Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
910 results about "Mr imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
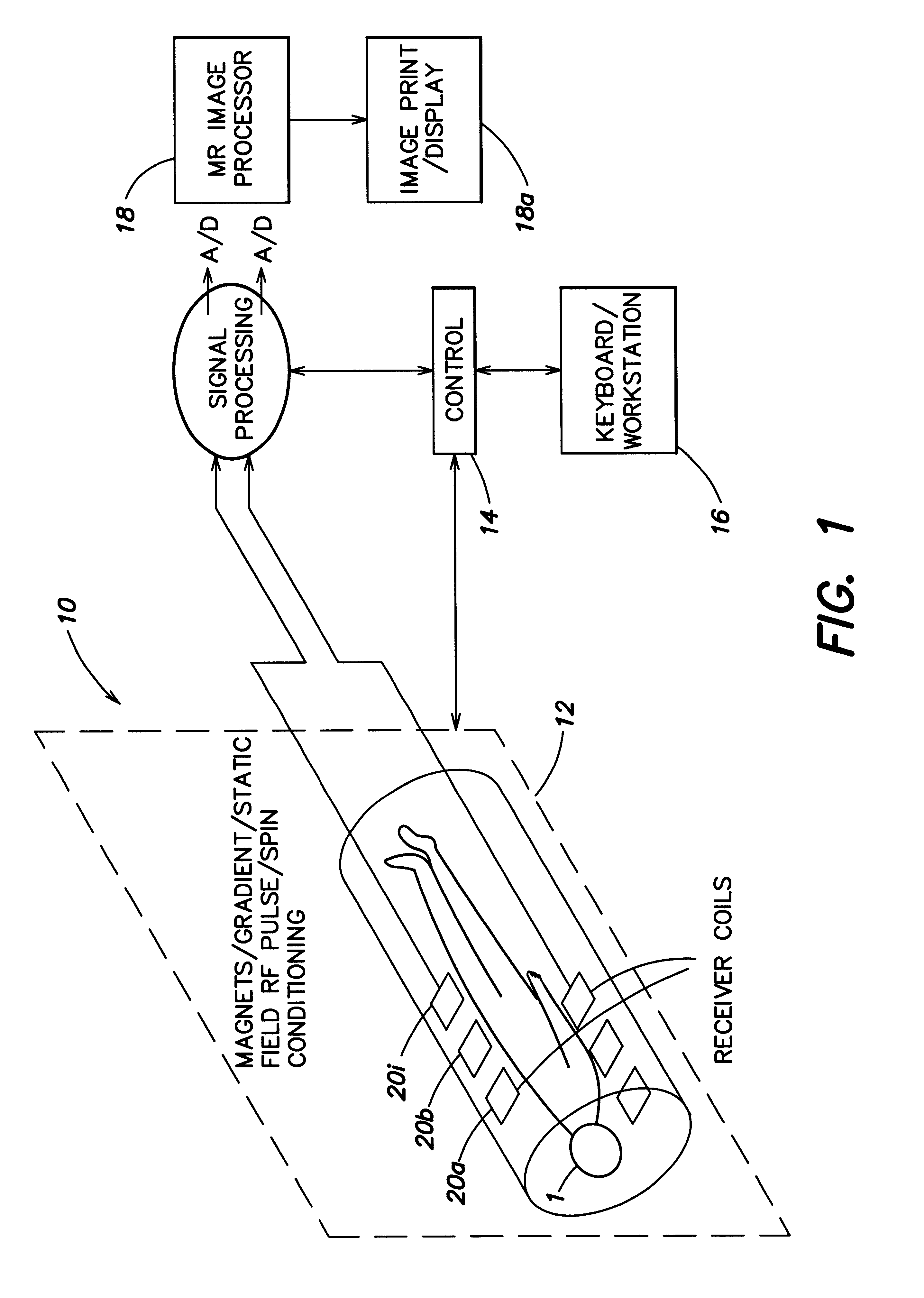
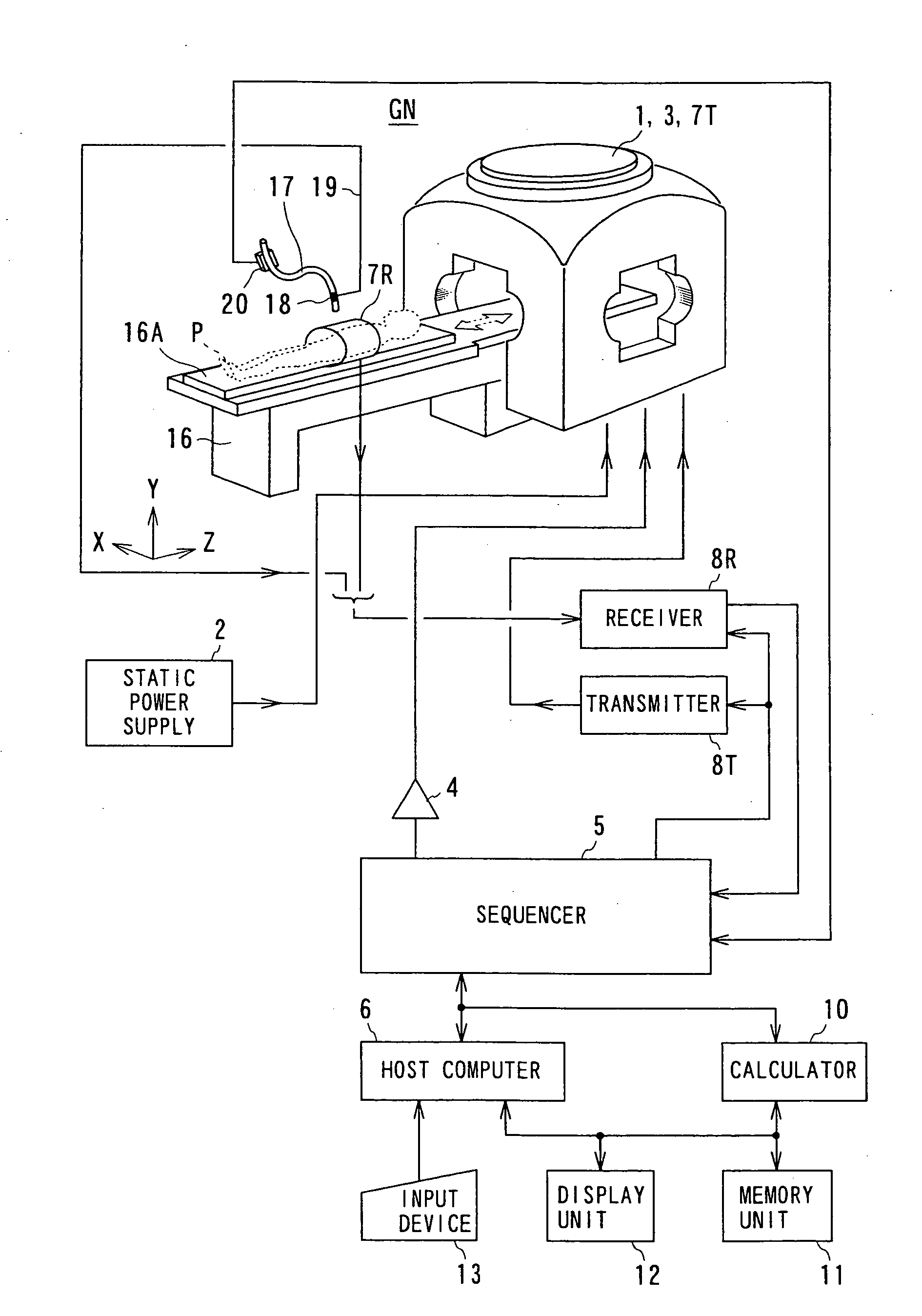
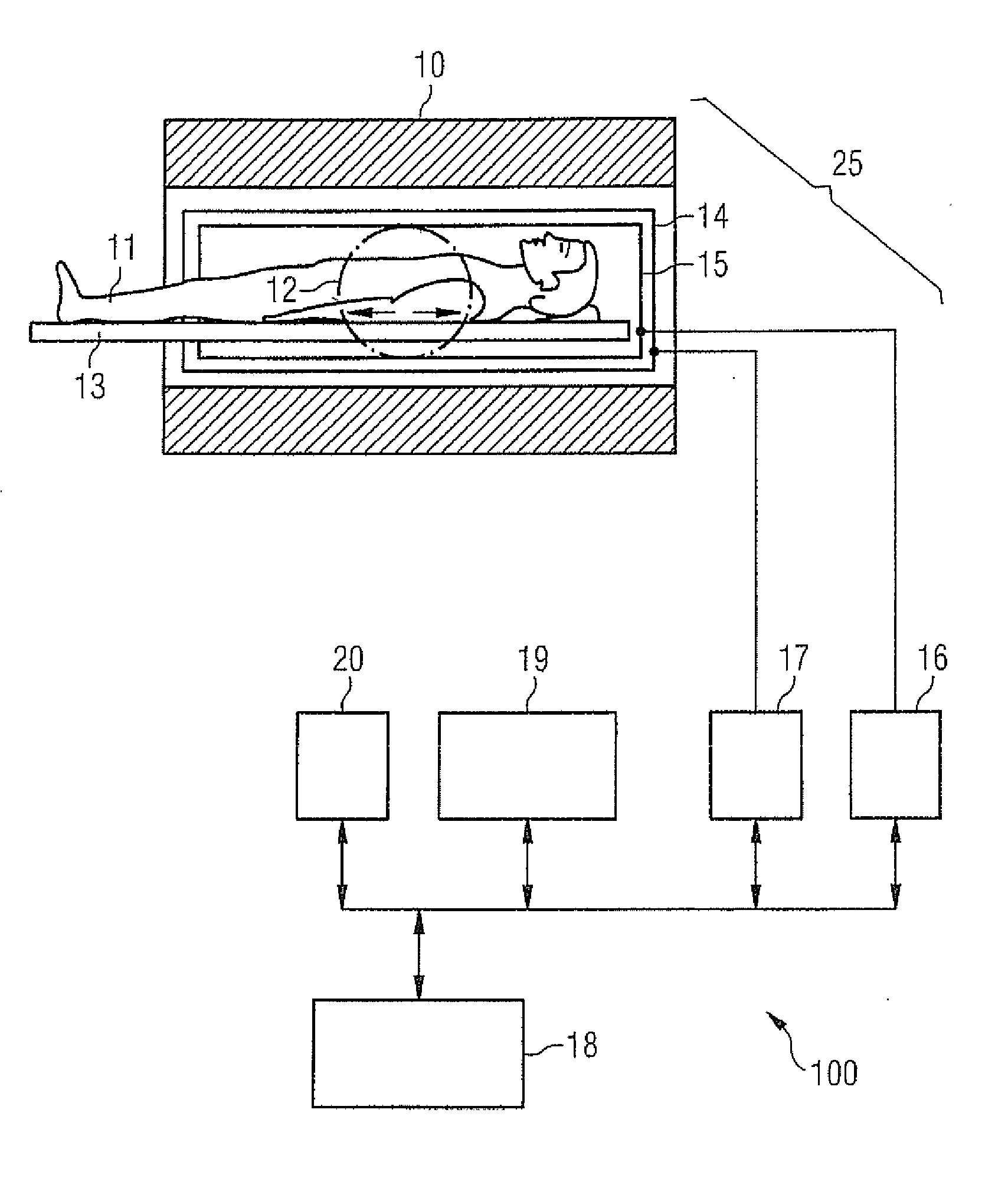
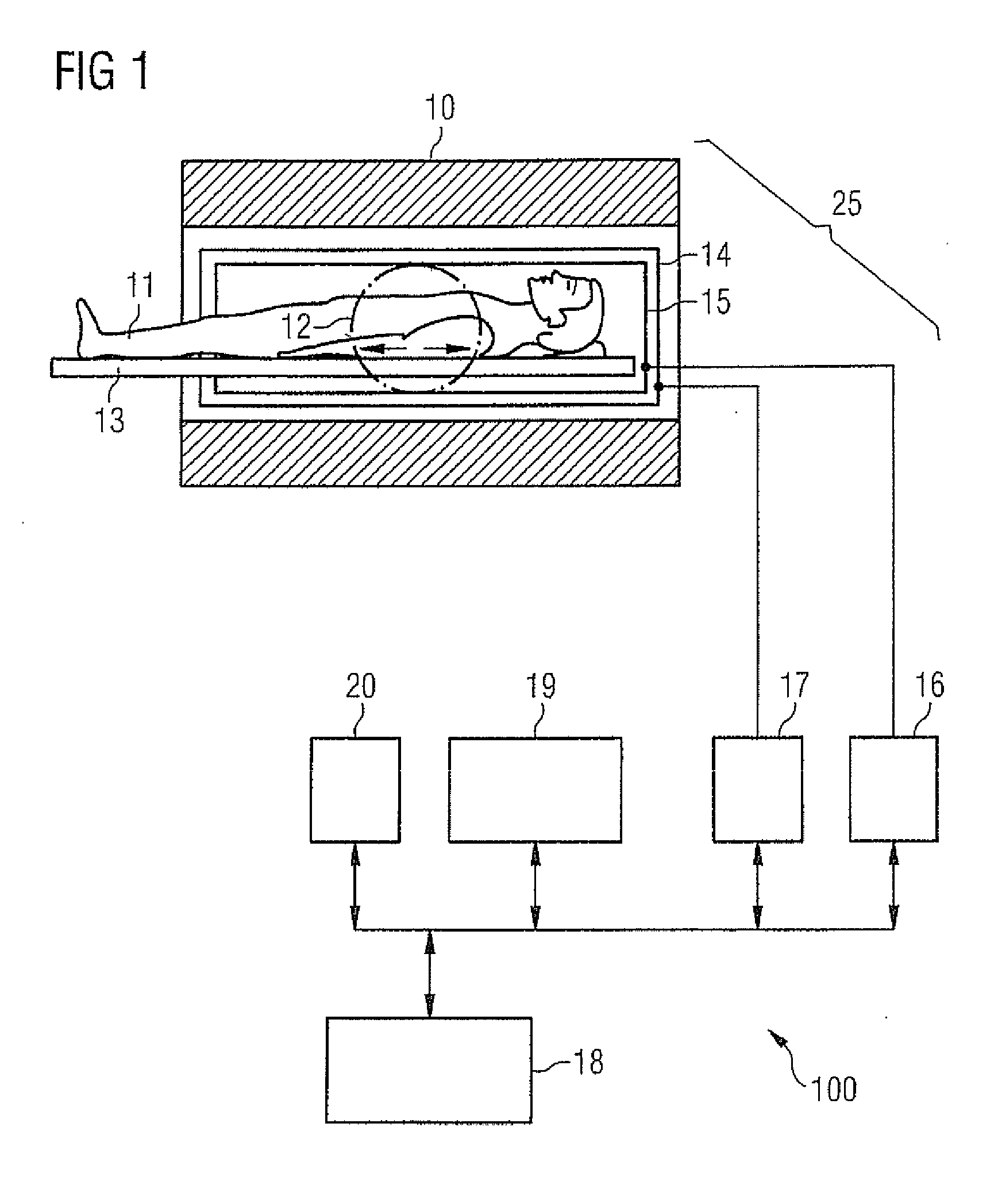
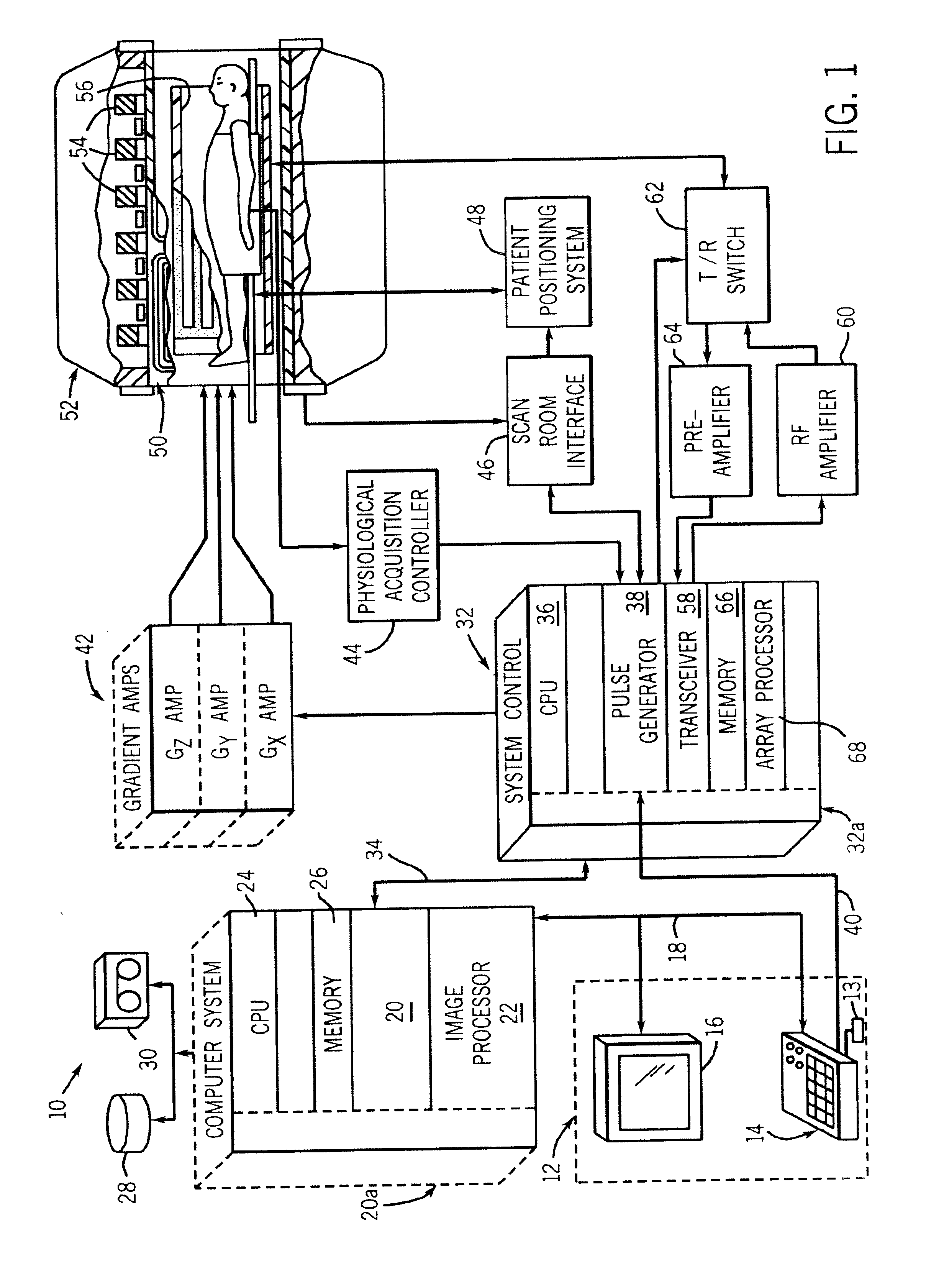
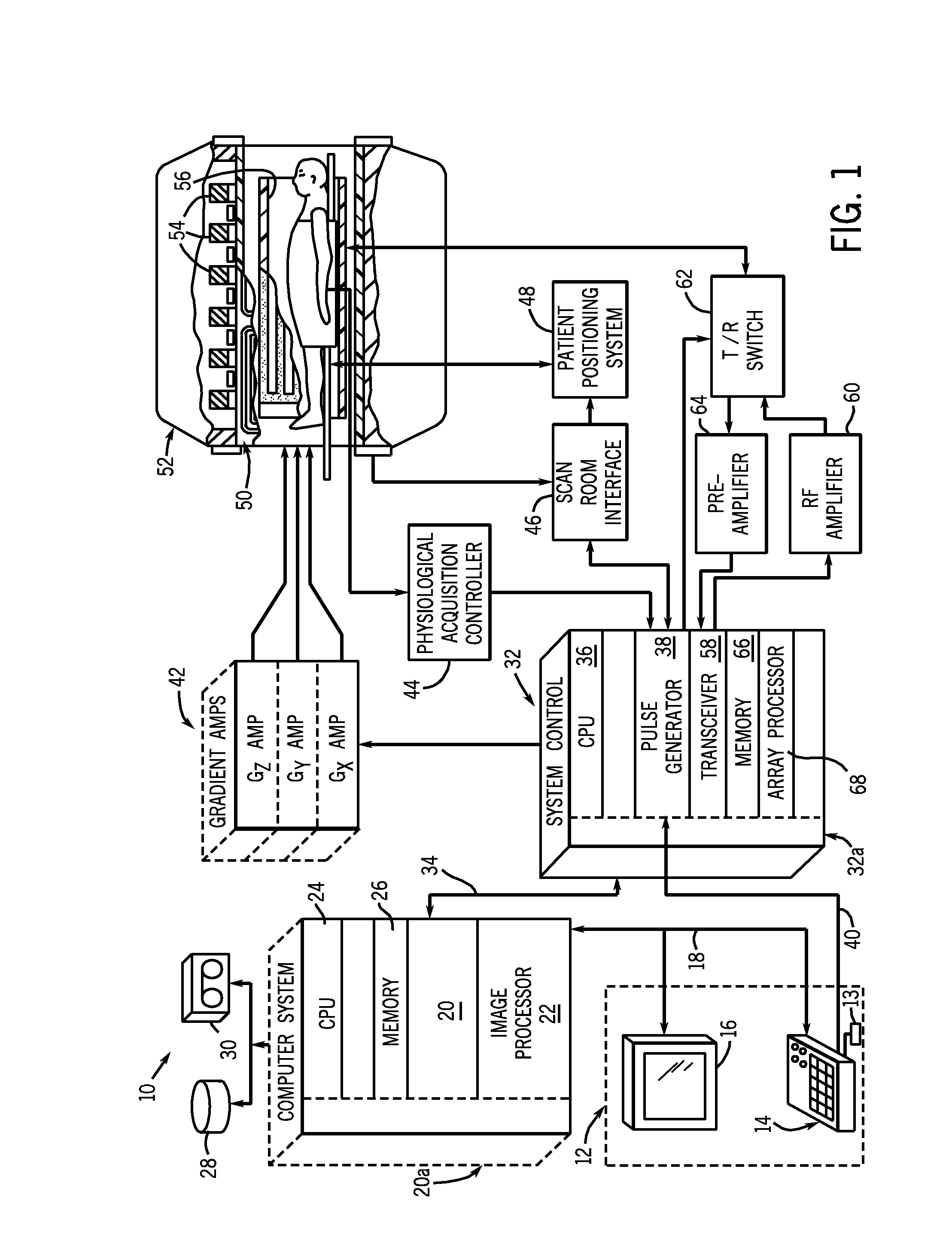
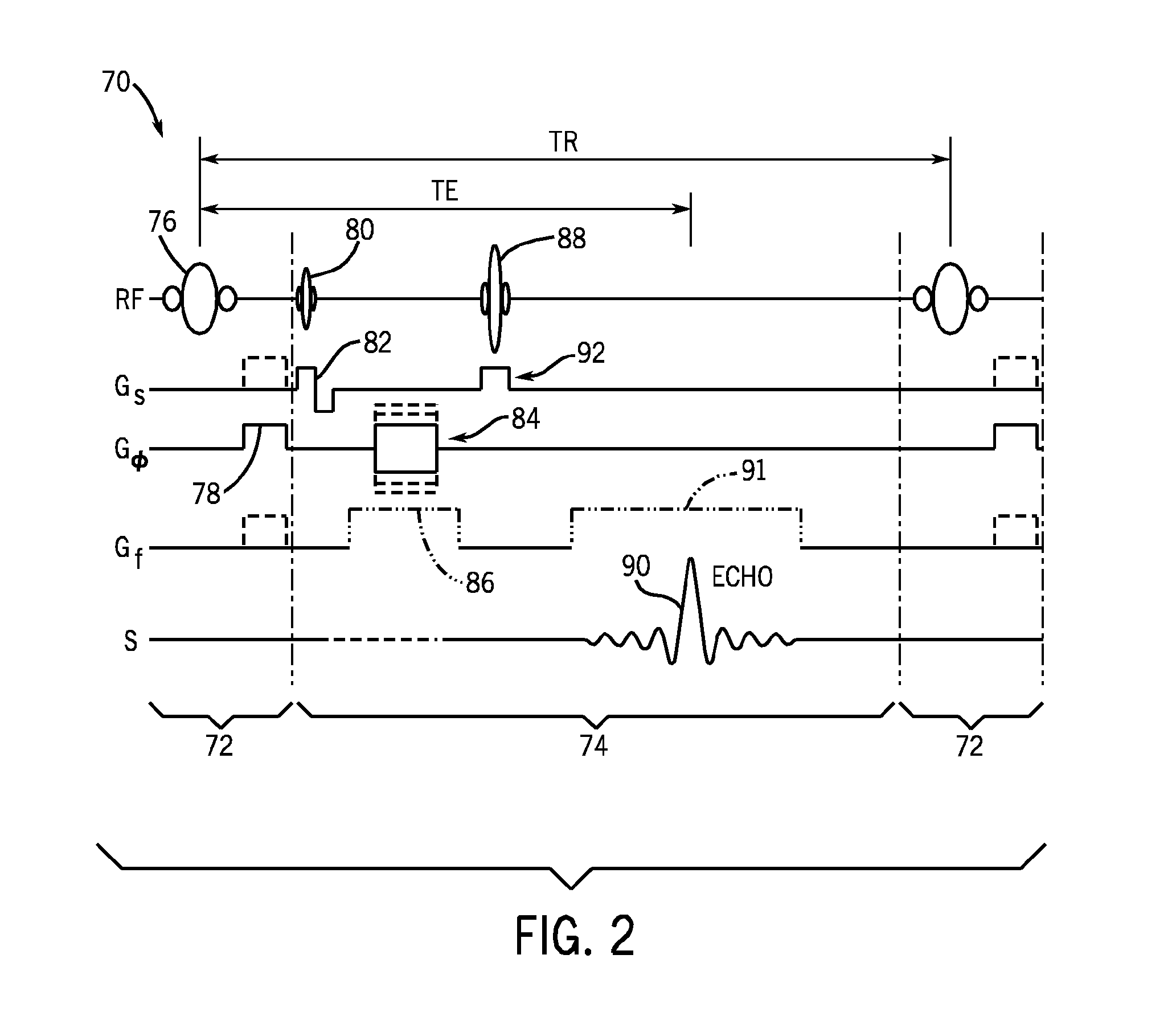
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has become established as a diagnostic and research tool in many areas of medicine because of its ability to provide excellent soft-tissue delineation in different areas of interest.
MR imaging method and medical device for use in method
InactiveUS6847837B1Precise positioningEasy flow measurementStentsDiagnostic recording/measuringImage resolutionResonance
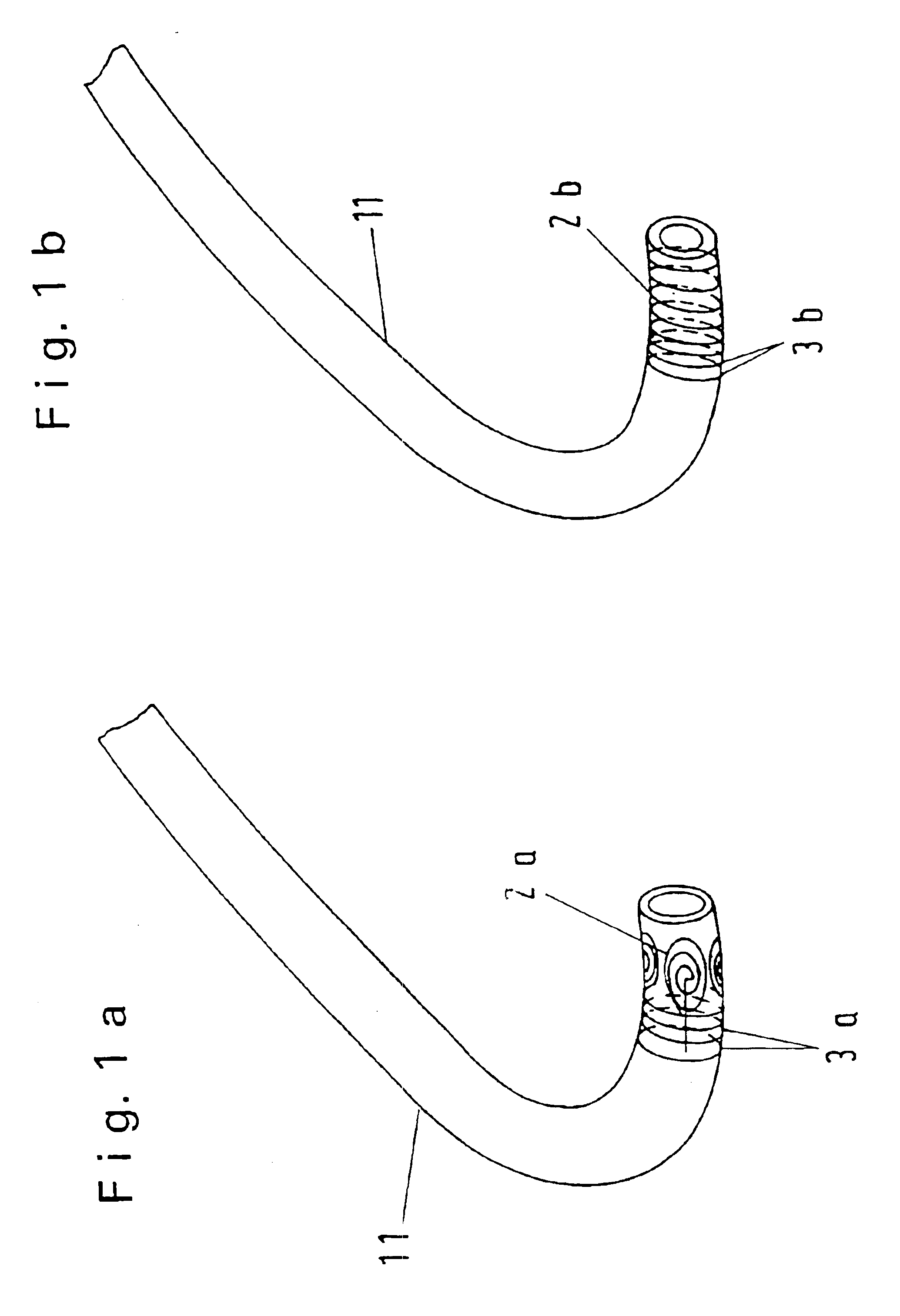
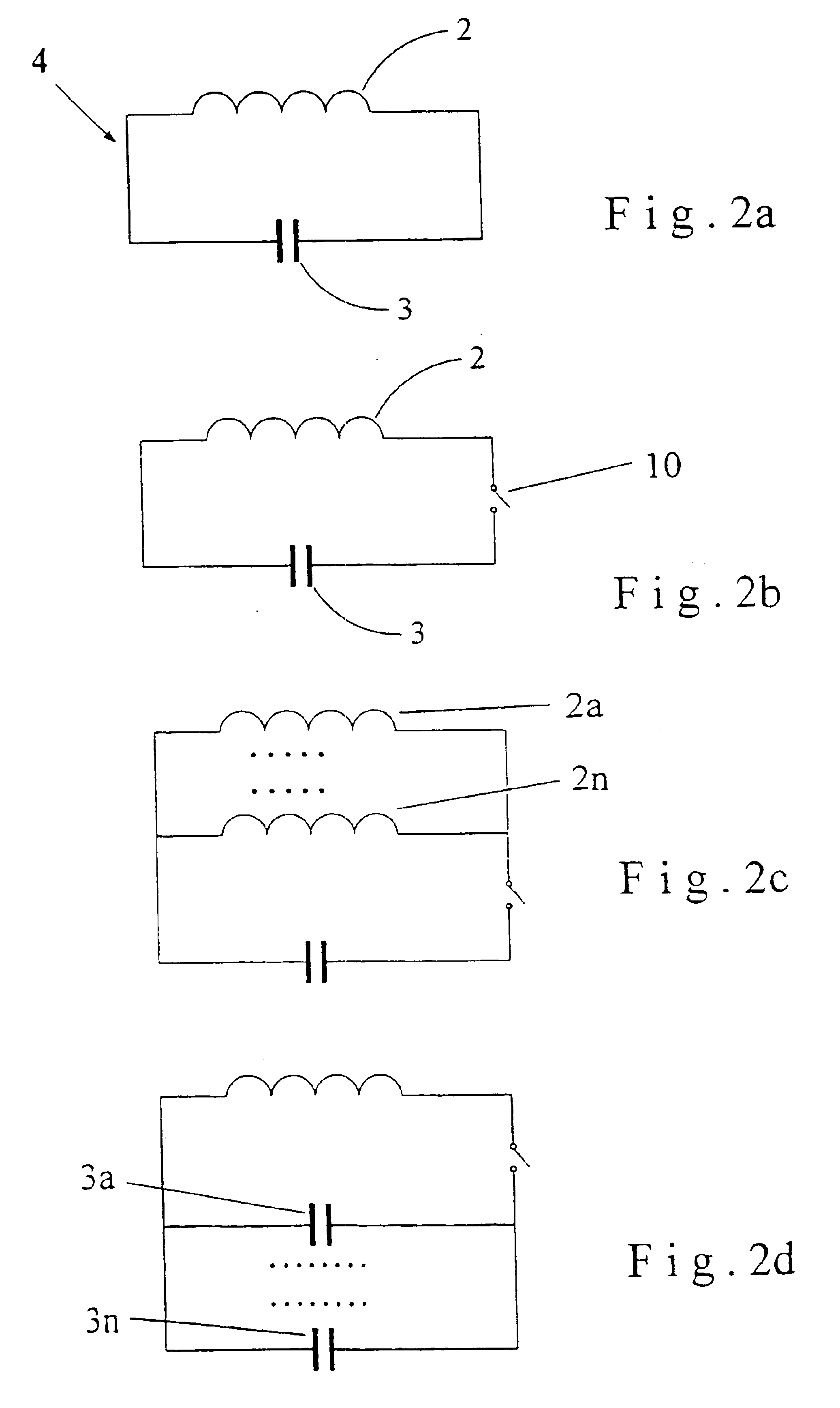
The invention relates to an MR imaging method for representing and determining the position of a medical device inserted in an examination object, and to a medical device used in the method. In accordance with the invention, the device (11) comprises at least one passive oscillating circuit with an inductor (2a, 2b) and a capacitor (3a, 3b). The resonance frequency of this circuit substantially corresponds to the resonance frequency of the injected high-frequency radiation from the MR system. In this way, in a locally limited area situated inside or around the device, a modified signal answer is generated which is represented with spatial resolution.
Owner:AMRIS PATENTE VERW
Hybrid imaging method to monitor medical device delivery and patient support for use in the method
ActiveUS20050080333A1Easy procedureConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesStretcherLiver and kidneySurgical removal
This invention discloses a method and apparatus to deliver medical devices to targeted locations within human tissues using imaging data. The method enables the target location to be obtained from one imaging system, followed by the use of a second imaging system to verify the final position of the device. In particular, the invention discloses a method based on the initial identification of tissue targets using MR imaging, followed by the use of ultrasound imaging to verify and monitor accurate needle positioning. The invention can be used for acquiring biopsy samples to determine the grade and stage of cancer in various tissues including the brain, breast, abdomen, spine, liver, and kidney. The method is also useful for delivery of markers to a specific site to facilitate surgical removal of diseased tissue, or for the targeted delivery of applicators that destroy diseased tissues in-situ.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Tomography-Based and MRI-Based Imaging Systems
InactiveUS20110142316A1Comparable image qualityImproved temporalReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisElastography
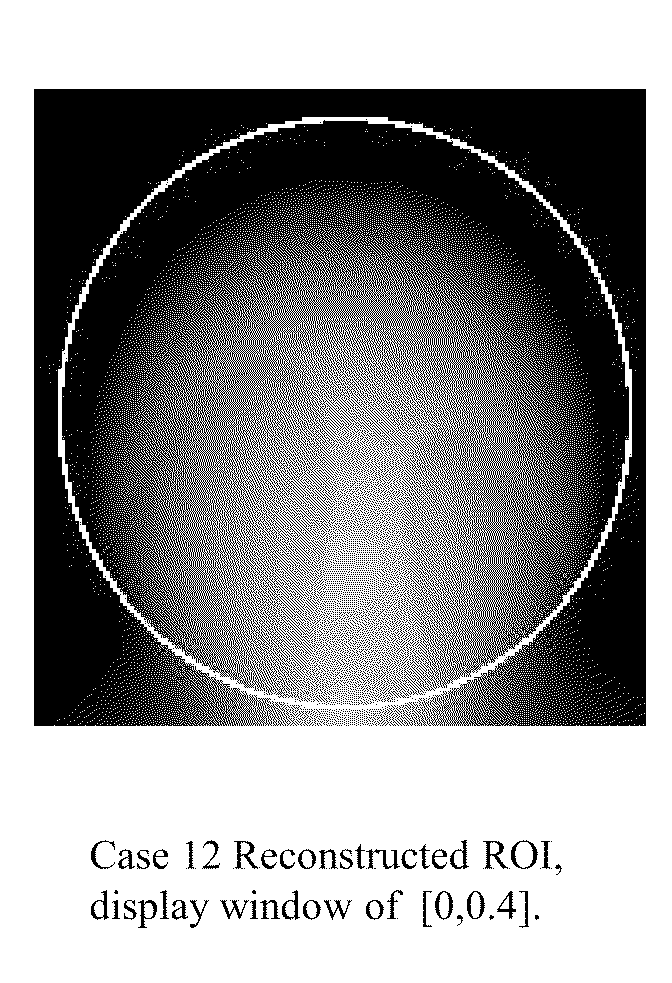
Tomography limitations in vivo due to incomplete, inconsistent and intricate measurements require solution of inverse problems. The new strategies disclosed in this application are capable of providing faster data acquisition, higher image quality, lower radiation dose, greater flexibility, and lower system cost. Such benefits can be used to advance research in cardiovascular diseases, regenerative medicine, inflammation, and nanotechnology. The present invention relates to the field of medical imaging. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to methods, systems, and devices for imaging, including tomography-based and MRI-based applications. For example, included in embodiments of the invention are compressive sampling based tomosynthesis methods, which have great potential to reduce the overall x-ray radiation dose for a patient. To name a few, compressive sensing based carbon nano-tube based interior tomosynthesis systems, tomography-based dynamic cardiac elastography systems, cardiac elastodynamic biomarkers from interior MR imaging, exact and stable interior ROI reconstructions for radial MRI, and interior reconstruction based ultrafast tomography systems are provided.
Owner:WANG GE +5
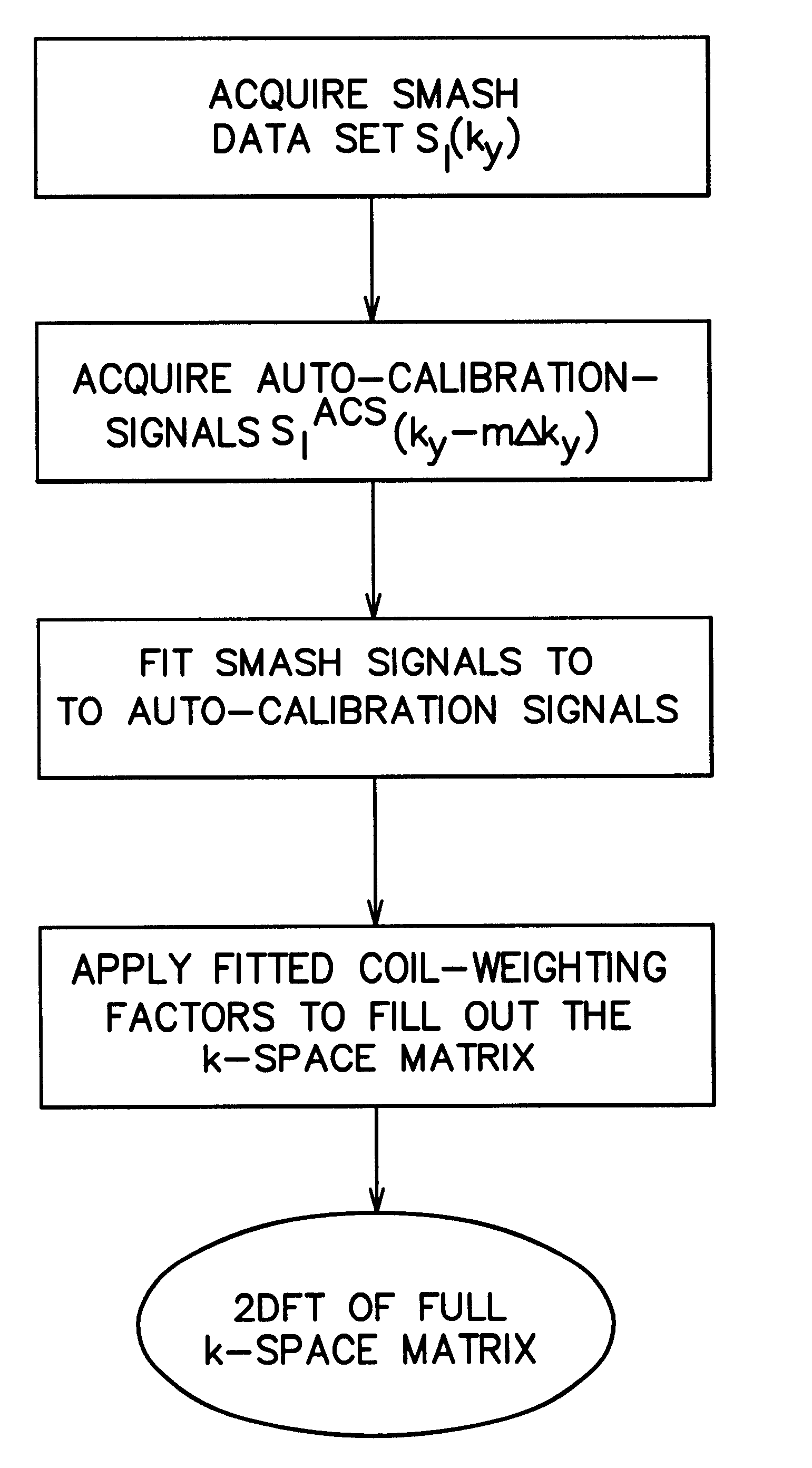
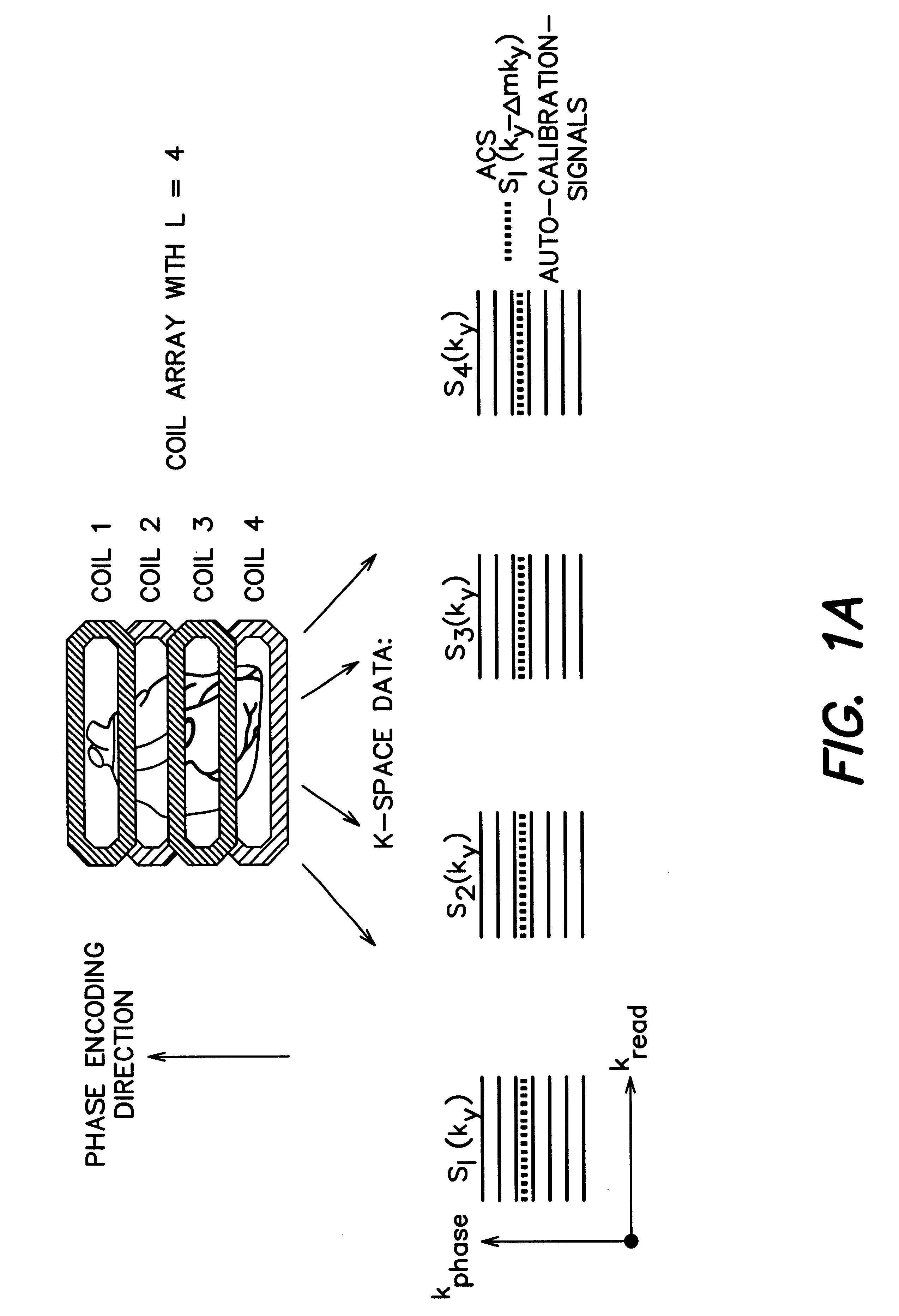
Coil array autocalibration MR imaging
InactiveUS6289232B1Shorten the timeEasy accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData spaceIn vivo
A magnetic resonance (MR) imaging apparatus and technique exploits spatial information inherent in a surface coil array to increase MR image acquisition speed, resolution and / or field of view. Magnetic resonance response signals are acquired simultaneously in the component coils of the array and, using an autocalibration procedure, are formed into two or more signals to fill a corresponding number of lines in the signal measurement data matrix. In a Fourier embodiment, lines of the k-space matrix required for image production are formed using a set of separate, preferably linear combinations of the component coil signals to substitute for spatial modulations normally produced by phase encoding gradients. One or a few additional gradients are applied to acquire autocalibration (ACS) signals extending elsewhere in the data space, and the measured signals are fitted to the ACS signals to develop weights or coefficients for filling additional lines of the matrix from each measurement set. The ACS lines may be taken offset from or in a different orientation than the measured signals, for example, between or across the measured lines. Furthermore, they may be acquired at different positions in k-space, may be performed at times before, during or after the principal imaging sequence, and may be selectively acquired to optimized the fitting for a particular tissue region or feature size. The in vivo fitting procedure is readily automated or implemented in hardware, and produces an enhancement of image speed and / or quality even in highly heterogeneous tissue. A dedicated coil assembly automatically performs the calibration procedure and applies it to measured lines to produce multiple correctly spaced output signals. One application of the internal calibration technique to a subencoding imaging process applies the ACS in the central region of a sparse set of measured signals to quickly form a full FOV low resolution image. The full FOV image is then used to determine coil sensitivity related information and dealias folded images produced from the sparse set.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Hybrid imaging method to monitor medical device delivery and patient support for use in the method
ActiveUS7379769B2Easy procedureConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesStretcherLiver and kidneySurgical removal
Owner:INVIVO CORP
System for delivering conformal radiation therapy while simultaneously imaging soft tissue
InactiveUS7907987B2Accurate guideIncrease speedMagnetic measurementsMicrowave therapyImage resolutionConformal radiation therapy
A device and a process for performing high temporal- and spatial-resolution MR imaging of the anatomy of a patient during intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to directly measure and control the highly conformal ionizing radiation dose delivered to the patient for the treatment of diseases caused by proliferative tissue disorders. This invention combines the technologies of open MRI, multileaf-collimator or compensating filter-based IMRT delivery, and cobalt teletherapy into a single co-registered and gantry mounted system.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic navigation systems and methods
InactiveUS20050182315A1Strong and uniformDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringStatic field
A system for magnetically imaging an operating region in a subject and magnetically navigating a medical device within the operating region includes a first magnet for applying a static magnetic field to the operating region of sufficient strength for magnetically imaging the operating region and sufficiently strong to permit a medical device to be oriented in the operating region by creating a magnetic moment at the distal end of the medical device, and a second magnet for applying a static magnetic field to the operating region of sufficient strength for magnetically imaging the operating region and sufficiently strong to permit a medical device to be oriented in the operating region by creating a magnetic moment at the distal end of the medical device. In an alternate construction, the system includes a first magnet that is movable between a first position to apply a first static magnetic field to the operating region and a second position to apply a second static magnetic field to the operating region. The method of the invention includes applying a first static magnetic field to the operating region and MR imaging and magnetically navigating a device in the first static field, and then applying a second static magnetic field to the operating region, in a different direction than the first direction, and MR imaging and magnetically navigating a device in the second static field.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Magnetic resonance-electrical impedance tomography
InactiveUS6397095B1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic resonance electrical impedance tomographyMR - Magnetic resonance
A magnetic resonance-electrical impedance tomography (MREIT) technique for determining the local conductivity of an object. The MREIT technique combines magnetic resonance current density imaging (MRCDI) with electrical impedance tomography (EIT) in order to obtain the benefits of both procedures. The MREIT technique includes the step of current density imaging by performing the steps of placing a series of electrodes around the patient or object to be imaged for the application of current, placing the patient or object in a strong magnetic field, and applying an MR imaging sequence which is synchronized with the application of current through the electrodes. Next, the electric potentials of the surface of the object or patient are measured simultaneously with the MR imaging sequence, as in EIT. Then, the MR imaging signal containing information about the current and the measured potential are processed to calculate the internal conductivity (impedance) of the object or patient.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method of magnetic resonance imaging of a sample with ex vivo polarization of an MR imaging agent
The present invention provides a method of magnetic resonance investigation of a sample, preferably of a human or non-human animal body, said method comprising the step of ex vivo polarisation of a high T1 agent and wherein the polarising agent is optionally seperated from the high T1 agent before the high T1 agent is administered to the sample.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
Interventional MR imaging with detection and display of device position
InactiveUS20060058633A1Easy to detectImprove presentationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInterventional imagingTip position
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
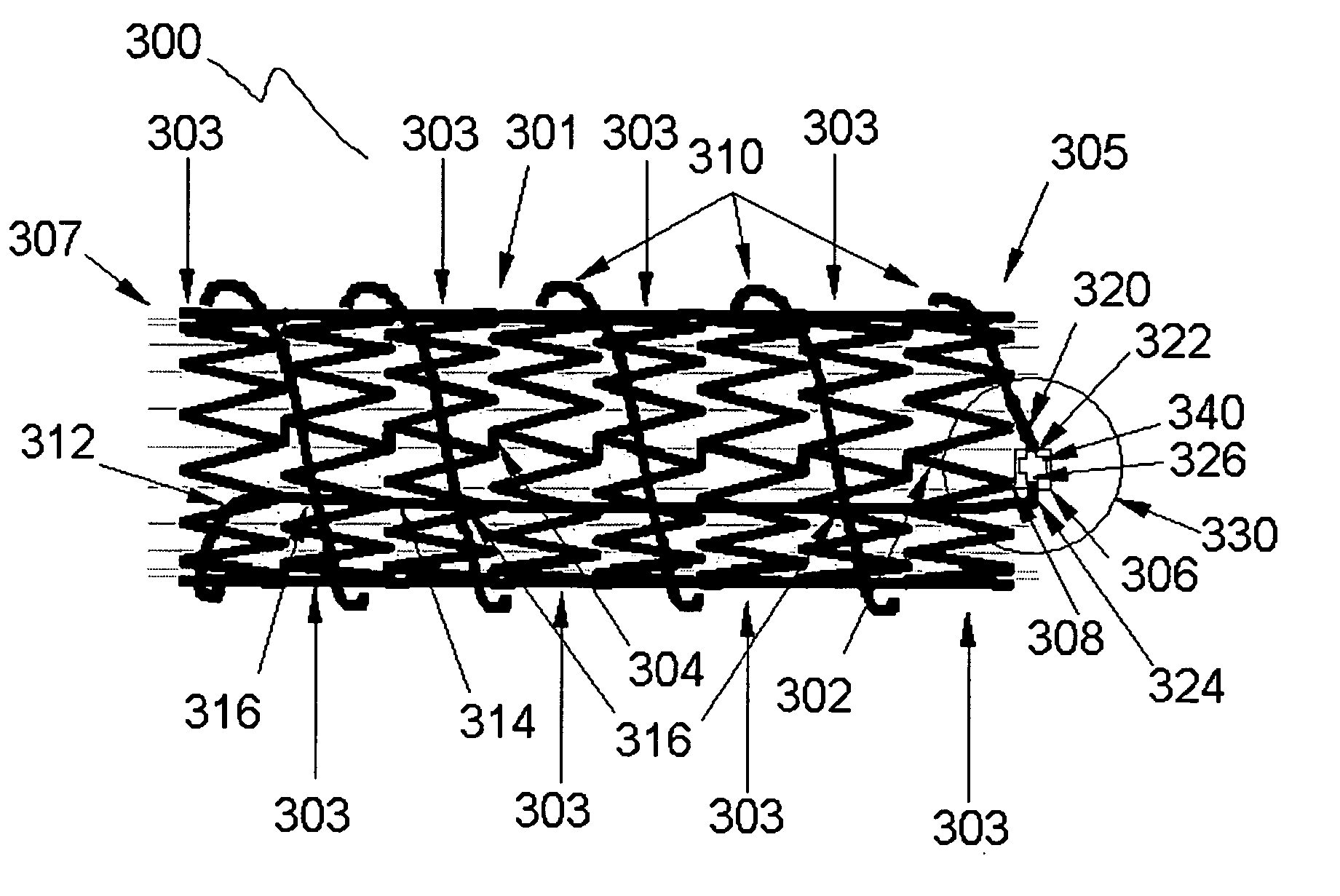
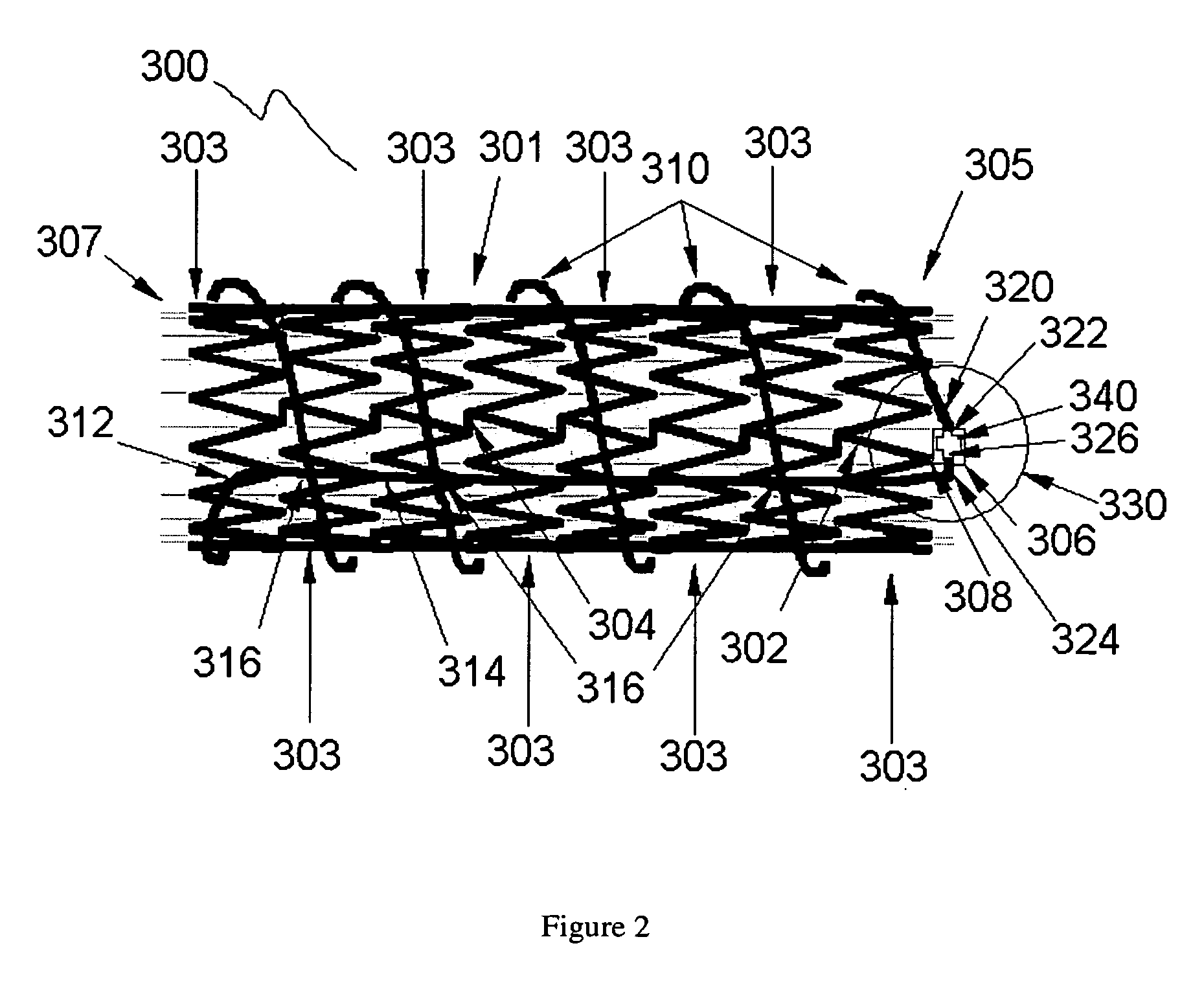
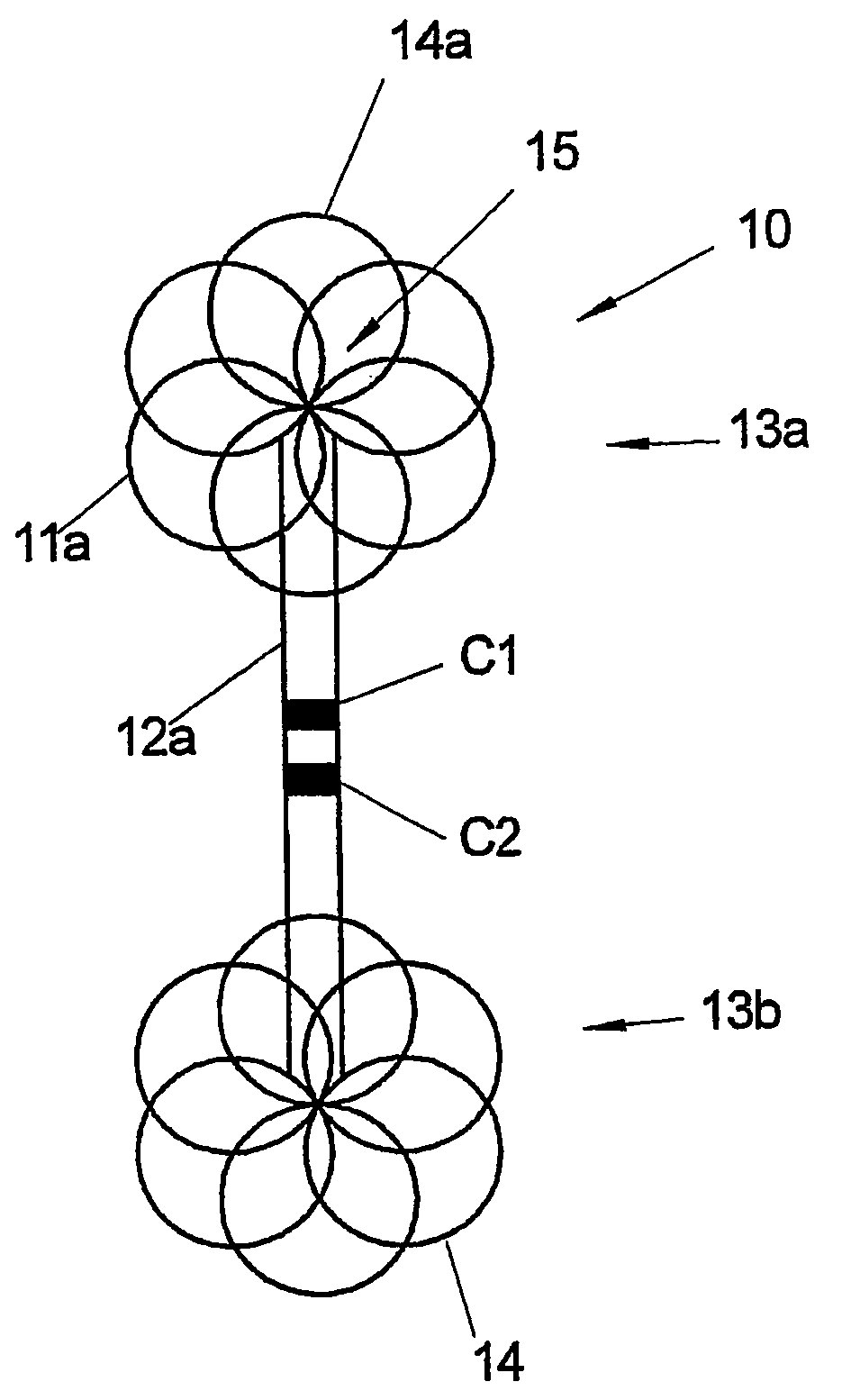
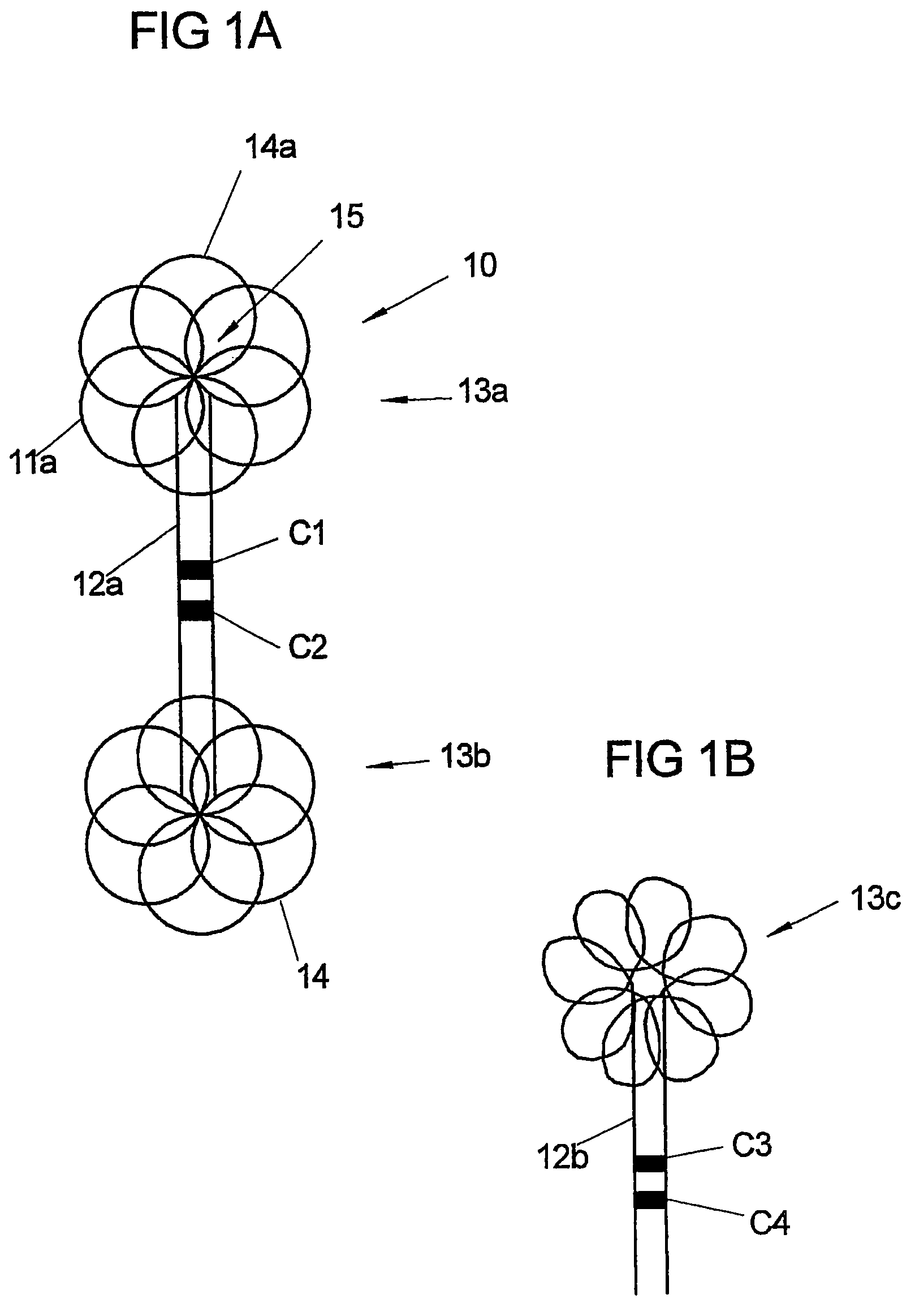
Stent and MR imaging process and device
A passive resonant circuit is disposed on an implanted stent. The materials, geomentry and electrical parameters of the stent with passive resonant circuit are chosen and arranged so that incident electromagnetic radiation induces currents in the passive resonant circuit that optimize imageability during MR scanning.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
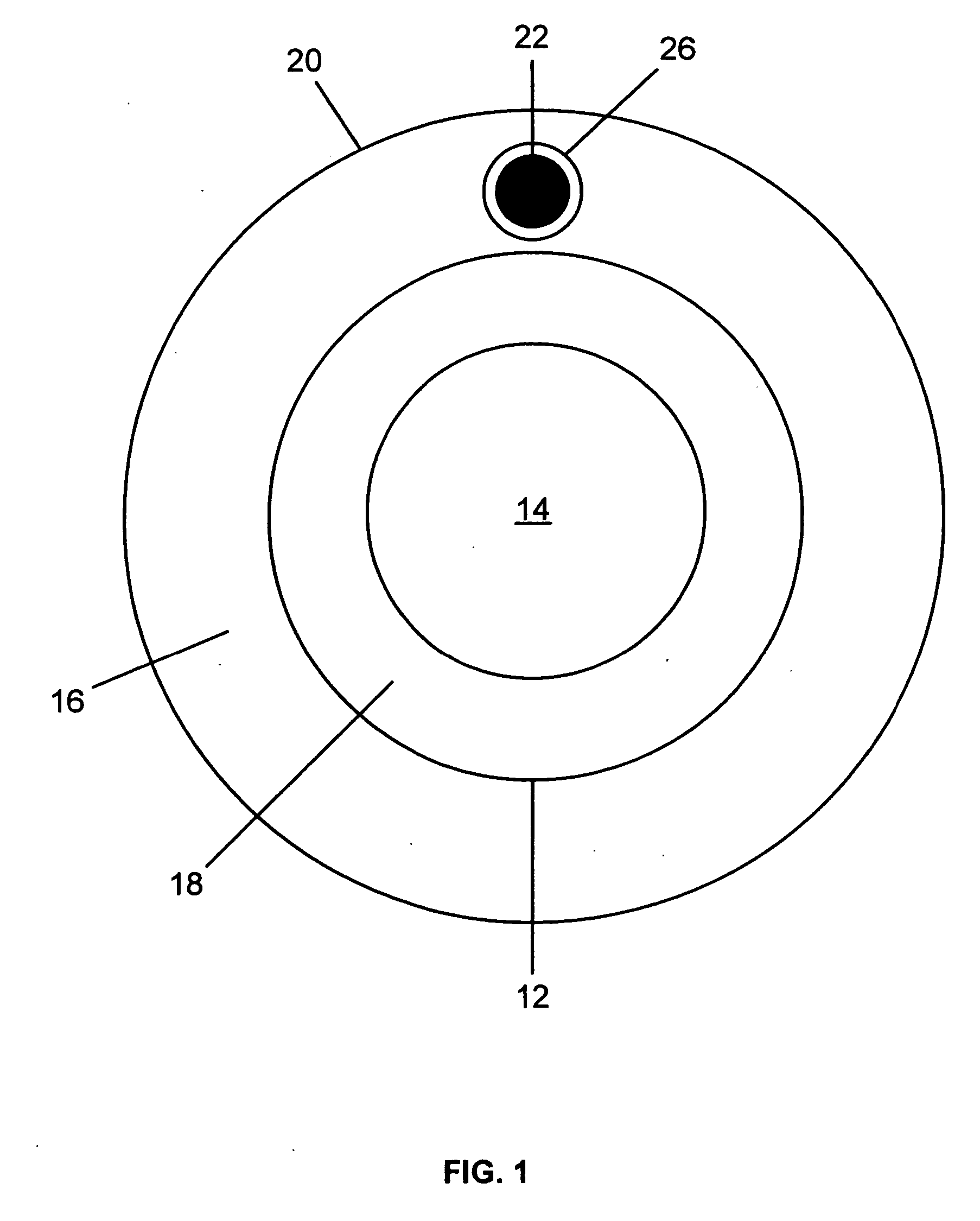
Marker device for X-ray, ultrasound and MR imaging
InactiveUS20060293581A1Sharp contrastEasily introduced into tissueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMicrosphere
An imaging marker comprised of glass and iron-containing aluminum microspheres in a gel matrix which shows uniformly good contrast with MR, US and X-Ray imaging. The marker is small and can be easily introduced into tissue through a 12-gauge biopsy needle. The concentration of glass microspheres and the size dictate the contrast for US imaging. The contrast seen in MRI resulting from susceptibility losses is dictated by the number of iron-containing aluminum microspheres; while the artifact of the marker also depends on its shape, orientation and echo time. By optimizing the size, iron concentration and gel binding, an implantable tissue marker is created which is clearly visible with all three imaging modalities.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT
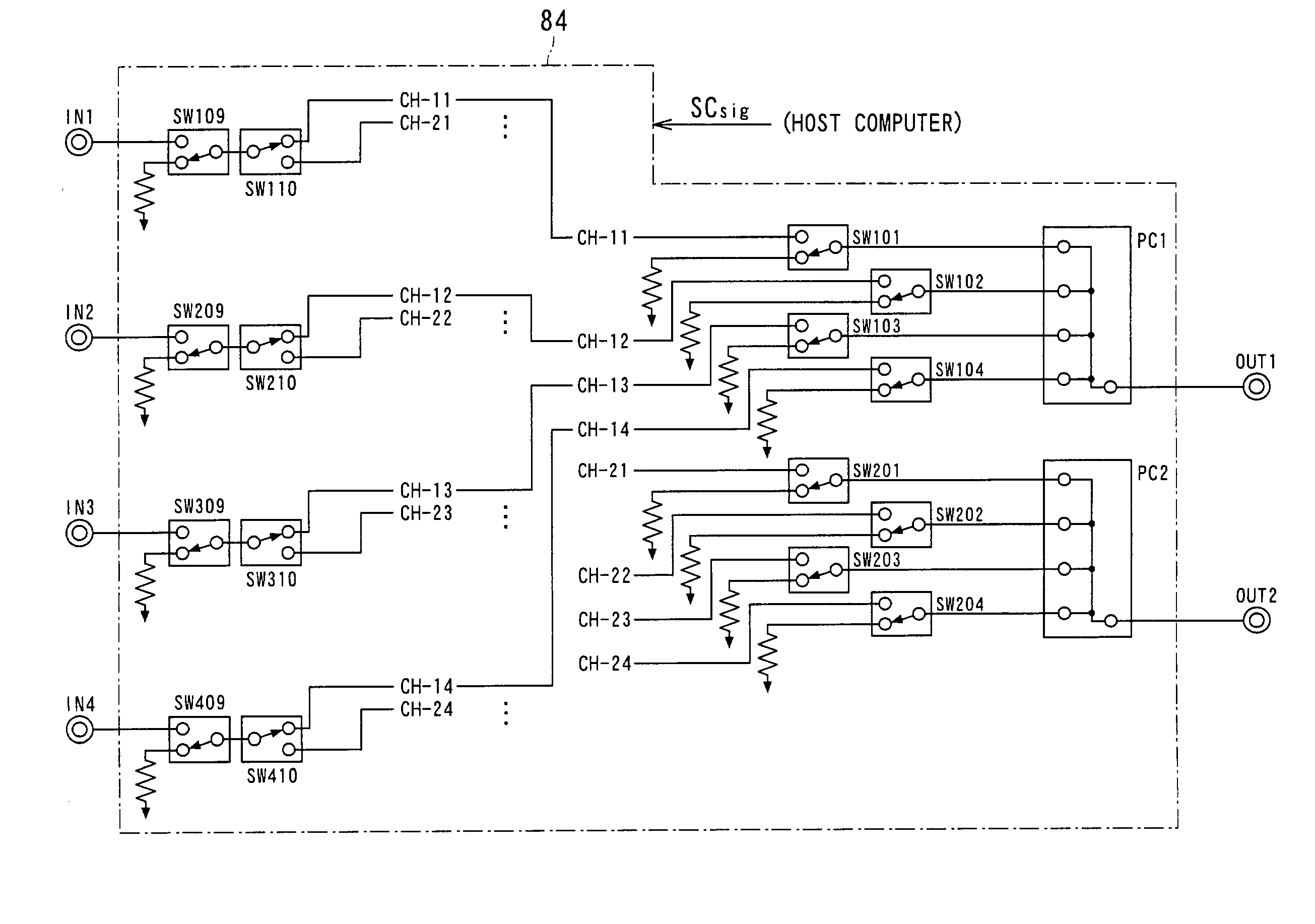
Parallel MR imaging with use of multi-coil made of plural element coils
InactiveUS7026818B2Simple wayHigher-quality MRDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging conditionEngineering
A magnetic resonance imaging system includes an MR signal reception apparatus comprising a receiving multi-coil and a switchover member. The receiving multi-coil receives MR signals and is composed of a plurality of element coils. The switchover member is configured to switch reception states of the MR signals received by the plurality of element coils in response to imaging conditions. The switchover member connects output paths of the MR signals from the plurality of element coils to a receiver, to reception channels in the receiver in response to the imaging conditions. The reception channels is less in number than the element coils. The imaging conditions are for example directed to parallel MR imaging.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
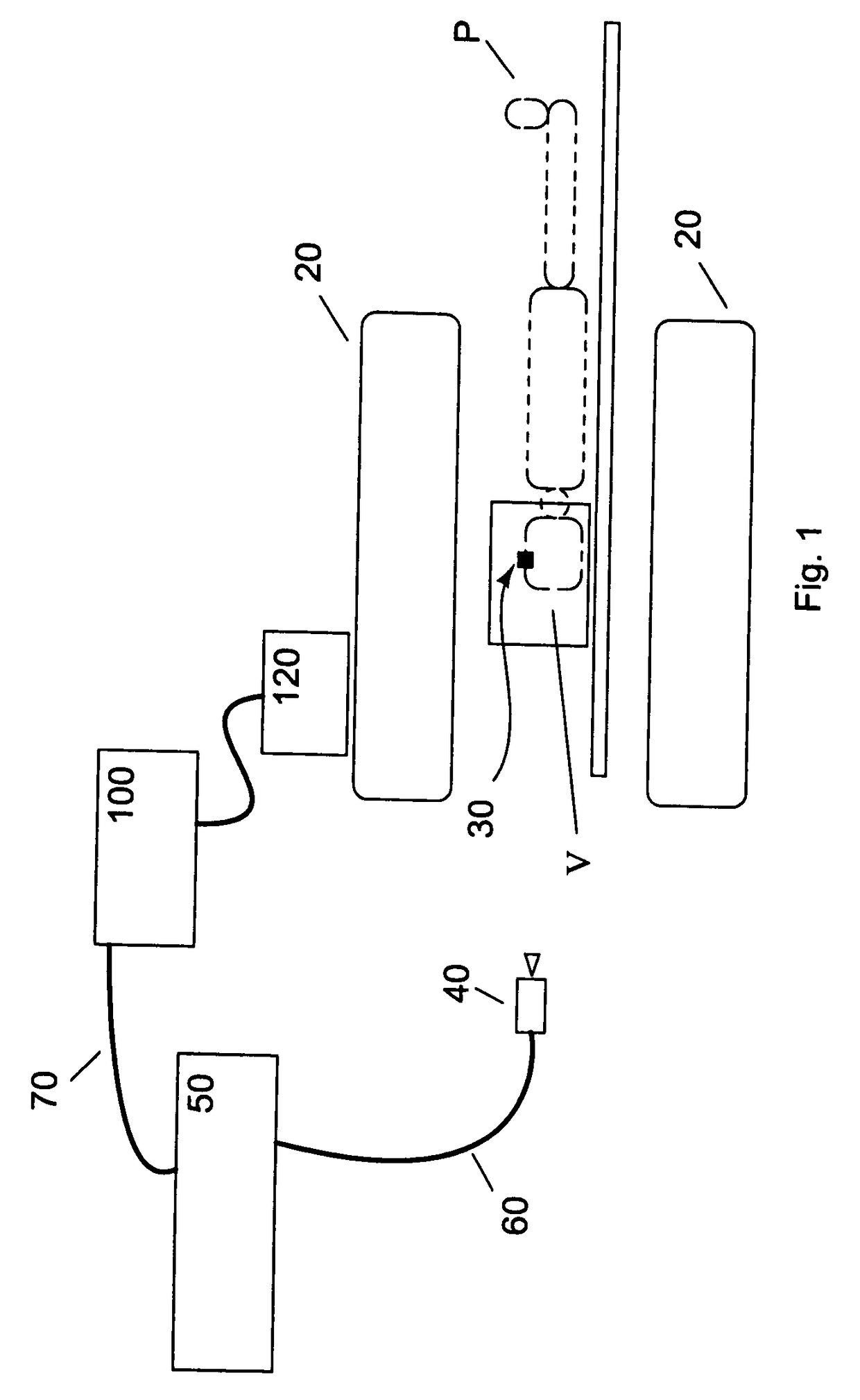
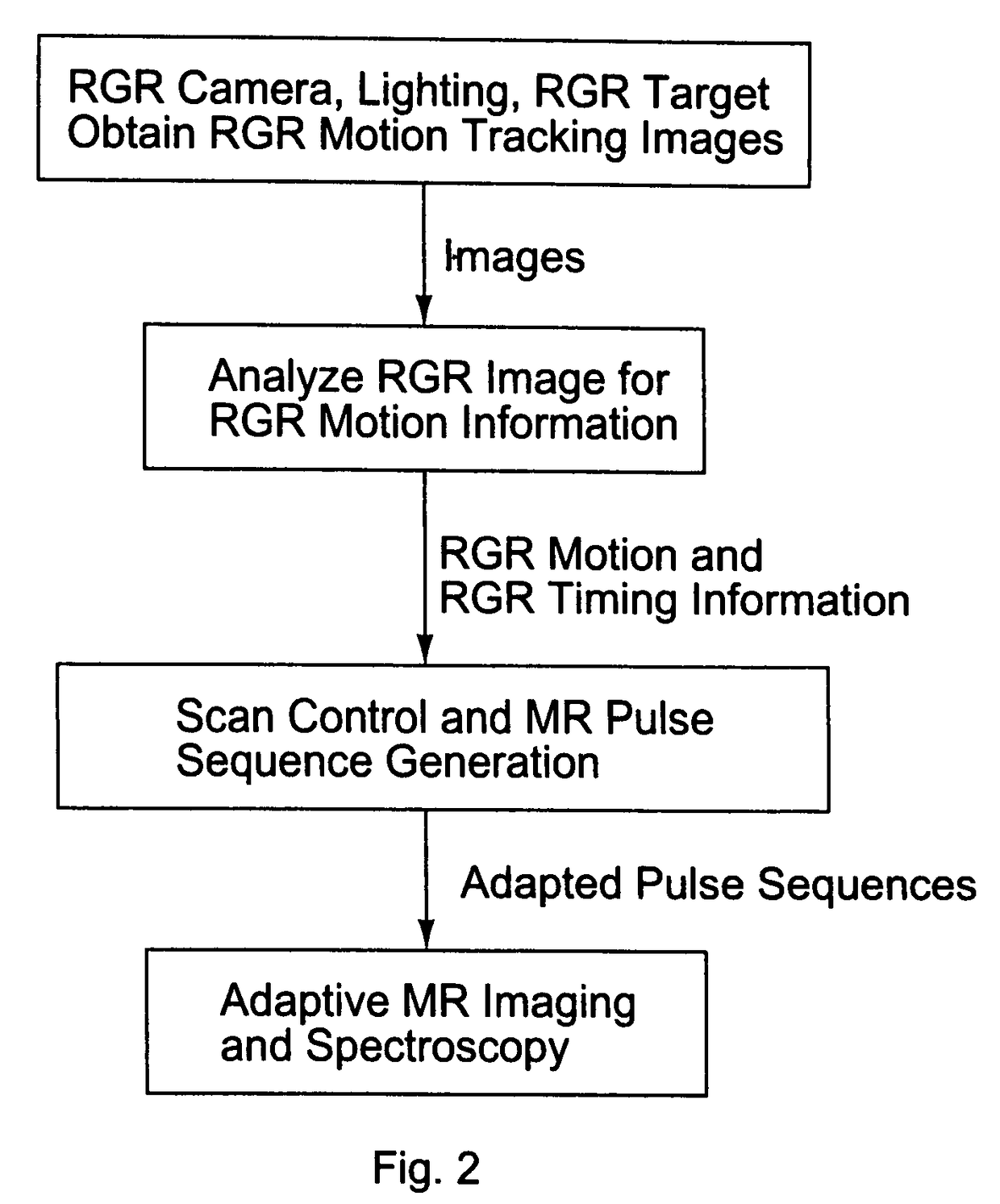
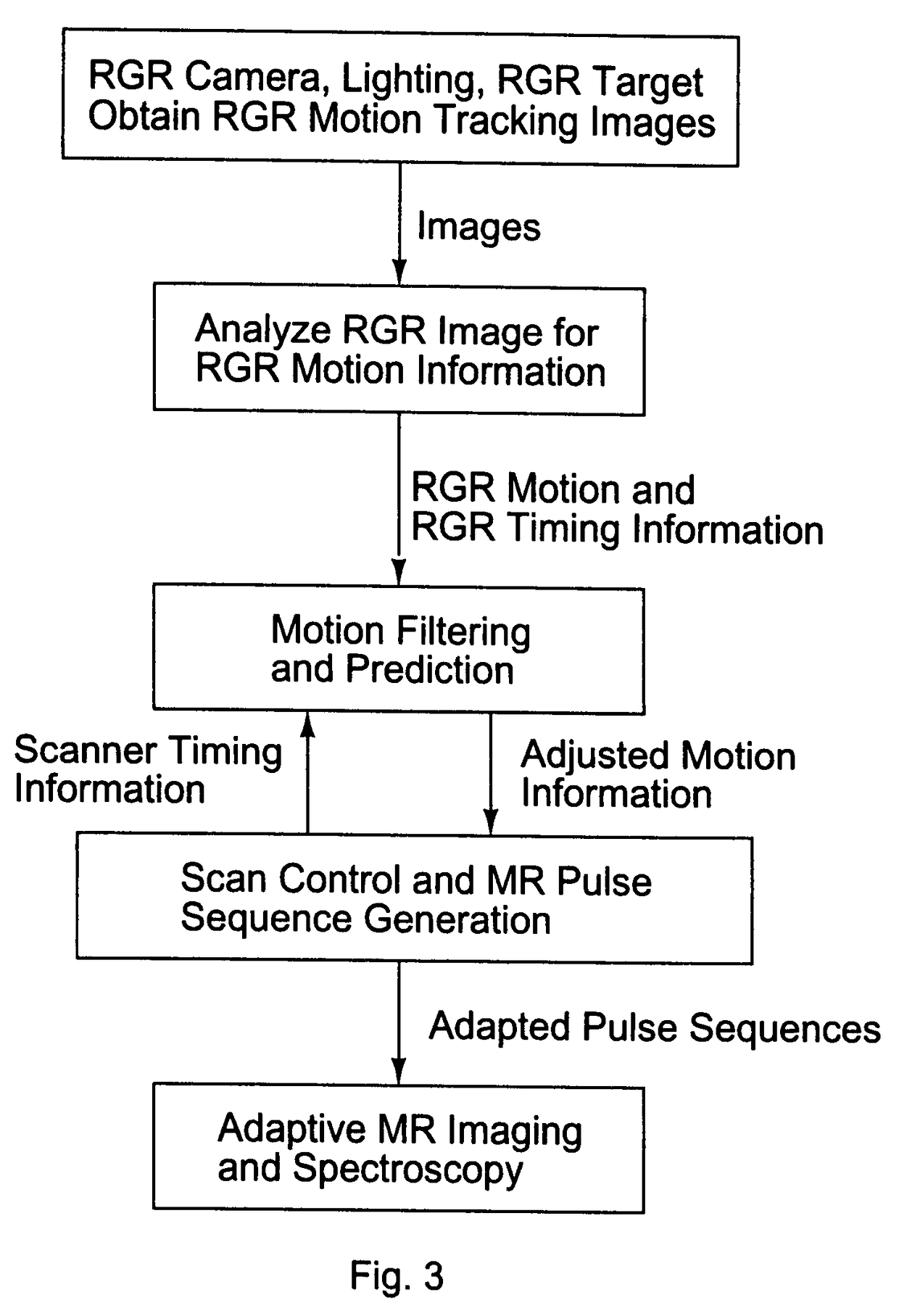
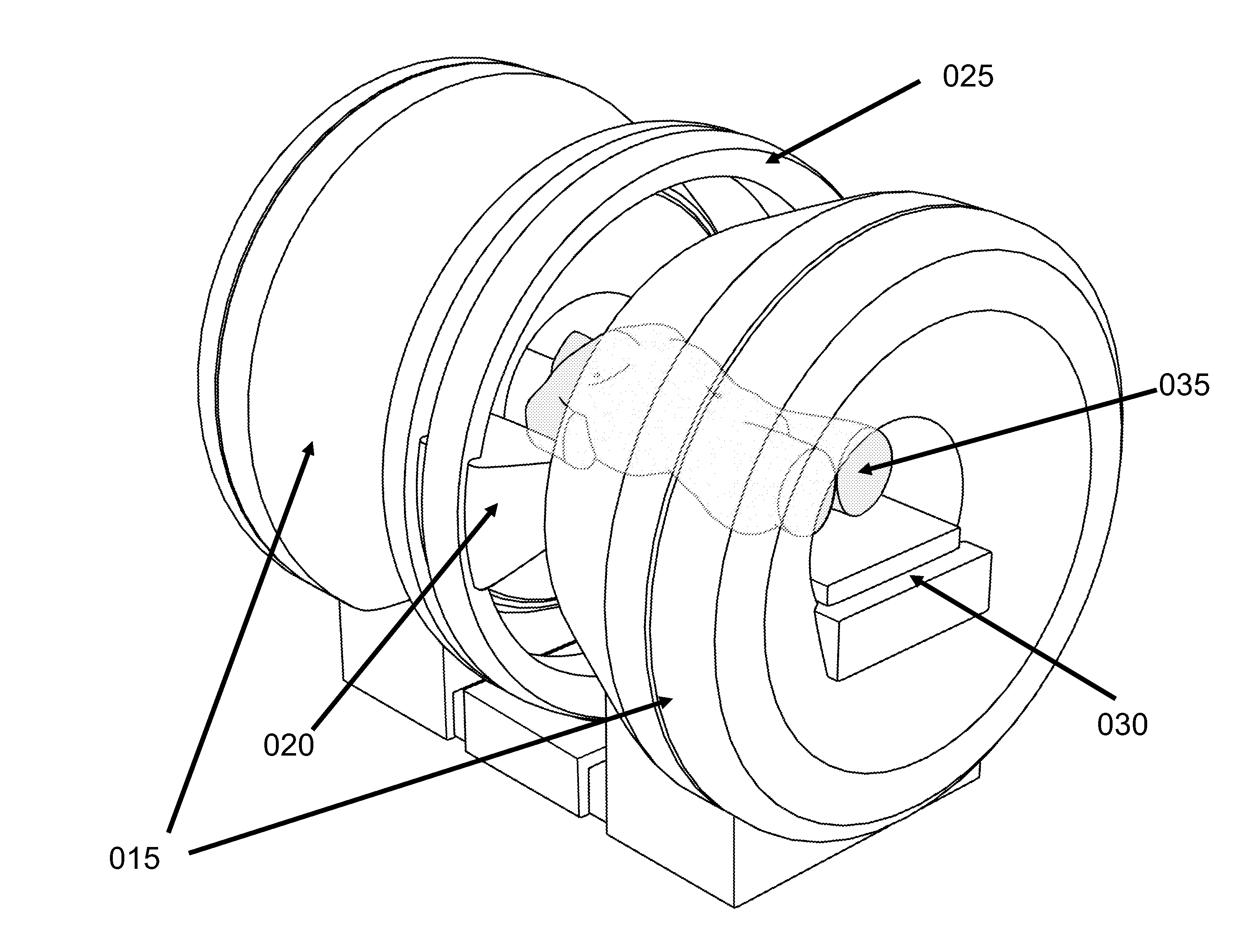
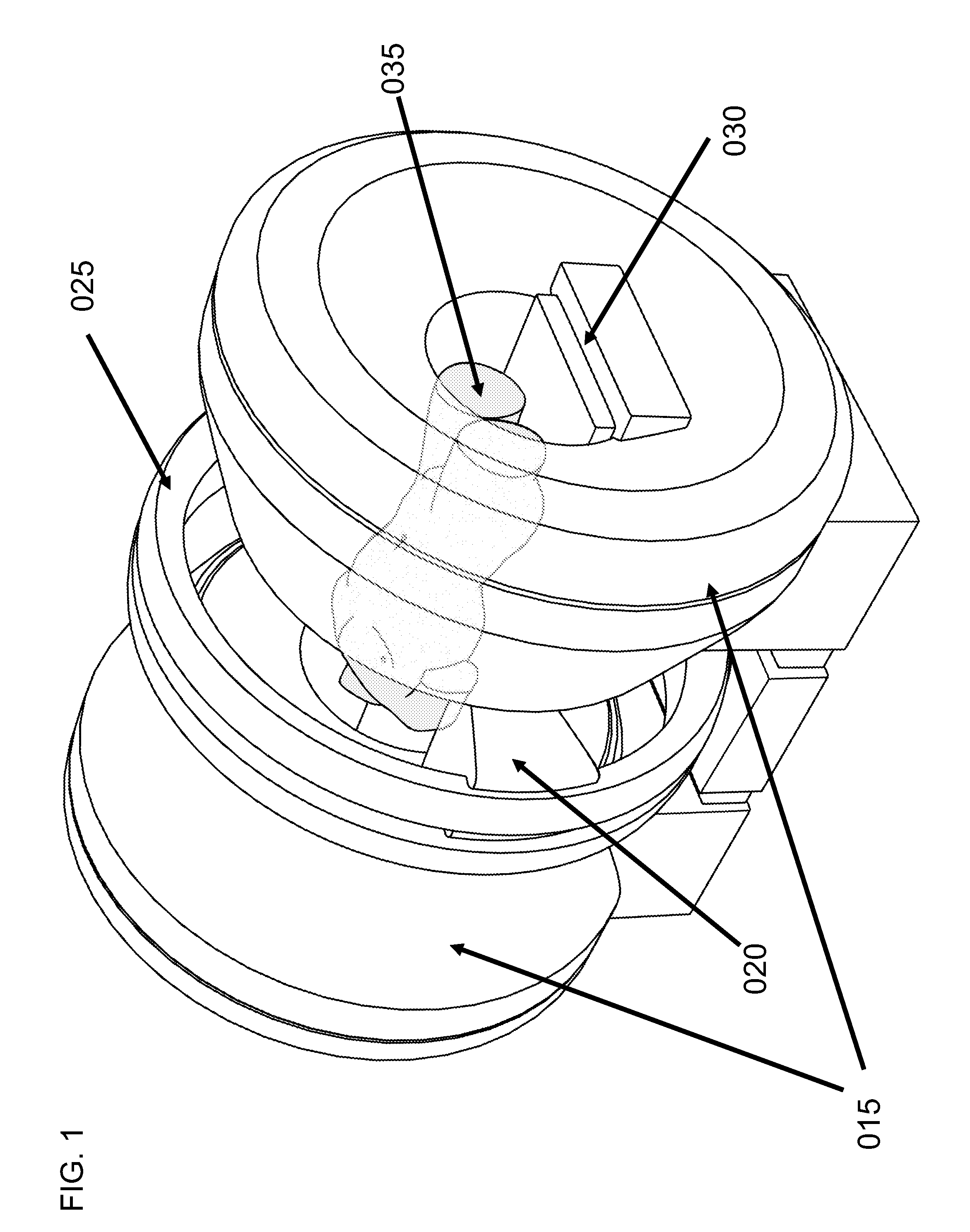
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS8121361B2Accurately determinedAccurately determineImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingSpectroscopy
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
System for Delivering Conformal Radiation Therapy While Simultaneously Imaging Soft Tissue
ActiveUS20100113911A1Accurate guideIncrease speedMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseTherapeutic Technique
A device and a process for performing high temporal- and spatial-resolution MR imaging of the anatomy of a patient during intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to directly measure and control the highly conformal ionizing radiation dose delivered to the patient for the treatment of diseases caused by proliferative tissue disorders. This invention combines the technologies of open MRI, multileaf-collimator or compensating filter-based IMRT delivery, and cobalt teletherapy into a single co-registered and gantry mounted system.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Techniques for temperature measurement and corrections in long-term magnetic resonance thermometry
ActiveUS20110046472A1Easy to correctUltrasound therapyMagnetic measurementsPhase shiftedMr thermometry
Techniques for temperature measurement and correction in long-term MR thermometry utilize a known temperature distribution in an MR imaging area as a baseline for absolute temperature measurement. Phase shifts that arise from magnetic field drifts are detected in one or more portions of the MR imaging area, facilitating correction of temperature measurements in an area of interest.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
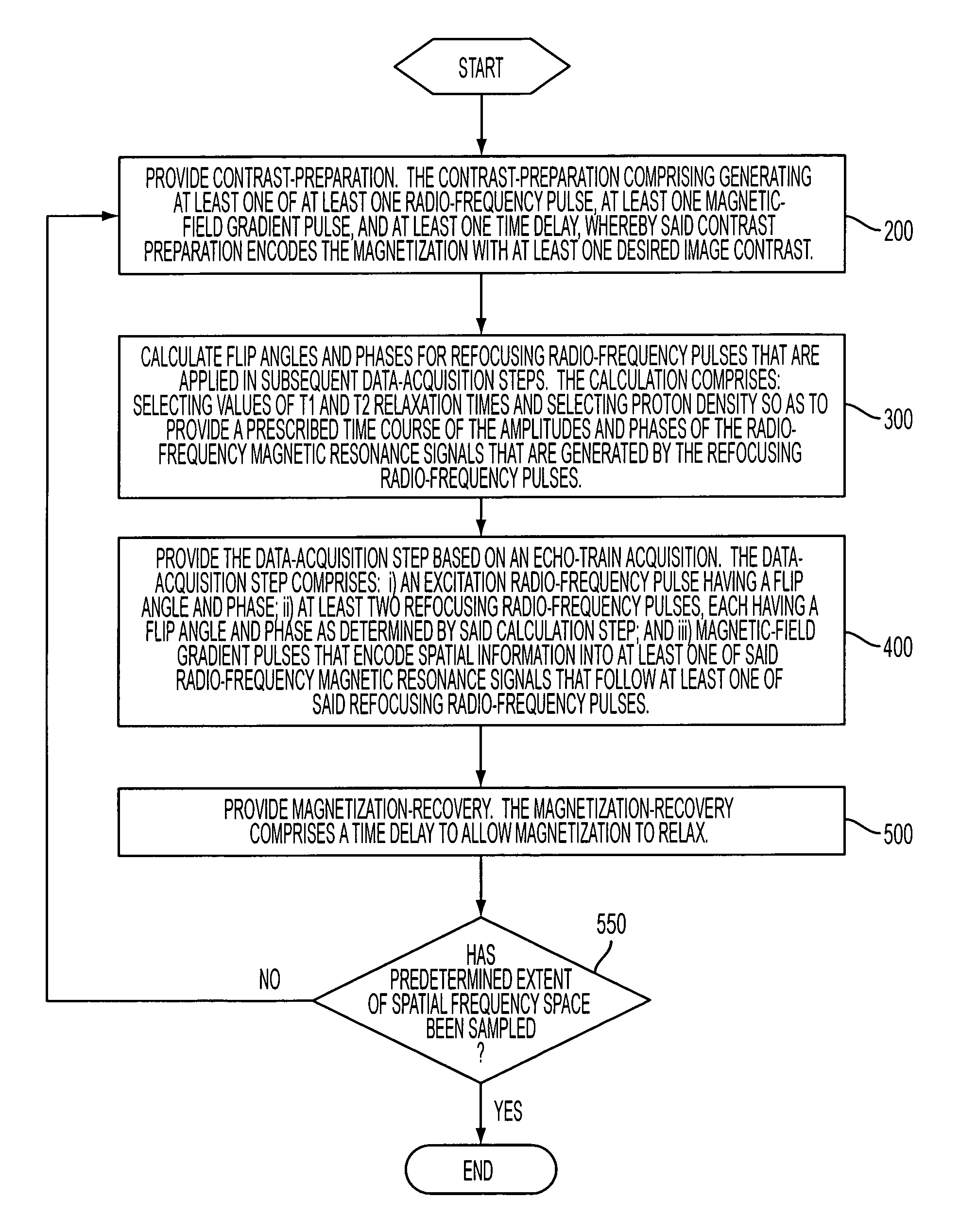
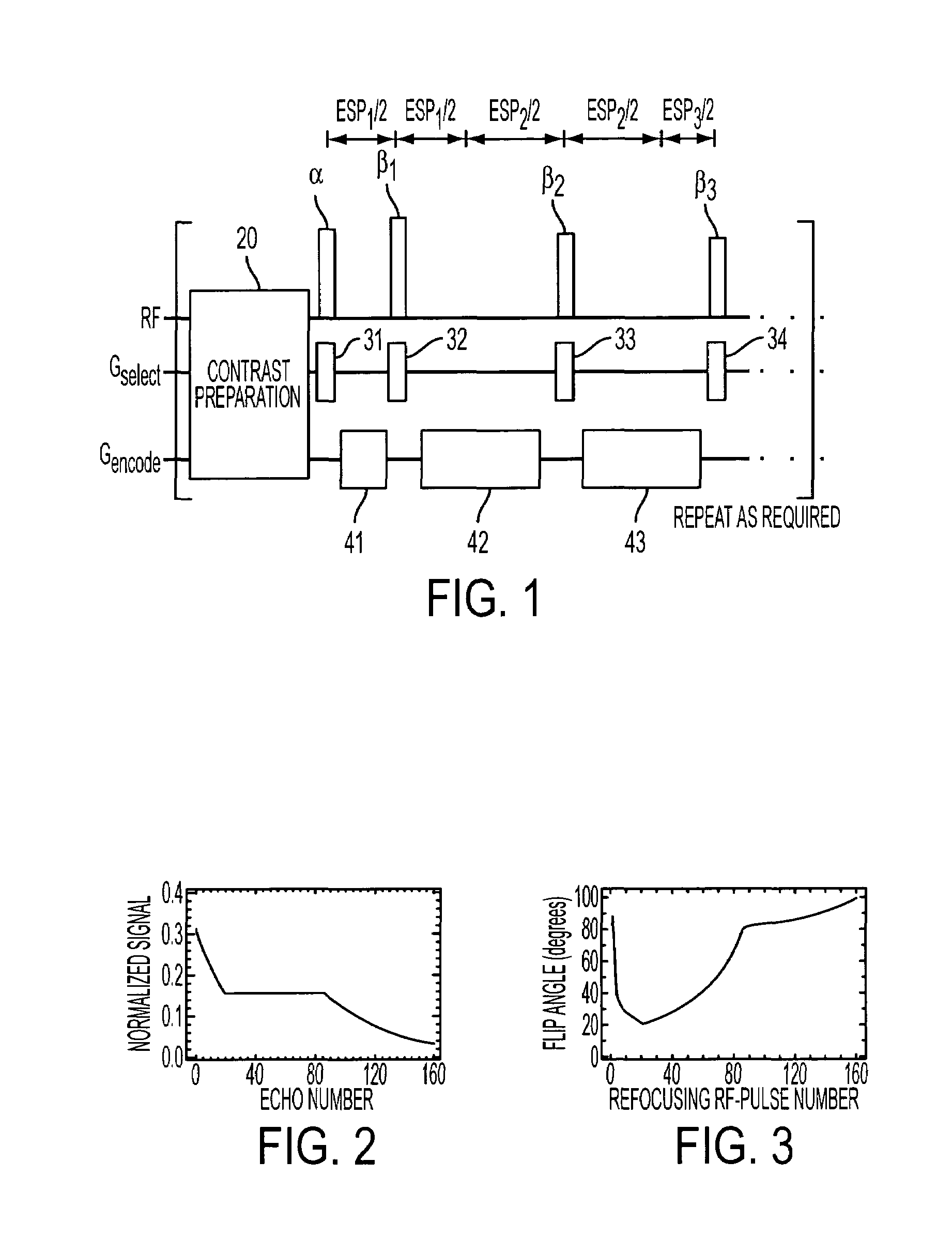
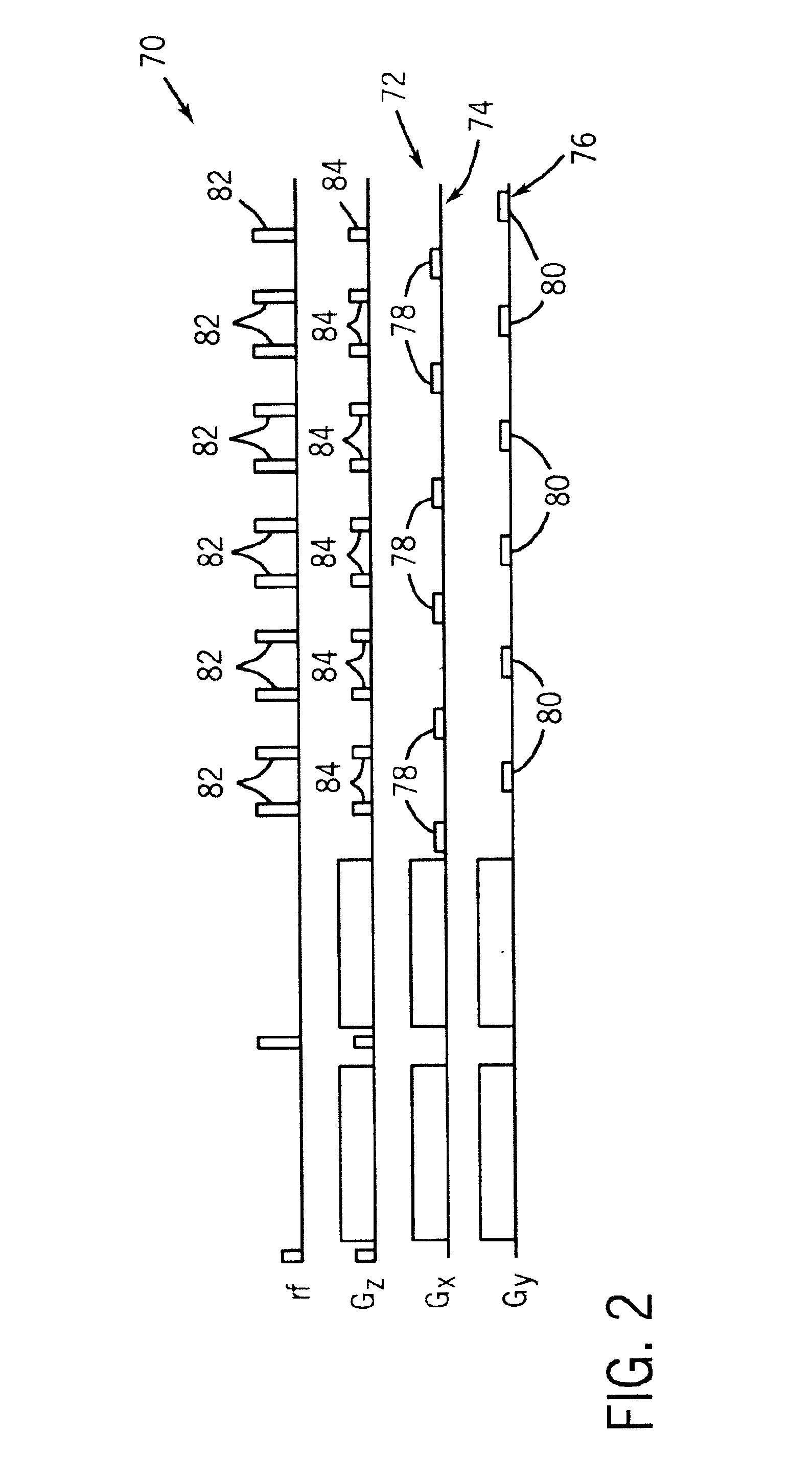
Method and apparatus for spin-echo-train MR imaging using prescribed signal evolutions
InactiveUS7164268B2Extended durationShorten Image Acquisition TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsHigh fieldMagnetic resonance technique
A magnetic resonance imaging “MRI” method and apparatus for lengthening the usable echo-train duration and reducing the power deposition for imaging is provided. The method explicitly considers the t1 and t2 relaxation times for the tissues of interest, and permits the desired image contrast to be incorporated into the tissue signal evolutions corresponding to the long echo train. The method provides a means to shorten image acquisition times and / or increase spatial resolution for widely-used spin-echo train magnetic resonance techniques, and enables high-field imaging within the safety guidelines established by the Food and Drug Administration for power deposition in human MRI.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
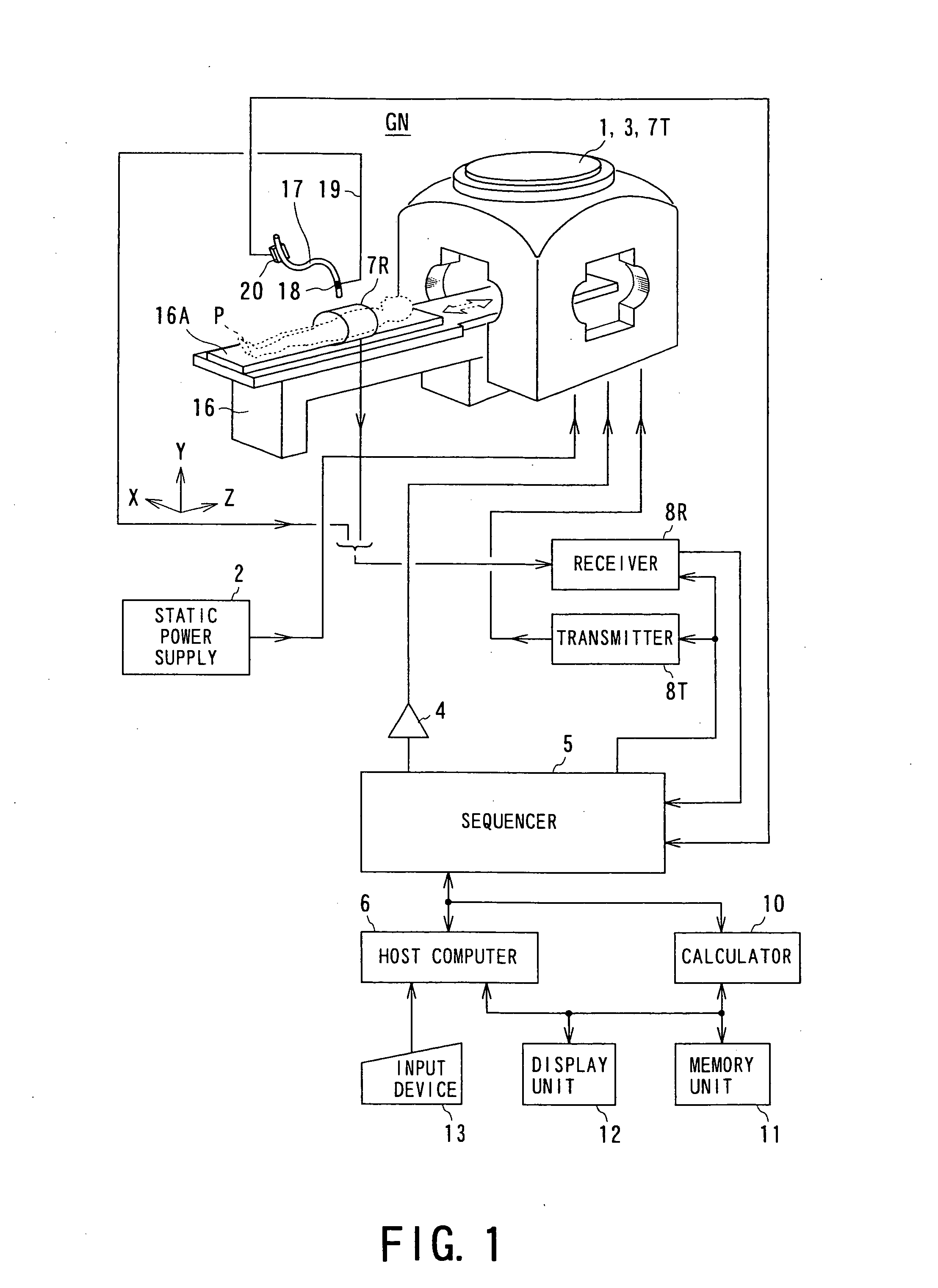
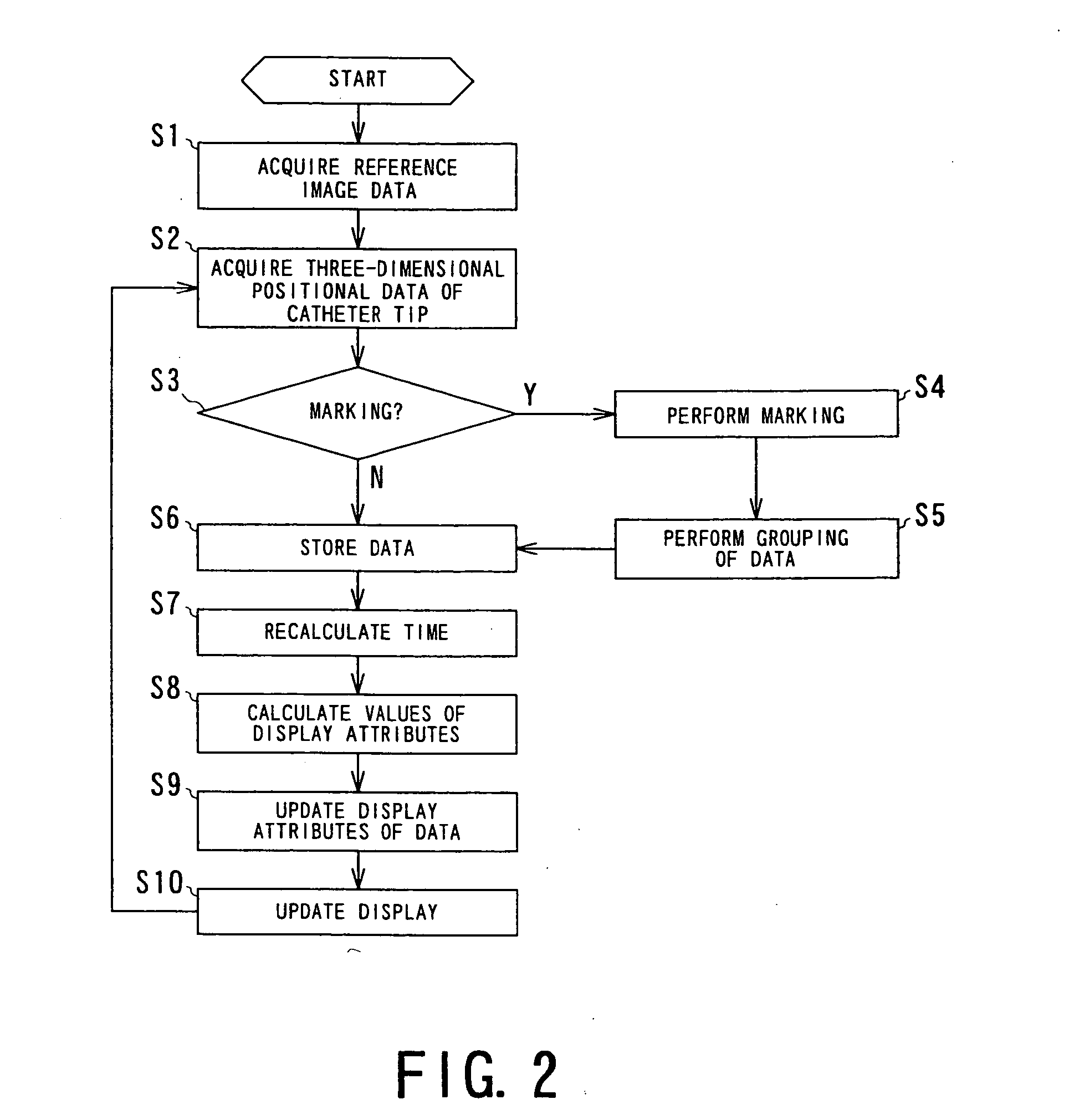
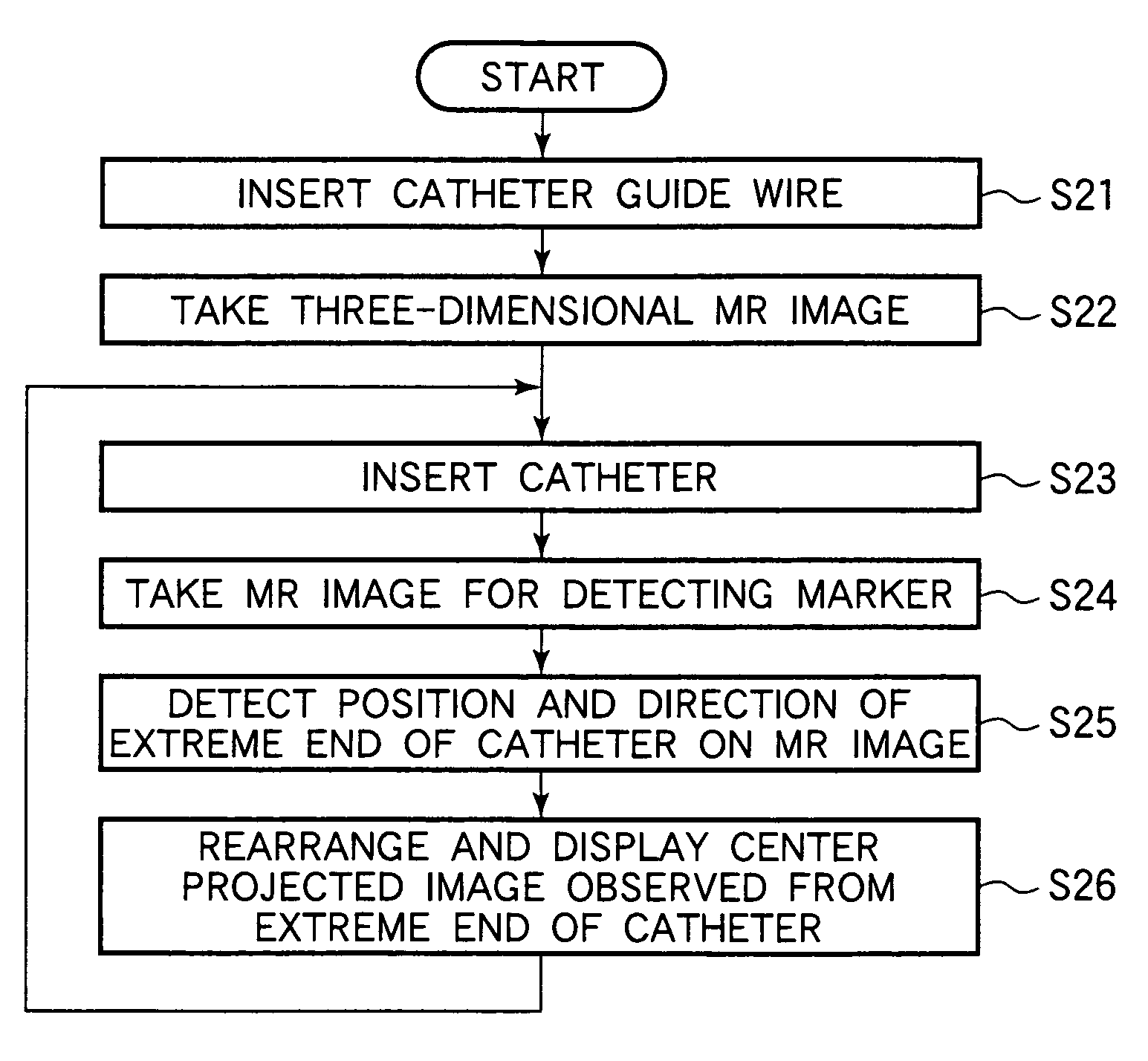
Endoscopic image pickup method and magnetic resonance imaging device using the same
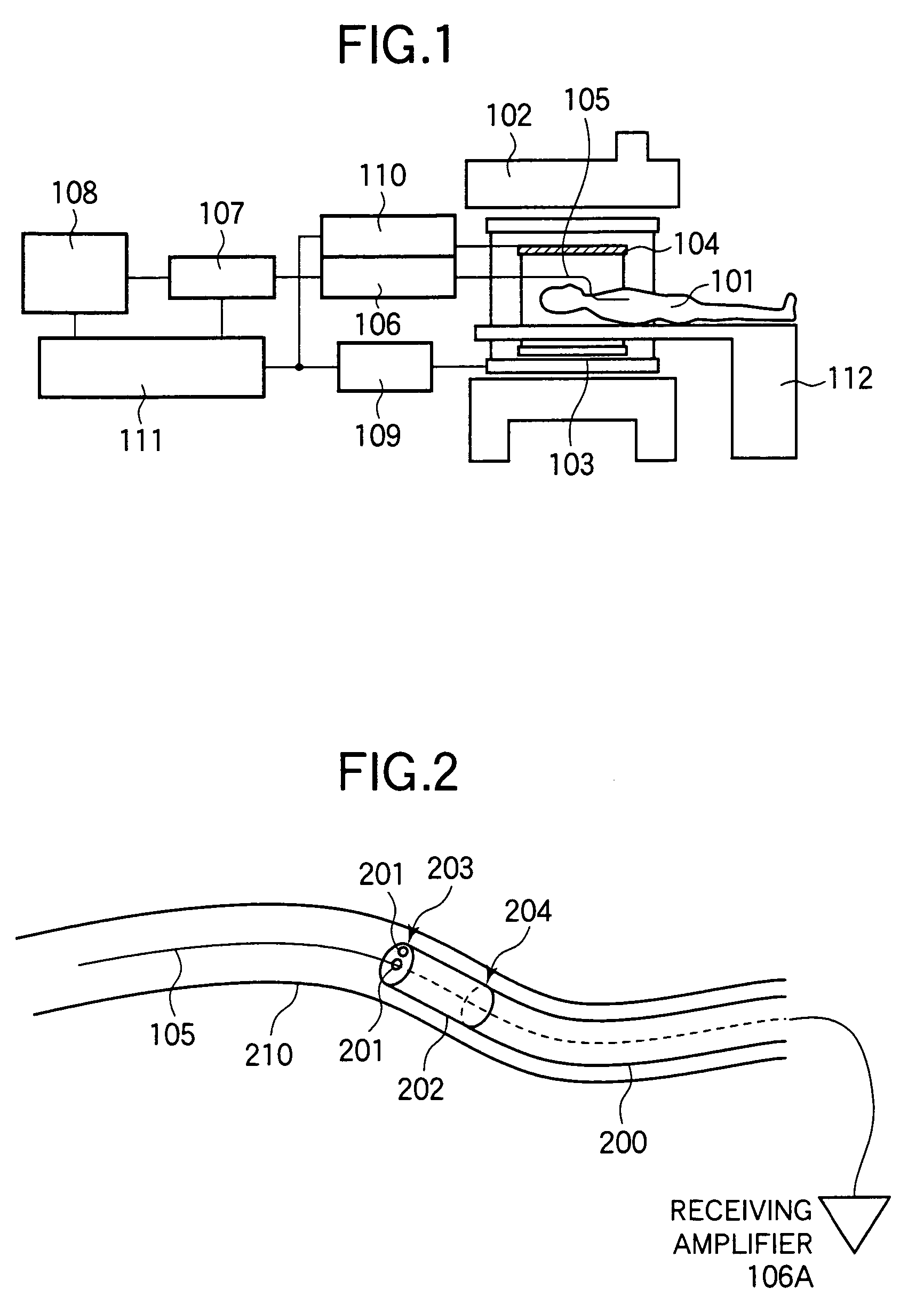
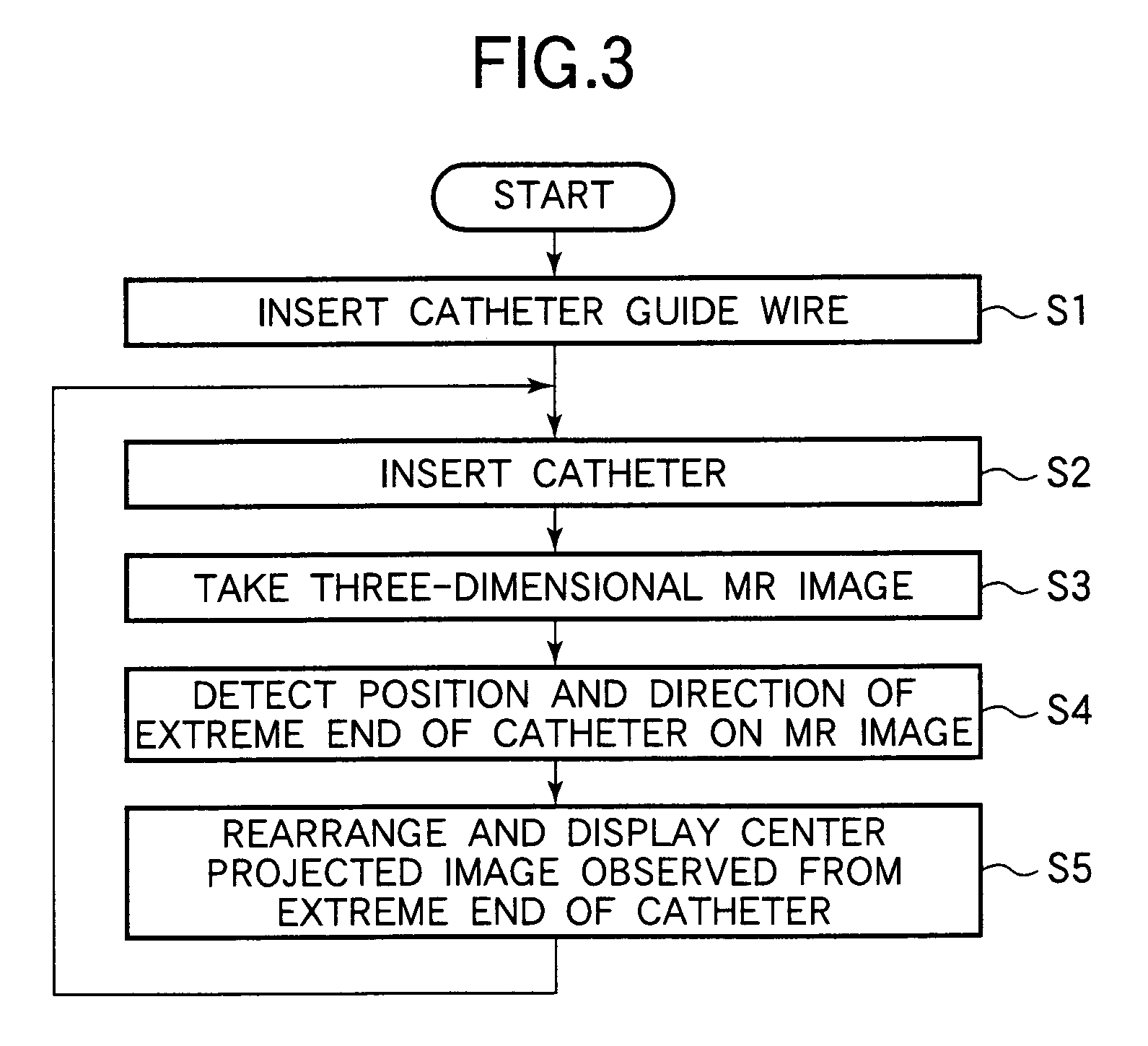
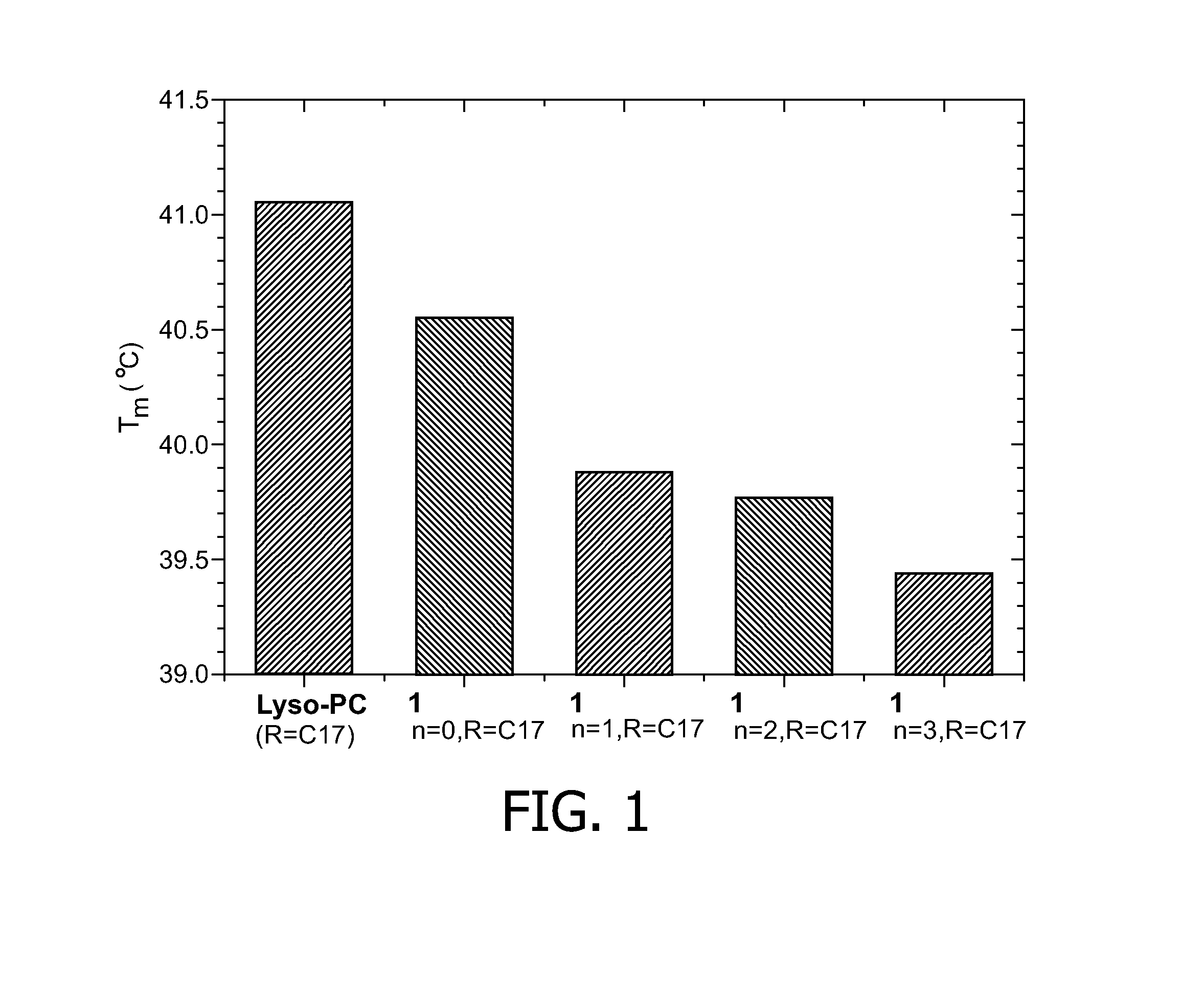
InactiveUS7653426B2Efficient insertionShort measurement timeImage enhancementElectrotherapyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceTip position
An endoscope-like image taking method includes providing at least one peculiar index, which can be discriminated from other portions on an MR image, at the tip of a catheter, previously inserting a metal guide wire for guiding the catheter into a body cavity of a patient inserting the catheter into the body cavity along the guide wire, executing an MR imaging sequence of a plurality of sliced images intersecting the guide wire, reconstructing three-dimensional image data based upon the nuclear magnetic resonance signals, which are received by the guide wire, and determining the tip position and the inserting direction of the catheter by detecting the peculiar index provided at the tip of the catheter based upon the three-dimensional image data, and reconstructing the center projected image using the three-dimensional image data and setting the tip position and the inserting direction of the catheter as a view point and a line-of-sight direction and displaying the center projected image on a display means.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Lipid bilayer carrier for drugs or imaging agents
InactiveUS20130108551A1Better addressMaximize MR contrast enhancementOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryChain lengthImaging agent
Disclosed are carriers for drugs and / or MR imaging agents having a lipid bilayer shell comprising a phospholipid having two terminal alkyl chains, one being a short chain having a chain length of at most seven carbon atoms, the other being a long chain having a chain length of at least fifteen carbon atoms. The mixed long / short chain phospholipids serve to tune the release properties of the carrier. Preferred phospholipids are phosphatidylcholines.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
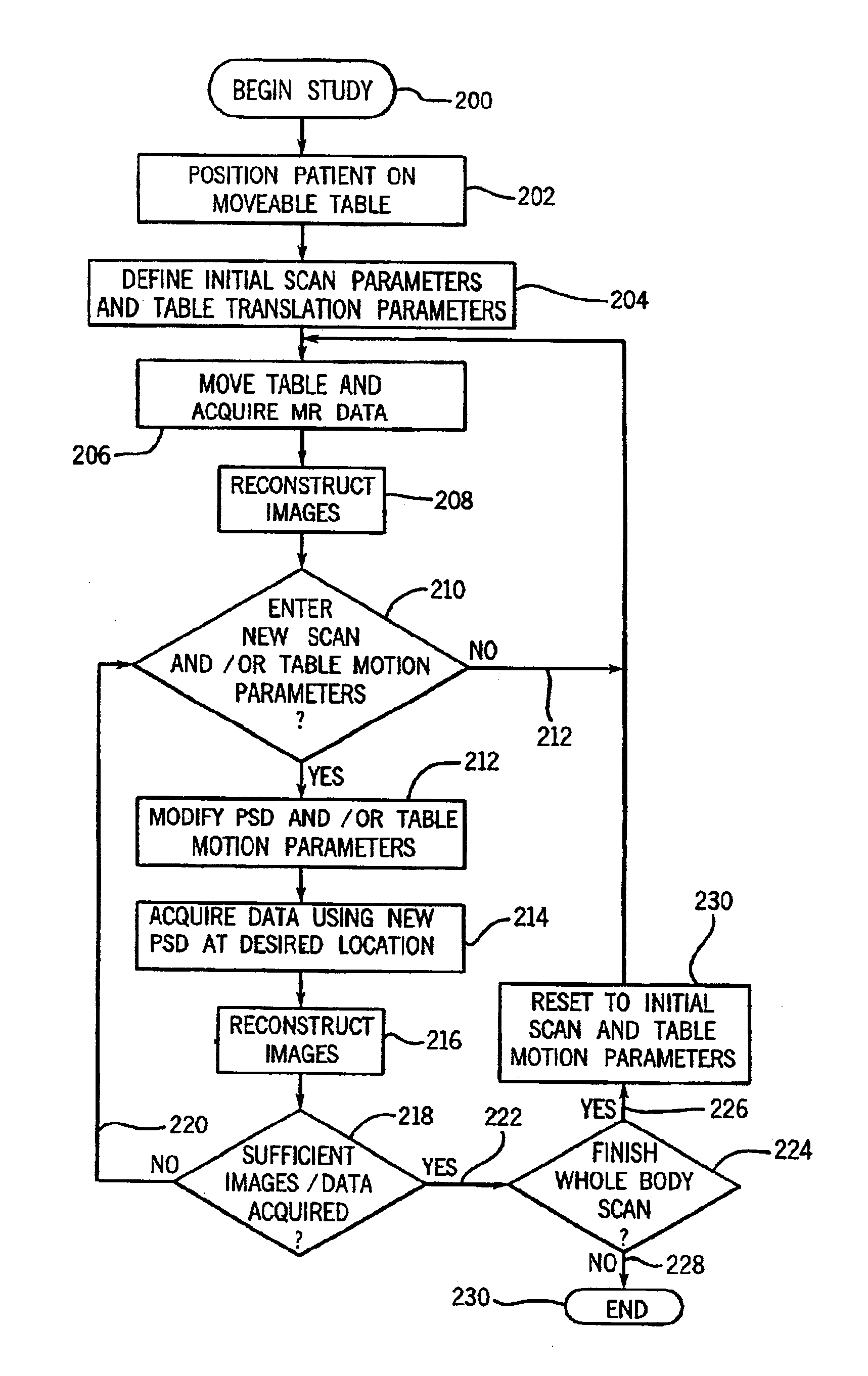
Whole body MRI scanning with moving table and interactive control
InactiveUS6963768B2Easy to useFast imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInteraction controlWhole body mri
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for high sensitivity whole body scanning using MR imaging. The invention includes acquiring MR data as the patient moves through the iso-center of the magnet while providing interactive control for the operator to change scan parameters and table motion and direction. The technique allows efficient whole body scanning for fast screening of abnormalities while allowing operator control during the screening process to interrupt table motion and redirect the speed and direction of the table while also allowing control over the acquisition plane, number of sections imaged, inter-section spacing, and the scan location.
Owner:UNIFORMED SERVICES UNIV OF HEALTH SCI DEPT OF DEFENSE US GOVERNMENT +1
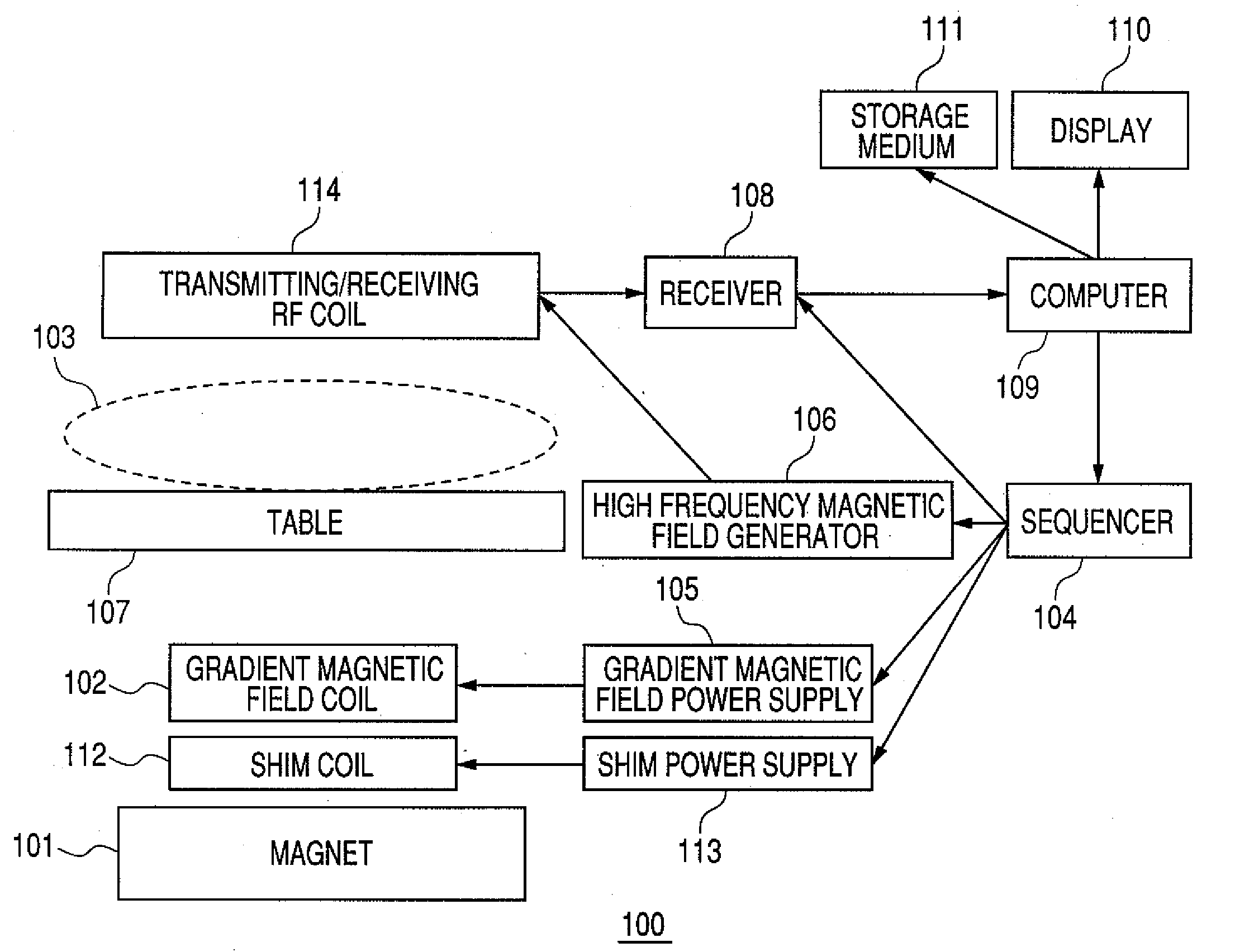
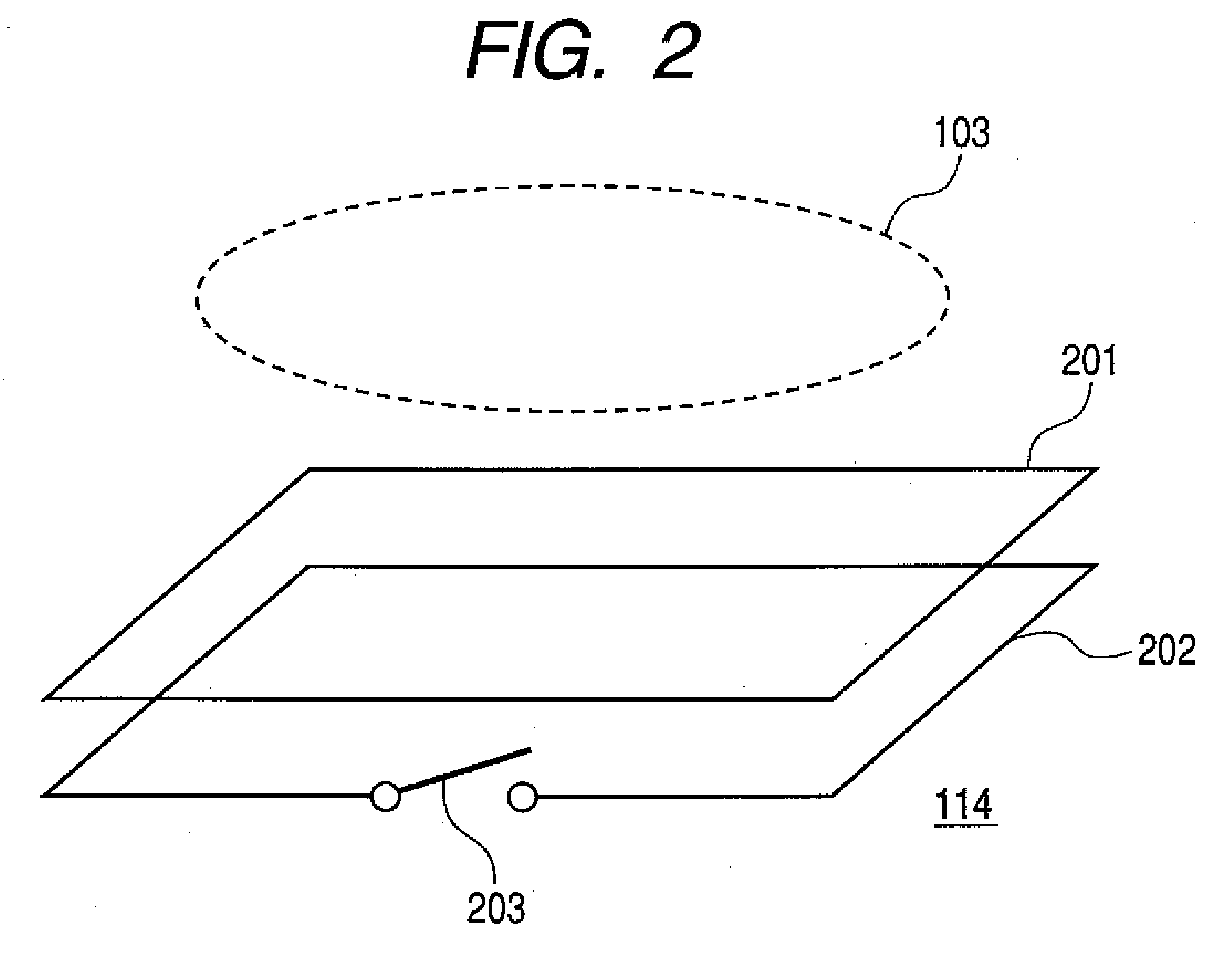
High frequency magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus with the same
InactiveUS20090251145A1Slight lowering in sensitivityMagnetic measurementsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceCouplingResonance
An RF coil for MR Imaging that can change a resonance frequency easily and instantaneously in response to a nuclide to be imaged without exchange and adjustment and that also causes only small lowering of sensitivity. The RF coil has a sub coil for changing a resonance frequency of the transmitting / receiving RF coil for transmitting and receiving an MR signal between itself and a nuclide that is an object to be imaged. The sub coil is equipped with a switch, and at the time of switching-on, shifts the resonance frequency of the RF coil by changing an inductance value of the RF coil in a noncontact manner using inductance coupling.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Synthesis and conjugation of iron oxide nanoparticles to antibodies for targeting specific cells using fluorescence and MR imaging techniques
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
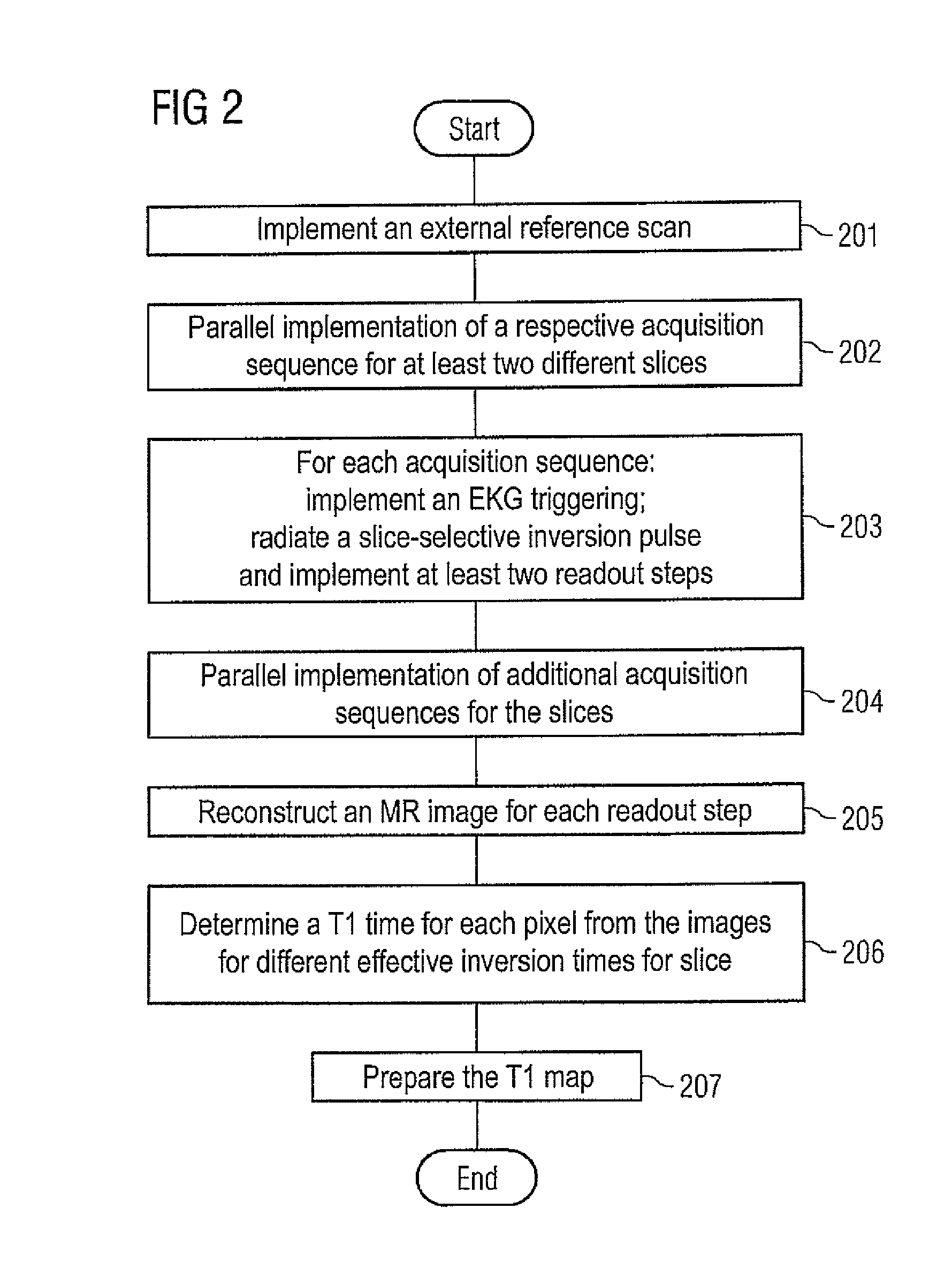
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create t1 maps
ActiveUS20110181285A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpatially resolvedProton magnetic resonance
In a method and apparatus for MR imaging, a data acquisition sequence is executed wherein at least two slices of an examination subject are imaged in parallel with a gradient echo method for spatially resolved quantification of the T1 relaxation time.At least one first acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a first slice of the examination subject and at least one second acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a second slice of the examination subject. The acquisition sequences each include an inversion pulse and at least two successive readout steps. The first and second acquisition sequences are temporally offset from one another such that they at least partially overlap.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
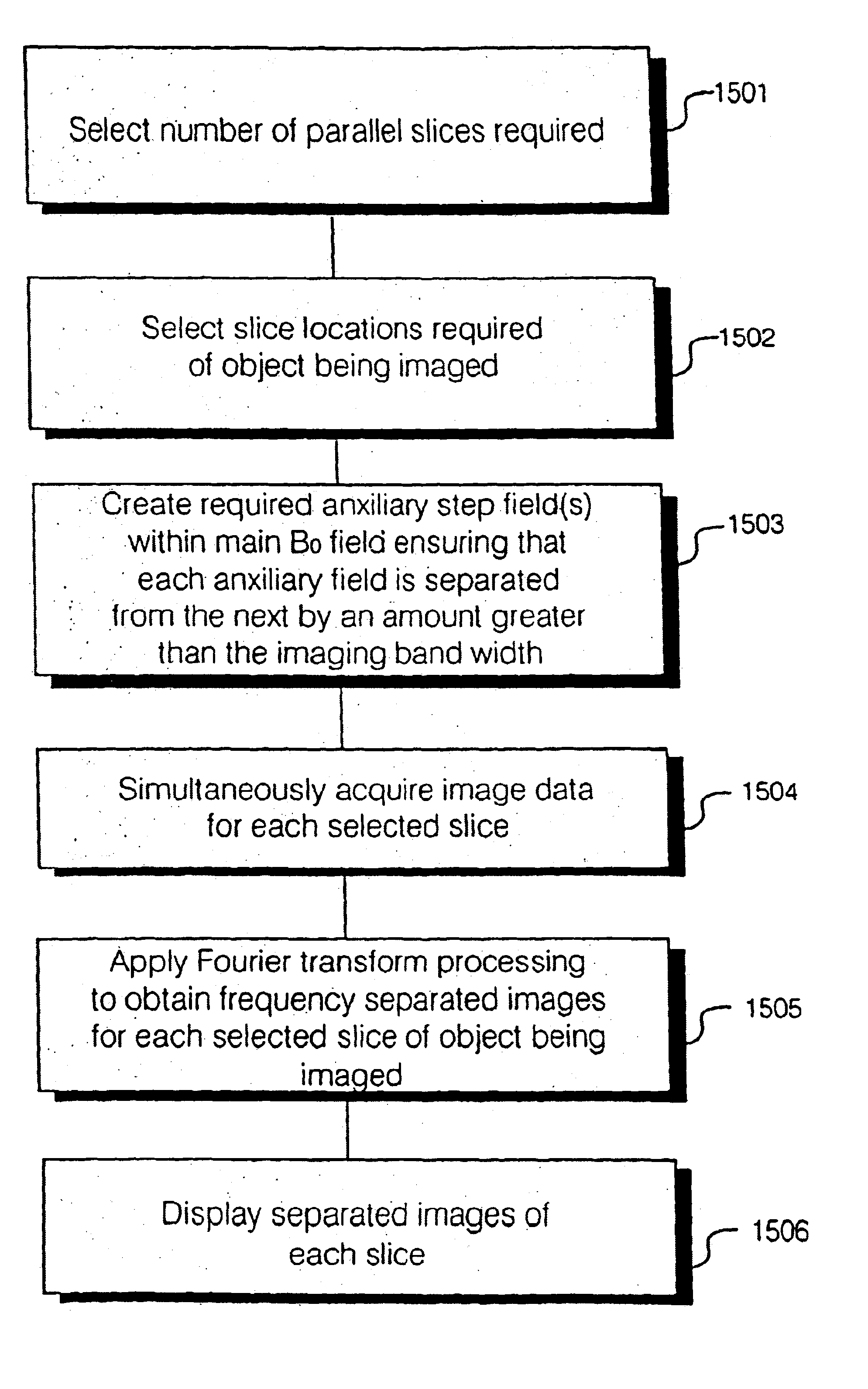
Methods & apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6980001B2Shorten Image Acquisition TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetizationPhysical entity
A parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus configurable to image a physical entity comprises:a main magnetic flux source for providing a uniform fixed magnetic field, B0;an RF array system comprising a plurality of RF coils and receivers, said RF system configured for:generating rotating RF excitation magnetic fields B1; andreceiving RF signals due to precessing nuclear magnetization on multiple spatially distinct radio frequency coils and associated receiver channels, said RF system being configured to operate in accordance with a B1 sensitivity encoding technique;a control processor for controlling imaging functionality, collecting image data and effecting data processing of the captured image data the control processor being configured with post processing capability for the B1 sensitivity encoding technique;an image display means for displaying processed image data as resultant images; andan auxiliary magnetic field means capable of producing at least one auxiliary uniform B0 step magnetic field imaging region within the main B0 magnetic field;wherein:the auxiliary magnetic field, means is configured to operate in combination with the RF coil system and the B1 sensitivity encoding technique, the imaging apparatus thereby providing faster image acquisition than that attributed to the speed up factor provided solely by the B1 sensitivity encoding technique.The invention also includes a method of imaging using this apparatus.Furthermore, the invention also includes a method and apparatus for three-dimensional MR imaging using a 1D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array coupled with a 2D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD AT WESTERN BANK THE
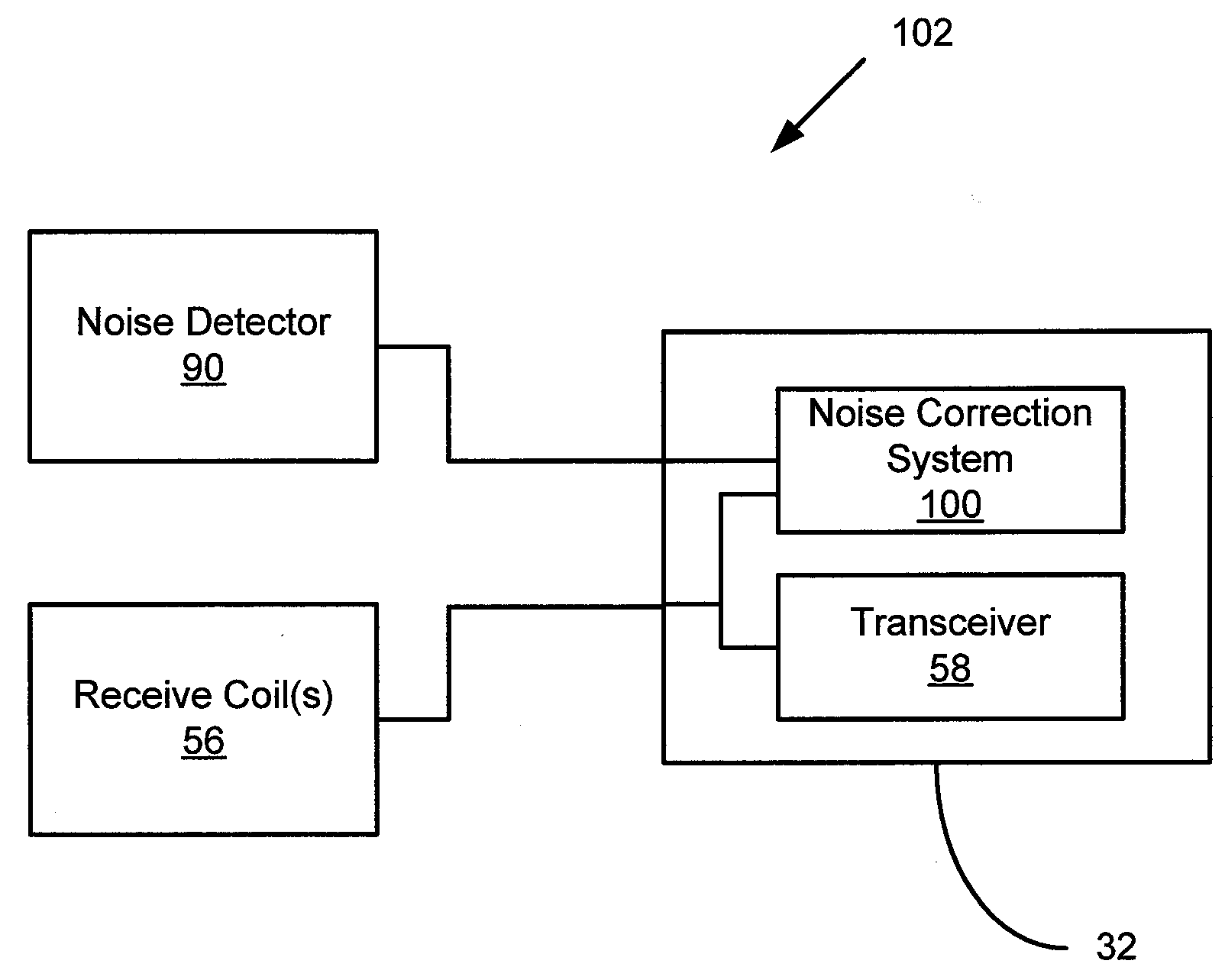
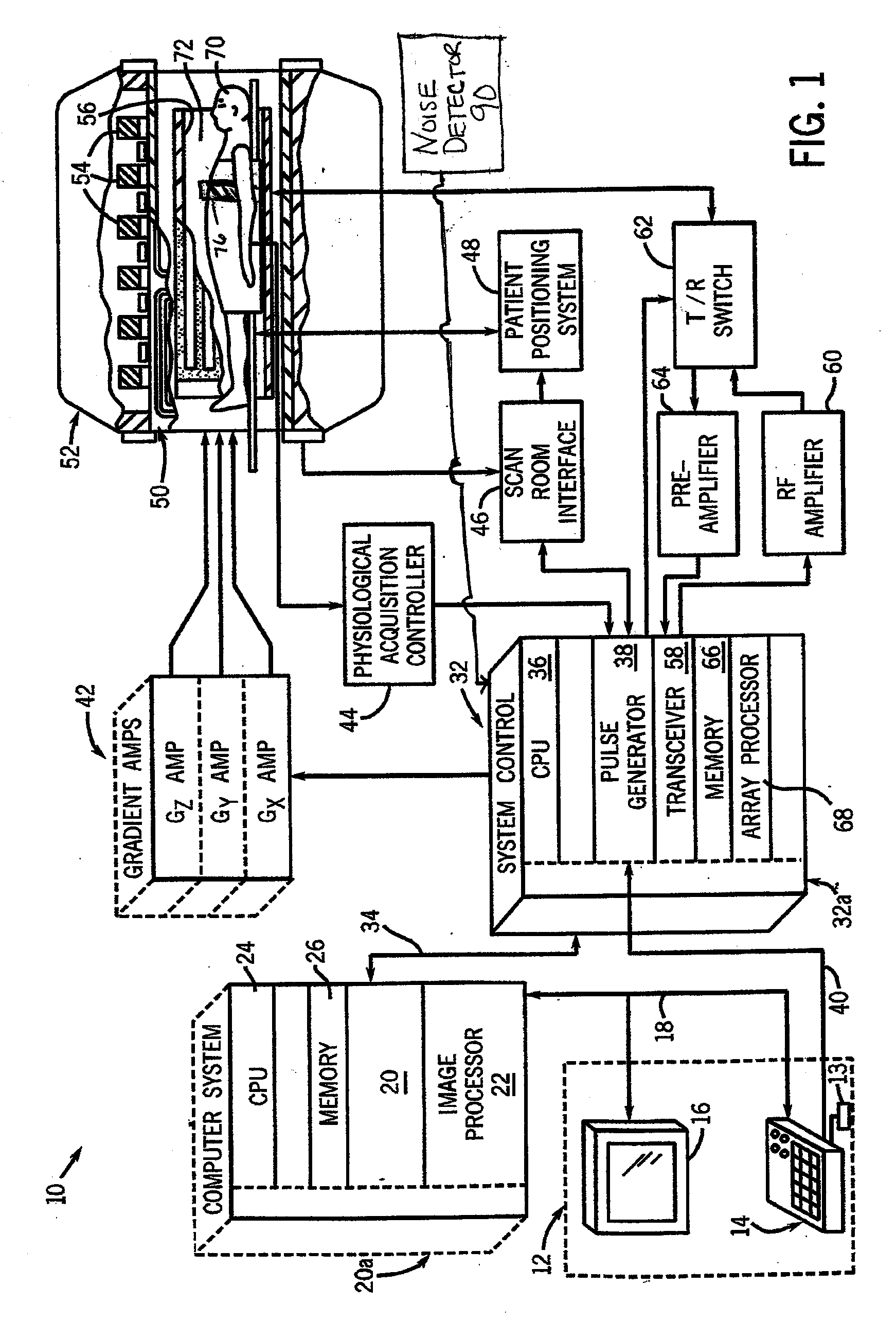
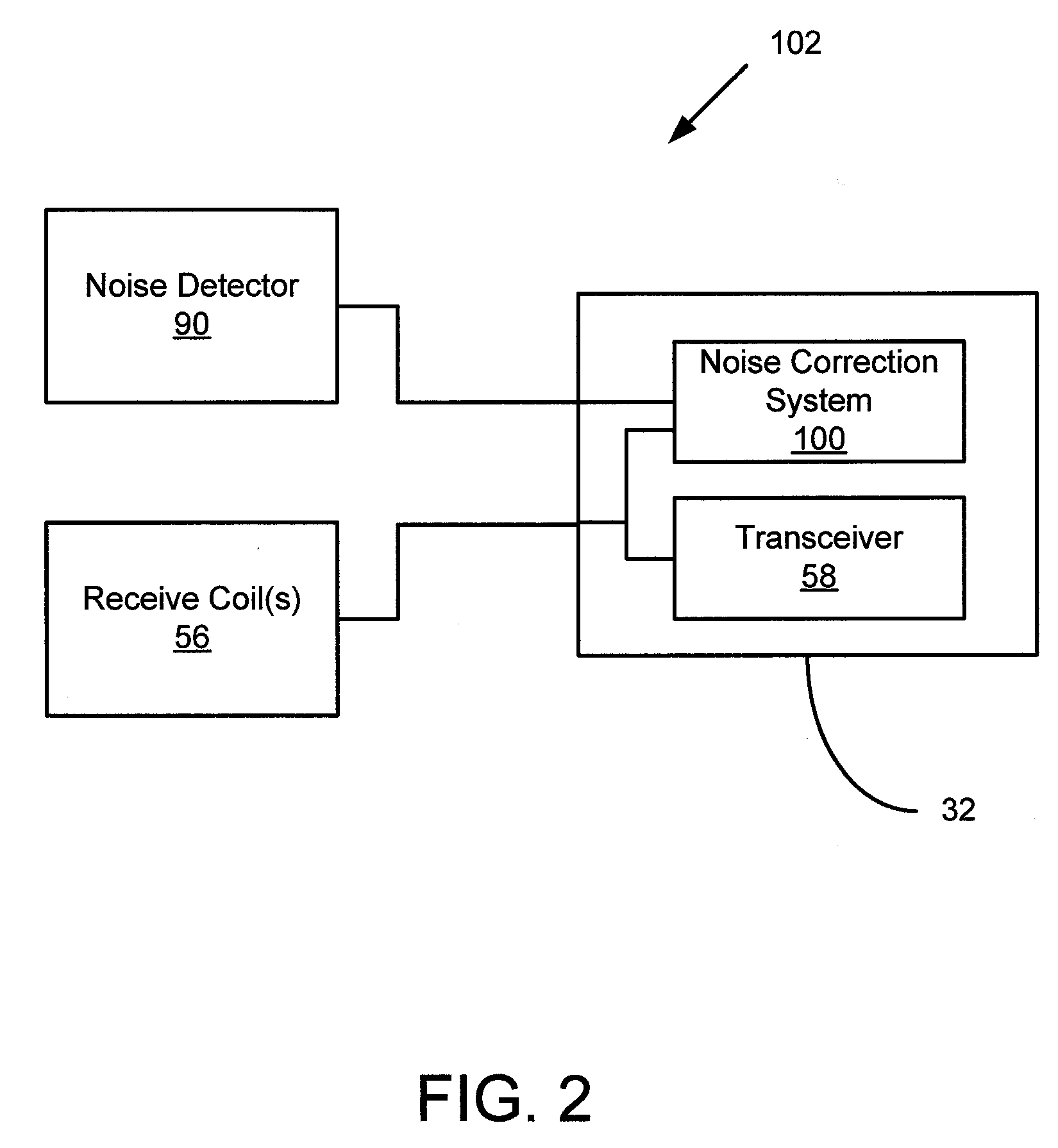
System and apparatus for electromagnetic noise detection in an mr imaging scanner environment
InactiveUS20080315879A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNoise correctionMagnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
A system for detecting electromagnetic noise in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner environment includes an antenna configured to detect electromagnetic noise. The antenna includes a first conducting loop and a second conducting loop oriented perpendicularly to the first conducting loop. The system also includes a noise correction system coupled to the antenna and configured to receive noise signals from the antenna.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
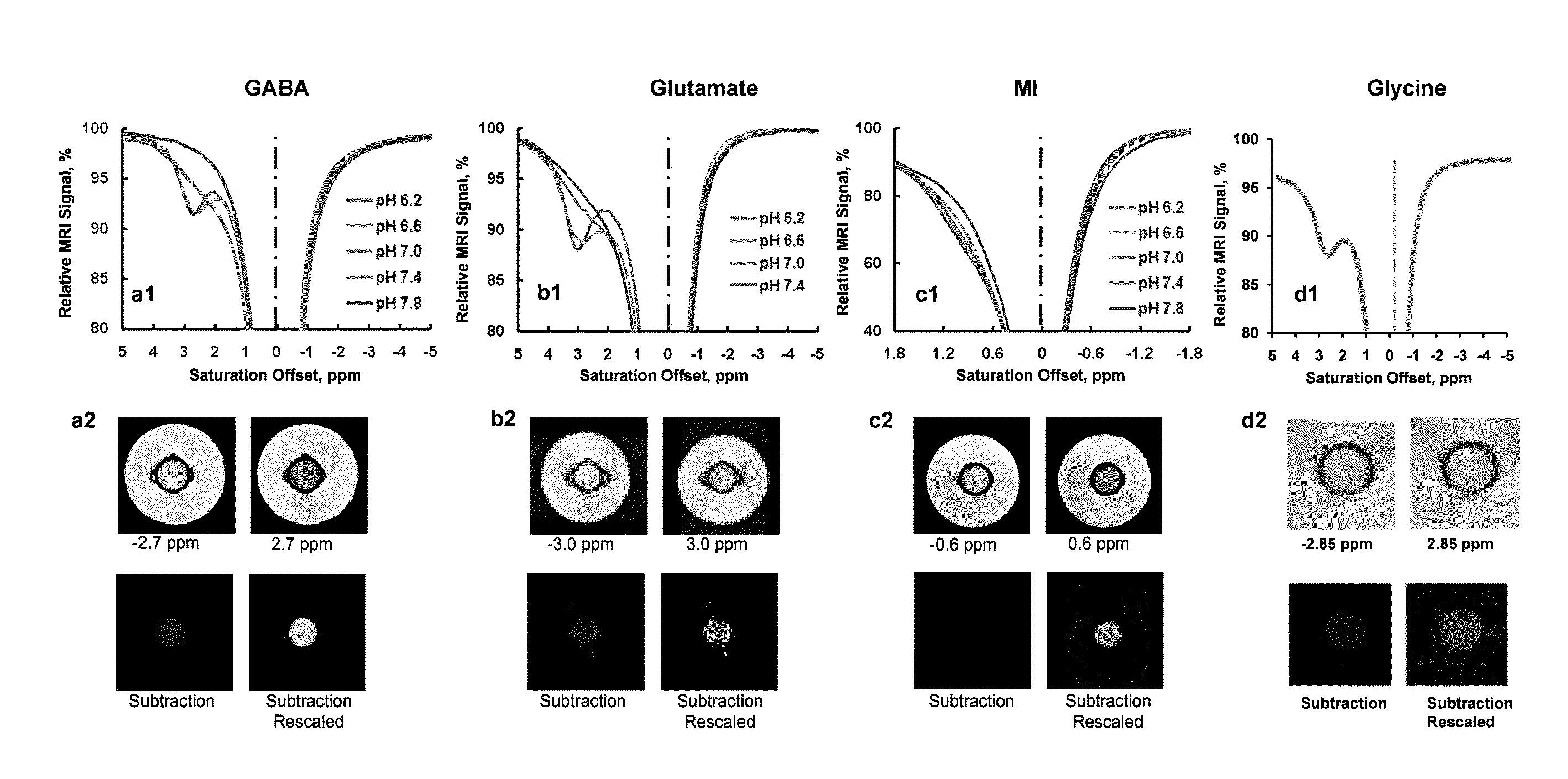
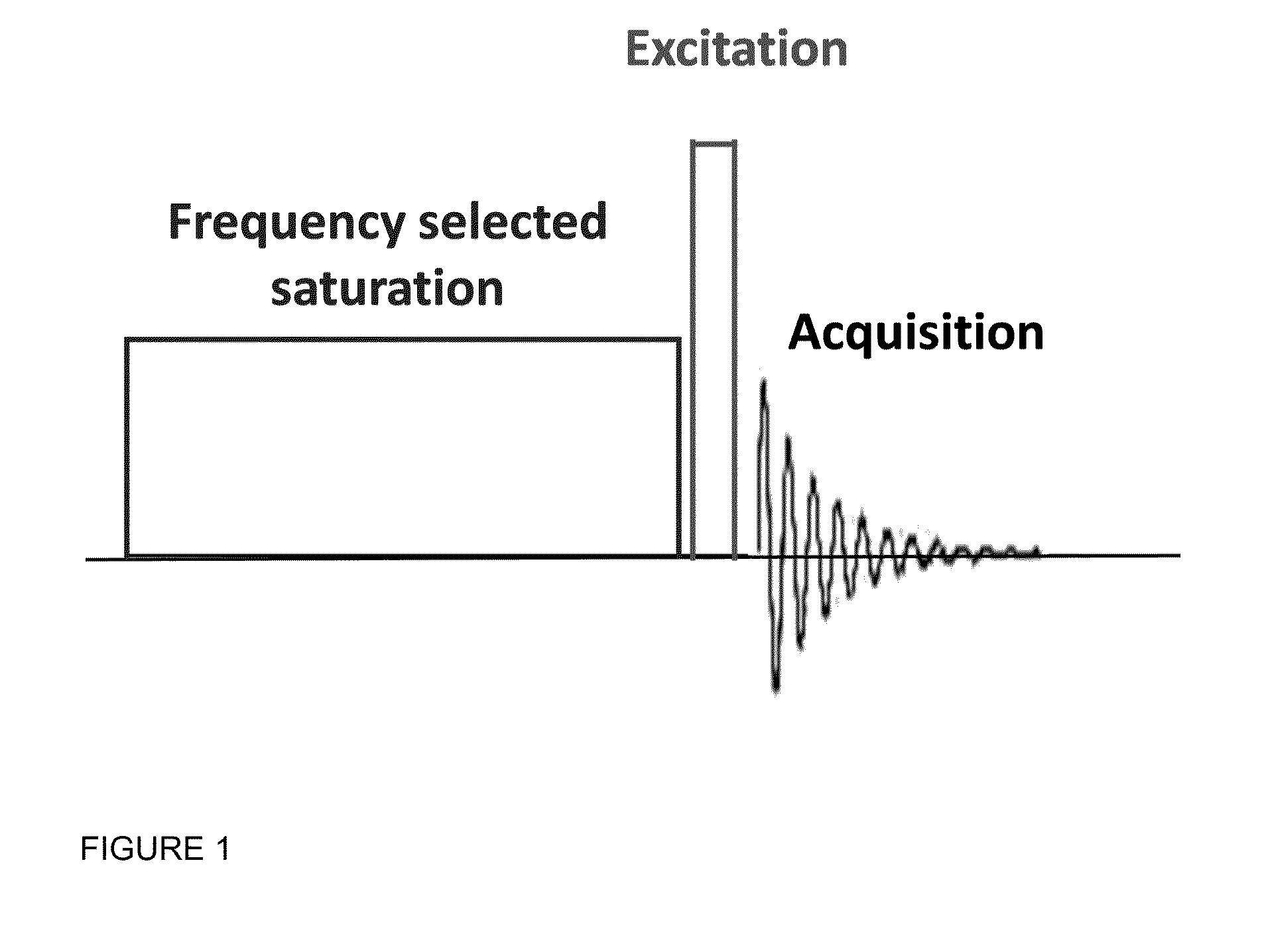
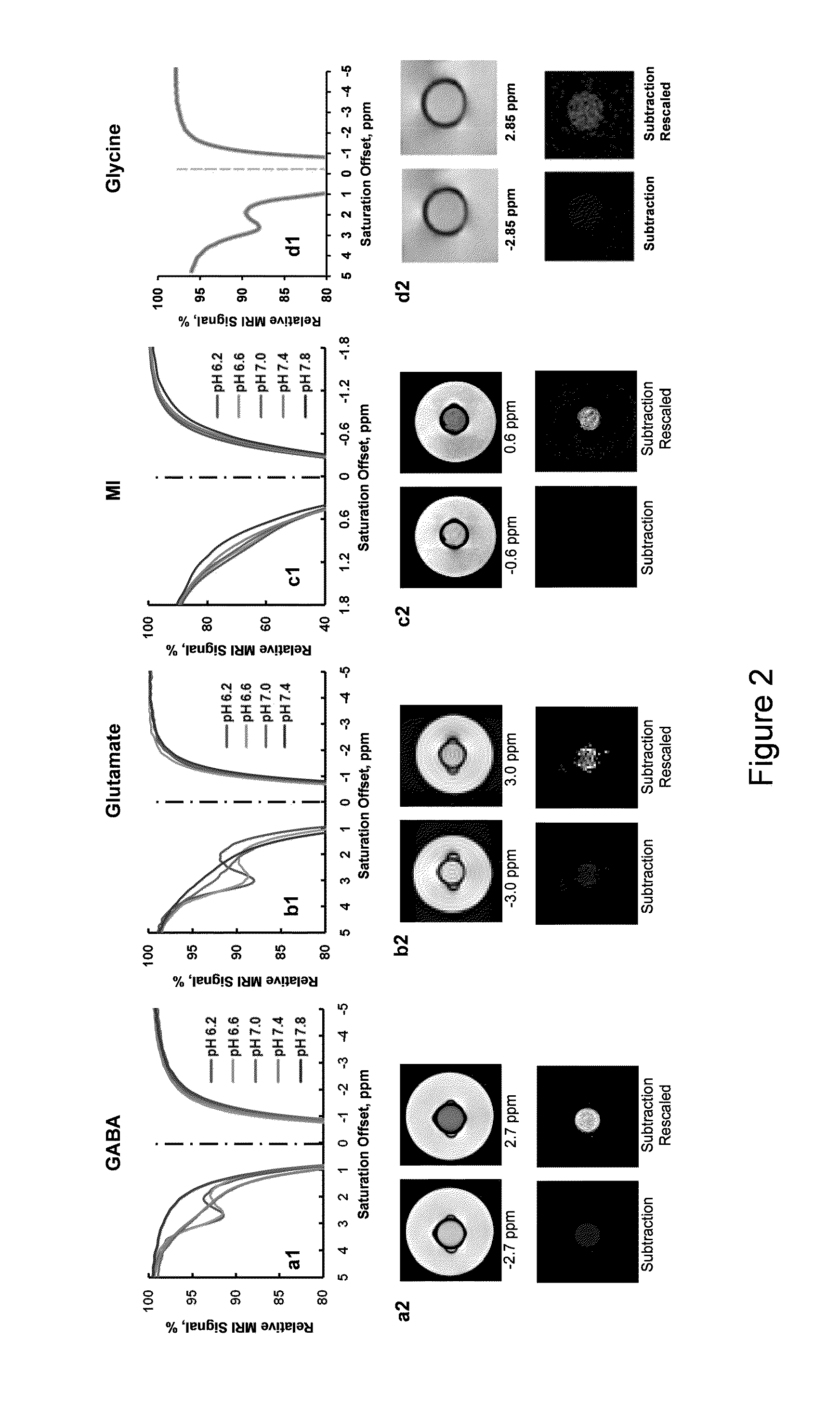
Cest MRI methods for imaging of metabolites and the use of same as biomarkers
ActiveUS20120019245A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to detectMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionEndogenous metabolismMetabolite
The CEST effect for various neurotransmitters and energy metabolites in the brain and muscles and various endogenous metabolites in the liver, brain, and myocardium are imaged using MR imaging to illustrate a unique CEST effect that may be used to monitor the concentration of the metabolite and hence to characterize and monitor various disease states in the body correlated to the concentration of that metabolite. By adjusting the timing, amplitude, and length of the RF pulse as well as other parameters of the CEST pulse sequence to address the unique chemical shifts and exchange rates of the target, new targets with unique characteristics may be acquired using CEST MR imaging.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Parallel collection image reconstruction method and device
InactiveCN101308202AImprove SNRMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
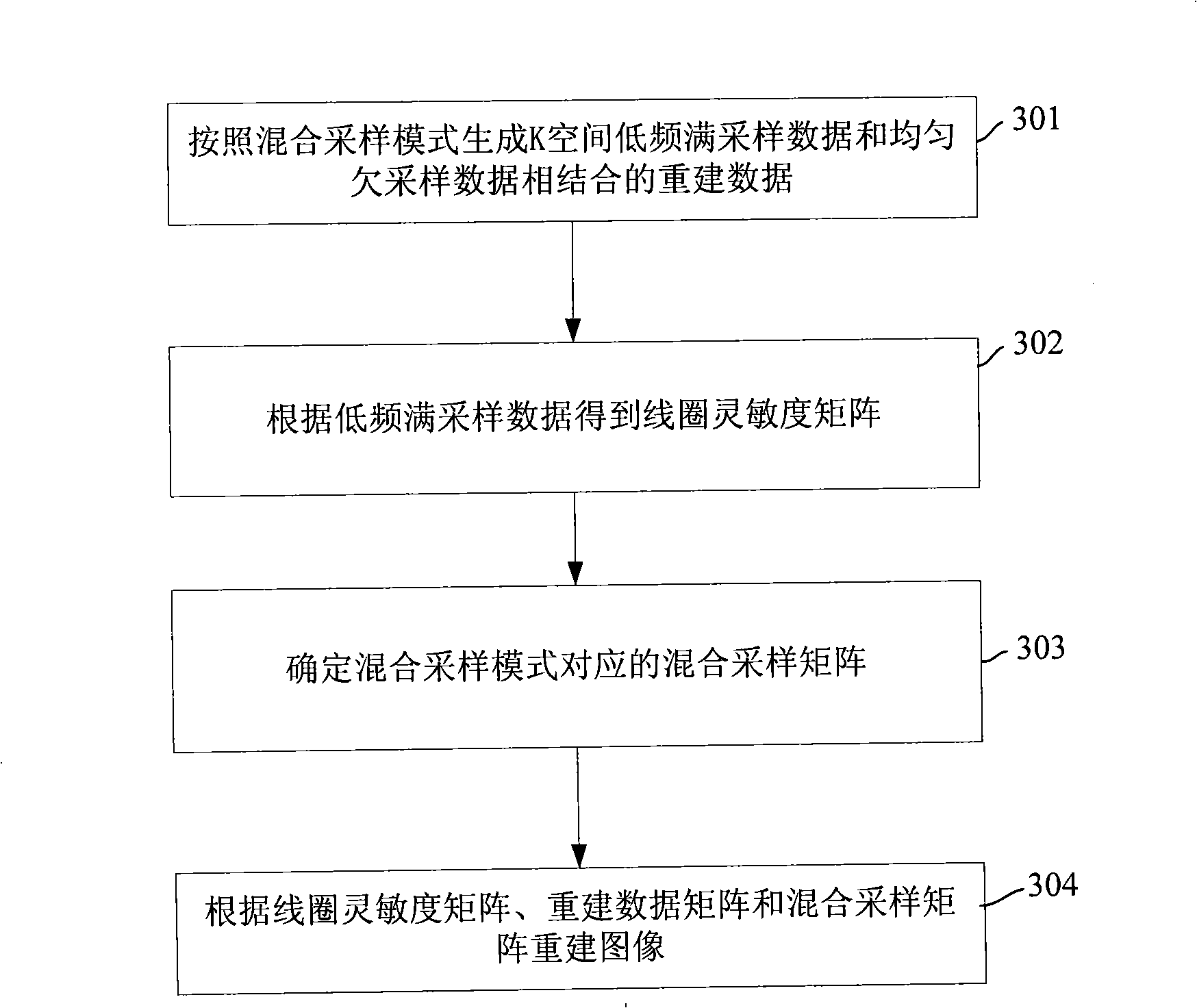
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing a parallel-acquired image, comprising: generating reconstruction data by combining uniformly under-sampled data and low-frequency fully-sampled data in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) K-space according to a hybrid sampling mode; calculating the sensitivity distribution of a coil according to the low-frequency fully-sampled data; and reconstructing an image according to the reconstruction data, the sensitivity distribution of the coil and the hybrid sampling mode. The invention also discloses an apparatus for reconstructing the parallel-acquired image. The method and the apparatus are adopted to generate reconstruction data by combining uniformly under-sampled data and low-frequency fully-sampled data in K-space according to the hybrid sampling mode and take the hybrid sampling mode into account during the image reconstruction, and the signal to noise ratio of the reconstructed image is effectively improved by using the reconstruction data combined with the low-frequency fully-sampled data in reconstructing the image since the low-frequency fully-sampled data contains more useful information.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Split-blade data collection for propeller MRI
InactiveUS6882148B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoPhase correction
The present invention provides a system and method of MR imaging particularly applicable with fast spin echo protocols. Odd and even echoes are used to create separate blades or strips in k-space. Preferably, each blade extends through the center of k-space. The blades are incrementally rotated about the center of k-space with each echo train until a full set of k-space data is acquired. After a phase correction, each odd and even blade is combined into a single k-space data set that is used for image reconstruction.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST CALIFORNIA NONPROFIT PUBLIC BENEFIT D B A ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENT
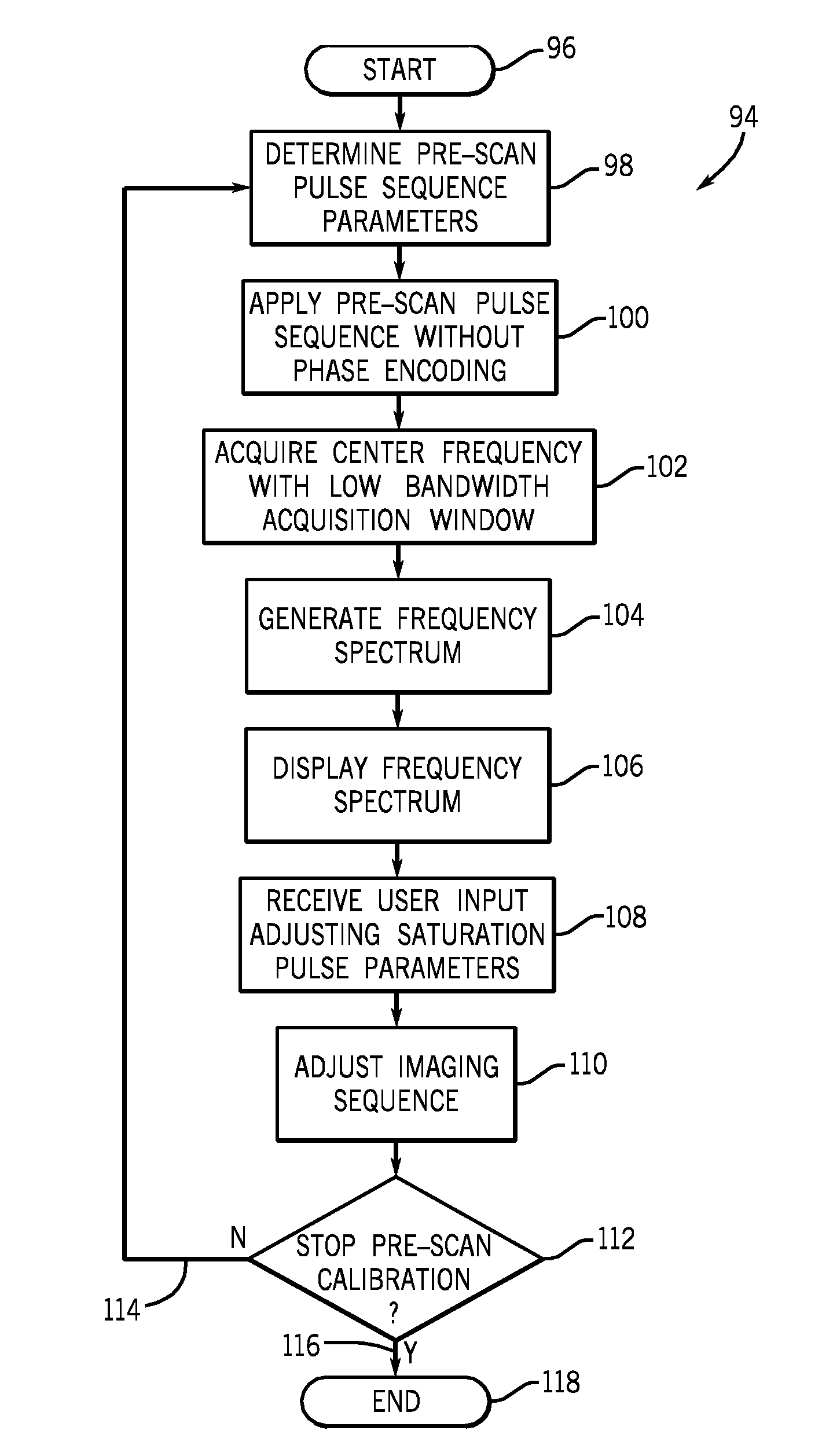
Method and apparatus for interactively setting parameters of an MR imaging sequence through inspection of frequency spectrum
ActiveUS8115485B1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumPulse sequence
A method of calibrating an imaging sequence includes the application of a pre-scan pulse sequence to acquire MR signals from a region-of-interest to be imaged with an imaging pulse sequence. The pre-scan pulse sequence is interrupted to acquire pre-scan data in a low bandwidth acquisition window. A frequency spectrum is generated from the pre-scan data and displayed to interactively allow a user to establish scan parameters for the imaging pulse sequence.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
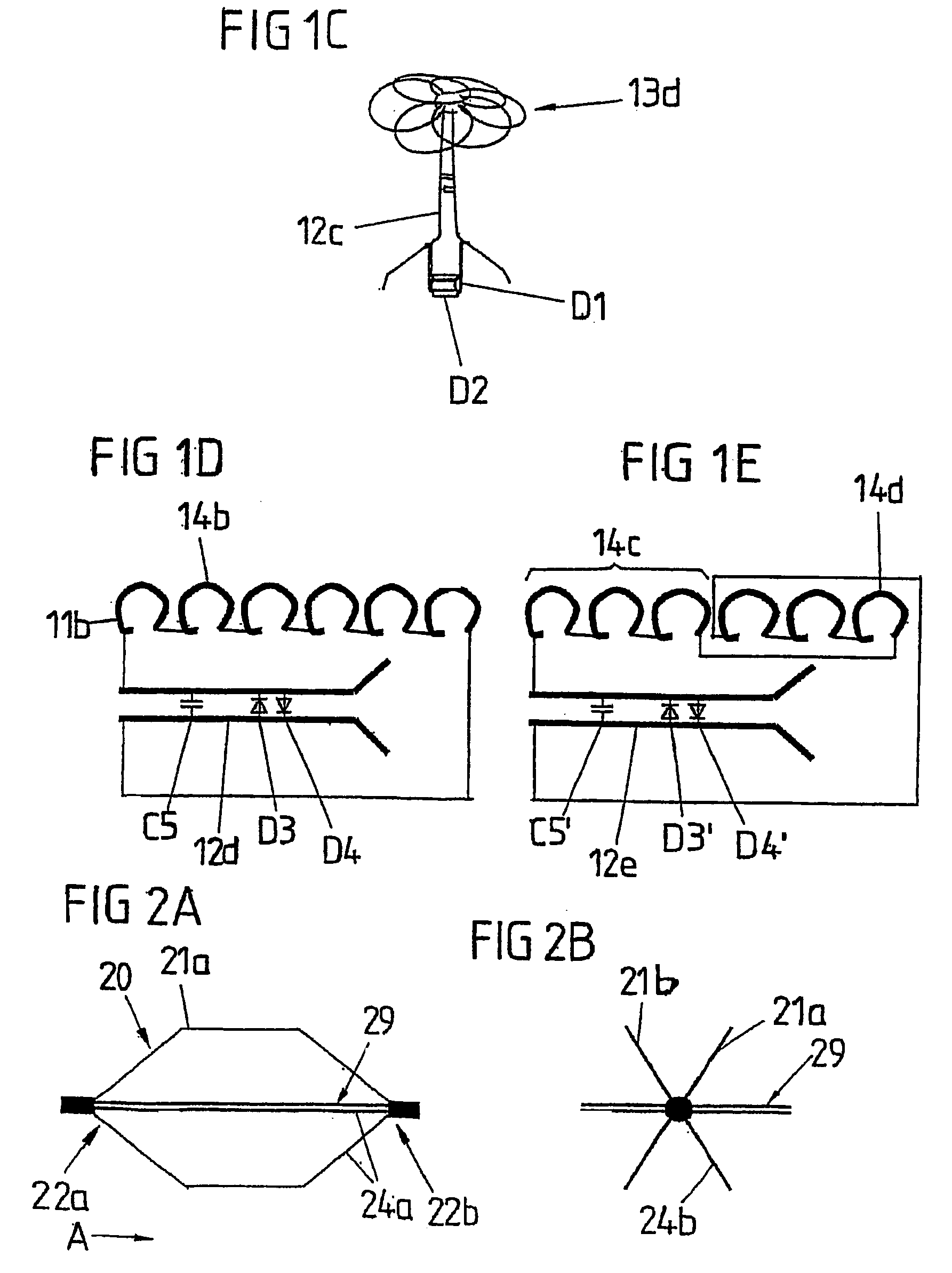
Vessel filter
The invention relates to a vessel filter comprising at least one conductor loop (21) which forms the inductance of an electric resonance circuit. According to the invention, the conductor loop (21) forms the vessel filter or parts of a vessel filter. The invention provides a vessel filter which is characterized by good mechanical properties, especially a high degree of flexibility and stability, offering good representability in MR imaging systems.
Owner:AMRIS PATENTE VERW
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com