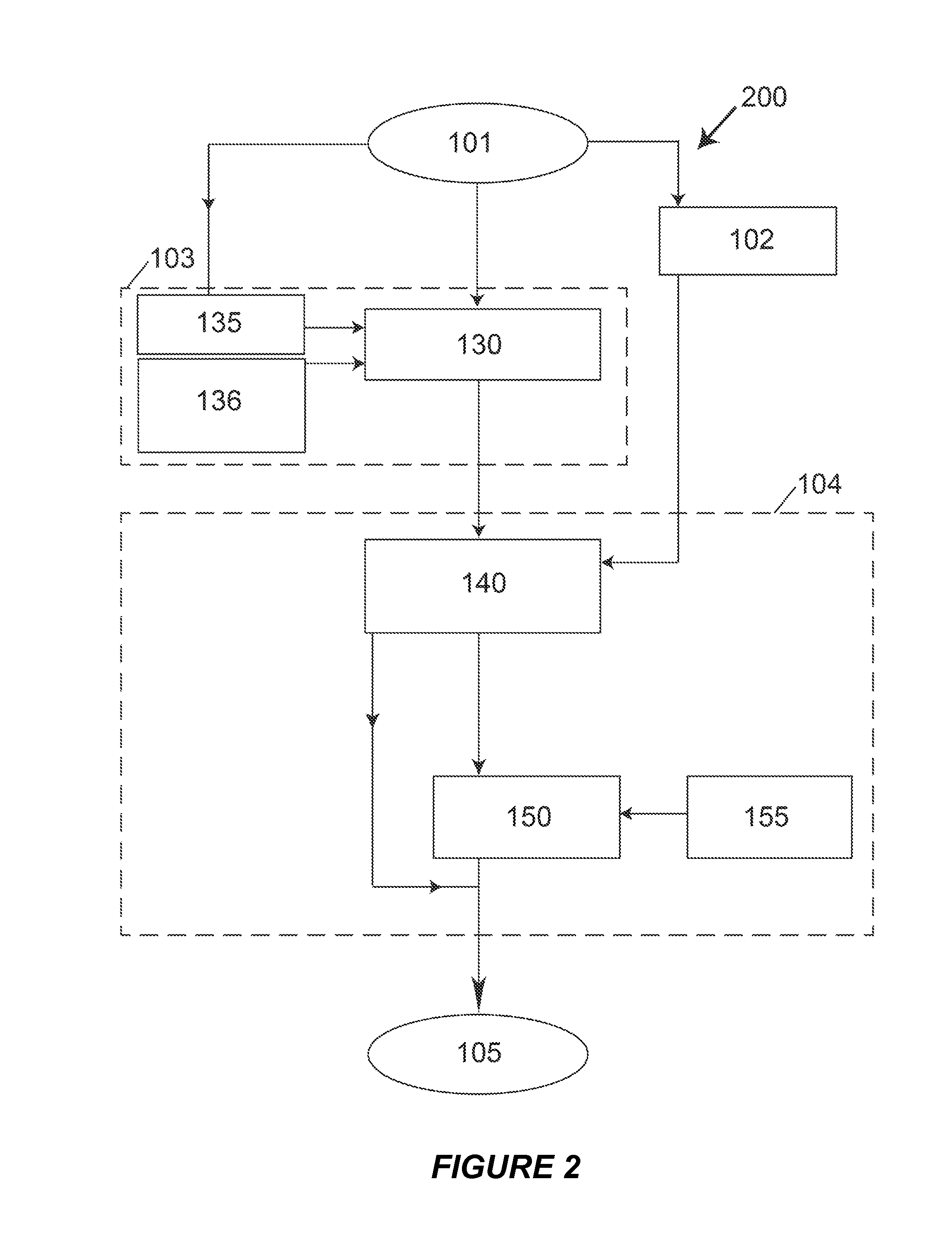
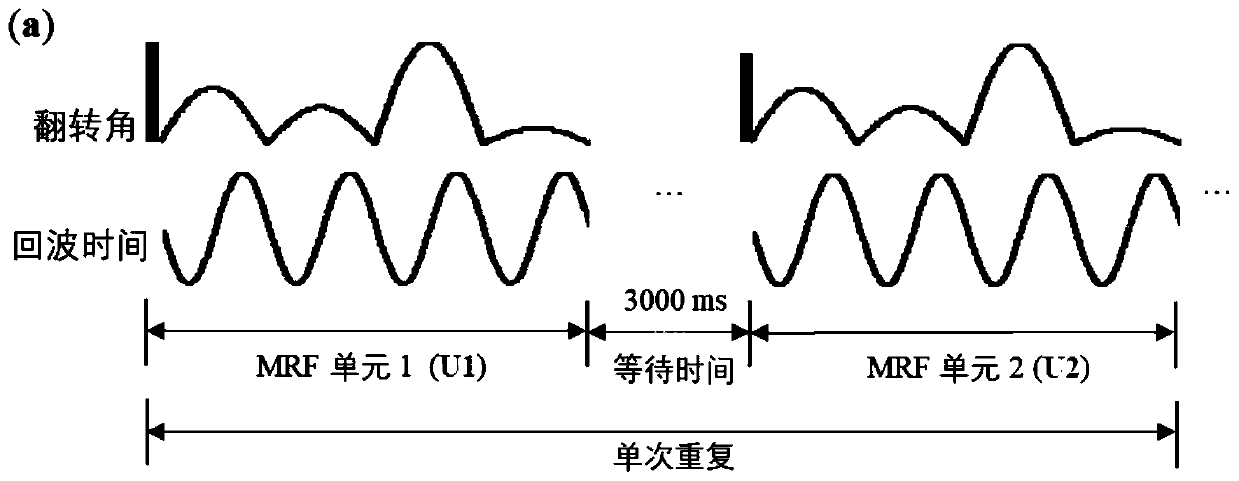
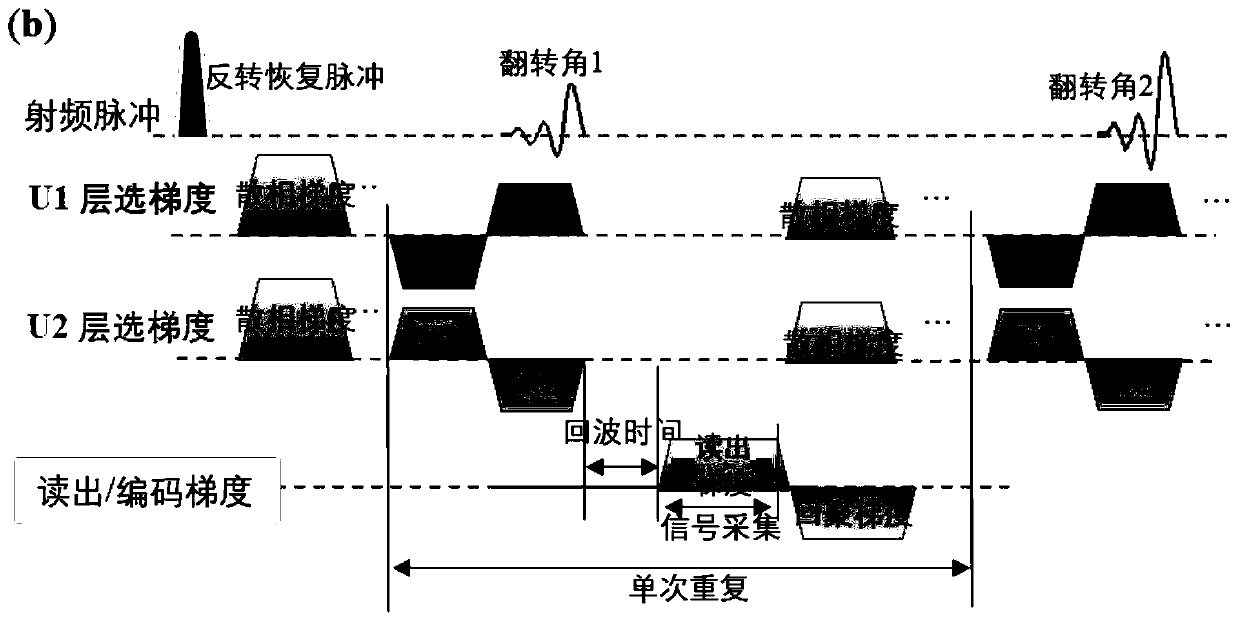
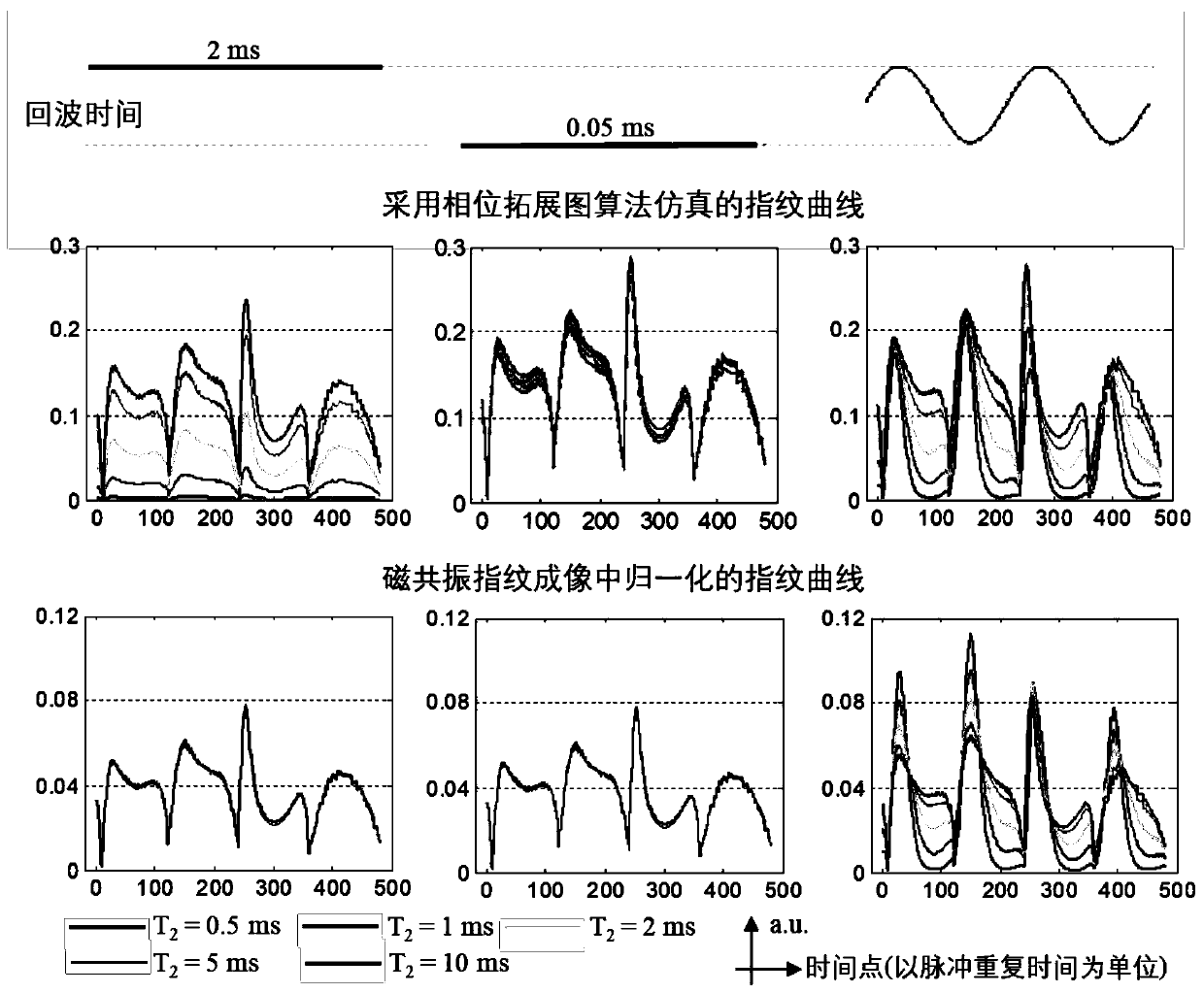
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
133 results about "White matter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
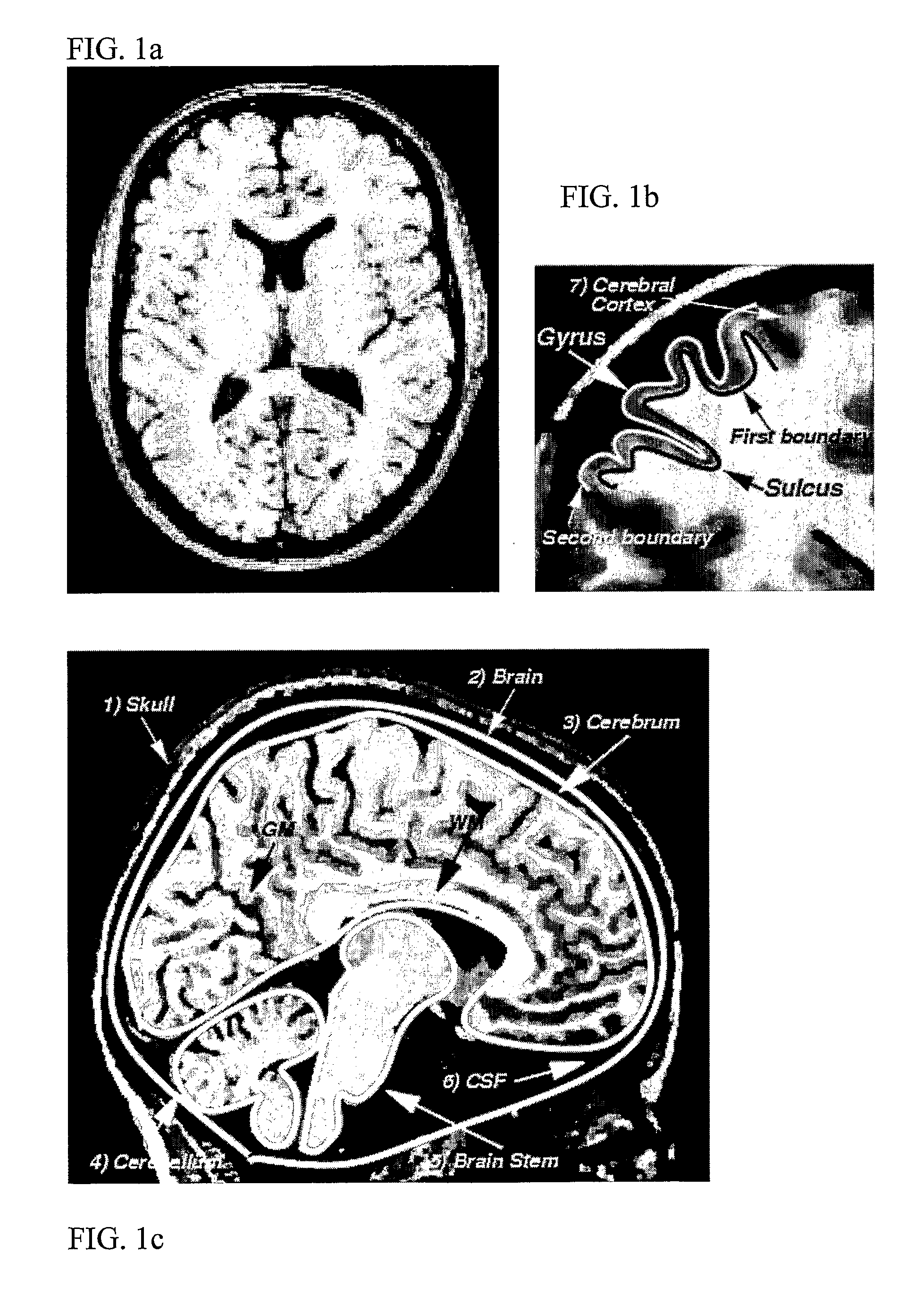
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions.
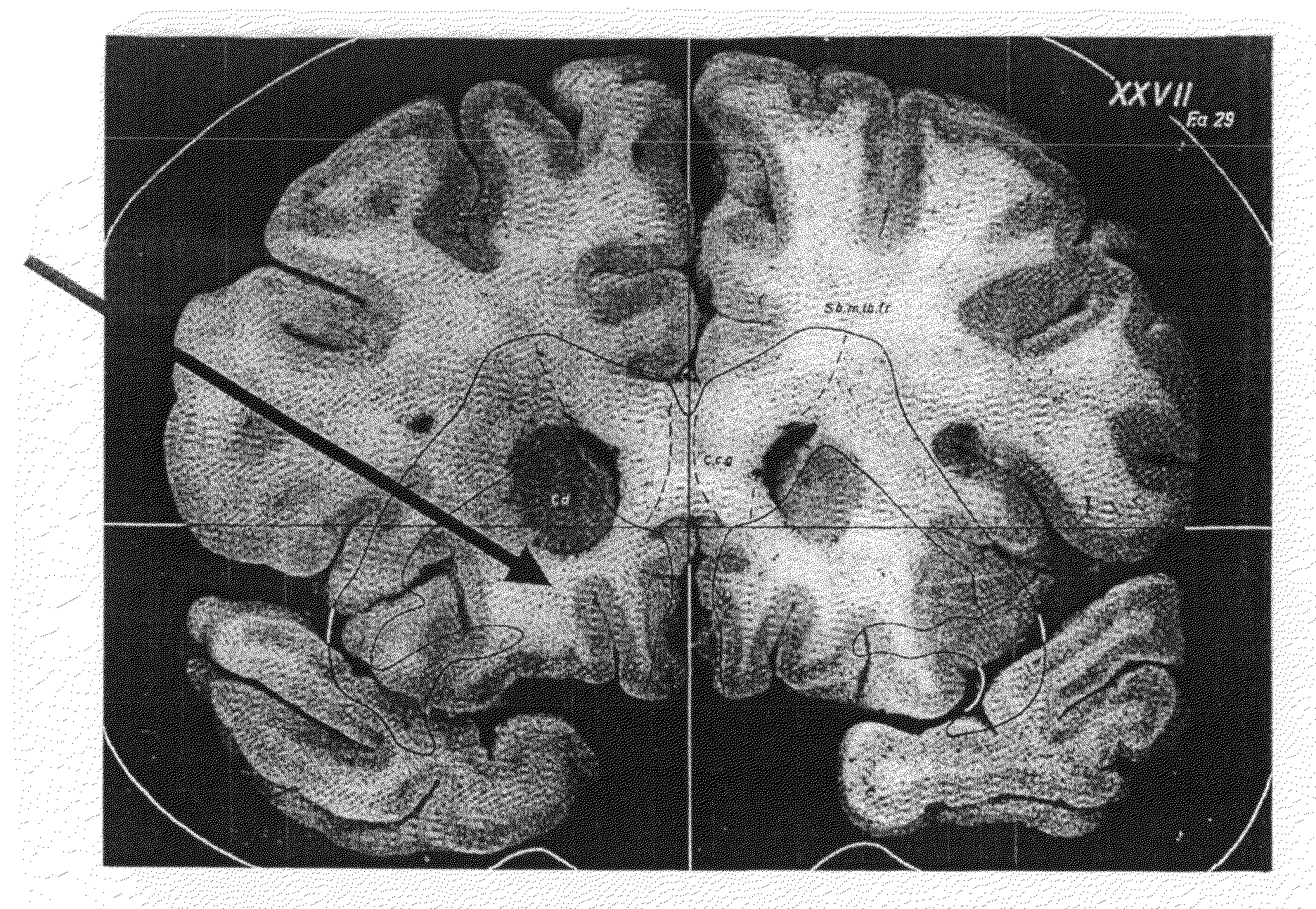
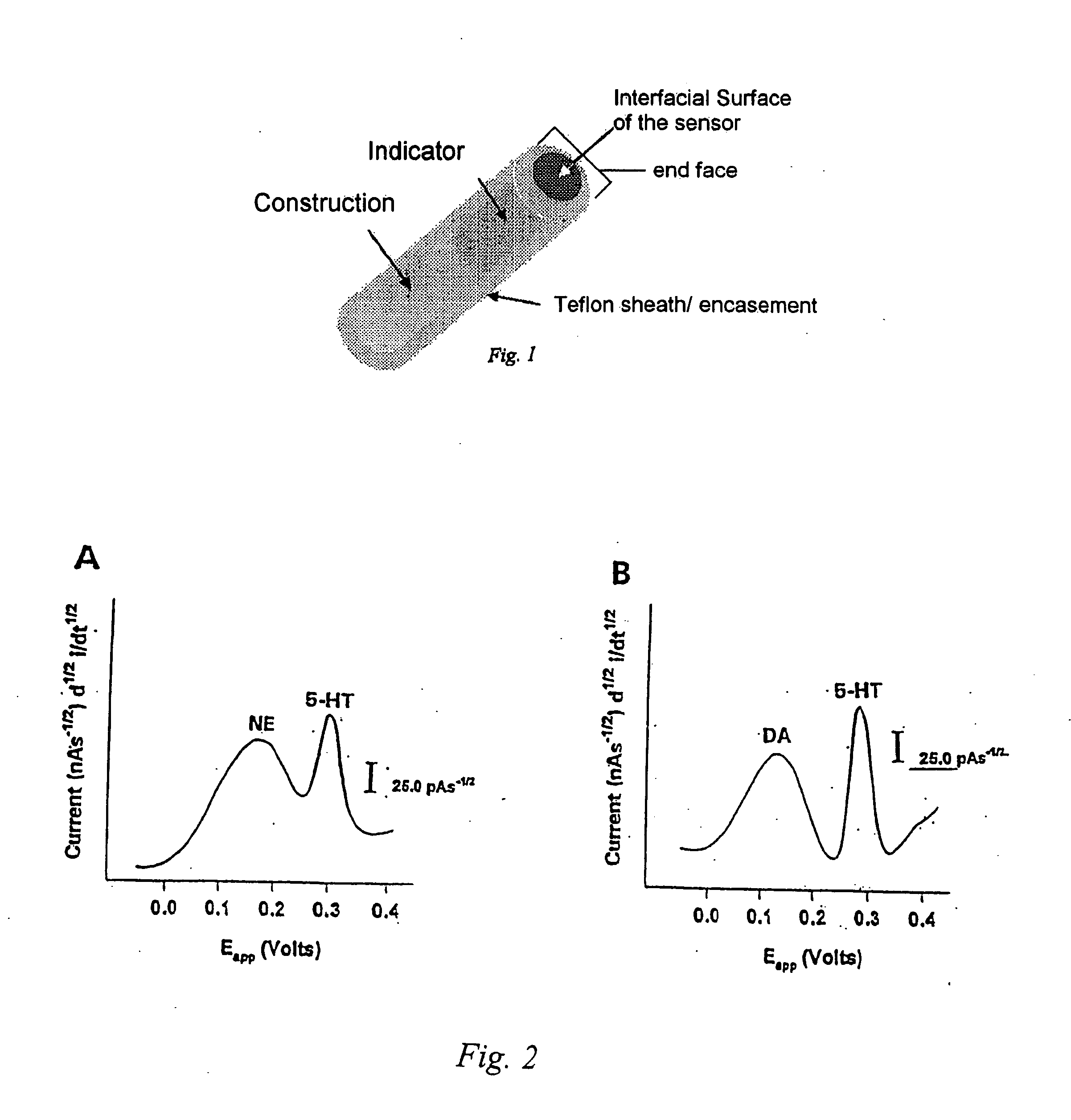
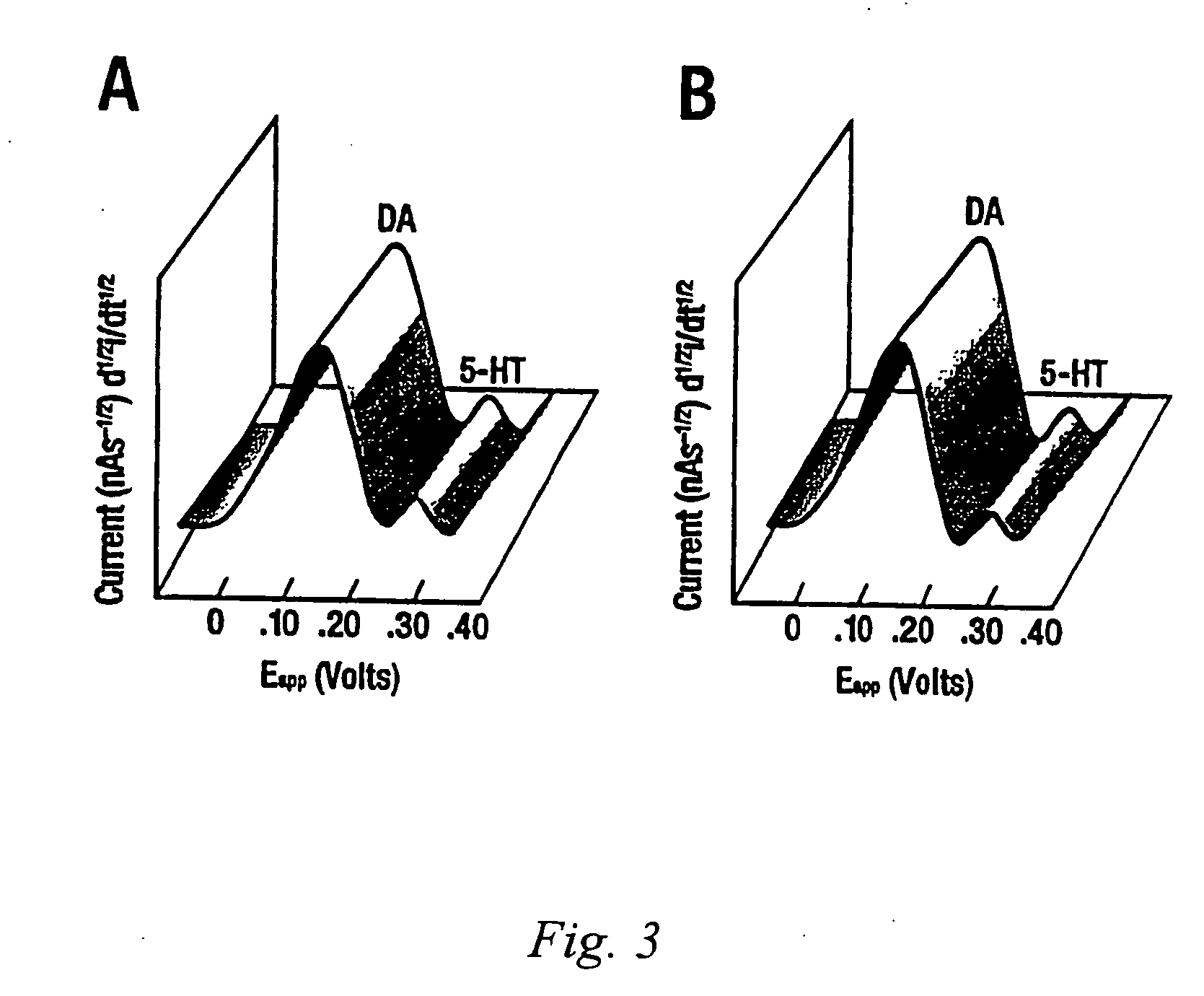
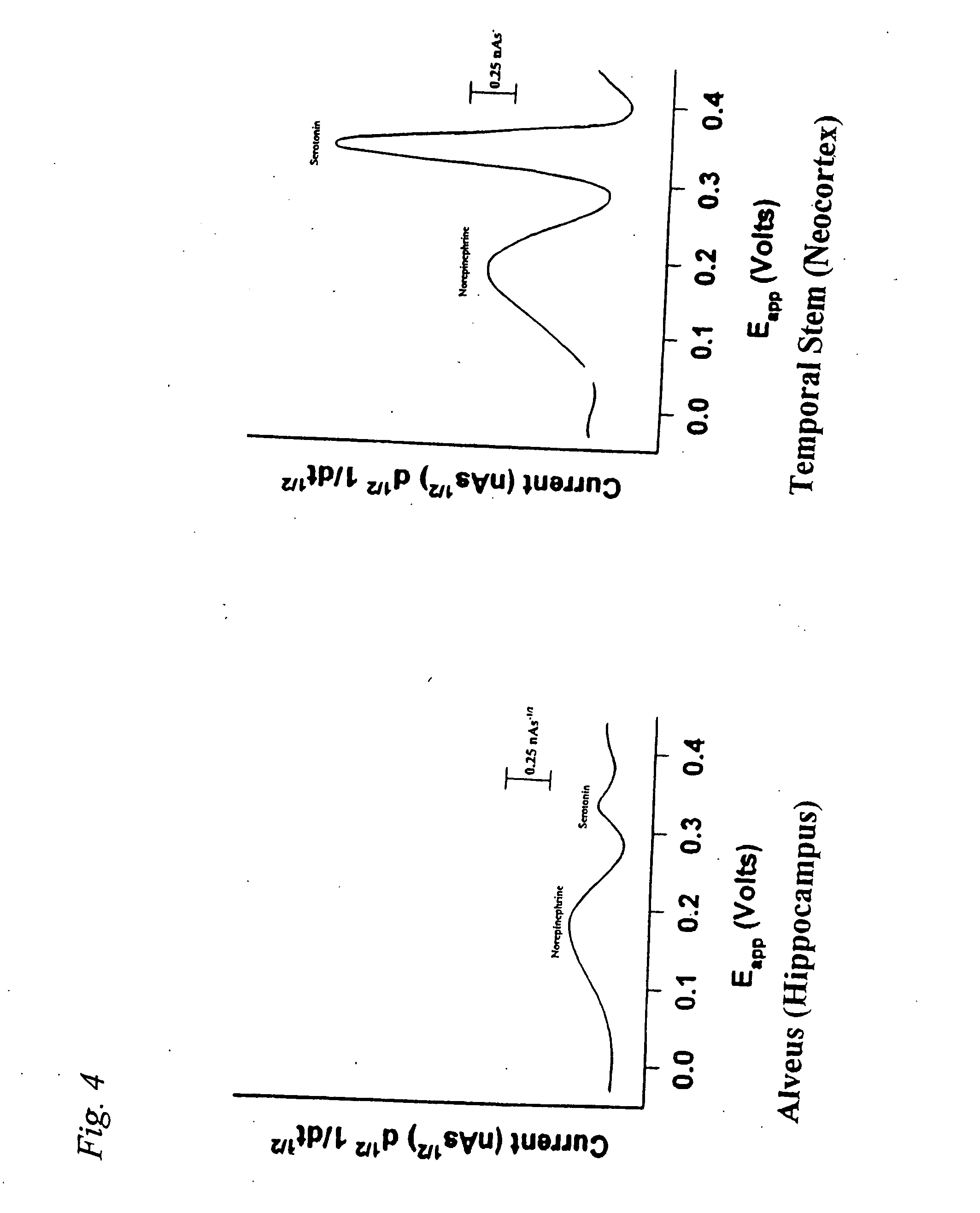
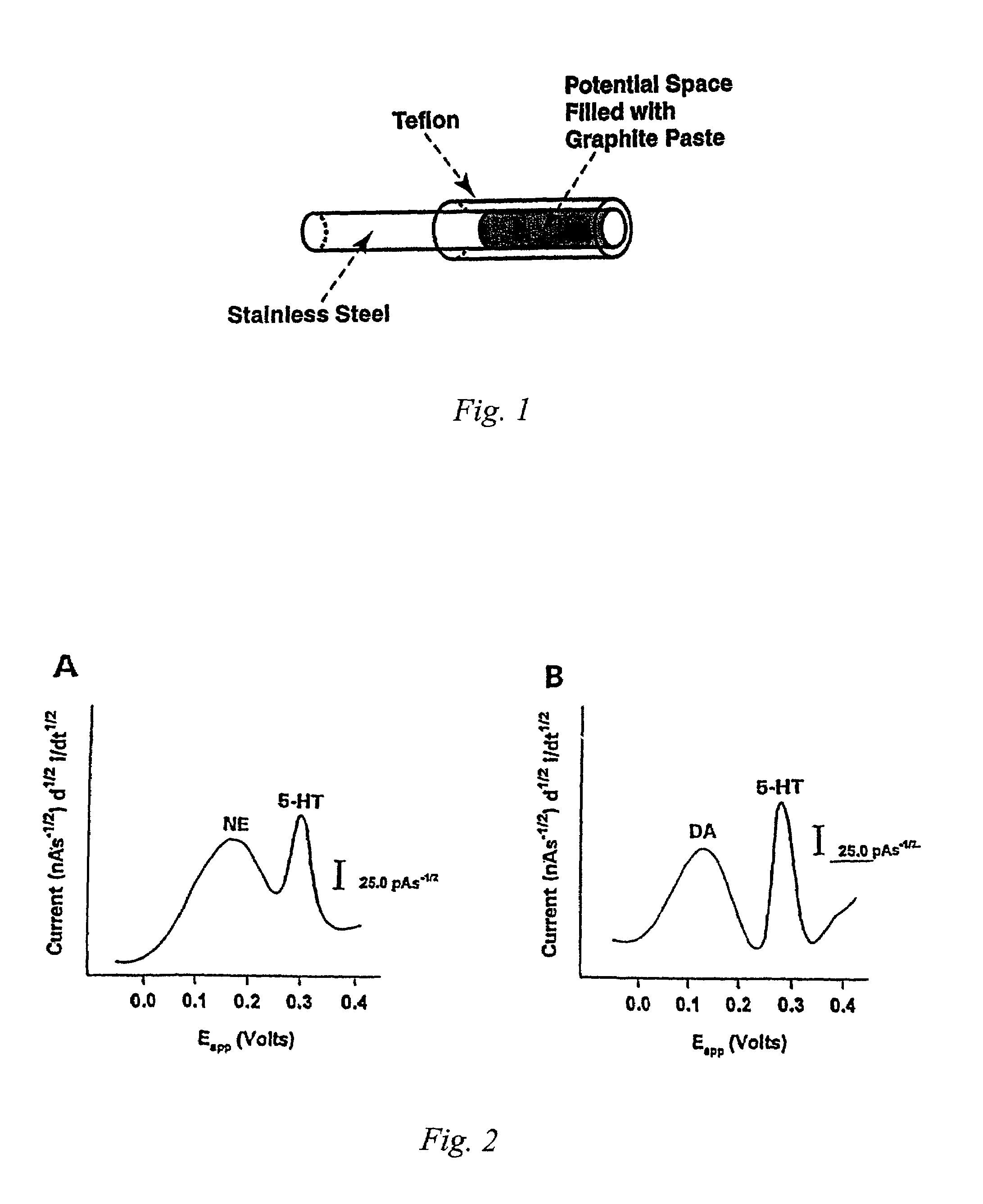
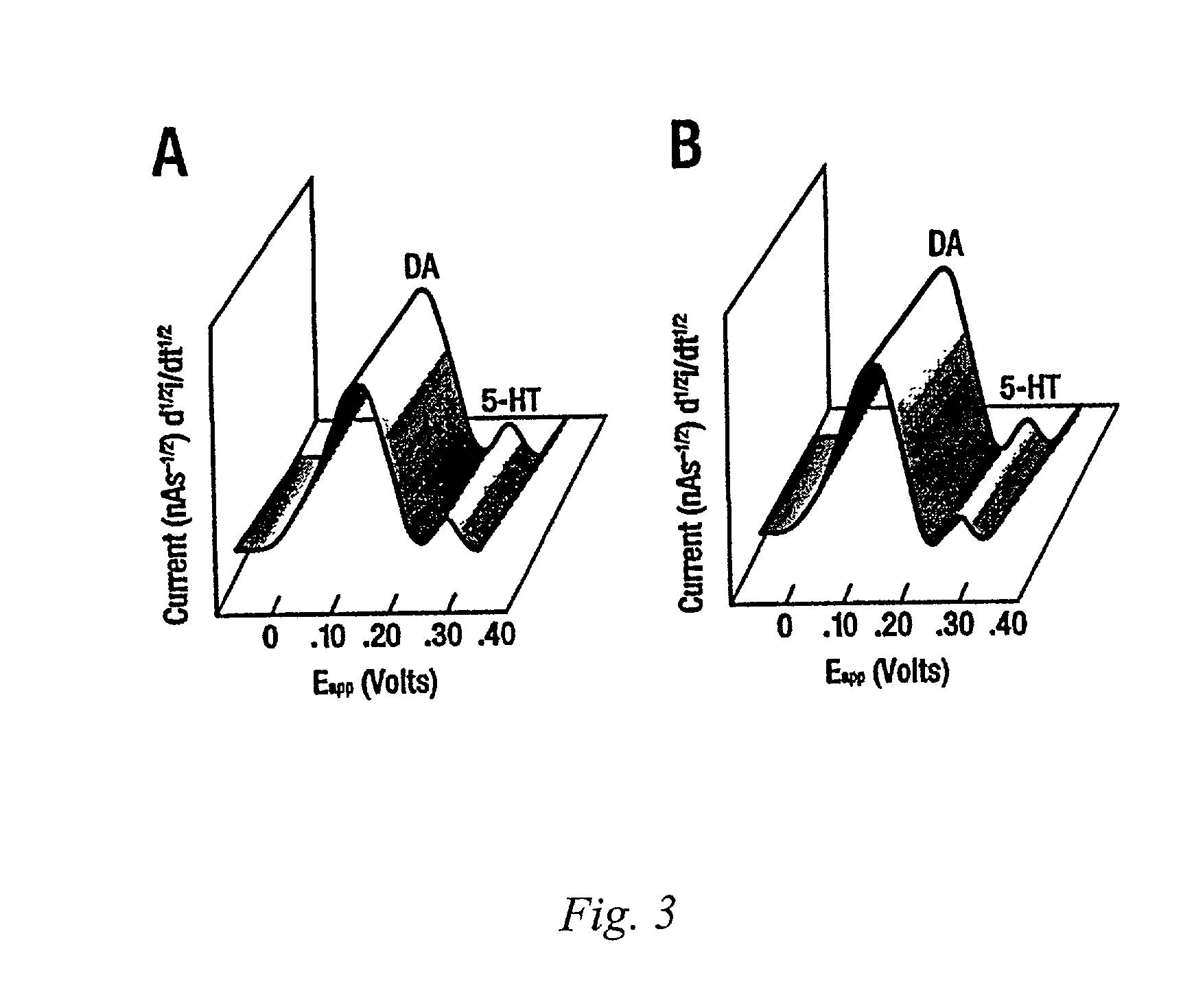
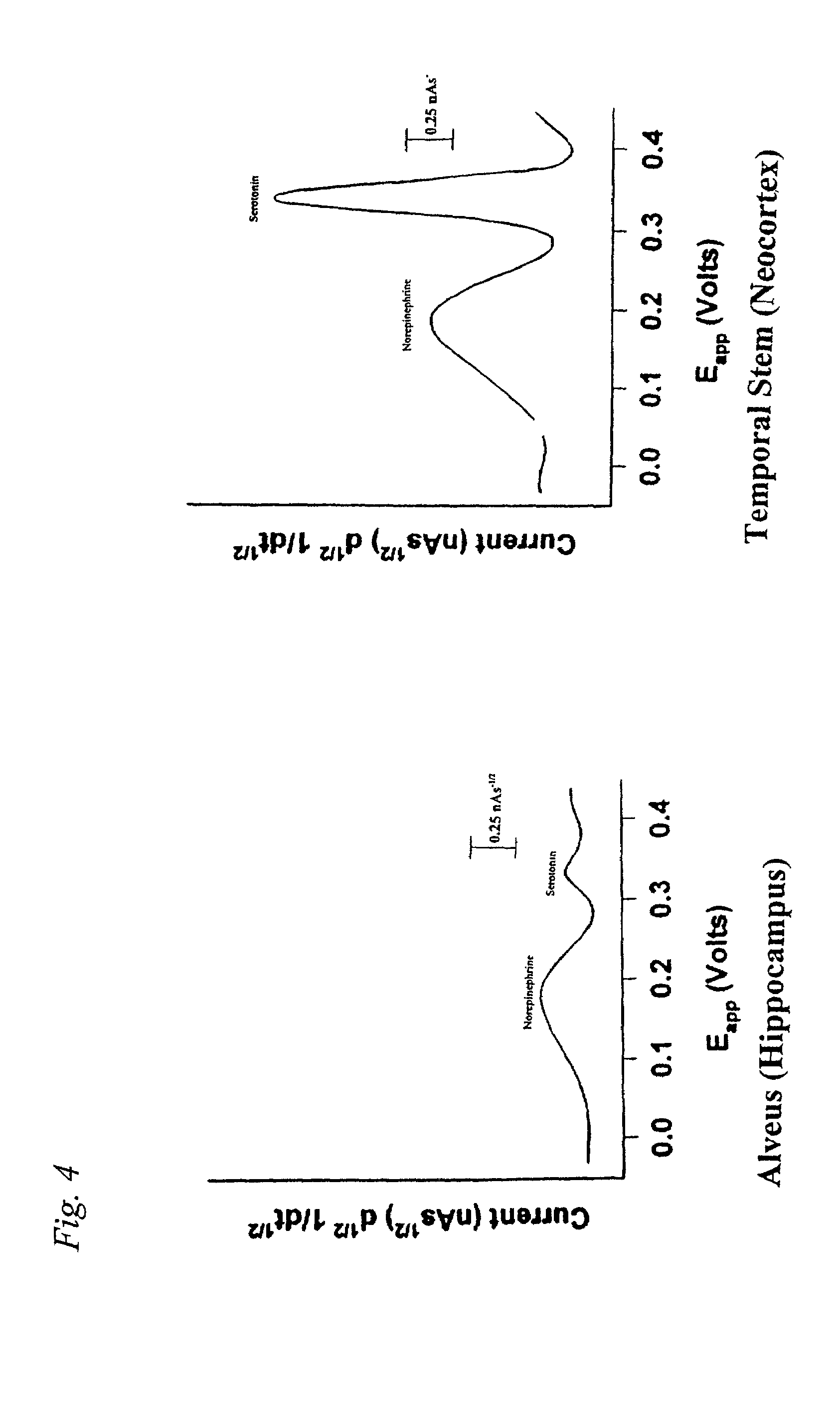
Identification, diagnosis, and treatment of neuropathologies, neurotoxicities, tumors, and brain and spinal cord injuries using electrodes with microvoltammetry
InactiveUS20070026440A1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementAbnormal tissue growthInjury brain
The present invention relates to devices and methods of use thereof for detection of biomolecules, in vitro, in vivo, or in situ. The invention relates to methods of diagnosing and / or treating a subject as having or being at risk of developing a disease or condition that is associated with abnormal levels of one or more biomolecules including, but not limited to, inter alia, epilepsy, diseases of the basal ganglia, athetoid, dystonic diseases, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, and cancer. The invention also provides methods of differentiating white matter from gray matter. In some embodiments, regions of the brain to be resected or targeted for pharmaceutical therapy are identified using sensors. The invention further provides methods of measuring the neurotoxicity of a material by comparing microvoltammograms of a neural tissue in the presence and absence of the material using the inventive sensors.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
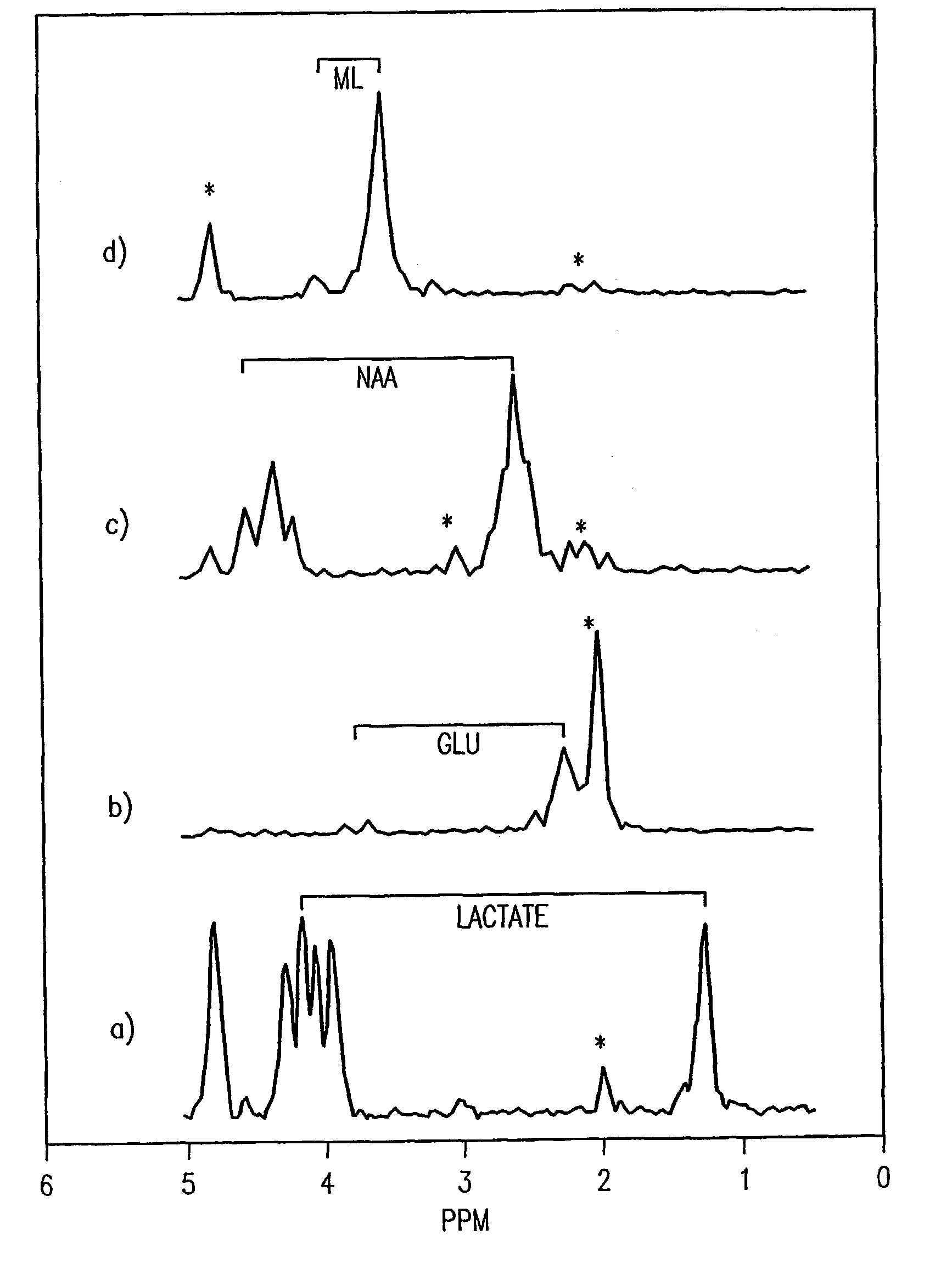
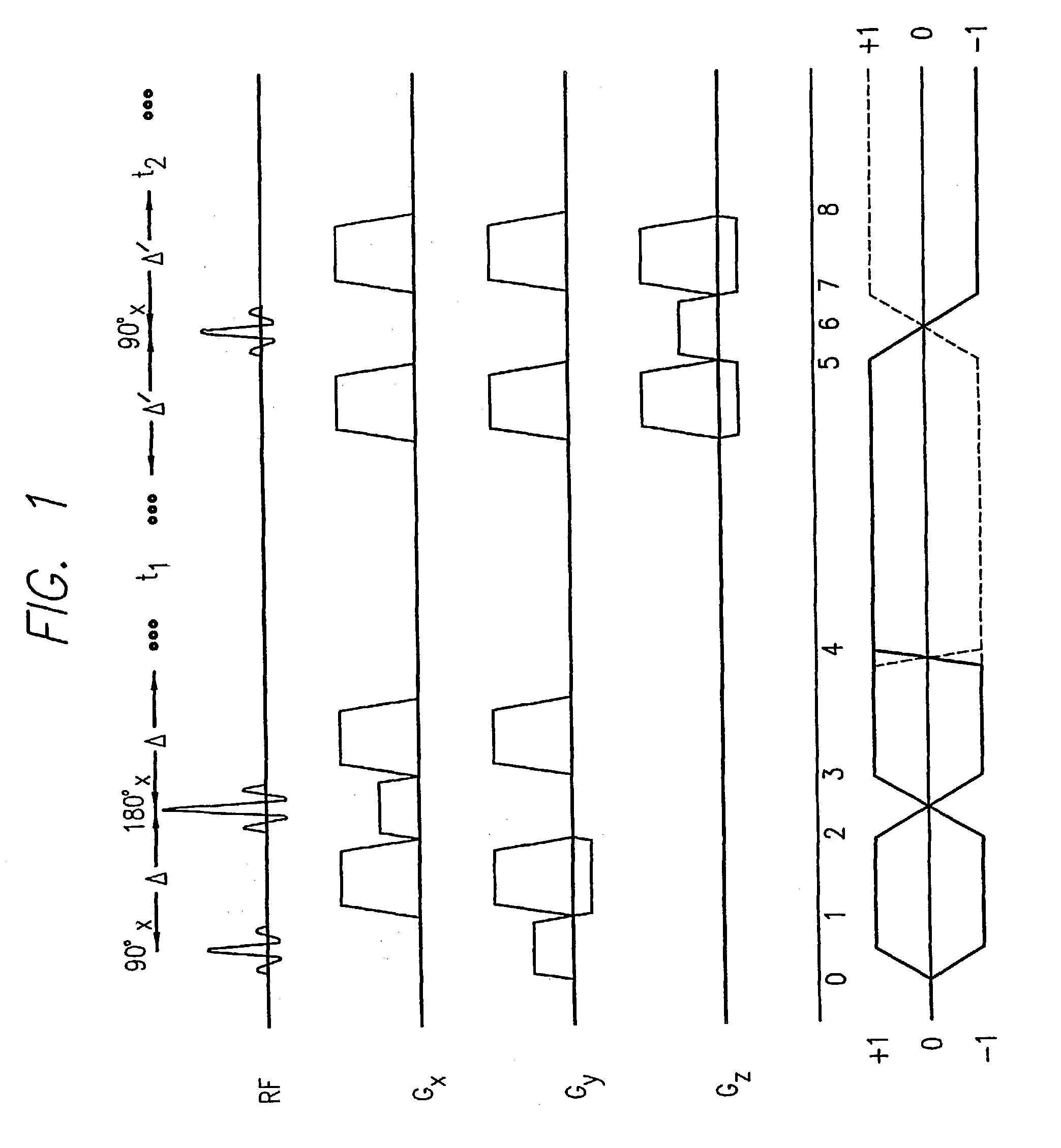
Localized two-dimensional shift correlated MR spectroscopy of human brain
InactiveUS7200430B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringWhole bodySpectroscopy
A two-dimensional (2D) chemical shift correlated MR spectroscopic (COSY) sequence integrated into a new volume localization technique (90°-180°-90°) for whole body MR Spectroscopy. Using the product operator formalism, a theoretical calculation of the volume localization as well as the coherence transfer efficiencies in 2D MRS is presented. A combination of different MRI transmit / receive rf coils is used. The cross peak intensities excited by the proposed 2D sequence are asymmetric with respect to the diagonal peaks. Localized COSY spectra of cerebral frontal and occipital gray / white matter regions in fifteen healthy controls are presented.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
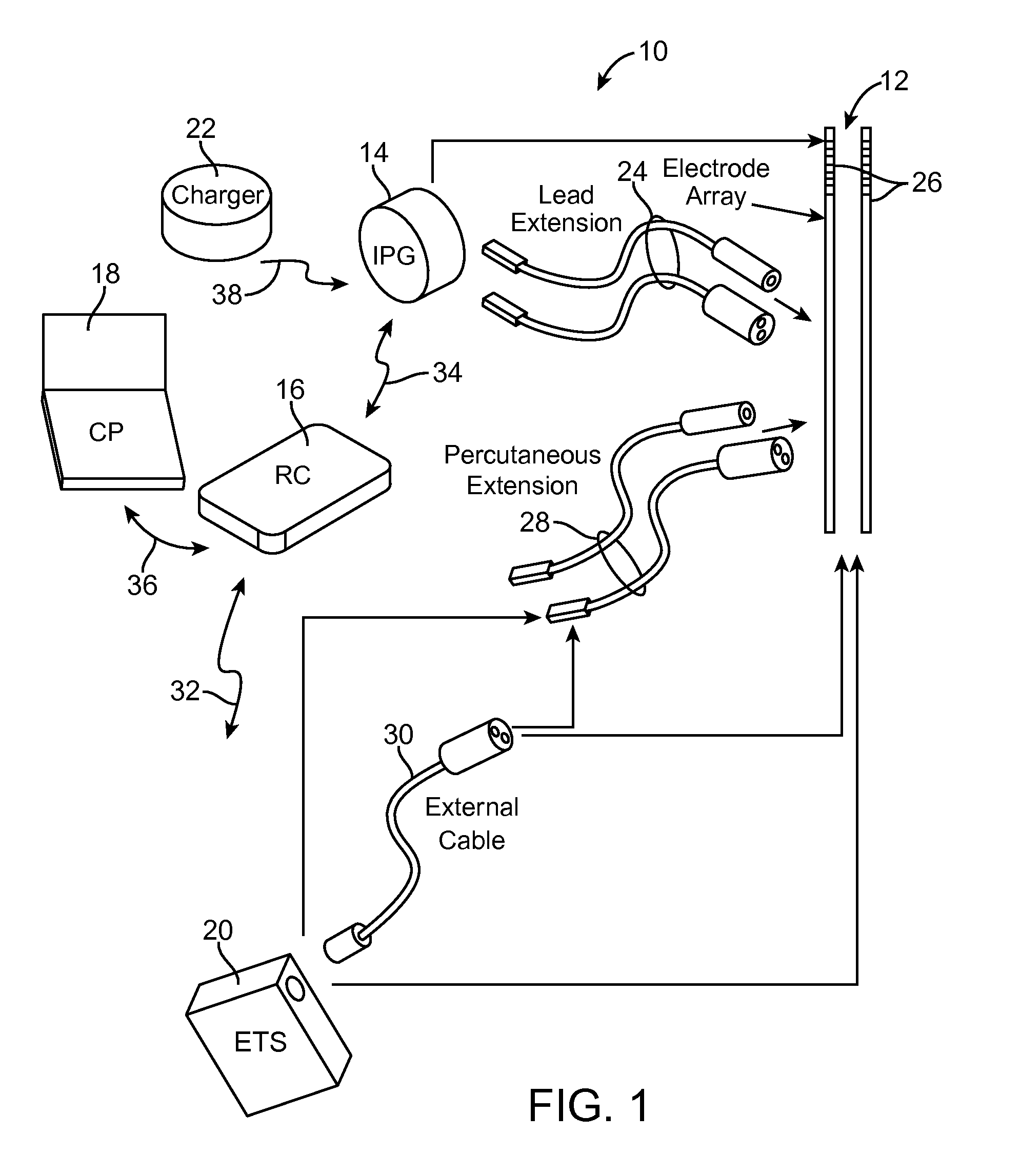
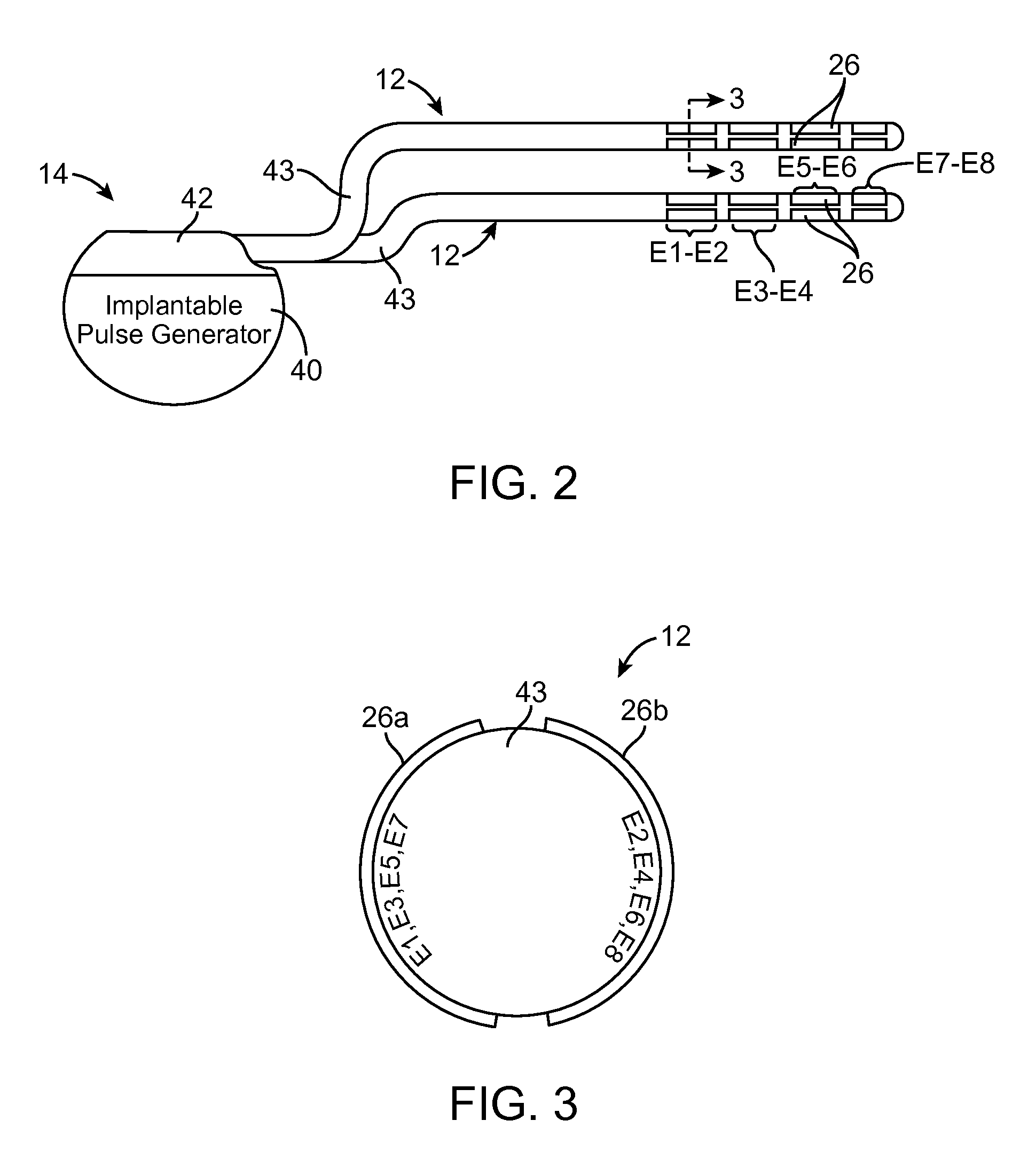
System and method for using impedance to determine proximity and orientation of segmented electrodes
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
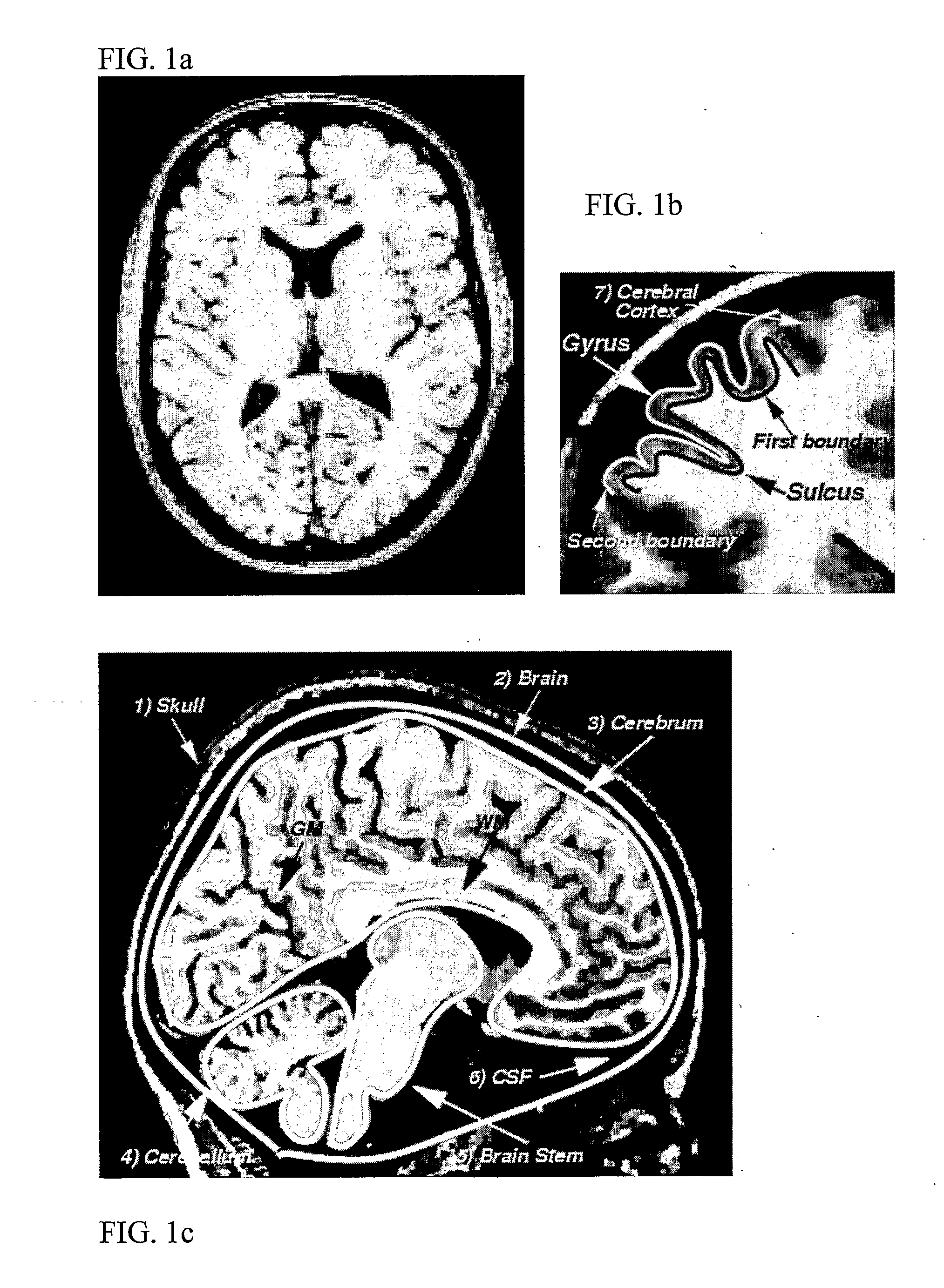
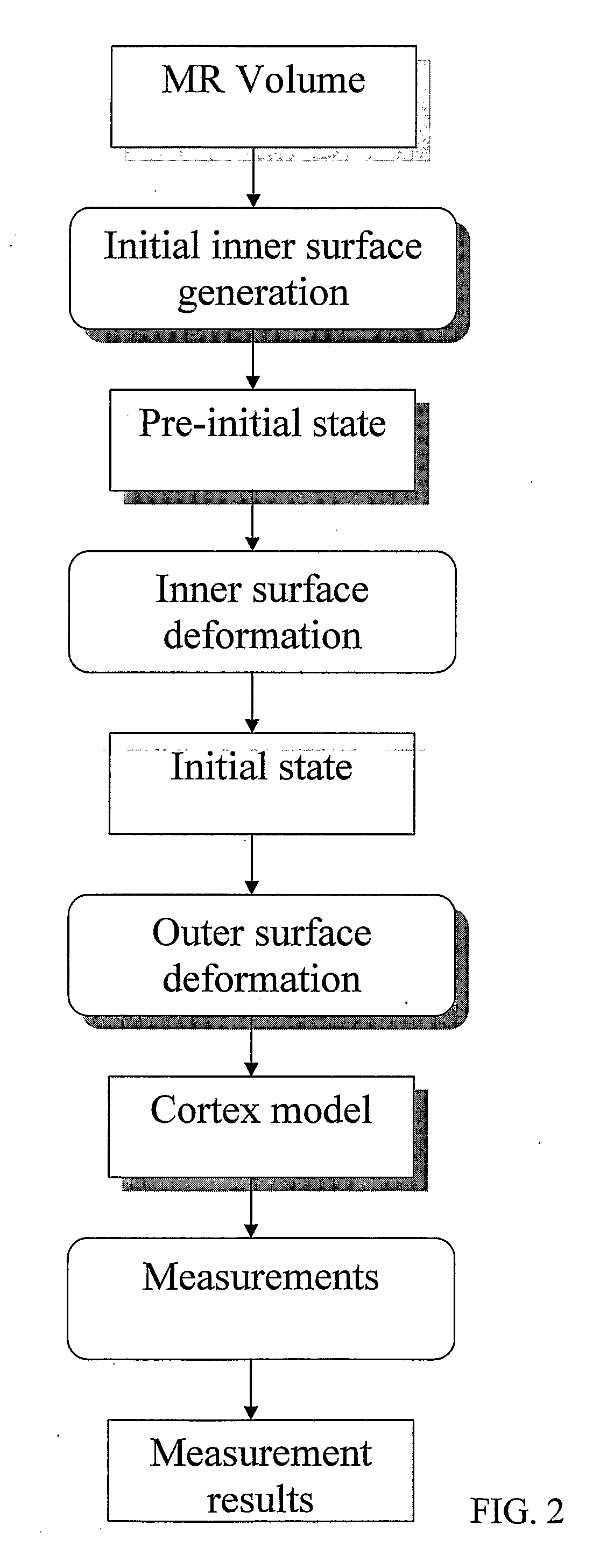
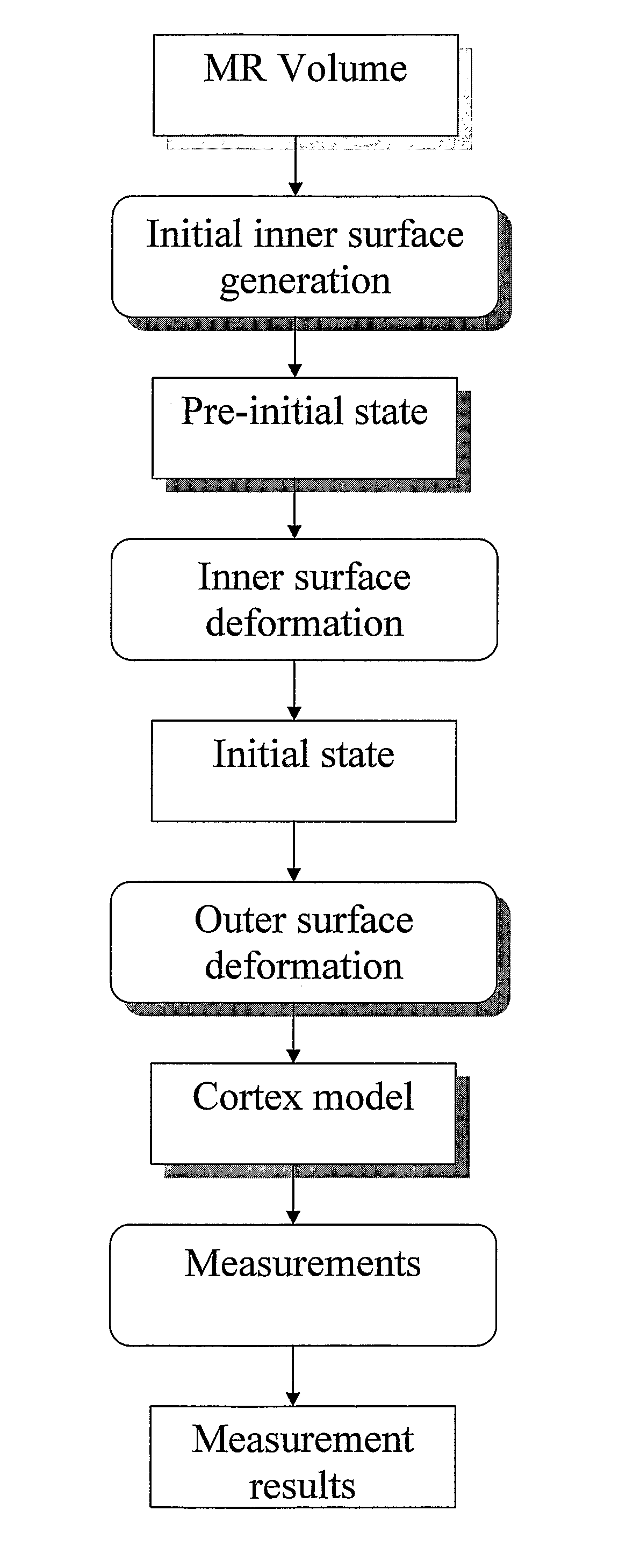
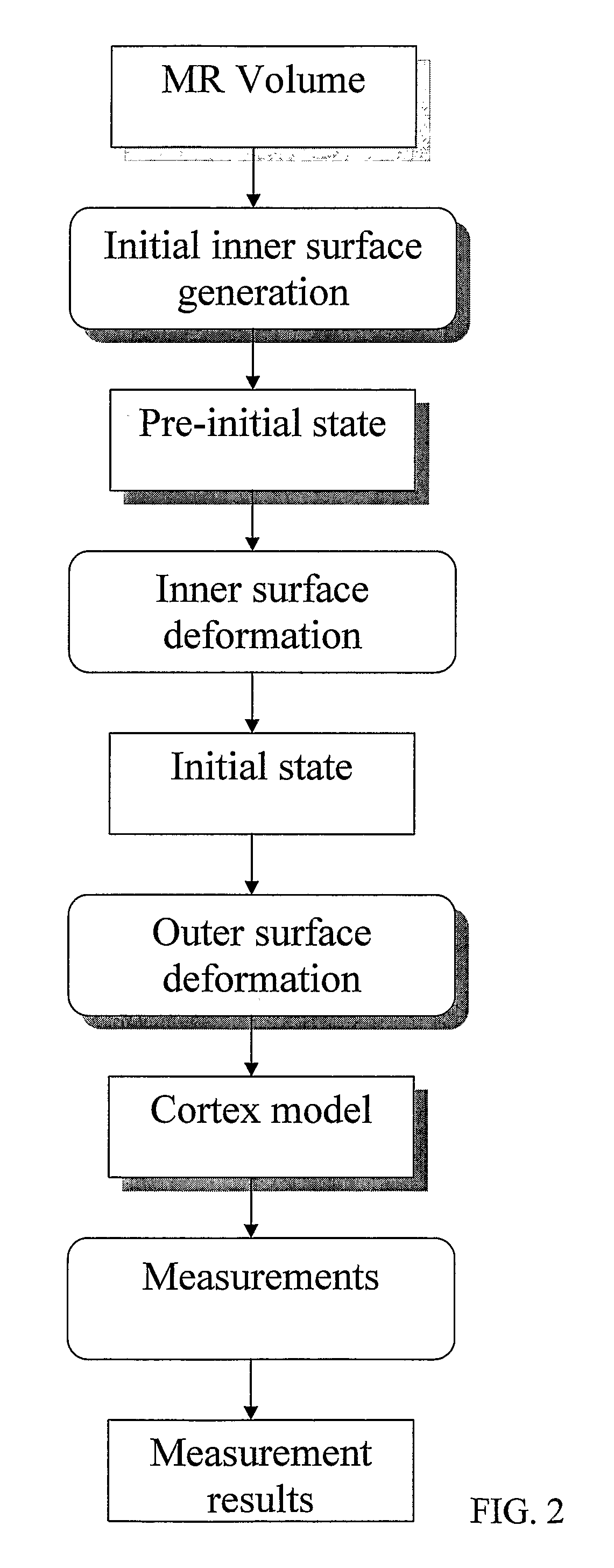
Computerised Cortex Boundary Extraction From Mr Images
InactiveUS20080170791A1Improved and robust and accurateAccurate modelingImage enhancementImage analysisDigital dataData set
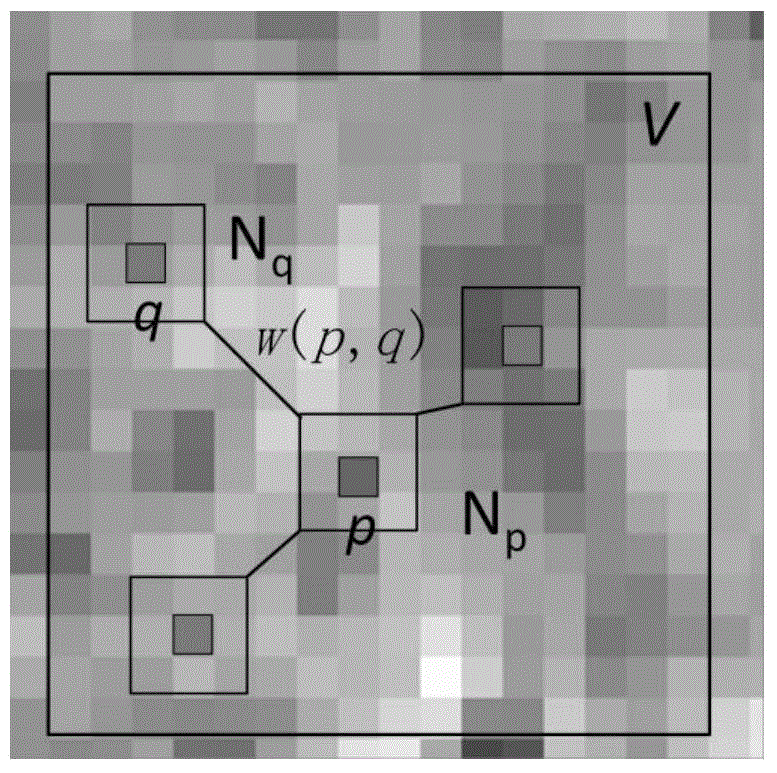
Method for processing digital images, such as magnetic resonance images of a brain. The images contain a first object, for example the cerebrum white matter, a second object, for example the cerebral cortex, and a third object, for example the cerebrospinal fluid. The method involves providing a digital dataset representing a deformable curve or surface that in an initial state approximates the boundary between the first object and the second object. Further, a vector force field is provided that for each point on the deformable curve or surface defines a direction from the point approximately towards the second boundary between the second and the third object, and this vector force field is applied for iteratively deforming the deformable curve or surface convergently towards the second boundary. In order to reconstruct a folded structure of the second object, for example the cortex, the vector force field also involves a normal vector field with a vector normal or approximately normal to the deformable curve or surface for each point on the deformable curve or surface.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging fiber bundle tracking device
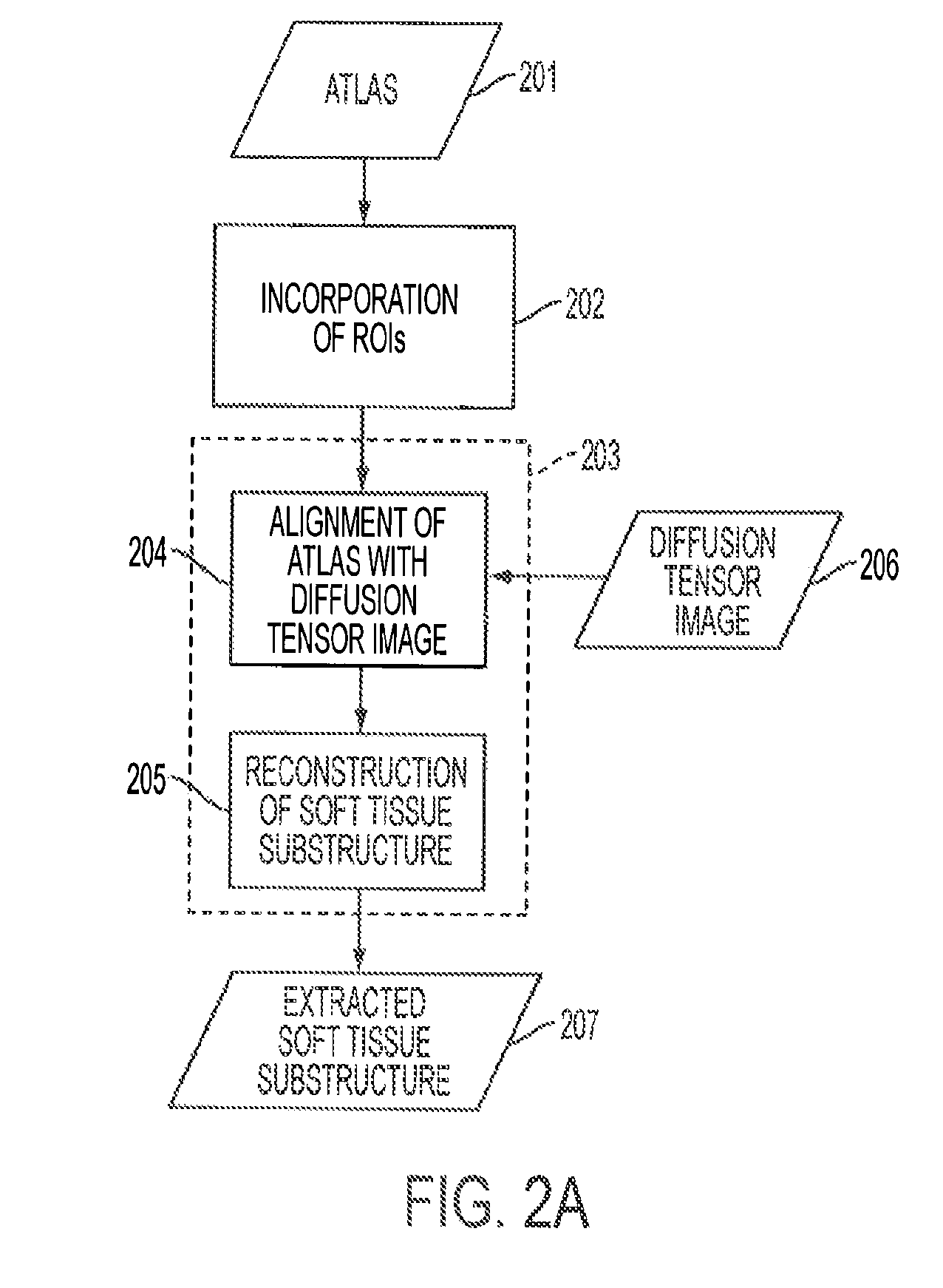
InactiveCN103049901AAccurate Tracking AlgorithmAccurate white matter fiber tractsImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringTensor fieldWhite matter
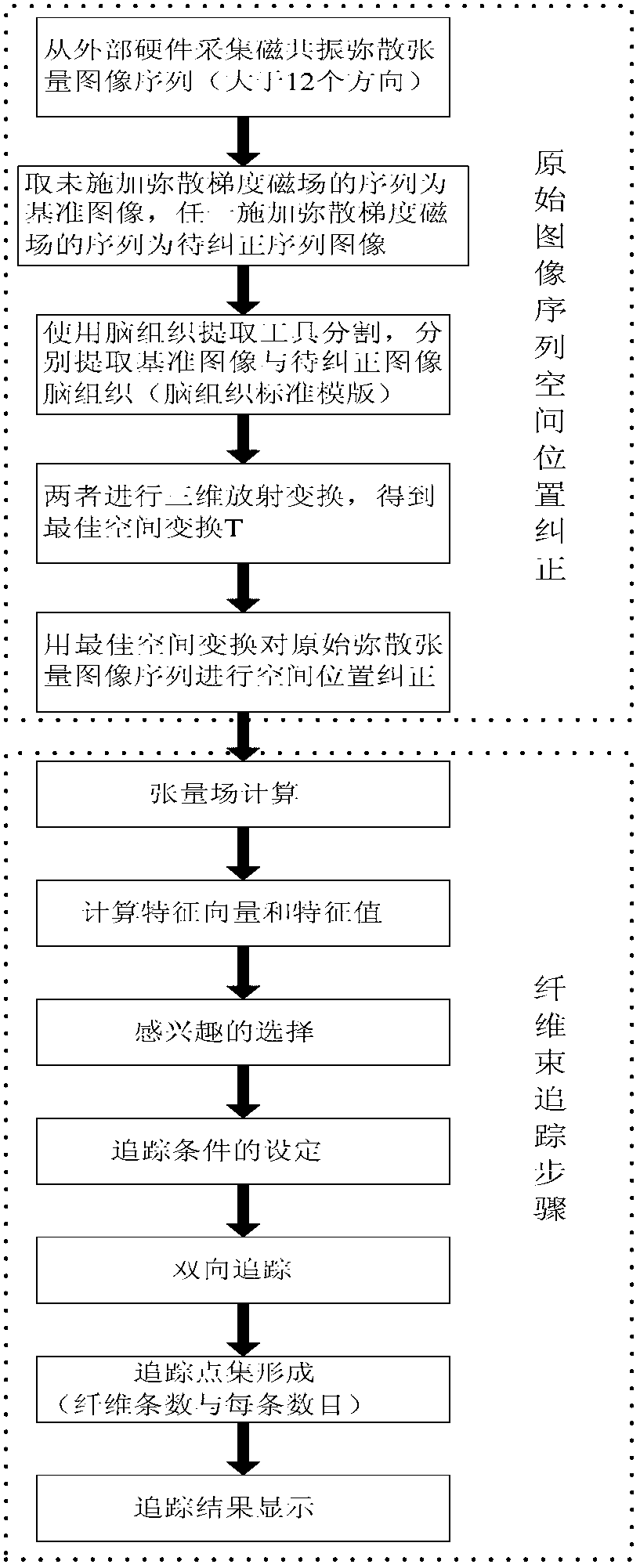
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging fiber bundle tracking device. The process is respectively completed by each component through the following steps of (1) collecting magnetic resonance diffusion tensor images; (2) carrying out brain issue dividing on a sequence without a diffusion gradient magnetic field and any sequence with the diffusion gradient magnetic field, and using the sequence without the diffusion gradient magnetic field as an image reference template of the brain tissues; (3) carrying out three-dimensional affine conversion on the two image sequences of the brain tissues after being extracted, to obtain a space conversion relationship; (4) carrying out space conversion on the remained diffusion tensor images by an optimum conversion relationship; (5) calculating tensor fields and feature vectors; (6) setting the interested areas and tracking conditions; and (7) carrying out the bidirectional tracking and displaying based on a fiber bundle with variable step size, so as to quickly and effectively carry out fiber bundle tracking and displaying on the white matters of human brain. In the diffusion tensor imaging process, the image deviation caused by space positions can be corrected, and the elastic step size is adopted in the tracking process, so as to ensure the reliable fiber bundle tracking.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Identification, diagnosis, and treatment of neuropathologies, neurotoxicities, tumors, and brain and spinal cord injuries using microelectrodes with microvoltammetry
InactiveUS7112319B2Reliable distinctionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteInjury brain
The present invention relates to devices and methods of use thereof for making semiderivative voltammetric and chronoamperometric measurements of chemicals, e.g. neurotransmitters, precursors, and metabolites, in vitro, in vivo, or in situ. The invention relates to methods of diagnosing and / or treating a subject as having or being at risk of developing a disease or condition that is associated with abnormal levels of one or more neurotransmitters including, inter alia, epilepsy, diseases of the basal ganglia, athetoid, dystonic diseases, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, and cancer. The invention provides methods of differentiating white matter from grey matter using microvoltammetry. In some embodiments, regions of the brain to be resected or targeted for pharmaceutical therapy are identified using Broderick probes. The invention further provides methods of measuring the neurotoxicity of a material by comparing Broderick probe microvoltammograms of a neural tissue in the presence and absence of the material.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
FMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method
ActiveCN106204562ANovel thinkingSimple processImage enhancementImage analysisClinical valueFiber bundle
The invention relates to an fMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method. The method includes the following steps that: fMRI and DTI magnetic resonance imaging data are pre-processed; regional segmentation is performed on a hippocampal encephalic region based on resting state function connections; an ROI is selected; and vault white matter segmentation is carried out based on a hippocampal sub-region and inter-thalamus white matter fiber bundle tracing technique. According to the method, the hippocampal encephalic region is segmented, and sub-regions obtained after segmentation are adopted as seed points; and the thalamus, adopted as a target encephalic region, is subjected to white matter fiber tracing, so that vault white matter can be segmented. The vault white matter is segmented based on the information of the function and structure of a human brain, and therefore, the fMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method has the advantages of novel thinking, simple process and important scientific and clinical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
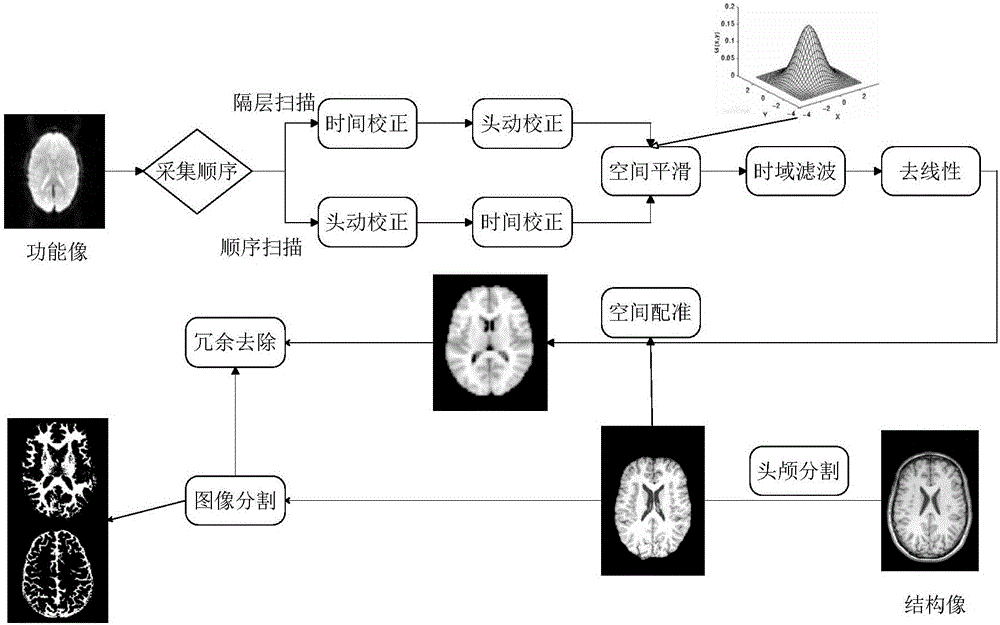
Method for three-dimensional registration and brain tissue extraction of individual human brain multimodality medical images
InactiveCN105816192AAchieve removalReduce distractionsRadiation diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPattern recognition
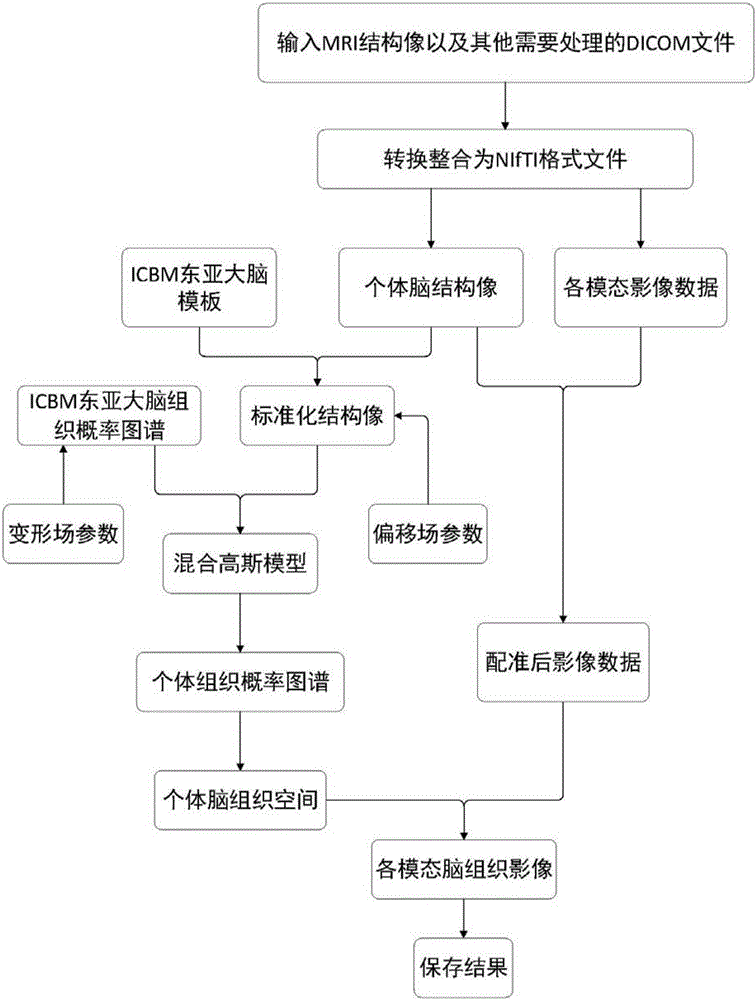
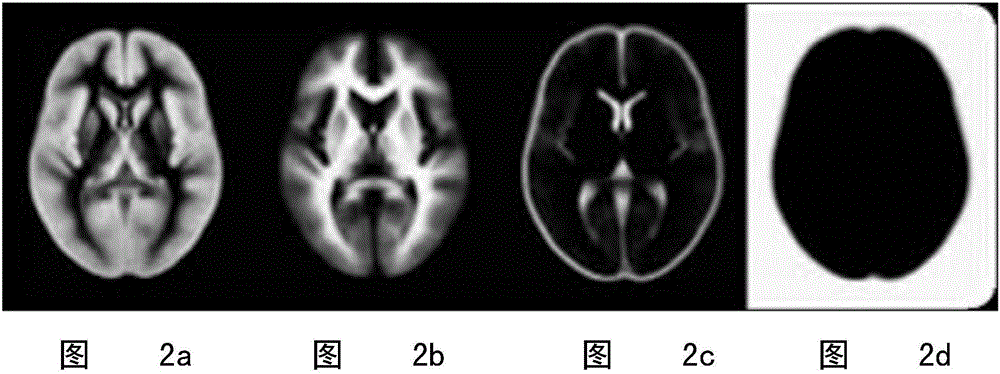
The invention relates to a method for three-dimensional registration and brain tissue extraction of individual human brain multimodality medical images. The method comprises the following steps: reading DICOM medical image data, and converting DICOM format data into NIfTI format data; layering images adopting a nuclear magnetic resonance structure; establishing a mixture gaussian model through an east Asia brain structure template and an east Asia brain tissue probability graph of ICBM, and dividing nuclear magnetic data into a grey matter part, a white matter part and a cerebrospinal fluid part; enabling the registration methods of other modality data and nuclear magnetic structure images to be the same; according to a layering and registration result, removing a skull and other parts outside the skull of each modality, and reserving the structure of parts inside the skull; adding weighting of three tissue probability graphs of the grey matter, the white matter and the cerebrospinal fluid obtained through layering of structure images so as to obtain a brain tissue probability graph, and performing Gaussian kernel smoothness; setting a threshold, applying the threshold to each modality image data after registration and resampling, and removing the cranium and parts outside the cranium; outputting a save result in an NIfTI format. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the registration of various structure images and multiplanar reconstruction images of a tested person can be completed at the same time.
Owner:王雪原 +1
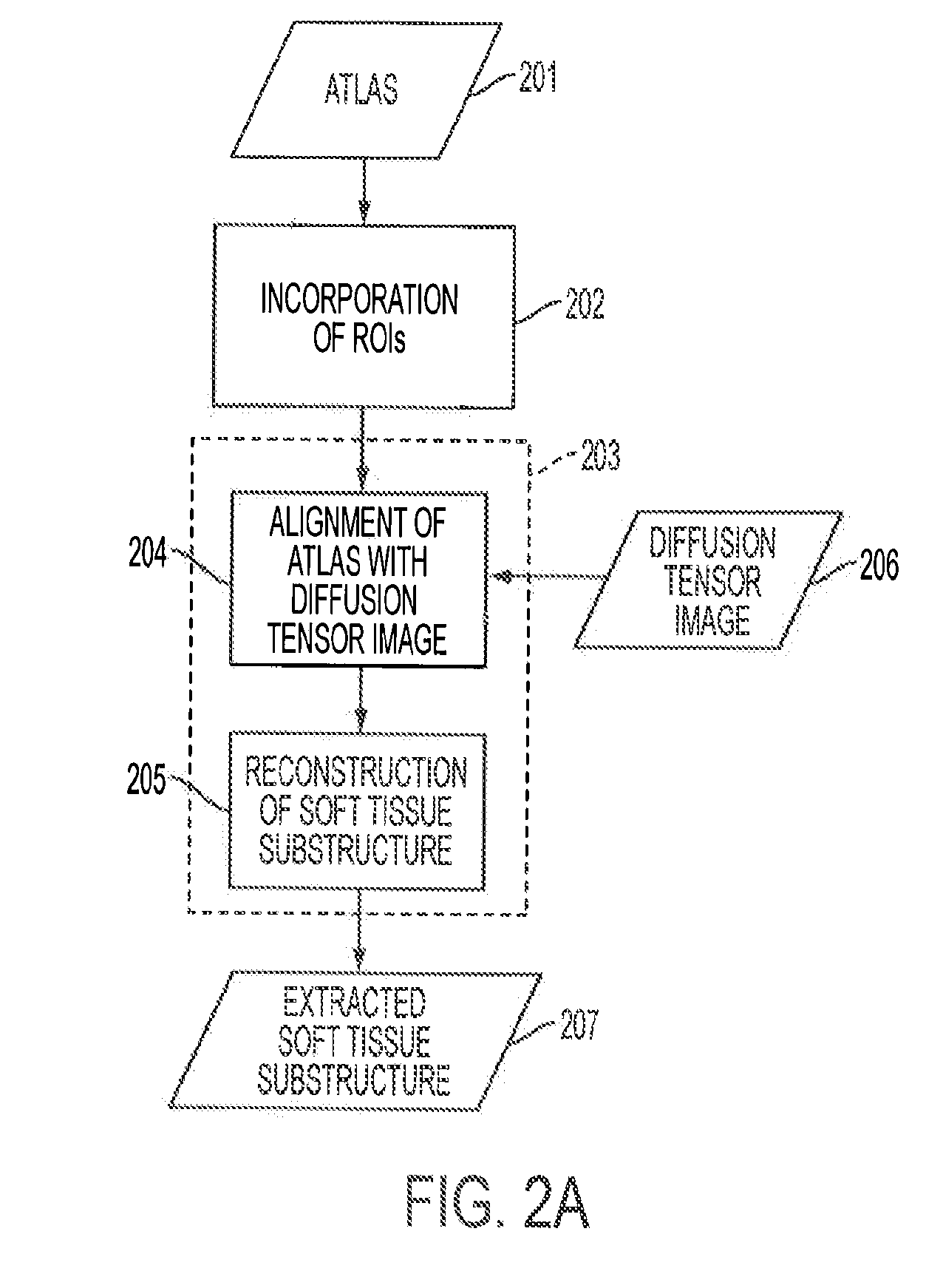
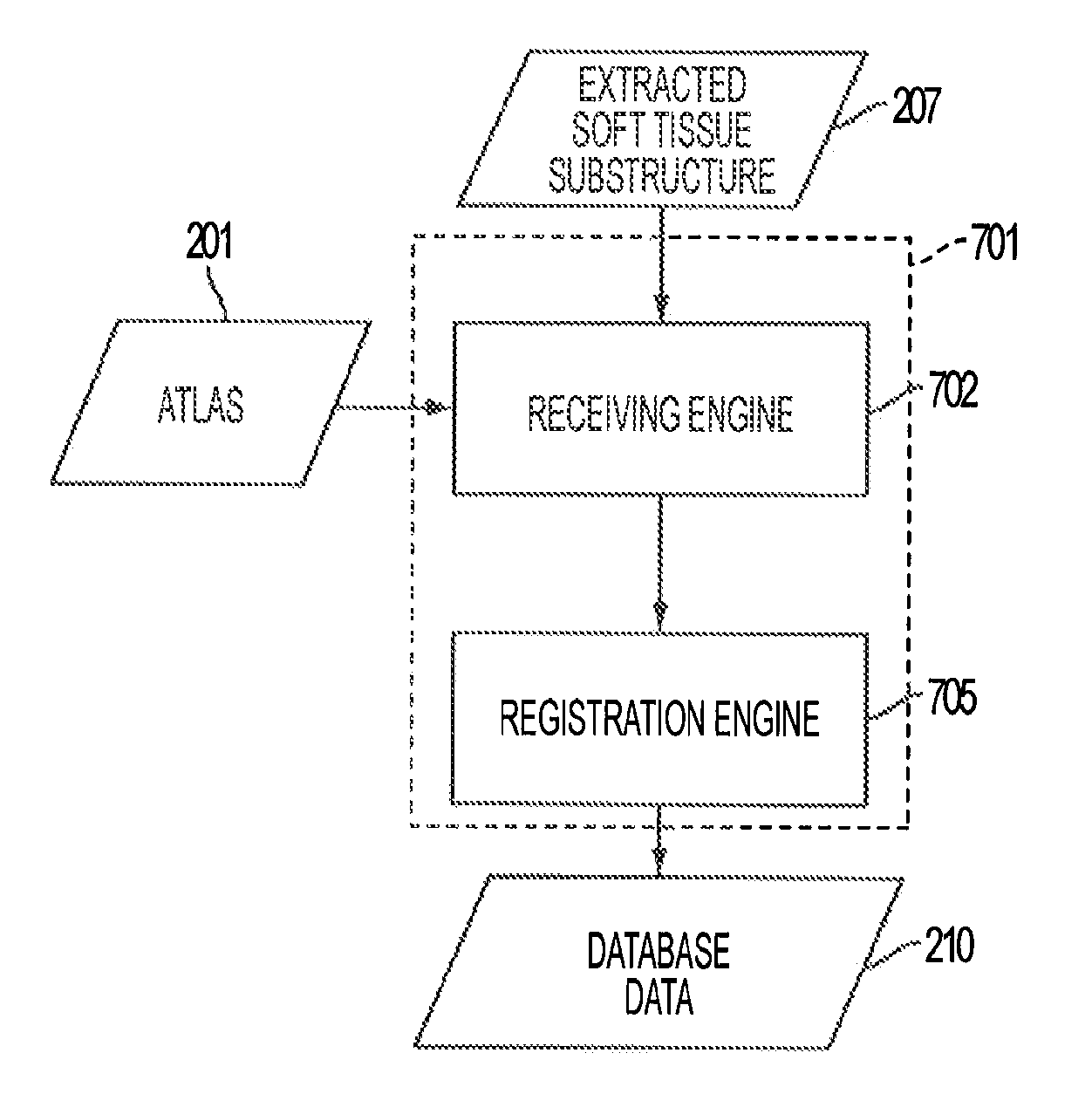
Automated fiber tracking of human brain white matter using diffusion tensor imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a MRI scanner; a signal processing system in communication with the magnetic resonance imaging scanner to receive magnetic resonance (MR) signals for forming magnetic resonance images of a subject under observations; a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit contains database data corresponding to a soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The database data includes information identifying at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The signal processing system is adapted to process MR signals received from the MRI scanner to automatically identify at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
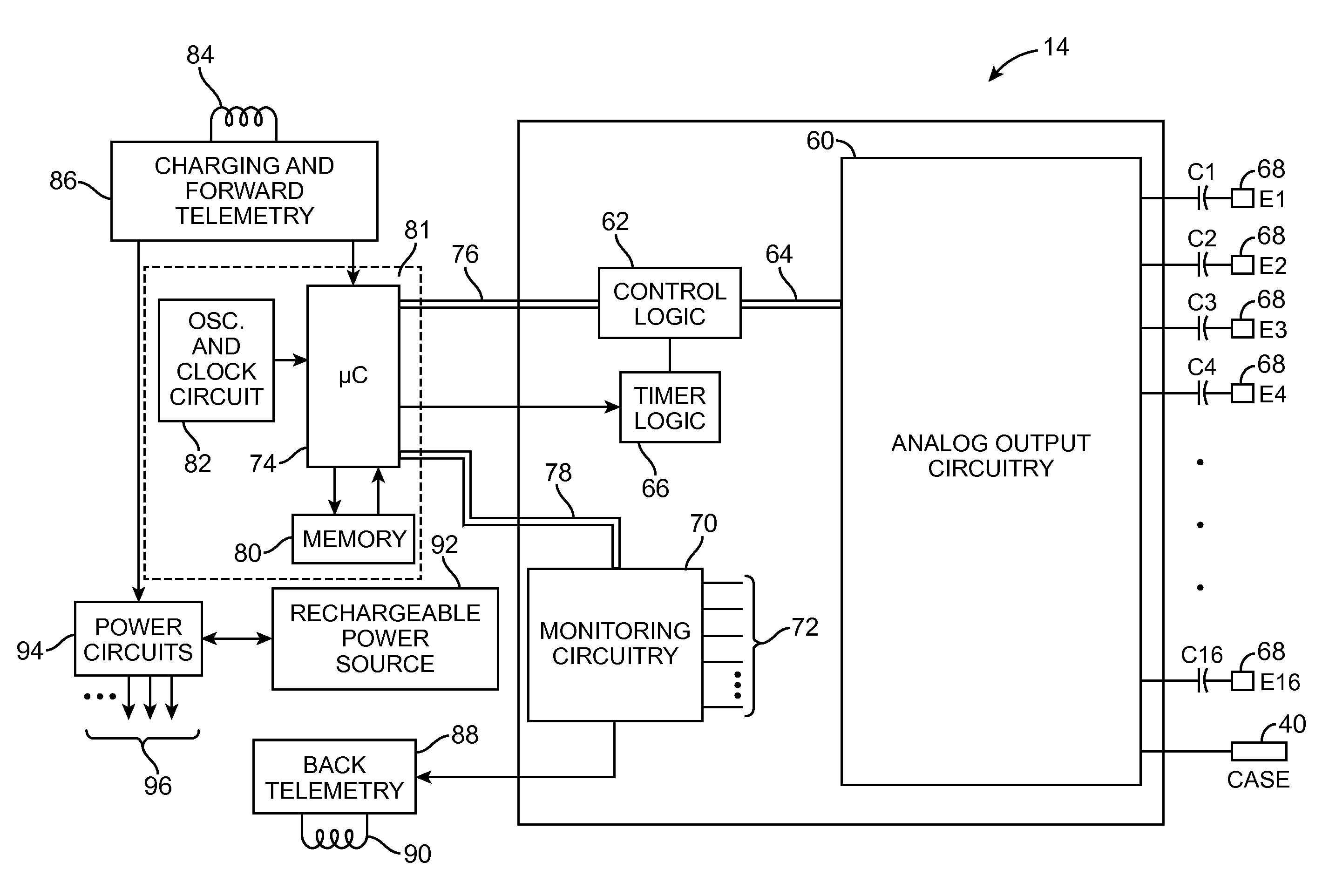
System for variably configurable, adaptable electrode arrays and effectuating software
ActiveUS20170087367A1Improve cognitive abilityAccurate informationElectroencephalographyUltrasound therapyDiseasePresent method
Electrical non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) delivers weak electrical currents to the brain via electrodes that are affixed to the scalp. NIBS can excite or inhibit the brain in areas that are impacted by that electrical current during and for a short time following stimulation. Electrical NIBS can be used to change brain structure in terms of increasing white matter integrity as measured by diffusion tensor imaging. Together the electrical NIBS can induce changes in brain structure and function. The present methods and devices are adaptable to and configurable for facilitating the enhancement of brain performance, and the treatment of neurological diseases and tissues. The present methods and devices are advantageously designed to utilize modern electrodes deployed with, inter alia, various spatial arrangements, polarities, and current strengths to target brain areas or networks to thereby enhance performance or deliver therapeutic interventions.
Owner:STIMSCI INC
Thin layer magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on deep learning
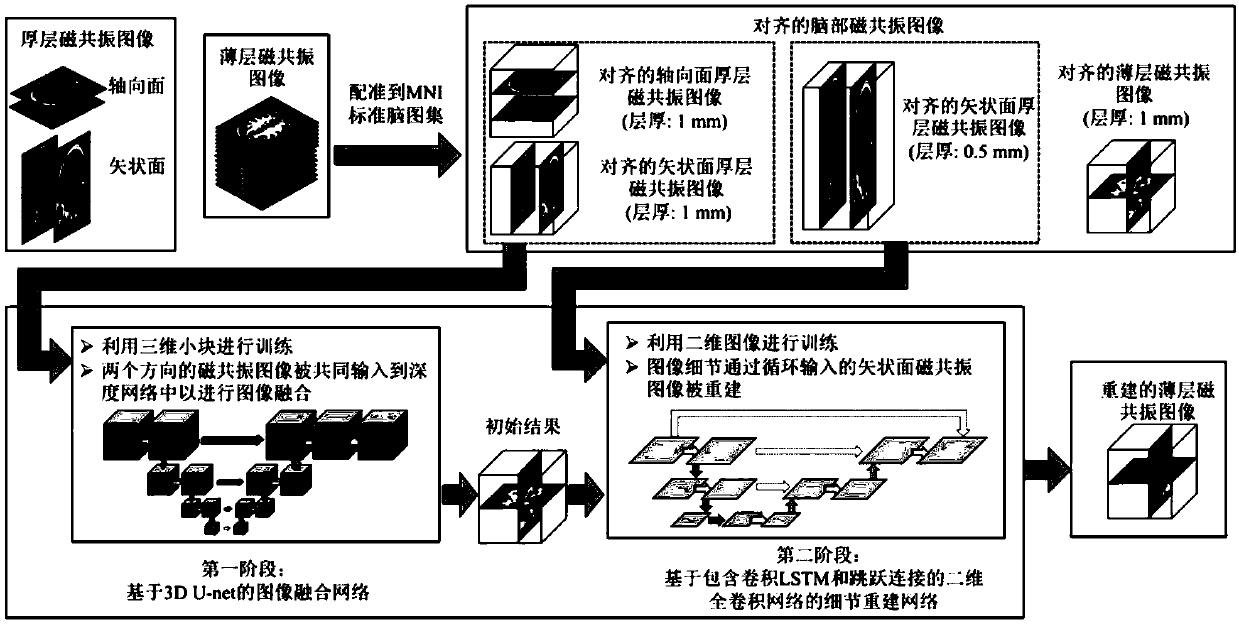
ActiveCN108629816AImprove reconstruction resultsReconstruction from projectionNeural architecturesData setSagittal plane
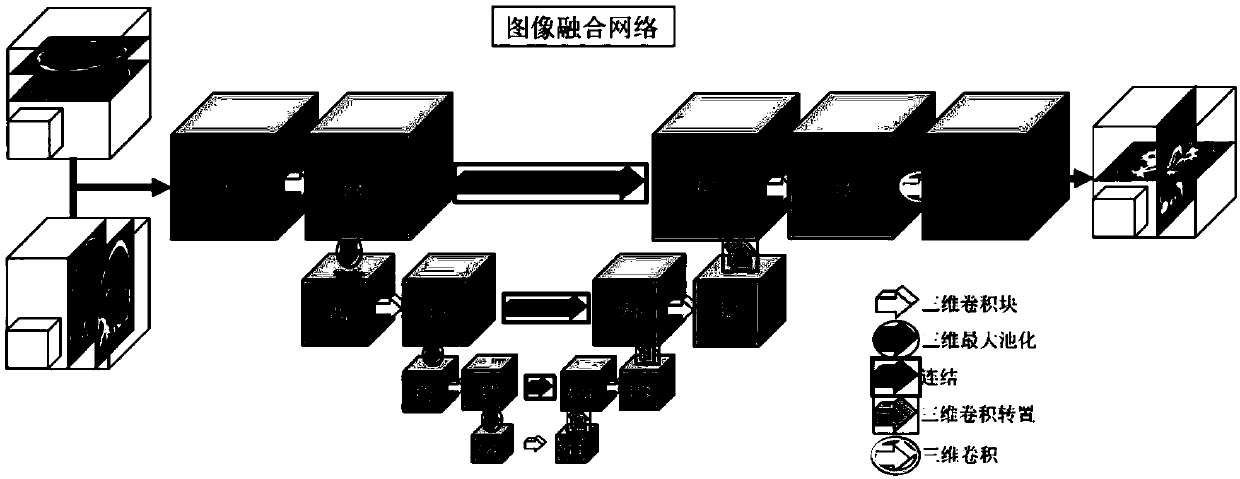
The invention discloses a thin layer magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on deep learning. The method comprises the specific steps that 1) thick layer magnetic resonance images are collected on the axial and sagittal planes of a brain; 2) the thick layer magnetic resonance images are registered and normalized; 3) the paired and registered thick layer magnetic resonance images areused to train an image fusion network based on 3D U-net to generate a preliminary reconstruction result of a thin layer magnetic resonance image; and 4) the preliminary reconstruction result of the thin layer magnetic resonance image and a corresponding sagittal thick layer magnetic resonance image are used to train details to reconstruct the network and acquire a final reconstruction result. In the data set of magnetic resonance images of adolescent brains, the method provided by the invention can provide a better thin layer magnetic resonance image reconstruction result, and the reconstructed magnetic resonance image can better show the structure and detail of a brain. The estimation accuracy of gray matters, white matters and total brain volume in the magnetic resonance image can be greatly improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Apparatus to simulate MR properties of human brain for MR applications evaluation
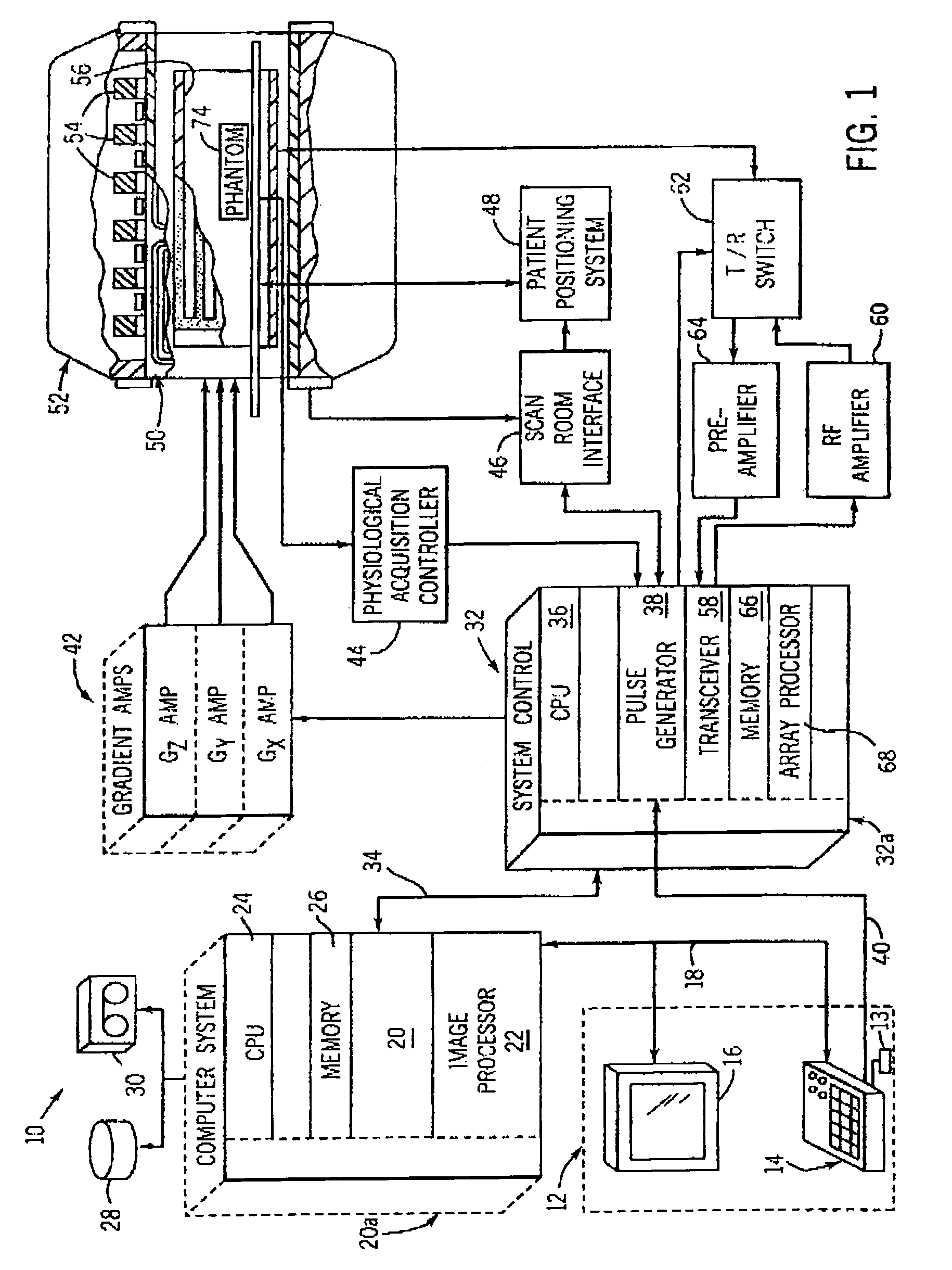
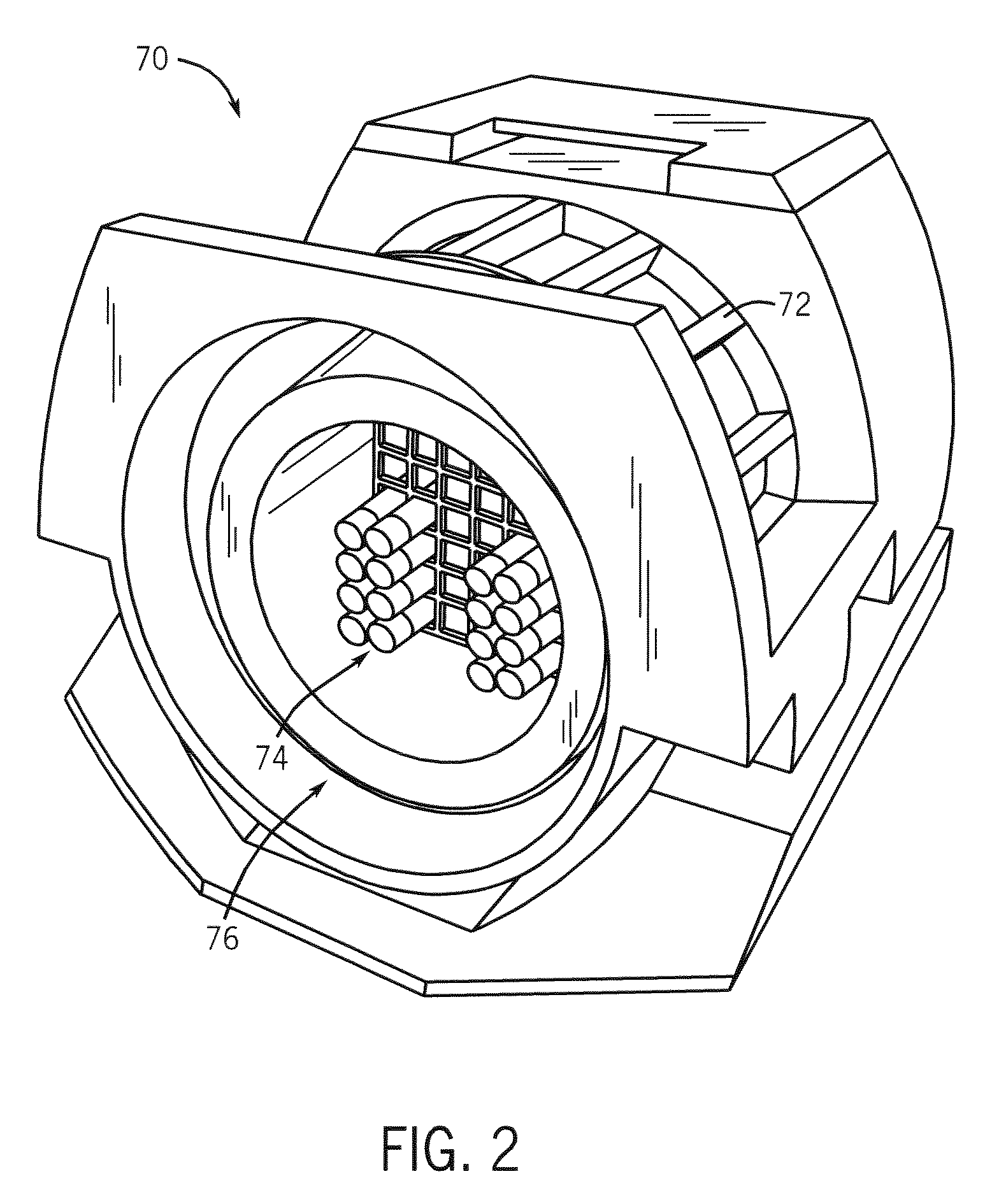
InactiveUS6965235B1Increase contrastImproves white matterMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionVolumetric Mass DensityT1 weighted
A system and method for mimicking a human brain for MR imaging at various magnetic field strengths is disclosed. A phantom is constructed of a structure having a number of sections. A first section contains a mixture of nickel chloride, agarose gel powder, potassium sorbate, deuterium oxide, and water such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the first section mimic white matter of the human brain. A second section contains different amounts of the same components such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the second section mimic gray matter of the human brain. As such, when the phantom is scanned in an MR imaging machine, an optimized flip angle for T1-weighted imaging to improve contrast between white matter and gray matter of the human brain that takes into account proton density differences therebetween can be determined.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-b-value DWI (diffusion weighted image) noise reduction method based on mutual information
ActiveCN104574298AReduce mistakesLess singular valueImage enhancementDiagnostic recording/measuringHead movementsImaging quality
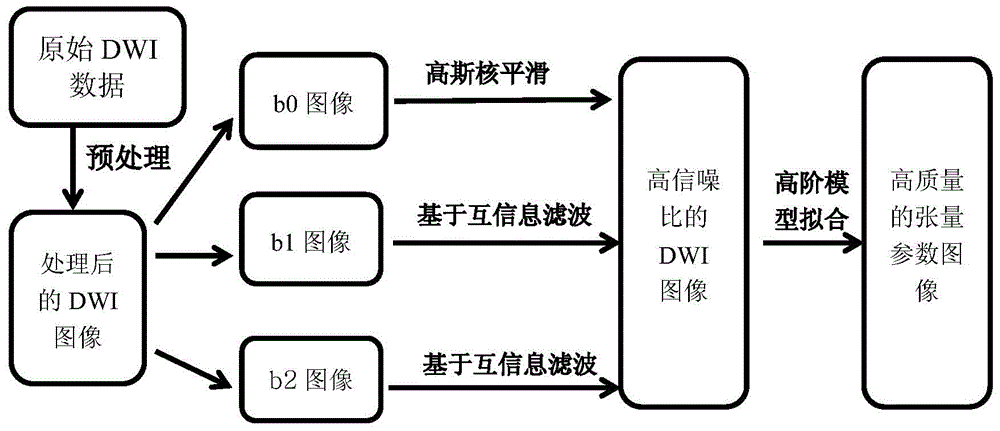
The invention discloses a multi-b-value DWI (diffusion weighted image) noise reduction method based on mutual information. The method comprises steps as follows: acquiring to-be-tested multi-b-value DWIs in multiple diffusion sensitive gradient directions by a magnetic resonance scanner; performing preprocessing such as head movement correction, eddy current correction and the like on the images; estimating different b-value image signal-to-noise ratios; performing noise reduction processing on the images through setting parameters of an optimal noise reduction algorithm so as to acquire DWIs with higher signal-to-noise ratios. The method fully considers features of different images, and three-dimensional structural features of the processed images are reserved as many as possible while noises are eliminated. During establishment of a high-order complex model, different b images have higher image quality, so that acquired high-order parameter images can have smaller errors and fewer singular values. The method can be better applied to preprocessing of a high-order model imaging technology and plays an active role in further research on white matter fiber structures.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Computerised cortex boundary extraction from MR images
InactiveUS8031919B2Accurate modelingImproved and robust and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisData setVector field
Method for processing digital images, such as magnetic resonance images of a brain. The images contain a first object, for example the cerebrum white matter, a second object, for example the cerebral cortex, and a third object, for example the cerebrospinal fluid. The method involves providing a digital dataset representing a deformable curve or surface that in an initial state approximates the boundary between the first object and the second object. Further, a vector force field is provided that for each point on the deformable curve or surface defines a direction from the point approximately towards the second boundary between the second and the third object, and this vector force field is applied for iteratively deforming the deformable curve or surface convergently towards the second boundary. In order to reconstruct a folded structure of the second object, for example the cortex, the vector force field also involves a normal vector field with a vector normal or approximately normal to the deformable curve or surface for each point on the deformable curve or surface.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
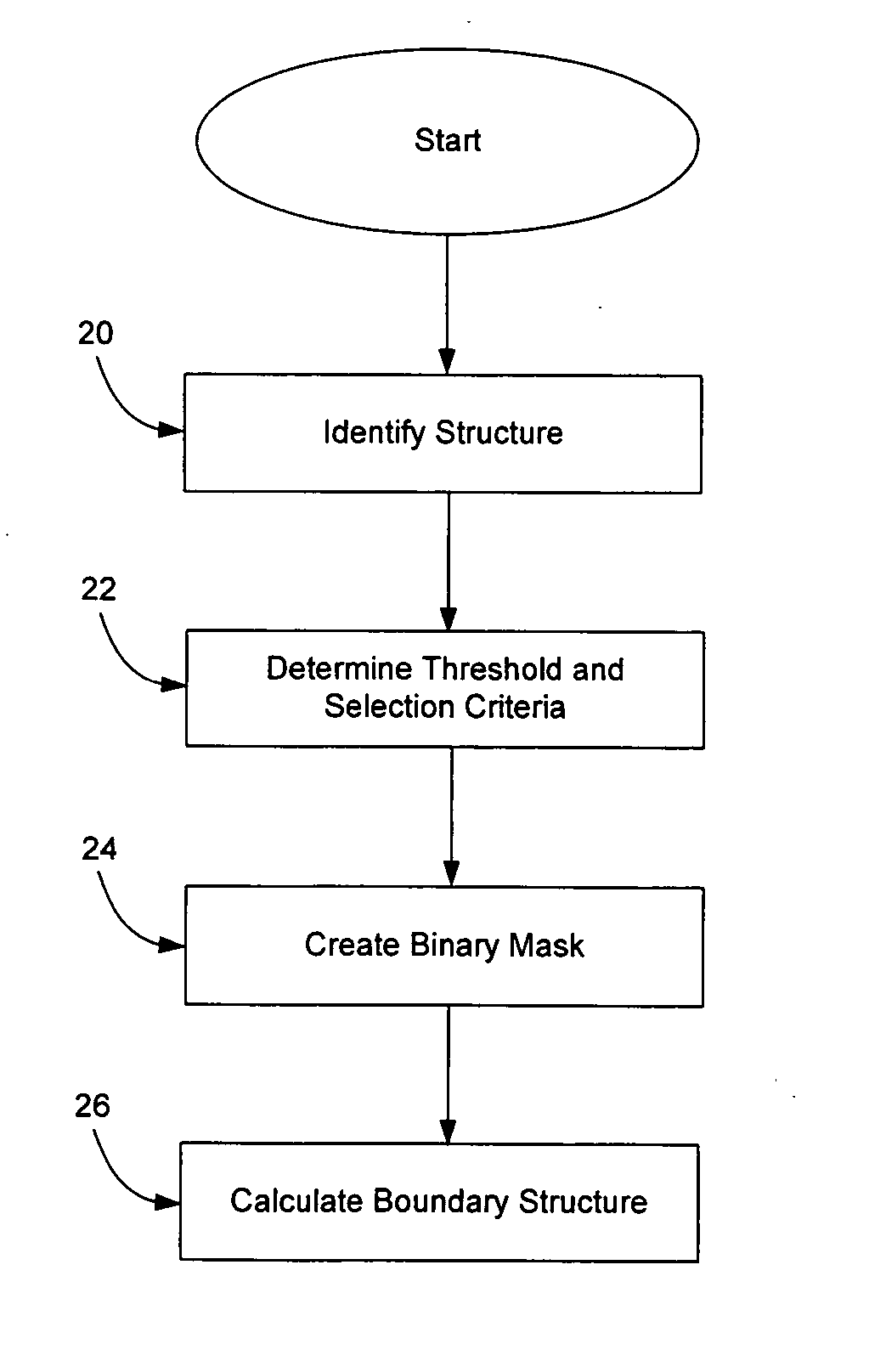
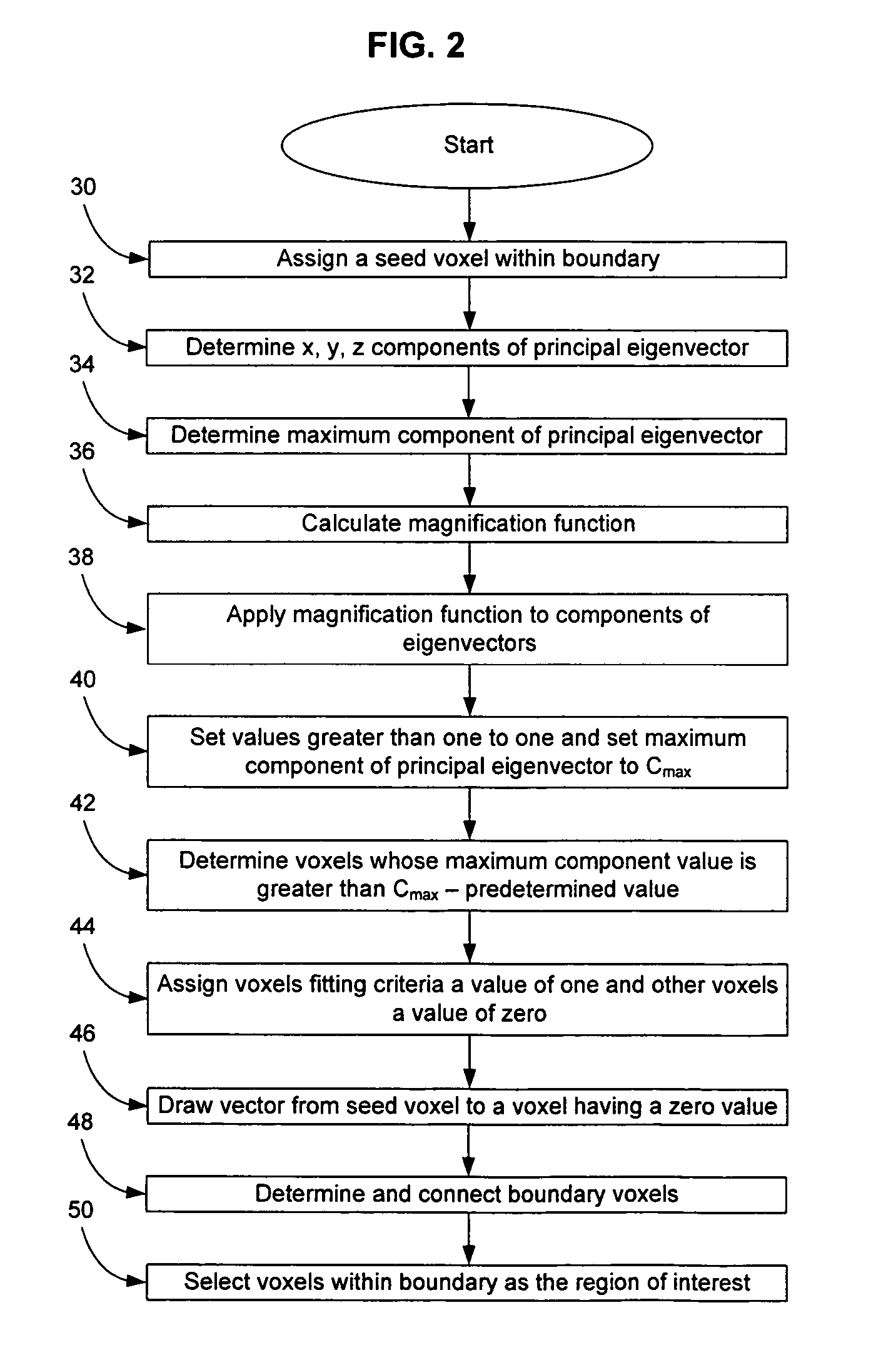
Reproducible objective quantification method to segment white matter structures
The invention provides a reproducible, objective quantification technique that reliably segments white matter structures. The technique receives a seed voxel within the white matter structure from an individual, determines thresholds and selection criteria, creates a binary mask based on the at least one threshold and the at least one selection criteria and calculates the boundary of the white matter structure based on the binary mask. A magnification factor is applied to each component of the eigenvectors of voxels. Boundary voxels are determined wherein each of the boundary voxels has a magnitude above a predetermined value and is located next to a voxel having a magnitude below the predetermined value. A vector is drawn from the seed voxel to a boundary voxel and the boundary voxels are connected together, thereby forming the region of interest within the connected boundary voxels.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Making method of color dough for dough modeling
The invention discloses a fabrication method for colourful dough used for dough molding, comprising 5 shares of rice flour, 2-3 shares of glutinous rice flour, 0.5-1 shares of glycerine, 0.2-0.5 shares of wheat starch and 0.6 shares of preservative and suitable quantity of water. The colourful dough is prepared with the components by the method as follows: the rice flour, the glutinous rice flour, the wheat starch and the preservative are arranged in a container, suitable quantity of water is also added in the container; the components and the water added in the container are uniformly mixed for 20-30 minutes. A disc is coated with one half of the glycerine and the mixed dough is arranged on the disc and steamed in boiled water for 40 minutes to obtain flour mud; when the flour mud is cooled and does not scald, the other half of the glycerine is mixed in the flour mud and coloring matter is then added in the flour. The wheat flour in traditional raw material is replaced by the rice flour, thus leading the prepared flour mud to be crystal-like and lucent and be easy to be colorized; meanwhile, the forming colourful dough has good elasticity and is easy to be formed during the nipping process; glue is not added when the colourful dough is being fabricated, and the health of the user is ensured; normal salt raw material is saved, then the preservation time of the finished product is long, no white matter separates out, the beauty of the finished product is not affected; and the honey is not used so as to lead the finished product to be mothproof; the processing is carried out by the steaming method, thus ensuring the deserved efficacies of all raw materials.
Owner:董晓红
Non human animals with human-glial chimeric brains
The present invention is directed to a non-human mammal with at least 30% of all of its glial cells in its corpus callosum being human glial cells and / or at least 5% of all of its glial cells in the white matter of its brain and / or brain stem being human glial cells. Methods of producing and using the non-human mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting grayscale nonuniformity of MR (Magnetic Resonance) image
InactiveCN102135606AAccurate divisionVolume effect suppressionMagnetic measurementsSorting algorithmNear neighbor
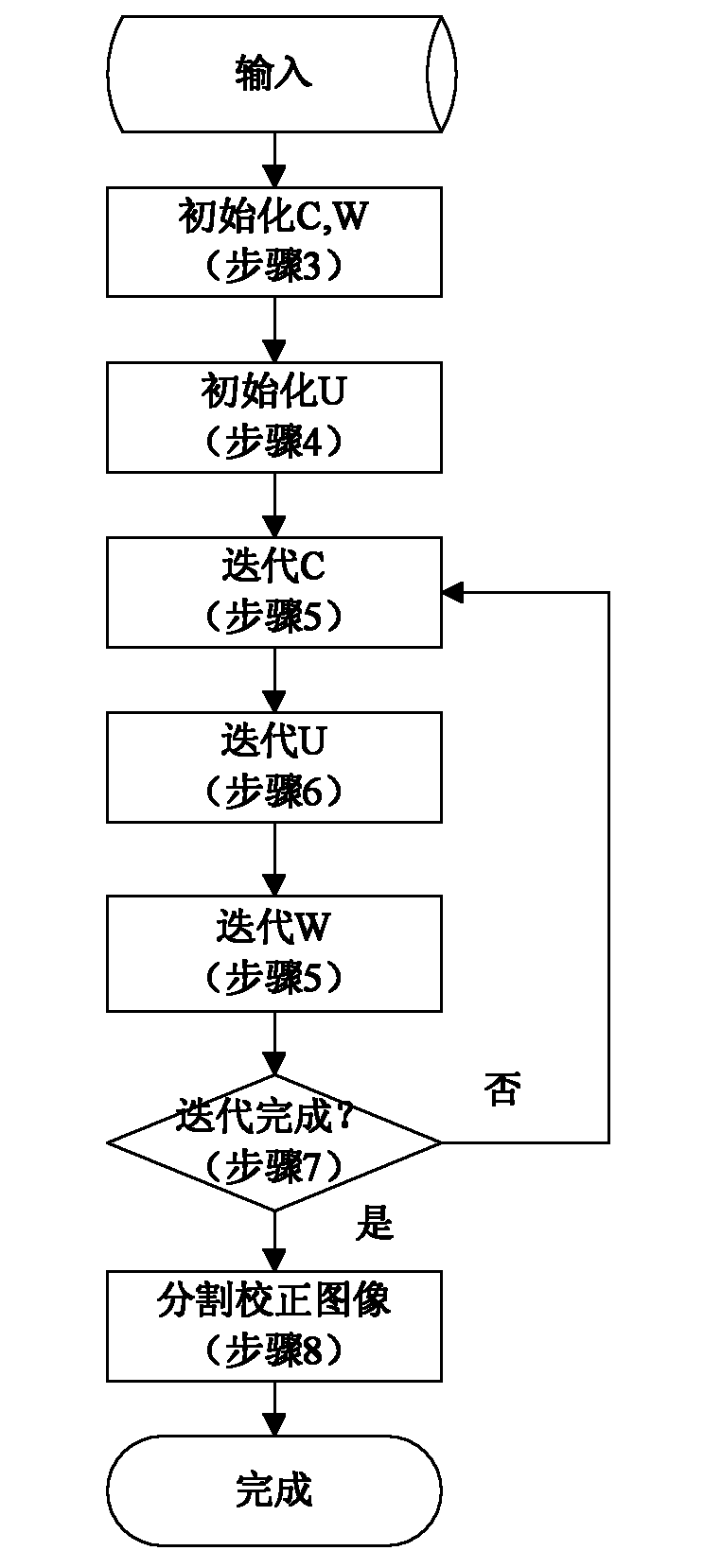
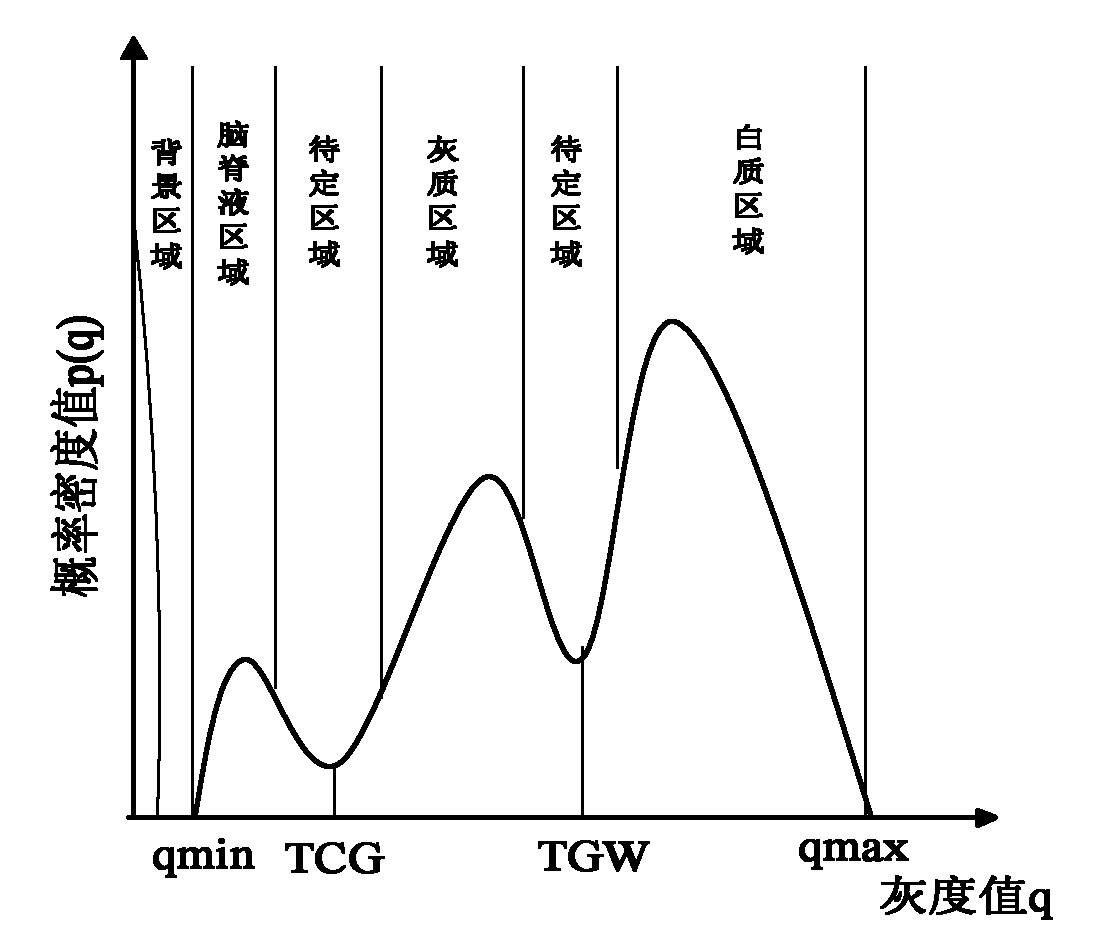
The invention relates to a KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting the grayscale nonuniformity of an MR (Magnetic Resonance) image, belonging to the field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly constructing a grayscale nonuniform field model by utilizing surface fitting knowledge and using a group of orthonormalization basis functions, and establishing energy functions; and then solving model parameters according to an energy function minimization principle to realize grayscale nonuniformity correction and image segmentation, wherein subordinate functions are solved by adopting an iterative algorithm and the KNN algorithm in the model parameter solving process, therefore a partial volume effect is greatly reduced while a grayscale nonuniform field is eliminated, and the influence of noises on the correction and the segmentation of the grayscale nonuniformity of the MR image is reduced. The subordinate functions are solved with KNN through the following steps of: firstly acquiring an accurate smooth normalization histogram by using a kernel estimation algorithm; then respectively solving a threshold value TCG between cerebrospinal fluids and gray matters and a threshold value TGW between the gray matters and white matters by using a maximum between-cluster variance method; carrying out rough sorting on the KNN sorting algorithm by utilizing the two threshold values; and finally accurately sorting points to be fixed by adopting the traditional KNN sorting algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Quantitative phantomless calibration of computed tomography scans
ActiveUS20140376701A1Improve consistencyEasily implemented clinicallyMedical automated diagnosisTomographySpinal columnComputed tomography
An apparatus, method, and computer program product for calibrating a CT scan without the use of an external calibration phantom, to enable quantitative assessment of internal body tissues and organs and additionally for any application that would benefit from a calibration of the scan attenuation data, such as viewing CT images in a consistent fashion. Embodiments are described with applications to quantitative assessment of bone density in the spine and hip, mineral content in blood vessels, hepatic-fat content in the liver, and gray-to-white matter ratio in the brain. The primary advantages of the method are that it does not require the use of an external calibration phantom, it is robust across different CT machines and scanner settings, and it is also highly precise, lending itself to a high degree of automation.
Owner:O N DIAGNOSTICS
Ultra-short time of echo magnetic resonance fingerprint relaxation time measuring method
ActiveCN110133553AImprove the ability to distinguishImprove Quantitative AccuracyMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrashort echo timeTime signal
The invention discloses an ultra-short time of echo magnetic resonance fingerprint relaxation time measuring method. According to the method, semi-pulse excitation and semi-projection readout are adopted to shorten TE to achieve acquisition of an ultra-short T2 time signal; and image acquisition and reconstruction are based on a magnetic resonance fingerprint imaging technology. A TE change mode of sinusoidal fluctuation is introduced, so that the distinguishing capability of a magnetic resonance fingerprint signal to short T2 and ultra-short T2 tissues is improved, and simultaneous multi-parameter quantitative imaging of the short T2 and ultra-short T2 tissues and long T2 tissues is realized. The non-uniformity of a magnetic field is modulated into phase information of the fingerprint signal through the TE of the sinusoidal fluctuation; a B0 graph is directly reconstructed according to an amplitude modulation signal demodulation principle; and the phase change caused by a B0 field iscompensated in the fingerprint signal, so that the accuracy of signal recognition is improved. In magnetic resonance skeletal muscle system imaging, simultaneous quantitative measurement of T1, T2, PDand B0 of the bone (ultra-short T2) and muscle (long T2) tissues can be realized; and the method can also be used for imaging the brain and measuring the grey / white matter relaxation time and the skull structure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
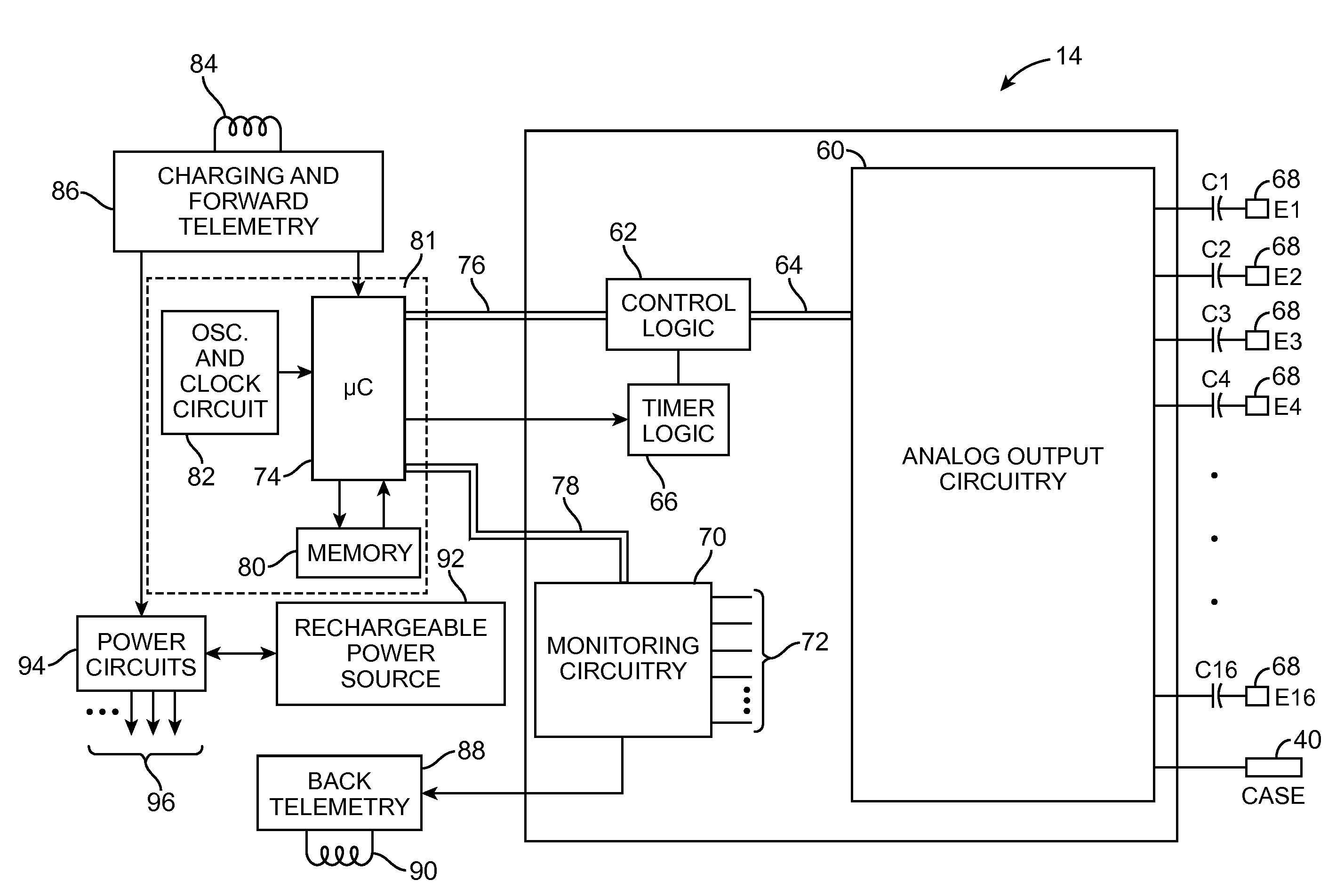
System and method for using impedance to determine proximity and orientation of segmented electrodes
ActiveUS20130006324A1Located very closeSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal cordTarget tissue
A method for implanting a neurostimulation lead within a patient includes measuring impedances of electrodes on the lead in order to correctly position the lead relative to a target tissue region. The electrodes are circumferentially segmented electrodes that are spaced from each other about the longitudinal axis of the lead. When the difference between the impedances of the electrodes exceeds a threshold value, the lead is in the correct position. In accordance with another embodiment, impedance measurements are used to select which one of the electrodes is closest to the target tissue region. By determining which electrode has the highest impedance and which electrode has the lowest impedance, the type of tissue adjacent to each electrode can be determined based on the conductivity properties of the tissue. The target tissue region may be a spinal cord, a posterior longitudinal ligament, white matter, or gray matter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Automatic tract extraction via atlas based adaptive connectivity-based clustering
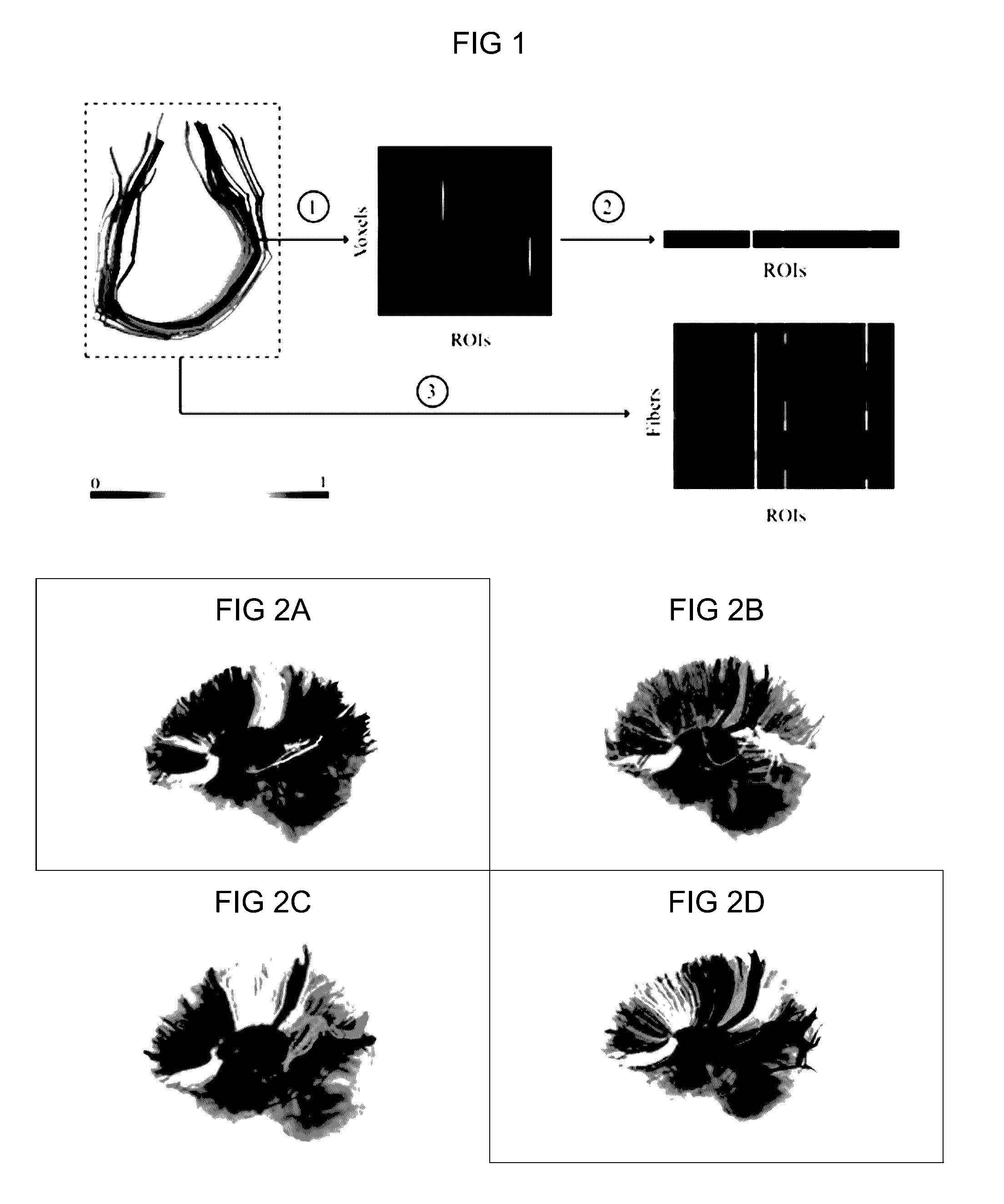
Method and apparatus for processing diffusion data for identification of white matter tracts in the brain of a patient is provided herein. The method involves, with a processor: generating a connectivity based representation of white matter fibers for multiple different subjects from the connectivity signatures of the fibers from a diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) without using the physical coordinates of the fibers; generating a fiber bundle atlas from the connectivity based fiber representation of (a) which define a model of the human brain; adaptively clustering fibers of a new patient utilizing the fiber bundle atlas of (b) to extract white matter tracts without manual intervention in the form of drawing regions of interest; and presenting the selected white matter tracts and diffusion data in a report or on a display device. This method and apparatus can be used even for patients having edema or brain perturbations.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Additive for crack self-repairing cement-base material, use method thereof and cement-base material
The invention provides an additive for a crack self-repairing cement-base material, a use method thereof and a cement-base material. The additive is composed of bacterial mud which is obtained by centrifuging 270-500g of carriers, 5-10g of calcium lactates and 100mL of bacterial liquid, wherein the bacterial liquid is obtained by inoculating bacterial strains, namely, Bacillus halodurans, to a culture medium for culturing according to a conventional method; the density of thallus contained in the bacterial liquid is (5-6)*106 pieces per mL; the carrier is slag or ceramsite; the calcium lactates are prepared into an aqueous solution with the weight percent of 1% and then are added; according to the cement-base material based on the additive for the crack self-repairing cement-base material, the weight of the additive is 20%-40% of the total weight of the cement plaster and additive; after the additive is cured for 24h, the additive is soaked in constant-temperature oxygen enrichment water bath at 30 DEG C; after 5 days, few white matters are generated in a crack; and after 40 days, the crack is fully filled, so that the crack is completely repaired.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
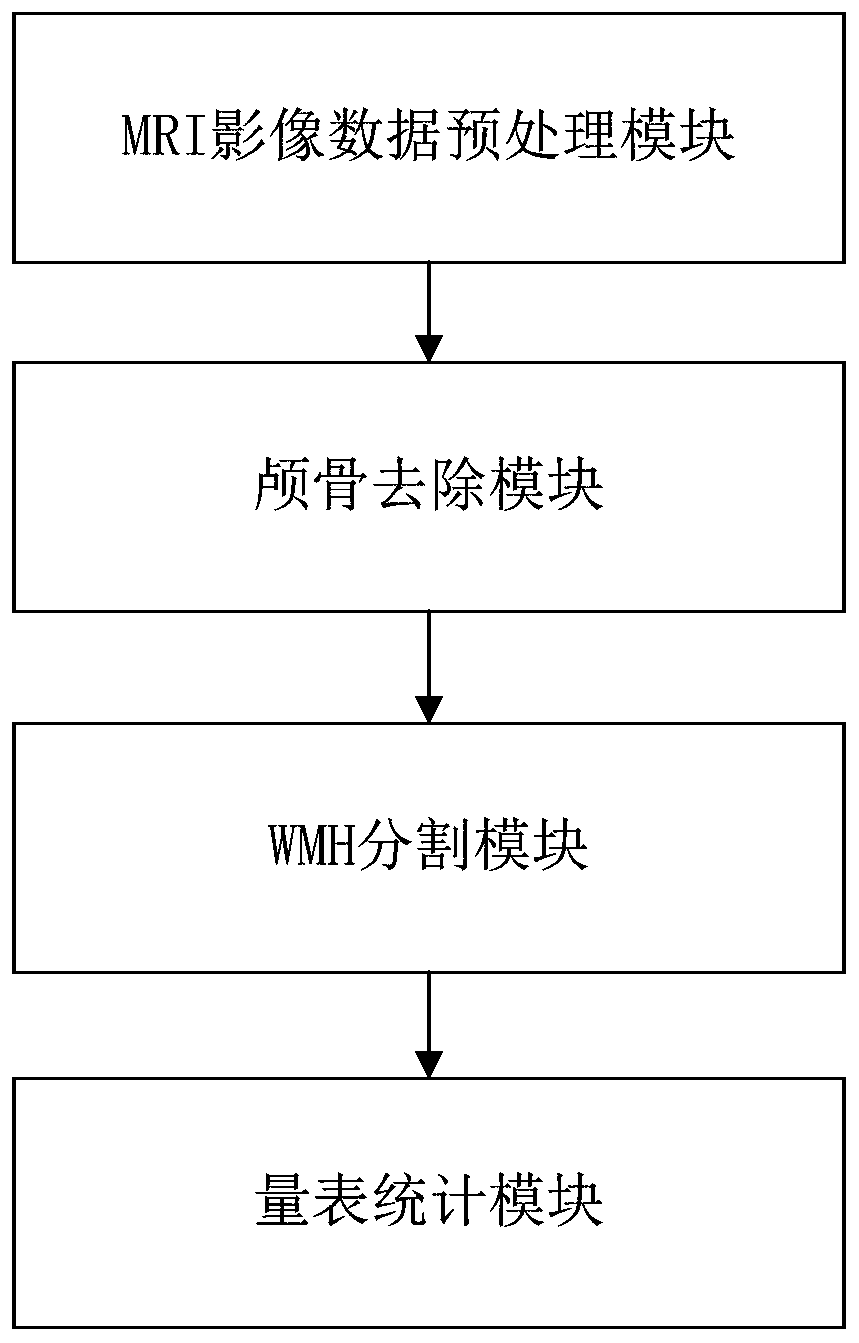
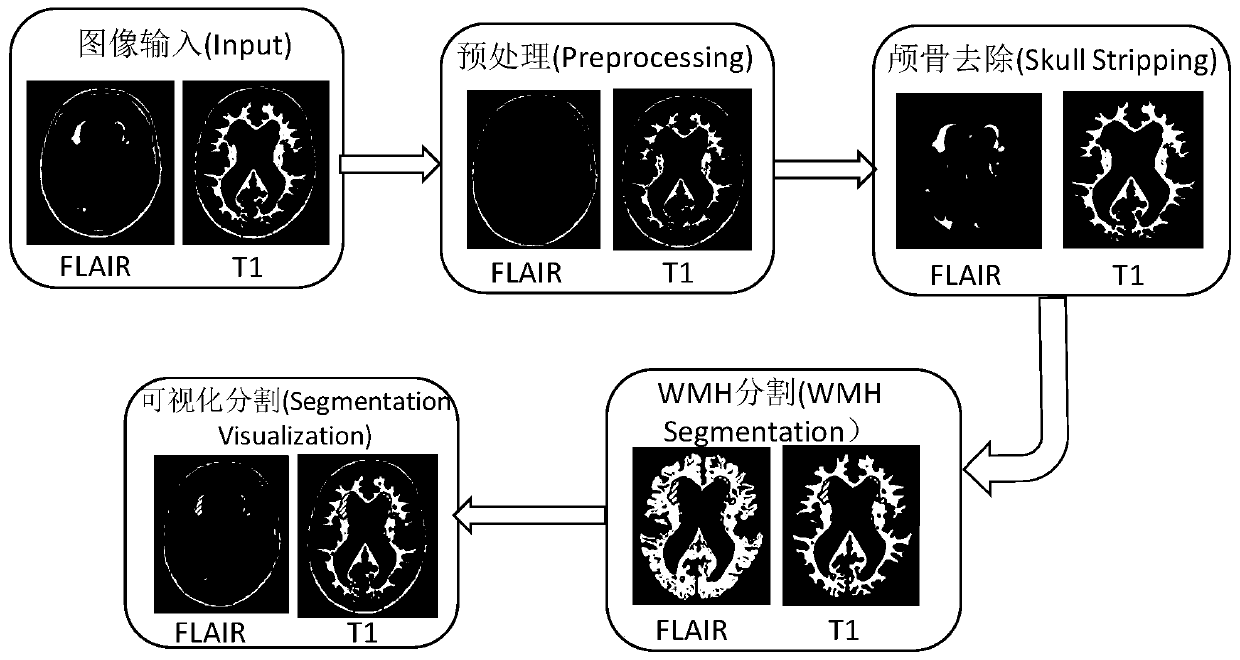
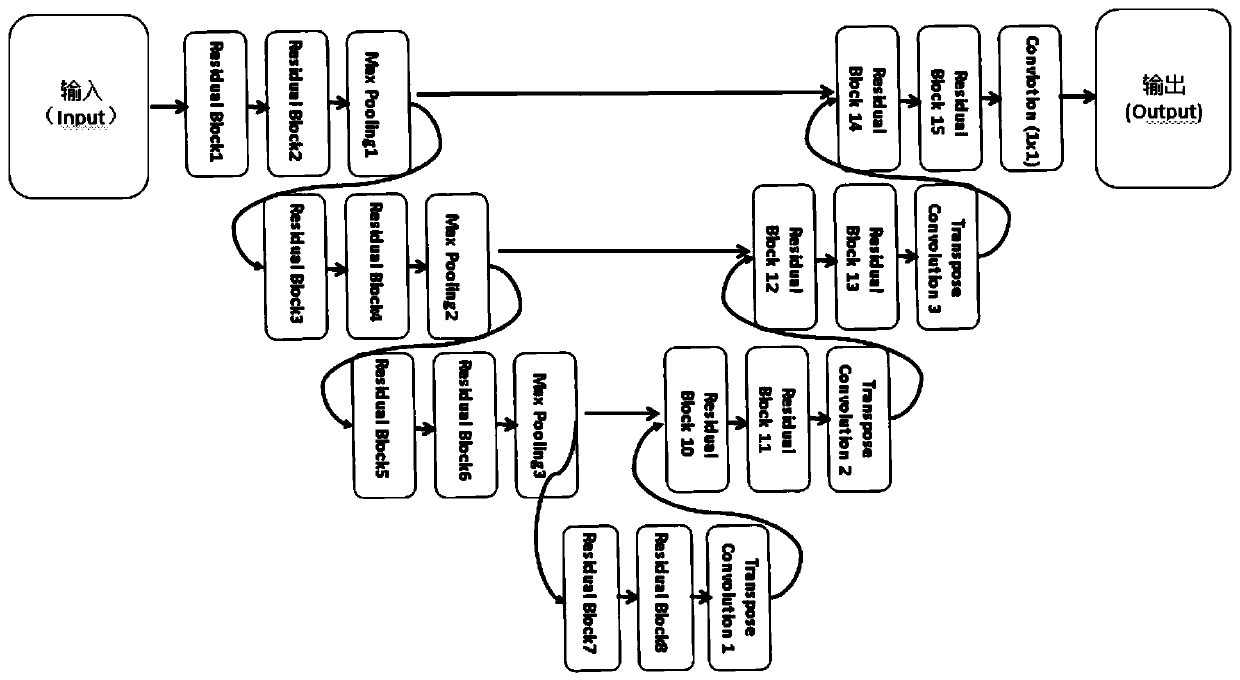
White matter hyperintensities automatic segmentation system and method based on Unet model
ActiveCN109859215AFast Auto SegmentationTime consuming to solveImage analysisAutomatic segmentationNetwork model
The invention discloses a white matter hyperintensitiesl automatic segmentation system and method based on a Unet model, and the system comprises an MRI image preprocessing module which is used for carrying out the normalization of inputted MRI image data, and removing the noise interference; a skull removing module which is used for removing the skull in the image by utilizing a skull removing algorithm so as to remove a non-brain tissue part and further remove noise interference; and a WMH segmentation module which is used for reading the MRI image data processed by the skull removal module,converting the MRI image data into image information data, transmitting the image information data to the neural network model for segmentation result prediction, and outputting an accurate segmentation result. By adopting the method, the WMH region can be automatically segmented by applying a deep learning algorithm in the process of automatically processing the image, so that the white matter hyperintensities focus of magnetic resonance imaging can be quantitatively and efficiently distinguished, and the aims of reducing the workload of doctors and facilitating subsequent diagnosis and research are fulfilled.
Owner:北京慧脑云计算有限公司
Automated fiber tracking of human brain white matter using diffusion tensor imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a MRI scanner; a signal processing system in communication with the magnetic resonance imaging scanner to receive magnetic resonance (MR) signals for forming magnetic resonance images of a subject under observations; a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit contains database data corresponding to a soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The database data includes information identifying at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The signal processing system is adapted to process MR signals received from the MRI scanner to automatically identify at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
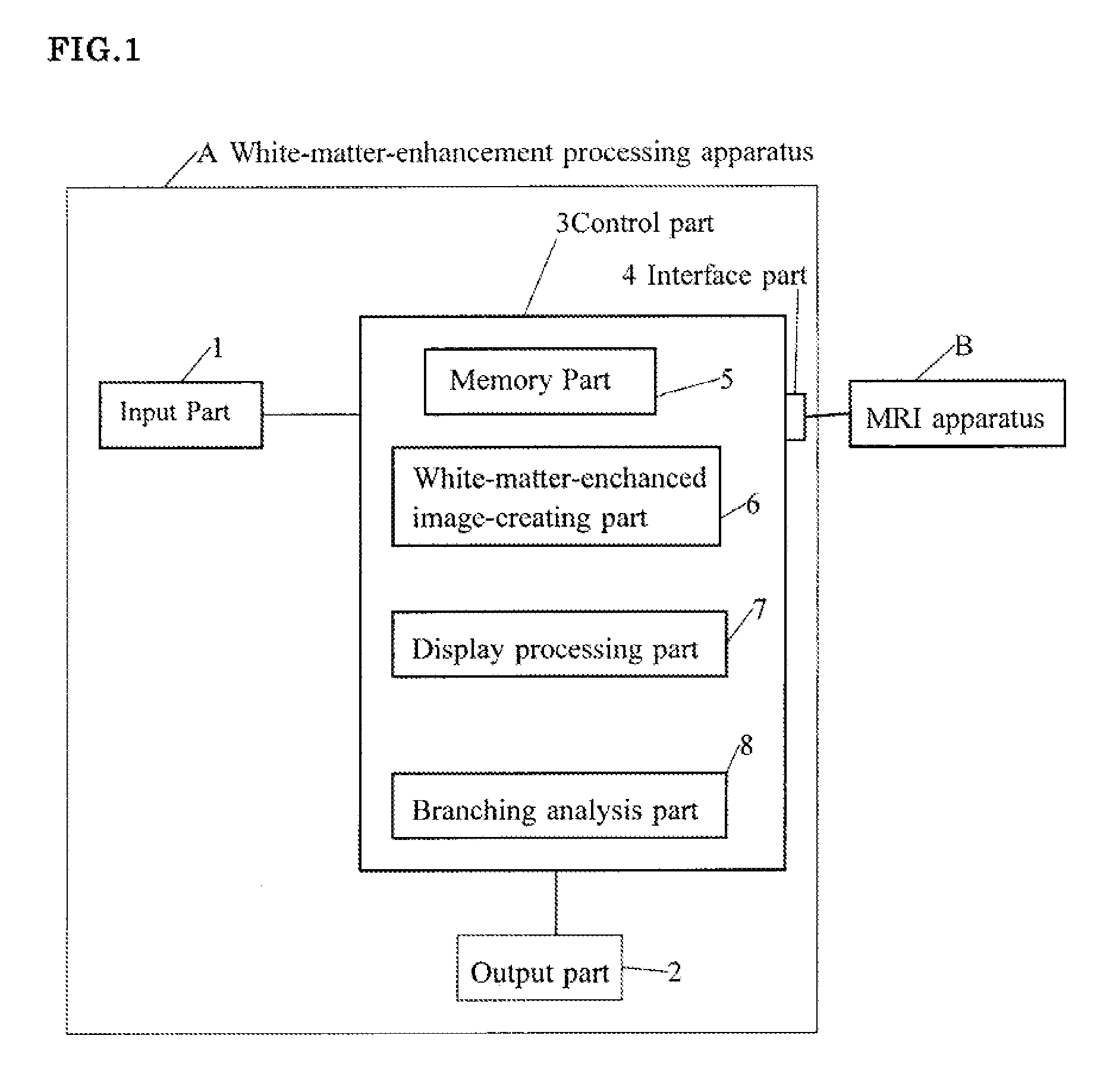
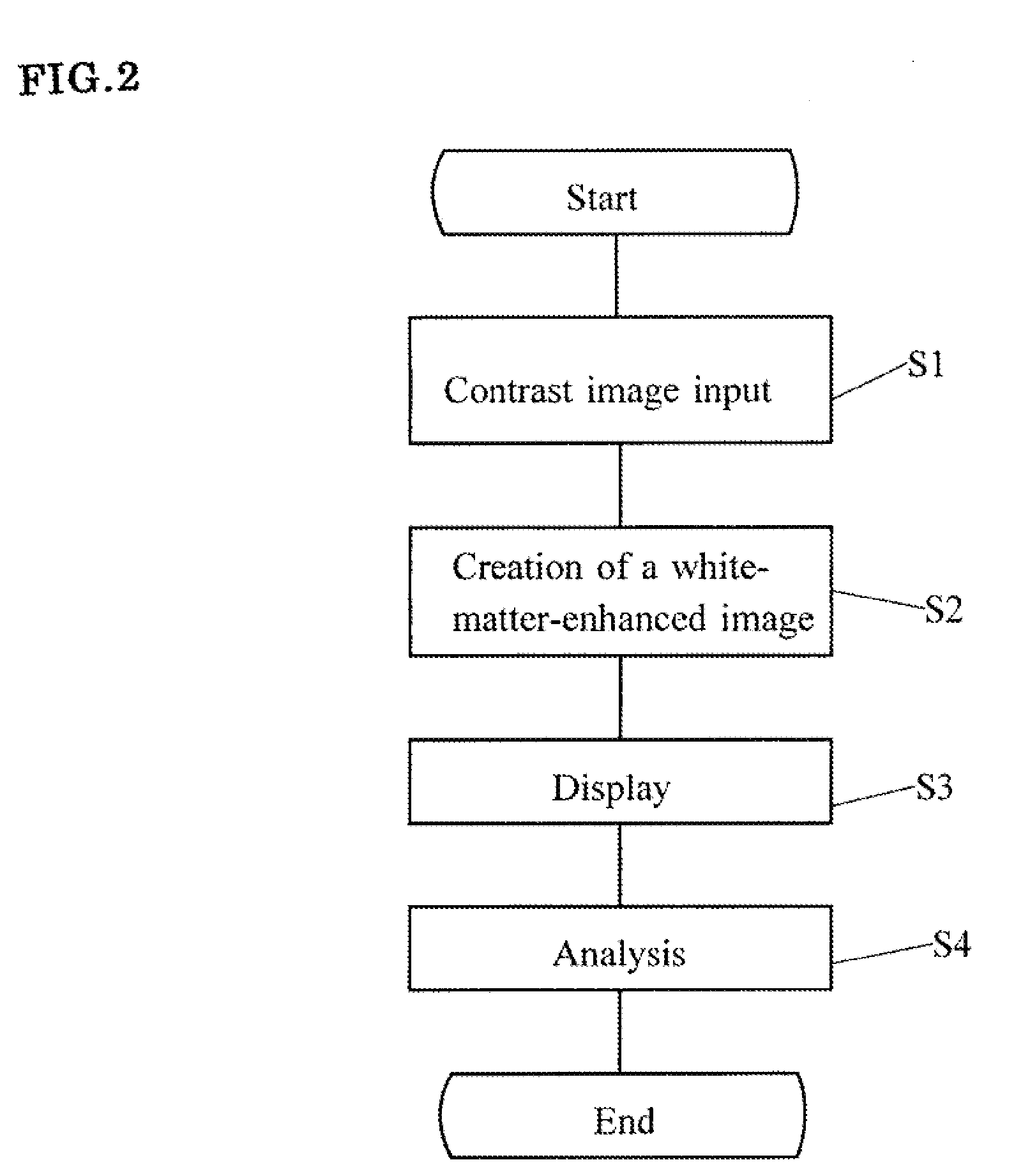
Apparatus for white-matter-enhancement processing, and method and program for white-matter-enhancement processing
The present invention provides an apparatus for white-matter-enhancement processing, and a method and a program for white-matter-enhancement processing that makes it possible to analyze distinguishing characteristics of the brain of a living body, such as degree of growth and development, left / right brain dominance, areas of strength and weakness, and personality traits. The apparatus for white-matter-enhancement processing of the present invention has a memory part for inputting and storing contrast images of a brain of a living body; a white-matter-enhanced image-creating part for creating white-matter-enhanced images, based on stored contrast images; a display processing part for displaying the white-matter-enhanced images thus created; and a branching analysis part for analyzing distinguishing characteristics of the brain of a living body, based on any one of or a combination of the characteristics of branches in the white-matter-enhanced images that are created: their number, thickness, length, location, intensity, shape and / or size.
Owner:KATO
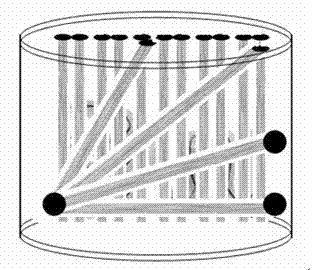
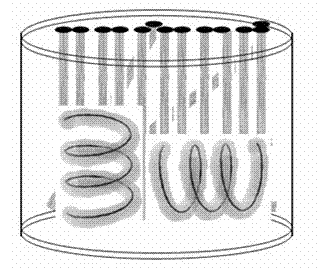
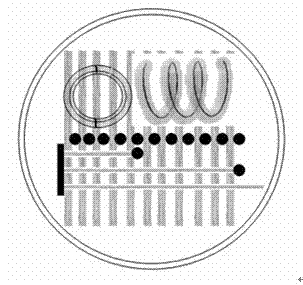
Comprehensive test phantom for controlling quality of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN102334991AAchieve precisionAchieve image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityLong axis
The invention discloses a comprehensive test phantom for controlling the quality of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging, which comprises a casing, wherein a test layer is arranged in the casing and is filled with a test solution. The comprehensive test phantom is characterized by further comprising a fiber bundle test region, a human brain simulation test region and a basic imaging quality test region; a fiber bundle test layer comprises three groups: the first group comprises two fiber bundle groups, wherein each group of fiber bundles is positioned on the same plane; the second group is a fiber bundle group; an included angle is formed between a straight line where each fiber bundle is positioned and a long axis of the phantom casing; the third group comprises helix tubes; and fiber bundles are arranged in the helix tubes. Compared with the prior art, the comprehensive test phantom has the advantages of multiple test parameters, high precision, high simulation degree of white matters of human brain and convenience for use.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
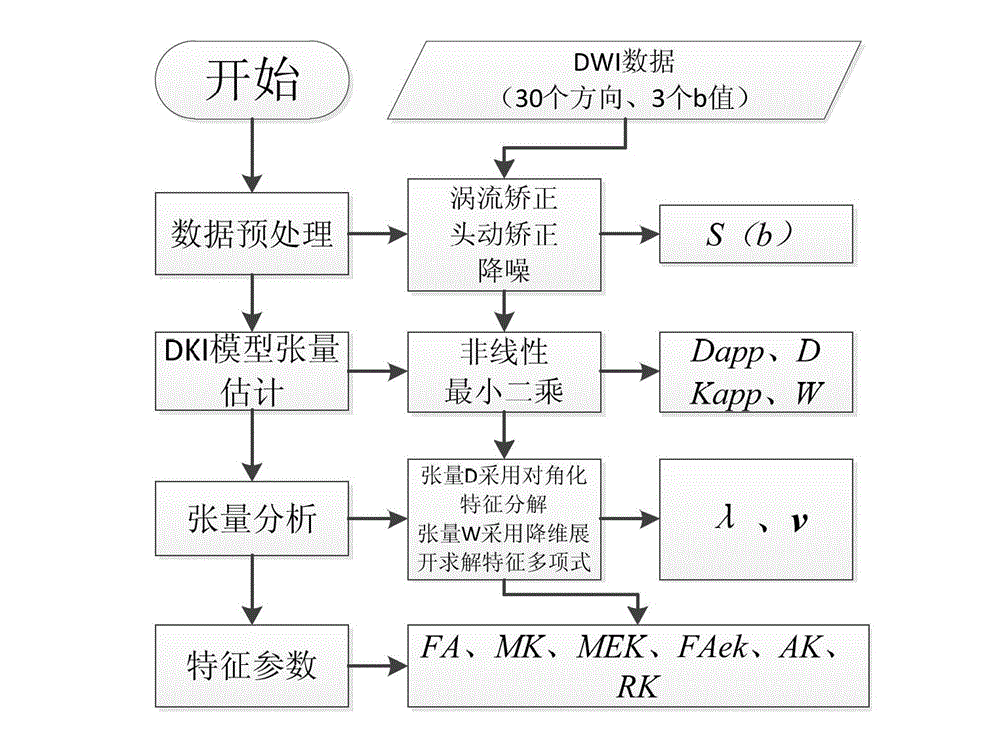
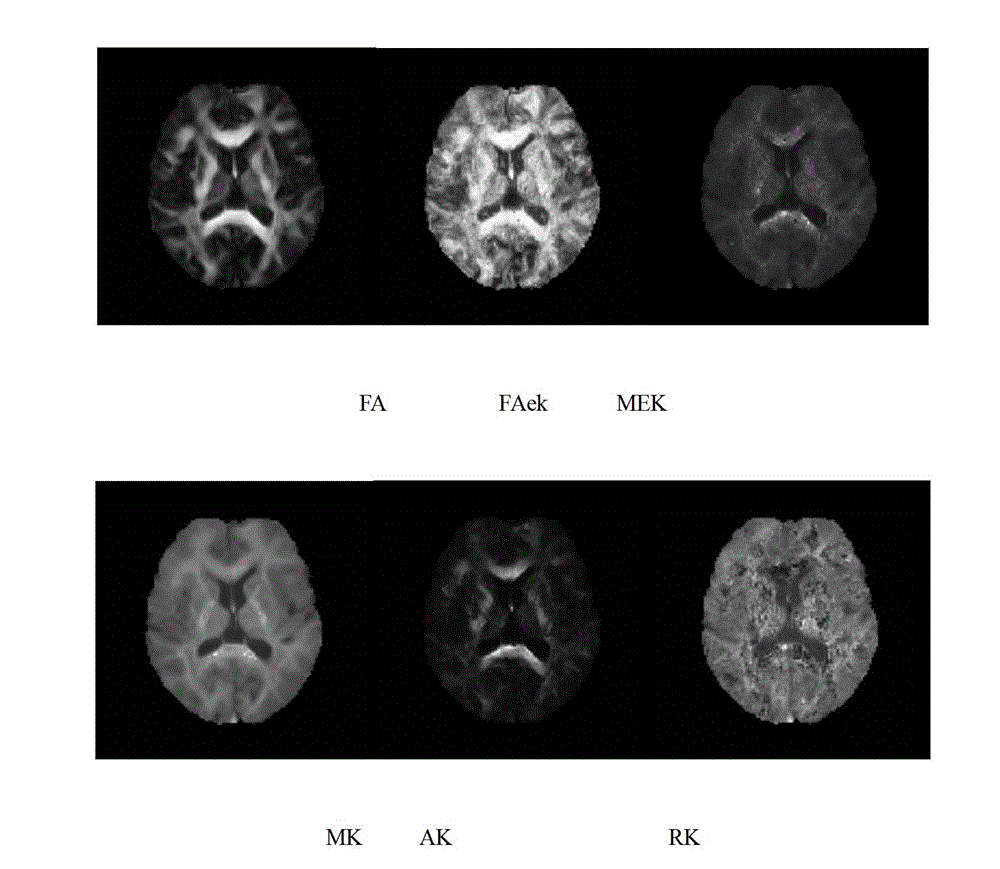
Method for extracting high-order tensor characteristic parameters of diffusion kurtosis tensor imaging
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, provides a novel practical method for extracting MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) parameters of structural abnormality of white matters of a human brain, and aims to achieve the purpose of objectively evaluate the lesion degree by analyzing anisotropy of tissues through a certain characteristic extraction method. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the method for extracting high-order tensor characteristic parameters of diffusion kurtosis tensor imaging comprises the following steps: a subject collects diffusion weighted signals of tissues along a plurality of directions on a magnetic resonance scanner, then a second-order or fourth-order tensor that reflects diffusion and distribution probability density function of water molecules in the tissues can be obtained through fitting, and lesion characteristics of diffusion and distribution abnormality of the water molecules, caused by structural abnormality of the tissues, can be obtained through certain tensor analysis, wherein parameters from two different angles, including diffusion coefficient and kurtosis coefficient, are mainly included. The invention is mainly applied to design and manufacture of medical instruments.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
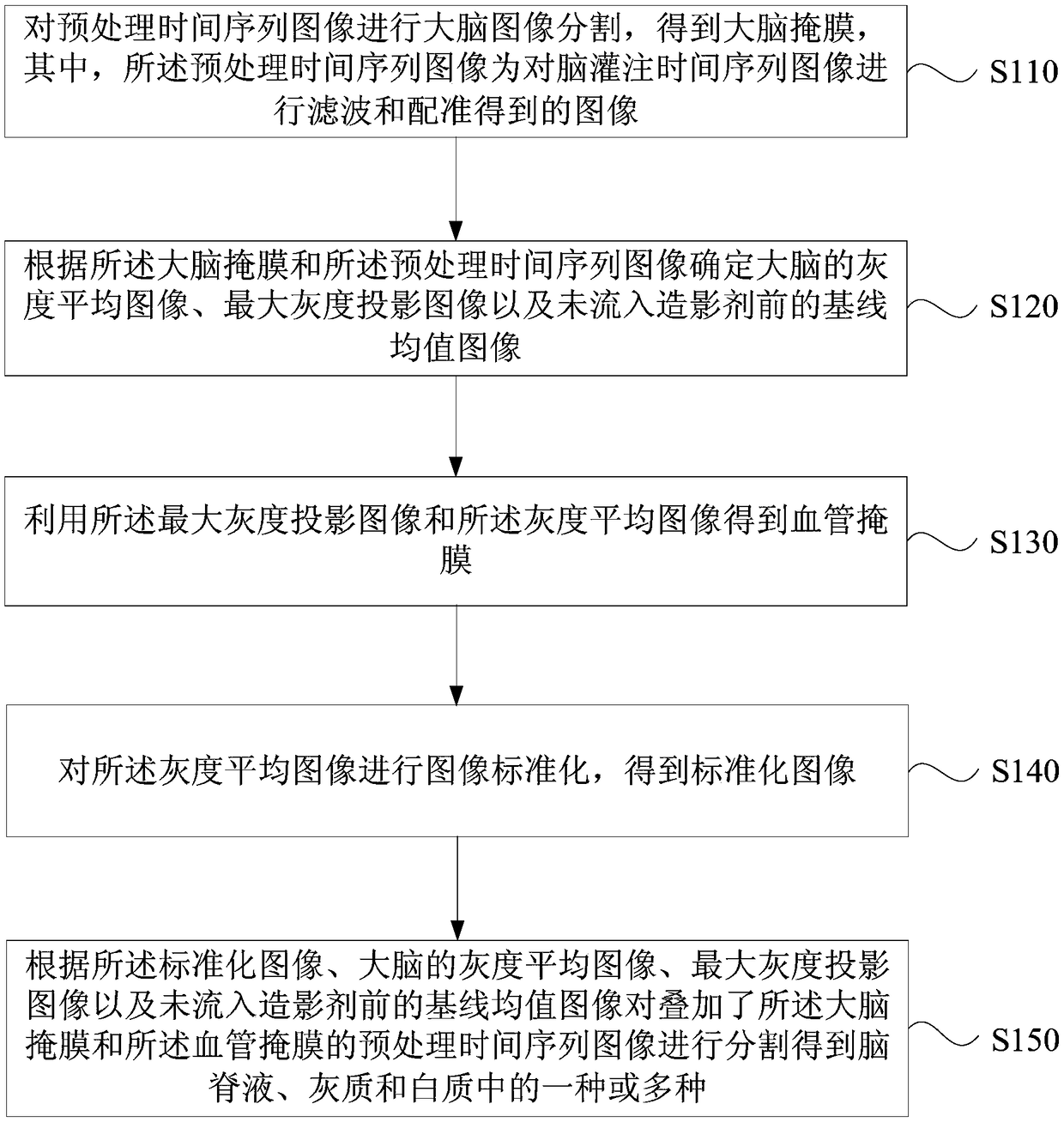
Brain perfusion image segmentation method and device, server and storage medium
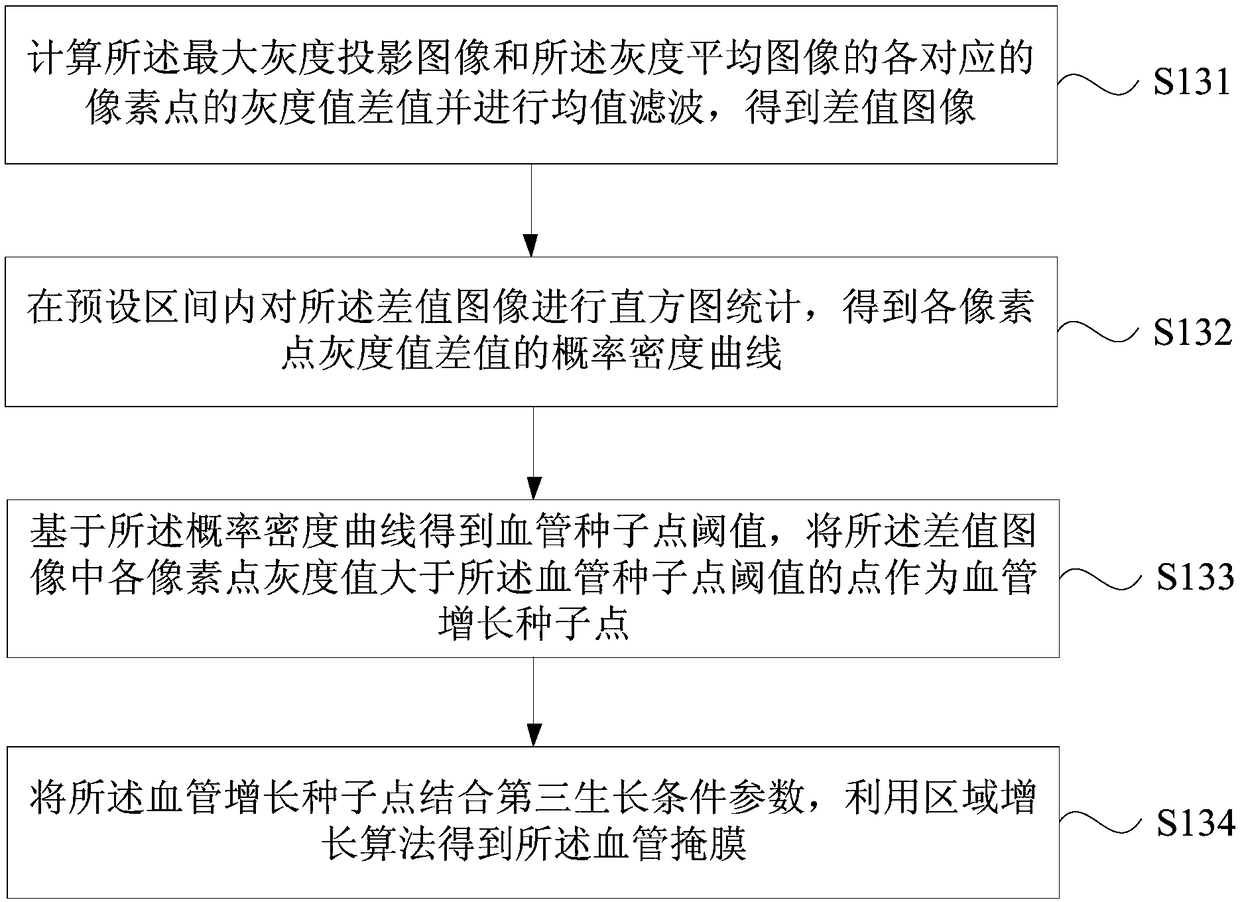
ActiveCN109410221ASolve the problem of poor edge segmentationAchieve precise segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPerfusionWhite matter
The embodiment of the invention discloses a brain perfusion image segmentation method and device, a server and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: performing brain image segmentation on a pre-processed time sequence image to obtain a brain mask; determining a feature image according to the brain mask and the pre-processing time sequence image; Using the maximum gray scale projection image and the gray scale average image in the feature image to obtain a blood vessel mask; performing image standardization on the gray average image to obtain a standardized image; and segmenting the pre-treatment time sequence image superposed with the brain mask and the blood vessel mask according to the standardized image, the gray average image of the brain, the maximum gray projection image and the baseline mean value image before flowing into the contrast agent to obtain one or more of cerebrospinal fluid, gray matter and white matter. According to the embodiment of the invention, the problem of poor edge segmentation effect of different brain tissues segmented by the brain perfusion image in the prior art is solved, and the accurate segmentation of different brain tissuesin the brain perfusion image and the automation of image processing are realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method for treating neurological /psychiatric disorders with stimulation to the subcaudate area of the brain
A method for treating a patient with a neurological or psychiatric disorder, comprising applying stimulation to at least a portion of the patient's subcaudate white matter of the subcaudate area under conditions effective to provide the patient with at least a partial relief from the neurological or psychiatric disorder. The stimulation may be electrical and / or pharmacological.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com