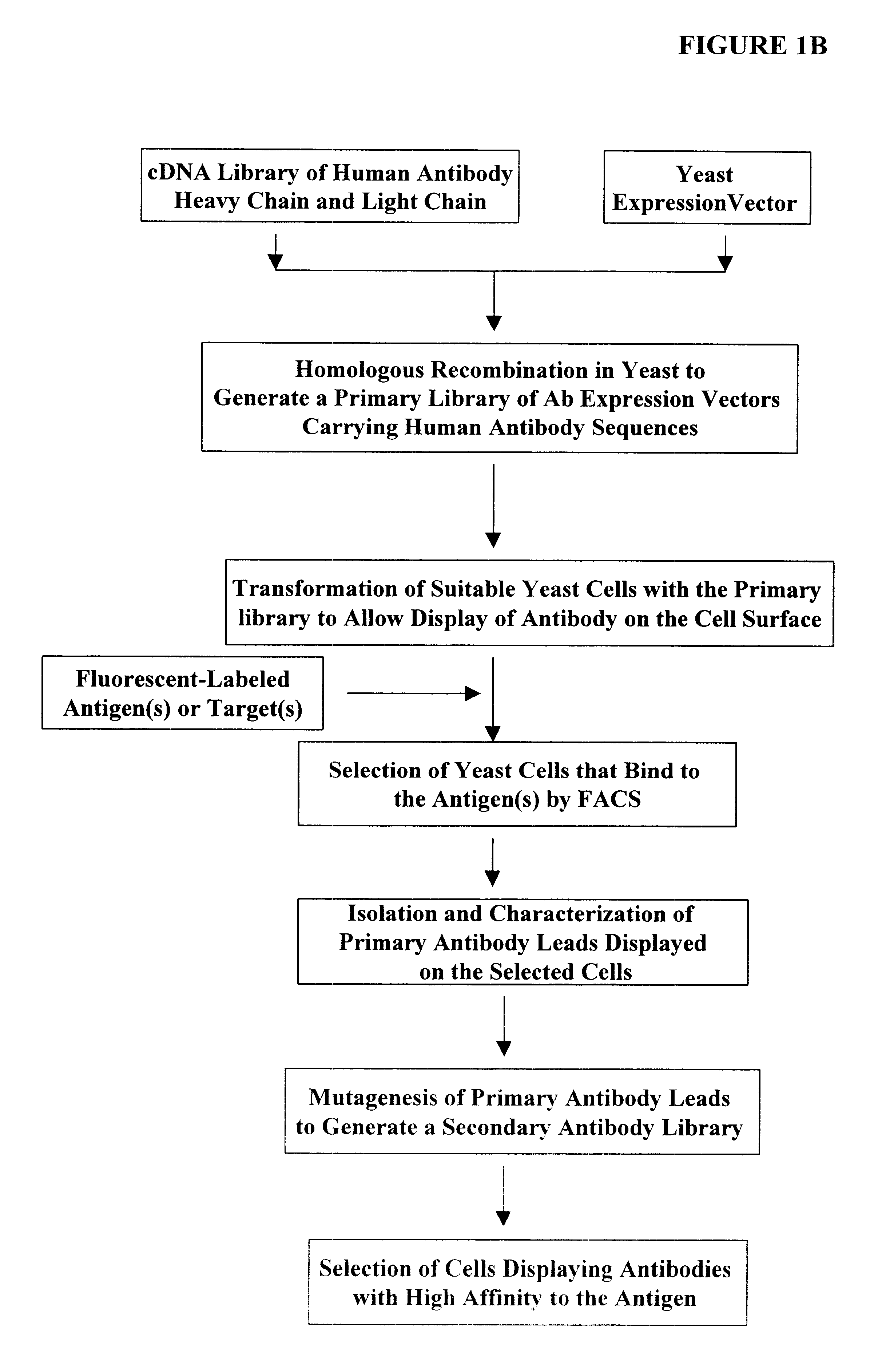
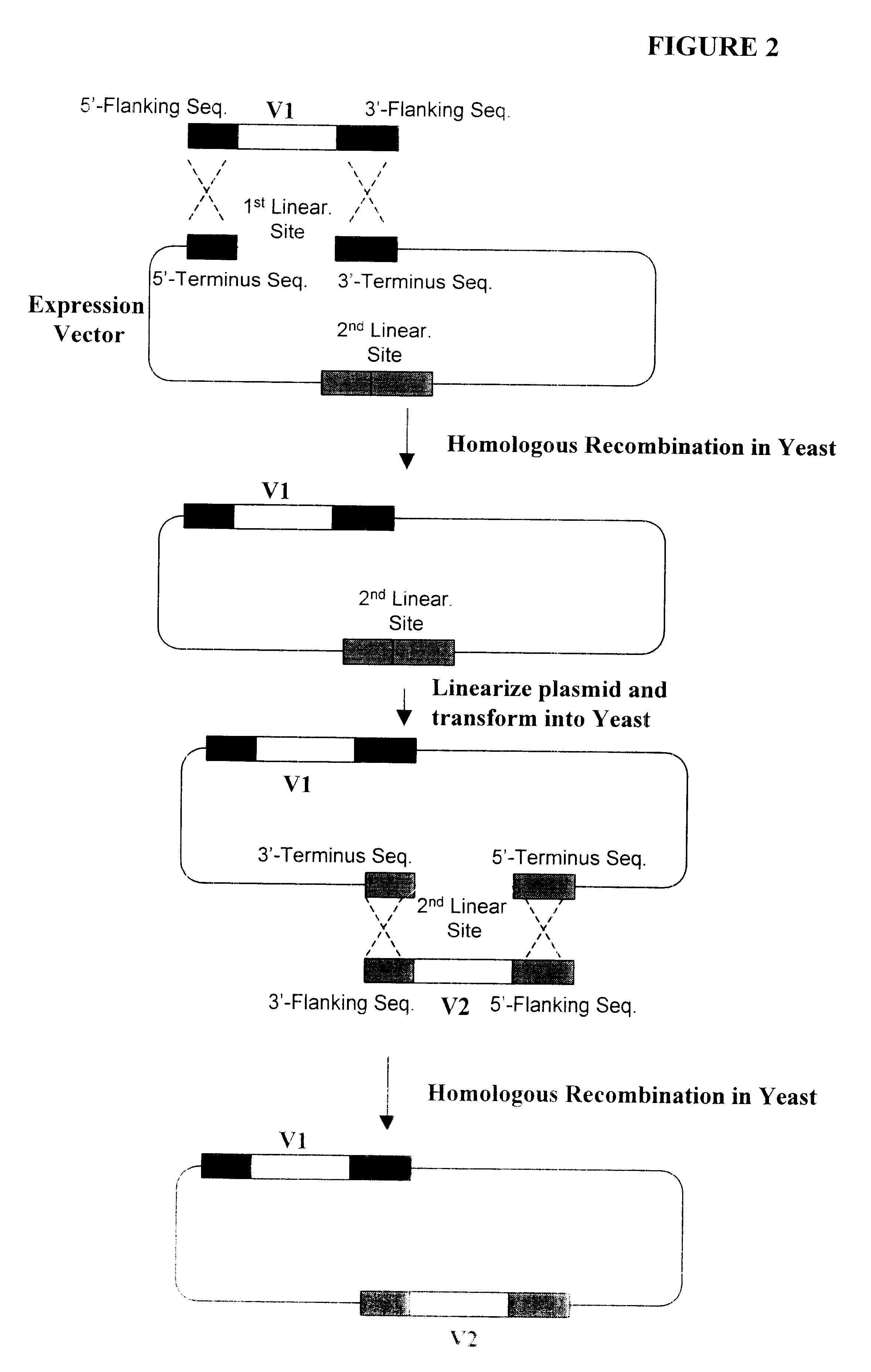
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening a library of highly diverse protein complexes for their ability to bind to other proteins or oligonucleotide sequences. In one aspect of the invention, a library of expression vectors is provided for expressing the library of protein complexes. The library comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit; and a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit. The first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors. In addition, the first and second polypeptide subunit are expressed as separate proteins which self-assemble to form a protein complex, such as a double-chain antibody fragment (dcFv or Fab) and a fully assembled antibody, in cells into which the library of expression vectors are introduced. The library of expression vectors can be efficiently generated in yeast cells through homologous recombination; and the encoded proteins complexes with high binding affinity to their target molecule can be selected by high throughput screening in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
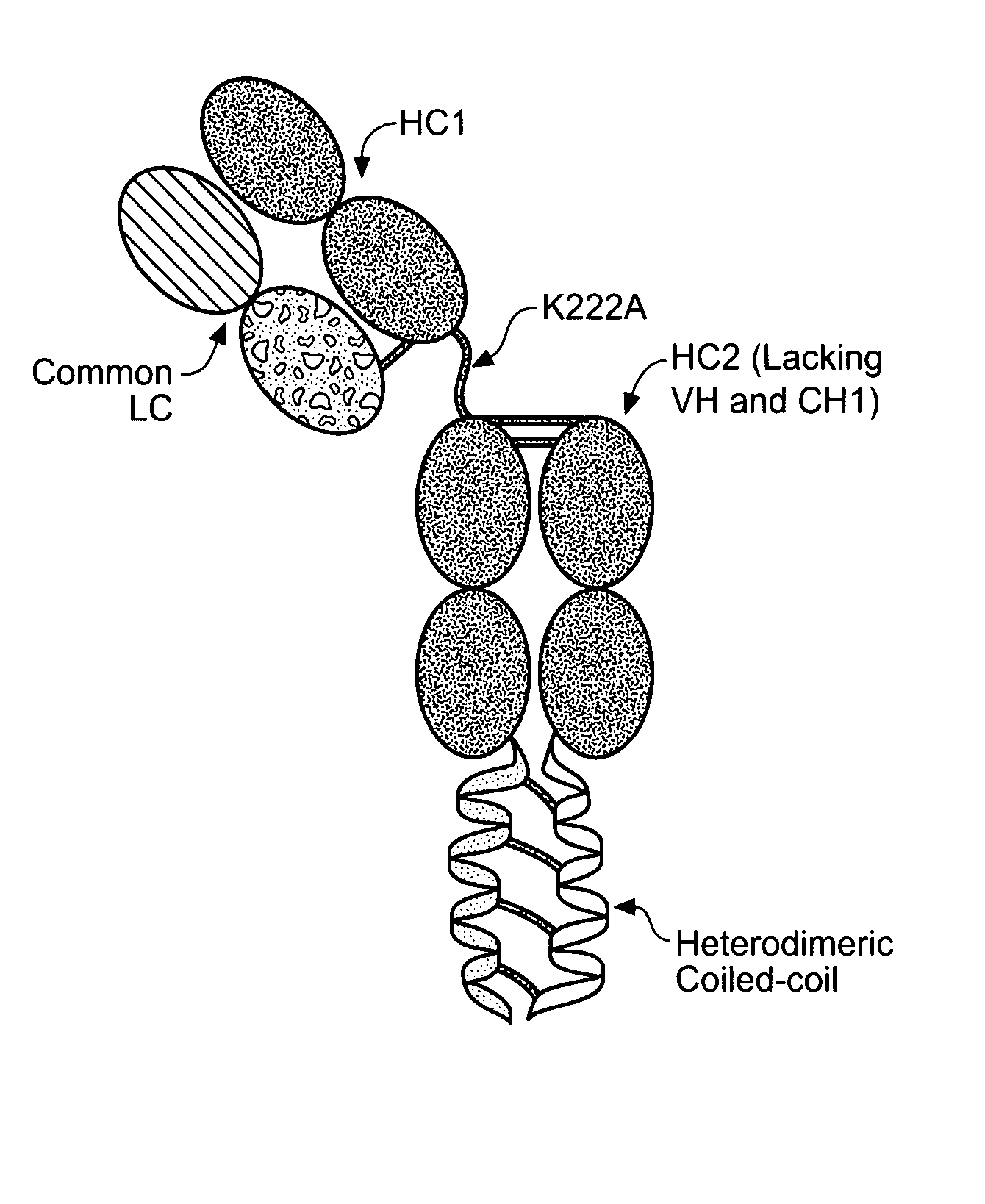
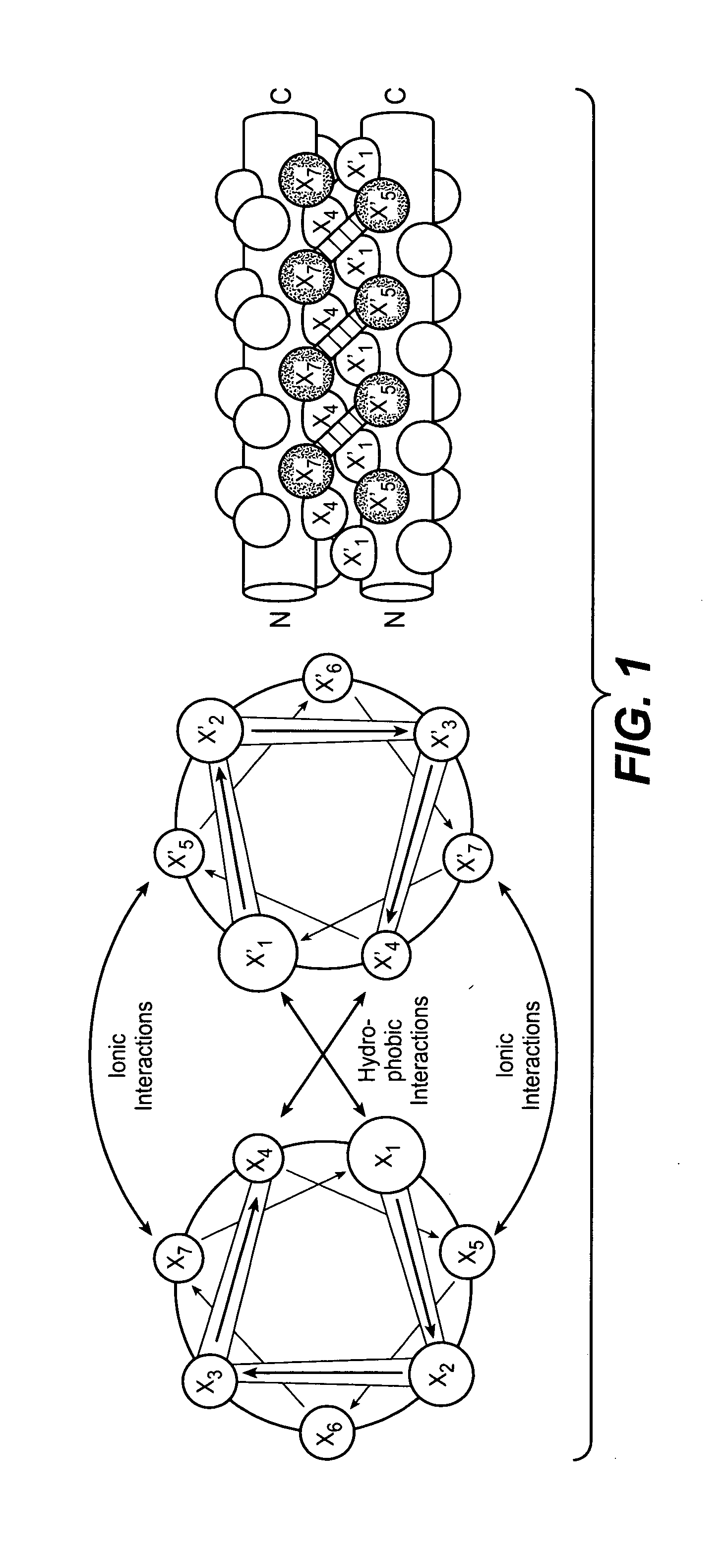
Coiled coil and/or tether containing protein complexes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120302737A1Simple structureSimple and efficient and high yieldHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesEngineering
The invention provides engineered protein complexes constructed using a coiled coil and / or a tether and methods for making, using, and purifying such complexes, such as multispecific antibodies or other multispecific Fc containing complexes.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathway analysis for diagnosis and therapy
ActiveUS20050131006A1BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPathway analysisProtein-protein complex
The invention provides a method for determining the activation status of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) pathways in either cell samples or patient samples by measuring receptor dimerization and relative amounts of protein-protein complexes or activated effector proteins that are characteristic of an RTK pathway. The invention also provides a method of using such status information to select patients responsive to pathway-specific drugs, and more particularly, to methods for measuring ErbB receptors and receptor complexes and using such information to select patients responsive to ErbB pathway-specific drugs. Preferably, methods of the invention are implemented by using sets of binding compounds having releasable molecular tags that are specific for multiple components of one or more complexes formed in RTK activation. After binding, molecular tags are released and separated from the assay mixture for analysis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Alleviation of non-specific binding in microarray assays
InactiveUS7258990B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysosomeSolid particle
A post-incubation treatment is employed to effectively remove targets, such as proteins / protein complexes, or other label-bearing moieties that may non-specifically bind to a microarray substrate during a binding assay. Following incubation, a one-step wash is carried out with a liquid containing digester, e.g., a digestive enzyme (protease) or lysosome, which is effective to remove non-specifically bound targets or at least labeled portions of such targets from the substrate. Proteases are bound to or coated onto large molecules or onto solid particles of such a size such that they are prohibited from entering the porous surfaces of 3-D hydrogel microspots and are unable to reach and digest labeled target-probe complexes that are disposed within such porous hydrogel microspots. Digested segments of such protein which contain labels (or of essentially the entire protein) are carried away in the wash liquid and thus are not present to create background noise during imaging.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
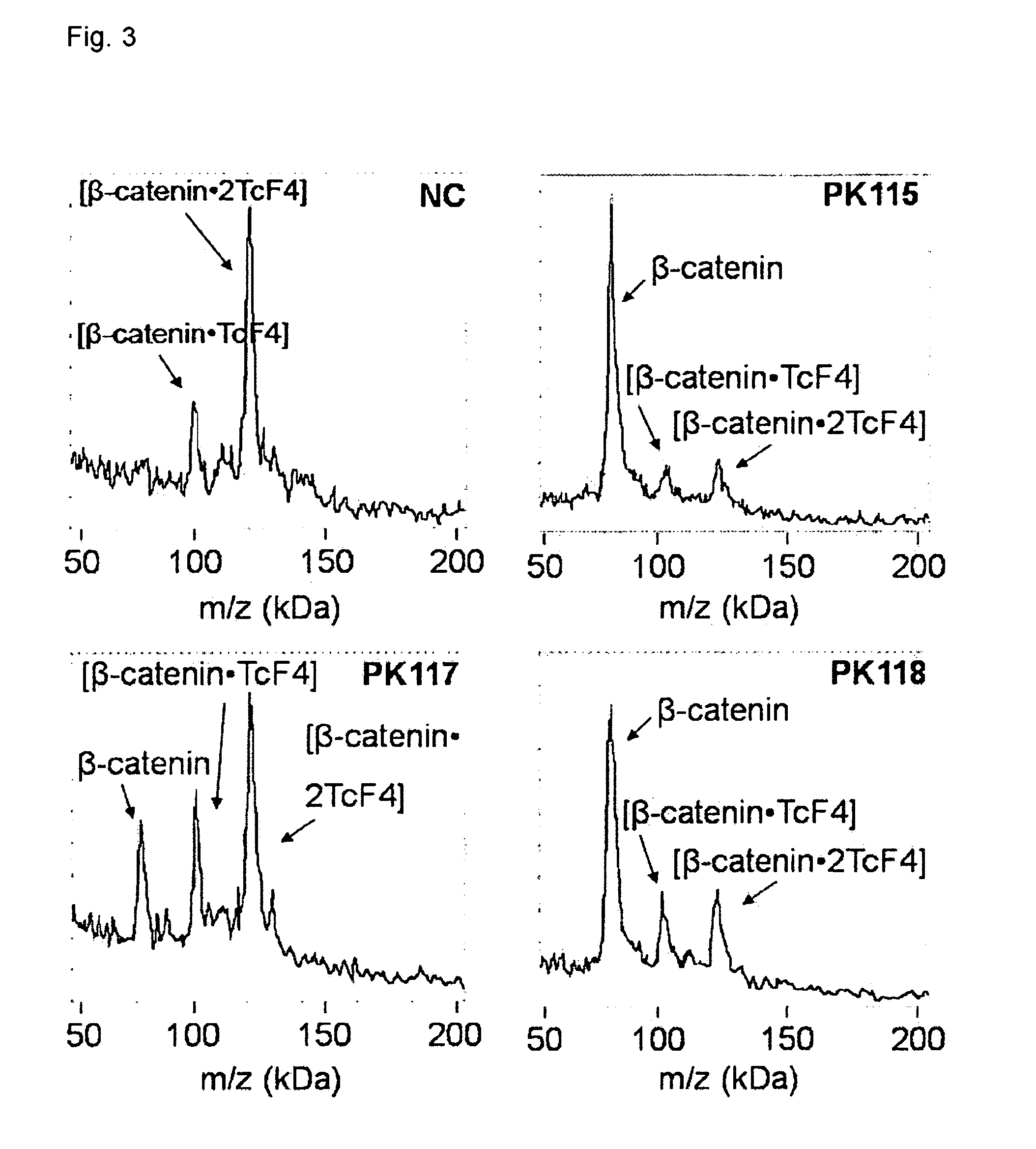
Direct mass spectrometric analysis of drug candidates targeting protein complexes
ActiveUS20100099200A1Improve throughputEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein targetProtein-protein complex
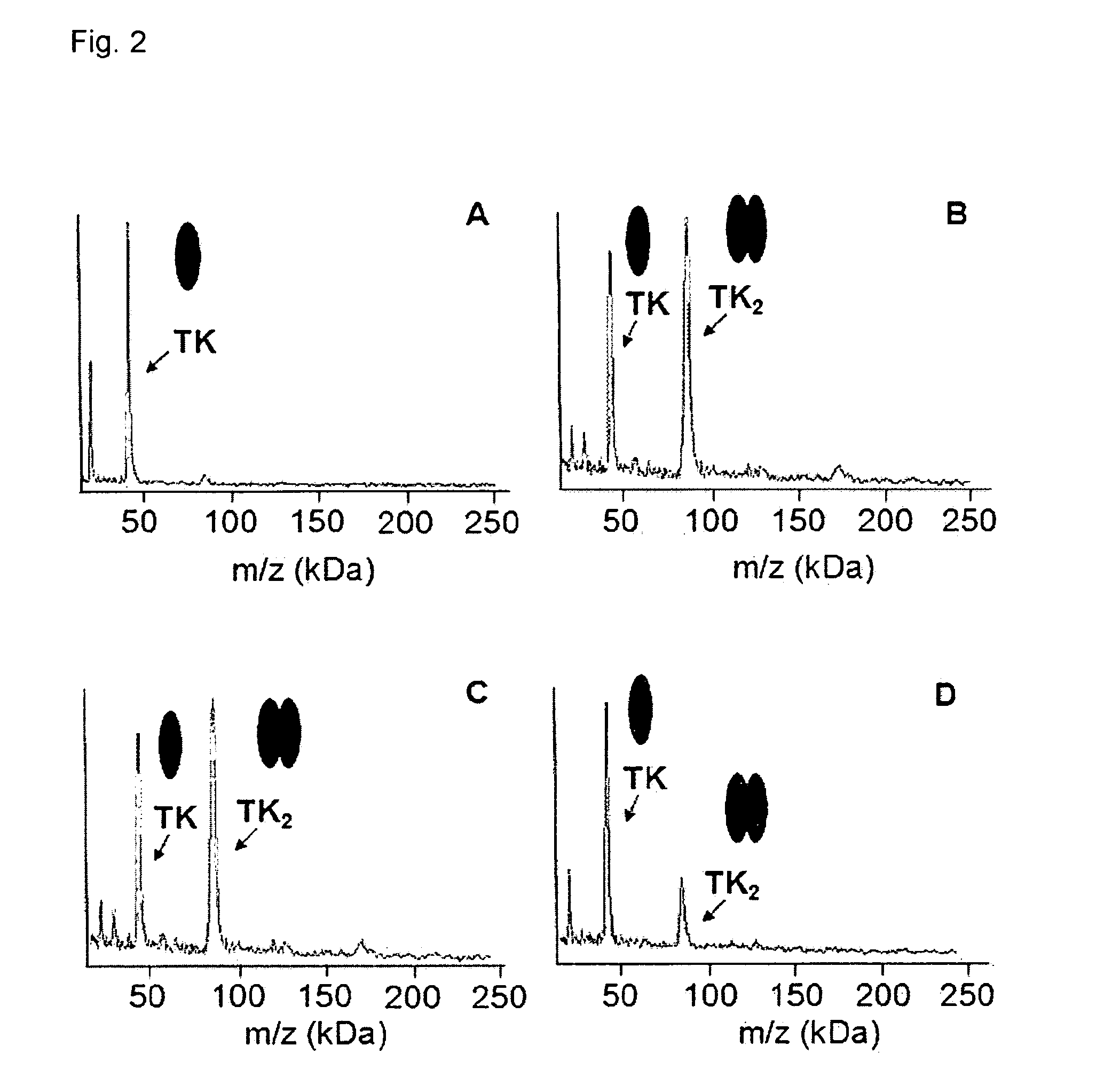
The invention relates to a method of using high mass matrix assisted laser desorption-ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the effect of drug candidates on protein complexes such as protein-protein interactions in purified samples or complex biological matrices, as well as to the use of this method for lead compound optimization, drug characterization, drug manufacturing processes, and drug quality control processes, including automated high throughput applications.
Owner:COVALX
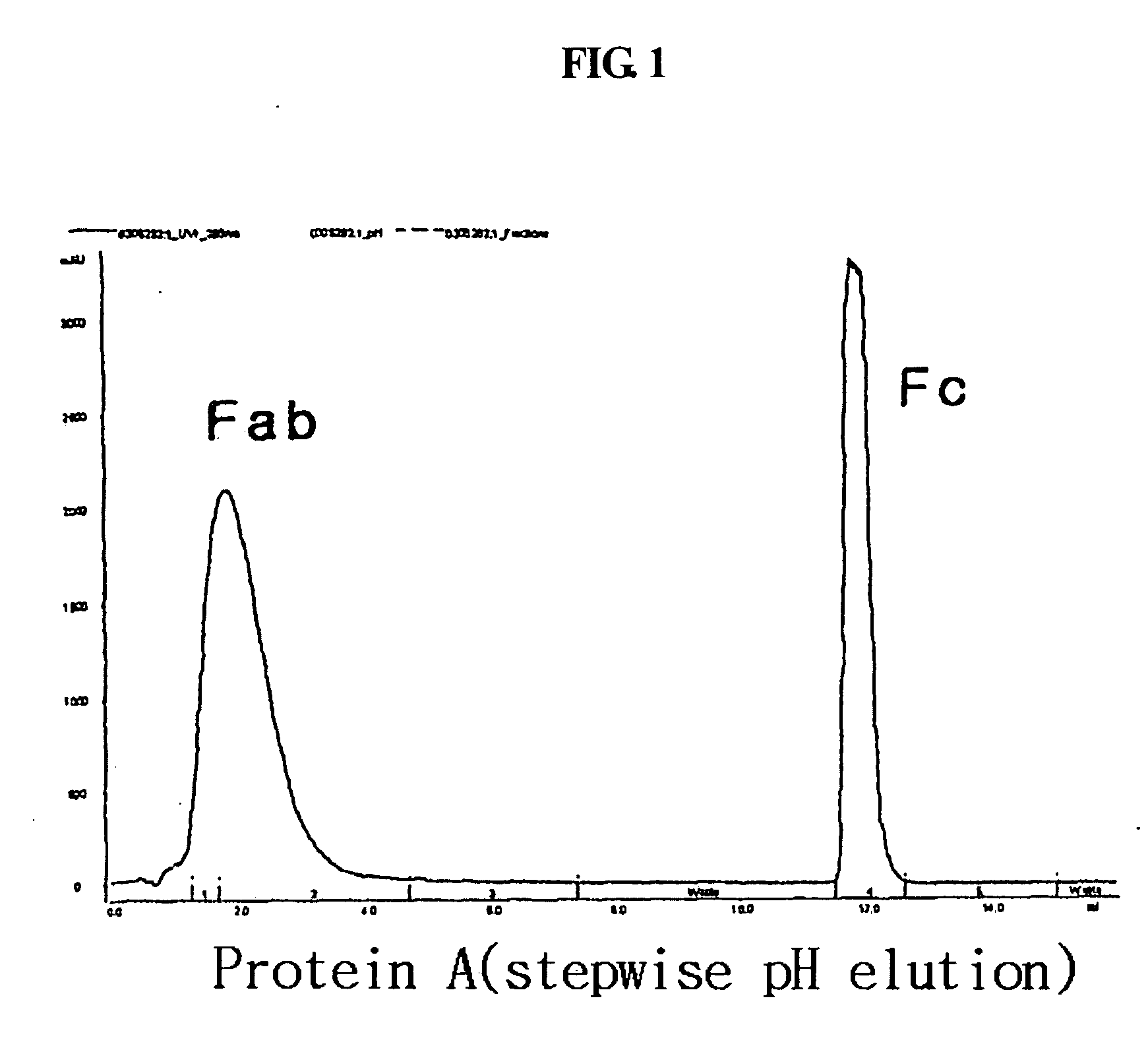
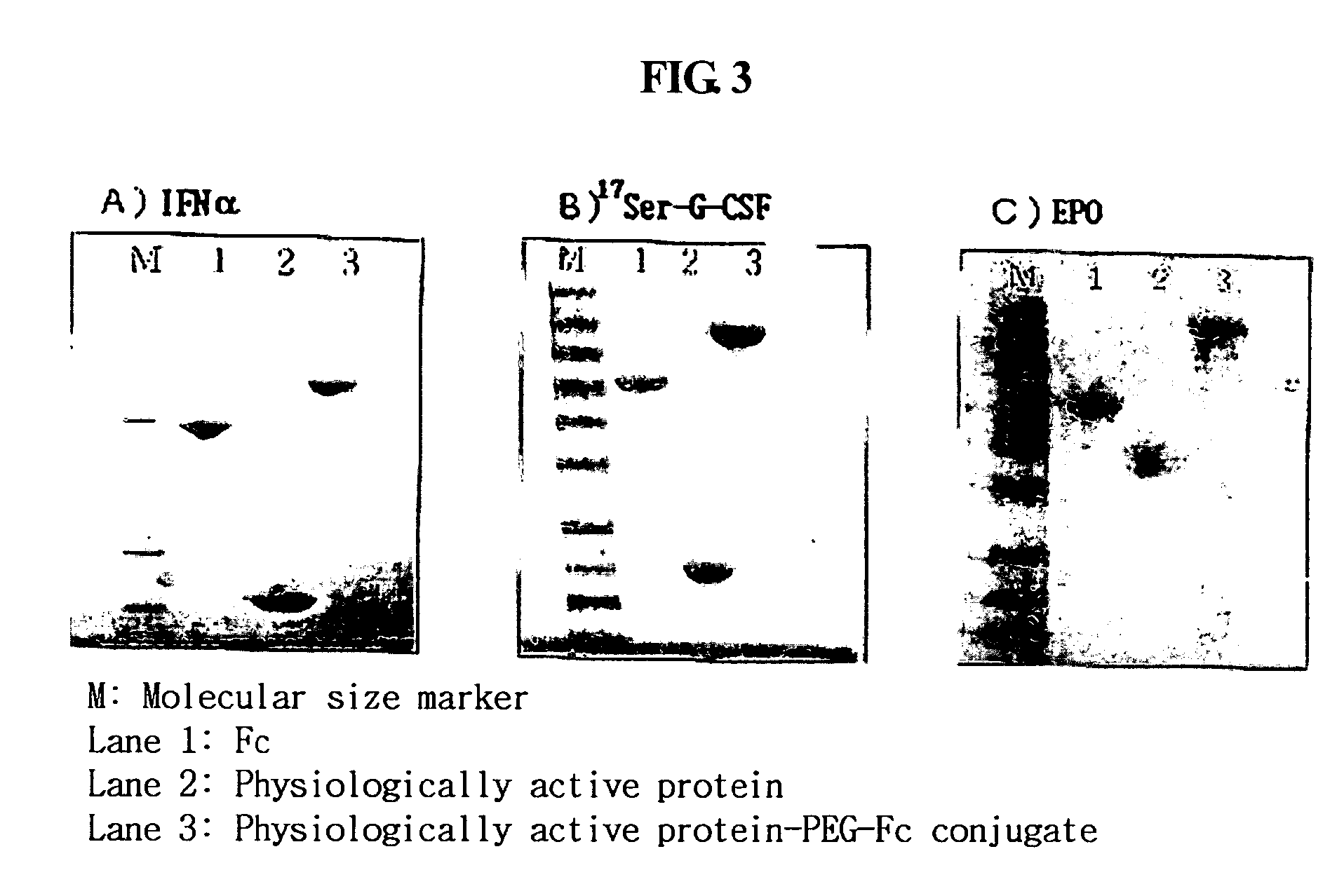
Protein complex using an immunoglobulin fragment and method for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20060269553A1Improve stabilityExtended durationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunological disordersHalf-lifeImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
Disclosed are a protein conjugate with improved in vivo duration and stability and the use thereof. The protein conjugate includes a physiologically active polypeptide, a non-peptide polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc fragment. Since the three components are covalently linked, the protein conjugate has extended in vivo duration and enhanced stability for the physiologically active polypeptide. The protein conjugate maintains the in vivo activity at relatively high levels and remarkably increases the serum half-life for the physiologically active polypeptide, with less risk of inducing undesirable immune responses. Thus, the protein conjugate is useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Glucose sensor and glucose level measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20060258959A1Advantageously in term of costCost advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementGlucose dehydrogenase activityGlucose sensors
The present invention relates to a glucose sensor (2) including an electrode (32) which includes a conductive component and glucose dehydrogenase immobilized to the conductive component. As the glucose dehydrogenase, use is made of a protein complex including a catalytic activity subunit which has glucose dehydrogenase activity, and an electron mediator subunit for supplying an electron donated from the catalytic activity subunit to the conductive component. Preferably, the glucose sensor (2) is designed to continuously measure the glucose level or successively measure the glucose level a plurality of times.
Owner:SODE
Compositions and methods for treating inflammatory disorders
InactiveUS20050112118A1Preventing and ameliorating diseaseEfficient modulationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsAssayProtein-protein complex
Protein complexes are provided comprising at least one interacting pair of proteins. The protein complexes are useful in screening assays for identifying compounds effective in modulating the protein complexes, and in treating and / or preventing diseases and disorders associated with the protein complexes and / or their constituent interacting members.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
Crystal structure of aurora-2 protein and binding pockets thereof
The present invention provides crystalline molecules or molecular complexes which comprise binding pockets of Aurora-2 or its homologues. The invention also provides crystals comprising Aurora-2. The present invention also relates to a computer comprising a data storage medium encoded with the structural coordinates of Aurora-2 binding pockets and methods of using a computer to evaluate the ability of a compound to bind to the molecule or molecular complex. This invention also provides methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure of homologous proteins or protein complexes. In addition, this invention provides methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for and design compounds, including inhibitory compounds, that bind to Aurora-2 or homologues thereof.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Pharmacological agent and method of treatment
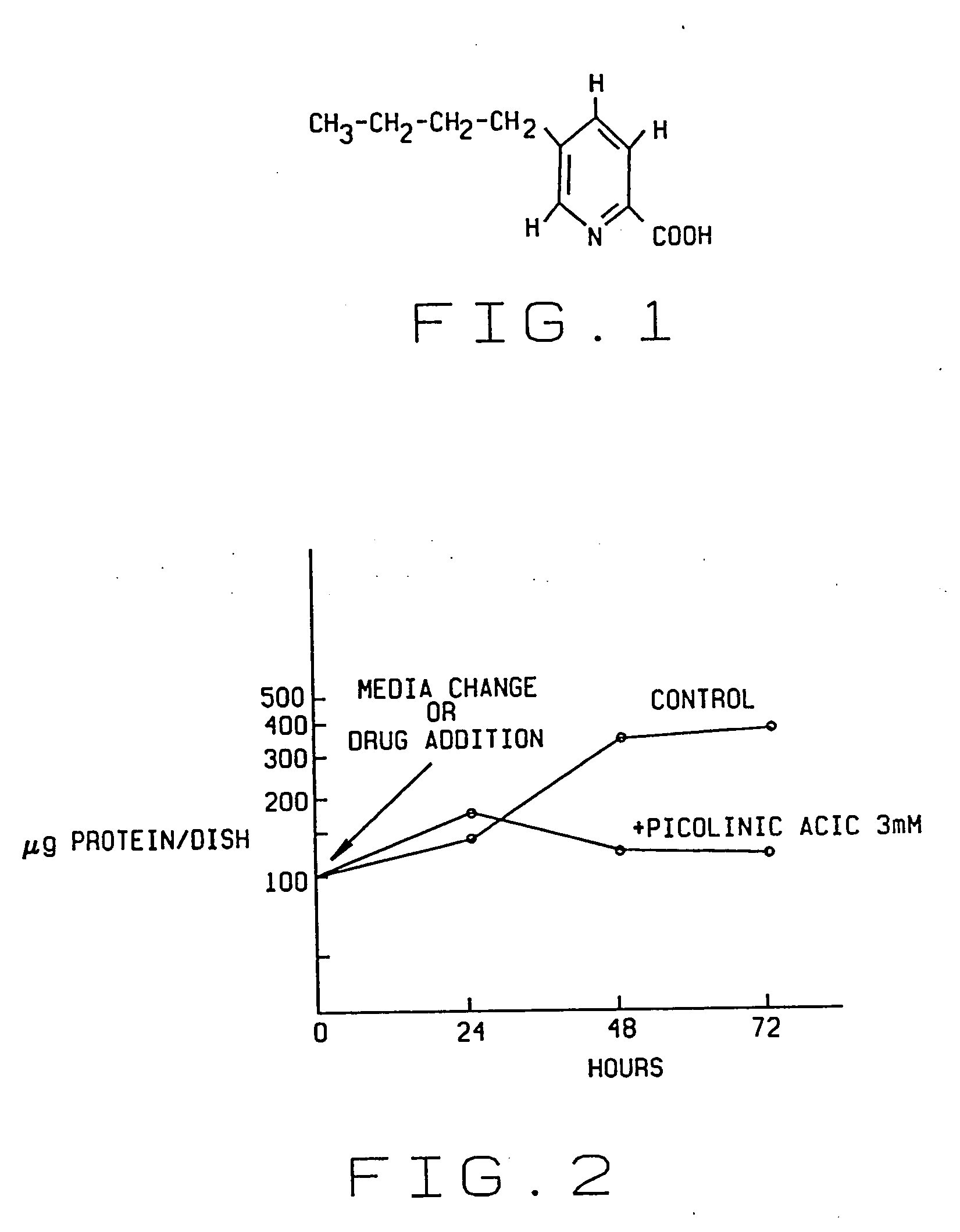
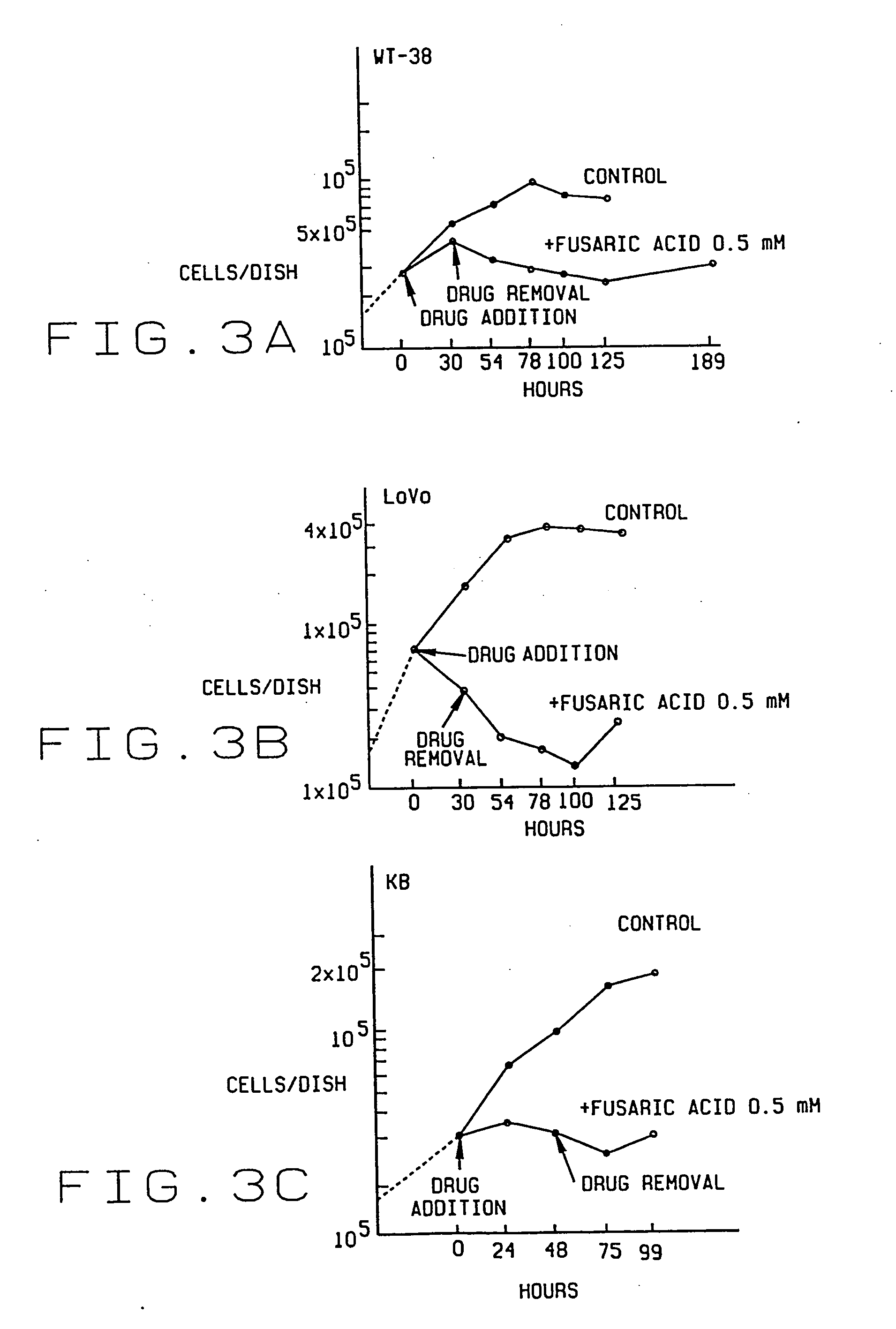
InactiveUS20060074063A1Eliminate effectiveEliminate energyBiocideGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsWhole bodyVirus warts
An antiproliferative, antiinflammatory, antiinfective, immunization agent of a metal ion chelating agent such as picolinic acid, analogs or derivatives thereof, and methods of using the same. The agents chelate metals in metal containing protein complexes and enzymes required for growth, replication or inflammatory response. The preparations can be administered systemically or topically. The products can be used to reduce systemic levels of metals in disease states such as Wilson's disease, iron or lead toxicity. The preparations have antineoplastic, antiviral, antiinflammatory, analgesic antiangiogenic and antiproliferative effects and are used in the treatment of warts, psoriasis, acne, cancers, sunburn, inflammatory responses, untoward angiogenesis and other diseases and in the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases such as genital warts, herpes and AIDS.
Owner:NOVACTYL
Methods and compositions for high throughput identification of protein/nucleic acid binding pairs
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Mutant proteins, high potency inhibitory antibodies and fimch crystal structure
InactiveUS20030199071A1Great functional inhibitory activityStrong inhibitory activityHydrolasesImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPassive ImmunizationsMutated protein
The present invention provides bacterial immunogenic agents for administration to humans and non-human animals to stimulate an immune response. It particularly relates to the vaccination of mammalian species, especially human patients, with variants of the E. coli FimCH protein that elicit antibodies that have better functional inhibitory activity than antibodies raised against wild type protein. In particular, such variants include mutations that promote a more open confirmation of the FimH protein, particularly in regions involved in mannose binding, to expose regions previously poorly exposed and mutations that abolish a significantly reduce mannose binding. In another aspect, the invention provides antibodies against such proteins and protein complexes that may be used in passive immunization to protect or treat pathogenic bacterial infections. The present invention also provides machine readable media embedded with the three-dimensional atomic structure coordinates of FimCH bound to mannose, and subsets thereof, and methods of using the crystal structure to provide candidate amino acid residues for mutation.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
Aptamer-Guided Gene Targeting
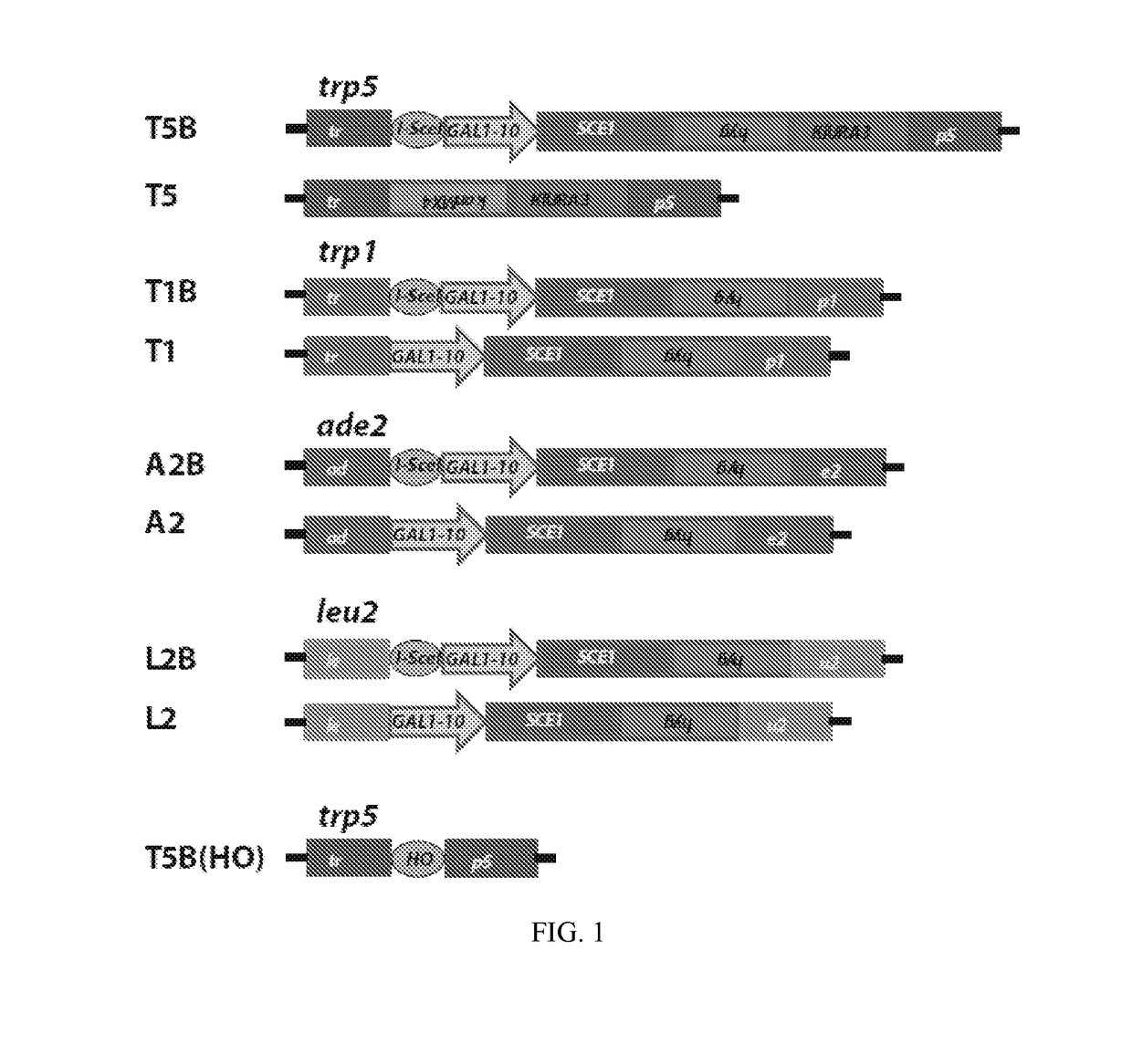
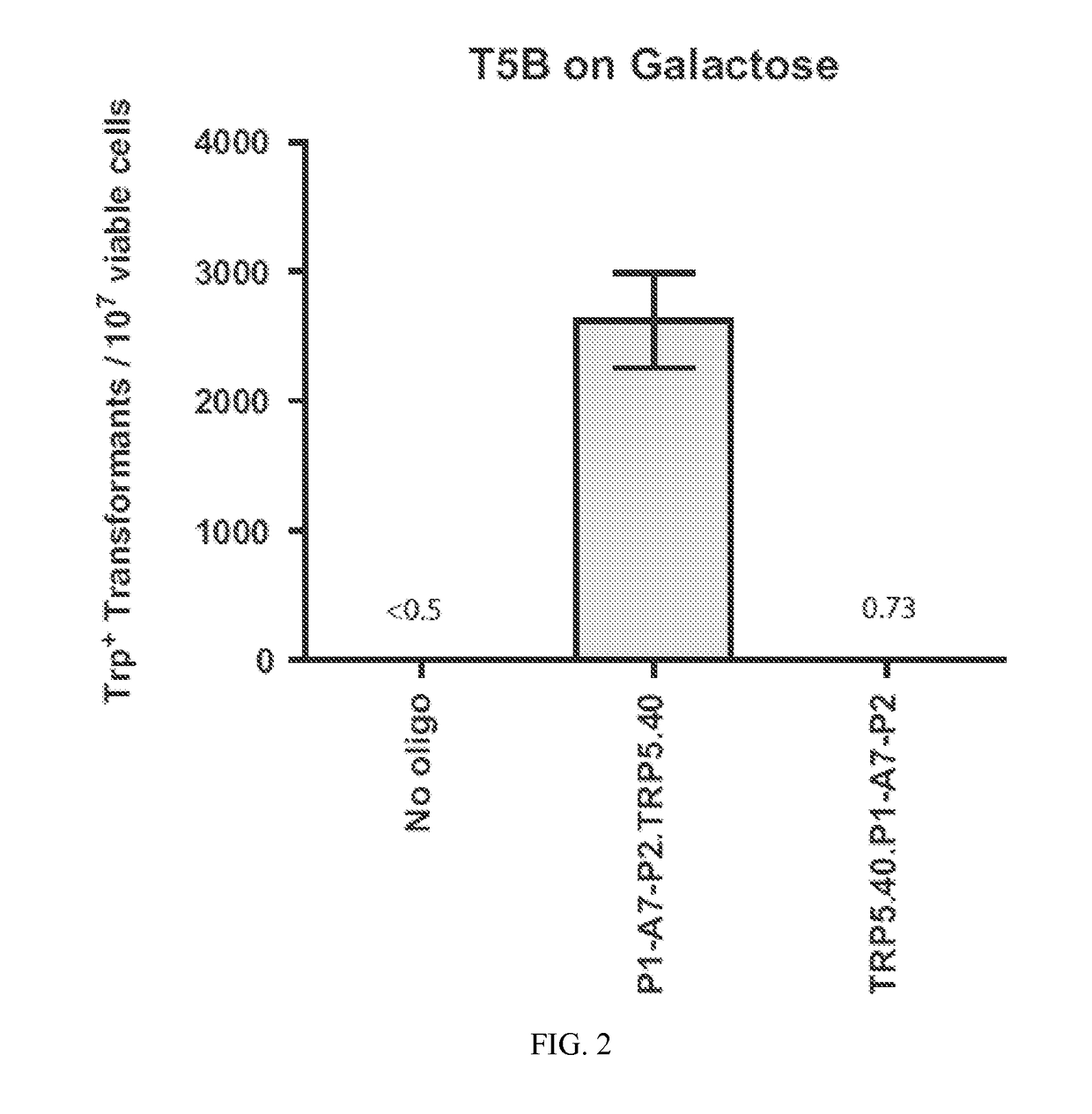
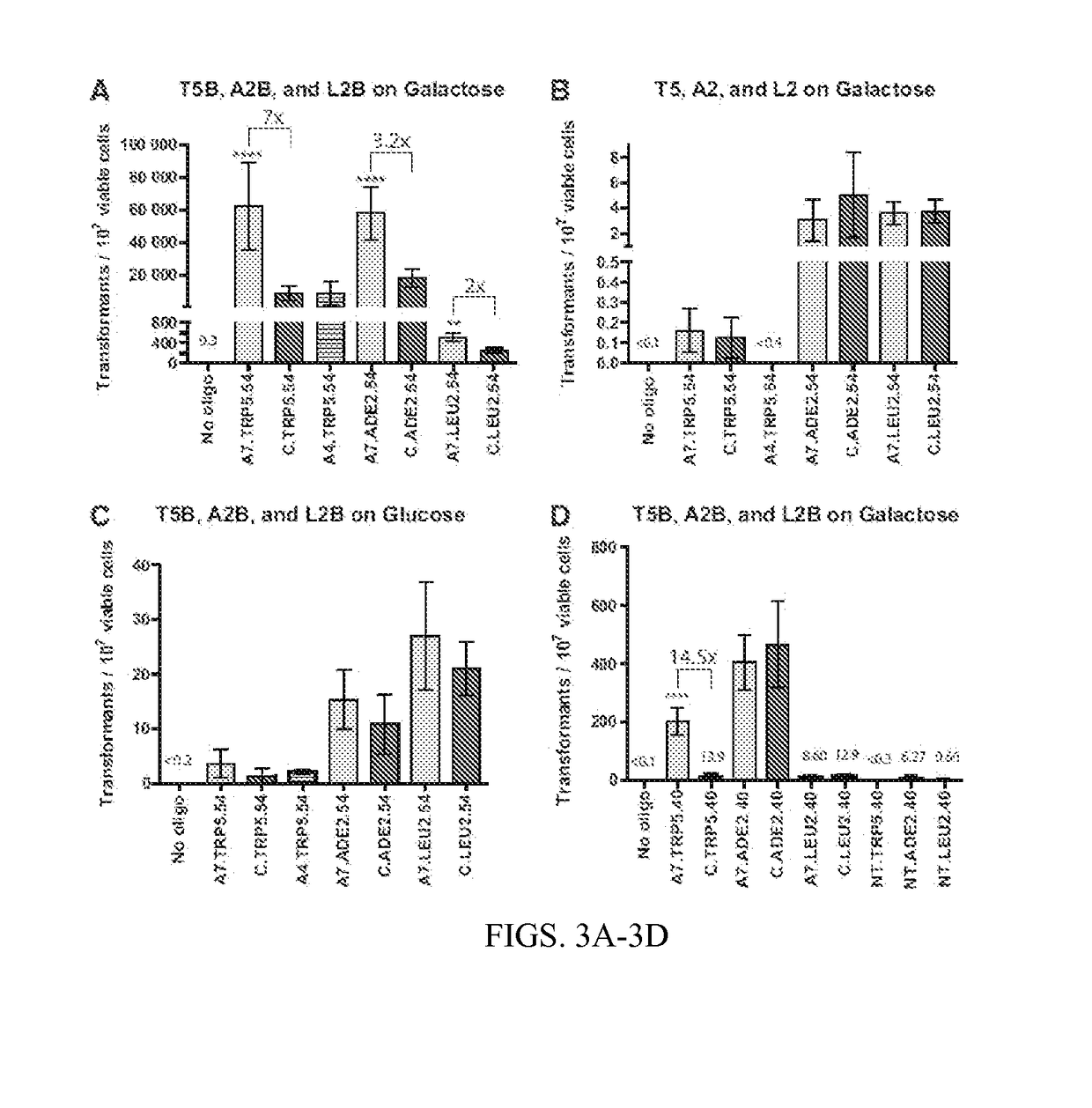
Compositions and methods for modifying genetic material are provided. One embodiment provides aptamers capable of binding to a site-specific DNA binding moiety to facilitate the exchange of homologous genetic information between a donor molecule and the desired target locus (aptamer-guided gene targeting or AGT). One embodiment provides an oligonucleotide containing a aptamer, preferably a DNA aptamer at the 5′ end. The oligonucleotide also contains a region of homology, also referred to as donor DNA, to a desired nucleic acid, locus, or gene. The DNA binding moiety can be a nucleic acid, a protein, or a complex of proteins. In a preferred embodiment the DNA binding moiety is a homing endonuclease that cuts DNA to facilitate the modification of the DNA by the donor DNA.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Kit for in vitro synthesis of protein and preparation method
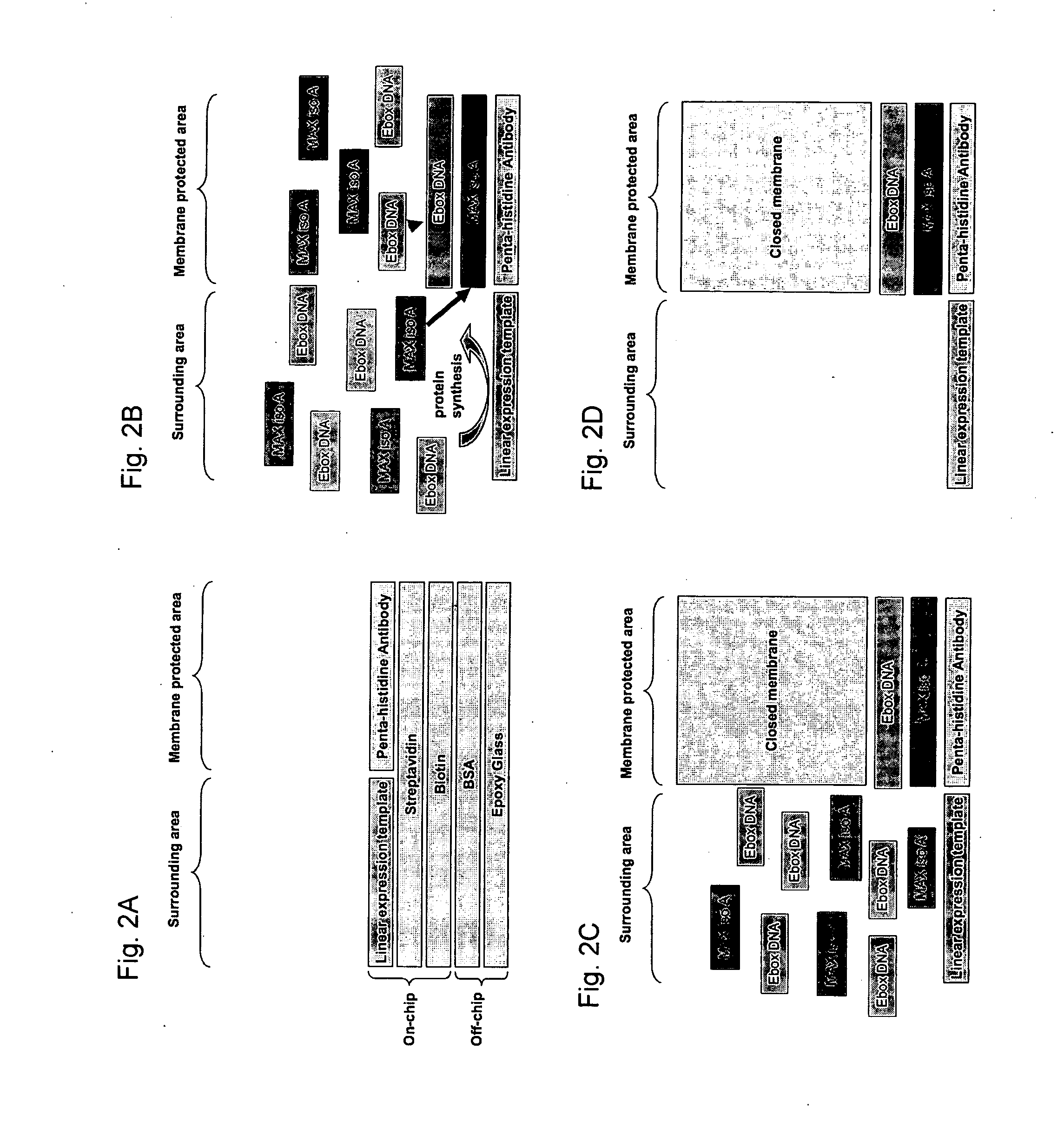
ActiveCN106978349ALow costEasy to operateMicroorganism lysisMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention provides a preparation method of a yeast cell extracting solution, the yeast cell extracting solution and a method for synthesizing protein in an in vitro system by virtue of the yeast cell extracting solution, as well as a kit containing the yeast cell extracting solution. The kit, which is more convenient than a conventional method, is applicable to protein synthesis in the in vitro system; transformation, culture and crushing can be prevented; a great amount of using time and cost can be saved; various types of proteins can be expressed, and influence of protein toxicity can be prevented; and a plurality of protein complexes can be expressed, without the use of a high temperature at 37 DEG C. In addition, as a raw material adopted by the invention, yeast cell is simple to cultivate, convenient to operate, rapid to propagate and relatively low in cost; a prepared yeast extract has a capacity of modifying translated protein, the yeast extract is suitable for large-scale preparation and has an advantage of industrial production; and the yeast cell extract, which is prepared into freeze-dried powder by virtue of a vacuum freeze-drying method and is preserved at low temperature or high temperature, is convenient to transport.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Multiple cytokine protein complexes
InactiveUS7141651B2Maintains balance of activityIncreases duration of activityOrganic active ingredientsFungiADAMTS ProteinsProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to protein complexes and fusion proteins including at least two different cytokine molecules. The protein complexes and fusion proteins may further include a targeting moiety such as a region of an immunoglobulin. Methods of using the protein complexes and fusion proteins are also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Biomarker detection in circulating cells
InactiveUS7537938B2Easy to detectRapid and efficient screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein-protein complexCirculating cancer cell
A method is provided for detecting biomarkers in rare circulating cells by forming an enriched population of cells immunomagnetically followed by biomarker detection using binding compounds having releasable molecular tags. Preferably, biomarkers comprising one or more protein-protein complexes are detected in circulating cancer cells metastasized from a solid tumor. In the presence of biomarkers, the molecular tags of the binding compounds are released and separated from the assay mixture for detection and / or quantification.
Owner:VIROLOGIC INCORPORATED
Formative agent of protein complex
InactiveUS20020119946A1Keep for a long timePromote resultsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCartilage cellsCuticle
The present invention proposes formative agent of protein complex, in which a polyphenol is useful component, and the agent is useful as gene complex, cell adhesion inhibitor or immune tolerogen. The polyphenol of forming the agent is selected from catechin group consisting of epigallocatechin-gallate, tannic acids, or proanto-dianisidine, a protein of the protein complex is selected from proteins consisting of animal proteins composed of polypeptide chain of peptide-combined amino acids, vegetative proteins, nucleus proteins, glycogen proteins, lipo-proteins and metal proteins, the gene complex comprises by compositing genes by polyphenol catechins in order to introduce genes to cells of animals or human bodies, a cell composed of the cell adhesion inhibitor is selected from cells consisting of an animal cell including a stem cell, skin cell, mucosa cell, hepatocyte, islet cell, neural cell, cartilage cell, endothelial cell, epidermal cell, osteocyte or muscle cell isolated from human or animal organism, or sperm, ovum or fertilized egg of domestic animals or fishes and a tissue or an organ for transplantation of the immune tolerogen is selected from the tissue or the organ consisting of skin, blood vessel, cornea, kidney, heart, liver, umbilical cord, bowels, nerve, lung, placenta or pancreas.
Owner:BERTELSMANN MUSIC GROUP
Production of high-quality protein isolates from defatted meals of Brassica seeds
The present invention provides a method for processing defatted oil seeds, comprising the steps of: (a) solubilizing at least a portion of the protein contained in the oil seeds to produce suspended residual solids and a first solution comprising protein, phenolic-protein complexes, and free phenolic compounds; (b) separating at least a portion of the free phenolic compounds from the first solution and recovering a free phenolic reduced solution; and (c) treating the free phenolic reduced solution to precipitate at least a portion of the protein as a precipitated protein isolate and recovering a treated solution containing a soluble protein isolate. Novel protein products are also disclosed. Food and drink products containing the novel protein products are also disclosed.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
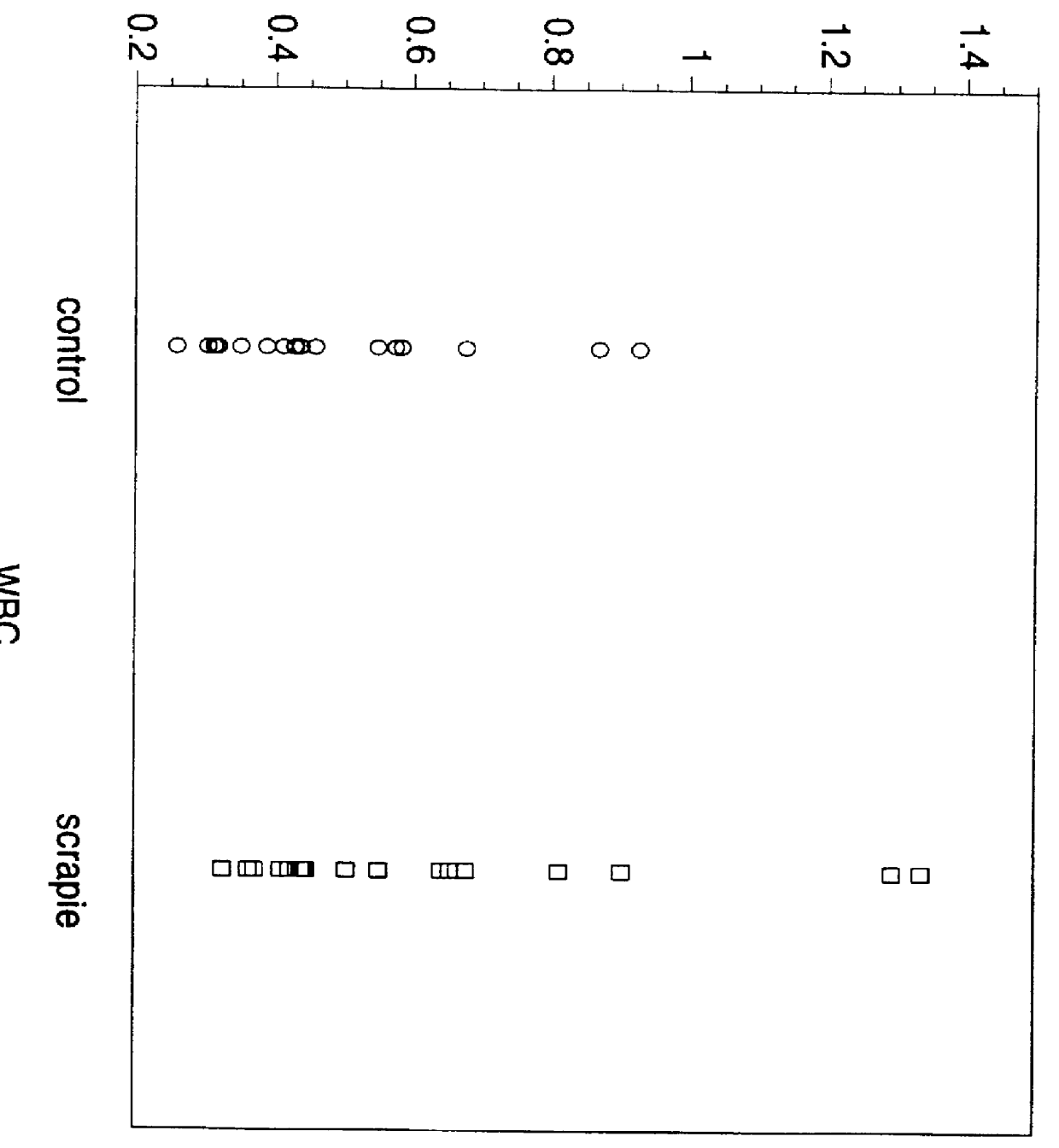
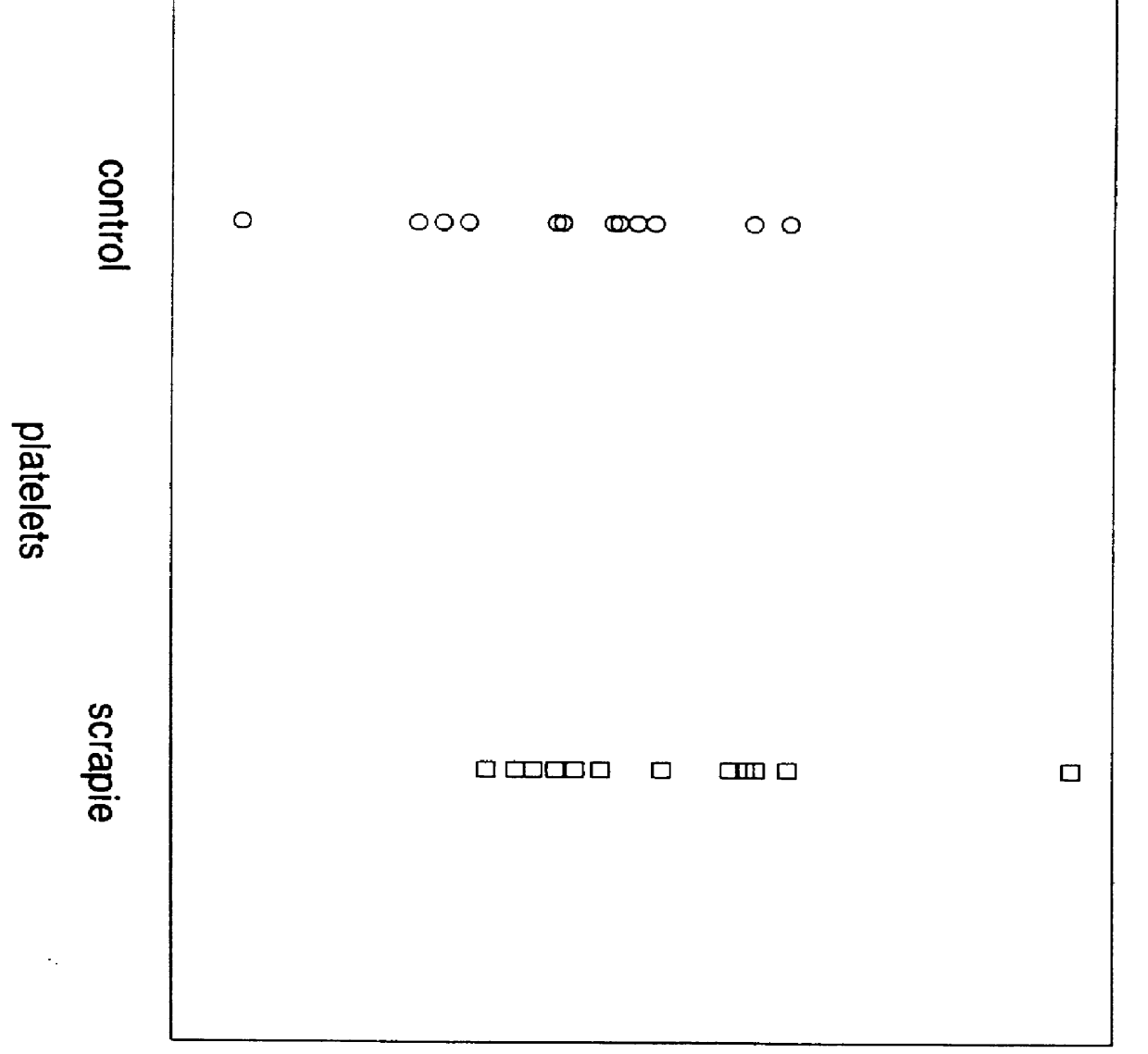
Method of concentrating prion proteins in blood samples
A sample is prepared from blood in a manner which makes it possible to further analyze proteins in the sample, e.g. to detect prions in the sample. Blood is extracted, allowed to clot and subjected to separation processing (e.g. centrifugation) to obtain serum. The serum is treated with a complexing agent which agent binds prions in the sample forming an agent / protein complex which makes it possible to concentrate the complex. Concentration of the complex results in a sample which can be successfully analyzed, e.g. assayed using a range of different types of assay methodologies for detecting prions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Human papillomavirus inhibitors
The present invention provides systems for identifying anti-viral agents. In particular, the invention encompasses reagents and strategies for identifying agents that inhibit or disrupt key protein-protein interactions that are important in the life cycle of papillomaviruses. The invention allows identification, production, and / or use of agents that reduce or inhibit the replication of HPV by inhibiting (e.g., precluding, reversing, or disrupting) the formation of the E1-E2 protein-protein complex. The invention also provides specific inhibitory agents, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of using these inhibitors and pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting viral replication in vitro. Methods are also described for the treatment and prevention of HPV infections and HPV-related diseases in patients.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method of administering FimH protein as a vaccine for urinary tract infections
InactiveUS20030138449A1Reduce morbidityInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseBacteroides
The present invention relates to methods of stimulating an immune response in a primate utilizing compositions comprising bacterial adhesin proteins and / or immunogenic fragments thereof. The compositions are useful for the prevention and treatment of bacterial induced diseases involving bacterial adherence to a target cell, such as diseases of the urinary tract. More specifically, the invention relates to the vaccination of primates, preferably humans, with protein complexes, such as a purified FimH polypeptides, a purified FimC-FimH (FimCH) polypeptide complex, or immunogenic fragments thereof, to stimulate protective immunity in the recipient against infection by pathogenic bacteria, including all types of Enterobacteriaceae, preferably E. coli to produce specific immunoglobin molecules in the serum and urine or mucosal secretions of the subject.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Aptamer-guided gene targeting
Compositions and methods for modifying genetic material are provided. One embodiment provides aptamers capable of binding to a site-specific DNA binding moiety to facilitate the exchange of homologous genetic information between a donor molecule and the desired target locus (aptamer-guided gene targeting or AGT). One embodiment provides an oligonucleotide containing a aptamer, preferably a DNA aptamer at the 5′ end. The oligonucleotide also contains a region of homology, also referred to as donor DNA, to a desired nucleic acid, locus, or gene. The DNA binding moiety can be a nucleic acid, a protein, or a complex of proteins. In a preferred embodiment the DNA binding moiety is a homing endonuclease that cuts DNA to facilitate the modification of the DNA by the donor DNA.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com