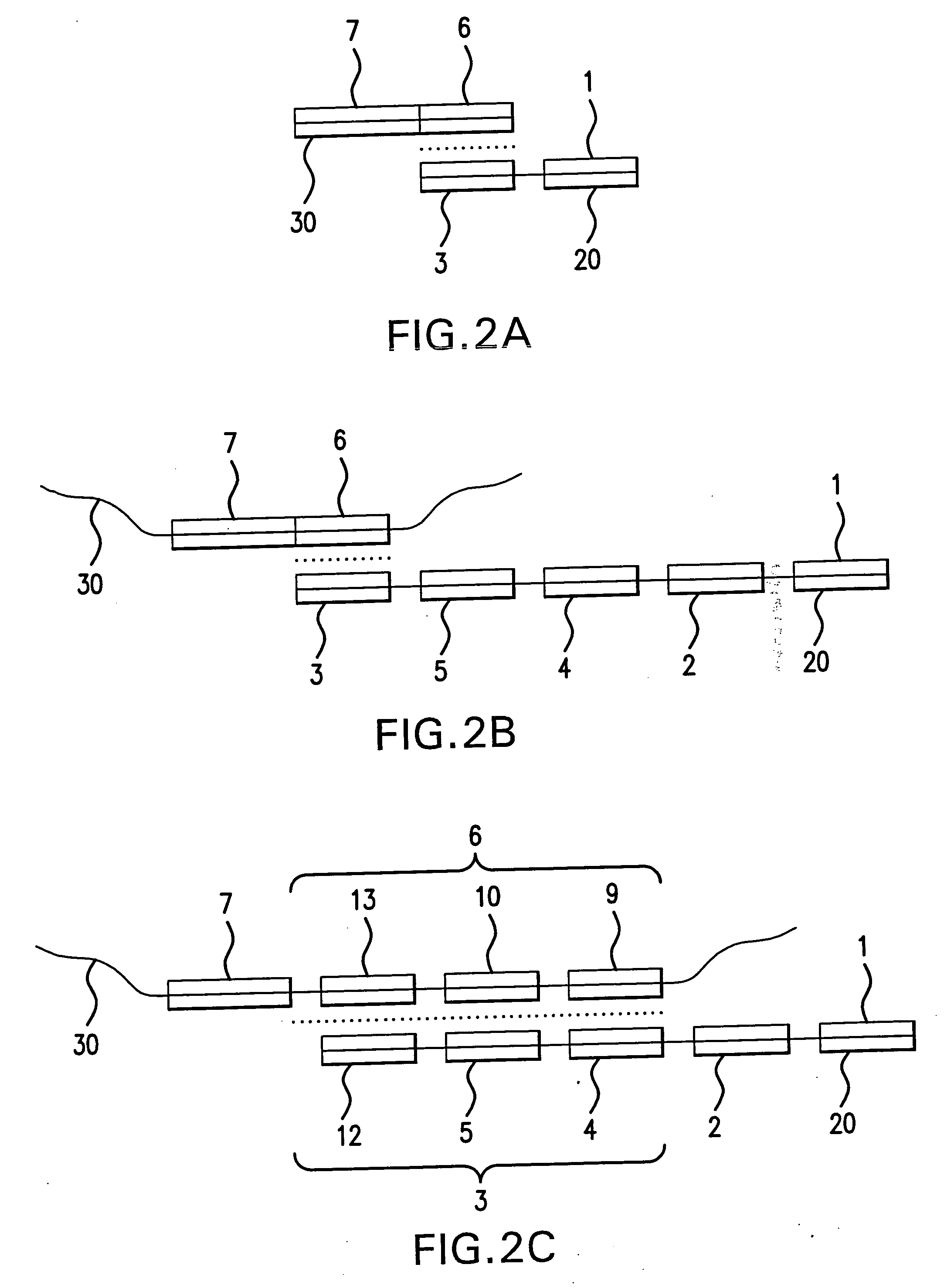
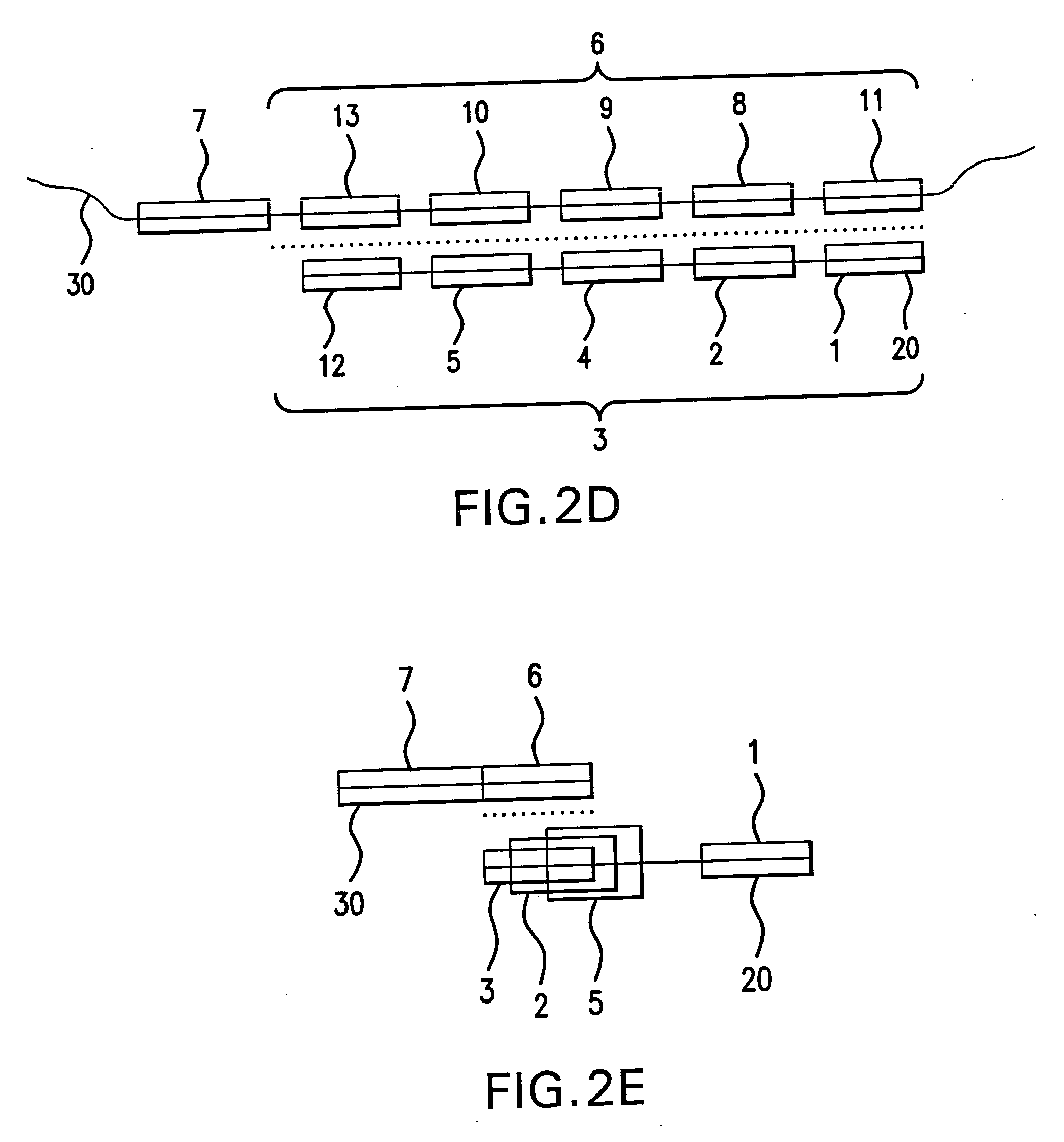
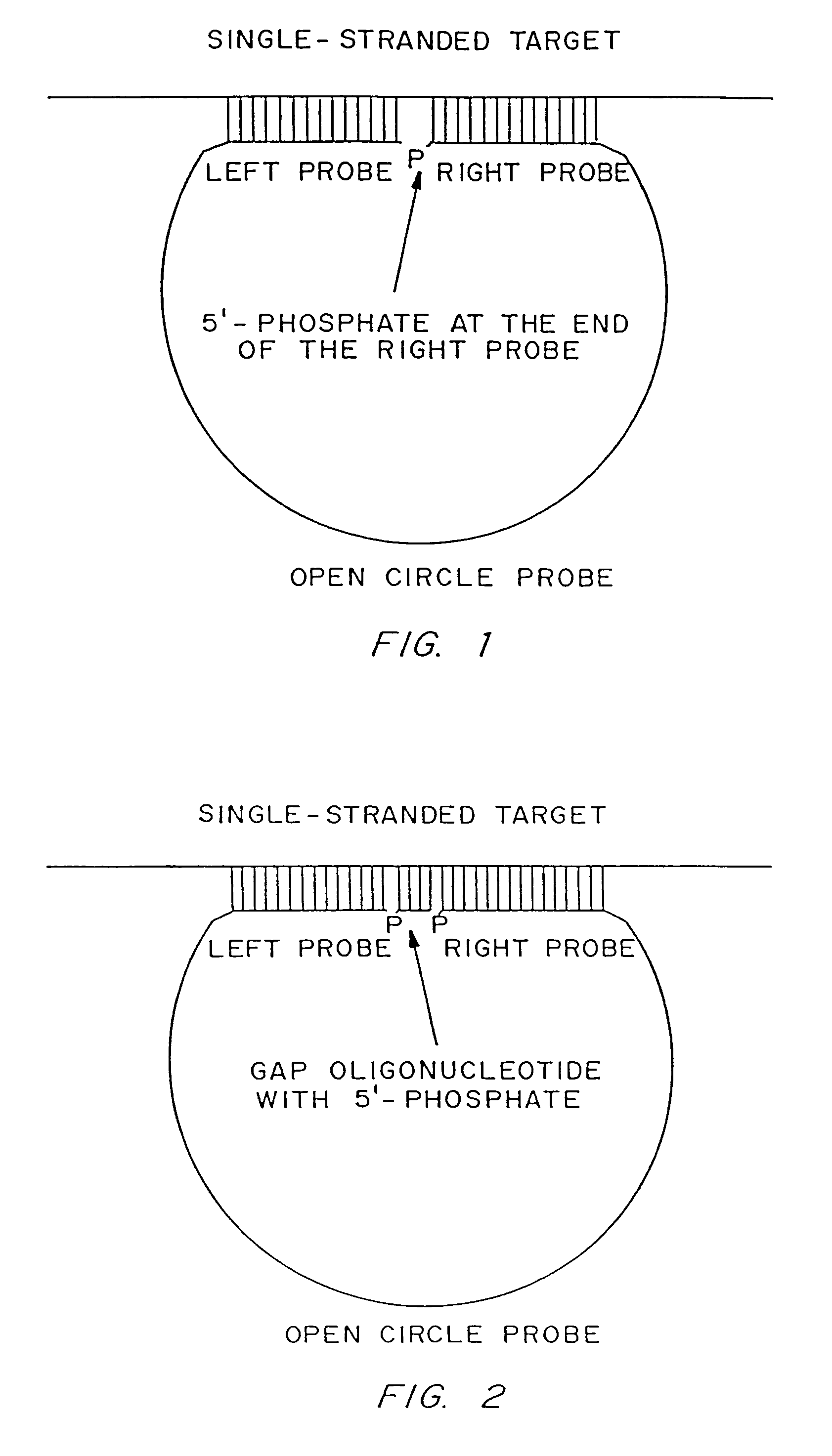
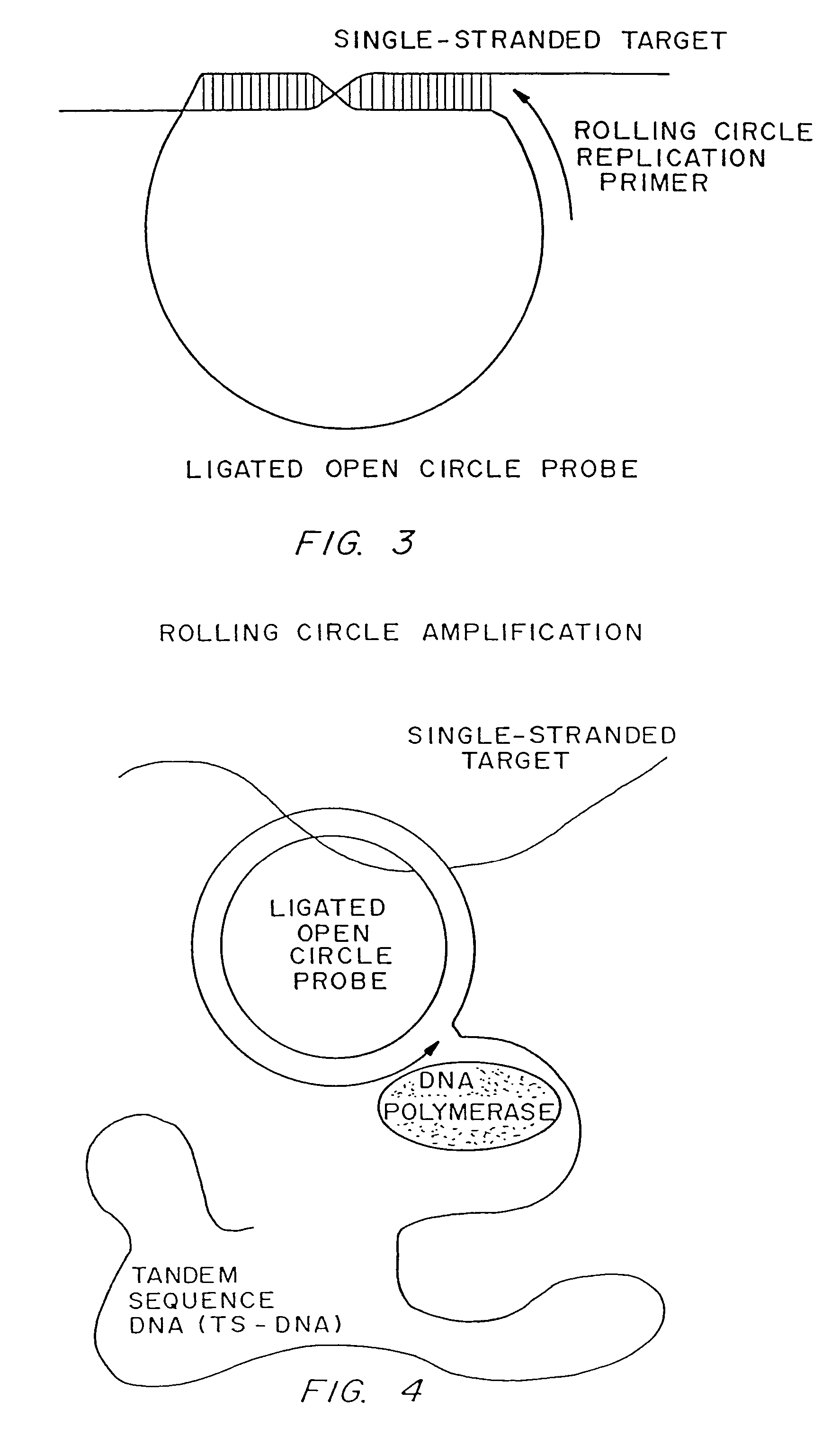
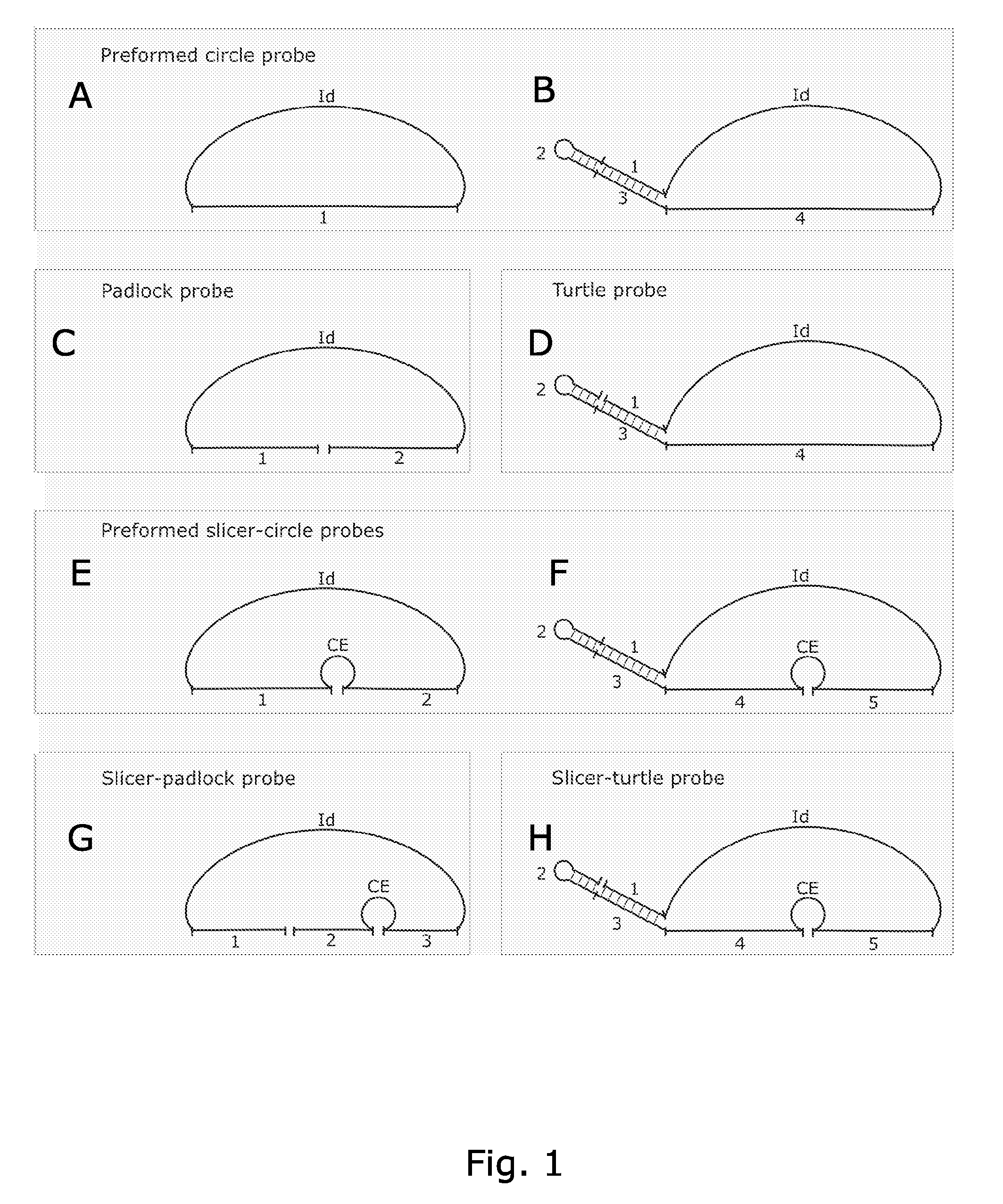
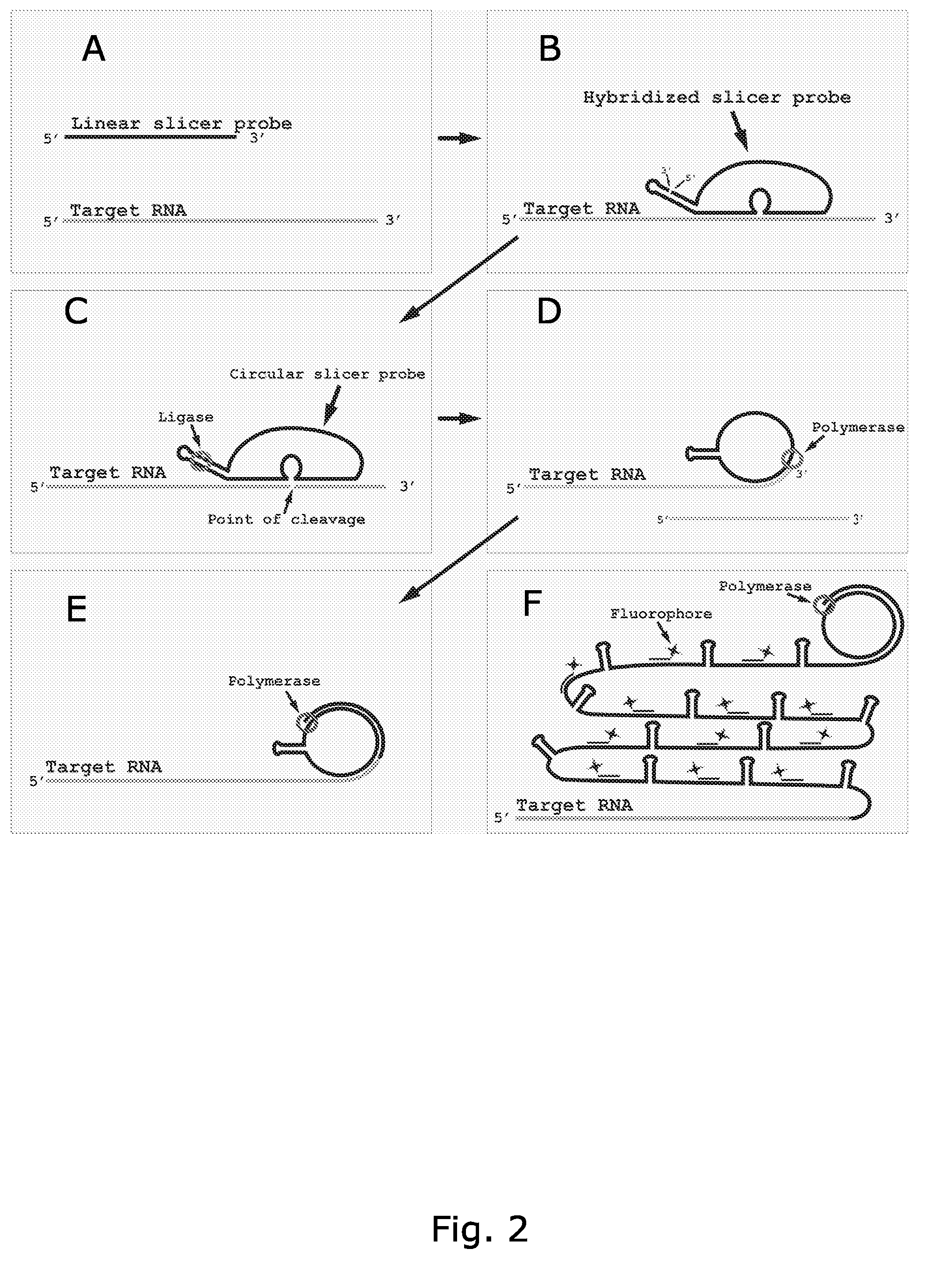
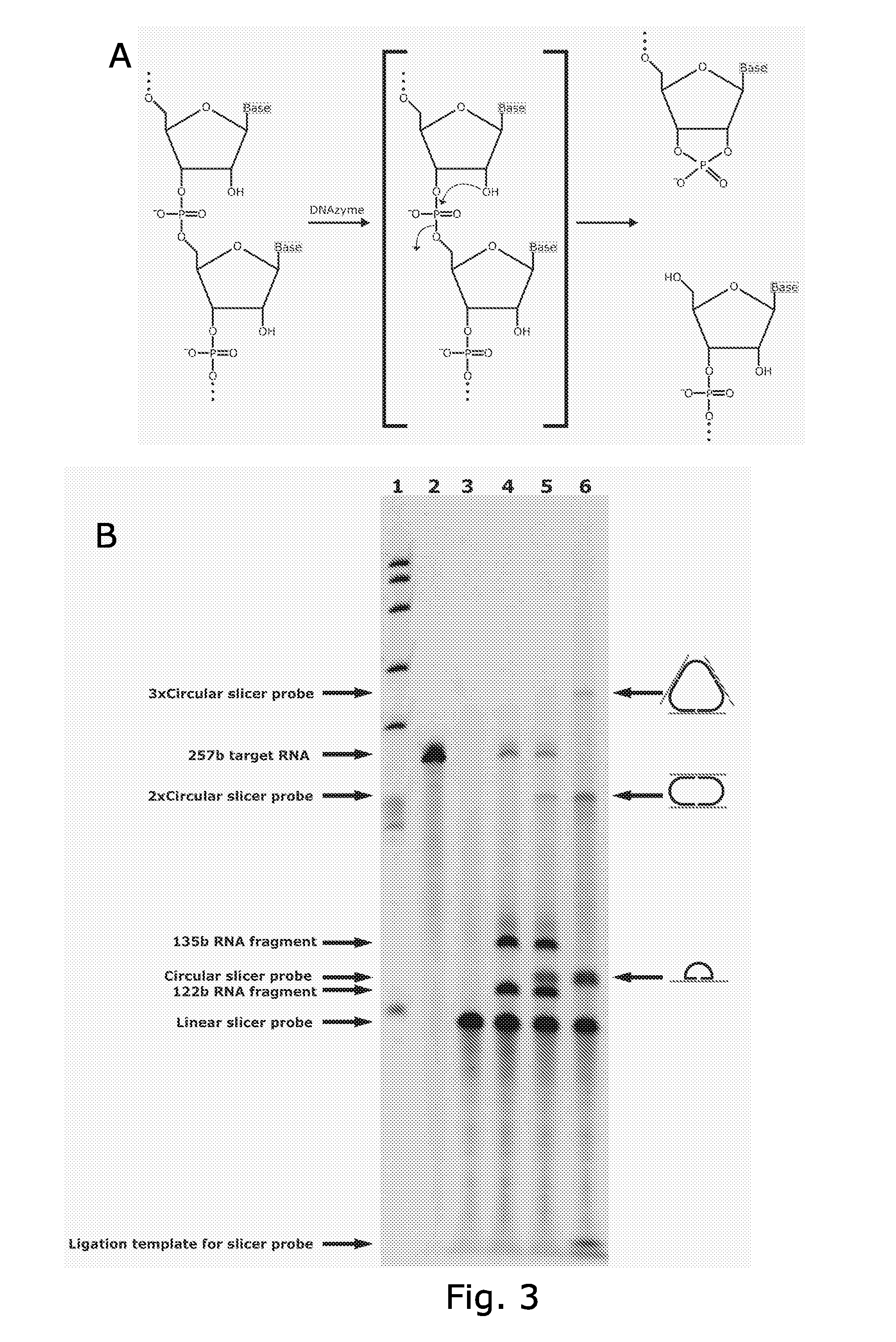
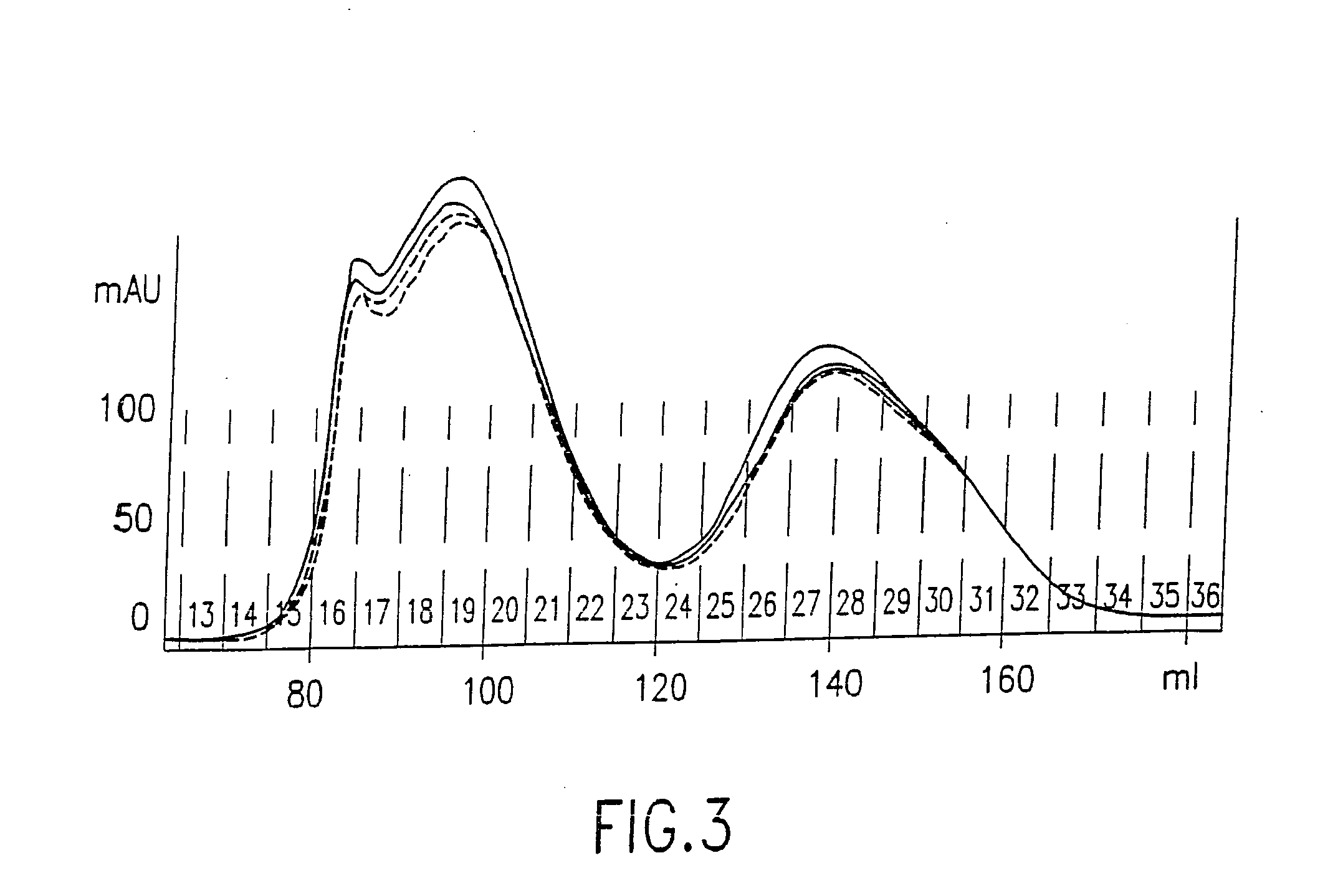
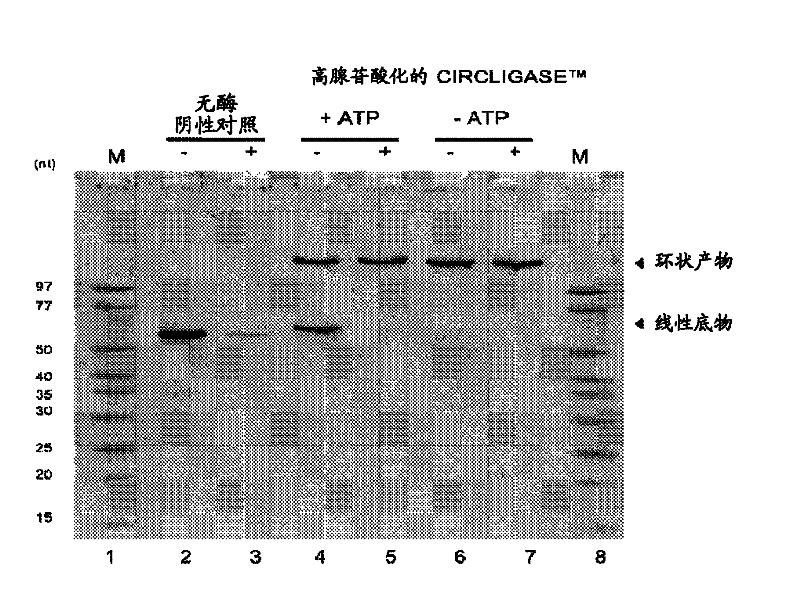
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Rolling circle replication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
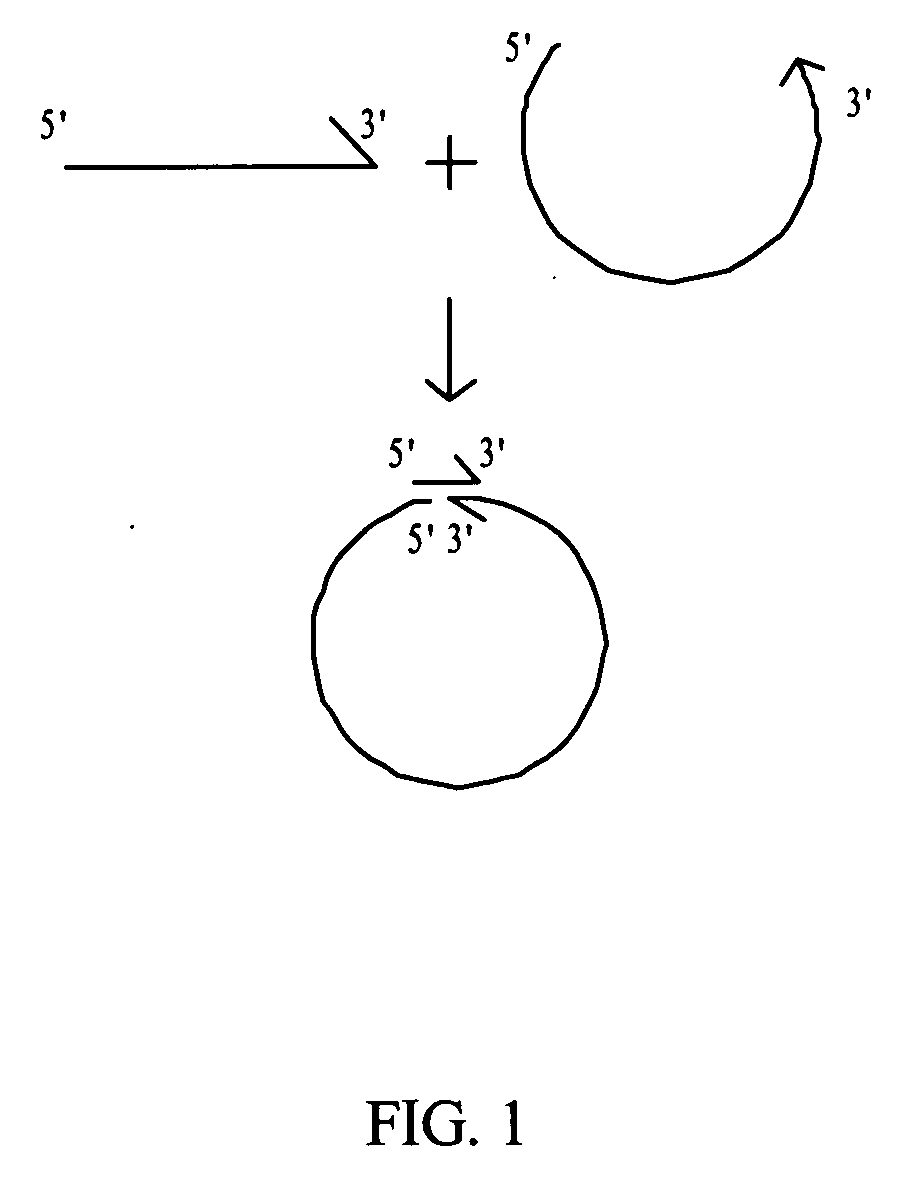
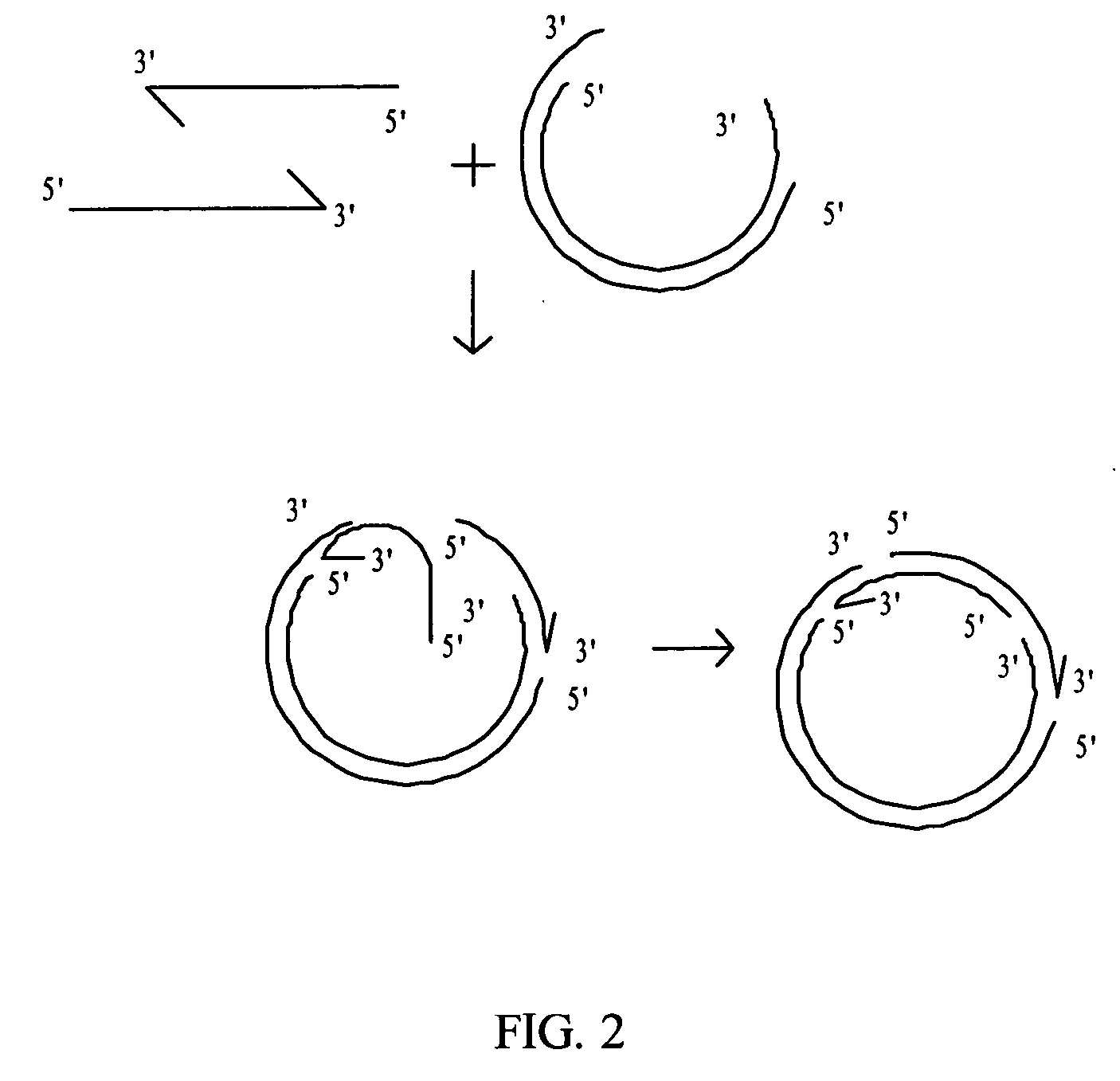
Rolling circle replication describes a process of unidirectional nucleic acid replication that can rapidly synthesize multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA or RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genome of viroids. Some eukaryotic viruses also replicate their DNA or RNA via the rolling circle mechanism.
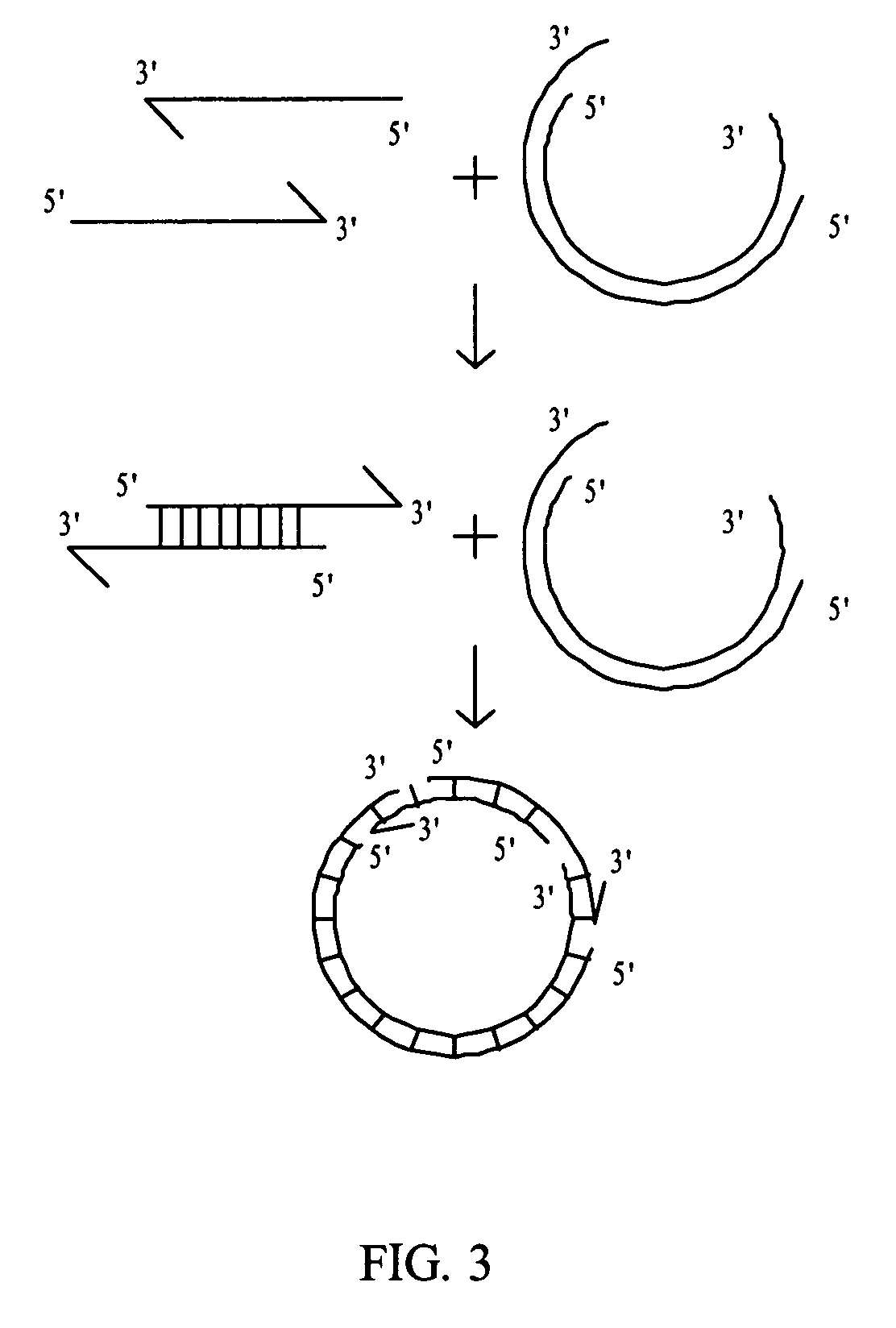
Rolling circle replication of padlock probes
InactiveUS6558928B1Avoid splittingStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid hybridisationOligonucleotide
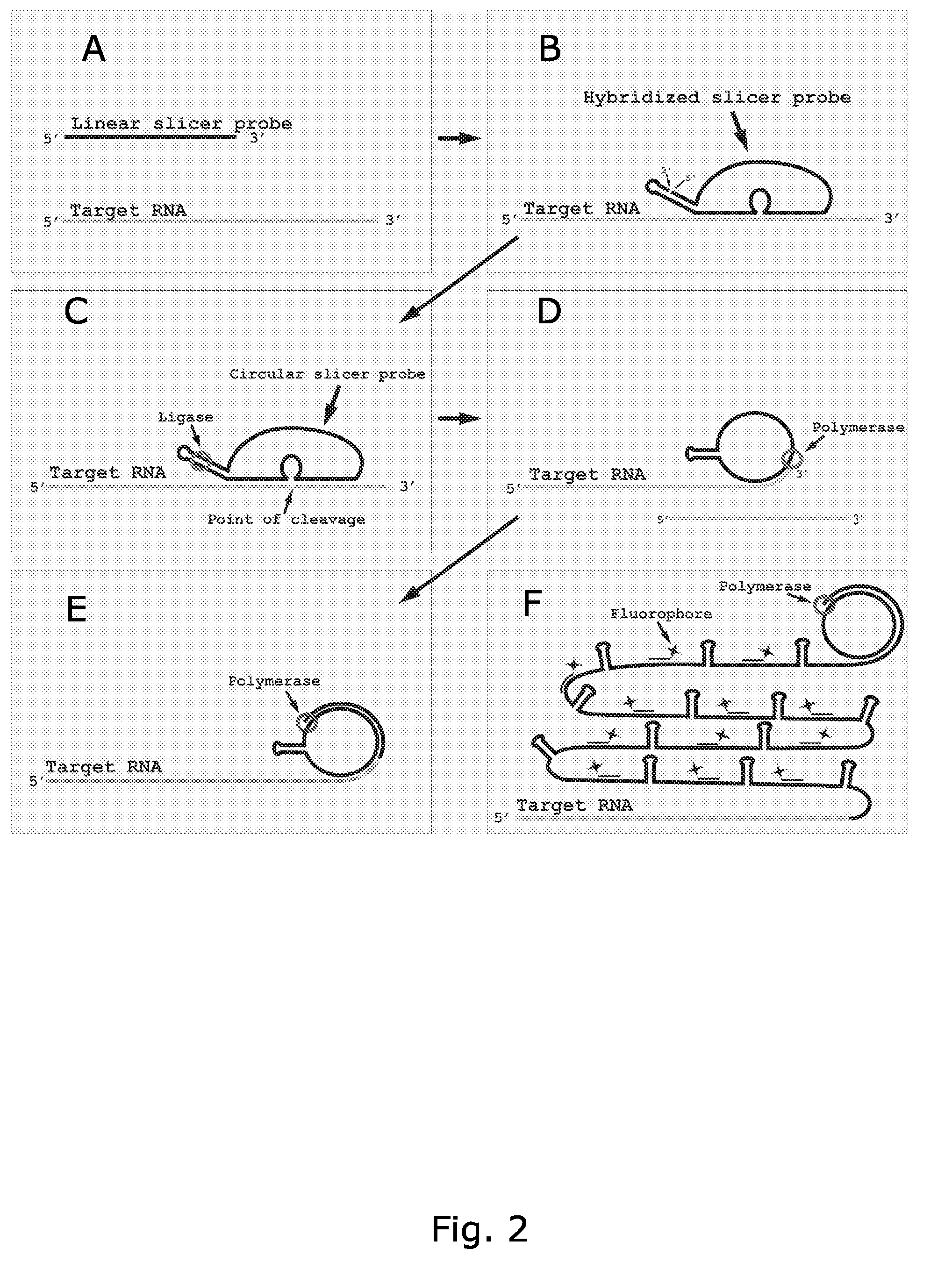
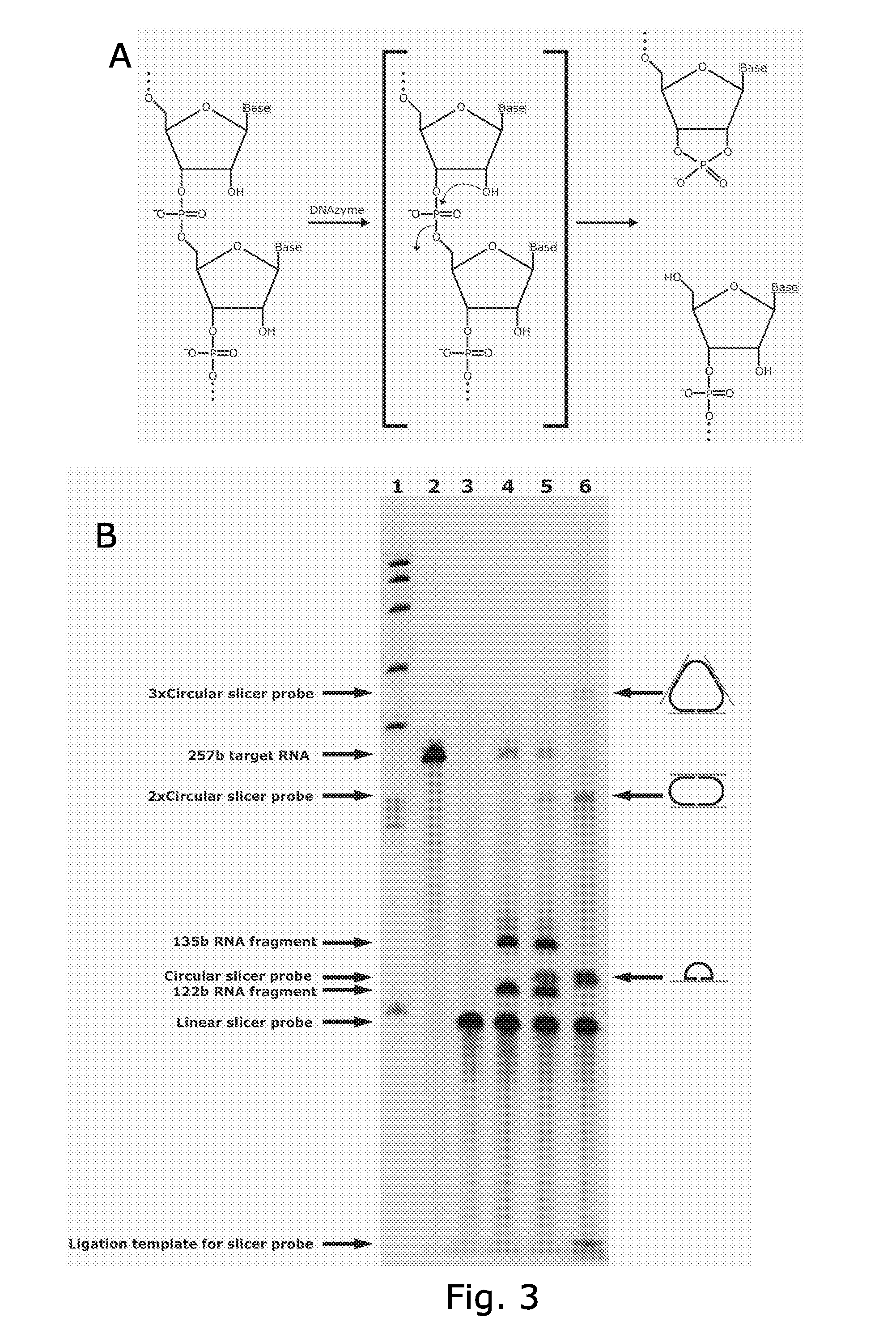
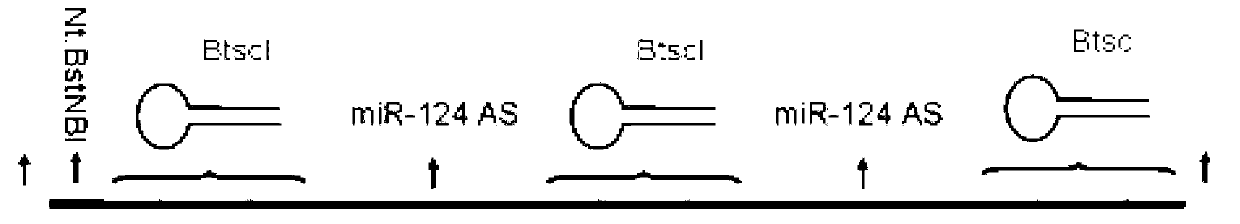
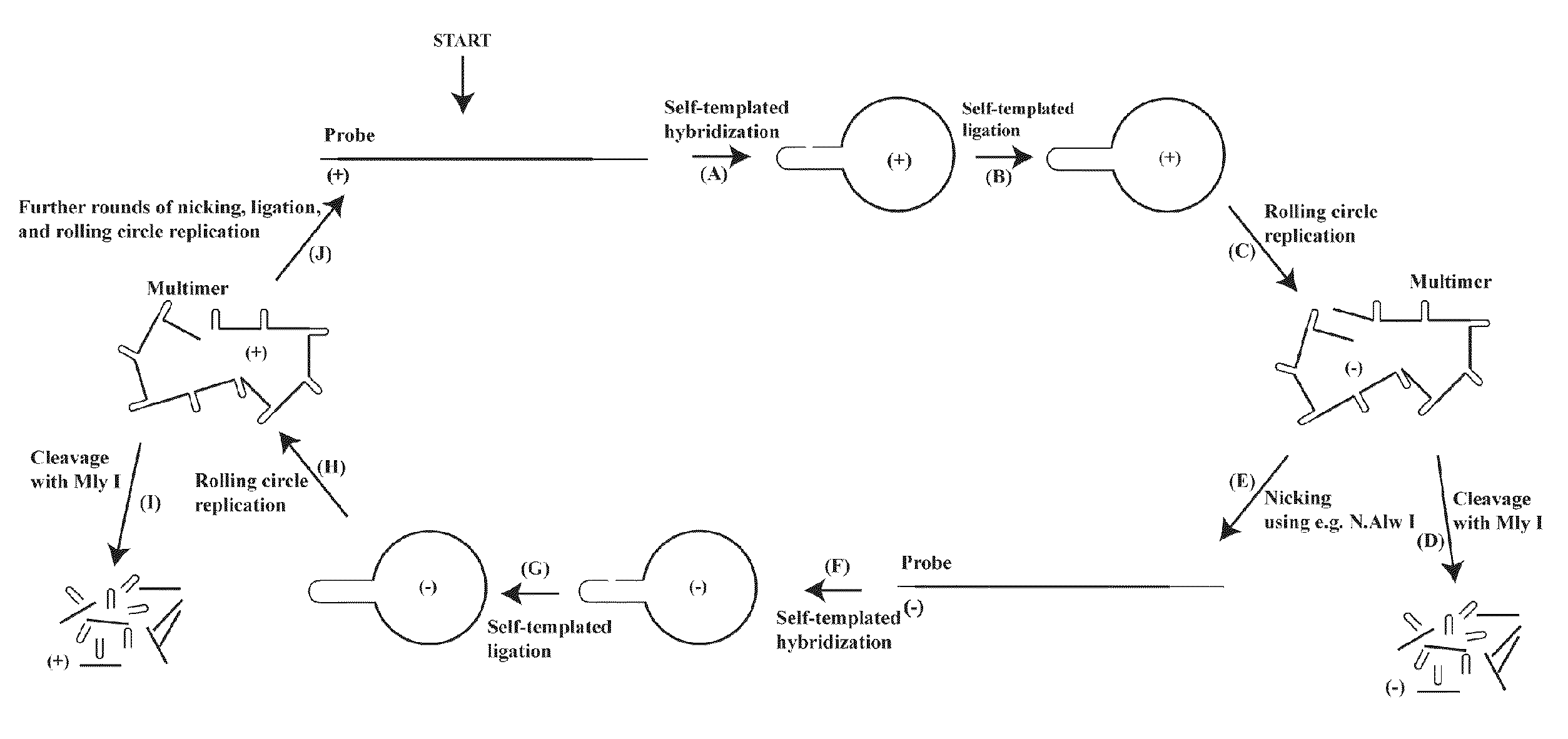
Rolling circle replication of a padlock primer is inhibited when it is hybridized to a target nucleic acid that is long or circular. The invention provides methods of addressing this problem including cutting the target nucleic acid near or preferably at the site which hybridizes with the padlock probe, whereby a 3'-end of the cut target nucleic acid acts as a primer for rolling circle replication of the padlock probe. Also included is a method of assaying for a polyepitopic target by the use of two affinity probes each carrying an oligonucleotide tag and of a padlock probe for rolling circle replication in association with the two affinity probes
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Protein expression profiling
InactiveUS6921642B2Easy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteProtein expression profile
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a primer with an analyte and subsequently using the primer to mediate rolling circle replication of a circular DNA molecule. Amplification of the DNA circle is dependent on the presence of the primer. Thus, the disclosed method produces an amplified signal, via rolling circle amplification, from any analyte of interest. The amplified DNA remains associated with the analyte, via the primer, and so allows spatial detection of the analyte. The disclosed method can be used to detect and analyze proteins and peptides. Multiple proteins can be analyzed using microarrays to which the various proteins are immobilized. A rolling circle replication primer is then associated with the various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule that specifically binds the proteins to be detectable. Rolling circle replication from the primers results in production of a large amount of DNA at the sites in the array where the proteins are immobilized. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the proteins. The disclosed method can also be used to compare the proteins expressed in two or more different samples. The information generated is analogous to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression profiles. The disclosed method allows sensitive and accurate detection and quantitation of proteins expressed in any cell or tissue.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Selected amplification of polynucleotides
InactiveUS8137936B2Reducing background and spurious amplificationSave materialMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolynucleotideDouble stranded
The invention provides methods and compositions for selectively amplifying one or more target polynucleotides in a sample. In one aspect, a plurality of selection oligonucleotides are provided that are capable of simultaneously annealing to separate regions of a target polynucleotide to form a complex that is enzymatically converted into a closed double stranded DNA circle that incorporates the sequence region between the two separate regions. Sequences that fail to form such complexes may be removed by nuclease digestion and the sequences of the remaining DNA circles may be amplified by a variety of techniques, such as rolling circle replication after nicking, PCR amplification after linearization, or the like.
Owner:MACEVICZ STEPHEN C
Rolling circle amplification of RNA
InactiveUS6977153B2Increase productionOptimization orderMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTandem repeatDouble strand
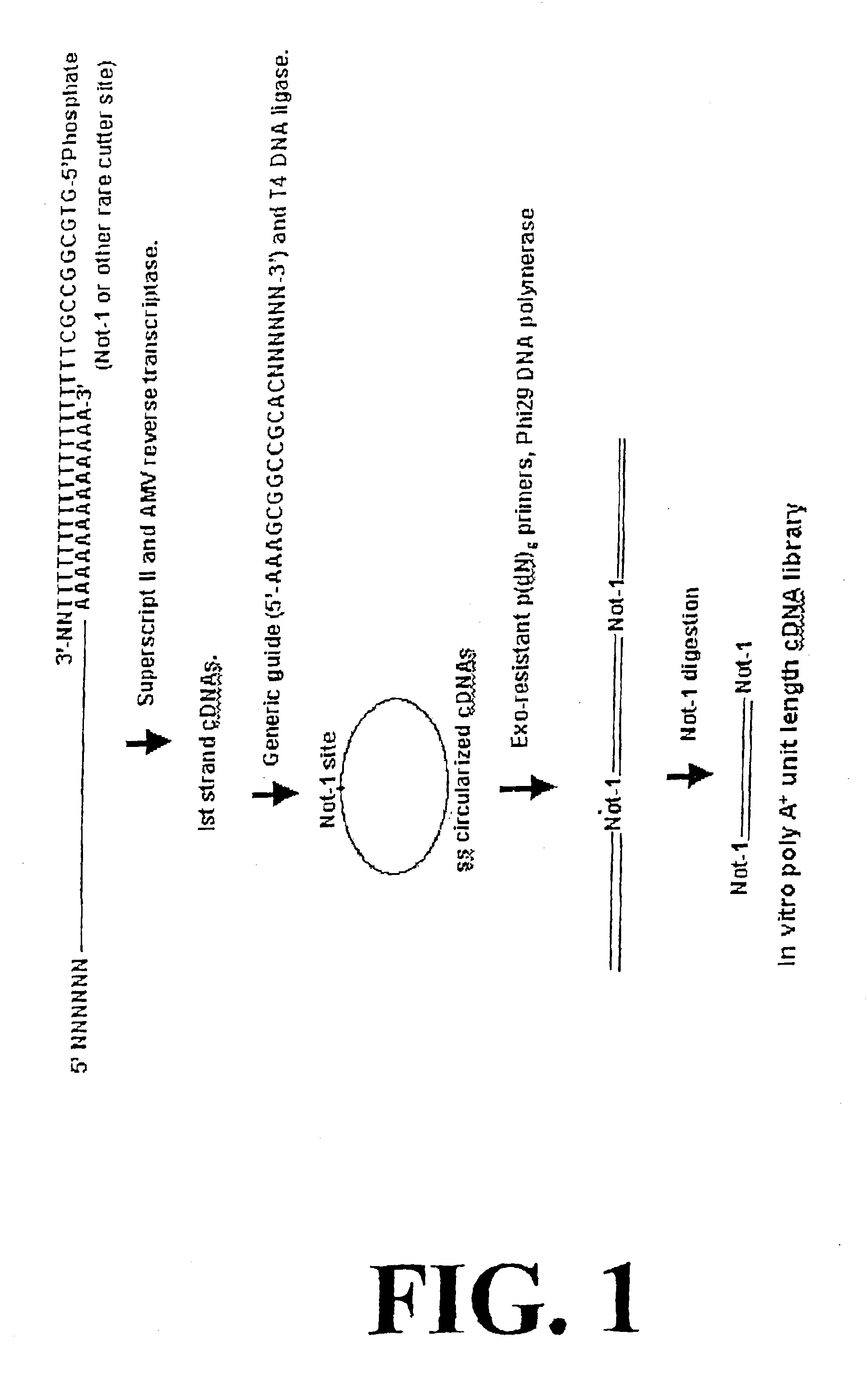
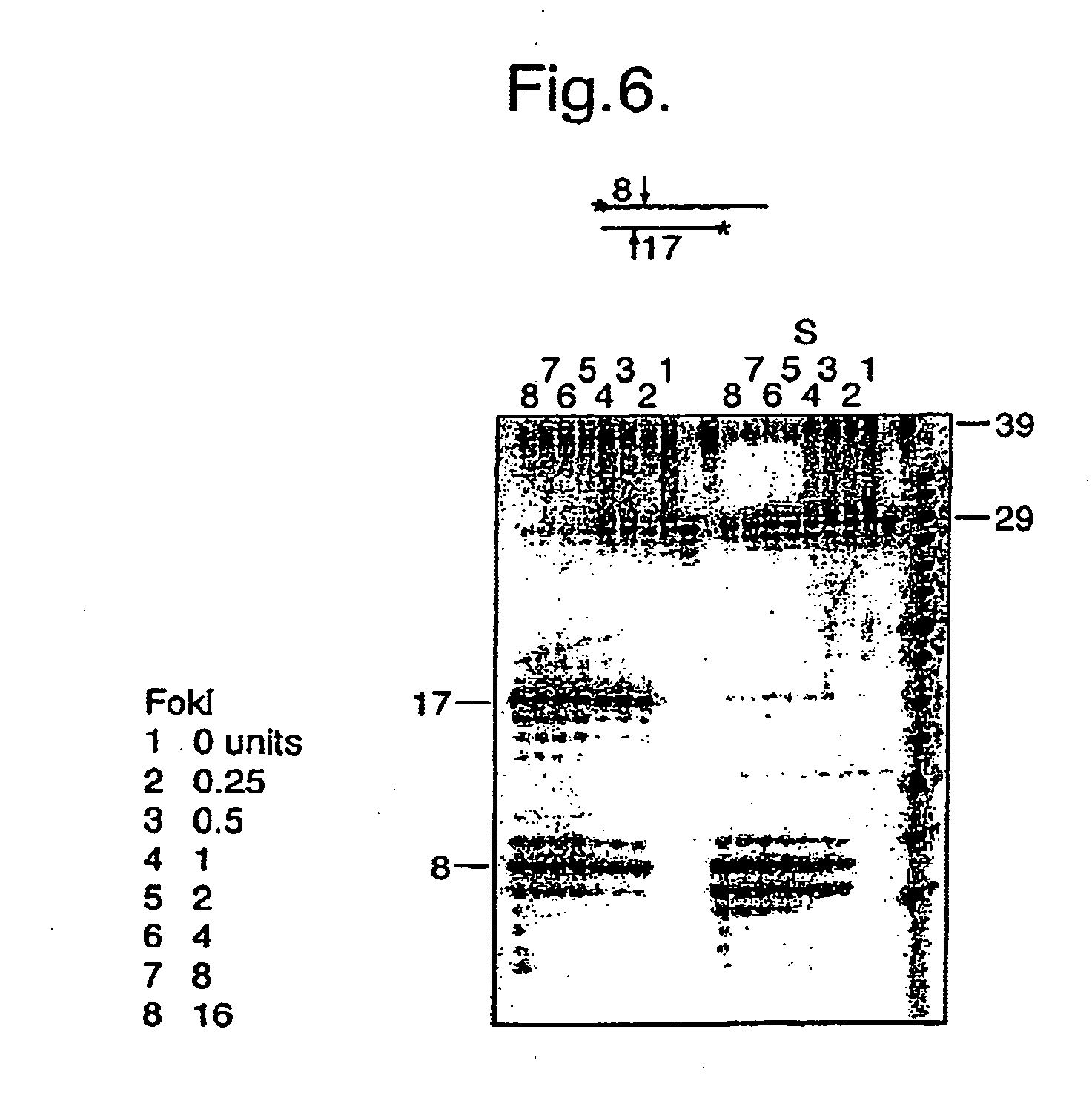
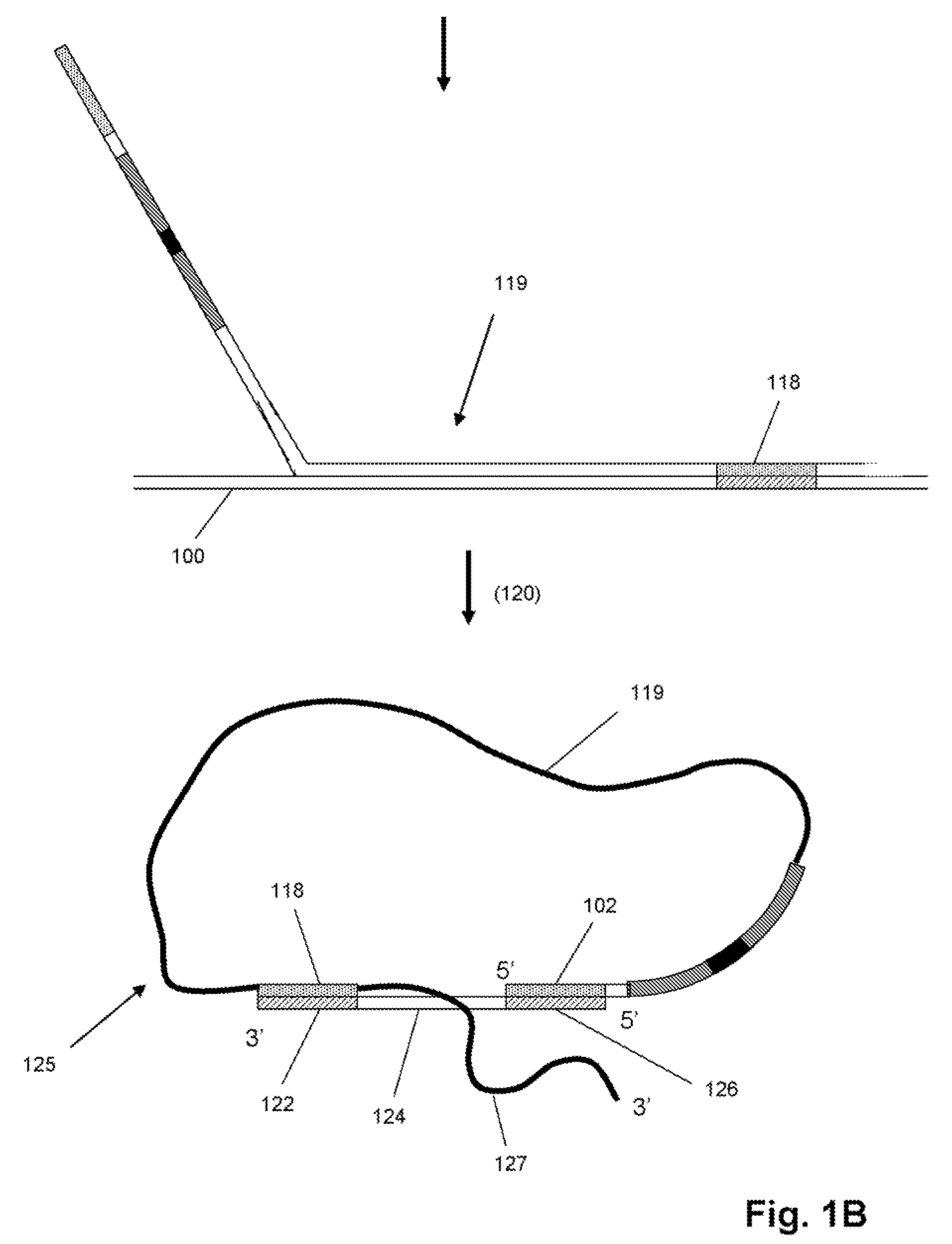
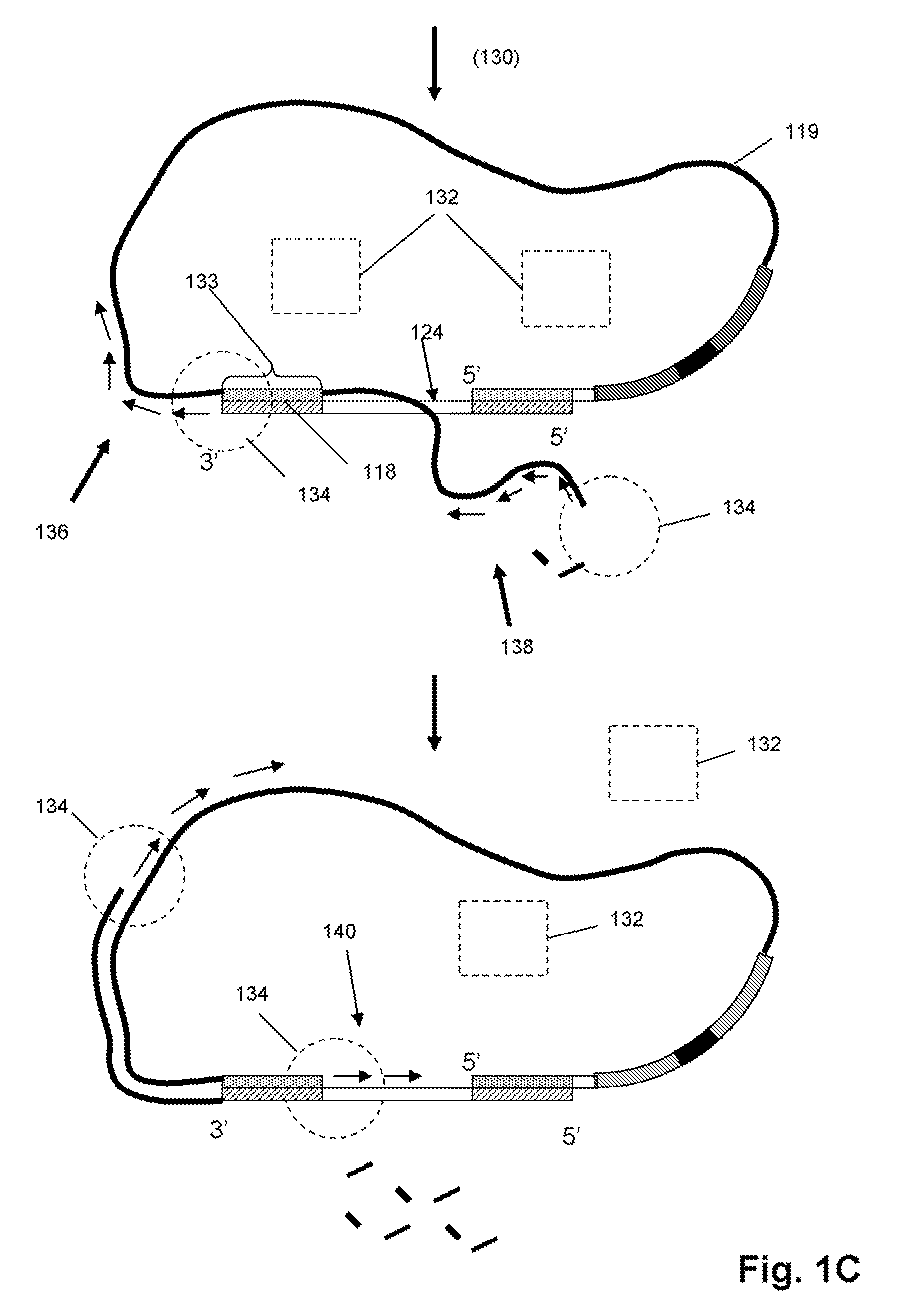
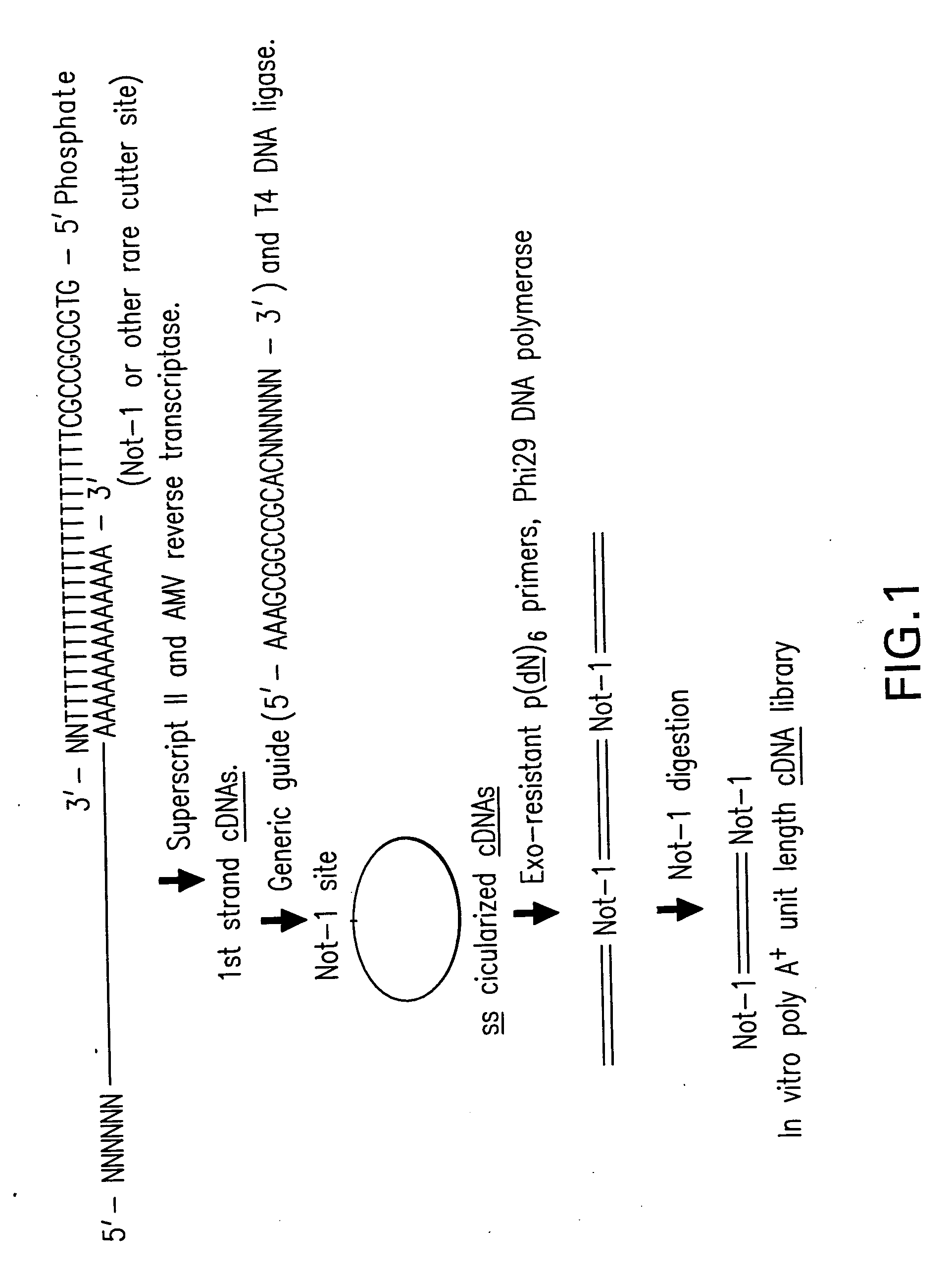
Disclosed are compositions and methods for amplification of RNA molecules. The disclosed method involves synthesizing first strand cDNA molecules from RNA molecules, circularizing the first strand cDNA molecules and replicating the circularized first strand cDNA molecules using rolling circle replication. The method can be aided by the use of specialized primers for cDNA synthesis and specialized probes for circularizing the first strand cDNA molecules. The method can be used to replicate and amplify multiple RNA molecules, such as all RNA molecules in a sample or all mRNA molecules in a sample, or be used to replicate and amplify specific RNA molecules. Rolling circle replication of the circularized first strand cDNA molecules results in long DNA strands containing tandem repeats of the cDNA sequence. The tandem sequence DNA can be used directly (for detection of sequences, for example), further amplified, or used any other purpose. Double-stranded tandem sequence DNA can be used to produce unit lengths of the cDNA sequence. Tandem sequence DNA can also be transcribed to produce transcripts having sequence complementary to or matching the sequence of RNA molecules.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Rolling circle replication of padlock probes
InactiveUS20050282158A1Limited amplificationInhibition of replicationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyOligonucleotideRolling circle replication
Rolling circle replication of a padlock primer is inhibited when it is hybridised to a target nucleic acid that is long or circular. The invention provides methods of addressing this problem including cutting the target nucleic acid near or preferably at the site which hybridises with the padlock probe, whereby a 3′-end of the cut target nucleic acid acts as a primer for rolling circle replication of the padlock probe. Also included is a method for assaying for a polyepitopic target by the use of two affinity probes each carrying an oligonucleotide tag and of padlock probe for rolling circle replication in association with the two affinity probes.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Selected amplification of polynucleotides
InactiveUS20070128635A1ConservingReduce backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideDouble strand
The invention provides methods and compositions for selectively amplifying one or more target polynucleotides in a sample. In one aspect, a plurality of selection oligonucleotides are provided that are capable of simultaneously annealing to separate regions of a target polynucleotide to form a complex that is enzymatically converted into a closed double stranded DNA circle that incorporates the sequence region between the two separate regions. Sequences that fail to form such complexes may be removed by nuclease digestion and the sequences of the remaining DNA circles may be amplified by a variety of techniques, such as rolling circle replication after nicking, PCR amplification after linearization, or the like.
Owner:MACEVICZ STEPHEN C
Rolling circle amplification of RNA
InactiveUS20060188893A1Optimization orderIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDouble strandTandem repeat
Owner:KUMAR GYANENDRA +1
Rolling circle replication reporter systems
InactiveUS7618776B2Consistent outputAmplification less complicatedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMultiplexNucleotide
Disclosed are compositions and a method for of amplifying nucleic acid sequences useful for detecting the presence of molecules of interest. The method is useful for detecting specific nucleic acids in a sample with high specificity and sensitivity. The method also has an inherently low level of background signal. A preferred form of the method consists of a DNA ligation operation, an amplification operation, and a detection operation. The DNA ligation operation circularizes a specially designed nucleic acid probe molecule. This operation is dependent on hybridization of the probe to a target sequence and forms circular probe molecules in proportion to the amount of target sequence present in a sample. The amplification operation is rolling circle replication of the circularized probe. A single round of amplification using rolling circle replication results in a large amplification of the circularized probe sequences. Following rolling circle replication, the amplified probe sequences are detected and quantified using any of the conventional detection systems for nucleic acids such as detection of fluorescent labels, enzyme-linked detection systems, antibody-mediated label detection, and detection of radioactive labels. Because, the amplified product is directly proportional to the amount of target sequence present in a sample, quantitative measurements reliably represent the amount of a target sequence in a sample. Major advantages of this method are that the ligation step can be manipulated to obtain allelic discrimination, the DNA replication step is isothermal, and signals are strictly quantitative because the amplification reaction is linear and is catalyzed by a highly processive enzyme. In multiplex assays, the primer oligonucleotide used for the DNA polymerase reaction can be the same for all probes. Also described are modes of the method in which additional amplification is obtained using a cascade of strand displacement reactions.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Novel circle probes and their use in the identification of biomolecules
ActiveUS20100047773A1Without efficiencyWithout hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideRolling circle replication
The present invention provides oligonucleotides and methods for efficient detection of target nucleic acids using rolling circle replication. In one aspect, the oligonucleotides of the invention are characteristic in that they can be circularised without an external ligation template. In another aspect, the oligonucleotides of the invention are characteristic in that they can generate a free 3′end of the target nucleic acid necessary for rolling circle replication. The oligonucleotides and detection methods of the invention are useful e.g. as research tool and for diagnosis.
Owner:OLINK AB
Protein expression profiling
InactiveUS20060166227A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAnalyteProtein Expression Profiling
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a primer with an analyte and subsequently using the primer to mediate rolling circle replication of a circular DNA molecule. Amplification of the DNA circle is dependent on the presence of the primer. Thus, the disclosed method produces an amplified signal, via rolling circle amplification, from any analyte of interest. The amplified DNA remains associated with the analyte, via the primer, and so allows spatial detection of the analyte. The disclosed method can be used to detect and analyze proteins and peptides. Multiple proteins can be analyzed using microarrays to which the various proteins are immobilized. A rolling circle replication primer is then associated with the various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule that specifically binds the proteins to be detectable. Rolling circle replication from the primers results in production of a large amount of DNA at the sites in the array where the proteins are immobilized. The DNA produced by rolling circle replication can be further amplified in secondary and higher order amplification processes using second-stage or higher order primers in conjunction with second-stage or higher order amplification target circles. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the proteins. The disclosed method can also be used to compare the proteins expressed in two or more different samples. The information generated is analogous to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression profiles. The disclosed method allows sensitive and accurate detection and quantitation of proteins expressed in any cell or tissue.
Owner:KINGSMORE STEPHEN +2
Method for detecting nucleic acid or cells based on enzymatic cycle amplification and nano-particle reinforced SPR (surface plasmon resonance)
InactiveCN105648070ARealize highly sensitive detectionIncrease loadMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMagnetic beadBarcode
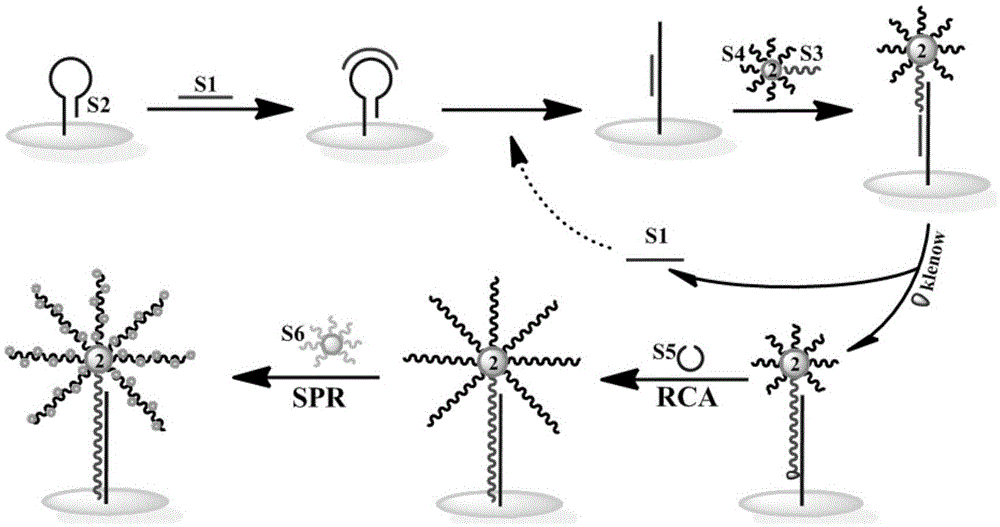
The invention discloses a method for detecting nucleic acid or cells based on enzymatic cycle amplification and nano-particle reinforced SPR (surface plasmon resonance). Strand displacement cycle amplification and rolling circle replication amplification are triggered by a target DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), a double-signal amplification reaction is formed, a magnetic bead is taken as a DNA carrier and serves as a transfer station for signal amplification, a magnetic bead bio-barcode probe has a strand displacement cycle amplification reaction as a reaction unit and also increases the load capacity of a rolling circle replication product as a signal amplification carrier, a multi-stage signal amplification system is formed, high-sensitivity detection of the target DNA is realized with gold nano-particles as signal probes with an SPR technique, and the limit of detection can reach 1fM.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
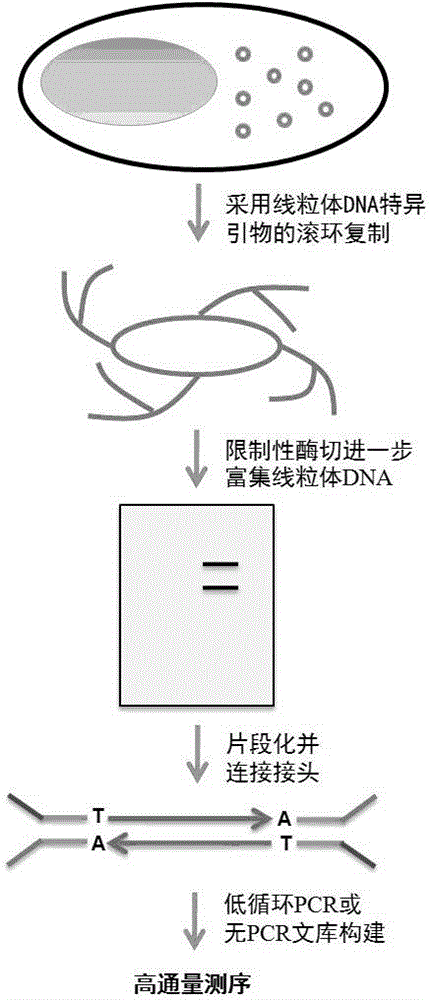
Method for precisely determining high-frequency and low-frequency mutations of mitochondrial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by high-throughput sequencing
ActiveCN103602735AGood repeatabilityIncrease coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsHigh throughput sequence
The invention belongs to the technical field of genomics and specifically relates to a method for precisely determining high-frequency and low-frequency mutations of mitochondrial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by high-throughput sequencing. According to the method provided by the invention, the purpose of determining the high-frequency and low-frequency mutations in a mitochondrial genome is achieved by designing a set of mitochondrial DNA-specific primers, enriching the mitochondrial DNA from total DNA by rolling-circle replication, further enriching the mitochondrial DNA through a specific restriction endonuclease, then constructing a sequencing library, performing high-throughput sequencing and developing a specific data analysis process flow. Mutation sites of which the frequency is as low as 0.3% can be detected to the greatest extent.
Owner:GRACELL BIOTECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Detection method using dissociated rolling circle amplification
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a DNA circle with the analyte and subsequent release and rolling circle replication of the circular DNA molecule. In the method, an amplification target circle is associated with analytes using a conjugate of the circle and a specific binding molecule that is specific for the analyte to be detected. Amplification target circles not associated with the proteins are removed, the amplification target circles that are associated with the proteins are decoupled from the specific binding molecule and amplified by rolling circle amplification. The amplification is isothermic and can result in the production of a large amount of nucleic acid from each primer. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the analytes.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Rolling circle amplification of micro-RNA samples
InactiveUS20060166245A1Efficient conversionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneticsSmall RNA
The compositions of the present invention find use in amplifying RNA obtained from subjects, particularly very small RNA samples. The methods allow conversion of RNA into circularized cDNA suitable for amplification by rolling circle replication. The amplified cDNA is then transcribed into RNA resulting in amplified RNA.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
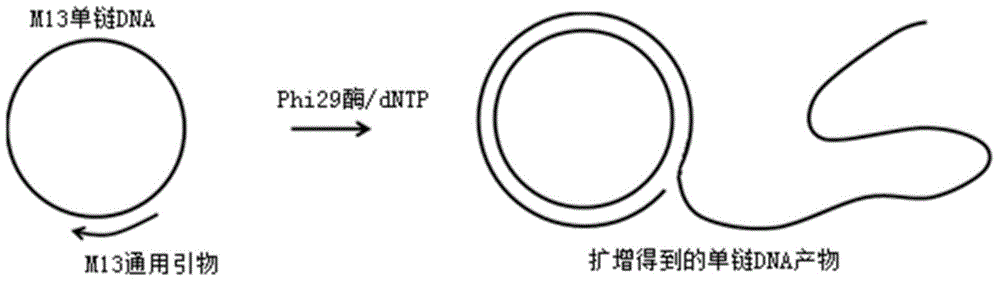
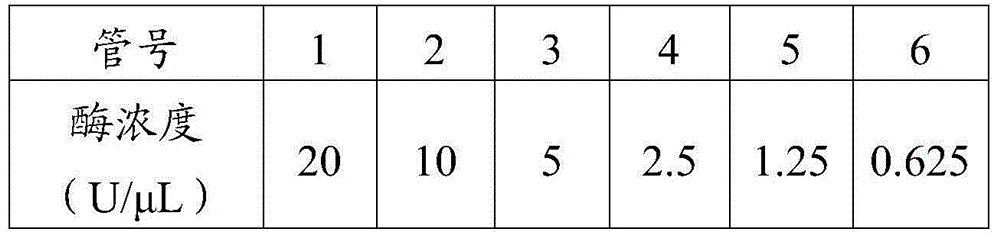
Method for measuring activity of Phi29 DNA polymerase and rolling circle sequencing method
InactiveCN106319032AEnhance aggregation abilityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh fluxFluorescence
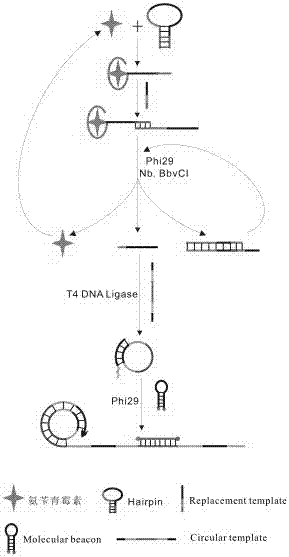
The invention discloses a method for measuring the activity of Phi29 DNA polymerase and a rolling circle sequencing method. The method for measuring the activity of Phi29 DNA polymerase comprises the following steps: taking a circular single-stranded DNA as a template; in the presence of an amplification primer, using Phi29 DNA polymerase to trigger rolling circle replication to generate a large amount of continuous single-stranded DNA copies; then doping fluorescent molecules into the amplification products, detecting the fluorescent signals of the amplification products to quantify the produced single-stranded DNA copy number, and thus calculating the activity of Phi29 DNA polymerase. The provided method has the advantages of no radioactive contamination, simpleness, rapidness, and high sensitivity, and can be applied to high-flux and automatic polymerase screening.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Circle probes and their use in the identification of biomolecules
ActiveUS7989166B2Without efficiencyWithout hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideBioinformatics
The present invention provides oligonucleotides and methods for efficient detection of target nucleic acids using rolling circle replication. In one aspect, the oligonucleotides of the invention are characteristic in that they can be circularised without an external ligation template. In another aspect, the oligonucleotides of the invention are characteristic in that they can generate a free 3′end of the target nucleic acid necessary for rolling circle replication. The oligonucleotides and detection methods of the invention are useful e.g. as research tool and for diagnosis.
Owner:OLINK AB
Protein expression profiling
InactiveCN1446050ABiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein insertionGene expression profiling
Compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and polypeptides are disclosed. The method involves linking a primer to an analyte, which is then used to mediate rolling circle replication of circular DNA molecules. The replication of DNA circles is dependent on the presence of primers. Thus, the methods disclosed herein can generate an amplified signal from any analyte of interest by rolling circle replication. The amplified DNA remains attached to the analyte via the primer, allowing stereoscopic detection of the analyte. The methods of the invention can be used to detect and analyze proteins or polypeptides. Various proteins can be analyzed by microarrays to which various proteins are immobilized. Thus, rolling circle replication primers are linked to various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule capable of specifically binding the protein to be tested. Rolling circle replication of the primers produces a large amount of DNA product at the site in the matrix where the protein is anchored. The amplified DNA serves as a signal for easy detection of the protein. The methods of the invention can also be used to compare proteins expressed in two or more samples. The resulting information is similar to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression systems. The method of the present invention can detect and quantify the protein expressed in any cell or tissue sensitively and accurately.
Owner:MOLECULAR STAGING
Method for synthesizing short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe
ActiveCN103276074AWide range of usesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseEnzyme digestion
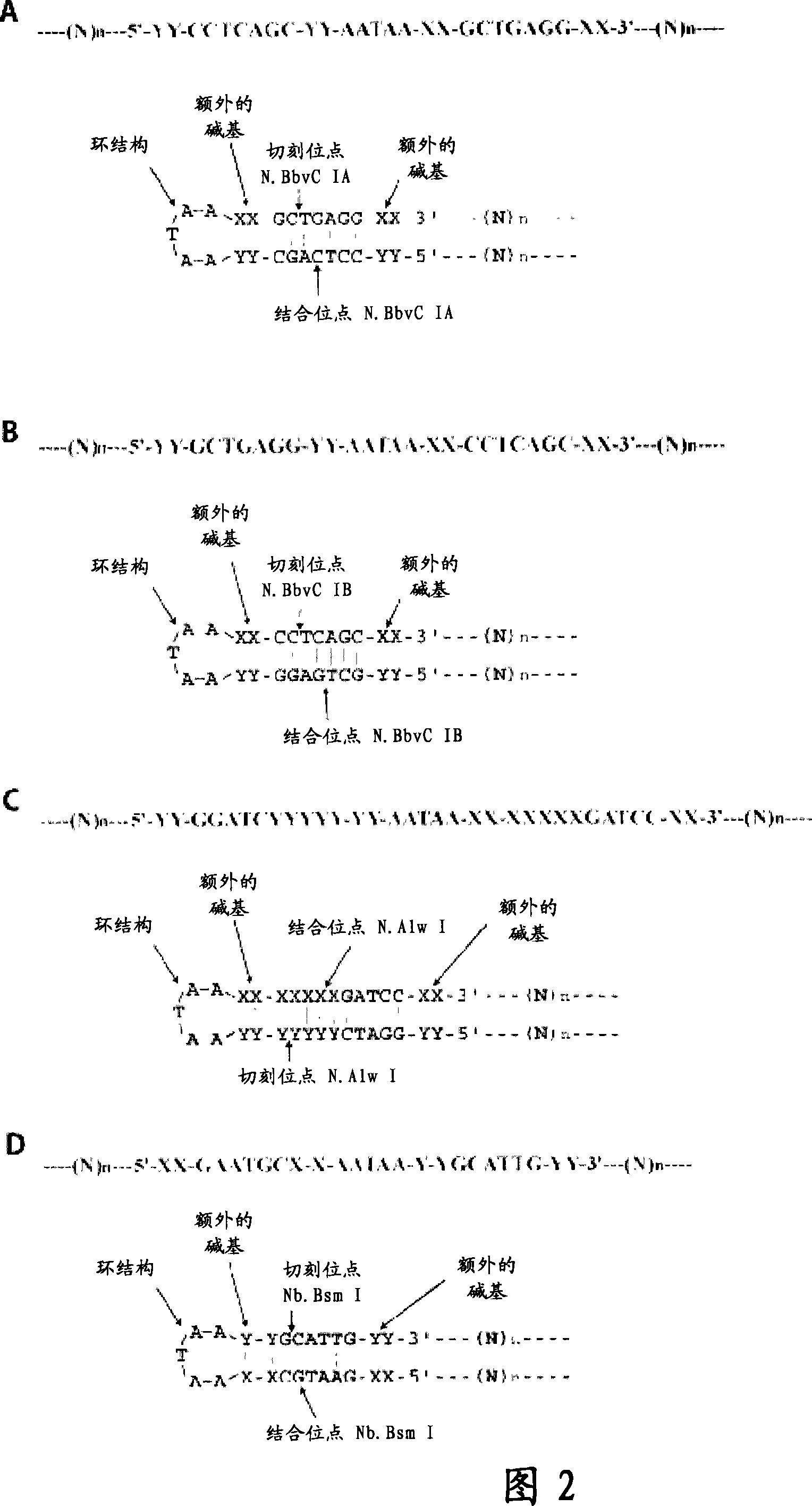
The invention belongs to the field of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) biosynthesis, and in particular relates to a method for synthesizing a short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe and application thereof. The short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe can be used for detecting small non-coding ribonucleic acid (RNA) such as micro ribonucleic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing plasmids recombined with template DNA; (2) cutting and connecting the template DNA, performing enzyme digestion on the recombined plasmids to obtain the template DNA, and connecting the template DNA end to end to form a ring; (3) cutting a single strand, performing rolling-circle replication, cutting one strand of the template DNA by using nickase, adding polymerase to perform rolling-circle replication by taking annular DNA with a nick as a template, and amplifying to obtain a DNA single strand containing a neck ring-probe structure; and (4) preparing target short single strand DNA, cutting the product of the step (3) by using a type II incision enzyme to form a target single strand DNA probe and a byproduct DNA, and separating and purifying through PAGE (polyacylamide gel electrophoresis) to obtain a single strand DNA probe without mutation. The short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe has wide applications in the fields of detection of small non-coding RNA and diagnosis and treatment of small non-coding RNA related diseases.
Owner:深圳弸福科技有限公司
Novel protein-DNA complex for detecting carcino-embryonic antigen as well as synthetic method and application thereof
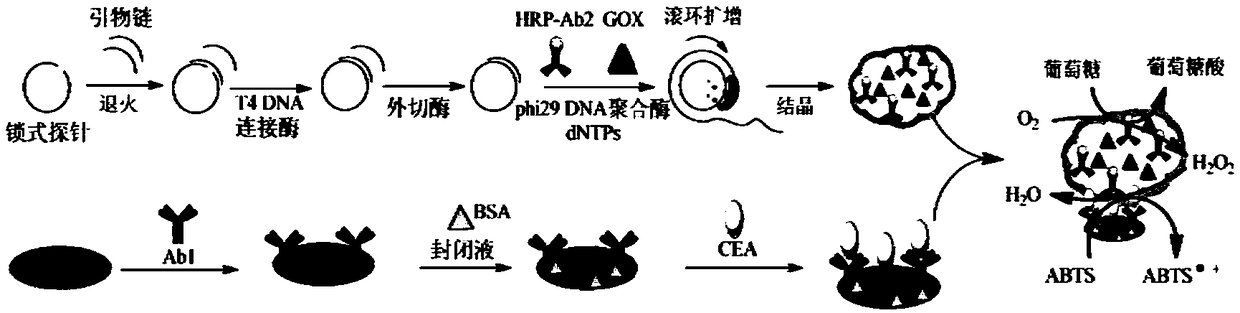
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and particularly relates to a novel protein-DNA complex for detecting a carcino-embryonic antigen as well as a synthetic method and application thereof. The novel protein-DNA complex comprises a horseradish peroxidase-marked carcino-embryonic antigen secondary antibody, glucose oxidase and a DNA structure. The novel protein-DNAcomplex structure encapsulated with a great amount of enzyme-labeled secondary antibodies and glucose oxidase is established on the basis of a rolling circle replication technology and is used as enzyme cascade signal amplification probe. A 96-pore plate is used for fixing carcino-embryonic antigen monoclonal antibody molecules, after the to-be-detected carcino-embryonic antigen is added, a sandwiched structure is formed. The encapsulated glucose oxidase is used for catalyzing the glucose to be oxidized to generate H2O2, then the H2O2 is catalyzed by virtue of the horseradish peroxidase to oxidize ABTS, so that the high-sensitivity and high-specificity colorimetry detection of the carcino-embryonic antigen can be realized, and the novel protein-DNA complex has important significance for the early diagnosis and clinical research of cancers.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
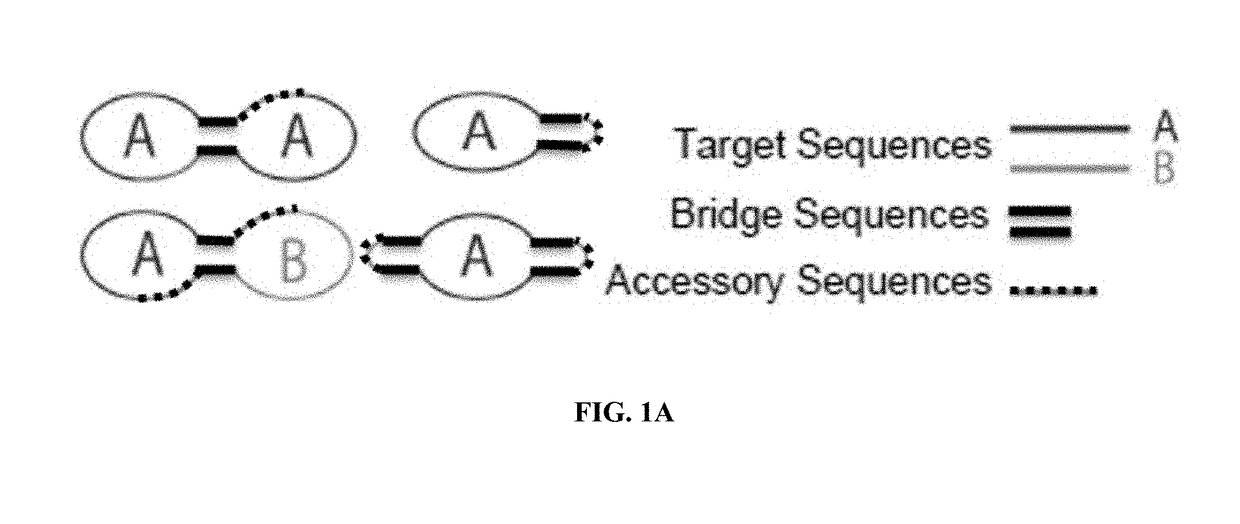
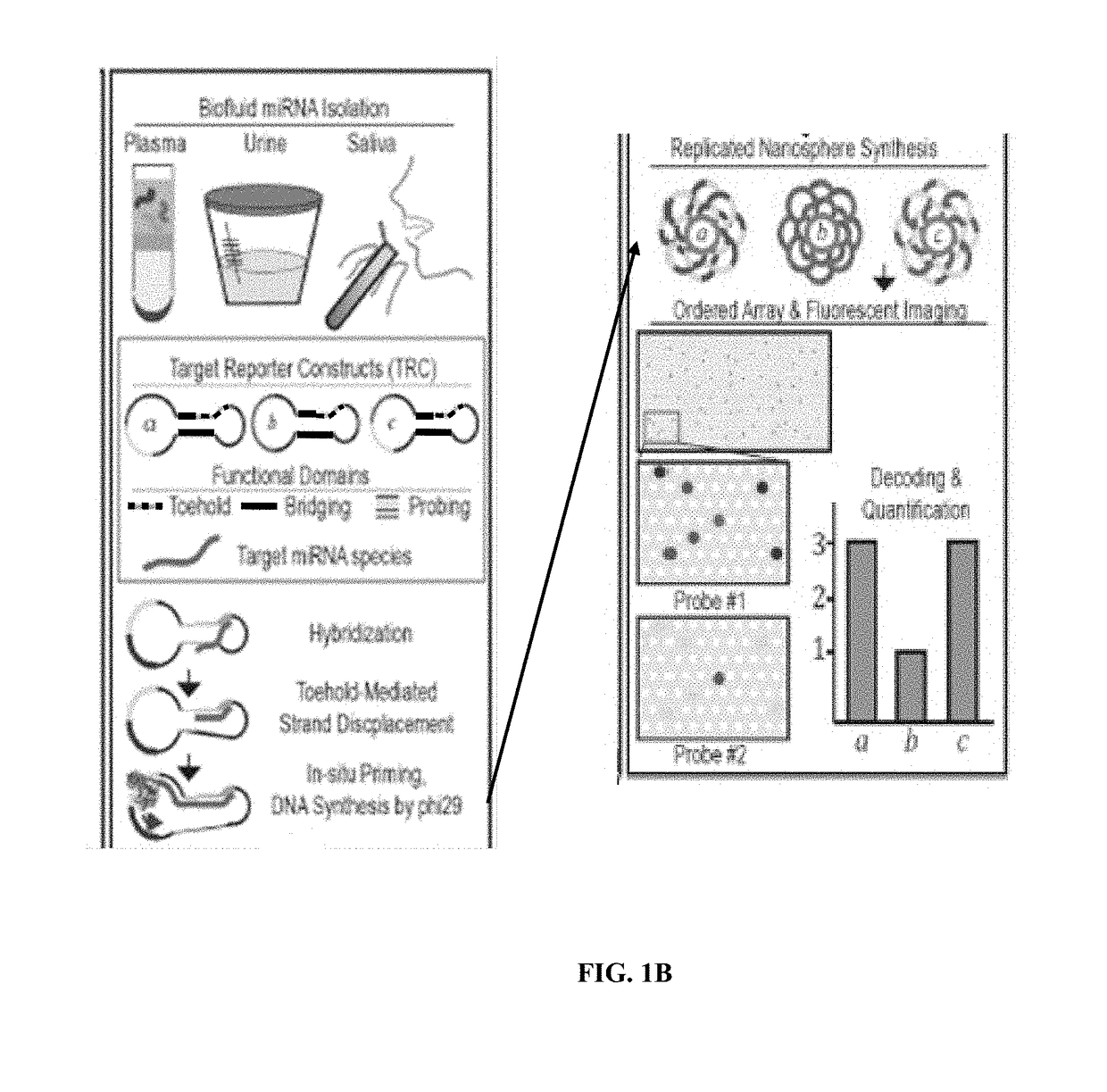
Target reporter constructs and uses thereof
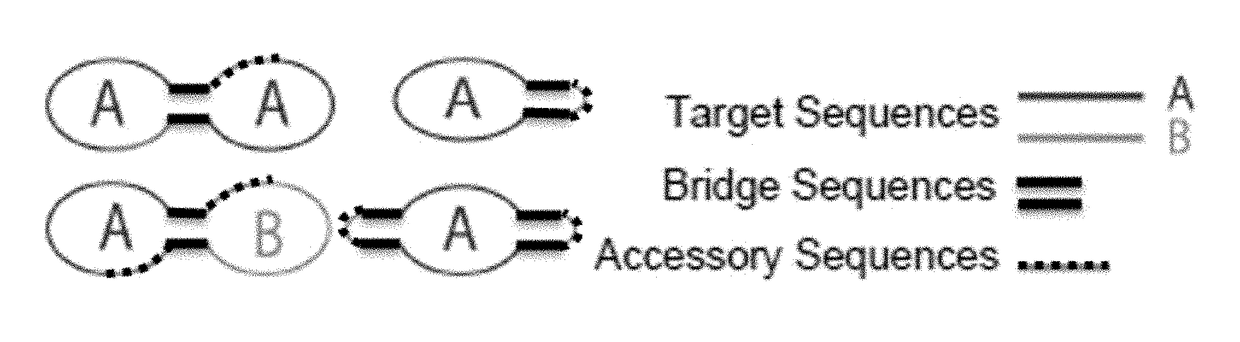
Provided herein are methods and compositions for the detection of target nucleic acids using target reporter constructs (TRCs) which comprise target sequences complementary to the target nucleic acid. Further provided are methods of replicating the TRCs using rolling circle replication and / or rolling circle amplification to produce replicated TRCs which can be detected using probe sequences within the replicated TRCs.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Template-independent ligation of single-stranded DNA
ActiveCN102317475AOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleic acid sequencingSingle strand dna
The invention provides ligation reaction mixtures, methods, and kits for improved template-independent intramolecular ligation (circularization) of linear ssDNA, including denatured gDNA fragments or first-strand cDNA made by reverse transcription of RNA, using, for example, a thermostable RNA ligase. The circular ssDNA molecules obtained using the improved ligation reaction mixtures and methods can be used, for example, as templates: for amplification by inverse PCR, rolling circle replication, transcription, or for massively parallel DNA sequencing. Applications include, for example: gene expression analysis by qPCR or using microarrays; analysis of gDNA copy number variation; and detection or quantification of specific nucleic acid sequences for research, screening, medical diagnostics, theranostics, personalized medical treatment or breeding, for purposes such as human or animal medicine, forensics, or agriculture.
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
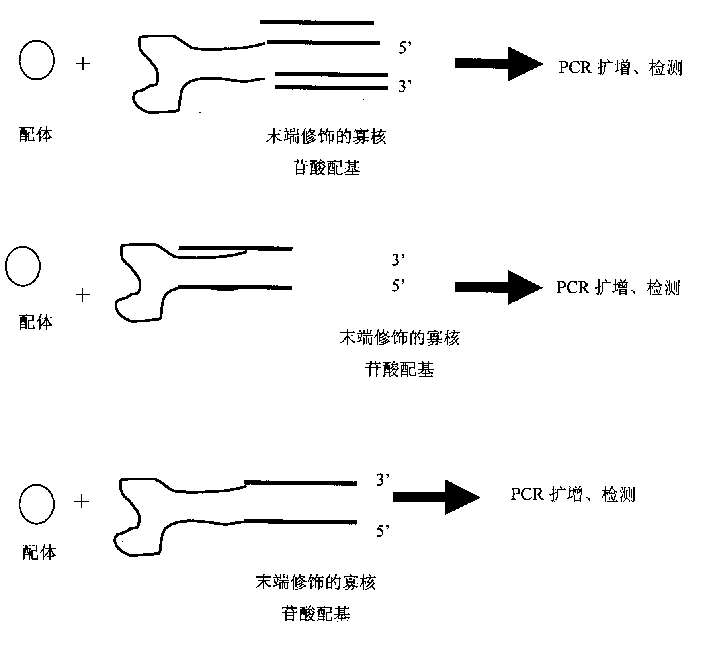
Novel ligand detecting method
InactiveCN1521272AHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingDirect binding
The present invention relates to one new kind o detecting ligand of nucleic acid aglucone. The method utilizes nucleic acid sequence modified ligand to specify oligonucleotide aglucone for direct binding with ligand and converting ligand signal into nucleic acid aglucone signal. The ligand is then determined via subsequent PCR proliferation and amplification and detection. The method of detecting ligand has the features of fast speed, high sensitivity, powerful specificity multi-ligand microarray detection.
Owner:甘肃省医学科学研究院
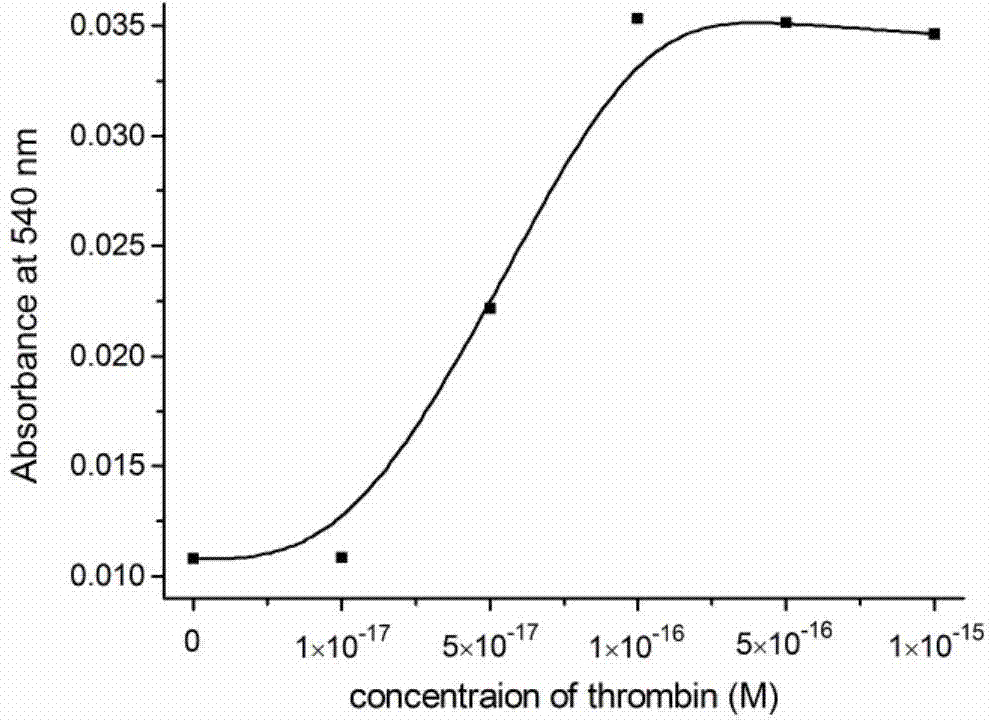
Ultra-high sensitive colorimetric method for detecting thrombin
ActiveCN104726560AHigh detection sensitivityAvoid smallMicrobiological testing/measurementHeminEnzyme
The invention provides an ultra-high sensitive colorimetric method for detecting thrombin; a lot of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) enzymes can be formed by adopting a rolling-circle replicating and amplifying technology; detection signals are amplified; therefore, the detection sensitivity of thrombin is increased; influence of unreacted hemin to reaction can be eliminated by adopting a 96-pore plate connection primer; the signal to noise ratio is increased; and therefore, the detection sensitivity is further increased. By adopting a sensitive colorimetric system, gold ions are reduced to be red or blue generated in a dispersed or united state by utilizing hydrogen peroxide; whether a target molecule exists can be judged directly; a nano gold solution is unnecessary to prepare in advance; the ultra-high sensitive colorimetric method is simple and feasible; complex apparatuses and equipment are unnecessary; by means of the ultra-high sensitive colorimetric method, ultra-high sensitive detection of thrombin can be realized; and the detection limit is up to 10-17 M (about six thrombin molecules).
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Methods for production of oligonucleotides
ActiveUS8080393B2Efficient amplificationEliminate needSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetics
The present invention relates to production of oligonucleotides using rolling circle replication, wherein synthesised multimeric oligonucleotides are reduced to mononucleotides using a nicking cassette. Thus, the invention provides a method for the production of oligonucleotides, enabling efficient amplification of oligonucleotides at lengths up to at least 1000 nucleotides and in high amounts contained within a nicking cassette.
Owner:OLINK AB +1
DNA nano flower-shaped composite structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110507818AEasy chemical modificationHuge development potentialPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImmunological disordersAdjuvantA-DNA
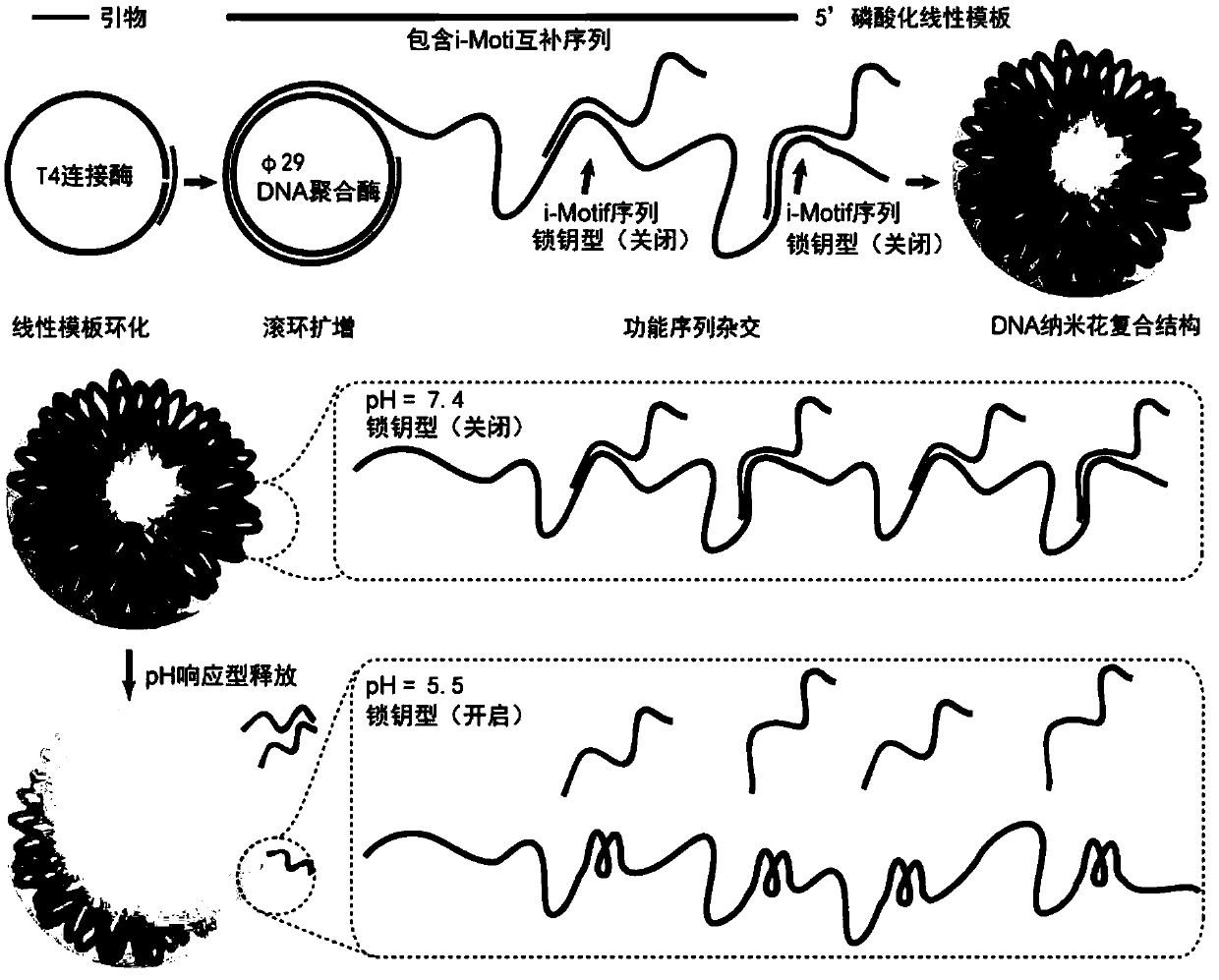
The invention provides a DNA nano flower-shaped composite structure as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The DNA nano flower-shaped composite structure comprises a DNA nano flower-shaped structure formed by amplification of a single-stranded DNA template and an immunostimulatory nucleic acid fragment hybridized with the DNA nano flower-shaped structure, according to the invention, primers and template sequences are ingeniously designed, a rolling circle replication method is used for amplifying the template DNA to form a nano flower shape, creatively fuses a pH-responsive i-motif into a hybridization site to realize hybridization and acid response release of an immunostimulatory nucleic acid sequence, optimizes the reaction conditions, and finally successfully prepares the composite structure. The composite structure provided by the present invention can be used as a carrier for loading immune stimulating nucleic acid fragments to be efficiently transported inside immune cells, by responsively releasing the immune stimulating nucleic acid fragments, the immune cells can be activated, which provides a powerful novel adjuvant material for tumor immunotherapy, and has broad application prospects and market value.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Methods for production of oligonucleotides
The present invention relates to production of oligonucleotides using rolling circle replication, wherein synthesised multimeric oligonucleotides are reduced to mononucleotides using a nicking cassette. Thus, the invention provides a method for the production of oligonucleotides, enabling efficient amplification of oligonucleotides at lengths up to at least 1000 nucleotides and in high amounts contained within a nicking cassette.
Owner:ON-SITE RCP CO UNDER THE NAME OF NOVIA CO
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
PendingUS20170067097A1Efficient productionCreate efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosomal regionHaplotype
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid-nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid-protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Improved sequencing library and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN105420348ARemoval of amplification errorsRemove sequencing errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDna amplificationSingle strand dna
The invention provides a sequencing library. An insertion fragment in the sequencing library is a conjugate alternate series body of a sequence to be measured and a label sequence. Preparation of the conjugate alternate series body of the sequence to be measured and the label sequence comprises the steps that the sequence to be measured is connected with the label sequence, and single-chain circulation and rolling circle replication are carried out, wherein rolling circle replication is completed in a reaction solution wrapped by oil drops. The invention further provides a preparing method of the sequencing library and a sequencing method. According to the sequencing library and the sequencing method, DNA amplification errors and sequencing errors can be effectively eliminated under any sequencing depth, and thus mutation existing on DNA molecules is detected super-precisely. The sequencing library is suitable for construction of microscale DNA short fragments and even a single-chain DNA sequencing library.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for detecting ampicillin based on aptamer
InactiveCN107058501AMeet the requirements of high sensitivity detectionLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerAmpicillin
The invention provides a method for detecting ampicillin based on an aptamer. According to the invention, signal amplification is realized by applying a target object circulation technology, a strand displacement reaction technology and a rolling circle replication amplifying technology. The method provided by the invention is low in price, high in analysis and detection speed, high in sensitivity and strong in specificity.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid - nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid - protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com