Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
163 results about "Static field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Static Field. Definition - What does Static Field mean? A static field is in programming languages is the declaration for a variable that will be held in common by all instances of a class. The static modifier determines the class variable as one that will be applied universally to all instances of a particular class.
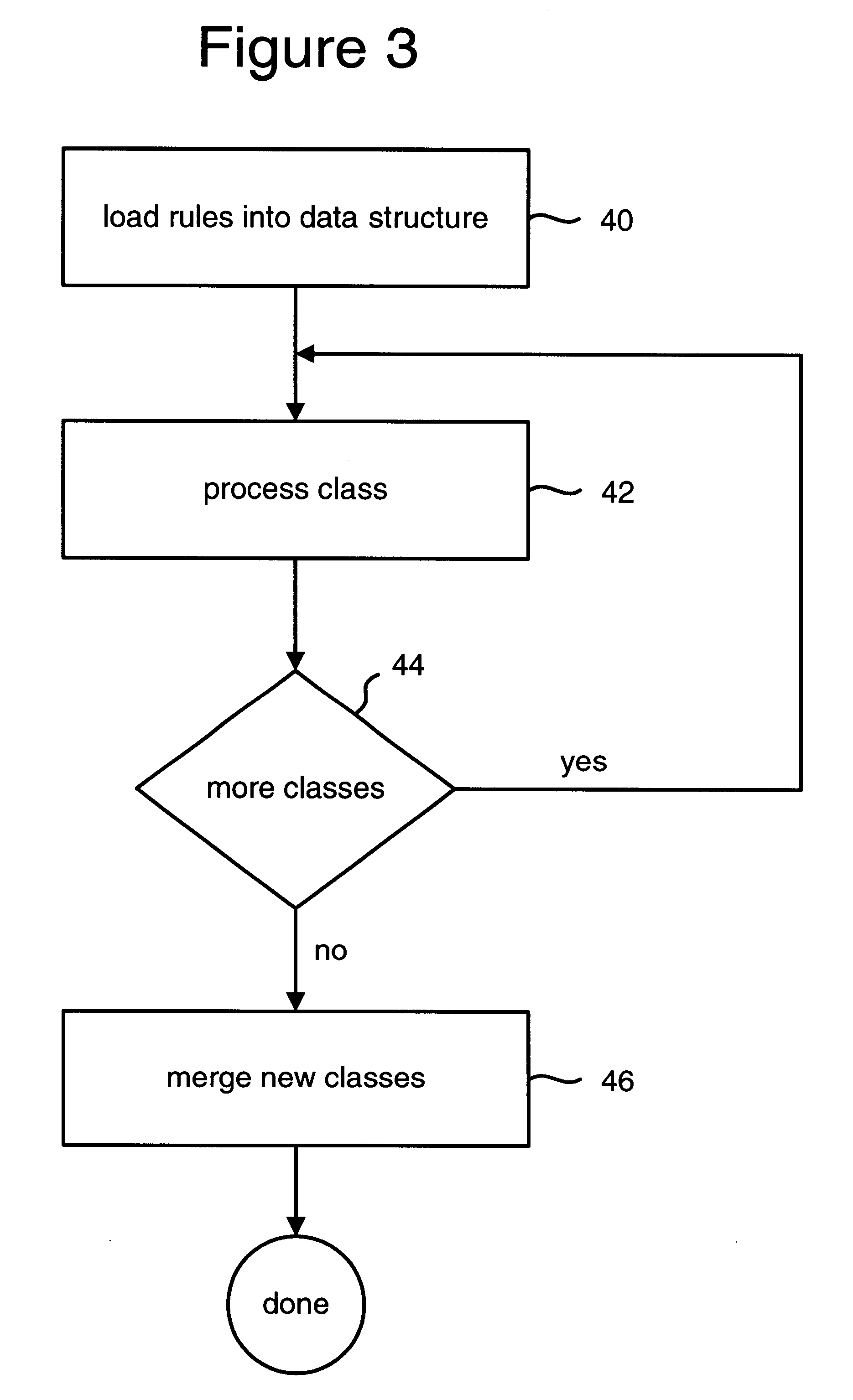
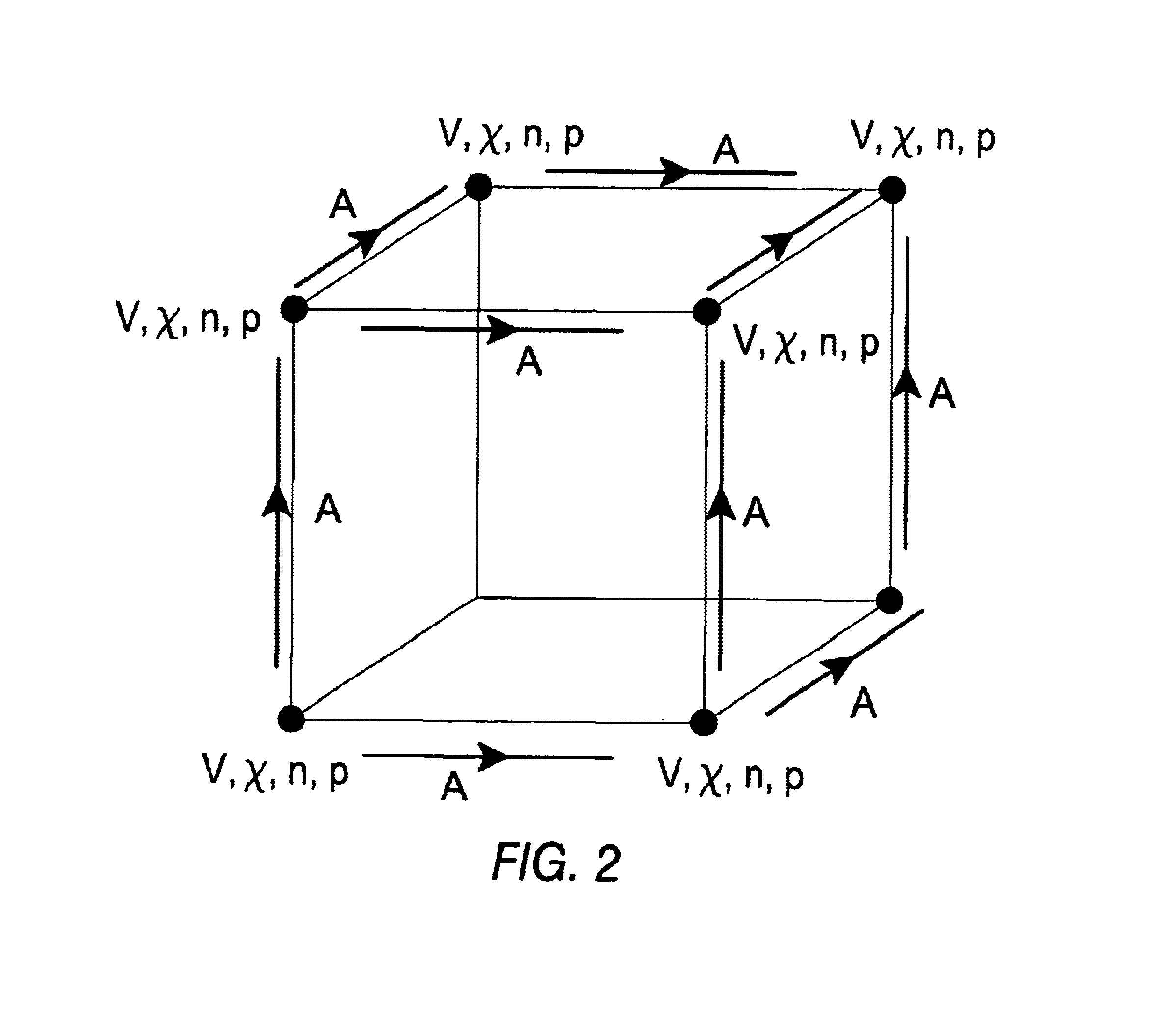
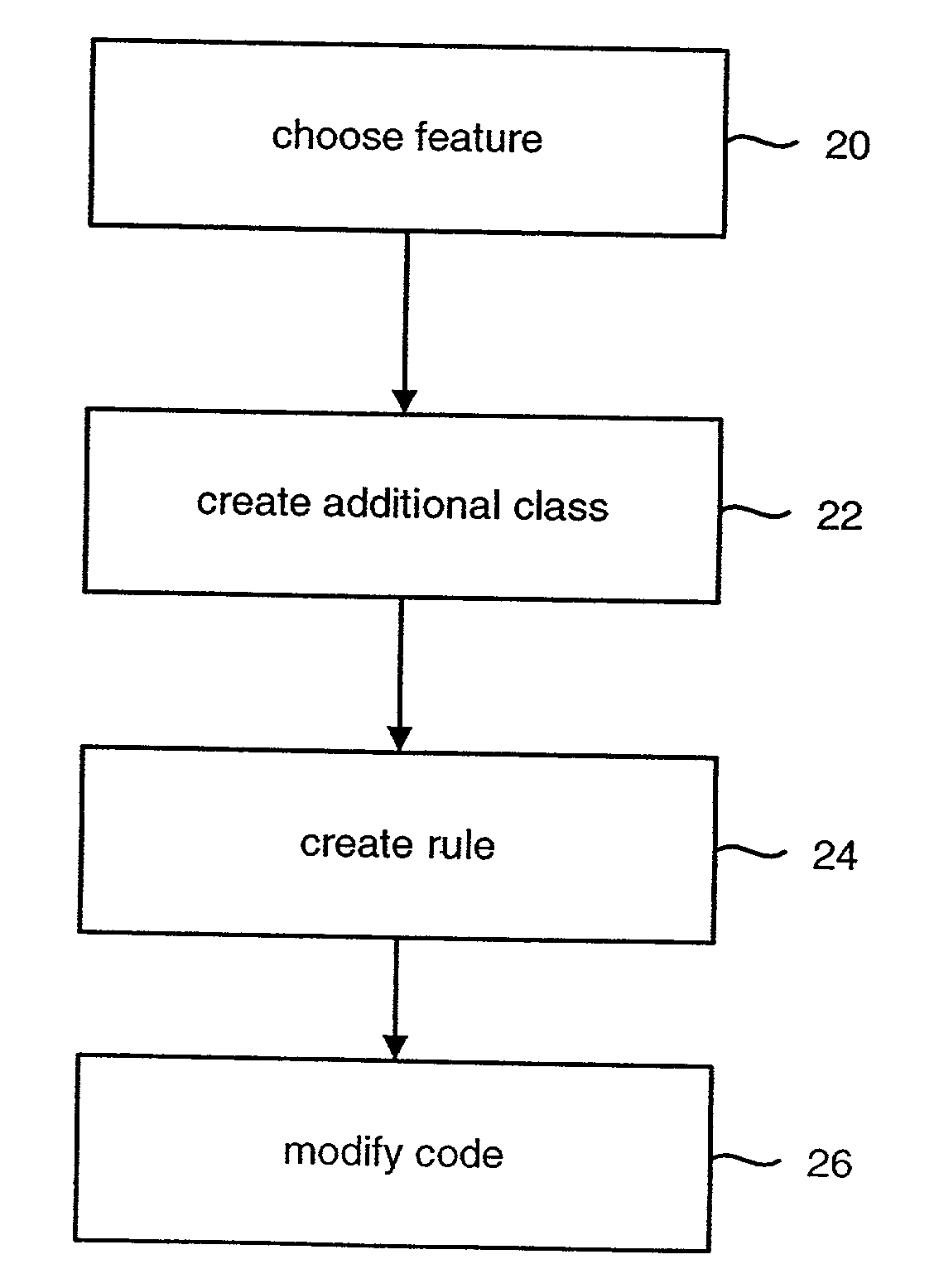
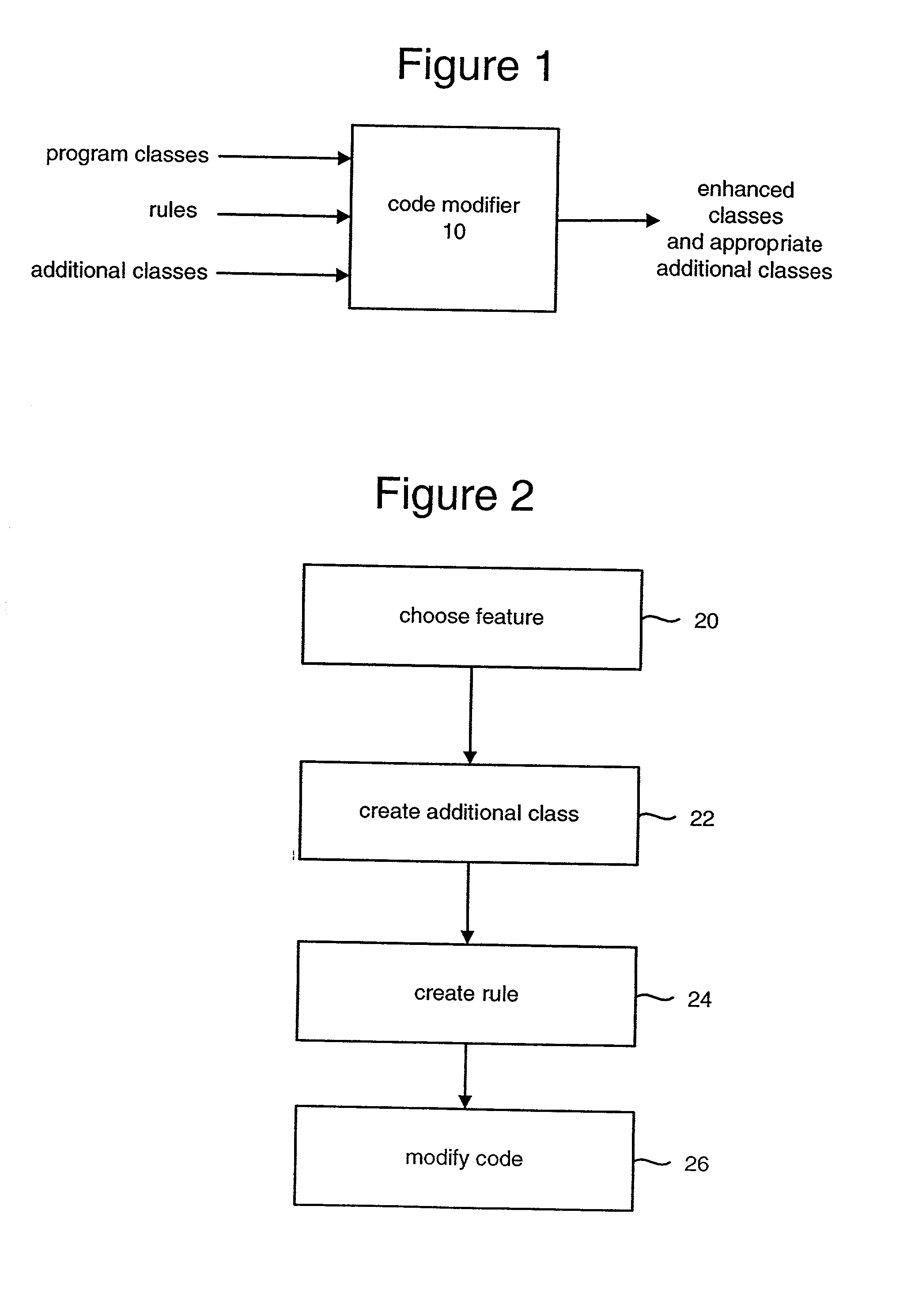
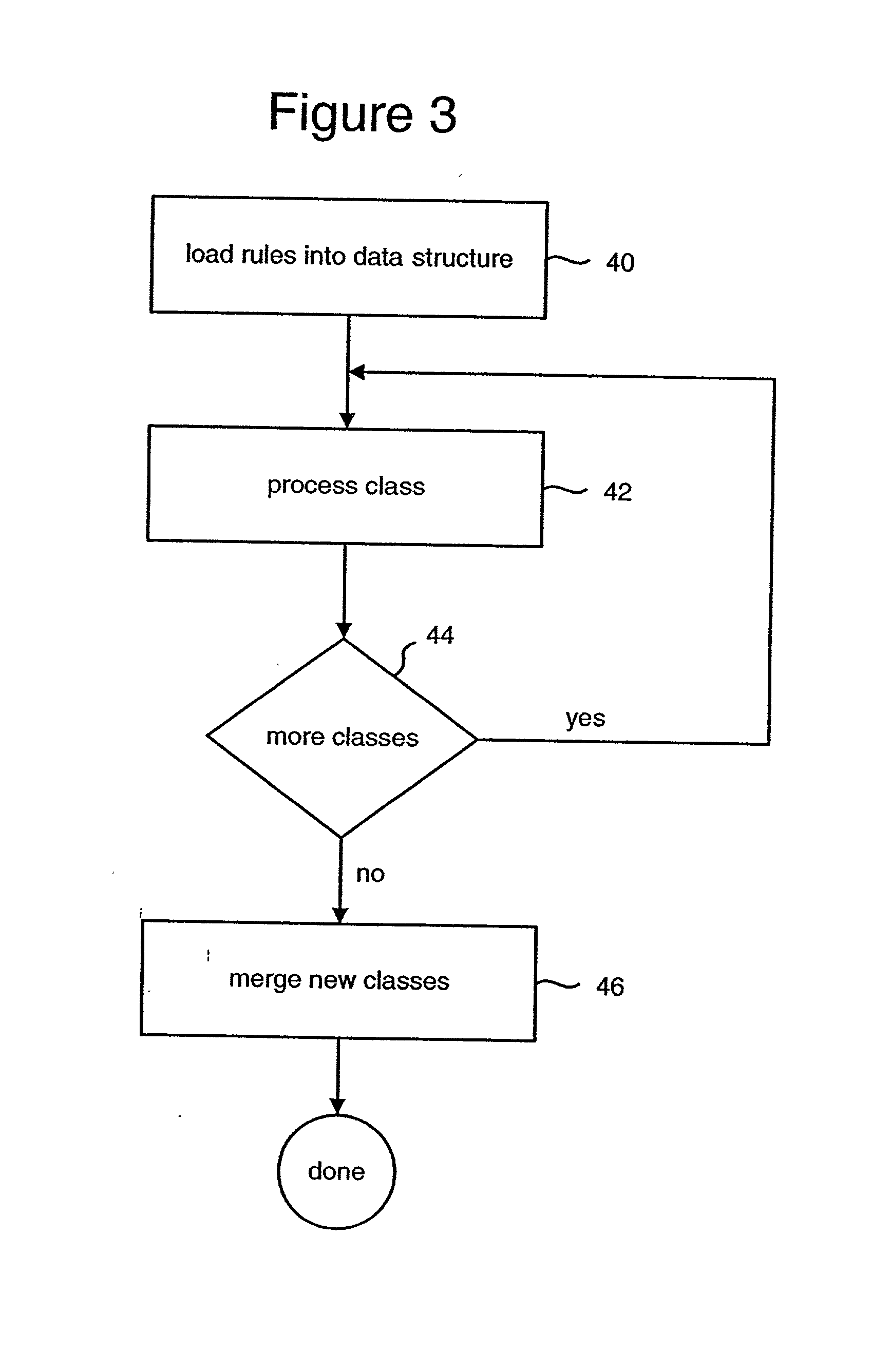
System for modifying object oriented code
The system receives three sets of inputs: program class definitions, a set of rules, and additional class definitions to be merged with the program class definitions. There are three types of rules: the first rule is used to substitute the allocation of an object of a new class for the allocation of the object based on an original class; the second rule is used to change code that allocates an object of an original class to code that calls a static method that allocates the object of the original class; and the third rule is used to a replace a new static field for an original static field. The system separately reads each of the original class definitions into a class data structure and performs the modifications to the class data structure according to the set of rules. The resulting class data structure is written to an output stream.
Owner:CA TECH INC
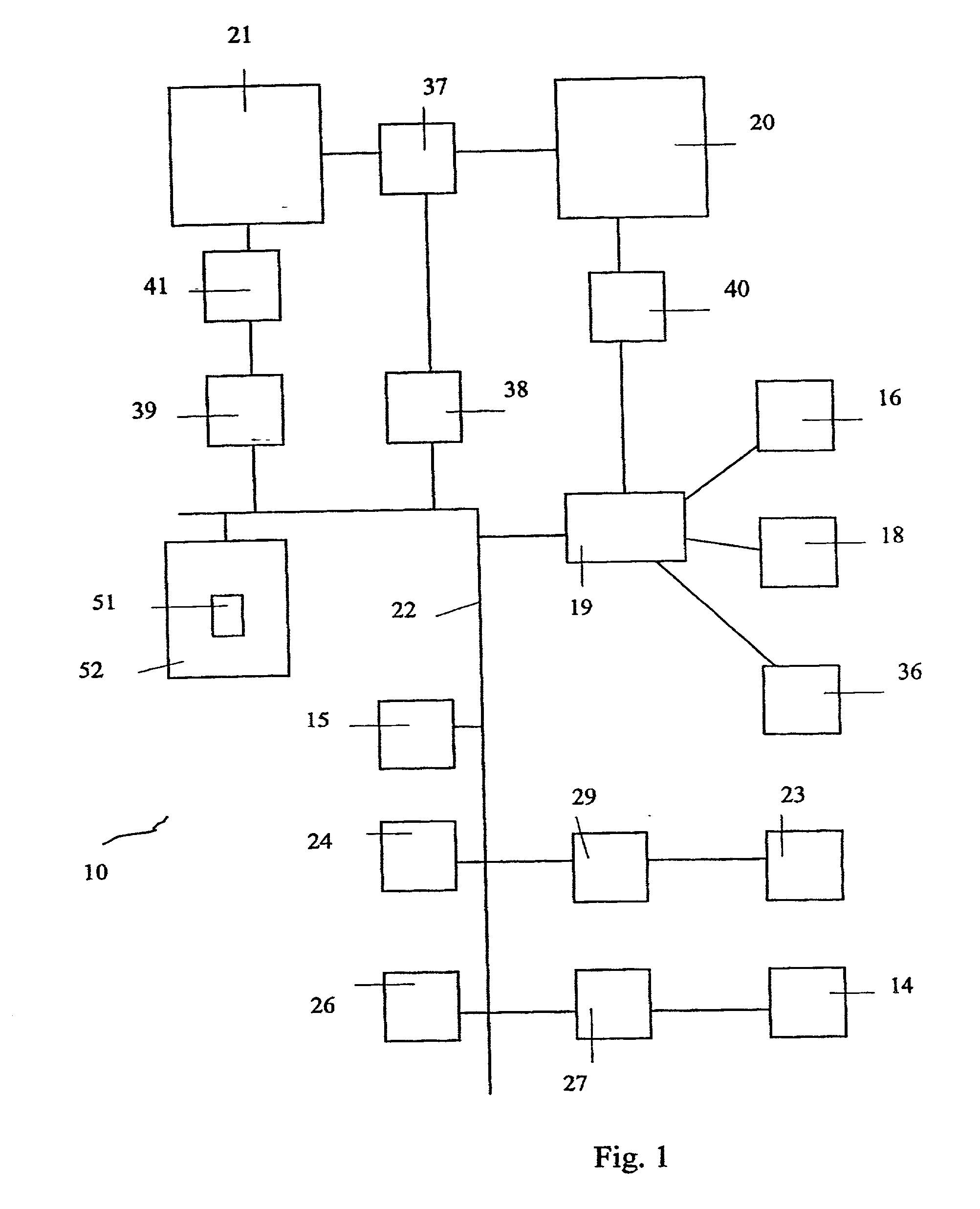
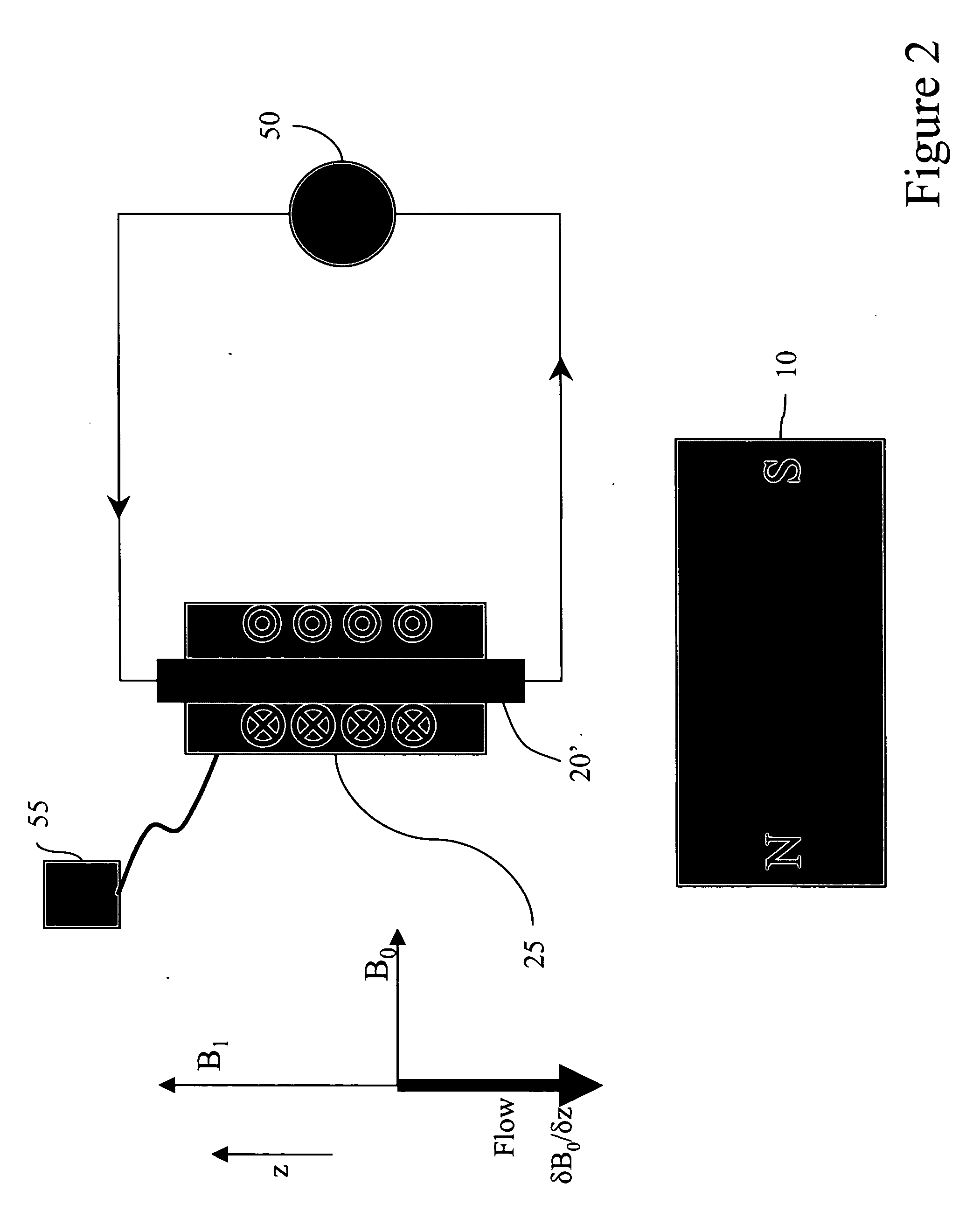
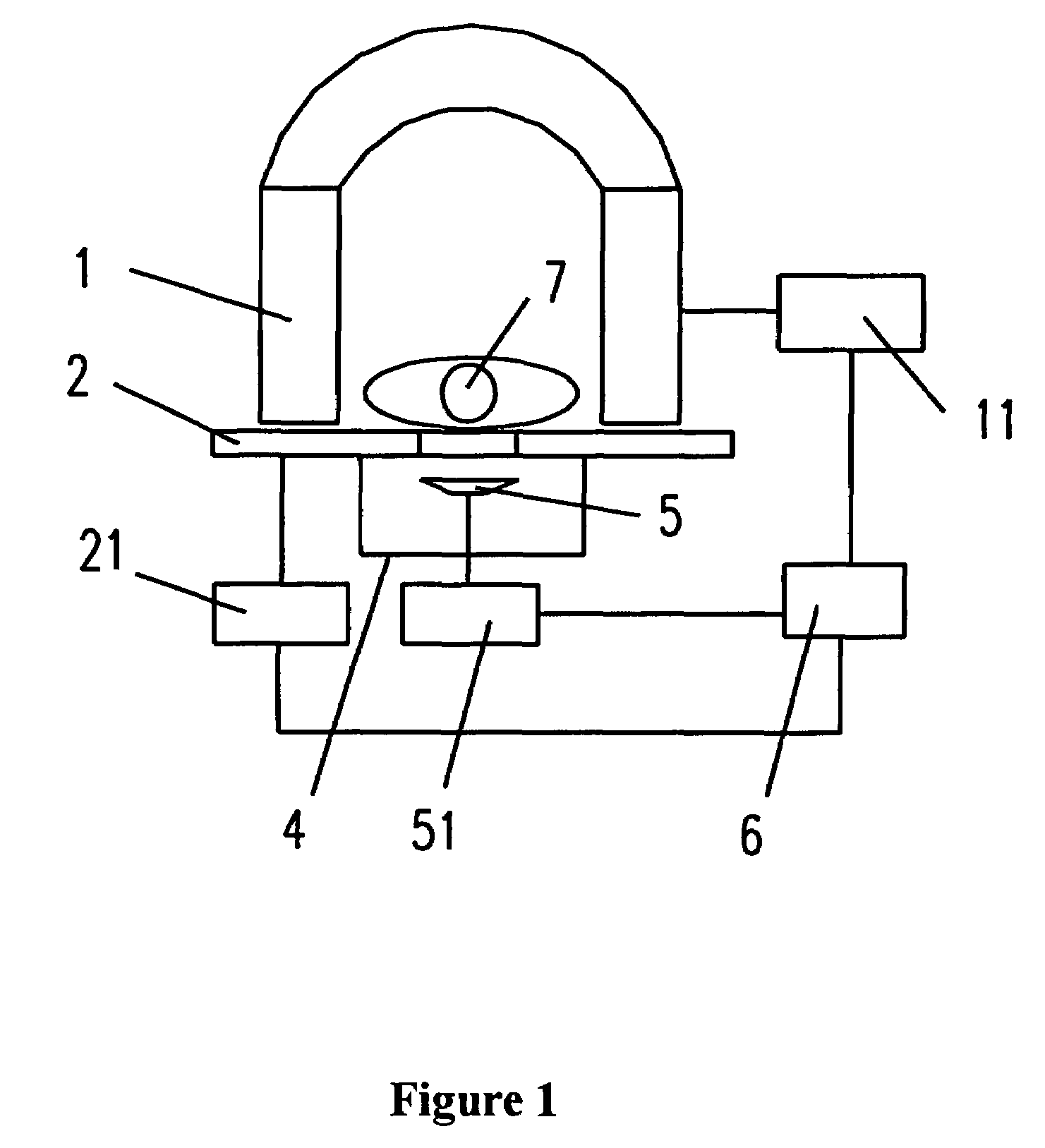
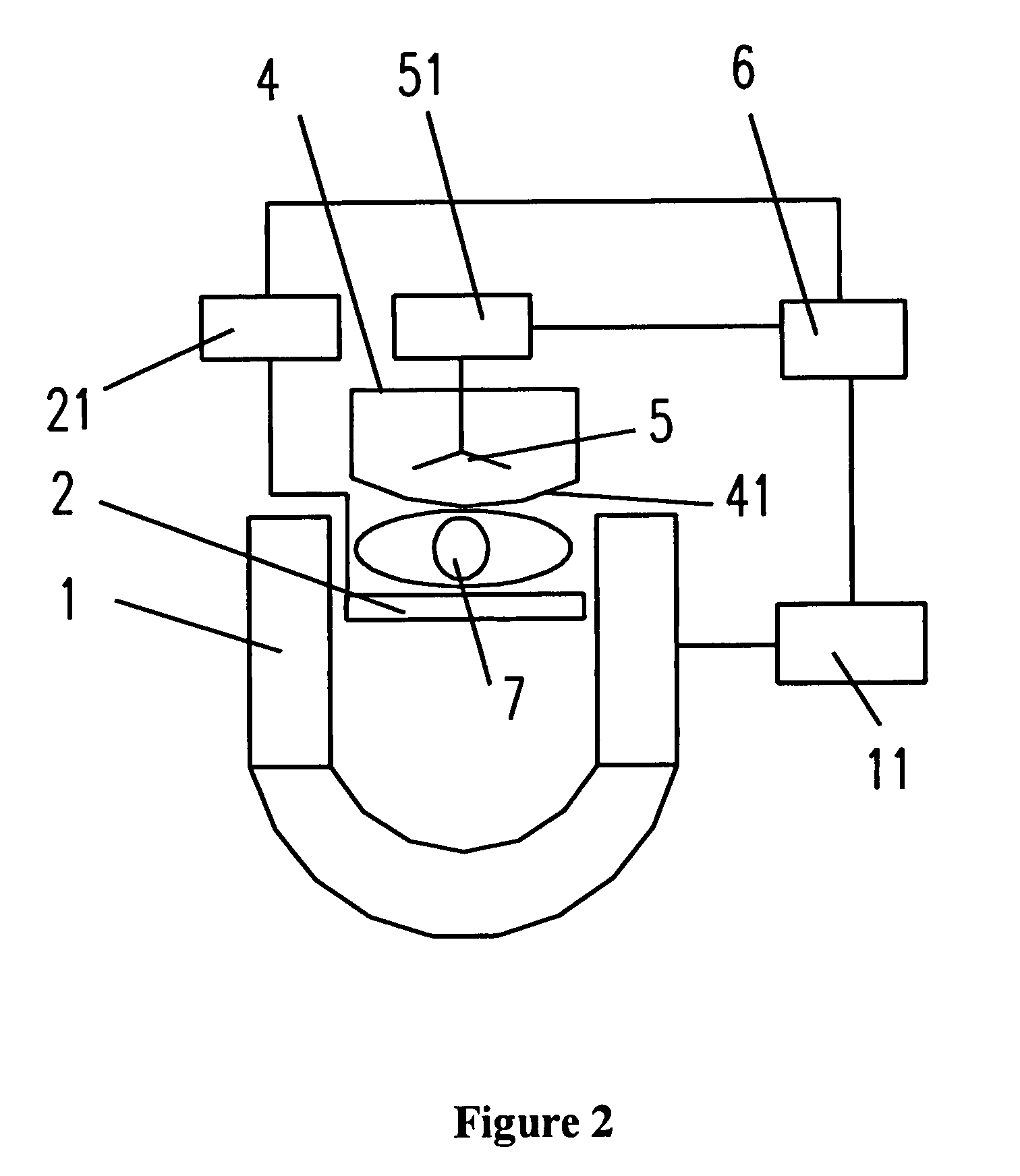
Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic navigation systems and methods
InactiveUS20050182315A1Strong and uniformDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringStatic field
A system for magnetically imaging an operating region in a subject and magnetically navigating a medical device within the operating region includes a first magnet for applying a static magnetic field to the operating region of sufficient strength for magnetically imaging the operating region and sufficiently strong to permit a medical device to be oriented in the operating region by creating a magnetic moment at the distal end of the medical device, and a second magnet for applying a static magnetic field to the operating region of sufficient strength for magnetically imaging the operating region and sufficiently strong to permit a medical device to be oriented in the operating region by creating a magnetic moment at the distal end of the medical device. In an alternate construction, the system includes a first magnet that is movable between a first position to apply a first static magnetic field to the operating region and a second position to apply a second static magnetic field to the operating region. The method of the invention includes applying a first static magnetic field to the operating region and MR imaging and magnetically navigating a device in the first static field, and then applying a second static magnetic field to the operating region, in a different direction than the first direction, and MR imaging and magnetically navigating a device in the second static field.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Switch for turning off therapy delivery of an active implantable medical device during MRI scans
InactiveUS20090163980A1Enhanced magnetic forceAvoid detectionElectrotherapyStatic fieldRadio frequency
An MRI-compatible electronic medical therapy system is provided for temporarily preventing current flow through an implanted lead wire in the presence of an induced radio frequency, magnetic, or static field. One or more normally closed switches are disposed in series between the AIMD and the one or more distal electrodes. The switch may be incorporated in the AIMD, lead wire, or within or adjacent to the electrode. The switch remains closed during normal AIMD-related therapy, but temporarily opens in the presence of an induced radio frequency, magnetic, or static field so as to prevent current flow through the electrode and lead wire. The switches prevent current from circulating that could be induced by a medical therapeutic diagnostic device, which can cause overheating of lead wires, excessive currents or temperatures and tissue damage.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
System and method for minimizing inter-application interference among static synchronized methods
InactiveUS6557168B1Multiple digital computer combinationsGenerating/distributing signalsStatic fieldApplication software
A system and method for isolating the execution of a plurality of applications. A plurality of monitors are provided for a plurality of applications to access a static synchronized method. The applications are enabled to call the static synchronized method concurrently by accessing the static synchronized method through the plurality of monitors. A plurality of threads within one of the applications are excluded from calling the static synchronized method concurrently. The source code or bytecode for the synchronized method may be transformed by removing a method-level monitor and adding the plurality of monitors inside the method. In one embodiment, each static synchronized method is replaced with a corresponding static non-synchronized method. The applications may be further isolated by placing the static fields of shared classes into a static field class, which has one instance per utilizing application. The static non-synchronized method includes the body of the corresponding static synchronized method, wherein the body is synchronized on the instance of the static field class that corresponds to the utilizing application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
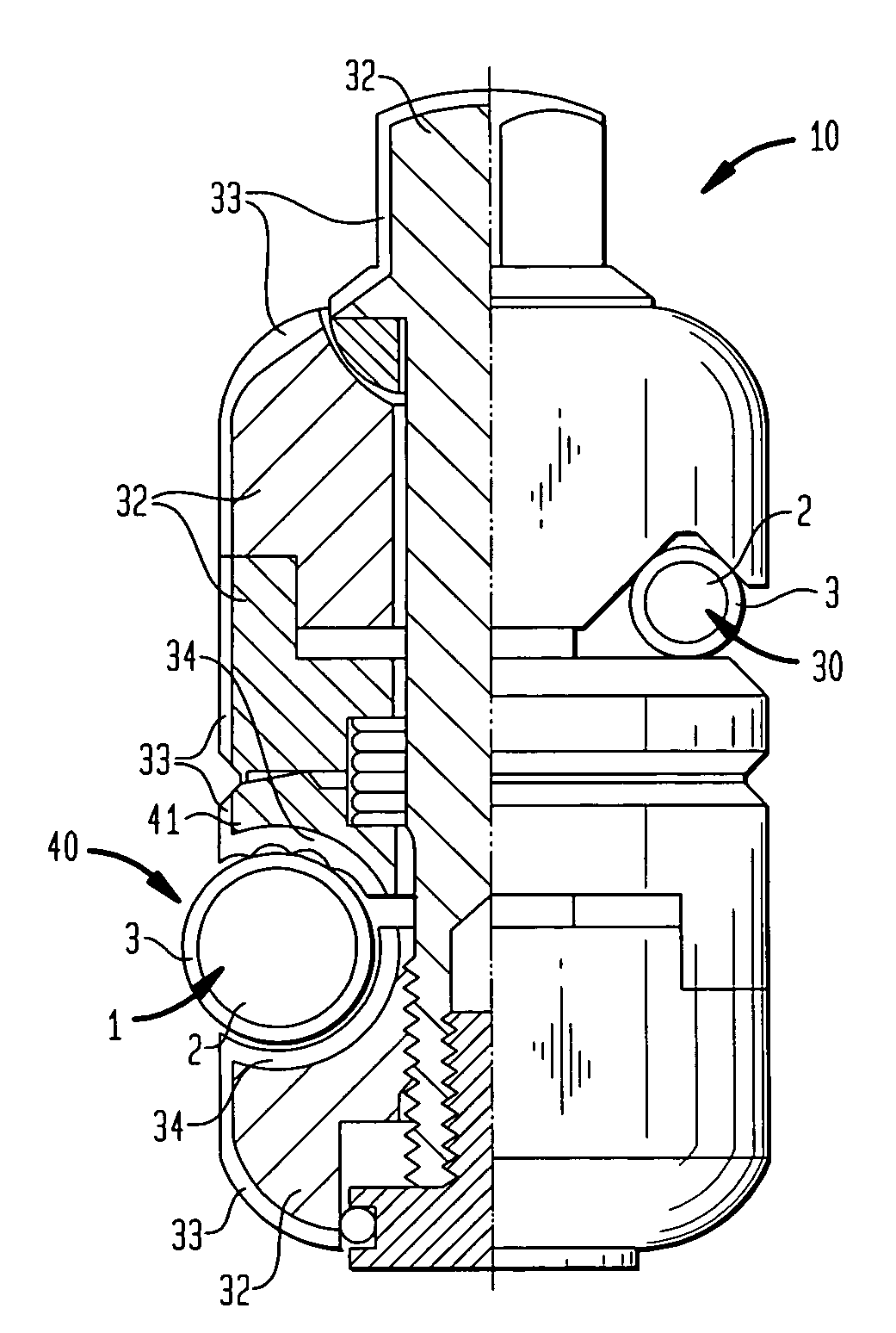
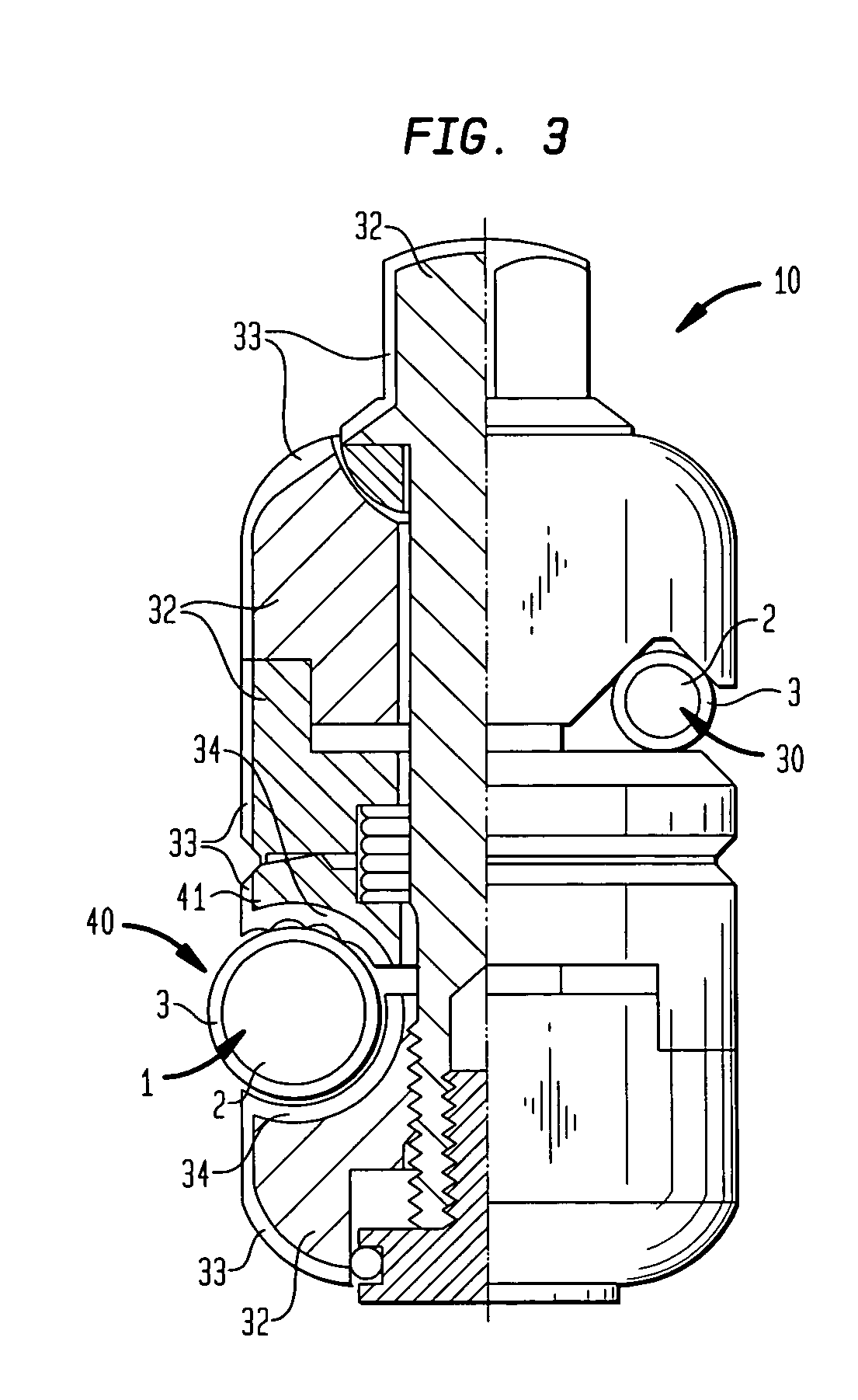
External fixation element
An external fixation system has clamps, rods and pins having anti-magnetic core parts and a non-conductive sheath part covering essentially the exterior surfaces of the core part. The rods, pins and clamps are especially MRI safe for a patient when used in any frame configuration for fractures of the upper and lower extremities and pelvis wherein the usual MRI field parameters of a static field of 2 Tesla, a time-varying filed of max. 20 Tesla / sec and a specific absorption rate (SAR) of max. 0.4 Watts / kg averaged over the whole body of the patient apply.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
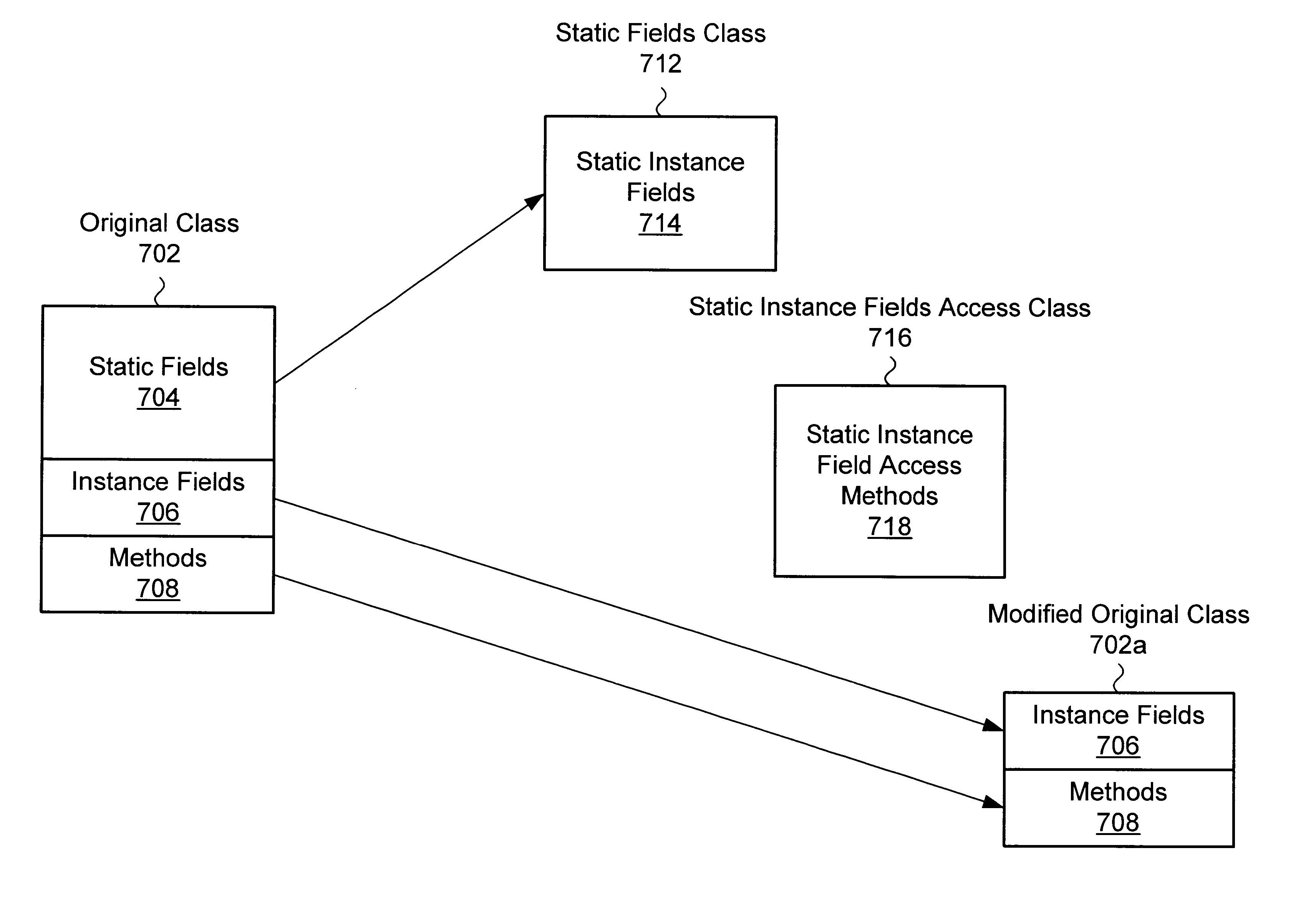
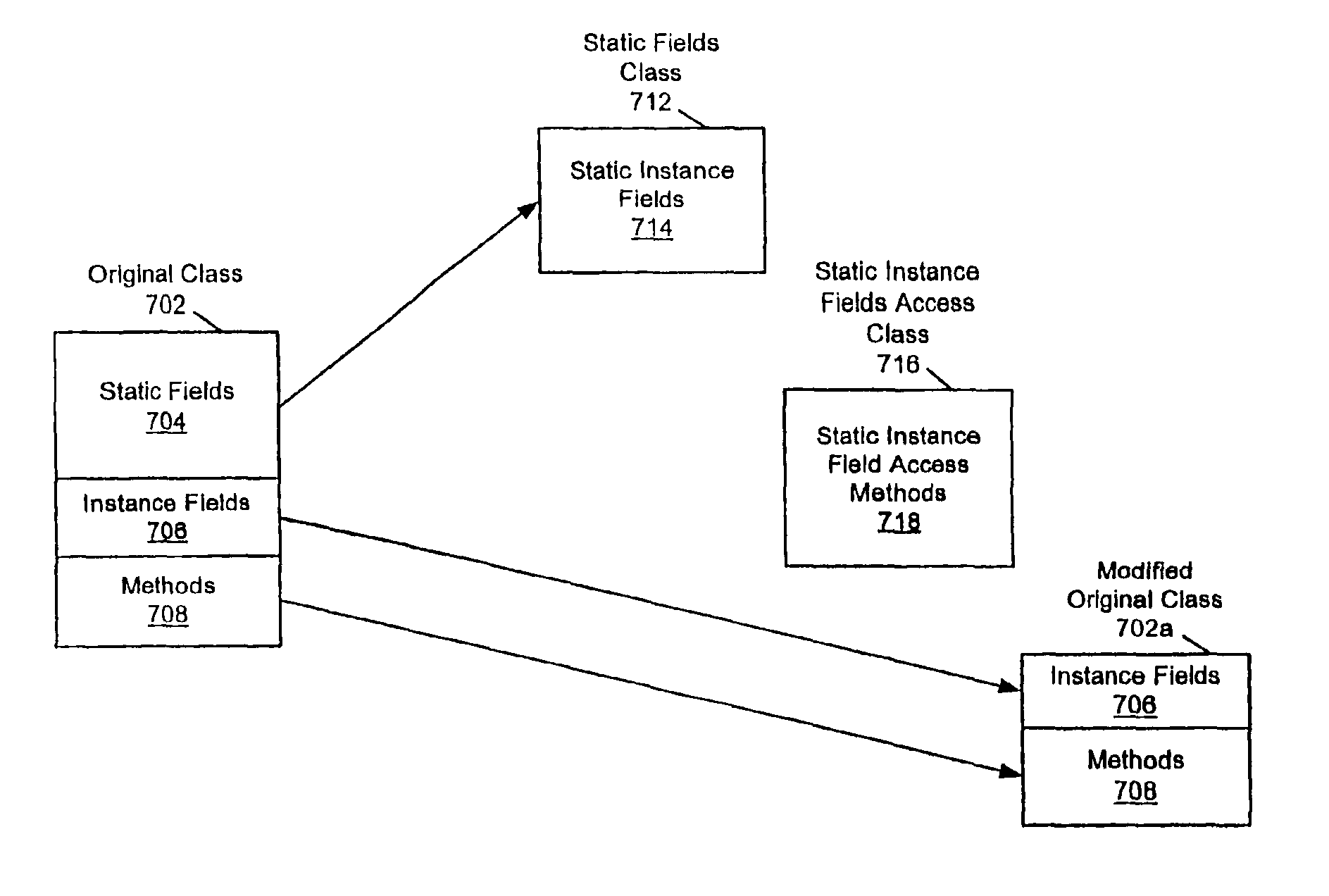
Small memory footprint system and method for separating applications within a single virtual machine
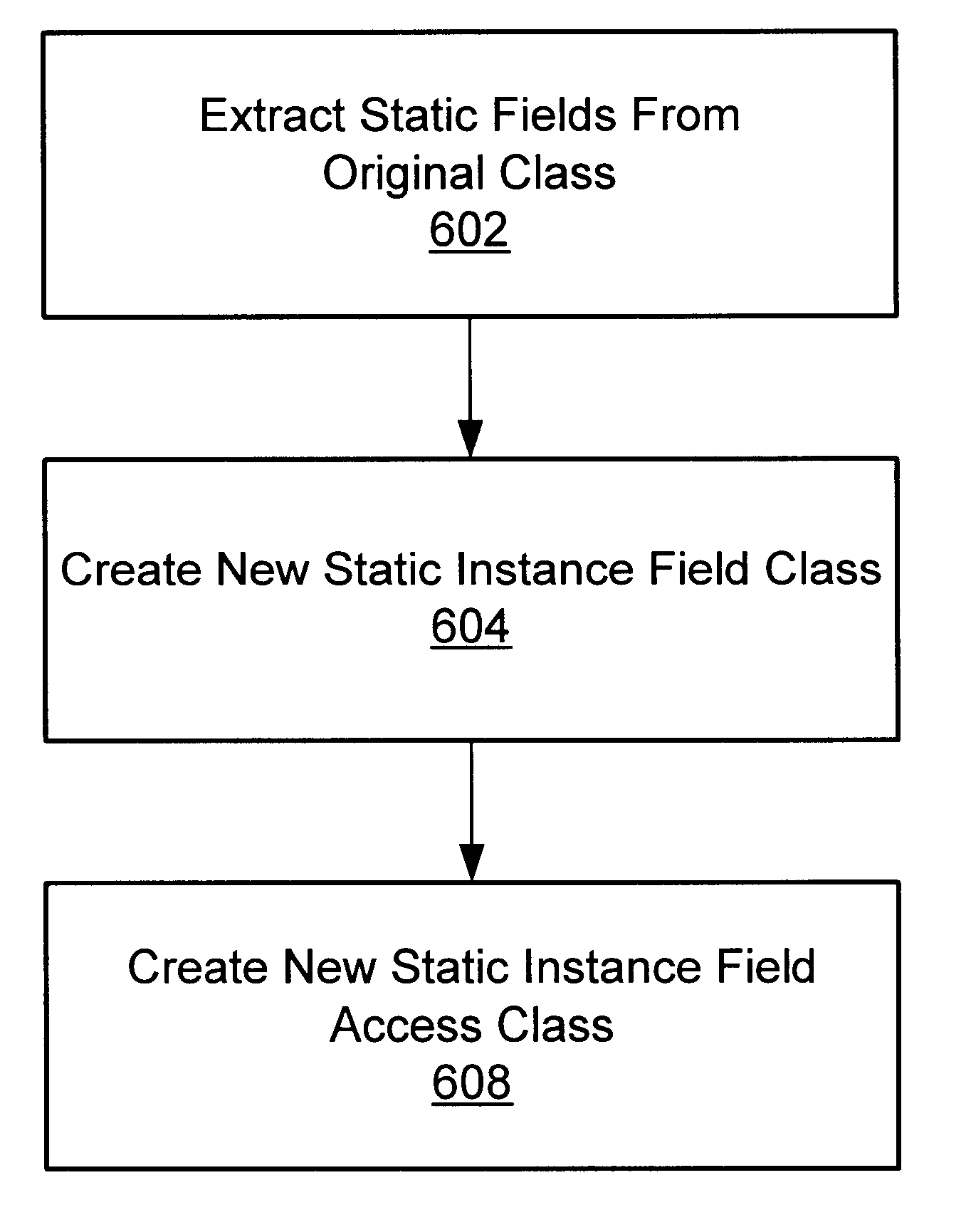
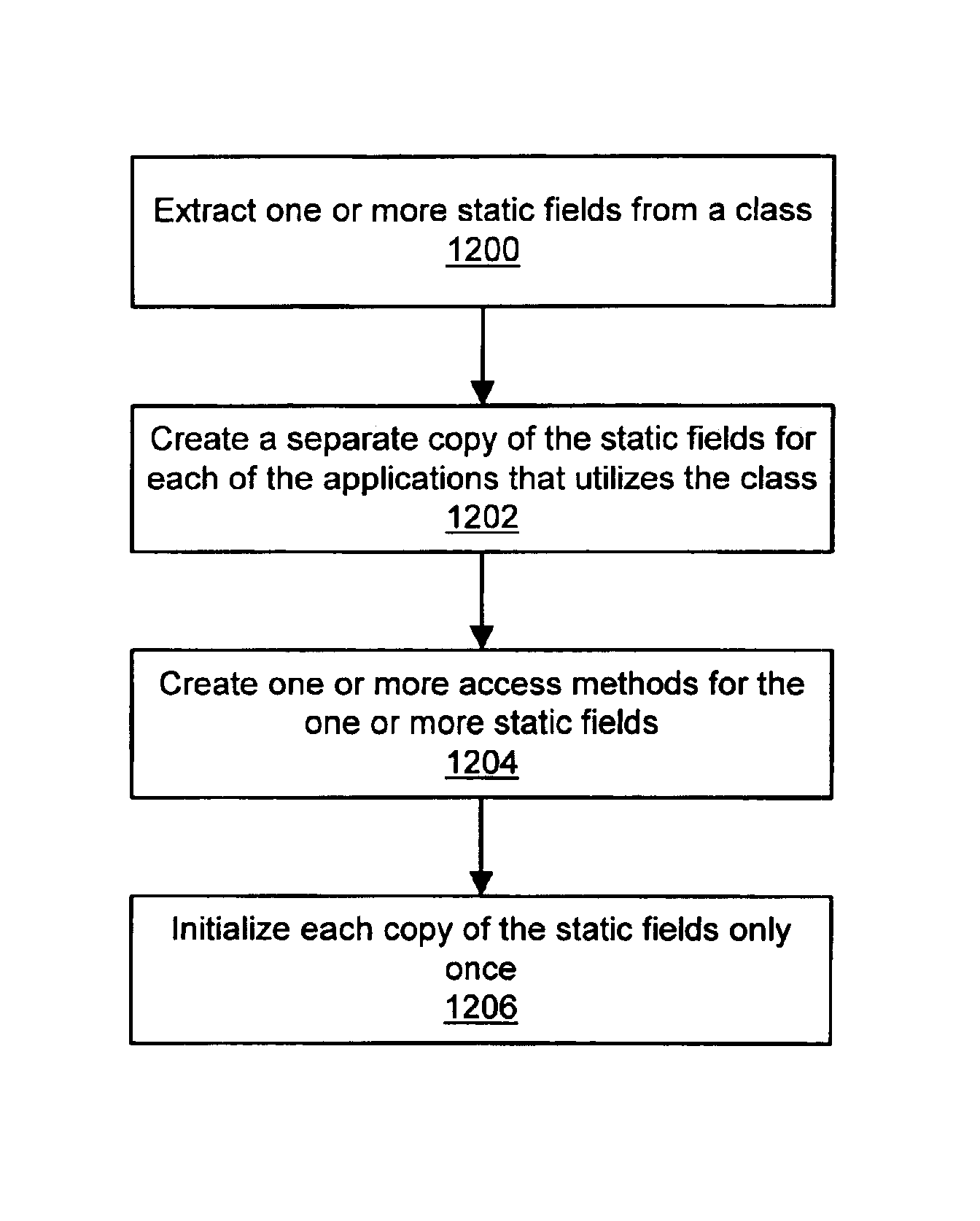
A system and method for isolating the execution of a plurality of applications. The applications may utilize or share one or more "original" classes. Only one copy of each original class is maintained, regardless of how many applications utilize it. Static fields are extracted from the original classes. A separate copy of the static fields is created for each of the utilizing applications. A static field class which includes instance fields corresponding to the static fields may be created, wherein each instance of the static field class corresponds to one of the utilizing applications. Access methods for the one or more static fields may be created, wherein the access methods are operable to access the corresponding separate copy of the static fields based upon the identity of the utilizing application. A single access methods class may be created for each original class, wherein the single access methods class includes the access methods for accessing the extracted fields from the original class. The method and system may be optimized by exempting from extraction static fields that are classified as secure for utilization by the plurality of applications without inter-application interference. The secure set of static fields may include final static fields of primitive types, final static strings, immutable arrays of primitive types, and / or other appropriate fields.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for simulating physical fields
InactiveUS6665849B2Less storage spaceAvoid excessive intensityDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhysical fieldEngineering
In order to design on-chip interconnect structures in a flexible way, a CAD approach is advocated in three dimensions, describing high frequency effects such as current redistribution due to the skin-effect or eddy currents and the occurrence of slow-wave modes. The electromagnetic environment is described by a scalar electric potential and a magnetic vector potential. These potentials are not uniquely defined, and in order to obtain a consistent discretization scheme, a gauge-transformation field is introduced. The displacement current is taken into account to describe current redistribution and a small-signal analysis solution scheme is proposed based upon existing techniques for static fields in semiconductors. In addition methods and apparatus for refining the mesh used for numerical analysis is described.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Small memory footprint system and method for separating applications within a single virtual machine
InactiveUS6938247B2Minimal collective footprintReliable isolationProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsArray data structureAccess method
A system and method for isolating the execution of a plurality of applications. The applications may utilize or share one or more “original” classes. Only one copy of each original class is maintained, regardless of how many applications utilize it. Static fields are extracted from the original classes. A separate copy of the static fields is created for each of the utilizing applications. A static field class which includes instance fields corresponding to the static fields may be created, wherein each instance of the static field class corresponds to one of the utilizing applications. Access methods for the one or more static fields may be created, wherein the access methods are operable to access the corresponding separate copy of the static fields based upon the identity of the utilizing application. A single access methods class may be created for each original class, wherein the single access methods class includes the access methods for accessing the extracted fields from the original class. The method and system may be optimized by exempting from extraction static fields that are classified as secure for utilization by the plurality of applications without inter-application interference. The secure set of static fields may include final static fields of primitive types, final static strings, immutable arrays of primitive types, and / or other appropriate fields.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Safe language static variables initialization in a multitasking system
InactiveUS6901586B1Multiprogramming arrangementsProgram loading/initiatingVirtualizationStatic field
A system and method are provided for thread-safe initialization of static variables in a multitasking system. In one embodiment, the static fields of a class may be “virtualized” such that each application that utilizes the class has its own copy of static fields. Each separate copy of the static fields is initialized only once. Instructions for performing the initialization may be embedded in a class constructor. The class constructor may be executed only once for each separate copy of the static fields. A template class may be loaded for each separate copy of the static fields when a copy of the static fields is sought to be initialized. The template class may include a static initializer for one of the separate copies of the static fields. The static initializer may be executed once for each separate copy of the static fields.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
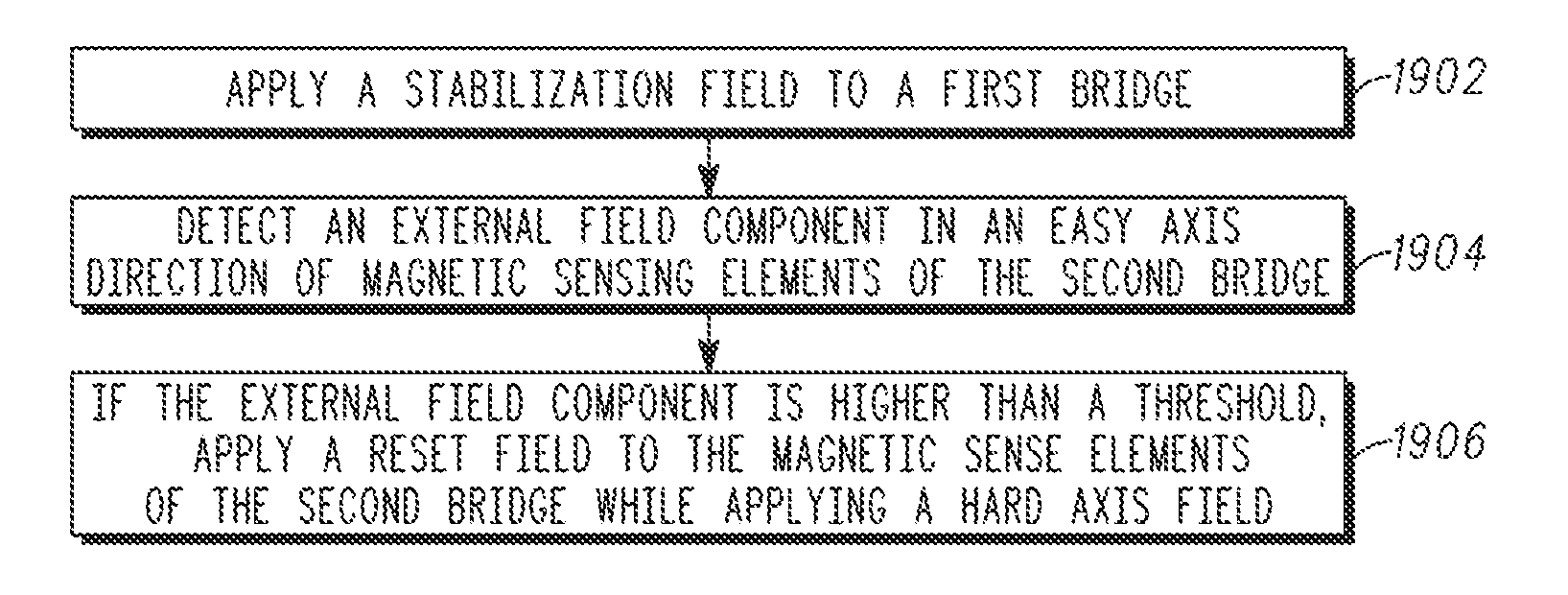
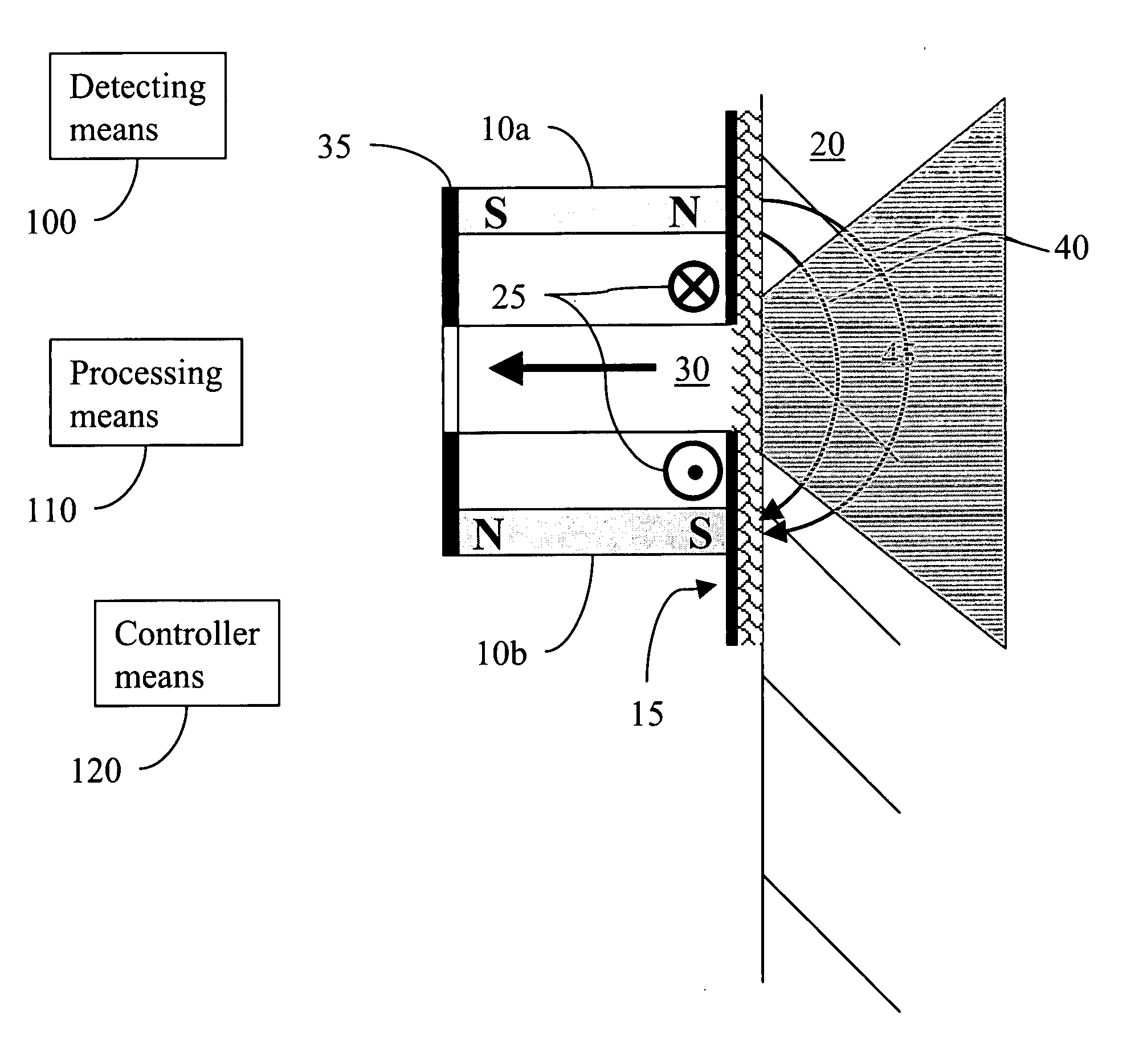
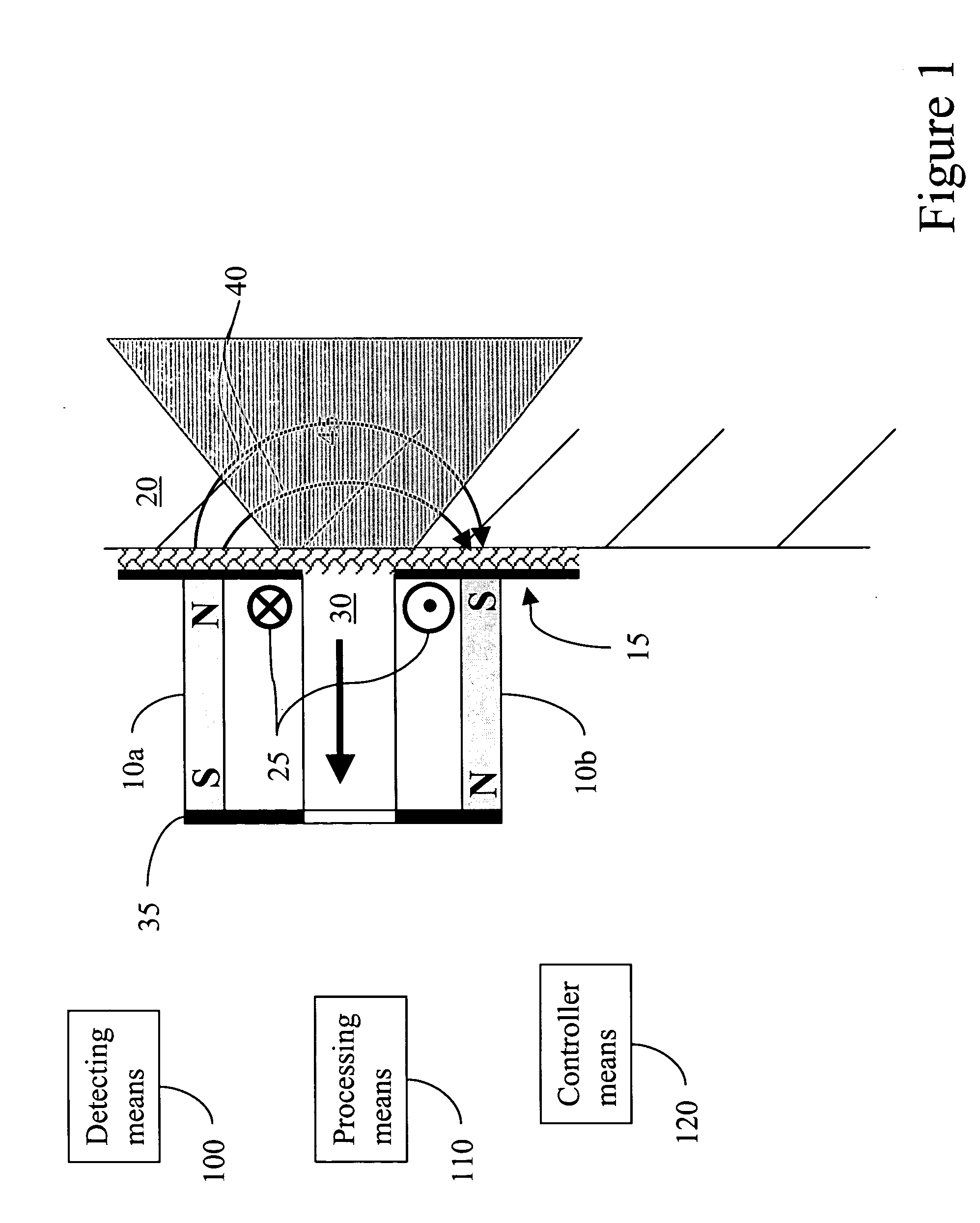
Apparatus and method for reset and stabilization control of a magnetic sensor
ActiveUS20130106410A1Magnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleOperating pointStabilization control
A magnitude and direction of at least one of a reset current and a second stabilization current (that produces a reset field and a second stabilization field, respectively) is determined that, when applied to an array of magnetic sense elements, minimizes the total required stabilization field and reset field during the operation of the magnetic sensor and the measurement of the external field. Therefore, the low field sensor operates optimally (with the highest sensitivity and the lowest power consumption) around the fixed external field operating point. The fixed external field is created by other components in the sensor device housing (such as speaker magnets) which have a high but static field with respect to the low (earth's) magnetic field that describes orientation information.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic memory device and manufacturing method of magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory device
ActiveUS7026671B2Improve rectangle propertyImprove coercive forceNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic anisotropyMagnetic memory
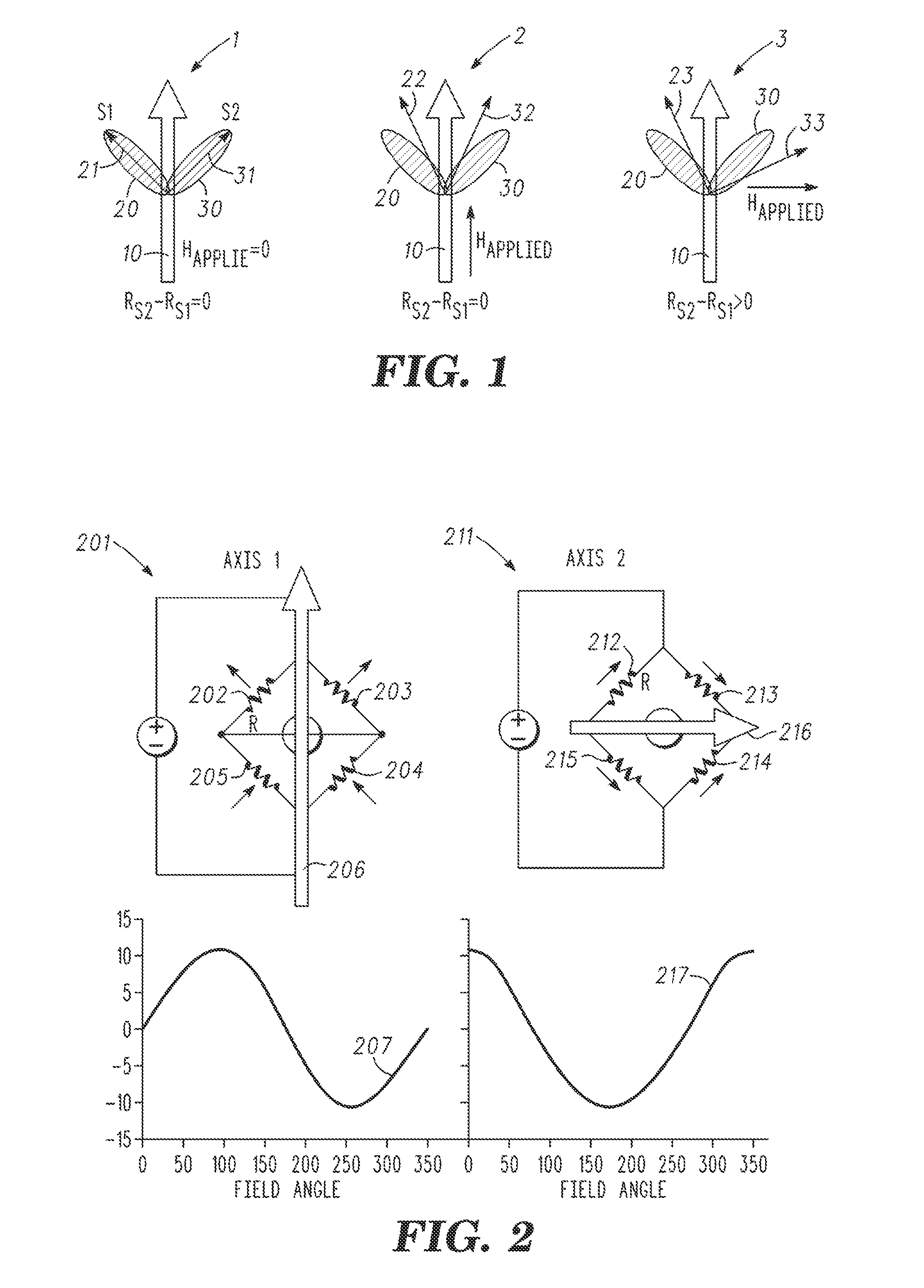
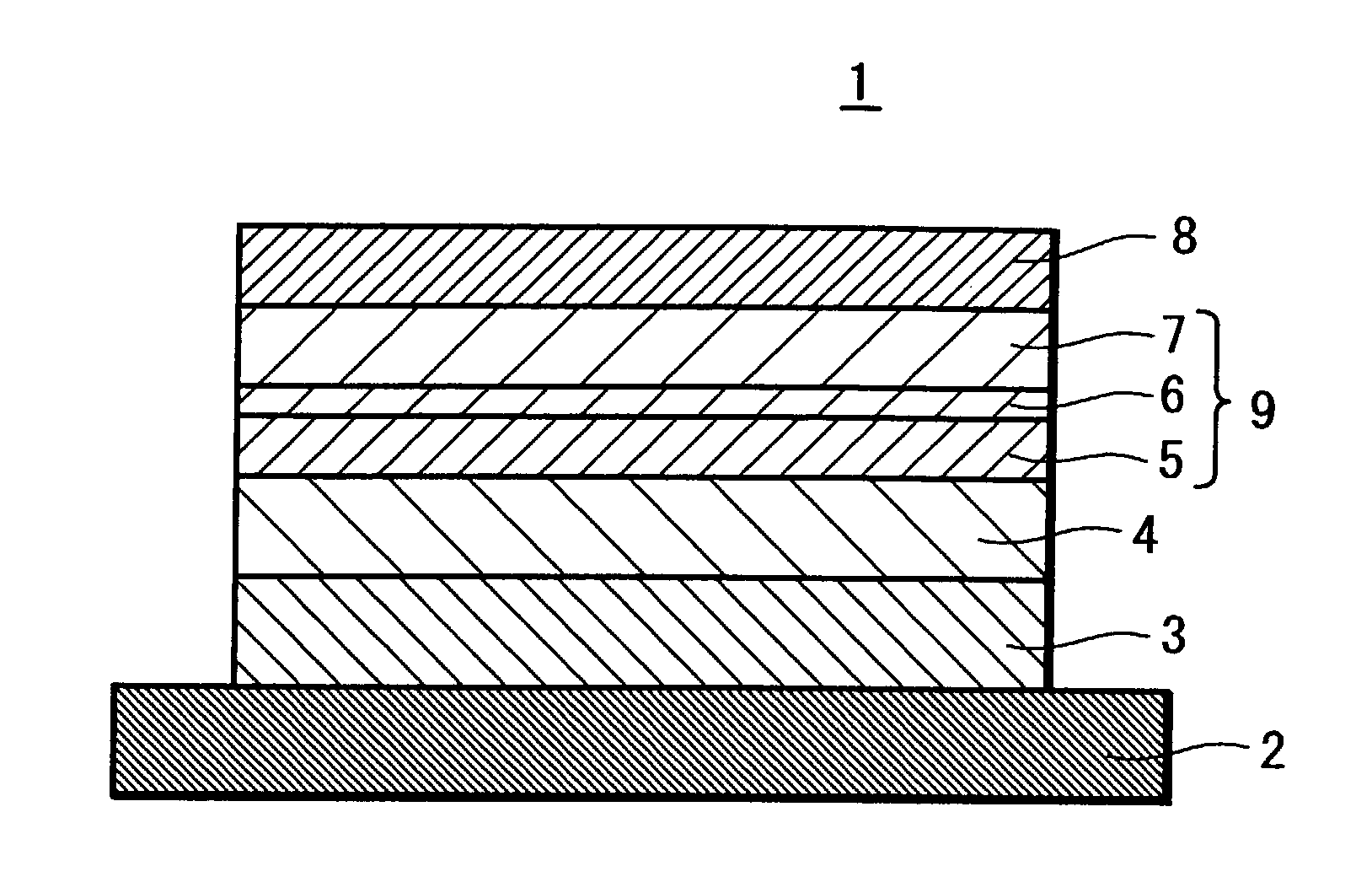
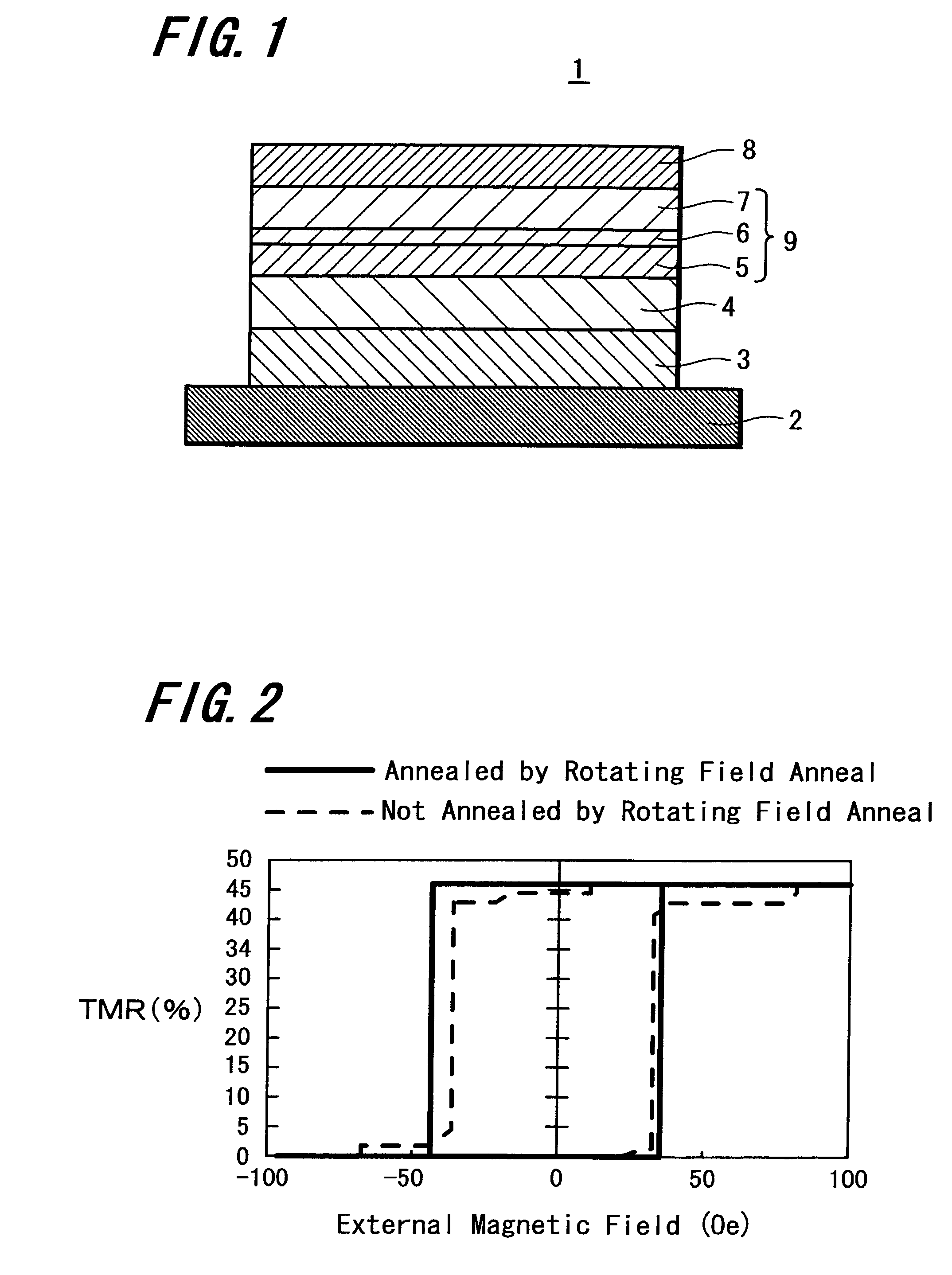
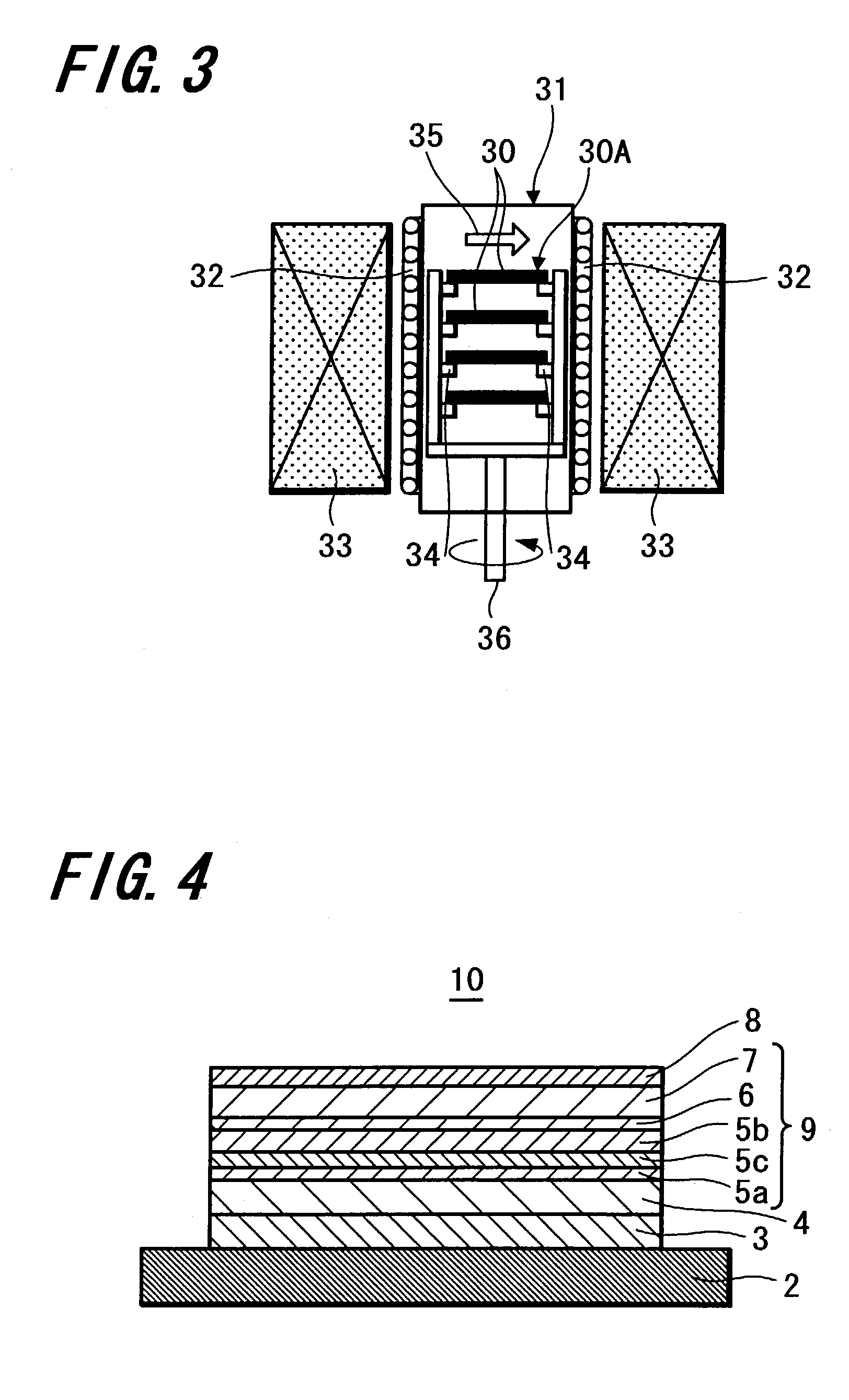
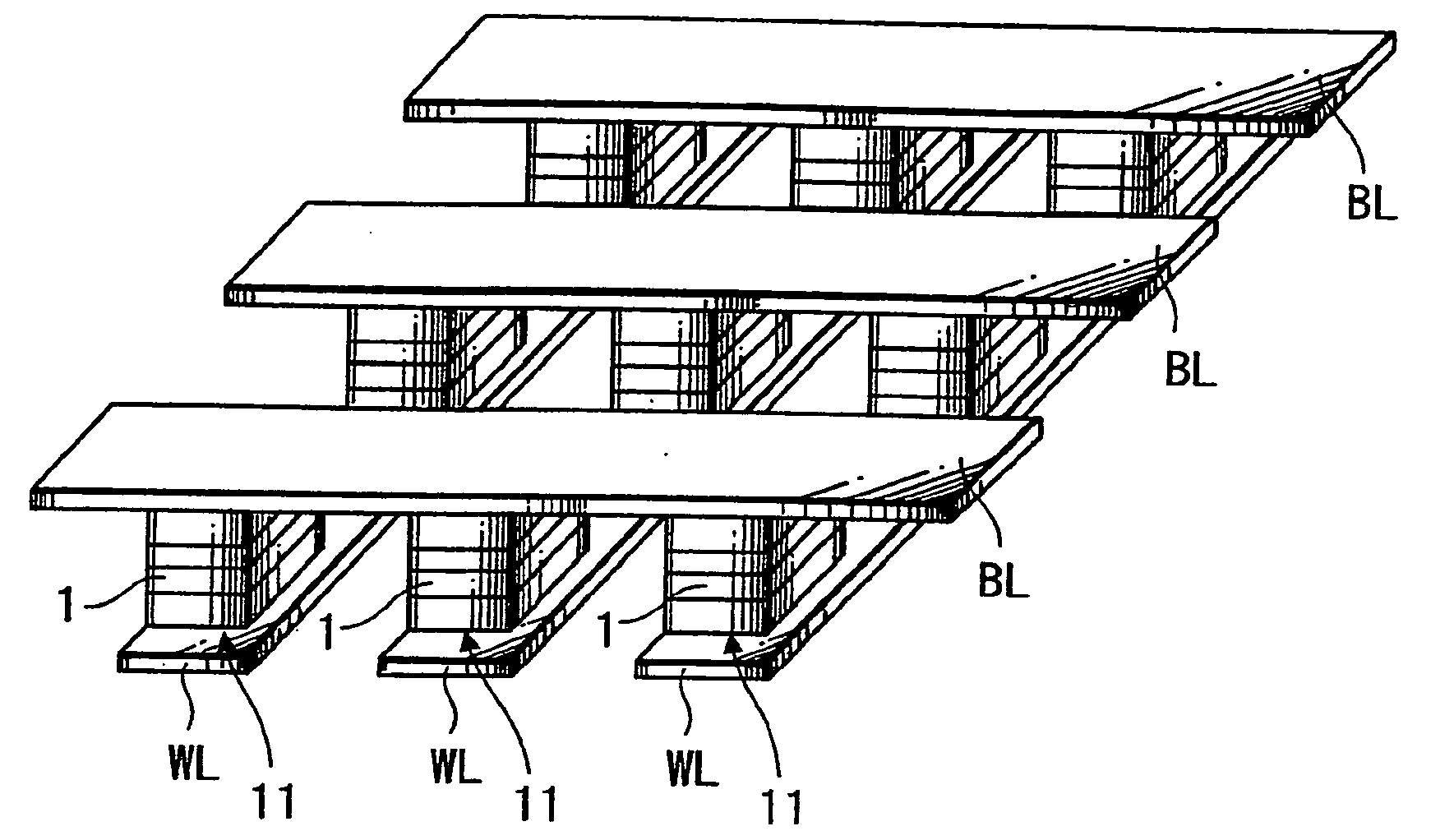
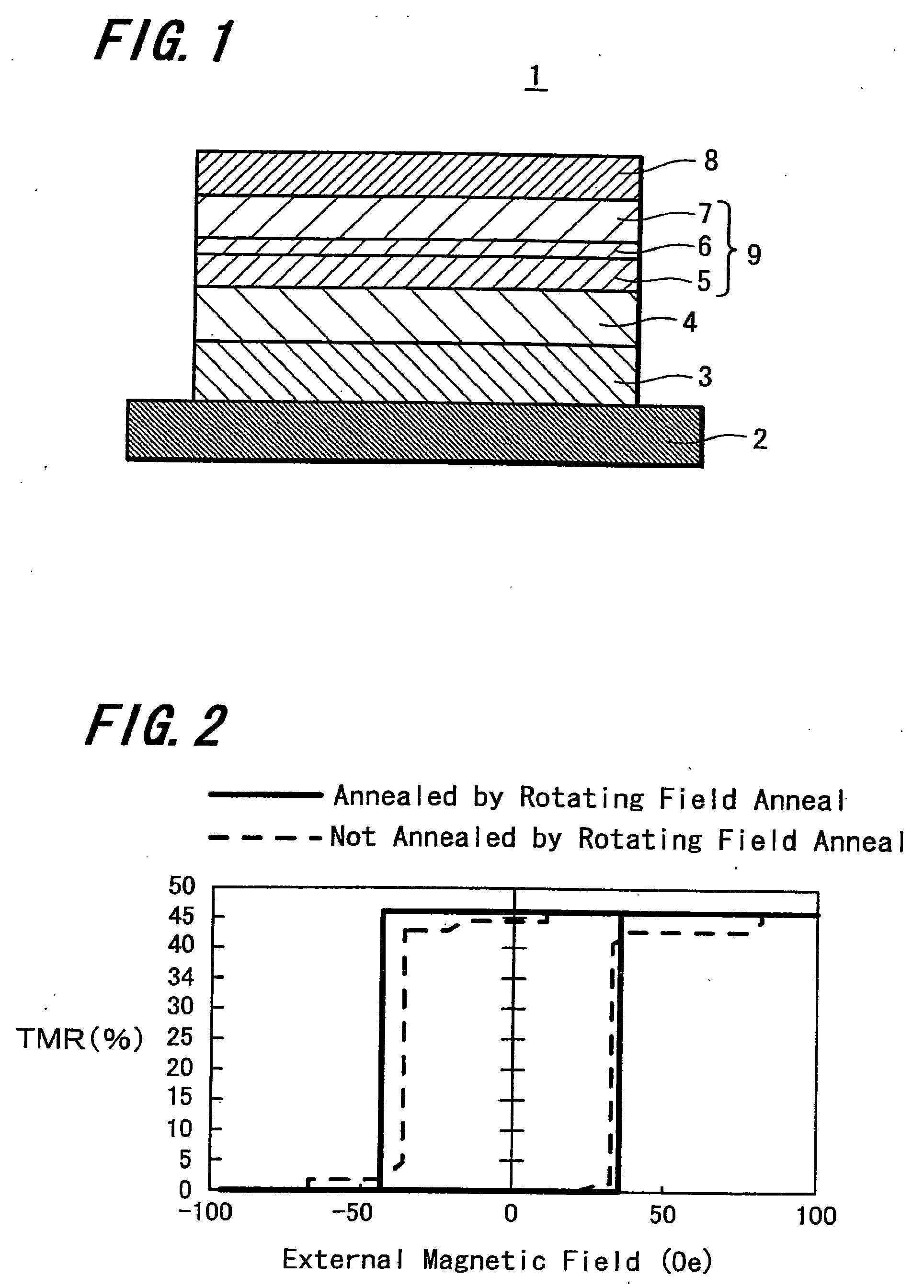
A magnetoresistive effect element (1) has an arrangement in which a pair of ferromagnetic material layers (magnetization fixed layer (5) and magnetization free layer (7)) is opposed to each other through an intermediate layer (6) to obtain a magnetoresistive change by causing a current to flow in the direction perpendicular to the layer surface and in which the ferromagnetic material layers are annealed by anneal including rotating field anneal and the following static field anneal. A magnetic memory device comprises this magnetoresistive effect element (1) and bit lines and word lines sandwiching the magnetoresistive effect element (1) in the thickness direction. When the magnetoresistive effect element (1) and the magnetic memory device are manufactured, the ferromagnetic material layers (5, 7) are annealed by rotating field anneal and the following static field anneal. There are provided the magnetoresistive effect element that can obtain excellent magnetic characteristics by controlling magnetic anisotropies of the ferromagnetic material layers, the magnetic memory device including this magnetoresistive effect element and which may have excellent write characteristics, and methods for manufacturing these magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory device.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
System and method for use of nanoparticles in imaging and temperature measurement
ActiveUS20090115415A1Improve rendering capabilitiesHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismMagnetic property measurementsBinding energyMagnetic particle imaging
This invention provides a system and method that improves the sensitivity and localization capabilities of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) by using combinations of time-varying and static magnetic fields. Combinations of magnetic fields can be used to distribute the signals coming from the magnetic particles among the harmonics and other frequencies in specific ways to improve sensitivity and to provide localization information to speed up or improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of imaging and / or eliminate the need for saturation fields currently used in MPI. In various embodiments, coils can be provided to extend the sub-saturation region in which nanoparticles reside; to provide a static field offset to bring nanoparticles nearer to saturation; to introduce even and odd harmonics that can be observed; and / or to introduce combinations of frequencies for more-defined observation of signals from nanoparticles. Further embodiments provide for reading of the signal produced by cyclically saturated magnetic nanoparticles in a sample so as to provide a measurement of the temperature of those nanoparticles. The spectral distribution of the signal generated provides estimates of the temperature of the nanoparticles. Related factors may also be estimated—binding energies of the nanoparticles, phase changes, bound fraction of the particles or stiffness of the materials in which the nanoparticles are imbedded.
Owner:DARTMOUTH HITCHCOCK CLINIC
Magnetoresistive effect element, magentic memory device and manufacturing method of magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory device
InactiveUS20060187703A1Excellent magnetic propertiesExcellent write characteristicNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismBit lineMagnetic anisotropy
A magnetoresistive effect element (1) has an arrangement in which a pair of ferromagnetic material layers (magnetization fixed layer (5) and magnetization free layer (7)) is opposed to each other through an intermediate layer (6) to obtain a magnetoresistive change by causing a current to flow in the direction perpendicular to the layer surface and in which the ferromagnetic material layers are annealed by anneal including rotating field anneal and the following static field anneal. A magnetic memory device comprises this magnetoresistive effect element (1) and bit lines and word lines sandwiching the magnetoresistive effect element (1) in the thickness direction. When the magnetoresistive effect element (1) and the magnetic memory device are manufactured, the ferromagnetic material layers (5, 7) are annealed by rotating field anneal and the following static field anneal. There are provided the magnetoresistive effect element that can obtain excellent magnetic characteristics by controlling magnetic anisotropies of the ferromagnetic material layers, the magnetic memory device including this magnetoresistive effect element and which may have excellent write characteristics, and methods for manufacturing these magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory device.
Owner:SONY CORP
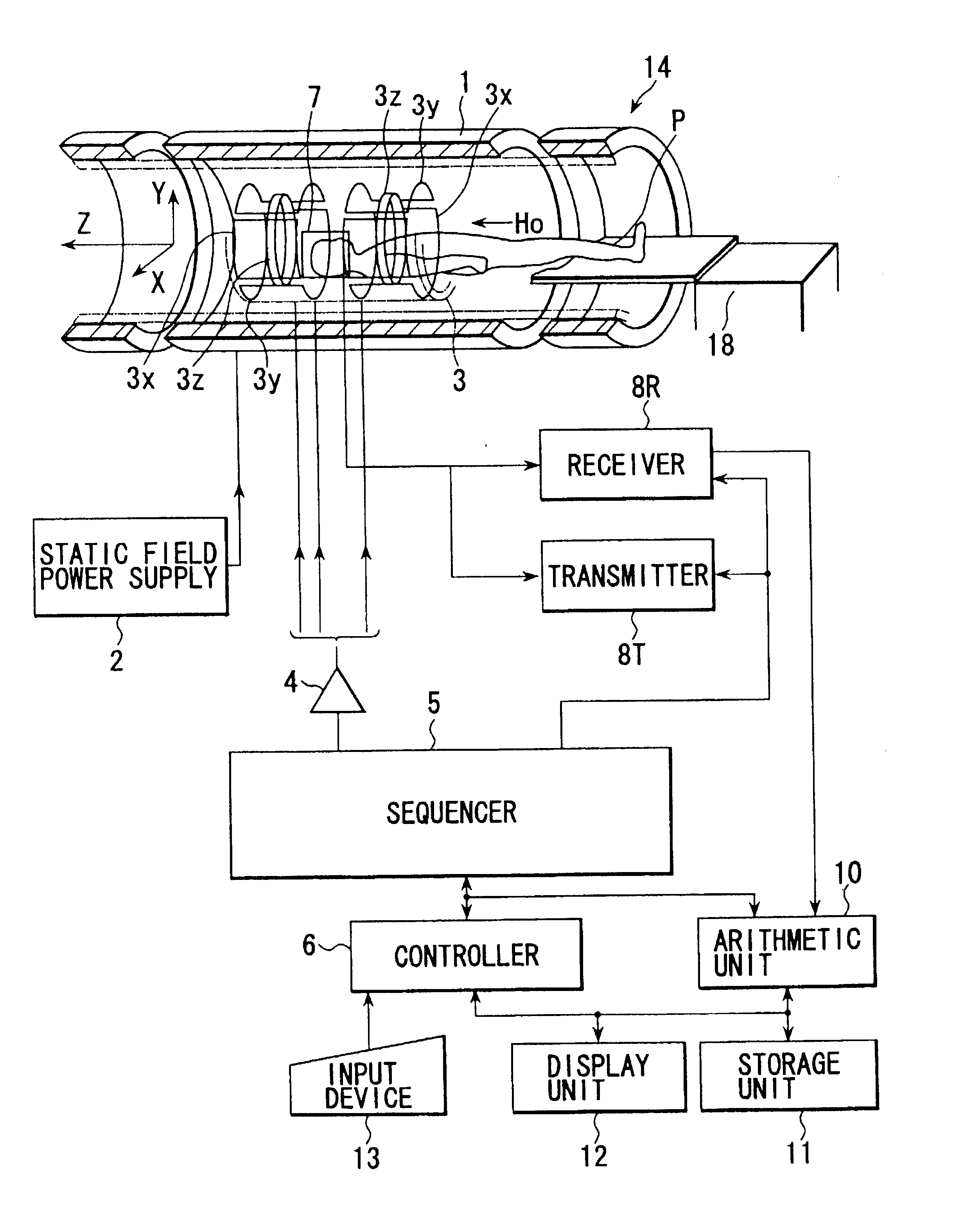
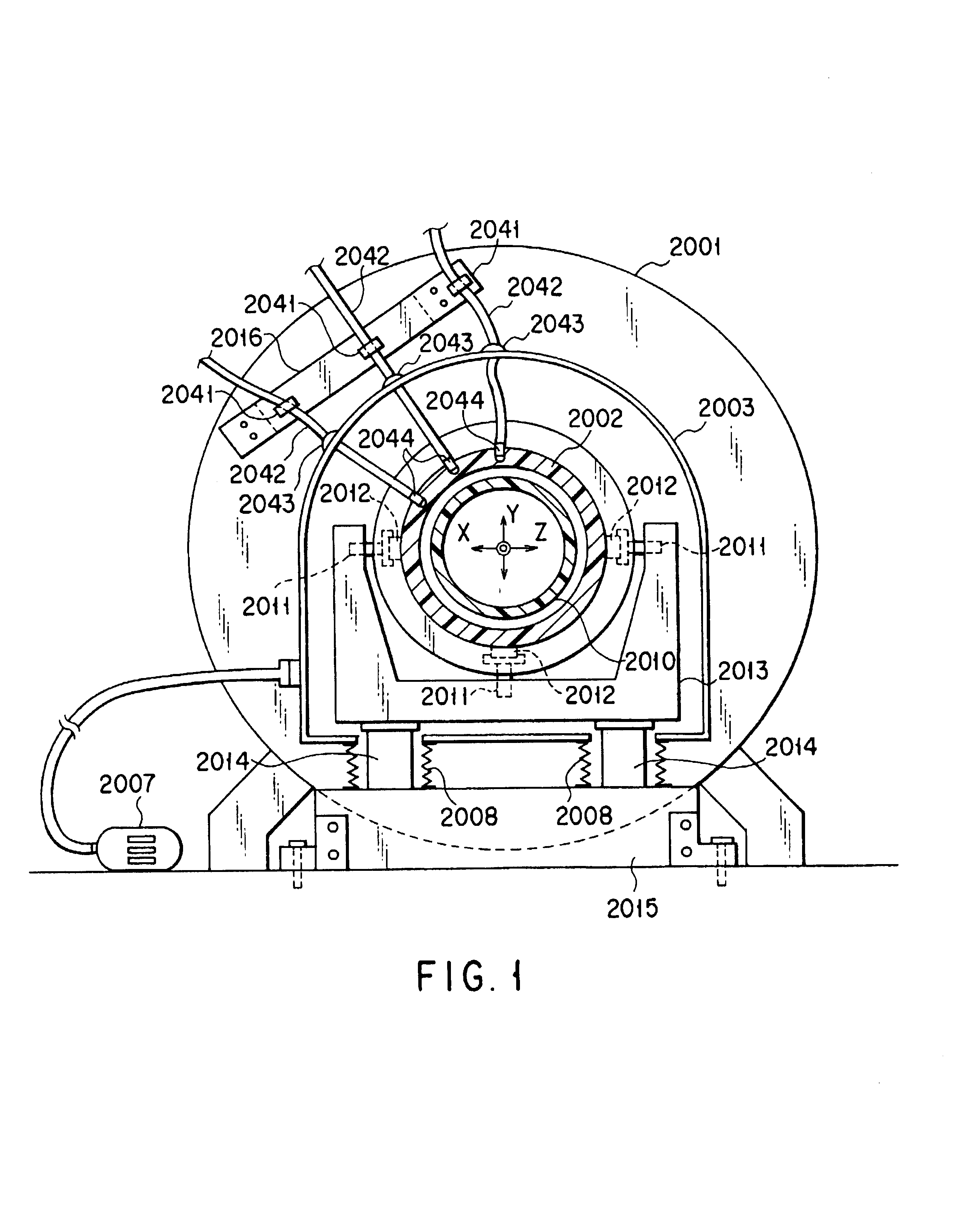
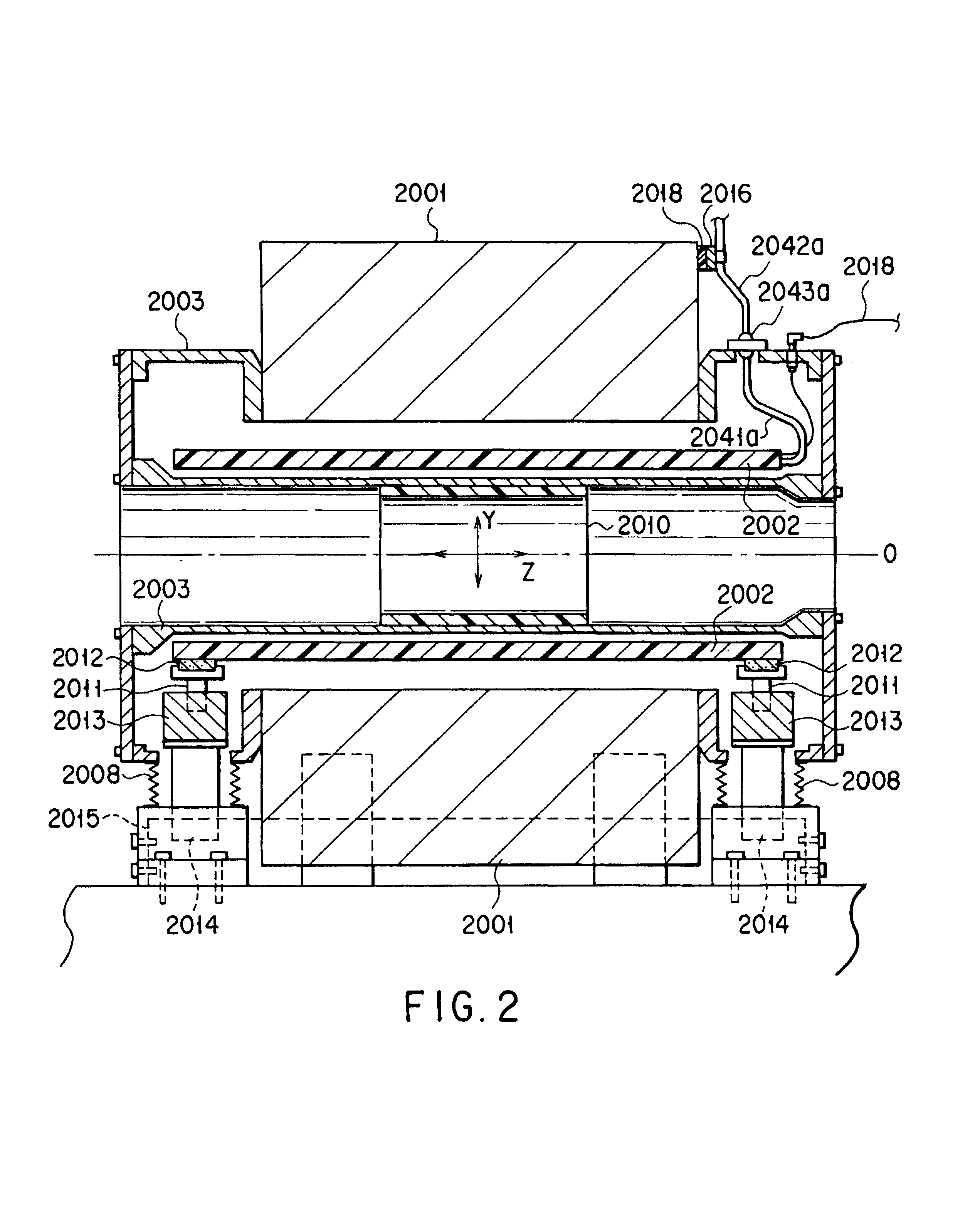
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080015430A1Avoid performancePrecise positioningMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringStatic fieldMovement control
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus has a static field magnet, gradient coils, a gantry including an opening and storing the static field magnet the gradient coils, a bed structure for advancing and retreating a table-top, on which an object can be placed, with respect to the opening, a lower coil formed by a radio frequency coil disposed below the table-top, and a movement control unit configured to control the lower coil to be movable.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for simulating physical fields
InactiveUS20020042698A1Simple structureLess storage spaceDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhysical fieldEngineering
In order to design on-chip interconnect structures in a flexible way, a CAD approach is advocated in three dimensions, describing high frequency effects such as current redistribution due to the skin-effect or eddy currents and the occurrence of slow-wave modes. The electromagnetic environment is described by a scalar electric potential and a magnetic vector potential. These potentials are not uniquely defined, and in order to obtain a consistent discretization scheme, a gauge-transformation field is introduced. The displacement current is taken into account to describe current redistribution and a small-signal analysis solution scheme is proposed based upon existing techniques for static fields in semiconductors. In addition methods and apparatus for refining the mesh used for numerical analysis is described.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
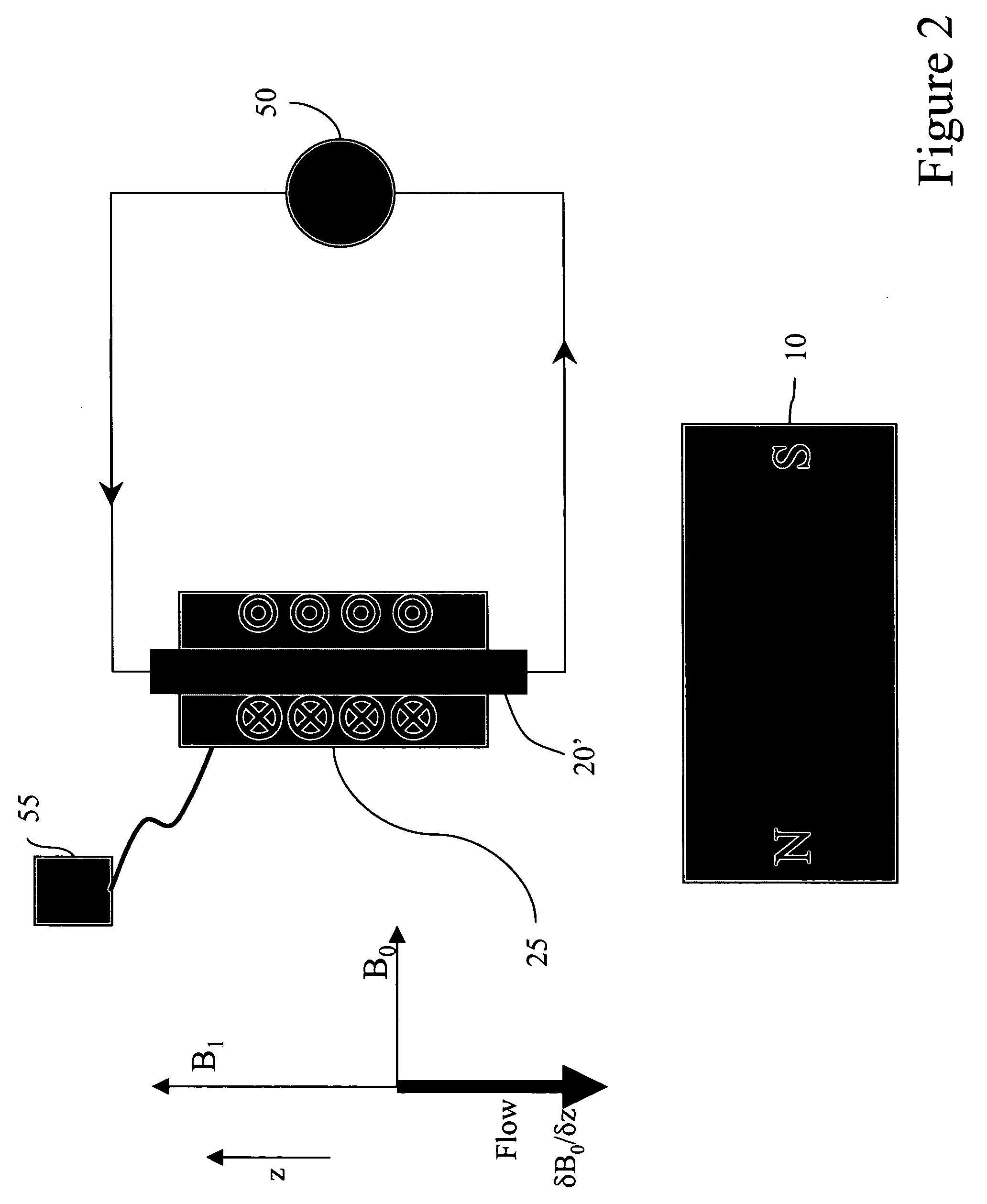
Downhole NMR flow and formation characterization while sampling fluids
ActiveUS7180288B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceStatic field
A method of measuring characteristics of a flowing fluid is described including: (a) providing a flowing fluid; (b) applying a static field gradient to the flowing fluid; (c) applying a series of nuclear magnetic resonance pulses to the flowing fluid; (d) detecting signals from the flowing fluid, wherein the signals are generated in response to the nuclear magnetic resonance pulses; and (e) analyzing the real and imaginary components of the signals to determine one or more characteristics of the flowing fluid. Also described is an apparatus for implementing this method.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7071693B2Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectron flowField coil
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus generates an MR signal from an object to be examined by applying a gradient field pulse generated by a gradient field coil and a high-frequency magnetic field pulse generated by a high-frequency coil to the object in a static field generated by a static field magnet, and reconstructs an image on the basis of the MR signal. The gradient field coil is housed in a sealed vessel. Numerous techniques are disclosed to reduce adverse effects of vibrations caused by rapidly changing gradient coil currents. By judicious use of non-conducting connection components between gantry components at some joint portions requiring electrical contact and at some other portions not requiring electrical contact, the generation of adverse B waves, and / or induced electron flow in response to physical vibration between joint components can be reduced.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Downhole NMR flow and formation characterization while sampling fluids
ActiveUS20060097722A1Readily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceStatic field
A method of measuring characteristics of a flowing fluid is described including: (a) providing a flowing fluid; (b) applying a static field gradient to the flowing fluid; (c) applying a series of nuclear magnetic resonance pulses to the flowing fluid; (d) detecting signals from the flowing fluid, wherein the signals are generated in response to the nuclear magnetic resonance pulses; and (e) analyzing the real and imaginary components of the signals to determine one or more characteristics of the flowing fluid. Also described is an apparatus for implementing this method.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
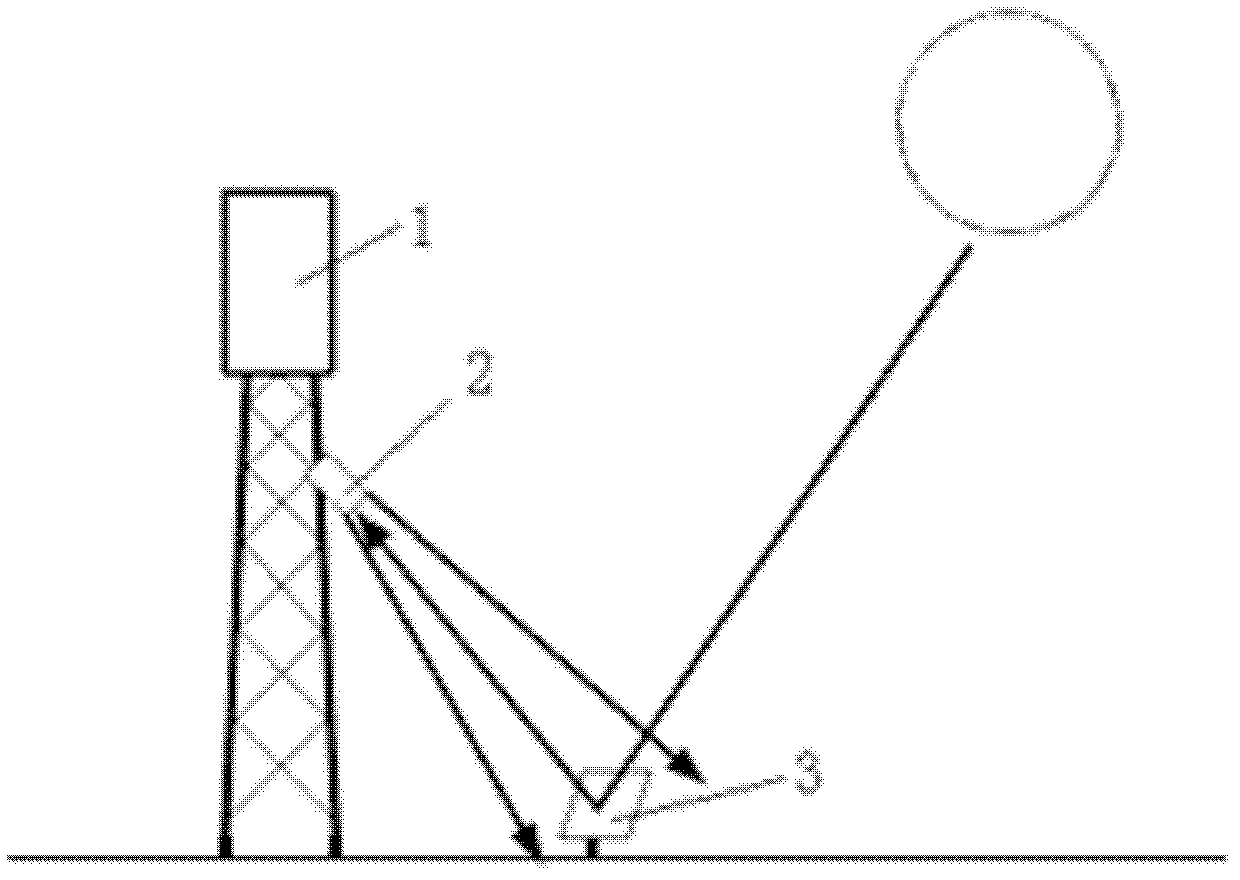
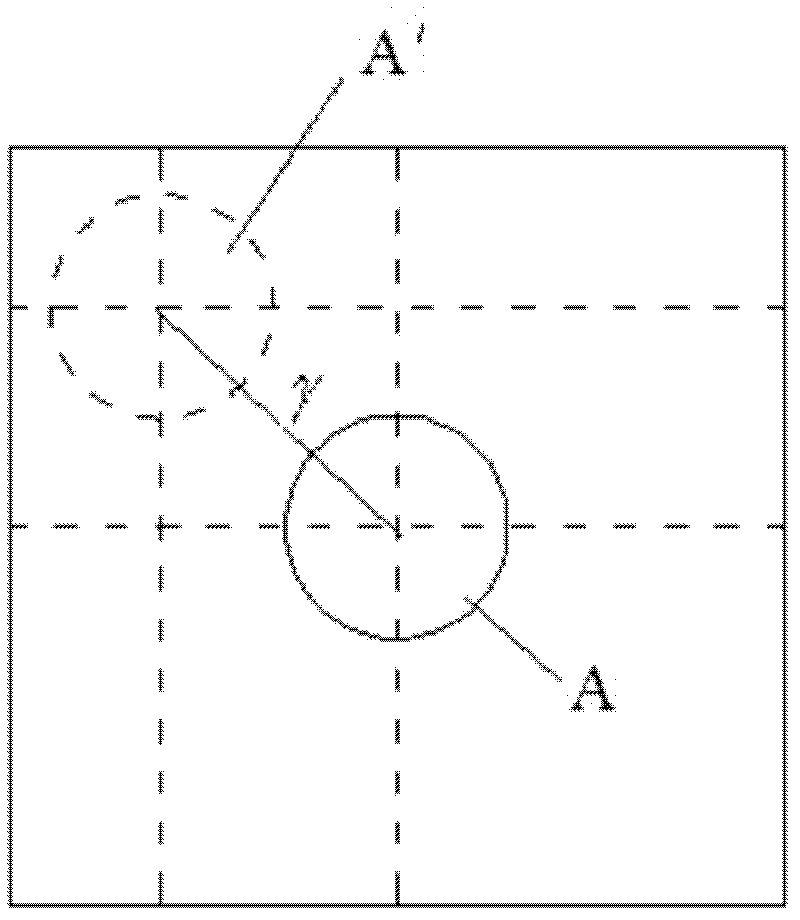
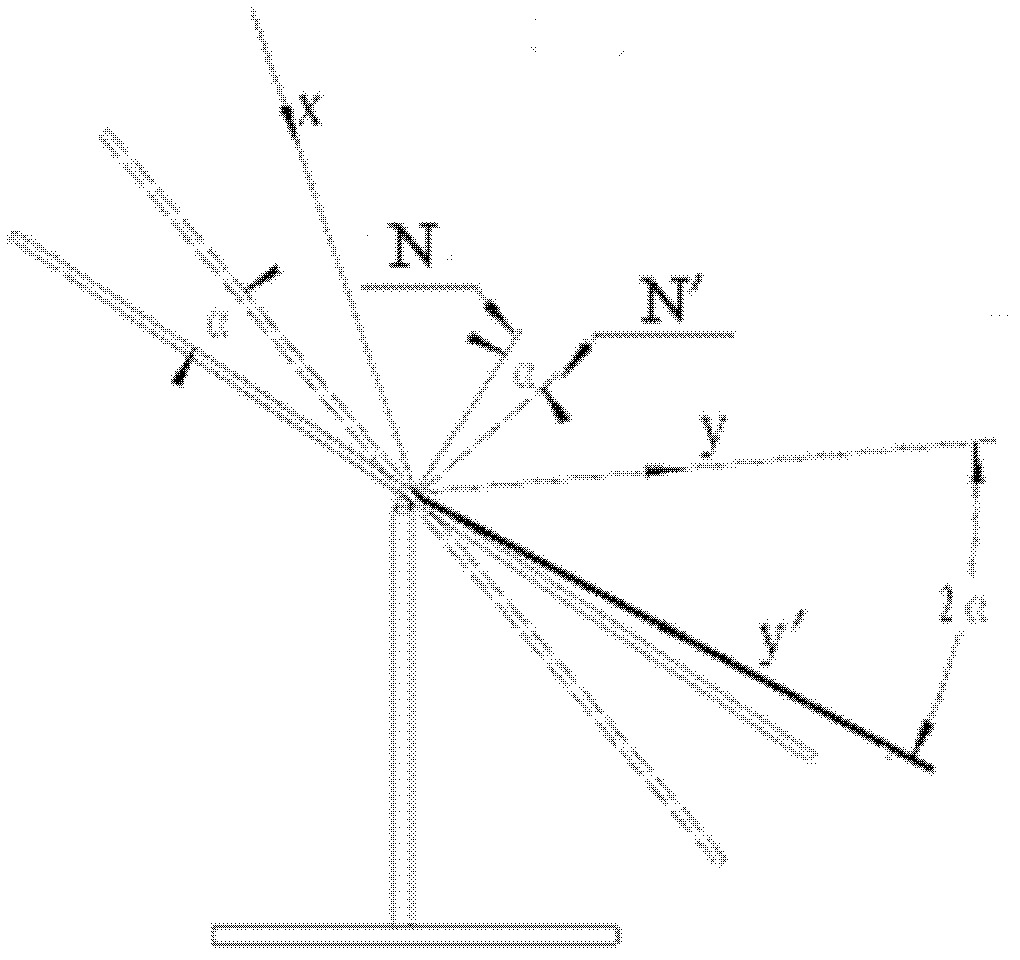
Image detection-based on-line detection and correction method of reflection angle of heliostat
ActiveCN102506811AThe results are direct and reliableGuaranteed accuracyAngle measurementSurveying instrumentsHeliostatImage detection
The invention discloses an image detection-based on-line detection and correction method of a reflection angle of a heliostat. Firstly, the heliostat to be corrected and a solar facula image in the heliostat are shot through a camera, the obtained image is processed, whether the solar facula image is positioned in the central position of the heliostat or not is judged, and if the solar facula image is positioned in the central position of the heliostat, the camera is aligned with the heliostat to be corrected; otherwise, the reflection angle deviation Theta of the heliostat is calculated according to the offset of the solar facula image from the central position of the heliostat, and a normal direction of the heliostat is controlled to rotate towards a direction in which the deviation is eliminated at an angle of half the Theta; and secondly, a declination angle Theta' between an angle for the camera to be aligned with the heliostat and an angle for the heliostat to be aligned with a heat collector is calculated, and the heliostat already aligned with the camera is rotated towards the heat collector for half the Theta'. By adopting the method, the heliostat can be accurately aligned with the heat collector when a static field is mounted, and errors caused by mechanical deformation and foundation settlement during long-term running of the static field can be corrected.
Owner:赵跃
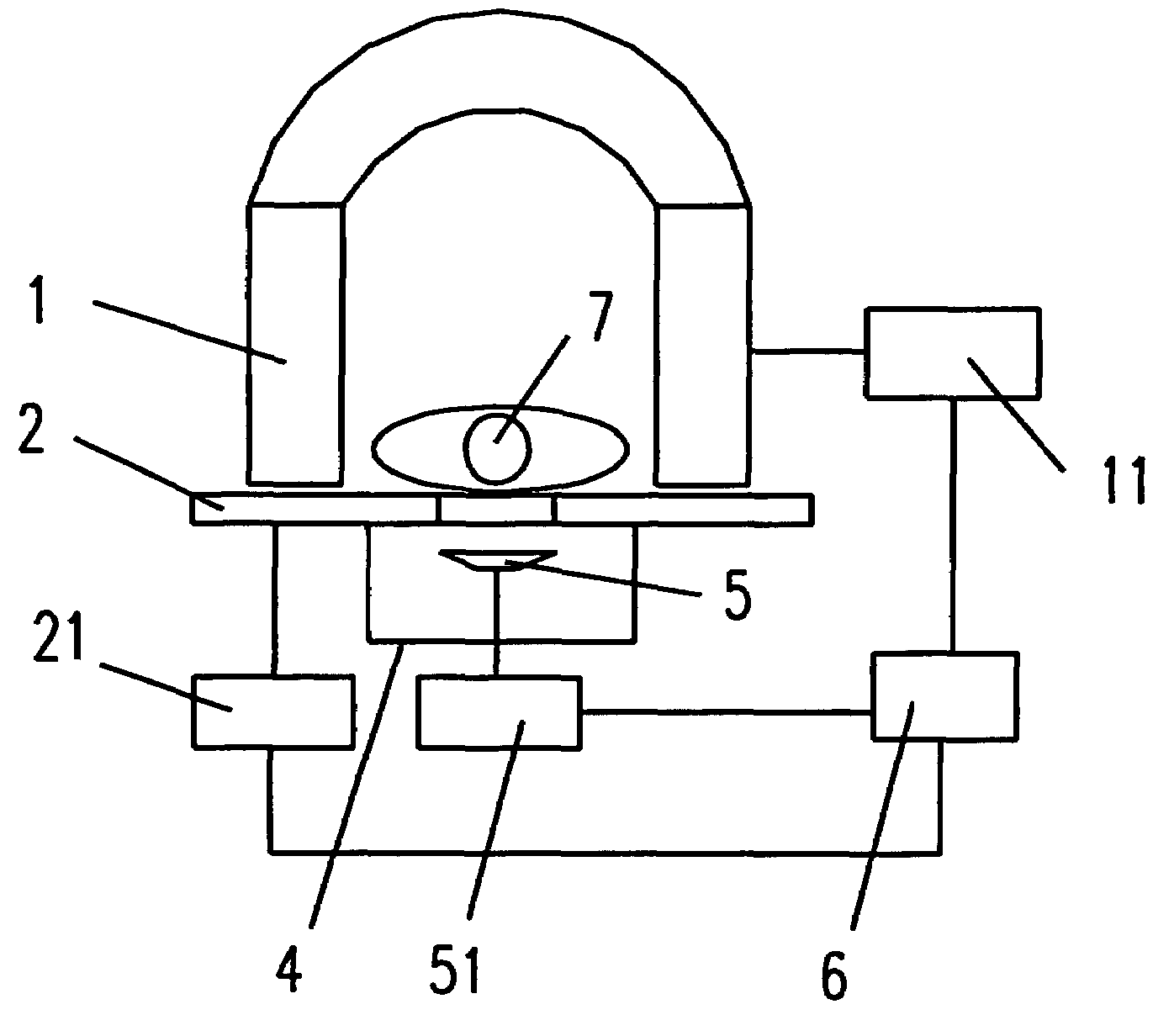
Mri Guided Ultrasound Therapy Apparatus
InactiveUS20080275330A1Reduce space constraintsReduce magnetic interferenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMri guidedPower flow
This invention provides a MRI guided ultrasound therapy apparatus. It comprises a static field magnet adapted to apply a static magnetic field in an magnetic resonance volume at a predetermined disposition; at least one ultrasound energy applicator adapted to apply energy within an energy application zone at a predetermined disposition; and The mechanical positioning means for moving said ultrasound energy applicator to position the applicator so that the energy application zone intersects said magnetic resonance volume within said region of the subject. In that apparatus, the static field magnet is open at both ends or open at side. The sided open is upward or downward and the mechanical positioning means of this ultrasound energy applicator is close to and is located outside of this sided open. This invention reduces the space limitation for the mechanical positioning means of the ultrasound transducer. Meanwhile, the non-magnetic requirement on the mechanical positioning means become less greatly and particularly the problem of interference from magnetic field produced by working current of the transducer power cord to MRI system can be solved.
Owner:RONGHAI SUPERSONIC MEDICINE EN
MRI apparatus
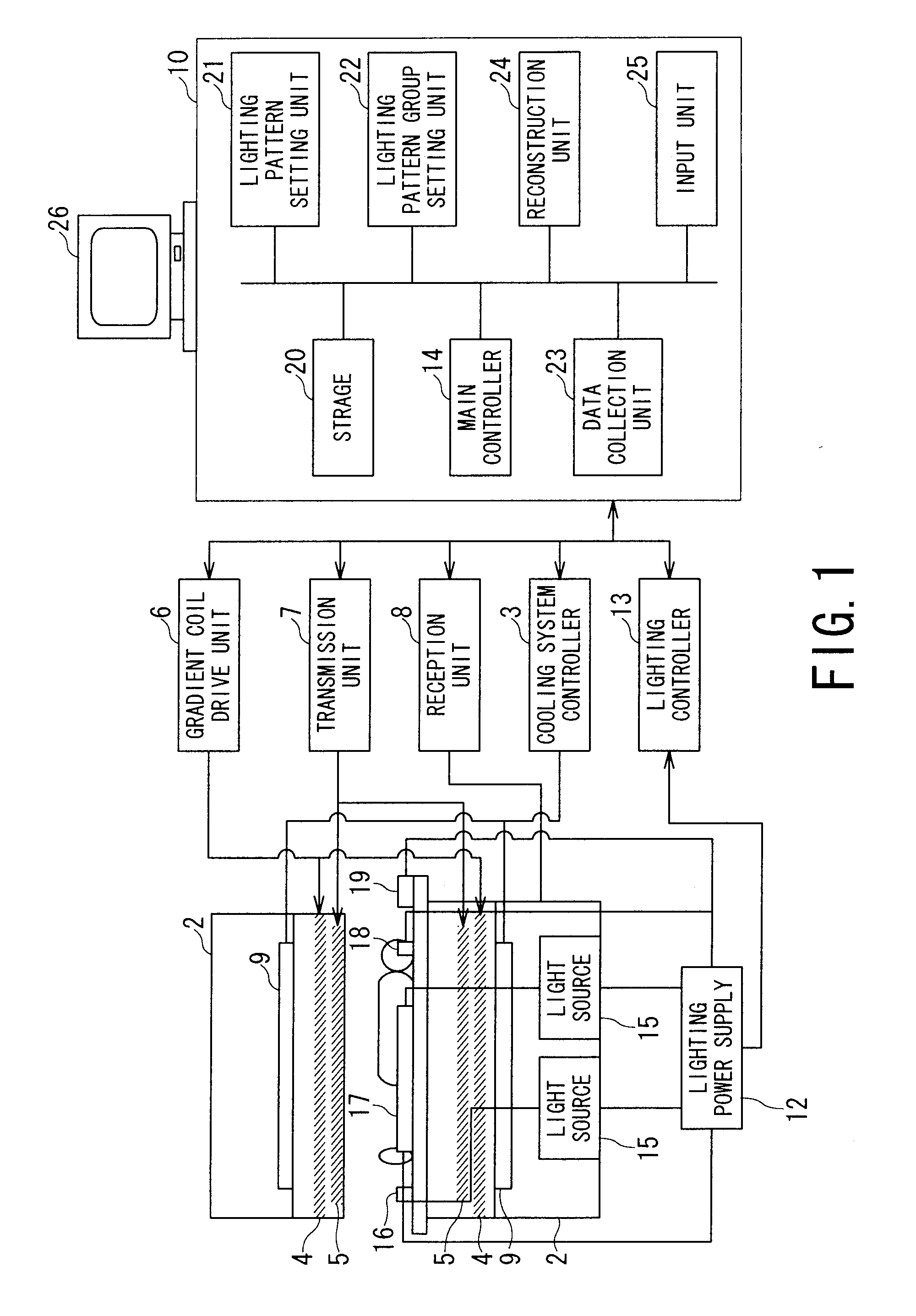
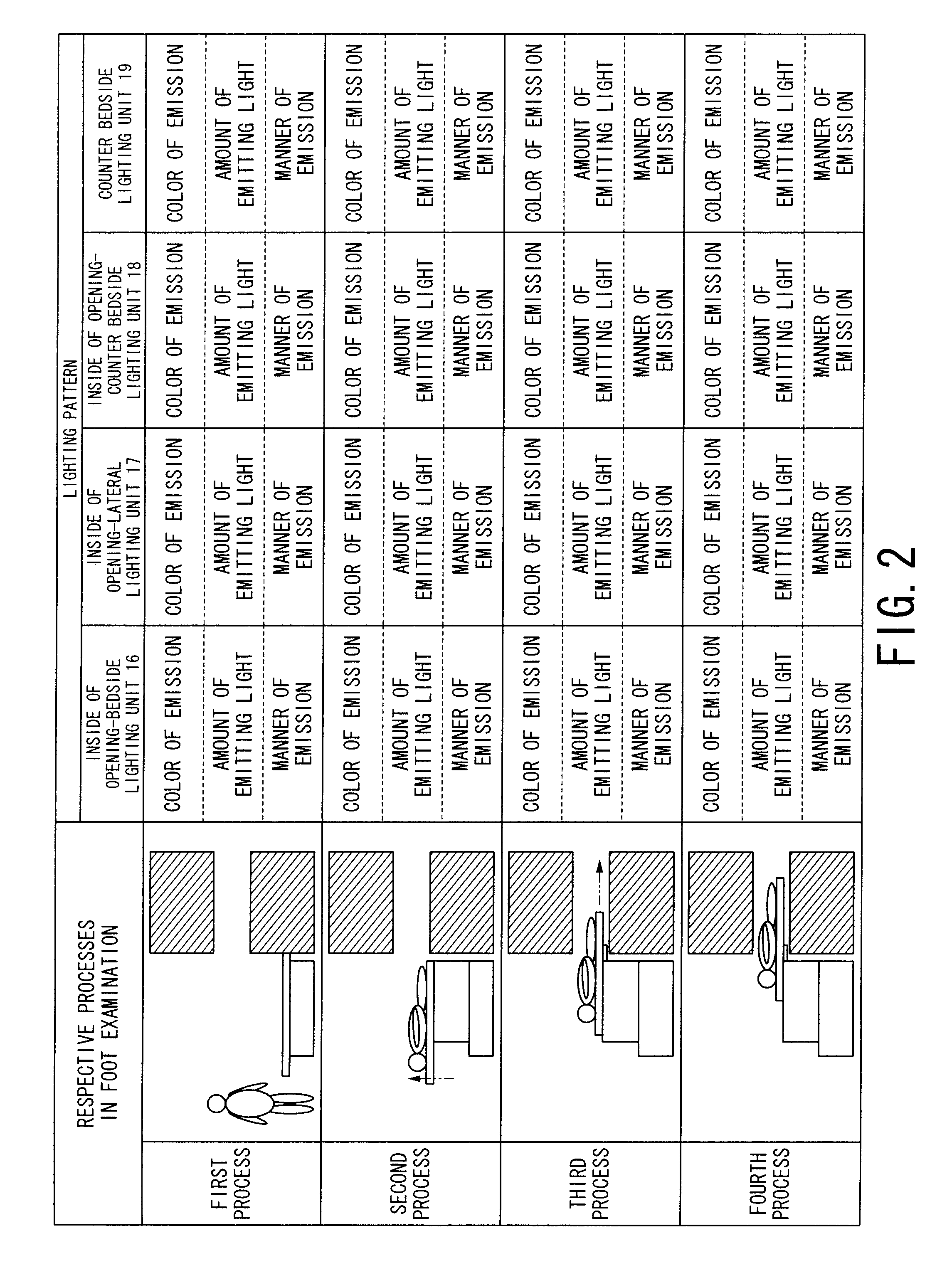
ActiveUS20080204017A1Improve securityIncreased sense of securityPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringStatic field
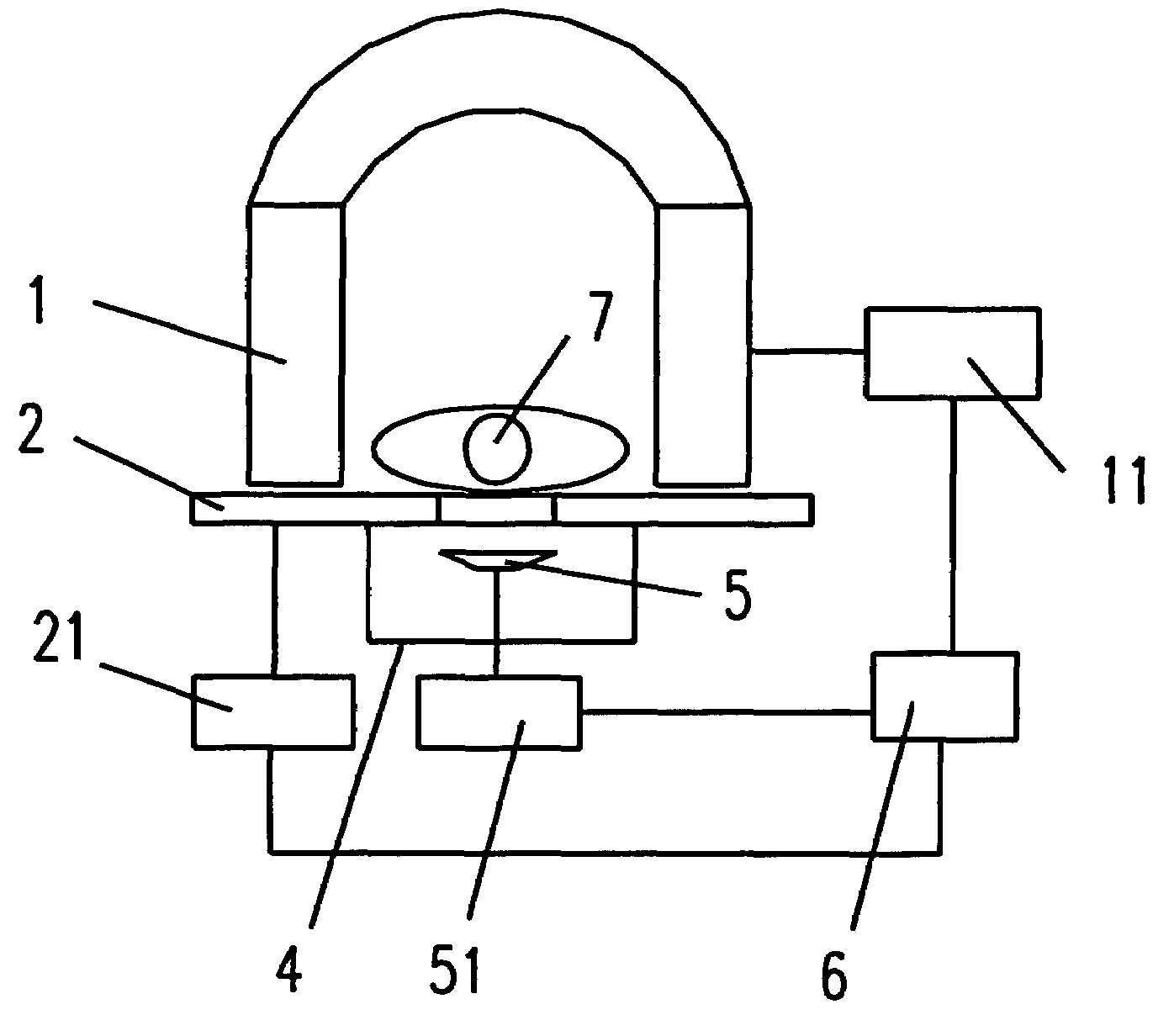
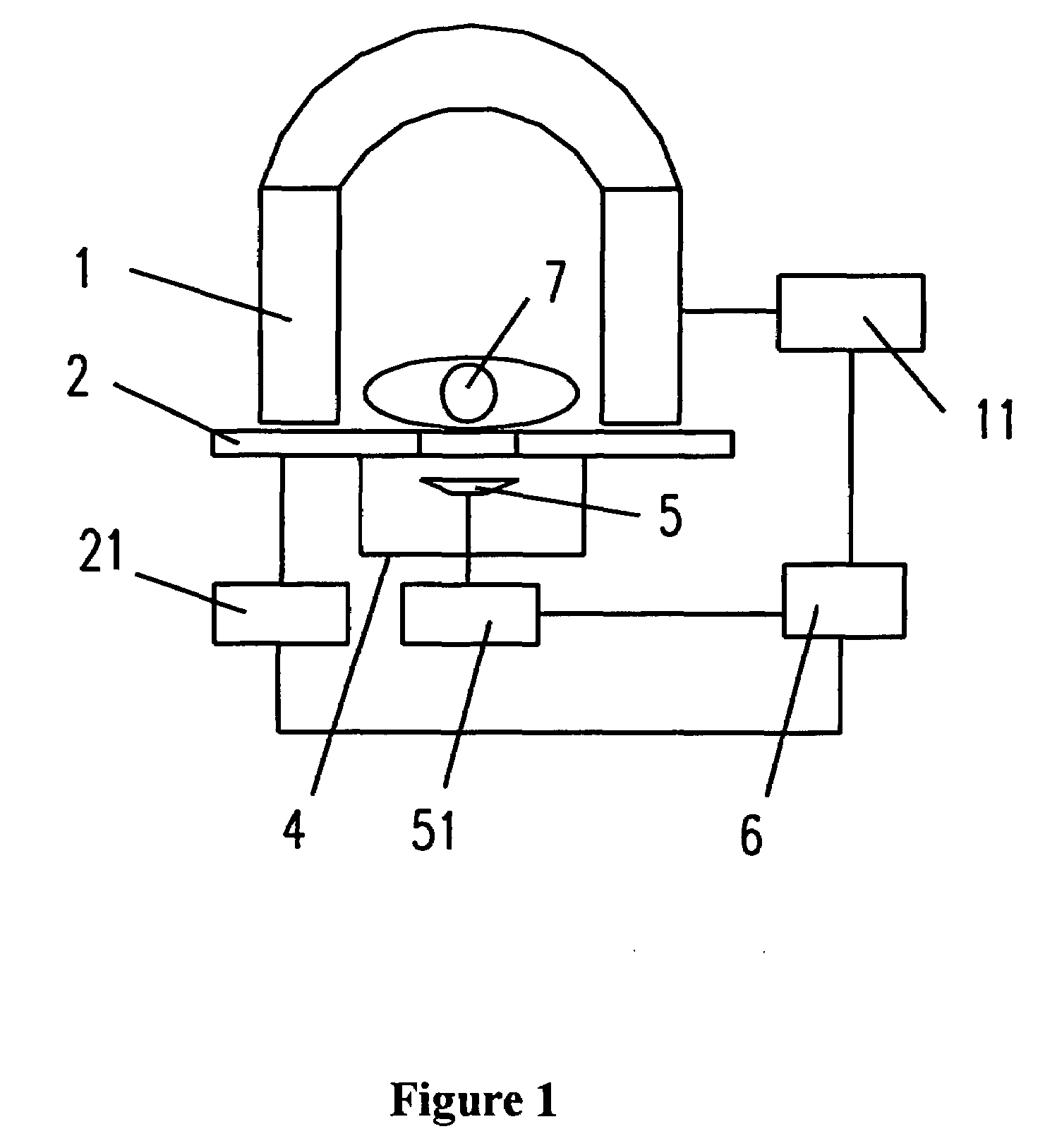
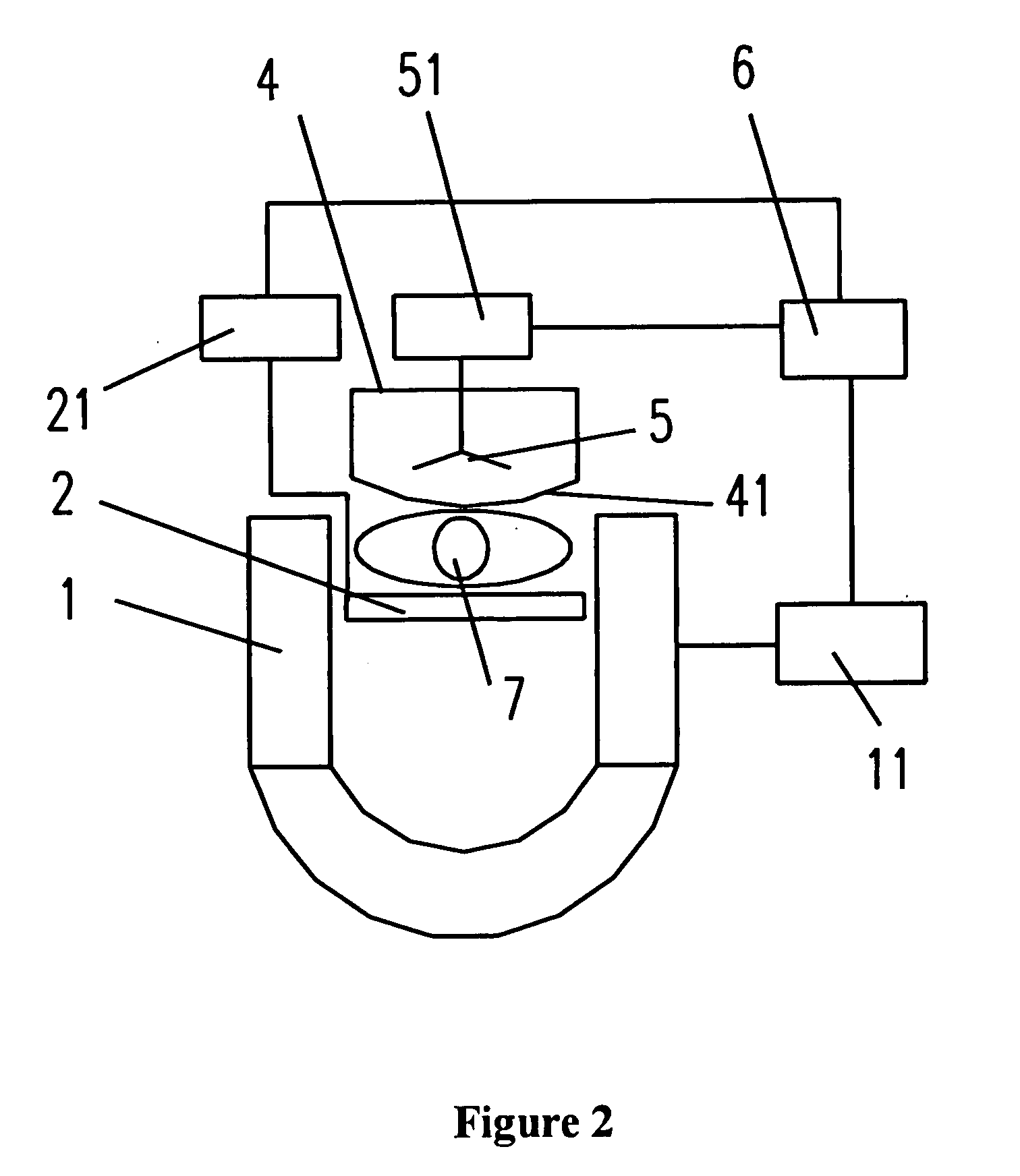
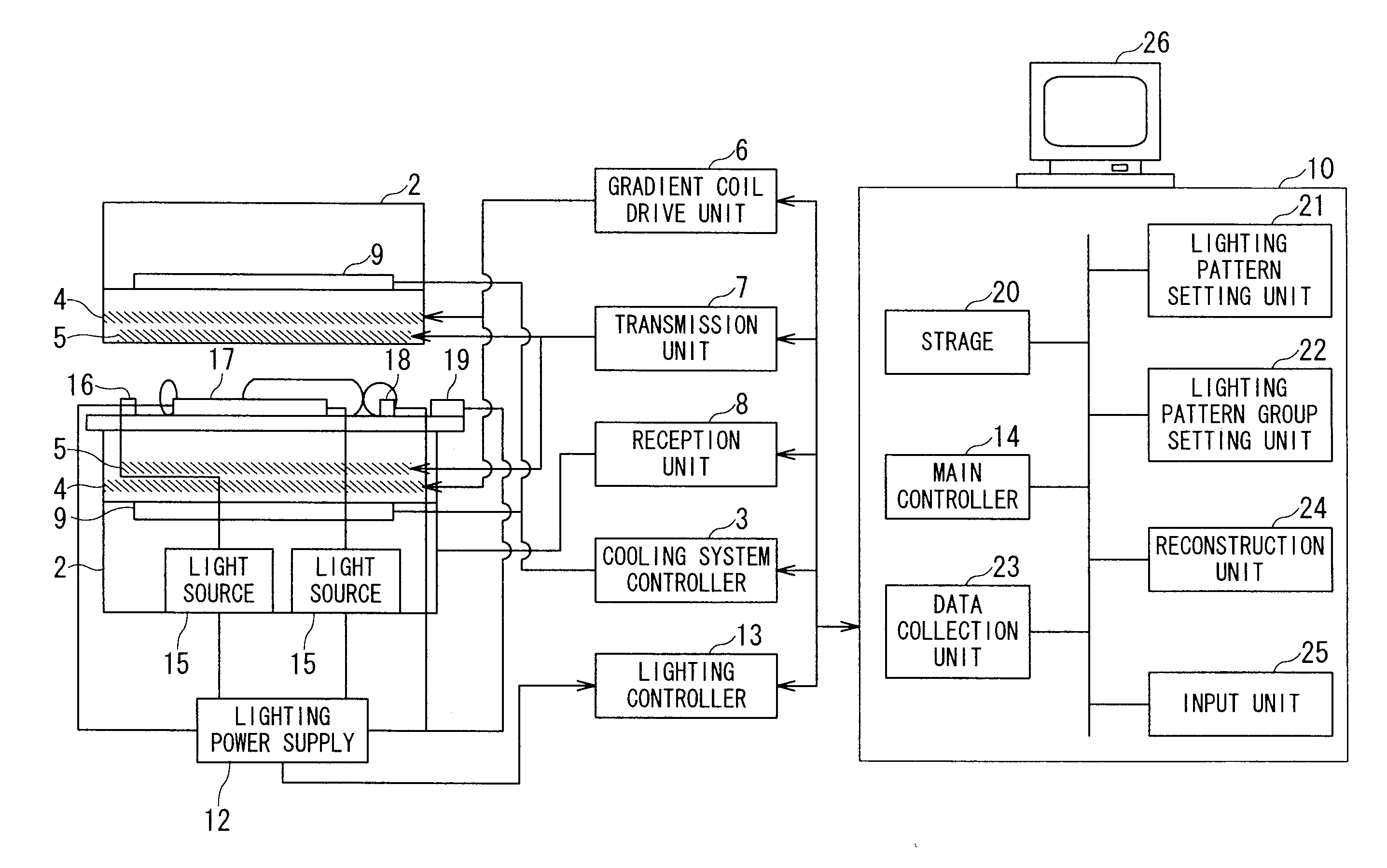
An MRI apparatus has a gantry, a bed and a lighting unit collective including a plurality of lighting units. The gantry accommodates a static field magnet configured to generate a static field, a gradient coil configured to generate a gradient magnetic field, and an RF coil configured to transmit or receive an RF pulse as well as having an opening into which a person is inserted. The bed has a removable table-top for an inside and an outside of the opening. The lighting unit group is disposed at at least one of an inside position of the opening and an outside position from which an inside of the opening can be lighted so that the lighting units can carry out lighting such that an amount of emitting light increases bit by bit from a bedside to a counter bedside opposite to the bedside across the opening.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Incremental updating method of an integrated Android application
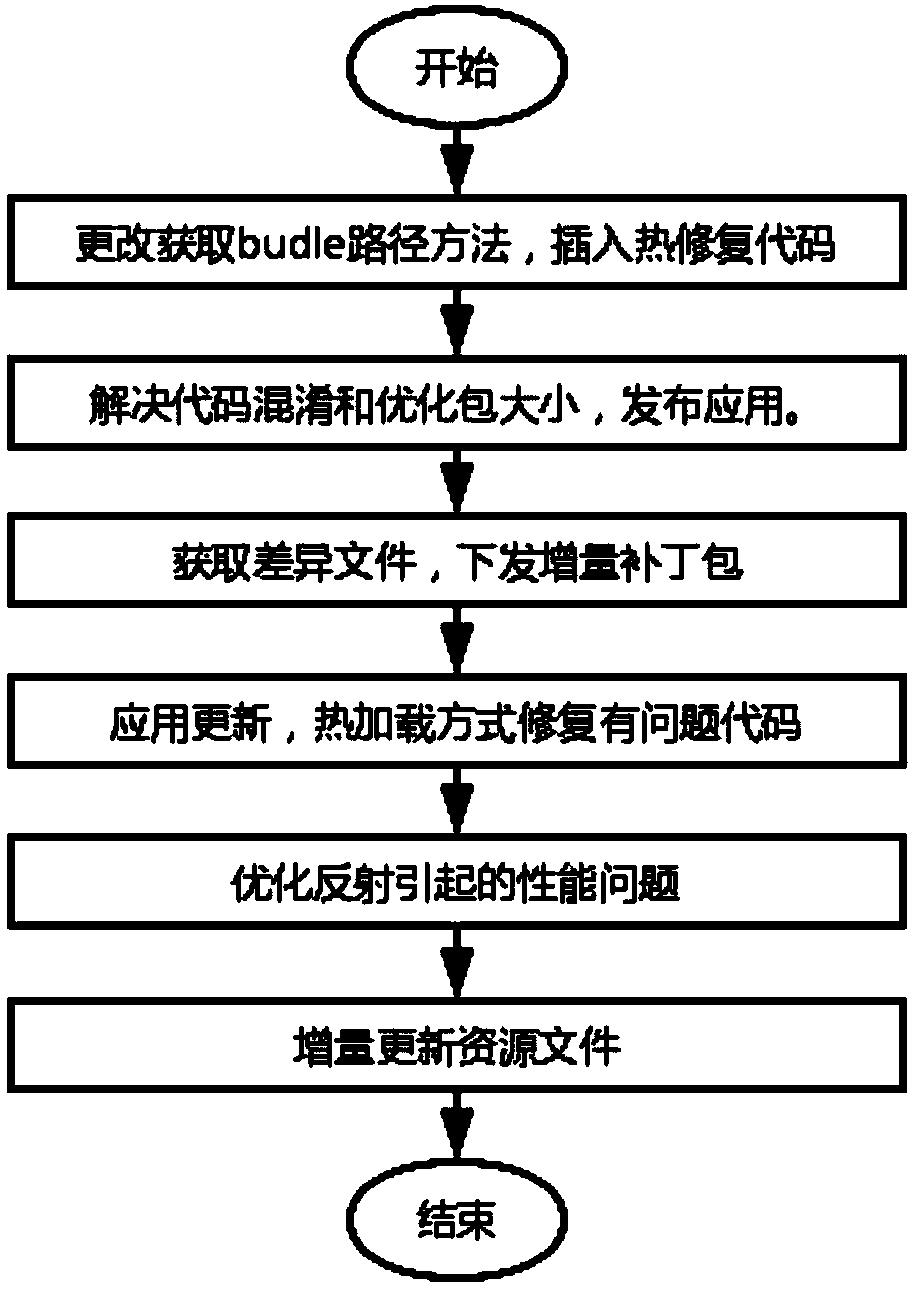
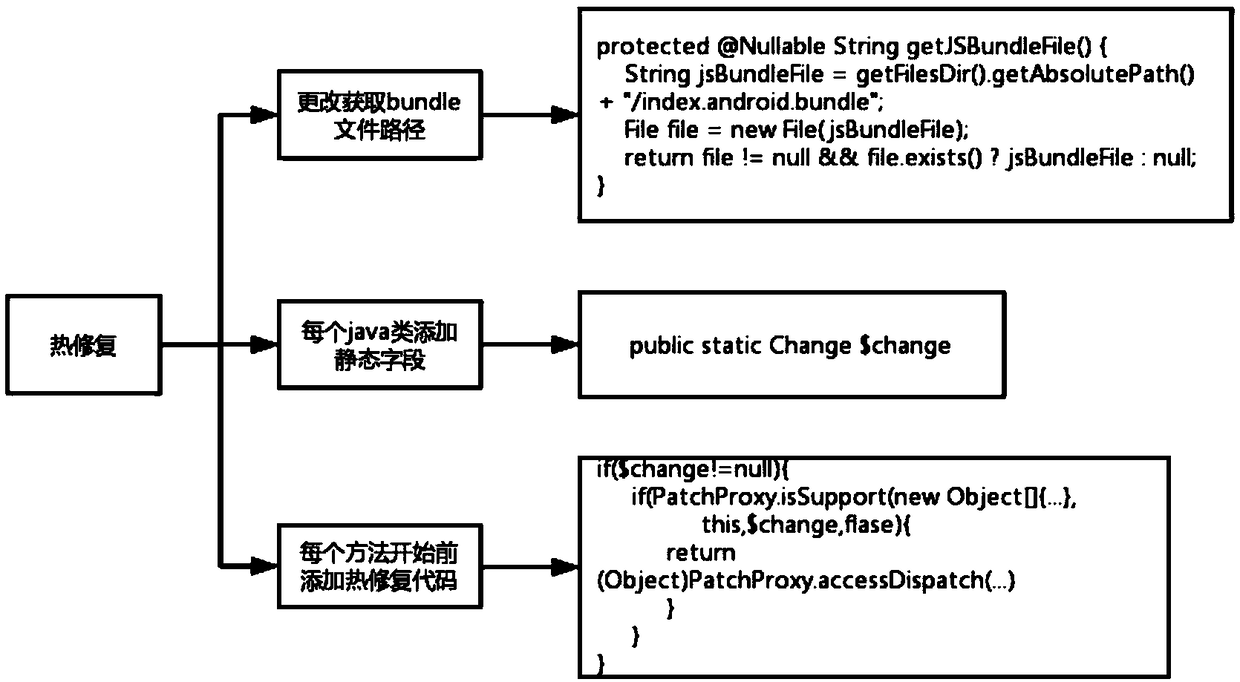
ActiveCN109491695AReduce trafficImprove application experienceCode compilationProgramming languageComputer compatibility
The invention discloses an incremental updating method of an integrated Android application, which is based on React Native, adds a static field to all classes in an Android native code serving as anapplication, inserts a skip code at an entrance of the method, and comprises condition judgment on the static field; in addition, the method for reading the bundle path is changed, and the bsdiff is used for achieving incremental updating of the application. According to the invention, the existing thermal remediation technology is optimized; a hot repair framework which is higher in compatibilityand can take effect in real time without restarting is achieved, online bugs can be repaired at any time without releasing a new version, resource files can be updated, discovered problems can be quickly repaired, great help is provided for developers, and great significance is achieved for improving the application use experience.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Liquid emanator device to deliver self-suspending insecticide droplets
A method and device for metered delivery of an insecticidal liquid into a room for the purpose of repelling or killing flying insects, wherein the liquid is ejected in small quantities from a bubble-jet type liquid emanator device at an ambient temperature. The ejected droplets may also be charged to (−1×10−4 C / Kg) by passing the droplets through a static field which will cause the droplets to be attracted to the positive charge which exists across the insects cuticle. Other applications include dispensation of fragrances and air fresheners into a room.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
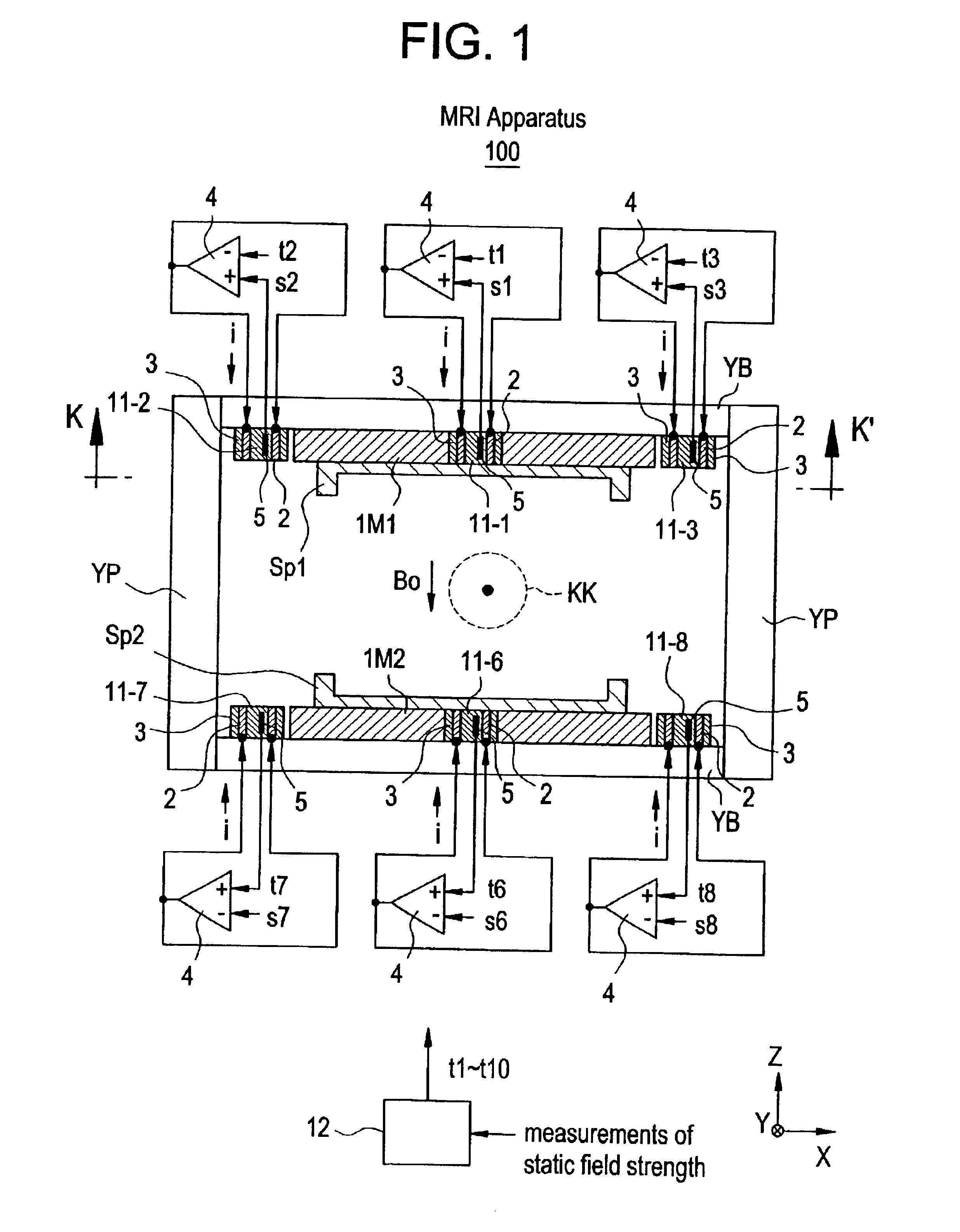
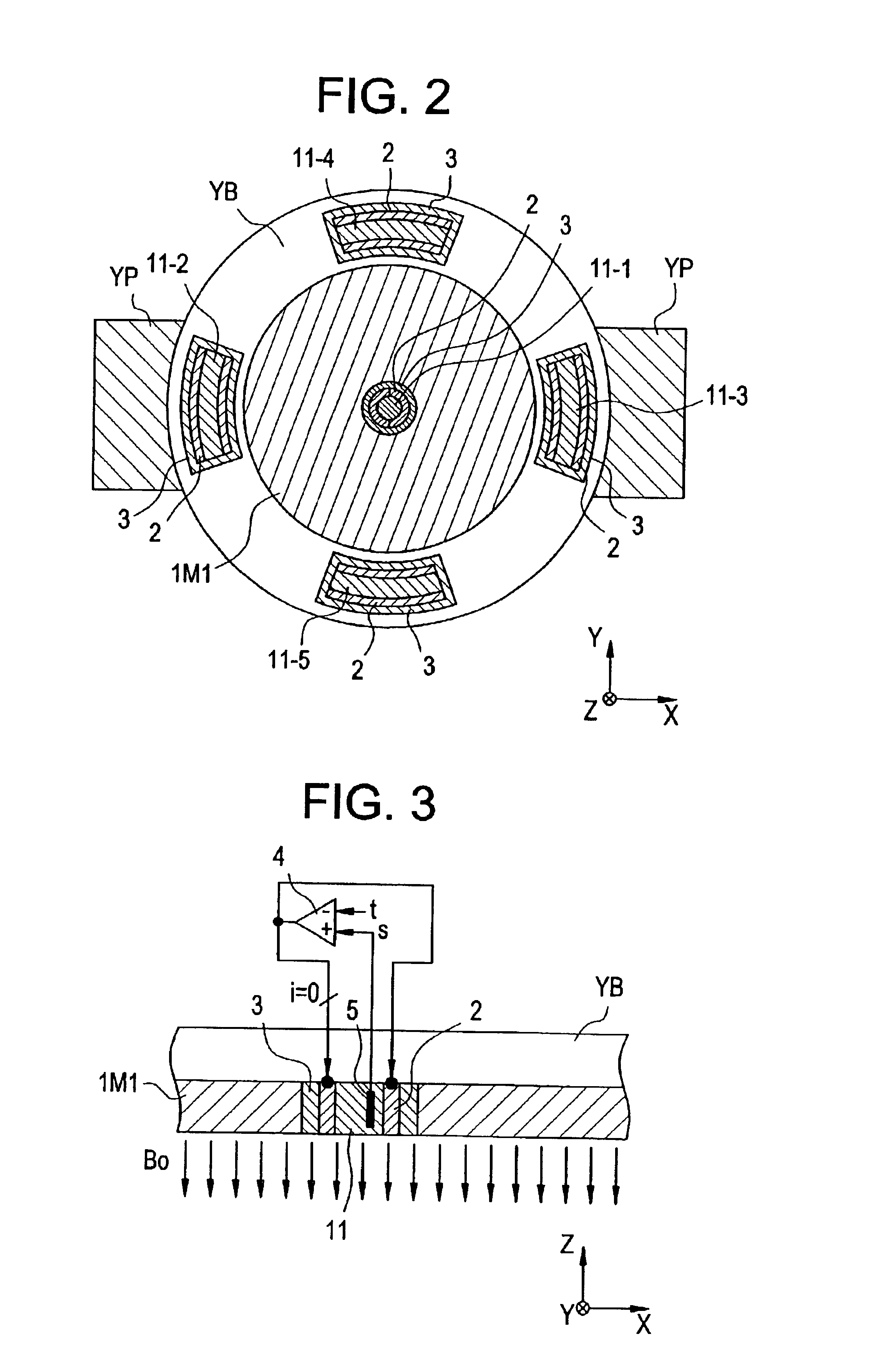
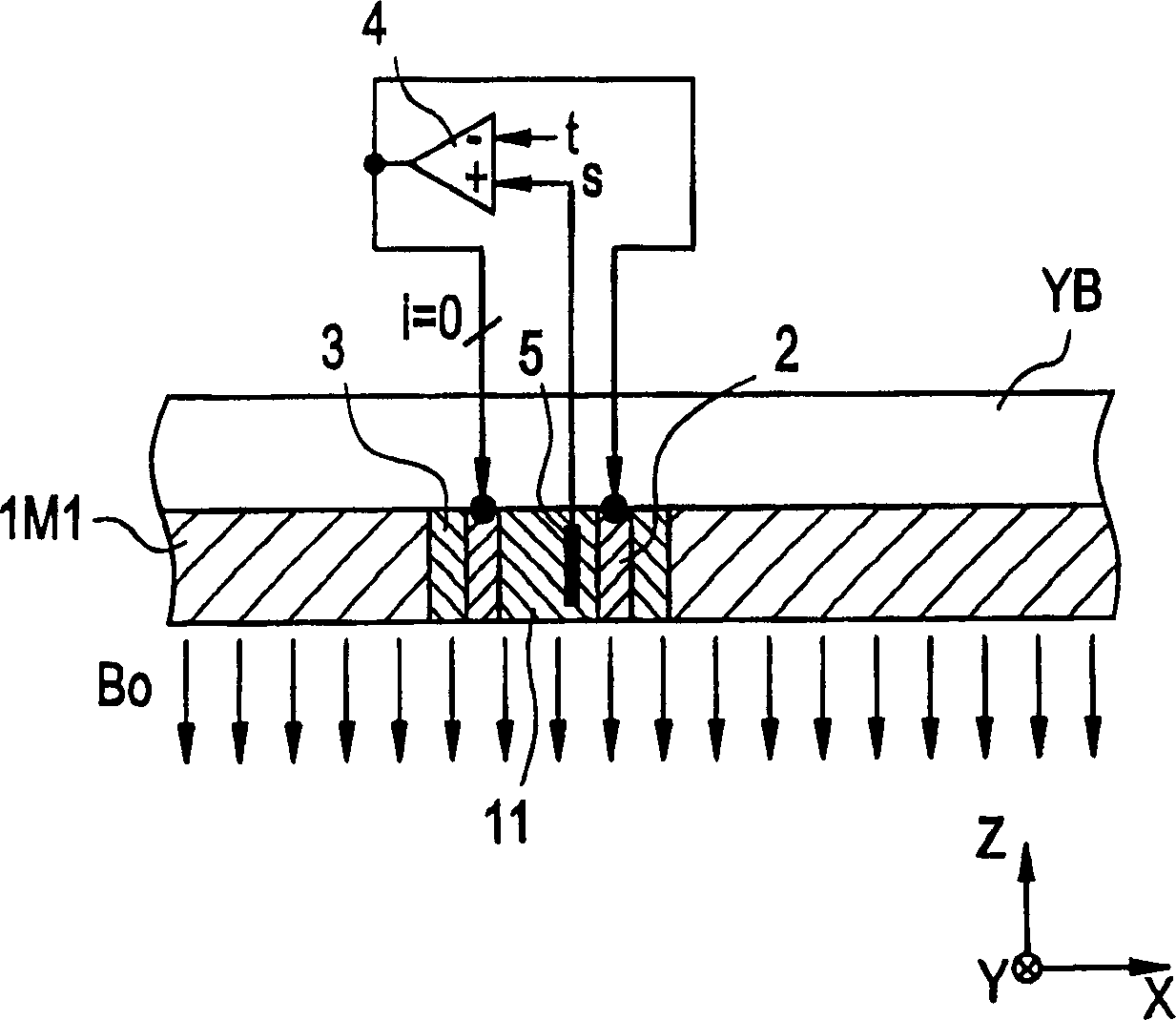
Static field controlling method and MRI apparatus
InactiveUS6891375B2Avoid interferenceControl UniformityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStatic fieldMagnet
The temperature of permanent magnet blocks embedded in several positions in permanent magnets and base yokes will be adjusted by device of a heater to improve the static field uniformity.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Static magnetic field control method and magnetic resonance imaging device
InactiveCN1394550AAvoid interferenceAdjust static magnetic field uniformityMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringStatic fieldMagnet
The temperature of permanent magnet blocks embedded in several positions in permanent magnets and base yokes will be adjusted by device of a heater to improve the static field uniformity.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
MRI guided ultrasound therapy apparatus
InactiveUS8224420B2Reduce space constraintsReduce magnetic interferenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMri guidedResonance
Owner:RONGHAI SUPERSONIC MEDICINE EN
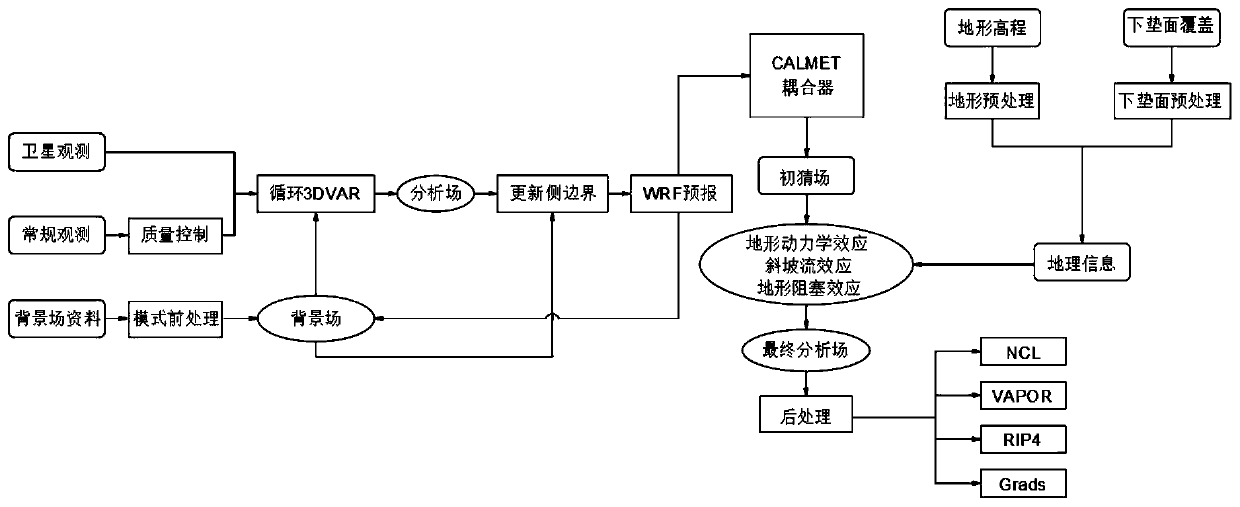
Refined meteorological element forecasting system of near-ground layer and forecasting method thereof
InactiveCN110275224AImprove initial field accuracyHigh-resolutionWeather condition predictionICT adaptationVariational assimilationObservation data
The invention, which relates to the field of meteorological element forecasting in the near-ground layer, discloses a refined meteorological element forecasting system of a near-ground layer and a forecasting method thereof. Different values of weather forecasting modes are integrated, coupled, and optimized to realize rapid cycle data assimilation. A forecasting area is designed and real-time dynamic refined near-ground meteorological element forecasting of an area and a single point under any landform is realized. The refined meteorological element forecasting system comprises a data downloading subsystem, a mesoscale weather forecasting mode subsystem, a three-dimensional variational assimilation subsystem, a CALMET small-scale meteorological model subsystem and a post-processing subsystem. In addition, the method includes: downloading grid data as well as conventional and unconventional meteorological observation data of the forecasting system; carrying out quality control and WRF mode pre-processing; carrying out rapid cycle data assimilation to obtain an optimized atmospheric initial field; carrying out area and single-point forecasting; acquiring an initial guess field and an underlying surface static field; carrying out downscaling forecasting based on a micro-topographic dynamics effect to obtain forecasting results of the near-ground layer at different heights; and carrying out post processing to obtain a final chart and a statistical result for outputting and displaying.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
System for modifying object oriented code
The system receives three sets of inputs: program class definitions, a set of rules, and additional class definitions to be merged with the program class definitions. There are three types of rules: the first rule is used to substitute the allocation of an object of a new class for the allocation of the object based on an original class; the second rule is used to change code that allocates an object of an original class to code that calls a static method that allocates the object of the original class; and the third rule is used to a replace a new static field for an original static field. The system separately reads each of the original class definitions into a class data structure and performs the modifications to the class data structure according to the set of rules. The resulting class data structure is written to an output stream.
Owner:WILY TECH
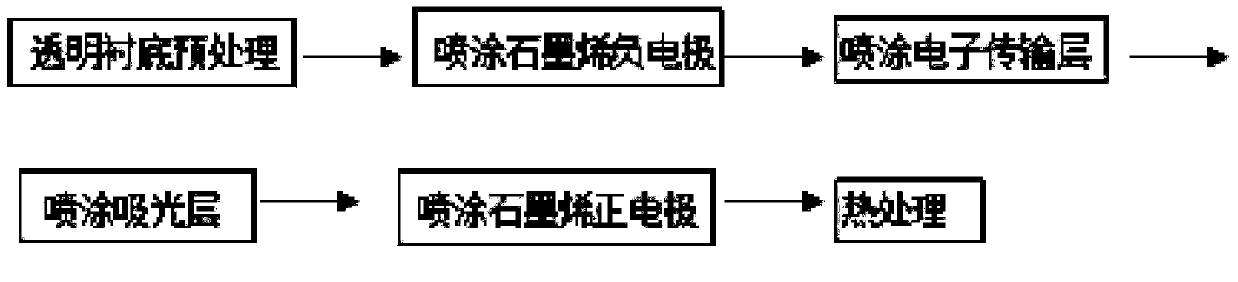
Perovskite based flexible film solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104201287AThickness is easy to controlEasy to makeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionSilicon solar cell
The invention discloses a perovskite based flexible film solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The perovskite based flexible film solar cell comprises a transparent substrate, a graphene negative electrode, an electronic transmission layer, a light-absorbing layer and a grapheme positive electrode. The preparation method of the perovskite based flexible film solar cell comprises the steps of: pre-treating the transparent substrate; spraying the graphene negative electrode; spraying the electronic transmission layer; spraying the light-absorbing layer; spraying the graphene positive electrode; performing heat treatment. According to the invention, static spraying way is adopted for molding; the static spraying way is to drive a raw material to pass through a nozzle by utilizing a strong static field and enable the raw material to be deposited on a base plate; a solvent is volatilized in the spraying process, and a coating with relatively high compactness can be shaped under the action of a relatively great acting force, so that the disadvantages in the prior art can be overcome efficiently. Through the static spraying way for molding, the cost is 80% lower than that of a silicon solar cell, the energy conversion efficiency is better than that of the traditional silicon solar cell and is up to 27%, so that the perovskite based flexible film solar cell can replace monocrystal to become a new generation of the flexible film solar cell.
Owner:湖南省天赐阳光太阳能有限责任公司
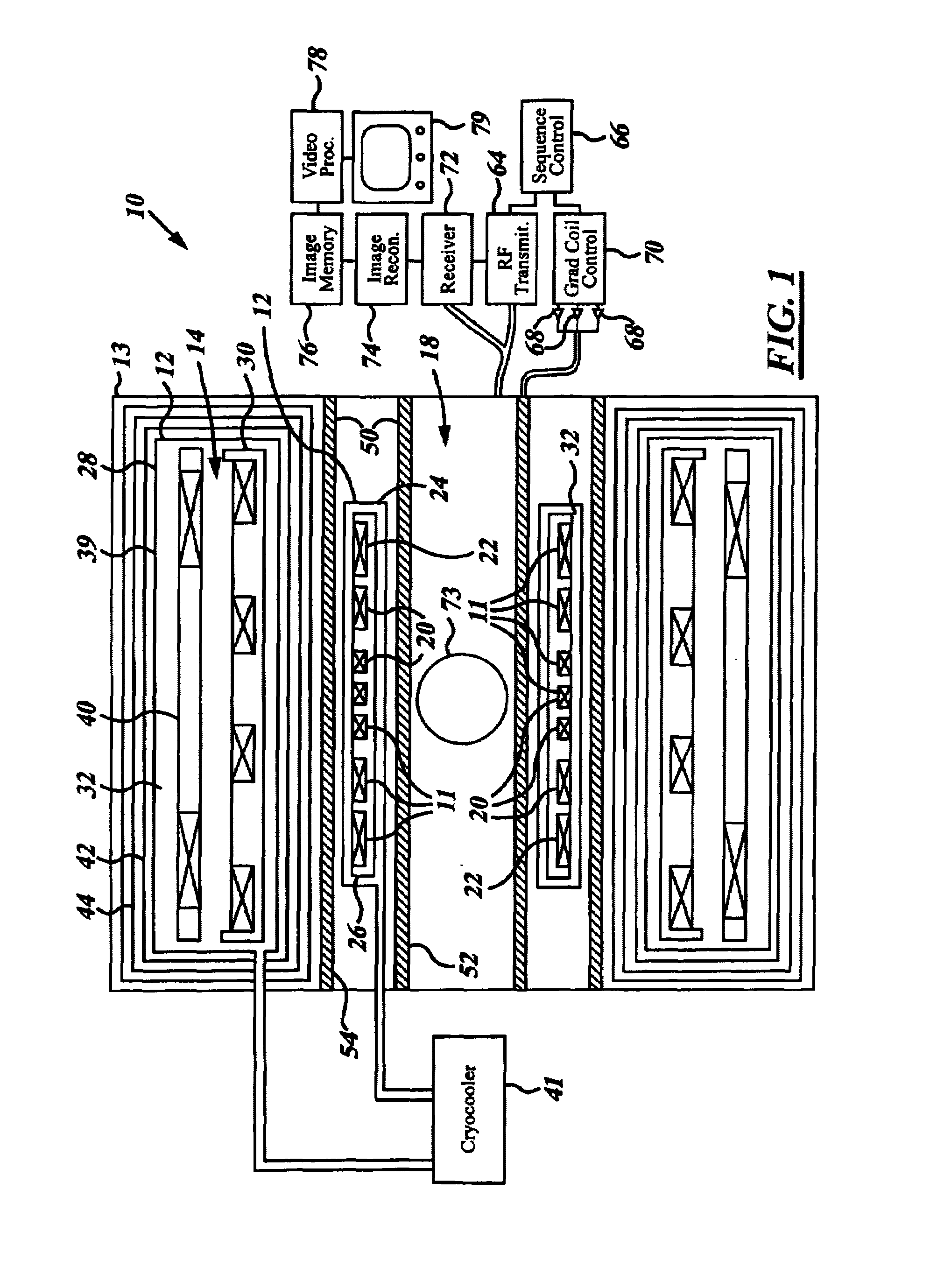
MRI system utilizing supplemental static field-shaping coils
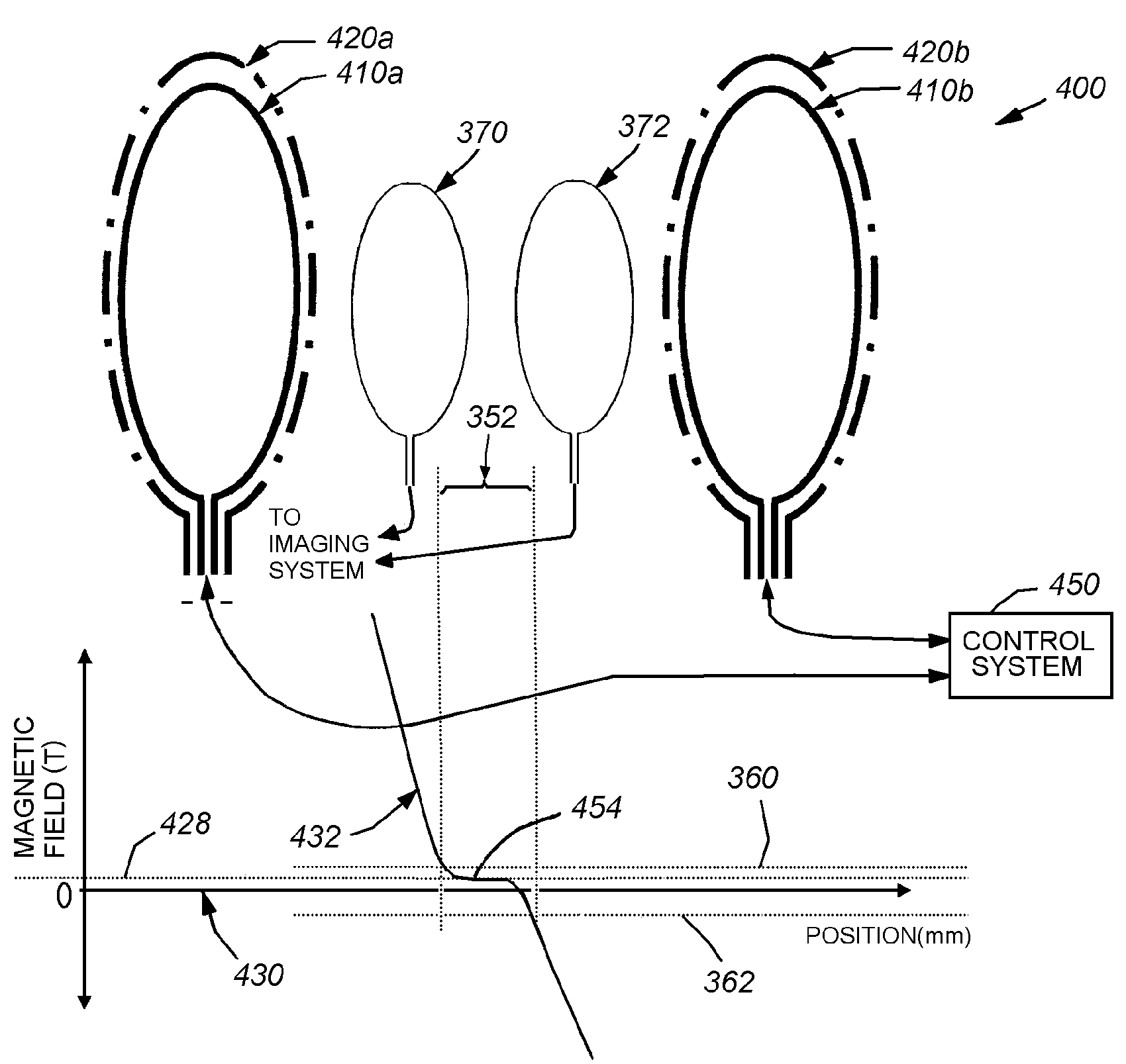
ActiveUS6965236B2Improves Strength and UniformityMinimizationMagnetsDiagnostic recording/measuringSuperconducting CoilsStatic field
A magnetic resonance imaging system (10) includes a superconducting magnet (14) that generates a static magnetic field. A gradient coil assembly (50) with an associated patient bore enclosure (18) and a gradient coil (52) that generates a gradient magnetic field in the patient bore (18). A static field-shaping coil (11) resides between the superconducting magnet (14) and the patient bore (18) and supplements the static magnetic field.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com