Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Short read" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
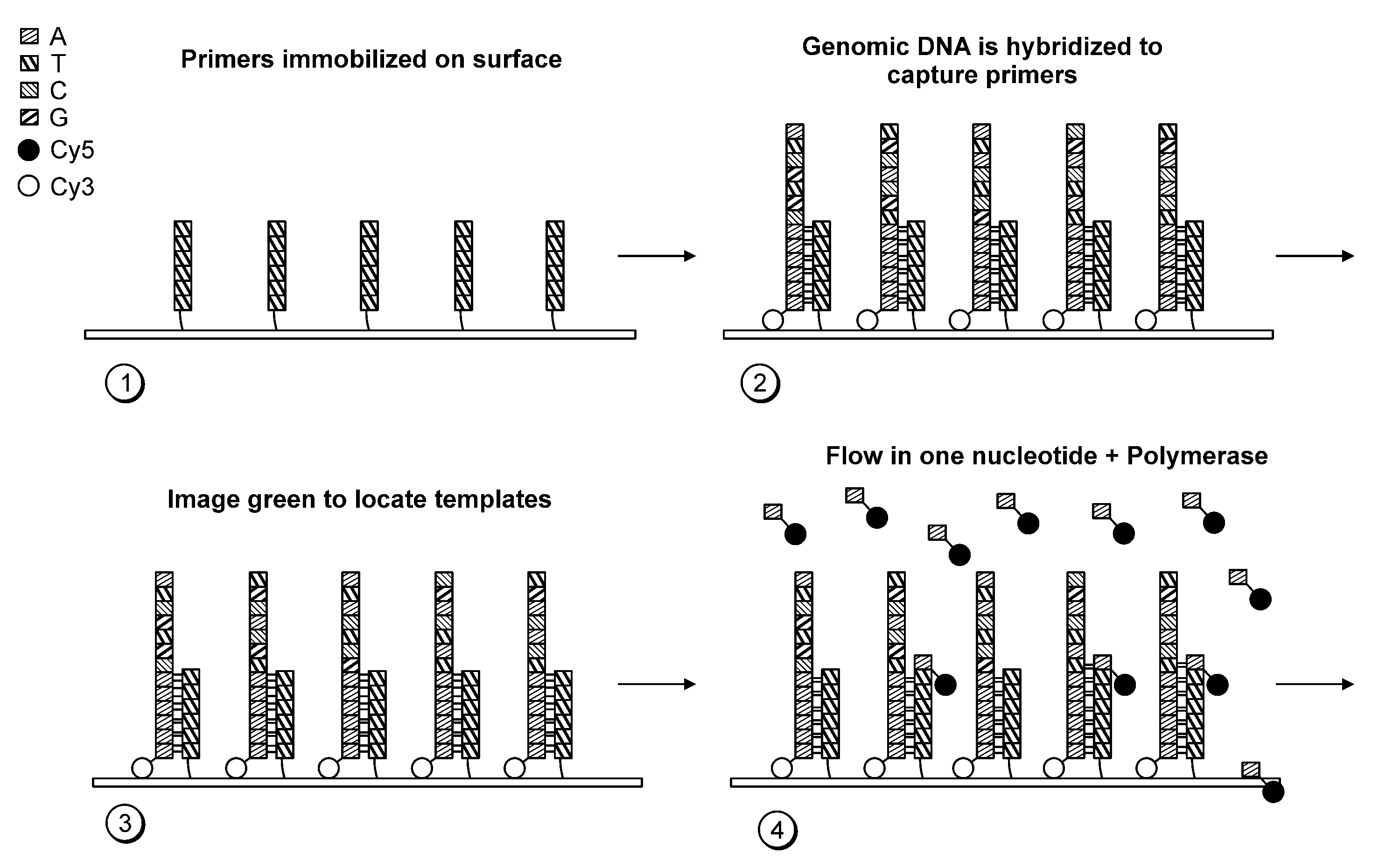
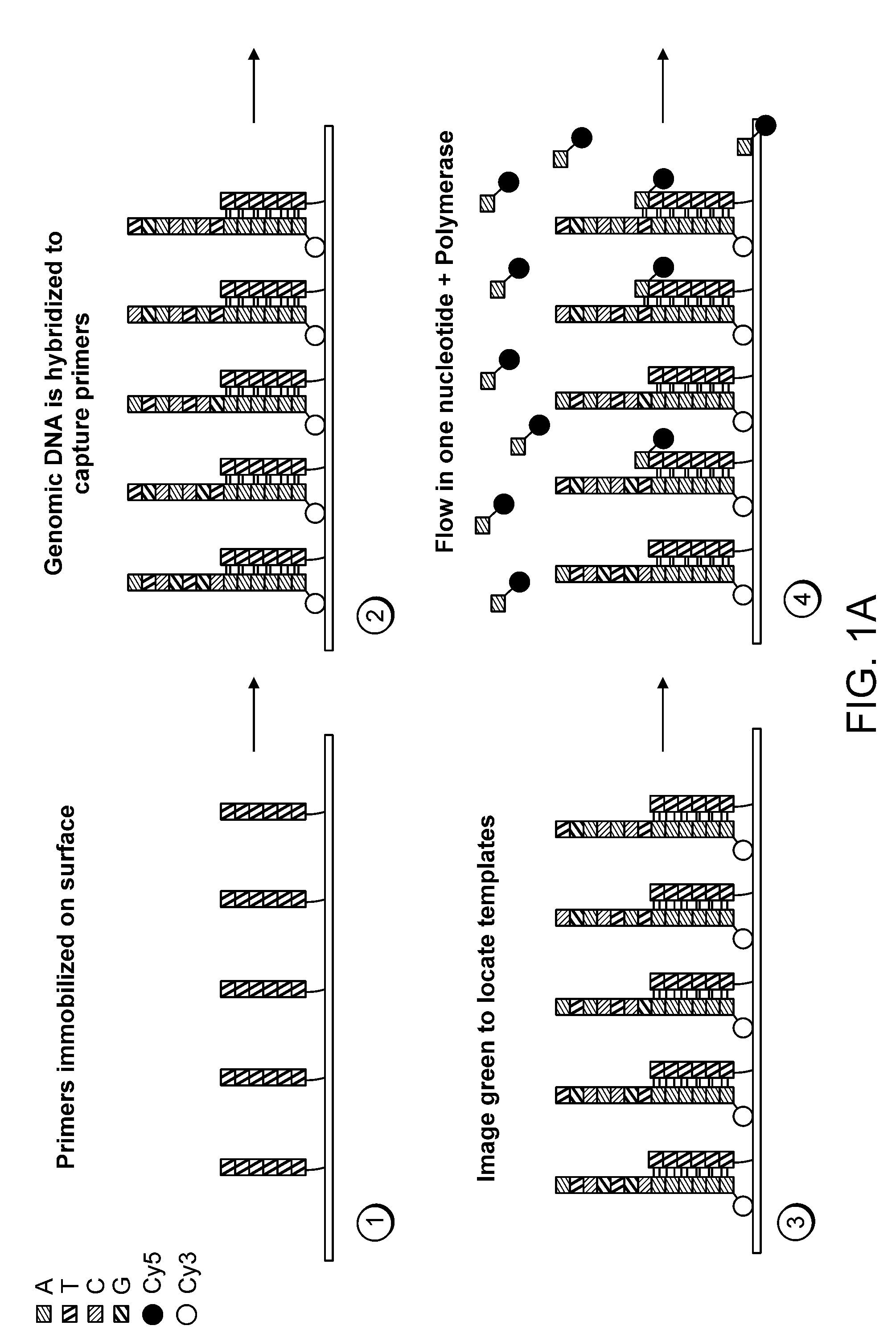
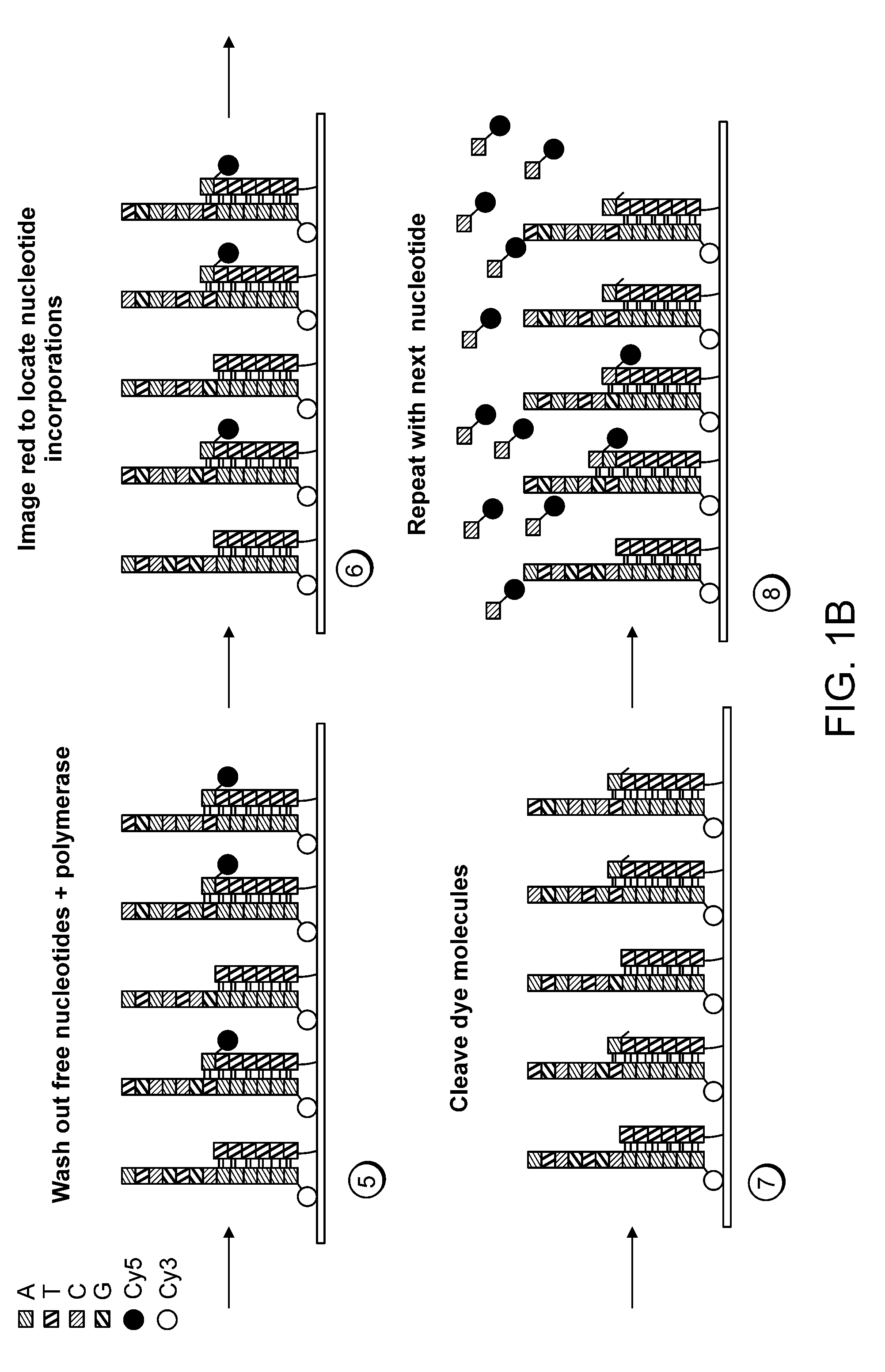
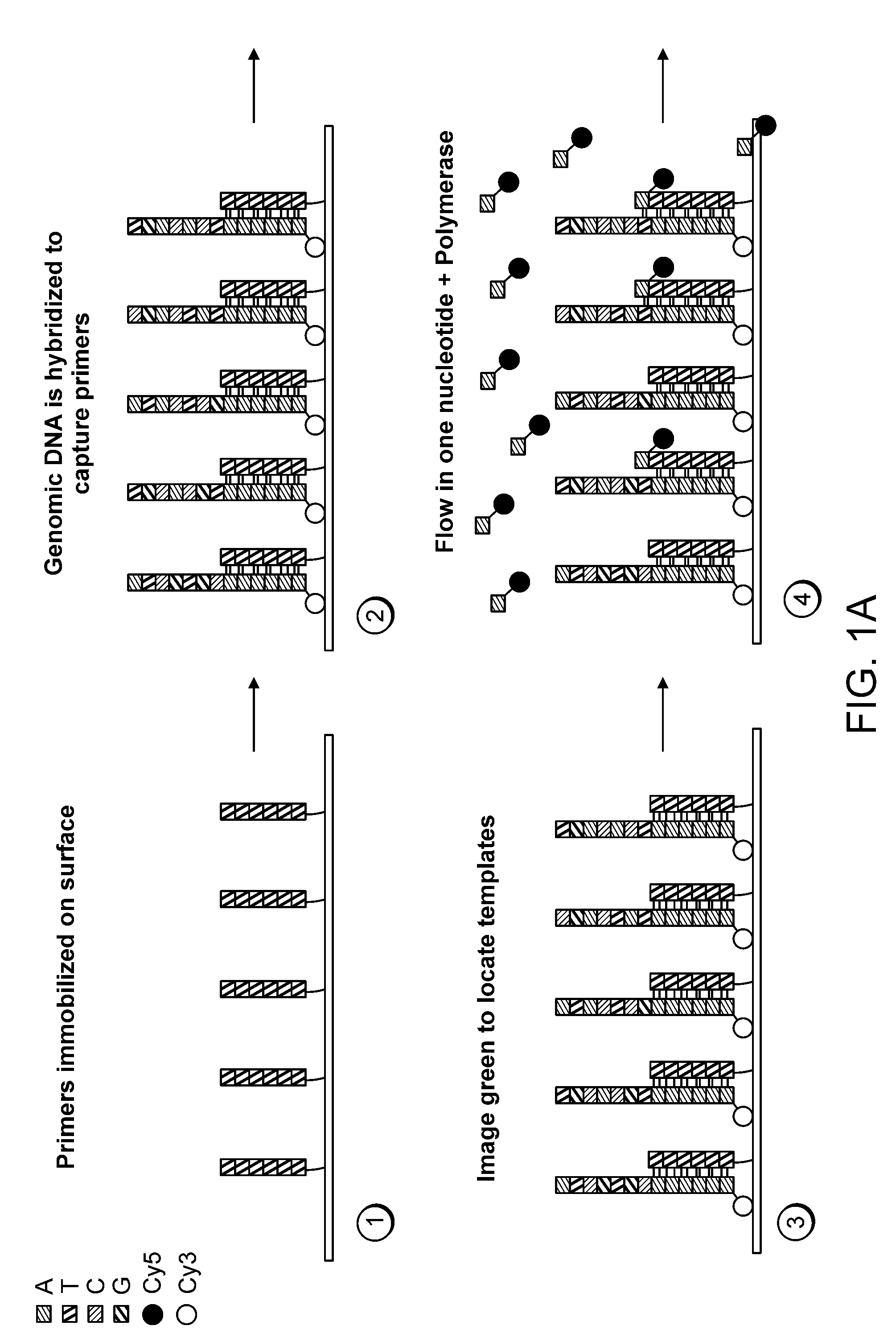
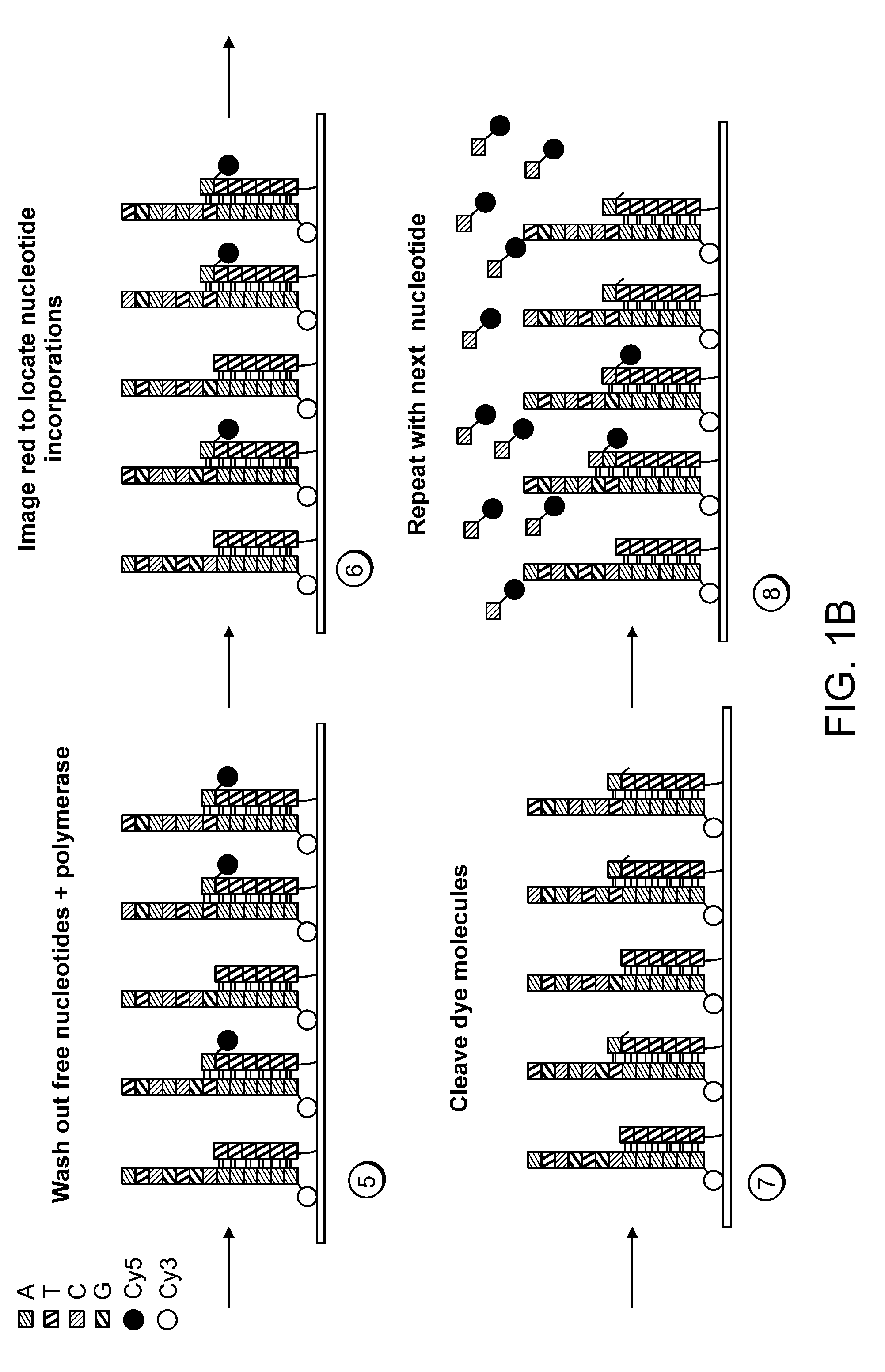
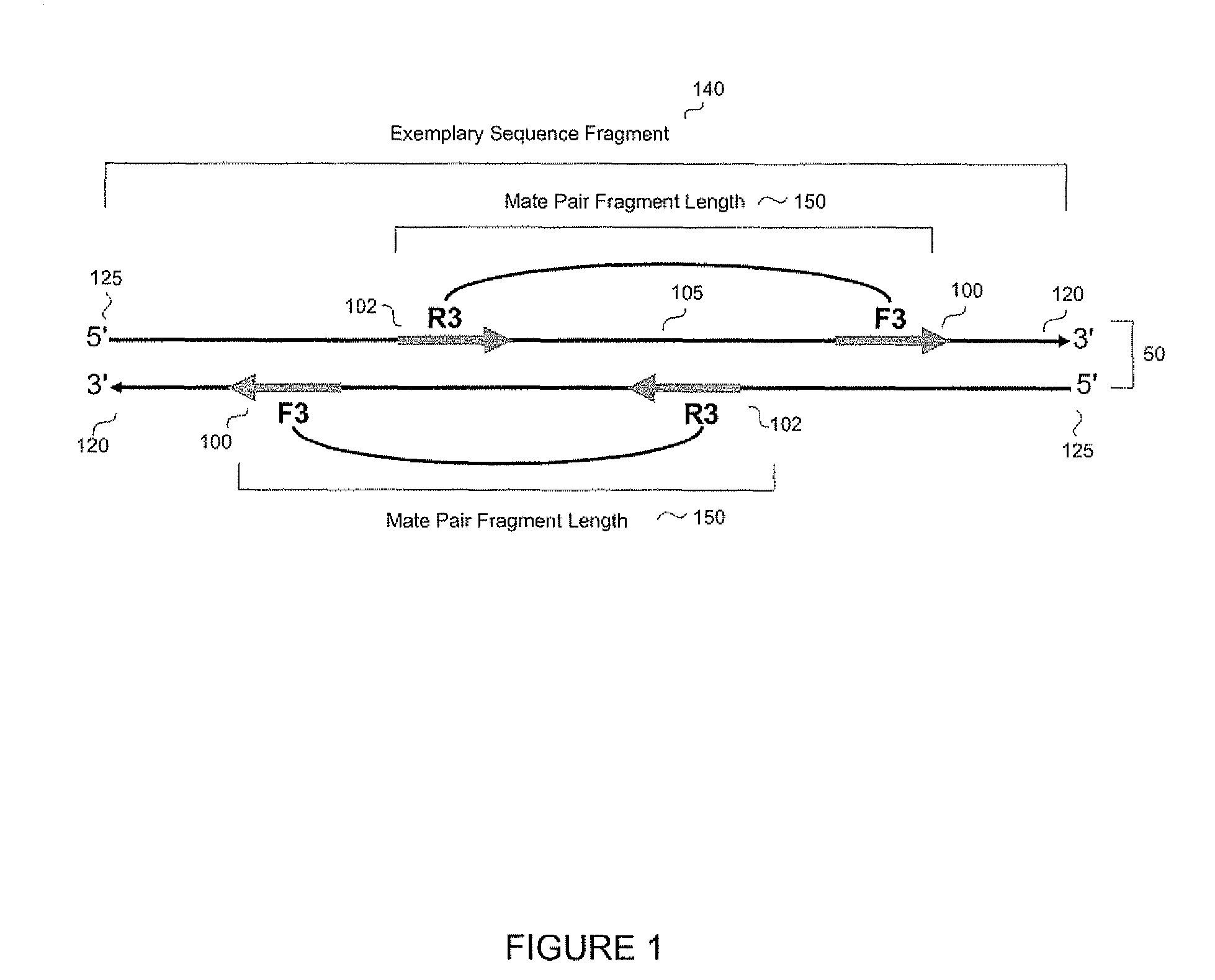
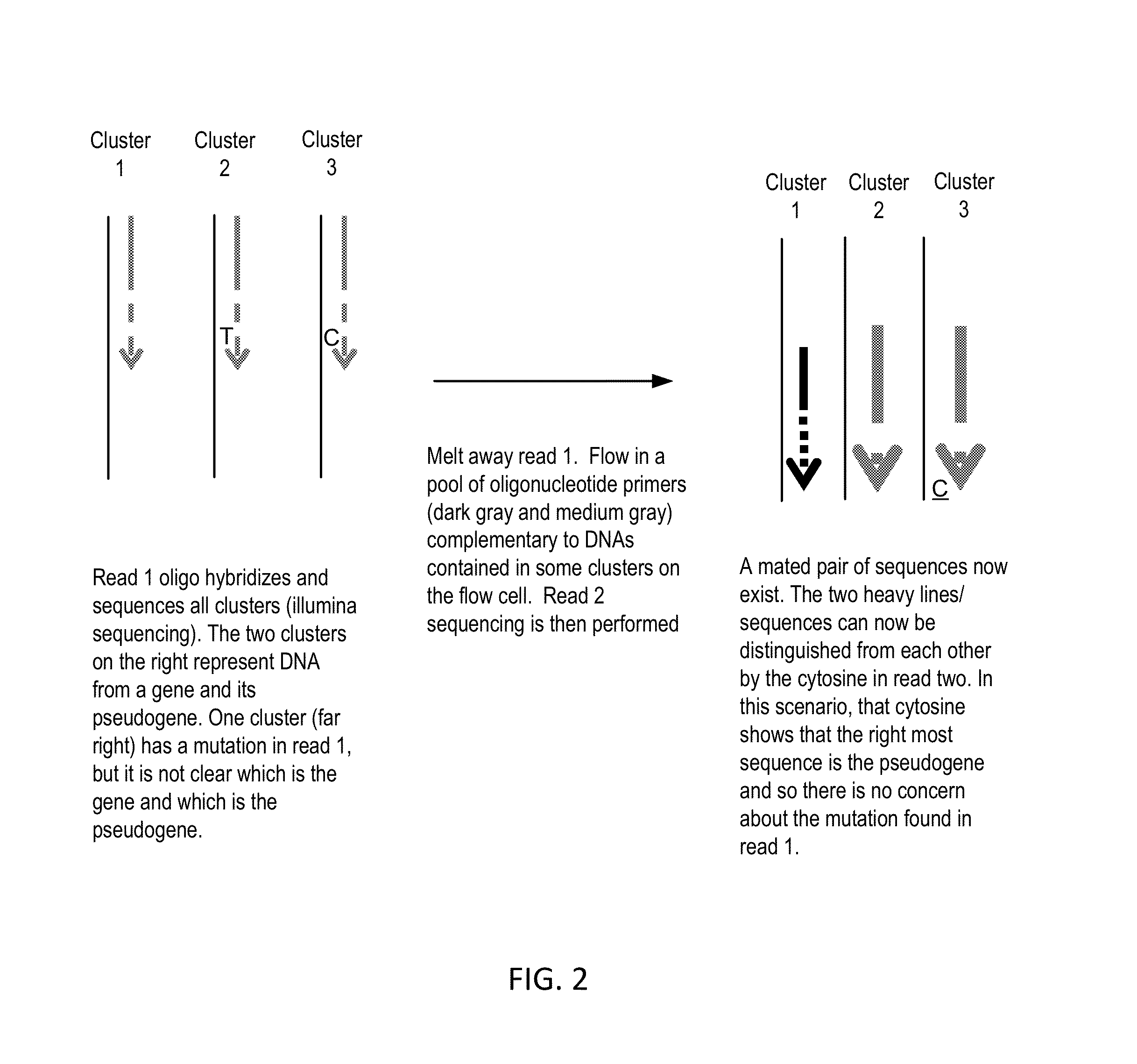
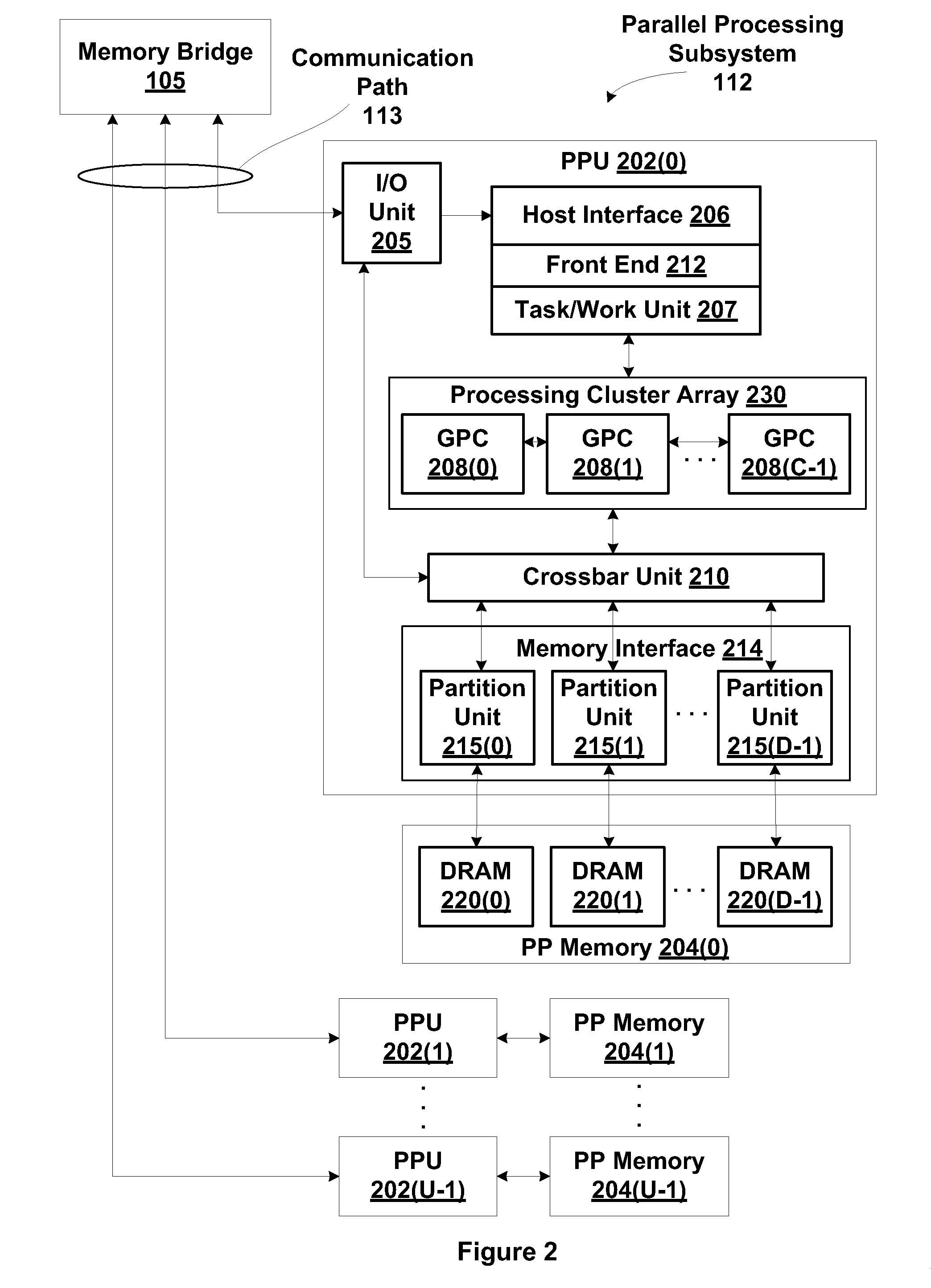
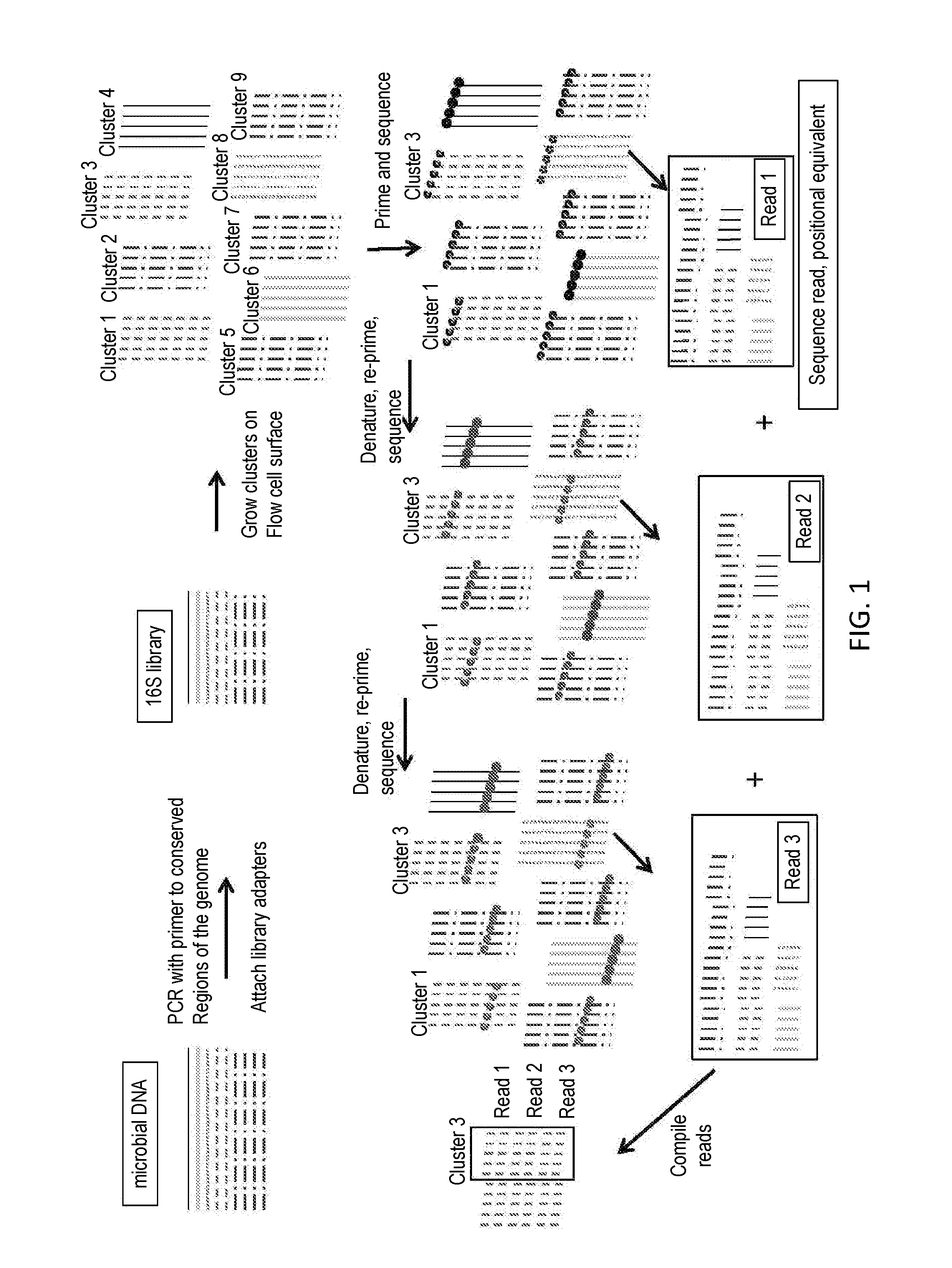
Paired-end reads in sequencing by synthesis
InactiveUS20090197257A1Yielding fewer sequencing errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRe sequencingShort read
The disclosure provides methods of generating paired reads in sequencing-by-synthesis process, particularly, in systems with relatively short read lengths (e.g., 15-35 bases), such as for example, in single molecule sequencing by synthesis. Several implementations of the methods are provided. Of particular advantage are the methods that permit re-sequencing of the template, which yields lower error rates. The invention further provides methods of using paired reads, for example, for positioning them over repeats or for assembly into large sequences, including whole genome assembly.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Paired-end reads in sequencing by synthesis
InactiveUS7767400B2Yielding fewer sequencing errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRe sequencingShort read
The disclosure provides methods of generating paired reads in sequencing-by-synthesis process, particularly, in systems with relatively short read lengths (e.g., 15-35bases), such as for example, in single molecule sequencing by synthesis. Several implementations of the methods are provided. Of particular advantage are the methods that permit re-sequencing of the template, which yields lower error rates. The invention further provides methods of using paired reads, for example, for positioning them over repeats or for assembly into large sequences, including whole genome assembly.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
DNA Sequence Assembly Methods of Short Reads
ActiveUS20090318310A1Shorten the counting processReducing sequenceSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsDNA fragmentationComputerized system
Certain embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for the automated assembly of DNA sequence data into contiguous DNA segments using a computer a system. DNA sequence data is entered into the system. The system indexes and groups a plurality of DNA fragment reads utilizing an anchor sequence and consolidates the fragments into larger sequences by merging the fragment reads within a group.
Owner:SOFTGENETICS
Systems, methods, and media for de novo assembly of whole genome sequence data
ActiveUS20170235876A1Sequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesNucleic acid sequencing
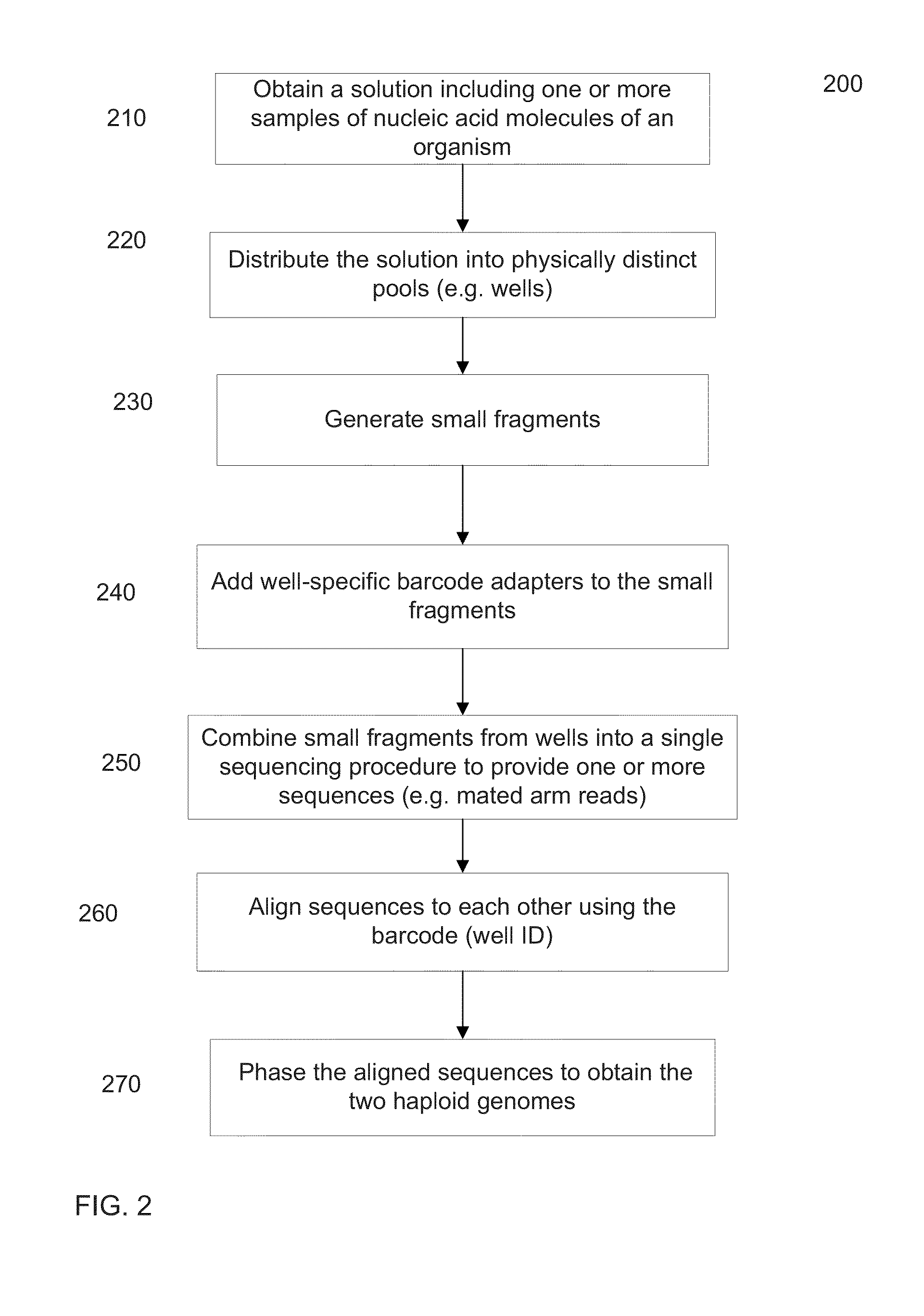
Described are computer-implemented methods, systems, and media for de novo phased diploid assembly of nucleic acid sequence data generated from a nucleic acid sample of an individual utilizing nucleic acid tags to preserve long-range sequence context for the individual such that a subset of short-read sequence data derived from a common starting sequence shares a common tag. The phased diploid assembly is achieved without alignment to a reference sequence derived from organisms other than the individual. The methods, systems, and media described are computer-resource efficient, allowing scale-up.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
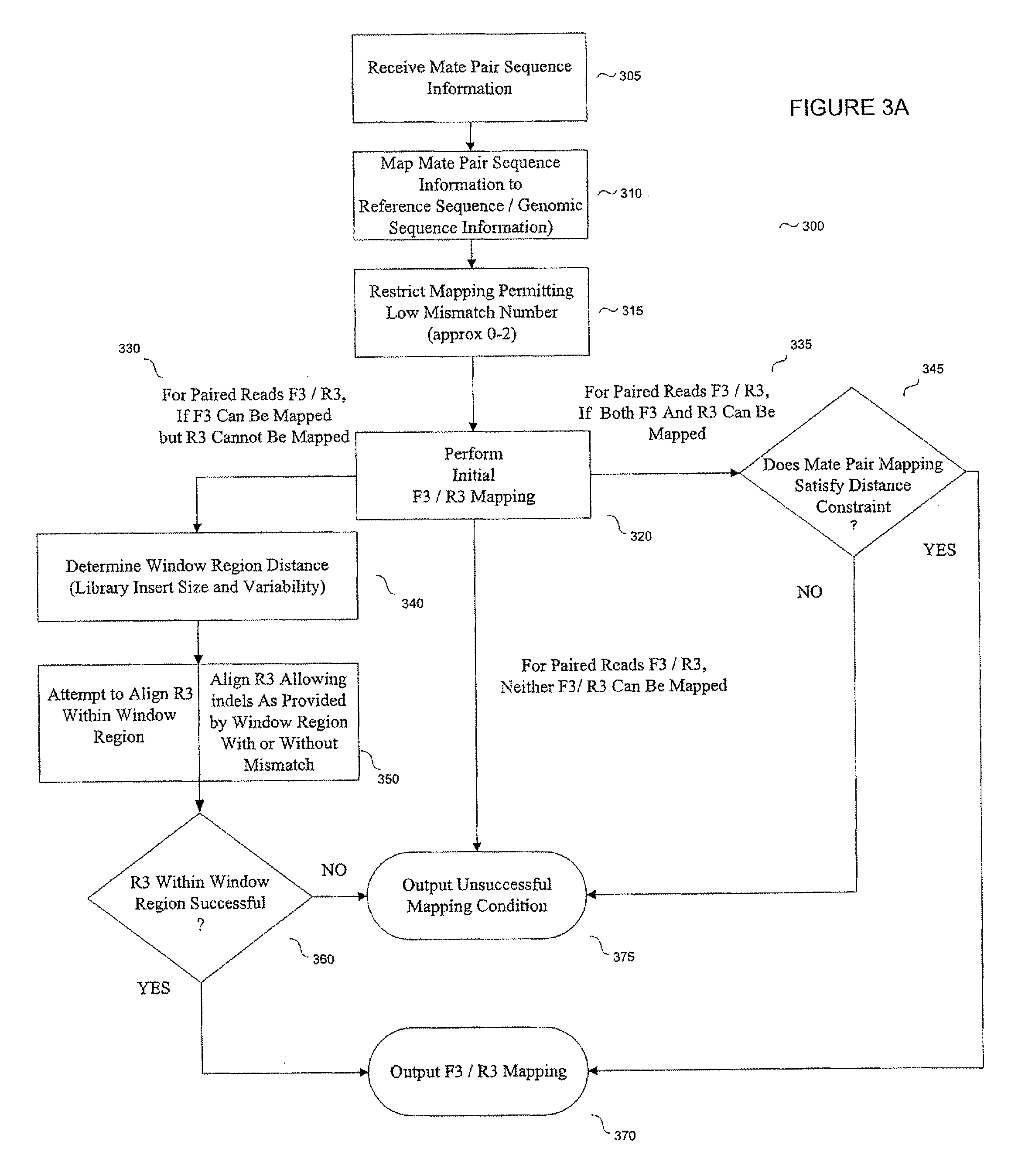
System and methods for indel identification using short read sequencing
ActiveUS8165821B2Reduce in quantityReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesParallel computingShort read
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
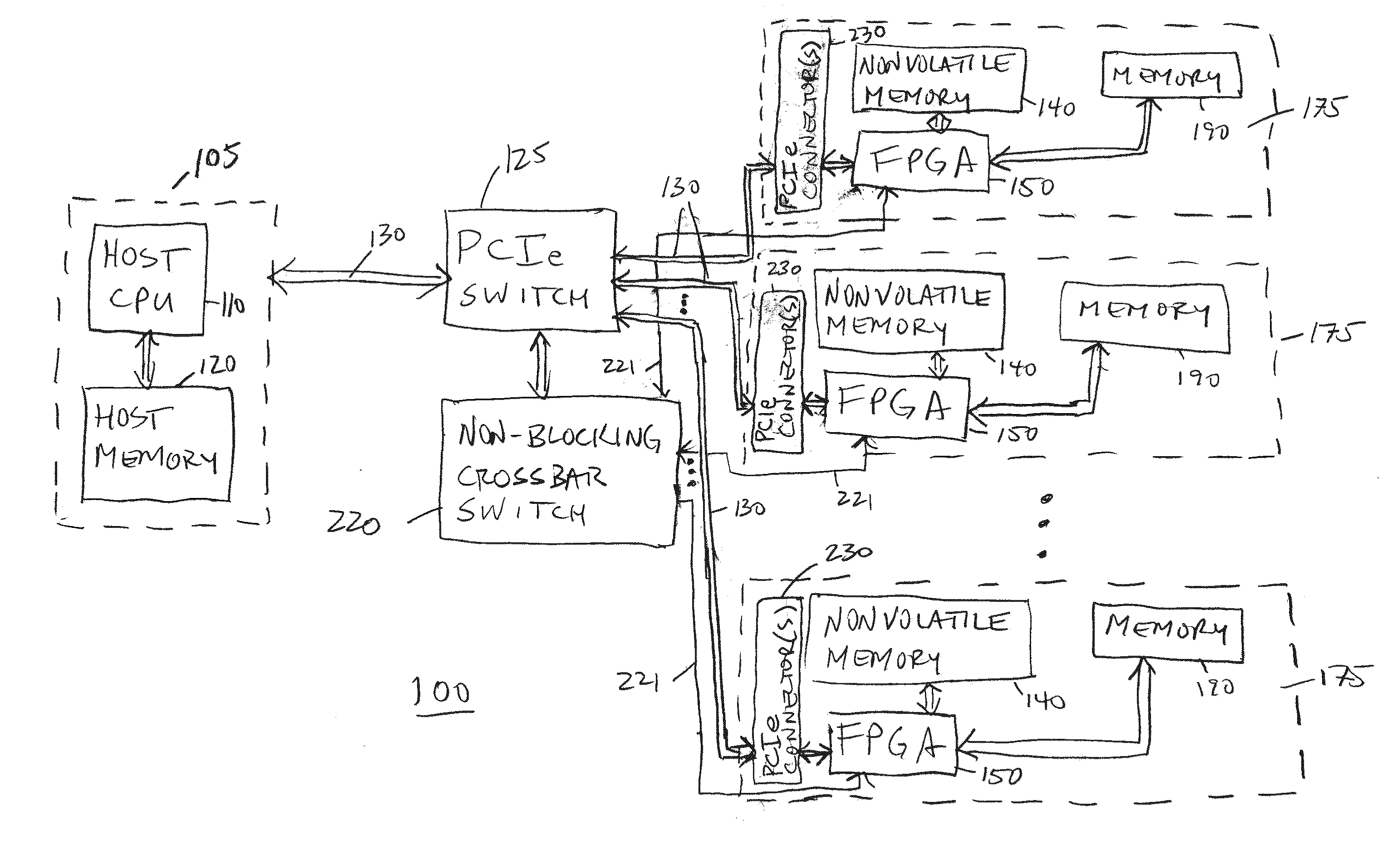
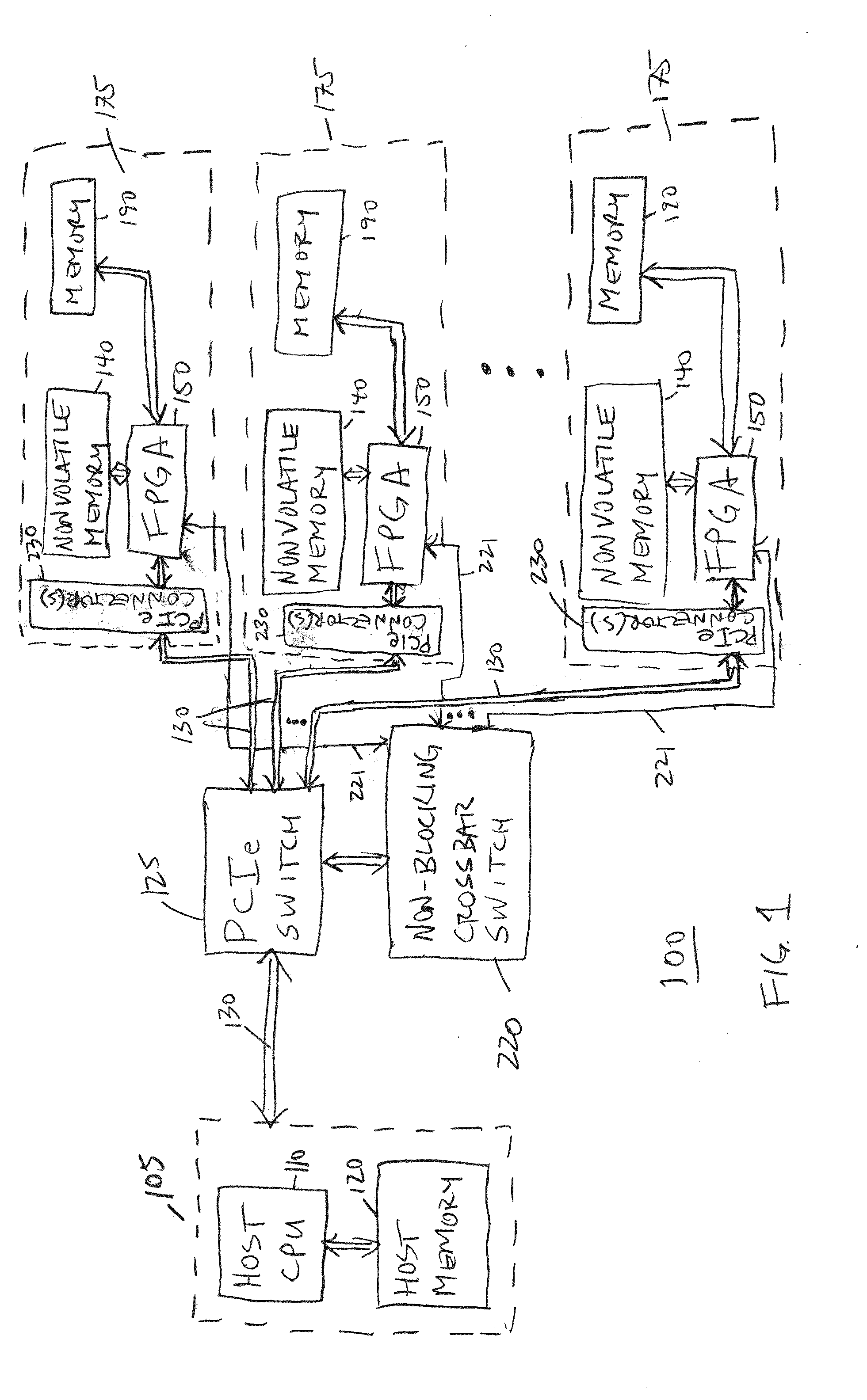
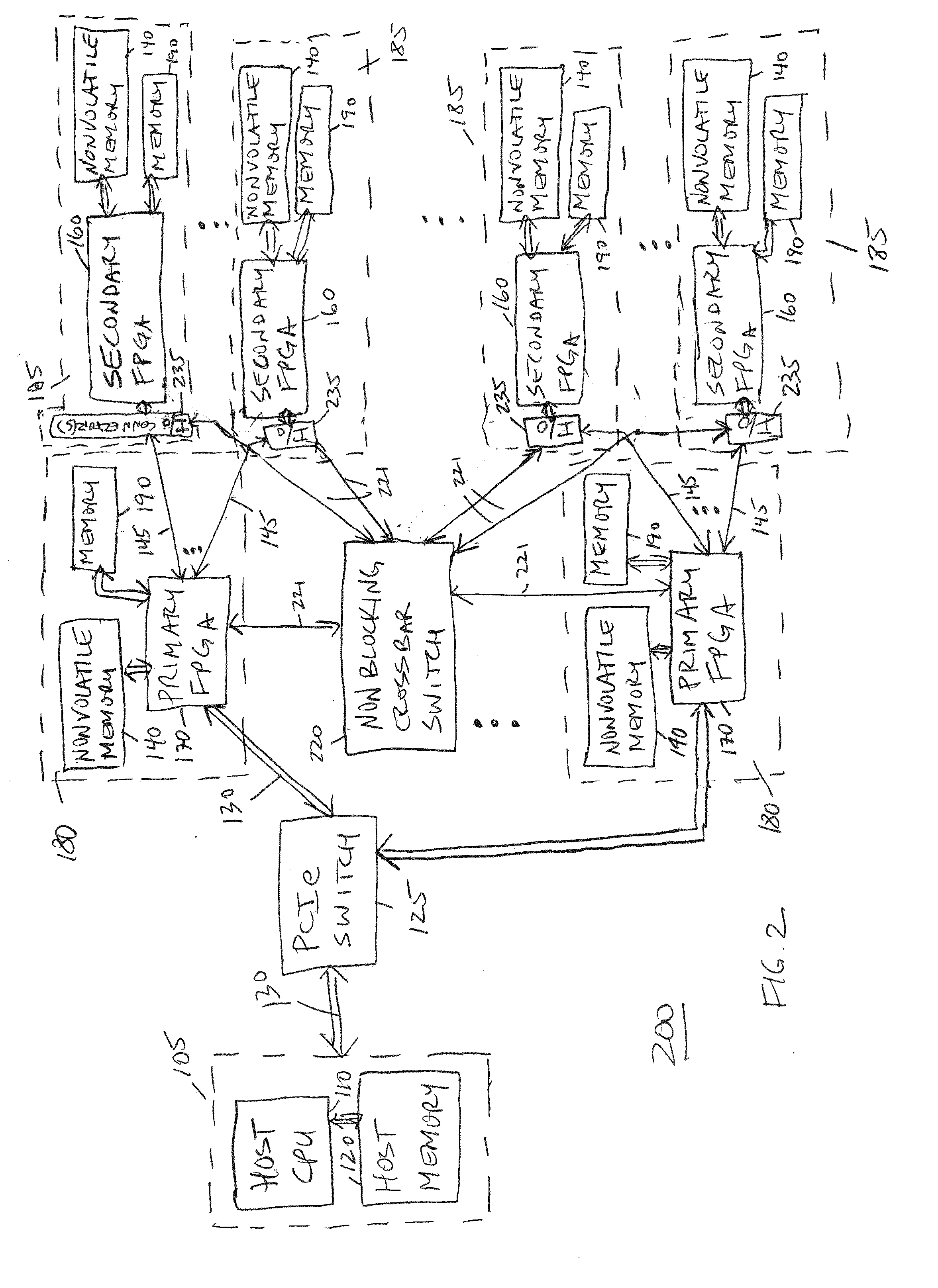
Hardware Acceleration of Short Read Mapping for Genomic and Other Types of Analyses
ActiveUS20140297196A1Reduce energy consumptionRapid genetic sequence analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingReference genome sequenceMemory circuits
A scalable FPGA-based solution to the short read mapping problem in DNA sequencing is disclosed which greatly accelerates the task of aligning short length reads to a known reference genome. A representative system comprises one or more memory circuits storing a plurality of short reads and a reference genome sequence; and one or more field programmable gate arrays configured to select a short read; to extract a plurality of seeds from the short read, each seed comprising a genetic subsequence of the short read; for each seed, to determine at least one candidate alignment location (CAL) in the reference genome sequence to form a plurality of CALs; for each CAL, to determine a likelihood of the short read matching the reference genome sequence in the vicinity of the CAL; and to select one or more CALs having the currently greater likelihood of the short read matching the reference genome sequence.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
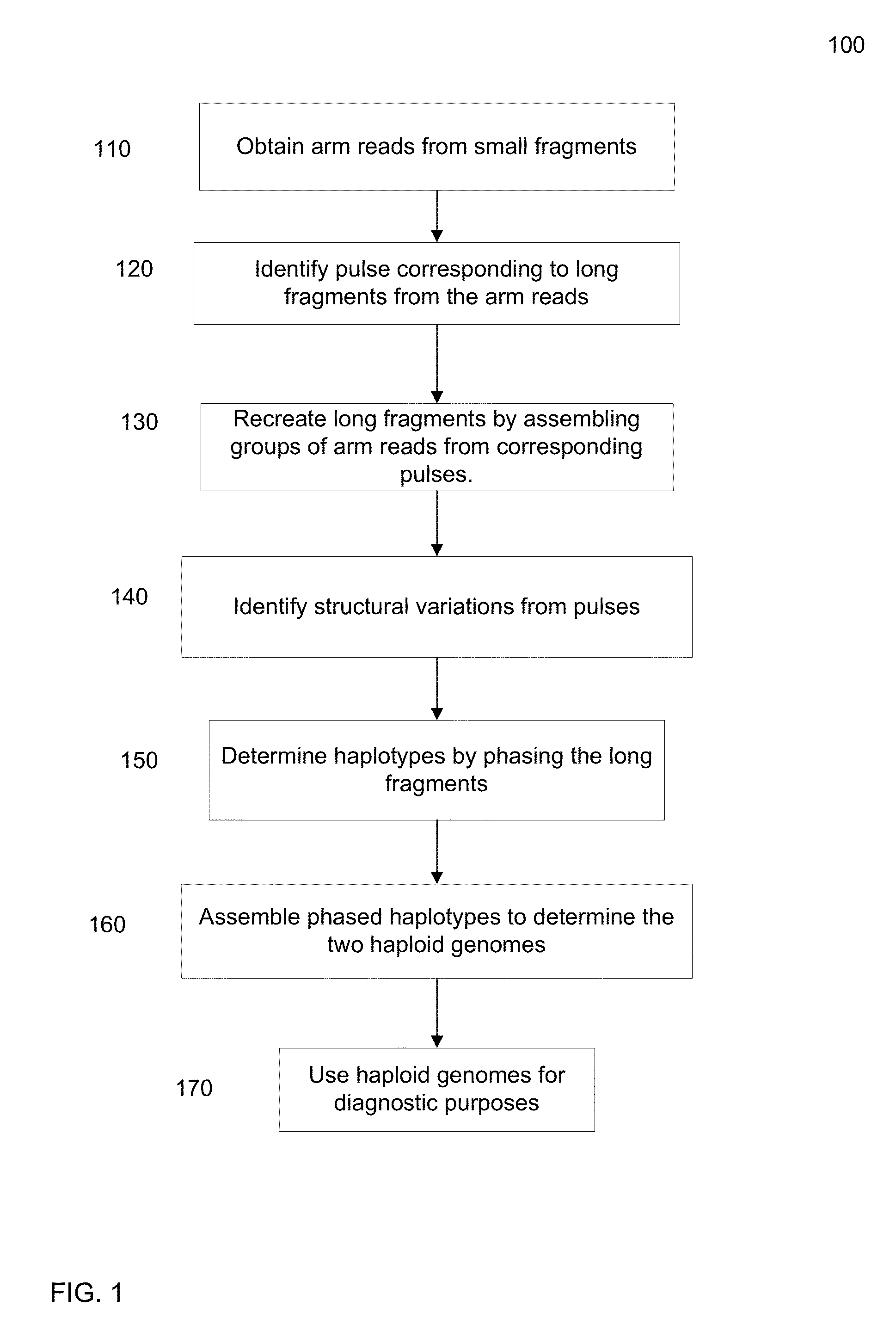
Identification of DNA fragments and structural variations
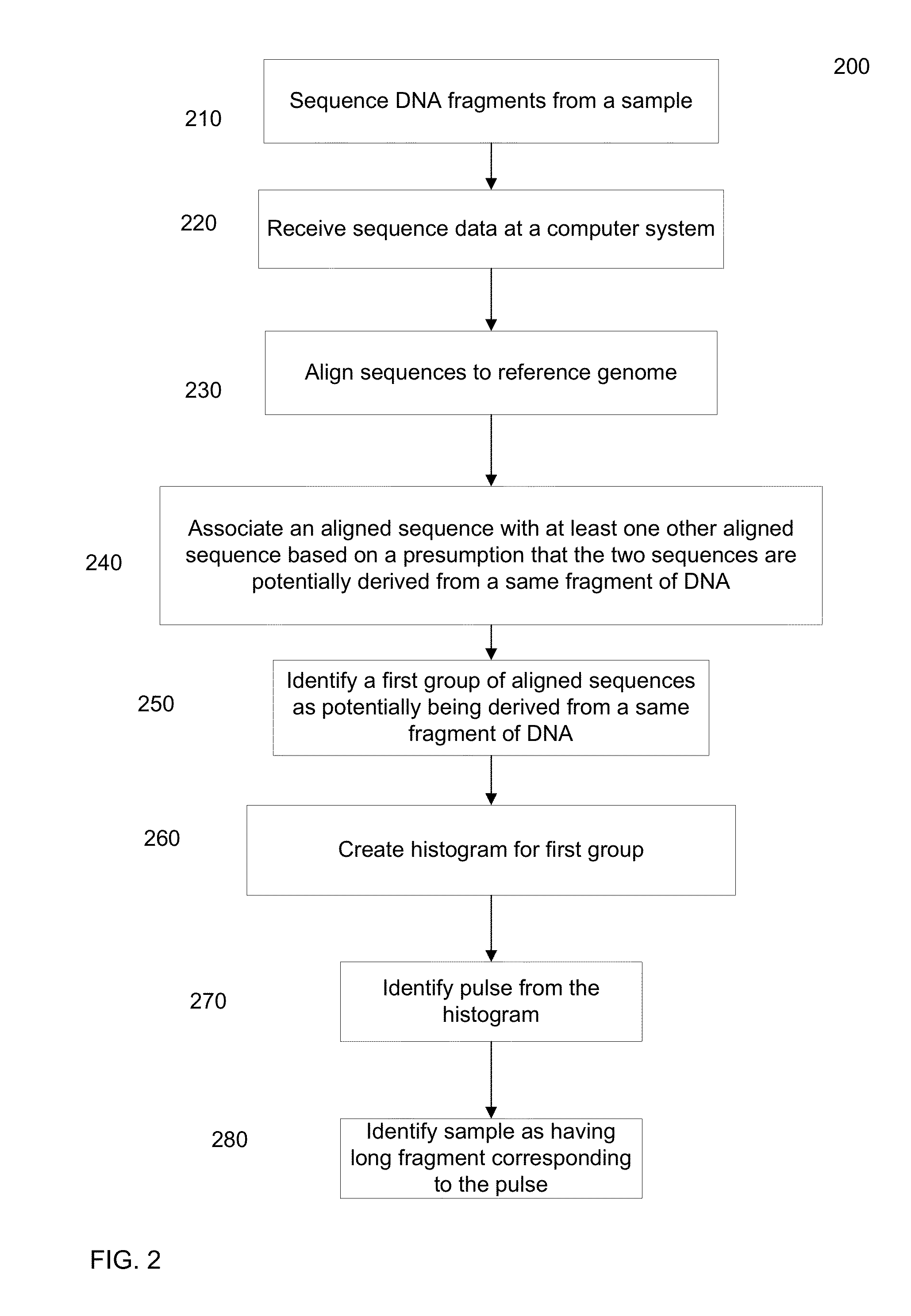
Various short reads can be grouped and identified as coming from a same long DNA fragment (e.g., by using wells with a relatively low-concentration of DNA). A histogram of the genomic coverage of a group of short reads can provide the edges of the corresponding long fragment (pulse). The knowledge of these pulses can provide an ability to determine the haploid genome and to identify structural variations.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Optical information detecting method, optical head, and optical disc apparatus
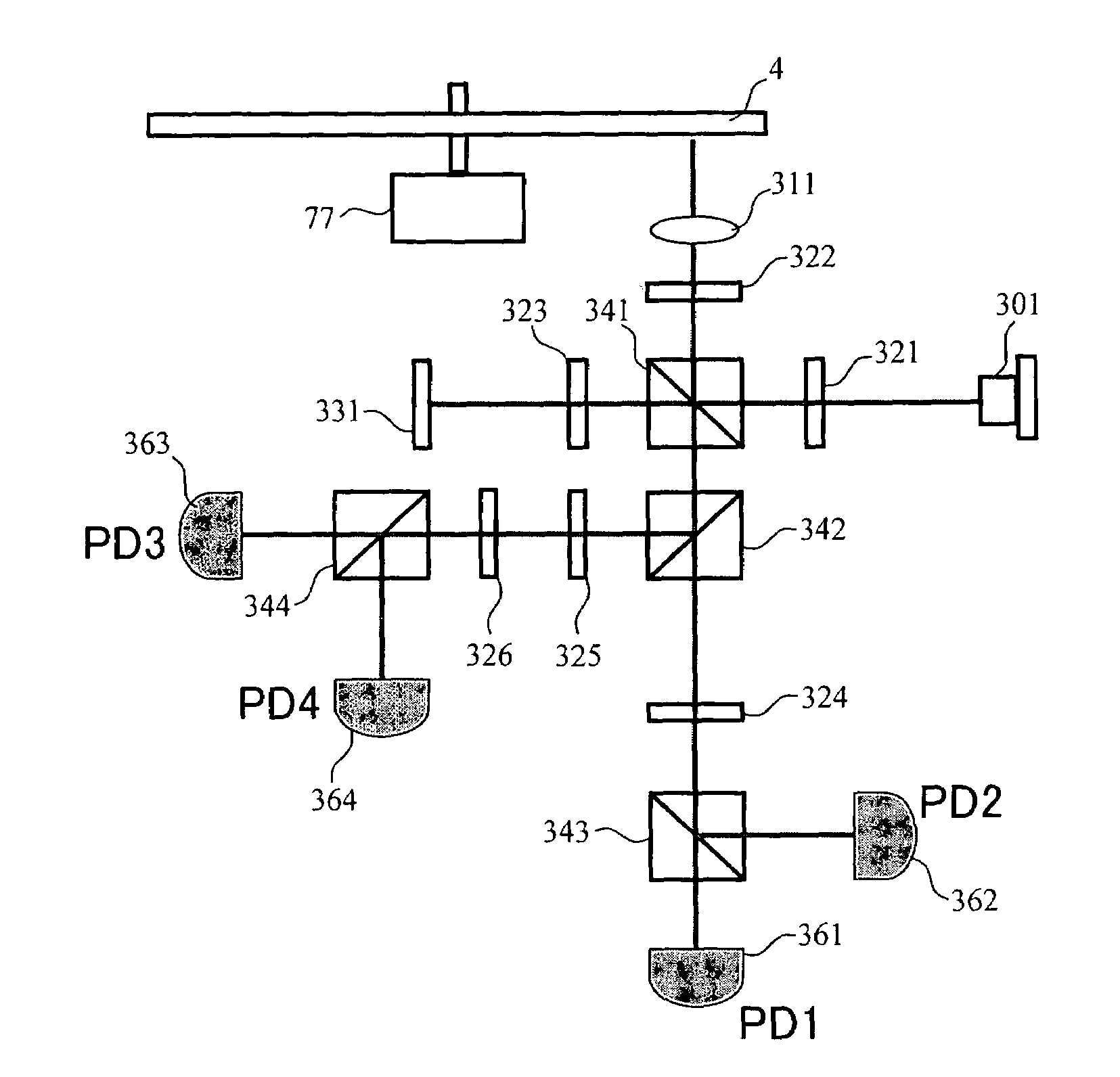
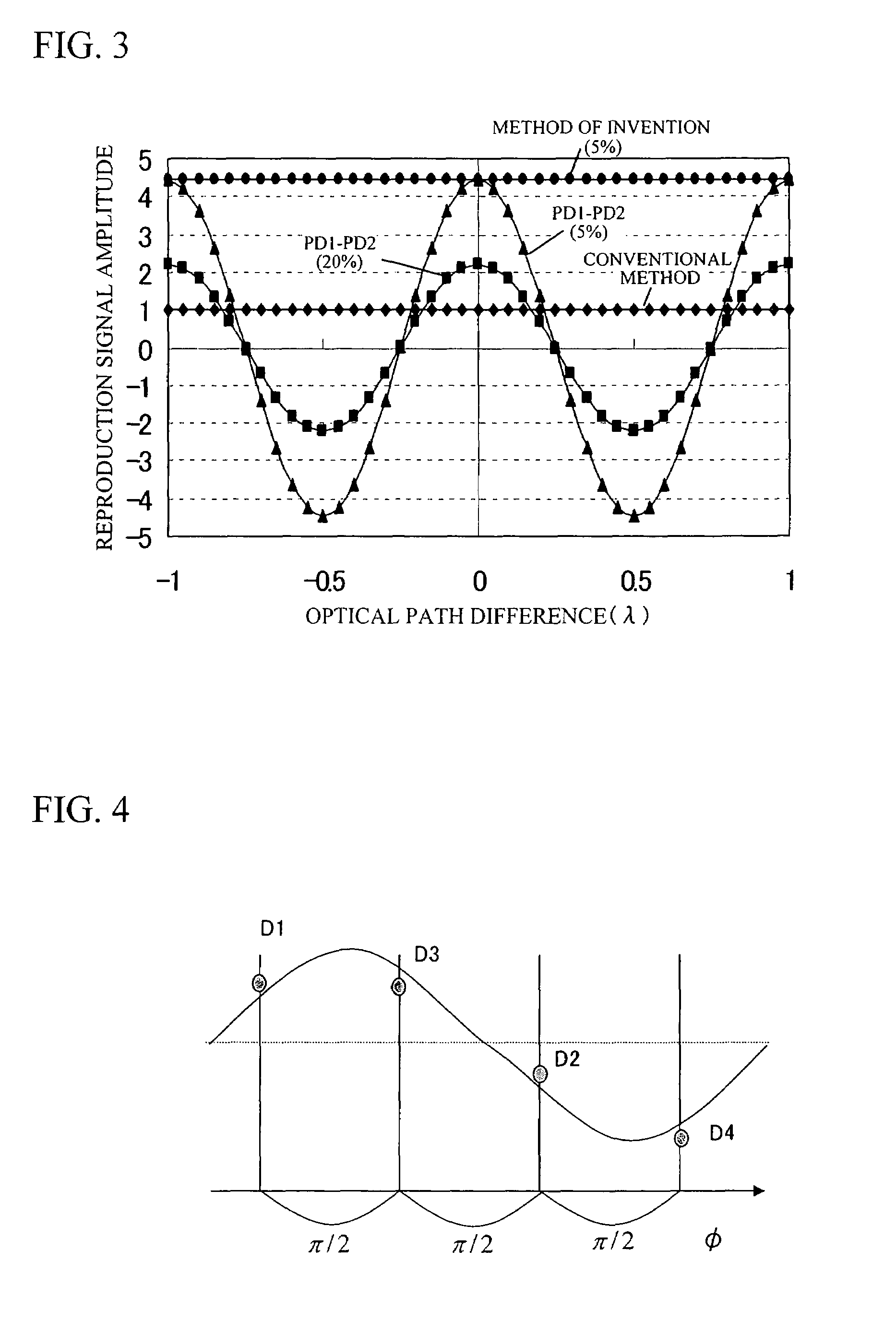
InactiveUS20080067321A1Small reflected signalImprove signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansRecord information storageSignal qualitySignal light
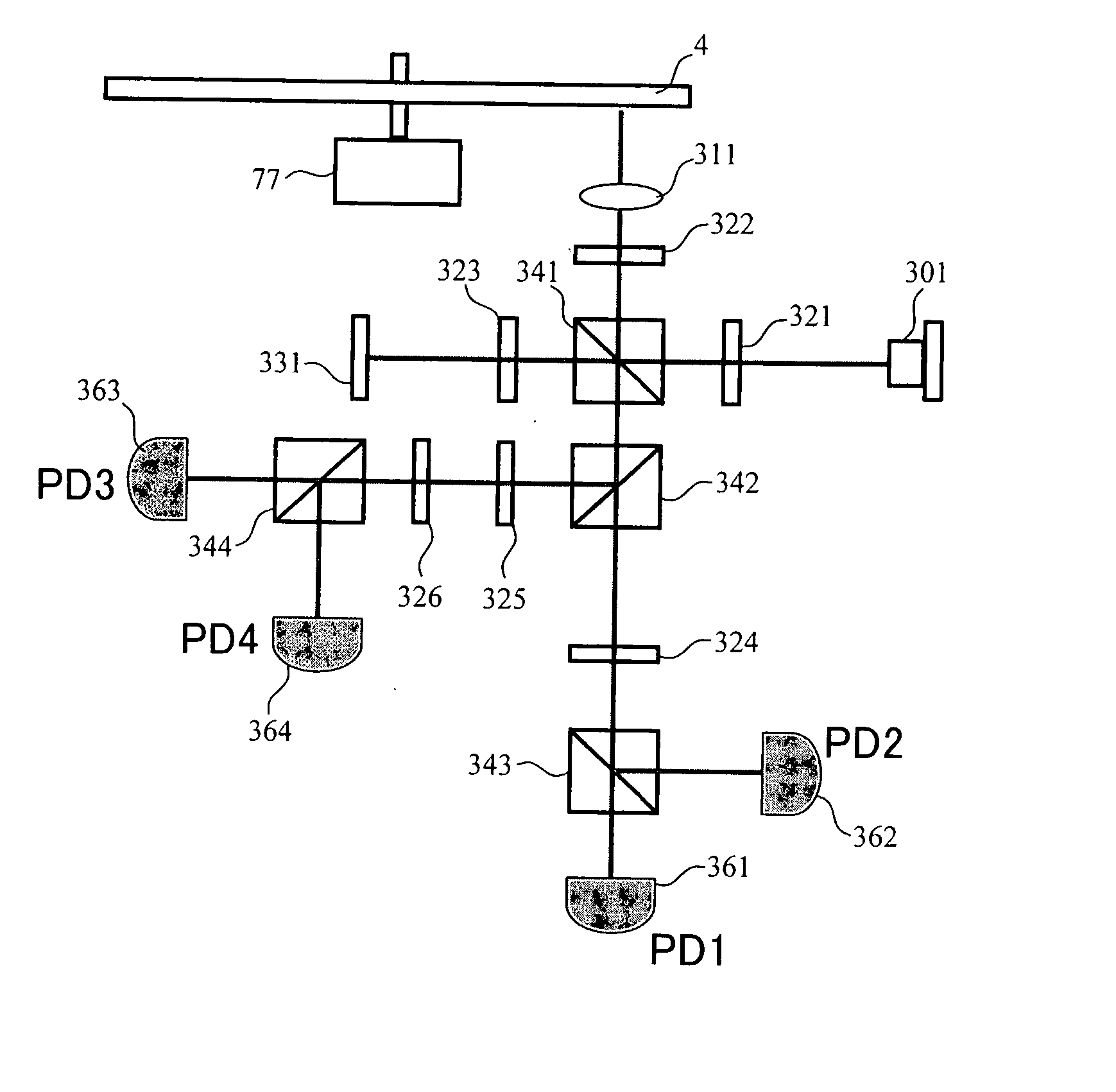
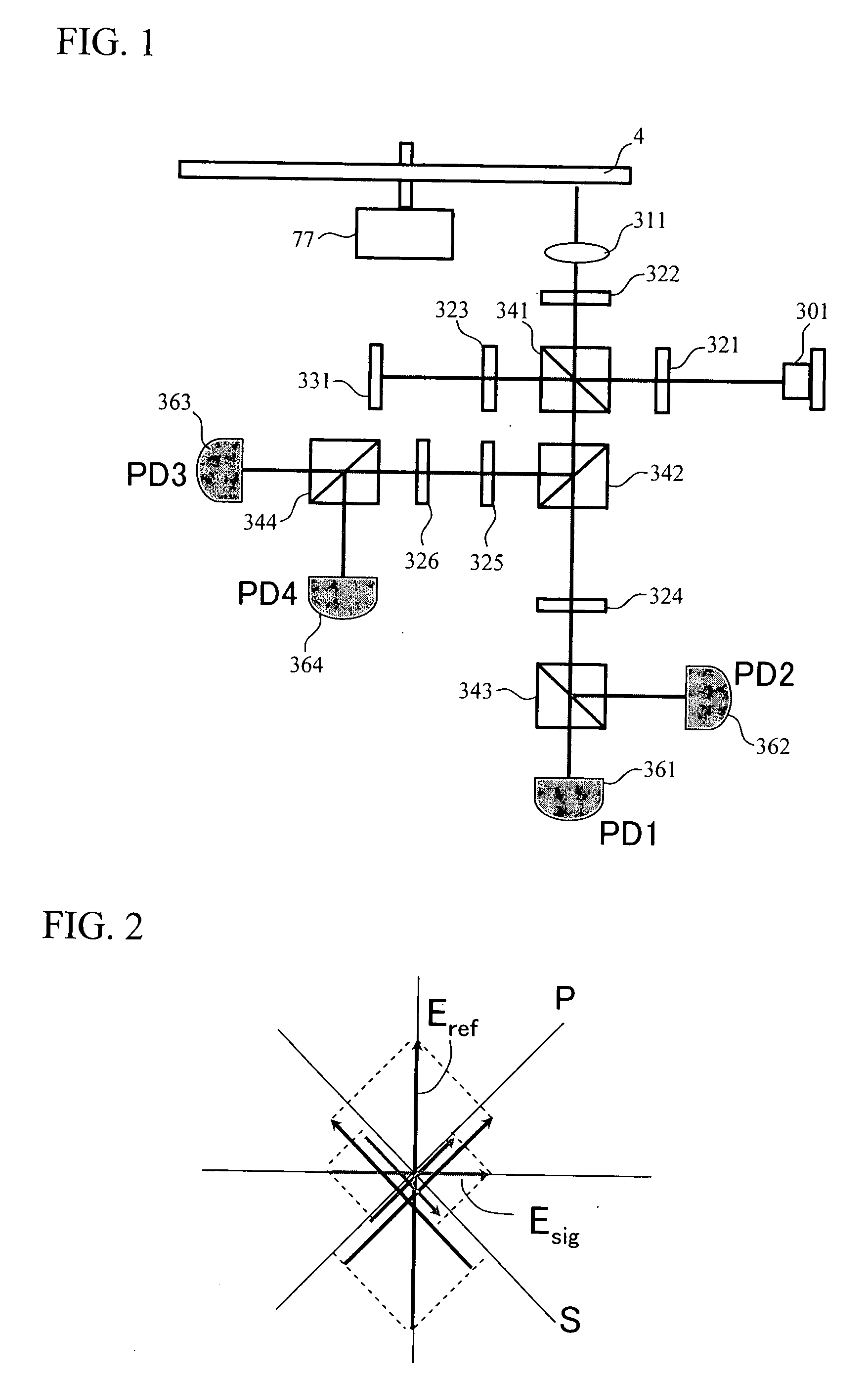
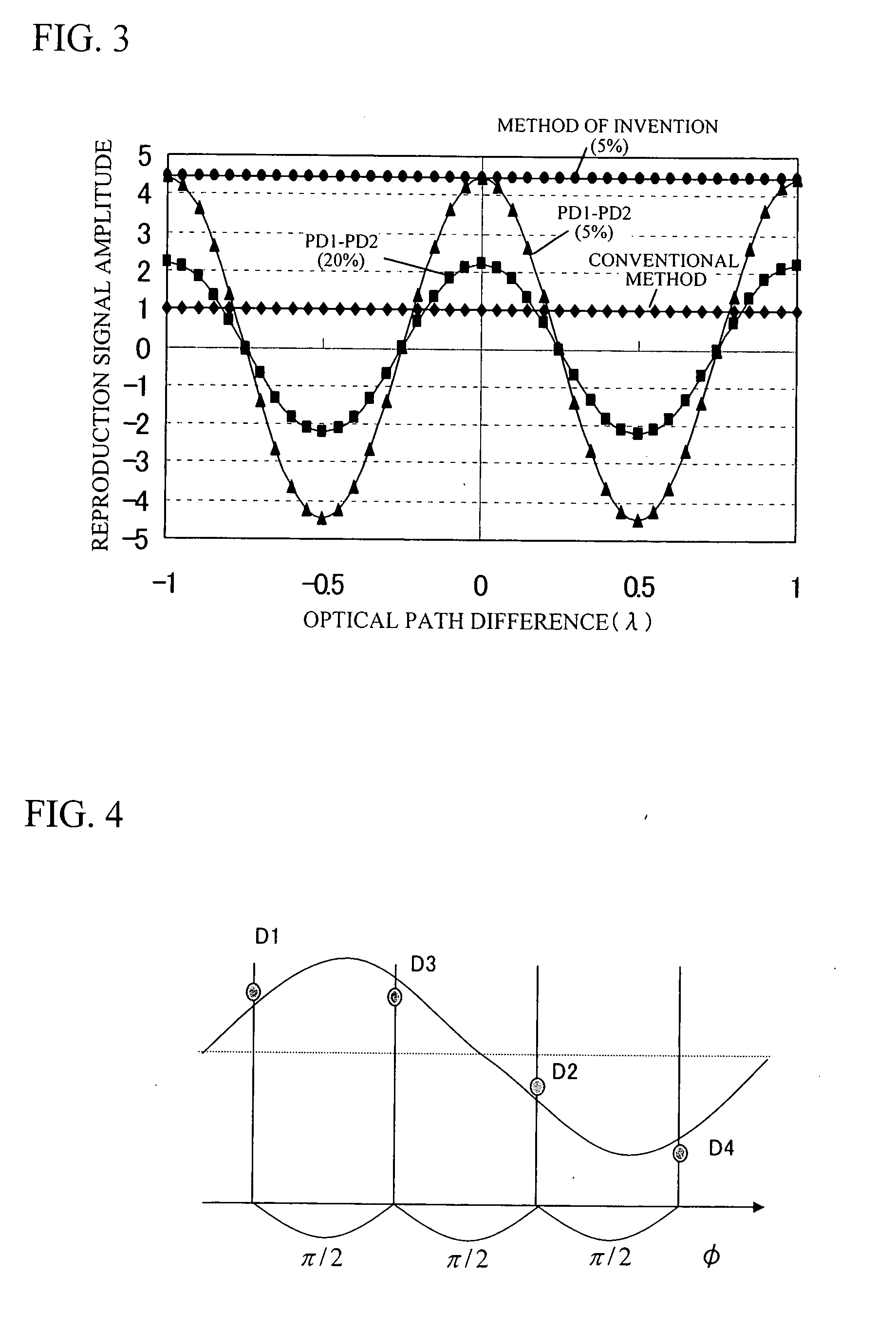
In multilayer optical discs and high-speed optical discs, the amount of reproduction light per unit time greatly decreases and the reproduction signal quality (S / N) significantly drops due to the low effective reflectivity and the short read time of the medium. These problems are solved by causing reflected signal light from the optical disc and reference light, which is separated from the same light source and introduced into a detector without being shone onto the optical disc, to interference with each other on the detector. Detector outputs having four different interference states are simultaneously obtained, the interference states being displaced at intervals of 90° in terms of the phase relationship between the reference light and the signal. Based on a operation of the four detector outputs, a reproduction signal can be obtained that is stable at all times and amplified with high quality, even when there is an optical path length variation due to disc undulations.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Transcriptome-based tumor neoantigen identification method
ActiveCN108491689AImprove accuracyComprehensive identificationSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSample sequenceTumor-specific antigen
The invention discloses a transcriptome-based tumor antigen identification method. The method comprises four steps of: obtaining an RNA sample of a patient tumor tissue, and carrying out library construction and amplification on the RNA sample to obtain an RNA sample sequencing result of the tumor tissue; aligning short read segments of the RNA sample sequencing result to a human reference genometo obtain an RNA alignment result; calculating gene expression quantity according to the RNA alignment result, and carrying out mutation detection and prediction of fusion gene events according to theRNA alignment result; and predicting transcriptome HLA typing according to the alignment result, wherein calculation of the gene expression quantity, mutation detection and prediction of the fusion gene events are carried out according to a specified order or simultaneously carried out; and using the gene expression quantity of a transcriptome sample, depth of transcriptome mutation sites in a whole-exon sequencing sample and binding force of neonatal short peptides and the patient HLA typing as an analysis result to submit the same to a downstream analyst. The invention provides the method capable of identifying a tumor-specific antigen of an individual sample from tumor patient transcriptome NGS data.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEOANTIGEN THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
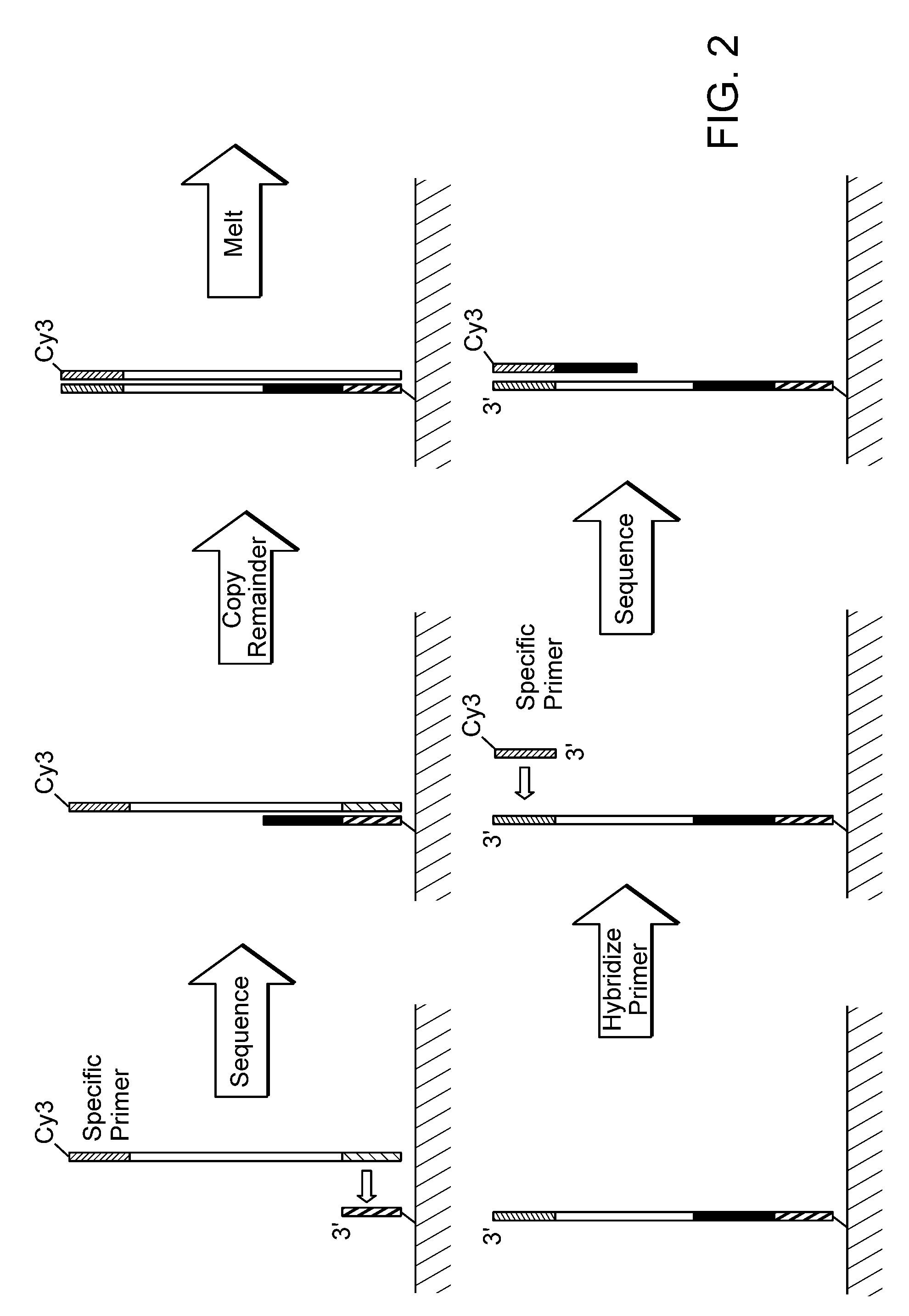
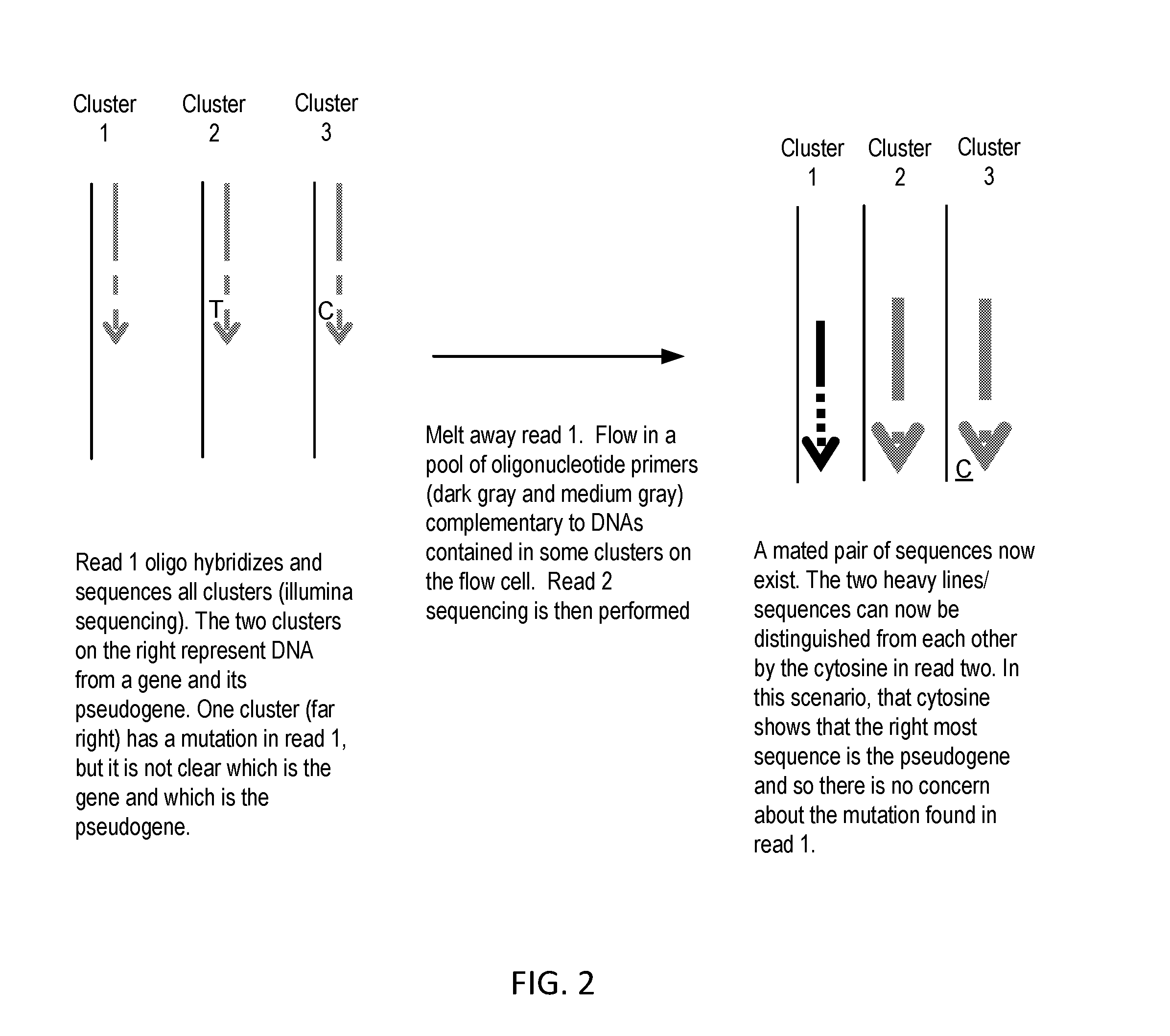
Sequential sequencing
InactiveUS20140274738A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleic acid sequencingExon
The present invention provides improved methods, compositions and kits for short read next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits of the present invention enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (typically comprising regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information is obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein are useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Non-volatile memories programmable by "hot carrier" tunnel effect and erasable by tunnel effect
A Flash-EPROM type memory cell with a short read time and a "very low supply voltage." The memory cell has the additional advantage of using less power, therefore generating less heat and allowing a denser integrated circuit. The memory cell comprises a floating-gate transistor whose source is coupled to the drain of a selection transistor. The floating-gate transistor is in a depleted state when the memory cell is "erased." The read voltage applied to the control gate of the floating-gate transistor is substantially equal to a general supply voltage which is in the range of 1.5 volts. The gate of the selection transistor receives a bias voltage at least equal to its conduction threshold. The gate of the selection transistor can also receive a bias voltage higher than the read voltage, which will speed up the read time further. A Flash-EPROM incorporating this memory cell is also provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
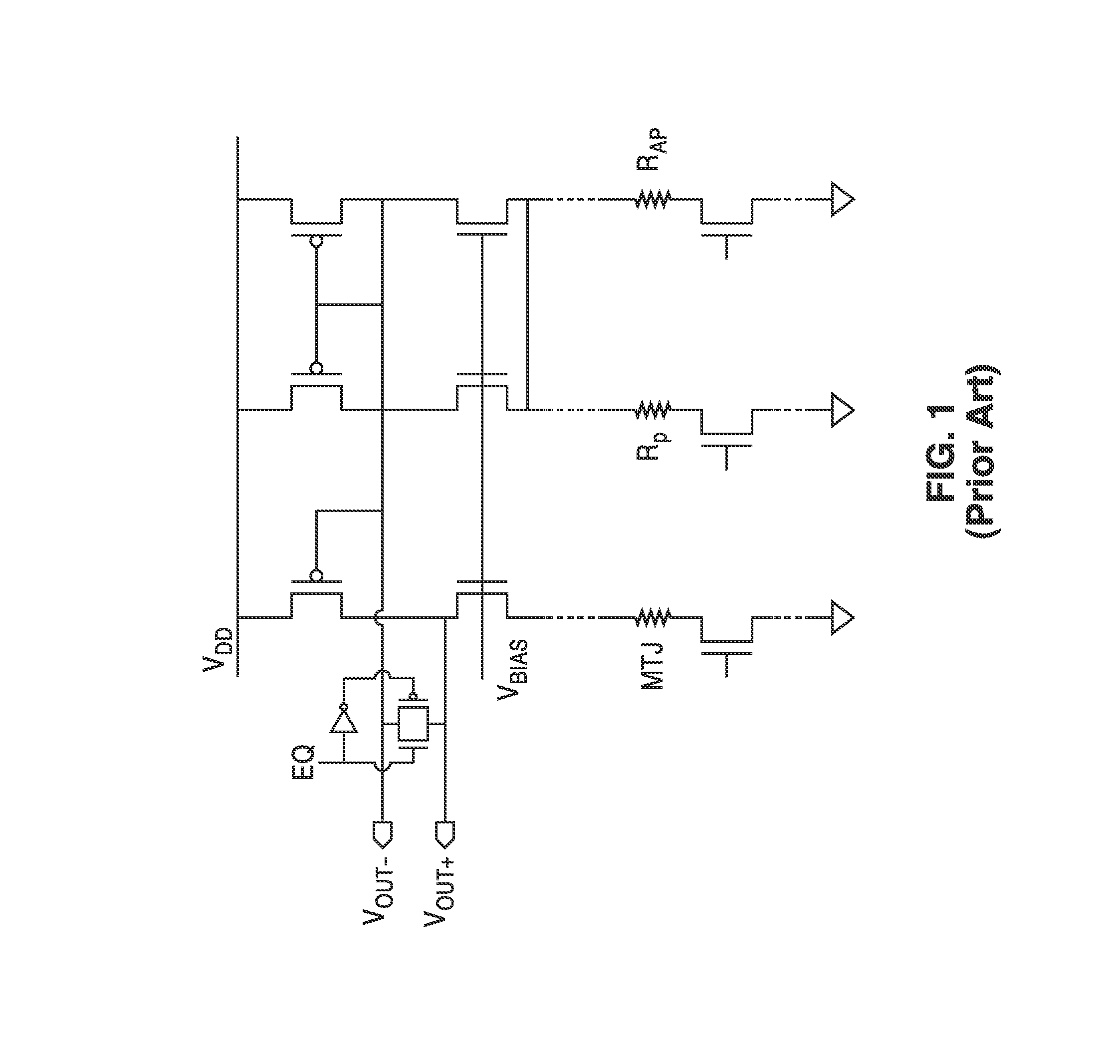
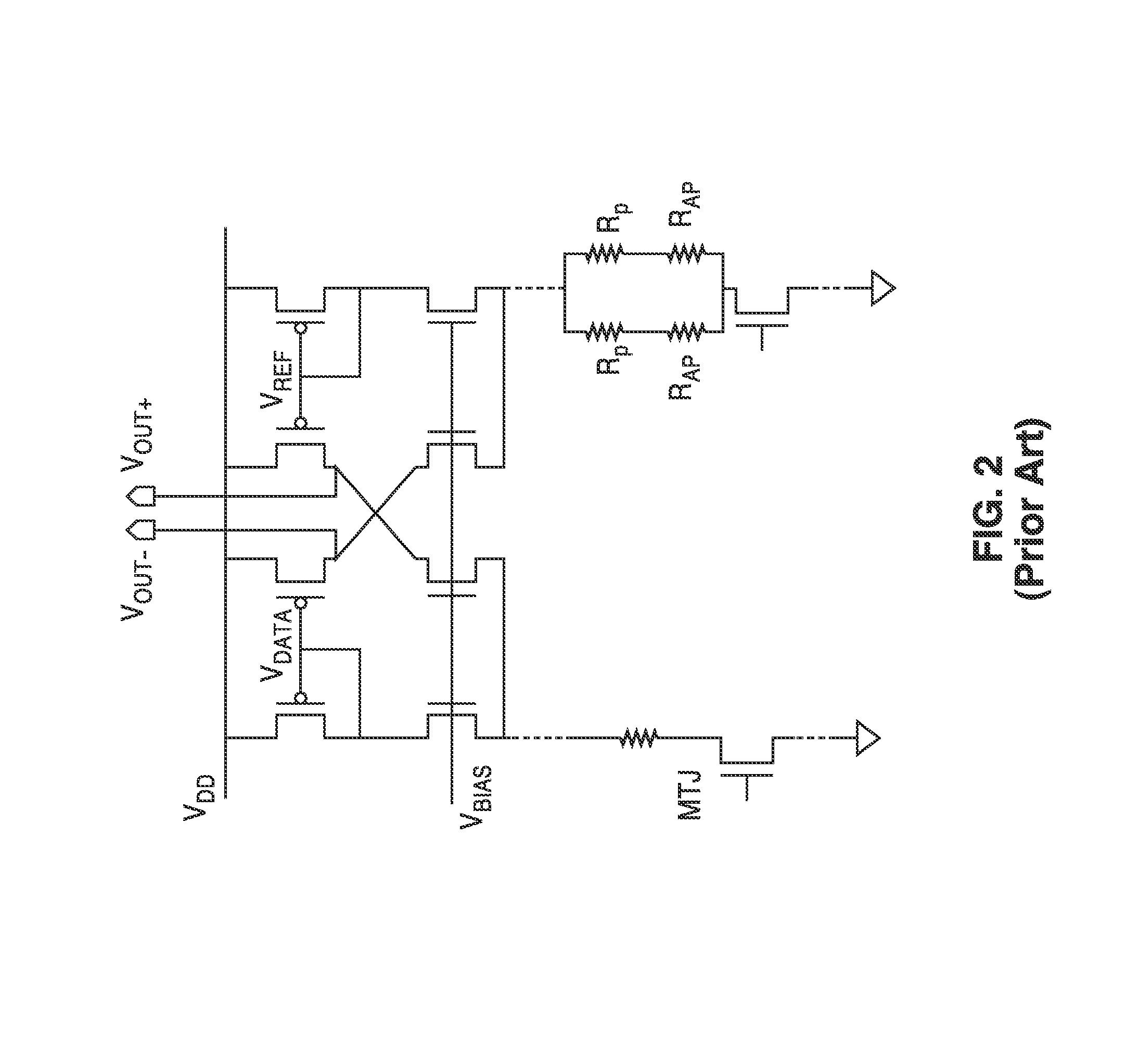
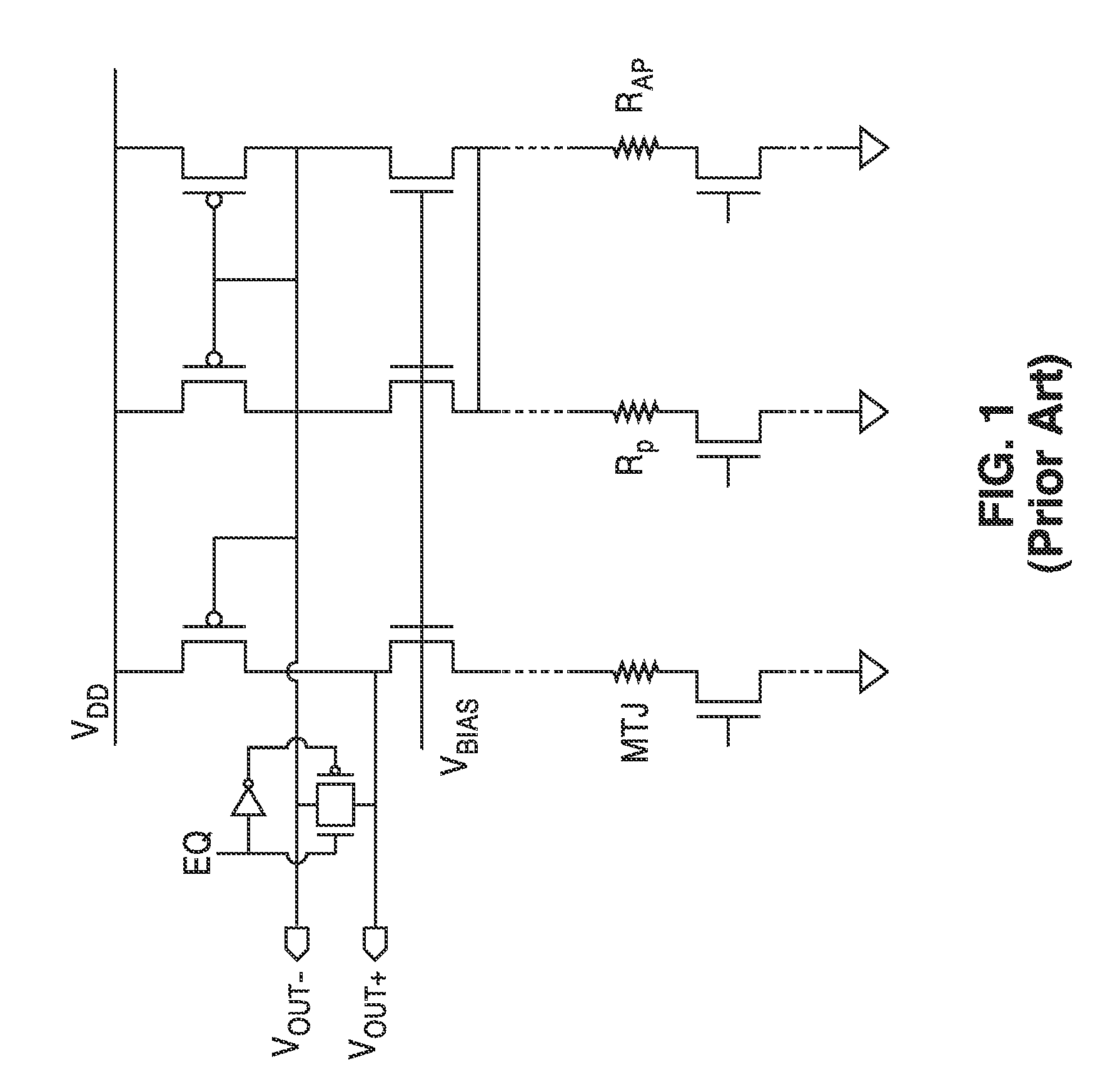
Body voltage sensing based short pulse reading circuit
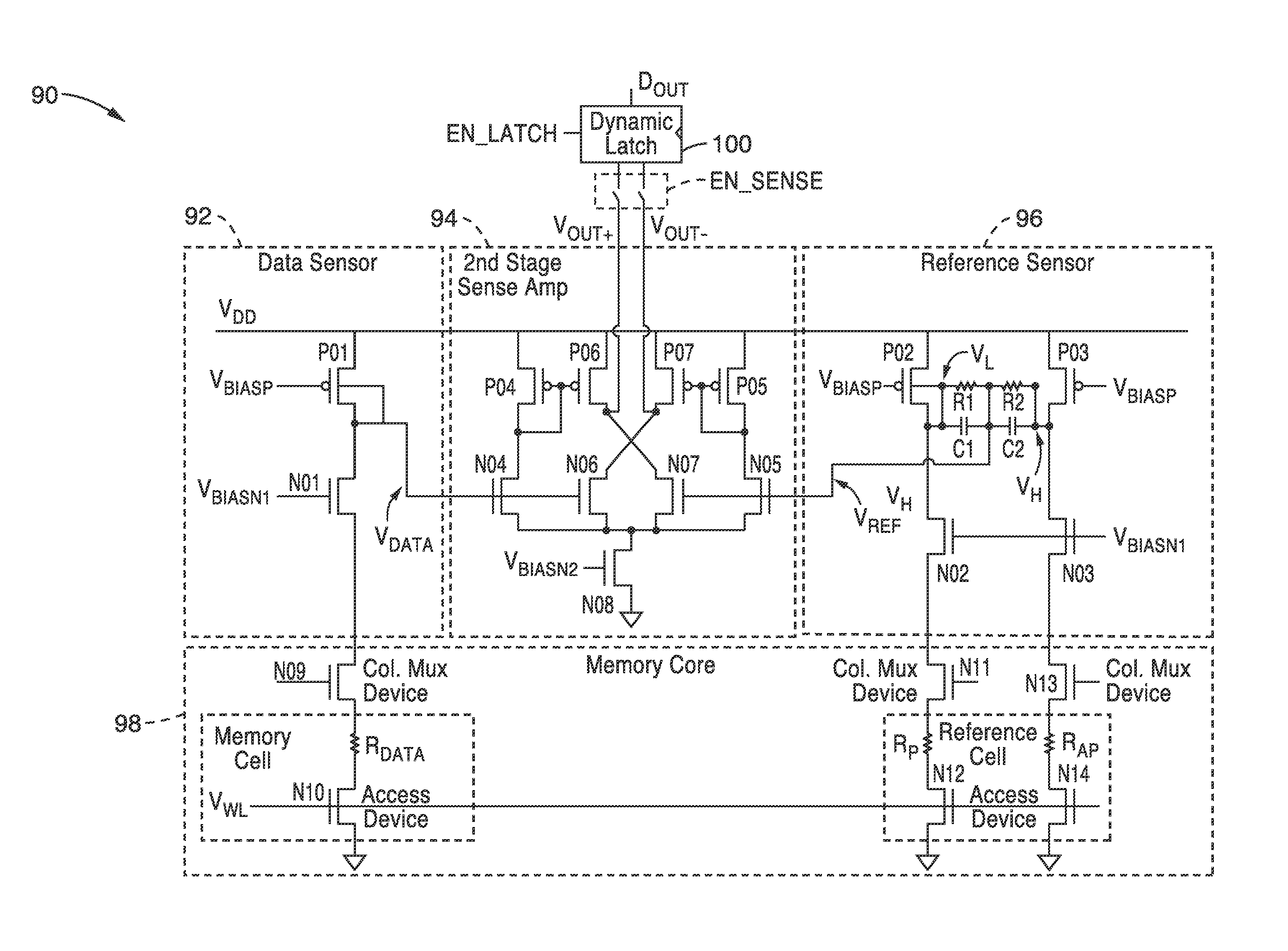
InactiveUS20140153325A1Decrease read disturbance probabilityImprove read reliabilityDigital storageEngineeringShort read
As memory geometries continue to scale down, current density of magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) make conventional low current reading scheme problematic with regard to performance and reliability. A body-voltage sense circuit (BVSC) short pulse reading (SPR) circuit is described using body connected load transistors and a novel sensing circuit with second stage amplifier which allows for very short read pulses providing much higher read margins, less sensing time, and shorter sensing current pulses. Simulation results (using 65-nm CMOS model SPICE simulations) show that our technique can achieve 550 mV of read margin at 1 ns performance under a 1V supply voltage, which is greater than reference designs achieve at 5 ns performance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
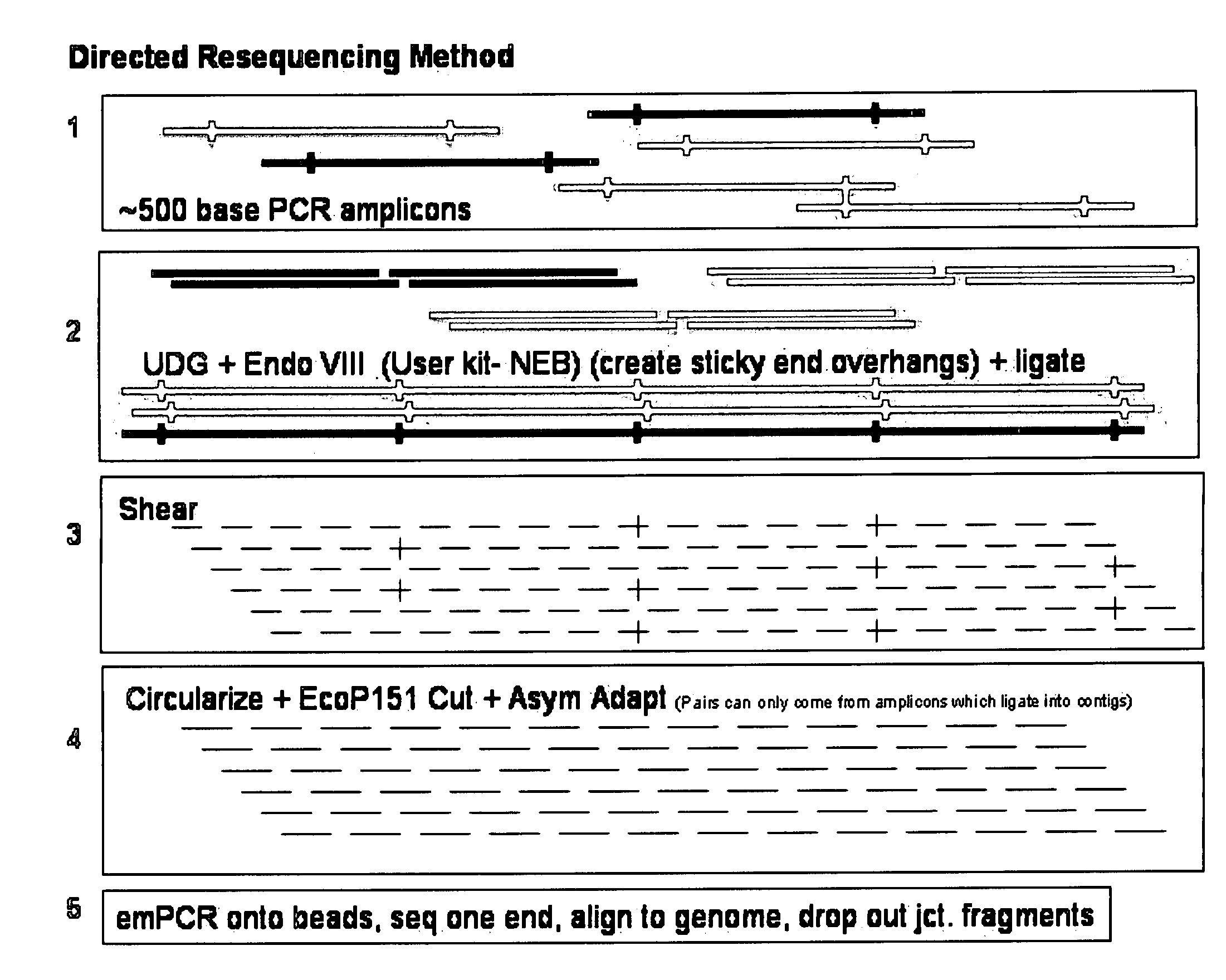
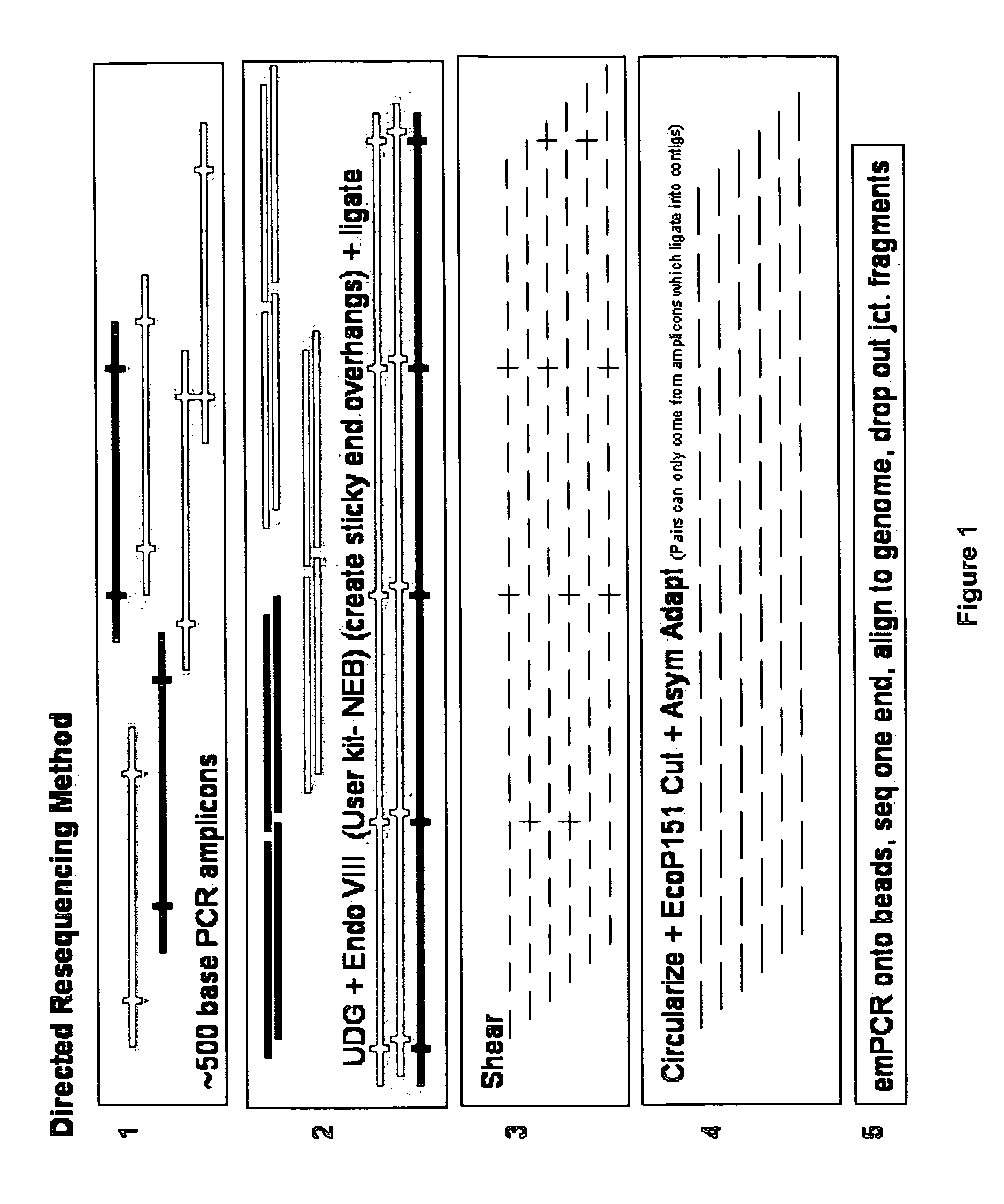
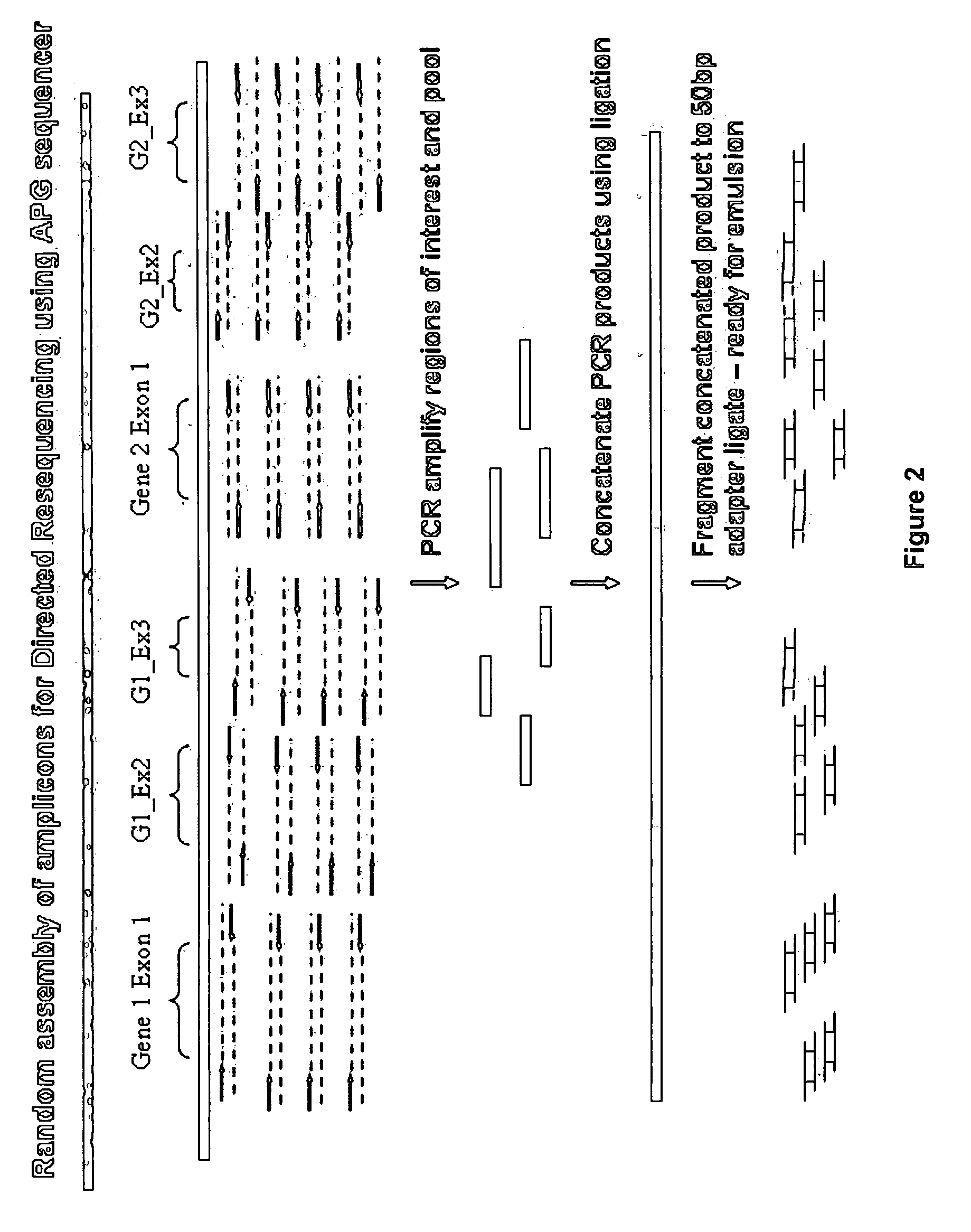
Directed assembly of amplicons to enhance read pairing signature with massively parallel short read sequencers
InactiveUS20090036325A1Easy to assembleFacilitate informatic assemblyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationShort readComputational biology
The present teachings relate to improved methods, kits, and compositions for making nucleic acid libraries and sequencing nucleic acids. In some embodiments, directionally defined concatamers are generated, facilitating sequencing efforts.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
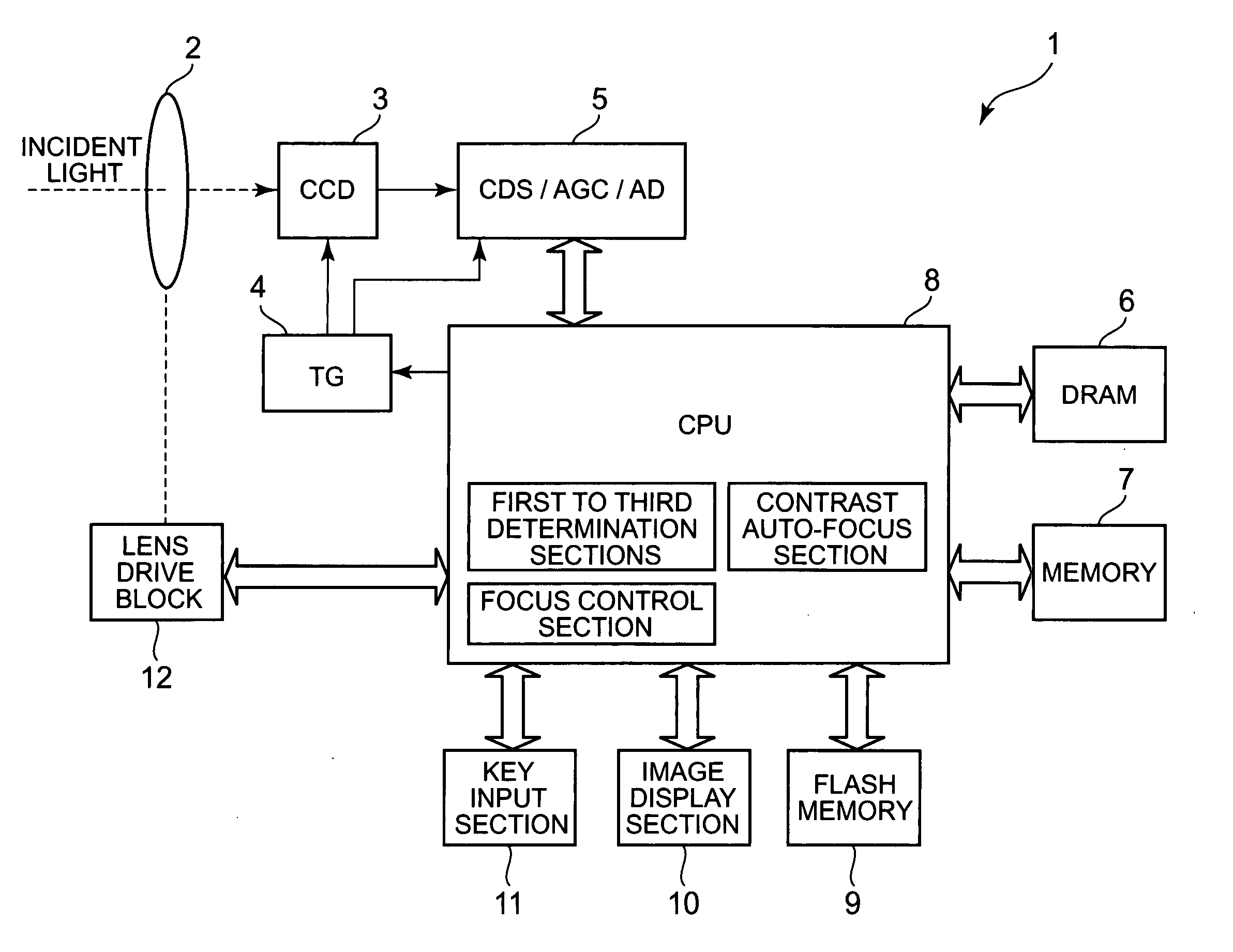
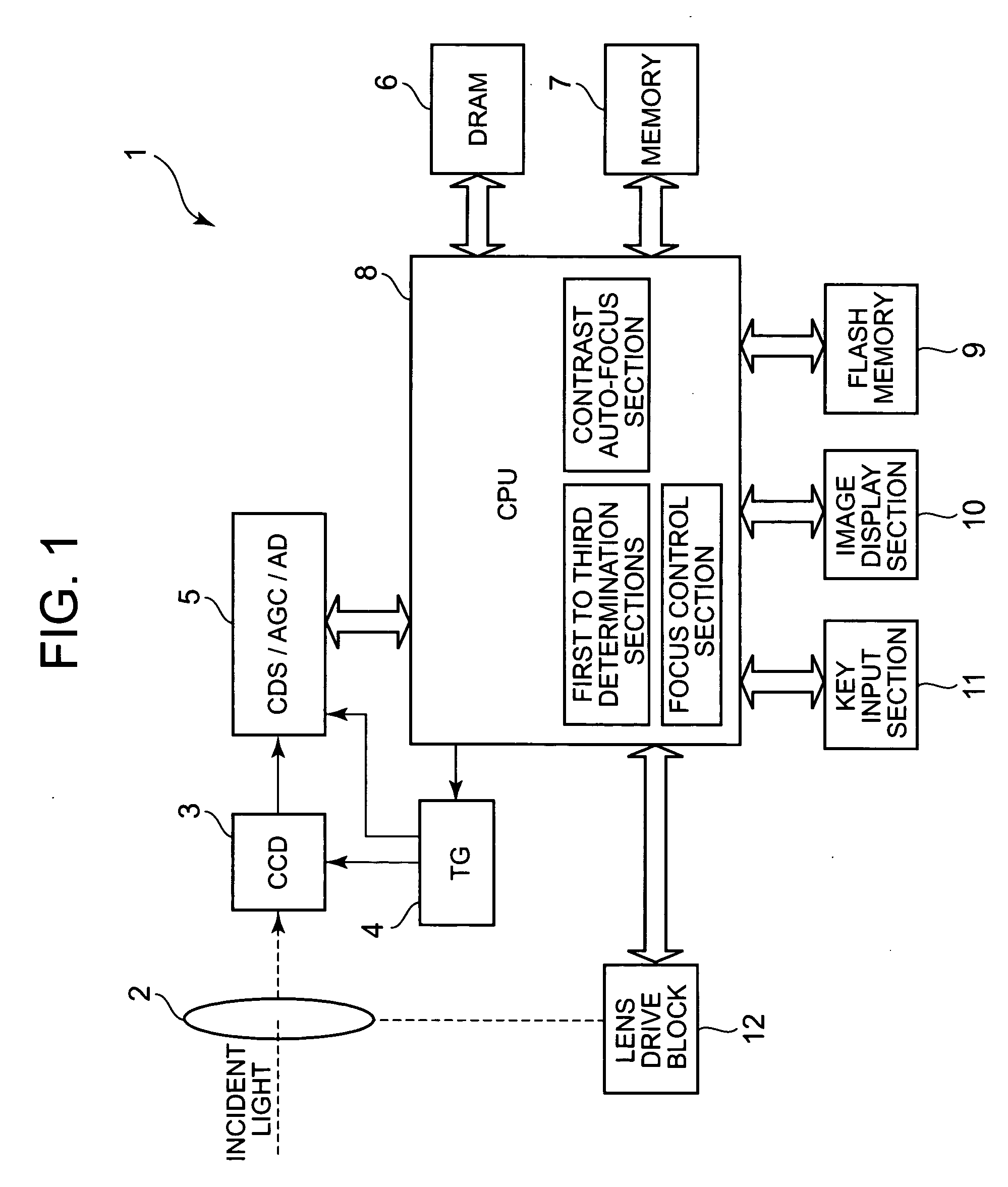
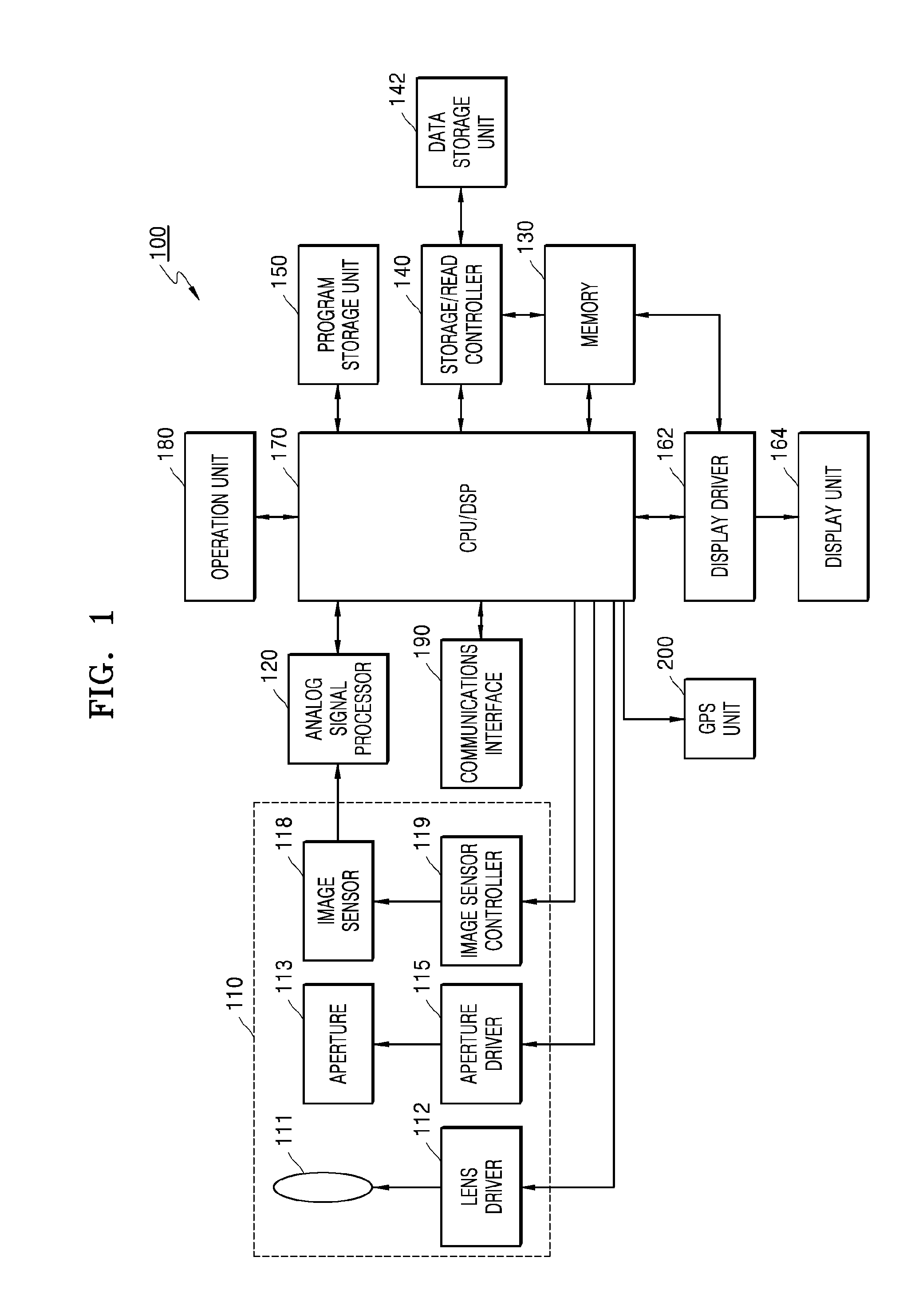
Imaging apparatus with auto-focus function
An imaging apparatus includes an image pickup device that converts light from a subject to image data a drive section that drives the image pickup device, an auto-focus section that performs an auto-focus operation, and a focus control section that controls the auto-focus section to perform an auto-focus operation while controlling the drive section so that the image data is read from the image pickup device at a predetermined read out cycle suitable for displaying a through image, when the first determination section determines that the shutter button is pressed halfway, and that controls the auto-focus section to perform an auto-focus operation while controlling the drive section so that the image data is read from the image pickup device at a shorter read out cycle than the redetermined read out cycle, when the second determination section determines that the shutter button is fully pressed at once.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Optical information detecting method, optical head, and optical disc apparatus utilizing plural photodetectors
InactiveUS7750276B2High amplification effectSmall sizeMaterial analysis by optical meansRecord information storageSignal qualityPhotovoltaic detectors
In multilayer optical discs and high-speed optical discs, the amount of reproduction light per unit time greatly decreases and the reproduction signal quality (S / N) significantly drops due to the low effective reflectivity and the short read time of the medium. These problems are solved by causing reflected signal light from the optical disc and reference light, which is separated from the same light source and introduced into a detector without being shone onto the optical disc, to interference with each other on the detector. Detector outputs having four different interference states are simultaneously obtained, the interference states being displaced at intervals of 90° in terms of the phase relationship between the reference light and the signal. Based on a operation of the four detector outputs, a reproduction signal can be obtained that is stable at all times and amplified with high quality, even when there is an optical path length variation due to disc undulations.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
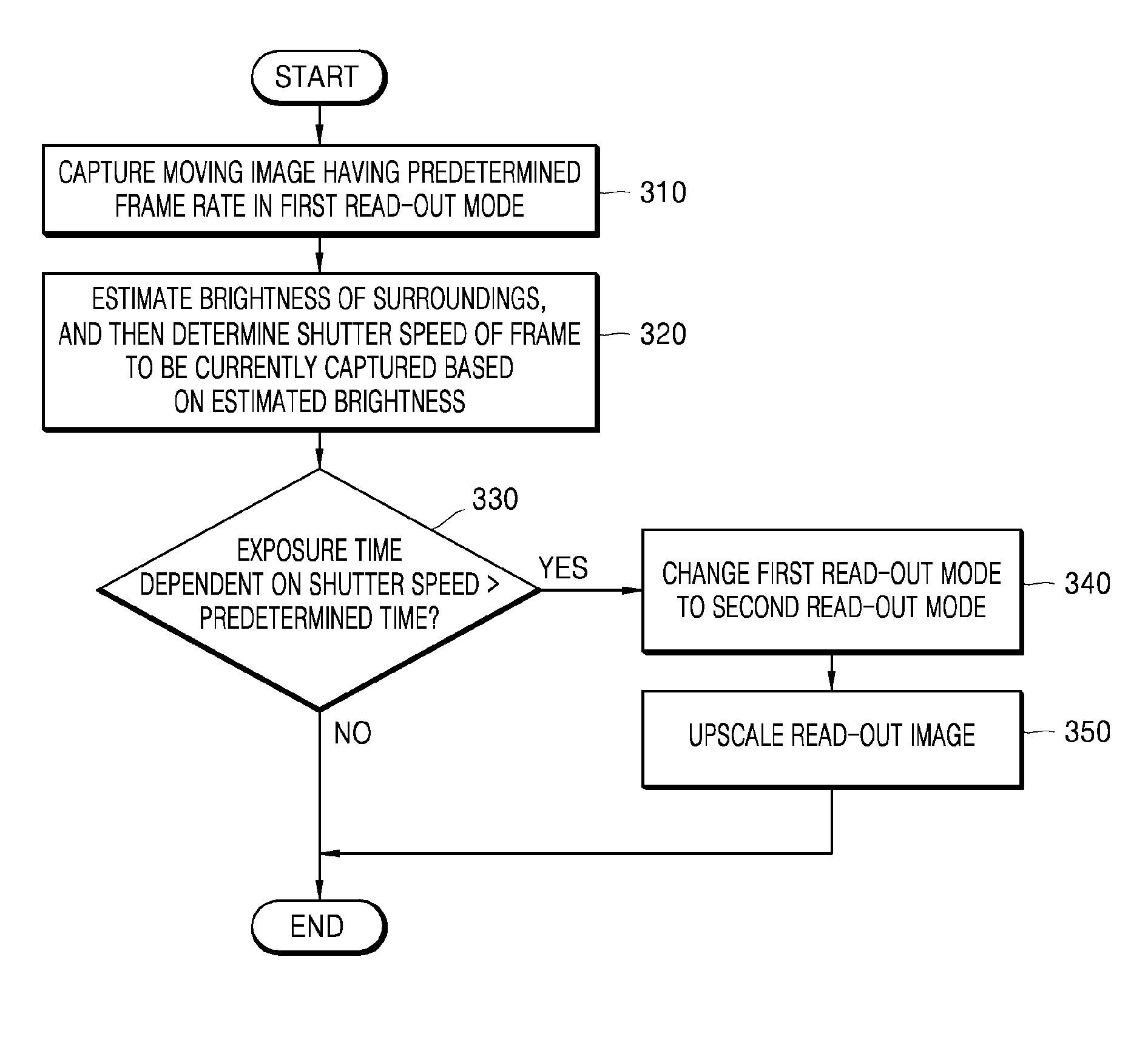
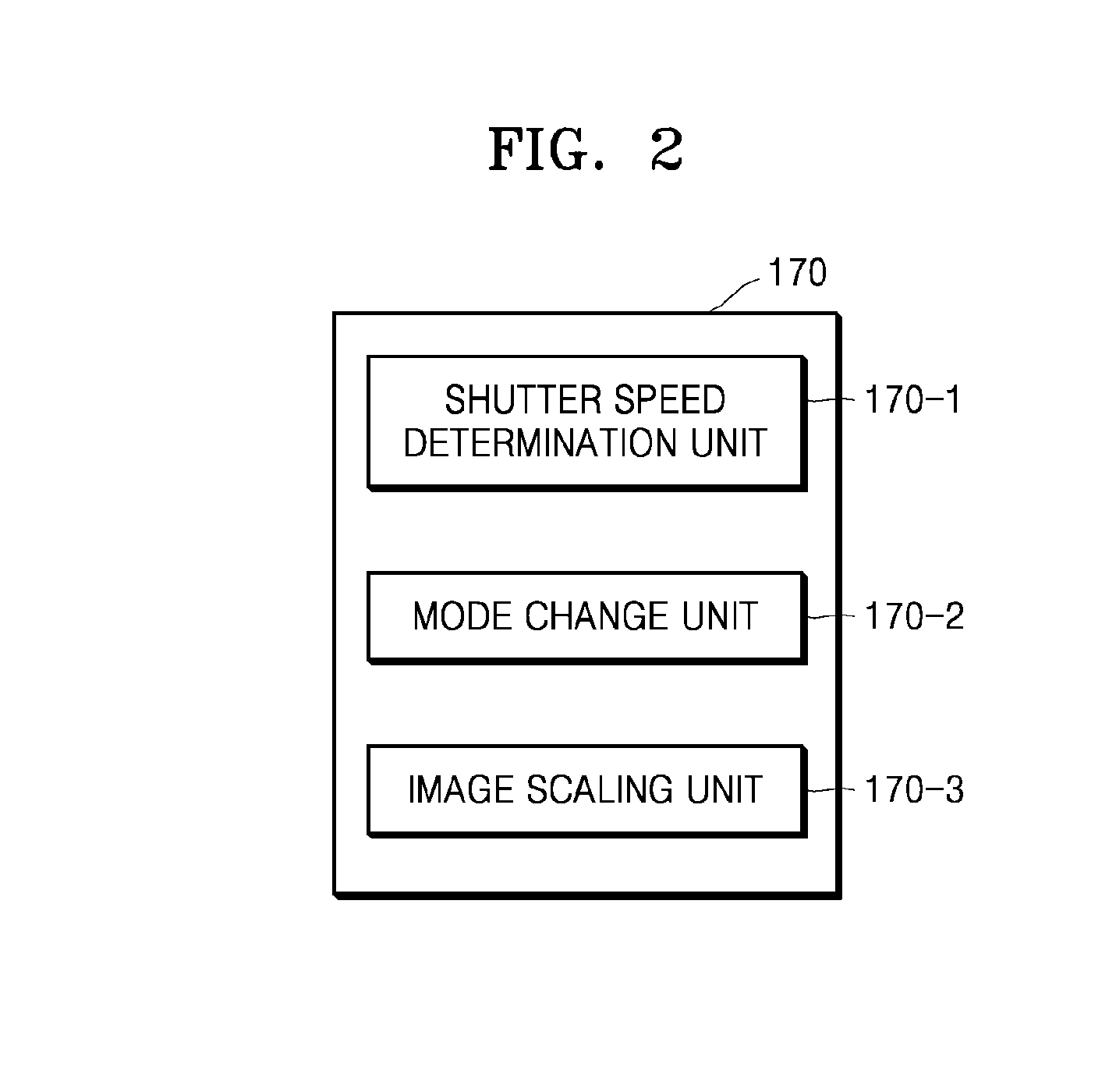
Read-out mode changeable digital photographing apparatus and method of controlling the same
Provided are a digital photographing apparatus in which a read-out mode may be changed when capturing a moving image, and a method of controlling the digital photographing apparatus. The method includes capturing a moving image having a predetermined frame rate in a first read-out mode, estimating a brightness of surroundings and then determining a shutter speed of a frame to be currently captured based on the estimated brightness of the surroundings, determining whether or not an exposure time that is dependent on the shutter speed is longer than a predetermined time period, and changing the first read-out mode to a second read-out mode that has a shorter read-out time than the first read-out mode when the exposure time is longer than the predetermined time period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
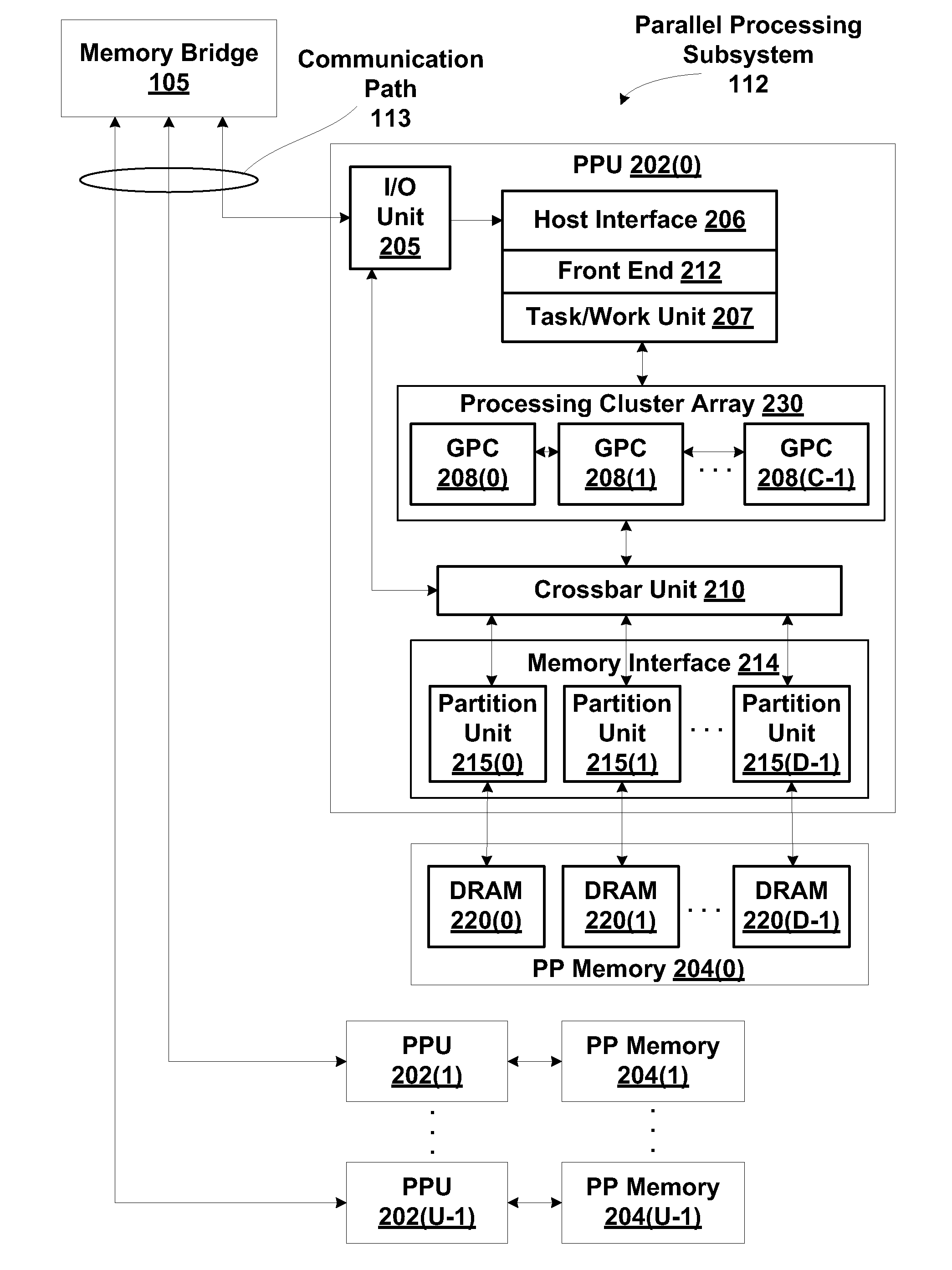
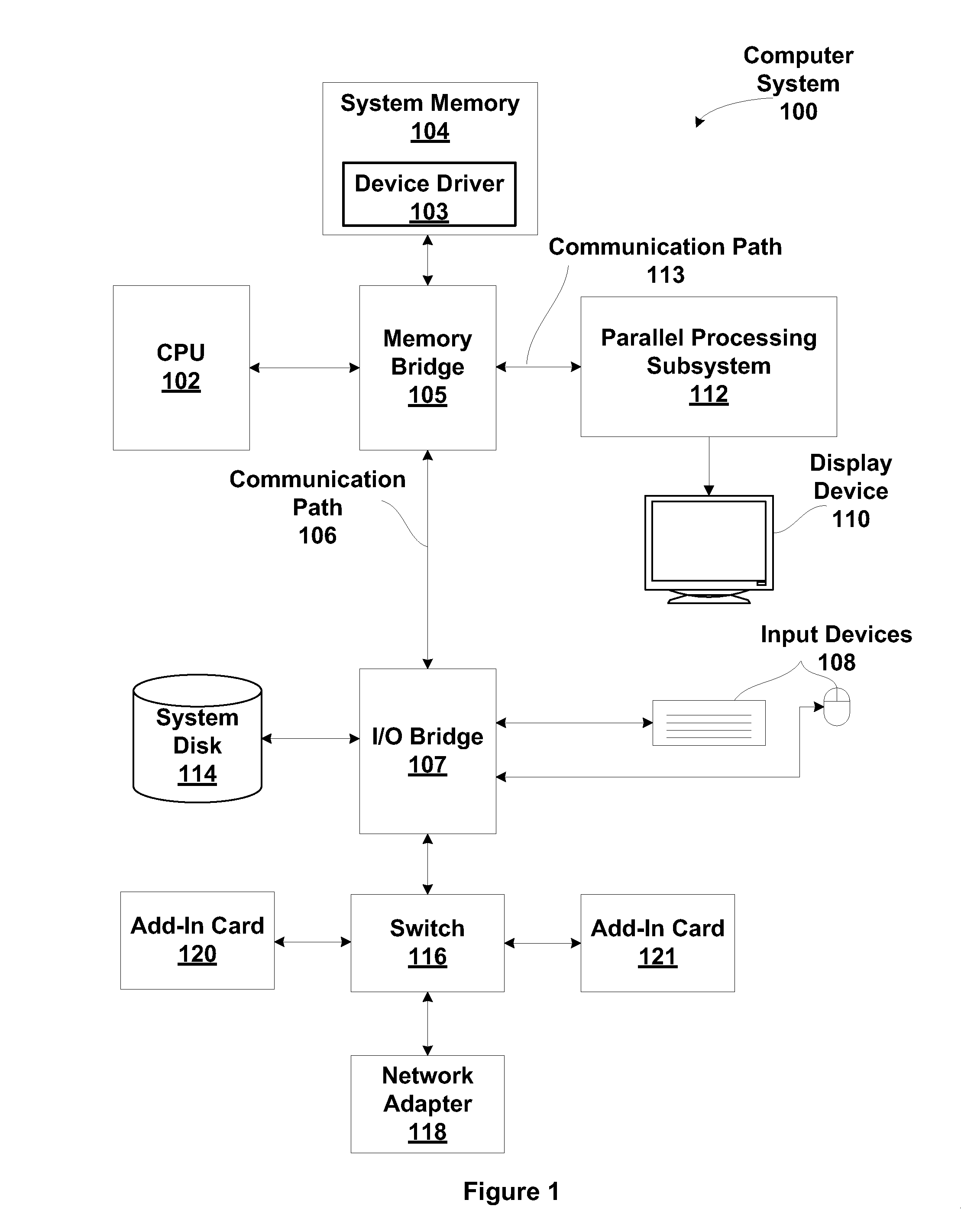
Streaming processing of short read alignment algorithms
InactiveUS20140173606A1Reduce in quantityMultiprogramming arrangementsSequence analysisShort readMultiple stages
A technique for executing alignment algorithms on a SIMT processing environment is disclosed. An alignment algorithm having multiple stages is executed within the SIMT environment such that a different thread group executes each stage of the algorithm. Each thread group performs a different set of alignment operations related to a different stage of alignment algorithm for a group of short reads. In such a manner, the thread groups operate in unison to perform all the operations related to each stage of the alignment algorithm on every short read in the group of short reads.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
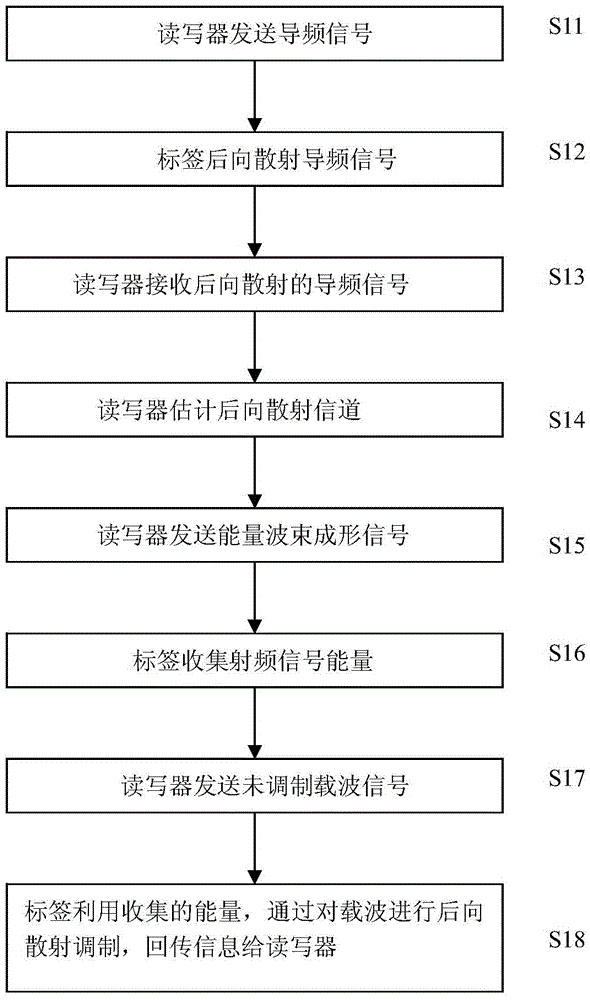
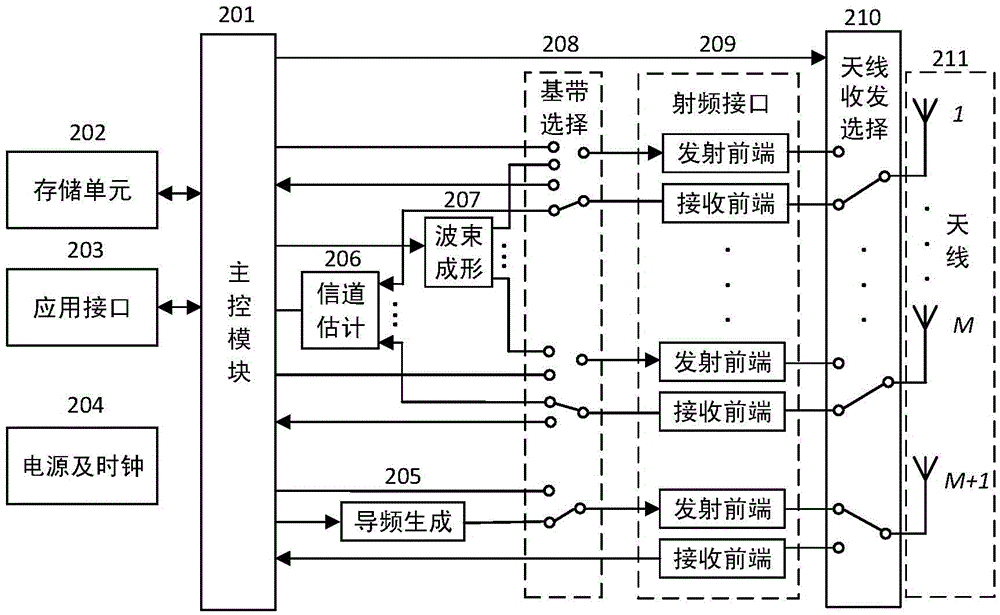
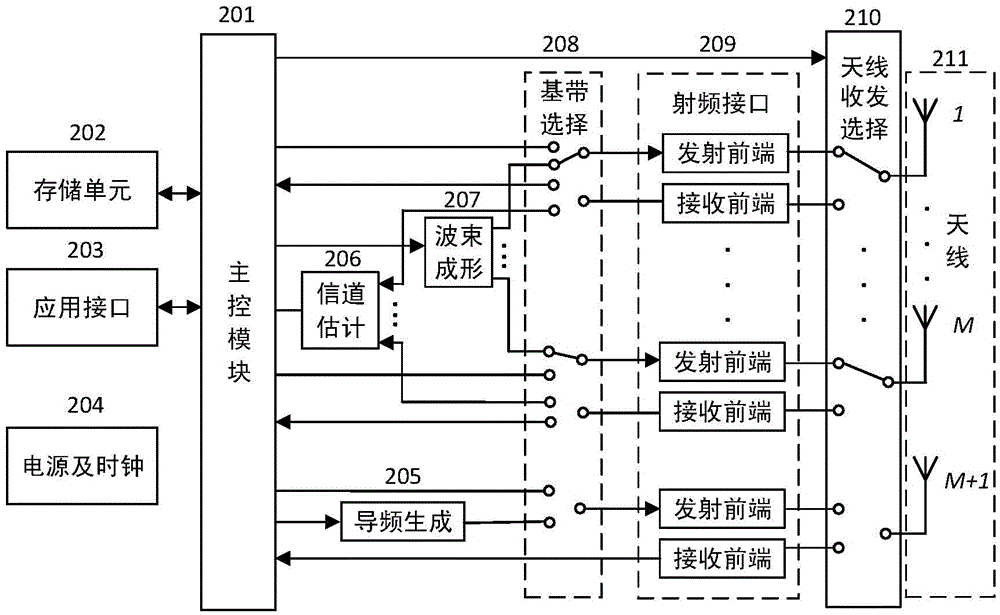
RFID system capable of enhancing read-write distance and read-write method thereof and energy distribution optimization method
ActiveCN105550720AAccurate estimateReduce intensityAutomatic card filesCommunications systemCarrier signal
The invention relates to the radio frequency automatic identification technology of the field of the backscattering communication system, discloses an RFID read-write system capable of enhancing RFID read-write distance and a read-write method thereof, and solves the problems in the prior art that a passive RFID system is short in read-write distance. The RFID read-write method comprises the following steps that a. a reader-writer transmits a pilot signal to a tag; b. the tag backscatters the pilot signal; c. the reader-writer receives the pilot signal backscattered by the tag; d. the reader-writer estimates a backscattering channel; e. the reader-writer transmits an energy beam forming signal to the tag; f. the tag collects radio frequency signal energy; g. the reader-writer transmits an unmodulated carrier signal; h. and the tag transmits information back to the reader-writer through backscattering modulation by utilizing the collected energy. The read-write range of the RFID reader-writer can be greatly enhanced without increasing energy consumption of the transmitting end or increasing complexity of the tag so that the severe defect of restriction of short read-write distance of the RFID system can be effectively solved, and thus the RFID read-write system and the read-write method are suitable for realization of long-distance RFID read-write.
Owner:杨刚
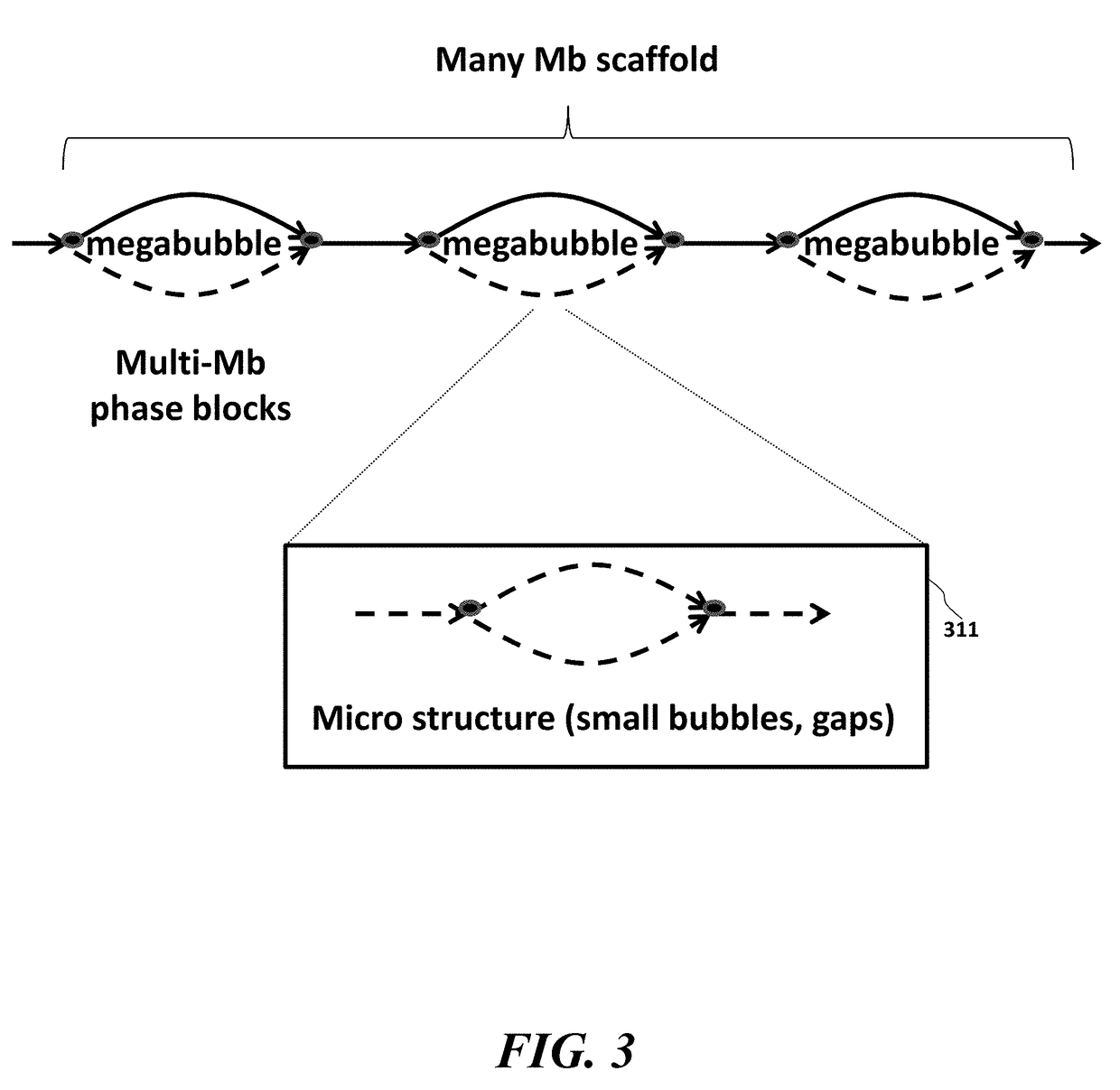
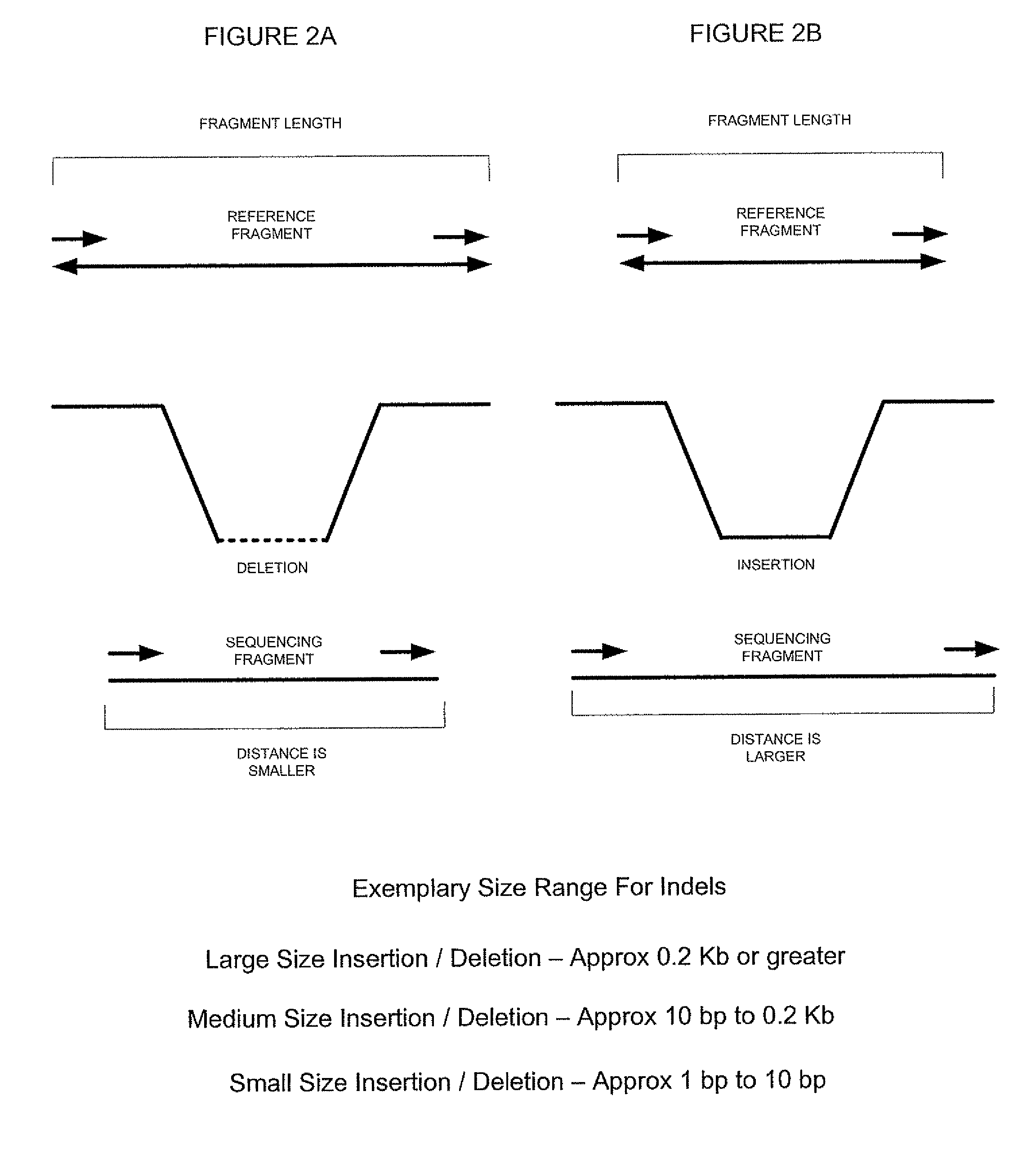
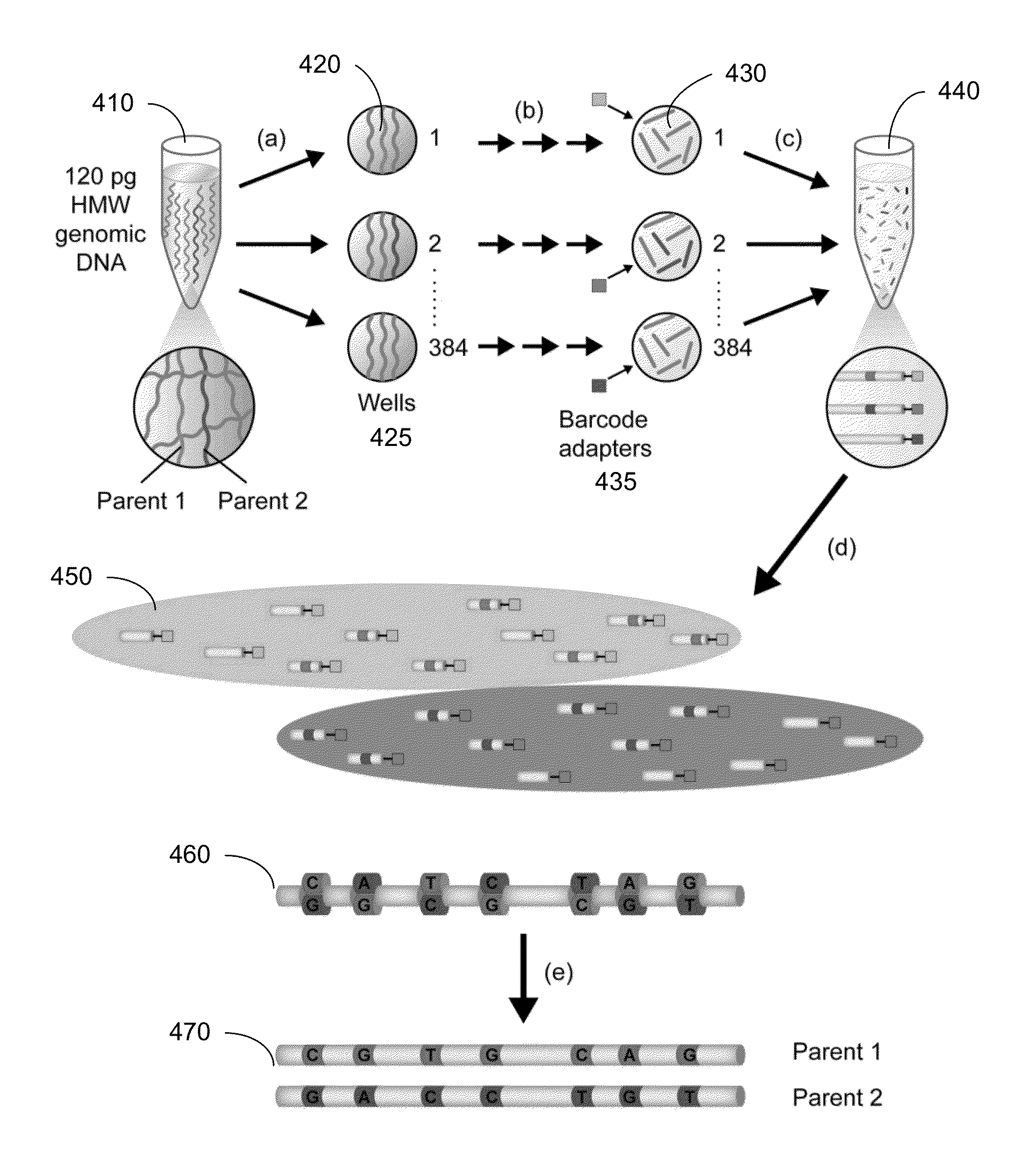
Long fragment de novo assembly using short reads
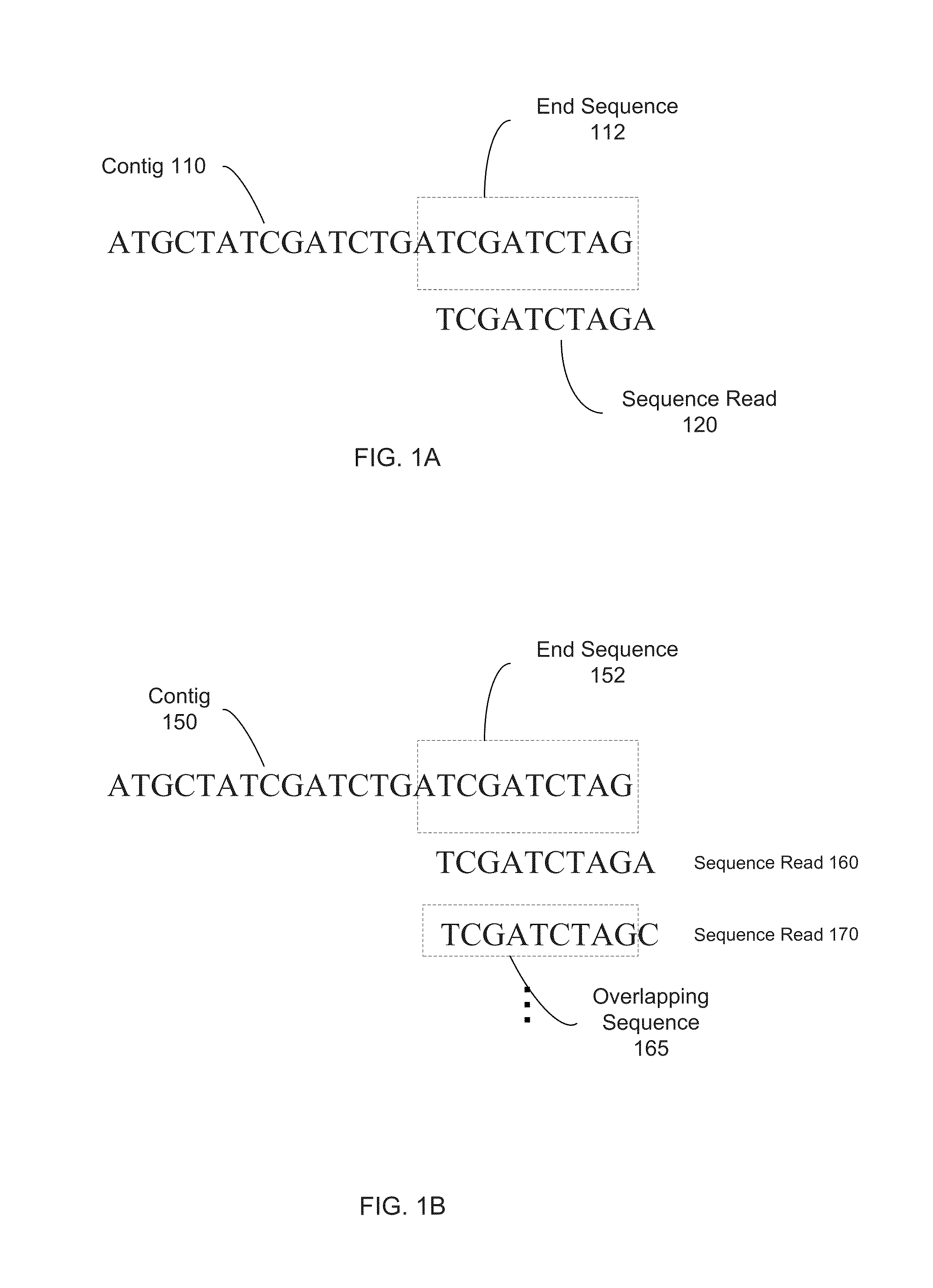
Techniques perform de novo assembly. The assembly can use labels that indicate origins of the nucleic acid molecules. For example, a representative set of labels identified from initial reads that overlap with a seed can be used. Mate pair information can be used. A sequence read that aligns to an end of a contig can lead to using the other sequence read of a mate pair, and the other sequence read can be used to determine which branch to use to extend, e.g., in an external cloud or helper contig. A kmer index can include labels indicating an origin of each of the nucleic acid molecules that include each kmer, memory addresses of the reads that correspond to each kmer in the index, and a position in each of the mate pairs that includes the kmer. Haploid seeds can also be determined using polymorphic loci identified in a population.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Method for Making Mate-Pair Libraries
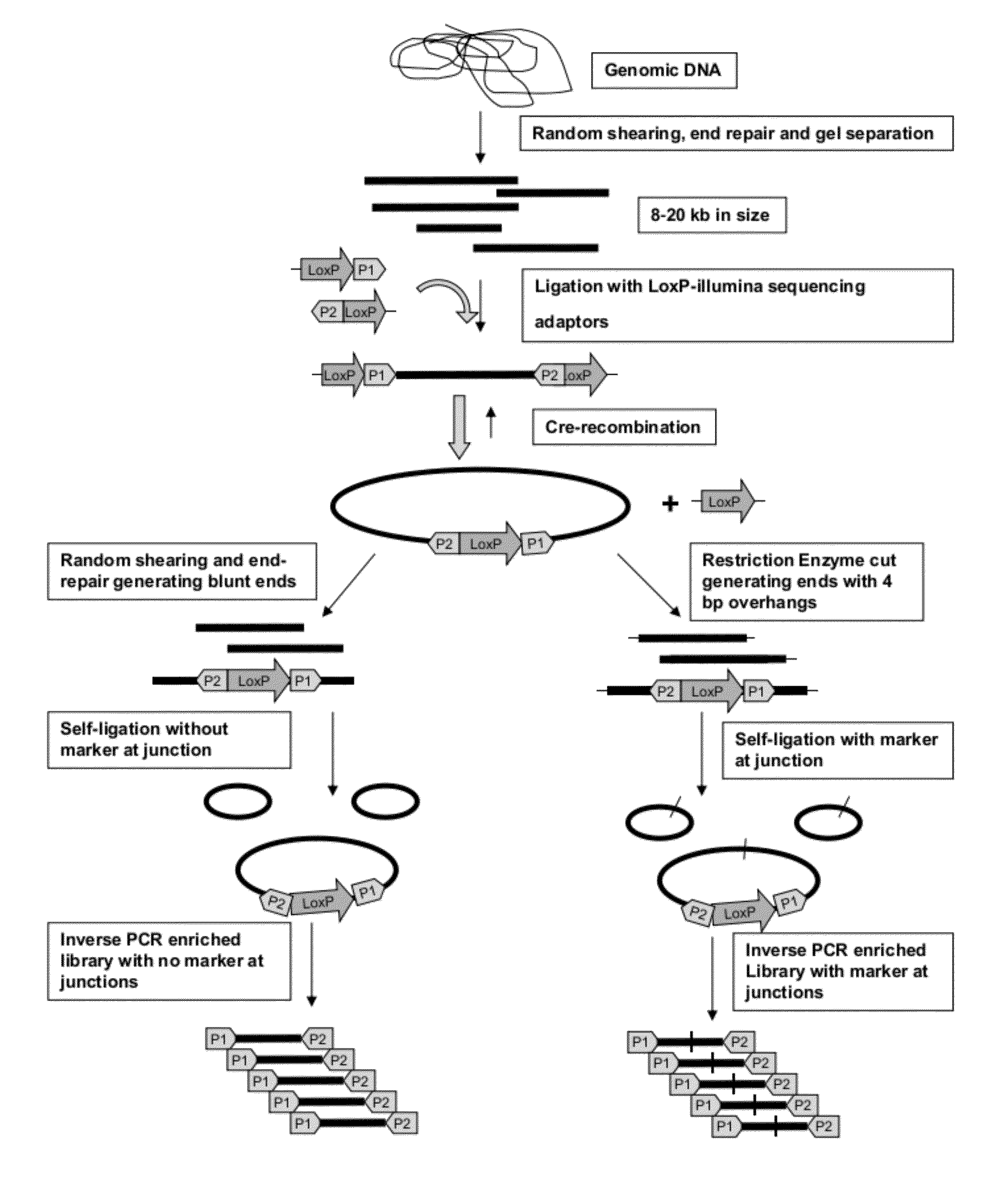
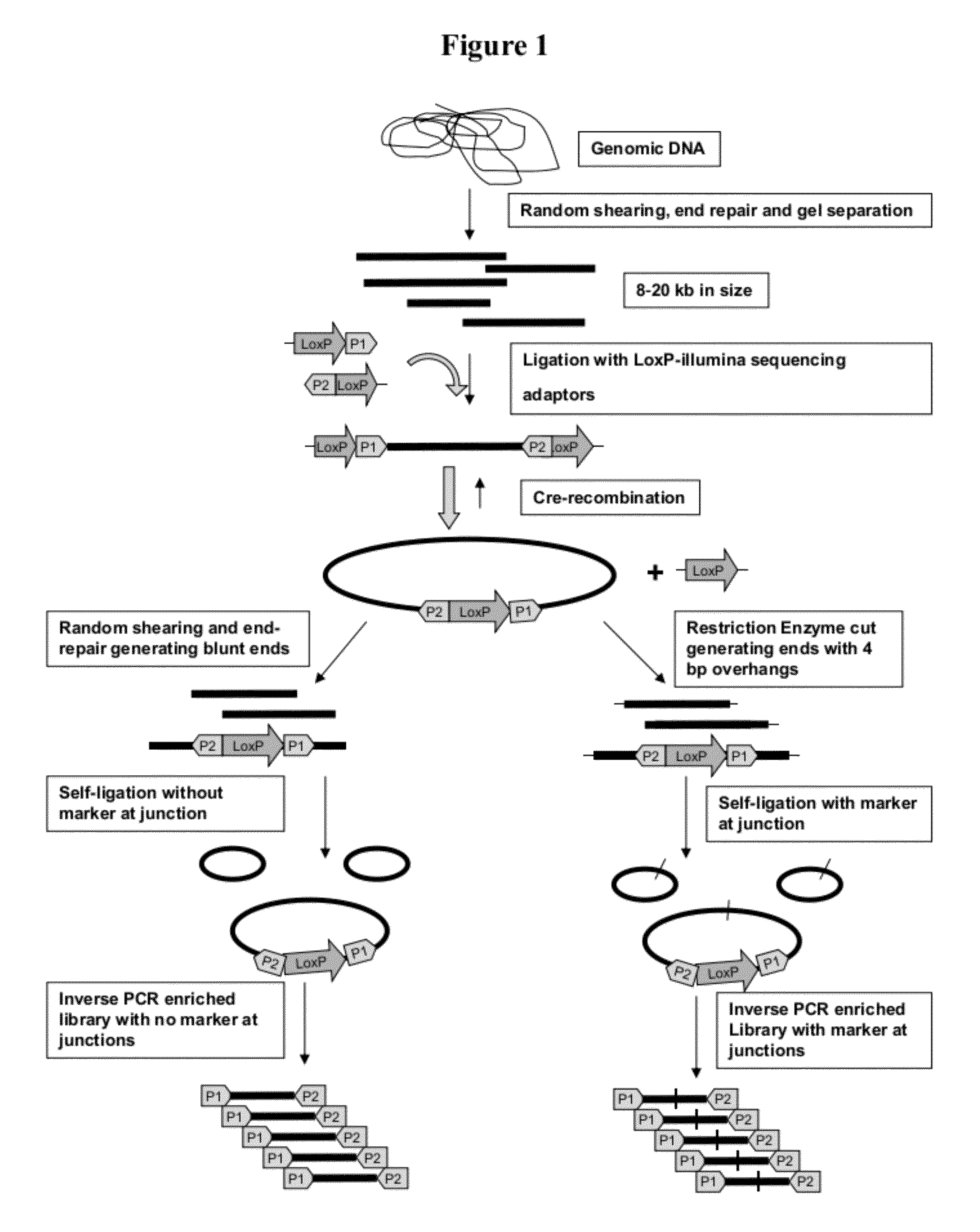
The present disclosure provides methods for generating mate-pair libraries using a recombinase / recombination site system. The method allows for increased insert size, improved efficiency and simplicity of the steps involved, and improved data generation. Mate-pair libraries are helpful in providing positional information for the assembly of sequence data from short read sequencing platforms. The disclosure also embodies the mate-pair libraries as generated from these methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Divide-and-conquer global alignment algorithm for finding highly similar candidates of a sequence in database
ActiveCN107798216AShorten the timeRelational databasesSequence analysisDivide and conquer algorithmsTheoretical computer science
A divide-and-conquer global alignment algorithm for finding highly similar candidates of a sequence in database is disclosed. The invention gives a divide-and-conquer algorithm called Kart, that separates the given sequence into smaller pieces whose alignment can be carried out independently, and their concatenated alignment constitutes the global alignment of the entire sequence. Kart could be viewed as aligning multiple seeds simultaneously in parallel. We illustrate the idea using the read mapping of Next-generation sequencing (NGS) as an example. NGS provides a great opportunity to investigate genome-wide variation at nucleotide resolution. Due to the huge amount of data, NGS applications require very fast alignment algorithms. The invention can process long reads as fast as short reads. Furthermore, it can tolerate much higher error rates. The experiments show that Kart spends much less time on longer reads than most aligners and still produce reliable alignments.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
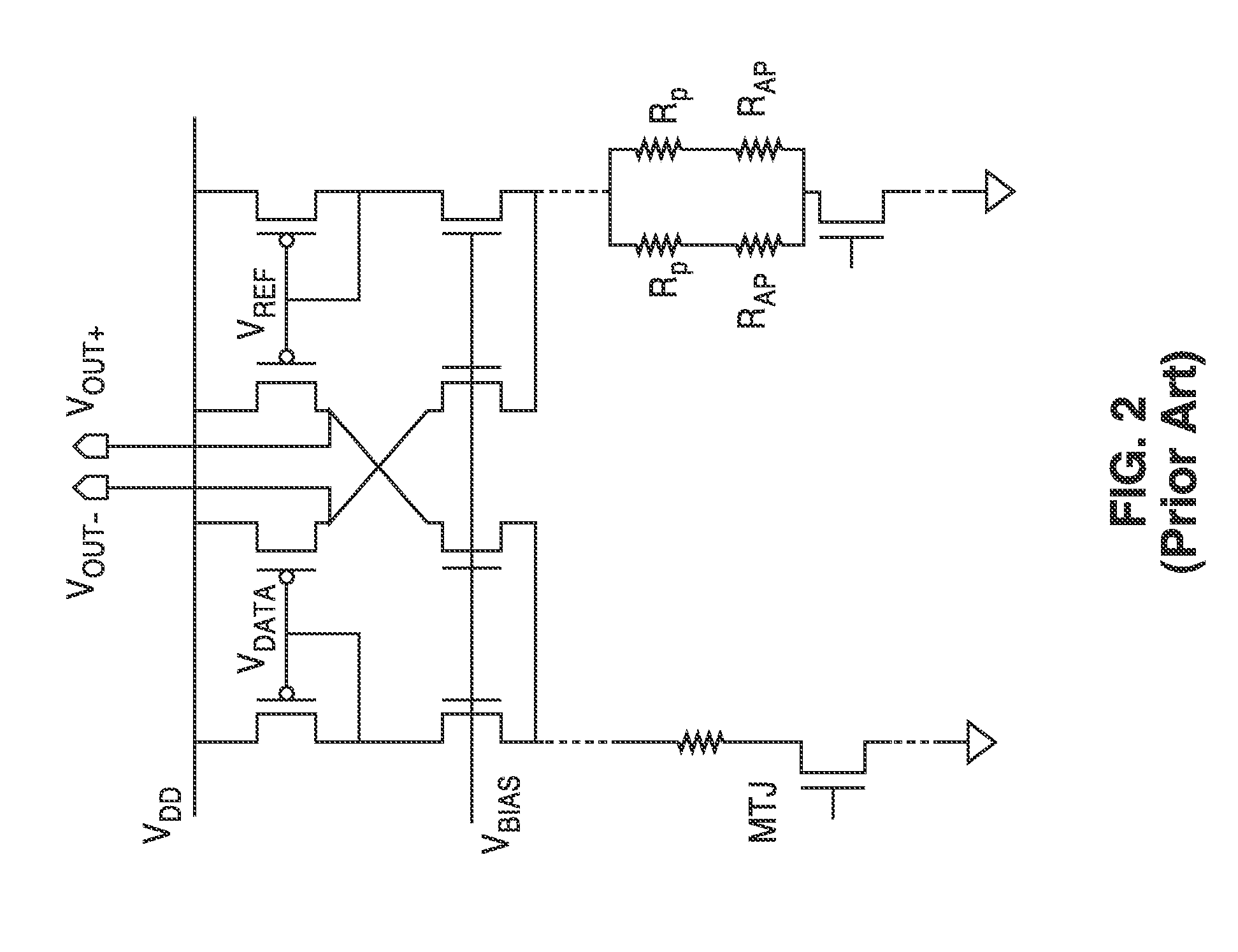
Body voltage sensing based short pulse reading circuit
InactiveUS8917562B2Large sensing marginImprove the sense of speedDigital storageEngineeringShort read
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sequential Sequencing
ActiveUS20160251712A1Microbiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingExon
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Method for sequence recombination and apparatus for ngs
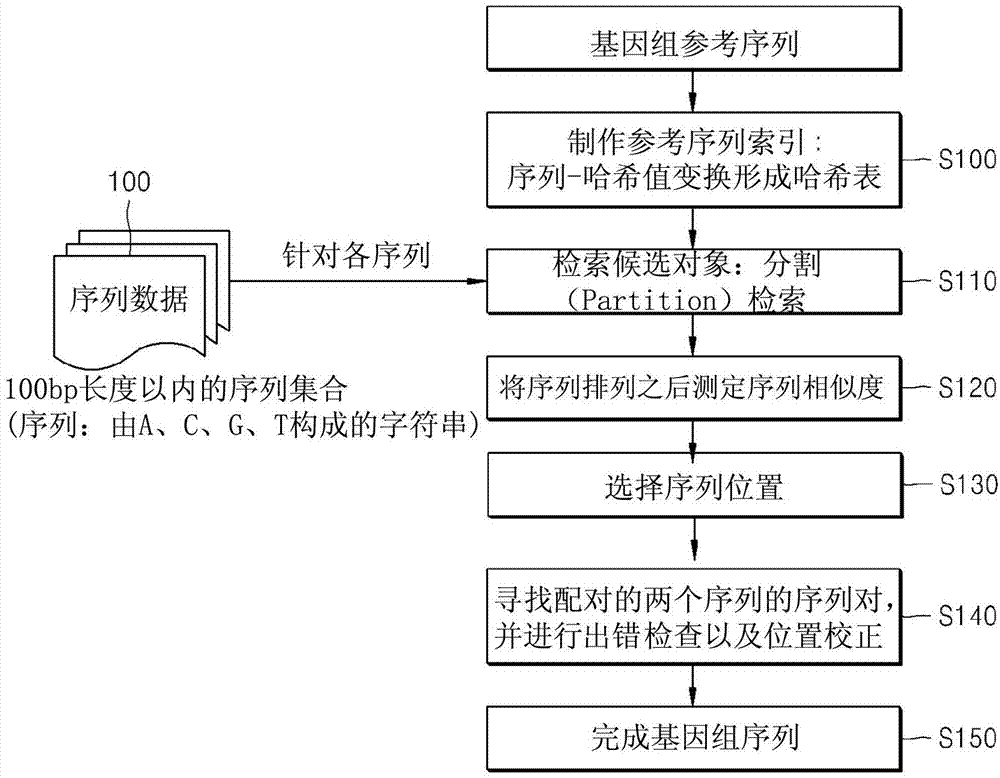
InactiveCN103946396AGuaranteed qualityHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisBiotechnologyGenetics
The present invention relates to a method for sequence recombination and to an apparatus for NGS. According to one preferred embodiment of the present invention, a short read having a sequence length of n is divided into six fragments, and then a candidate matching position is searched for by looking up a hash table which is created on the basis of a reference sequence using only the first three fragments as seeds.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD
DNA sequence assembly methods of short reads
Certain embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for the automated assembly of DNA sequence data into contiguous DNA segments using a computer a system. DNA sequence data is entered into the system. The system indexes and groups a plurality of DNA fragment reads utilizing an anchor sequence and consolidates the fragments into larger sequences by merging the fragment reads within a group.
Owner:SOFTGENETICS
Automatically adjustable radio frequency carrier cancellation RFID reader-writer
PendingCN106339731ARF Carrier Cancellation ImplementationCo-operative working arrangementsCarrier signalShort read
The invention discloses an automatically adjustable radio frequency carrier cancellation RFID reader-writer. The phase and the amplitude of a cancellation signal are adjusted through a vector modulator so that the leakage carrier of the cancellation signal and a receiving channel is enabled to be different for 180 degrees; the amplitude is enabled to be consistent with that of the leakage carrier of the receiving channel so as to realize radio frequency carrier cancellation; besides, the radio frequency carrier cancellation effect is inspected through a detector, and the radio frequency carrier cancellation effect is enabled to reach the standard by adjusting the phase and the amplitude of the vector modulator if the radio frequency carrier cancellation effect is not standard. The common problems of short read-write distance, saturated receiving channel and other defects of the common UHF RFID reader-writers can be compensated; and the defects of the present UHF RFID reader-writers can be greatly compensated and thus the RFID reader-writer has wide application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU JIUZHOU ELECTRONIC INFORMATION SYSTEM CO LTD
Method for developing simple sequence repeats molecular markers of genome of ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Maxim.) Chengf. plant
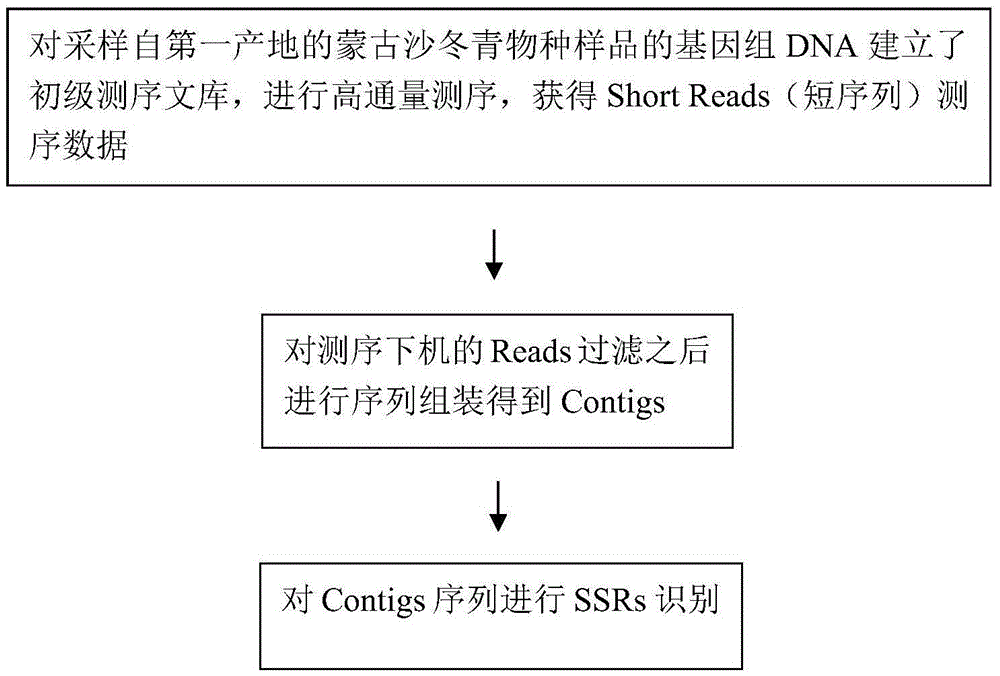
ActiveCN106282330AImprove efficiencyShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic diversityShort read
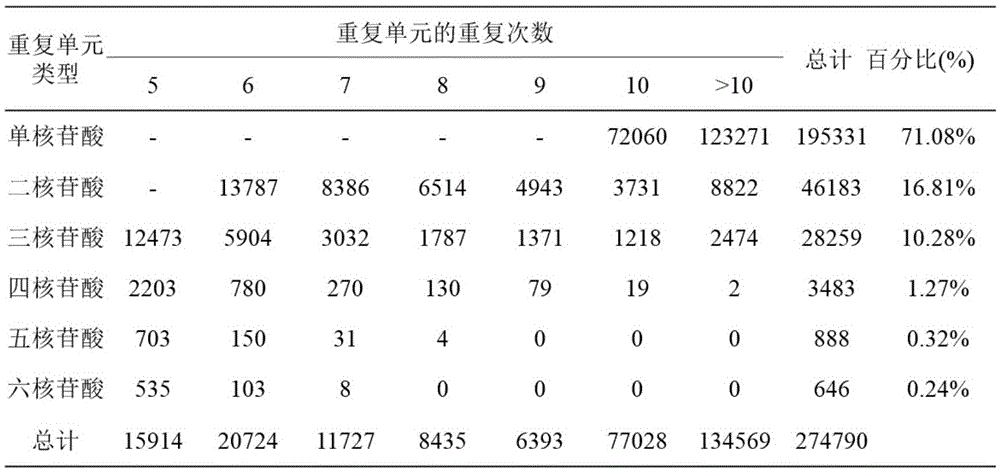
The invention relates to a method for developing SSRs (simple sequence repeats) molecular markers of genome of an ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Maxim.) Chengf. plant, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a primary sequencing library for genome DNA of a species sample sampled from a first production area, and conducting high-throughput sequencing so as to obtain Short Reads sequencing data; (2) filtering Reads obtained from sequencing and conducting sequence assembling so as to obtain Contigs; (3) conducting SSRs identification on Contigs sequences; and (4) verifying the SSRs in a Unigene sequence of a same species derived from a second production area, and conducting screening so as to obtain the SSRs having polymorphism. The high-throughput SSRs molecular marker discovering method provided by the invention is applicable to such researches as genetic map construction, QTL (quantitative trait loci) location, genetic diversity analysis and the like of the plant species.
Owner:SHENZHEN RES INST THE CHINESE UNIV OF HONG KONG
Zr:Fe:LiNbO3 crystal and its preparing method
InactiveCN101024902ADecreased diffraction efficiencyWeakening rangePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltHolographic memoryCzochralski method
The invention relates to a Zr:Fe:LiNbO3 crystal and the preparing method thereof, relating to a crystal and the preparing method thereof. And the crystal is made of ZrO2, Fe2O3, LiCO3 and Nb2O5 with the same purity of 99.99%, where the ZrO2 doping quantity is 2-6mol%, the Fe2O3 doping concentration is 0.01-0.04wt%, and the molar ratio of Li to Nb is 0.946. and the preparing method comprises the steps of: 1. weighing ZrO2, Fe2O3, LiCO3 and Nb2O5 and fully mixing them; 2. placing the ready-mixed raw materials into a Pt pot, and making crystal growth by Czochralski method; 3. polarizing the obtained crystals in the step 2; then accurately orienting the polarized crystals and cutting by Y surface and making optical quality polishing on the crystal surfaces and obtaining Zr:Fe:LiNbO3 crystals. And the Zr:Fe:LiNbO3 crystal can act as huge-capacity holographic memory. And the invention has advantages of small reduced amplitude of diffraction efficiency, short read-in time, high flexibility and strong optical loss resistance.
Owner:YIBIN UNIV
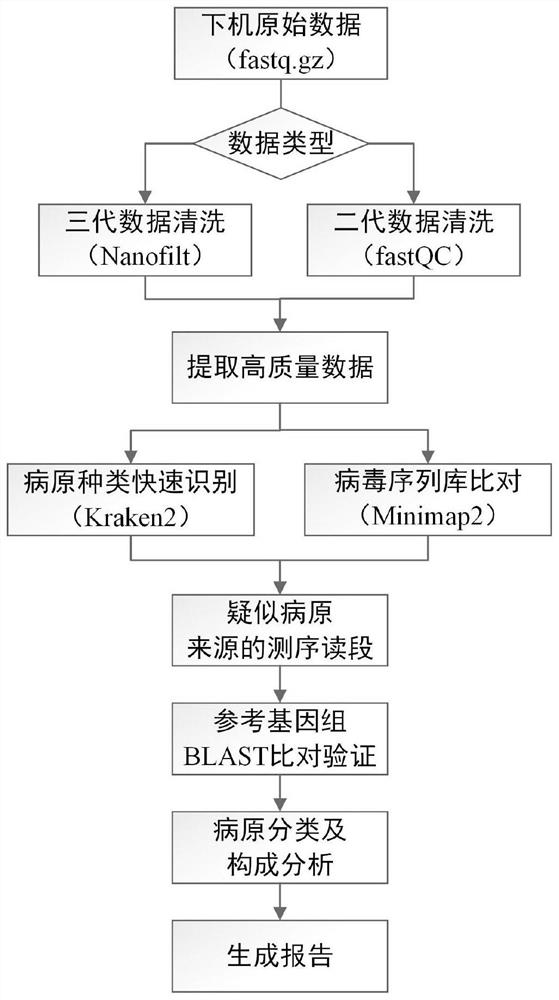
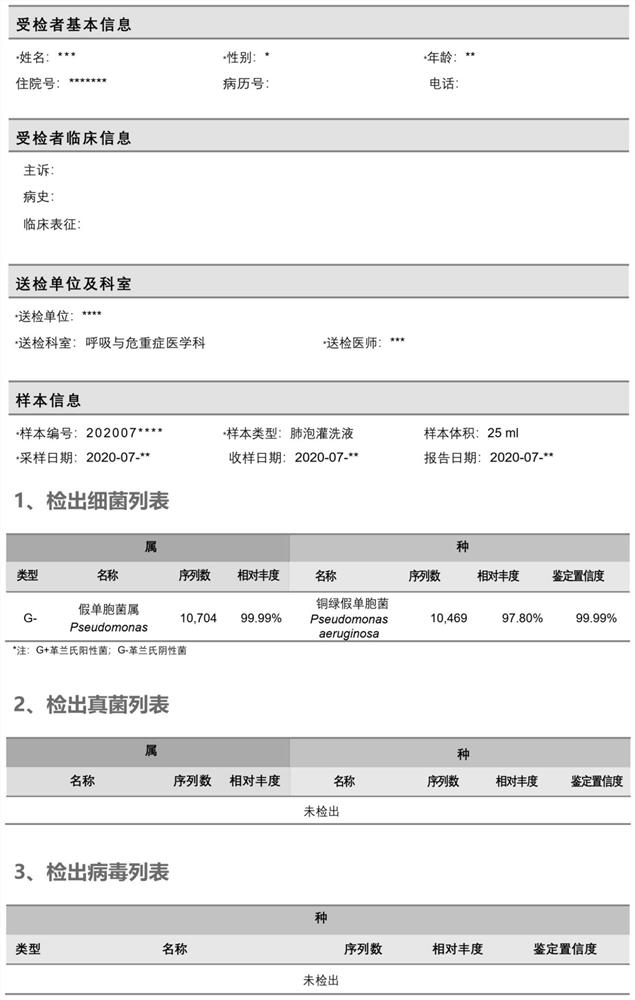
Method and system for automatically analyzing pathogen types
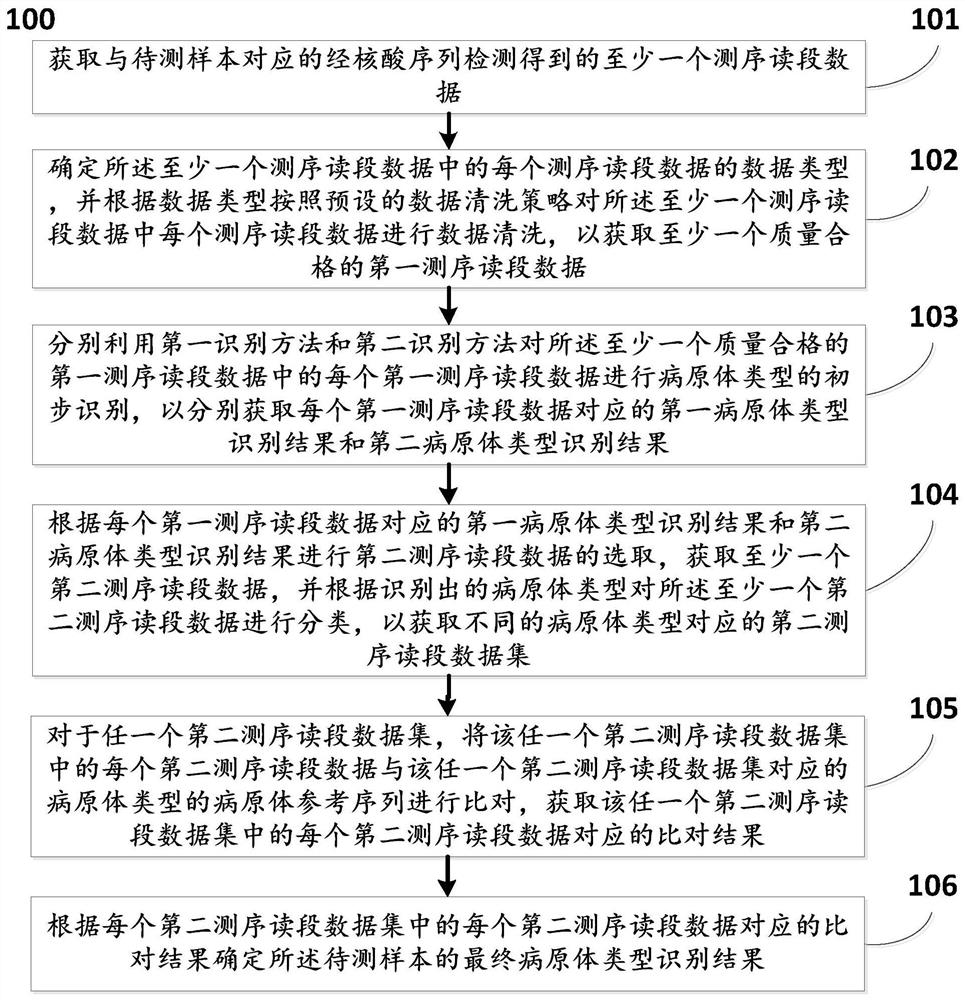
PendingCN113096737AMeet the needs of rapid pathogen detection and analysisEasy to handleProteomicsGenomicsThird generation sequencingShort read
The invention discloses a method and system for automatically analyzing pathogen types. The and comprises the following steps that: pathogen types of first sequencing read data of different data types of a to-be-detected sample are preliminarily judged through two different algorithms, and second sequencing read data are selected; then comparison verification and screening are performed on the identified second sequencing read data of the different pathogen types and corresponding pathogen reference sequences, and therefore, pathogen types existing in the to-be-detected sample can be determined. According to the method, long read length data generated based on a third-generation sequencing technology can be effectively processed, the calculation amount of accurate comparison is reduced, accurate analysis and report generation of typical third-generation metagenome or metatranscriptome data within 30 minutes can be achieved, and the requirement for rapid pathogen detection and analysis is met; and meanwhile, the method can be used for analyzing short read length data obtained by next-generation sequencing, and has relatively good data compatibility.
Owner:北京源生康泰基因科技有限公司
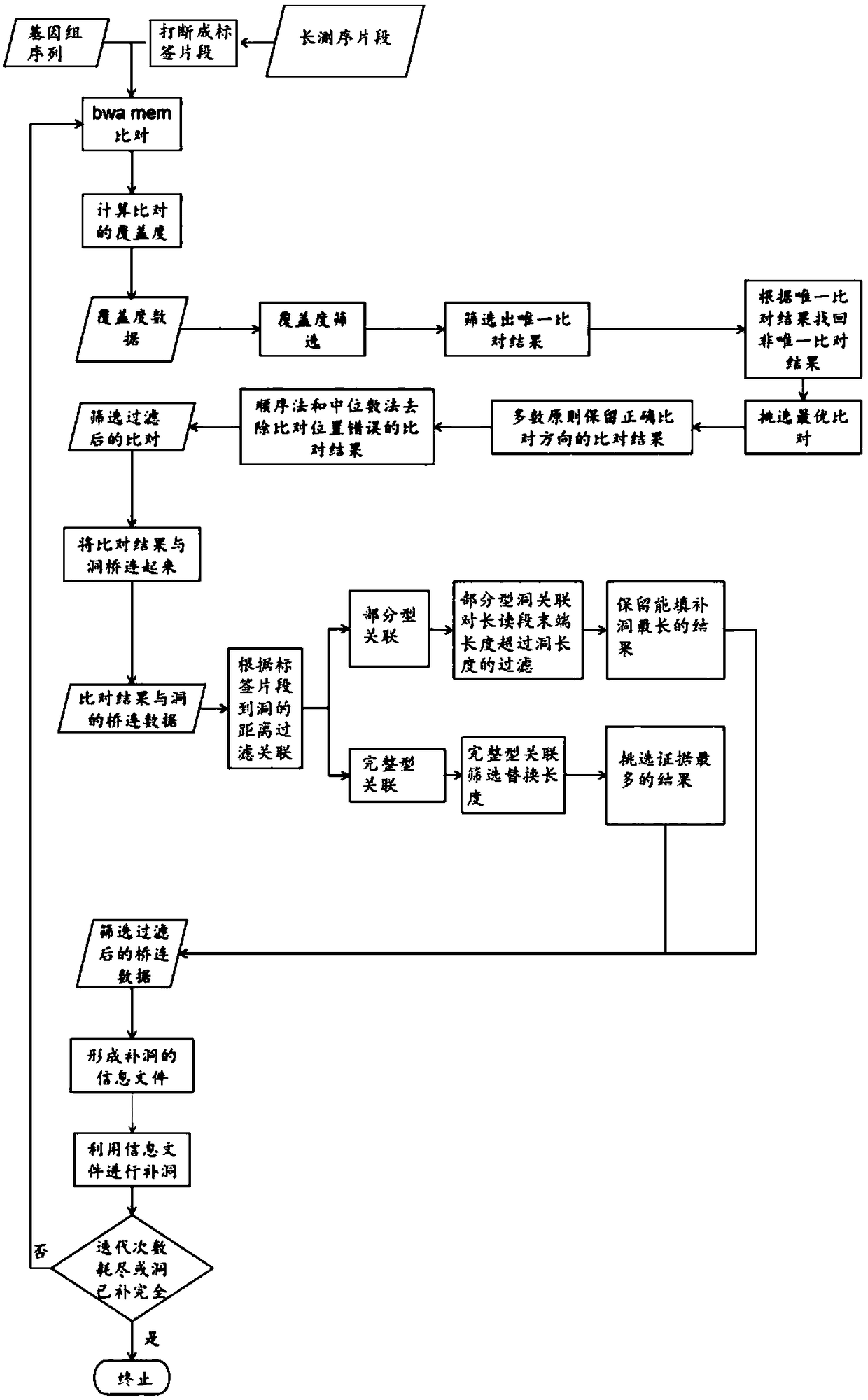
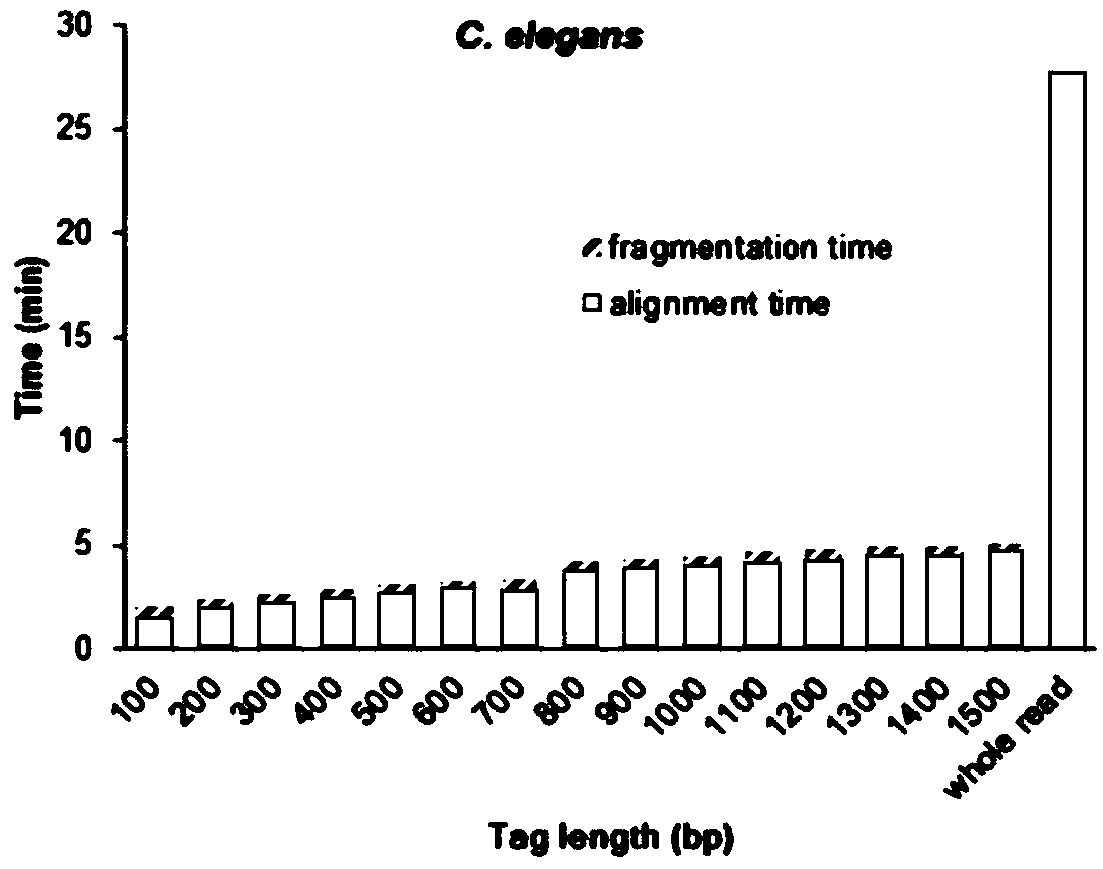
Method for performing full genome sequence hole filling by means of long sequencing read segment
The invention discloses a method for performing full genome sequence hole filling by means of a long sequencing read segment. The method comprises the following steps of 1, dividing the long sequencing read segment to a plurality of label fragments which are successively connected, then comparing the plurality of label segments with the full genome which requires hole filling; 2, determining a comparing direction and a comparing position of the label segment which matches the full genome sequence on the full genome sequence; 3, according to the comparing position of the label segment and the position relation of the hole, establishing an association relation between the corresponding long sequencing read segment and the hole; and 4, according to the association relation between the long sequencing read segment and the hole, and performing hole filling on the unknown sequence of the hole by means of the long sequencing read segment. According to the method of the invention, a short readsegment comparison method is applied to a long sequencing read segment comparison genome, the short read segment is compared with the genome sequence, thereby realizing short operation time and low memory requirement, and improving hole filling speed and memory requirement of the long segment.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com