Methods of diagnosing alzheimer's disease and markers identified by set association
a technology of genetic markers and alzheimer's disease, applied in the field of detection of genetic markers and methods of diagnosing and screening for alzheimer's disease, can solve the problems of reducing life quality, overproduction of toxic a-1-42, etc., and achieve the effects of decreasing and reducing or preventing neuronal cell deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design
[0092]The software program STRUCTURE (Pritchard et al. (2000) Genetics 155:945-59) was used to test for underlying genetic stratification, using 5000 randomly selected SNPs with at least 100 SNPs per chromosome. Initial analysis yielded empirical evidence of three populations (K=3). One, which contained fourteen samples and was far removed from the rest of the study population, was eliminated from further analyses. STRUCTURE was re-run with K=2, and each sample was assigned an admixture of the resulting populations. Comparison of the resulting case and control populations defined by these admixture vectors yielded a silhouette score of 0.06, indicating that while the samples in this study are the likely result of admixture of two populations, the distribution of those populations is equivalent in cases and controls (Pritchard et al. (2000) Genetics 155(2):945-59).
example 2
Introduction to High-Density Genome-Wide Association Study
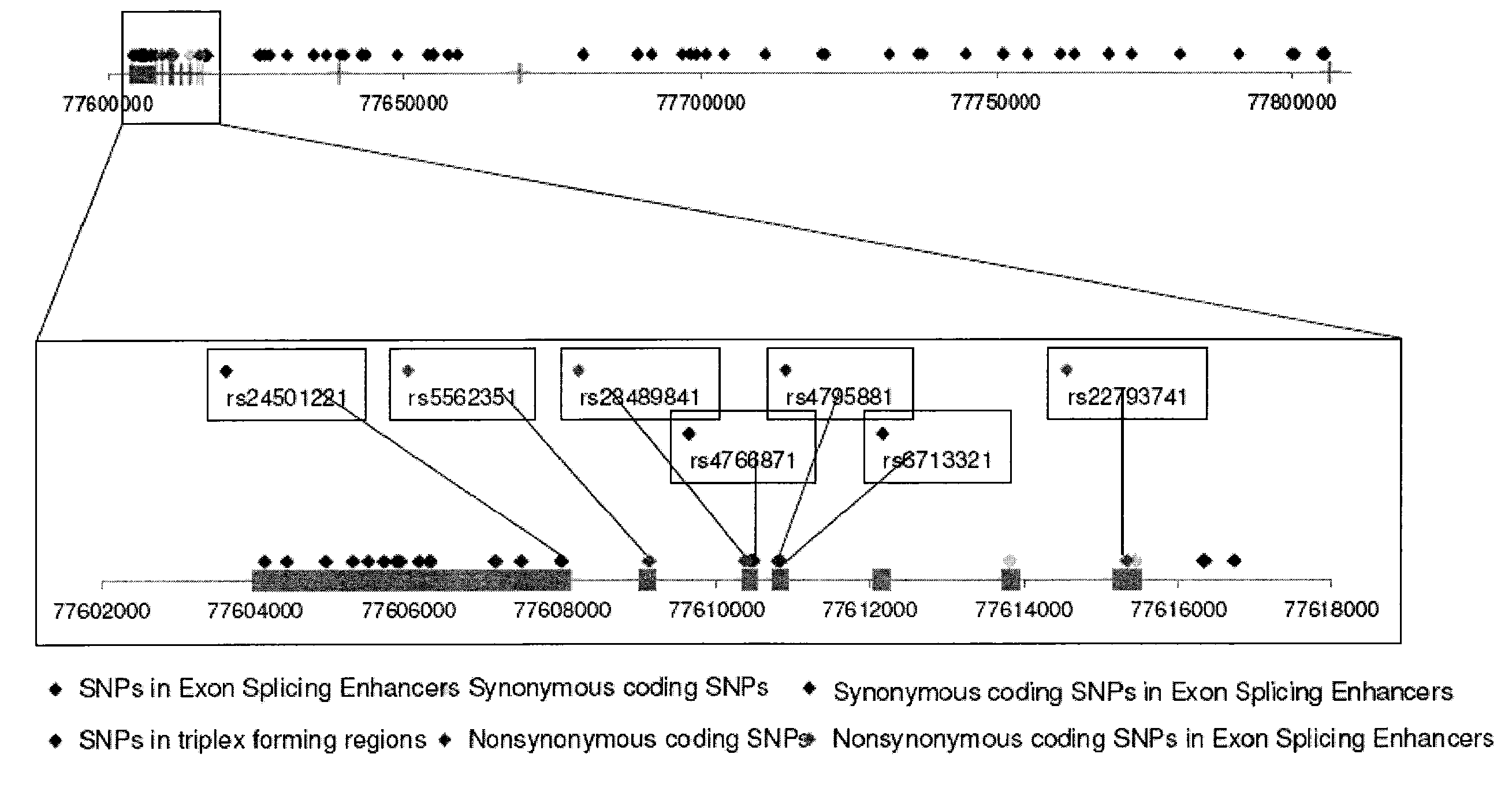
[0093]The genome-wide association study was performed using 502,627 SNPs on DNA samples extracted from brain tissue or blood of donors who were at least 65 years of age at the time of their death. The donors included a postmortem cohort of 664 patients who satisfied clinical and neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of AD and 422 persons that did not meet clinical or neuropathological criteria for AD as controls (broken up into a 70% “discovery cohort” and a 30% “replication cohort 1” design). Tissue and neuropathological diagnoses were supplied by investigators from twenty National Institute on Aging Alzheimer's Disease Centers (ADCs) in accordance with an agreement with these Centers, the National Institute on Aging, and the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center (NACC). Additional post-mortem samples were received from Sun Health Research Institute and the Netherlands Brain Bank. An additional sample series includ...
example 3
High-Density Genome-Wide Association Study Specifics
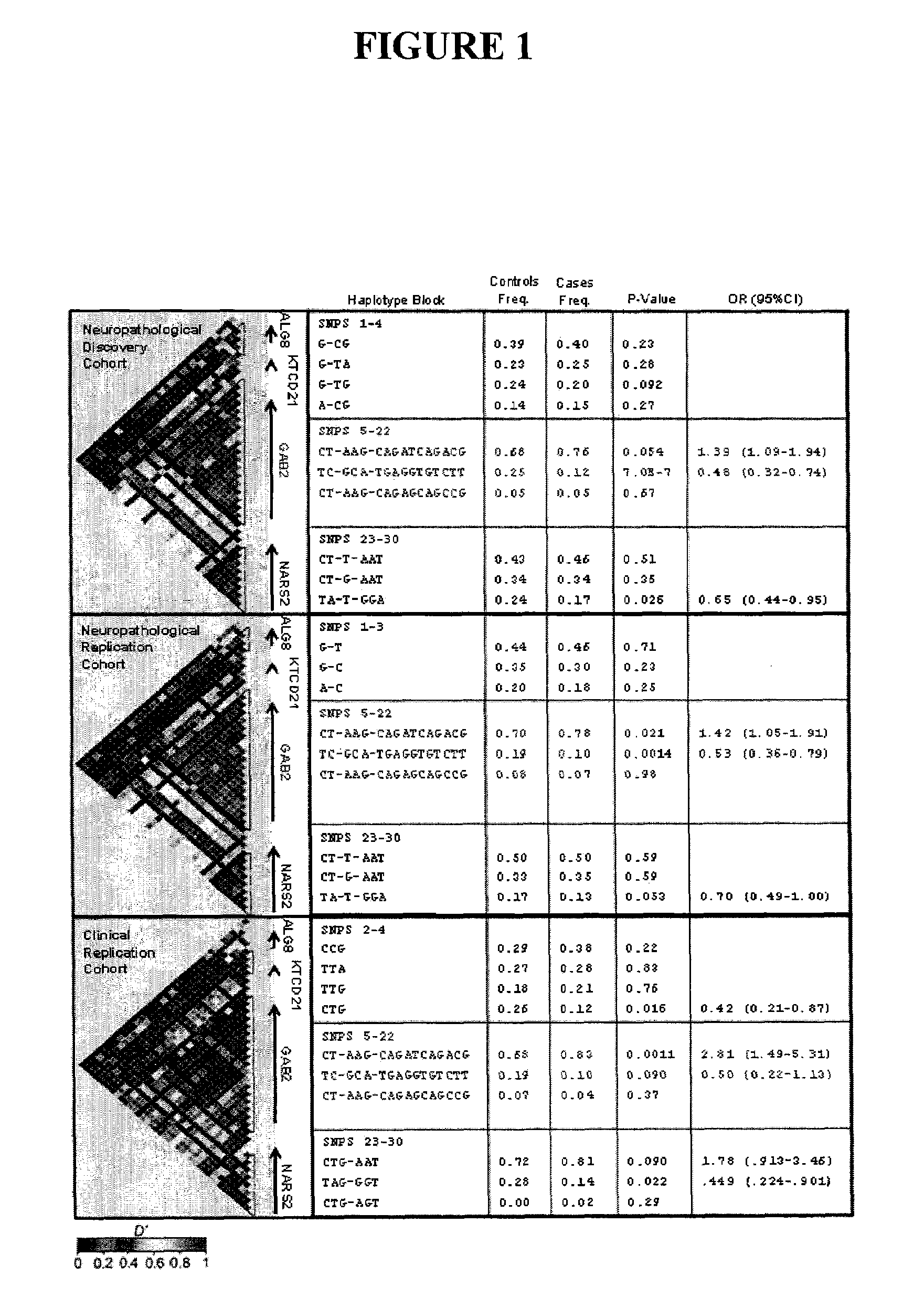
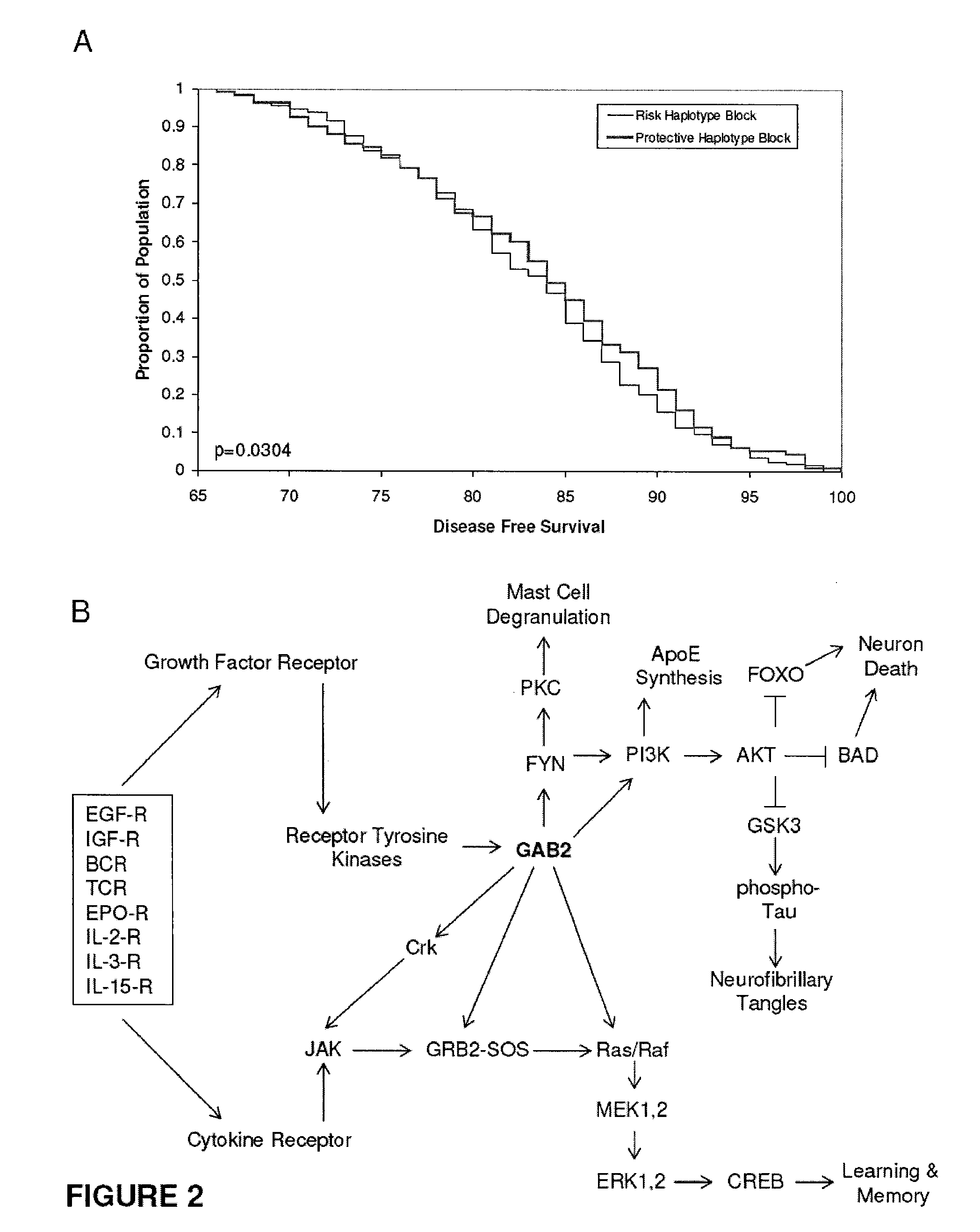
[0096]Individualized genome-wide surveys were performed in a “neuropathological discovery cohort” of 749 expired brain donors, a “neuropathological replication cohort” of 307 expired brain donors, and an additional “clinical replication cohort” of 369 living subjects who were at least 65 years old at the time of their death or last clinical assessment and who were independently assessed for their APOE genotype. For the two neuropathological cohorts, brain tissue for DNA extraction, neuropathological diagnoses and data were supplied by investigators from twenty of the National Institute on Aging (NIA) sponsored Alzheimer's Disease Centers (ADCs) (in accordance with agreements with the NIA, the ADCs and the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center) and from the Netherlands Brain Bank. 70% of the 1,056 expired LOAD cases and controls were randomly assigned to the hypothesis-generating neuropathological discovery cohort and the remaini...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid hybridization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pharmaceutical composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid sequence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com