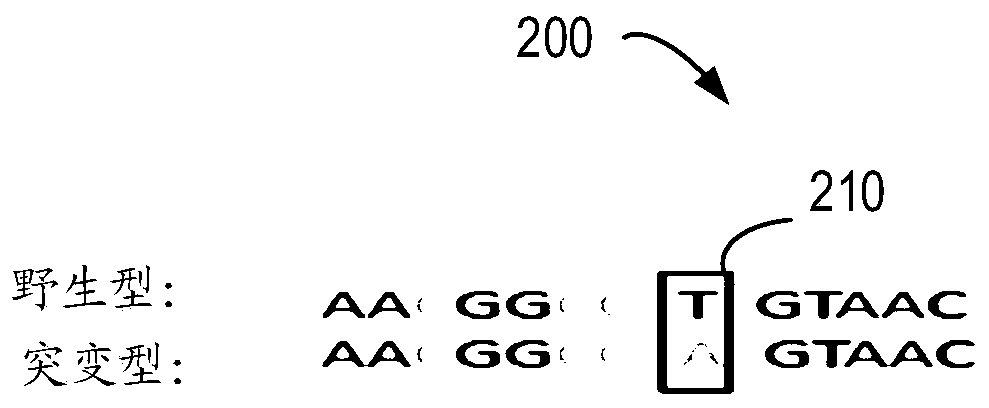
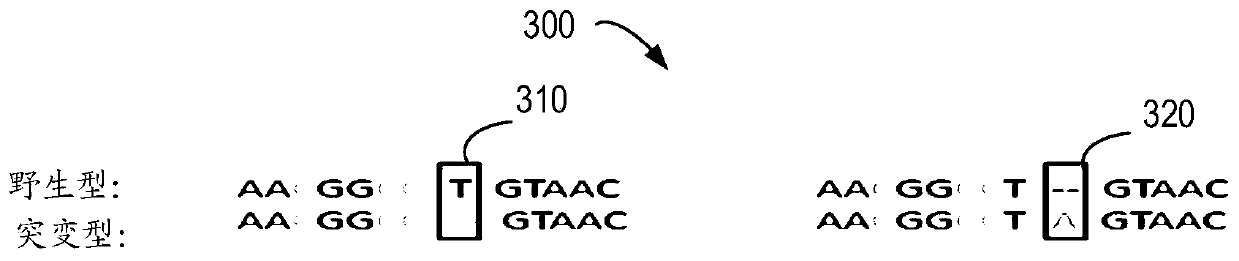
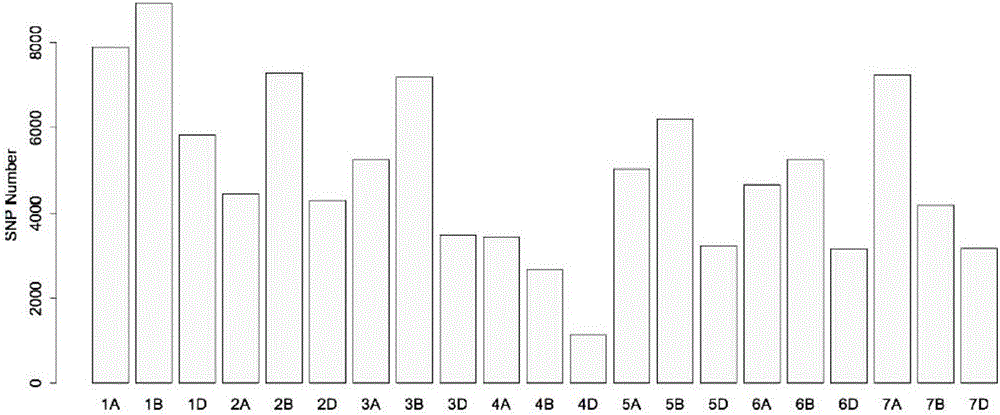
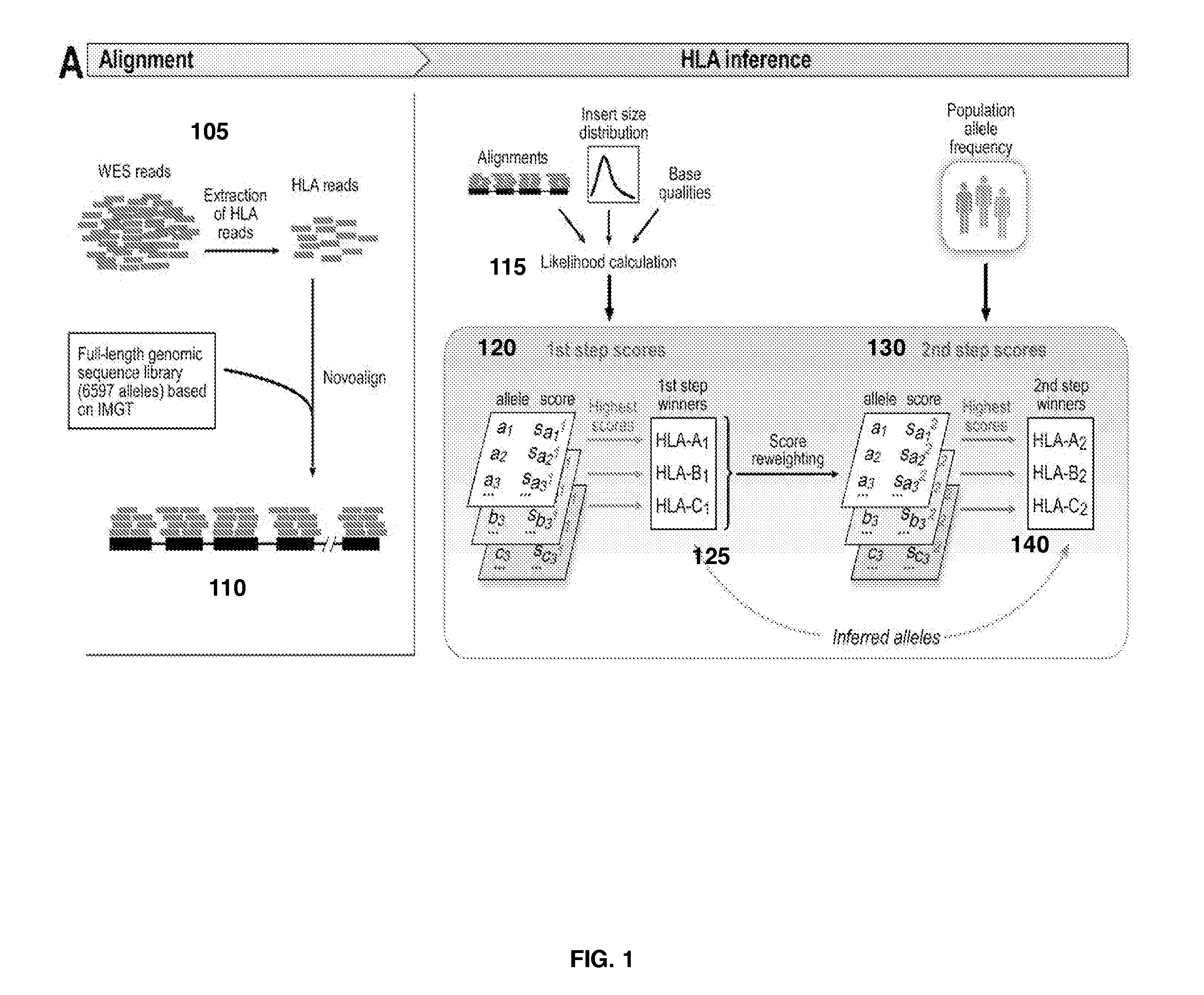
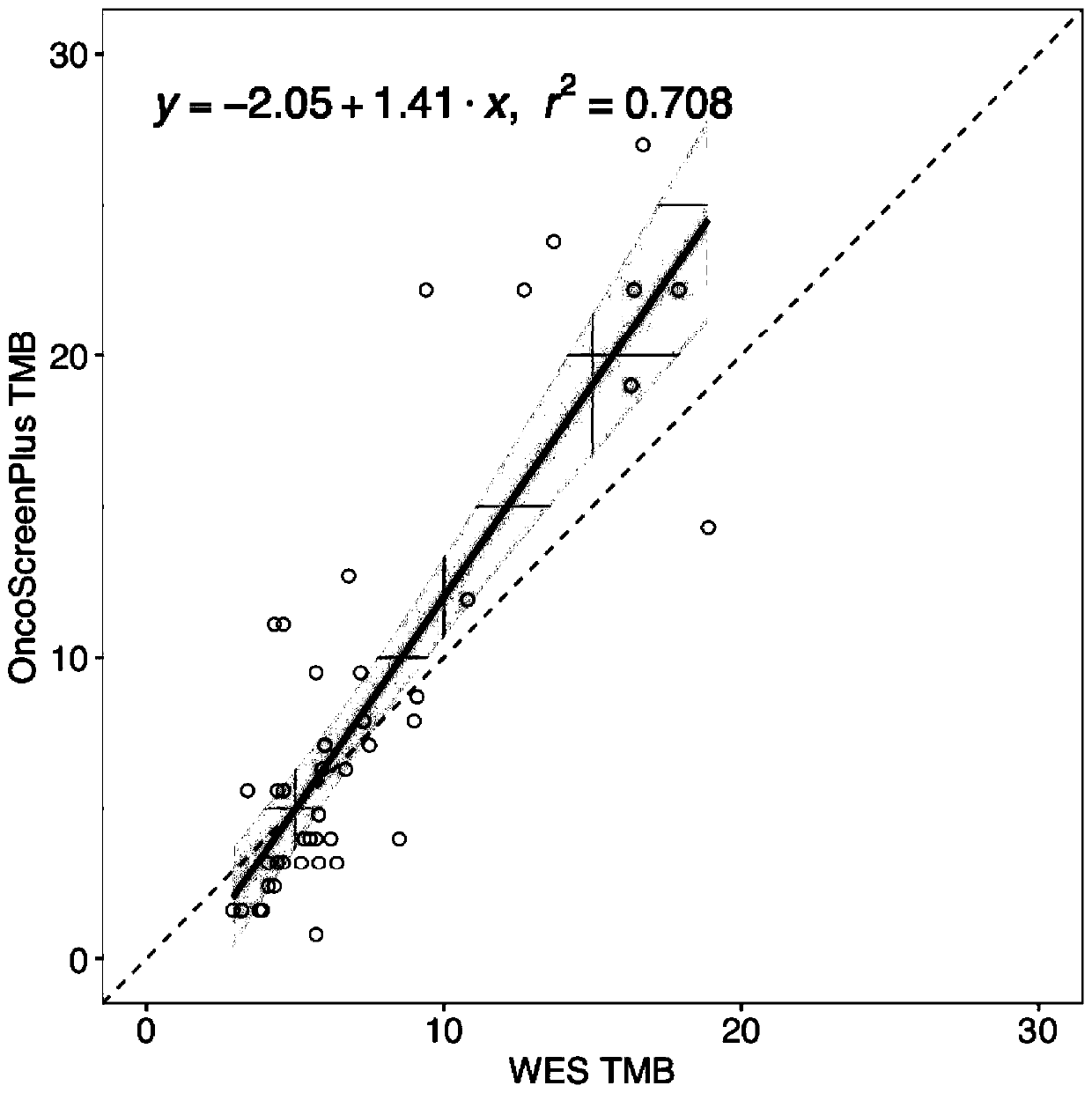
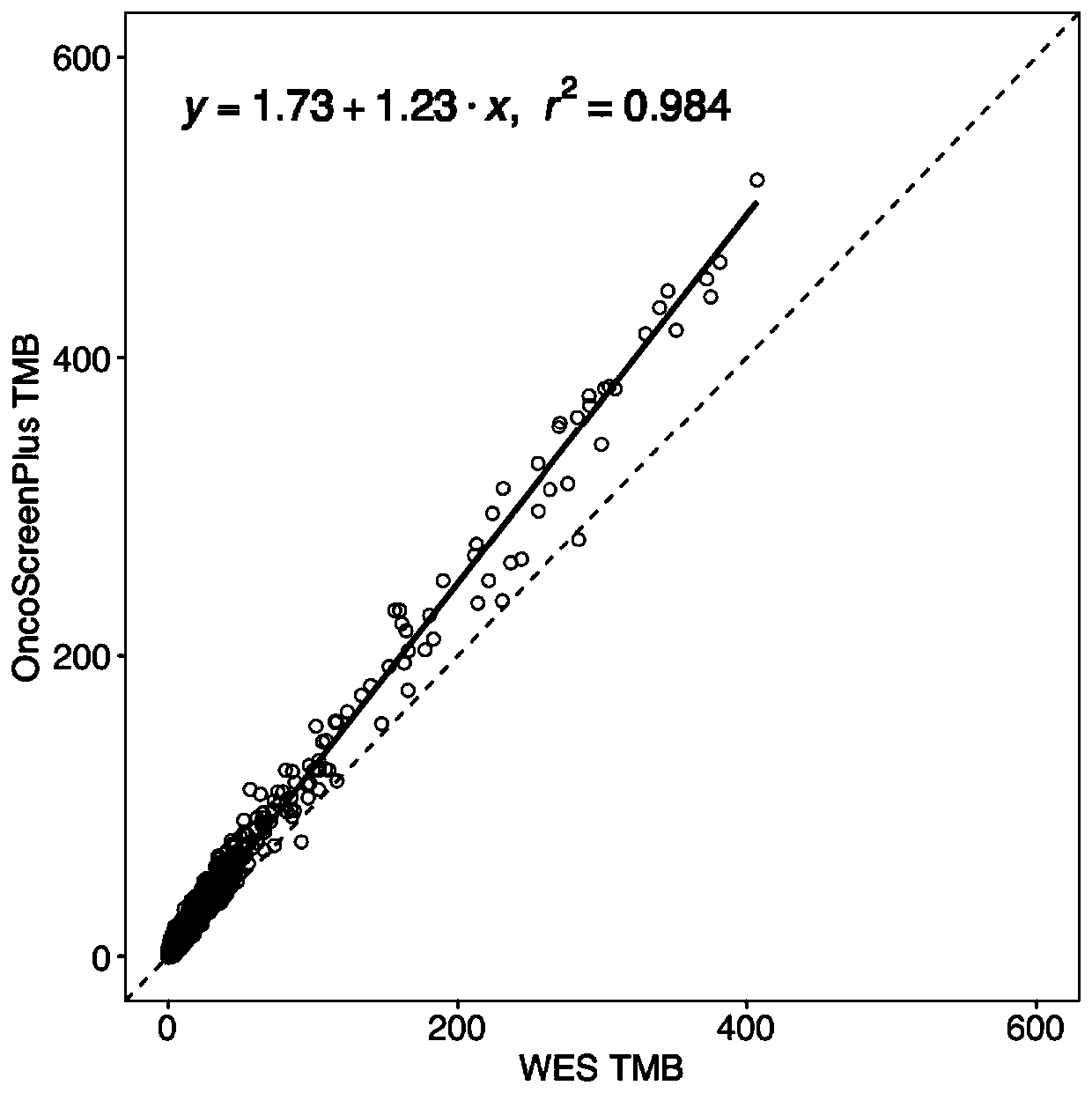
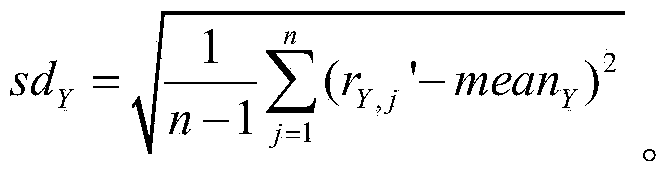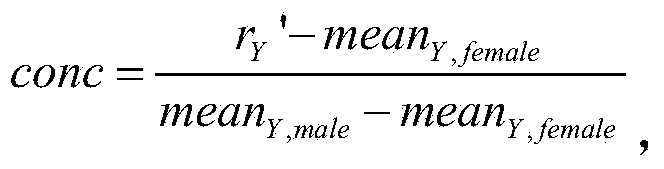Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
129 results about "Reference genome sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
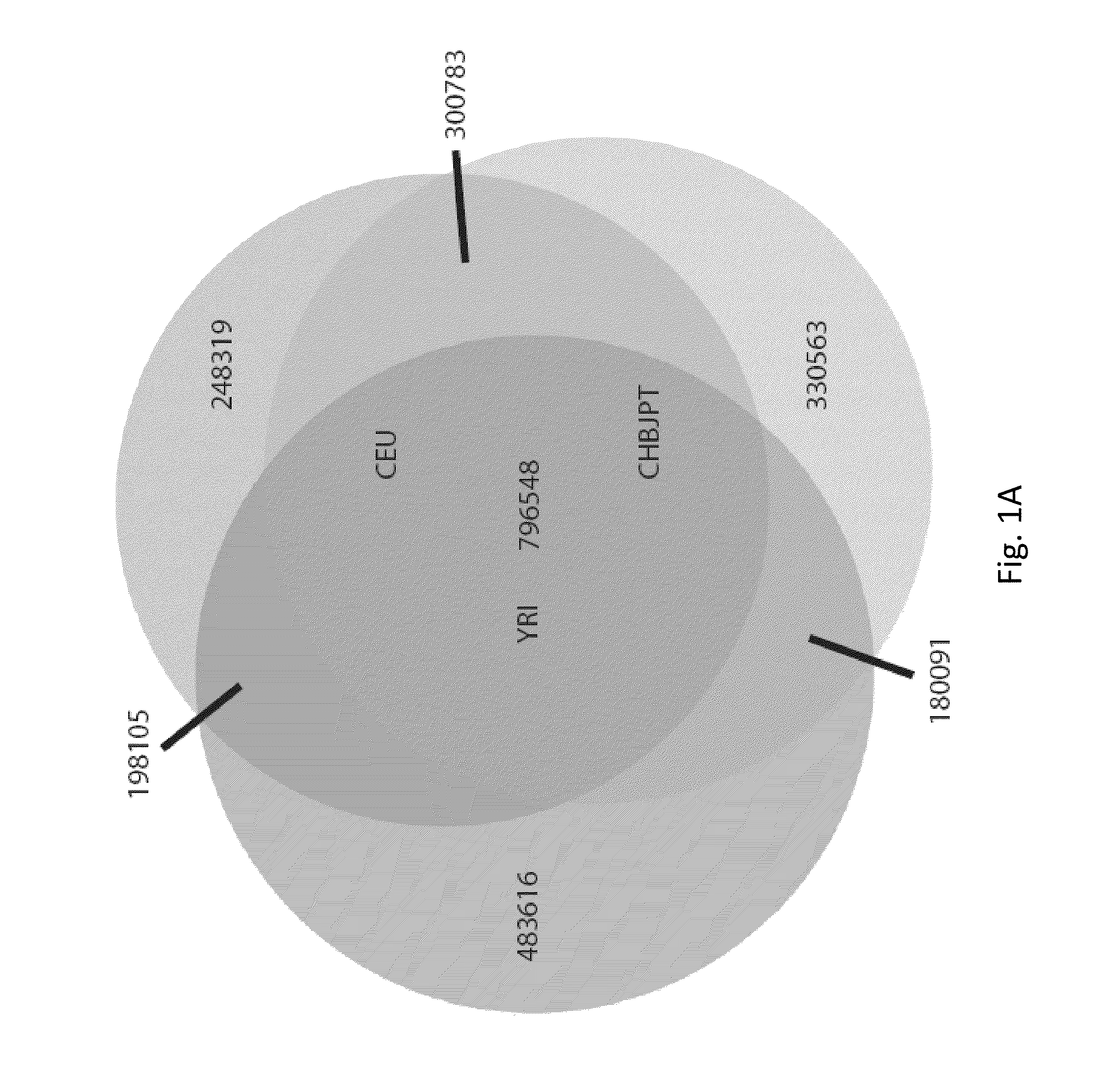
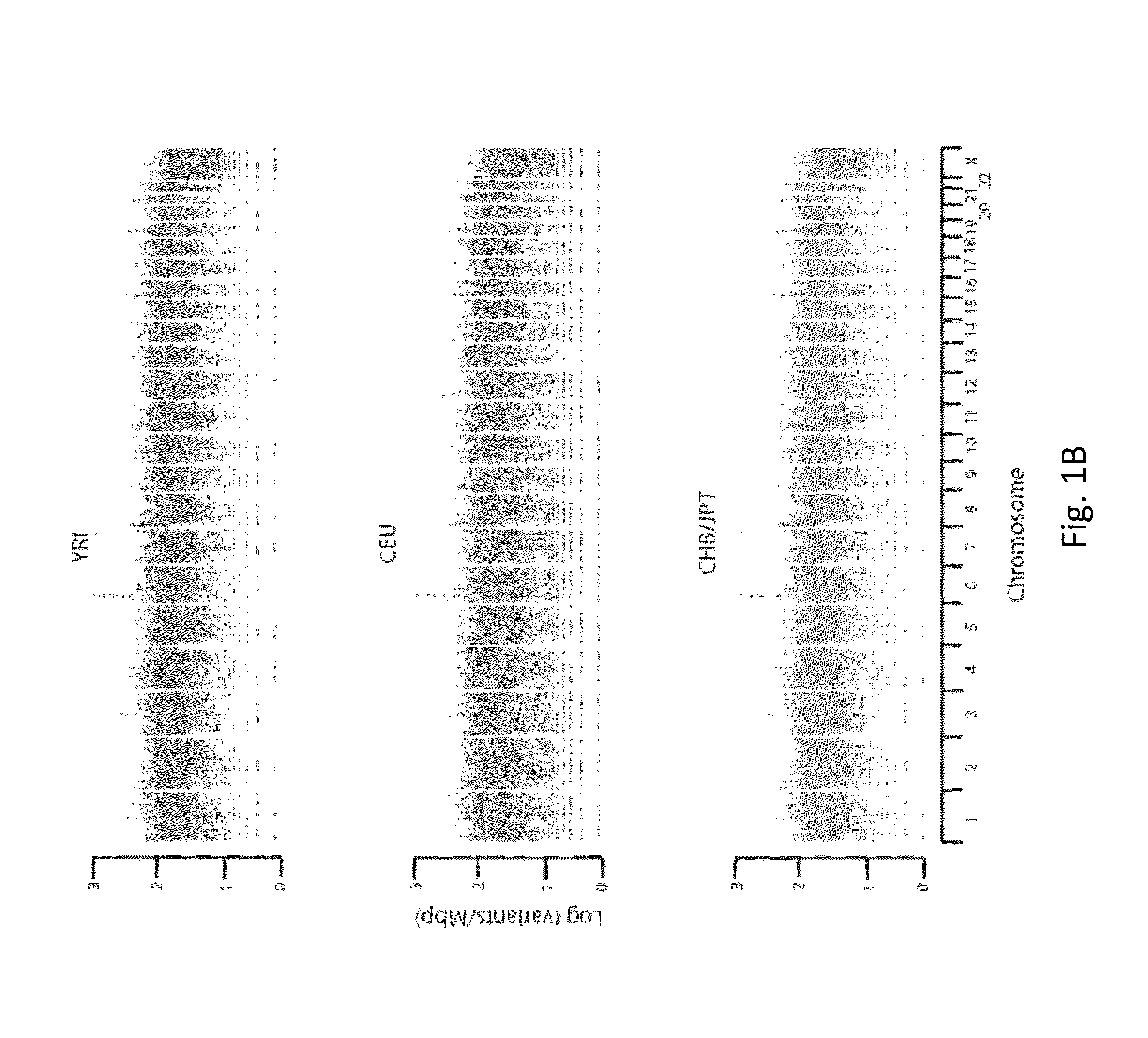
A reference genome is the initial sequence to which all subsequent sequences are ultimately compared, and therefore must be as complete as possible given fiscal and technical constraints. Reference genome sequences result from the de novo sequencing and assembly of a haploid complement of an organism’s genome.
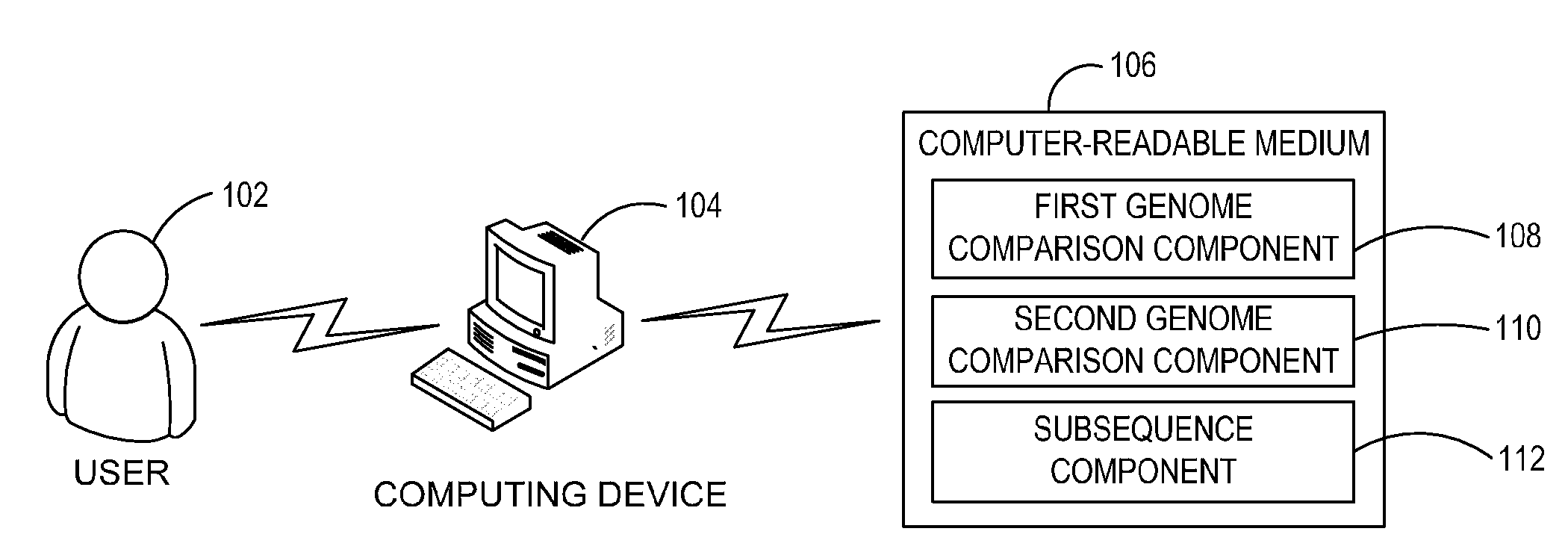
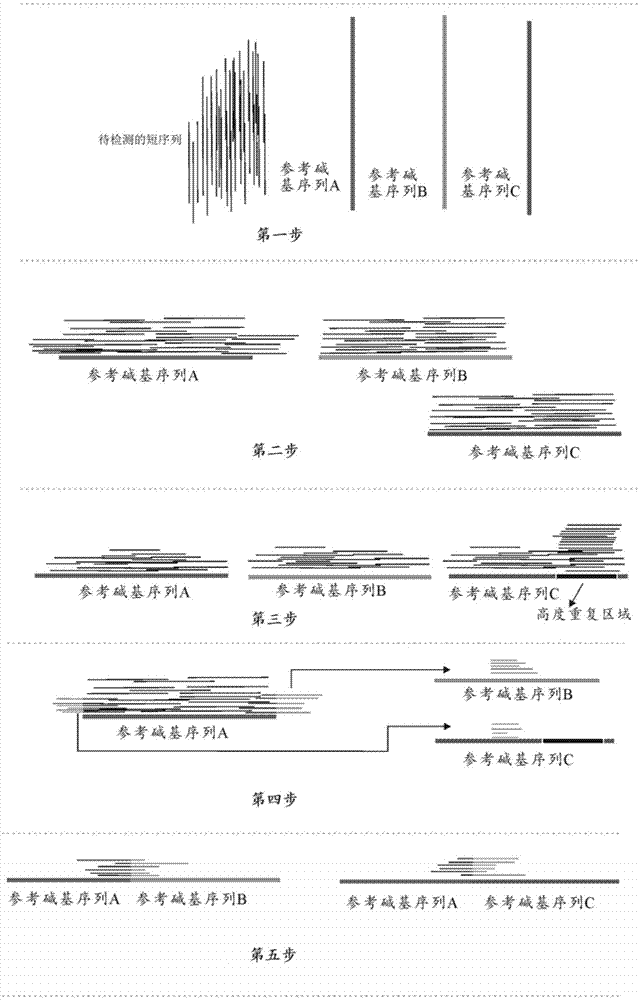
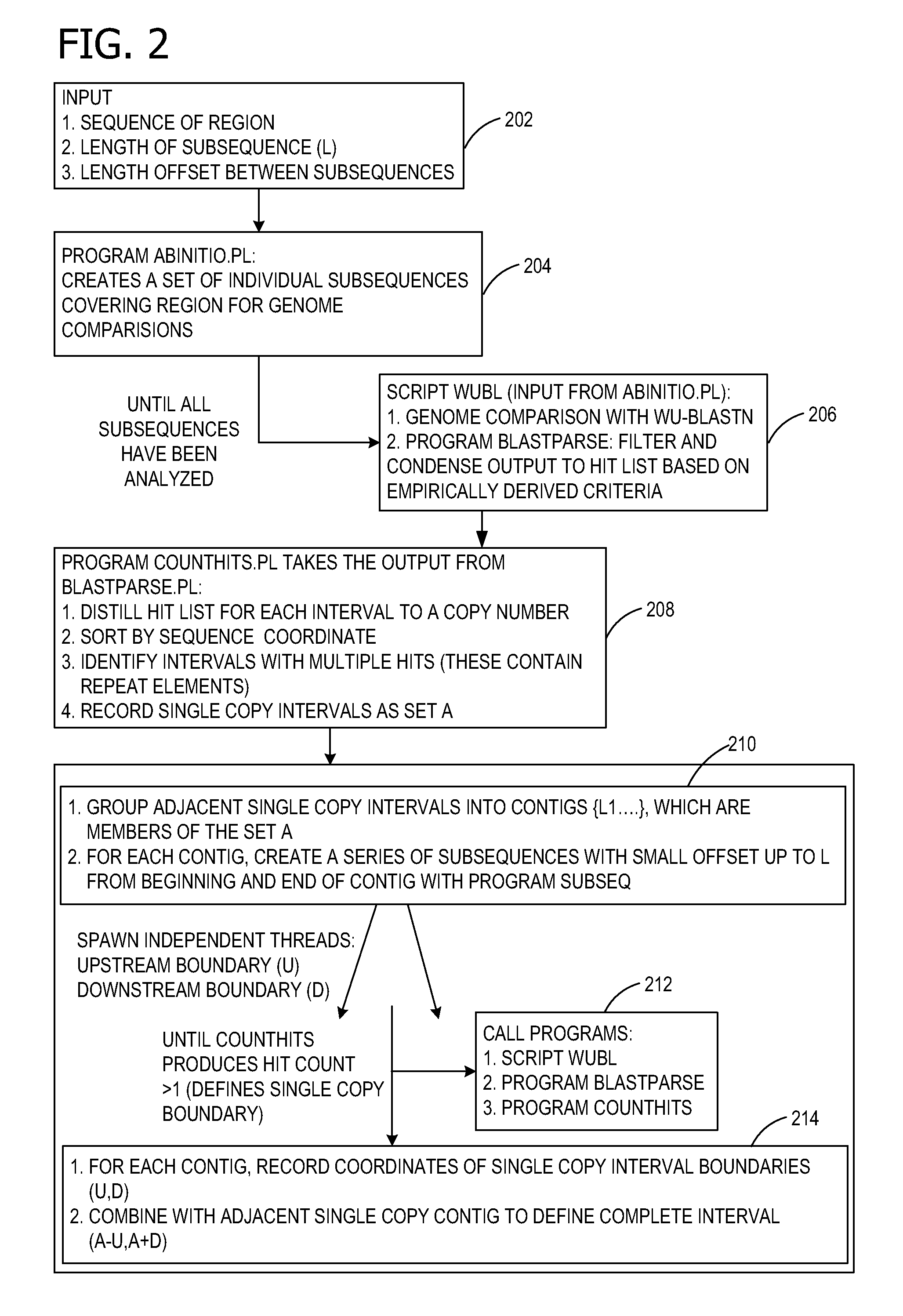
Ab initio generation of single copy genomic probes
Single copy sequences suitable for use as DNA probes can be defined by computational analysis of genomic sequences. The present invention provides an ab initio method for identification of single copy sequences for use as probes which obviates the need to compare genomic sequences with existing catalogs of repetitive sequences. By dividing a target reference sequence into a series of shorter contiguous sequence windows and comparing these sequences with the reference genome sequence, one can identify single copy sequences in a genome. Probes can then be designed and produced from these single copy intervals.
Owner:ROGAN PETER K
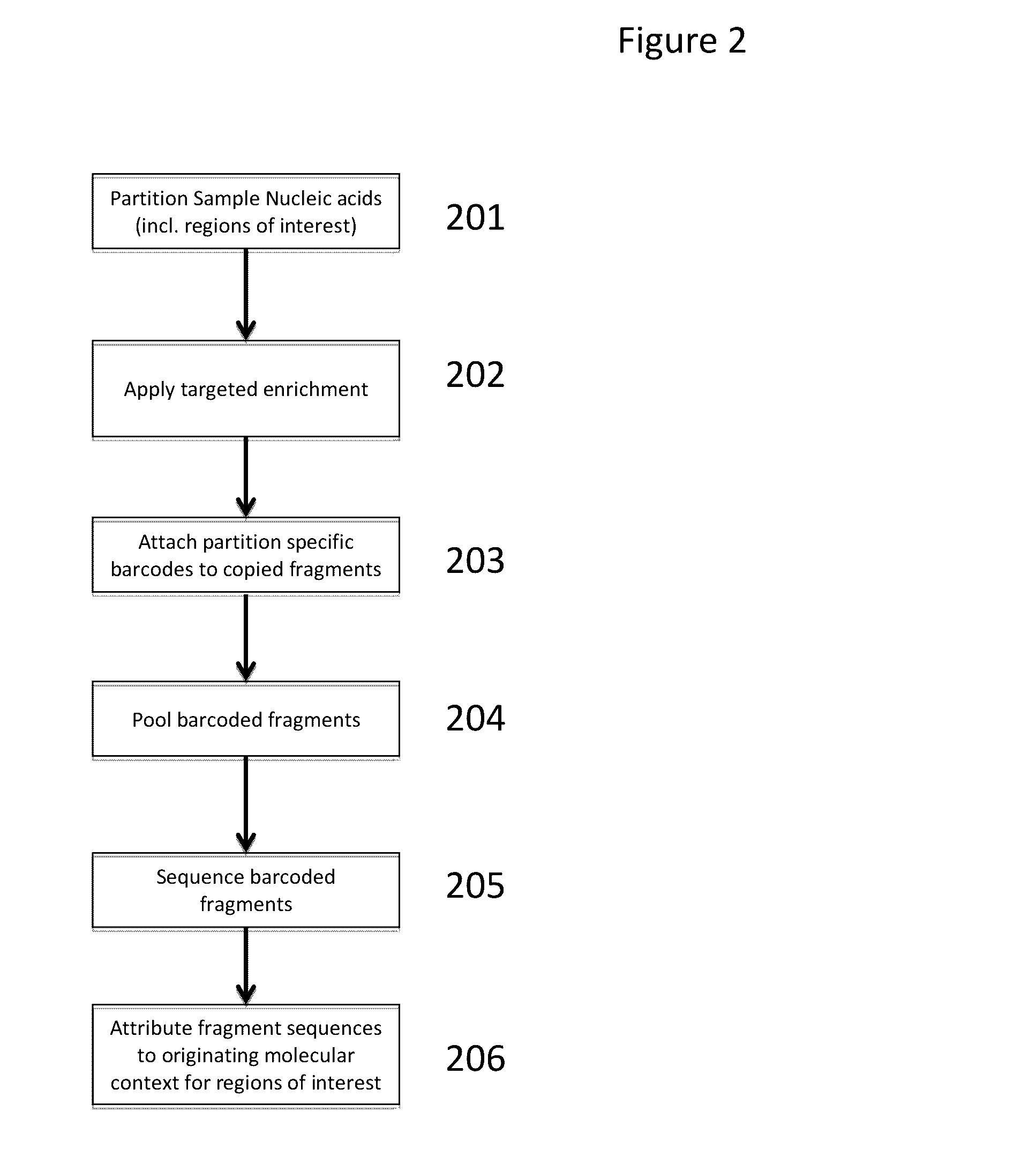
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequence coverage
ActiveUS20160281160A1Improve throughputImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genome sequenceNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and systems for analyzing sequence information from targeted regions of a genome. Such targeted regions may include regions of the genome that are poorly characterized, highly polymorphic, or divergent from reference genome sequences.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Method for detecting mononucleotide polymorphism
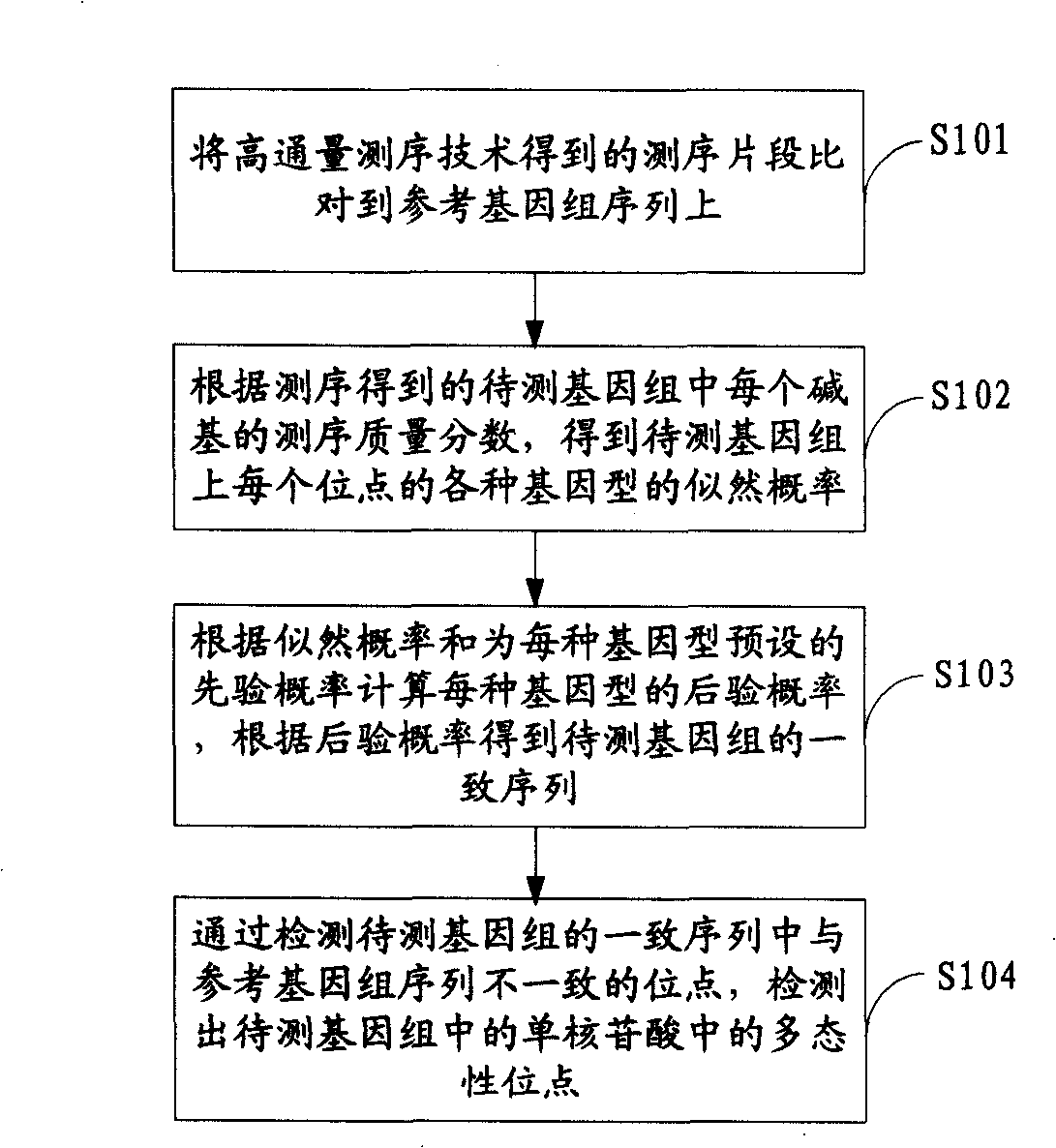
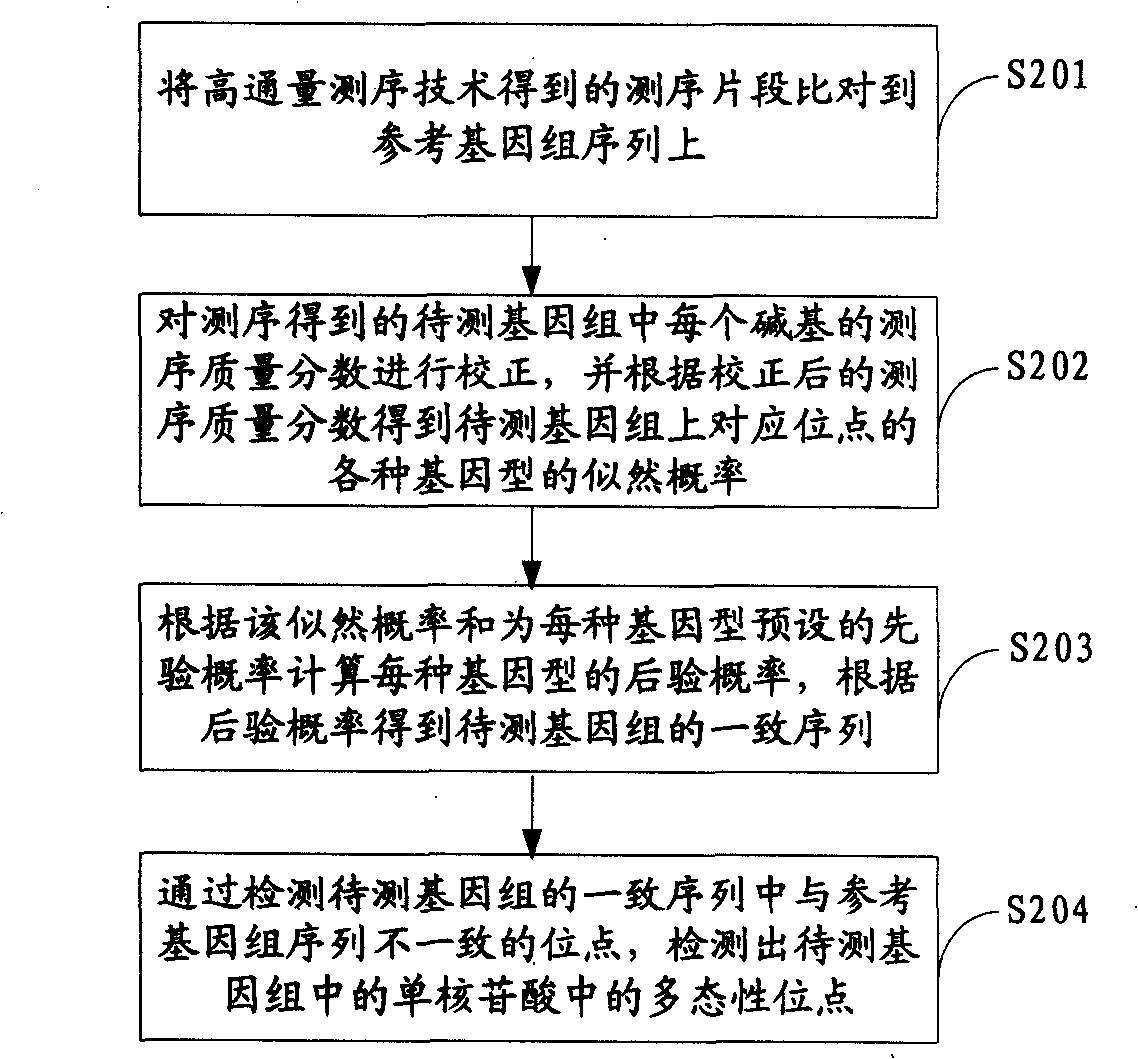
ActiveCN101539967AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGenotype determination
The invention is applicable to the field of biological engineering and provides a method for detecting mononucleotide polymorphism. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing fragments obtained by high throughput sequencing technology are compared on a referenced genome sequence; the likelihood ratio of various genotypes of the corresponding sites on the genome to be tested is obtained according to the sequencing mass fraction of each basic group in the genome to be tested and obtained by sequencing; the posterior probability of each genotype of each site on the referenced genome is calculated according to the likelihood ratio and the prior probability preset for each genotype, and the genotype which has the highest posterior probability is determined as the most likely right genotype of the corresponding sites on the genome to be tested to obtain the consistent sequence of the genome to be tested; and the sites of the genome to be tested, which are inconsistent with the sequence of the referenced genome in the consistent sequence are detected to obtain the polymorphism sites of the genome to be tested. The embodiment of the invention can achieve a more accurate test result as the influence of the prior probability on mononucleotide polymorphism test result is considered in advance.
Owner:WUHAN BGI CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
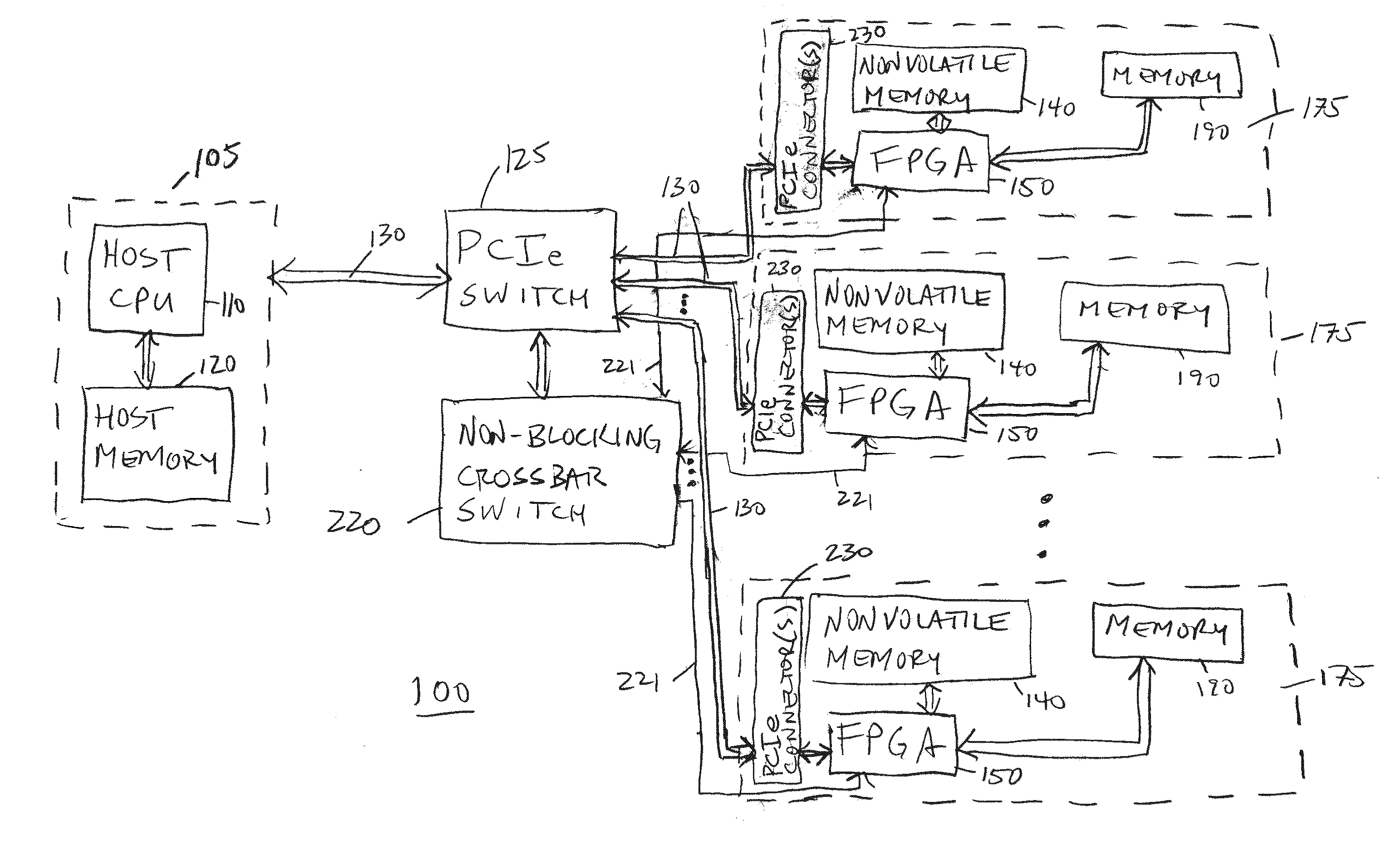
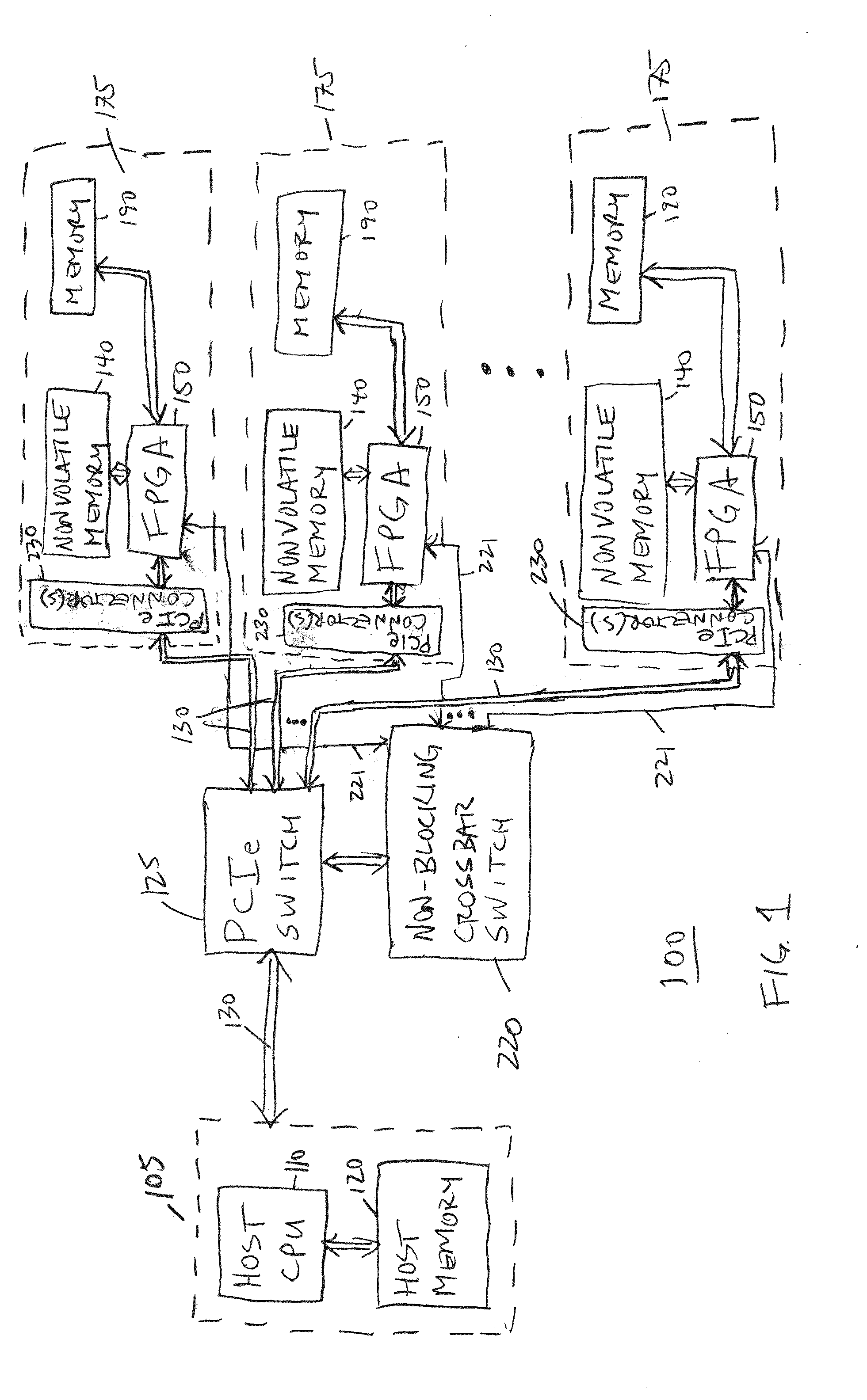
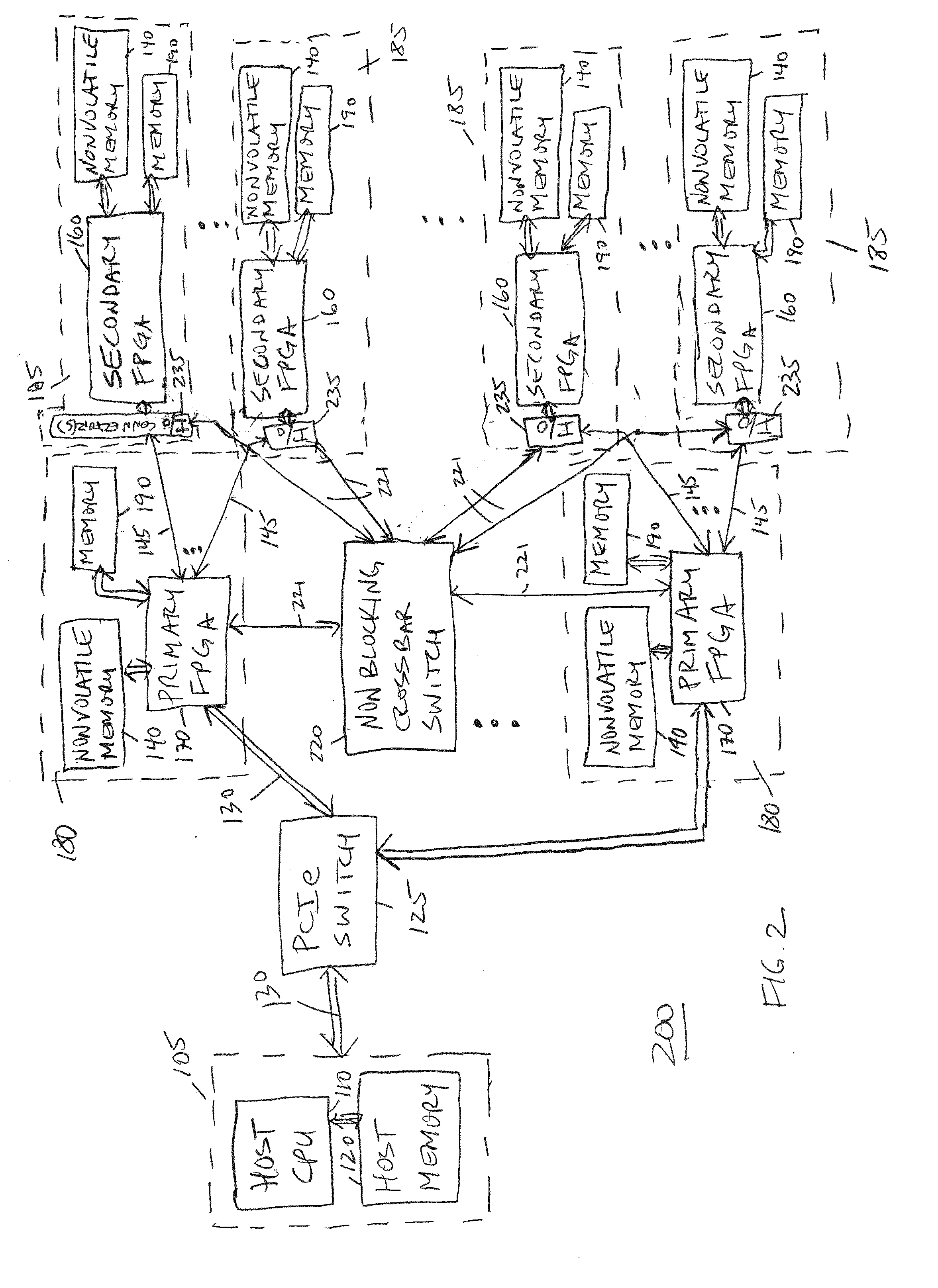
Hardware Acceleration of Short Read Mapping for Genomic and Other Types of Analyses
ActiveUS20140297196A1Reduce energy consumptionRapid genetic sequence analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingReference genome sequenceMemory circuits
A scalable FPGA-based solution to the short read mapping problem in DNA sequencing is disclosed which greatly accelerates the task of aligning short length reads to a known reference genome. A representative system comprises one or more memory circuits storing a plurality of short reads and a reference genome sequence; and one or more field programmable gate arrays configured to select a short read; to extract a plurality of seeds from the short read, each seed comprising a genetic subsequence of the short read; for each seed, to determine at least one candidate alignment location (CAL) in the reference genome sequence to form a plurality of CALs; for each CAL, to determine a likelihood of the short read matching the reference genome sequence in the vicinity of the CAL; and to select one or more CALs having the currently greater likelihood of the short read matching the reference genome sequence.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
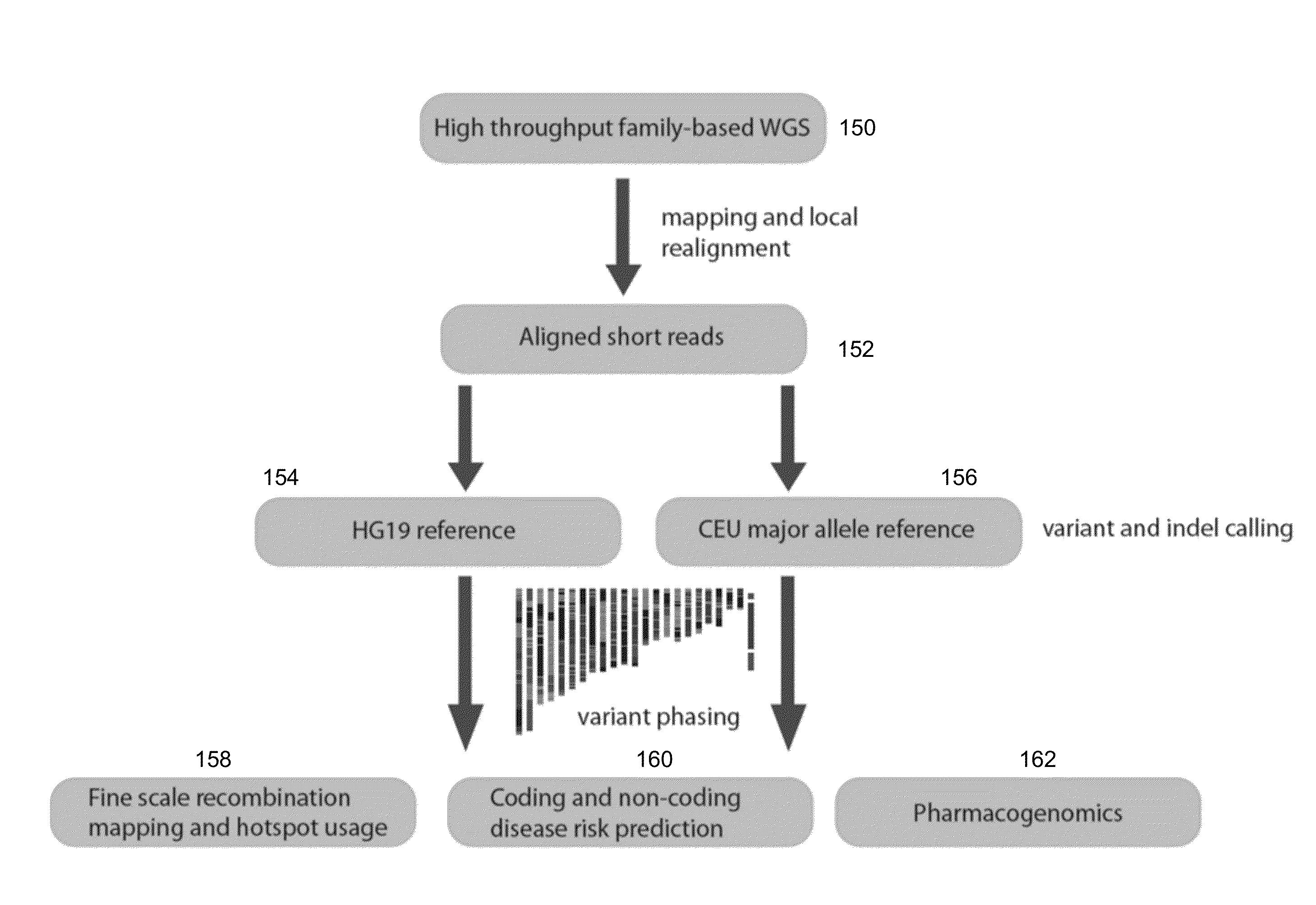
Phased Whole Genome Genetic Risk In A Family Quartet
In an embodiment of the present invention, three novel human reference genome sequences were developed based on the most common population-specific DNA sequence (“major allele”). Methods were developed for their integration into interpretation pipelines for highthroughput whole genome sequencing.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for rapid assessment of similarity between sequences
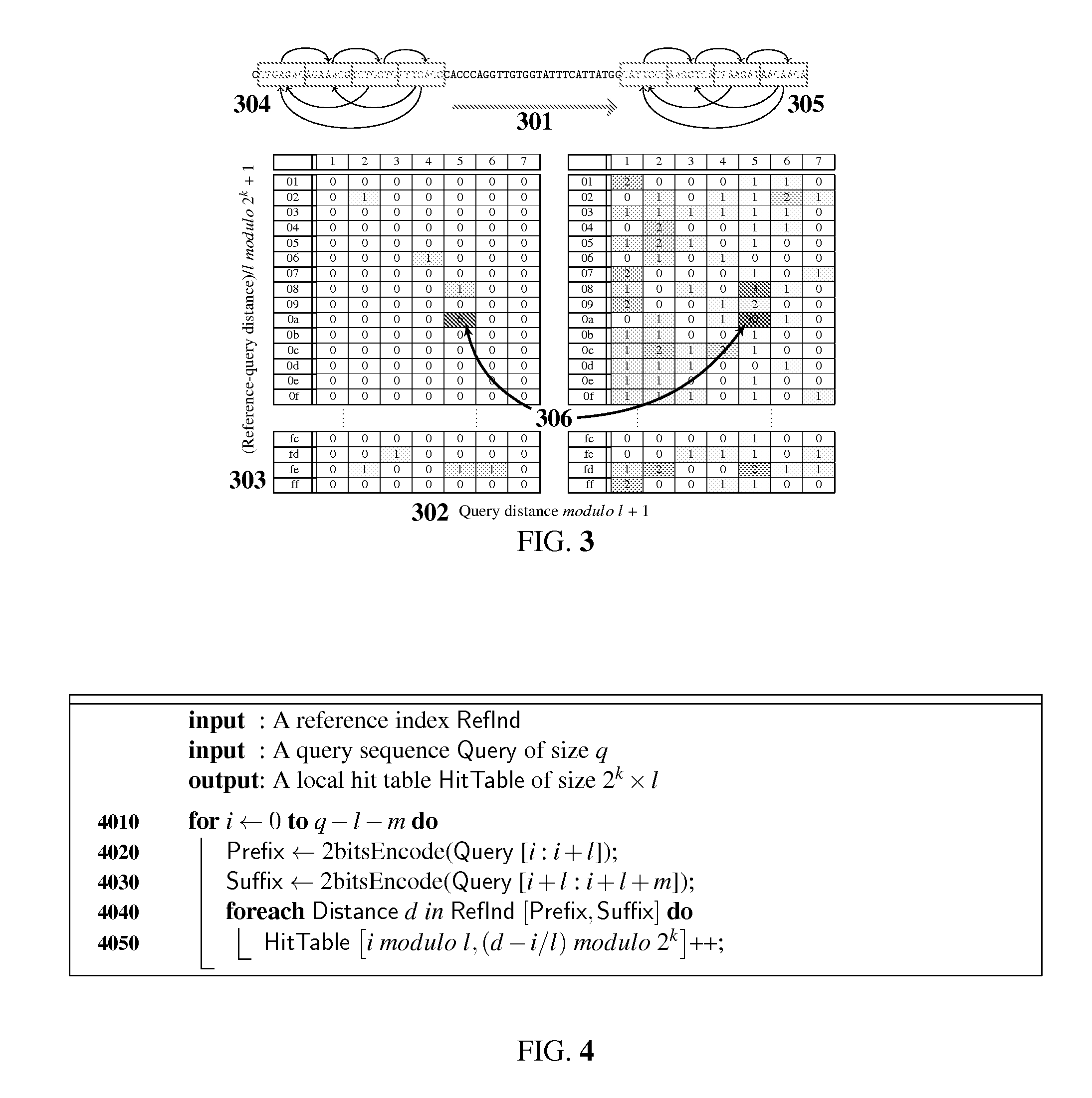
InactiveUS20130091121A1Increase query sensitivityImprove error toleranceDigital data processing detailsSequence analysisReference genome sequenceData mining
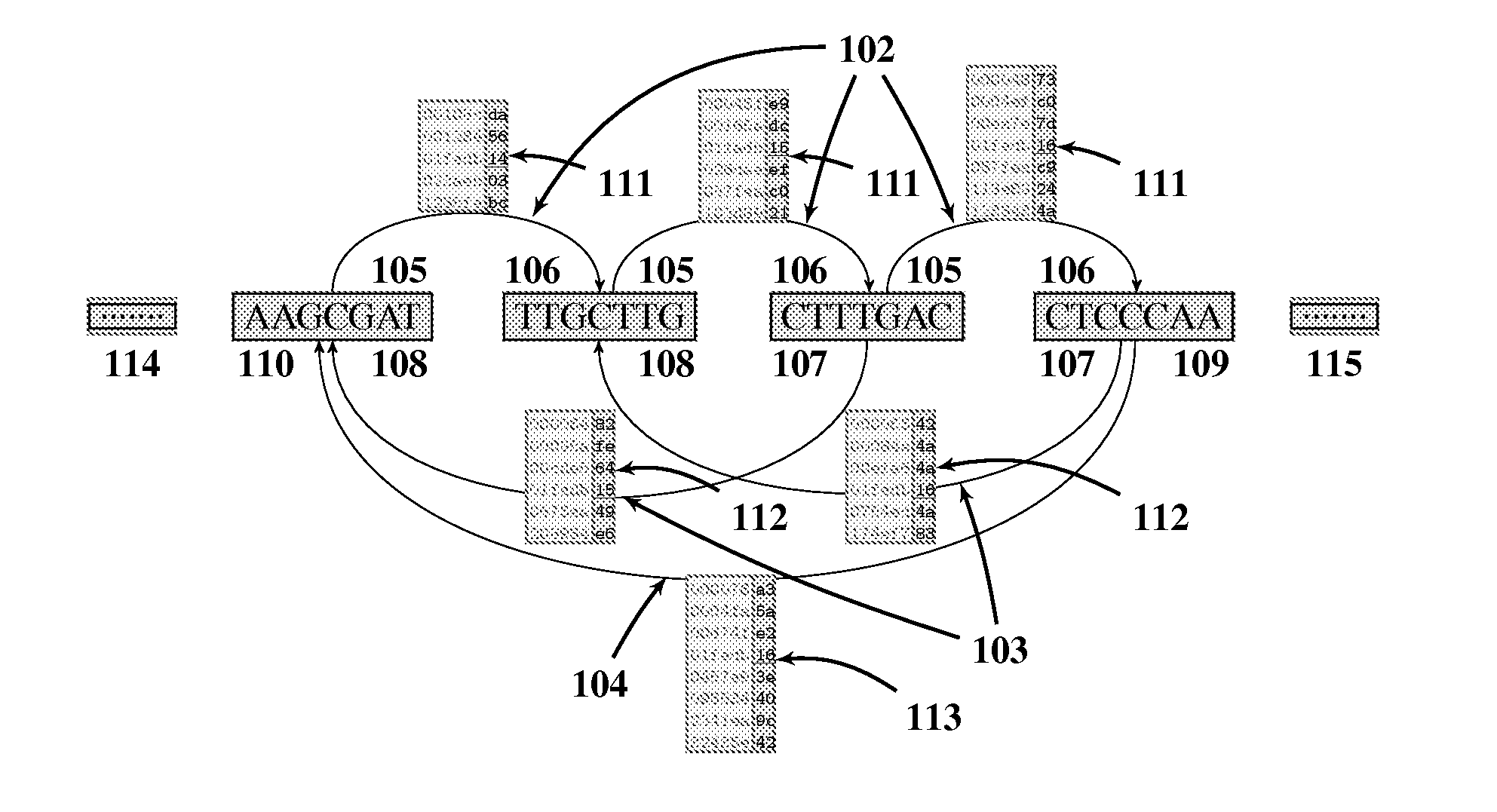
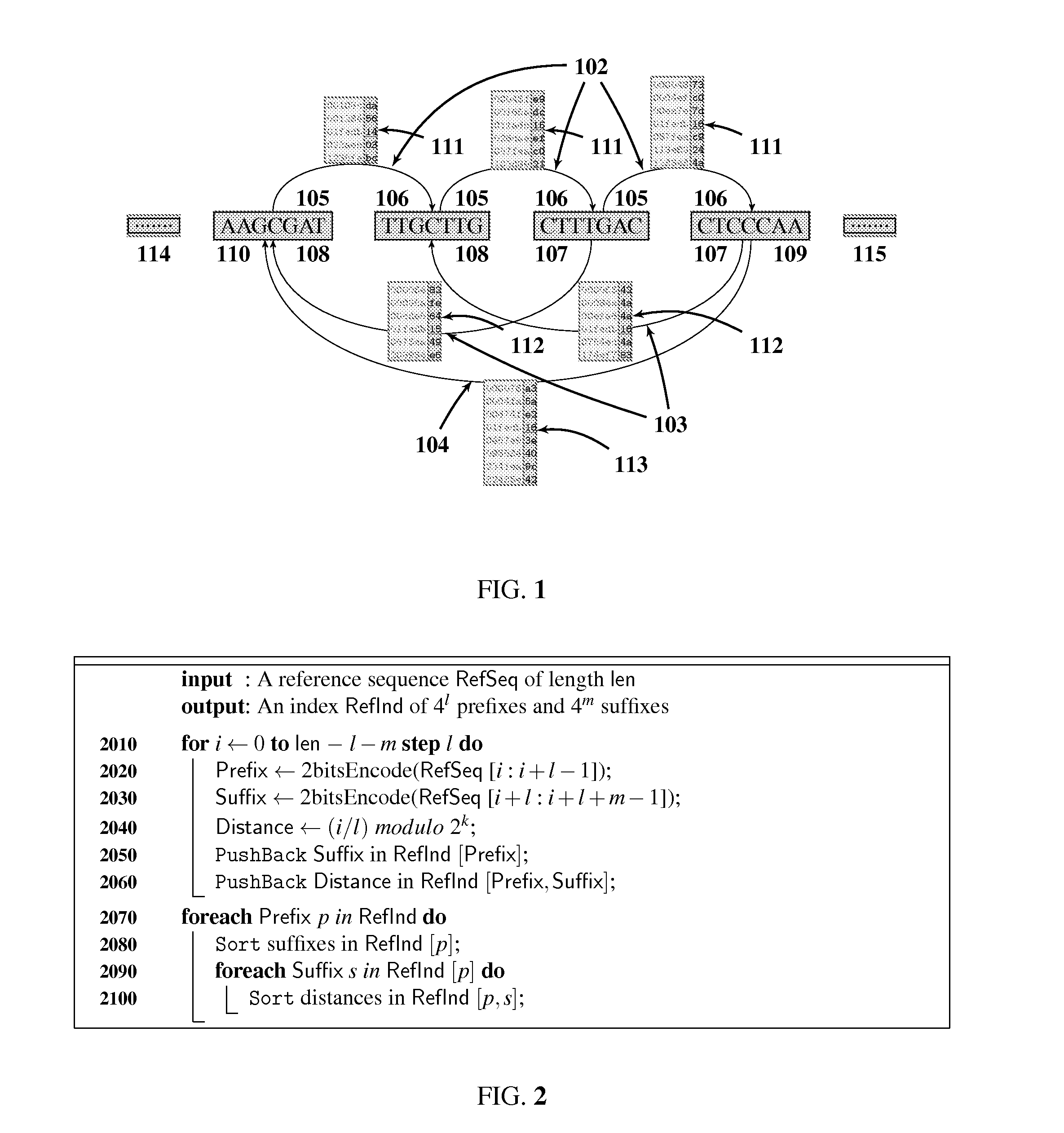
Genomic sequence matching and alignment techniques are disclosed. In one embodiment, an index of a reference sequence is constructed that represents all transitions from a single l-mer prefix to multiple m-mer suffixes. This index data structure may take a variety of forms, including an array or a tree. The base position of each transition from l-prefix to m-suffix is recorded in k-bit masked form. The positions data structure may take a variety of forms as well, including an array or a tree. The l-prefix, m-suffix and k-position index is used for rapid assessment of similarity between a query and a reference genomic sequence by means of a table of local hits.
Owner:QUALG
Method for rapidly detecting human genome single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion
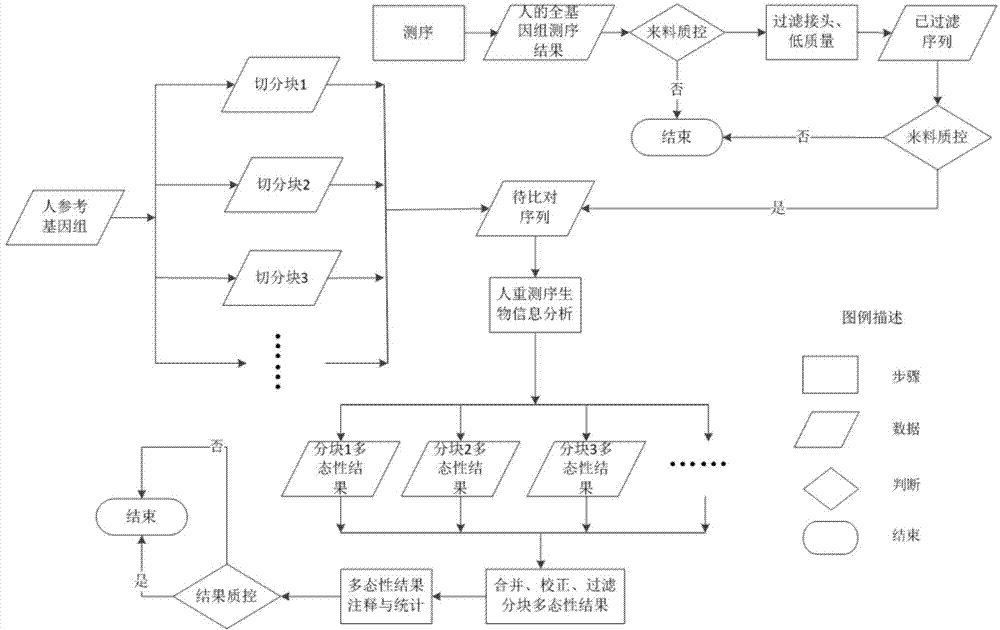
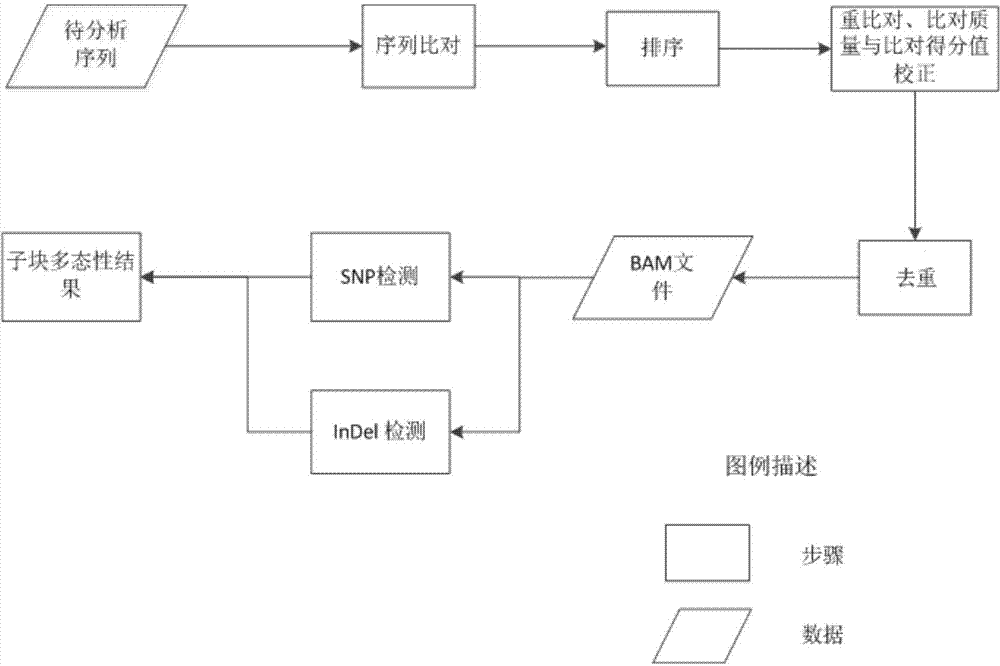
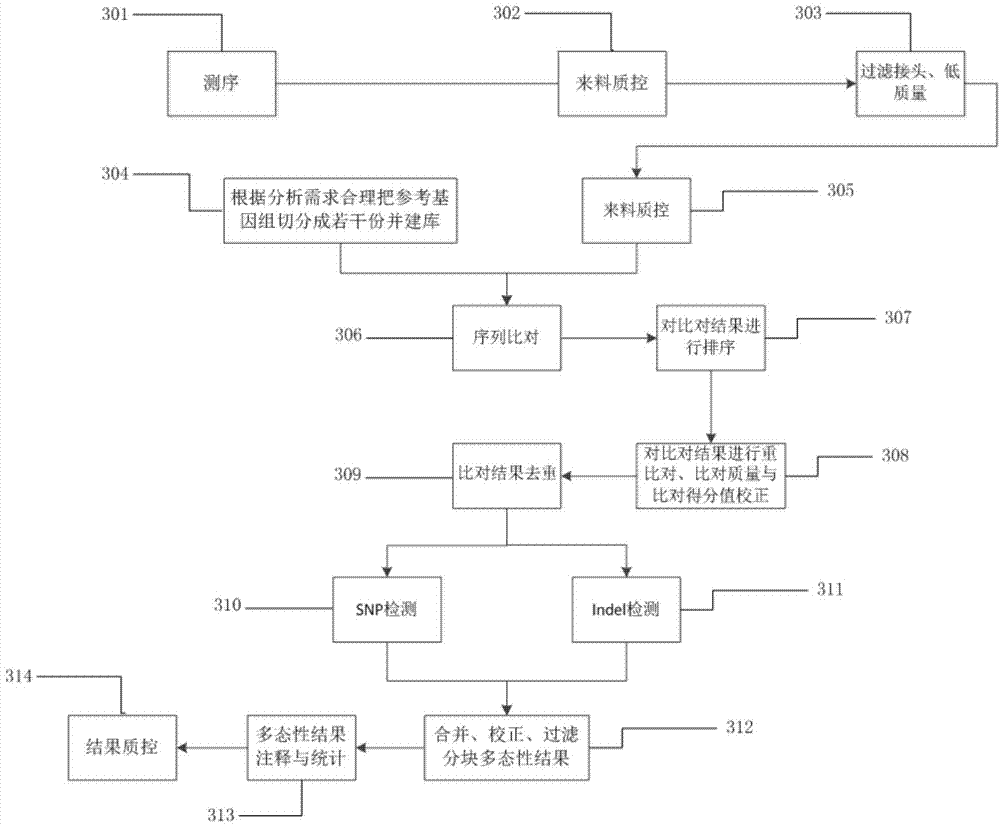
ActiveCN104762402AReduce memory requirementsShort analysis timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsInsertion deletionHuman DNA sequencing
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting human genome single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion. The method is a feasible method for rapidly detecting single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion from a human genome DNA sequencing result. According to the invention, a human reference genome sequence is scientifically and effectively split into small sub reference sequence blocks; almost all steps (including steps with relatively long analysis time) of human resequencing are divided into sub task blocks with greatly reduced computational complexity, wherein the sub task blocks do not influence each other; polymorphism information obtained from the sub reference sequence blocks is subjected to redundancy-removing, correction and filtering, such that the polymorphism information needed by an original human resequencing process is obtained. With the method provided by the invention, a problem of long human resequencing biological information analysis time is solved, and a novel analysis mode is created.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGDING INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and device for assembling genome sequence
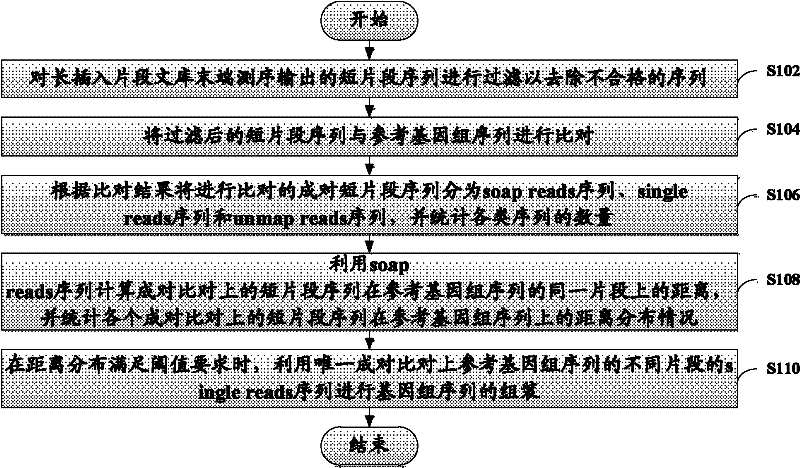
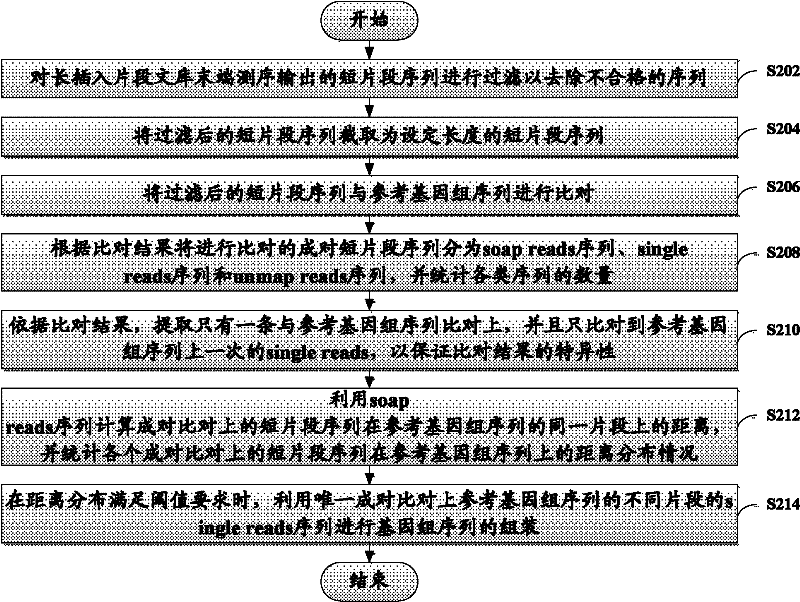
ActiveCN102206704AEasy to assembleImprove assembly efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference genome sequenceComputer science
The invention discloses a method and device for assembling a genome sequence. The method comprises the following steps: filtering short segment sequences output after long insertion segment library tail end sequencing, thereby removing unqualified sequences; comparing the short segment sequences after filtering with a reference genome sequence; dividing paired short segment sequences for comparison into soap reads sequences, single reads sequences and unmap reads sequences according to the comparison result, and making statistics on the quantity of each type of sequences; calculating the distance between the paired short segment sequences on the same segment of the reference genome sequence by utilizing the soap reads sequences, and making statistics on the distance distribution of all the paired short segment sequences on the reference genome sequence; and when the distance distribution satisfies the threshold requirement, assembling the genome sequence by utilizing the unique paired single reads sequences with different segments on the reference genome sequence.
Owner:WUXI QINGLAN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
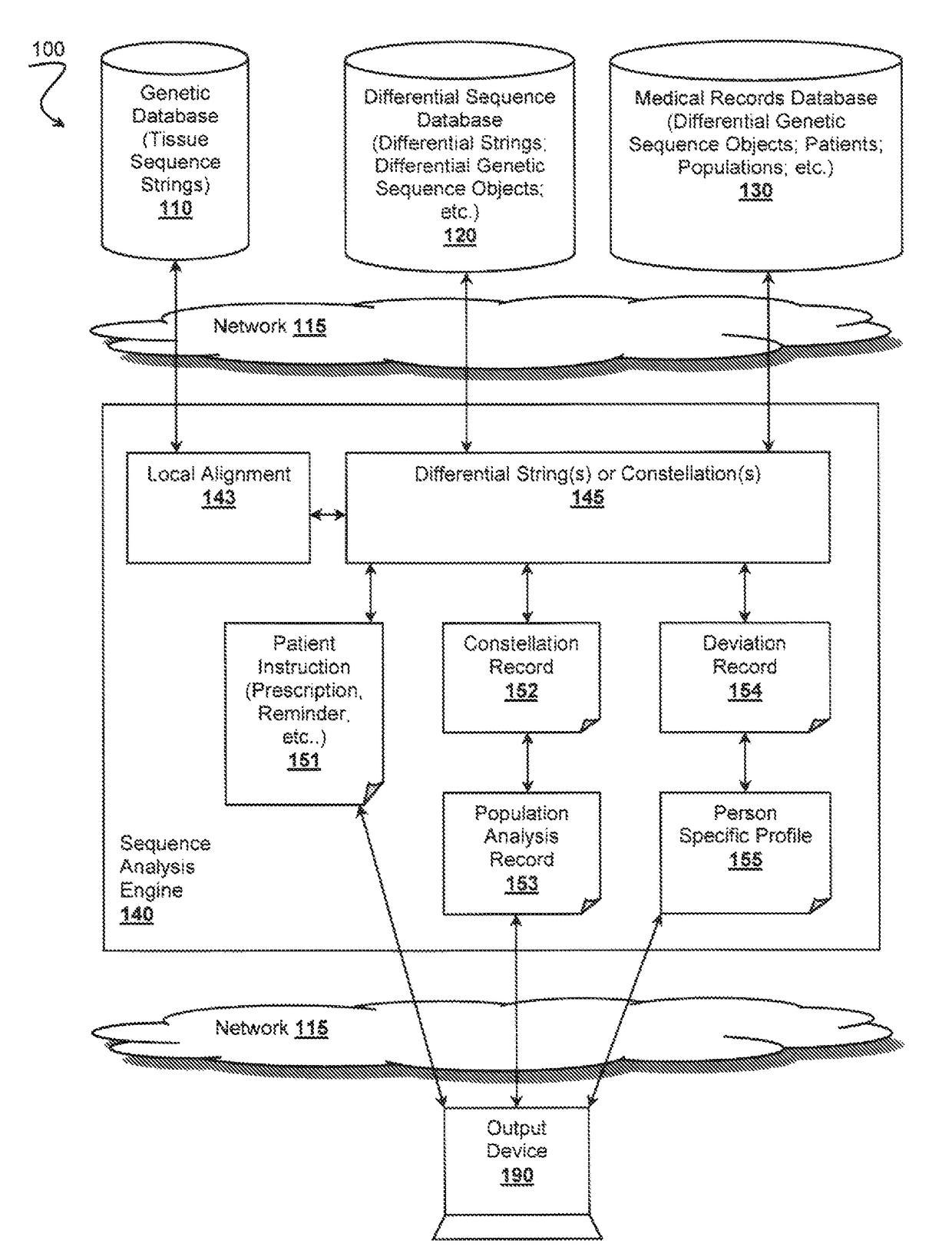
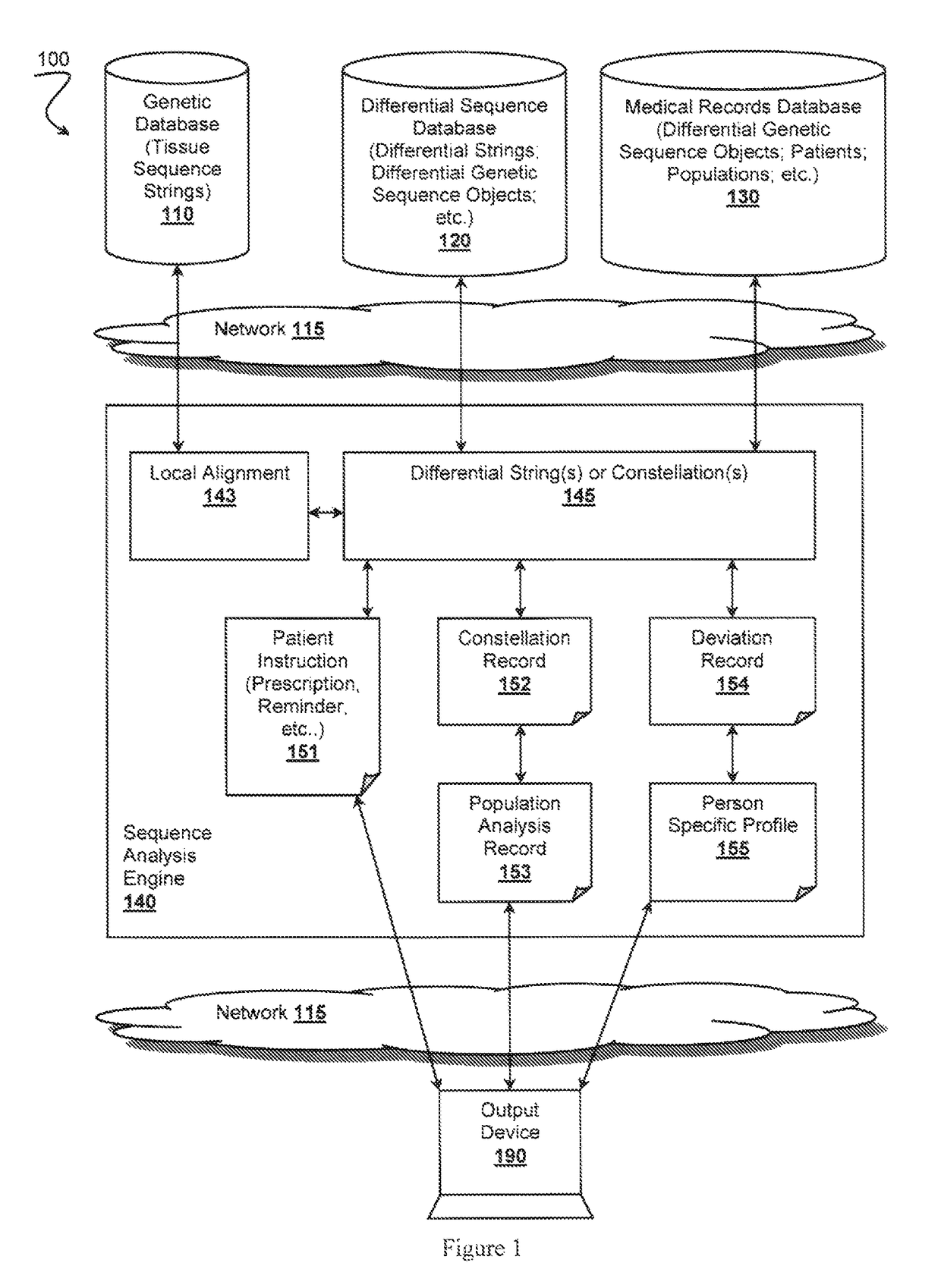
Bambam: parallel comparative analysis of high-throughput sequencing data
ActiveUS9646134B2Quick buildLow densityBiostatisticsProbabilistic networksReference genome sequenceThroughput
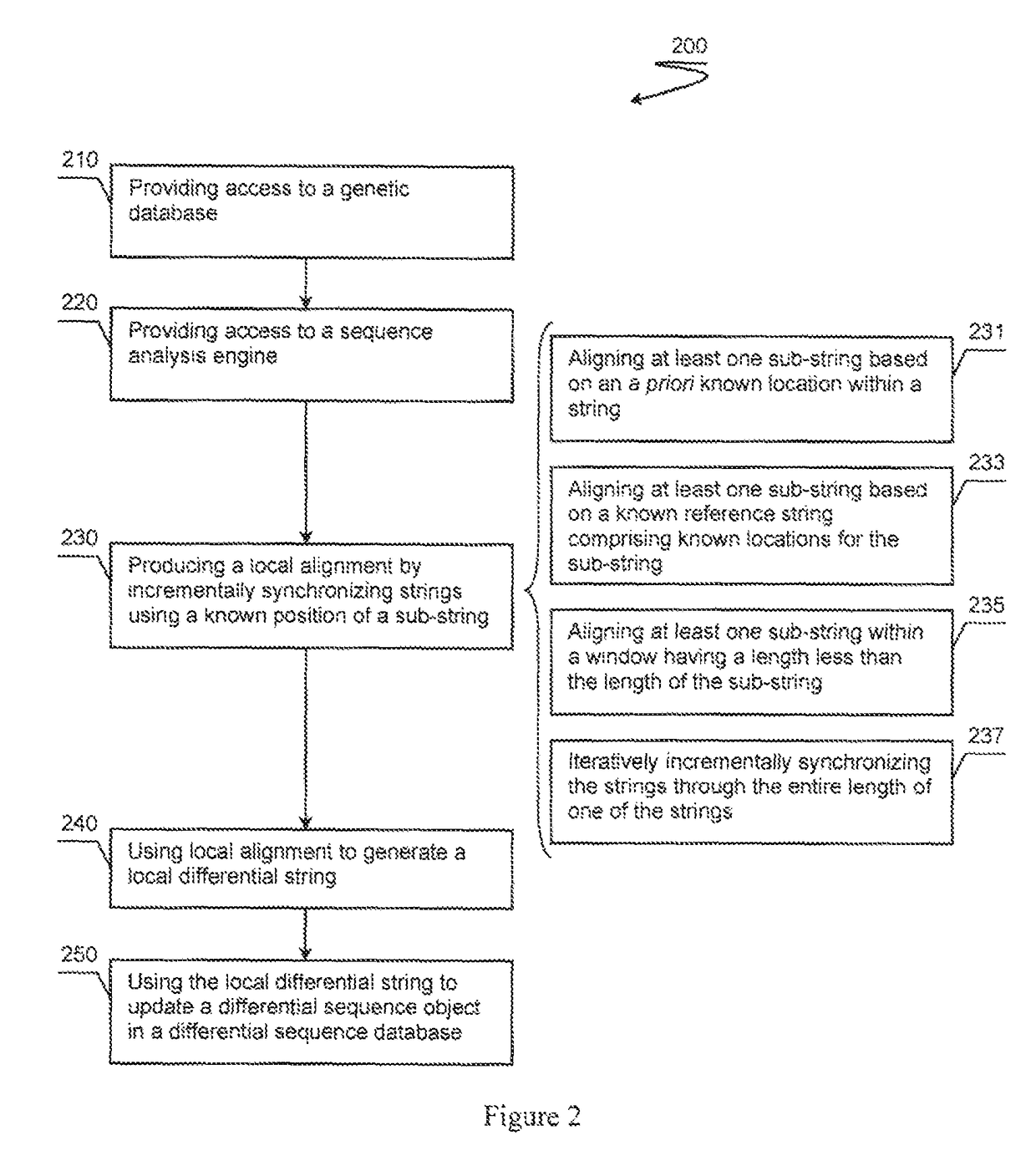
A differential sequence object is constructed on the basis of alignment of sub-strings via incremental synchronization of sequence strings using known positions of the sub-strings relative to a reference genome sequence. An output file is then generated that comprises only relevant changes with respect to the reference genome.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Detection method of chromosome copy number variation
InactiveCN105349678AOvercoming the pitfalls of noninvasive testingThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genome sequenceAbsolute volume
The invention provides a detection method of chromosome copy number variation. The detection method comprises the following steps: preparing cell-free DNA from body fluid of a parent body with an appendage and taking the cell-free DNA as a sample to be detected; preparing cell-free DNA from body fluid of a normal parent body without appendages and taking the cell-free DNA as a check sample; comparing to a reference genome sequence after all sequencing is finished; counting matching number and calculating z value; determining that cnv originates from the appendage if the length of the sample to be detected is smaller than the absolute value of the z value of a DNA sequence of N bp and greater than the absolute value of the z value of all DNA sequences of the sample to be detected in the same window; and determining that the cnv originates from the parent body if the length of the sample to be detected is not smaller than the absolute value of the z value of the DNA sequence of N bp and not greater than the absolute value of the z value of all the DNA sequences of the sample to be detected in the same window. By the detection method, whether the cnv originates from the parent body or the appendage can be judged effectively, accuracy of the result of existing non-invasive detection can be the same with that of the result of the traditional intrusion detection, loss caused by false positive is avoided effectively, and meanwhile, the detection method is easy to operate and has application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Method for detecting variable spliceosome in third generation full-length transcriptome
ActiveCN105389481AEfficient access to shear structuresPerfect commentSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGene model
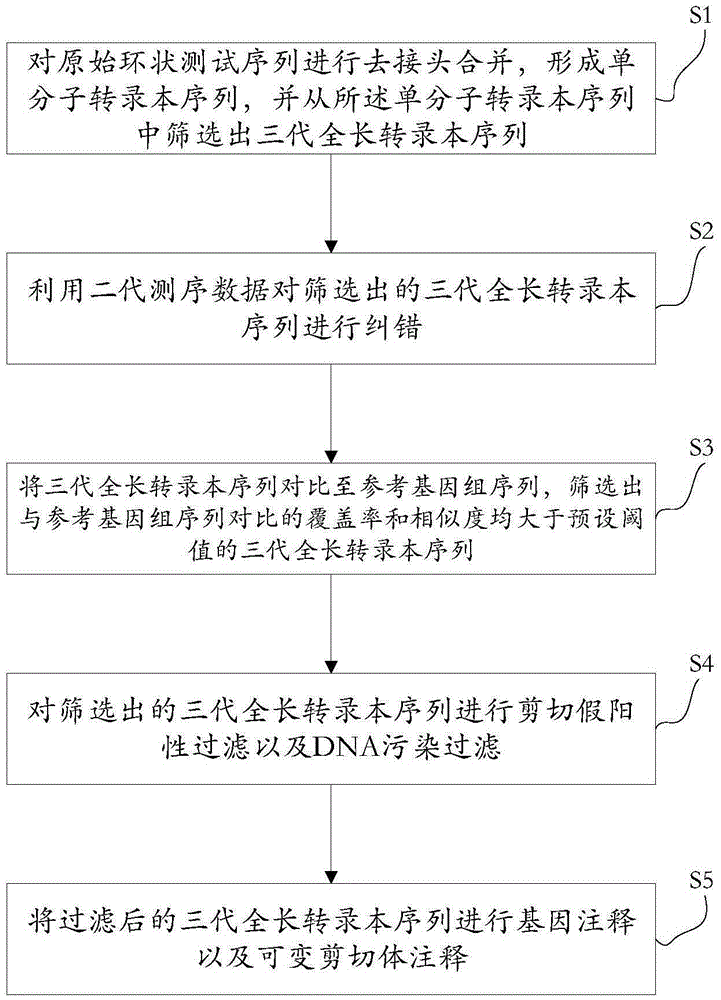
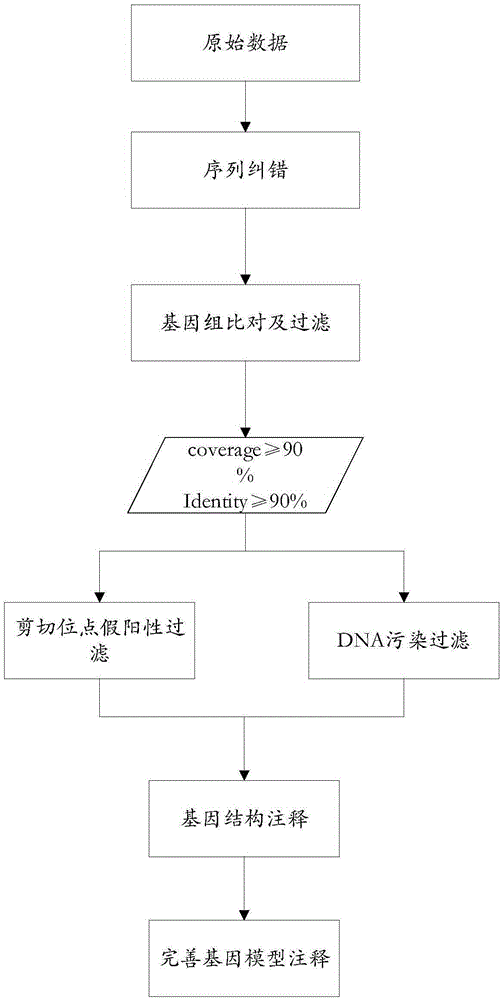
The invention discloses a method for detecting a variable spliceosome in a third generation full-length transcriptome. The method comprises the following steps: merging original annular test sequences with joints removed to form a monomolecular transcript sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence; comparing the third generation full-length transcript sequence with a reference genome sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence having coverage and similarity with the reference genome sequence larger than preset thresholds; carrying out splicing false positive filtration and DNA contamination filtration on the screened third generation full-length transcript sequence; and carrying out gene annotation and variable spliceosome annotation on the filtered third generation full-length transcript sequence. An overlong read length of a third generation sequencing technology mentioned in the method disclosed by the invention is large enough to cover most RNA, the third generation full-length transcript sequence can be obtained by SMRT sequencing transcriptomes without being assembled, and a splicing structure of a gene can be effectively obtained by third generation transcriptome sequencing, and more perfect gene model annotation can be constructed.
Owner:嘉兴菲沙基因信息有限公司
Processing method and processing device of high-throughput sequencing data, storage medium and processor
ActiveCN108280325AReduce false positive processing resultsImprove accuracySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceOriginal data
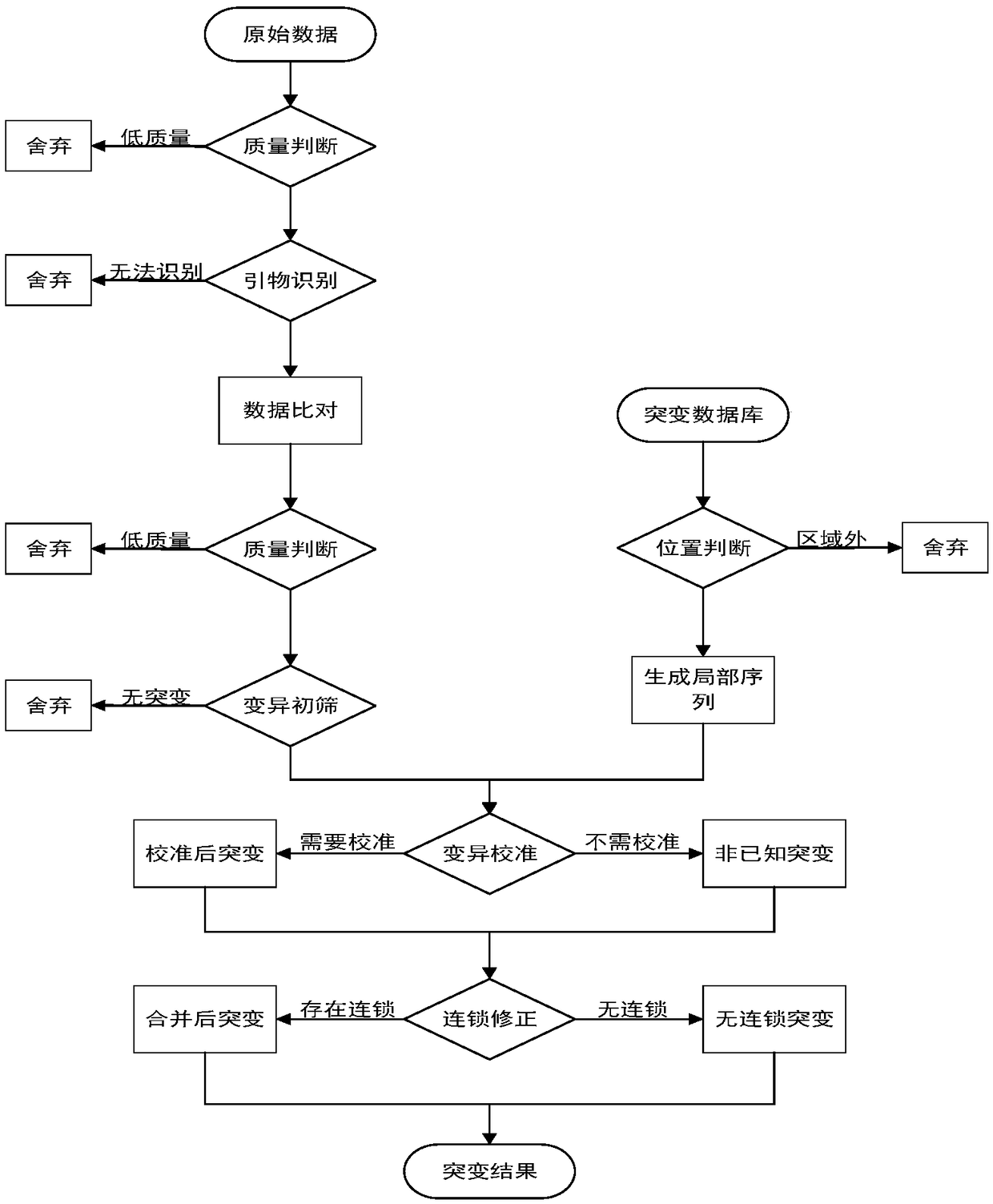
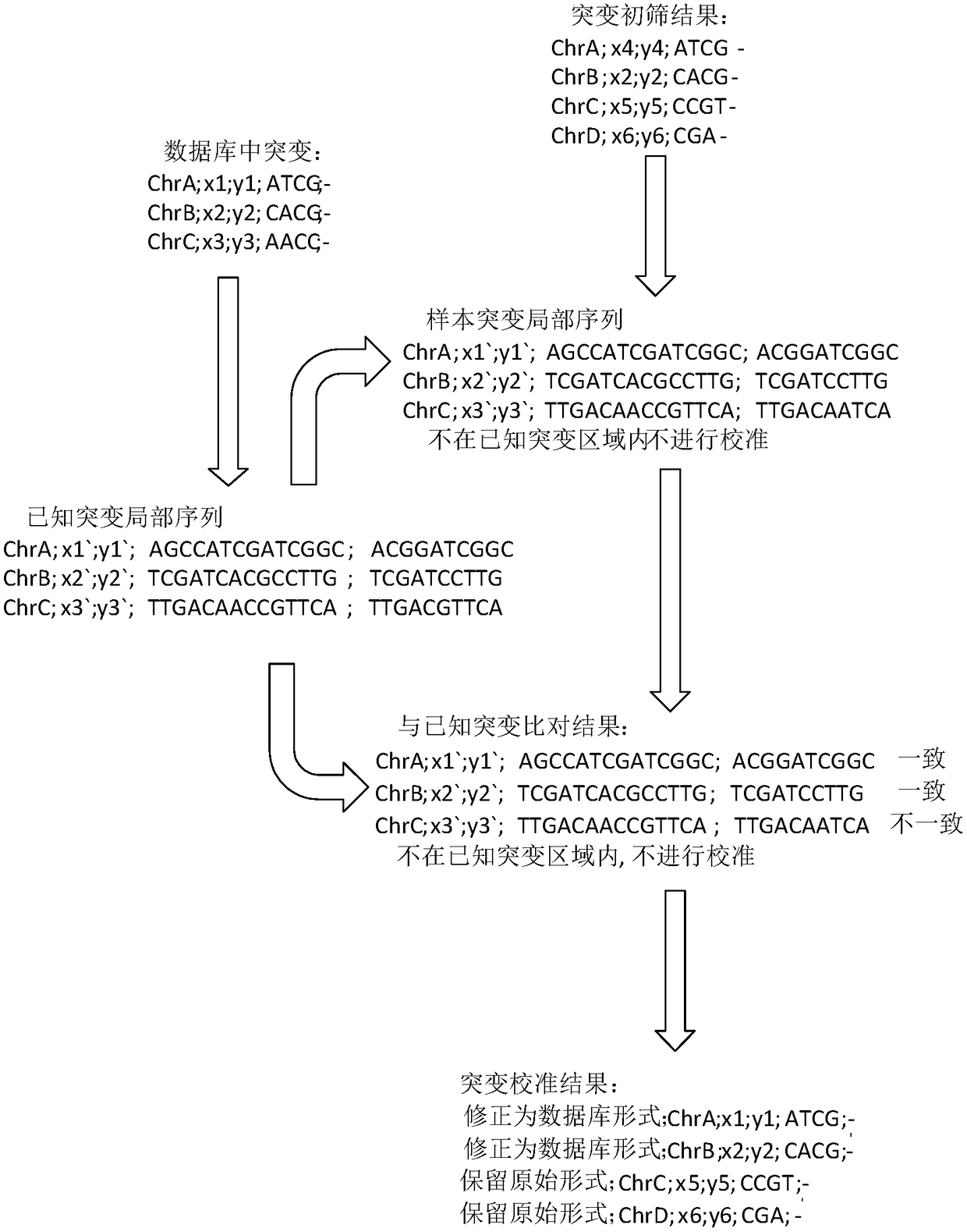
The invention provides a processing method and a processing device of high-throughput sequencing data, a storage medium and a processor. The processing method includes: acquiring secondary sequencingsequences, wherein the secondary sequencing sequences are sequencing sequences which are in the high-throughput sequencing data, can be recognized by amplification primers of a target fragment and areafter removing corresponding amplification primers; carrying out alignment on the secondary sequencing sequences and a reference genome sequence to obtain a primary variation result; and utilizing mutation data in known mutation data to correct the primary variation result to obtain a processing result. False positive processing results caused by primer mutation existing in amplification productoverlapping regions are reduced through partially removing the primers in all the sequences from the original data, which are obtained by high-throughput sequencing, according to known primer information. Certain erroneously-amplified sequences in the high-throughput sequencing data can also be removed, accuracy of subsequent analysis is improved, and decreasing of an overall data amount and improving of analysis efficiency are also facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING ACCB BIOTECH
Genomic sequence alignment method and genomic sequence alignment device
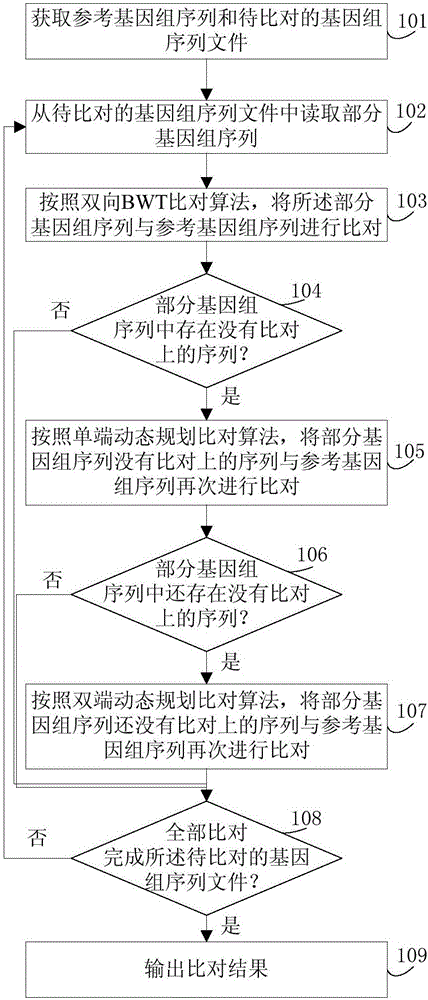
ActiveCN106682393AShorten comparison timeHigh speedProteomicsGenomicsReference genome sequenceSequence alignment algorithm
The invention discloses a genomic sequence alignment method and a genomic sequence alignment device. The method includes: reading part of genomic sequences from to-be-aligned genomic sequence files; subjecting the part of the genomic sequences and a reference genomic sequence to alignment according to a two-way BWT alignment algorithm, a single-end dynamic programming alignment algorithm and a double-end dynamic programming alignment algorithm; after alignment is finished according to any of the alignment algorithms, if no sequence failed in alignment exists in the part of the genomic sequences, reading new part of genomic sequences from the to-be-aligned genomic sequence files, and performing alignment according to the steps; repeating the steps until alignment of all of the to-be-aligned genomic sequence files is finished, and outputting alignment results. By the genomic sequence alignment method and the genomic sequence alignment device, problems of high time consumption, low processing speed and high resource consumption of the genomic sequence alignment algorithms can be solved.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
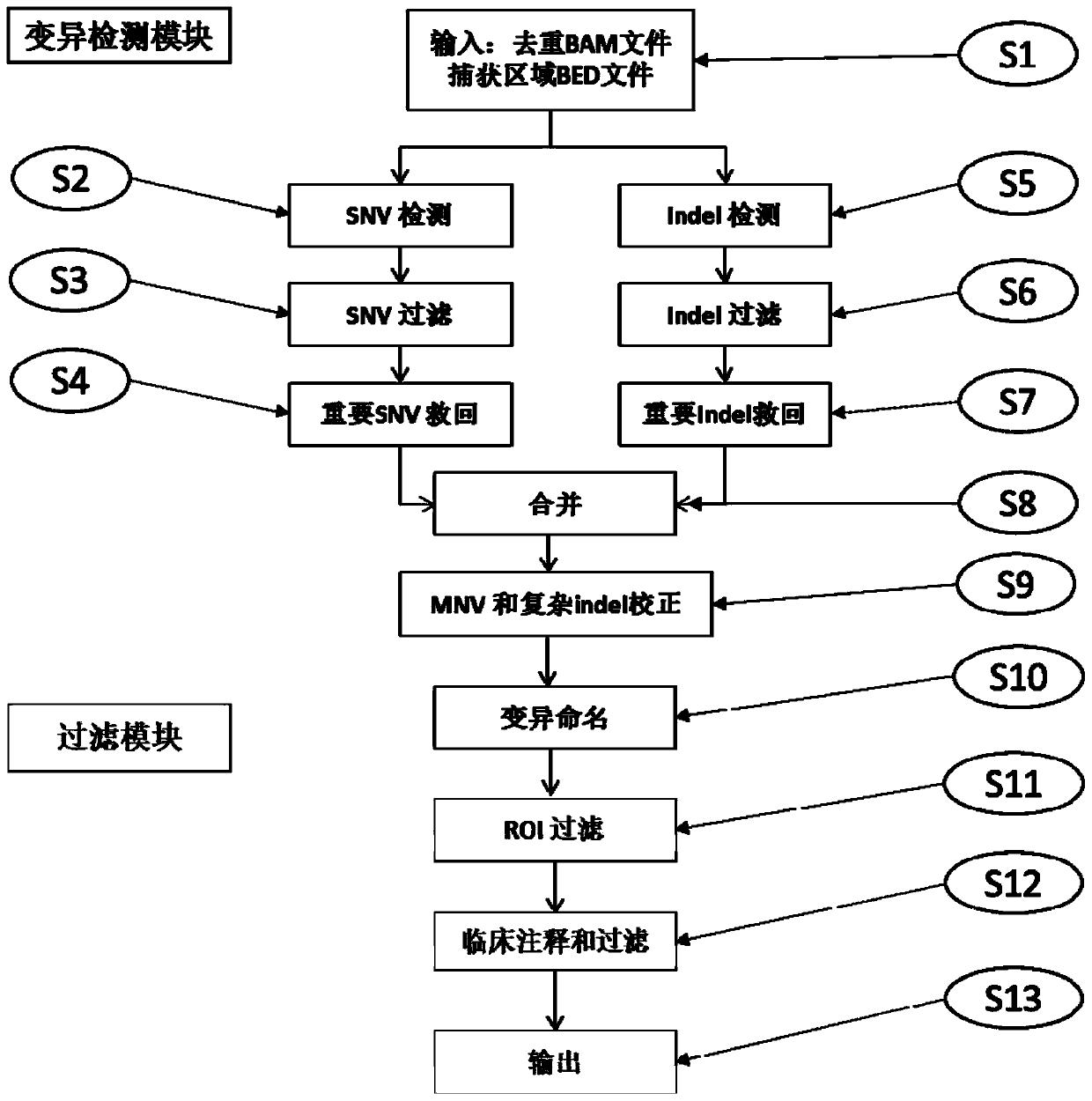
Method for detecting mutation, electronic equipment and computer storage medium
The invention relates to a method for detecting mutation, electronic equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring comparison result information about asequence of a to-be-detected sample and a reference genome sequence, wherein the to-be-detected sample comprises at least one of a to-be-detected blood sample and a to-be-detected tissue sample; basedon the comparison result information, generating mutation site base information, wherein the mutation site base information comprises at least one of base mass and comparison quality; extracting feature values of mutation site base information based on a prediction model, the prediction model being generated by machine learning of a plurality of training samples; and predicting mutation information based on the extracted feature value. According to the invention, the mutation detection efficiency and accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
Wheat BSR-Seq gene locating method
ActiveCN106202995ALow costHigh precisionSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceAllele frequency
The invention discloses a wheat BSR-Seq gene locating method. The wheat BSR-Seq gene locating method comprises the following steps of: constructing and sequencing mixing pools, performing quality variation mining, screening a transcript tightly linked to a target gene, developing and locating a molecular marker, etc. The next-generation transcriptome sequencing technology (transcriptome sequencing, RNA-Seq) and a mixing pool technology (Bulked Segregant Analysis BSA) are combined; a wheat sequencing draft sequence is used as a reference sequence at first; then, a lot of high-quality SNP heritable variations on the transcript is mined at high throughput by adopting the next-generation sequencing technology; the allele frequency is precisely calculated in combination with the mixing pool technology, so that the transcript tightly linked to the target gene possibly can be rapidly screened out; false positive is precisely checked and controlled through Fish; the method is independent of a reference genomic sequence, low in cost, rapid and high in precision; the wheat gene locating efficiency and precision are increased; the wheat polymorphic molecular marker developing cost is reduced; therefore, the wheat gene fine locating working time is reduced to several months from several years; the locating precision is reduced to a fraction or 0 cM from several cM; and the fine locating cost is reduced to several thousands from several ten thousands.
Owner:北京麦美瑞生物科技有限公司
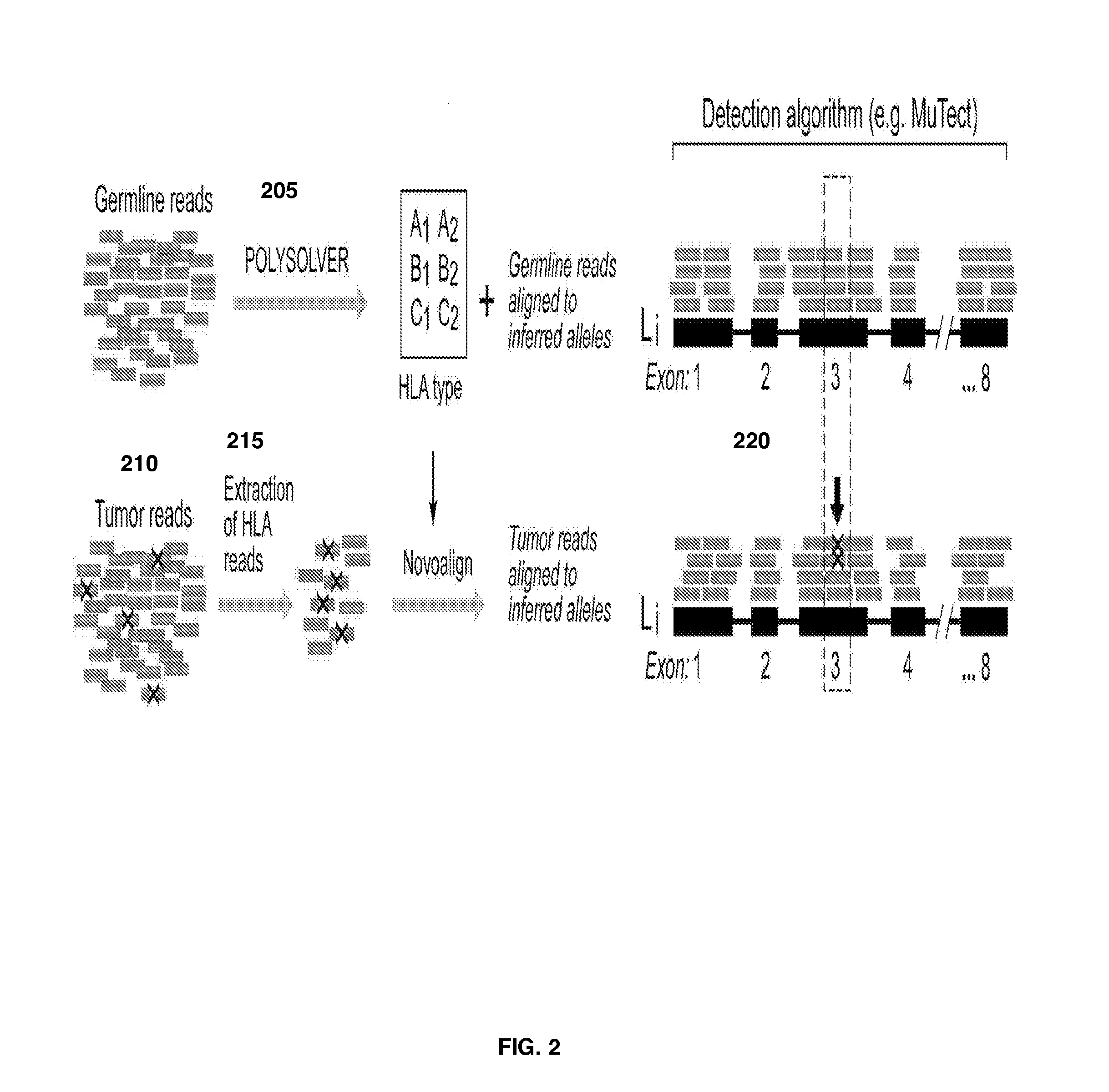
Polymorphic gene typing and somatic change detection using sequencing data
ActiveUS20160298185A1High affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsReference genome sequenceData set
A system and method for determining the exact pair of alleles corresponding to polymorphic genes from sequencing data and for using the polymorphic gene information in formulating an immunogenic composition. Reads from a sequencing data set mapping to the target polymorphic genes in a canonical reference genome sequence, and reads mapping within a defined threshold of the target gene sequence locations are extracted from the sequencing data set. Additionally, all reads from the set data set are matched against a probe reference set, and those reads that match with a high degree of similarity are extracted. Either one, or a union of both these sets of extracted reads are included in a final extracted set for further analysis. Ethnicity of the individual may be inferred based on the available sequencing data which may then serve as a basis for assigning prior probabilities to the allele variants. The extracted reads are aligned to a gene reference set of all known allele variants. The allele variant that maximizes a first posterior probability or posterior probability derived score is selected as the first allele variant. A second posterior probability or posterior probability derived score is calculated for reads that map to one or more other allele variants and the first allele variant using a weighting factor. The allele that maximizes the second posterior probability or posterior probability score is selected as the second allele variant.A system and method for identifying somatic changes in polymorphic loci using WES data. The exact pair of alleles corresponding to the polymorphic gene are determined as described using a normal or germline sample from an individual. A tumor or otherwise diseased sample is also retrieved from the individual and the corresponding WES data is generated. Reads corresponding to the polymorphic gene are extracted as described in the paragraph above. These reads are then aligned to the inferred pair of allele sequences. The alignment of the germline or normal reads to the inferred pair of alleles, along with the alignment of the tumor or diseased reads to the inferred pair of alleles are simultaneously used as inputs to somatic change detection algorithms to identify somatic changes with greater precision and sensitivity.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +2
Tumor mutation analysis method and system, terminal and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110570904APrecision therapyAutomatic detectionProteomicsGenomicsInsertion deletionGenomic sequencing
A tumor mutation analysis method based on next-generation sequencing is characterized by comprising filtering a sample genome sequencing sequence; comparing the filtered sample genome sequencing sequence with a reference genome sequence; controlling the tumor sample comparison quality, wherein the type of the tumor sample is one of a tumor single sample or a tumor / control paired sample; performingsingle nucleic acid variation detection and insertion deletion marker detection according to the type of the tumor sample; and performing fusion detection according to the type of the tumor sample. The present invention provides an automated process for tumor variation biological information analysis, which can quickly and automatically detect variation markers such as SNV (single nucleic acid variation), indel (insertion deletion marker), fusion, CNV (gene copy number variation), TMB (tumor mutation load) and MSI, can obtain more information about the precise target of tumor treatment, and provides more help for patients to select targeted drugs with potential benefits.
Owner:深圳百诺精准医疗科技有限公司
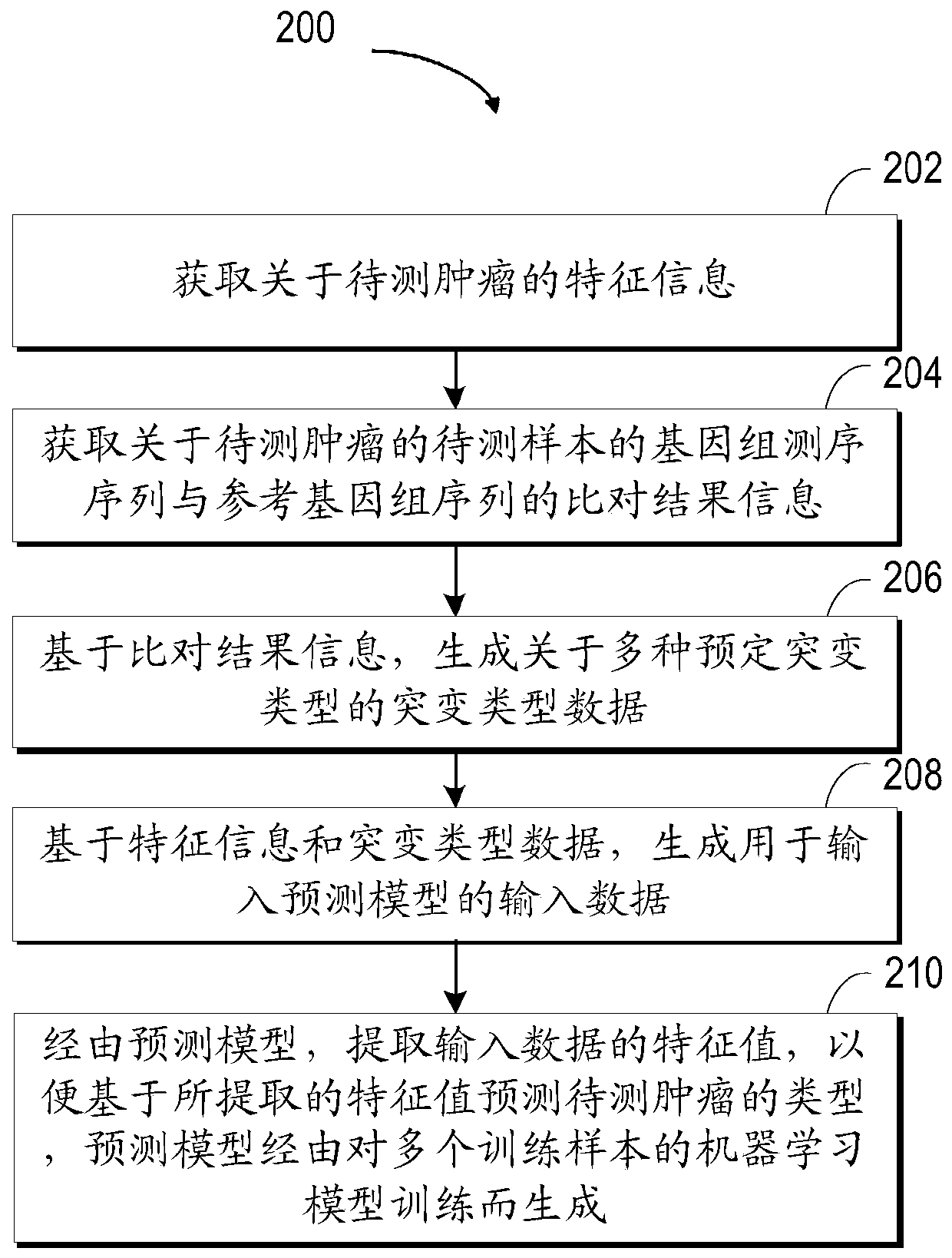
Method for predicting the type of tumors, electronic apparatus, and computer storage medium
The invention relates to a method for predicting the type of tumors, an electronic apparatus, and a computer storage medium. The method includes following steps: 1) acquiring the feature information of to-be-detected tumors; 2) acquiring the comparing result information between the genome detected sequence and reference genome sequence of a to-be-detection sample of the to-be-detected tumors; 3) based on the comparing result information, generating mutation type data related to the various preset mutation types; 4) based on the feature information and the mutation type data, generating the input data for inputting a prediction model; 5) through the prediction model, extracting a feature value of the input data, and predicting the type of the to-be-detection tumors on the basis of the extracted feature value, wherein the prediction model is generated by training machine learning models of a plurality of training samples. The disclosure is used for improving the prediction accuracy on the type of tumors in primary sites.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
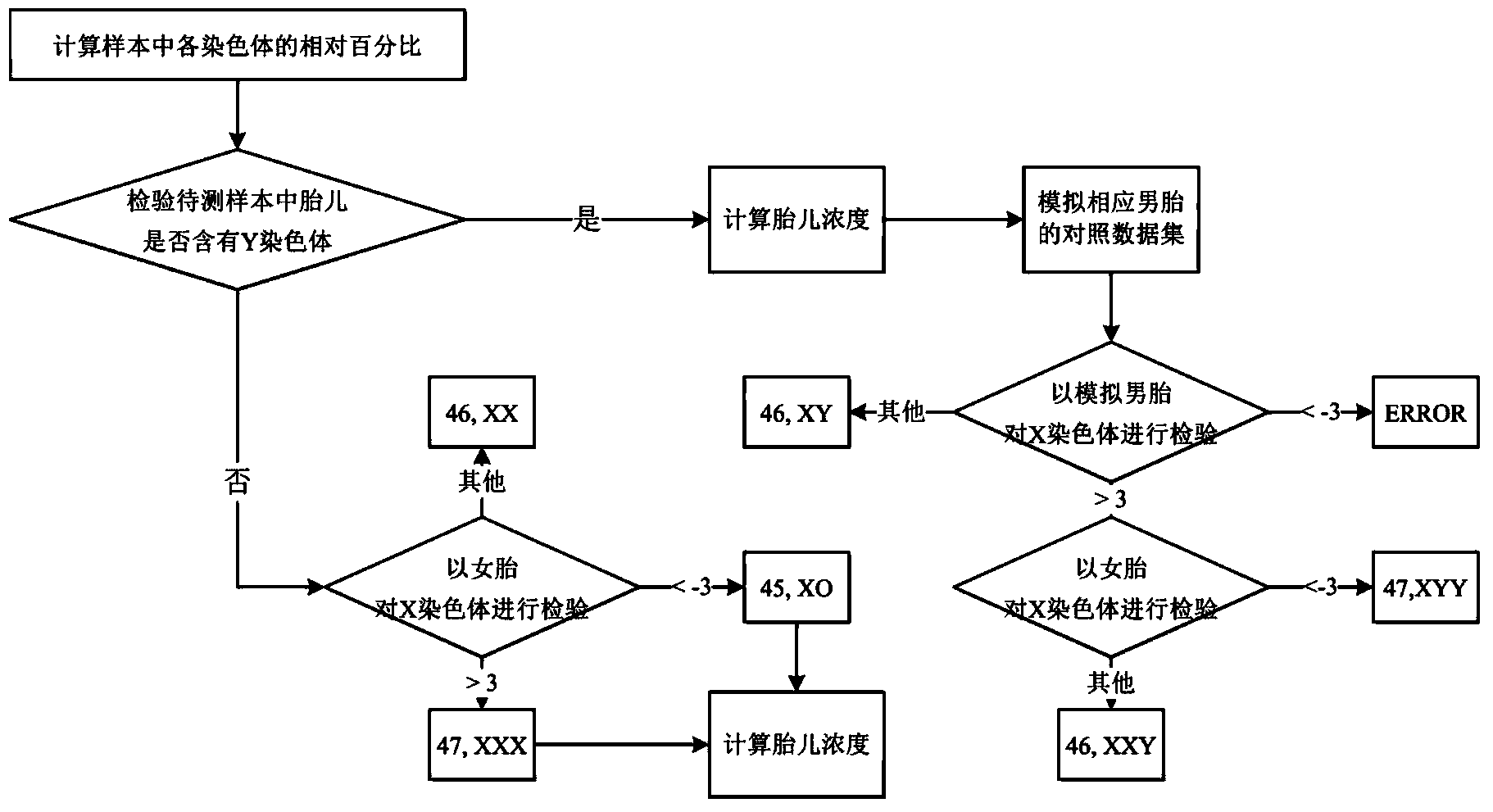
Method used for determining whether the number of sex chromosomes of fetus is abnormal, system and computer readable medium
ActiveCN104169929AAccurate and effective determinationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsReference genome sequenceX chromosome
A method used for determining whether the number of sex chromosomes of fetus is abnormal, system and computer readable medium are provided. The method used for determining whether the number of sex chromosomes of fetus is abnormal, comprises the steps of: performing nucleic acid sequence detection for a pregnant woman sample containing nucleic acid of a fetus, so as to obtain a plurality of sequence detection data; comparing the sequence detection data with reference genome sequence of human, so as to obtain comparison sequence detection dataset; determining the number Q of comparison sequence detection data contained in the comparison sequence detection dataset; determining the number Ni of sequence detection data from i-th chromosome in the comparison sequence detection dataset, wherein i represents the serial number of the chromosome, the i-th chromosome at least comprises a Y chromosome and an optional X chromosome; determining sex of the fetus on the basis of the number Ny of the sequence detection data from the Y chromosome; and determining whether the number of sex chromosomes of the fetus is abnormal.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
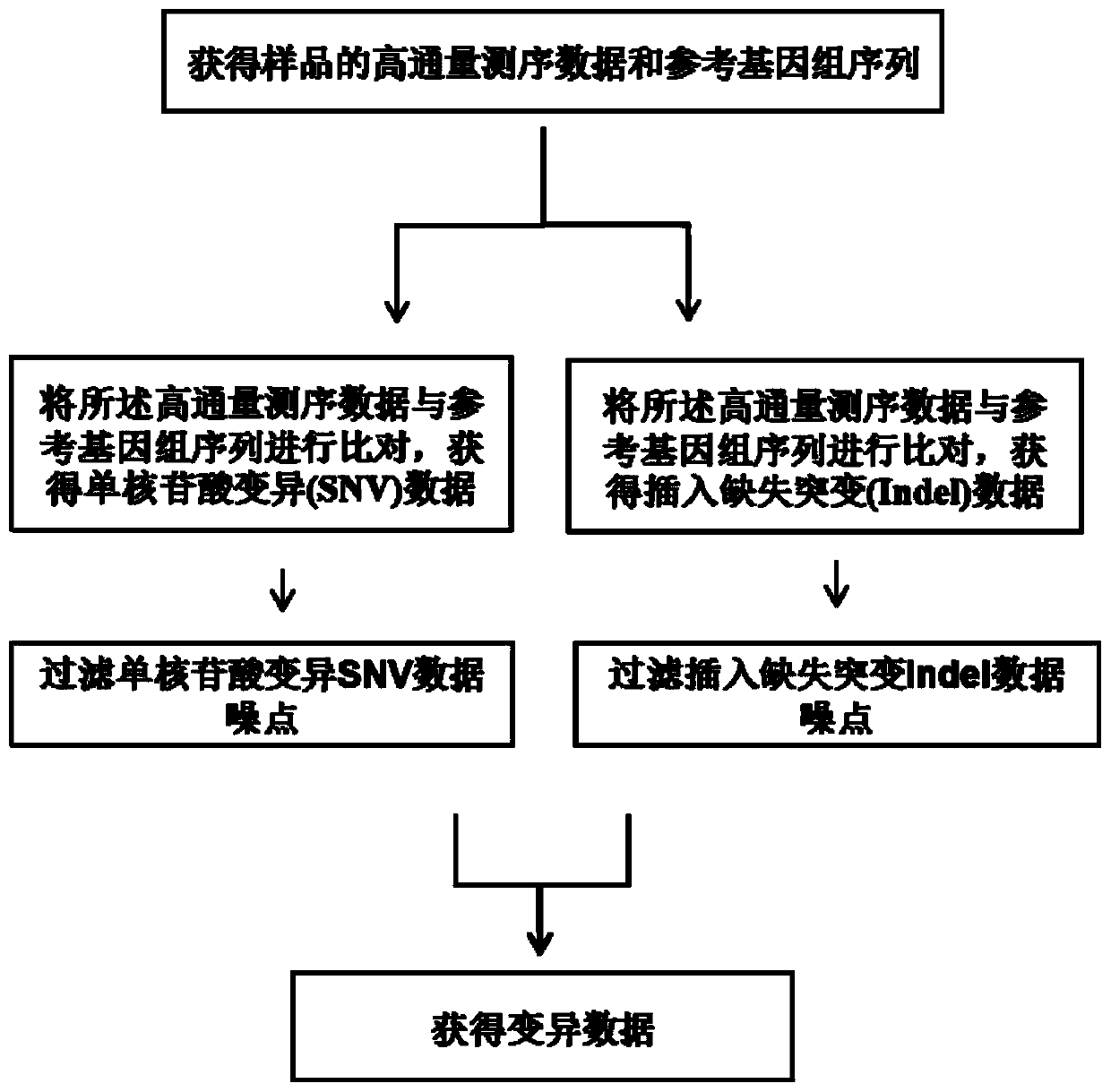
High-flux sequencing data analysis method and device
ActiveCN109767810AAccurate calculationVariation detection is fastProteomicsGenomicsInsertion deletionReference genome sequence
The invention relates to a high-flux sequencing data analysis method and a device. The high-flux sequencing data analysis method comprises the steps of acquiring high-flux sequencing data of a sampleand a reference genome sequence, comparing the high-flux sequencing data with the reference genome sequence, and respectively acquiring locus data of single nucleotide variation (SNV) and locus data of insertion deletion mutation (Indel), and respectively filtering noise points of the SNV data and the Indel data through comparing the difference substantial degrees of the variation and the background, thereby obtaining the variation data. The invention further provides a device for analyzing the high-flux sequencing data and a computer-readable storage medium for storing instructions.
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
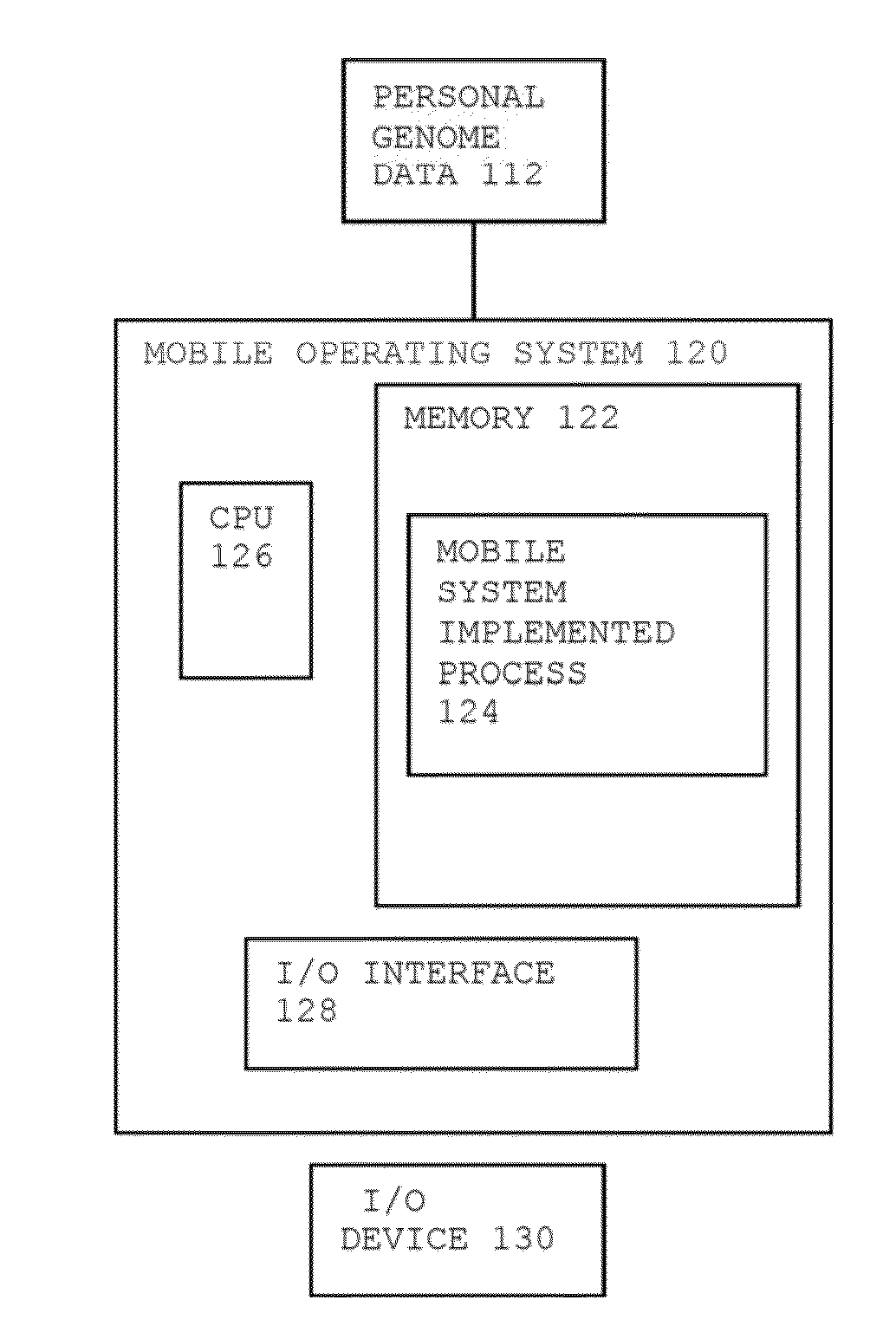
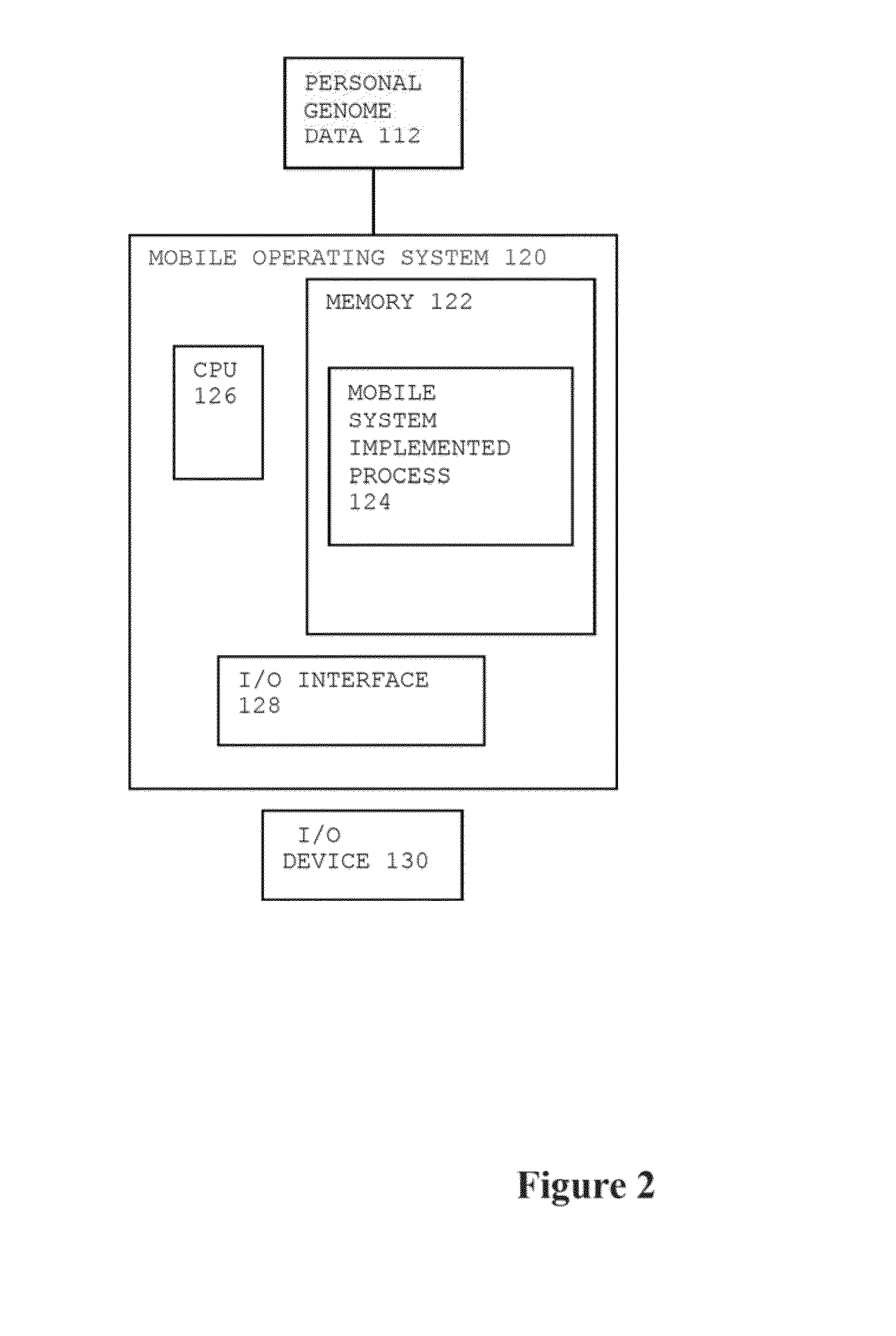
Method for Personal Genome Data Management
InactiveUS20140089009A1Add depthImprove risk variation assessmentData processing applicationsData visualisationReference genome sequenceData management
A method for personal genome information management includes receiving personal genome sequence data at a mobile device. The personal genome sequence data is compared to a reference genome sequence data to identify one or more sequence variants from the personal genome sequence data. One or more sequence variants from the personal genome sequence data are assigned to categories of hierarchical lists. One or more visual displays are provided to the user based upon the assignment of the sequence variants in the categories of hierarchical lists.
Owner:WOBBLEBASE
Method and device for processing circulating tumor DNA repetitive sequence
ActiveCN108229103AImprove processing accuracySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceCirculating tumor DNA
The invention discloses a method and device for processing a circulating tumor DNA repetitive sequence. The method comprises the steps that sequencing data and a reference genome sequence of to-be-detected circulating tumor DNA are obtained, wherein the sequencing data is obtained by carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the to-be-detected circulating tumor DNA and comprises a plurality of pairs of double-ended sequences; the sequencing data is compared with the reference genome sequence to obtain a first comparison result, wherein the first comparison result at least comprises genome positions, base sequences and corresponding base quality value sequences of the double-ended sequences; the type of each pair of double-ended sequences is determined on the basis of the first comparisonresult, wherein the types comprise independent sequences and repeated sequences. The method and the device solve the problem that a sequencing data processing method in the prior art is used for sequencing samples to delete or mark repetitive sequences and accordingly the accuracy is low.
Owner:GENE CRAB BIOTECH CO
Kit and probe for measuring instability of genome and application of kit and probe
ActiveCN112662767AEfficient analysisLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genome sequenceGenome instability
The invention provides a kit for measuring genome instability and application thereof, and a probe set contained in the kit is determined by the following steps: dividing a reference genome sequence into a plurality of first-level regions, wherein the first-level regions contain at least one known SNP site; performing SNP filtering on each of the plurality of primary regions; selecting a notch region; dividing the gap region into at least one secondary region based on an expected interval; for each of the at least one secondary region, respectively carrying out secondary high-frequency SNP search: carrying out extension treatment from the central point of the secondary region to two sides for at least one time, and after extending for a preset length for at least one time, searching for the SNP with the highest frequency in the obtained region, and determining a third-level region on the basis of taking the summary of the first-level high-frequency SNP and the second-level high-frequency SNP as the starting point SNP; and based on the third-level region, constructing a probe for specifically identifying the third-level region. By utilizing the method, the probe combination which can be effectively used for analyzing the instability of the genome can be effectively obtained.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +2
Tumor somatic cell mutation site detection method and device
ActiveCN111180010AFalse-positive situations caused by variant sitesAvoid false positivesProteomicsGenomicsReference genome sequenceWhite blood cell
The invention provides a tumor somatic cell mutation site detection method and a tumor somatic cell mutation site detection device. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing a tumor somaticcell sample and a leukocyte sample taken from the same tumor patient, and comparing a sequencing result with a reference genome sequence to generate a corresponding bam file; removing deviation caused by PCR amplification in the bam file to obtain a corrected bam file; comparing the corrected tumor somatic cell sample bam file with the corrected leukocyte sample bam file to generate a vcf file ofall mutation detection information of the tumor somatic cell sample, and annotating the vcf file; and filtering the variation detection information of the tumor somatic cell sample according to a preset filtering condition to obtain a real tumor somatic cell mutation site information result. According to the method, one-step filtering operation is realized, so that the filtering accuracy is ensured, and tumor somatic cell mutation site information can be rapidly obtained; the result is real and reliable; and an important basis is provided for accurate treatment of tumor patients.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
Method for genotyping forest populations on basis of gene CNV (copy number variation) sites
ActiveCN106480221AAccurate discoveryAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genome sequenceRead depth
The invention provides a method for genotyping forest populations on basis of gene CNV (copy number variation) sites. Compared with published reference genome sequences of species, a large quantity of reads obtained by sequencing on different individuals is mapped to a pre-segmented reference genome for comparison; the number of reads matched in each window is taken as a read depth signal; read depth signal values are subjected to data standardized treatment according to GC content and deviation in windows and on the basis of the median value of a data set of read depth signal values of different individuals in the windows; varied copy numbers of the different individuals in the windows are predicted by means of corrected read depth signal values, and genotyping is performed on each CNV site according to the read depth signal values. The method is applicable to forests with different population sizes, genotypes of the CNV sites are determined on the basis of the read depth signals of high-throughput sequencing results, the algorithm is simple, the operation is simple and convenient, and the genotypes of the CNV sites are discovered and detected more accurately.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
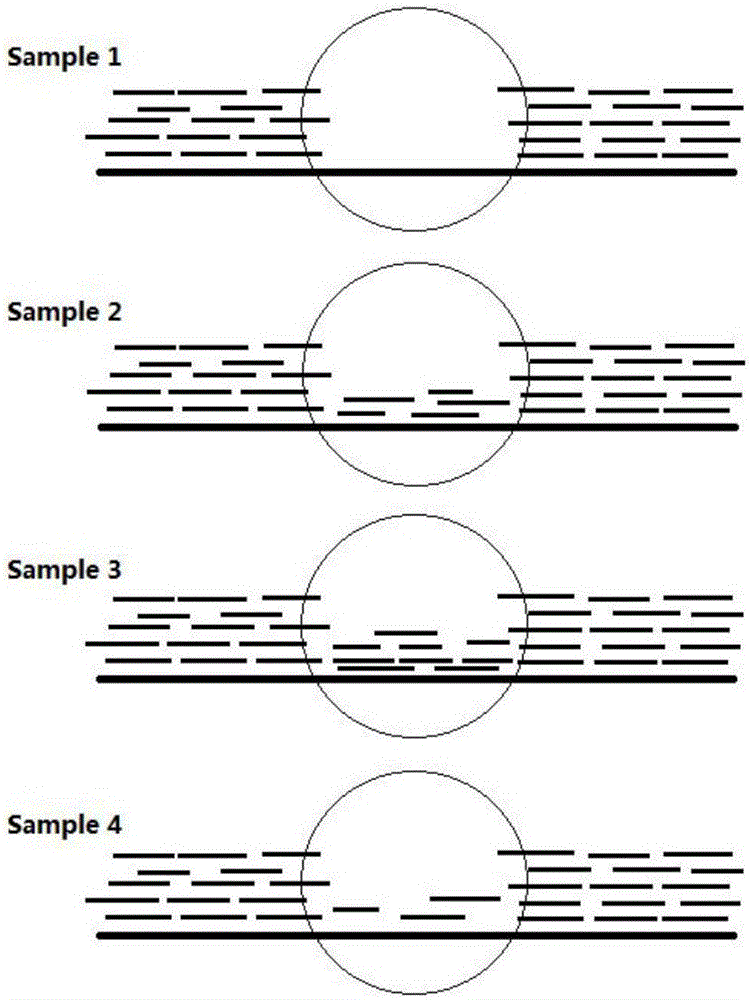
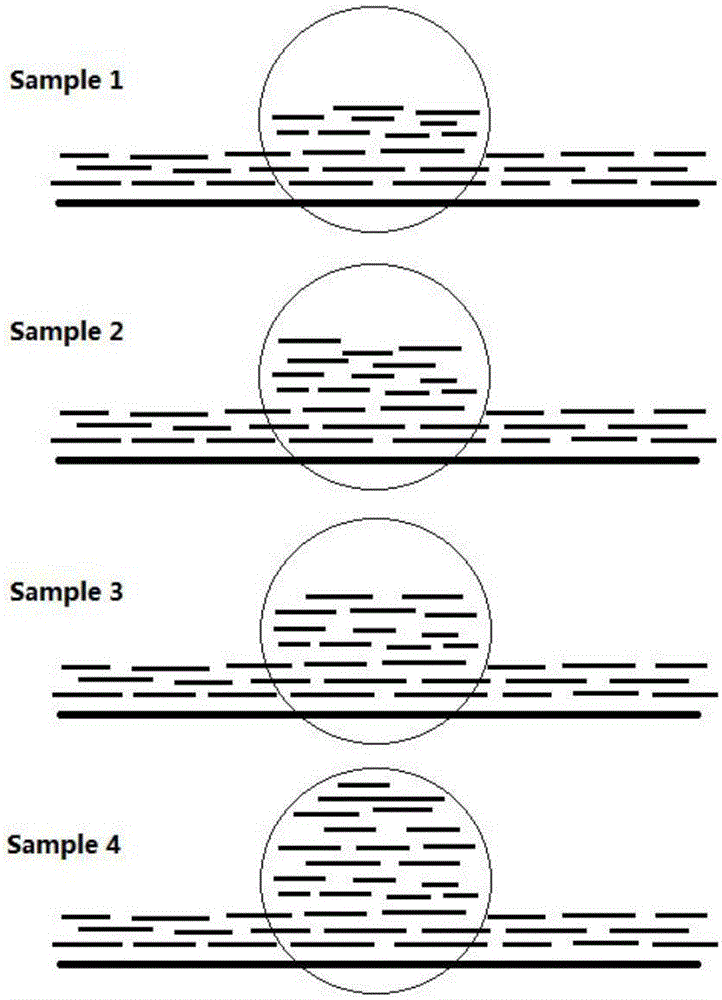
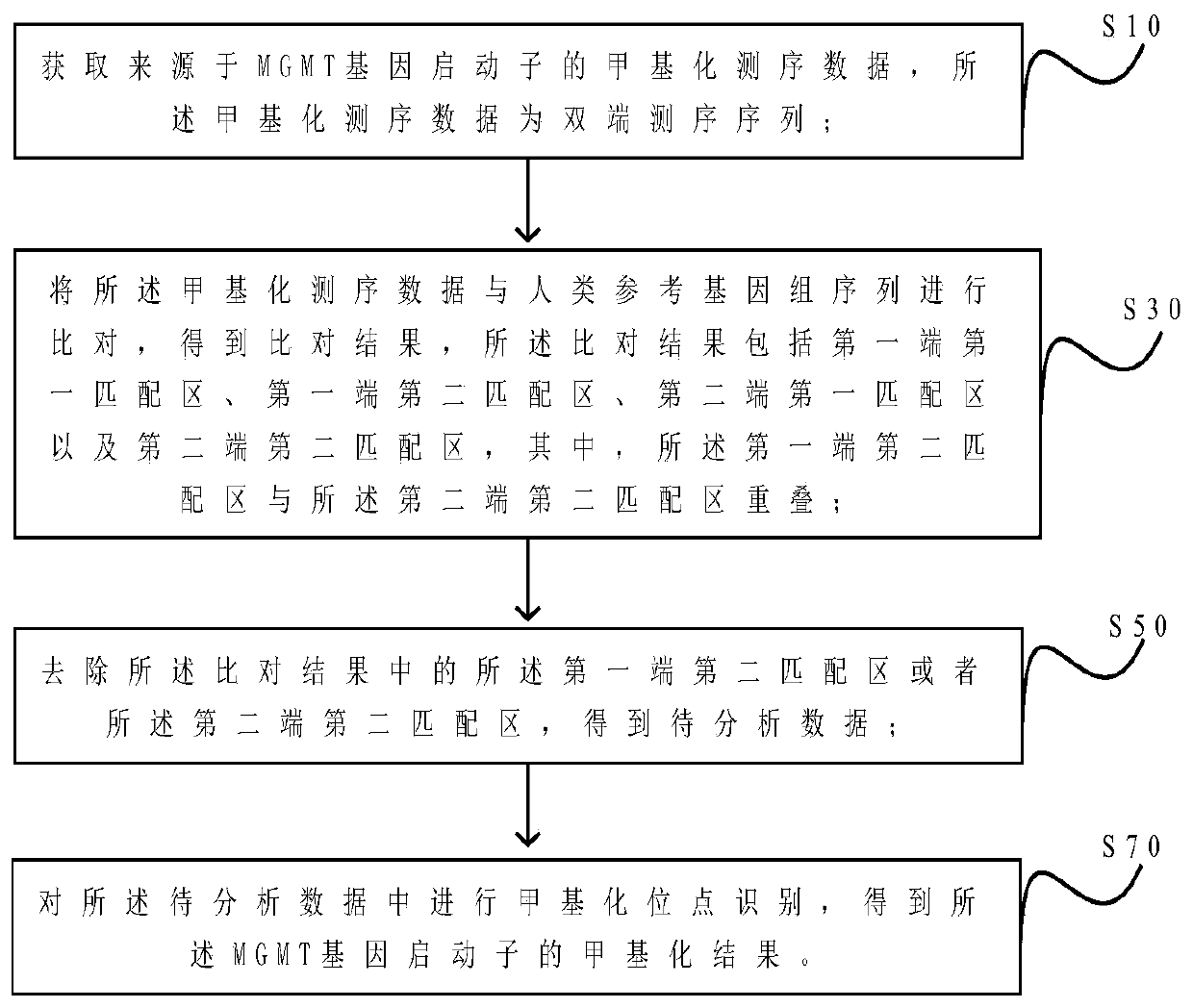
MGMT gene promoter methylation detecting method, sequencing data processing method and processing device
ActiveCN110211633AImprove accuracyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsReference genome sequencePromoter methylation
The invention provides an MGMT gene promoter methylation detecting method, a sequencing data processing method and a processing device. The processing method comprises the steps of acquiring methylation sequencing data from the MGMT gene promoter, wherein the methylation sequencing data are a double-end sequencing sequence; comparing the methylation sequencing data with a human reference genome sequence for obtaining a comparing result, wherein a comparing result comprises a first-end first matching area, a first-end second matching area, a second-end first matching area and a second-end second matching area, the first-end second matching area is overlapped with the second-end second matching area; eliminating the first-end second matching area or the second-end second matching area in a comparing result for obtaining to-be-analyzed data; and performing methylation site identification on to-be-analyzed data for obtaining a methylation result of the MGMT gene promoter. The methylation site which is detected by the processing method has relatively high accuracy and relatively high flux, thereby facilitating evaluation of methylation level in an integral manner.
Owner:GENECAST WUXI PRECISION MEDICAL DIGNOSTIC LAB
Method and device for detection of gene fusion
ActiveCN107480472AAccurate detectionImprove accuracySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceBioinformatics
The invention discloses a method for detection of gene fusion. The method includes the following steps that 1, the sequences of to-be-detected gene fragments are provided, and sequence comparison with a reference genome is conducted; 2, the to-be-detected gene fragments which are partially same as the sequence of the reference genome are extracted, and consensus sequence portions are labeled; 3, sequence comparison is conducted again on the to-be-detected gene fragments extracted in the step 2 and the reference genome, and if the obtained consensus sequence is not same as the consensus sequence labeled in the step 2, it is speculated that the to-be-detected gene fragments extracted in the step 2 have a gene fusion phenomenon; 4, the authenticity of gene fusion is verified. At the same time, the method and the device further discloses a device for the detection of gene fusion. By means of the method and the device, the gene fusion sequence (less than 1%) with the extremely low concentration can be accurately detected out, and the method and the device are more sensitive to the gene fusion sequence high in fusion concentration.
Owner:武汉安至康永医疗科技有限公司
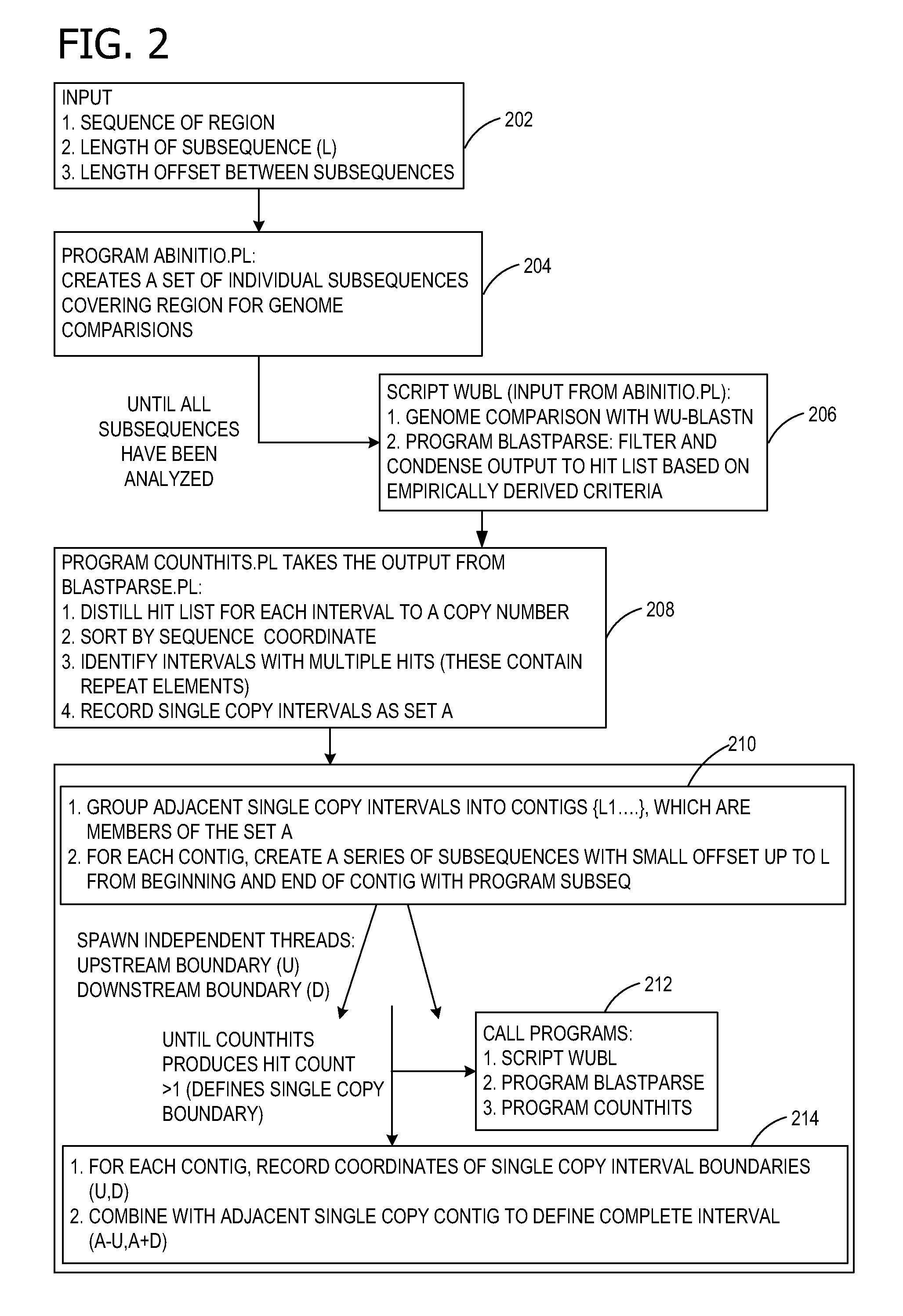
AB initio generation of single copy genomic probes
ActiveUS8407013B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genome sequenceAb initio
Single copy sequences suitable for use as DNA probes can be defined by computational analysis of genomic sequences. The present invention provides an ab initio method for identification of single copy sequences for use as probes which obviates the need to compare genomic sequences with existing catalogs of repetitive sequences. By dividing a target reference sequence into a series of shorter contiguous sequence windows and comparing these sequences with the reference genome sequence, one can identify single copy sequences in a genome. Probes can then be designed and produced from these single copy intervals.
Owner:ROGAN PETER K
Gene sequence alignment method and system
PendingCN112735528AHigh speedHigh precisionBiostatisticsSequence analysisReference genome sequenceData set
The invention discloses a gene sequence alignment method and system. The method comprises the following steps: storing a reference genome sequence and a query genome sequence in a distributed storage system; under a Spark heterogeneous distributed computing platform framework, segmenting a reference genome sequence according to row offset, and preprocessing to obtain a plurality of preprocessed reference data sets; establishing an index for each preprocessing reference data set by adopting a suffix array algorithm, and combining all the preprocessing reference data sets after the index is established to obtain a reference sequence index file; carrying out CUDA fine-grained sequence comparison on each fragment in the query genome sequence and a reference sequence index file by adopting a seed extension algorithm, and determining position information of each fragment in the reference sequence index file; and combining the position information of all the fragments in the reference sequence index file to obtain a gene sequence comparison result. According to the invention, the calculation speed and precision of a large-scale sequence alignment algorithm are improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
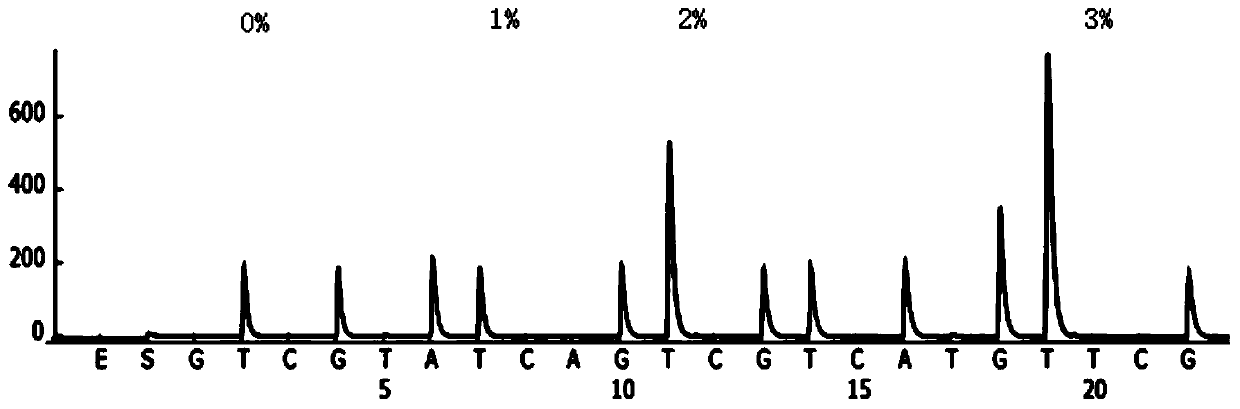
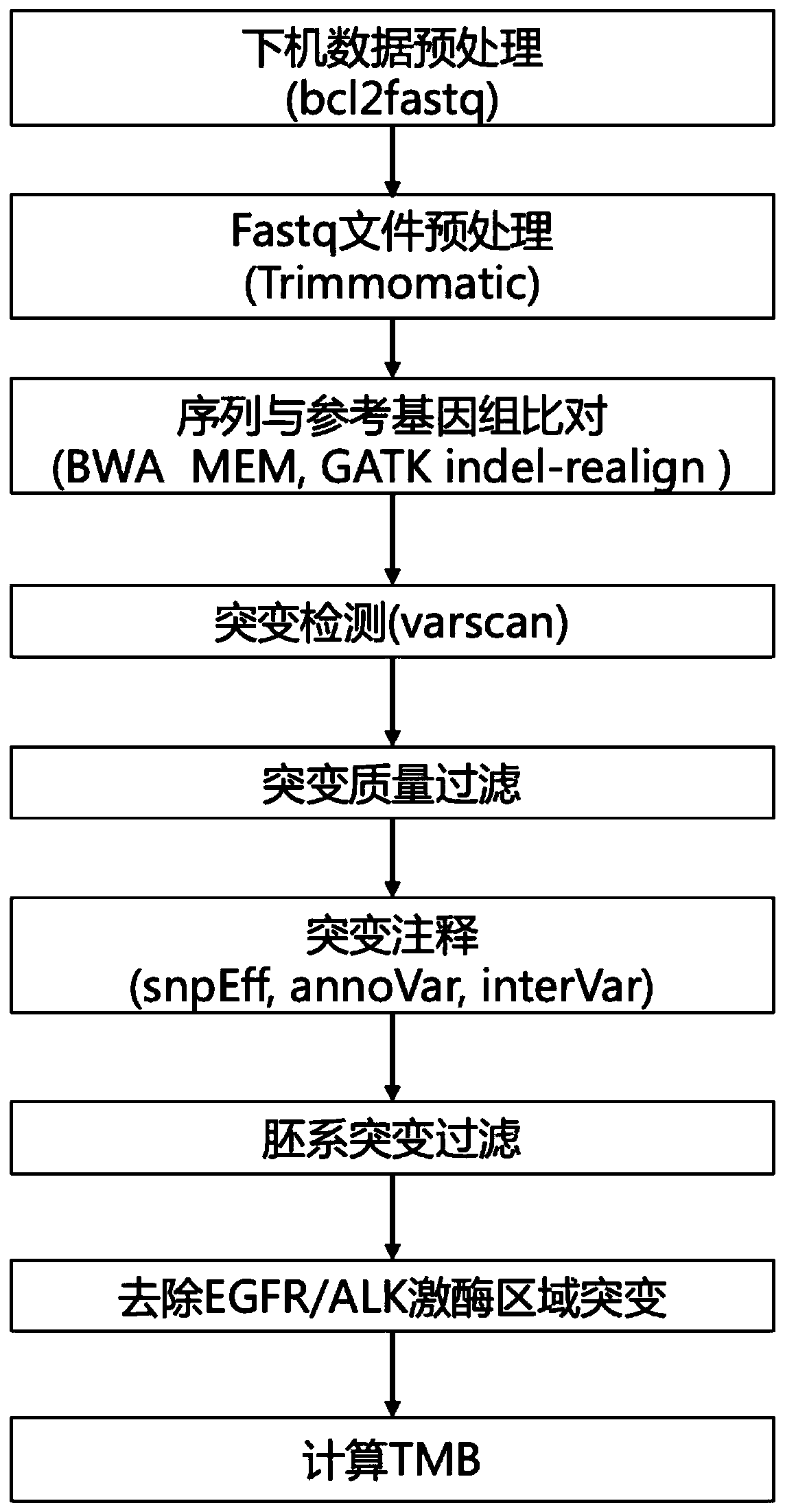
Method for analyzing tumor mutation load based on high-flux targeted sequencing
ActiveCN110343748ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference genome sequenceHigh flux
The invention relates to a method and system for analyzing a tumor mutation load based on high-flux targeted sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps that through high-flux targeted sequencing, sequences of selected exons and upstream and downstream areas of target genes in a tumor sample and a pairing contrast sample are subjected to sequencing; sequencing data obtained from thetumor sample and the pairing contrast sample is compared with a human reference genome sequence, and the number of mutated somatic cells in the sequences of the selected exons and the upstream and downstream areas of the target genes in the tumor sample is calculated; the mutation numbers of the somatic cells in the selected exons and the upstream and downstream areas of the target genes are addedto obtain a total mutation number, the lengths of the selected exons and the upstream and downstream areas of the target genes are added to obtain a total area length (Mb), and TMB is calculated through the following formula: TMB=the total mutation number / the total area length.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BURNING ROCK DX CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com