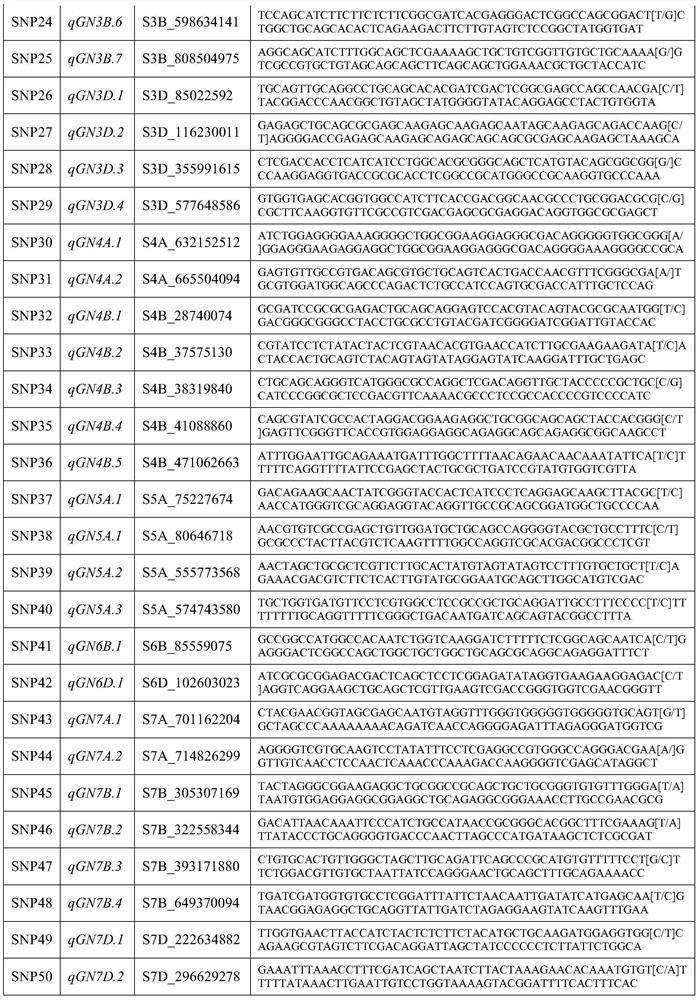
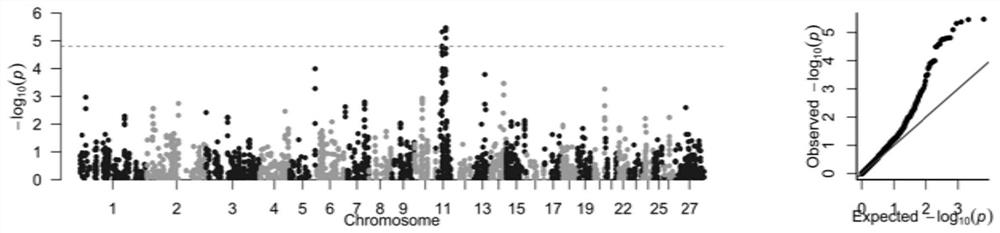
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Whole Genome Association Analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Construction method of pulmonary thromboembolism risk prediction model based on single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP locus combination and application
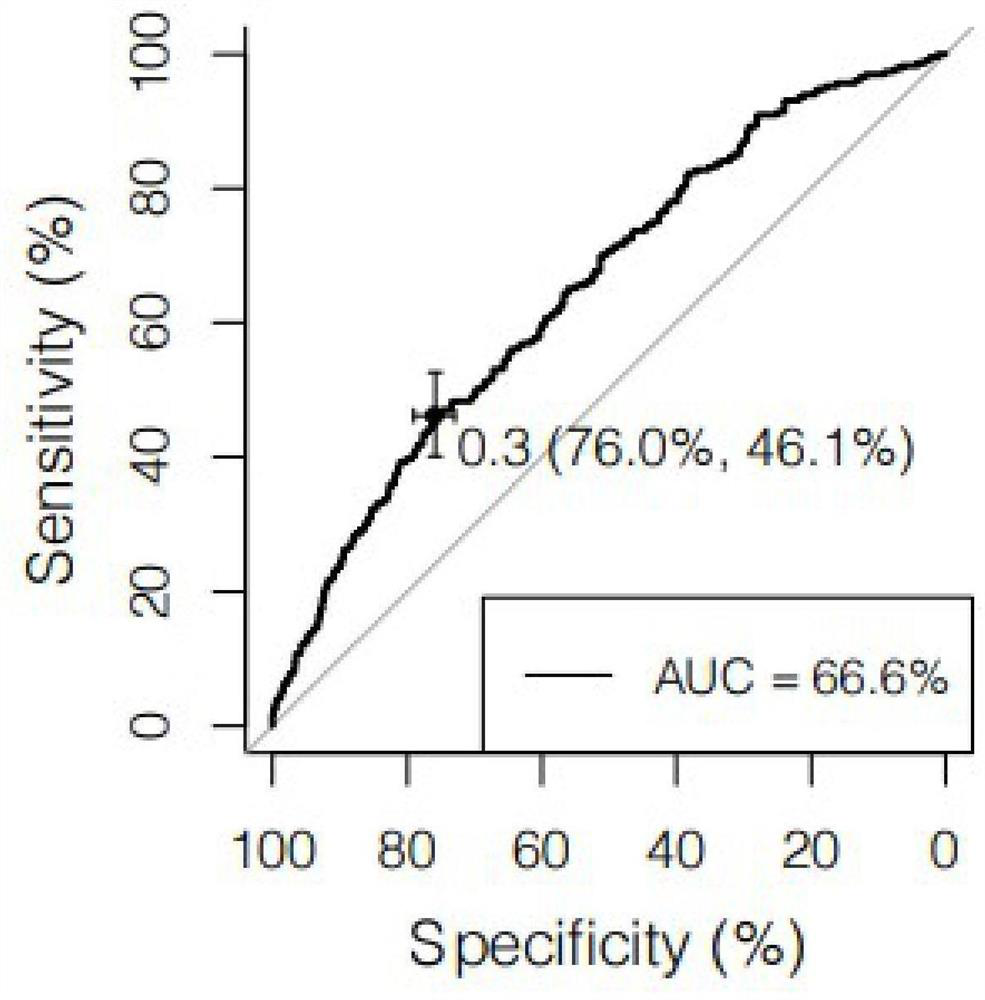
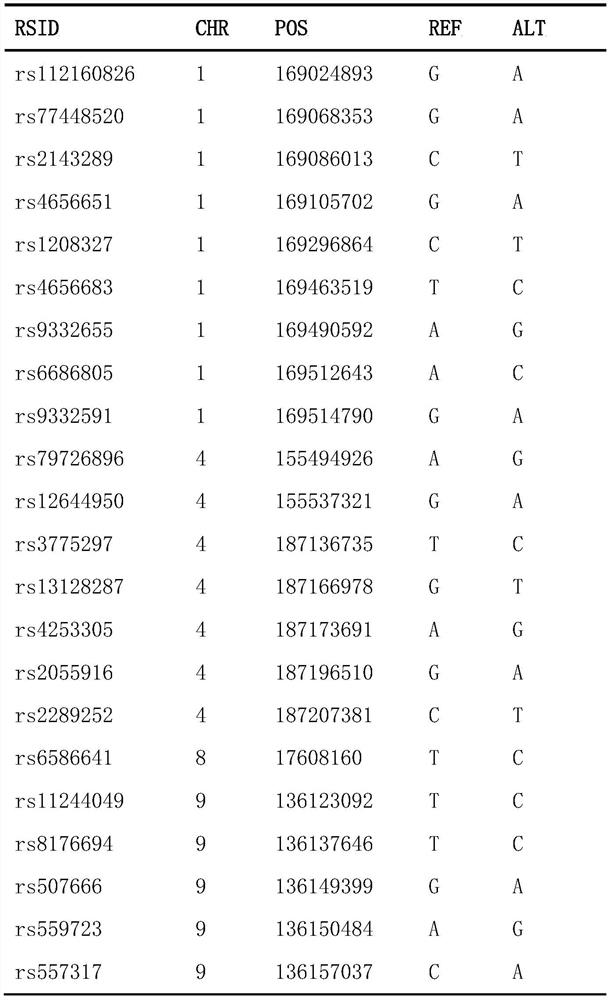
ActiveCN112553327AReduce incidenceReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWhole Genome Association AnalysisNucleotide
The invention discloses a construction method of a pulmonary thromboembolism risk prediction model based on single nucleotide polymorphism, an SNP locus combination and application. The construction method of the prediction model comprises the following specific steps of S1, carrying out sample collection and gene detection; S2, carrying out data quality control and whole genome association analysis (GWAS); S3, carrying out meta analysis by combining the genome data of an external population; S4, screening an SNP locus combination with a prediction value; and S5, building a regression model, and carrying out training and testing. According to the prediction model, 48 SNP site combinations are obtained, at least one SNP site combination can be applied to pulmonary thromboembolism risk assessment or screening products, pulmonary thromboembolism risk prediction of Asian people, especially Chinese people can be achieved, and the detection method is simple, convenient and easy to implementand convenient to use clinically.
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL +1
Whole genome association analysis method, system and electronic equipment
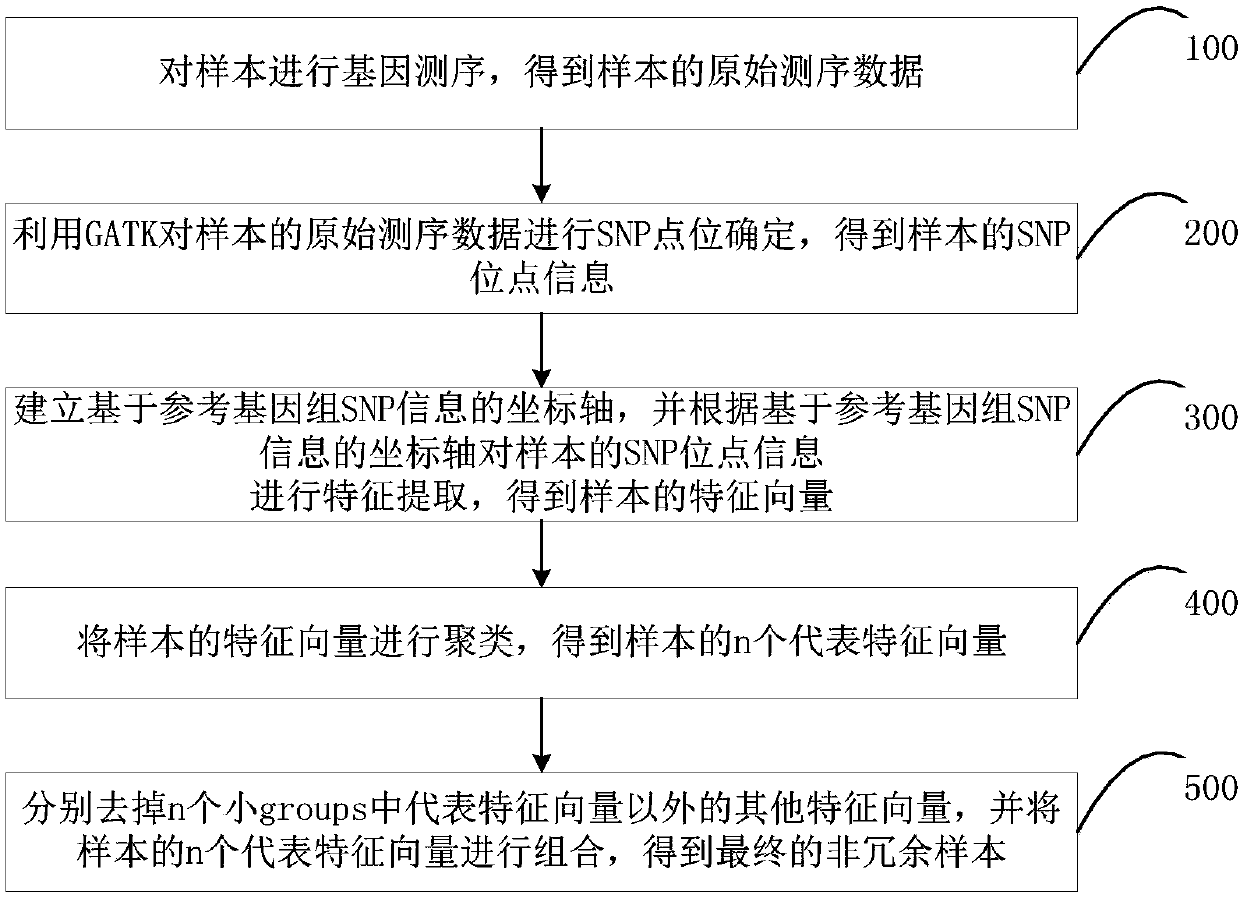
PendingCN110211631ASmall amount of calculationAchieve understandingBiostatisticsProteomicsFeature vectorWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention belongs to the field of gene data processing technology, and particularly relates to a whole genome association analysis method, a system and electronic equipment. The whole genome association analysis method comprises the steps of a, performing SNP site determining on original sequencing data of a sample, and obtaining SNP site information of the sample; b, establishing a coordinateaxis based on reference genome SNP information, and performing characteristic extraction on the SNP site information of the sample according to the coordinate axis based on the reference genome SNP information, and obtaining a characteristic vector of the sample; and c, clustering the characteristic vectors of the sample, obtaining the representative vectors of the sample, and combining the representative characteristic vectors for obtaining a non-redundancy sample. According to the method, through clustering the original data, characteristic expression of the sample is performed, and important characteristics are found, thereby reducing data computing amount; according to the similarity between the samples, the samples with high similarity are combined, and the rest samples are removed,thereby greatly reducing a memory requirement and improving efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Screening method and application of SNP molecular marker associated with Nandan Yao egg shell color
ActiveCN111705139AImprove color uniformityEasy to filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a screening method of an SNP molecular marker associated with Nandan Yao egg shell color. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1) finding out genes related to egg quality from known literatures, designing primers, taking Nandan Yao chicken, collecting blood, extracting genomic DNA, and performing sequencing in a mixed pool; (2) taking Nandan Yao hens as testchickens, measuring eggshell color and shape indexes of eggs from 24 weeks old and to 60 weeks old; (3) collecting blood of the 60-week-old test chicken, extracting genome DNA, and performing PCR sequencing on detected SNP sites; and (4) sorting sequencing data and eggshell color data, screening out candidate SNP loci significantly associated with eggshell colors, and providing an SNP molecular marker theoretical basis for eggshell color breeding. The method can be applied to rapid and simple cultivation for improving the eggshell color of Nandan Yao chicken eggs, simplifies whole genome association analysis, directly performs SNP marker screening on trait-related genes, and is suitable for breeding of quantitative traits with high heredity.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
SNP locus related to birth weight of sheep, application, molecular marker and primer
ActiveCN111485026AImprove reliabilityShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWhole Genome Association AnalysisPhysiology
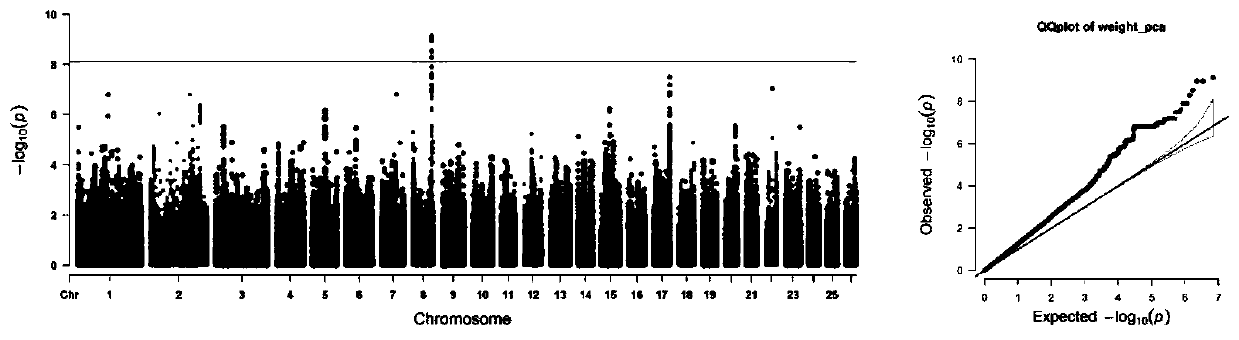
The invention relates to an SNP locus related to birth weight of sheep. The locus is positioned at the 8th chromosome and the 81799821st chromosome of a sheep genome, the original basic group is G, and the mutation form is A. According to the method, a simplified genome sequencing means and sheep birth weight information are utilized, and the marker related to the sheep birth weight is positionedby combining whole genome association analysis (GWAS), so that the method has important guiding significance for increasing the birth weight of sheep and improving the production performance of sheepflocks, and provides a scientific basis for sustainable development of the sheep breeding industry.
Owner:天津奥群牧业有限公司
Molecular marker related to cow perinatal period metabolic disease resistance and application
ActiveCN110106250AStrong disease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceWhole Genome Association Analysis
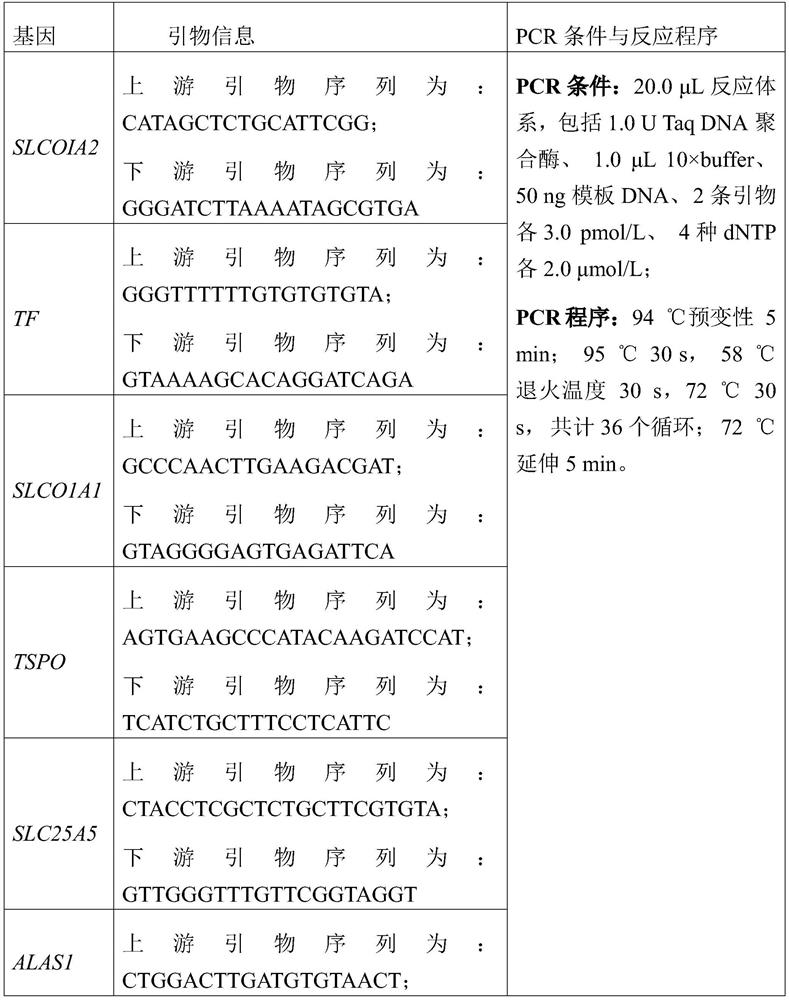
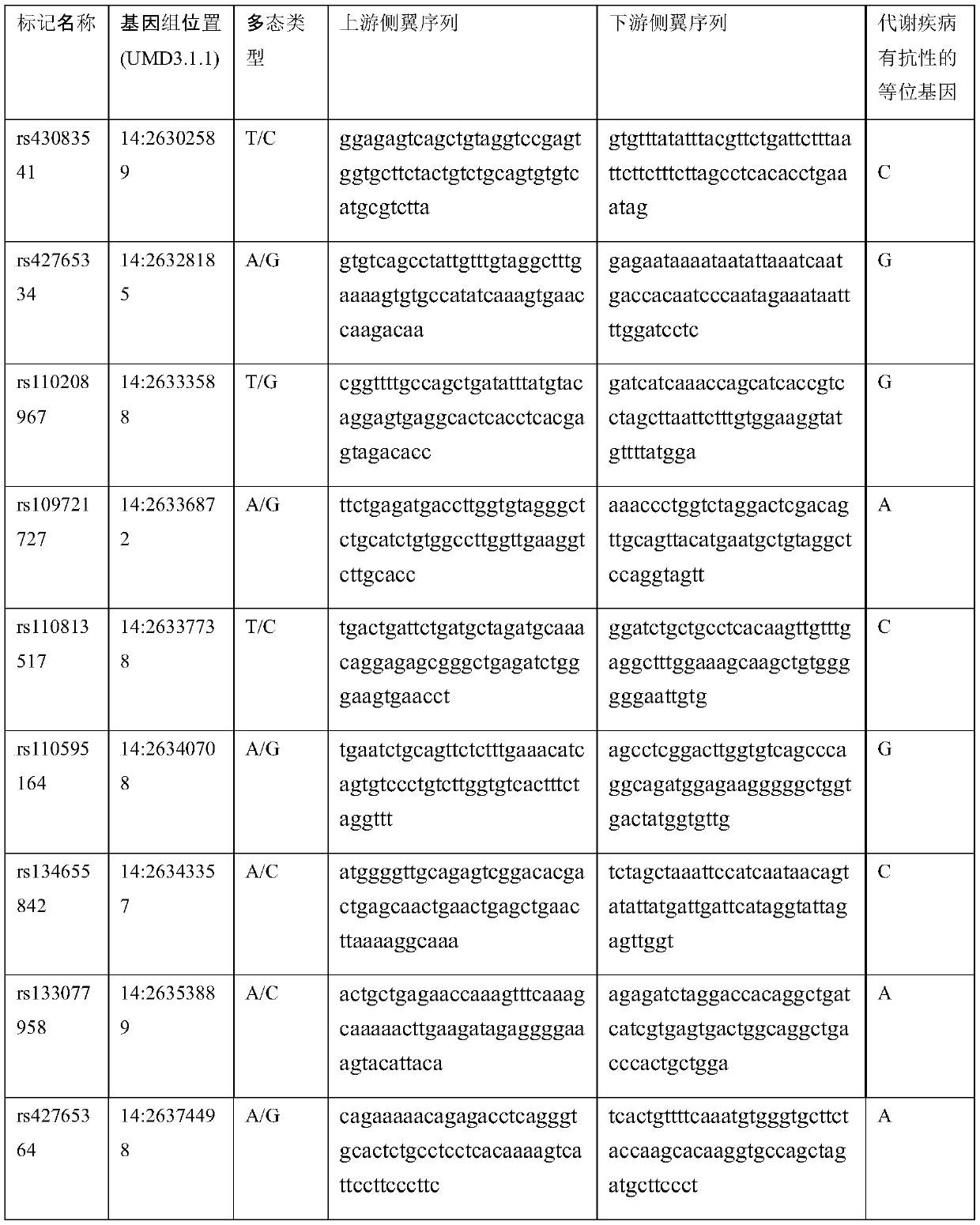
The invention provides a molecular marker related to cow perinatal period metabolic disease resistance and application. The molecular marker is obtained on the basis of cow whole-genome association analysis development, 10 SNP molecular markers are involved, and upstream and downstream flanking sequences of SNP loci are shown in SEQ ID NO.1-2, SEQ ID NO.3-4,..., and SEQ ID NO.19-20. The molecularmarker can be used for identifying cow metabolism disease resistance genetically, cows with the poor metabolism resistance are eliminated, the cows with the high metabolism disease resistance are cultured, and the effective method is supplied to marker auxiliary selection for cow perinatal period energy metabolism disease genetic resistance.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Medicament reutilization method based on omics data
The invention discloses a novel method for medicament reutilization, and particularly relates to a method for integrating data analysis results of human diabetes-associated whole-genome association analysis, proteomics and metabonomics, screening human diabetes-associated risk proteins, exploring information of marking medicaments or clinical experiment medicaments working on the human diabetes-associated risk proteins by combining a medicament development database, and integrating pathogenesis information of human diabetes through a public database. According to the method, 58 marking medicaments or clinical experiment medicaments aiming at other diseases are excavated, and a novel purpose for treating the human diabetes is achieved.
Owner:奚正蕊 +1
Methods of diagnosing alzheimer's disease and markers identified by set association
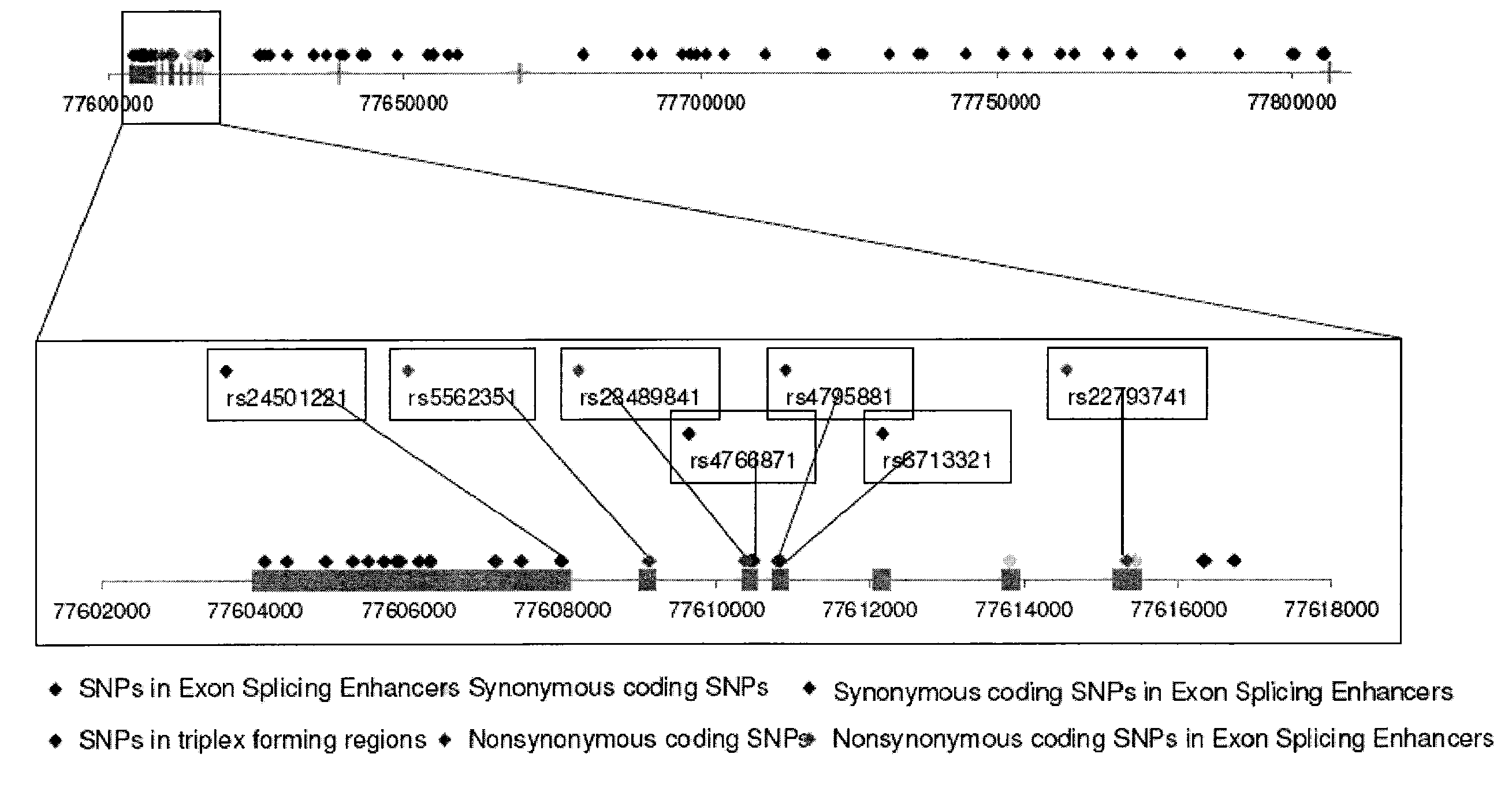
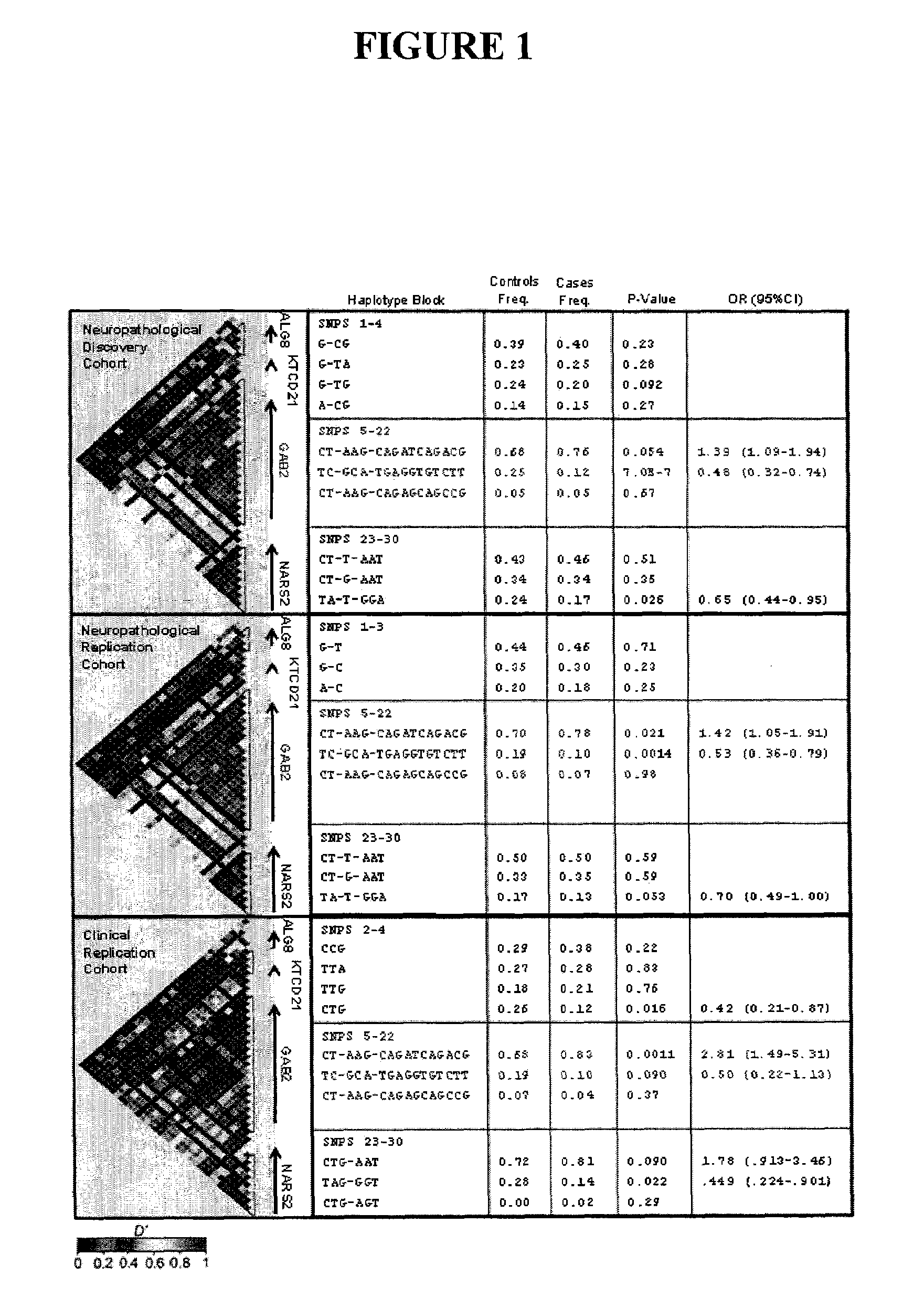
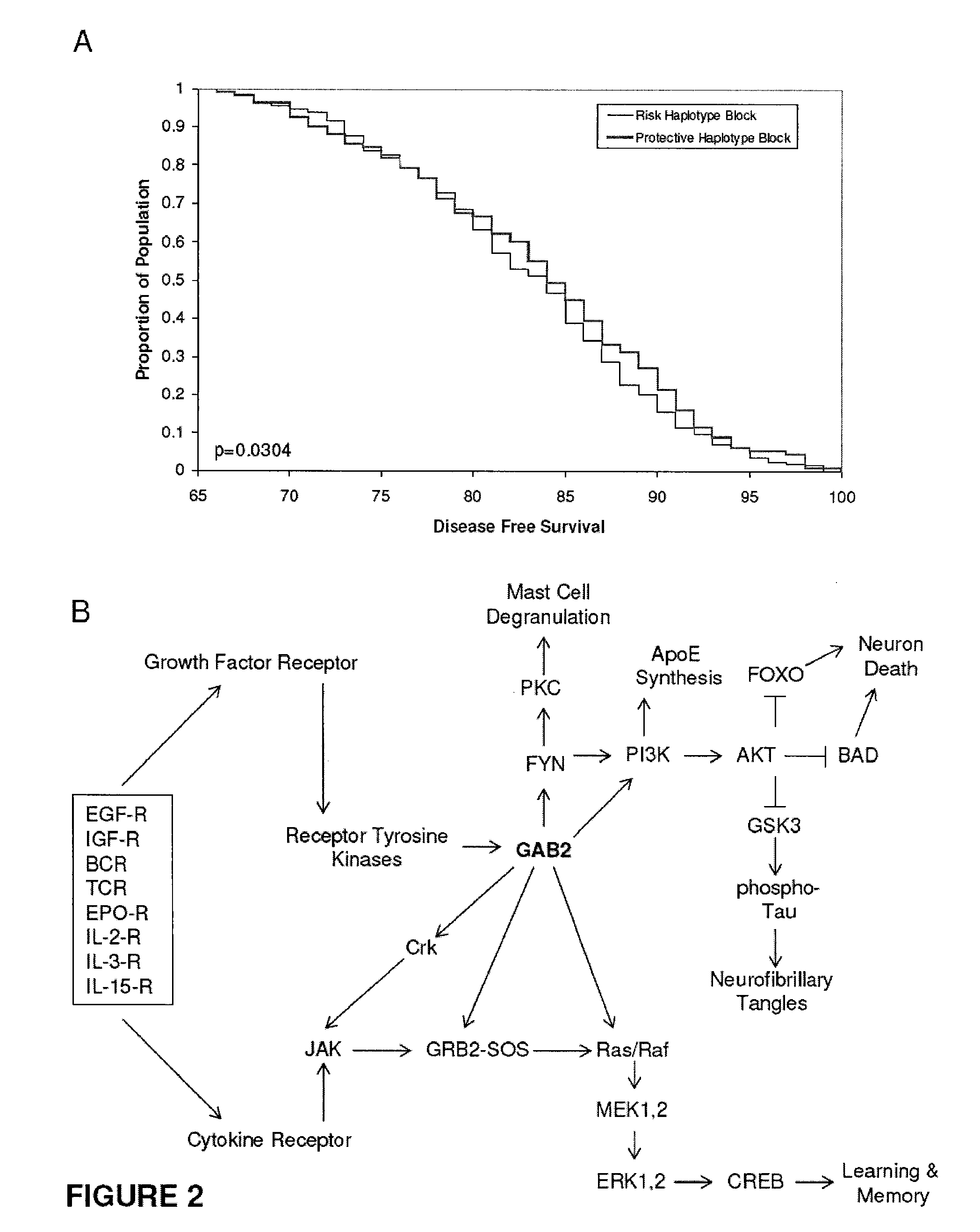
InactiveUS20090260092A1Reduce riskReduce the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderWhole Genome Association AnalysisLate onset
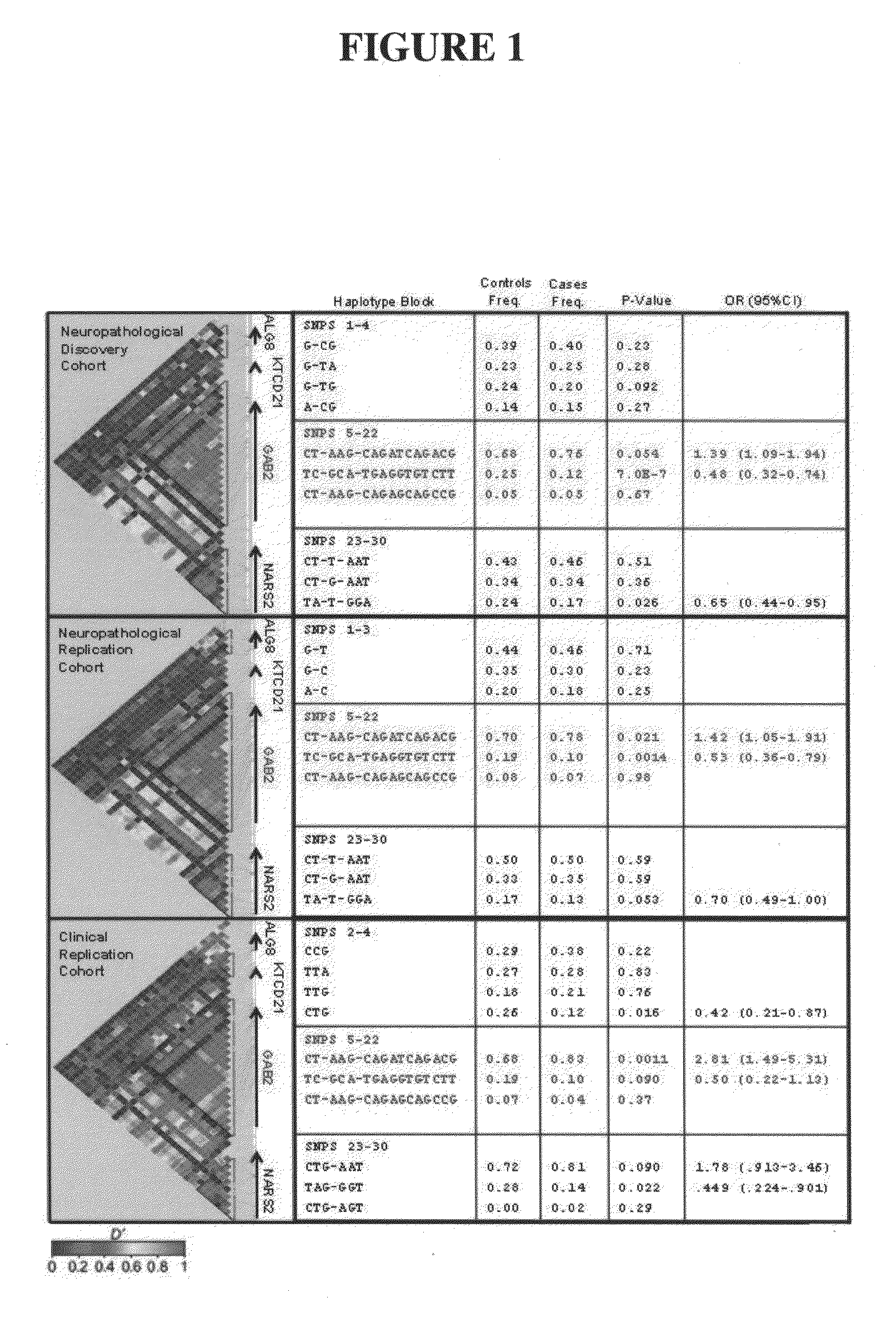
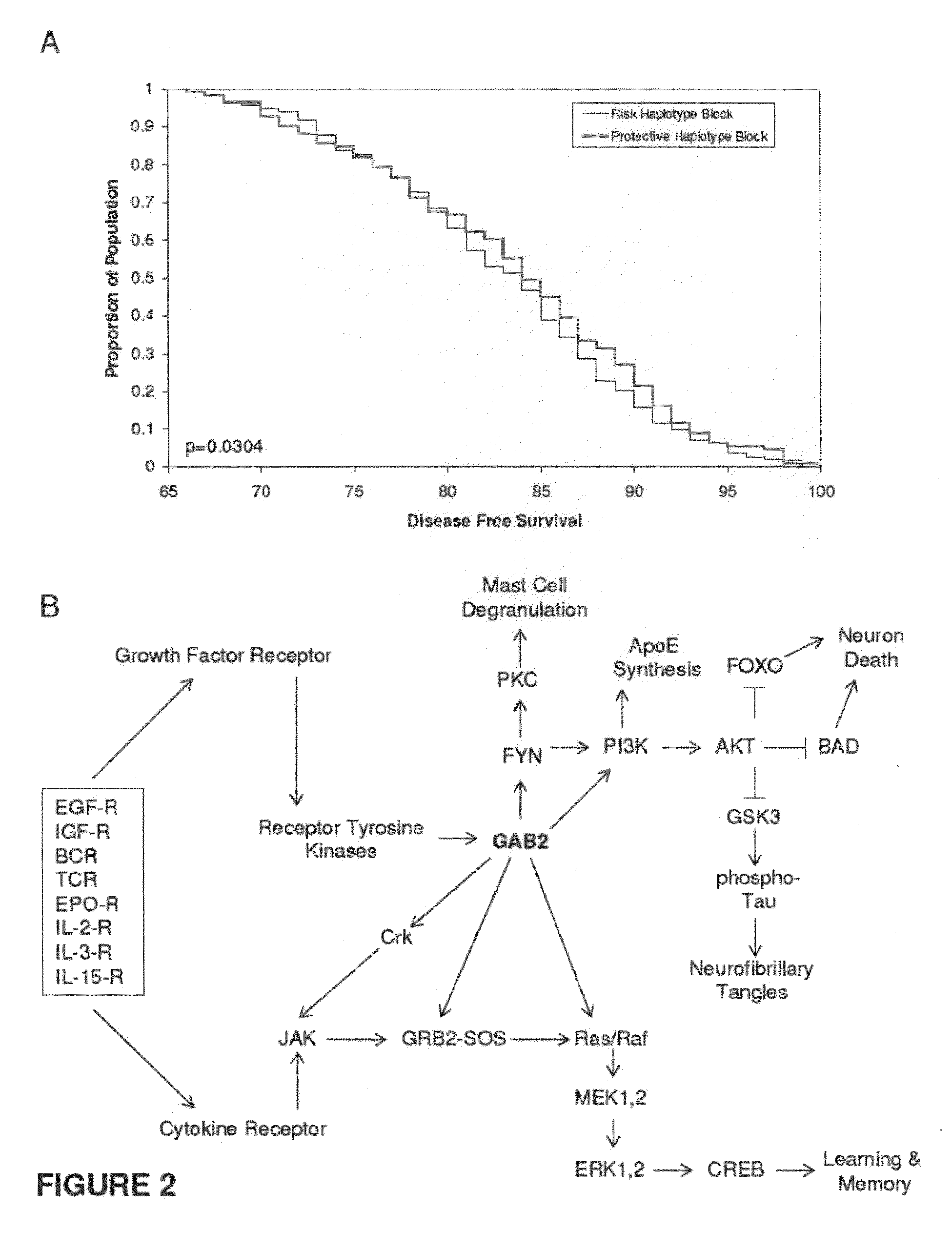
The present disclosure relates to genetic markers and methods of diagnosing and screening for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). As such, the disclosure encompasses a whole-genome association analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of which a number are located within the GRB2-associated binding protein 2 (GAB2) gene as well as other markers associated with other genes. The disclosure identifies two novel haplotypes within the GAB2 gene, i.e., a LOAD risk-enhancing and a LOAD risk-decreasing haplotype. These haplotypes modify LOAD risk differentially in combination with APOE alleles. Further encompassed are therapeutic methods and agents of decreasing the deterioration of cells associated with LOAD.
Owner:TRANSLATIONAL GENOMICS RESEARCH INSTITUTE +1
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites remarkably associated with grain number per ear of wheat and application of SNP sites in genetic breeding of wheat
PendingCN113684300AImprove breeding efficiencyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyReference genome sequence
The invention discloses a group (50) of SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) loci obviously associated with the grain number per ear of wheat and an application method of the SNP loci in inheritance and breeding. The SNPs are identified by performing simplified genome sequencing (GBS) on 768 wheat varieties and excellent strains from main wheat producing areas in China, comparing reference genome sequences to explore single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and then performing whole genome association analysis. The SNP site is high in accuracy, can be used for being converted into a KASP marker and an SNP chip, and is widely applied to positioning of related genes of the grain number per ear of wheat, fine mapping and candidate gene identification as well as marker-assisted selective breeding and whole-genome selective breeding of the grain number per ear of wheat, new germplasm and new species of wheat with increased grain number per ear of wheat are bred, and the yield of wheat is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sheep liquid phase chip and application thereof
InactiveCN113249495ALow parting costIncrease flexibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a sheep liquid phase chip and application thereof, 935 SNP loci for chip design are found and screened, and sheep genotyping can be realized by utilizing the designed liquid phase chip through a targeted capture sequencing technology. Experimental results show that the chip designed by the invention can be used for sheep genetic diversity analysis, variety identification, genetic relationship identification, whole genome association analysis and genome selective breeding.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
SNP marker for identifying apricot peel hair traits, primer and application
ActiveCN113684301AEnables early screeningShorten the breeding periodFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention provides an SNP marker for identifying apricot peel hair traits, a primer and application. According to the SNP marker related to the hairy / hair-free character of the apricot fruit epidermis, the SNP marker related to the hairy / hair-free character of the apricot fruit epidermis is obtained through a whole genome association analysis method, the polymorphic site is located at the 15954845bp position of the No. 7 chromosome of an apricot genome and is a basic group G or C, and a detection primer is designed aiming at the site; according to the method, one pair of primers is utilized, whether apricot fruit epidermis is hairy or not can be identified in the seedling stage, early screening of hairy / hair-free characters is achieved, the breeding age limit is shortened, through verification of 244 parts of apricot resources, the result shows that the identification accuracy of the method on the hairy / hair-free character of the surface skin of the apricot fruit reaches 100%; and the method the hairy / hair-free character of the apricot fruit epidermis has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness, high efficiency, low cost and the like, and has an important application value in fresh apricot breeding.
Owner:北京市林业果树科学研究院
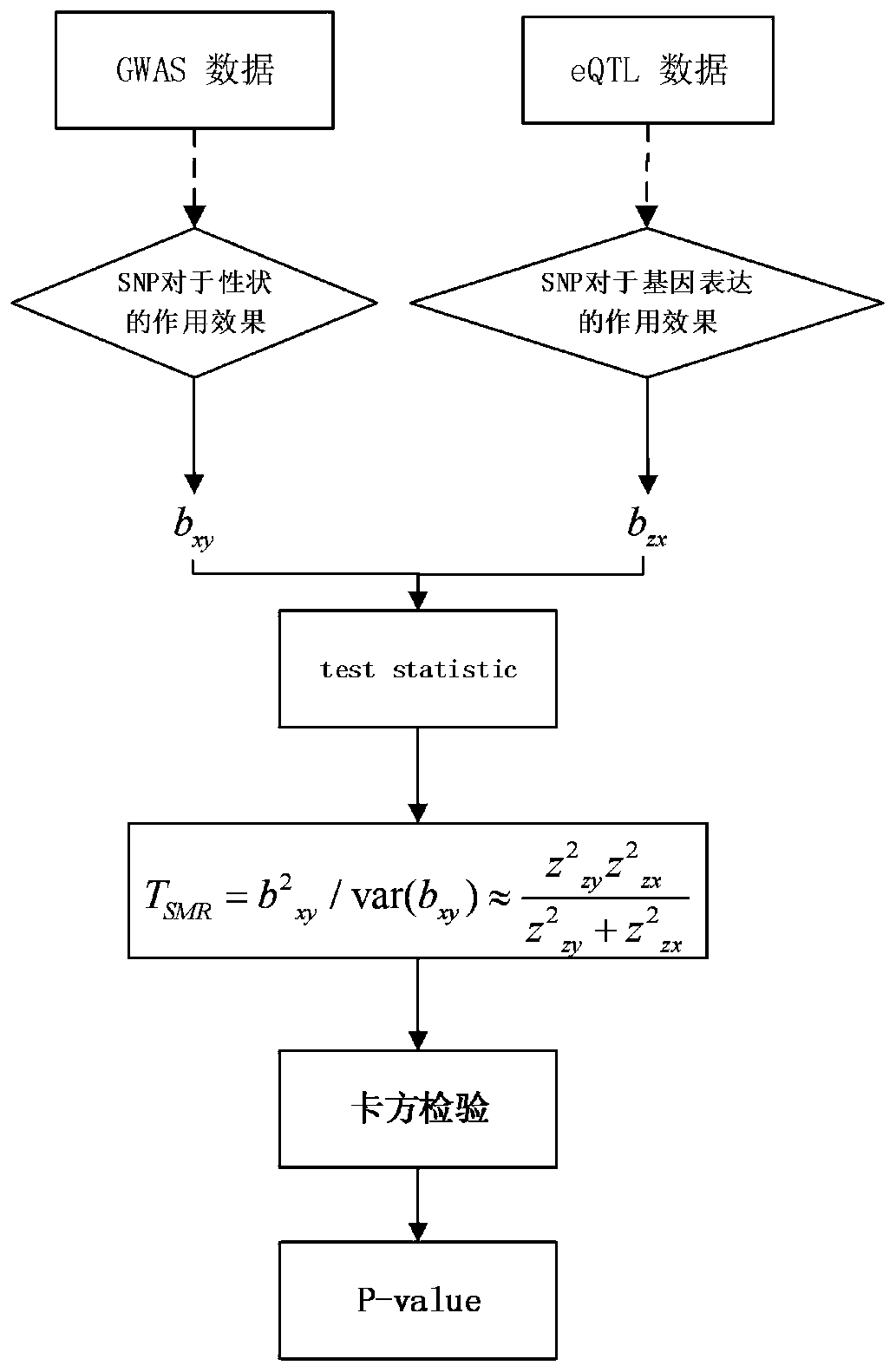
Gene recognition method based on empirical Bayesian and Mendel randomization fusion
PendingCN111180012AFast recognitionTake advantage ofBiostatisticsSequence analysisWhole Genome Association AnalysisMendelian randomization
The invention relates to a gene recognition method based on empirical Bayesian and Mendel randomization fusion. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing whole genome association analysis data by adopting empirical Bayesian meta-information to obtain an analysis result; correcting a statistical value of each SNP in the whole genome based on comprehensive hierarchical meta-information analysis of empirical Bayesian; integrating the whole genome association analysis data based on the Mendel randomization with the eQTL data and the mQTL data respectively, and obtaining a gene recognition result according to the overlapping part of the integration results of the whole genome association analysis data based on the Mendel randomization integrating with the eQTL data and the mQTL data.According to the method, the recognition speed of AD related genes can be greatly increased, existing data are fully utilized and the recognition speed of disease related genes is increased, and the research and development cost is saved; and the calculation result can screen out a great part of genes, so that a valuable research range is provided for subsequent biological experiments.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
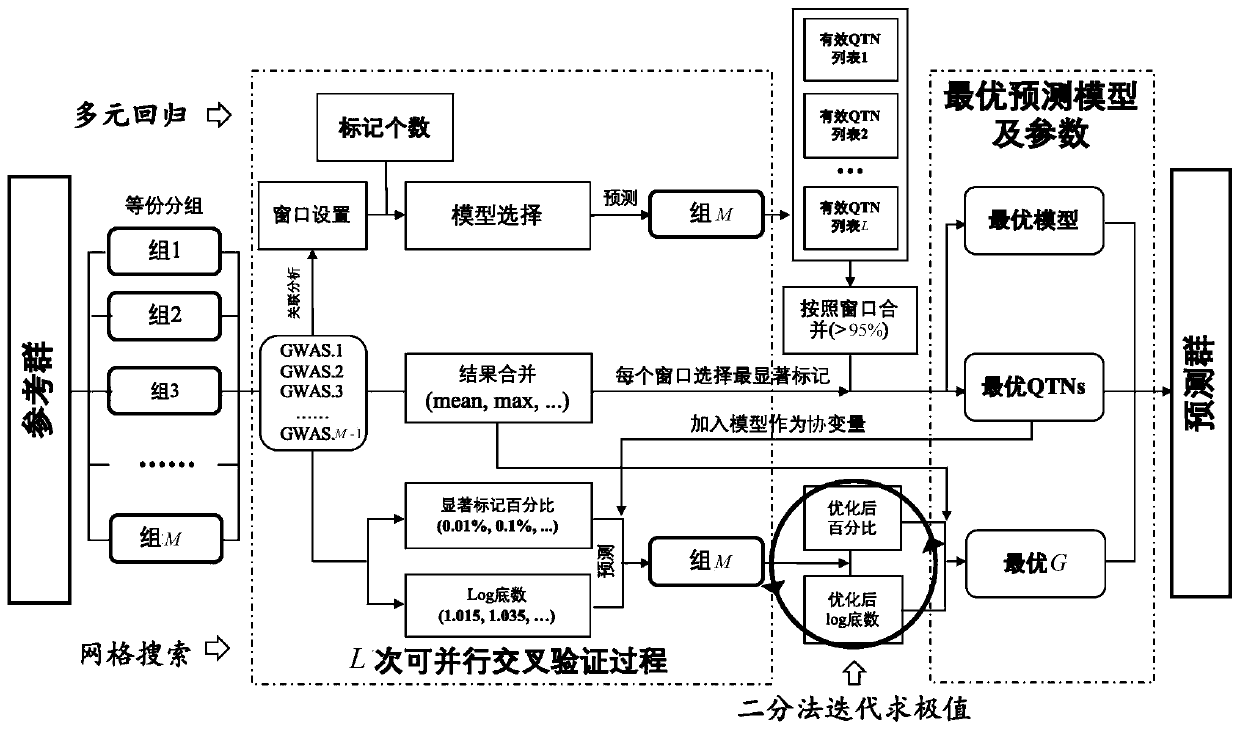
Efficient high-accuracy whole-genome selection method capable of performing parallel operation
ActiveCN110610744AImprove accuracyImprove computing efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsWhole Genome Association AnalysisAlgorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of animal and plant breeding and human disease prediction, and provides an efficient high-accuracy whole-genome selection method capable of performing parallel operation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading an original genotype file and a phenotype file, constructing a new genotype file and a new phenotype file, and calculating agenetic relationship matrix of all individuals; then, extracting all individuals in the new phenotypic file as a reference group, and extracting all individuals without phenotypic data in the originalgenotypic file as a prediction group; carrying out whole genome association analysis by utilizing the reference group data, and extracting result characteristics of the whole genome association analysis; constructing a model library with specific characters, sequentially optimizing an optimal fixed effect and an optimal random effect by adopting a cross validation strategy, and selecting an optimal prediction model from the model library; and finally, calculating genome estimated breeding values of the prediction group by utilizing the optimal prediction model. The method can quickly, accurately and stably predict individual genome breeding values, and thus the accuracy and efficiency of whole genome selection are improved.
Owner:武汉影子基因科技有限公司
SNP sites remarkably associated with wheat powdery mildew resistance and application thereof in genetic breeding
InactiveCN112501345AReduce in quantityQuantitatively lowMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a group (58 wheat varieties) of SNP sites remarkably associated with wheat powdery mildew resistance and an application method thereof in genetic breeding. The SNP sites are identified by performing simplified genome sequencing (GBS) on 768 wheat varieties and excellent strains to explore SNP sites and then performing disease resistance identification and whole genome association analysis. The group of SNP sites are high in accuracy, can be converted into KASP markers and SNP chips, and are used for positioning, fine mapping and candidate gene identification of wheat powdery mildew resistance genes and wheat powdery mildew resistance whole genome selective breeding.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker linked with cucumis sativus peel gloss regulation gene and application
ActiveCN112592999ASolve the problem of long conventional breeding cycle and easy to be affected by the environmentReduce planting sizeFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a molecular marker linked with a cucumis sativus peel gloss regulation gene and application. The molecular marker is mutation from T to C at a 26138107 bp position on a chromosome 3 of cucumis sativus genome. 289 parts of seed resources collected by a project group are utilized, methods of whole genome association analysis (GWAS) combined with QTL positioning and the like are adopted, key variation sites influencing cucumis sativus peel gloss regulation and control are identified, and the molecular marker is developed according to the variation. One KASP molecular marker is designed, the marker is used for carrying out genotype identification on 295 single plants in a segregation population, and coincidence rate reaches 100%. Research results not only are beneficialto early identification and assisted breeding of cucumis sativus with glossy peels, but also provide a basis for map-based cloning of peel gloss regulation and control genes and analysis of molecularmechanisms of gloss regulation and control, and have a wide popularization value.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST OF VEGETABLE
Whole genome association analysis method based on comparison of multiple genomes and next-generation sequencing data
ActiveCN113628685AImplementation of association analysisEasy to understandProteomicsGenomicsGene PositionWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a whole genome association analysis method based on comparison of multiple genomes and next-generation sequencing data, which comprises the following steps of: 1, comparing a reference genome with a de novo assembly genome file by using comparison software; and updating the annotation gene positions or structures in the reference genomes; 3, if a plurality of de novo assembly genomes exist, sequentially iteratively updating the reference genomes; 4, comparing the next-generation sequencing data of the samples to the updated reference genome by using comparison software; 5, collecting demarcation point position information of all structural variations of all the samples into a set, constructing a population genotype; and 6, performing functional gene candidate according to the association site and the updated reference genome annotation file. According to the method, the whole genome association analysis is performed by using the structure variation genotype data.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
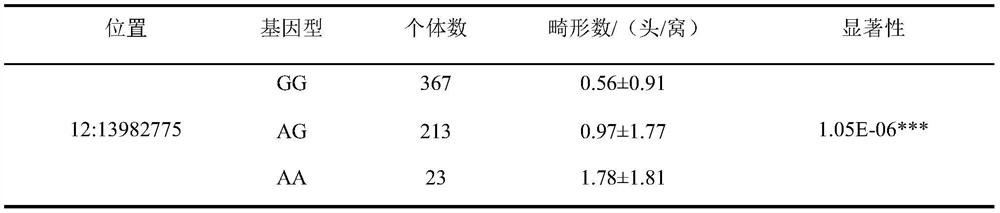
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker located on 12 # chromosome of pig and related to piglet malformation number and application of SNP molecular marker
PendingCN113584185AGuaranteed profitReduced number of piglet deformitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWhole Genome Association AnalysisGenetics
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
SNP molecular marker related to wheat stem rot resistance and application of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN113005213AImprove selection efficiencyReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention provides an SNP molecular marker related to wheat stem rot resistance and an application of the SNP molecular marker. Whole genome association analysis is carried out on a natural population composed of 358 Chinese wheat germplasm resources, and five SNP loci closely associated with stem rot resistance are found on a hexaploid wheat 5D chromosome long arm for the first time. KASP primers capable of being used for large-scale material screening are further developed for the SNP loci, and the close association degree of the developed molecular marker and disease resistance is verified in F2 and F2: 3 populations constructed by using an anti-infection material as a parent. The five SNP molecular markers provide an effective means for screening of wheat anti-FCR germplasm resources.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Barley 40K SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) liquid phase chip
PendingCN114807410AImprove breeding efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHigh throughput genotyping
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant molecular markers, and relates to a barley 40K SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) liquid chip. The barley 40K SNP liquid phase chip is obtained by the following method: 1, selecting barley and highland barley as germplasm materials for re-sequencing, then performing quality control on a sequencing result, mapping with a reference genome, and identifying and screening out SNP loci; 2, according to the indexes of the SNP sites, combining the positions of the sites on chromosomes, analyzing upstream and downstream sequences of the sites, designing sequencing primers, and selecting the SNP sites which can be used for chip development; and 3, developing the barley 40K SNP liquid phase chip by using a targeted sequencing genotyping technology. The barley 40K SNP liquid phase chip belongs to an SNP chip for DNA detection, is a barley whole genome liquid phase chip which is developed based on a targeted capture high-throughput sequencing technology and contains 40519 SNP marker sites, and provides an important tool for barley high-density genetic map construction, barley germplasm identification, high-throughput genotyping, QTL positioning, whole genome association analysis and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Marker related to earliness or lateness of flowering period of Siberian apricot and detection primer, method and application thereof
ActiveCN111826462AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a marker related to the earliness or lateness of the flowering period of Siberian apricot and a detection primer, a detection method and application thereof, 7 SNP markers related to earliness or lateness of the flowering period of Siberian apricot exist in chromosome 6 of Siberian apricot, 6 pairs of primers for detecting earliness or lateness of the flowering period of Siberian apricot are designed; and PCR amplification is performed through the 6 pairs of primers, to detect a marker site related to the earliness or lateness of the flowering period of Siberian apricot, and carry out sequencing on the genotype of the marker site, thereby judging the earliness or lateness of the flowering period of the Siberian apricot. Whole genome association analysis of the Siberian apricot in China finds that the site is remarkably related to the earliness or lateness of the flowering period of the Siberian apricot, the marker is further developed for the site, and a methodand a special primer for detecting the earliness or lateness of the flowering period of the Siberian apricot are provided. And the marker provided by the invention can be used for specifically detecting the genotype of the marker site of the Siberian apricot, can also be used as a new tool for selecting the marker in an assisted mode in breeding in different flowering periods, and has very important positive significance.
Owner:中国林业科学研究院经济林研究所
Whole genome association analysis algorithm based on parent genotypes and progeny phenotypes
ActiveCN113793637ATrait high associationReduce material costsProteomicsGenomicsWhole Genome Association AnalysisGenetics
The invention discloses a whole genome association analysis algorithm based on parent genotypes and progeny phenotypes, the algorithm comprises the following steps: acquiring parent genotypes, progeny phenotypes and progeny phenotype parent information of a group to be analyzed, and establishing a combined genotype matrix of progeny according to genotypes of parent pairs, obtaining possible genotype combination information of different progenies of each SNP site and corresponding progeny group grouping phenotype data, constructing a statistical model of a progeny combination genotype and a corresponding progeny phenotype for correlation analysis, and obtaining a correlation P value of the phenotype and each SNP site; then, distinguishing correlation types of the SNP sites, calculating whether conforming to additive or complete dominant effects or not, and screening candidate sites; obtaining the average distance of the strong correlation markers according to LD attenuation of the whole genome SNP markers for screening of a final marker set.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Methods of diagnosing alzheimer's disease and markers identified by set association
ActiveUS20090249498A1Decreasing and preventing deteriorationAvoid developmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderWhole Genome Association AnalysisLate onset
The present disclosure relates to genetic markers and methods of diagnosing and screening for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). As such, the disclosure encompasses a whole-genome association analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of which a number are located within the GRB2-associated binding protein 2 (GAB2) gene as well as other markers associated with other genes. The disclosure identifies two novel haplotypes within the GAB2 gene, i.e., a LOAD risk-enhancing and a LOAD risk-decreasing haplotype. These haplotypes modify LOAD risk differentially in combination with APOE alleles. Further encompassed are therapeutic methods and agents of decreasing the deterioration of cells associated with LOAD.
Owner:TRANSLATIONAL GENOMICS RESEARCH INSTITUTE +1
Rice blast resistance related gene OsPLUS3 and application thereof in gene engineering
PendingCN114181947AIncrease resistanceReduced blast resistanceTransferasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and relates to a rice blast resistance related gene OsPLUS3 and application thereof in gene engineering. The rice gene OsPLUS3 is a transcription factor with a plus-3 structural domain, the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention discloses a rice gene OsPLUS3 which is reported for the first time in rice, and the gene is a rice gene which is screened through 240 parts of natural population whole genome association analysis and is significantly related to seedling blast resistance and has haplotype significant difference. MRNA expression analysis shows that the gene is obviously induced by inoculation of magnaporthe oryzae, and the seedling blast resistance of a rice plant with the T-NDA inserted mutant is lower than that of a wild Dongjin material. Therefore, the gene can be used as a target gene to be introduced into a susceptible material to improve the plant disease resistance so as to improve the plant variety.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
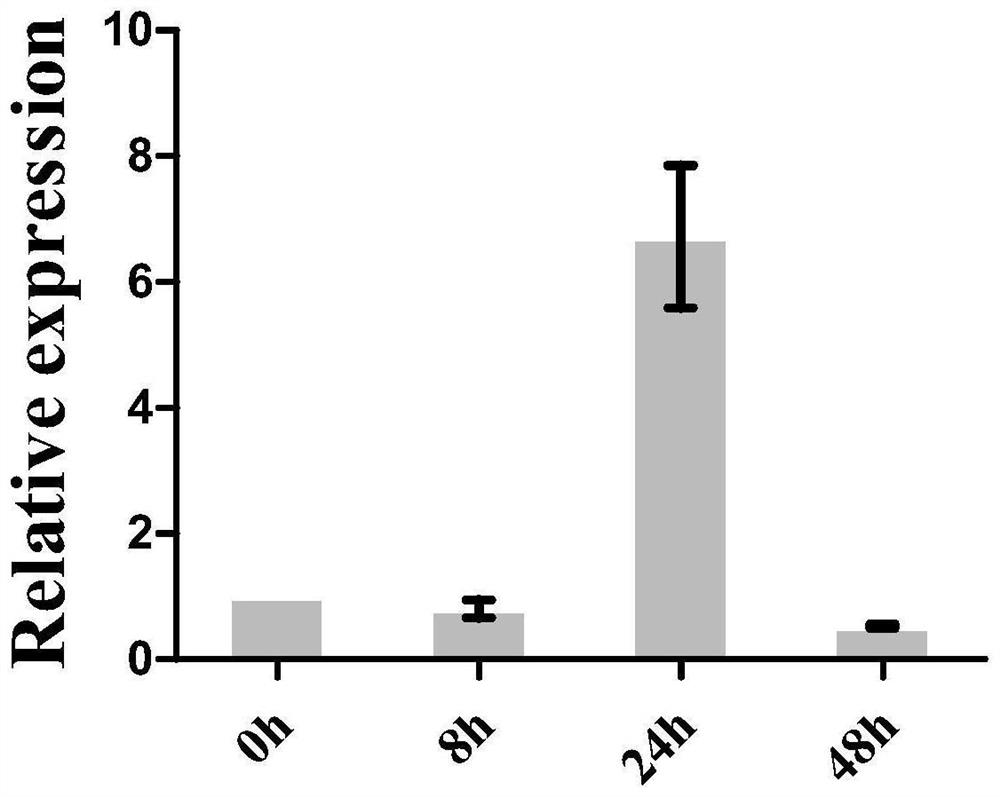
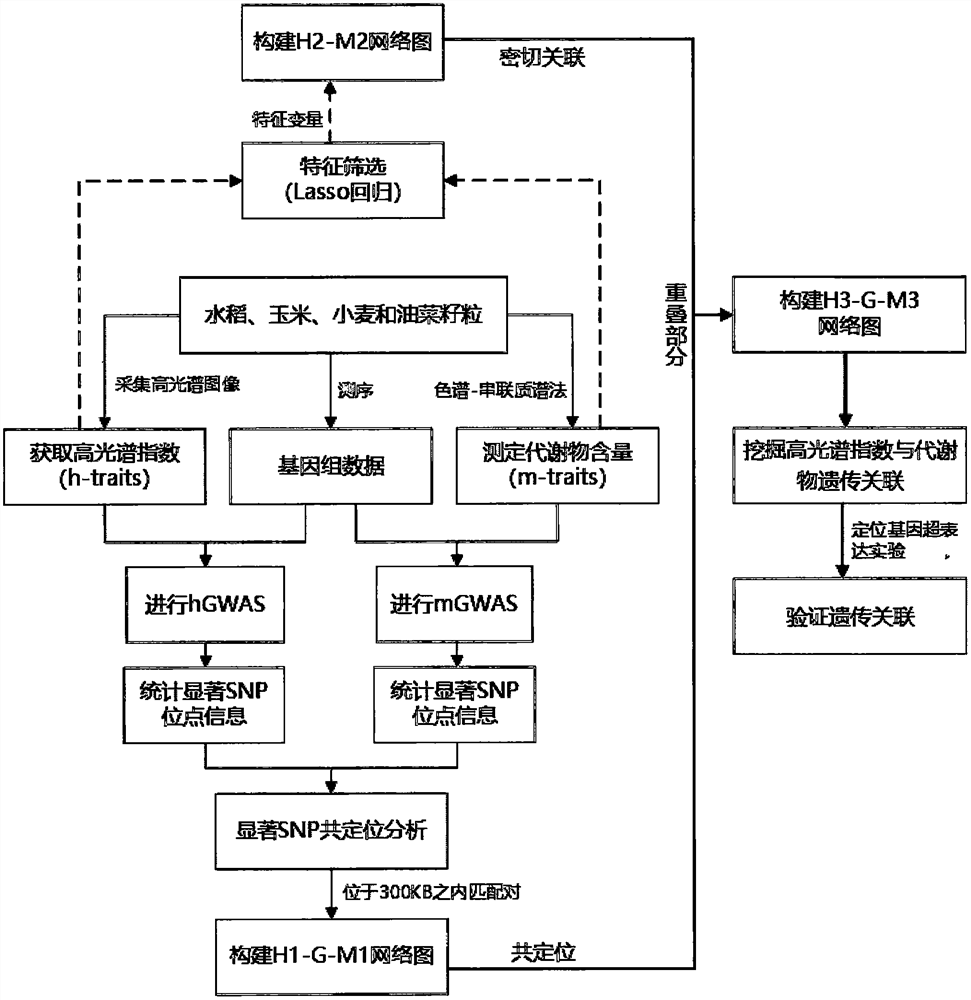
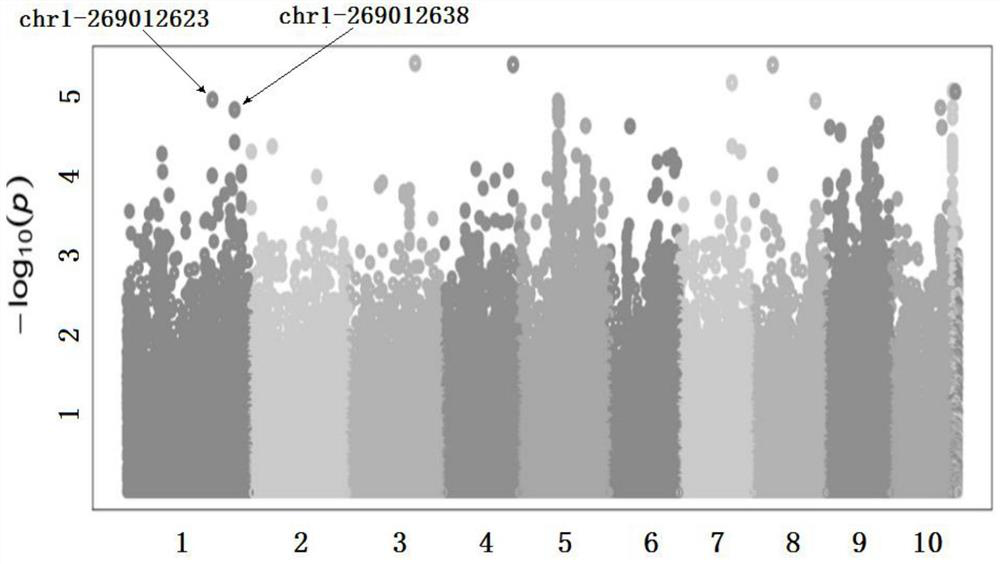
Crop grain metabolism character detection and genetic analysis method based on hyperspectral imaging
ActiveCN113393897AAddressing Insufficient Genetic AnalysisImprove throughputProteomicsGenomicsPhenotype genotypeWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a crop grain metabolic trait detection and genetic analysis method based on hyperspectral imaging. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring hyperspectral images of crop grains by using a hyperspectral camera to obtain hyperspectral indexes of thousands of crop grains, and secondly, detecting thousands of metabolites by using a gas phase / high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method; based on genetic typing information of each strain of a population, carrying out whole genome association analysis by respectively taking a hyperspectral index and metabolite content as crop grain phenotypic characters, screening significant SNP sites, carrying out co-localization analysis on the two groups of significant SNP sites, and constructing a hyperspectral phenotype-genotype-metabolic phenotype association network H1-G-M1; carrying out feature screening on the hyperspectral index and the metabolite content by using Lasso regression, and constructing a hyperspectral-metabolic phenotype association network H2-M2; analyzinfg the H1-G-M1 network and the H2-M2 network are comprehensively, and integrating the H1-G-M1 network and the H2-M2 network to construct the hyperspectral phenotype-genotype-metabolite phenotype associated network H3-G-M3, and futher mining the new information of the metabolic genetic structure of the crop grains.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
ZmGNAT19 gene SNP molecular marker related to corn leaf blight resistance and application
ActiveCN112662807ASimplified sequencingQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention relates to a ZmGNAT19 gene SNP molecular marker related to corn leaf blight resistance and application, and belongs to the technical field of crop genetic breeding molecular marker application. The invention particularly relates to two extremely remarkale genes related to the leaf spot AUDPC (P<0.0001) ZmGNAT19 gene (Zm001d033620) 3'-UTR region on a corn chromosome 1 , an SNP molecular marker thereof and the application thereof. The ZmGNAT19 gene SNP molecular marker disclosed by the invention is obtained from whole genome association analysis of a maize inbred line group, and the nucleotide sequence of the ZmGNAT19 gene SNP molecular marker is shown as SEQ ID N01. The ZmGNAT19 gene SNP molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for auxiliary selection of corn leaf blight resistant varieties, the selection accuracy can be improved, and the cultivation process of disease-resistant varieties is accelerated.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Molecular marker related to salt tolerance of rice and application of molecular marker
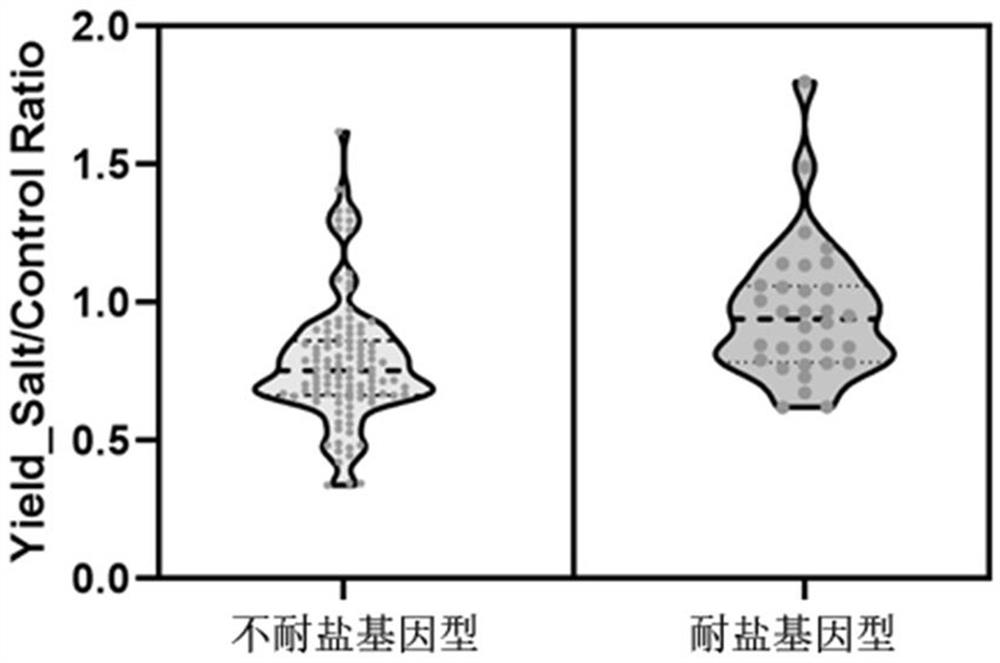
ActiveCN114317812AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWhole Genome Association AnalysisNucleotide
The invention discloses a molecular marker related to salt tolerance of rice and application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is obtained through whole genome association analysis, and comprises nucleotide single base mutation at the 1796216bp position, nucleotide single base mutation at the 1797072bp position, two nucleotide base mutations at the 1797131bp position and the 1797132bp position, and nine nucleotide base deletion at the 1797233bp position on the No.3 chromosome of a rice reference genome. By utilizing the molecular marker provided by the invention, the salt-tolerant genotype of the rice OsDSK2a gene can be rapidly and accurately detected, and efficient application of the gene in rice salt-tolerant molecular breeding is facilitated.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
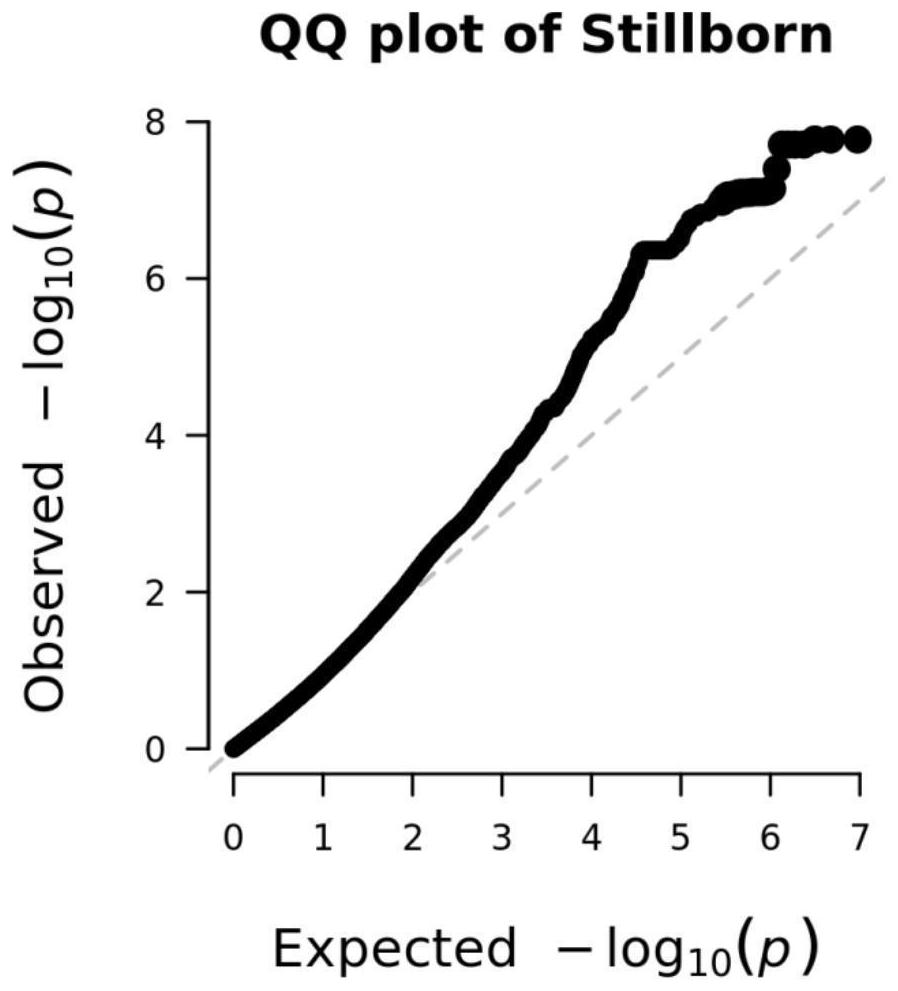
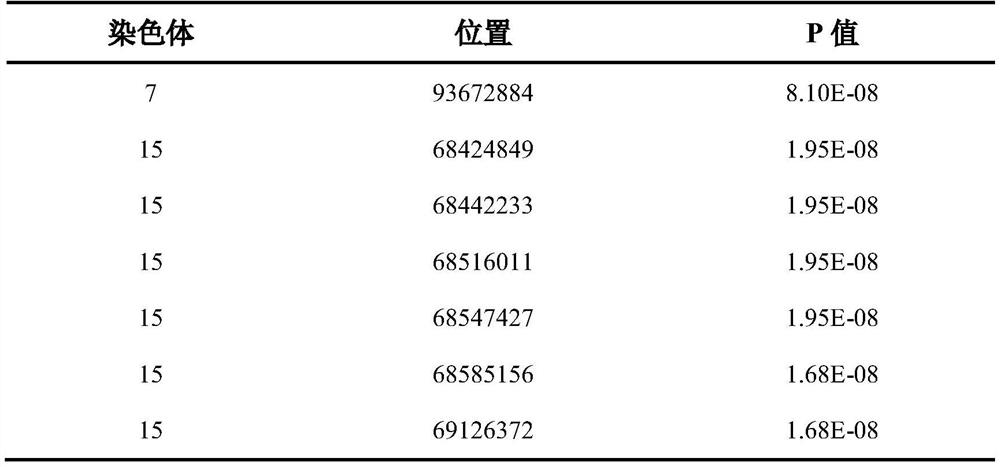
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related to stillbirth character of sow and application thereof
PendingCN114717329AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWhole Genome Association AnalysisMarker-assisted selection
The invention belongs to the technical field of pig molecular markers, and particularly relates to an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related to a stillbirth character of a sow and application of the SNP molecular marker. Gene typing is carried out by utilizing a gene chip technology, whole genome association analysis is carried out based on SNP molecular markers, and six SNP molecular marker sites related to the stillbirth character of the large white sow are screened out through the analysis. The sites of the SNP molecular marker are respectively positioned on SLC4A10 gene segments of the 15 # chromosome of the sow. A new SNP molecular marker resource is provided for the stillbirth character of the sow, and the SNP molecular marker can be applied to marker-assisted selection of genetic breeding of the sow.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
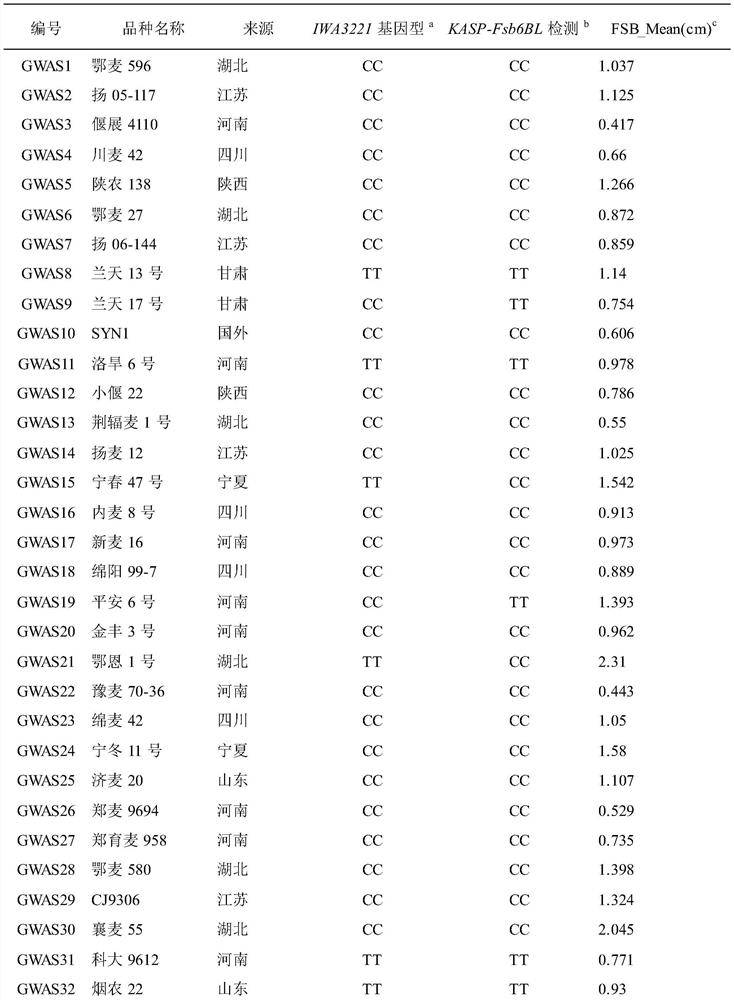
Molecular marker for detecting wheat fusarium blight QTL Qfsb.hbaas-6BL and application of molecular marker
PendingCN113699272AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a molecular marker for detecting a wheat fusarium blight resistant QTL Qfsb.hbaas-6BL and application of the molecular marker. The invention provides application of a substance for detecting the genotype of an SNP IWA3221 site of a wheat chromosome 6BL in identification or auxiliary identification of wheat fusarium blight resistance. The invention also provides application of a substance for detecting the genotype of the SNP IWA3221 site of the wheat chromosome 6BL in preparation of a product for identification or auxiliary identification of wheat fusarium blight resistance. The fusarium blight resistant locus Qfsb.hbaas-6BL located on a wheat 1D chromosome long arm is found through whole genome association analysis (GWAS), the associated SNP IWA3221 is further converted into a common PCR marker KASP-Fsb6BL, and the typing consistency rate of the two to 240 parts of materials is 97.5%. The marker can be used for detecting the genotype of the fusarium blight resistant QTL Qfsb.hbaas-6BL, and can be used for molecular breeding of fusarium blight resistance.
Owner:INST OF FOOD CROPS HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP molecular marker for detecting porcine T cell subset character
ActiveCN104711346AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWhole Genome Association AnalysisGenetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular marker preparation, particularly relates to an SNP molecular marker for detecting porcine T cell subset character. The SNP molecular marker comprises an SNP molecular marker related to the T cell subset character as well as location and application of a haplotype formed by two SNPs. The SNP molecular marker provided by the invention is obtained through whole genome association analysis; the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2; and an allelic mutation exists at the 26bp of the SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 so that polymorphism is caused. By utilizing the obtained SNP molecular marker, a corresponding haplotype as shown in figure 6 is obtained through haplotype analysis. The marker and the haplotype can be applied to the related detection of porcine T cell subset character.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Tomato whole genome chip and application thereof
PendingCN114736985ALow parting costIncrease flexibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a tomato whole genome chip and application thereof, gene typing objects capable of being used for chip design are found and screened out, the gene typing objects comprise 1377 SNP loci and 80 Indel loci located on a tomato reference genome SL2.50, and tomato gene typing can be achieved through a targeted capture sequencing technology by means of a liquid phase chip; experimental results show that the chip designed by the invention can be used for tomato genetic diversity analysis, variety identification, genetic relationship identification, whole genome association analysis and genome selective breeding.
Owner:河南七度农业科技有限公司 +3
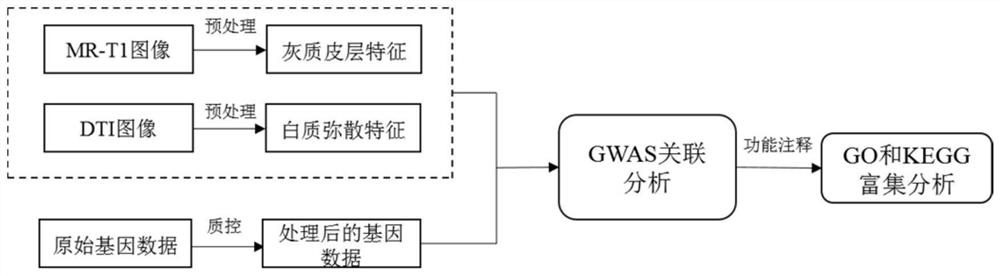
Imaging phenotype-based whole genome association analysis method, medium and equipment
ActiveCN113380379AImprove reliabilityAccurate processingMedical imagesComplex mathematical operationsWhole Genome Association AnalysisFiber bundle
The invention relates to an imaging phenotype-based whole genome association analysis method, a medium and equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a multi-modal magnetic resonance image of a brain; preprocessing the multi-modal magnetic resonance image to obtain related cortex features and white matter fiber bundle dispersion features, and forming an imaging phenotype file; acquiring original gene data corresponding to the multi-modal magnetic resonance image, and screening the original gene data to obtain effective gene data and form a gene file; performing correlation analysis based on the imaging phenotype file and the gene file by adopting an additive genetic regression model to obtain a correlation result; and carrying out visualization processing on the association result. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of high analysis accuracy and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF MEDICINE & HEALTH SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com