Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Spliceosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
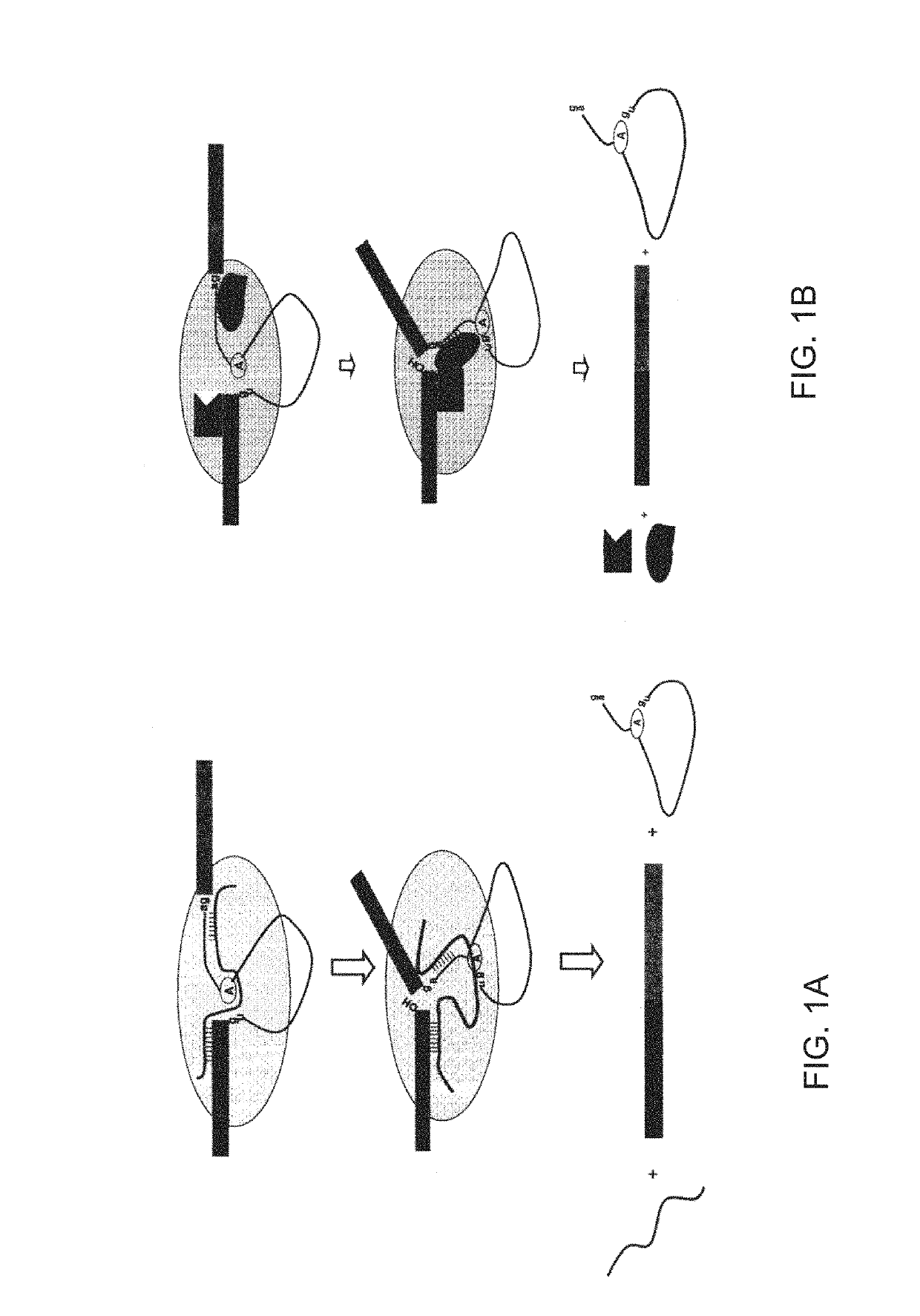
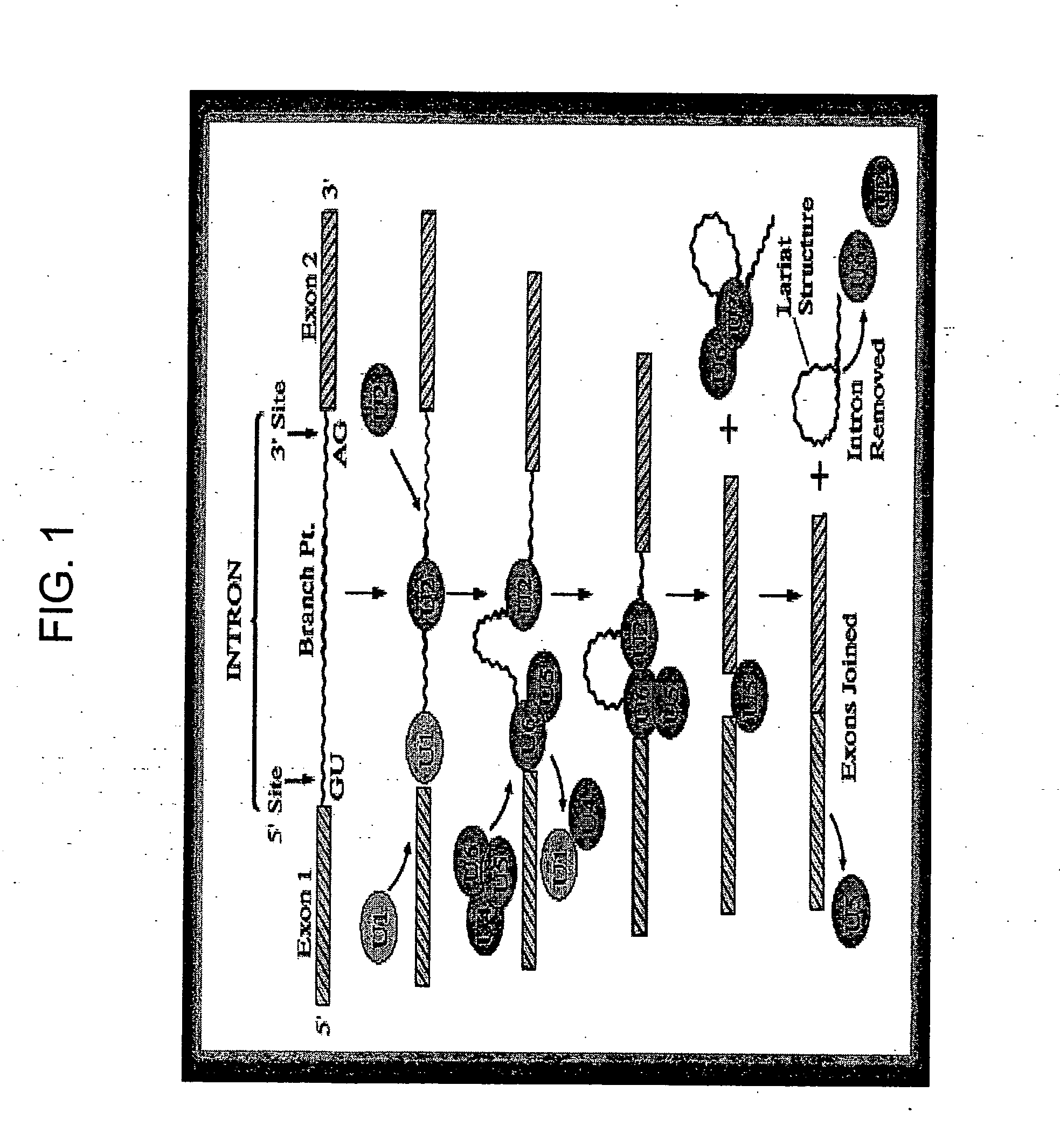
A spliceosome is a large and complex molecular machine found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) and approximately 80 proteins. The spliceosome removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA, a type of primary transcript. This process is generally referred to as splicing. An analogy is a film editor, who selectively cuts out irrelevant or incorrect material (equivalent to the introns) from the initial film and sends the cleaned-up version to the director for the final cut.
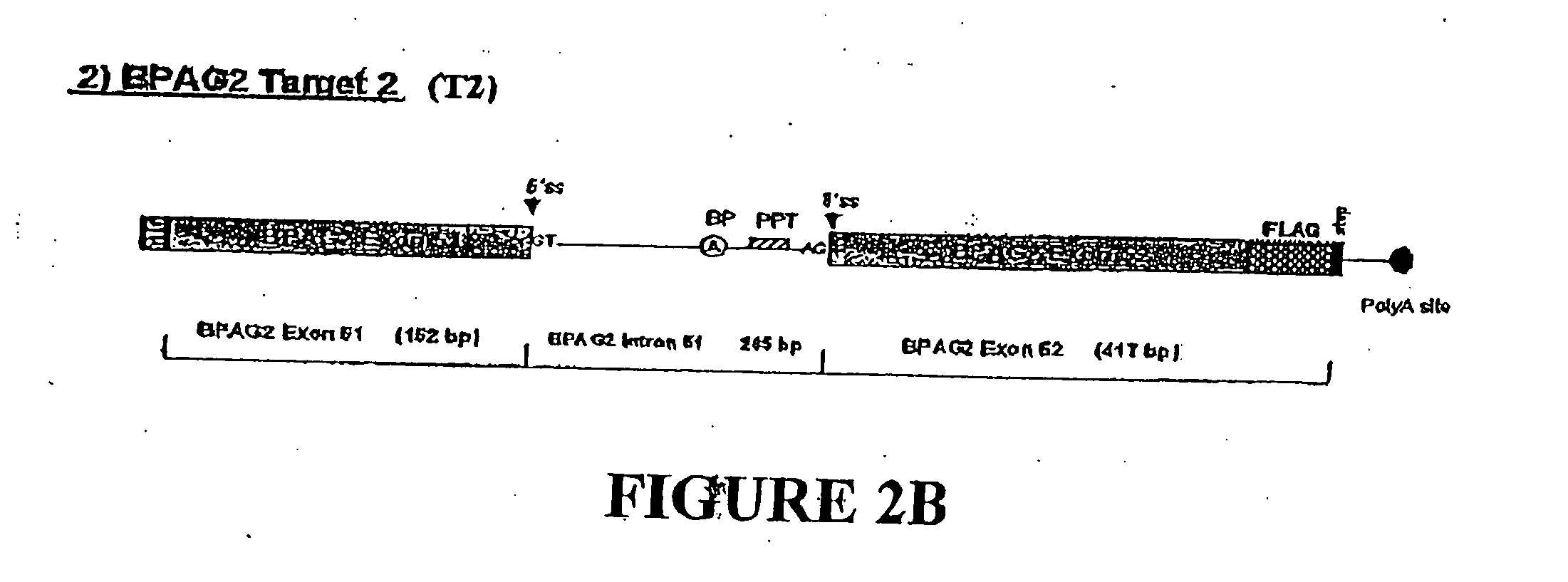
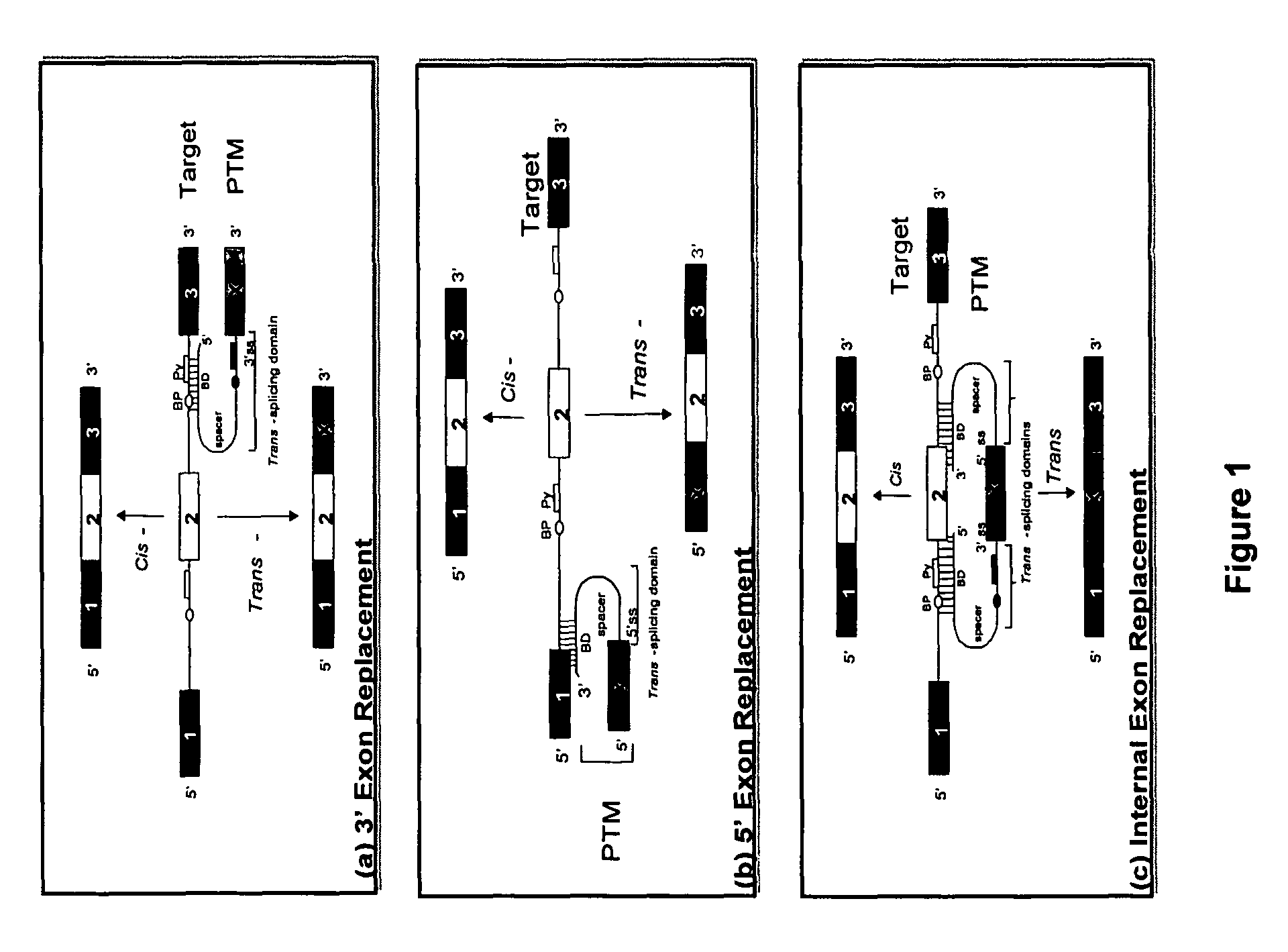
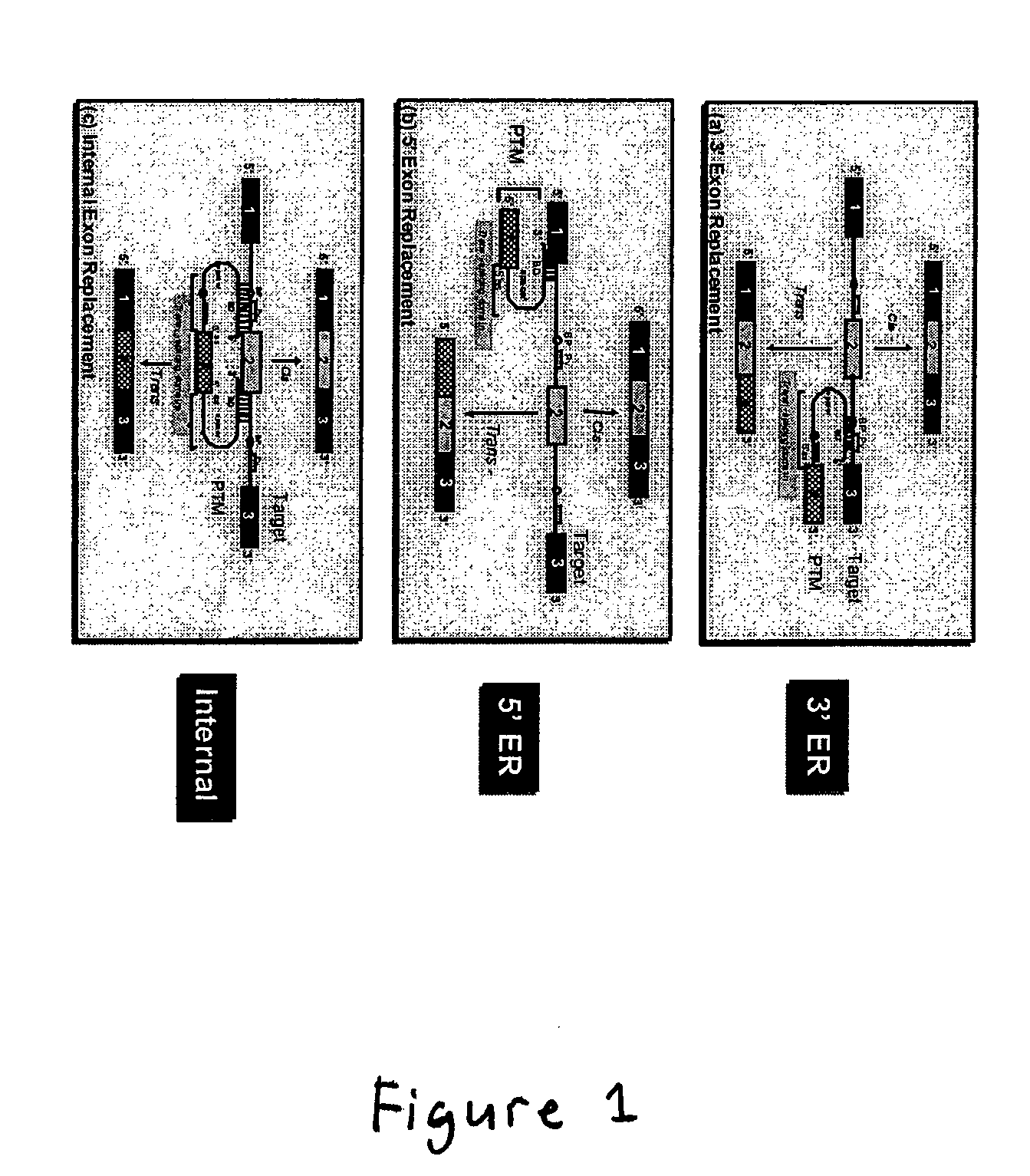
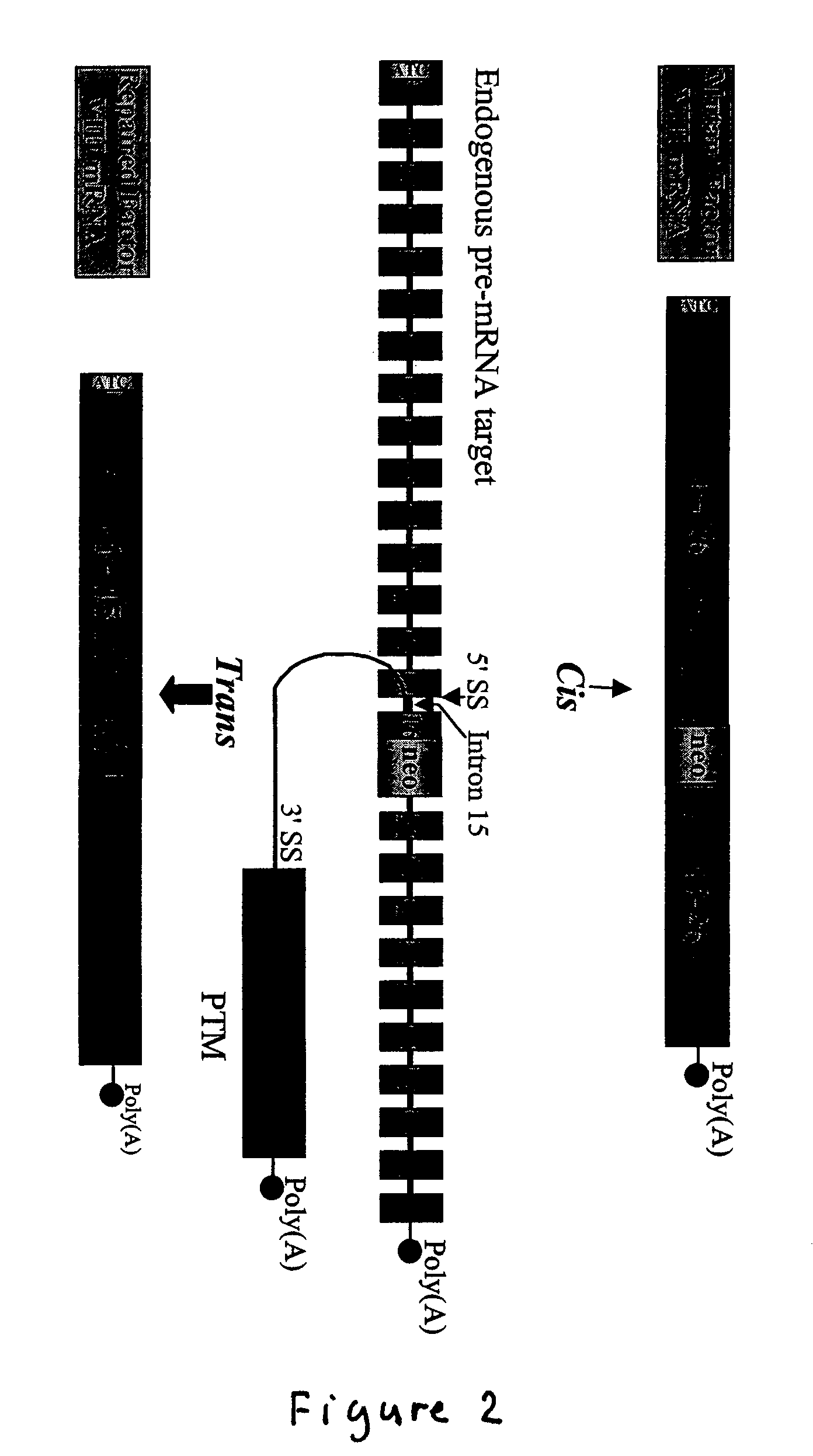
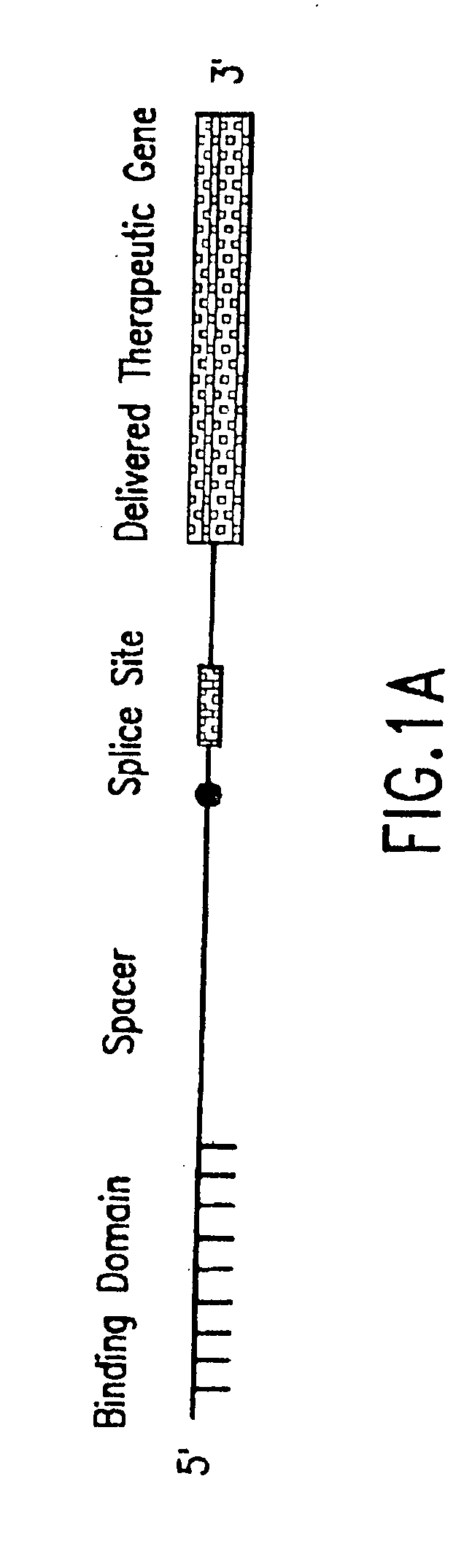
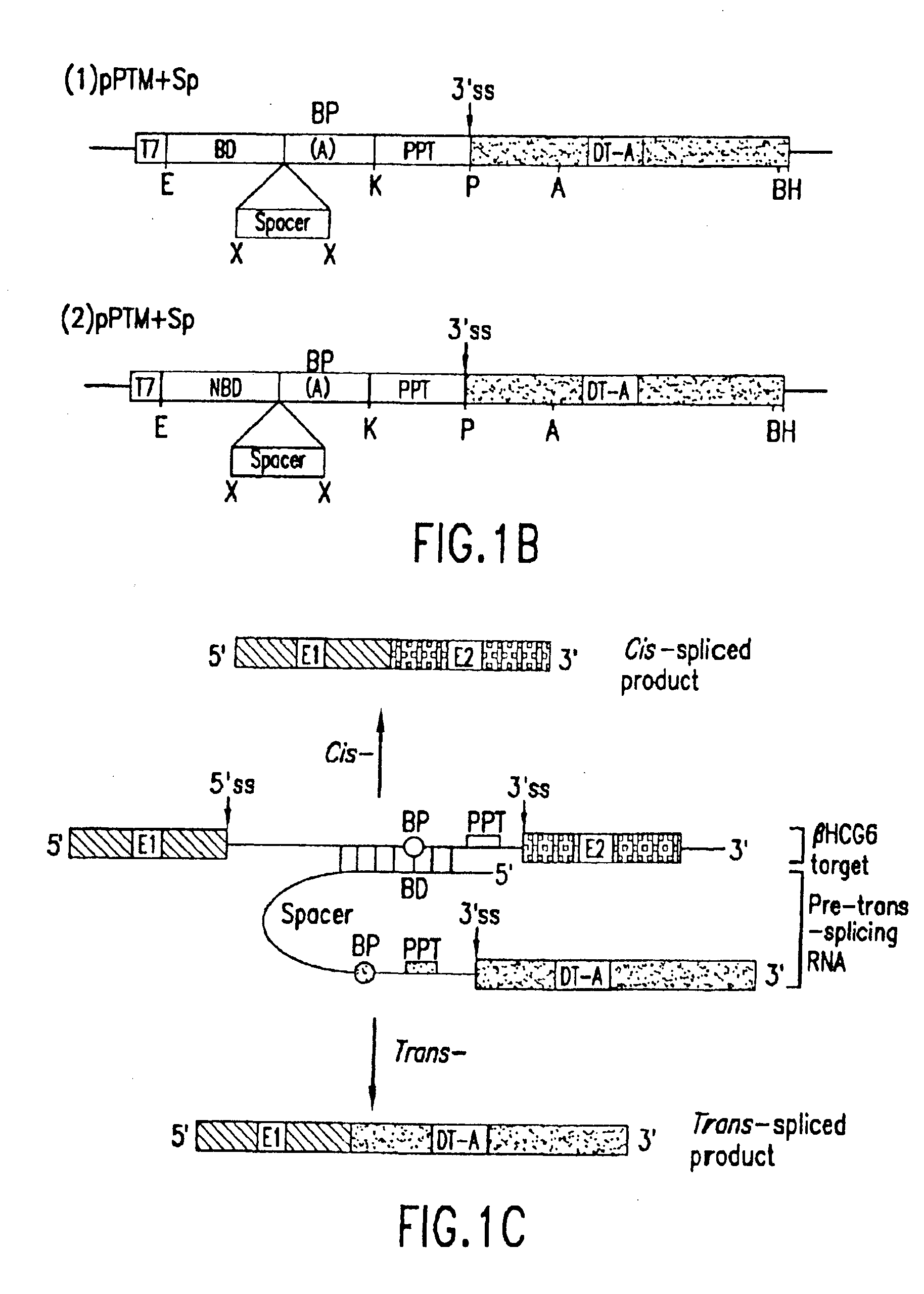
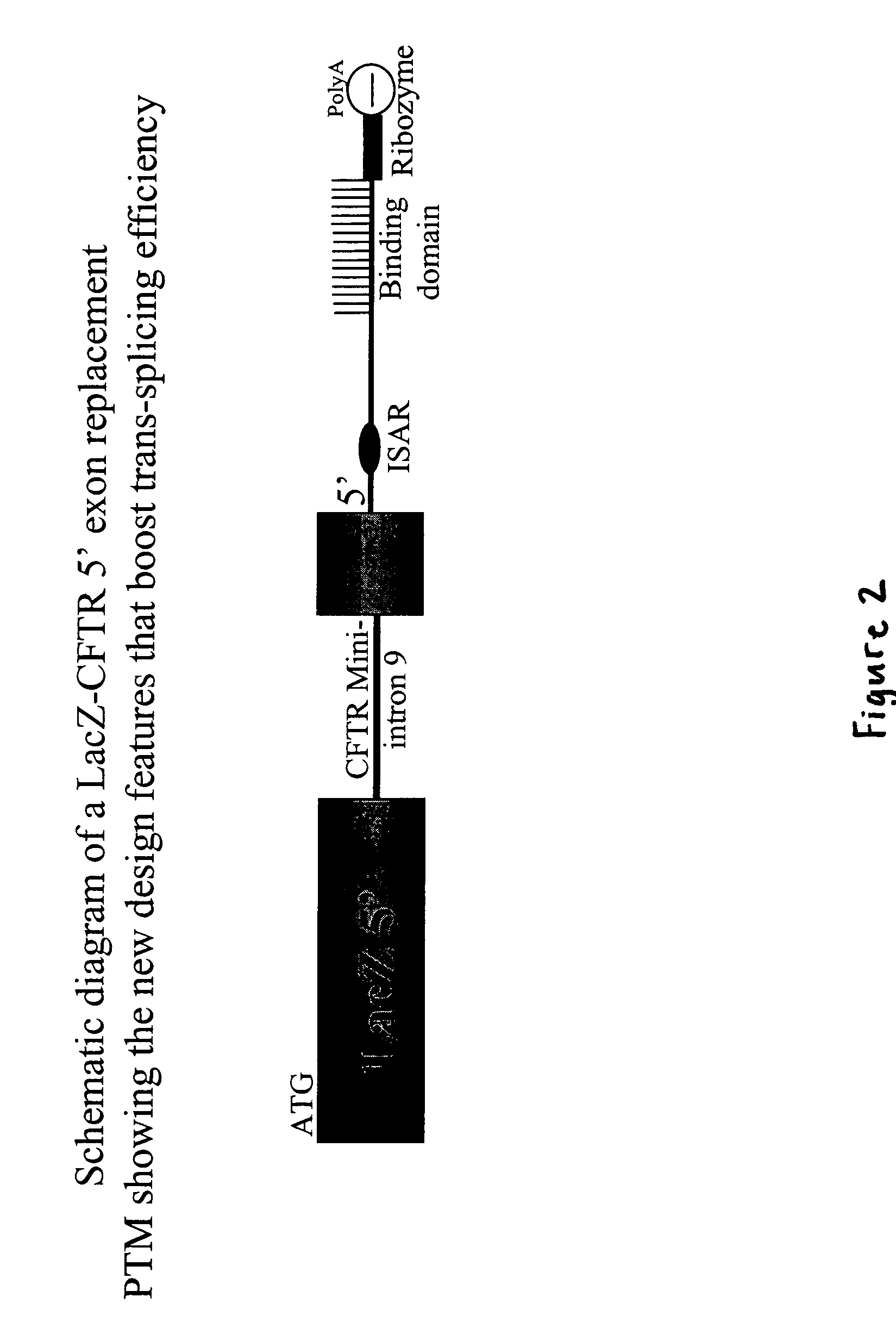
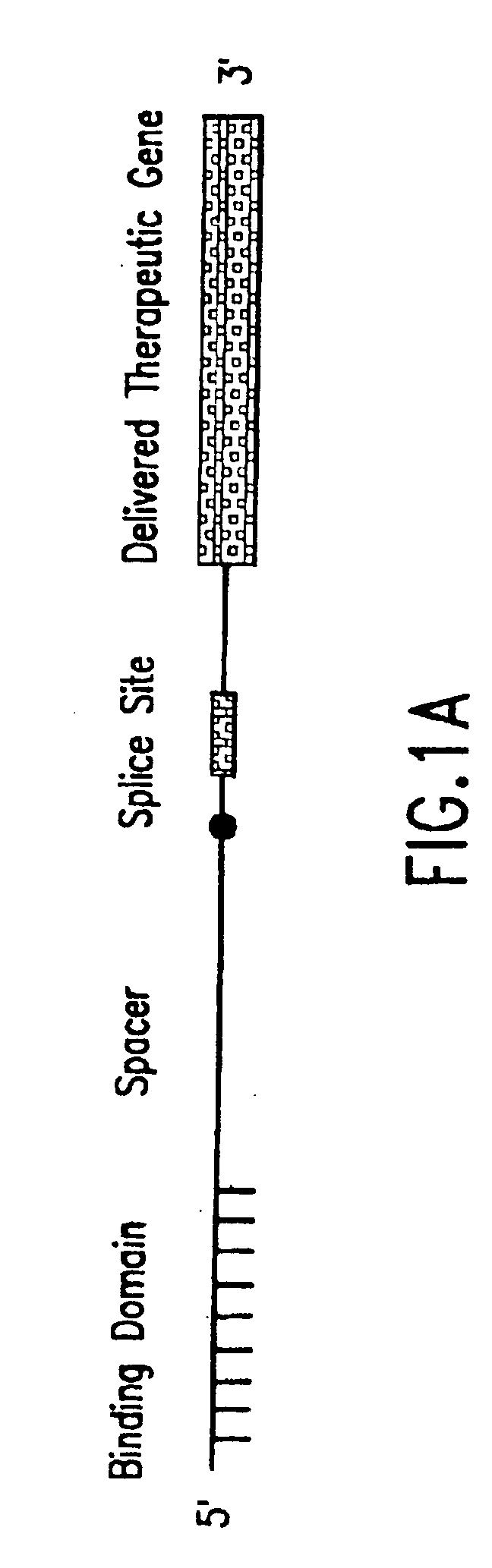
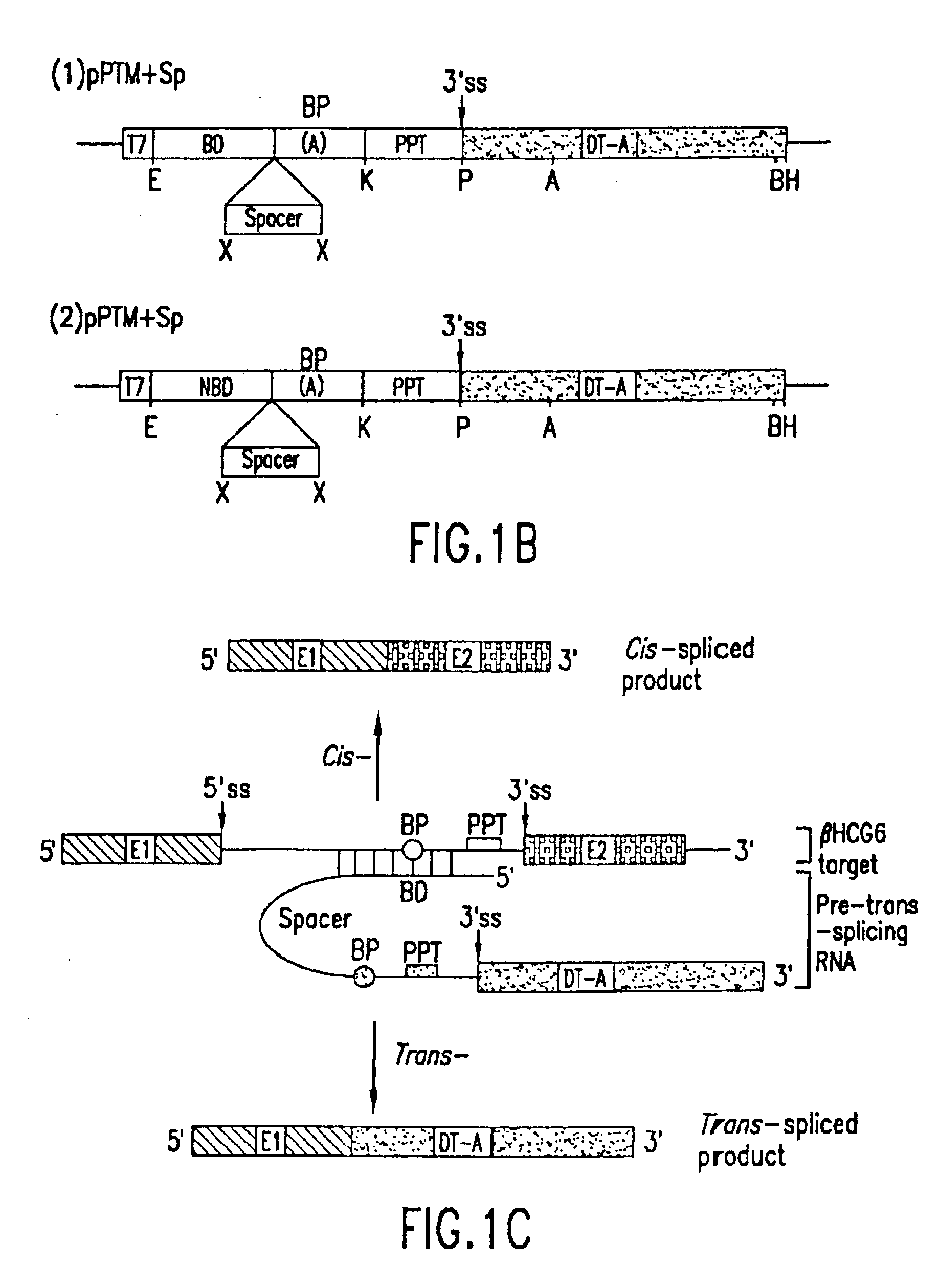
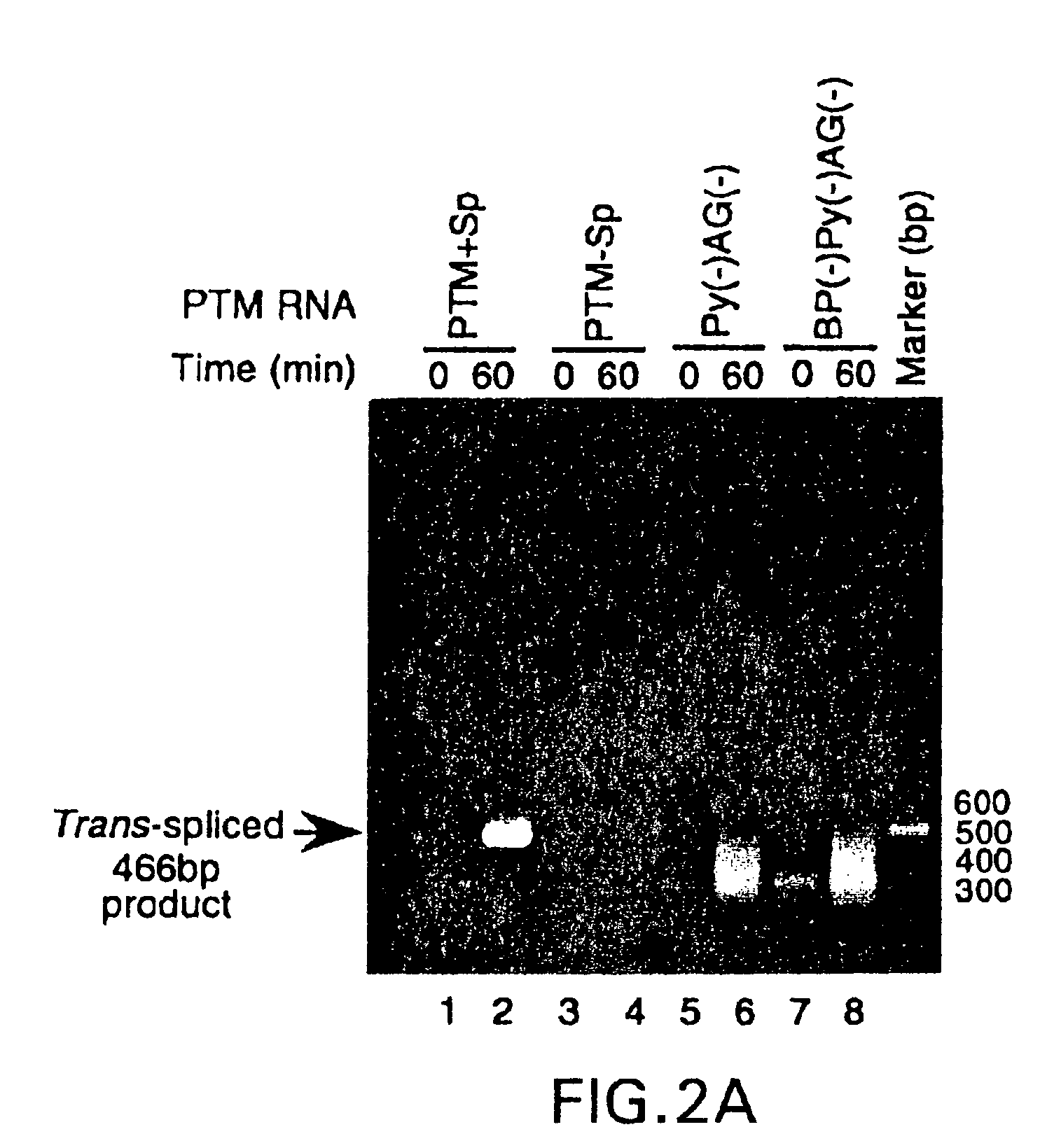
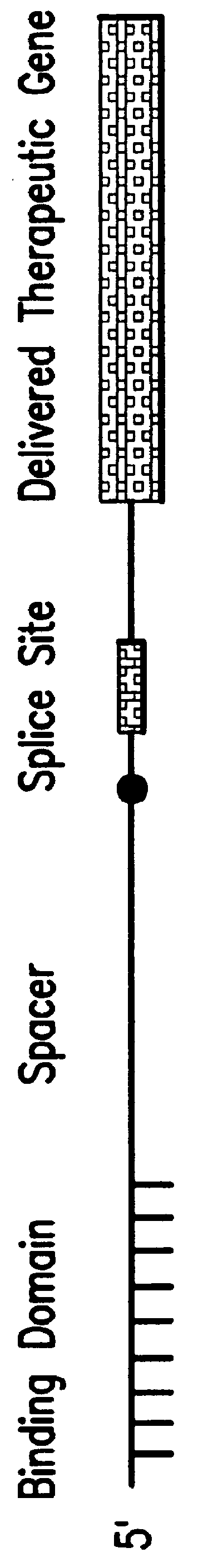
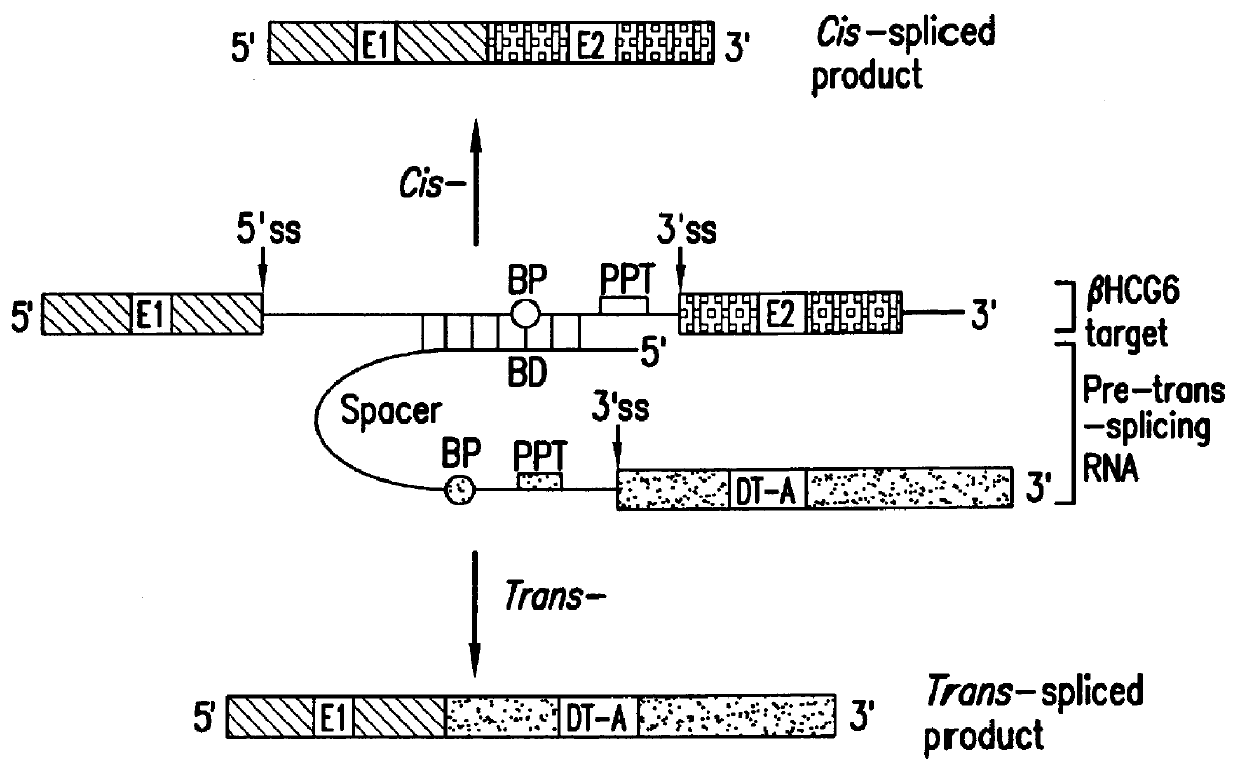
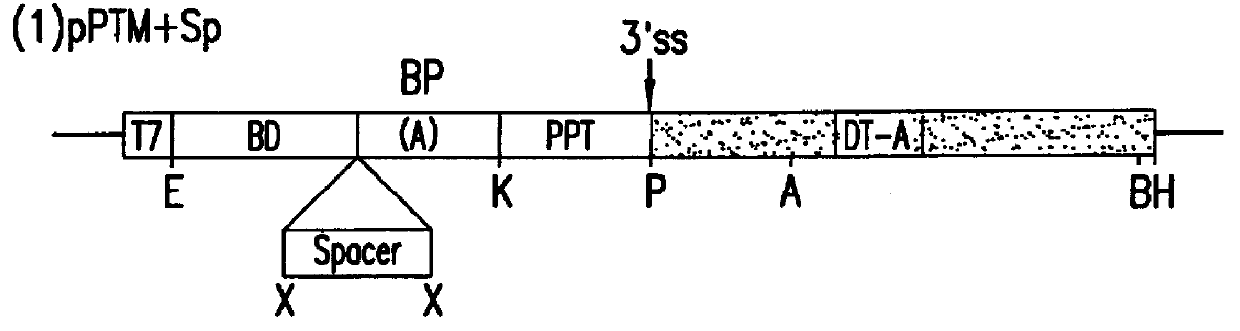
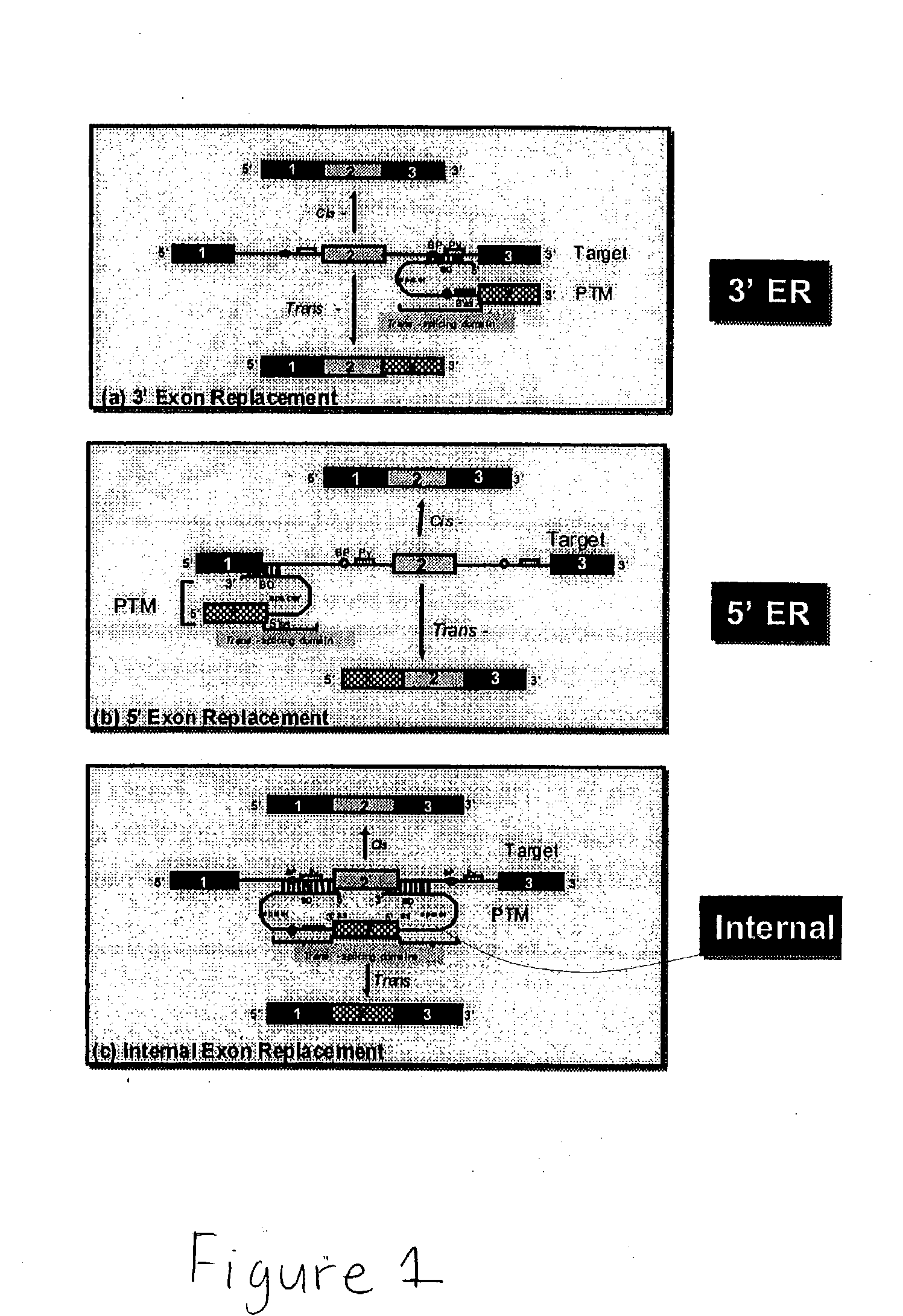
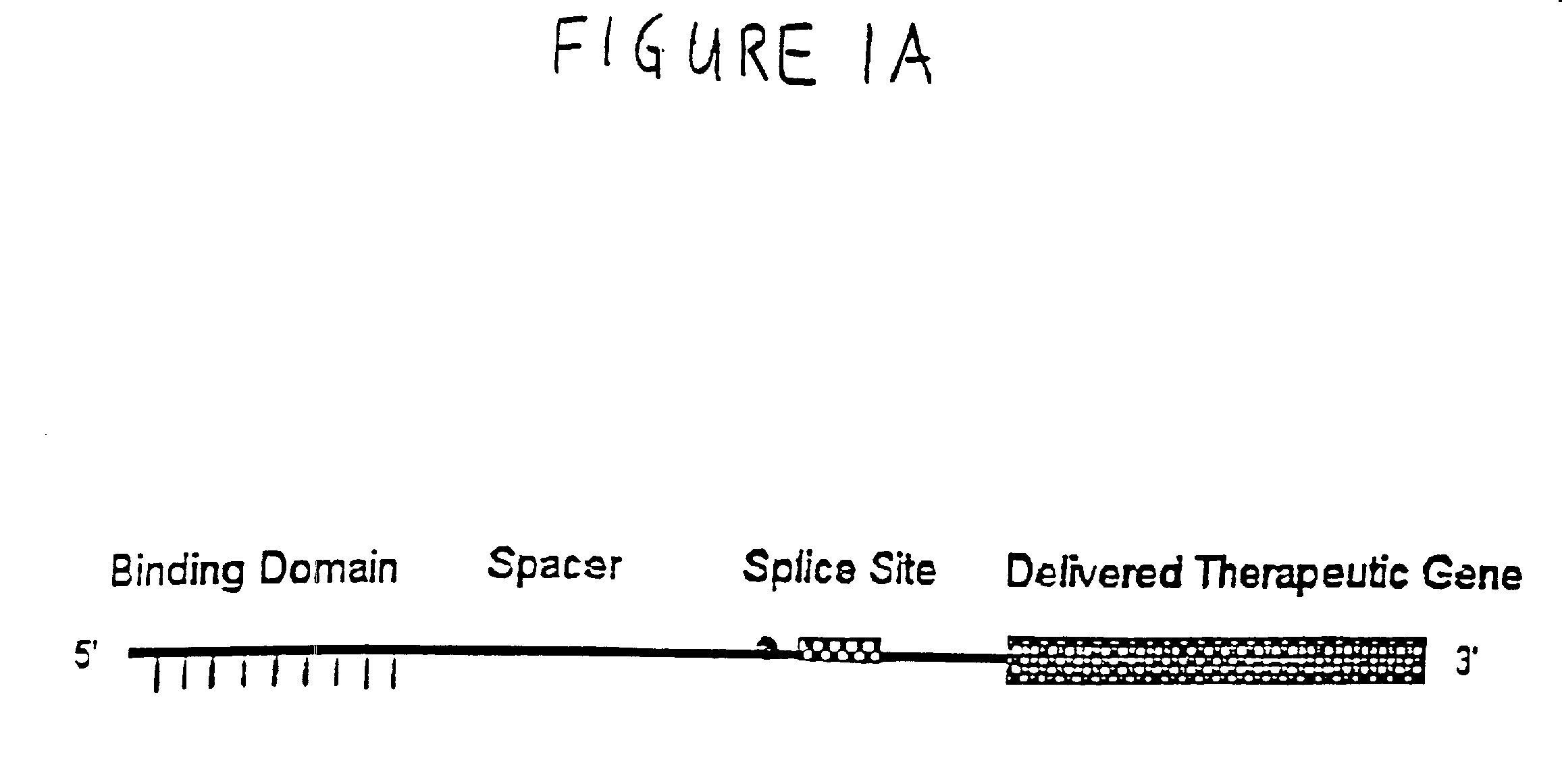
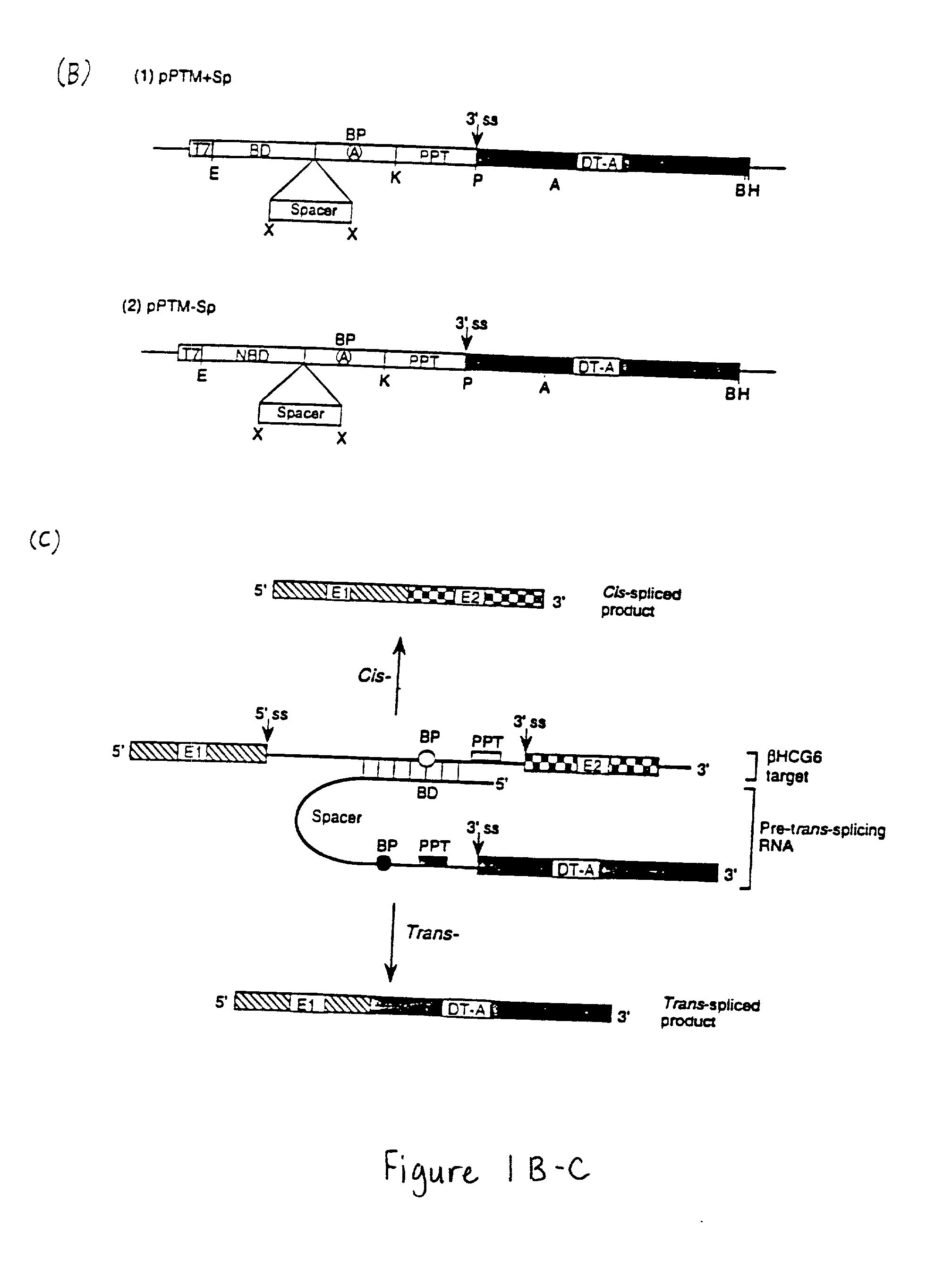
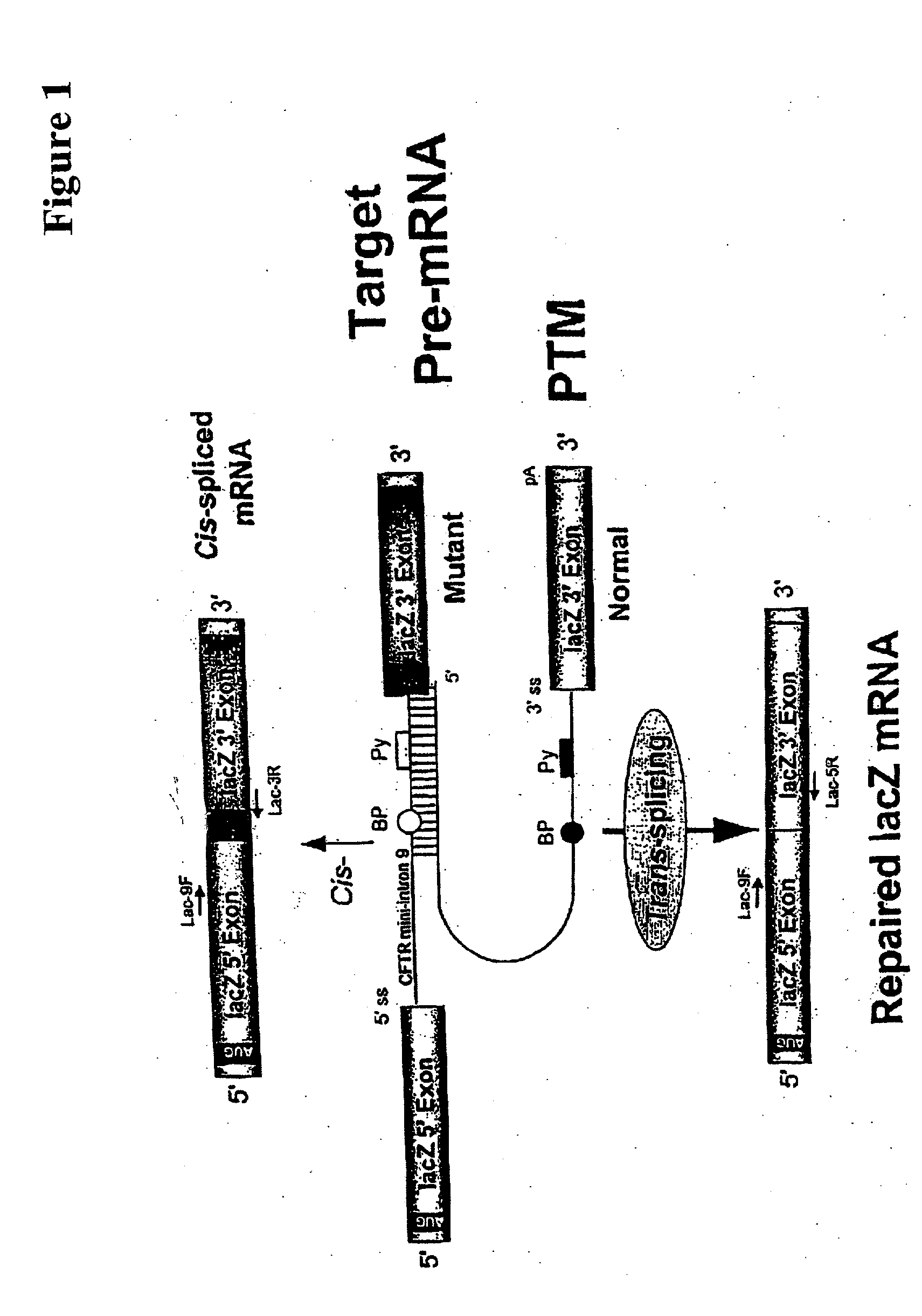
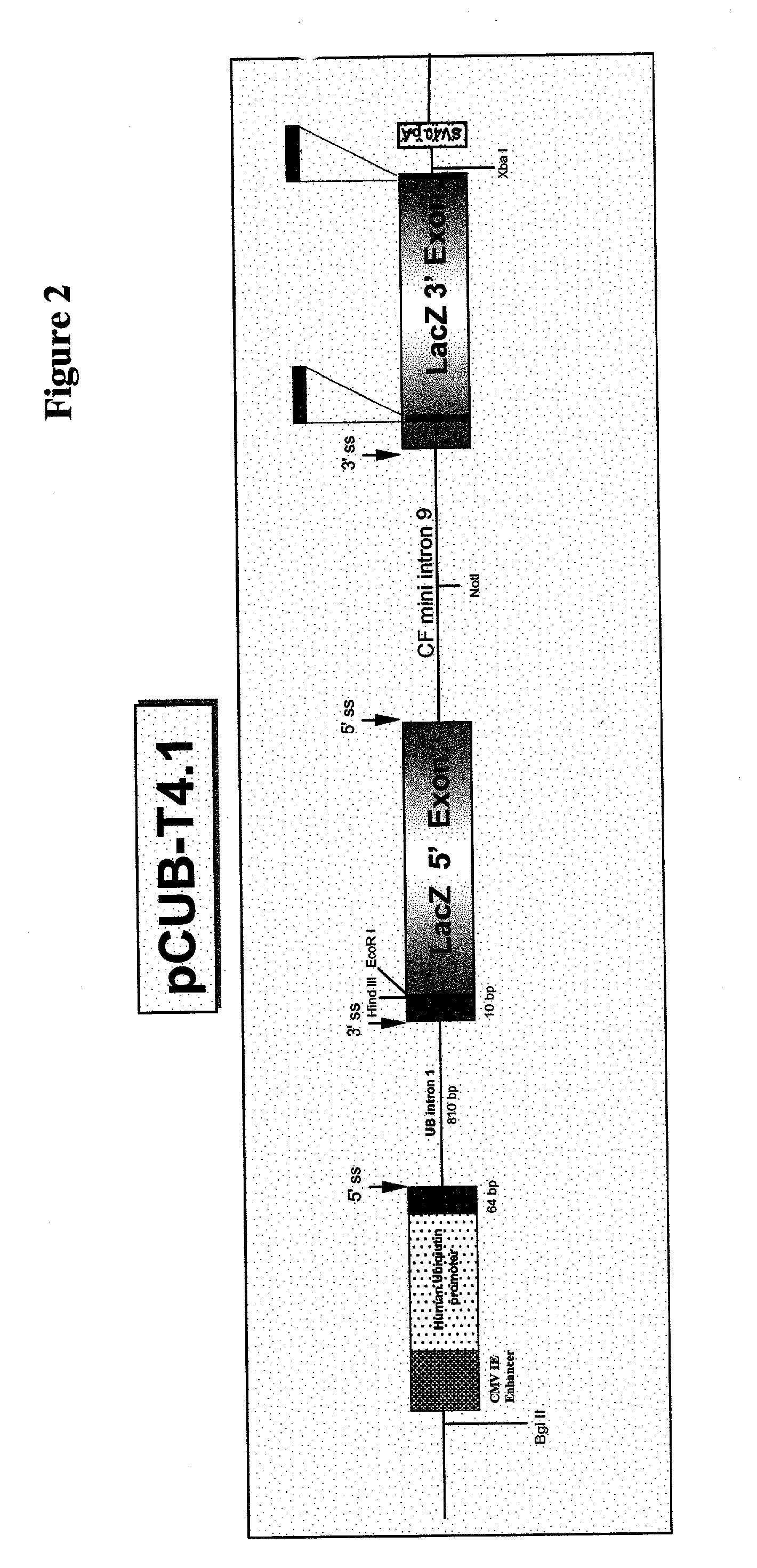
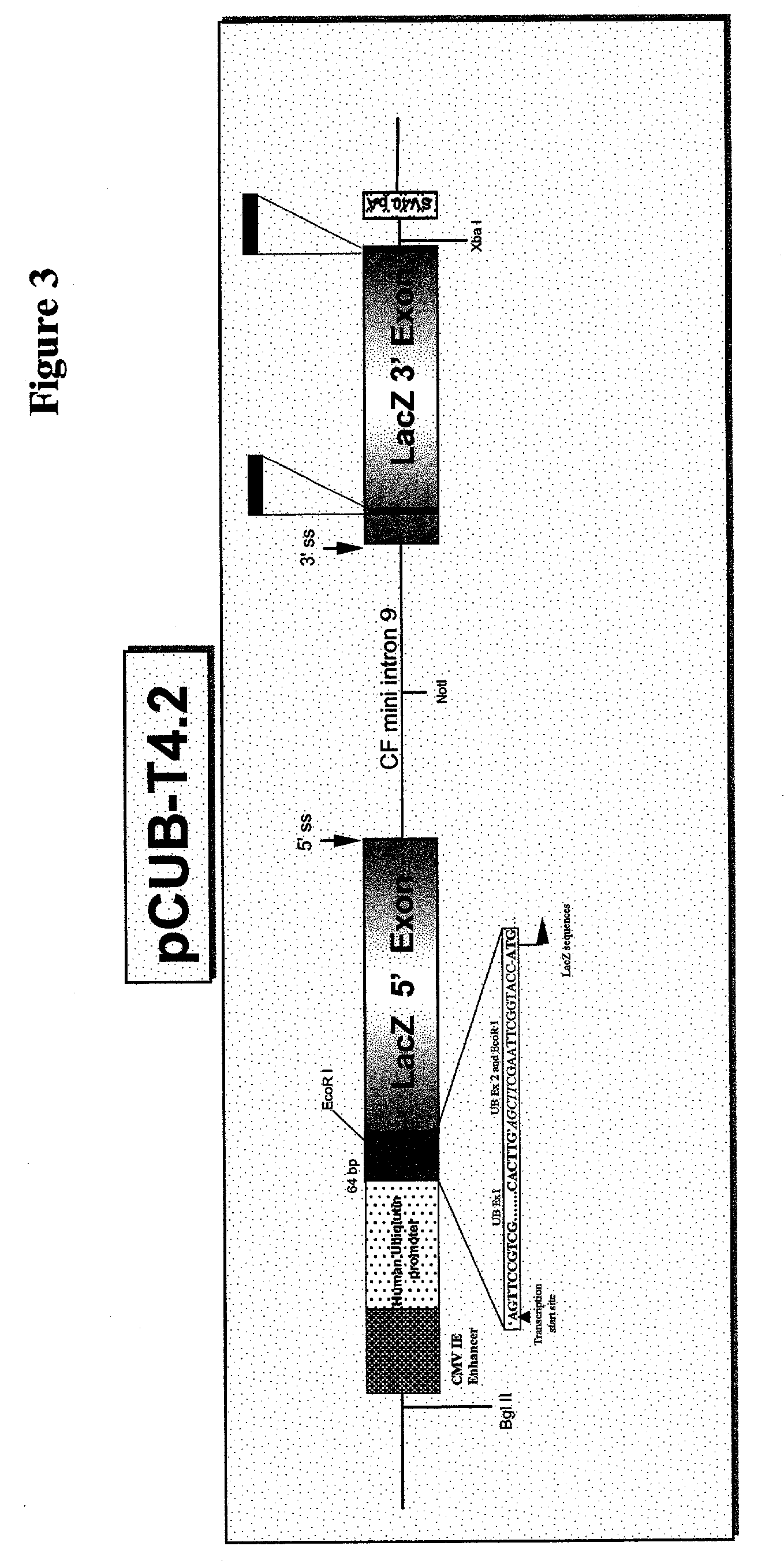
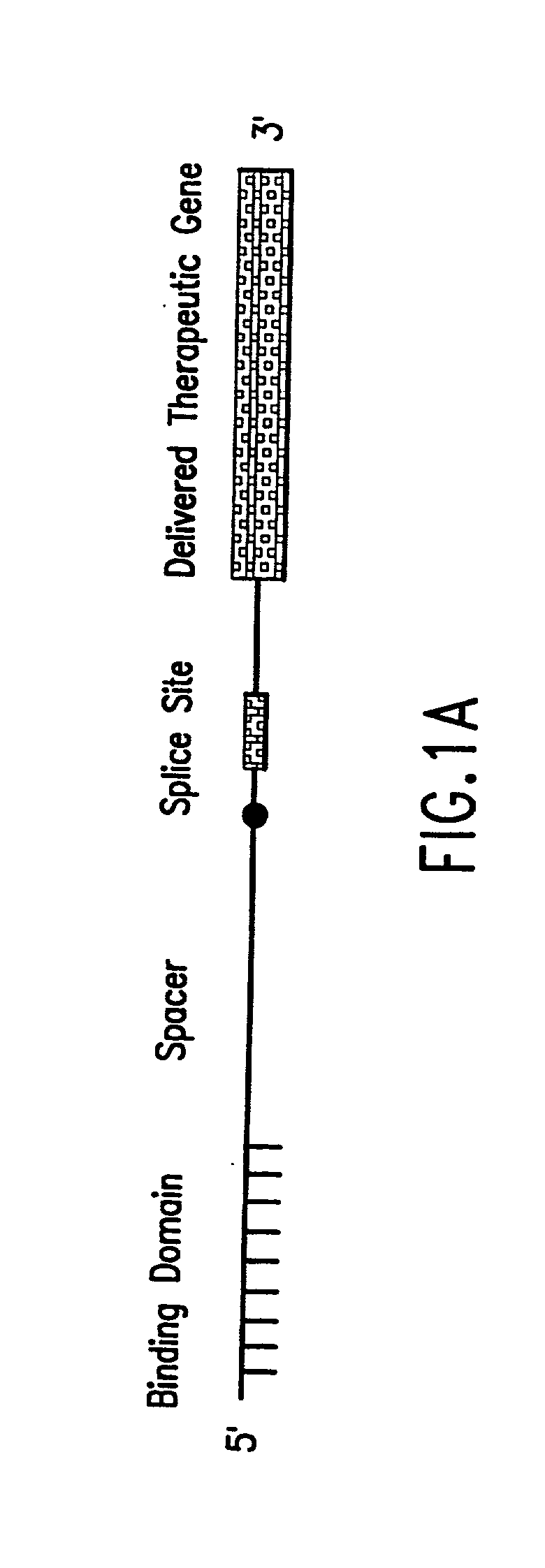
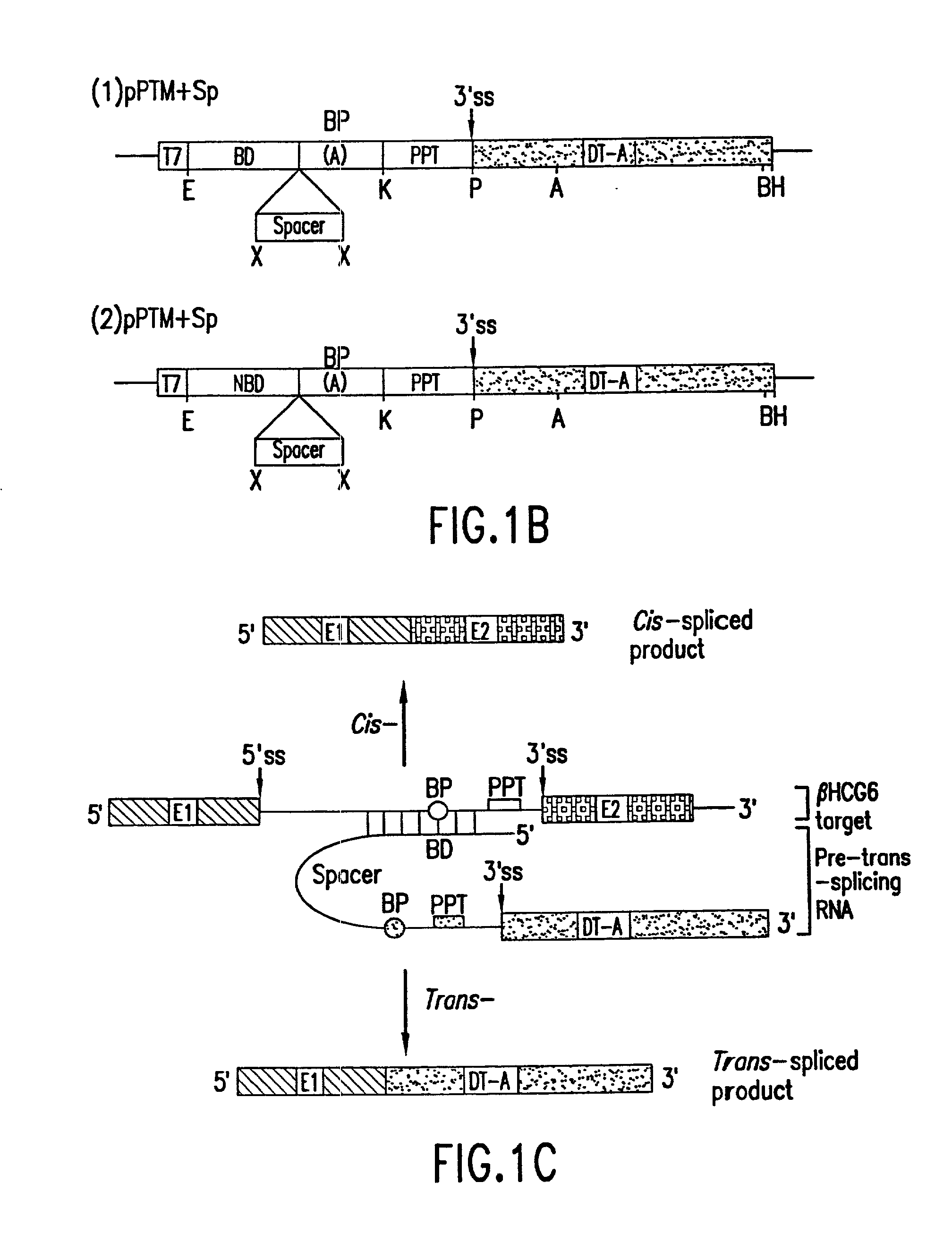
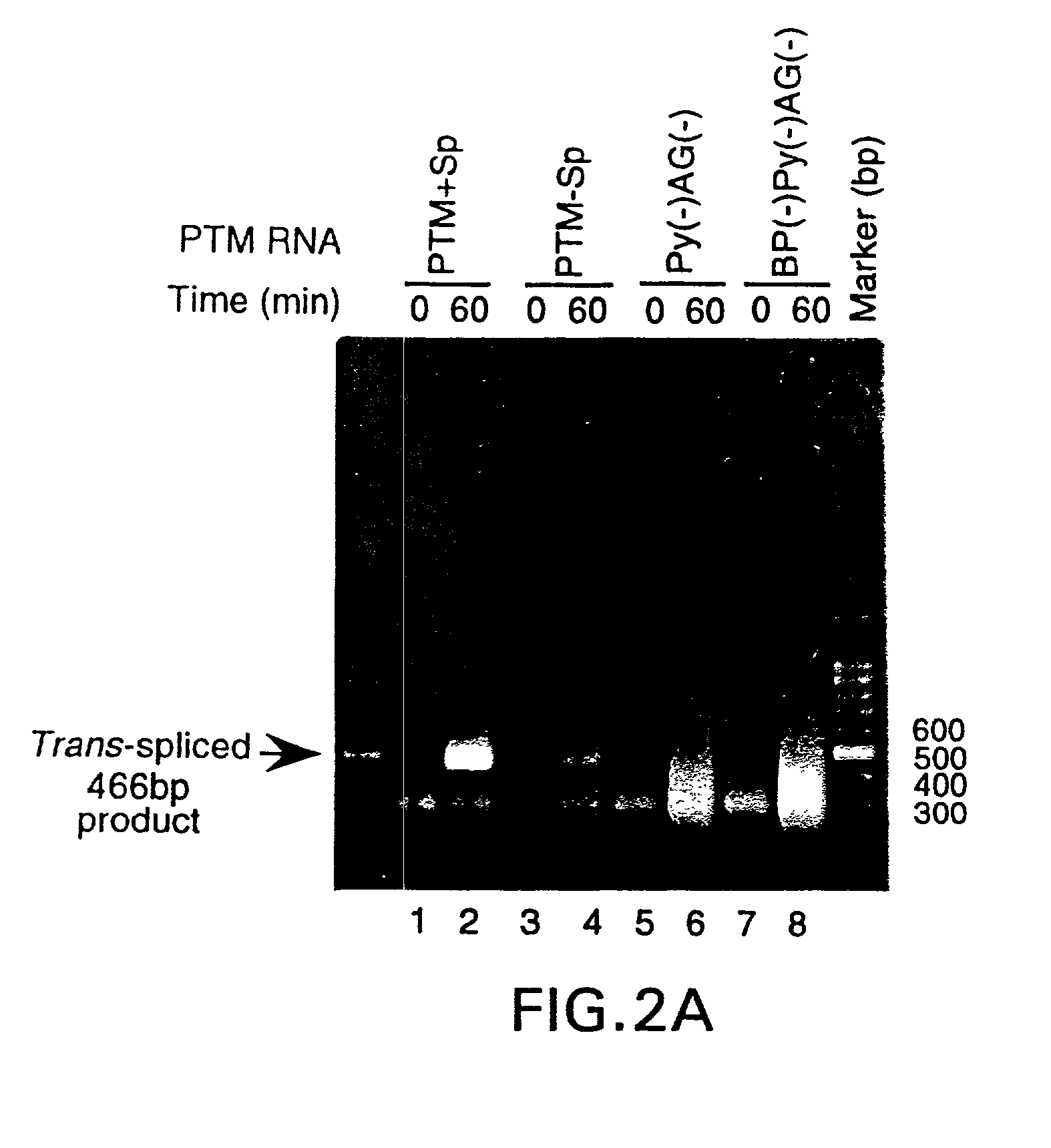
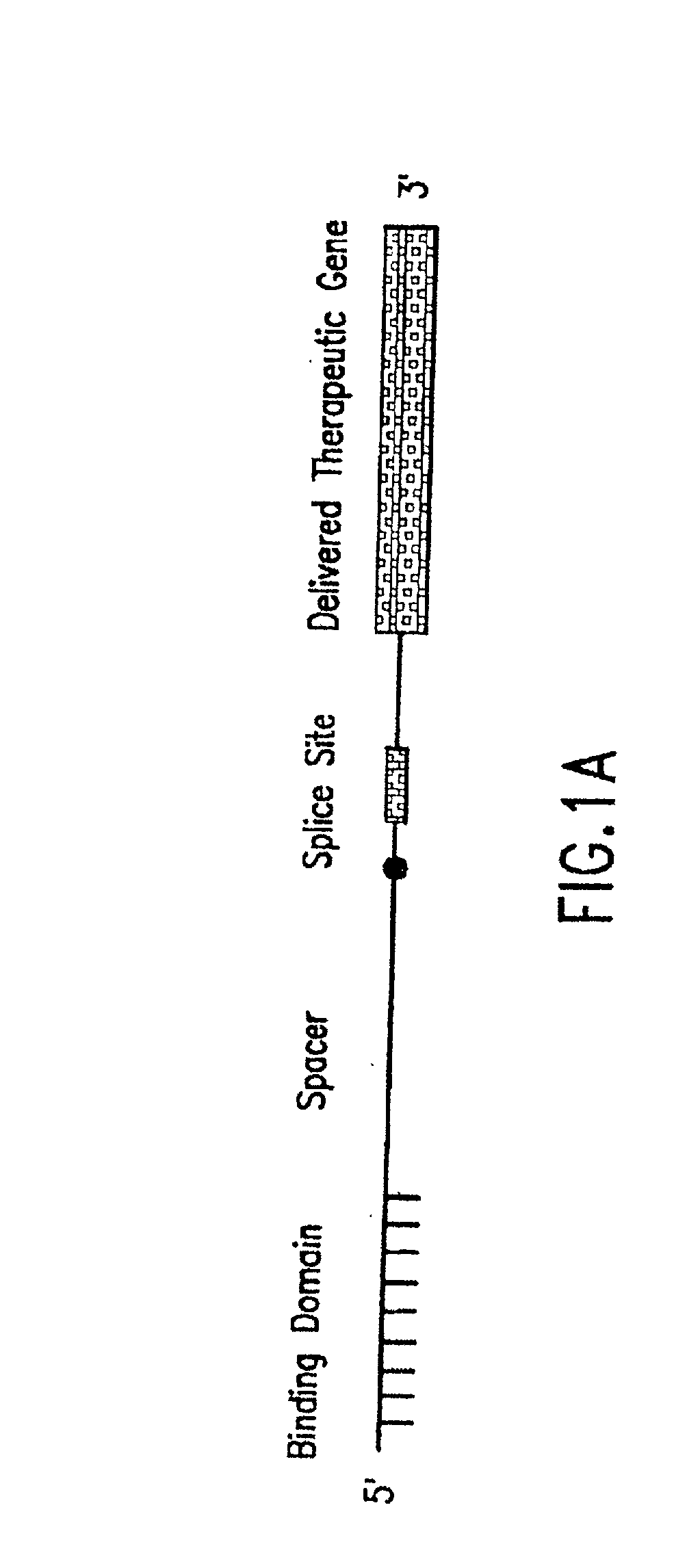
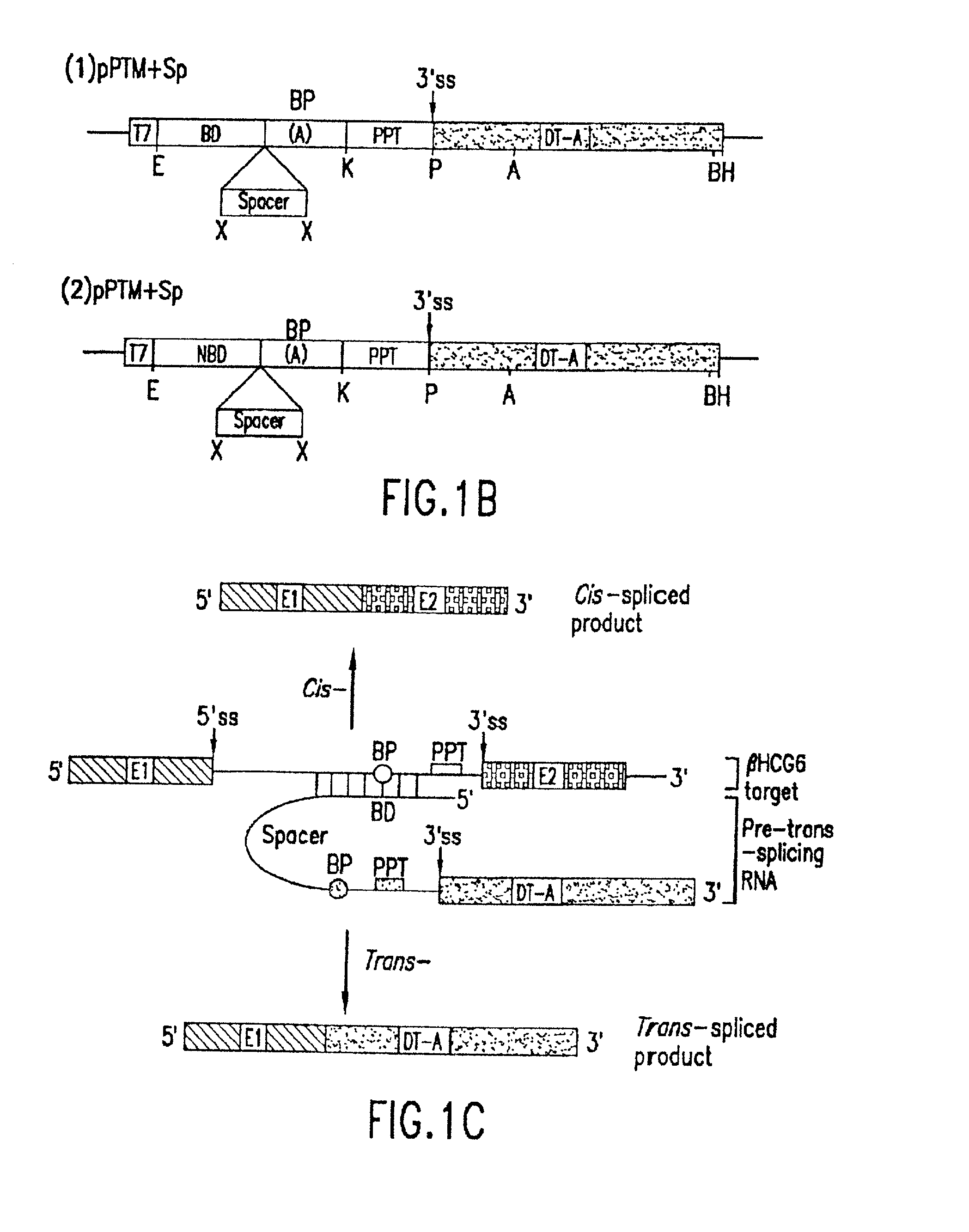
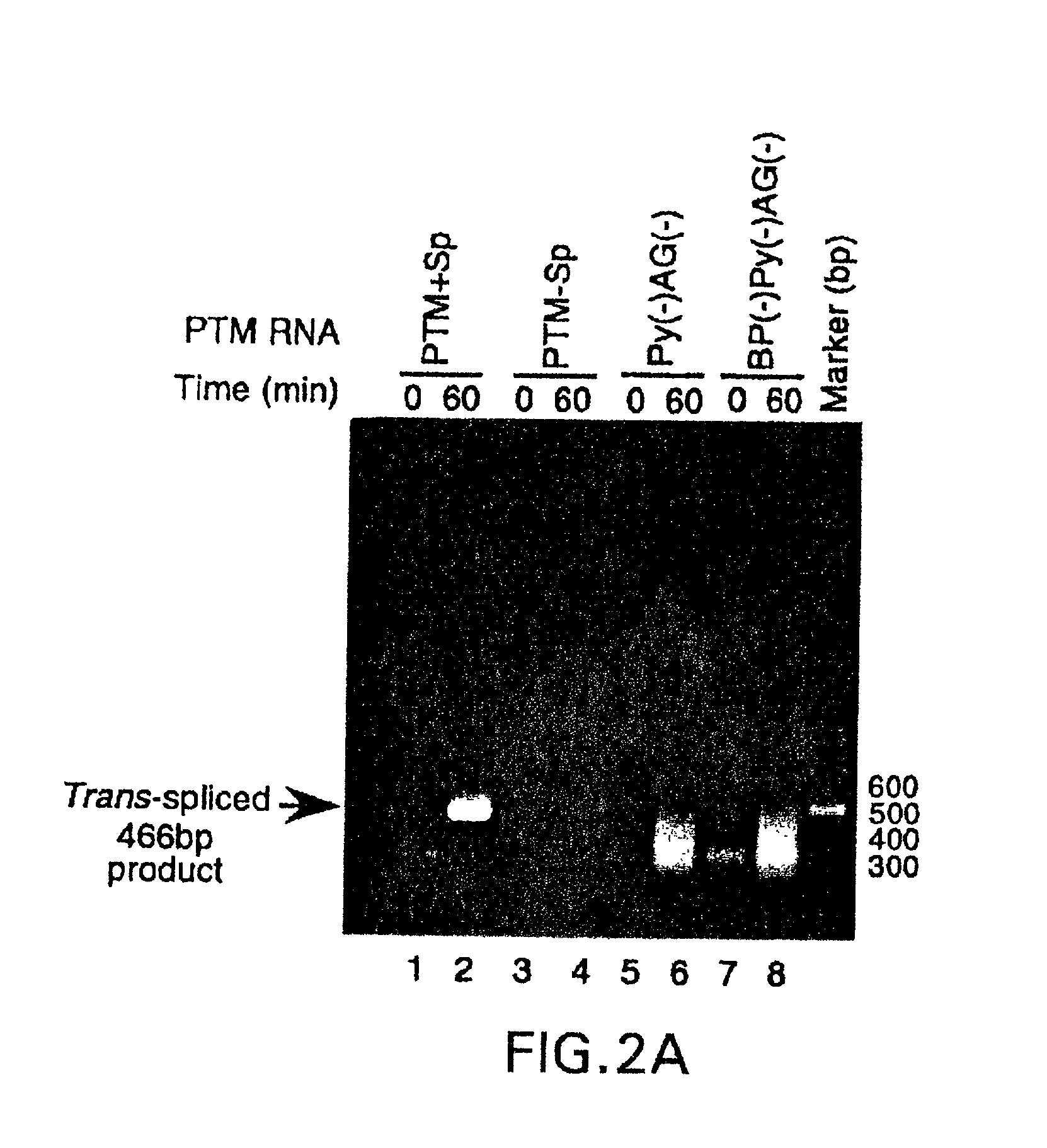
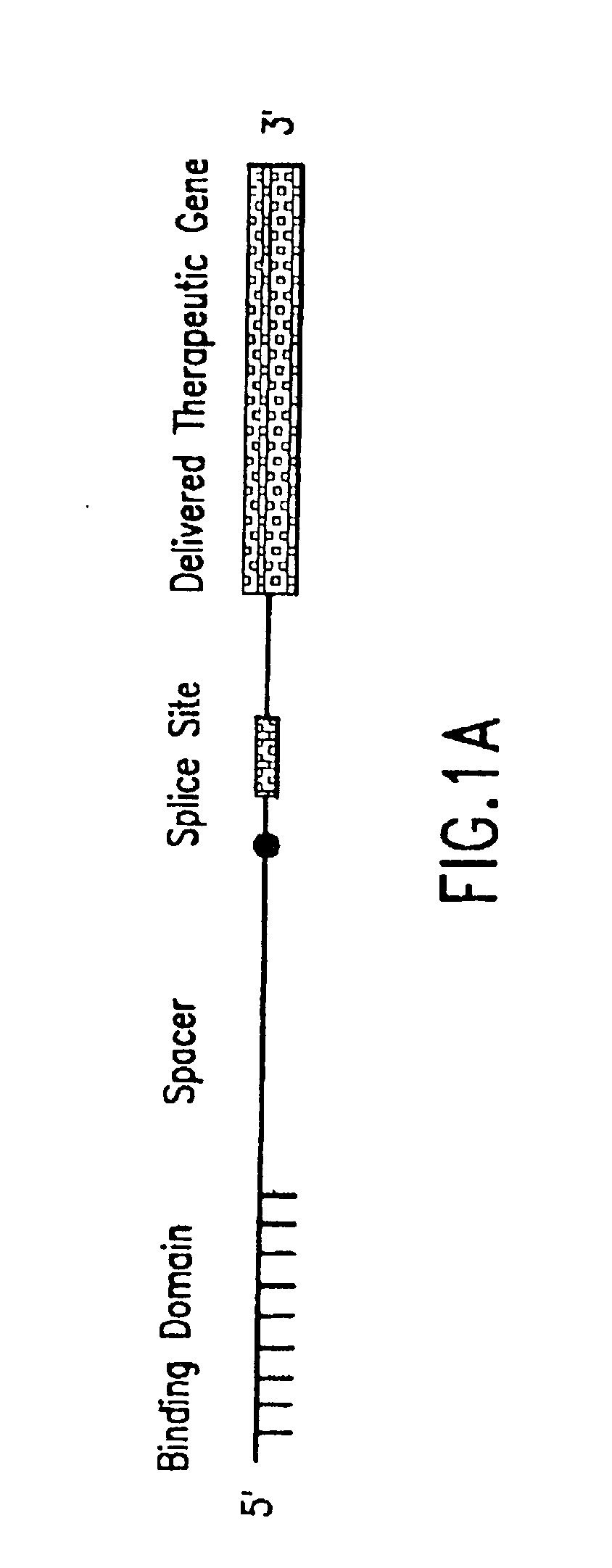
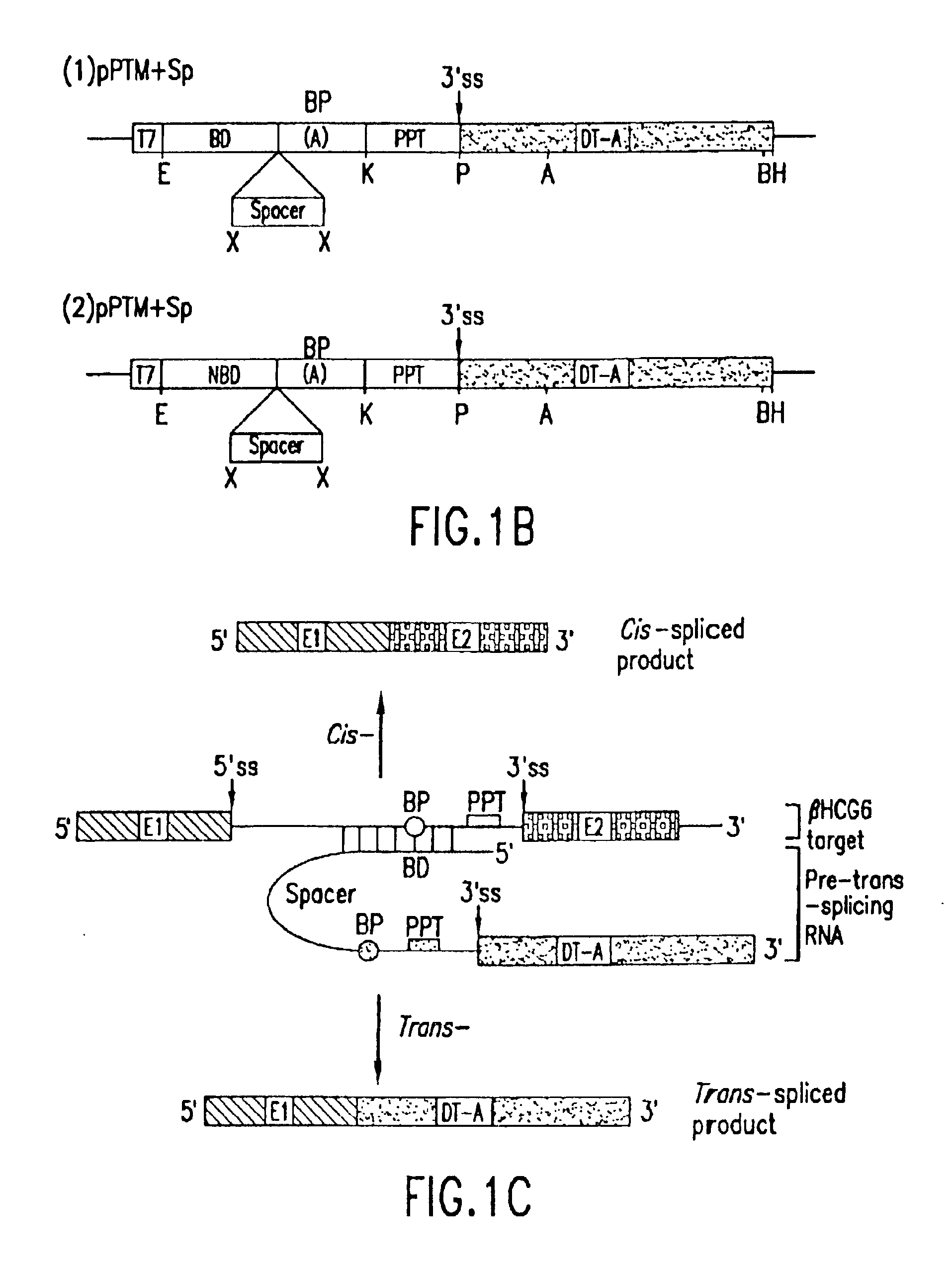
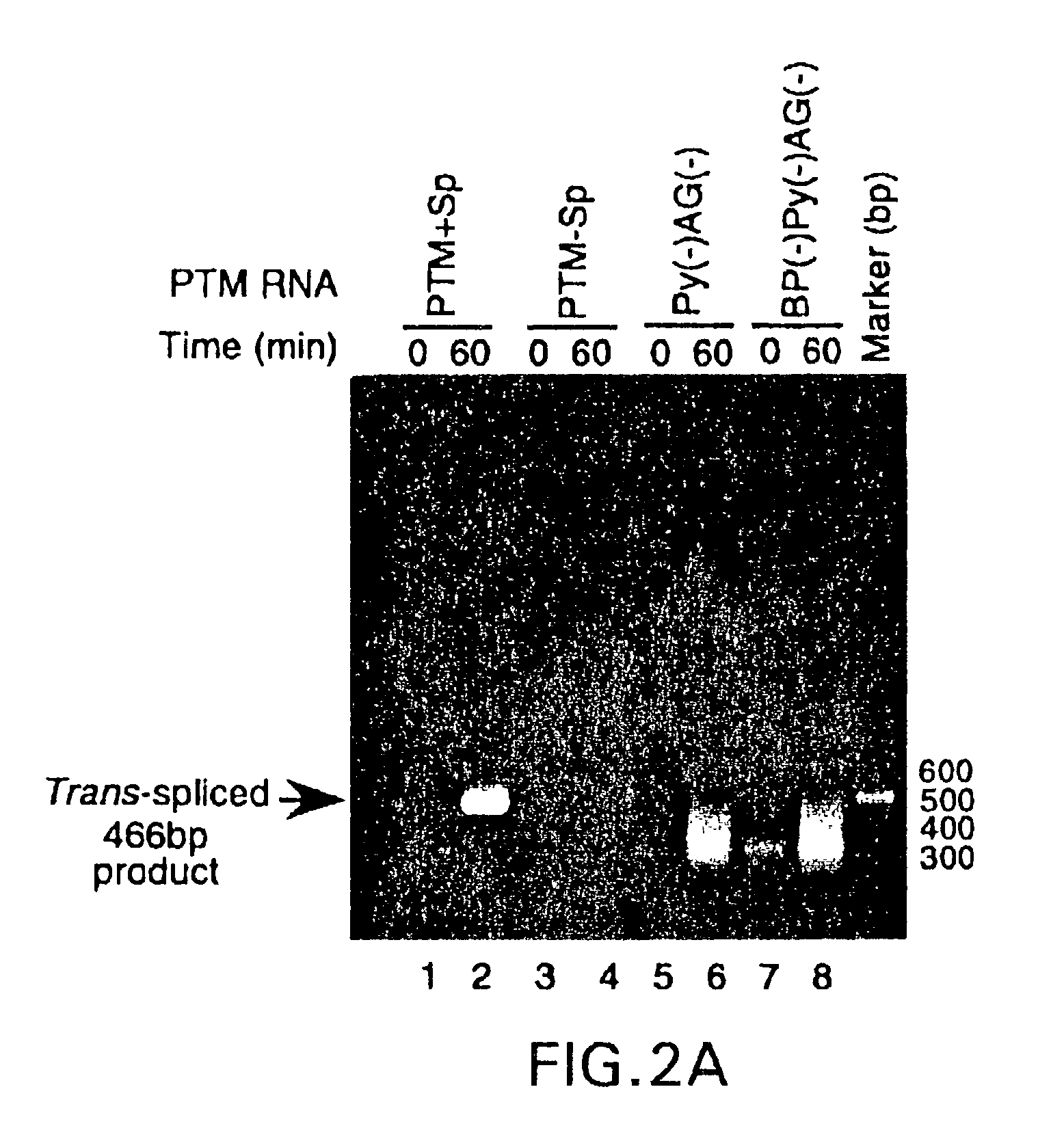
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
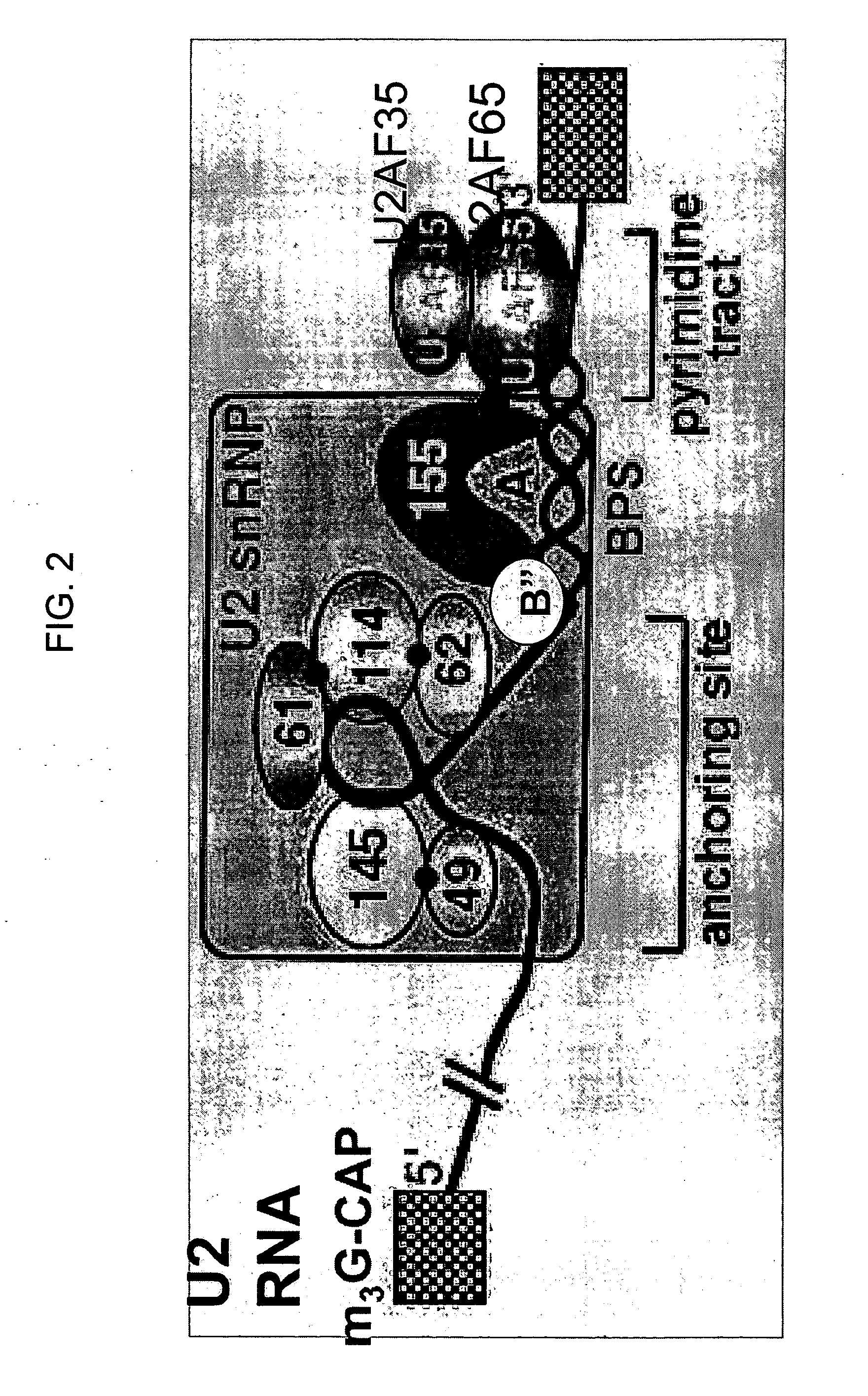
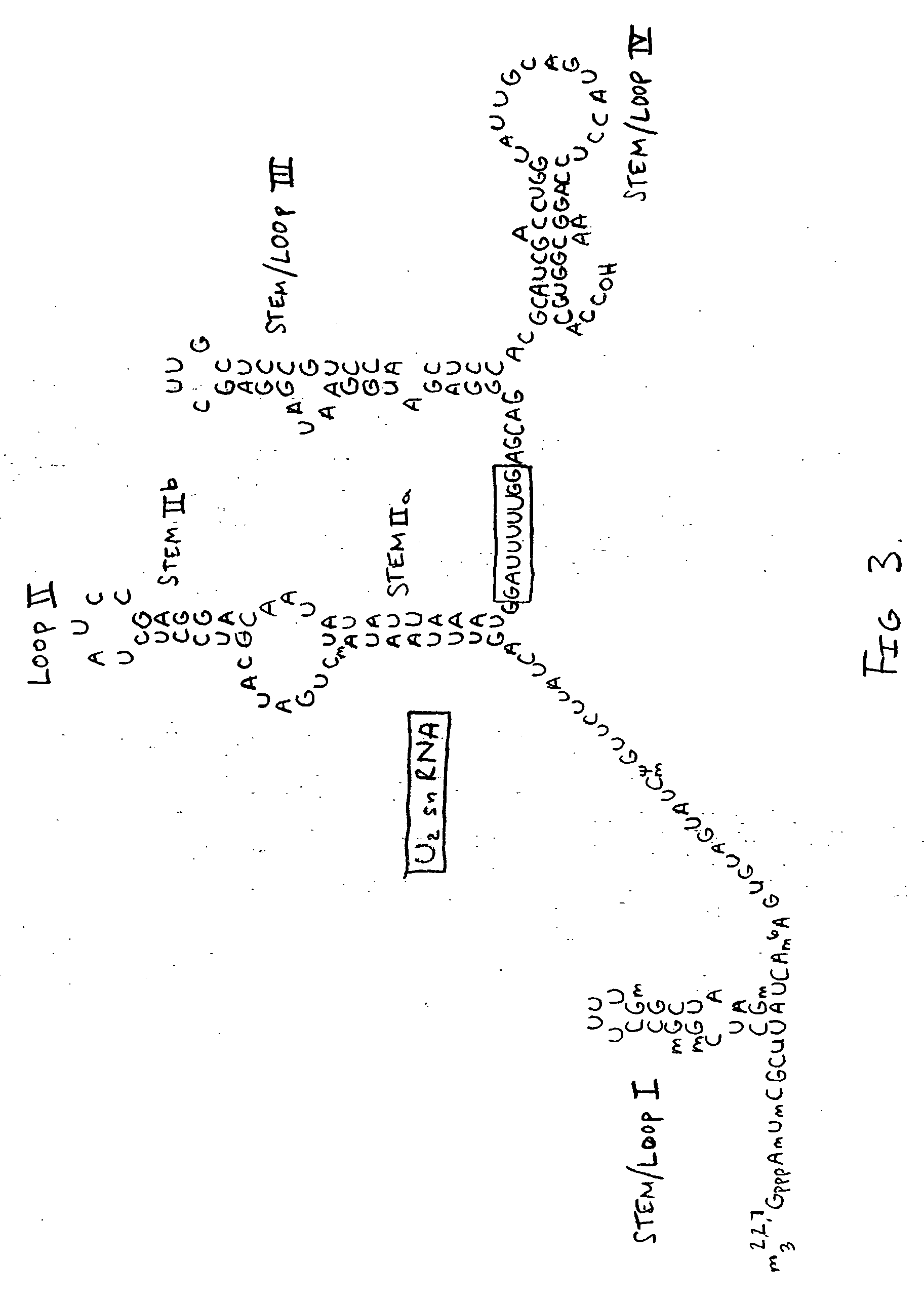
Methods and compositions for detecting cancer using components of the U2 spliceosomal particle
InactiveUS20060068434A1Easy to detectEasy to measureMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCancer detectionBiology
The present invention relates to cancer-associated proteins and nucleic acids that encode or bind specifically to cancer-associated proteins, which represent markers for cancer detection. Specifically, the invention provides a family of methods and compositions for detecting cancer, for example, breast cancer, in an individual using components of the U2 spliceosomal particle. A target cancer-associated protein may be detected, for example, by reacting the sample with a labeled binding moiety, for example, a labeled antibody capable of binding specifically to the protein. The invention also provides kits useful in the detection of cancer in an individual.
Owner:MILANO ACQUISITION CORP
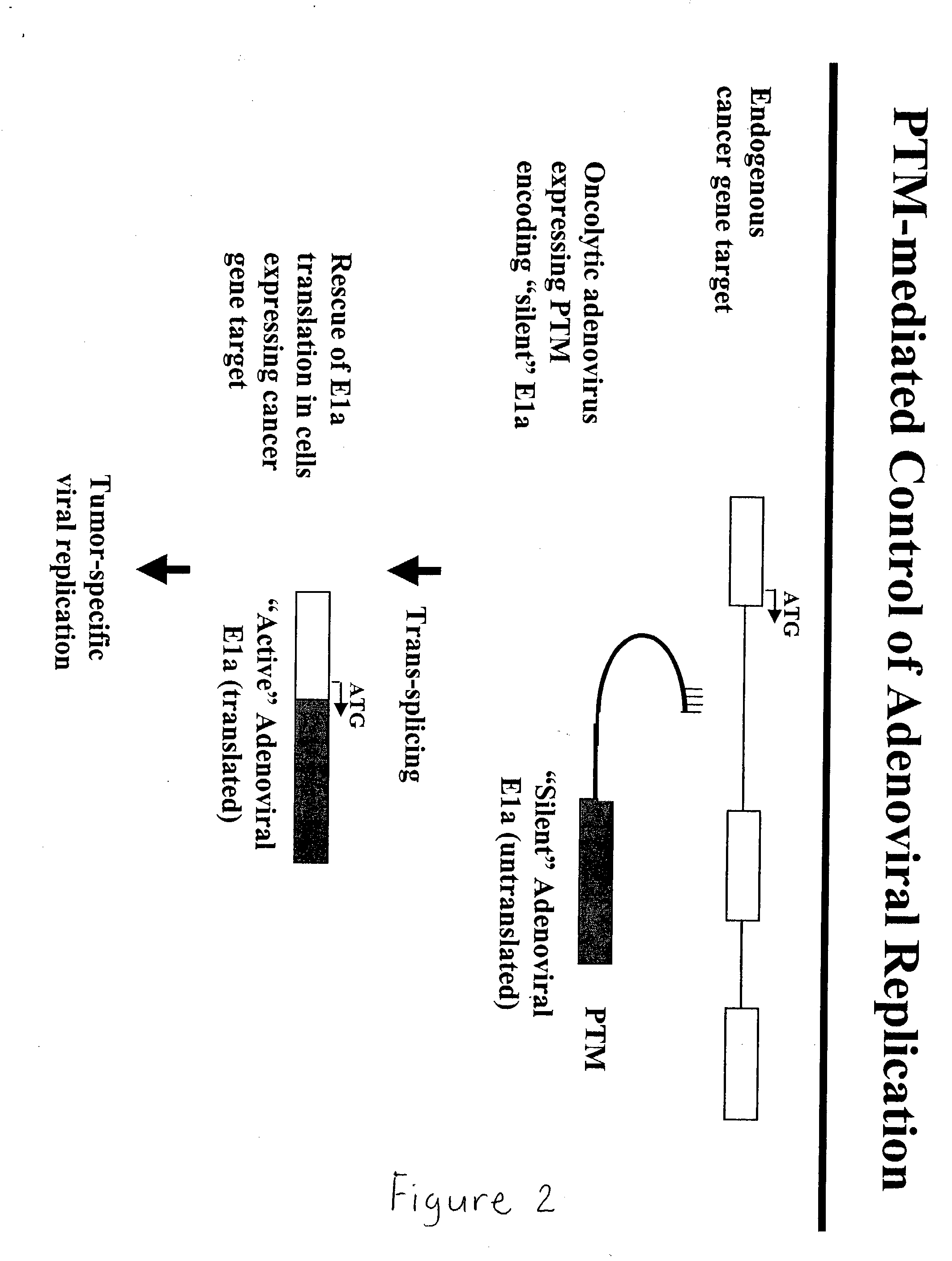
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing to confer cell selective replication to adenoviruses
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring tumor selective cell death on cancer cells expressing specific target precursor messenger RNA molecules (cancer cell selective target pre-mRNAs). The compositions of the invention include conditionally replicative adenoviruses that have been genetically engineered to express one or more pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with one or more cancer cell target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecules (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding adenovirus specific protein(s). Adenovirus specific proteins include those proteins complementing an essential activity necessary for replication of a defective adenovirus. The methods and compositions of the invention may be used to target a lytic adenovirus infection to cancer cells thereby providing a method for selective destruction of cancer cells. In addition, the adenoviruses of the invention may be engineered to encode PTMs designed to interact with target pre-mRNAs encoded by infectious agents within a cell, thereby targeting selective destruction of cells infected with such agents.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing to confer cell selective replication to adenoviruses
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring tumor selective cell death on cancer cells expressing specific target precursor messenger RNA molecules (cancer cell selective target pre-mRNAs). The compositions of the invention include conditionally replicative adenoviruses that have been genetically engineered to express one or more pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with one or more cancer cell target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of novel chimeric RNA molecules (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding adenovirus specific protein(s). Adenovirus specific proteins include those proteins complementing an essential activity necessary for replication of a defective adenovirus. The methods and compositions of the invention may be used to target a lytic adenovirus infection to cancer cells thereby providing a method for selective destruction of cancer cells. In addition, the adenoviruses of the invention may be engineered to encode PTMs designed to interact with target pre-mRNAs encoded by infectious agents within a cell, thereby targeting selective destruction of cells infected with such agents.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20020115207A1Inhibition of translationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSpliceosomeExon intron
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Selection in fungi
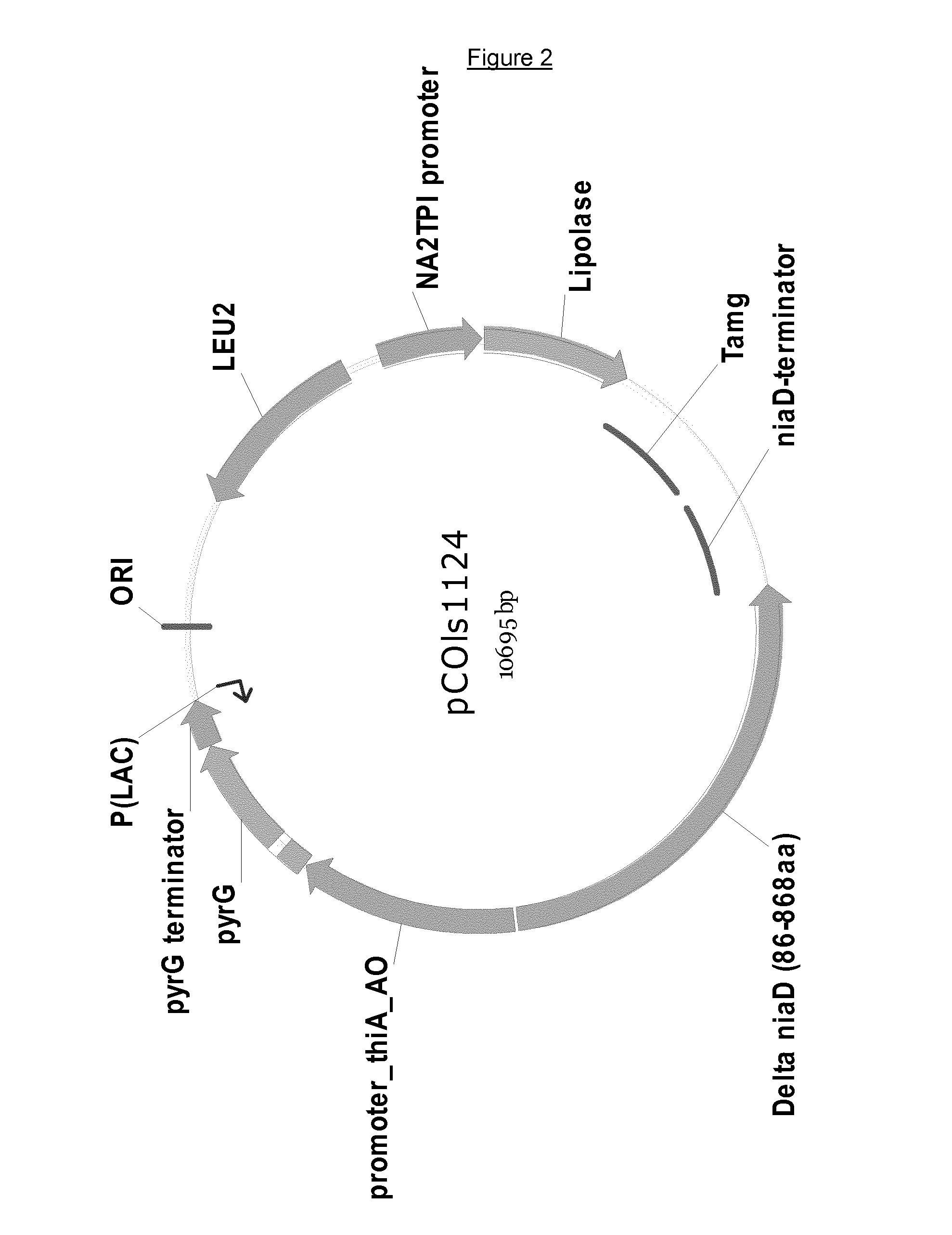
The present invention relates to methods for constructing a recombinant fungal host cell comprising one or more copies of a polynucleotide construct integrated in its genome, said method comprising transforming a fungal host cell with an integrative polynucleotide construct comprising a first polynucleotide encoding a selectable marker, wherein the first polynucleotide, a 5′ untranslated region thereof and / or a riboswitch operably linked therewith comprises a spliceosomal intron which has 5 nucleotides or less between its branch site and its acceptor site; and a second polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide of interest; as well as suitable polynucleotide constructs, resulting fungal host cells and methods of manufacture.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Eriocheir sinensis EsSXL gene, amplification primer group thereof and amplification method
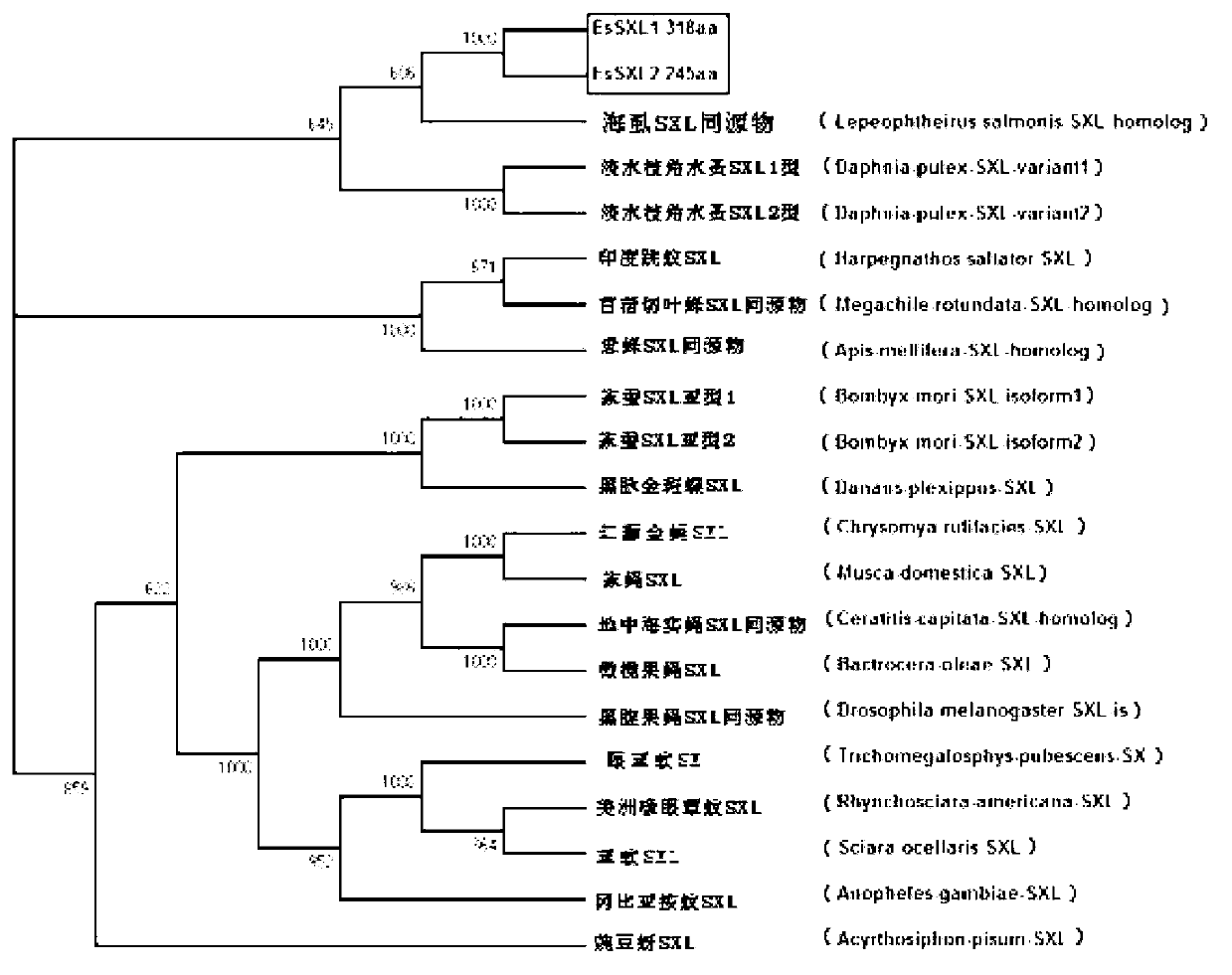
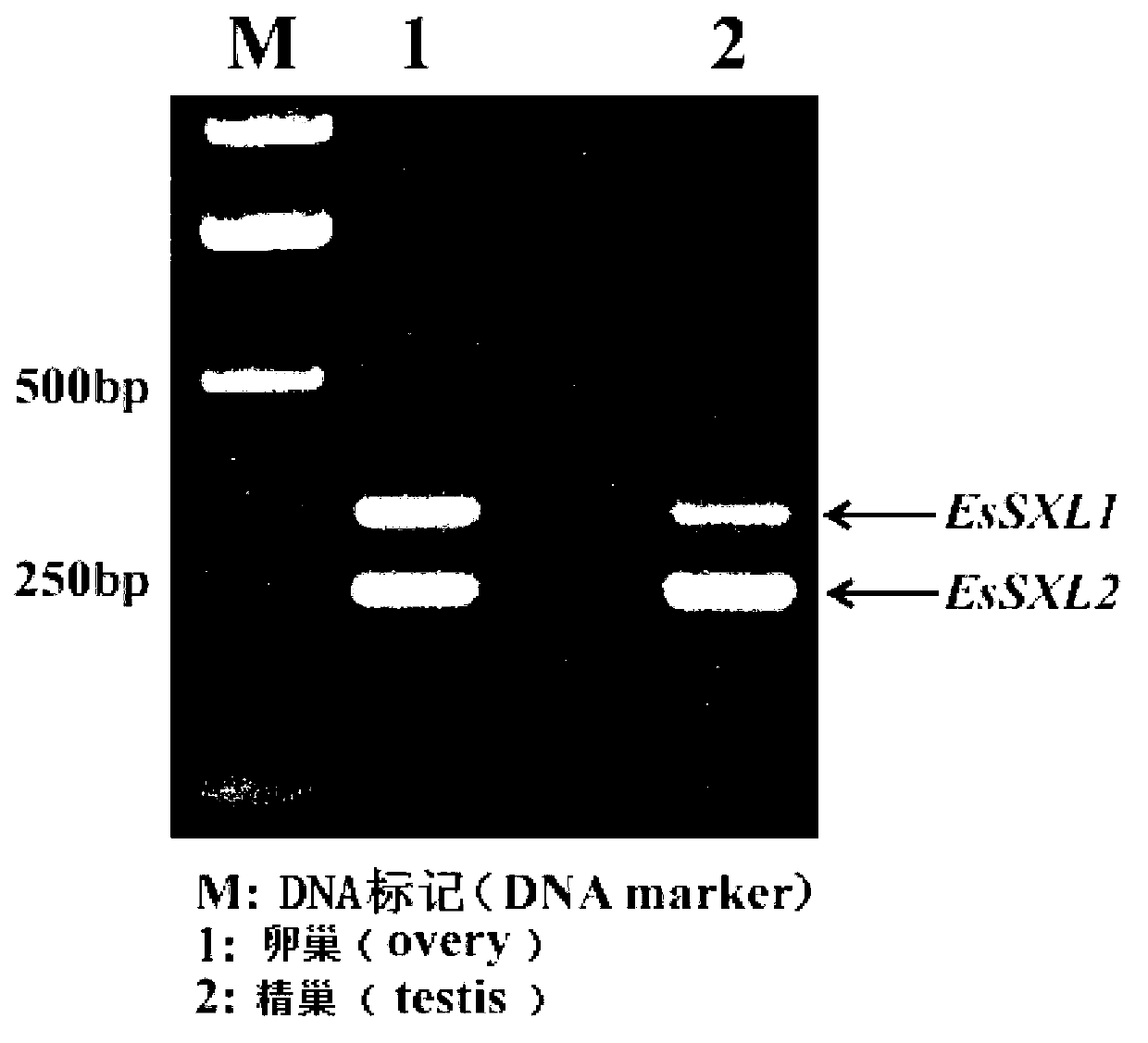
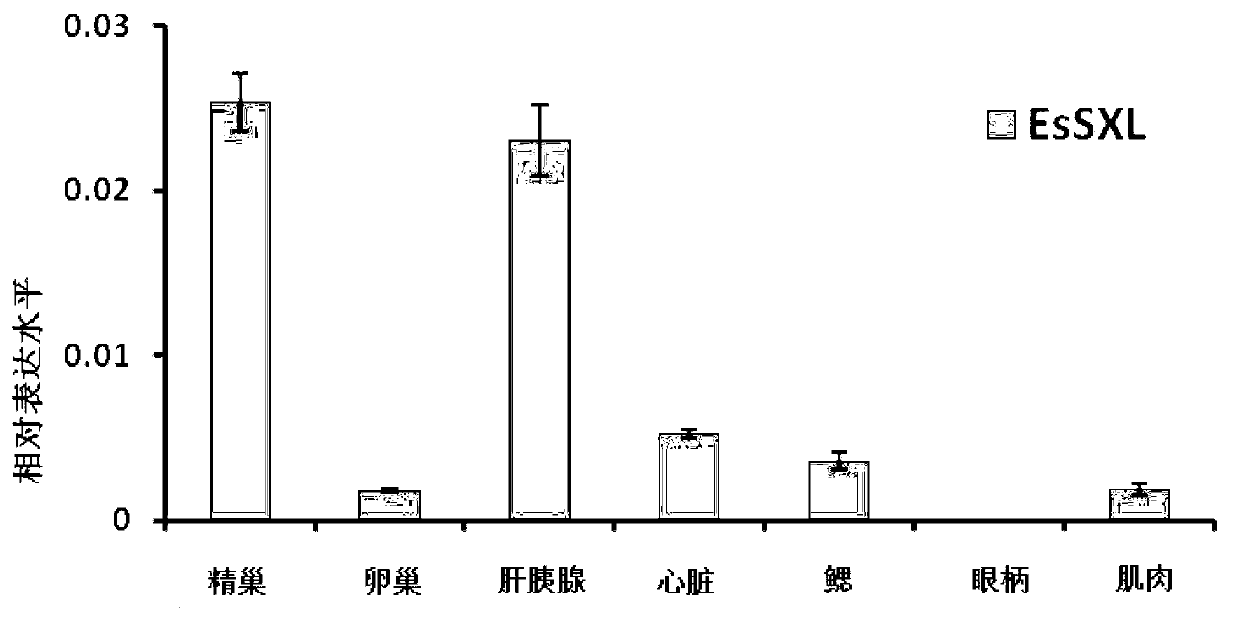
The invention discloses an Eriocheir sinensis EsSXL gene, an amplification primer group thereof and an amplification method. A full-length cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence of the EsSXL gene is cloned from an Eriocheir sinensis testis tissue by using the primer group provided by the invention, and the EsSXL gene comprises two variable spliceosomes EsSXL1 and EsSXL2, and lays an important foundation for the research of the important function of the function of the Eriocheir sinensis EsSXL gene in a sex differentiation process of the Eriocheir sinensis EsSXL gene.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Transgenic animal model for spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20030204861A1Efficiently mediate trans-splicingMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorPrecursor mRNAFhit gene
The present invention relates to development of an animal model system for in vivo testing of spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing reactions. The present invention provides transgenic animals, and methods for generating such animals, that have been genetically engineered to expresses a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) that serves as a substrate for a trans-splicing reaction. Specifically, the transgenic animals contain at least one transgene capable of expressing a target pre-mRNA molecule. The invention provides methods, based on utilization of the transgenic animals, for assessing the specificity and efficiency of a pre-trans-splicing molecule (PTM) designed to interact with a target pre-mRNA and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule. The present invention further relates to the transgenic expression of PTM molecules in animals to determine gene function, i.e, functional genetics. The present invention is based on the successful generation of a transgenic animal expressing a target pre-mRNA and, moreover, the use of that animal to detect accurate in vivo trans-splicing reactions in the presence of a PTM.
Owner:VIRXSYS +1
Selection in fungi
ActiveUS9487767B2High product yieldHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAFungal microorganismsNucleotide
The present invention relates to methods for constructing a recombinant fungal host cell comprising one or more copies of a polynucleotide construct integrated in its genome, said method comprising transforming a fungal host cell with an integrative polynucleotide construct comprising a first polynucleotide encoding a selectable marker, wherein the first polynucleotide, a 5′ untranslated region thereof and / or a riboswitch operably linked therewith comprises a spliceosomal intron which has 5 nucleotides or less between its branch site and its acceptor site; and a second polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide of interest; as well as suitable polynucleotide constructs, resulting fungal host cells and methods of manufacture.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20030027250A1Inhibition of translationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRNA Trans-SplicingIntein
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20030148937A1Inhibition of translationFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsRNA Trans-SplicingIntein
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
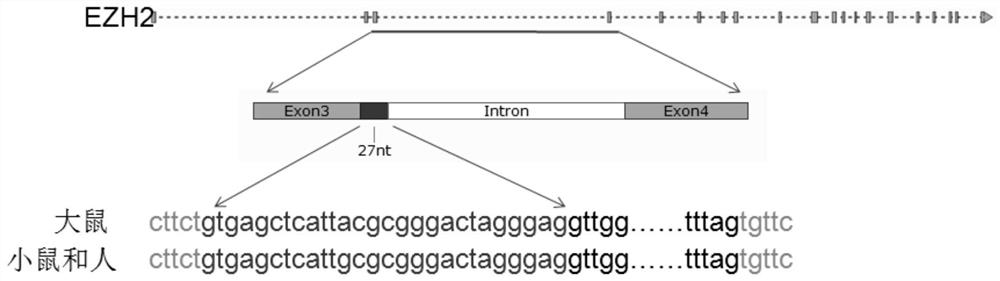
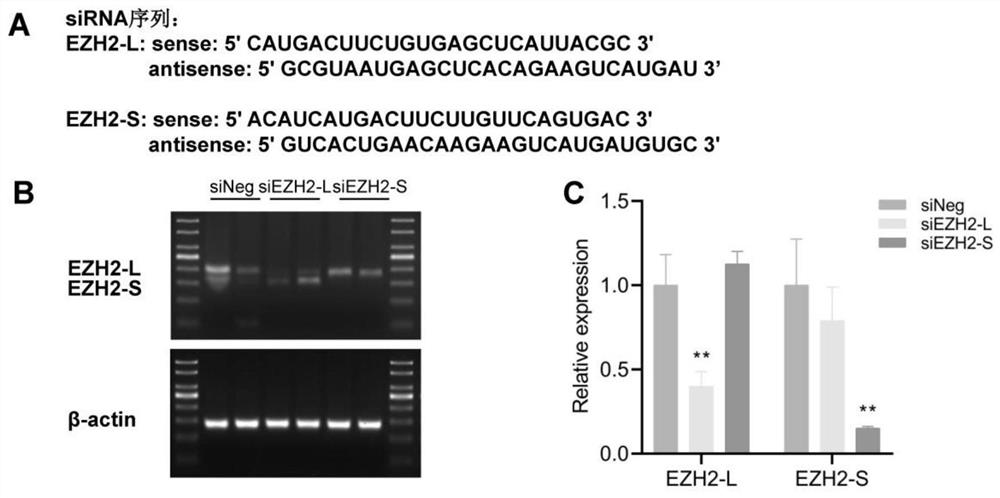
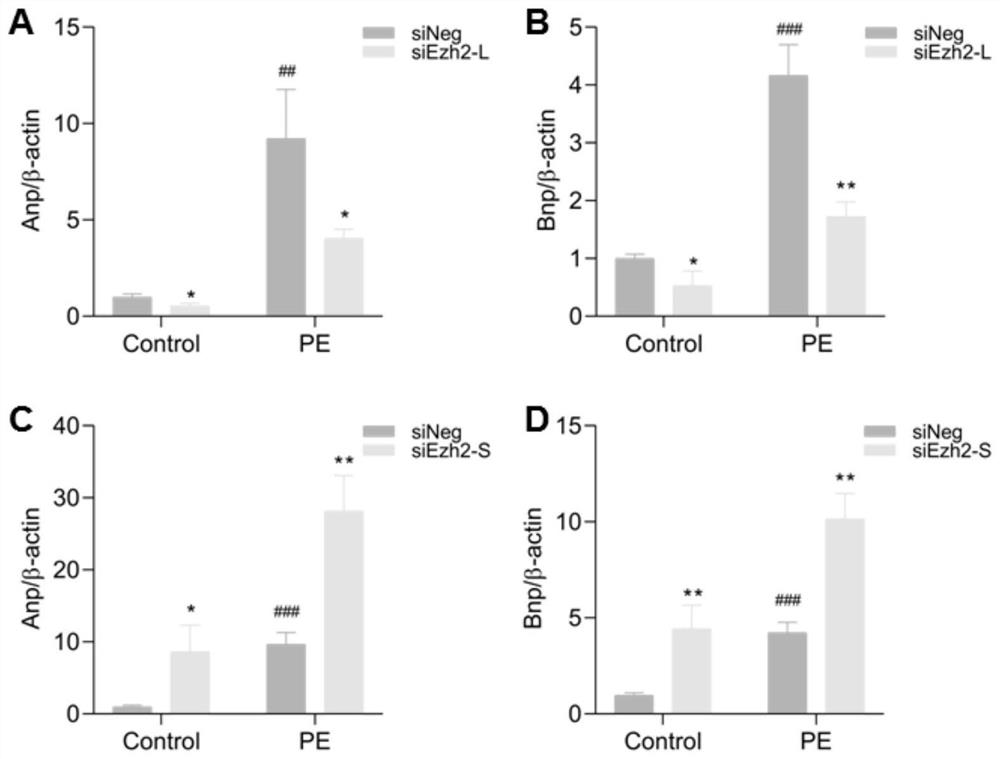
EZH2 variable spliceosome and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to an EZH2 variable splicing site and an application thereof. Specific siRNA is used for knocking down two subtypes ofEZH2-L and EZH2-S respectively, and myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure models are established at the cellular level and the animal level respectively. Results show that after the EZH2-L is knocked down, the expression level of a myocardial hypertrophy pathological gene is obviously reduced, the myocardial cell area is reduced, and the heart weight is reduced; and after the EZH2-S is knockeddown, the expression level of the myocardial hypertrophy pathological gene is remarkably increased, the myocardial cell area is increased, the heart weight is increased, and the situation prompts that the EZH2-L and the EZH2-S have the effects of promoting and inhibiting myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure respectively. In addition, after the EZH2-L is knocked down, tumor cell proliferationis inhibited, and knock-down of the EZH2-S has no influence on tumor cell proliferation. The invention provides a new target and a new strategy for research and development of medicines for treating EZH2 gene related diseases.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
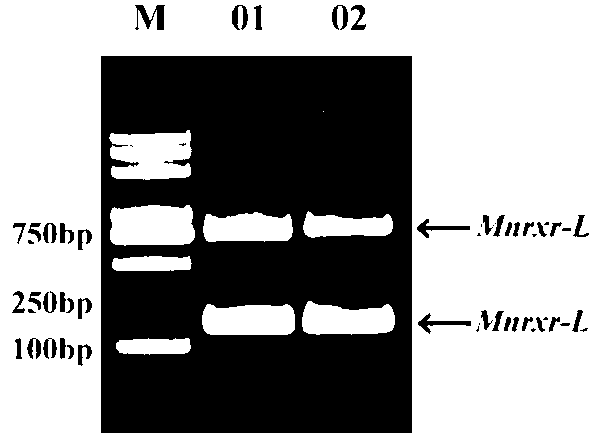
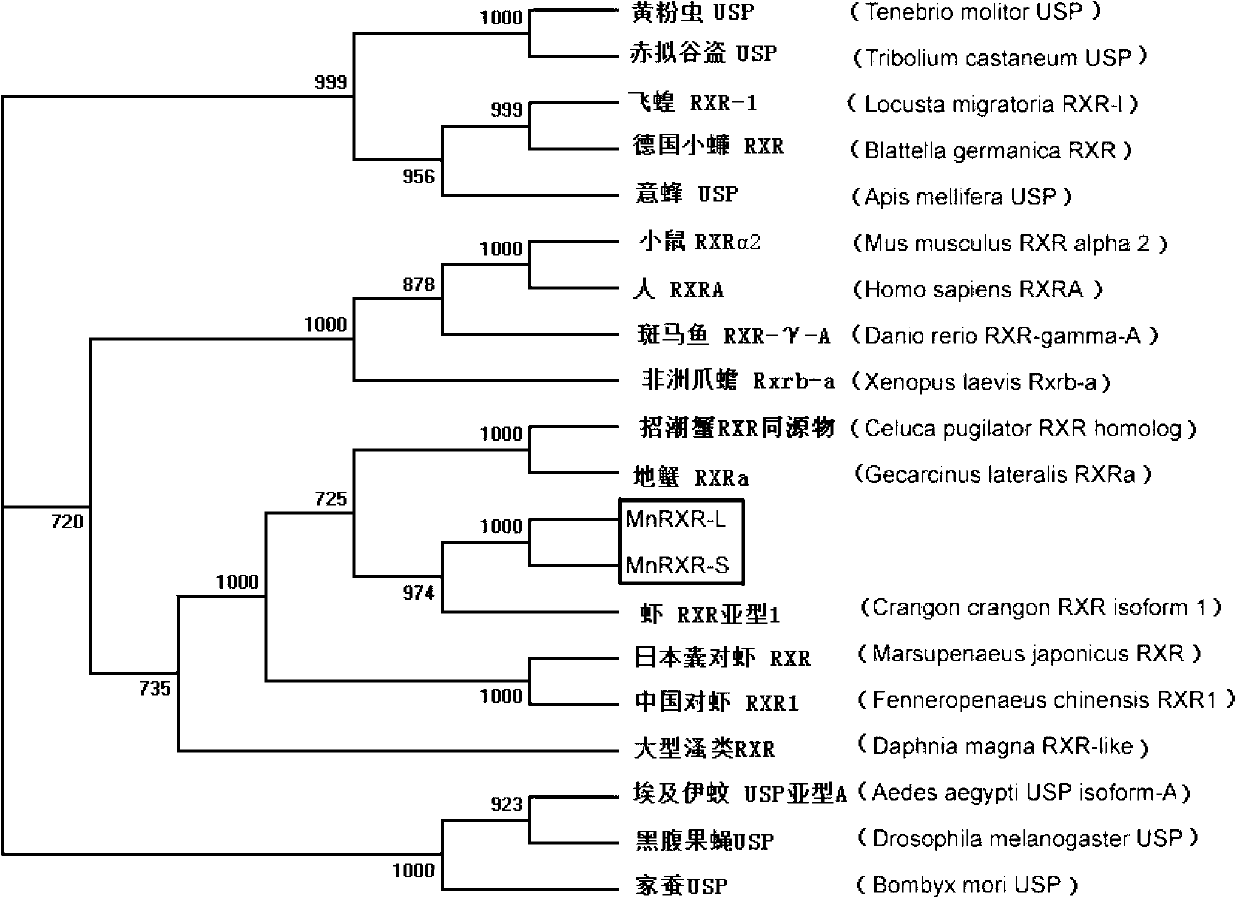
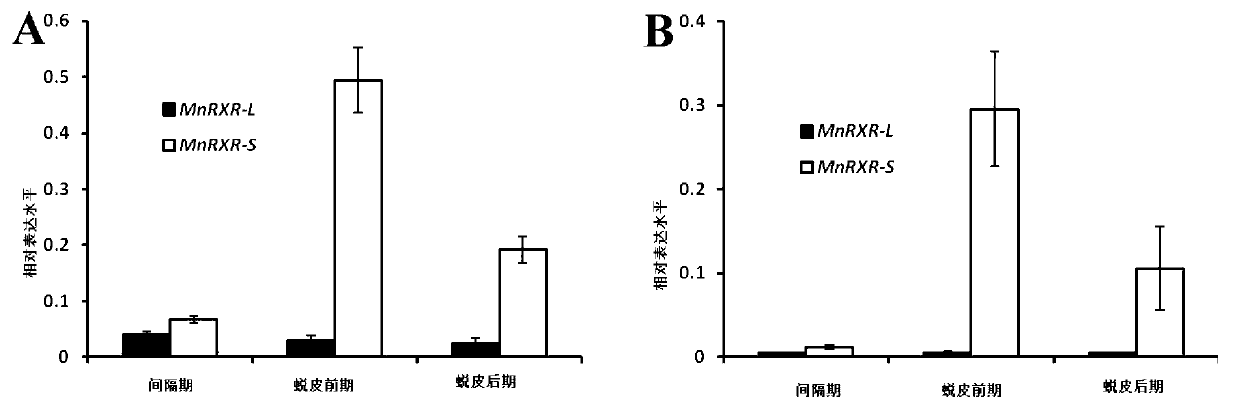
MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, and amplification primer group and amplification method thereof
The invention discloses a MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, and an amplification primer group and an amplification method thereof. A full-length cDAN sequence of the MnRXR gene is cloned from the hepatopancreas tissue of macrobrachium nipponensis. The gene comprises two variable spliceosomes: MnRXR-L and MnRXR-S. The invention lays an important base for research on functions of the MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, in particularon important effects in a moult cycle.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS20030077754A1Inhibition of translationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSpliceosomeExon intron
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
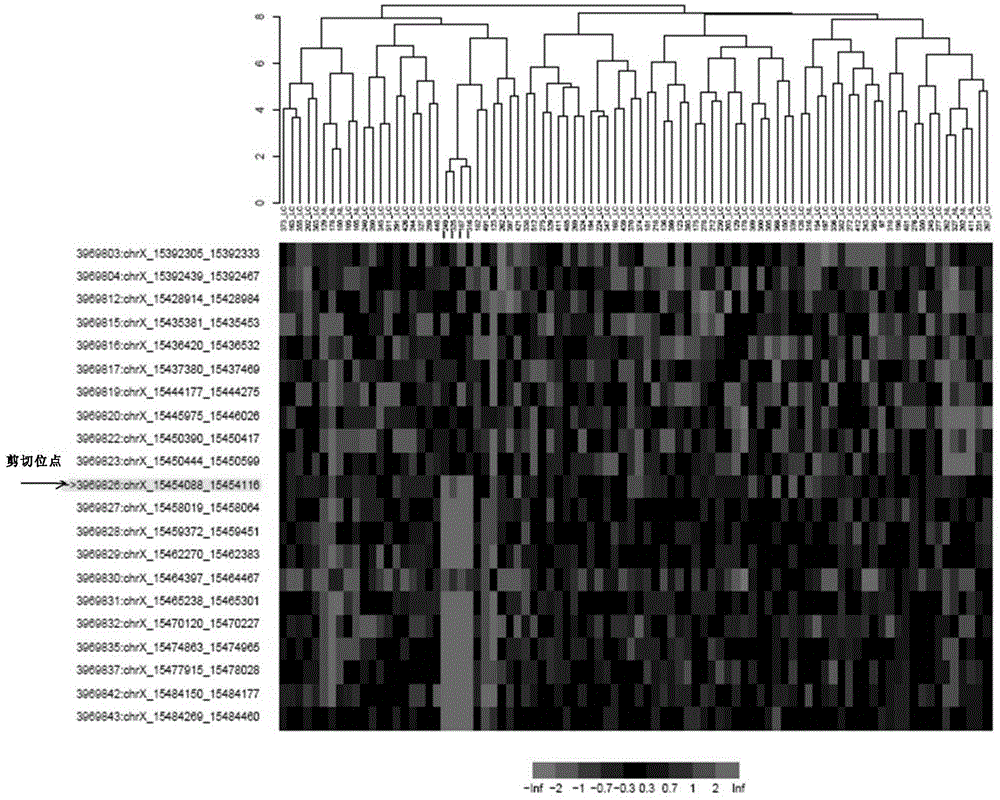
Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group
ActiveCN111733238AStrong specificityFacilitates molecular diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerFluoProbes
The invention discloses a primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of a PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and a test kit and application of the primer group. The primer group for identifyingthree kinds of spliceosomes of the PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene comprises a specific forward primer, a reverse primer, a specific fluorescent probe and a competitive primer which are used for detectingPML-RAR[alpha] fusion genes bcr1, bcr2 and bcr3 spliceosomes; according to the invention, a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology is applied, multiple PCR primers and the specific fluorescent probe are adopted, and the three spliceosomes bcr1, bcr2 and bcr3 of the PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene in a sample can be simultaneously detected in one reaction through the competitive primer; the primer group can be widely applied to multiple fields such as clinical early diagnosis, drug curative effect, after-healing monitoring and scientific research of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene related diseases, and has the characteristics of semi-automatic detection, high detection speed, high sensitivity and wide sample application range.
Owner:广州血康陆道培生物技术有限公司
Spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing for correction of skin disorders
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated RNA trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention can be genetically engineered to interact with a specific target pre-mRNA expressed in cells of the skin so as to result in correction of genetic defects responsible for a variety of different skin disorders to encode a reporter molecule or protein that may have therapeutic benefit. The compositions of the invention further include recombinant vectors systems capable of expressing the PTMs of the invention and cells expressing said PTMs. The methods of the invention encompass contacting the PTMs of the invention with specific target pre-mRNA expressed within cells of the skin under conditions in which a portion of the PTM is trans-spliced to a portion of the target pre-mRNA to form a chimeric RNA molecule wherein the genetic defect in the specific gene has been corrected. The present invention is based on the successful trans-splicing of the collagen XVII pre-mRNA thereby establishing the usefulness of trans-splicing for correction of skin specific genetic defects. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for treatment of specific disorders of the skin, i.e., genodermatoses, such as epidermal fragility disorders, keratinization disorders, hair disorders and pigmentation disorders as well as cancers of the skin.
Owner:VIRXSYS
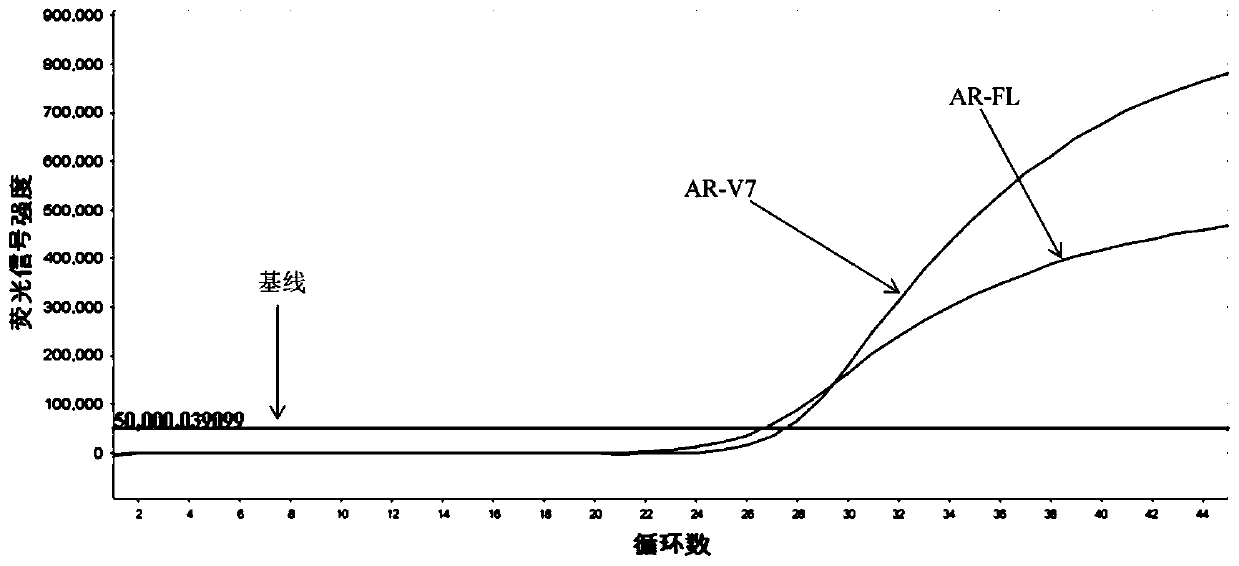
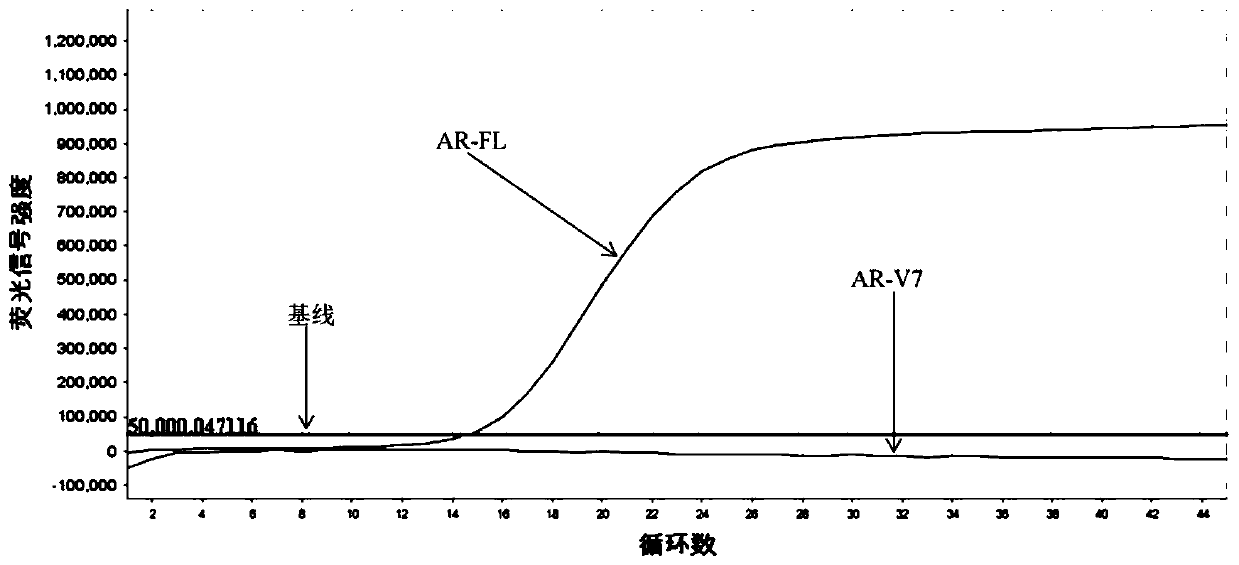
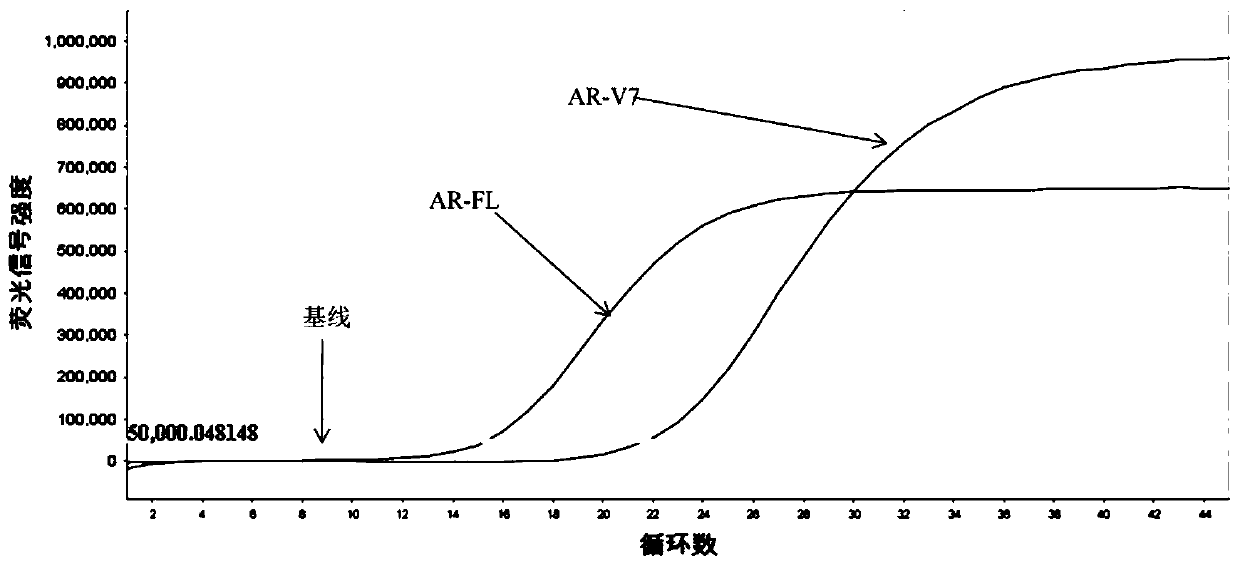
Primer probe composition, kit and detection method for detecting human AR-V7 and AR gene expression
InactiveCN111500728AEasy accessHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerSpliceosome
The invention provides a primer probe composition, a kit and a detection method for detecting human AR-V7 and AR gene expression. The primer probe composition comprises an AR-V7 forward primer with anucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, an AR-V7 reverse primer with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2, an AR-V7 probe with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3, an AR forward primer with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 4, an AR reverse primer with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 5, an AR probe with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.6 and an internal reference primer probe. According to the invention, the specific primers and probes are used for respectively amplifying AR full length and AR-V7 spliceosome molecules in blood cellRNA, and has the advantages of rapidness, high sensitivity, simplicity and convenience in operation, reduction of sample pollution in the intermediate process, low misoperation risk and the like.
Owner:WUXI SHENRUI BIO PHARMA
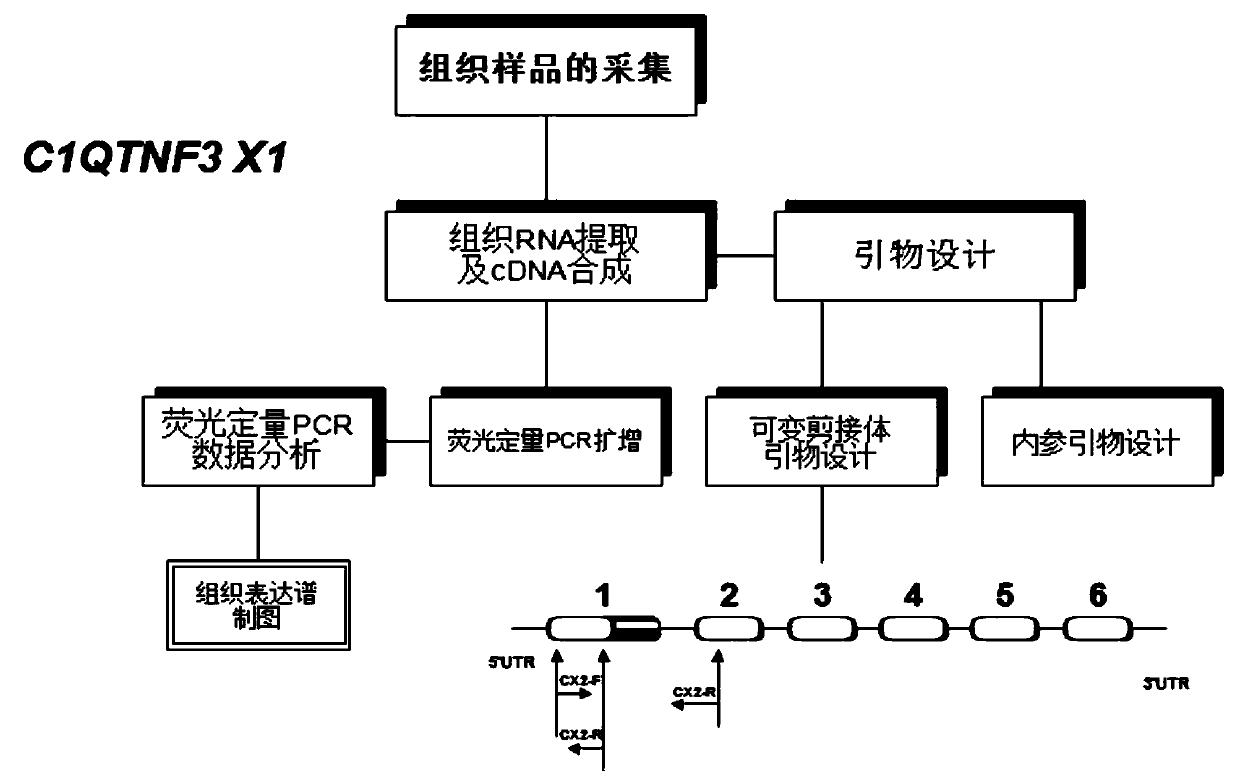
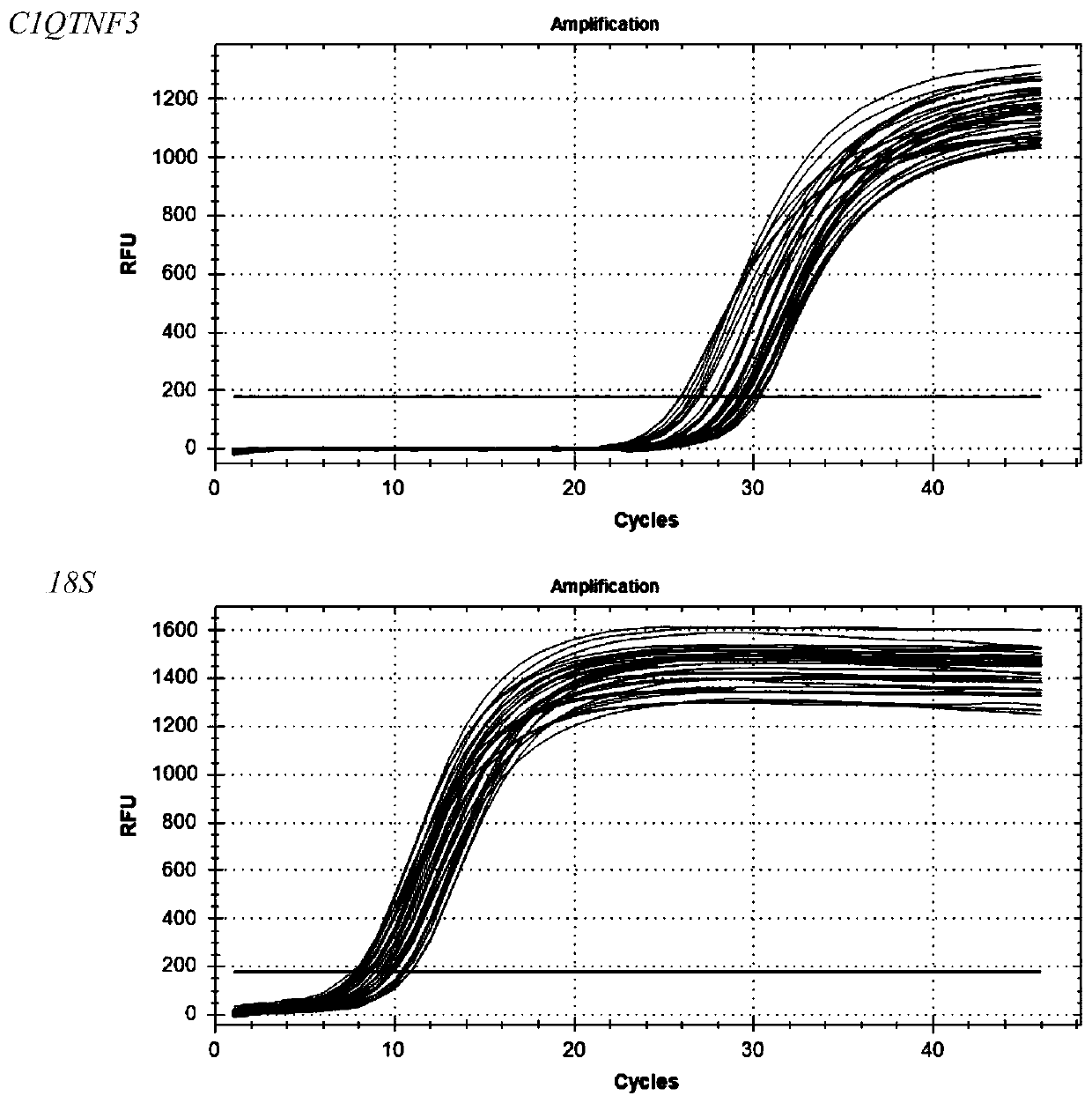
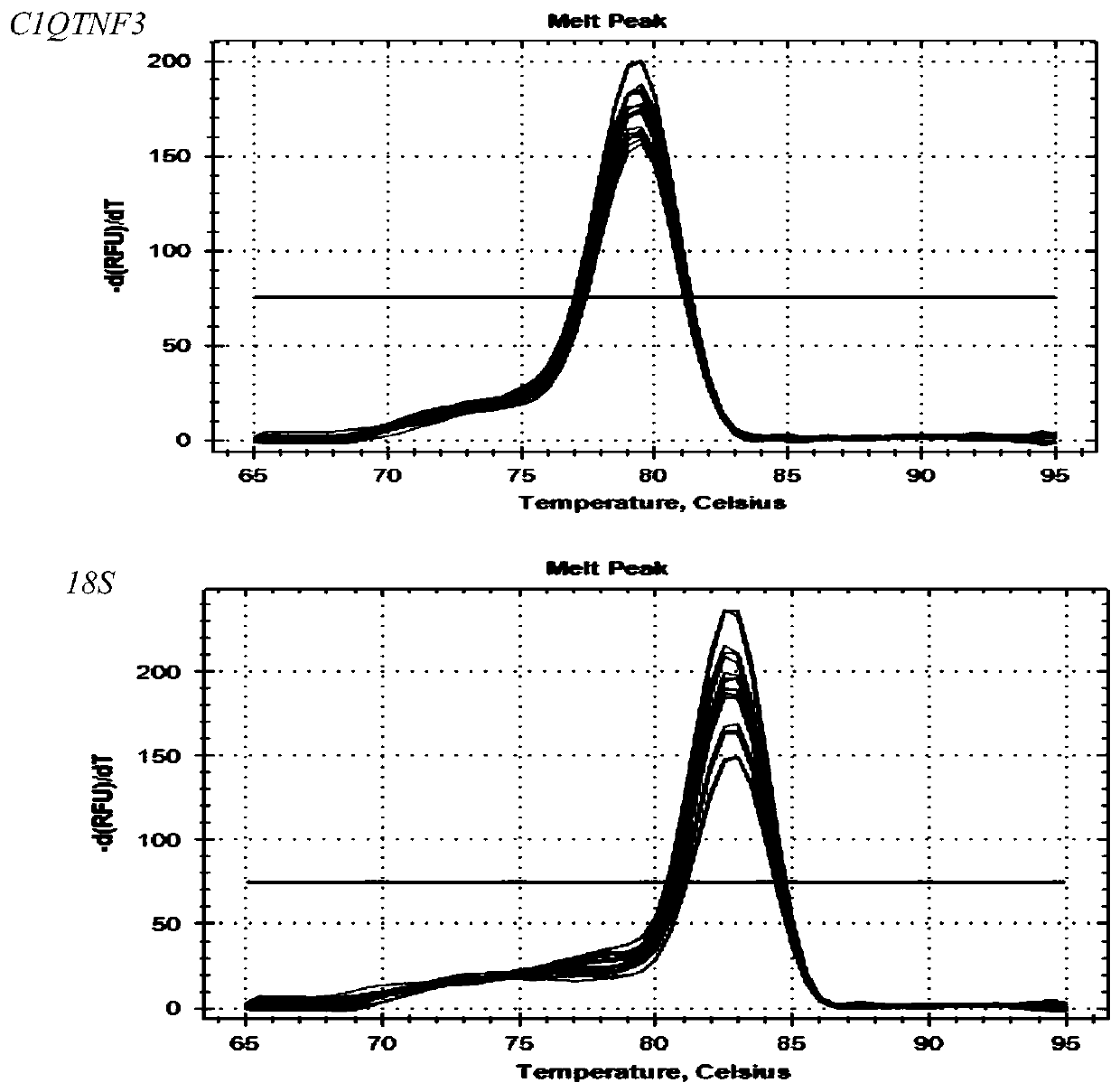
Primer, kit and detection method for detecting C1QTNF3 gene 219bp-deletion variable spliceosome
PendingCN109825560APracticalMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpliceosome complexGene
The invention provides a primer, kit and detection method for detecting C1QTNF3 gene 219bp-deletion variable spliceosome. The sequence of the primer for detecting the C1QTNF3 gene 219bp-deletion variable spliceosome is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and 2. The for detecting C1QTNF3 gene 219bp-deletion variable spliceosome is separated from various splicing forms of the gene , the expression level of the C1QTNF3 gene 219bp-deletion variable spliceosome is quantitatively analyzed, the detection method is accurate, quick, convenient to use and high in practicability.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
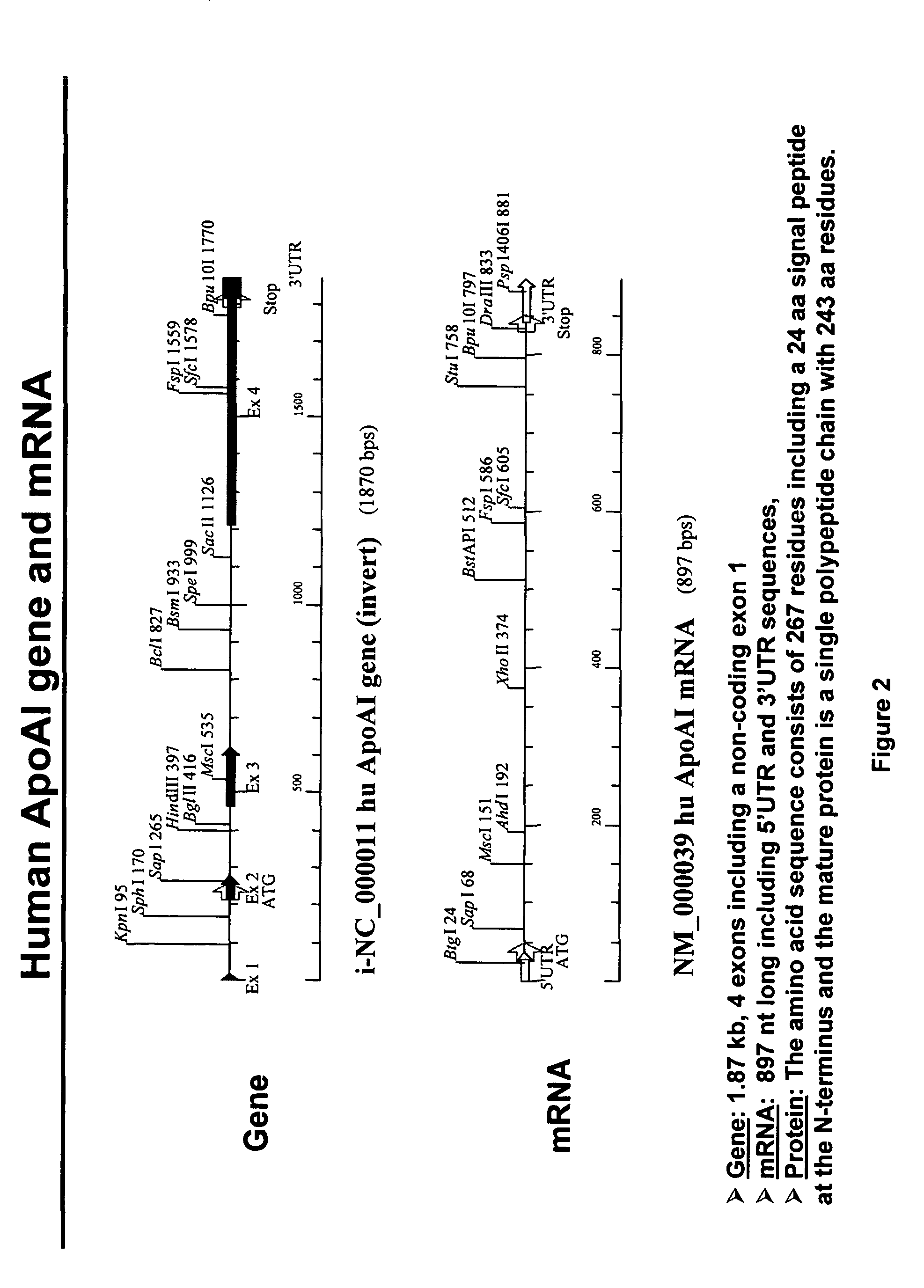
Expression of apoAI and variants thereof using spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
InactiveUS7968334B2Reduce buildReduce usageSplicing alterationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRNA Trans-SplicingMessenger RNA
Methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing that result in expression of a apoAI protein, an apoAI variant, the preferred embodiment referred to herein as the apoAI Milano variant, a pre-pro-apoAI or an analogue of apoAI. The methods and compositions include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding apoAI, the apoAI Milano variant, or an analogue of apoAI. The expression of this apoAI protein results in protection against vascular disorders resulting from plaque build up, i.e., atherosclerosis, strokes and heart attacks.
Owner:VIRXSYS
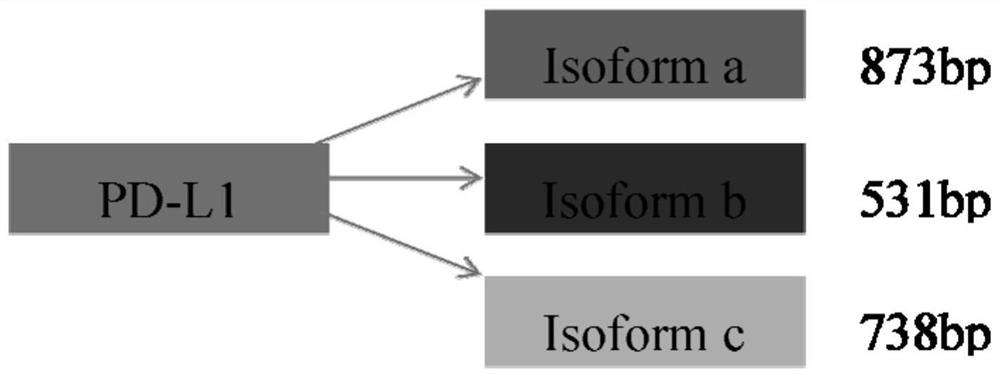
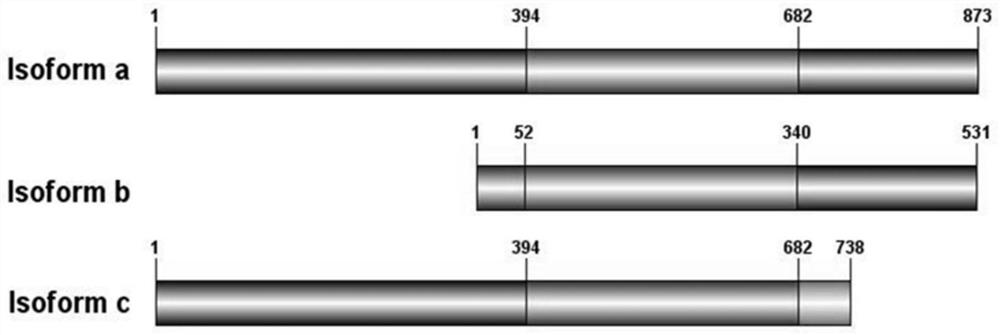
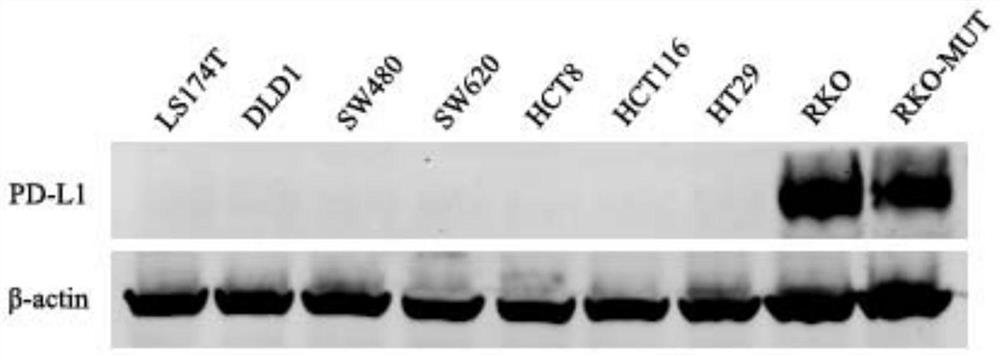
Use of PD-L1 spliceosome B as a marker to guide the dosing of anti-PD-L1/PD1 immunotherapy
The invention discloses application of a PD-L1 (Programmed Death-Ligand 1) spliceosome B as a marker for instructing administration of PD-L1 / PD1 immunotherapy. Expression of three different variable spliceosomes of PD-L1 can be observed in normal and mutant colorectal cancer cell systems, and eukaryotic expression vectors of the three spliceosomes are established and transfected into tumor cells without or with low PD-L1 expression. Tests further show that in co-culture of a tumor cell system with isoform b over-expression and immune cells, apoptosis of the immune cells is promoted, secretionof immune cell factors is inhibited, inhibition of immunoreactions in bodies of patients can be reminded, and clinical sample testing shows that isoform b of PD-L1 is a monitoring target of poor prognosis of tumor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
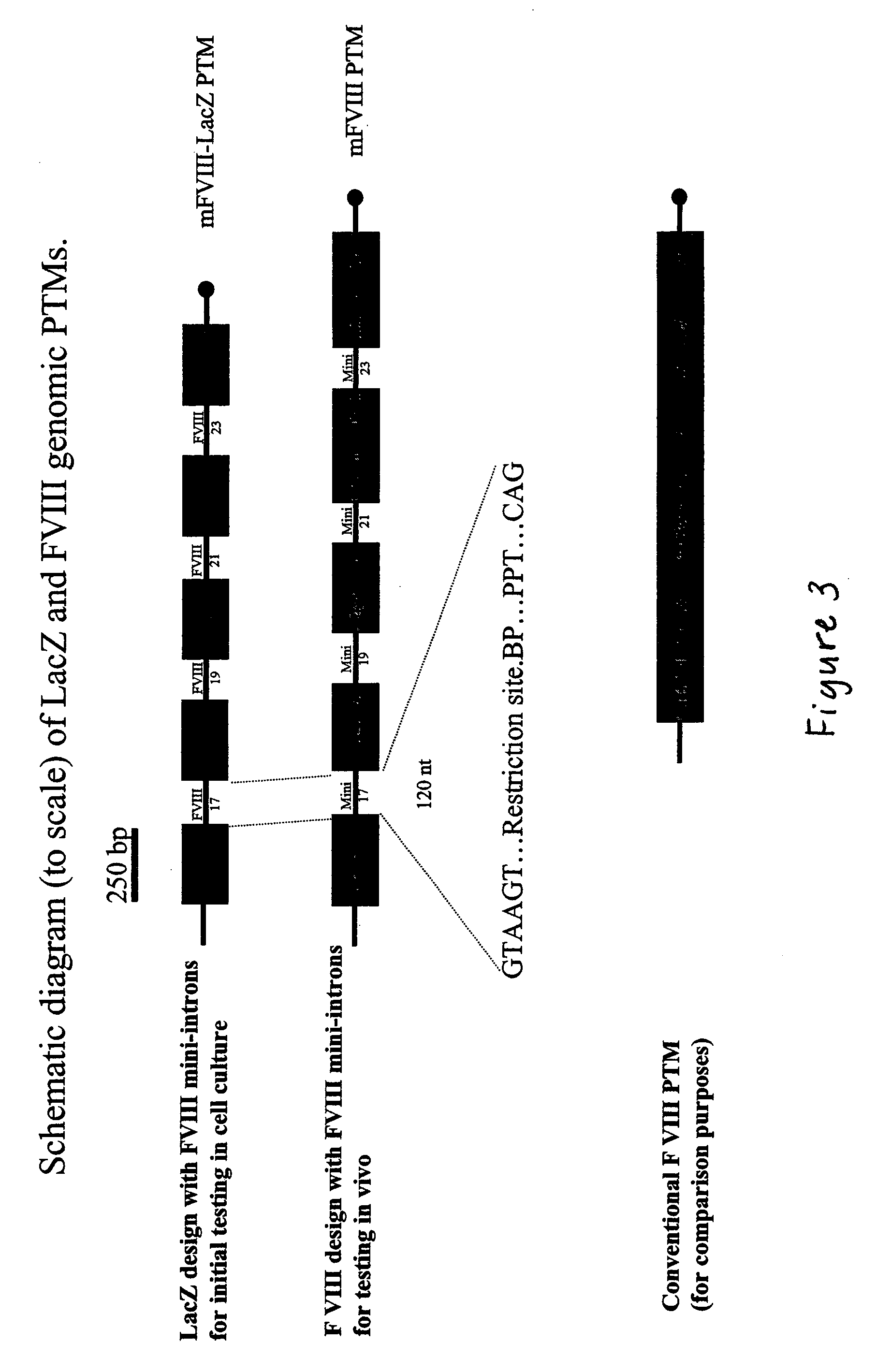
Spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing for correction of factor VIII genetic defects
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention are genetically engineered to interact with factor VIII (FVIII) target pre-mRNA so as to result in correction of clotting FVIII genetic defects responsible for hemophilia A. The compositions of the invention further include recombinant vector systems capable of expressing the PTMs of the invention and cells expressing said PTMs. The methods of the invention encompass contacting the PTMs of the invention with a FVIII target pre-mRNA under conditions in which a portion of the PTM is trans-spliced to a portion of the target pre-mRNA to form a RNA molecule wherein the genetic defect in the FVIII gene has been corrected. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for correction of FVIII disorders such as hemophilia A.
Owner:MITCHELL LLOYD G +1
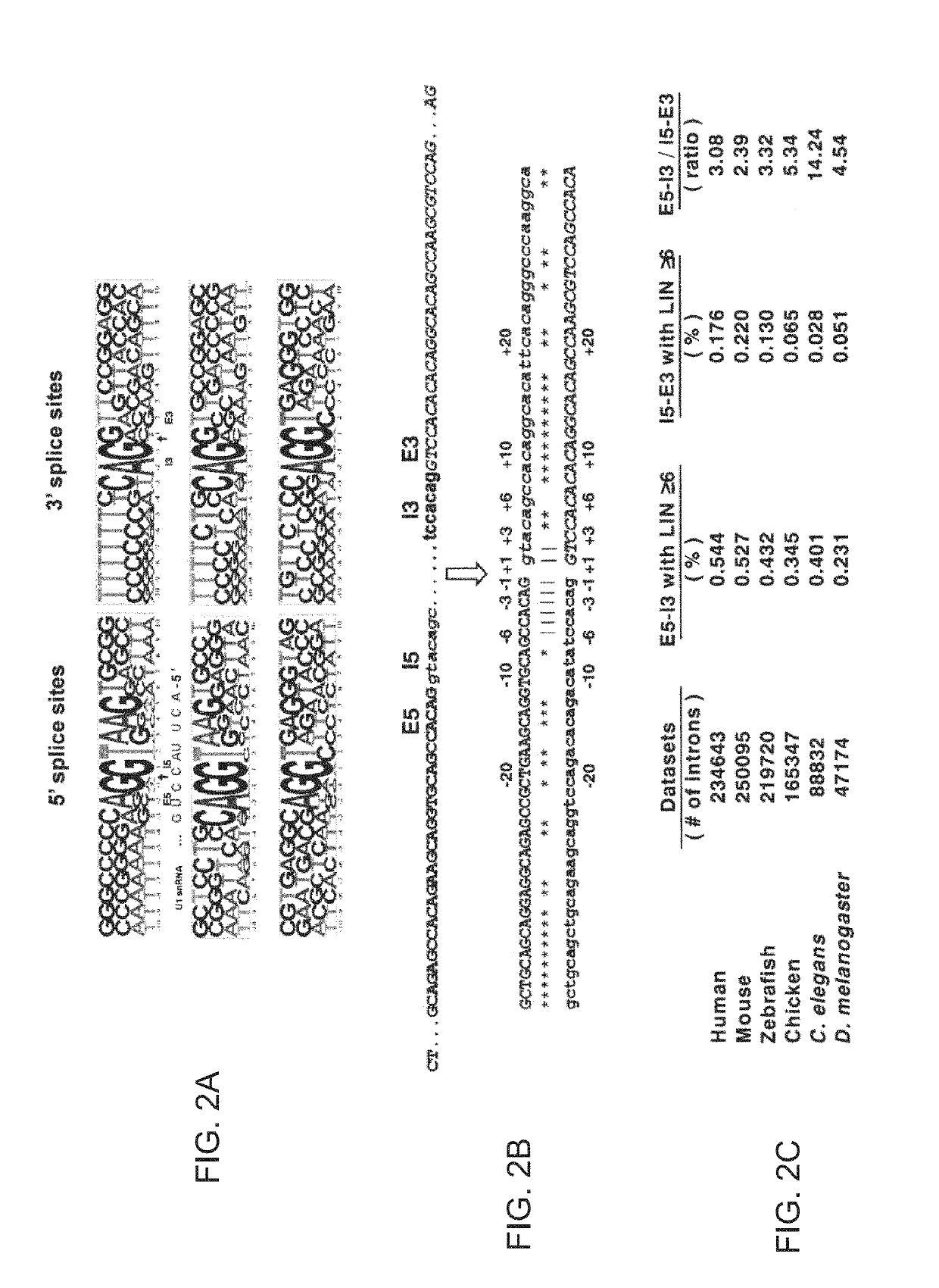
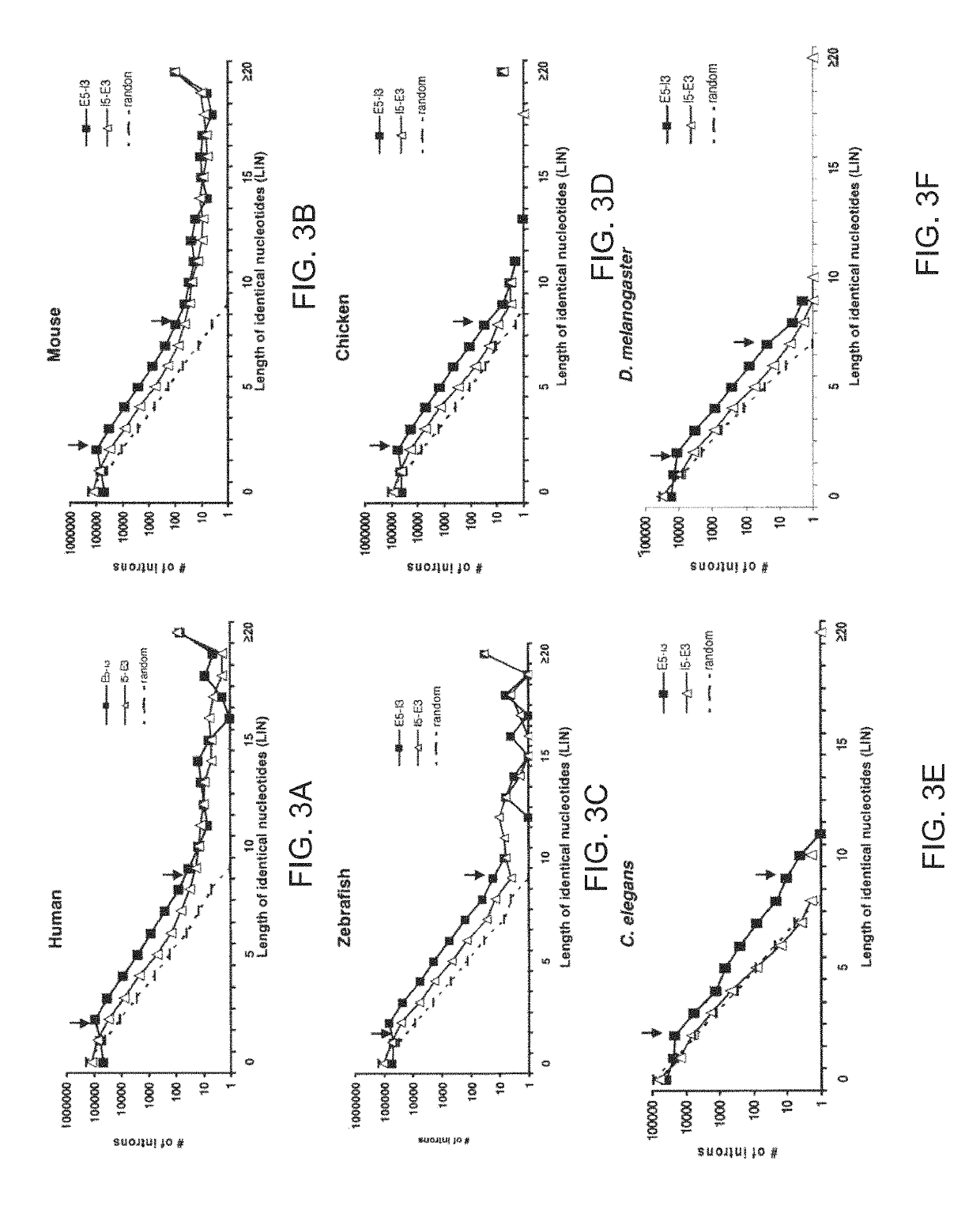
System and method for analyzing splicing codes of spliceosomal introns
ActiveUS10446261B1Lower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDiseaseGenomic DNA
A system and method for analyzing splicing codes of spliceosomal introns is disclosed. One embodiment comprises methods of identifying introns and exons in genomic DNA or pre-mRNA sequences by locating characteristic markers in splicing junctions by computation and / or manually. Exon sequences predicted by computation can be verified and characterized by employing standard amplification methods, such as comparative genomic, RNA-seq, next-generation sequencing, RT-PCR. DNA / RNA / oligo, electrophoretic or protein chip technologies. If a given sample is verified, its polypeptide can be translated based on genetic codons. Its functions can be deduced based on its characteristics, computation predictions and related knowledge databases. These data can be used to compare databases which correlate the characterized intron or exon or gene to characterized diseases or genetic mutations. Isoforms can be detected and analyzed at mRNA and protein levels alone and with other isoforms predicted by computation, characterized by experiments and stored in existing databases.
Owner:BIOTAILOR
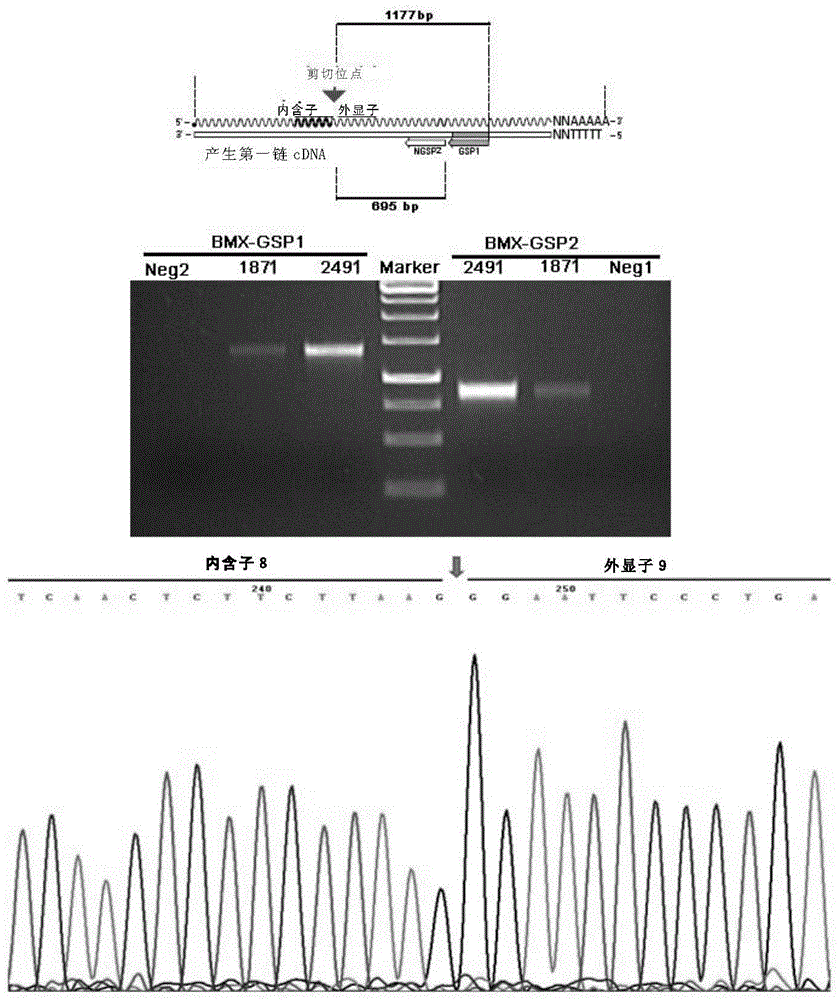
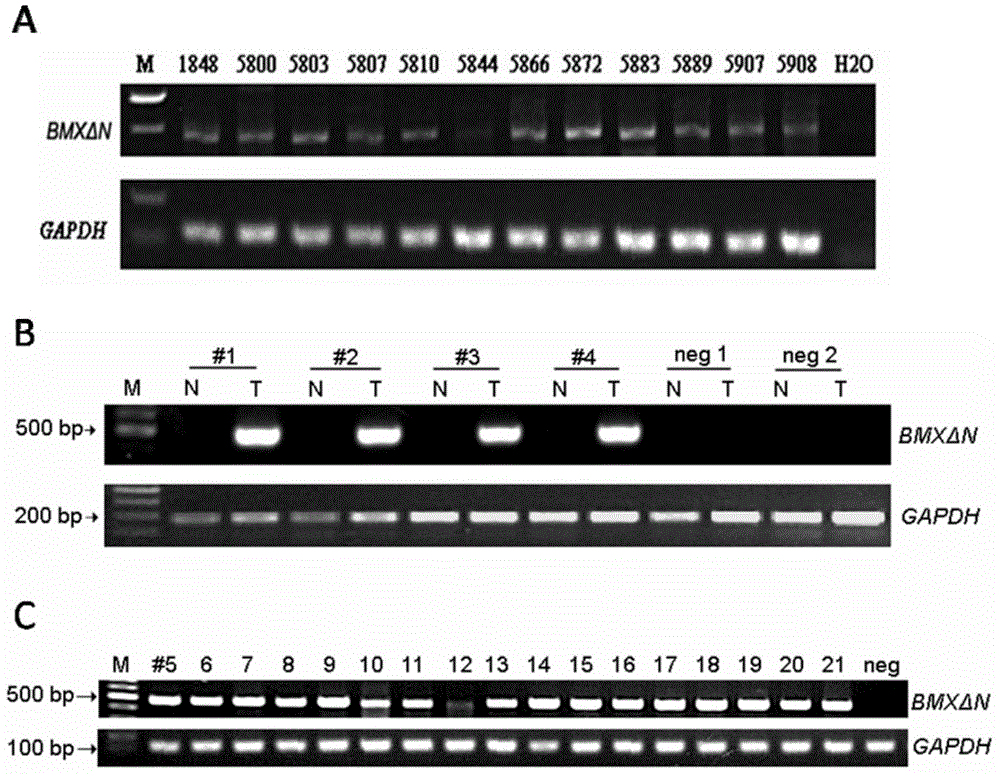
A BMX spliceosome and applications thereof in lung cancer drug resistance
ActiveCN105441405AMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesSpliceosome complexNucleotide sequencing
A BMX spliceosome is provided. The nucleotide sequence of the BMX spliceosome is shown as SEQ ID NO:3. A host cell containing a gene coding the BMX spliceosome and a method of detecting functions of the BMX spliceosome by utilization of the host cell are also provided by the invention. The BMX spliceosome or the host cell containing the BMX spliceosome can be used for testing drug resistance of lung cancer cells.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
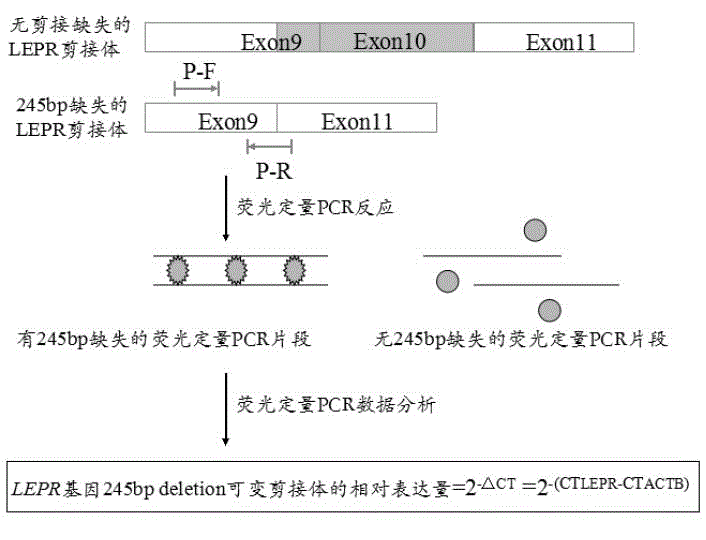
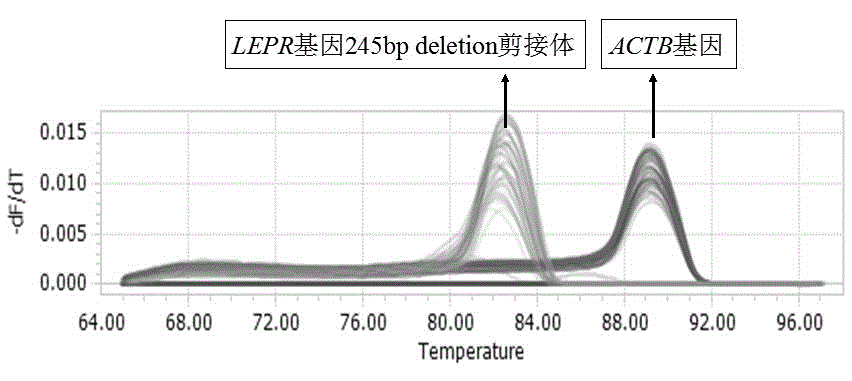
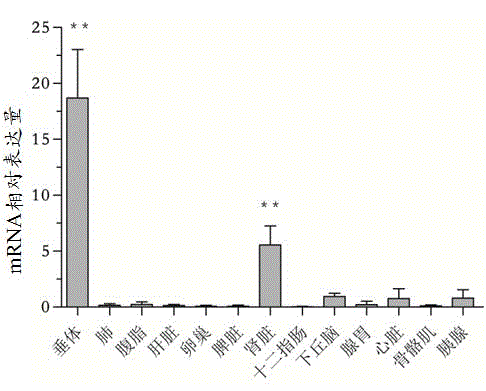
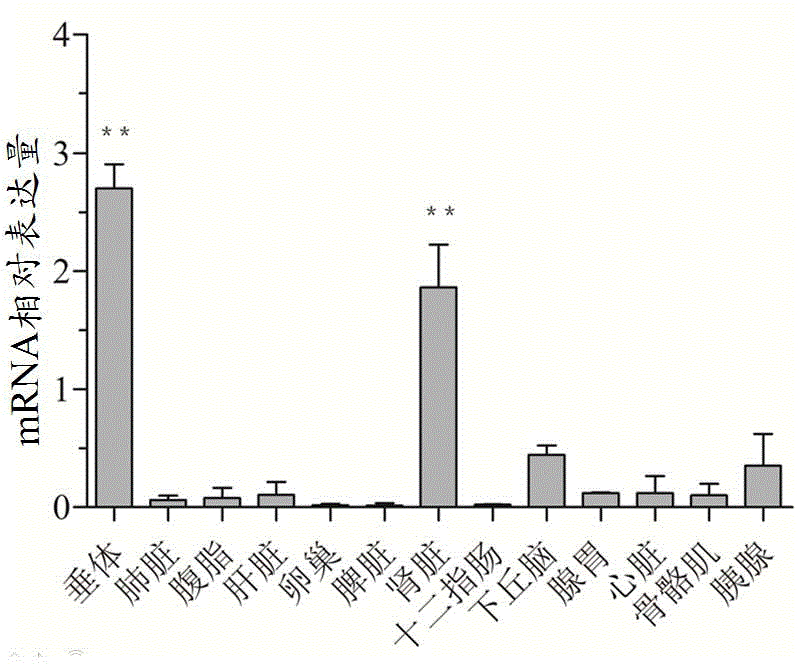
Primer, kit and detection method for detecting 245bp deletion alternative spliceosome of LEPR gene
ActiveCN104673912AImprove applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpliceosomeGenetics
The invention relates to a primer, a kit comprising the primer and a detection method for detecting a 245bp deletion alternative spliceosome of an LEPR gene and aims at solving the problems of tedious program, long consumed time and low accuracy. The detection method comprises the following steps: with cDNA as a tempelate and a primer pair ACTB as a primer, and amplifying an ACTB reference gene by virtue of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR; with a primer pair P as a primer, carrying out real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification, wherein the reaction system of the real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification consists of 2*SYBR@Premix Ex TaqTMII, ultrapure water with RNase removed, a primer P-F or ACTB-F, a primer P-R or ACTB-R, and the cDNA tempelate, and the reaction method comprises the following steps: initial denaturation, denaturation, annealing and extension; and analyzing a qPCR real-time monitoring result, calculating by using 2-delta CT relative quantification, and carrying out difference significance test by SPSS version 20.0. The primer, the kit and the detection method are accurate, rapid and convenient and strong in applicability.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
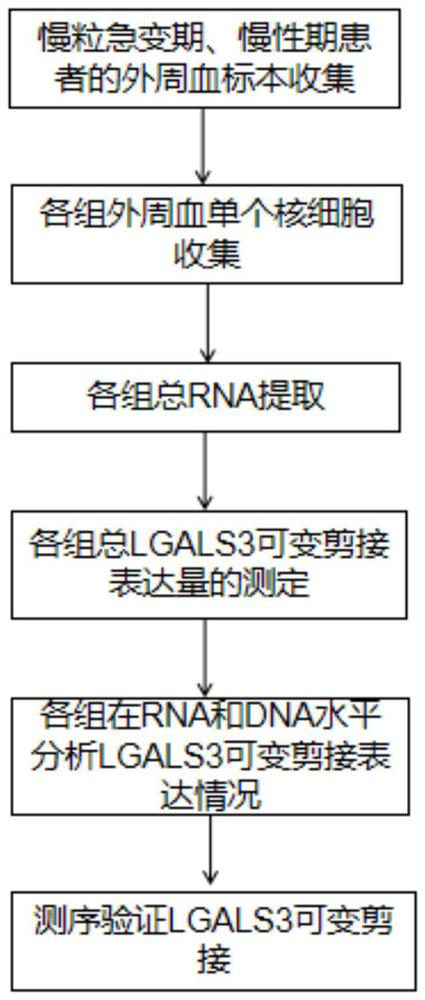
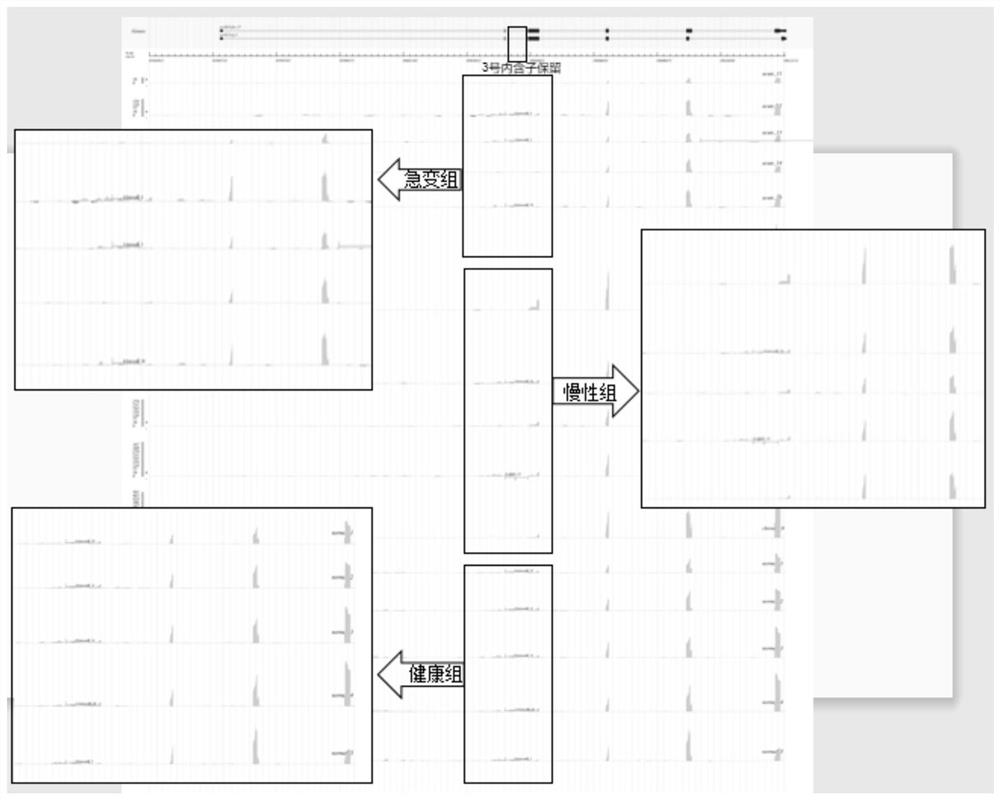
Reagent and kit for diagnosing acute change period of chronic myeloid leukemia based on LGALS3 splicing variant
ActiveCN112522415AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMyeloid leukemiaSpliceosome
The invention discloses application of 3# intron retention and / or loss spliceosome LGALS3-R and / or LGALS3-M of LGALS3 in preparation of a reagent for diagnosing the acute change period of chronic myeloid leukemia or a kit containing the diagnostic reagent. The invention has relatively high sensitivity and specificity, and can observe the acute change period of chronic myeloid leukemia more simplyand accurately as soon as possible; therefore, treatment means can be adopted in time; and relatively high clinical application value is achieved.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL TO NANCHANG UNIV
Spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
The invention provides molecules and methods for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in selected cells. Pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The mRNA expression product is a therapeutic protein, a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells, or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides genetically engineered PTMs for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to produce chimeric RNA encoding peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing in plants
InactiveUS20060088938A1Inhibition of translationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRNA Trans-SplicingExon intron
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Human platelet-derived growth factor A homologous dimers and production method thereof
InactiveCN102154305AImprove biological activityMaintain biological activityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationBiotechnologyHuman platelet
The invention discloses a human platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) A homologous dimers and a high-efficiency production method thereof. The method mainly comprises the following steps: cloning a human platelet-derived growth factor A spliceosome 2 gene; constructing an eukaryotic expression vector and transferring the eukaryotic expression vector into an eukaryotic yeast host; screening a yeast transformant for high level secretion expression, wherein the PDGF-As expressed by the yeast are in a glycosylated form and a non-glycosylated form; and performing amplified culture in a shake flask, dialyzing supernate of culture solution, purifying the supernate efficiency by using a chromatography (CM) cation exchange column and G-75 molecular sieve, and obtaining the novel modified protein of the PDGF-AA dimers, of which one PDGF-A monomer is glycosylated and of which the other PDGF-A monomer is not glycosylated, by using a CM cation exchange process and optimizing the pH value of dislysate, wherein the separated and purified new glycosylation modified protein of the PDGF-AA dimers has high uniformity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of arabidopsis thaliana MAPKKK kinase in breeding
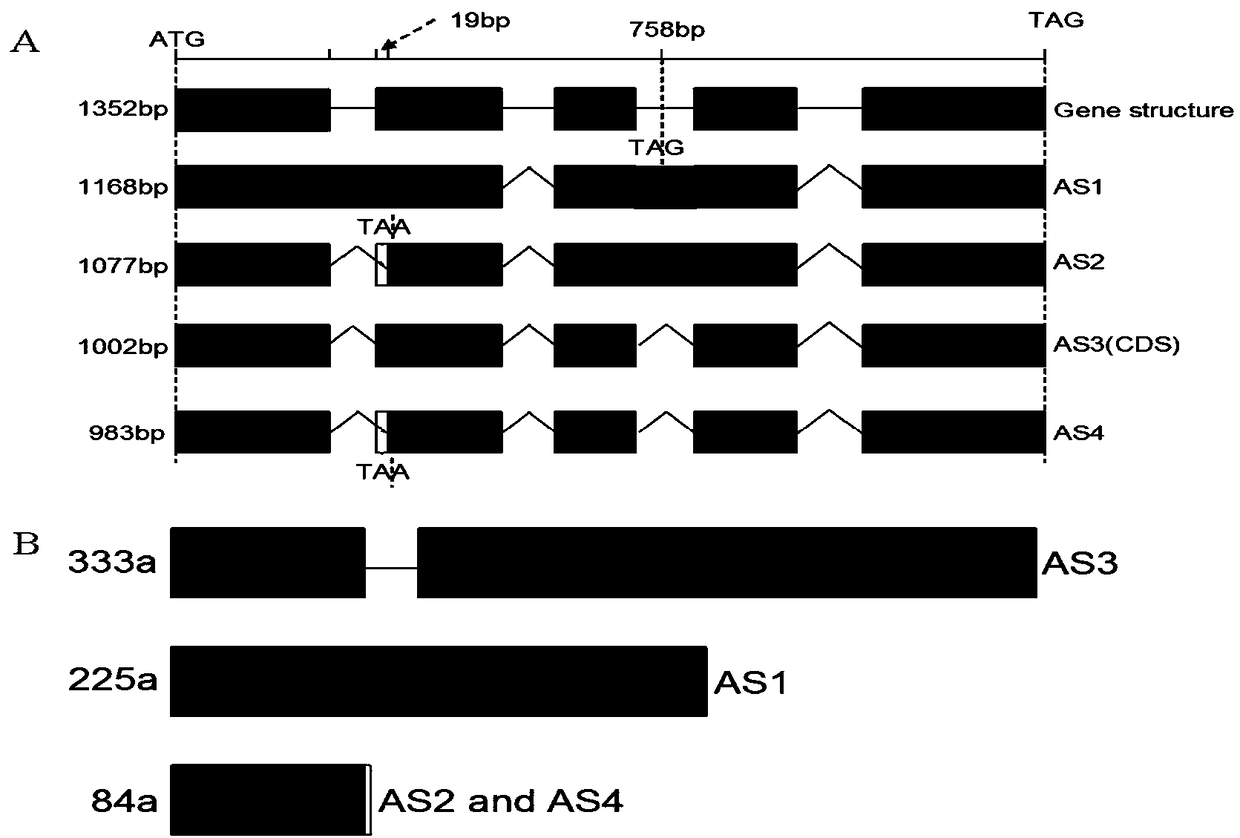
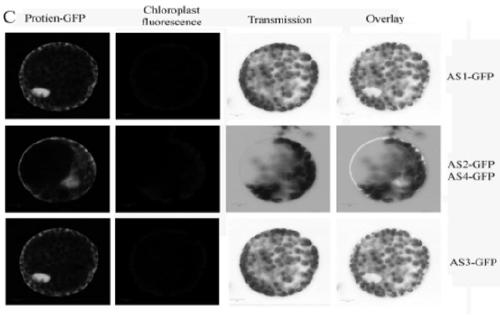
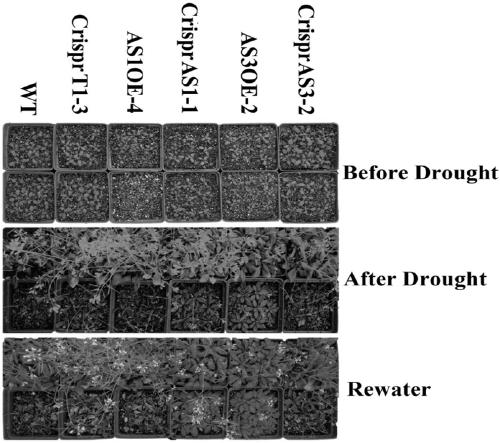
ActiveCN109486839AAccurate selectionShorten the timeTransferasesFermentationCruciferSpliceosome complex
The invention discloses an application of arabidopsis thaliana MAPKKK kinase in breeding, and relates to the technical field of agricultural breeding. The breeding includes creation of the drought resistant idioplasm and early blossoming idioplasm of crucifer by a transgenic technology. The crucifer includes oilseed rape and broccoli. The MAPKKK kinase has four spliceosomes, named as AS1, AS2, AS3and AD4; an overexpression plant AS1-OE of AS1 and a mutant CRISPPAS3-2 lost by AS3 both express the non-drought resistant phenotype; AS3-OE plant and a mutant CRISPRAS1-1 lost by AS1 both express the drought resistant phenotype; AS1-OE plant and AS2 / 4-OE plant express the early blossoming phenotype, and AS3-OE plant expresses the late blossoming phenotype. The research can provide theoretical basis for the crucifer transgene breeding operation.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
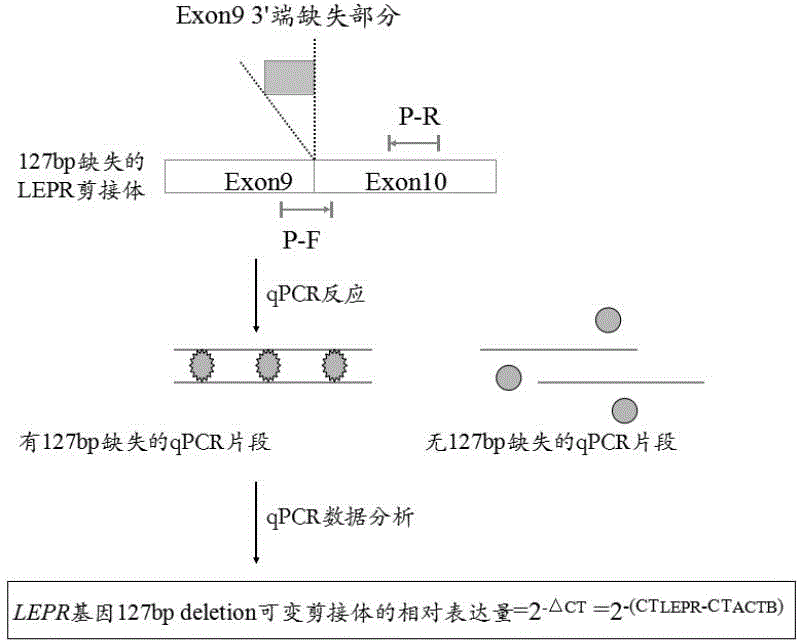
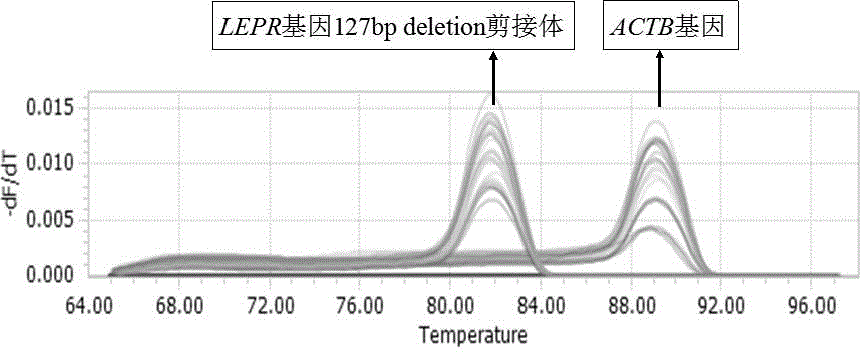
Primer and kit for detecting 127bp deletion variable spliceosome of LEPR gene and detecting method
ActiveCN104673910AImprove applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesSpliceosome
The invention discloses a primer for detecting 127bp deletion variable spliceosome of LEPR gene and a kit containing the same and a detecting method. The problems of tedious procedure, long time consumption and low accuracy can be effectively solved. The detecting method comprises the following steps: by taking a cDNA to be tested as a template and taking a primer pair ACTB as a primer, carrying out real-time fluorescence quantification PCR amplification on an ACTB reference gene; and by taking a primer pair P as a primer, carrying out real-time fluorescence quantification PCR amplification on 127bp deletion alternative spliceosome of LEPR gene, wherein the reaction system of the fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification includes ultrapure water for removing the RNA enzyme, a primer P-F or ACTB-F, a primer P-R or ACTB-R and a cDNA template, and the reaction method comprises the steps of pre-denaturing, denaturing, annealing, extending and circulating for 35-45 times, analyzing the qPCR real-time monitoring result, calculating by 2-Delta CT relative quantification method and performing SPSS version 20.0 significance test of difference. The method is accurate, rapid, convenient and strong in applicability.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com









![Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6029d53e-ea98-49aa-a5c2-bab9888ead7a/RE-HDA0002624759740000011.png)
![Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6029d53e-ea98-49aa-a5c2-bab9888ead7a/RE-HDA0002624759740000012.png)
![Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group Primer group for identifying three kinds of spliceosomes of PML-RAR[alpha] fusion gene and test kit and application of primer group](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6029d53e-ea98-49aa-a5c2-bab9888ead7a/RE-HDA0002624759740000013.png)