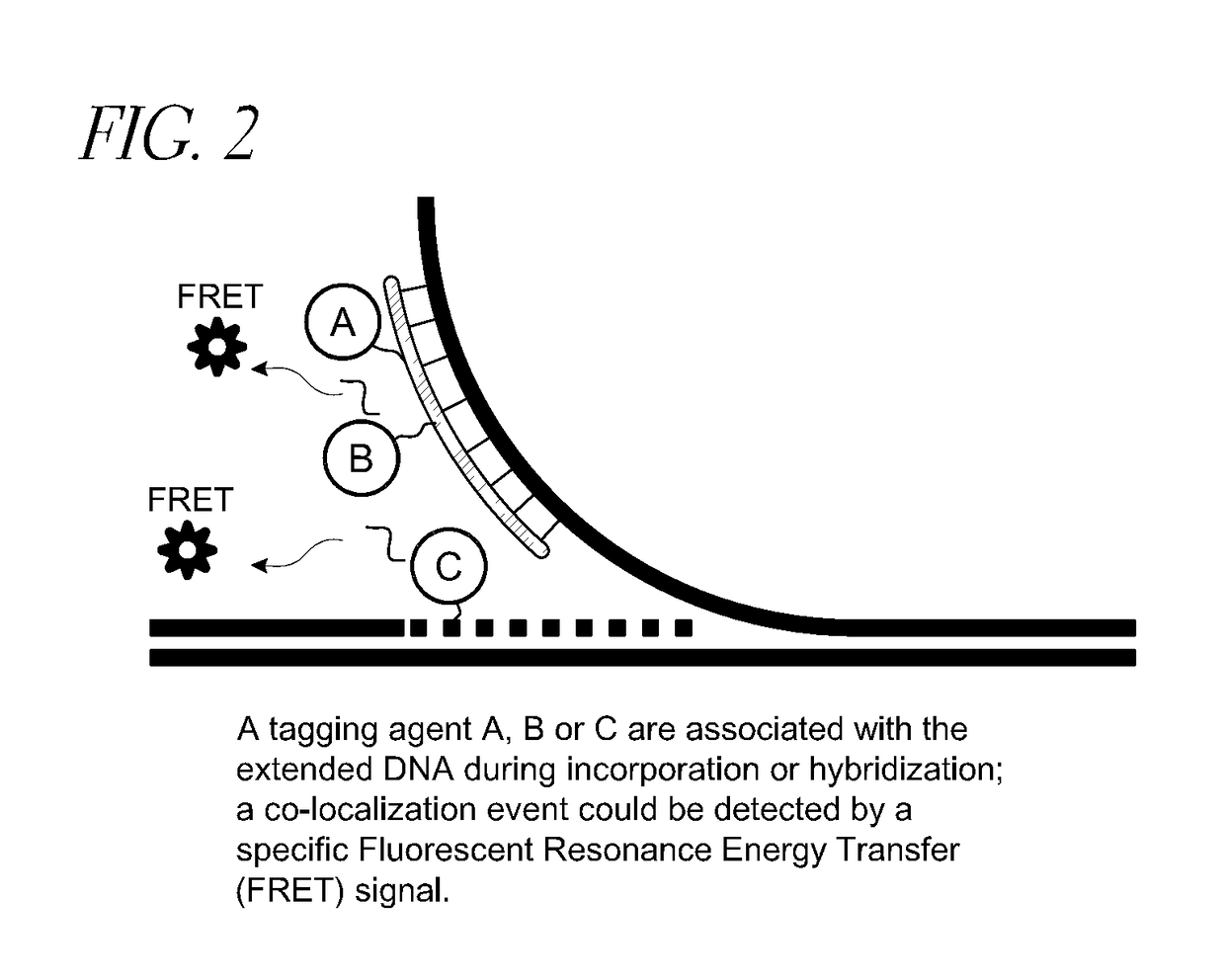
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Structural variant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
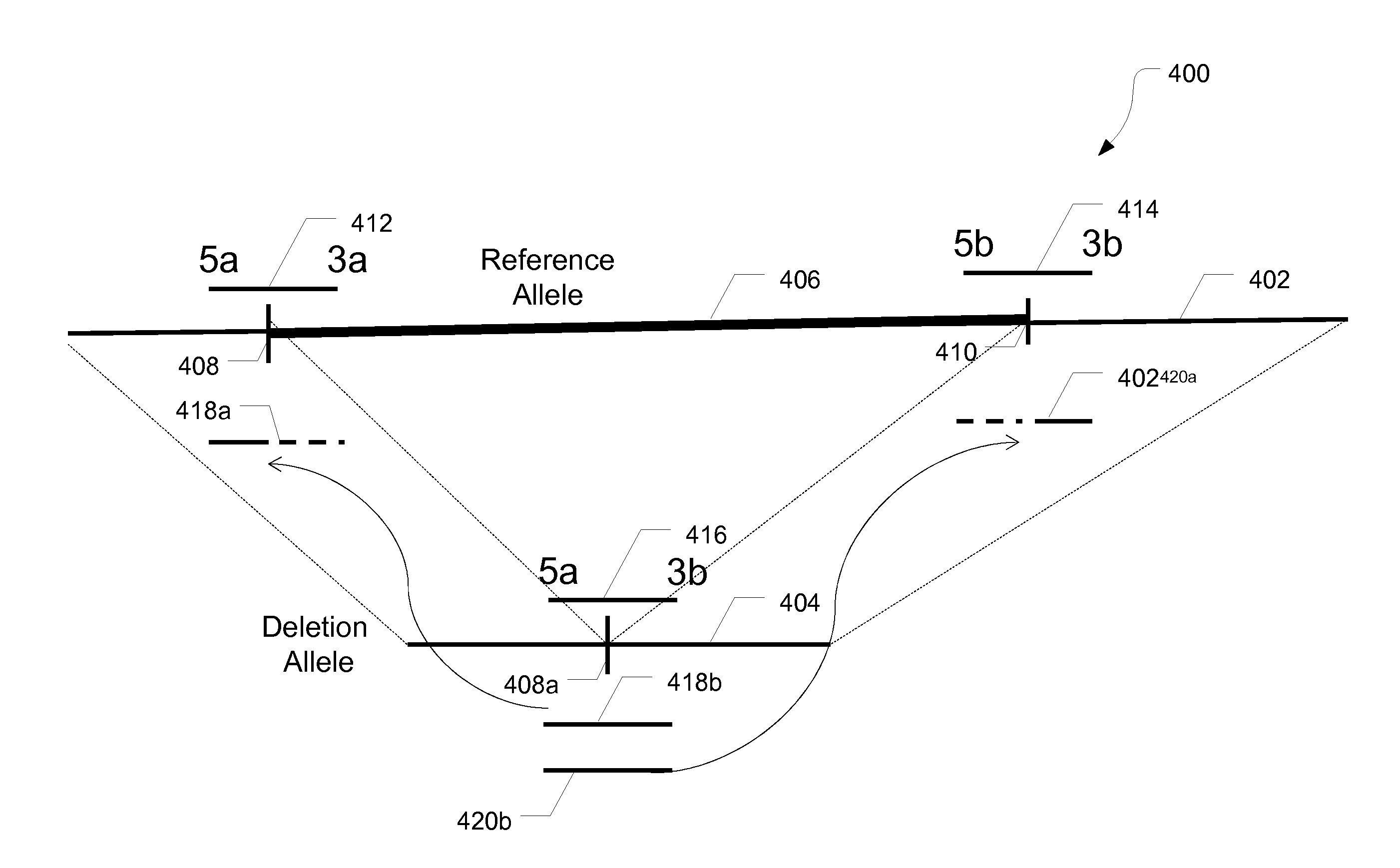
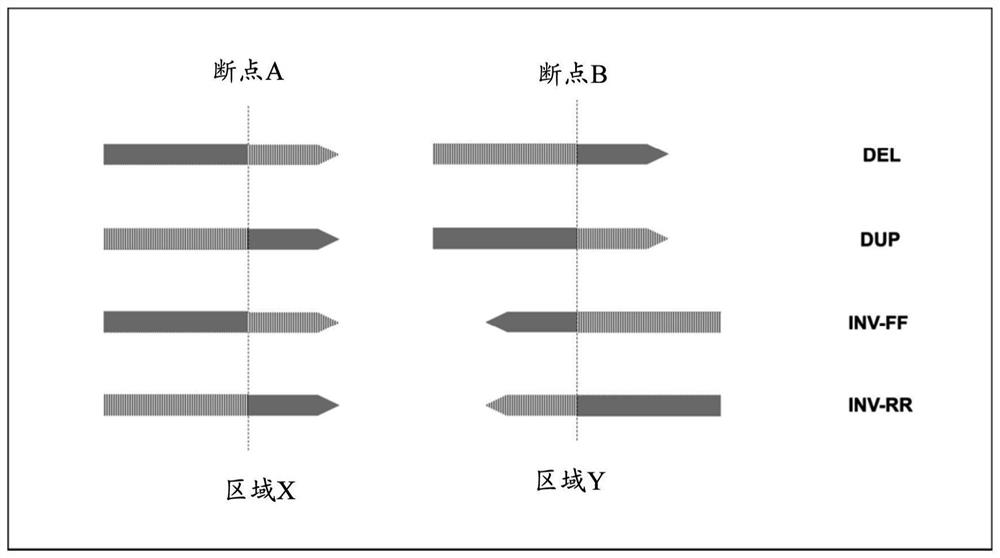
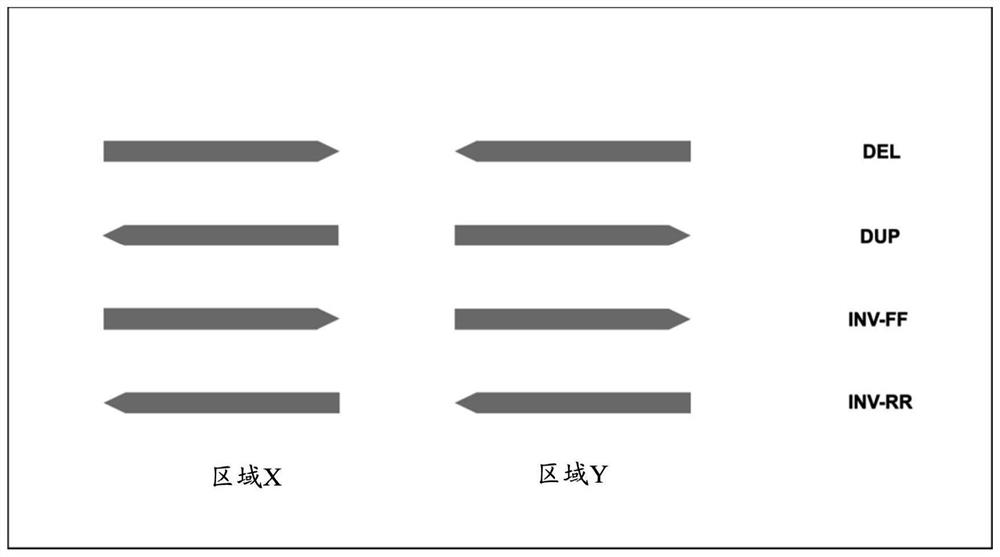
Structural variation (also genomic structural variation) is the variation in structure of an organism's chromosome. It consists of many kinds of variation in the genome of one species, and usually includes microscopic and submicroscopic types, such as deletions, duplications, copy-number variants, insertions, inversions and translocations.
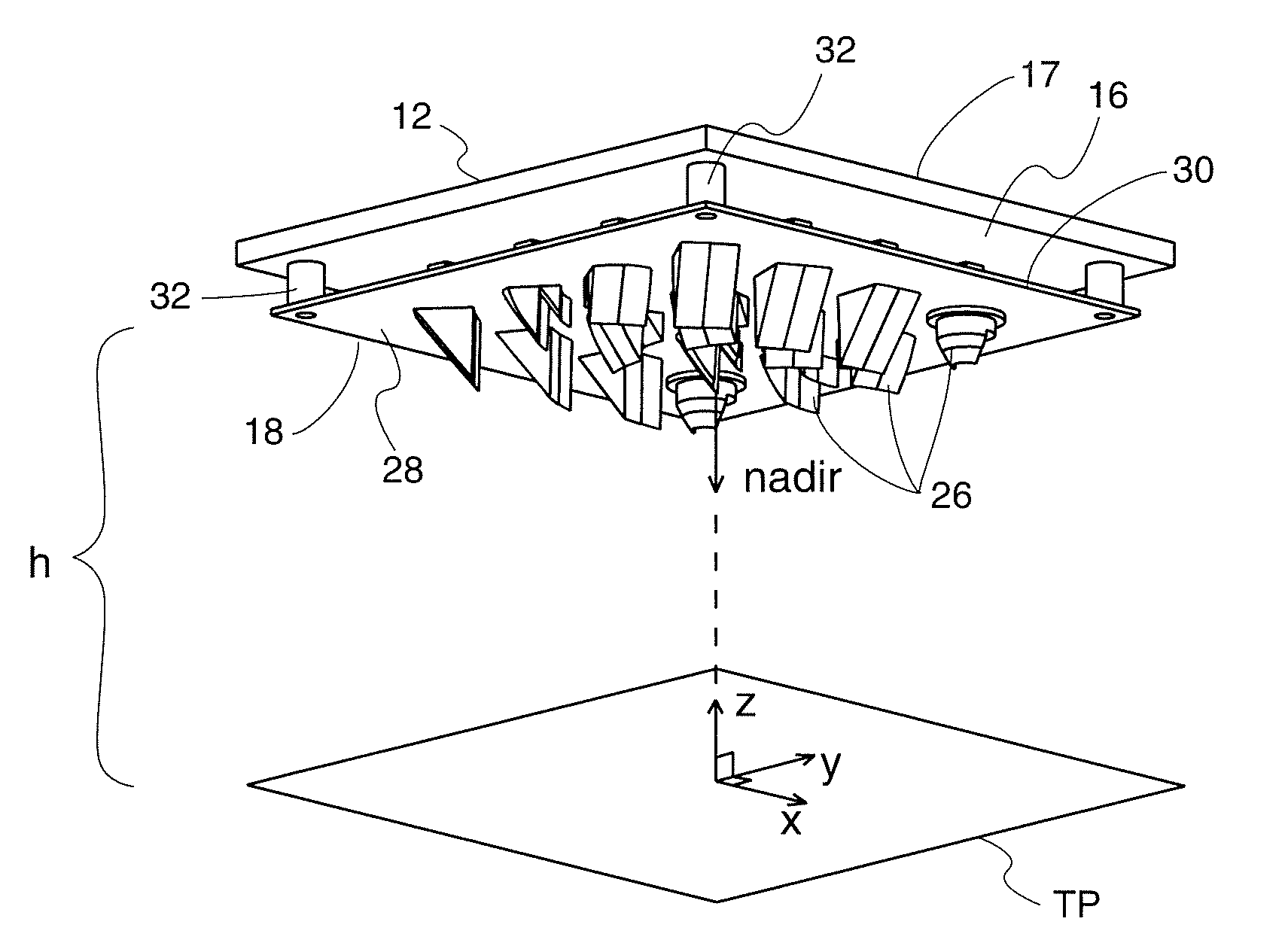
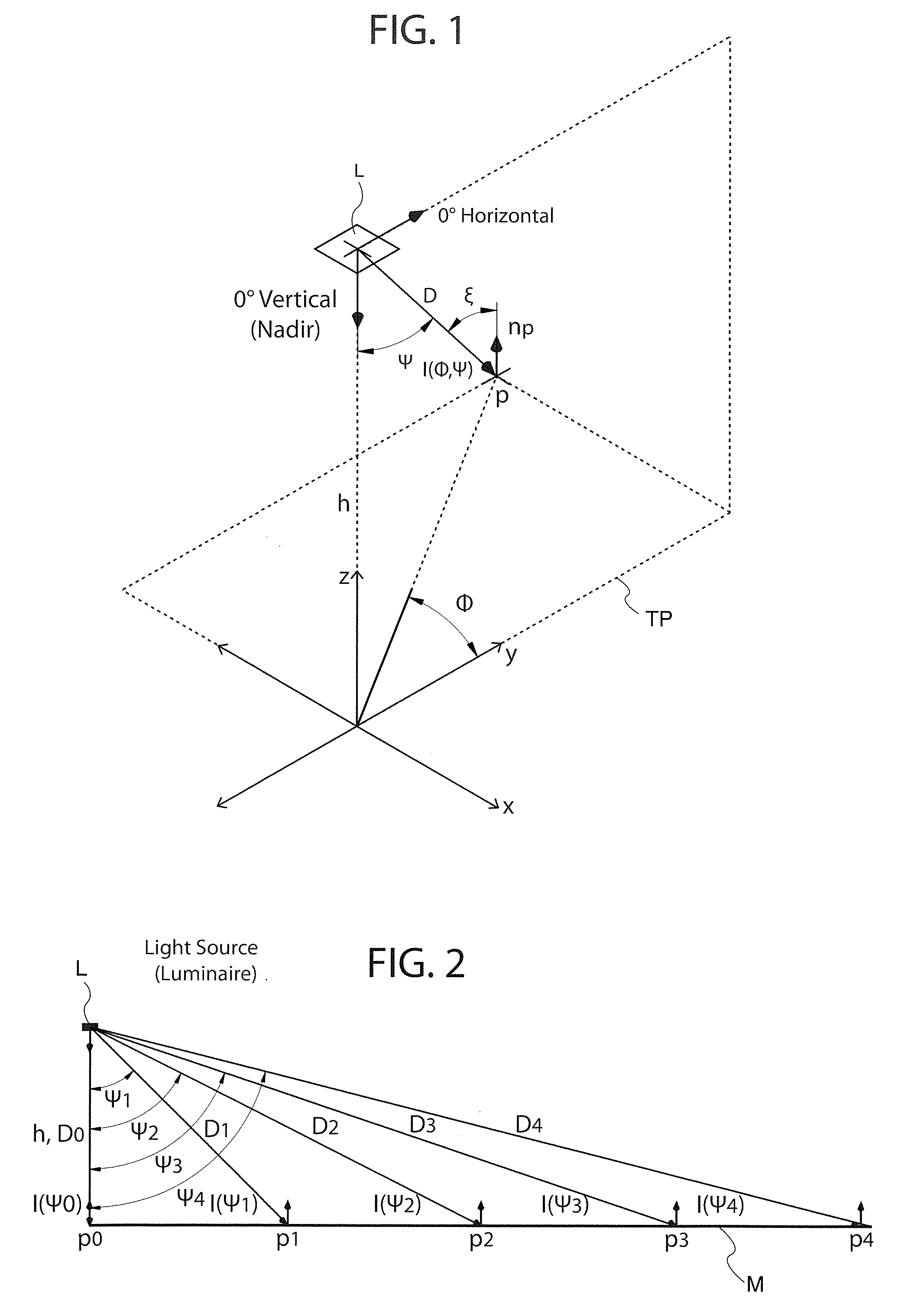
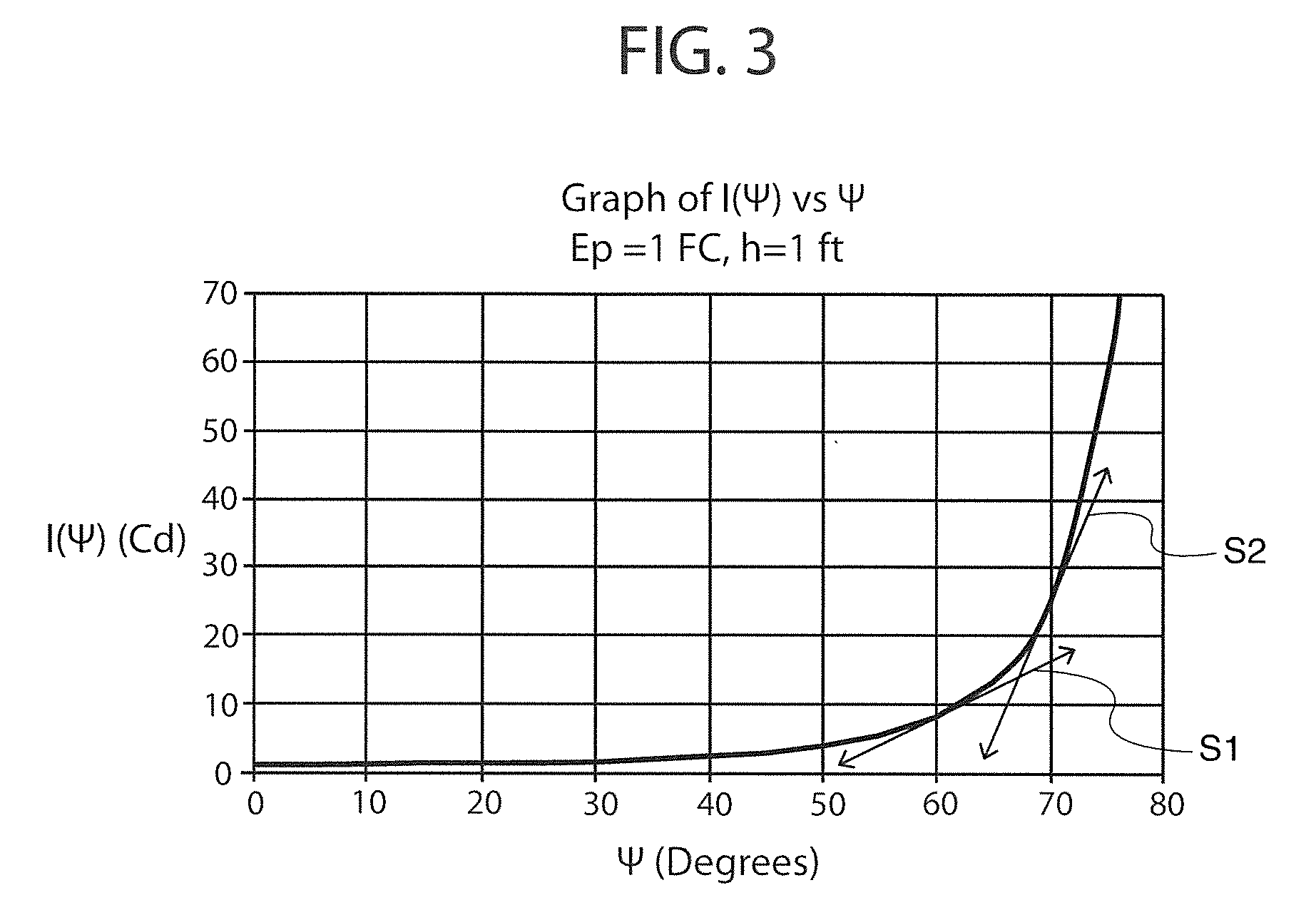
LED optical system
ActiveUS20110038151A1Eliminate all waste lightEffective distributionPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusTarget surfaceEffect light
An optical system for lighting fixtures uses light emitting diodes arranged in a 2-D array. In one embodiment, a lighting system comprises a framework carrying a plurality of diodes, where each diode has an associated optic that projects the light with a “high,”“medium” or “low” vertical throw, as provided by prismatic “teeth” that refract and reflect light rays in a predetermined manner so that the combined illumination patterns of each diode can blend to generally uniformly illuminate a target surface without dark spots or regions. Each optic has a common primary portion and a selected secondary portion whose tooth / teeth have a “swept” geometry for better angular (vertical and / or horizontal) control of light rays. Structural variations between different secondary portions reside in various factors, including plurality of teeth, length of the tooth along the longitudinal axis A, curvature(s) in the vertical and / or horizontal directions, and angularity or tightness of curvature of the swept geometry.
Owner:U S POLE
Systems and Methods for Detecting Structural Variants
ActiveUS20150094212A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationStructural variantComputational biology
Systems and method for identifying long deletions can obtain sequencing information for a plurality of amplicons in and around a potential region from a nucleic acid sample. The sequencing information can include a plurality of reads that can be mapped to a reference sequence. Using information, such as where reads map to a reference sequence and relative abundance of reads for the amplicons, structural variants can be identified and a determination can be made if the nucleic acid sample is homozygous or heterozygous for the structural variant.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Device and method for hoisting entire oversized steel reinforcement cage in one step
InactiveCN102328881AGuaranteed deformationGuaranteed deformation controlCranesLoad-engaging elementsOperabilityRebar
The invention discloses a method for hoisting an entire oversized steel reinforcement cage in one step. The method mainly comprises the steps of: binding a steel reinforcement cage; arranging hoisting points and configuring a crane; connecting a main hoisting hook with the hoisting points; completing horizontal hoisting of the steel reinforcement cage; converting the steel reinforcement cage froma horizontal state to a vertical state; and directly hoisting the steel reinforcement cage in the vertical standing state to be in place by using a third crane. According to the invention, by jointlyhoisting the oversized steel reinforcement cage by using three hoisting equipment and by skillfully transforming the hoisting points in the angle transformation from the horizontal state to the vertical state, the oversized steel reinforcement cage is hoisted in one step without segmentation and structural variation, so that the efficiency in hoisting operation is increased, in addition, concretecan be poured, so that the advantages of construction safety, operability, capability of meeting construction period requirement and increased efficiency are achieved.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR SECOND ENG BUREAU LTD
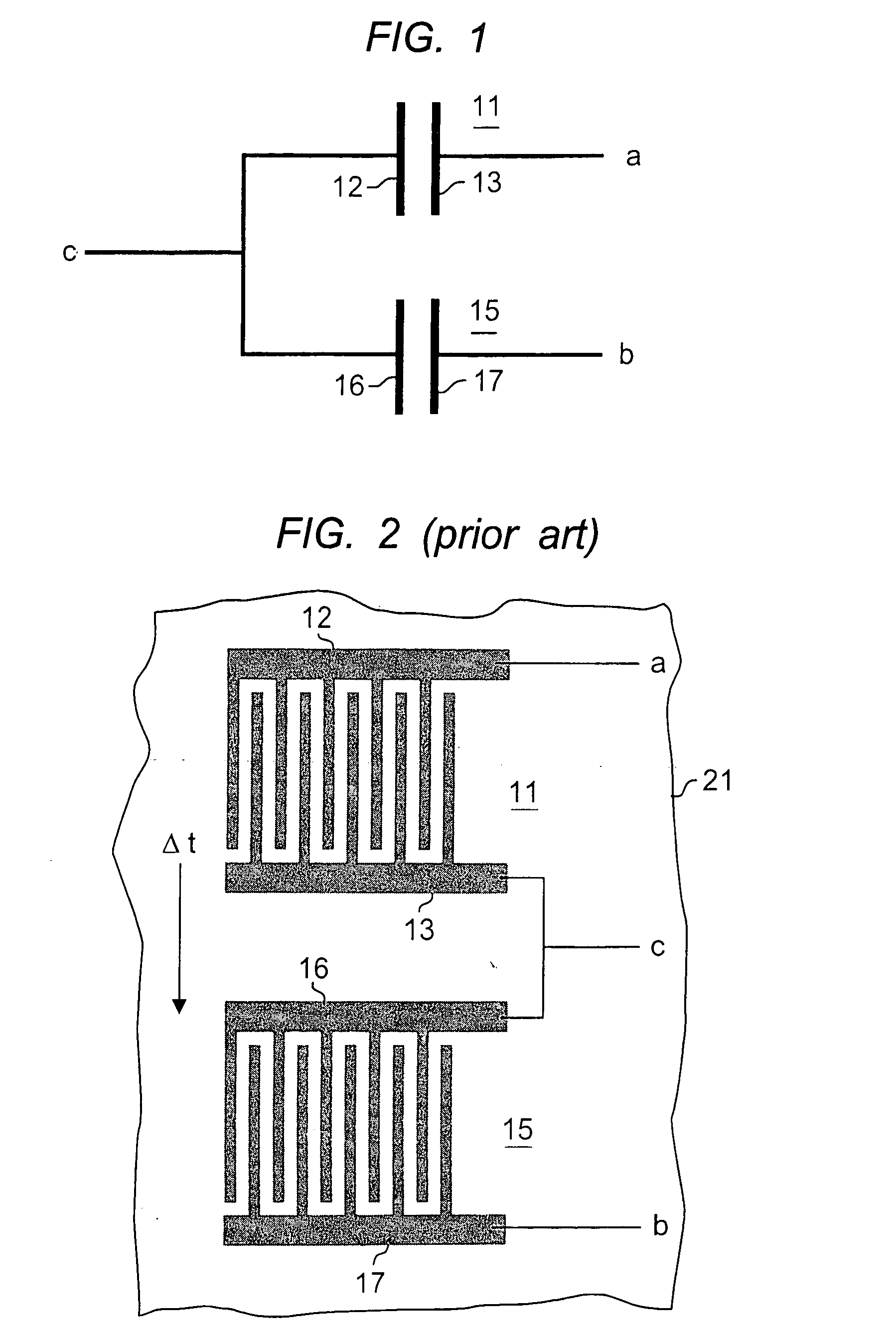
Interdigitaded capacitors
ActiveUS20060054994A1Reduce variationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStructural variantProcess conditions
The specification describes matched capacitor pairs that employ interconnect metal in an interdigitated form, and are made with an area efficient configuration. In addition, structural variations between capacitors in the capacitor pair are minimized to provide optimum matching. According to the invention, the capacitor pairs are interdigitated in a manner that ensures that the plates of each pair occupy common area on the substrate. Structural anomalies due to process conditions are compensated in that a given anomaly affects both capacitors in the same way. Two of the capacitor plates, one in each pair, are formed of comb structures, with the fingers of the combs interdigitated. The other plates are formed using one or more plates interleaved between the interdigitated plates.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
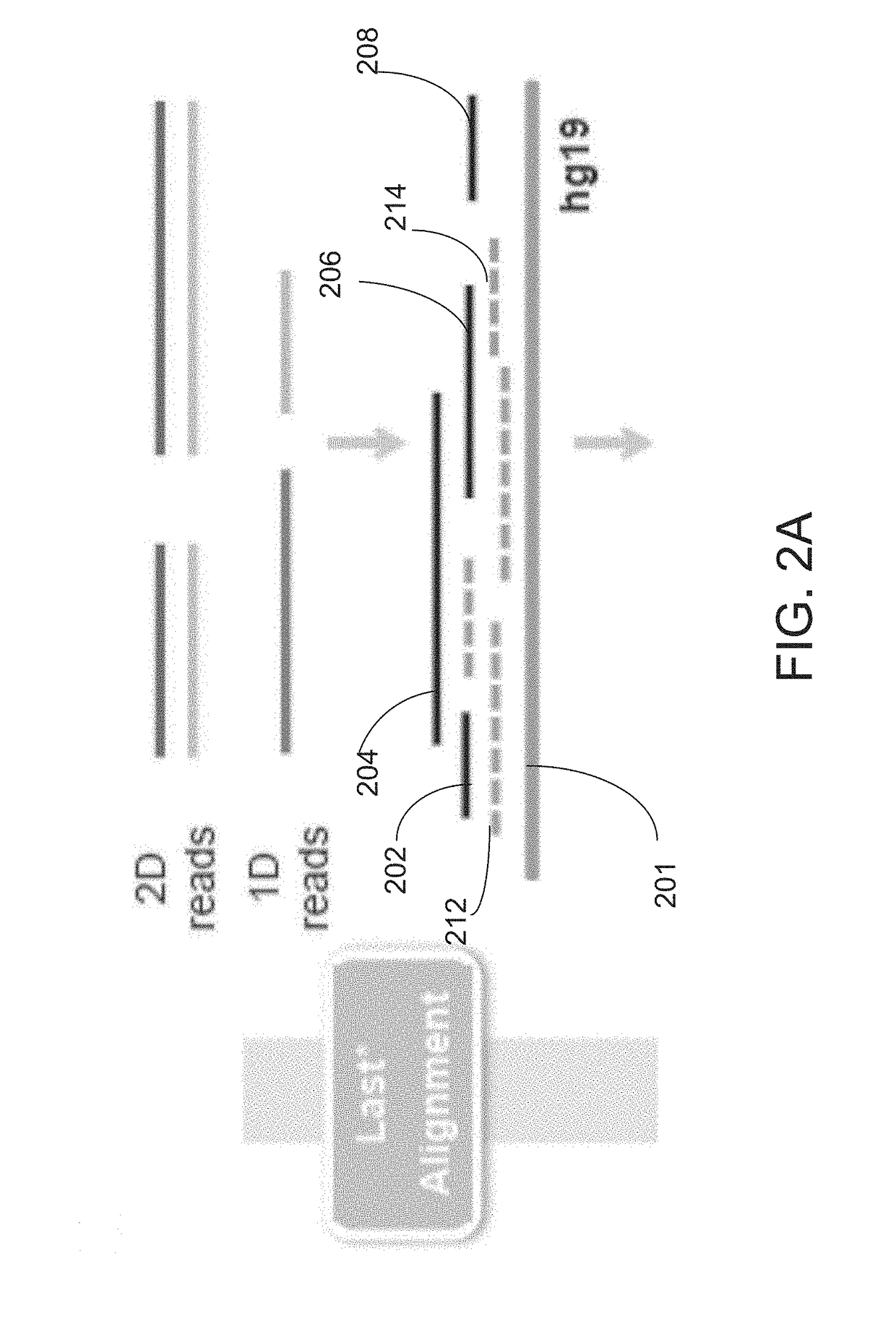
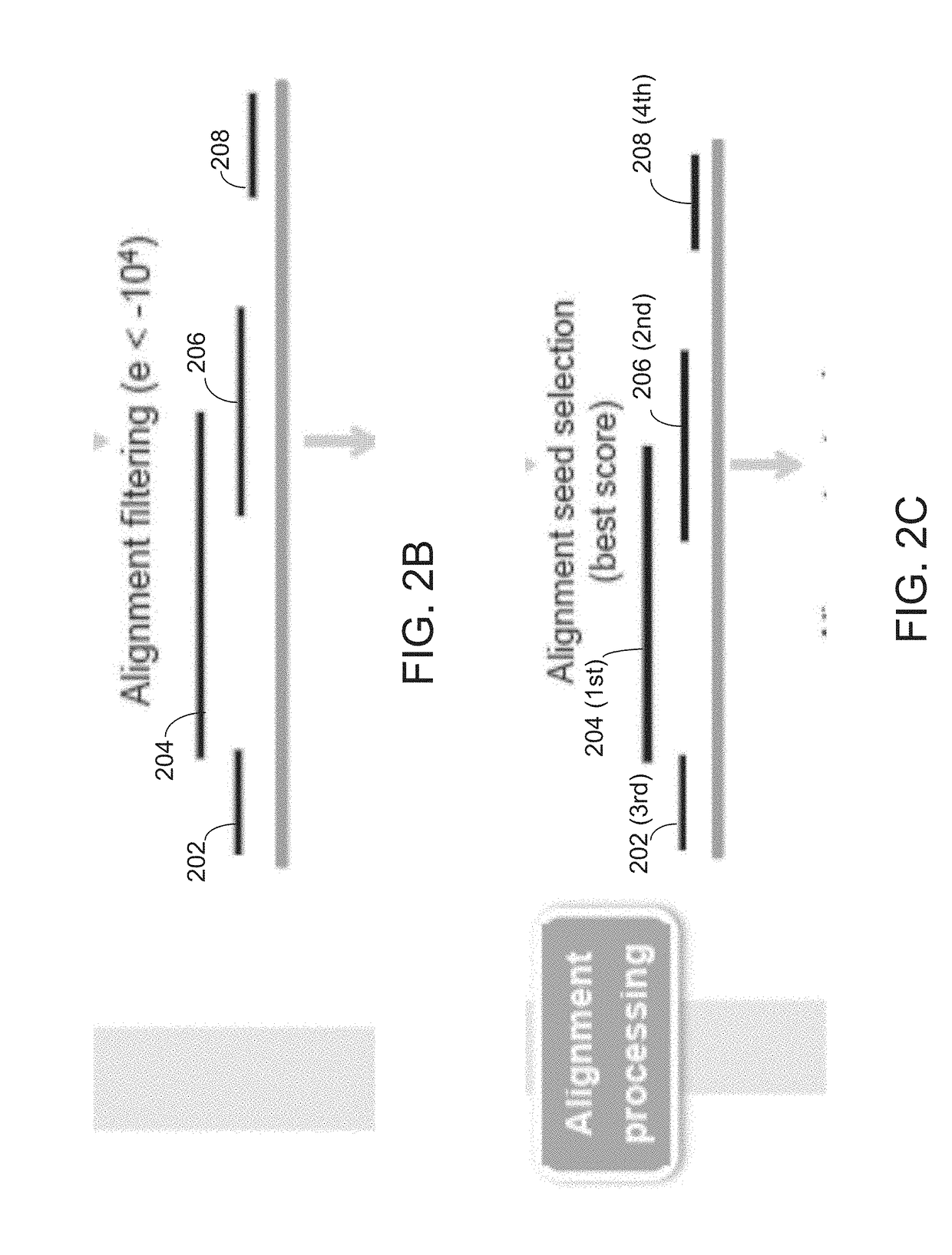
Detection of high-resolution structural variants using long-read genome sequence analysis
A method of determining the presence of a novel structural variation in a genome using long-read genome sequence fragments includes a process of aligning, filtering ranking and linking long-read sequence fragments against a reference genome. Presence of a novel structural variation is present in said genome can be determined when said linked alignment contains multiple linked fragments that are mapped to a single locus, referred to as a split-read.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
Systems and methods for detecting structural variants
Systems and method for identifying gene fusions can obtain sequencing information for a plurality of amplicons from a nucleic acid sample. The sequencing information can include a plurality of reads that are initially partially mapped to a reference sequence. Fragments may be generated by splitting the partially mapped reads into mapped and unmapped fragments, and the fragments may be remapped to the reference sequence. Gene fusions can be identified based on reads where the first fragment maps to a first gene and the second fragment maps to a second gene.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method and device for simultaneously detecting methylation level, genome variation and insert fragment
ActiveCN111755072AEasy to distinguishImprove the comparison rateProteomicsGenomicsGenes mutationBisulfite sequencing
The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting a methylation level, genome variation and an insert fragment by utilizing a methylation non-bisulfite sequencing technology. The genome variation comprises gene mutation, copy number variation and structural variation. The invention also provides a device and equipment for implementing the method, and a corresponding computer readable medium. According to the invention, for methylated non-bisulfite sequencing data, one-step detection and analysis from offline data to multiple dimensions of methylation level, genome variation and insert fragments are realized, the method is suitable for whole genome and targeted capture data types of methylated non-bisulfite, and analysis of a single cancer sample and paired samples (cancer samples containing control samples) can be carried out.
Owner:深圳吉因加医学检验实验室
Method for detecting multiple mutation types of genome
InactiveCN109337957AHigh precisionIncrease linearlyMicrobiological testing/measurementLinear growthSingle nucleotide mutation
The invention relates to a method for detecting multiple mutation types of a genome. A BAM file is used as an input file, a tumor tissue sample is detected, multiple mutation information of differentsample types is detected, and detection of the tumor tissue sample comprises the steps as follows: 1) detection of mononucleotide mutation; 2) detection of insertion and deletion; 3) detection of structural variants; 4) detection of complex variants. According to the method for detecting multiple mutation types of the genome, insertion and deletion are detected with a GeneReader algorithm obtainedthrough combination of a supervised method and an unsupervised method, the local comparison precision is optimized, linear growth with increase of the sequencing depth is realized in the aspect of speed, the detection effect is good, the detection result is accurate, and actual application demands can be well met.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
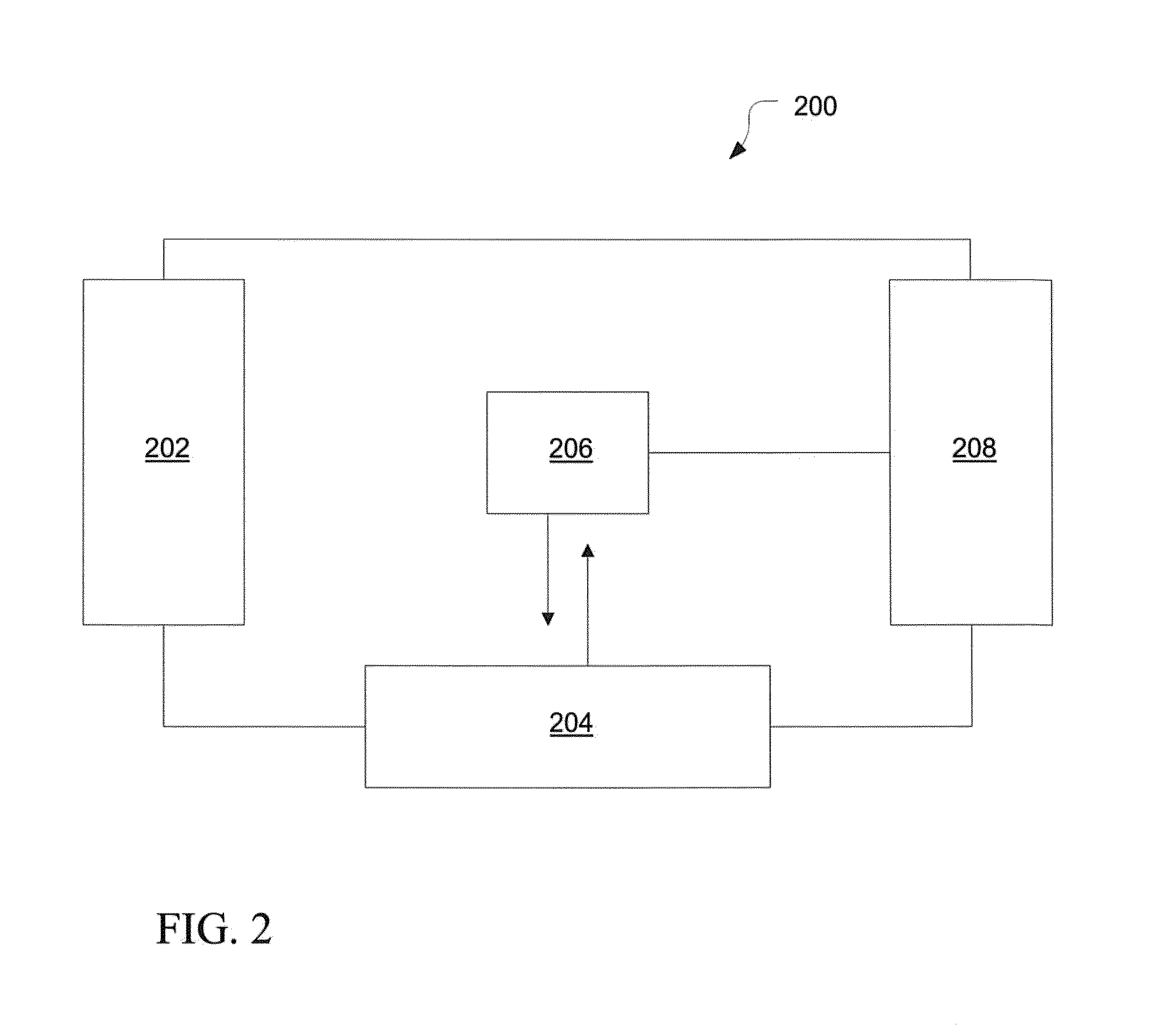
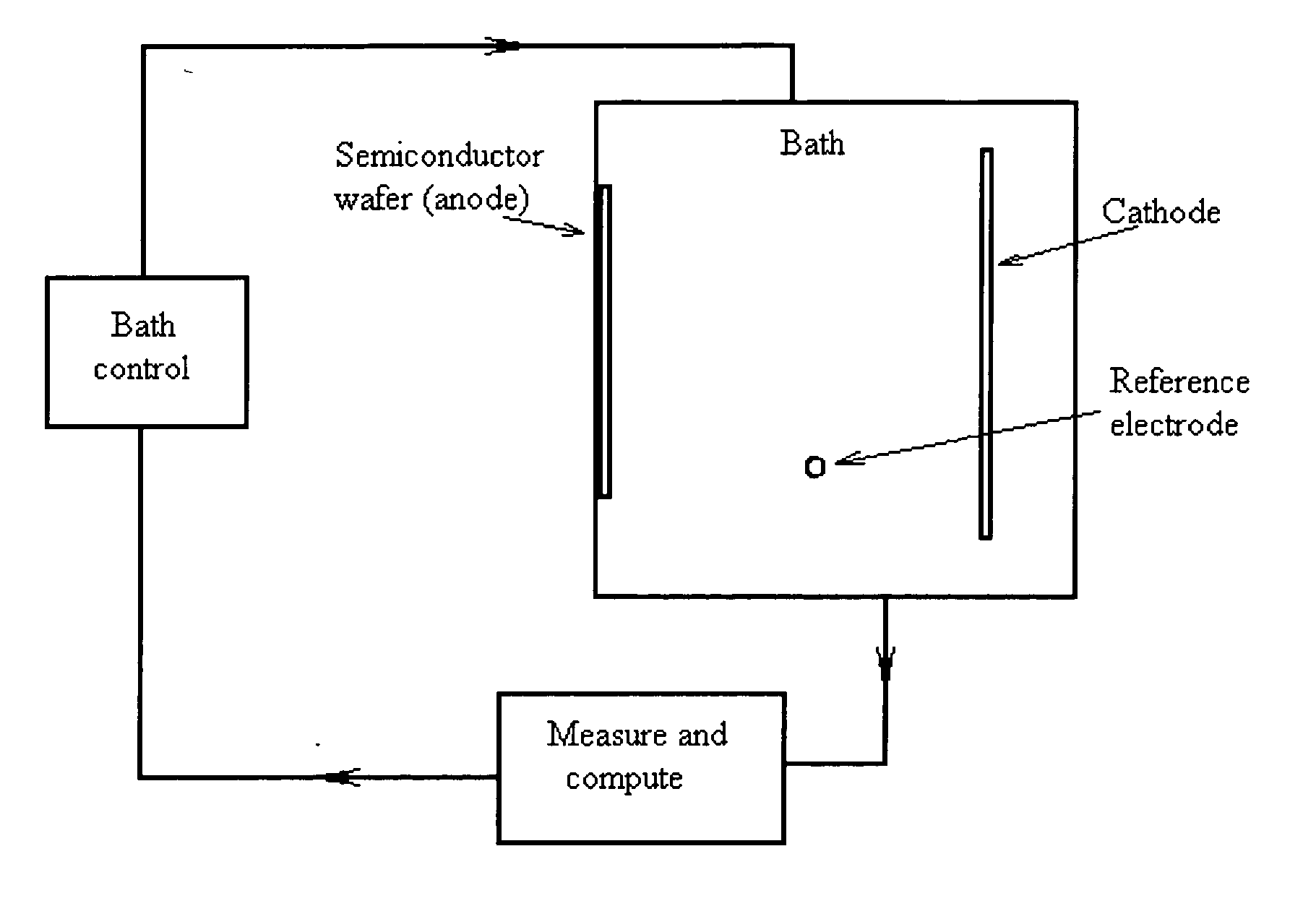
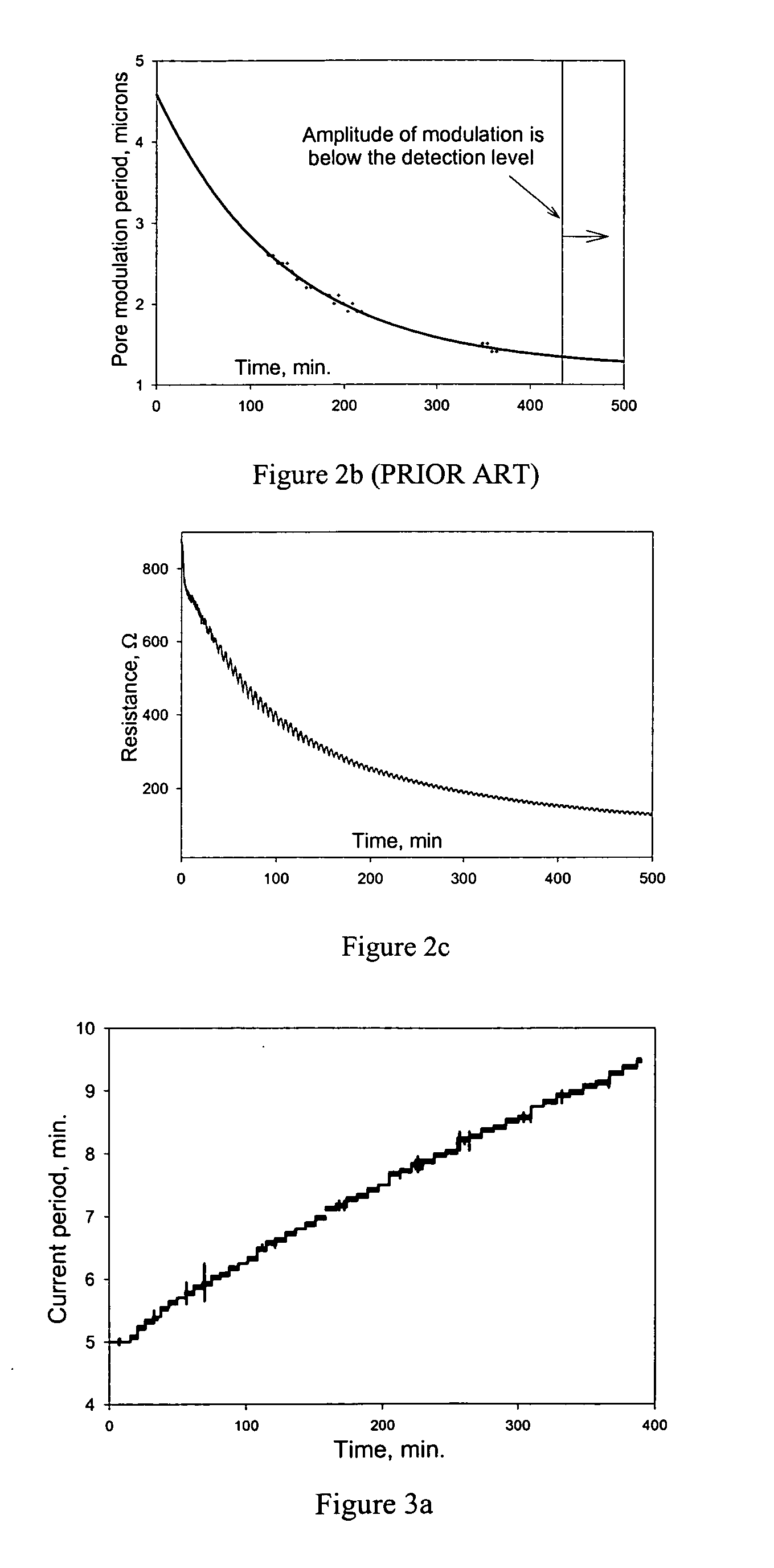
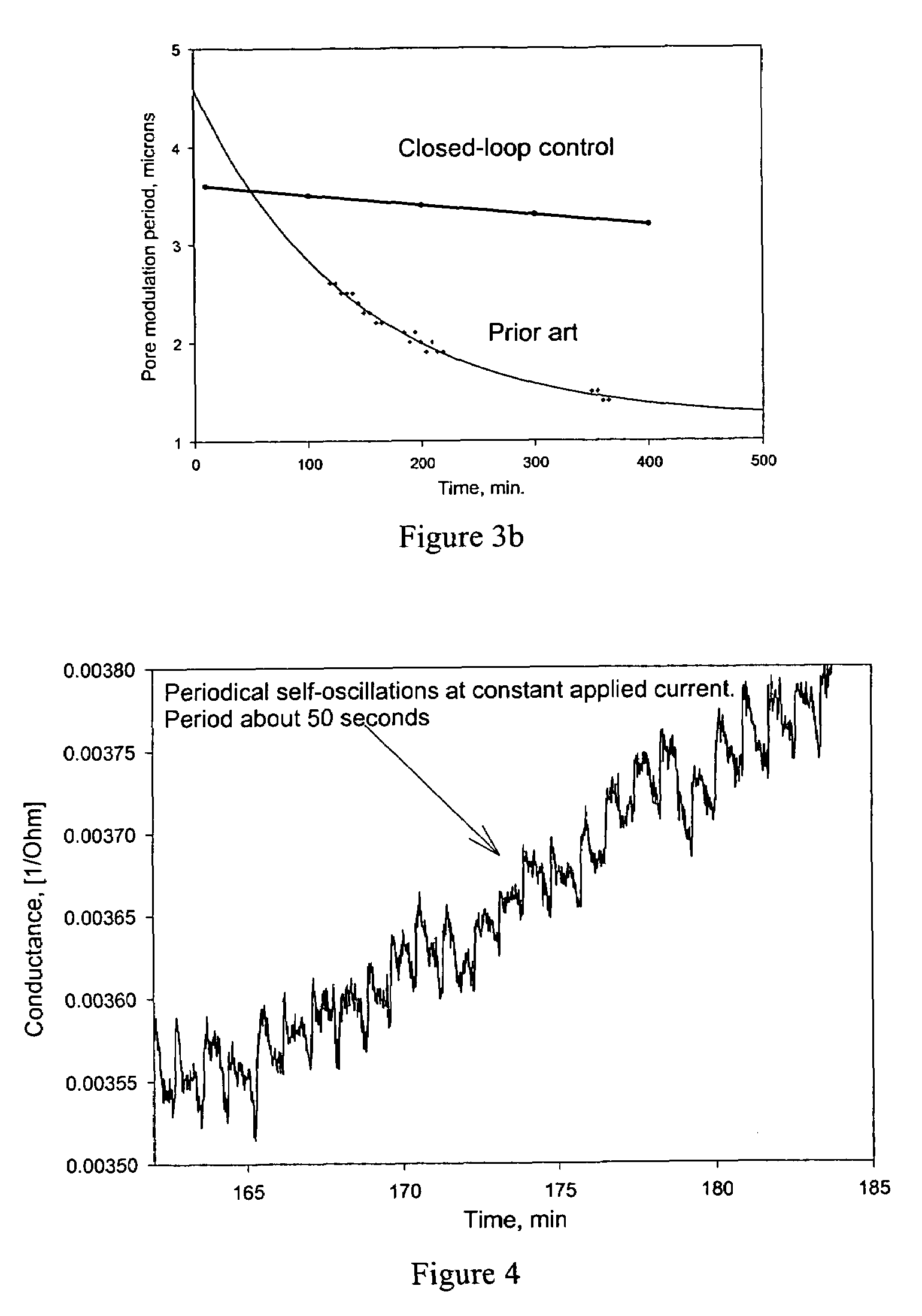
Semiconductor electrochemical etching processes employing closed loop control
InactiveUS20050199511A1Quality improvementElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPorosityClosed loop
Methods and apparatus for providing closed-loop control over an electrochemical etching process during porous semiconductor fabrication enhance the quality of the porous semiconductor materials, especially those contained structural variations (such as porosity or morphology variations) along the thickness of said porous semiconductors. Such enhancement of the control over the electrochemical etching process is highly desired for many applications of porous semiconductor materials.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Systems and methods for detecting structural variants
ActiveUS9953130B2Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsStructural variantComputational biology
Systems and method for identifying long deletions can obtain sequencing information for a plurality of amplicons in and around a potential region from a nucleic acid sample. The sequencing information can include a plurality of reads that can be mapped to a reference sequence. Using information, such as where reads map to a reference sequence and relative abundance of reads for the amplicons, structural variants can be identified and a determination can be made if the nucleic acid sample is homozygous or heterozygous for the structural variant.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Fiducial calibration method and system for assembling parts
InactiveUS7073239B2Reducing positioning and alignment errorMeasurement/indication equipmentsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesStructural variantManufacturing engineering
Fiducial calibration systems and methods for precisely and accurately manufacturing a part from a workpiece, inspecting or measuring a part, and / or assembling a plurality of manufactured parts including providing a workpiece, wherein the workpiece and the associated processes are subject to environmental and structural variations, and disposing a plurality of datums on a surface of or within the workpiece. The systems and methods also including calibrating the separation distance between each of the plurality of datums to workpiece distance units and disposing the workpiece in a machine, wherein the machine is subject to environmental and structural variations. The systems and methods further including calibrating a coordinate system of the machine to the workpiece distance units, manufacturing the part from the workpiece, inspecting or measuring the part, and / or assembling the plurality of manufactured parts utilizing the calibrated machine, and intermittently recalibrating the machine to the workpiece distance units.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Methods of detecting structural variations in genomic regions
PendingCN112349346ASmall Intragenic Structural VariationsHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsGeneticsHigh throughput sequence
The present disclosure relates to methods of detecting structural variations in genomic regions, including deletions, repetitions, inversions, and translocations, using high throughput sequencing data. The present disclosure also provides systems, devices, and computer-readable media for detecting structural variations in genomic regions.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BURNING ROCK DX CO LTD
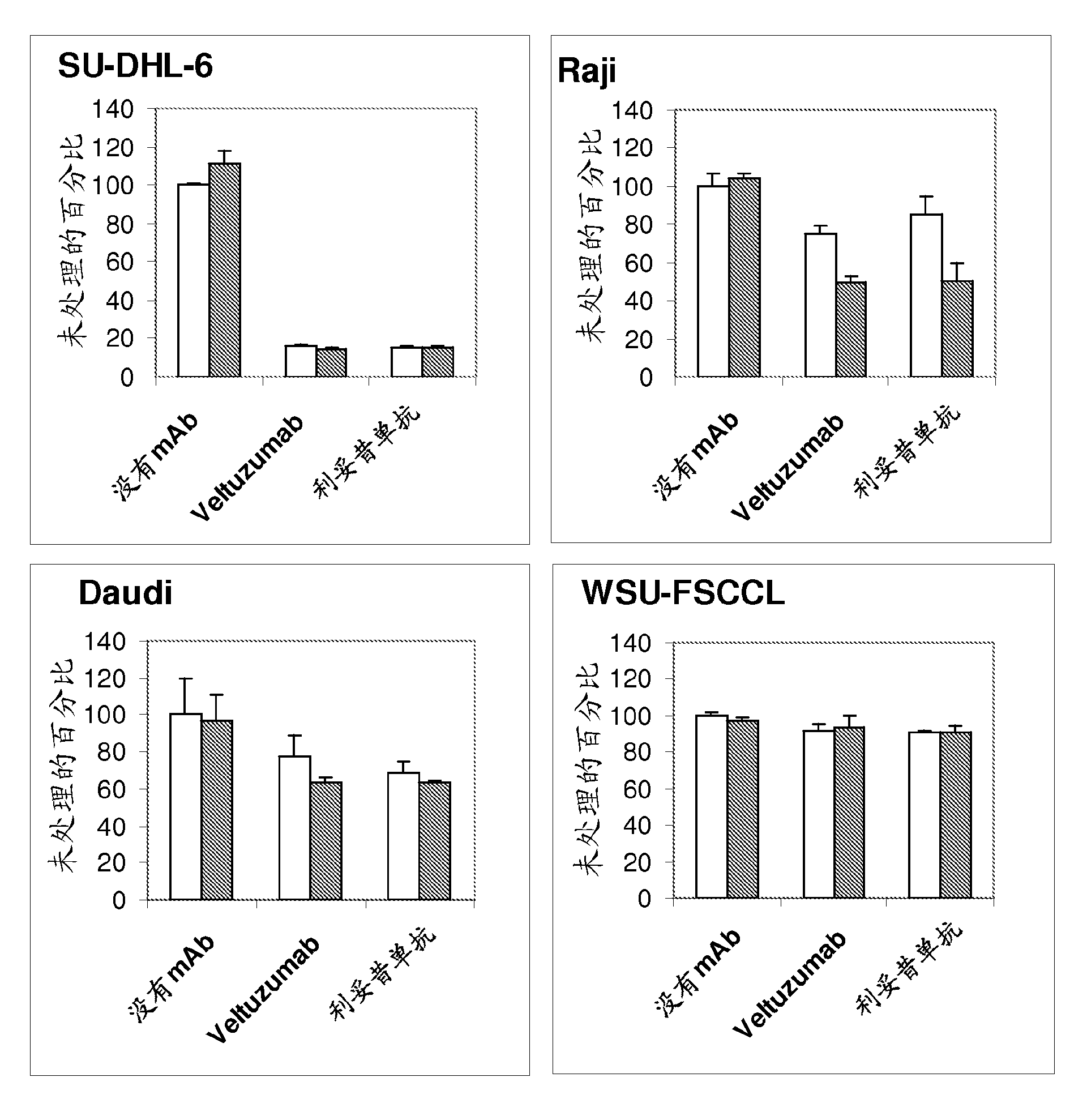
Structural variants of antibodies for improved therapeutic characteristics
The present invention provides substituted humanized, chimeric or human anti-CD20 antibodies or antigen binding fragments thereof and bispecific antibodies or fusion proteins comprising the substituted antibodies or antigen binding fragments thereof. The antibodies, fusion proteins or fragments are useful for treatment of B-cell disorders, such as B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases, as well as GVHD, organ transplant rejection, and hemolytic anemia and cryoglobulinemia. Amino acid substitutions, particularly substitution of an aspartate residue at Kabat position 101 of CDR3 VH (CDRH3), result in improved therapeutic properties, such as decreased dissociation rates, improved CDC activity, improved apoptosis, improved B-cell depletion and improved therapeutic efficacy at very low dosages. Veltuzumab, a humanized anti-CD20 antibody that incorporates such sequence variations, exhibits improved therapeutic efficacy compared to similar antibodies of different CDRH3 sequence, allowing therapeutic effect at dosages as low as 200 mg or less, more preferably 100 mg or less, more preferably 80 mg or less, more preferably 50 mg or less, most preferably 30 mg or less of naked antibody when administered i.v. or s.c.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
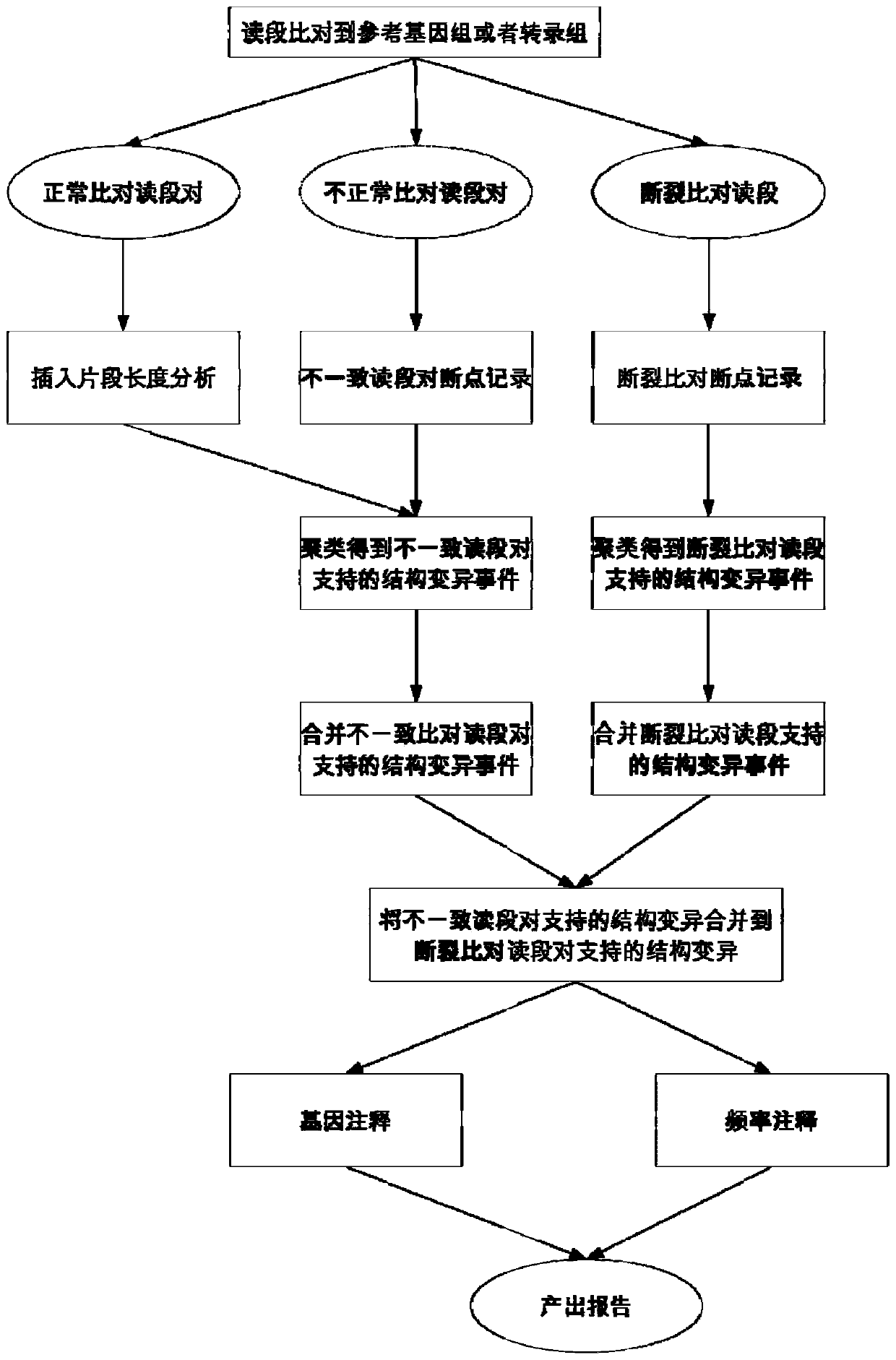
Structural variation detection method
The invention discloses a method for detecting structural variation. The method supports structural variation recognition of RNA and DNA at the same time, and is high in sensitivity, specificity and speed and small in resource consumption. The invention further provides a complete system or device established based on the method, a computer readable storage medium and equipment.
Owner:BERRY ONCOLOGY CO LTD
Determination of top-plate structural variation and separating layer
InactiveCN1818235AEasy to operateSmall amount of test engineeringMining devicesFoundation testingStructural variantPhysics
This is a method to detect strata shifting for bord. Two holes of the same diameter and height are drilled along any fracture surface of the bord, one is for detecting strata shifting and the other is for viewing of structure transform of strata to figure out the ratio of structure transform to total shifting.
Owner:TIANDI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
PendingUS20170067097A1Efficient productionCreate efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosomal regionHaplotype
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid-nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid-protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Stochastic molecular binding simulation
InactiveUS20100138205A1Molecular designAnalogue computers for chemical processesMolecular bindingBiomolecular complex
The invention provides methods of dynamically simulating molecular interactions between a target molecule and a plurality of ligand molecules. The ligand molecules may be presented in the model as a homogeneous set of identical ligands or as a heterogeneous set of different ligands, such as, for example, a set of structural variants of a ligand molecule. Typically, the ligand molecule will be a small organic compound, such as a drug or other small molecule, and the ligand will be a protein or a protein domain, a nucleic acid (i.e., DNA, RNA), or a biomolecular complex of proteins and / or nucleic acid molecules. Unlike all known molecular dynamics simulation methods, the invention provides ligand molecules to the simulation's interaction environment(s) in excess relative to the target molecule.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY +1
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid - nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid - protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
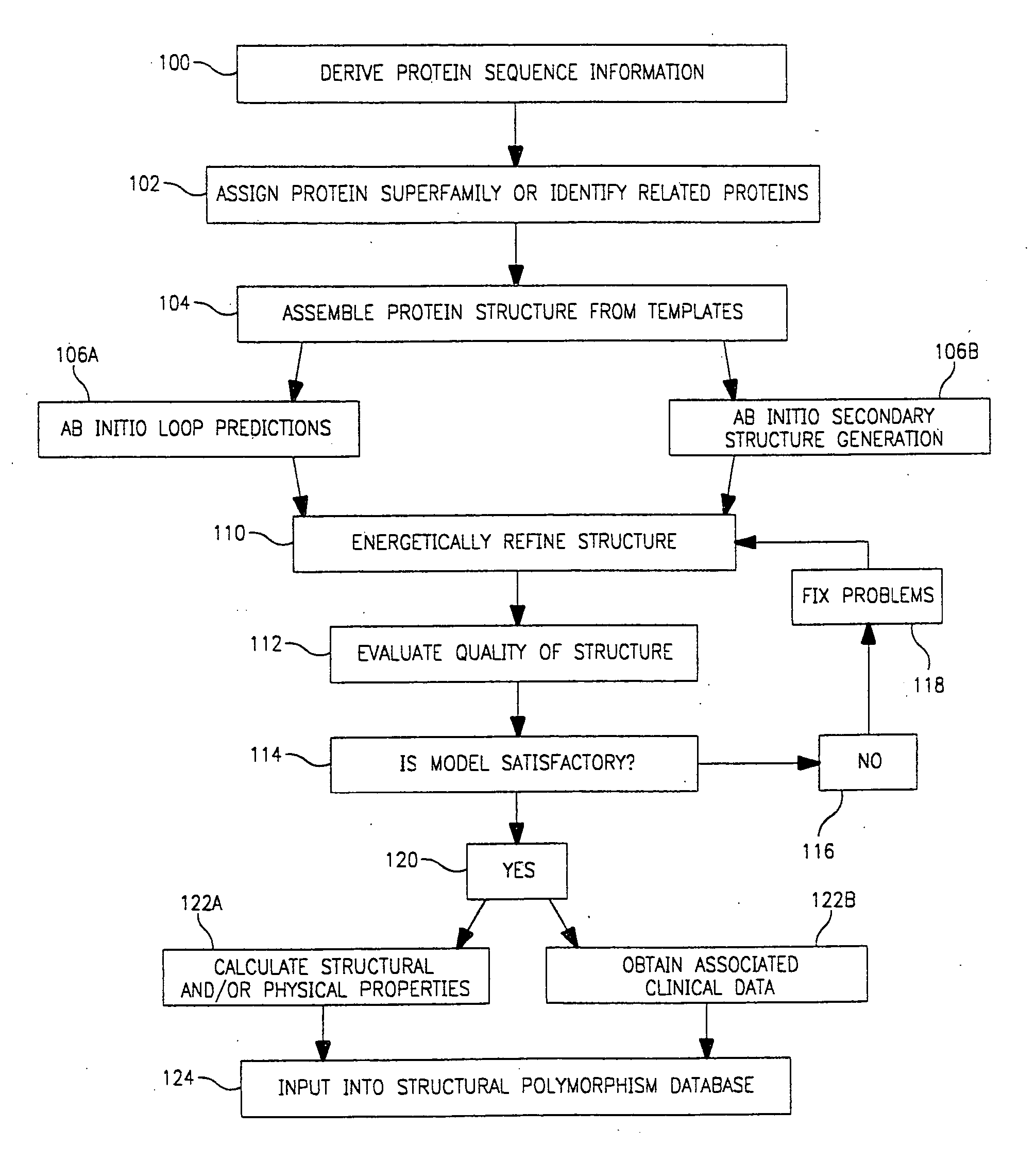
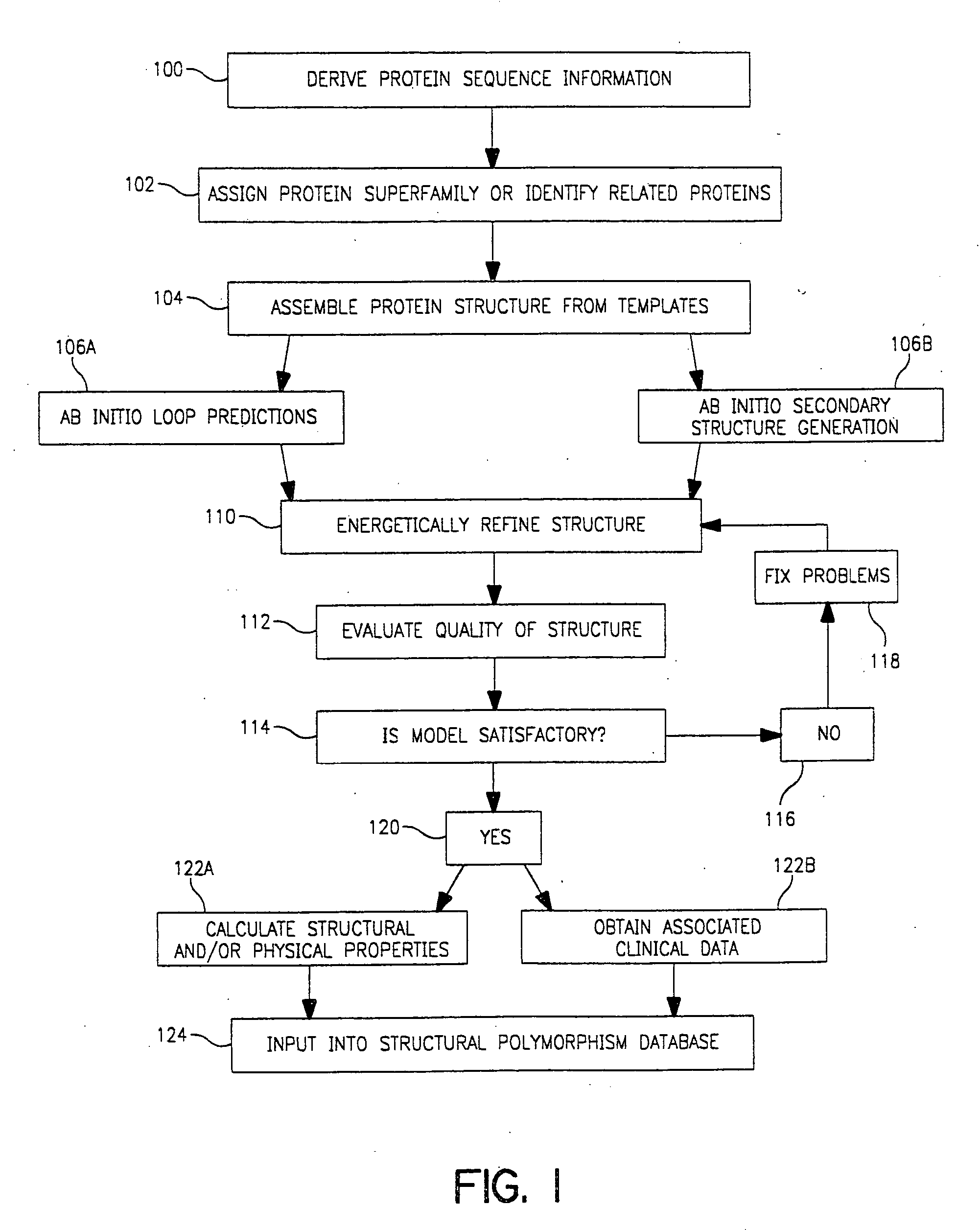
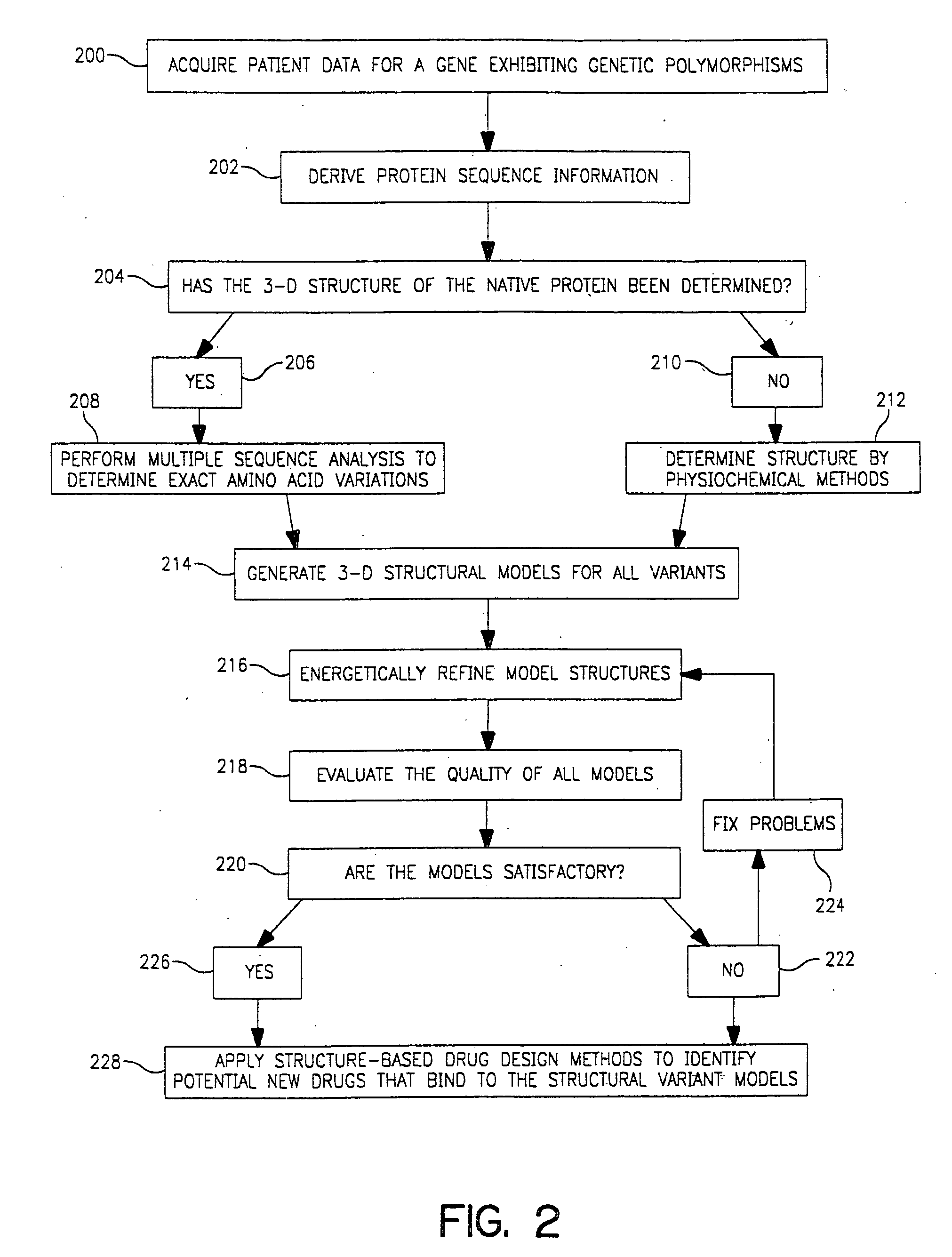
Use of computationally derived protein structures of genetic polymorphisms in pharmacogenomics for drug design and clinical applications
InactiveUS20060217894A1Expand the populationReduce adverse side effectsMolecular designProteomicsGenomicsProtein structure
Provided herein are computer-based methods for generating and using three-dimensional (3-D) structural models of target molecules and databases containing the models. The targets can be protein structural variants derived from genes containing polymorphisms. The models are generated using molecular modeling techniques and are used in structure-based drug design studies for identifying drugs that bind to particular structural variants in structure-based drug design studies, for designing allele-specific drugs and population-specific drugs and for predicting clinical responses in patients. Computer-based methods for predicting drug resistance or sensitivity via computational phenotyping are also provided. Databases containing protein structural variant models are also provided.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC +2
Model-independent genome structure variation detection system and method
ActiveCN111583996ALow detection sensitivityReduce error rateBiostatisticsProteomicsData miningStructural variant
The invention provides a model-independent genome structure variation detection system and method, wherein a model-independent structure variation detection theory is used as a core, and structure variation detection without depending on any variation model is achieved through a variation signal extraction module, a frequent maximum subgraph mining module and a classification module. According tothe system, a frequent variation pattern mining module is used for capturing the characteristics of structural variation left on a genome, and judging a potential structural variation region only by mining abnormal points in a large amount of normal data; and according to different genome disturbance modes of different variation types, different arrangement sequences of variation signals are further caused, and the different variation types are classified on the basis of the different arrangement sequences in combination with a deep learning model with a memory function. According to the invention, the system does not depend on any variation model, so that the variation detection sensitivity and error rate are greatly reduced; and the system is suitable for detection of complex variation types, and an additional structural variation model does not need to be established.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Methods and devices for single-molecule whole genome analysis
Provided are methods and devices for single-molecule genomic analysis. In one embodiment, the methods entail processing a double-stranded nucleic acid and characterizing said nucleic acid. These methods are useful in, e.g. determining structural variations and copy number variations between individuals.
Owner:BIONANO GENOMICS
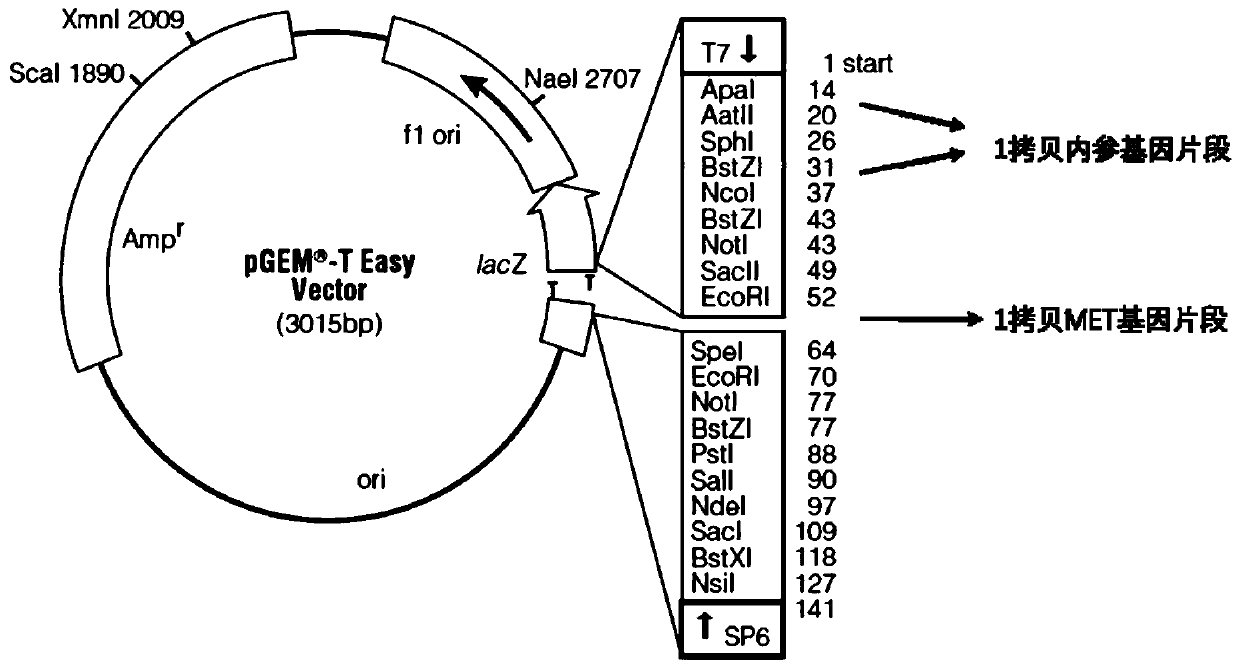
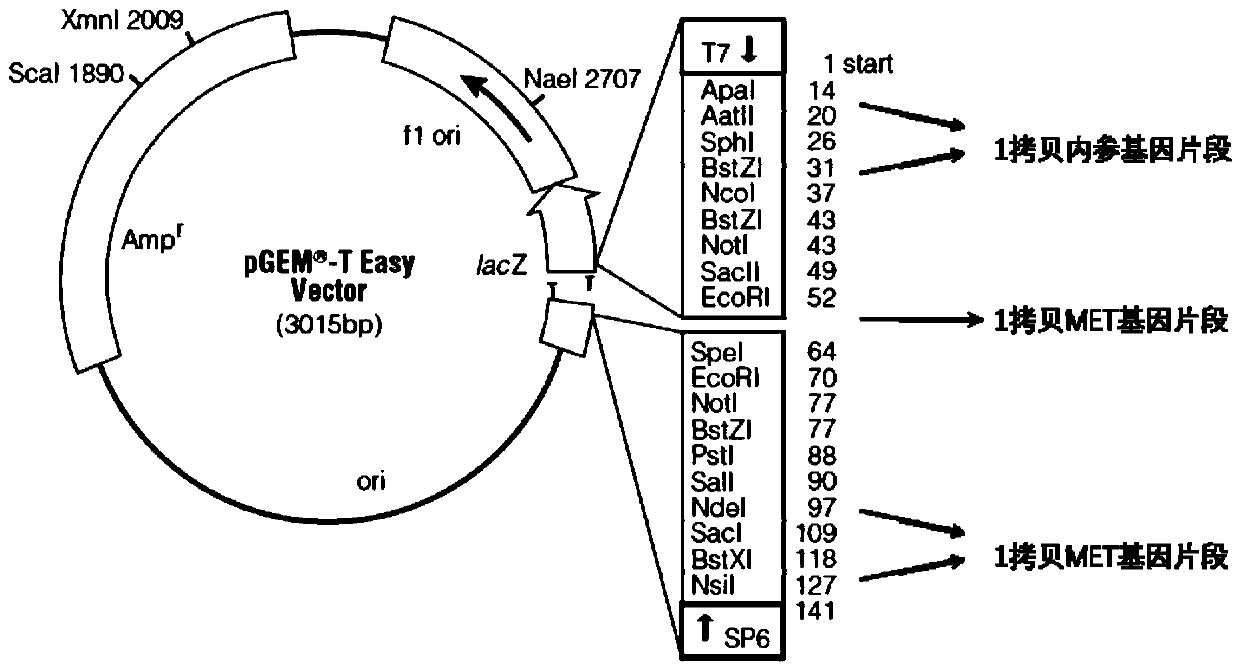
Primer, system and kit for MET gene amplification detection
ActiveCN110863051AImproved prognosisSolve the difficult problem of not easy to detect gene copy numberMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroorganismPlant microbe
The invention discloses a primer group for MET gene amplification detection, a kit and a related medication guidance system, and is characterized by constructing calibration plasmids and standard plasmids for correcting errors of primers and an amplification system, and the accuracy of the kit is improved. A 2-Ct method is adopted, is suitable for gene copy number detection of diploid animals, andis also suitable for determining the copy number of a certain gene of polyploid animals, plants, microorganisms and the like, so that the problem that PCR methods are not easy to detect the gene copynumber is solved. The method is simple and easy to operate, a result is easy to interpret, and a very beneficial thought is provided for other application of gene copy number detection (such as geneamplification and chromosome structural variation).
Owner:广州迈景基因医学科技有限公司
Semiconductor electrochemical etching processes employing closed loop control
InactiveUS7560018B2Electrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPorosityClosed loop
Methods and apparatus for providing closed-loop control over an electrochemical etching process during porous semiconductor fabrication enhance the quality of the porous semiconductor materials, especially those contained structural variations (such as porosity or morphology variations) along the thickness of said porous semiconductors. Such enhancement of the control over the electrochemical etching process is highly desired for many applications of porous semiconductor materials.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Method for detecting CAH related true and false genes
ActiveCN112442530AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPseudogeneStructural variant
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a method for detecting CAH related true and false genes. Specifically, the invention discloses the detection methodfor determining the mutation condition of the CAH related genes. The CAH related genes comprise a CYP21A2 gene and a CYP11B1 gene. The method comprises the following steps of S1, extracting DNA in asample and carrying out PCR amplification by using a primer group; S2, detecting an amplification product by using a third-generation sequencing platform; and S3, analyzing the sequencing result to obtain the mutation condition of the CAH related genes. According to the method, the true and false genes are expanded together by designing the primer group, a mutation type can be detected by long-fragment library building sequencing, known CYP21A2 and CYP11B1 gene pathogenic mutations can be detected at the same time, the sensitivity is high, only 1-50ng of DNA is required to be contained in thesample, the operation is convenient, the deletion of long fragments can be detected, the true and false genes can be distinguished, and meanwhile, the unknown chromosome structural variation can be detected.
Owner:BEIJING GRANDOMICS BIOTECH
Systems and methods for karyotyping by sequencing
Owner:PHASE GENOMICS INC
A computer-implemented and reference-free method for identifying variants in nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20200005898A1Type accurateUnprecedented performanceData visualisationProteomicsNucleotideVariome
There is provided a computer-implemented method for identifying of nucleic acid variants between two cells, such as a normal cell vs. a pathological cell of a patient, or a cell at two different stages of development. The method is alignment-free, as it does not depend on the use of a reference genome, and is based on the generation and comparison of polymorphic k-mers derived from the nucleotide sequence reads of both biological states. The invention accurately identifies all sorts of genetic variants, ranging from single nucleotide substitutions (SNVs) to large structural variants with great sensitivity and specificity. As a major novelty, it also identifies non-human insertions, such as those derived from retroviruses. Altogether, this invention allows the integration with specific hardware architectures in order to speed up the executions to an unprecedented level.
Owner:BARCELONA SUPERCOMPUTING CENT CENT NAT DE SUPERCOMPUTACION +2
Whole genome association analysis method based on comparison of multiple genomes and next-generation sequencing data
ActiveCN113628685AImplementation of association analysisEasy to understandProteomicsGenomicsGene PositionWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a whole genome association analysis method based on comparison of multiple genomes and next-generation sequencing data, which comprises the following steps of: 1, comparing a reference genome with a de novo assembly genome file by using comparison software; and updating the annotation gene positions or structures in the reference genomes; 3, if a plurality of de novo assembly genomes exist, sequentially iteratively updating the reference genomes; 4, comparing the next-generation sequencing data of the samples to the updated reference genome by using comparison software; 5, collecting demarcation point position information of all structural variations of all the samples into a set, constructing a population genotype; and 6, performing functional gene candidate according to the association site and the updated reference genome annotation file. According to the method, the whole genome association analysis is performed by using the structure variation genotype data.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
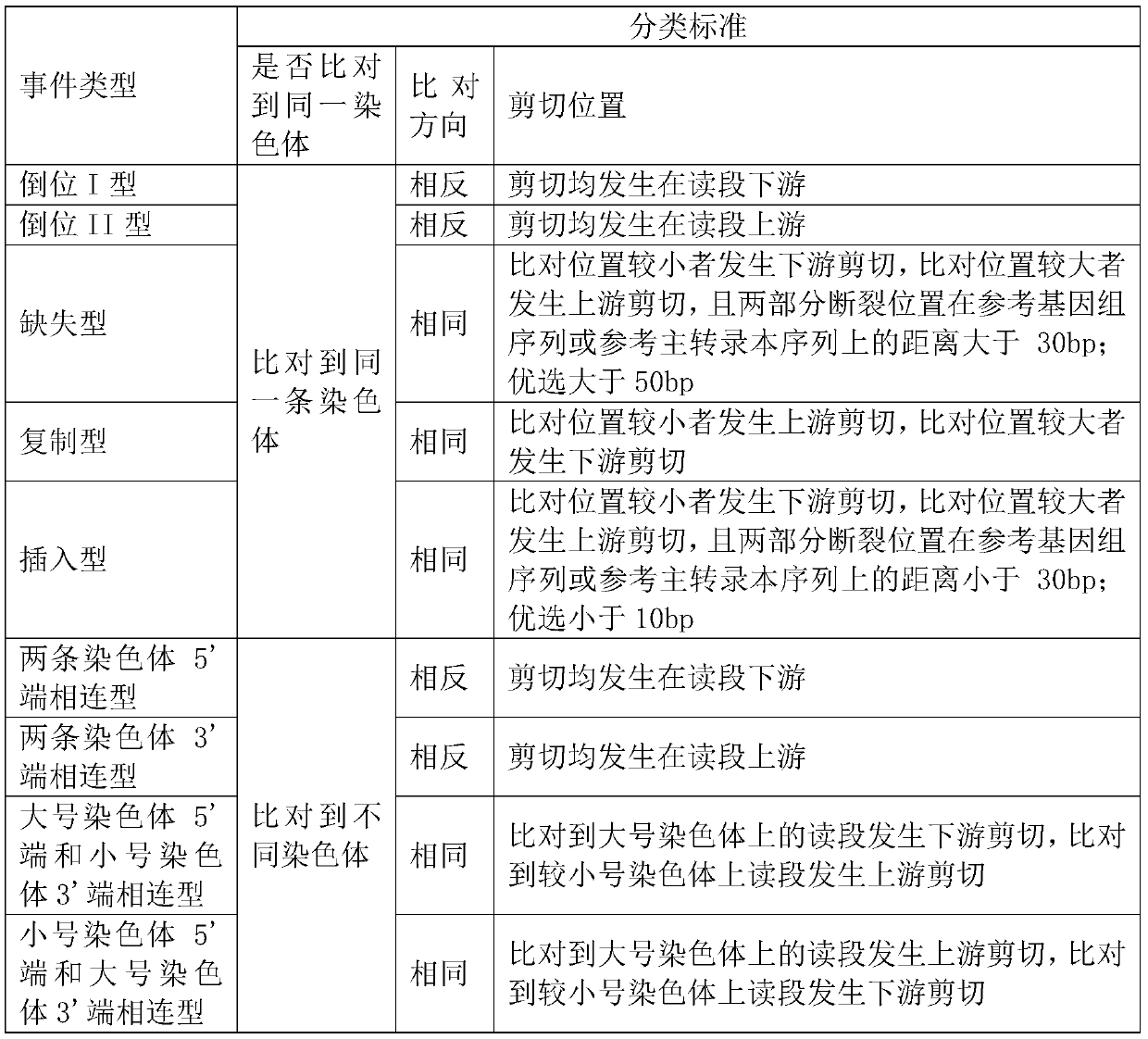
A Breakpoint-Centric Approach for Chromosomal Structural Variation Identification
The invention relates to a method for identifying chromosome structure variation centered on breakpoints. In particular, the present invention relates to a computer-implementable breakpoint-centric method for identifying structural variations in chromosomes. The invention also relates to a computer system or apparatus for implementing the method, and a computer-readable medium storing a computer program capable of implementing the method.
Owner:上海思路迪医学检验所有限公司
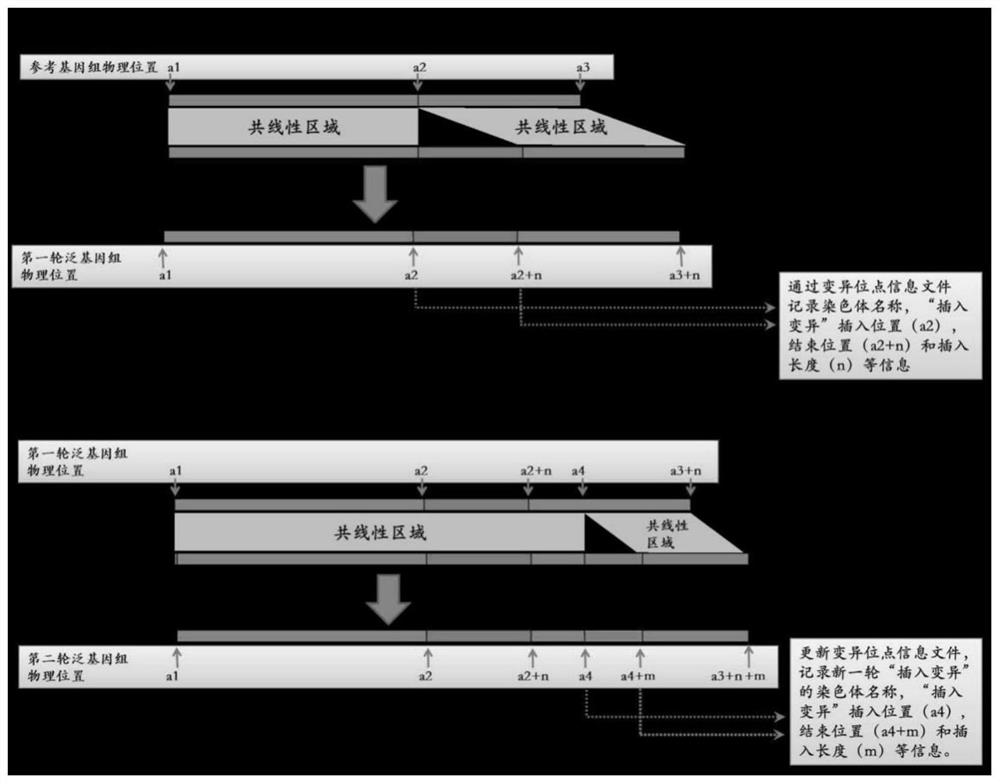
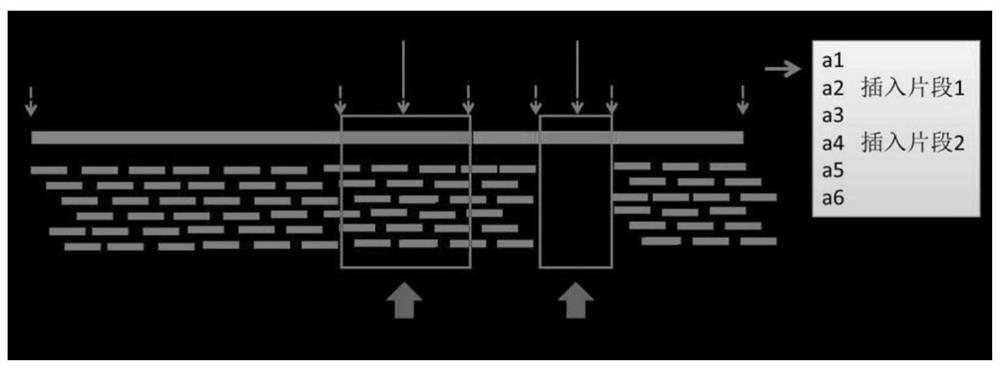
Generic genome construction method and corresponding structural variation mining method thereof
ActiveCN113571131AQuality improvementAchieve large-scale applicationBiostatisticsProteomicsTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genome data analysis, and particularly relates to a generic genome construction method and a corresponding structural variation mining method thereof, structural variation obtained through genome comparison is put back to a linear genome, meanwhile, a structural variation site information file is added, and an efficient analysis generic genome which is linearized in the form and considers various structure variation forms is constructed. The generic genome not only can capture more brand-new structural variations which are not found by a reference genome, but also better displays the captured structural variations by combining a linearization method with a variation site information file, so that the constructed generic genome is easier to understand and analyze, and is more beneficial to subsequent application; according to the method and the process for analyzing the genome structure variation based on the generic genome and the second-generation sequencing data, a complete program code is compiled, and the efficient and accurate mining of the structure variation based on the relatively low-cost second-generation sequencing data is realized.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Sequencing joint, construction method, nano-hole library building kit and application
PendingCN113736778AAccurate identificationNo need for purificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBiotechnologyChemical reaction
The invention discloses a sequencing joint, a construction method, a nano-hole library building kit and application. The sequencing joint comprises a joint top chain and a target connector. The joint top chain comprises a nano-hole guide chain and a first linking group which are arranged in a preset sequencing direction. The nano-hole guide chain is used for guiding a to-be-detected sequence to pass through a nano-hole sequencing channel. The target connector comprises a second linking group which is subjected to a click chemical reaction with the first linking group. The second linking group is used for being connected to the to-be-detected sequence. The sequencing joint can avoid the use of ligase, so that a purification treatment step before on-machine sequencing is omitted, the sequencing efficiency is improved, and template self-connection, artificial introduction of chimeric sequences and influence on structural variation analysis caused by the use of ligase can also be avoided.
Owner:QITAN TECH LTD CHENGDU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com