Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2349results about "Weather condition prediction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
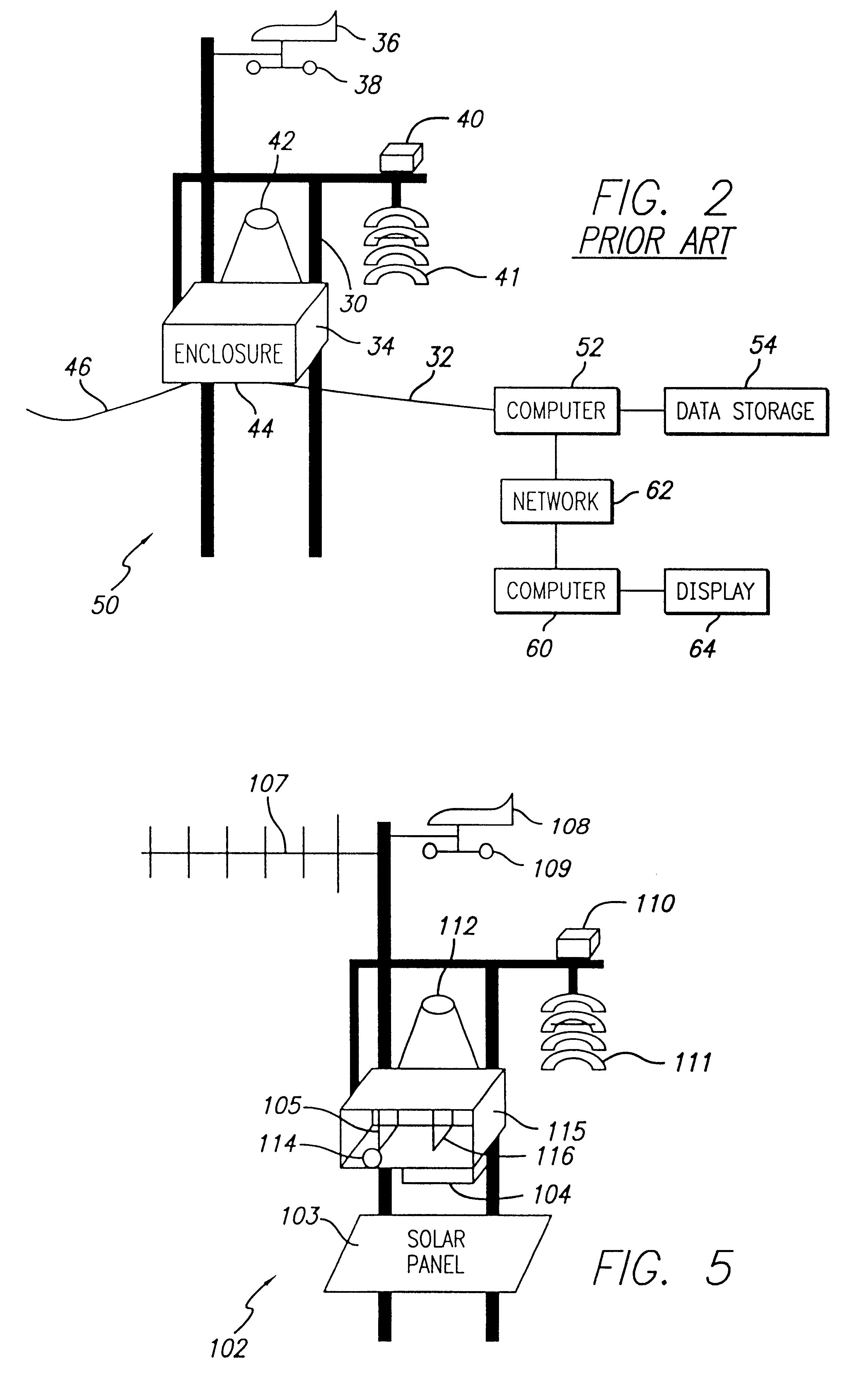
Method and Apparatus of Transmitting, Receiving, Displaying and Playing Weather Data
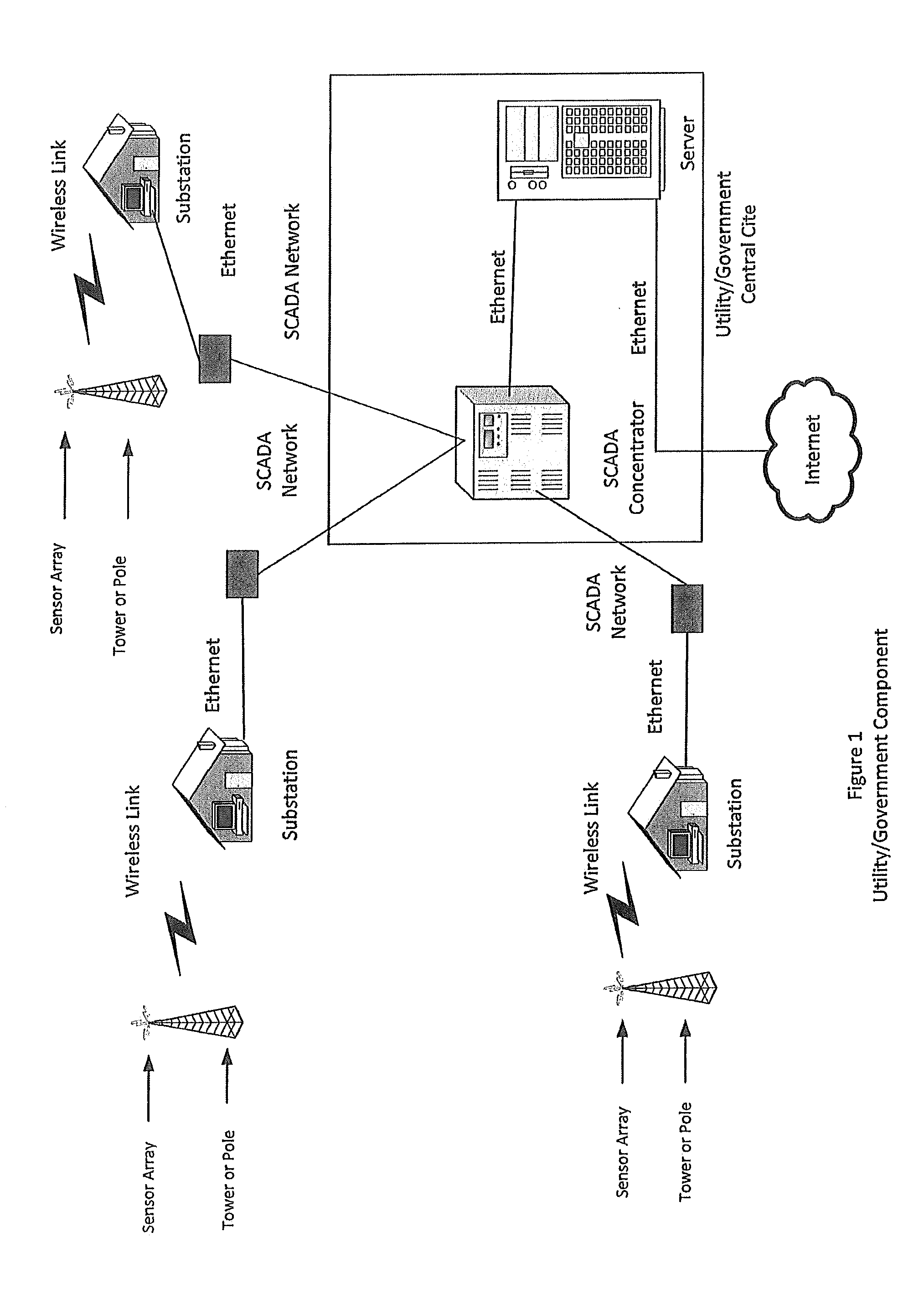
ActiveUS20090316671A1Low costReception problemWeather condition predictionWireless commuication servicesData synchronizationTransceiver
A transmitter transmits time synchronized data via a pager / WiMax / 802.x access to a receiver system, wherein the receiver system is programmed to receive data for specific geographic locations. The geographic locations may be specified by the user or by the receiver system, and includes state, zip codes, towns, counties, towns, or cardinal regions. The receiver is able to find its location when outside its cell region and is able to synchronize to the data transmitted in the new cell region. Further, the receiver system is able to remotely monitor weather data and other information at a different location via wireless Internet or voice over IP. A transceiver may also be used to receive weather or alert data. In response to receiving data, the transceiver transmits the data to low powered devices in a house using a different frequency band than the frequency band it received the data.
Owner:LA CROSSE TECH
Monitoring Fitness Using a Mobile Device
ActiveUS20150324751A1Physical therapies and activitiesWeather condition predictionTerrainExercise performance
Athletic performance monitoring and tracking may provide multiple ways in which to track athletic movement and activity. Workouts may also be tagged with various parameters including mood, weather, terrain, athletic equipment, friends used and the like. Workout information may be shared to social messaging and networking outlets. Workout information shared may include map information including images of maps, interactive maps, links to maps, route information and the like and / or combinations thereof. Additionally or alternatively, an application may be configured to execute within a context of a social networking system to facilitate athletic activity data transfer and generation of workout entries in the social networking site. Recommended activities to be performed or a recommended time to perform an activity may be determined based on a user's schedule, weather or conditions forecasts, or a location of the user or the potential activity.
Owner:NIKE INC
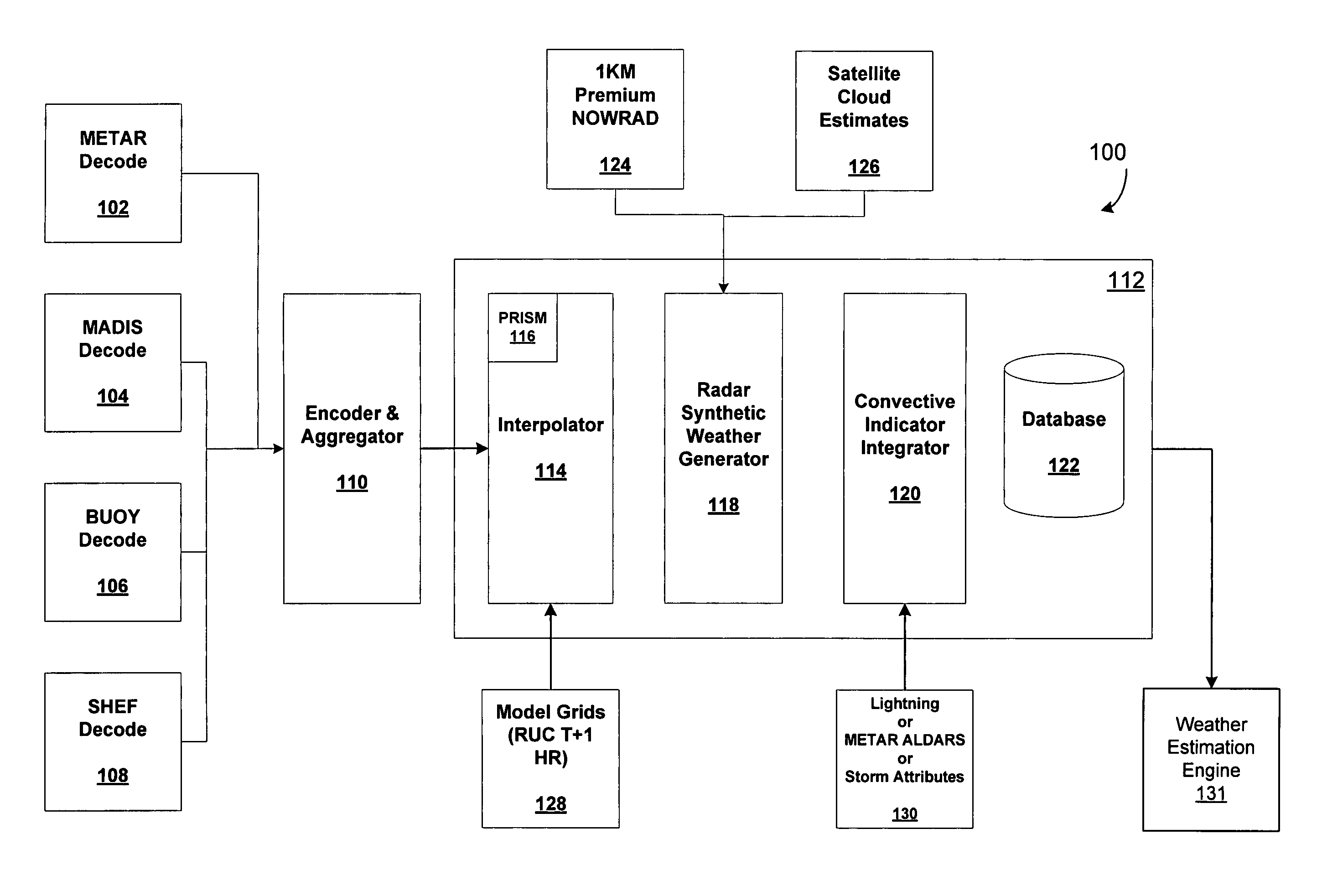
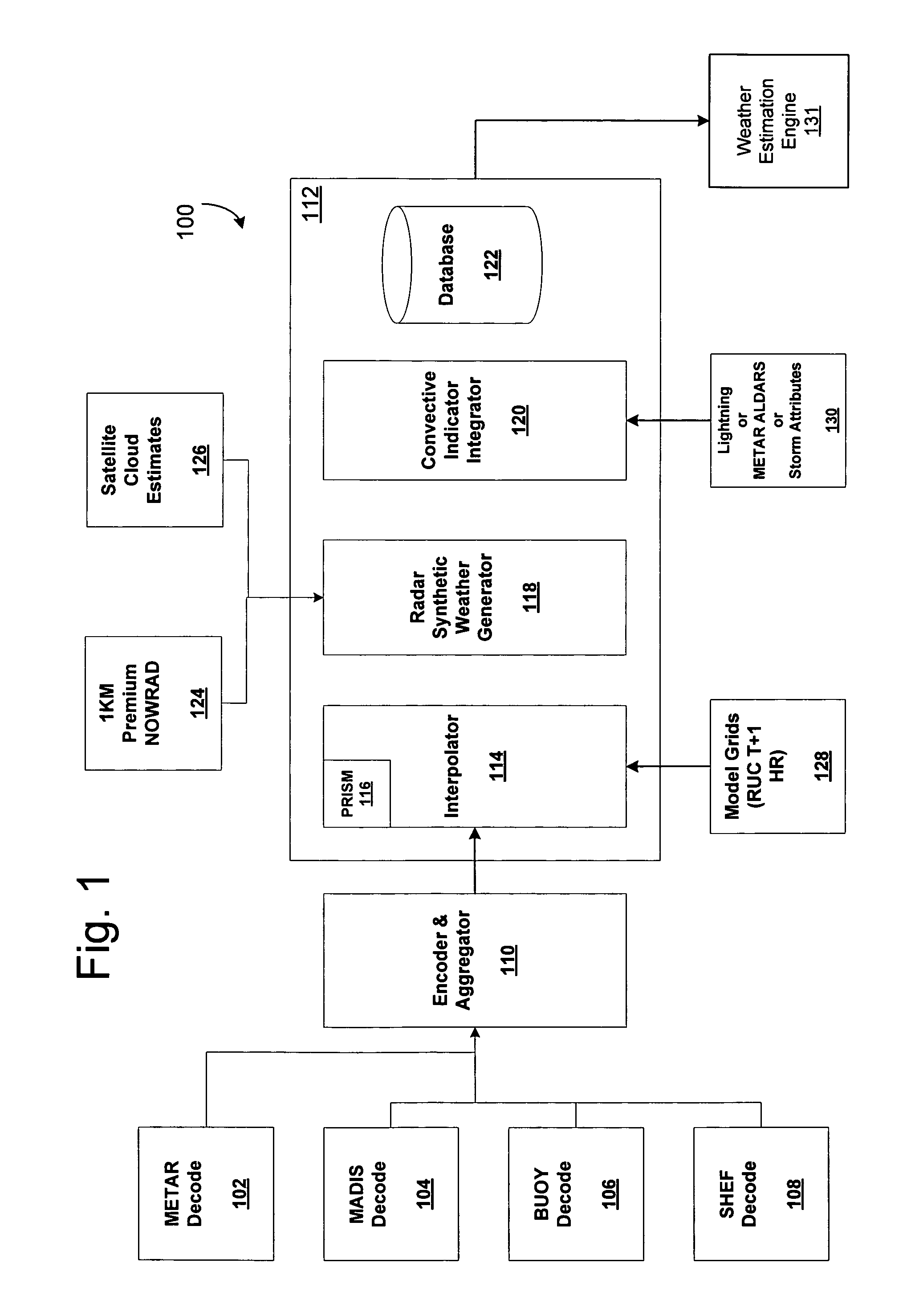
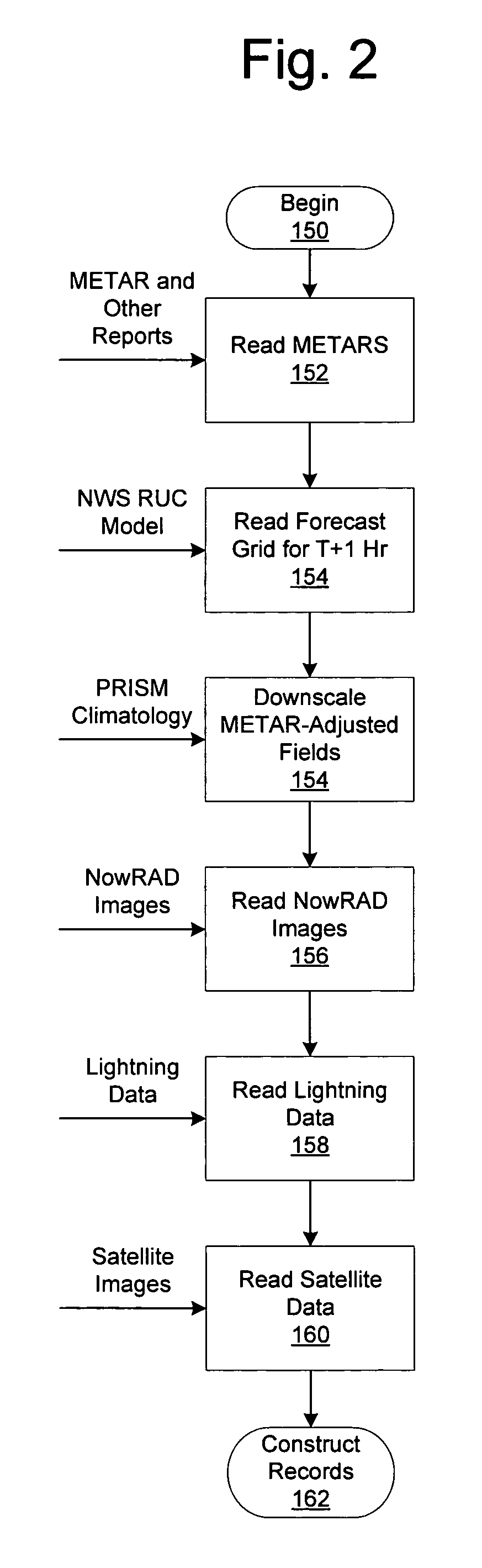
System for producing high-resolution, real-time synthetic meteorological conditions for a specified location
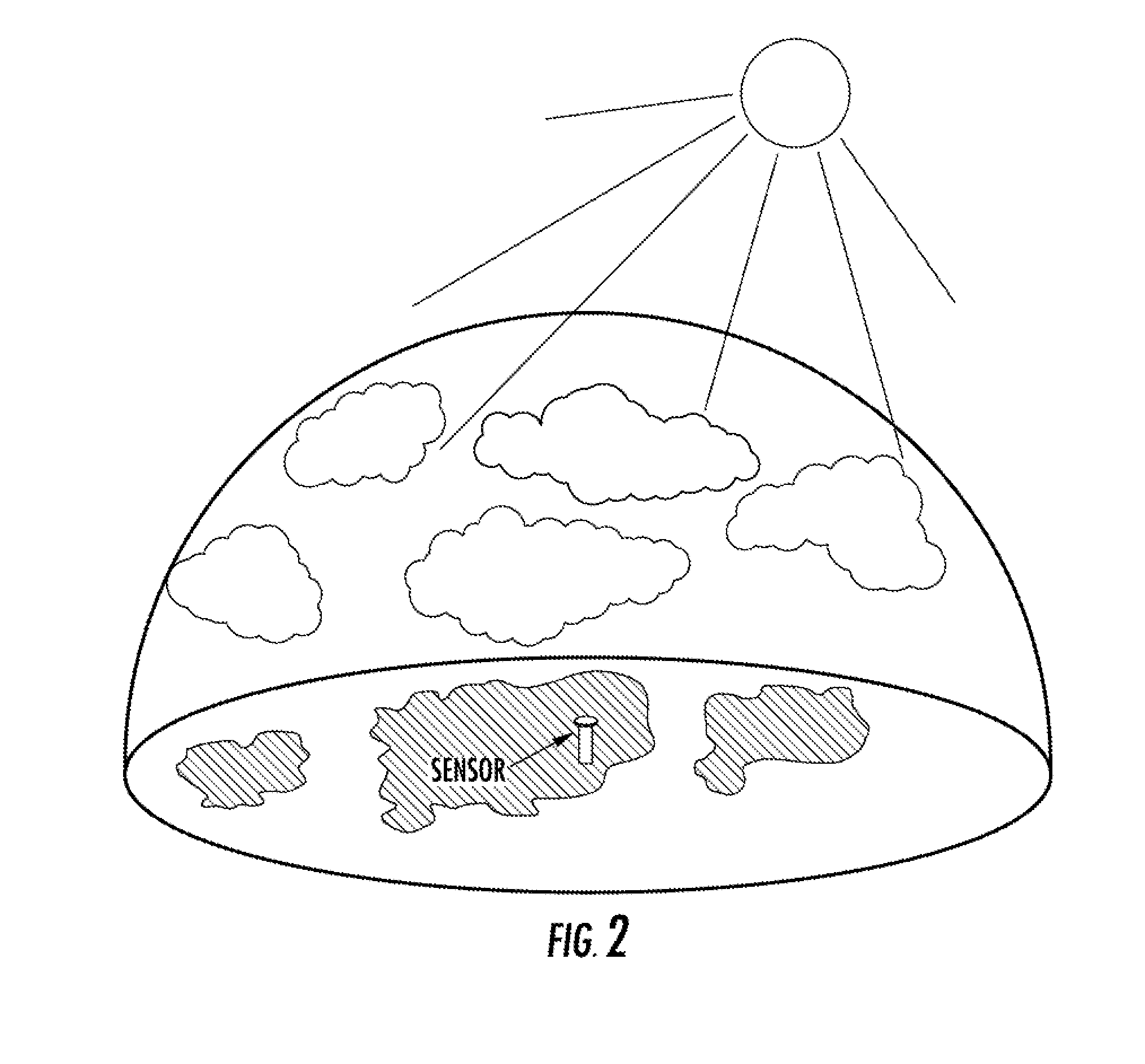
ActiveUS7082382B1Weather condition predictionDigital computer detailsAtmospheric sciencesSatellite imagery
Methods and articles of manufacture for estimating or deriving weather observations / conditions for any given location using observed weather conditions from neighboring locations, radar data, lightning data, satellite imagery, etc. An initial estimate of weather conditions for a location is made based on a downscaling process using the current conditions the neighboring locations. A measure of corroboration between the radar data and surface weather conditions at official observing stations may be established. Through the results of the downscaling process, radar calibration statistics and estimates of ground-based precipitation, the corroboration can be iteratively tuned, resulting in a weather conditions vector containing associated meteorological fields for locations that lie between or near the sparse network of official observing sites from which an estimate of the weather conditions may be made.
Owner:DTN LLC
Severe weather detector and alarm
InactiveUSRE45514E1Protection lifeProtect propertyHuman health protectionWeather condition predictionExtreme weatherRadio receiver
A compact, portable weather station for predicting local extreme weather conditions and for reporting remote weather conditions. The weather station has sensors for determining local temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, ambient light, and ambient static charge. A microprocessor has memory for storing data relating to past weather conditions and data processing apparatus and algorithms for determining probable developing weather conditions responsive to sensed local conditions. The weather station has a radio receiver for communicating with global weather reporting communications systems utilizing cellular communications. Operating commands, predicted local weather conditions, and remote weather conditions are annunciated in synthesized voice in any one of a variety of predetermined languages. The weather station includes voice synthesizing and recognition apparatus for annunciating verbal prompts and weather conditions, and for responding to vocal control. The weather station is formed in two separable components, one having sensors and the other having radio communications apparatus.
Owner:LA CROSSE TECH IP HLDG
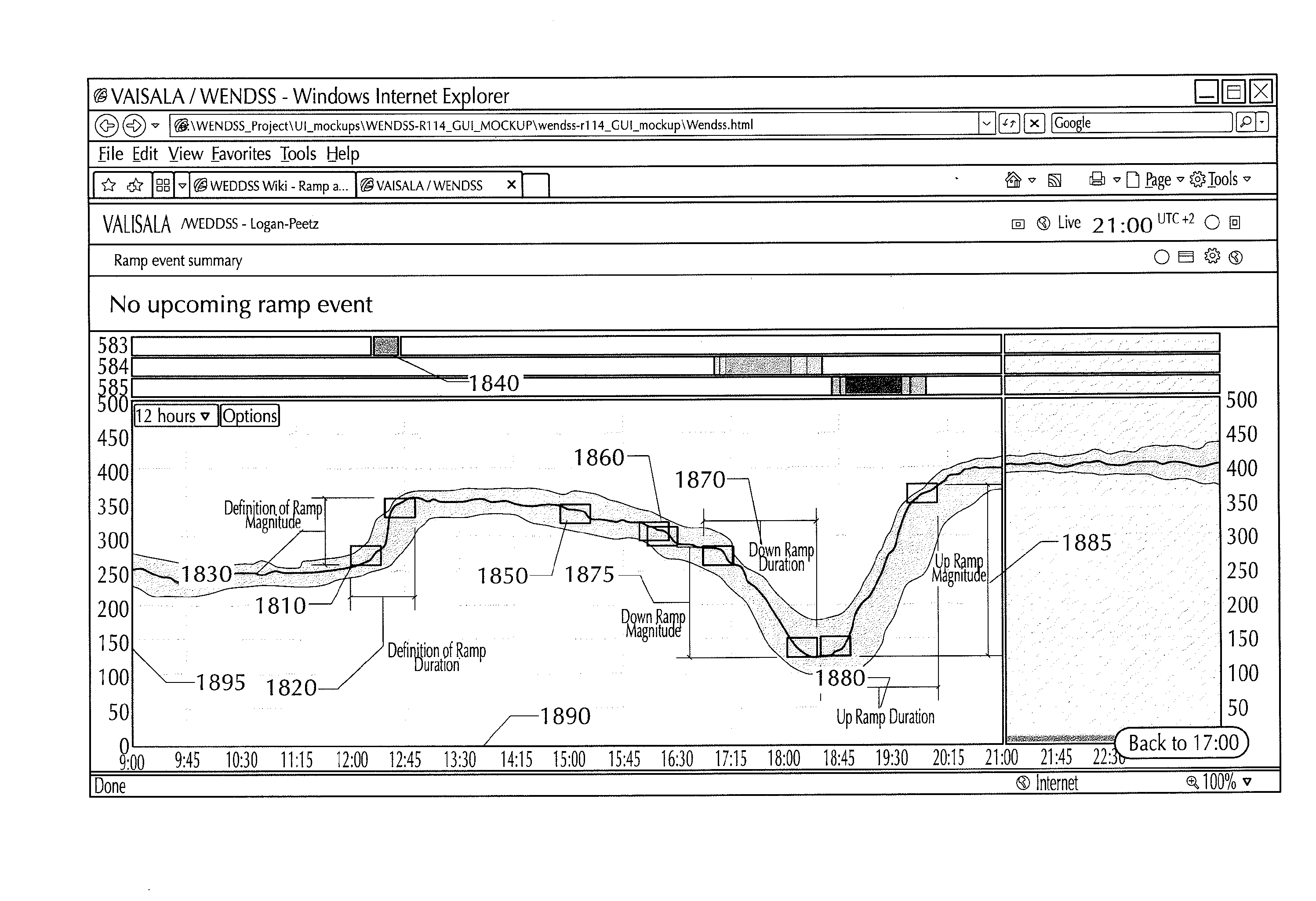
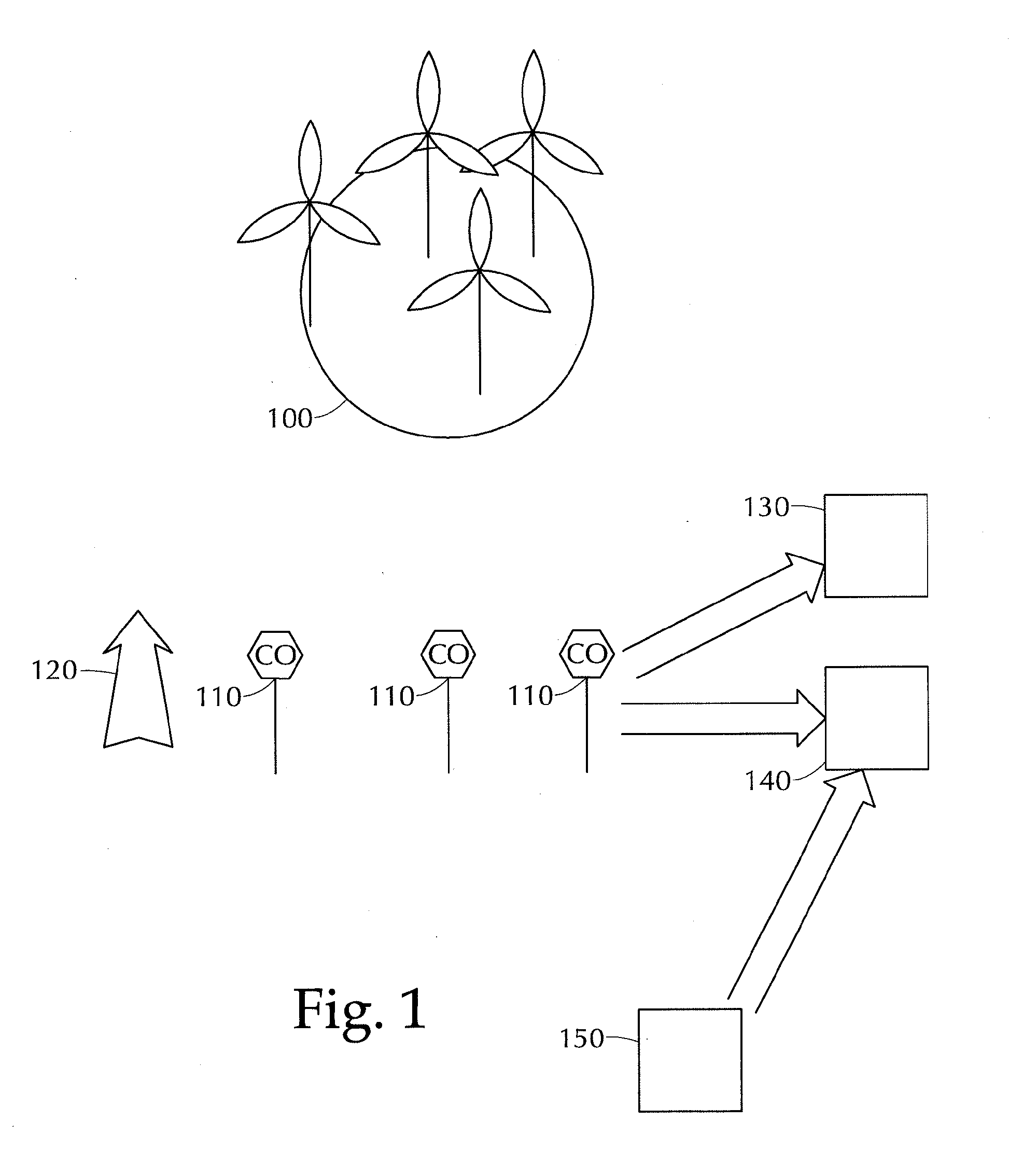
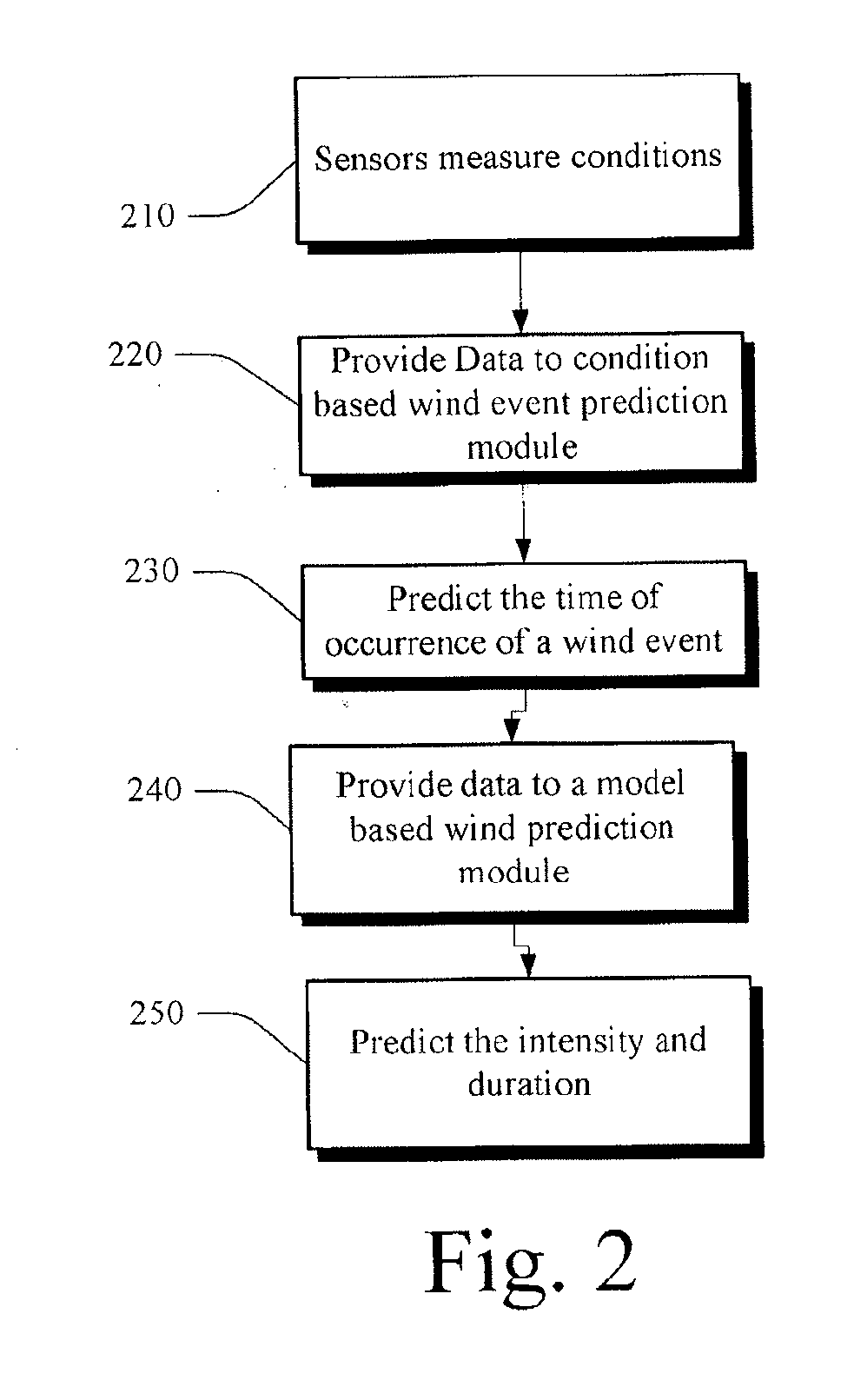
Systems and methods for wind forecasting and grid management
In one embodiment, a wind power ramp event nowcasting system includes a wind condition analyzer for detecting a wind power ramp signal; a sensor array, situated in an area relative to a wind farm, the sensor array providing data to the wind condition analyzer; a mesoscale numerical model; a neural network pattern recognizer; and a statistical forecast model, wherein the statistical model receives input from the wind condition analyzer, the mesoscale numerical model, and the neural network pattern recognizer; and the statistical forecast model outputs a time and duration for the wind power ramp event (WPRE) for the wind farm.
Owner:VAISALA
Weather prediction method for forecasting selected events
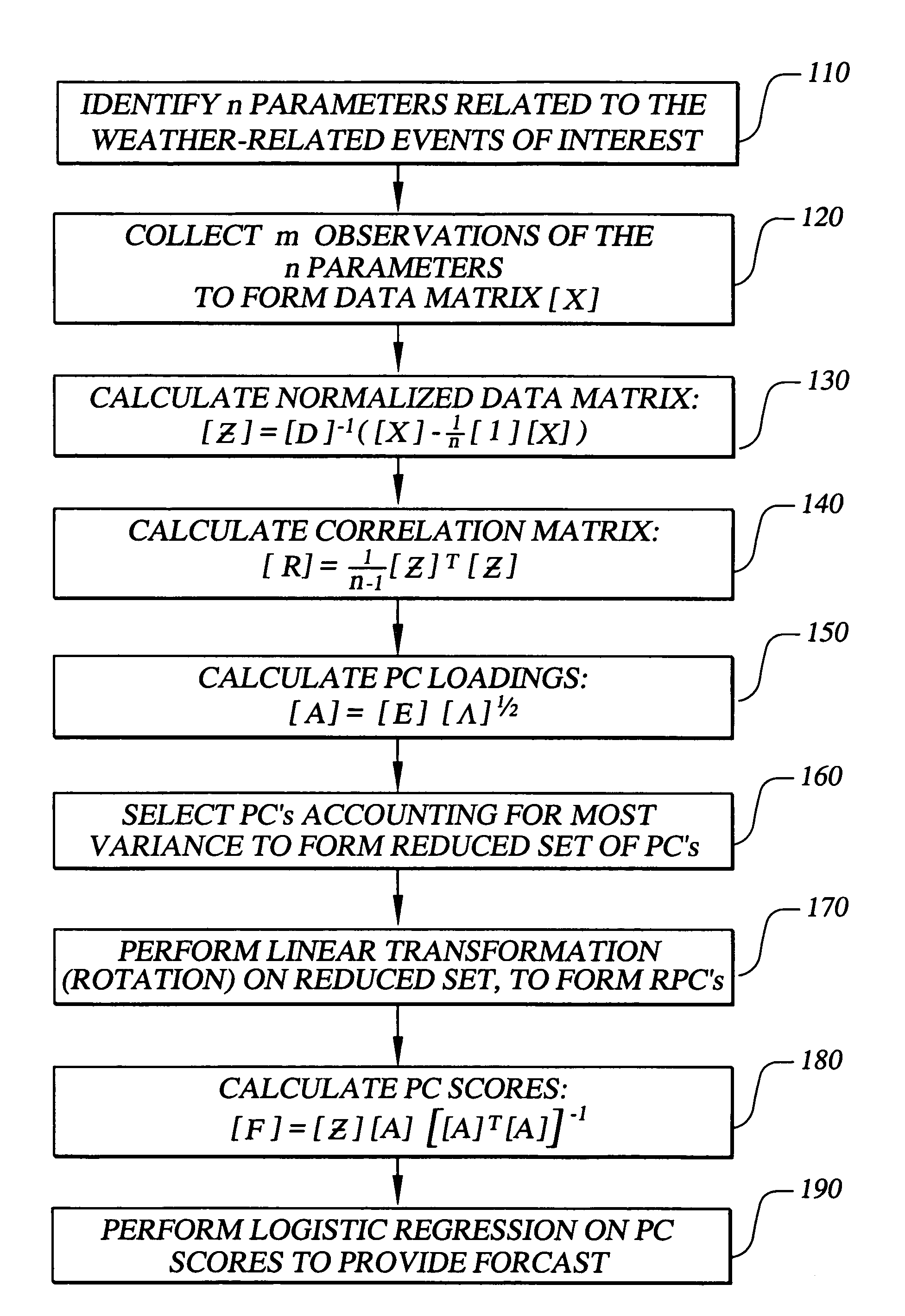
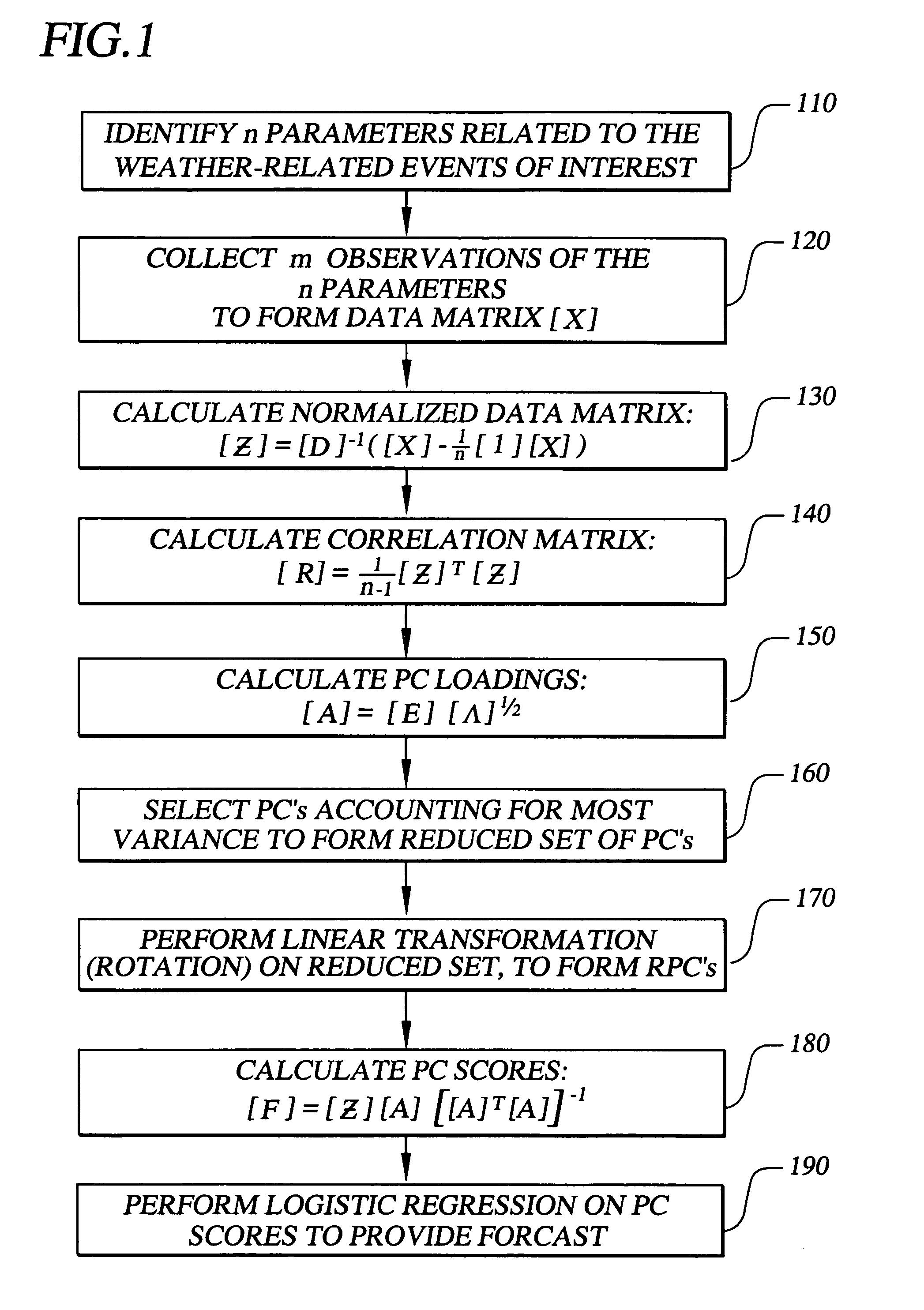
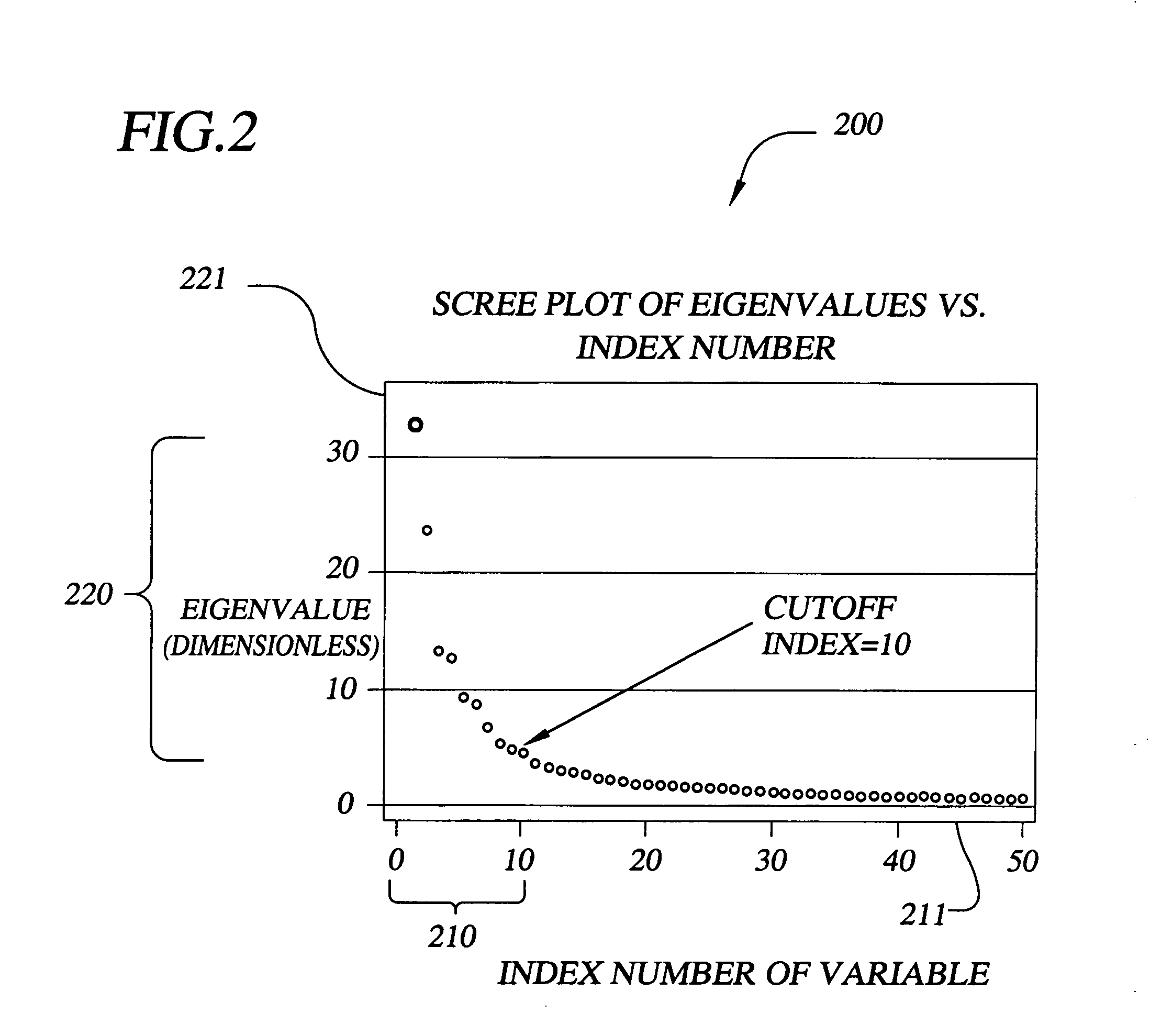
InactiveUS7069258B1Accurate predictionWeather condition predictionDigital computer detailsData setPrincipal component analysis
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer program products for short term probability forecasting of selected weather-related events. These embodiments are adaptable for any geographical region that can be identified and for which a reasonable number of data points exist. The inventive method uses a data set of n observations of m parameters, where the parameters may be statistically correlated. A Principal Component Analysis may be performed, with the data set as input, to provide a reduced set of principal components that are uncorrelated and account for most of the variance in the input data set. An orthogonal transformation may be performed on the reduced set of principal components to provide a rotated set of principal components that are aligned with the corresponding parameters in the input data set. Finally a logistic regression may be performed on the rotated set of principal components to derive an S-shaped predictive equation for the probability of a binary weather-related event of interest. An illustrative embodiment of the invention is given for forecasting the probability for the number of lightning flashes exceeding a selected value, for the western United States climatological area.
Owner:BOTHWELL PHILLIP D
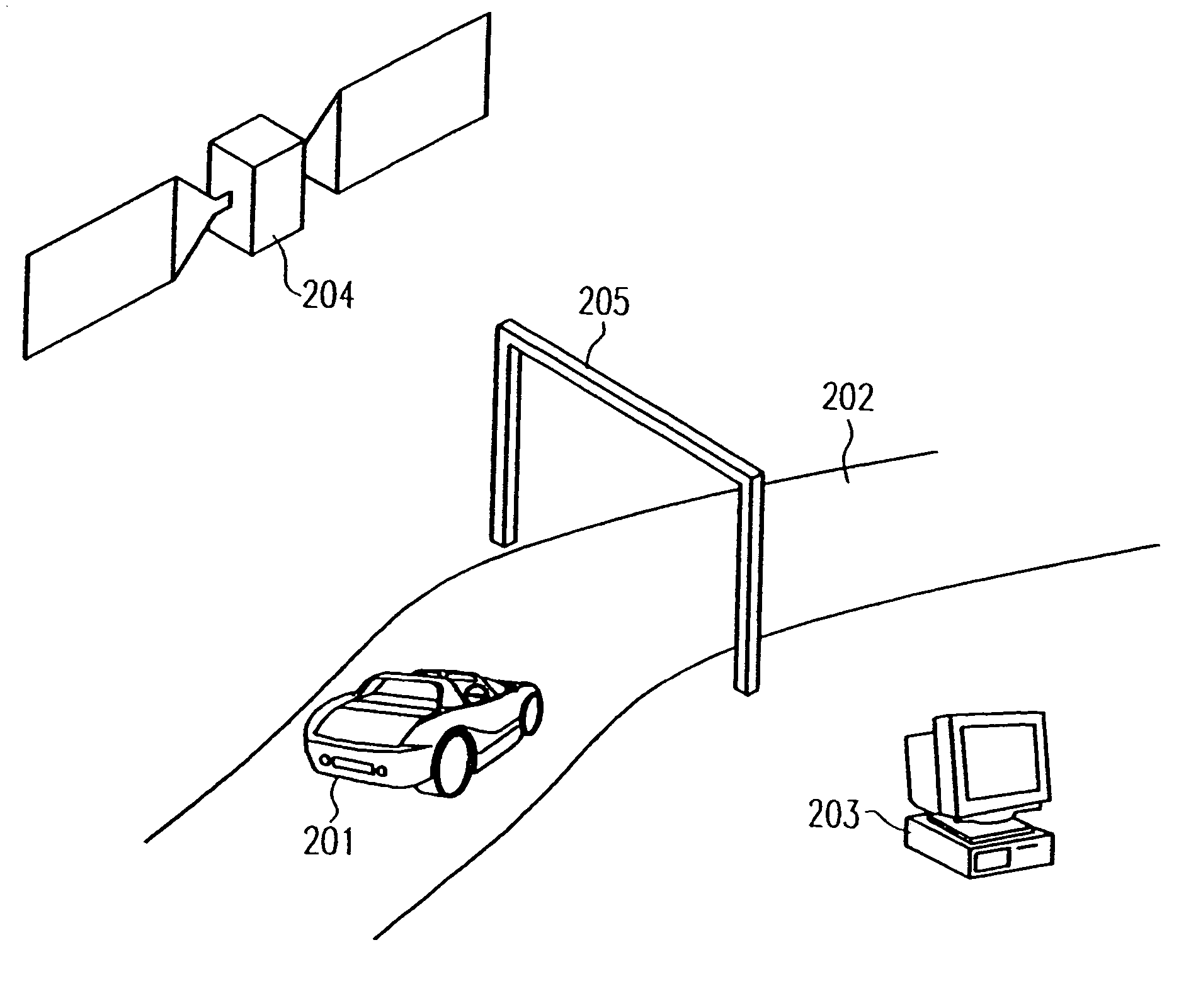
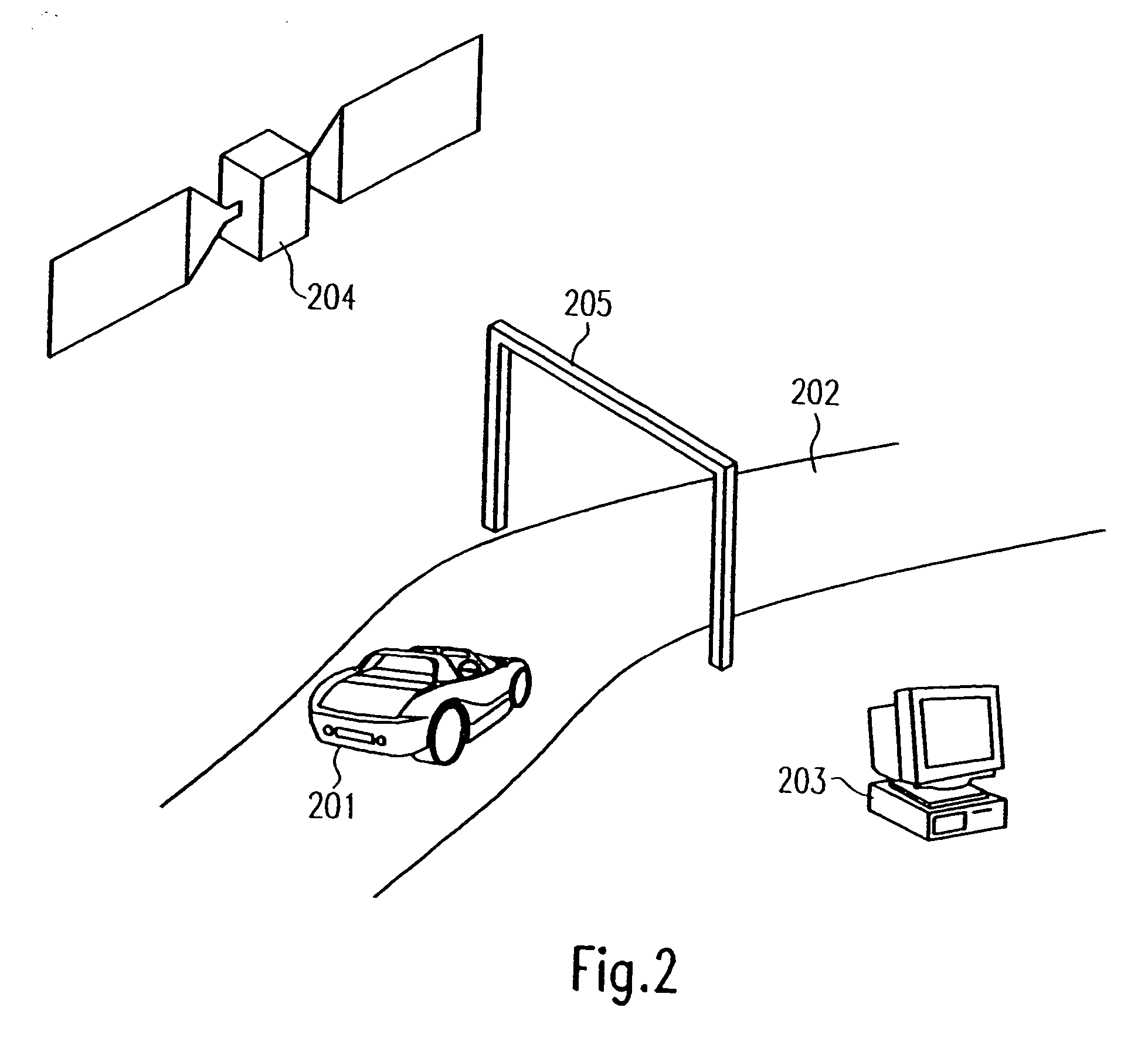
Method and system for providing weather information over the internet using data supplied through the internet and a wireless cellular data system
InactiveUS6343255B1Weather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsCellular digital packet dataThe Internet
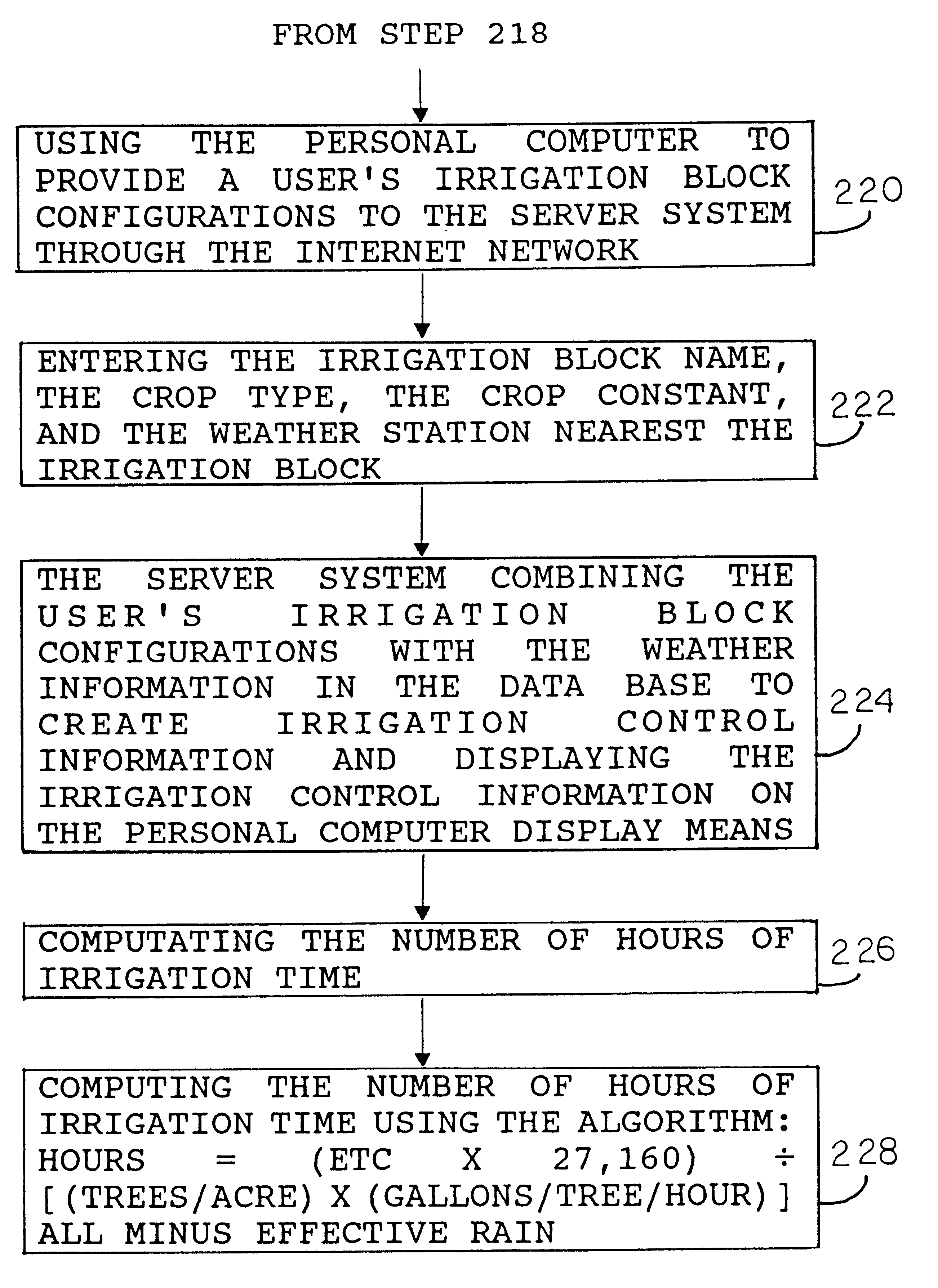
A system and method for accessing and displaying weather information are shown. A weather station (102) collects weather information data from sensors (108-114) using a collection program and assembles the data as a data string in a memory. A station access system (140) is used to call the weather station through the Internet (150) and a wireless cellular digital packet data system (154). The weather station downloads the weather data string to a data base (164). A user contacts the access computer through the Internet using his personal computer (170) to ask for the weather information. The information is compiled from the data base and transmitted to the user's display (172) over the Internet. A user such as a farmer can also supply the system with his particular field and crop conditions and the system will apply the conditions to the weather information and return customized crop production and control information to the farmer over the Internet.
Owner:INVESTMENTSIGNALS
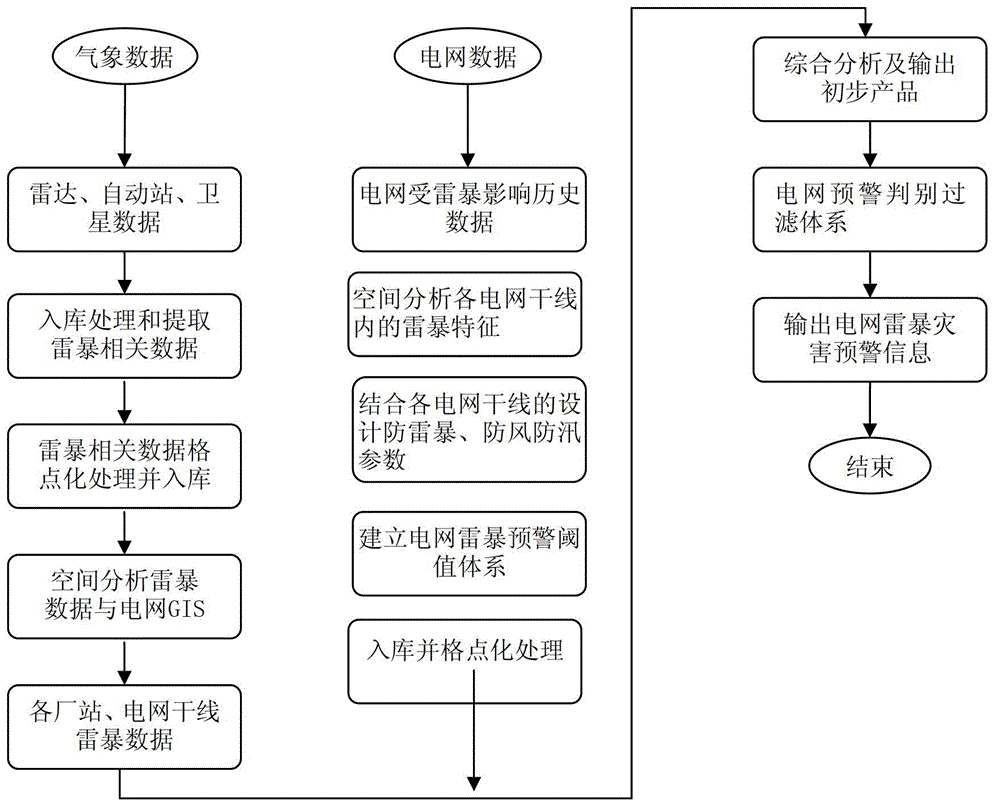
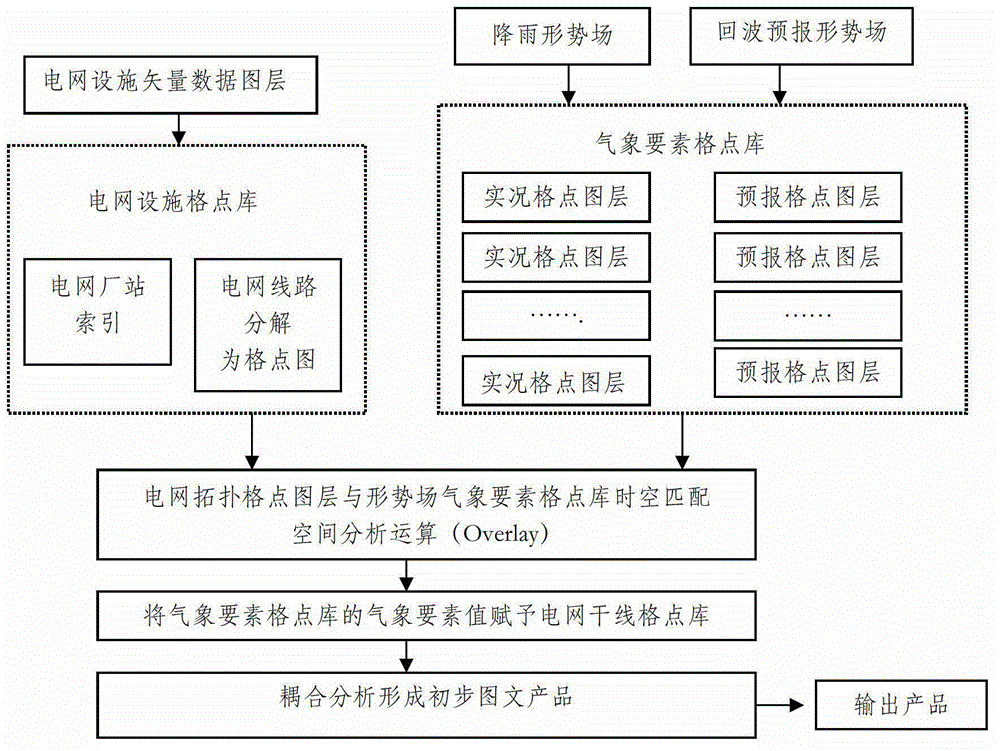
System and method for power grid thunderstorm disaster early warning based on recognition and forecast
ActiveCN103337133ARealize automatic monitoringRealize scientific disaster preventionWeather condition predictionAlarmsThunderstormPower grid
The invention relates to a system for power grid thunderstorm disaster warning based on recognition and forecast. The system is characterized by comprising a thunderstorm forecast information module, an early warning data analyzing module, a power grid thunderstorm risk early warning module and a display module all connected with one another in sequence. The invention further relates to a method which adopts the system to perform power grid thunderstorm disaster early warning. The system and the method utilize region thunderstorm characteristic and regional power grid characteristic, and combine the anti-thunderstorm design parameters and the on-site geographical conditions of power grid equipment including various transformer substations, electric transmission lines, pole and the like, so as to realize real-time automatic monitoring on the thunderstorm disaster, perform actual condition analysis quantitatively at a specific time and location and near-disaster early warning and perform fine instructional functions on production and scheduling of power grid.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Apparatus and method for providing environmental predictive indicators to emergency response managers
ActiveUS20140324351A1Good effectIncrease probabilityWeather condition predictionAlarmsAtmospheric sciencesPrediction system
A method of predicting weather-exacerbated threats, said method comprising inputting localized weather measurement data into a weather threat prediction system; predicting future localized weather conditions based on said localized weather measurement data combined with modeling from large scale weather data including National Weather Service Data; inputting natural environment and infrastructure data into said weather threat prediction system; correlating said infrastructure data with said predicted future localized weather conditions; and determining a threat level index over a region, a threat level indicating an area having a certain probabilistic likelihood of being harmed by said future weather conditions.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Analysis system and hydrology management for basin rivers
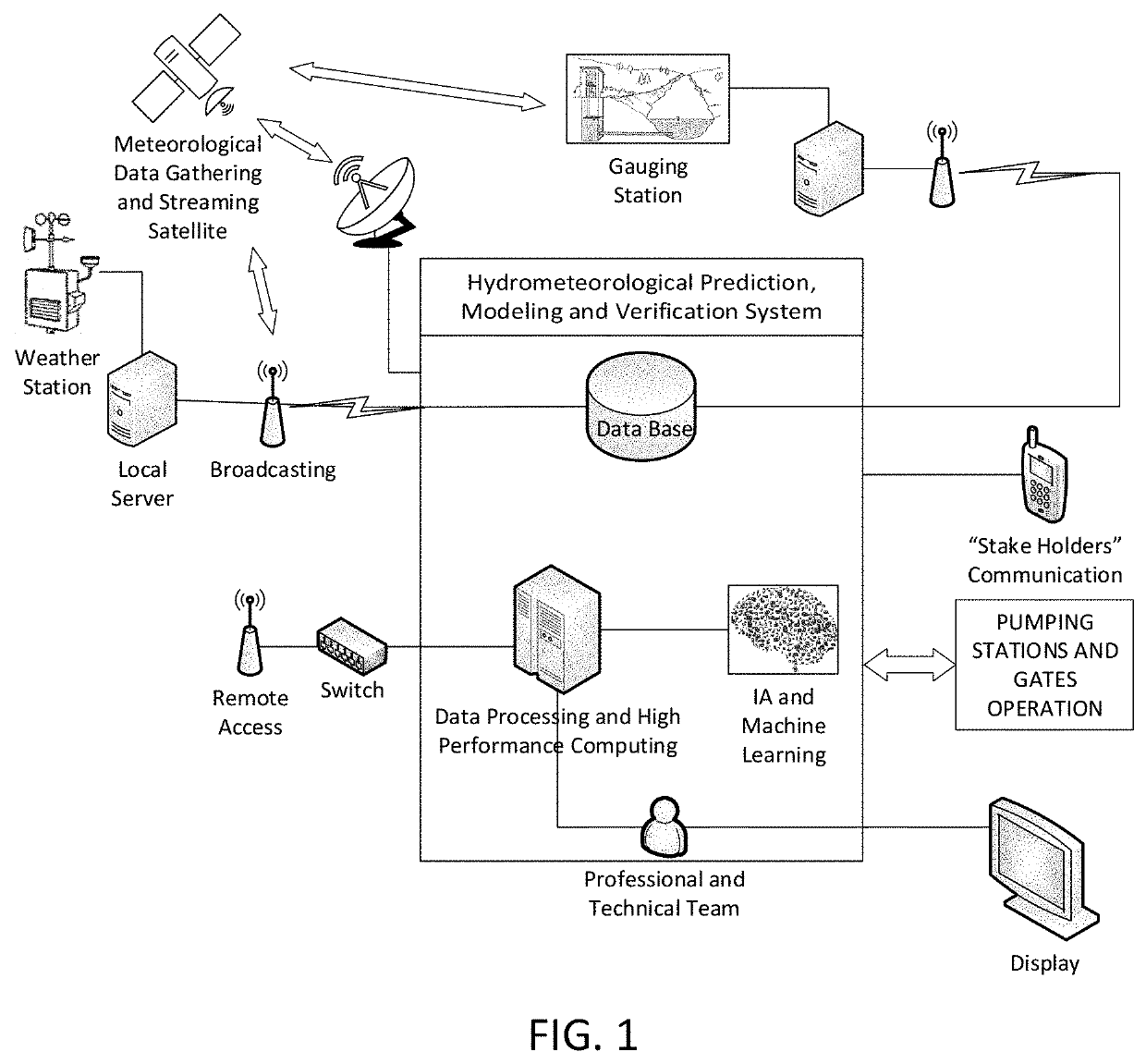
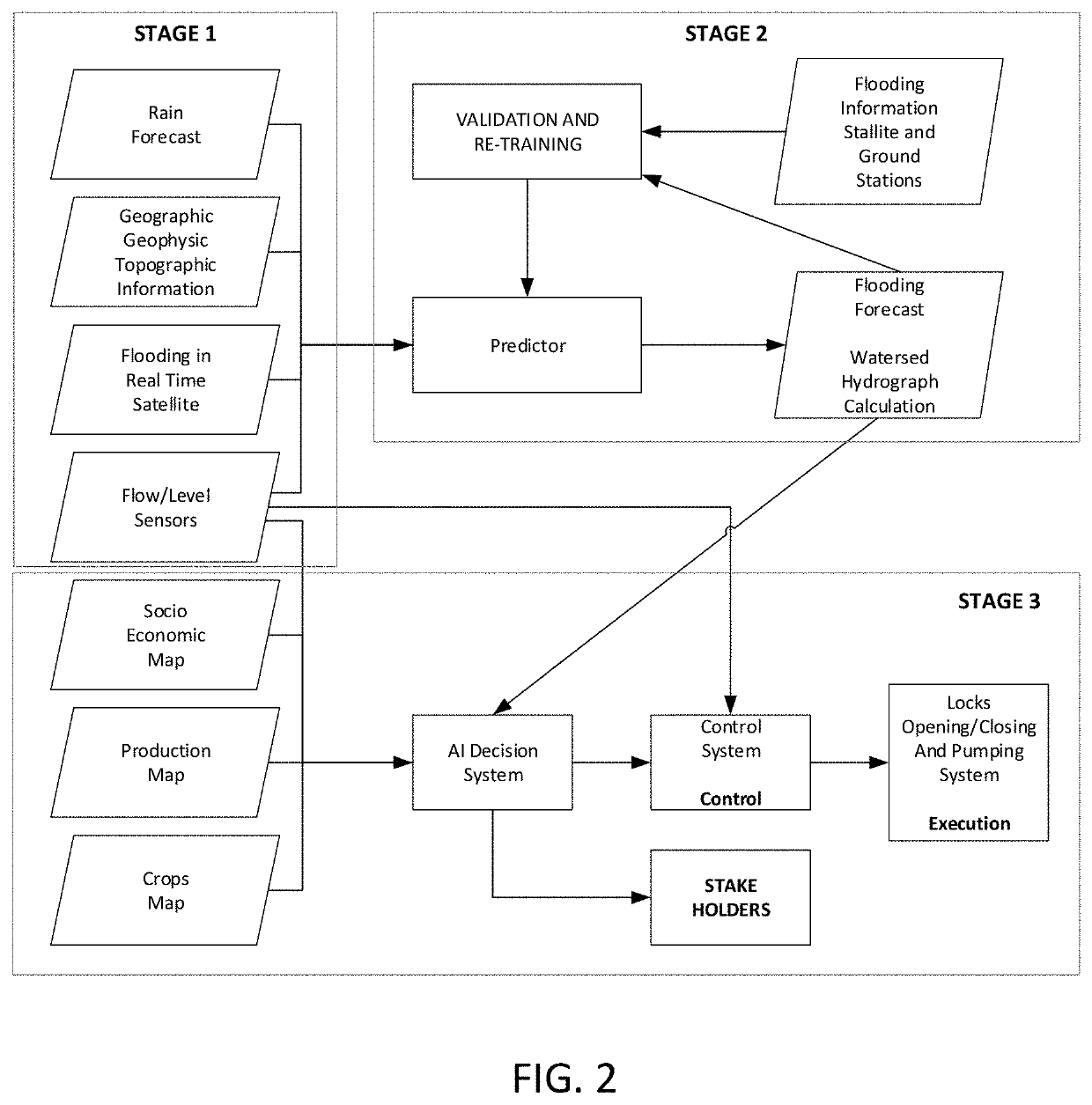
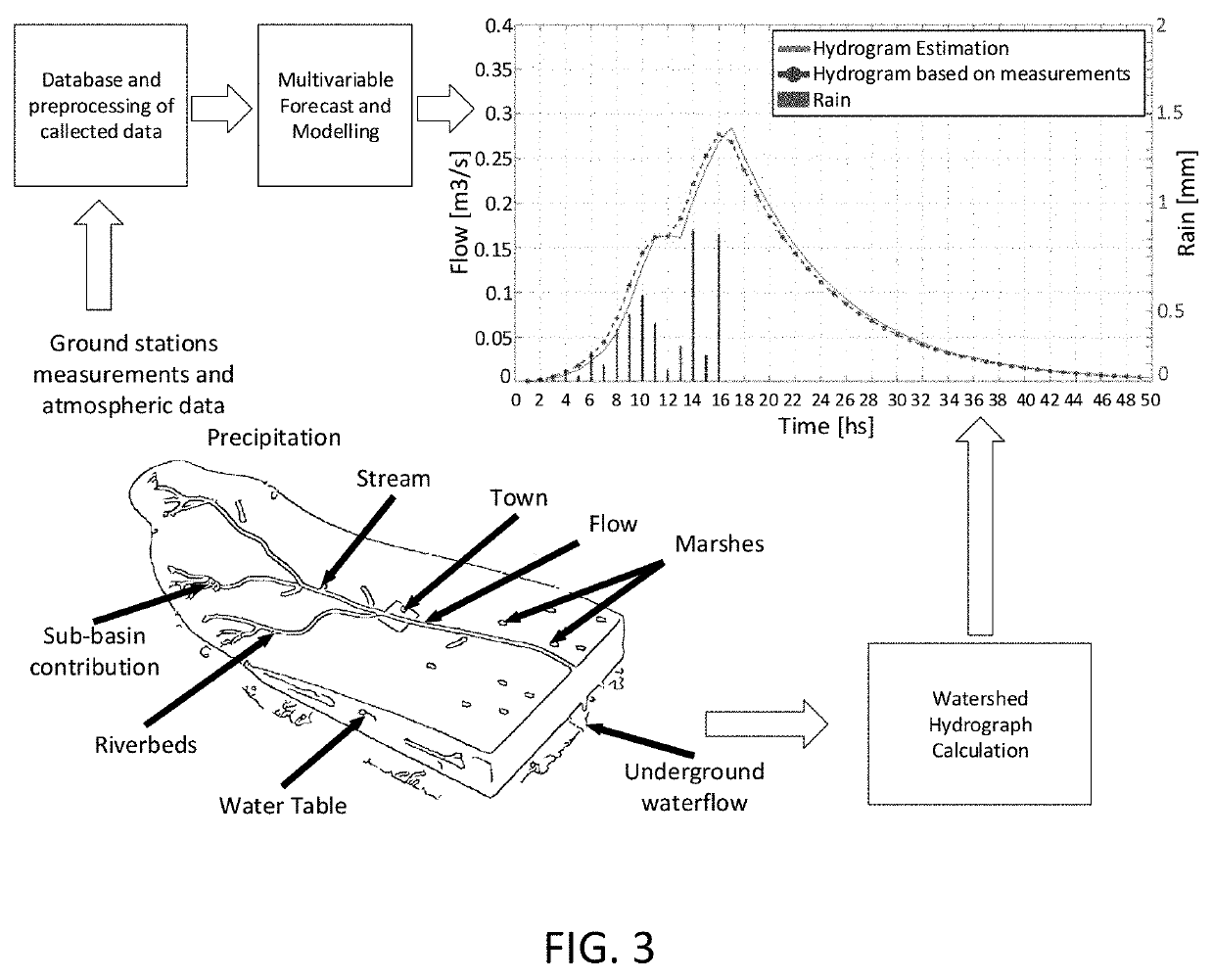
ActiveUS20190354873A1Minimize impactWeather condition predictionClimate change adaptationSocio economyWater quality
Watershed hydrology analysis and management process and system with a network of weather stations and artificial drainage systems with artificial and natural reservoir management through locks and pumping stations. It evaluates potential hydrologic risk in each area and analyses the possible consequences of future precipitations using simulations. To make the simulation, it calculates hydrographs for each sub-basin, streams and rivers in the basin. It simulates the behavior of the basin under different scenarios corresponding to different types of management of the operation of locks and / or pumps and compares its results in terms of loss of flooded area, economic loss in each area, loss for flooding of urban areas, etc. Optimization of the simulation through artificial intelligence (AI, meta-heuristic algorithms, neural networks, etc.) allows it to act as a search engine to find better solutions and the best configuration of resource management that allows minimizing the socio-economic impact on each basin.
Owner:PESCARMONA LUCAS
Forecasting output power of wind turbine in wind farm
A method and apparatus for forecasting output power of wind turbine in a wind farm. The present invention provides a method for forecasting output power of a wind turbine in a wind farm, including: generating a corrected data set based on environmental data collected from at least one sensor in the wind farm; correcting a weather forecasting model by using the corrected data set; obtaining a forecast value of wind information at the wind turbine based on the corrected weather forecasting model; and forecasting the output power of the wind turbine based on the forecast value and a power forecasting model.
Owner:UTOPUS INSIGHTS INC
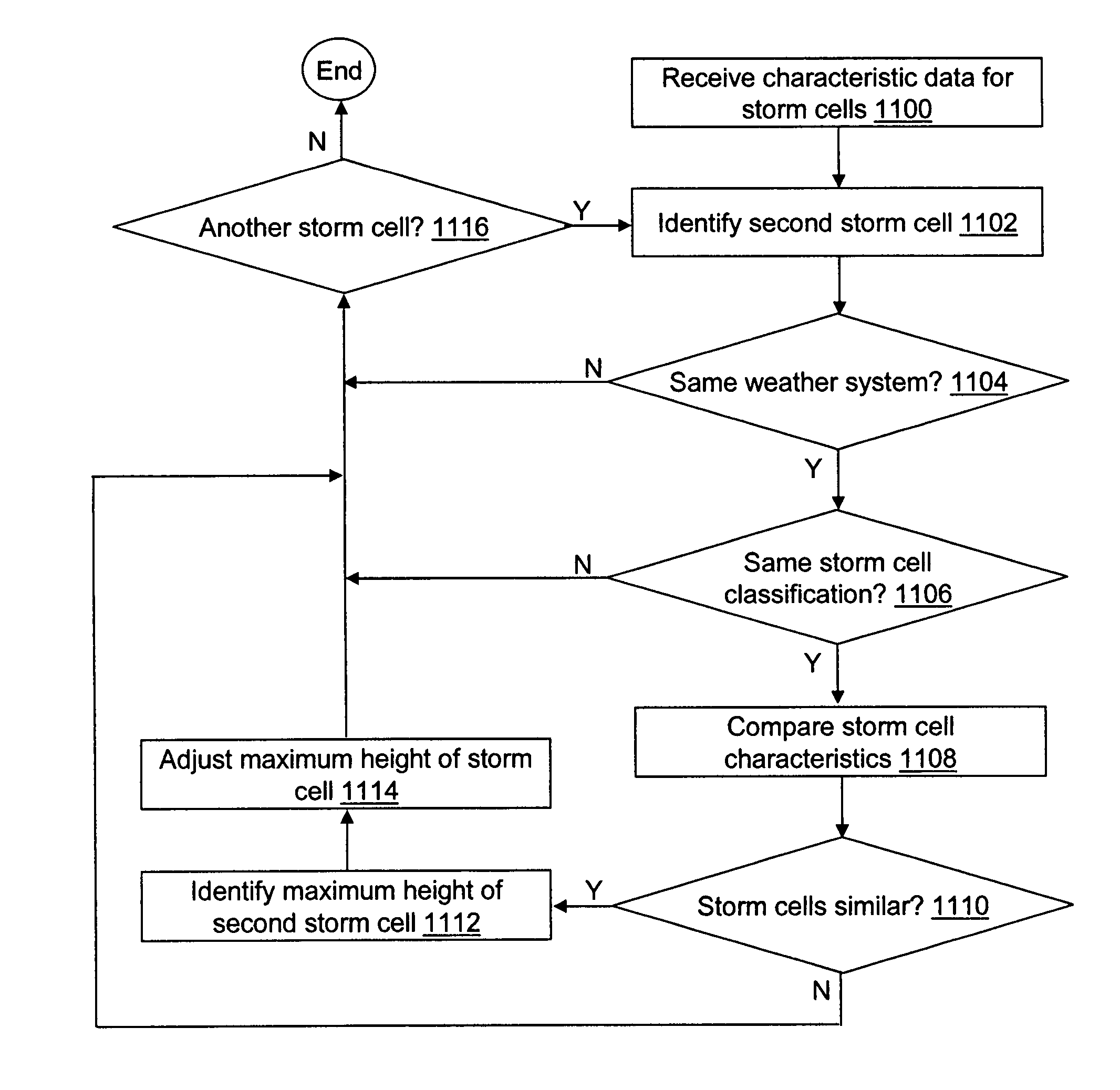
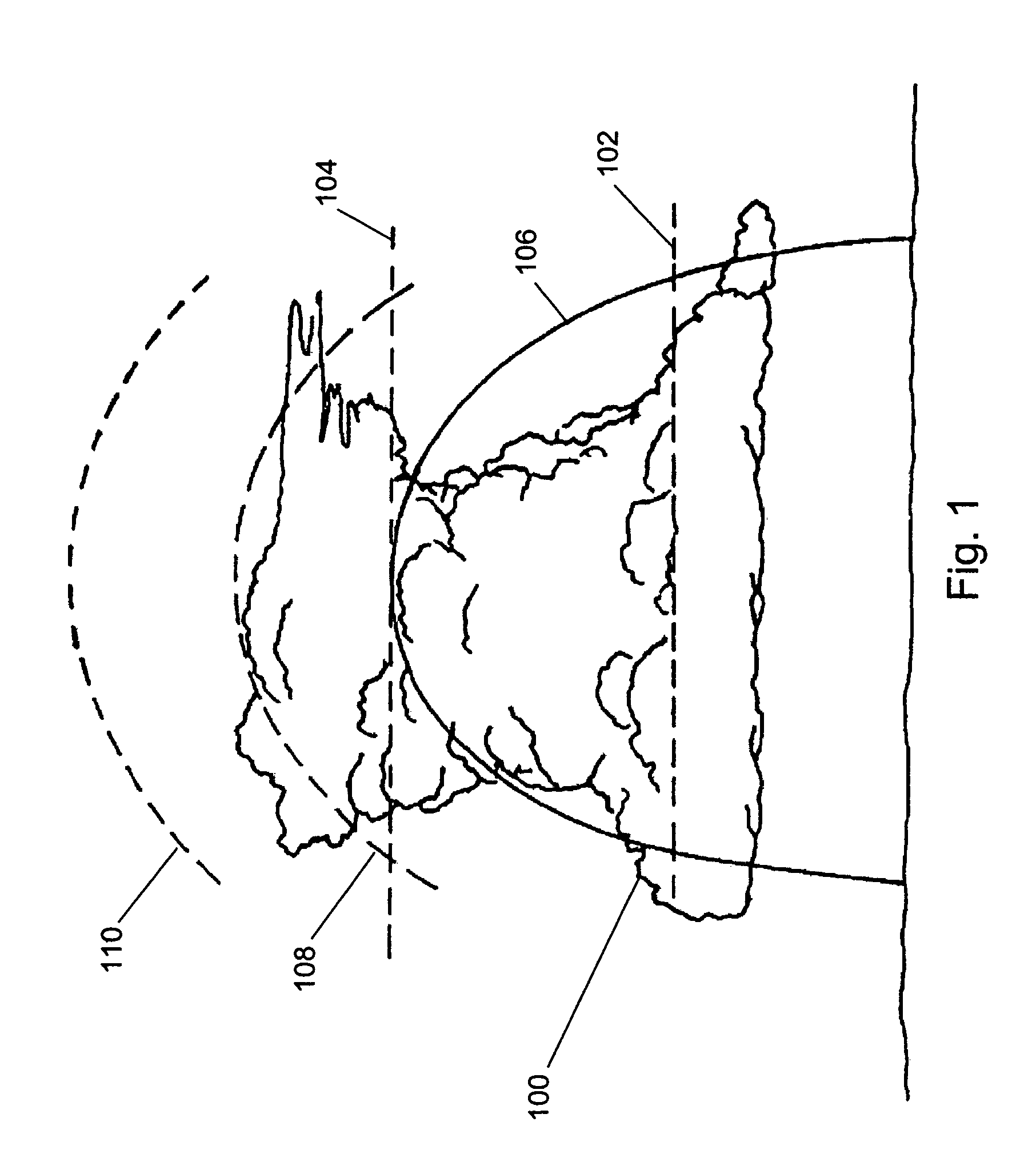
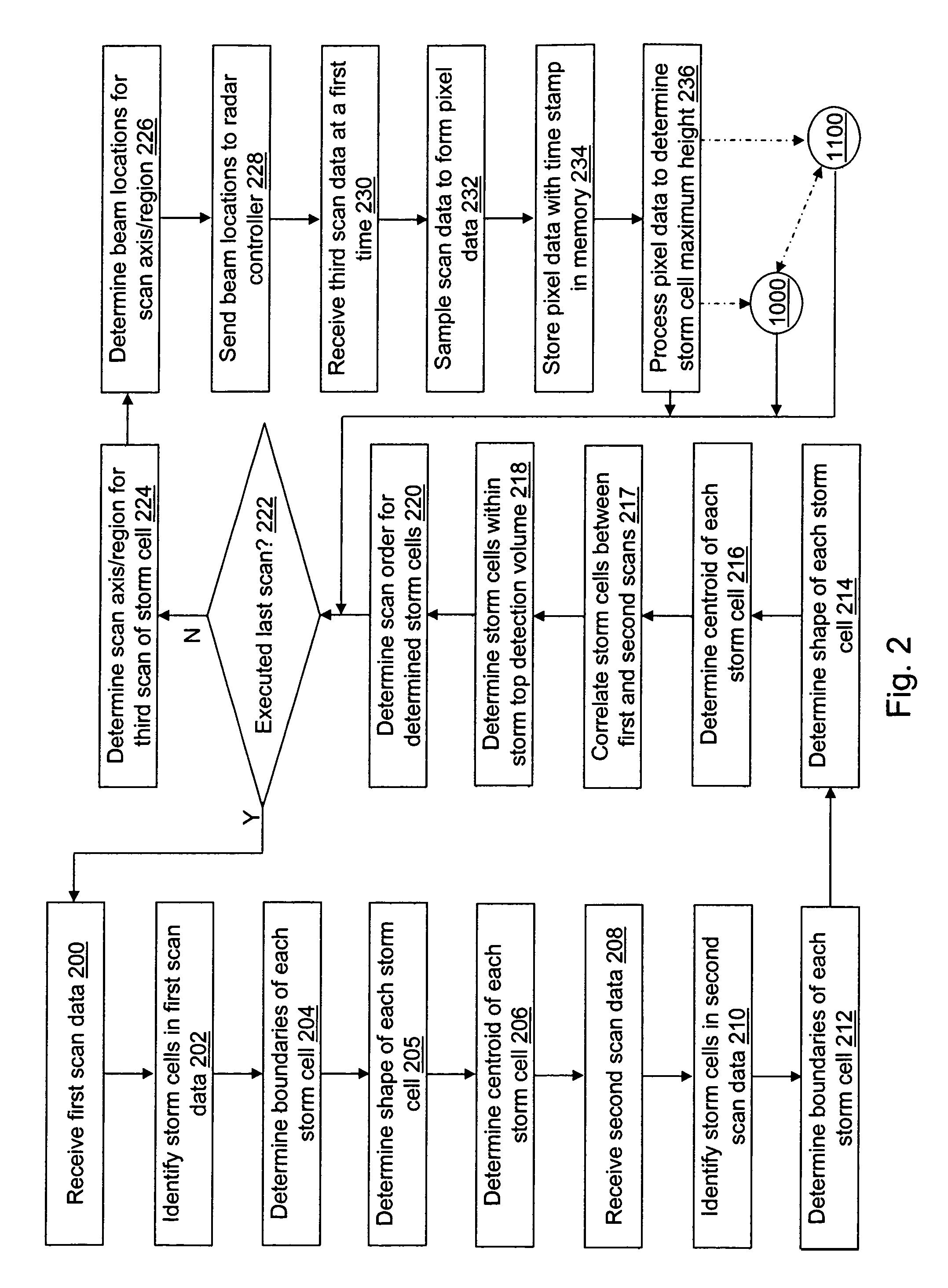
Storm top detection and prediction
ActiveUS7486220B1Efficient detectionDirection finders using radio wavesWeather condition predictionRadarGrowth ratio
A method of predicting storm cell characteristics at a future time is provided. A value relating to a characteristic of the storm cell is determined from reflectivity data processed from signals received from a radar scan of the storm cell. A second storm cell is identified that is part of the same weather system as the storm cell. A plurality of values relating to the characteristic for the identified second storm cell is received from a memory wherein the plurality of values were determined at a plurality of different times. The determined value of the storm cell is compared with the determined plurality of values of the identified second storm cell. A growth rate of the storm cell is determined. A maximum height of the storm cell at a third time in the future is calculated based on the comparison and the determined growth rate and presented to a user.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
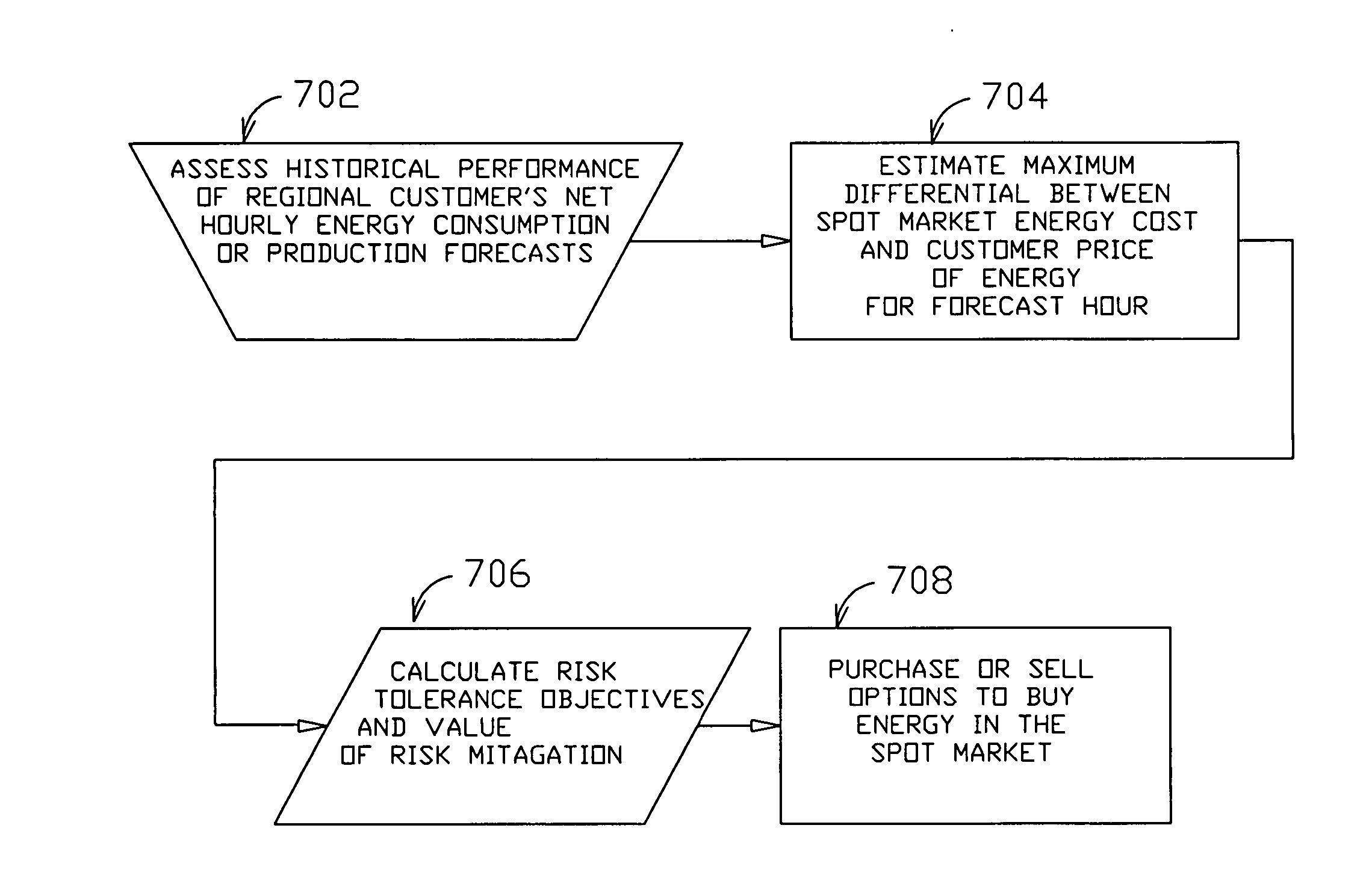
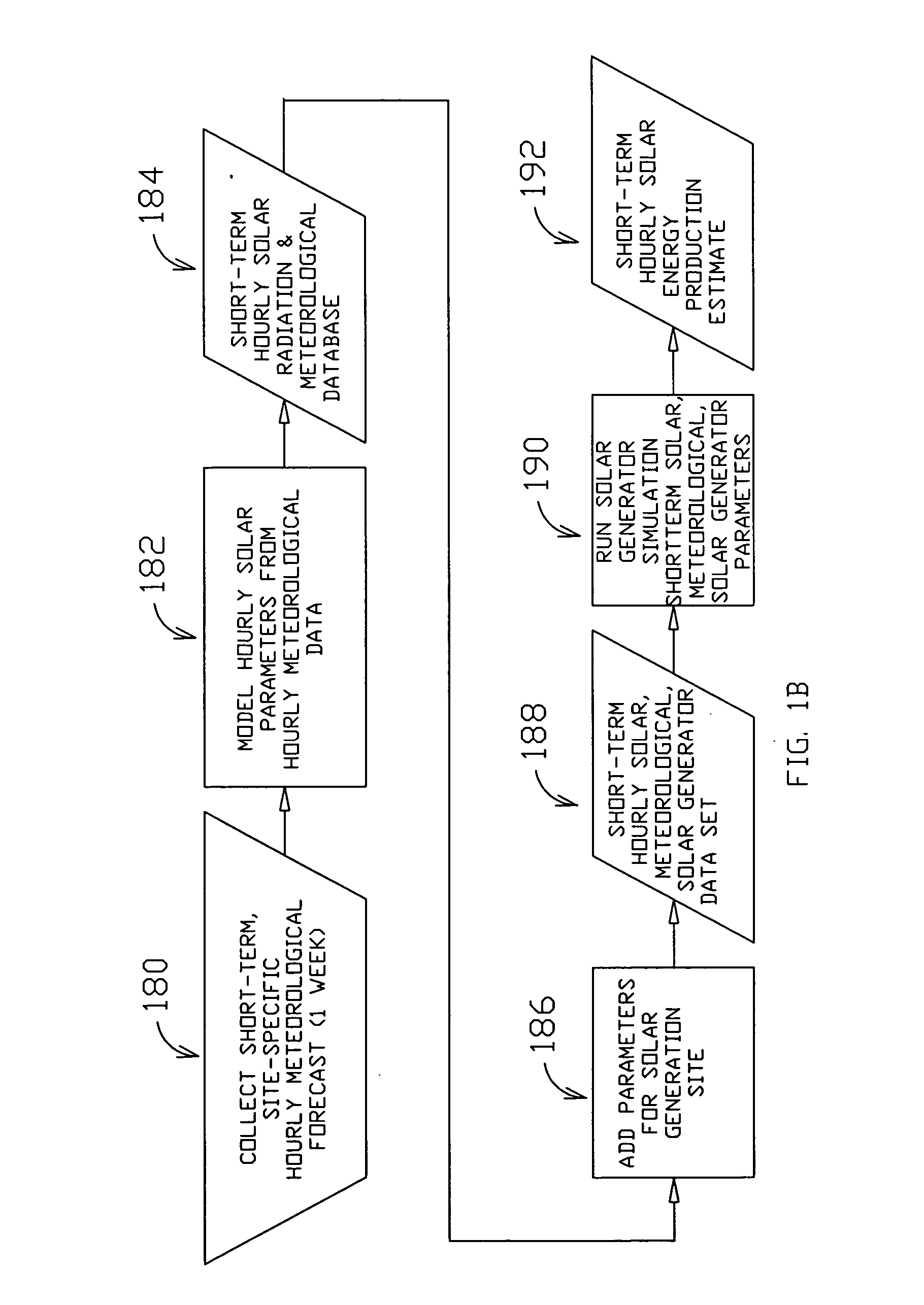
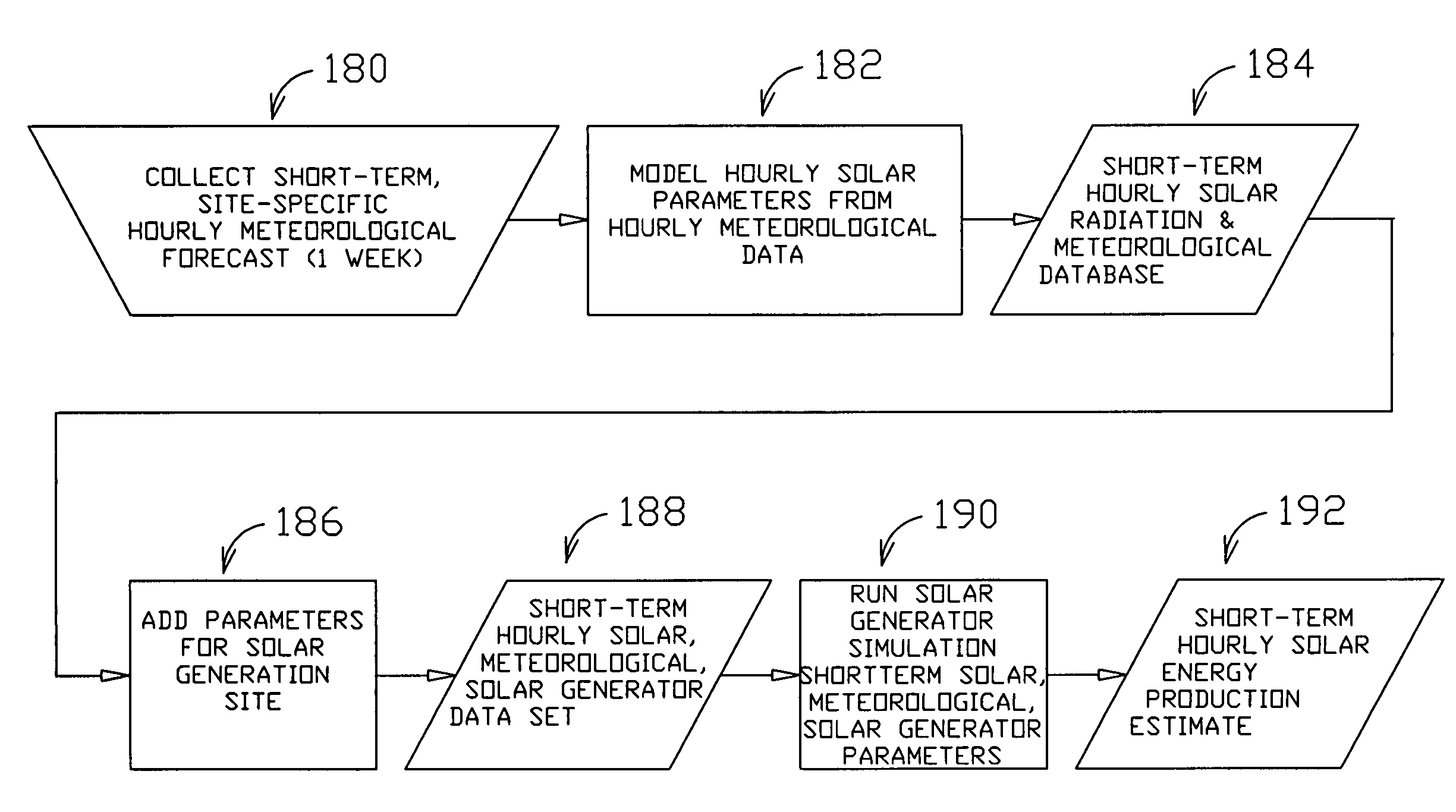
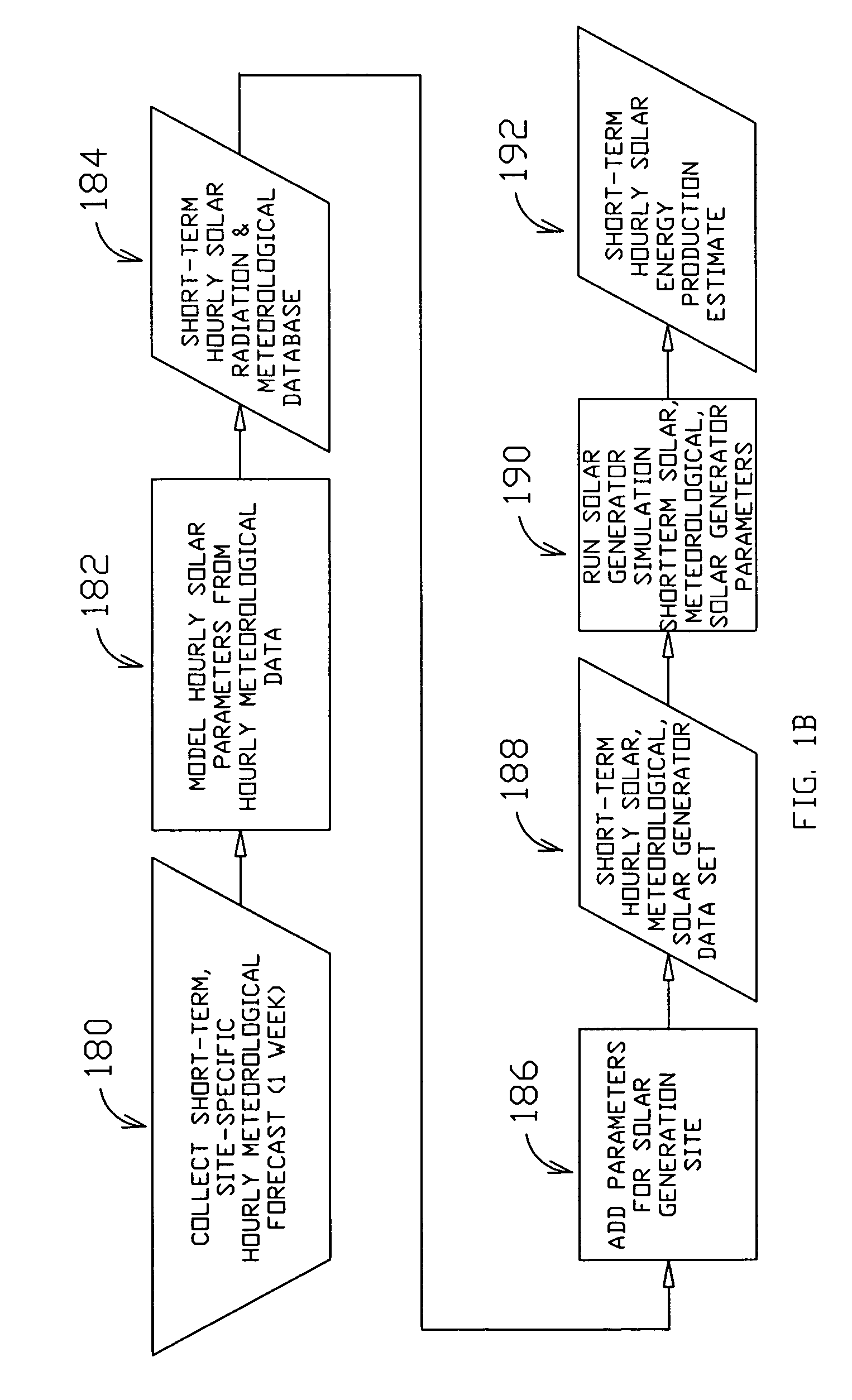
Method and system for predicting solar energy production
A system, method and computer program product to assist in managing the physical plant mechanisms and market finances for a deregulated electricity grid or regulated utility grid, populated with solar electric generation capacity. This system provides tools to assist grid operators in the scheduling and dispatch of generation resources in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity, a week in advance, on an hourly basis. It also provides tools to assist companies engaged in generation, distribution and energy marketing, in the electrical power industry, to manage their contractual supply obligations in the day-ahead hourly wholesale market and the spot market, in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity. This process can also be used to predict solar loading of building structures, using forecast irradiance data as inputs to common building energy modeling programs, a week in advance, on an hourly basis.
Owner:NEO VIRTUS ENG
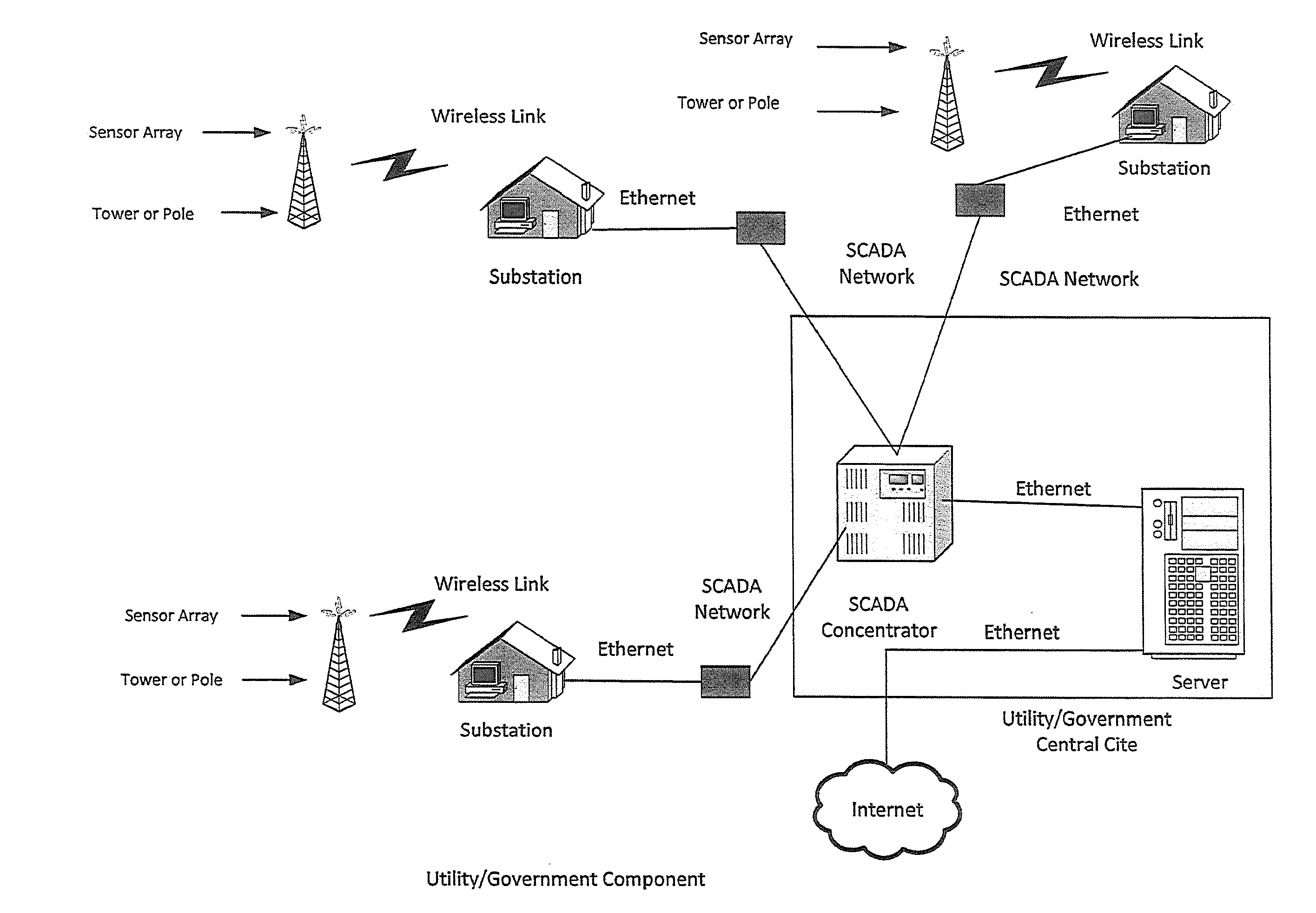
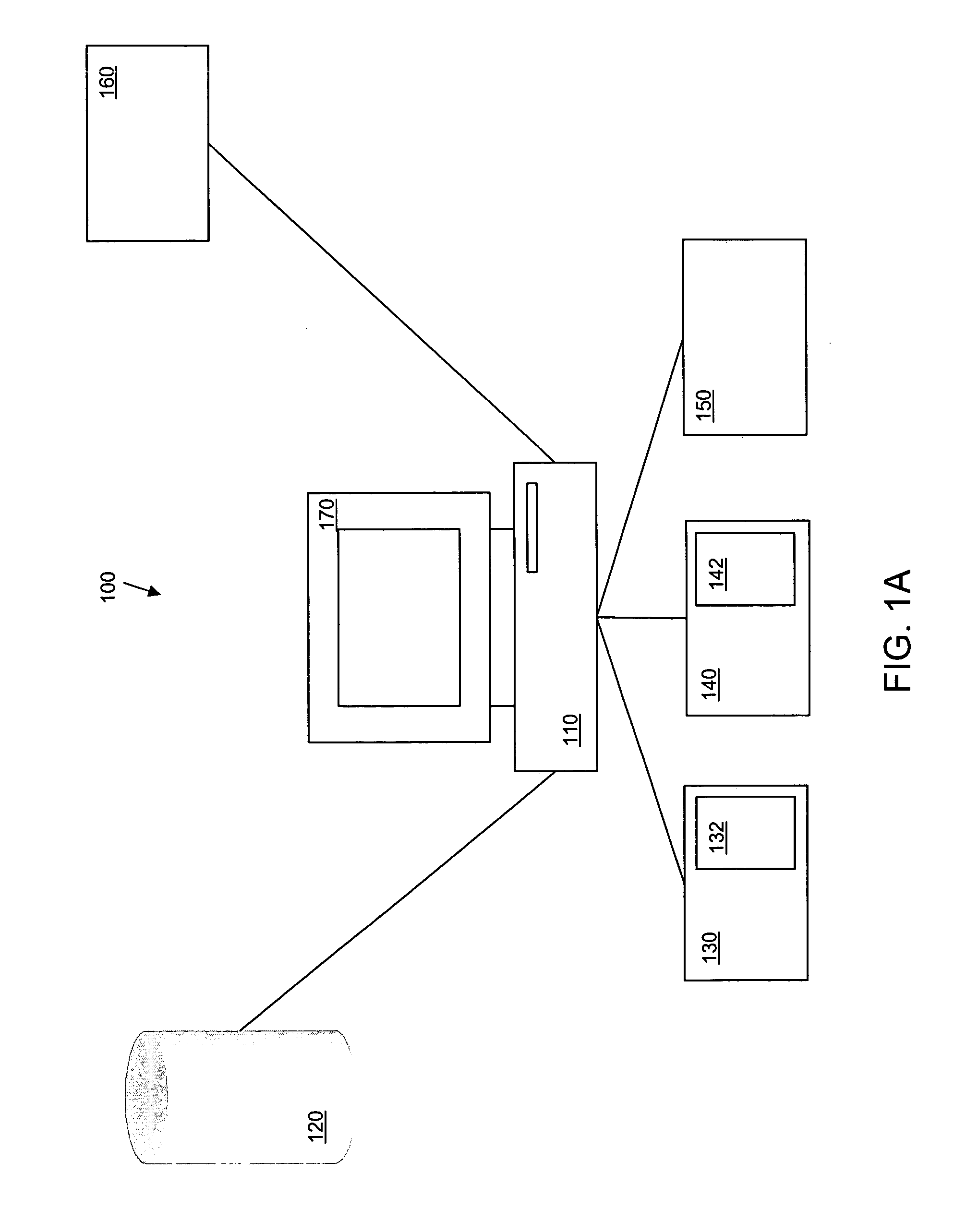
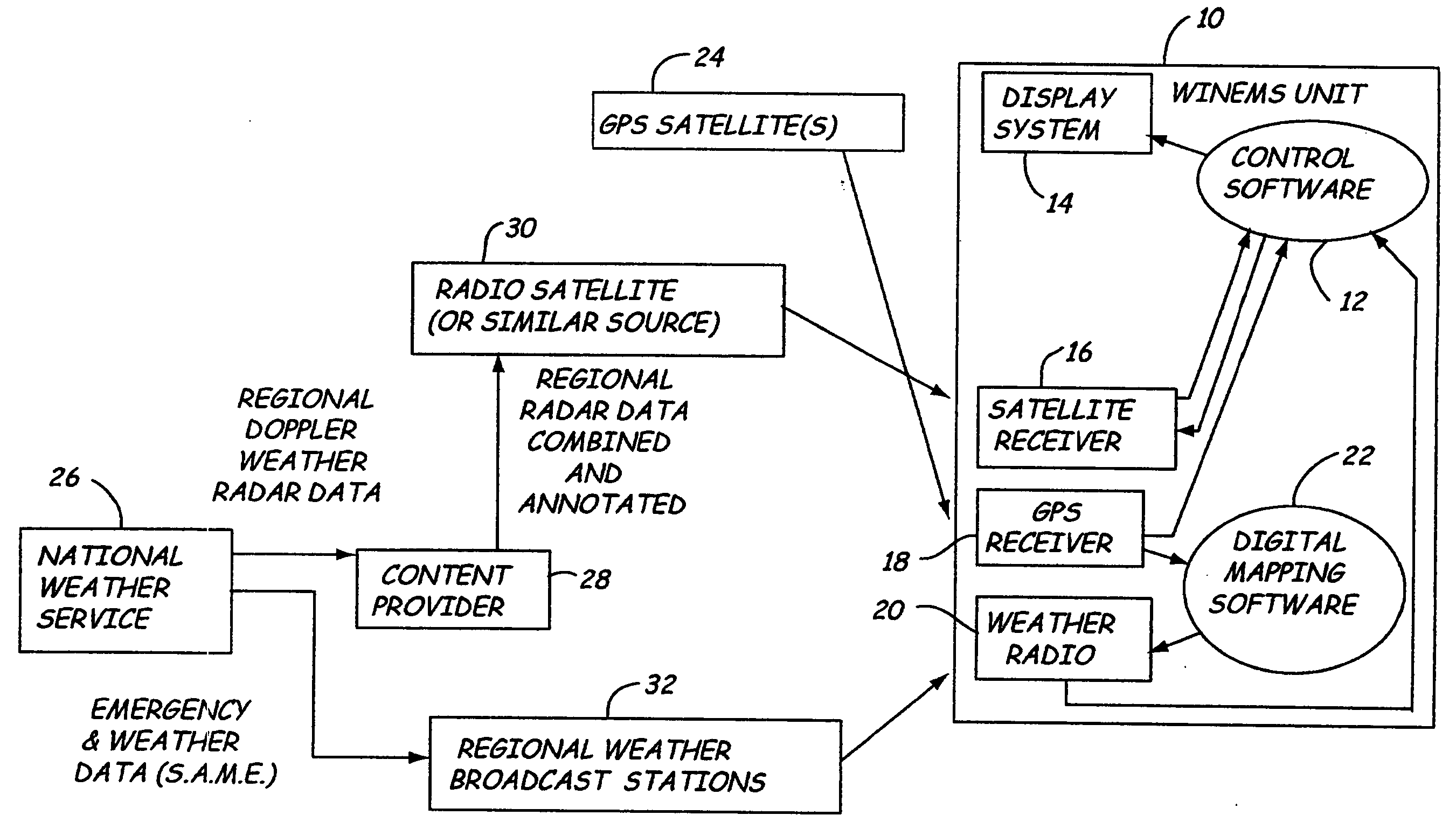
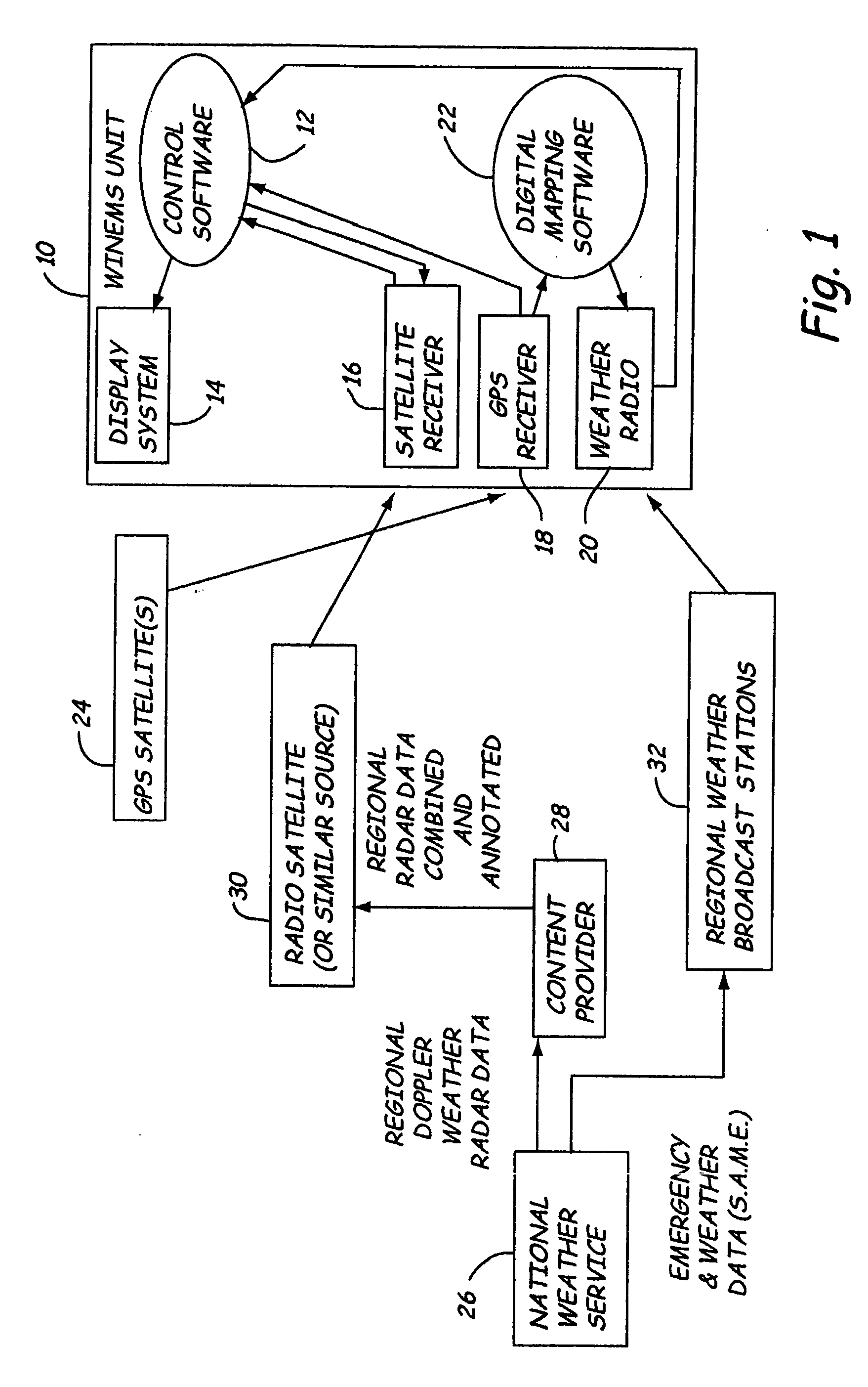
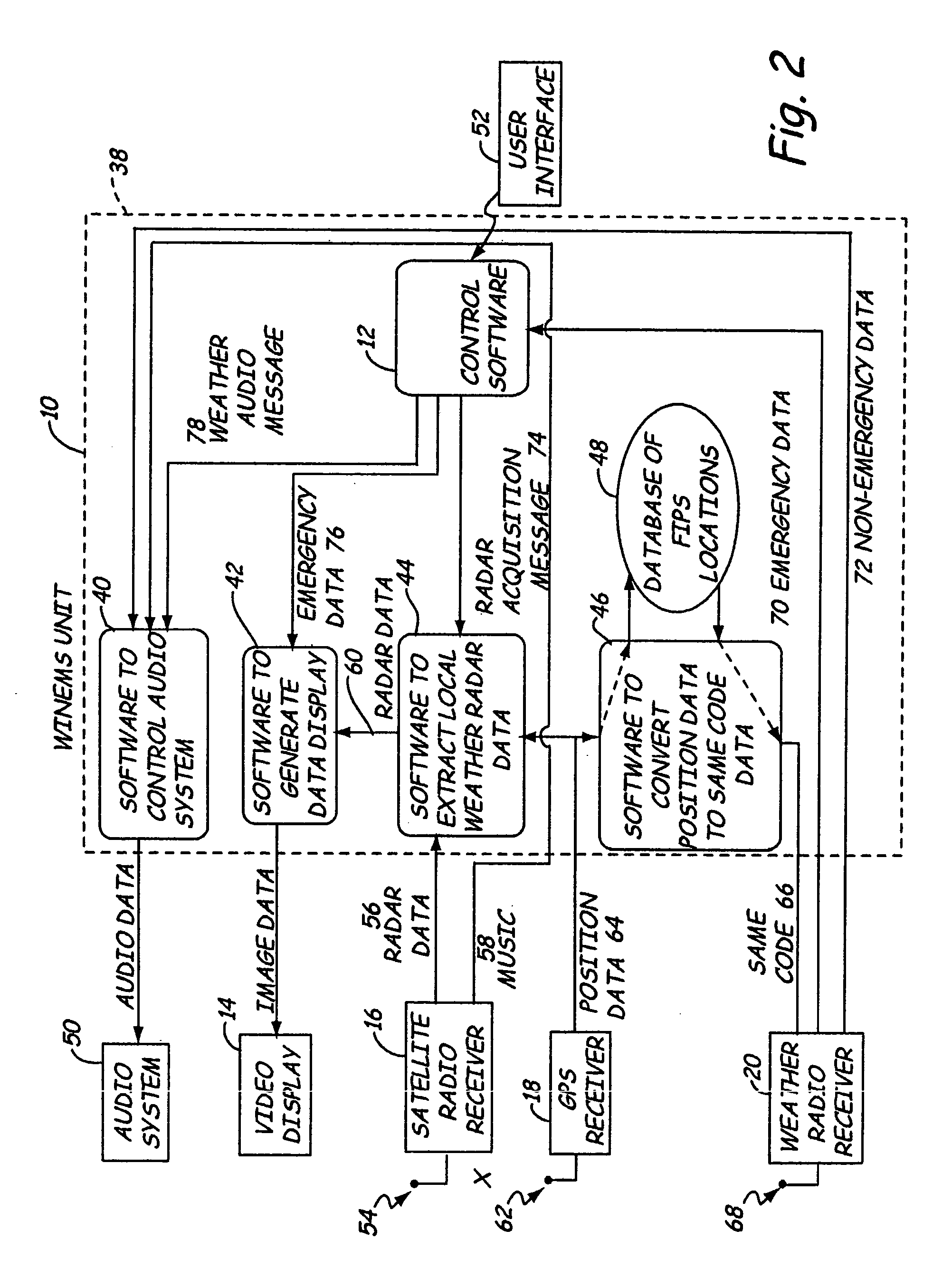
Weather information network enabled mobile system (WINEMS)
InactiveUS20050027449A1Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsWeather condition predictionInformation networksInformation system
A Weather Information Network Enabled Mobile System for providing information to a user regarding an emergency event. The WINEMS system receives location data, such as from a GPS system, and correlates the location data with the emergency alert to display a map showing both a location of the WINEMS system and a location of the emergency event. Preferably, the locations are displayed on a digital map.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA UNIV OF
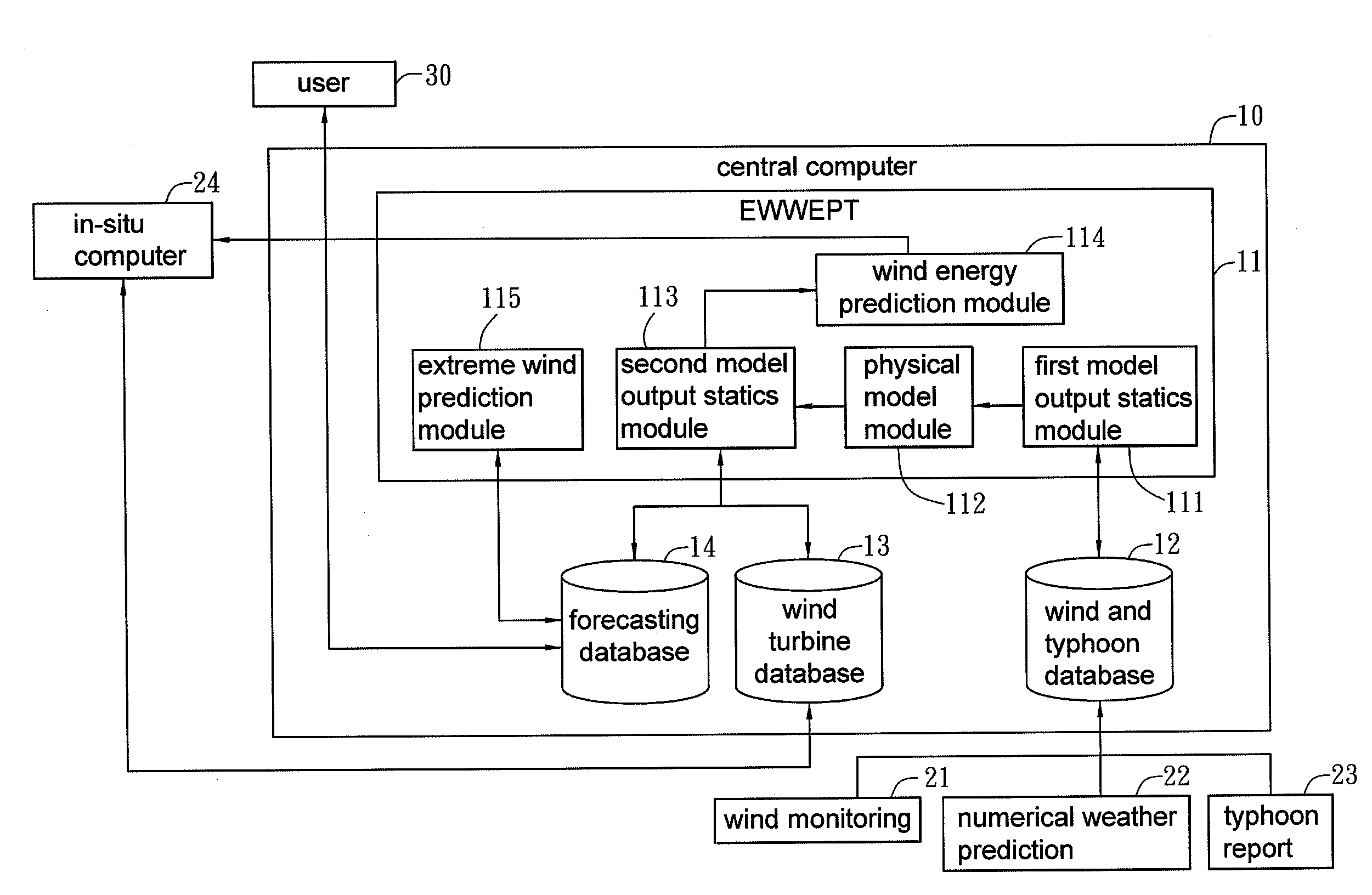
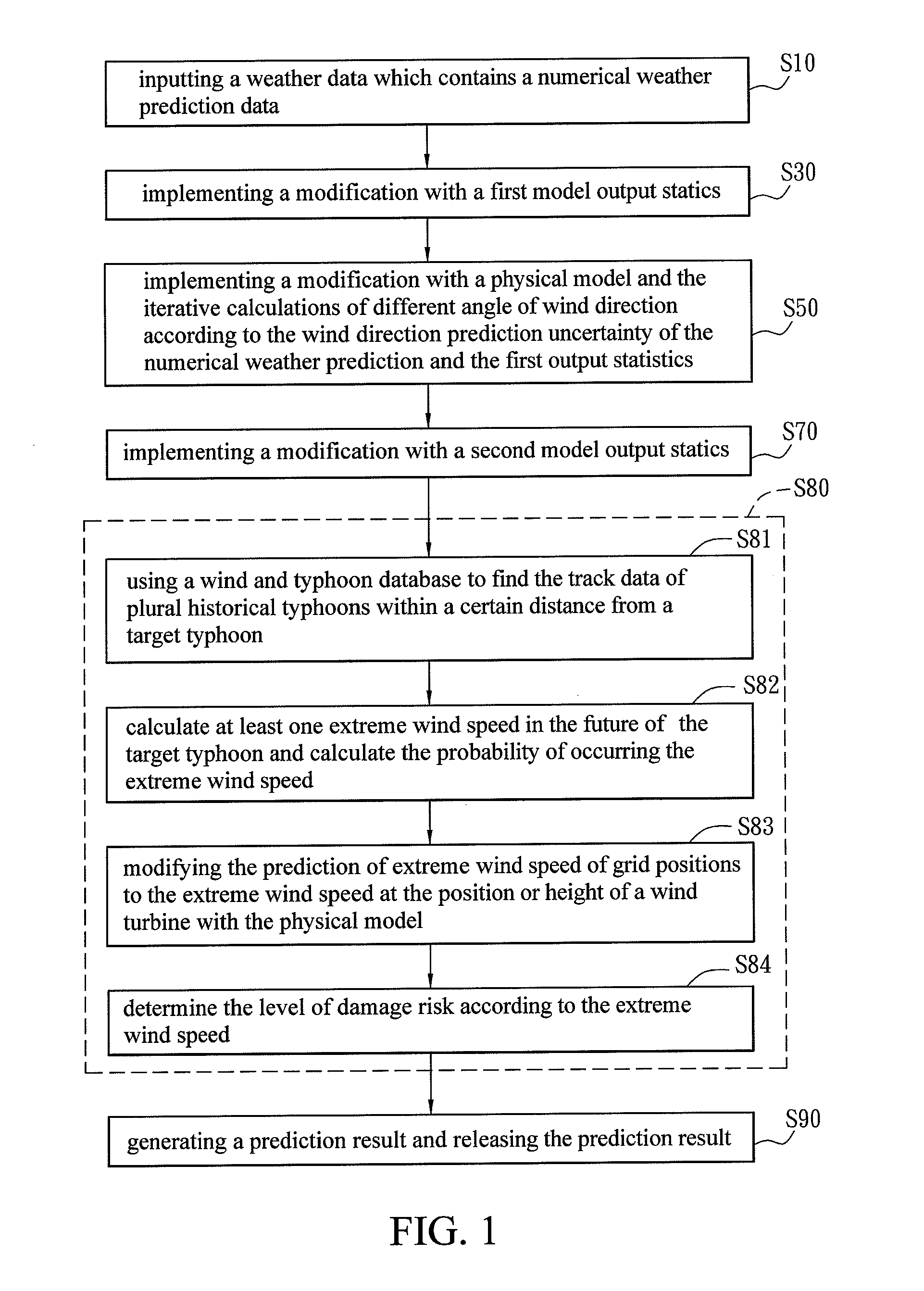
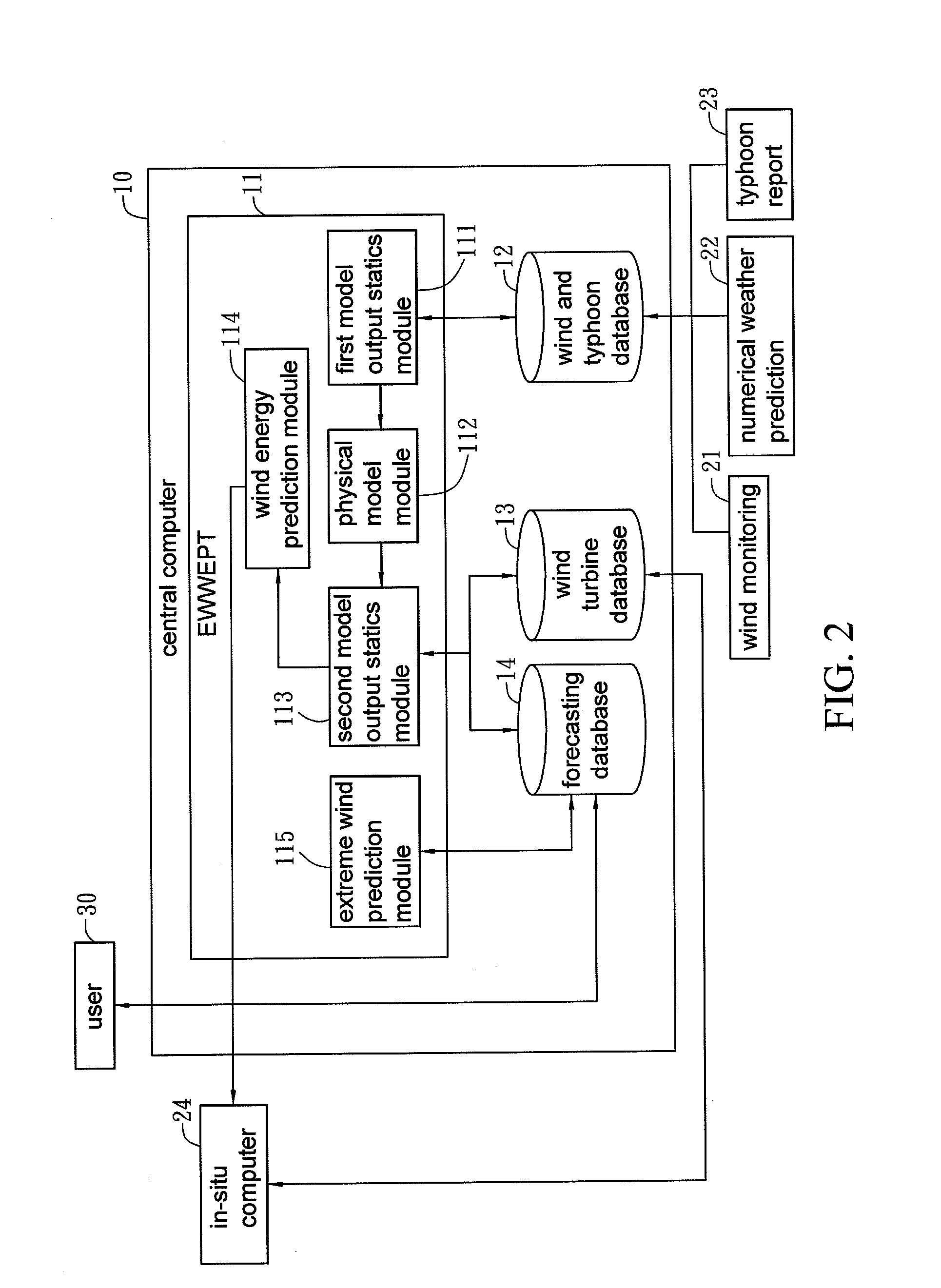
Wind energy forecasting method with extreme wind speed prediction function
InactiveUS20120046917A1Improve efficiencyProcess safetyWeather condition predictionEngine fuctionsNumerical weather predictionPhysical model
A wind energy forecasting method with extreme wind speed prediction function cooperated with a central computer, comprising the steps of: inputting a weather data which contains a numerical weather prediction data; implementing a modification with a first model output statistics; implementing a modification with a physical model in accordance with the output of the first model output statistics that can iteratively calculate the results by varying the angles of wind direction; implementing a modification with a second model output statistics; and implementing a prediction of extreme wind speed caused by typhoon, which comprises the following sub-steps of: using a wind and typhoon database to find track data of plural historical typhoons within a certain distance from a target typhoon; using an extreme wind and wind energy prediction tool to calculate at least one extreme wind speed in the future of the target typhoon and calculate the probability of occurring the extreme wind speed; and modifying the extreme wind speed with the physical model to the extreme wind speed at the position or height of a wind turbine.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Weather and satellite model for estimating solar irradiance
ActiveUS20130166266A1Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkNatural satelliteThe Internet
Solar irradiance, the energy from the Sun's electromagnetic radiation, has a wide range of applications from meteorology to agronomy to solar power. Solar irradiance is primarily determined by a location's spatial relationship with the Sun and the atmospheric conditions that impact the transmission of the radiation. The spatial relationship between the Sun and a location on Earth is determined by established astronomical formulas. The impact of atmospheric conditions may be estimated via proxy using pixels from satellite imagery. While satellite-based irradiance estimation has proven effective, availability of the input data can be limited and the resolution is often incapable of capturing local weather phenomena. Brief qualitative descriptions of general atmospheric conditions are widely available from internet weather services at higher granularity than satellite imagery. This methodology provides logic for quantifying the impact of qualitative weather observations upon solar irradiance, and the integration of this methodology into solar irradiance estimation models.
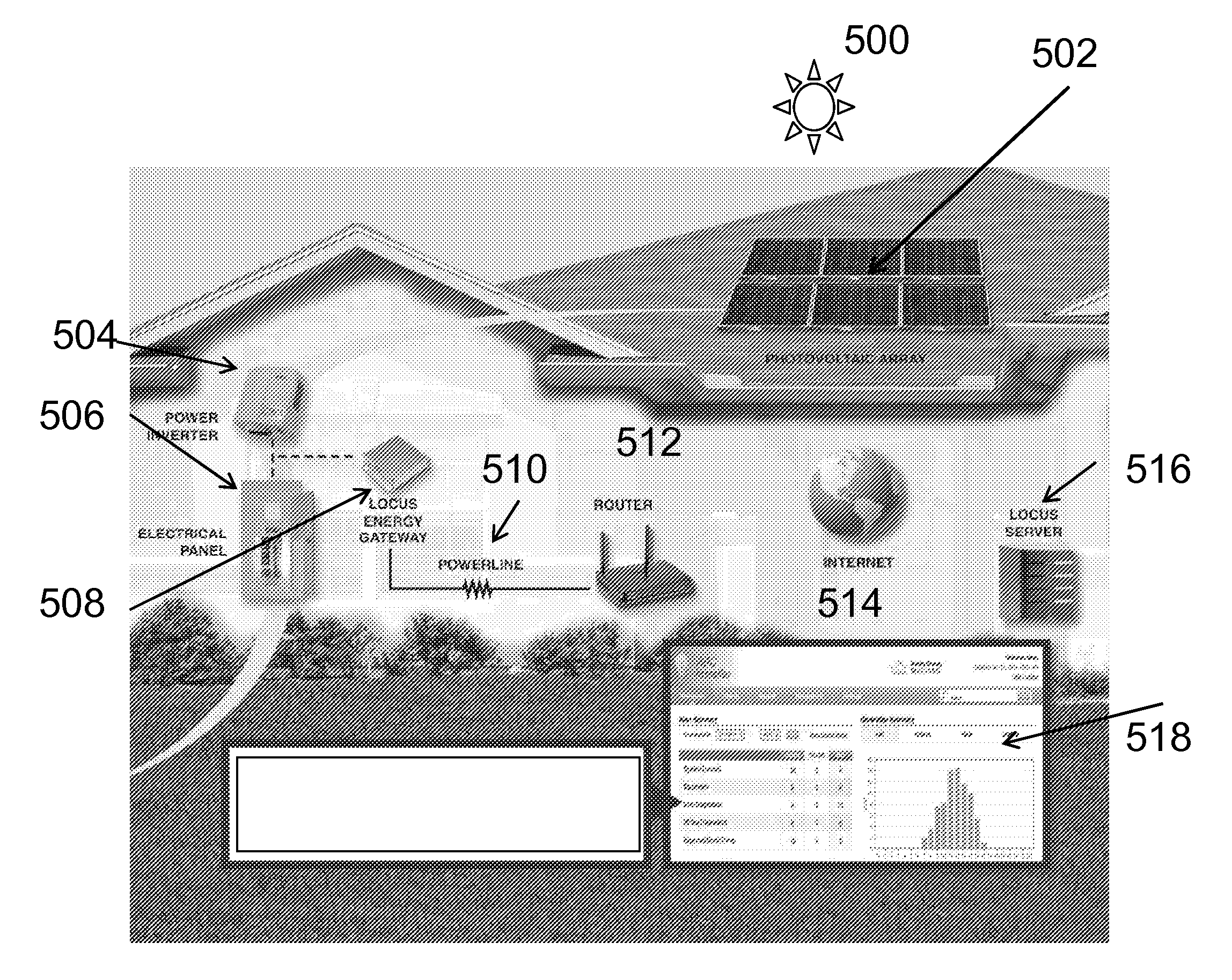
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
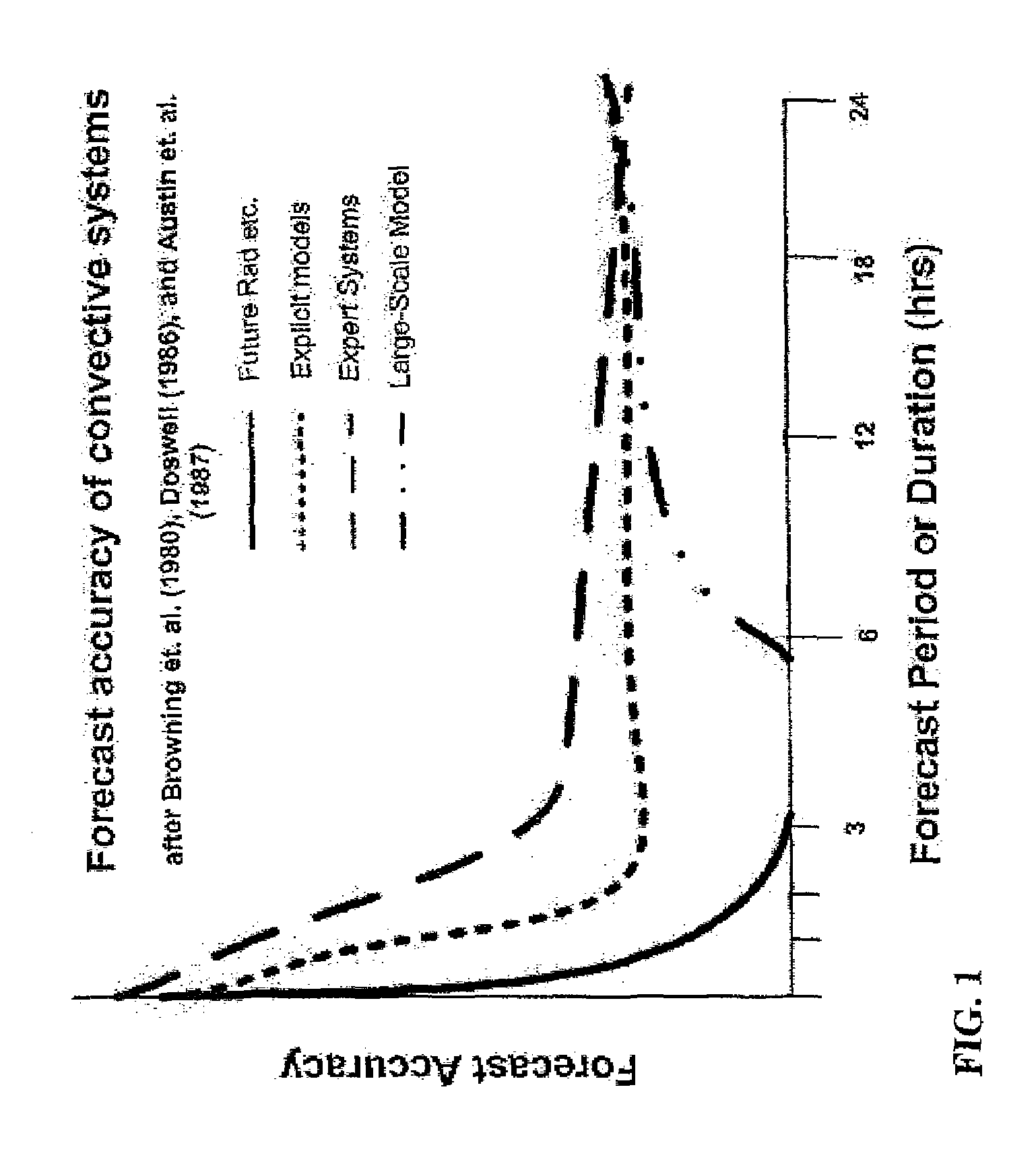
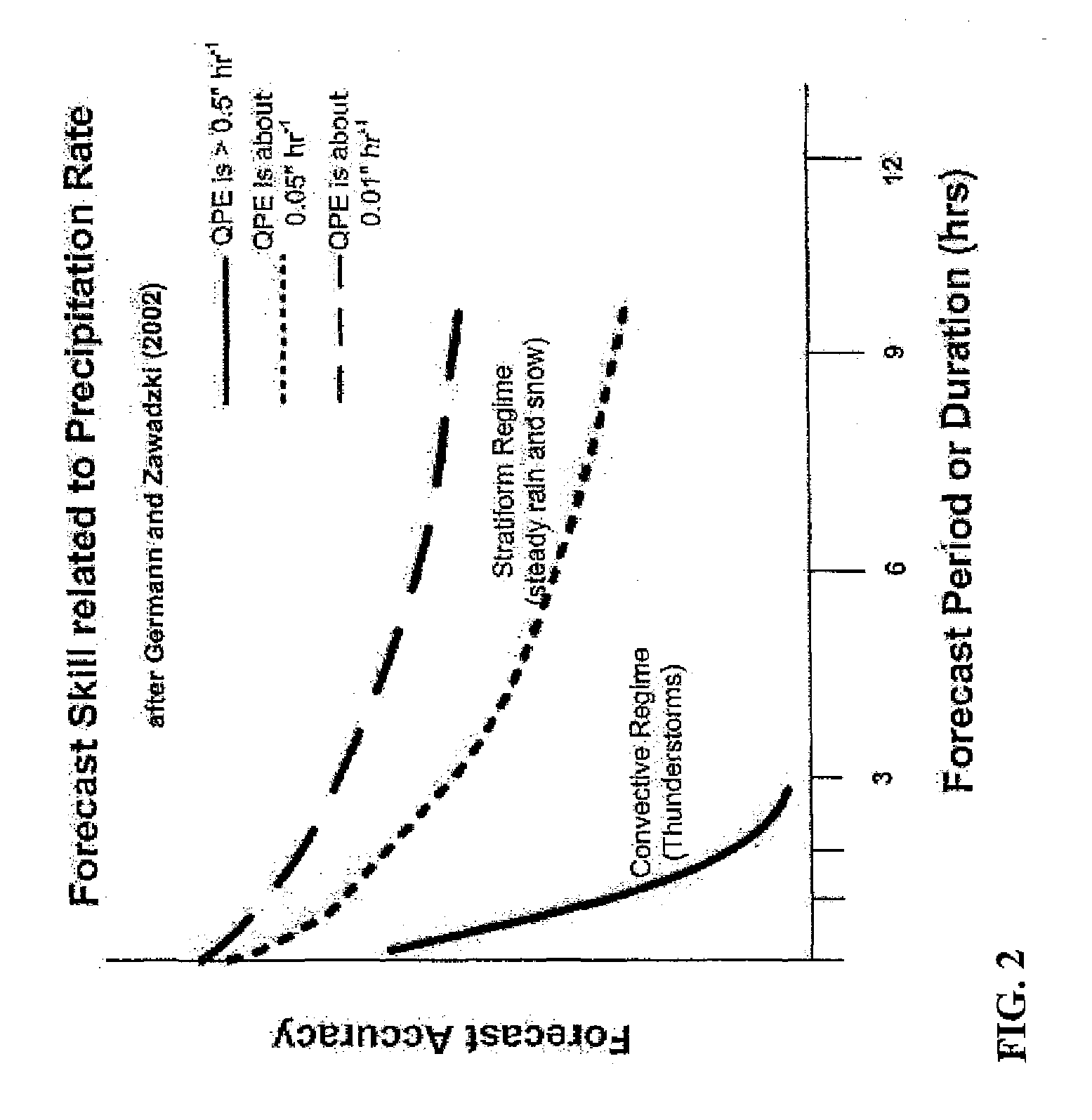
Derivation and production of high-resolution, very short-term weather forecasts
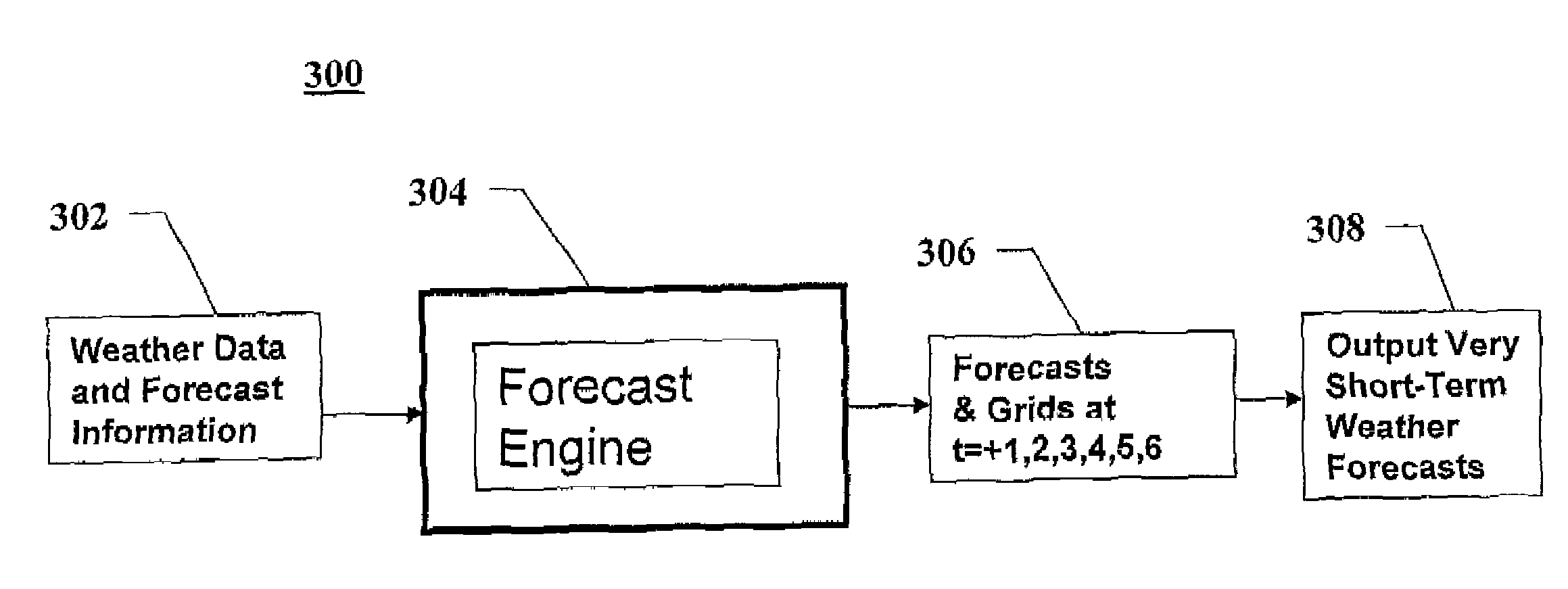
ActiveUS7542852B1Improve accuracyImproved prediction of timing and location and severityNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementWeather condition predictionGround truthAtmospheric sciences
Weather forecasting systems and methods for deriving and producing very short-term weather forecasts. Weather data and forecast information maybe input to derive very short-term weather forecasts in the 0-6 hour time frame. The system and methods include an expert system employing a hybrid or blending of forecasting approaches, with dynamic or intelligent arbitration of the different numerical, statistical, and human-driven techniques to produce more accurate weather forecasts for very short-term time periods. A calibration or internal verification against ground truth may be run independently with a time lag to produce more accurate future predictions of atmospheric state. The systems and methods may run in modes that produce either high resolution weather forecasts in the short-term period of 0-6 hours or a combination of synthetic, real-time weather observations / conditions and high resolution, short-term weather forecasts.
Owner:DTN LLC
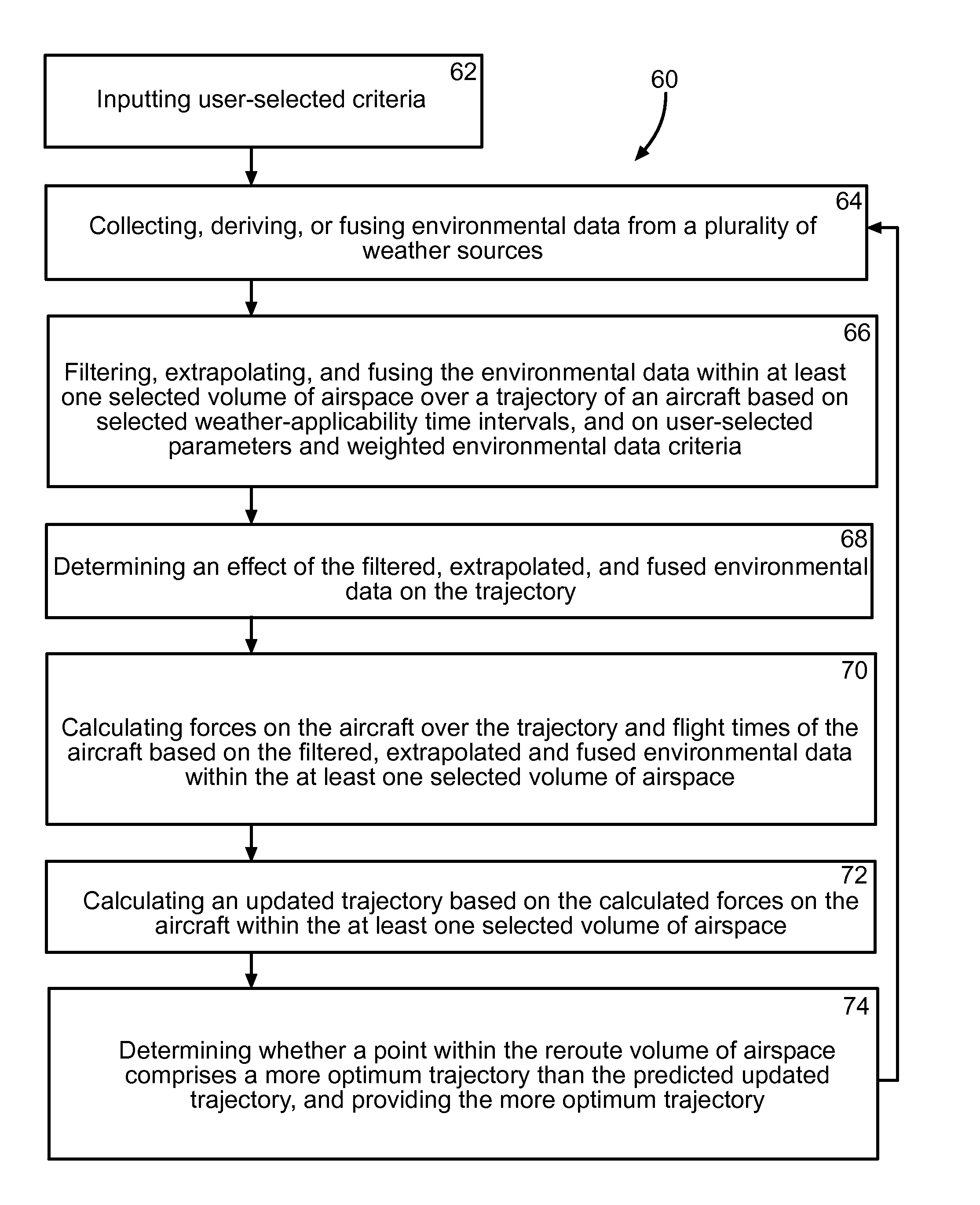
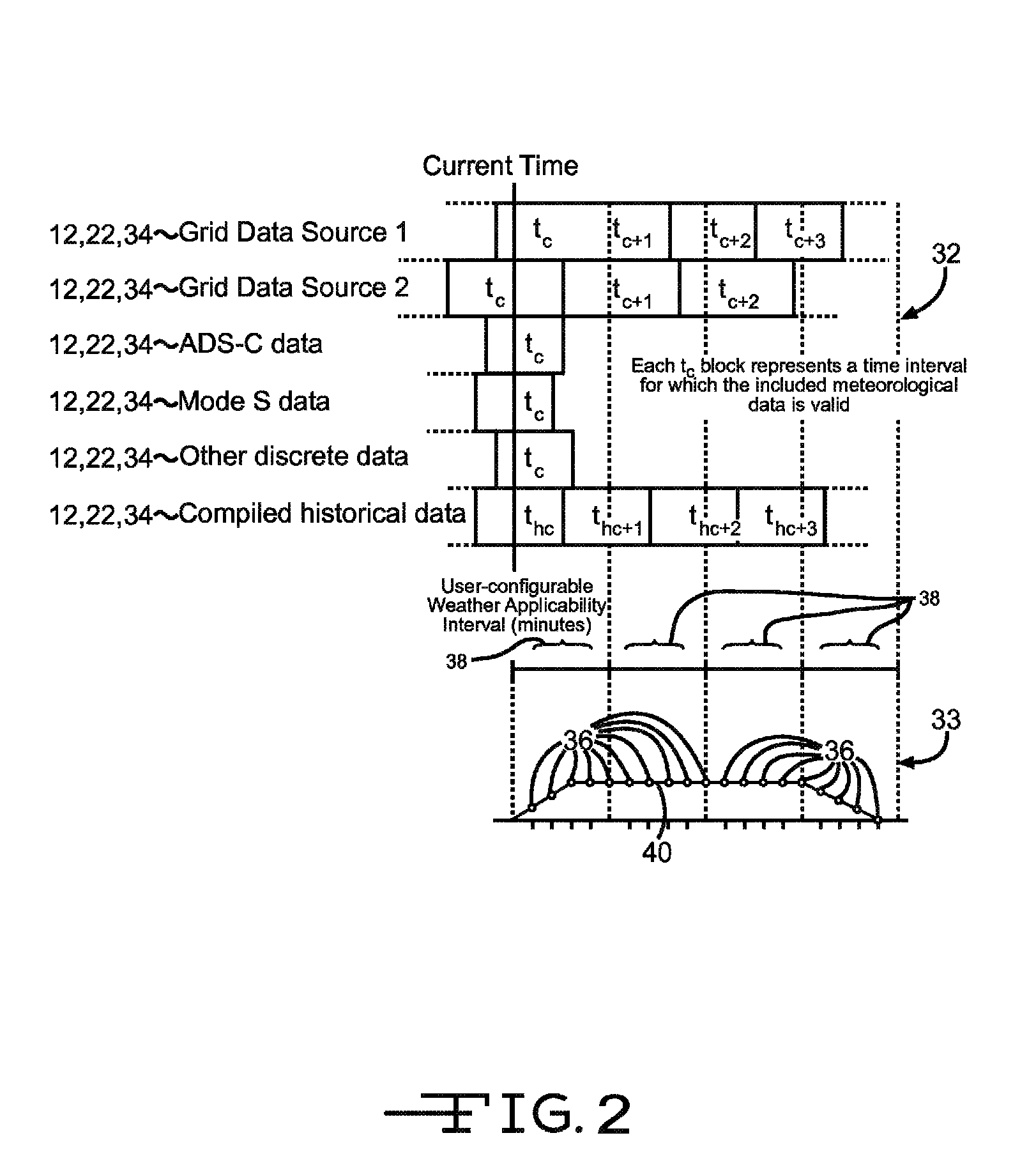
Four-dimensional weather predictor based on aircraft trajectory
ActiveUS8332084B1Instruments for road network navigationAnalogue computers for trafficFlight vehicleEnvironmental data
A method of determining environmental data along a trajectory of an aircraft may assist in the evaluation of flight conditions along the trajectory. Environmental data may be at least one of collected, derived, and fused from a plurality of weather sources using at least one processor. The environmental data may be filtered, extrapolated, and fused, using the at least one processor, within at least one selected volume of airspace over a trajectory of the aircraft based on selected weather-applicability time intervals, and on at least one of user-selected parameters and weighted environmental data criteria. The trajectory may comprise at least one of a planned trajectory, a current trajectory, and an intent trajectory of the aircraft. An effect of the filtered, extrapolated, and fused environmental data on the trajectory may be determined using the at least one processor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Interactive weather advisory system
InactiveUS6985813B2Special service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalWeather analysisPersonalization
A broadcast network for selectively transmitting individualized weather forecast signals to remote communicator devices. The broadcast network comprising a user input database, a communicator location database, a weather analysis unit and a communication network. The user input database contains user-defined parameters, each of the user-defined parameters includes a user profile. The user profile utilizes a user identifier code and identifies a communicator device associated with a particular user. The communicator location database contains data indicative of the real-time spatial locations of the communicator devices. The weather analysis unit compares the spatial location of each communicator device contained in the communicator location database with real-time weather forecast data or weather data and generates an individualized weather forecast signal upon demand of a user. The communication network receives the individualized weather output signals and transmits the individualized weather output signals to the communicator devices identified by the user identifier codes.
Owner:LOCATOR IP
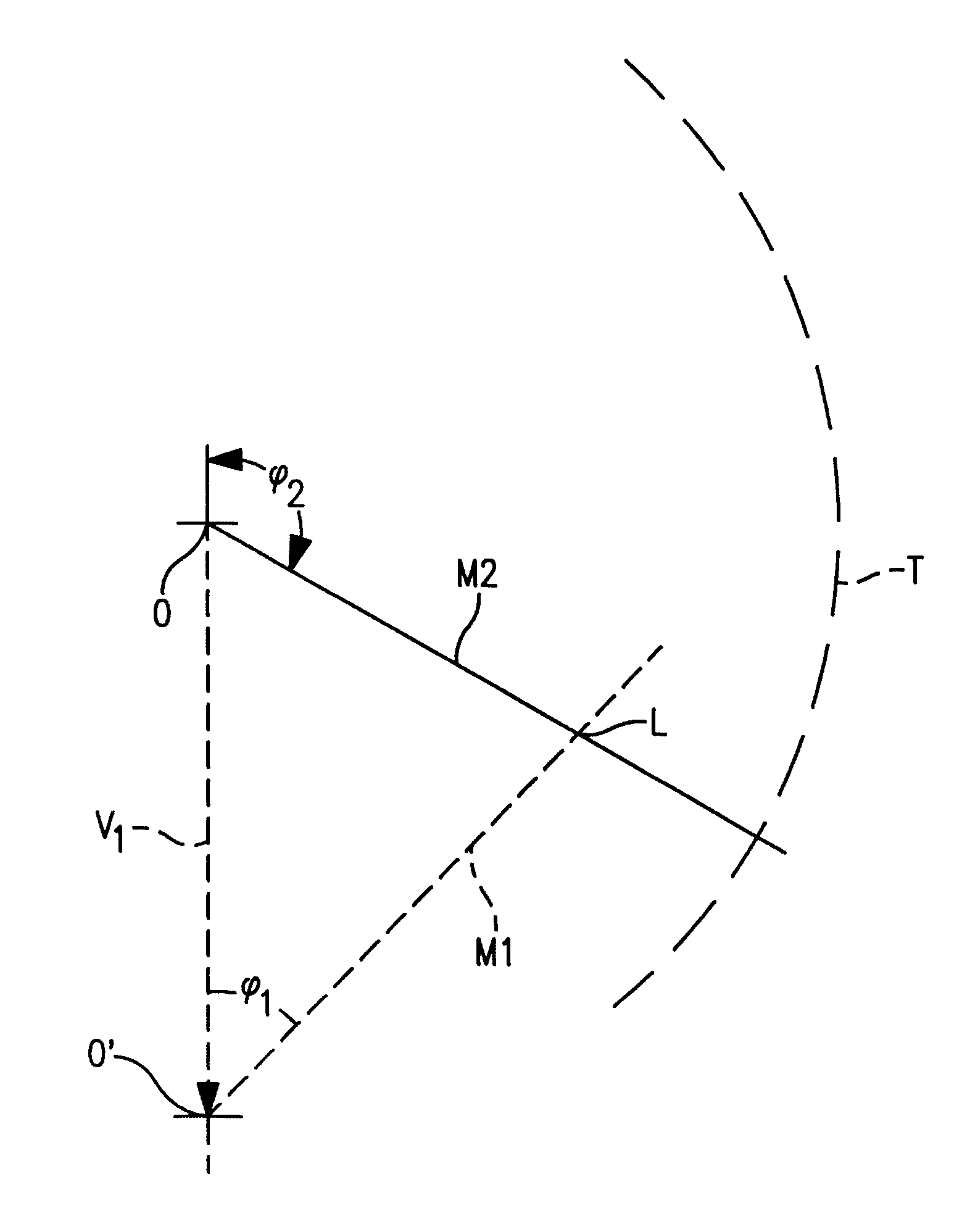
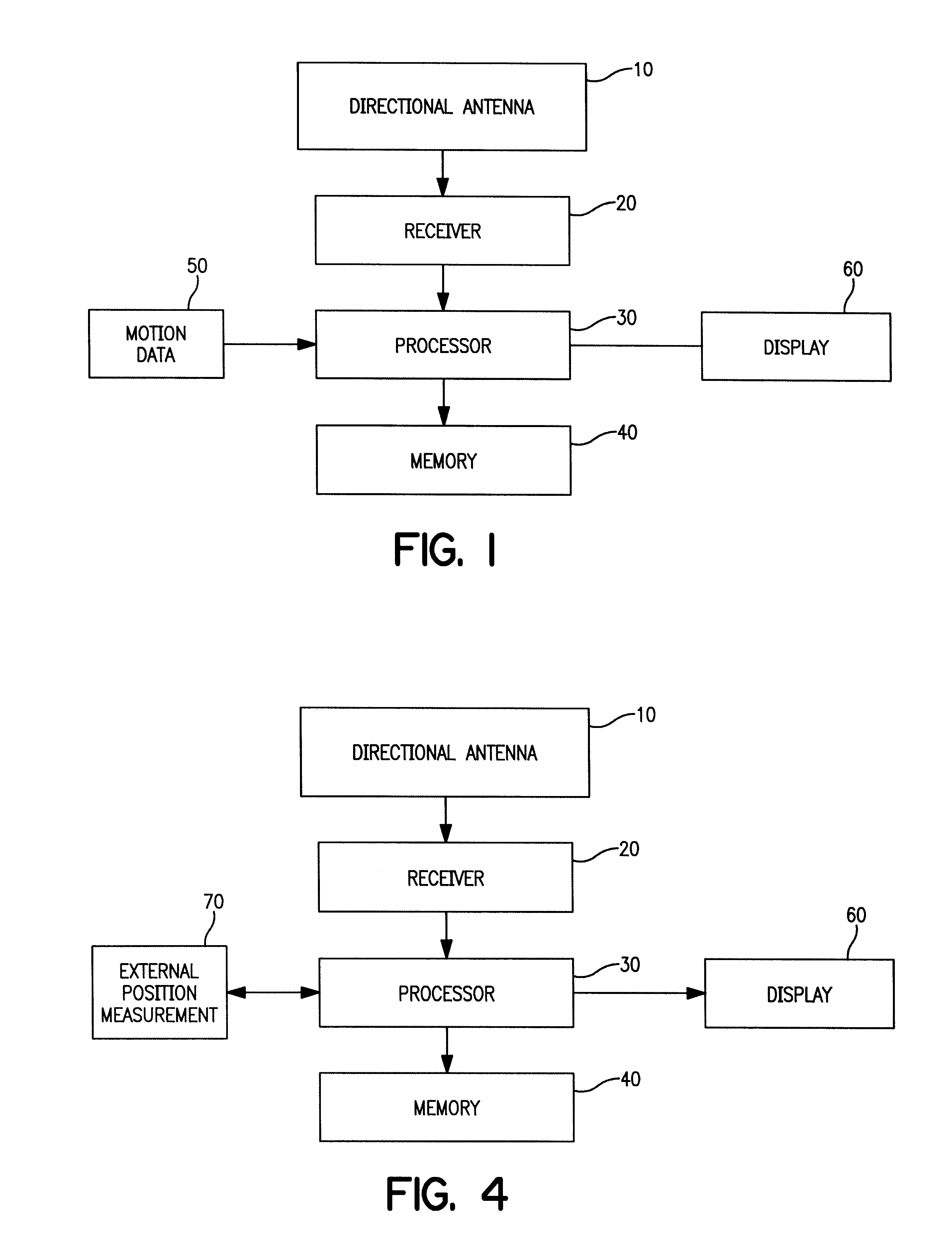
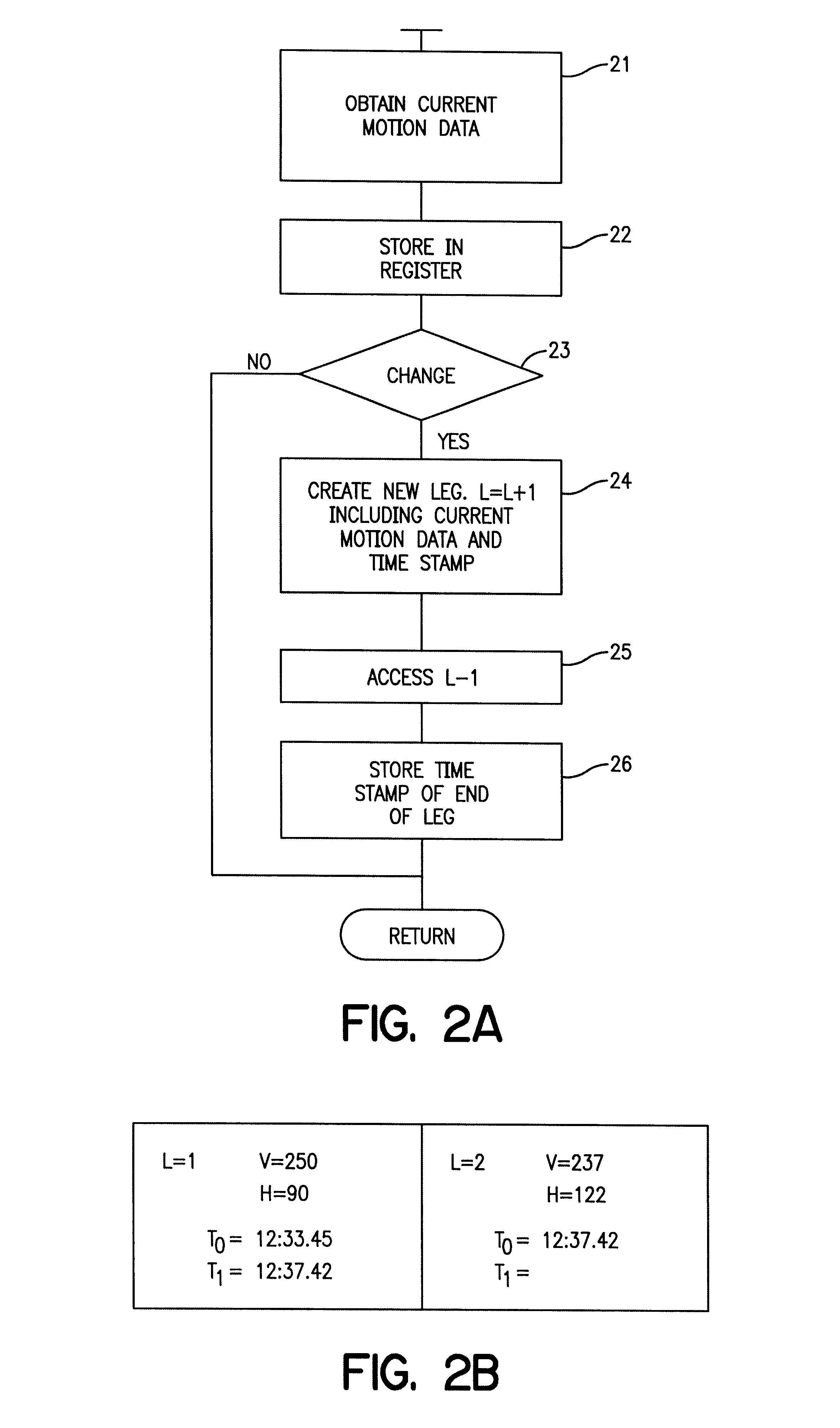
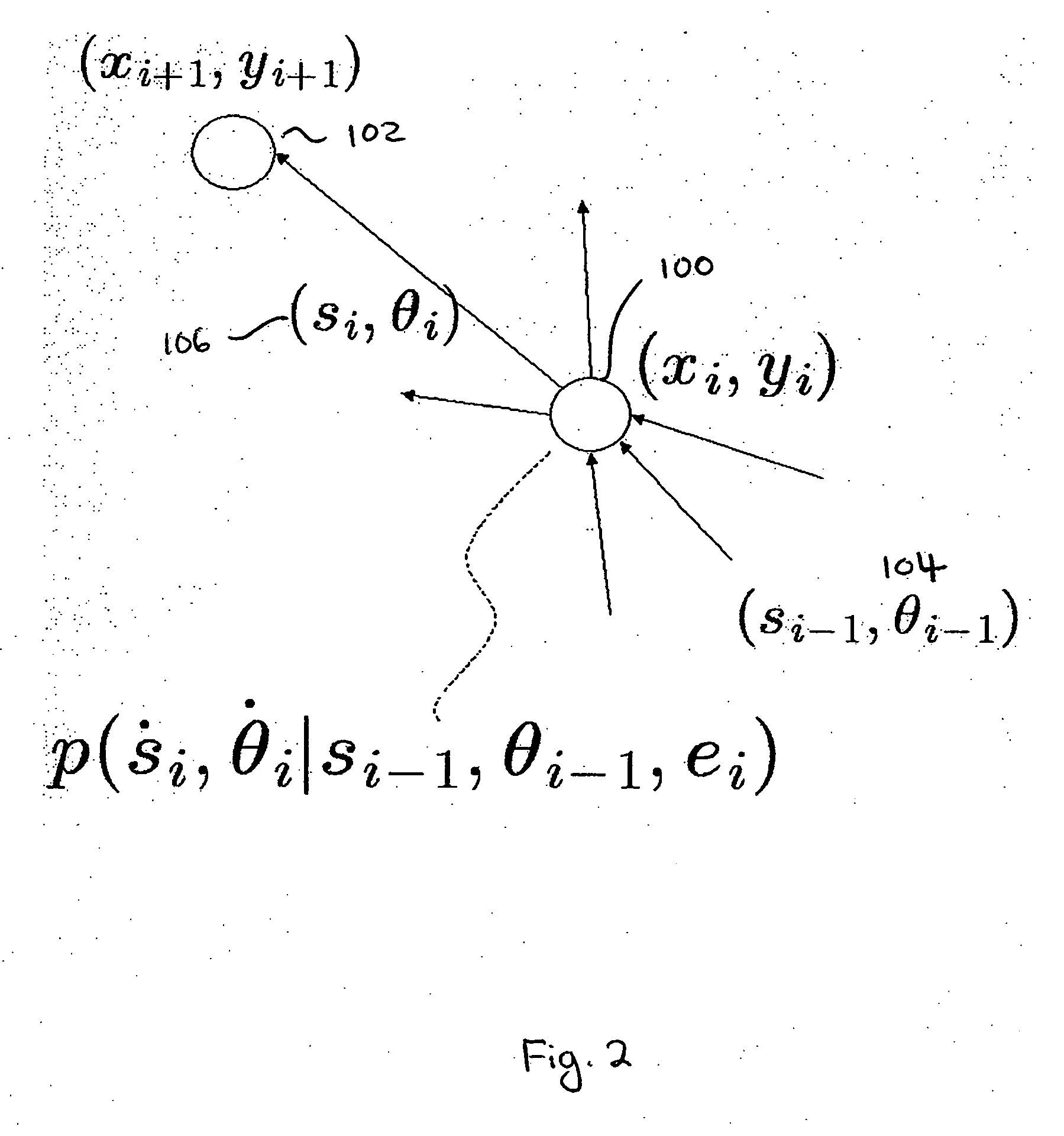
Enhancement of storm location from a single moving platform
InactiveUS6347549B1Reduce motion errorsMinimum errorWeather condition predictionTriangulationAtmospheric sciences
The location of weather activity from a moving platform such as an aircraft is enhanced using triangulation in time. More particularly, a first measurement of the weather activity is made relative to the aircraft at a first time. A second measurement of the location of the weather activity is made from the aircraft at a second period in time. The first measurement is modified or updated to correct for the change in position of the aircraft between the first and second measurements and then the modified data is compared with the data of the second measurement to enhance the location of the weather activity.
Owner:RYAN INT OHIO
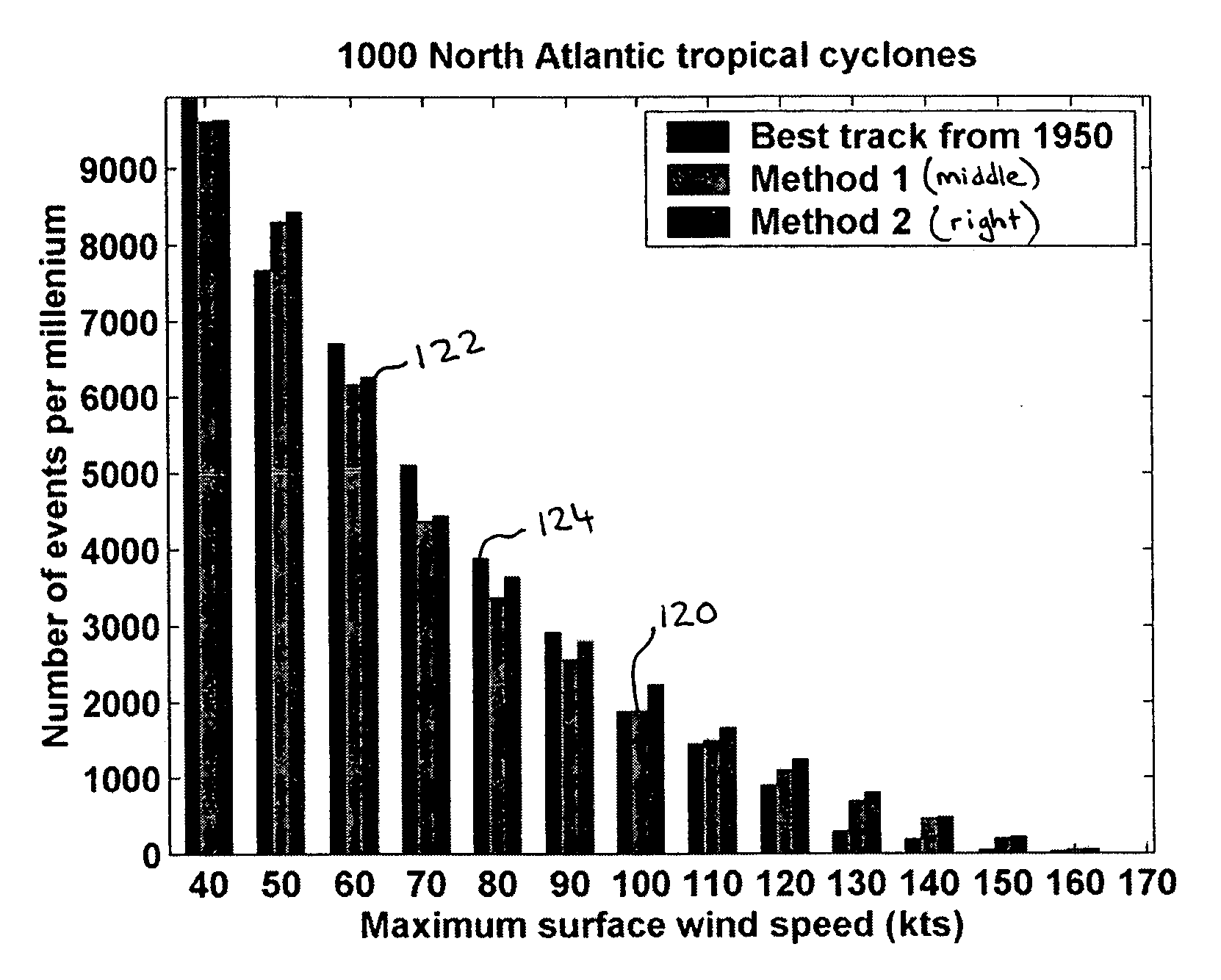
Statistical-deterministic approach to natural disaster prediction
ActiveUS20070168155A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsWeather condition predictionDeterministic methodNatural disaster
A combined statistical-deterministic approach to methods and systems for assessing risk associated with natural disasters, in particular, hurricane wind risk. One example of a method of predicting wind speed distribution within a predetermined distance from a point of interest includes steps of statistically synthesizing a large plurality of wind storm tracks that pass within a predetermined radius of the point of interest, running a deterministic simulation of wind intensity along each one of the large plurality of wind storm tracks to produce an output representative of wind speed distribution along each track, and using the output to estimate an overall wind speed probability distribution from a combination of the wind speed distributions along each track within the predetermined distance from the point of interest.
Owner:RAVELA SAI +1
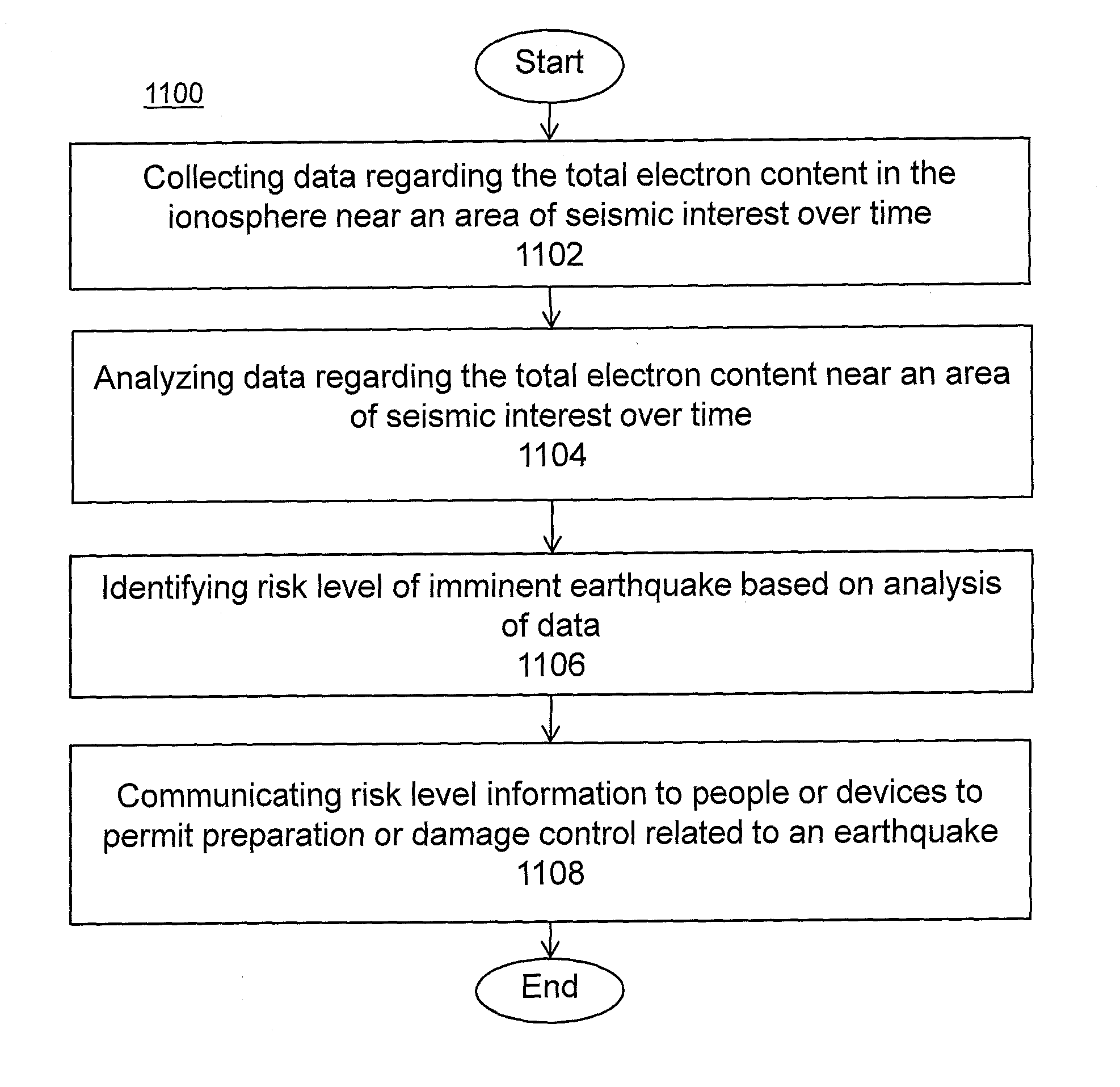
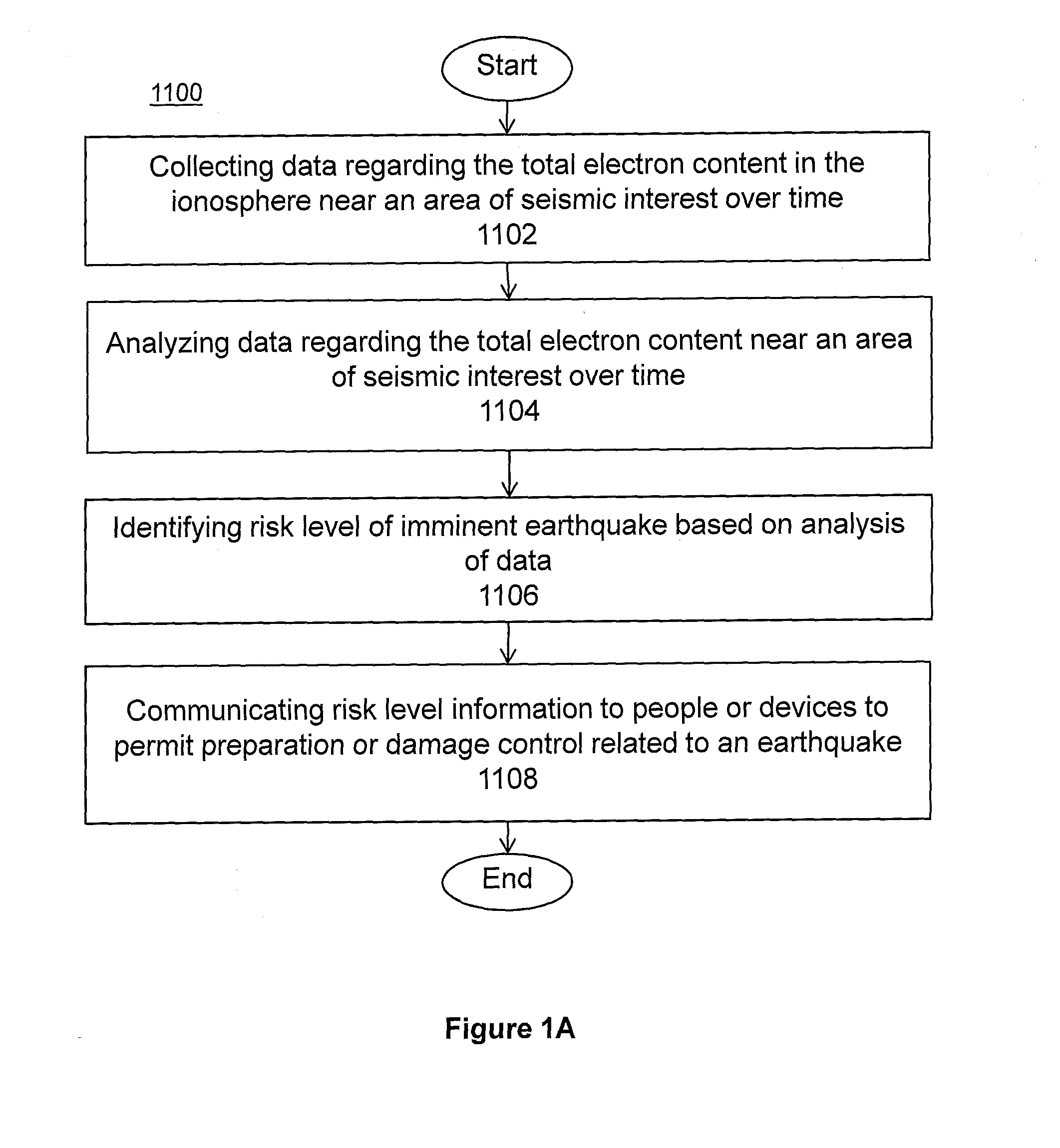
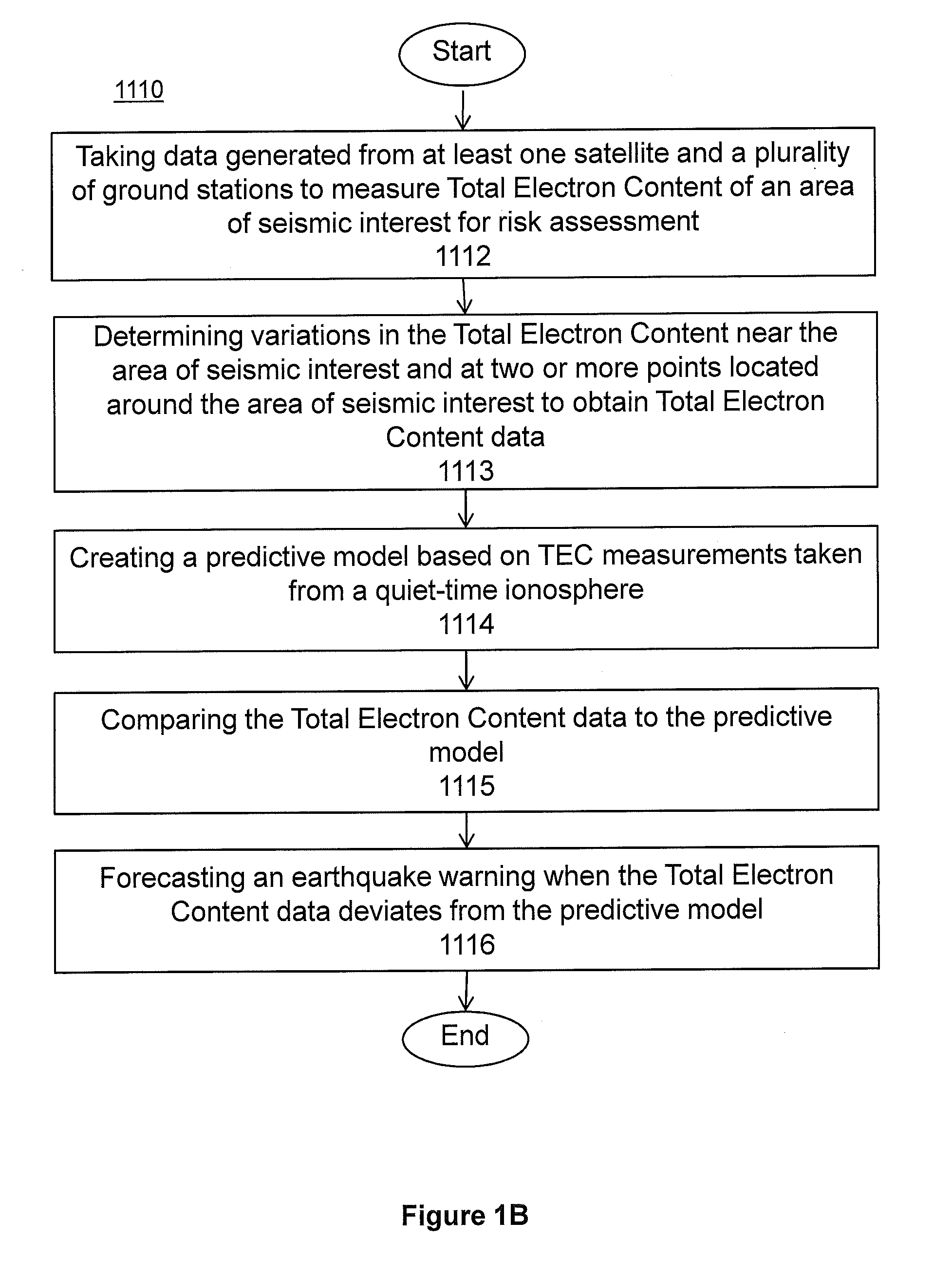
System and methods for risk prediction and assessment
InactiveUS20150051837A1Weather condition predictionEarthquake measurementIonosphereTotal electron content
A system and methods for predicting and assessing risk before an event occurs. More particularly, the present invention predicts and assesses risk such as the occurrence of an earthquake prior to the event by collecting and analyzing changes in Total Electron Content (“TEC”) in the ionosphere.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CORNELL CENT FOR TECH ENTERPRISE & COMMLIZATION CCTEC
Methods and systems for monitoring atmospheric conditions, predicting turbulent atmospheric conditions and optimizing flight paths of aircraft
InactiveUS20060155432A1Energy saving arrangementsNavigational calculation instrumentsInformation dataAirplane
A method for optimizing the flight path of an aircraft is performed by collecting atmospheric information data from one or more sensors mounted on an aircraft; processing the collected atmospheric information; predicting an atmospheric condition in a flight path of the aircraft based upon the collected atmospheric information; and modifying the flight path in anticipation of the atmospheric condition.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
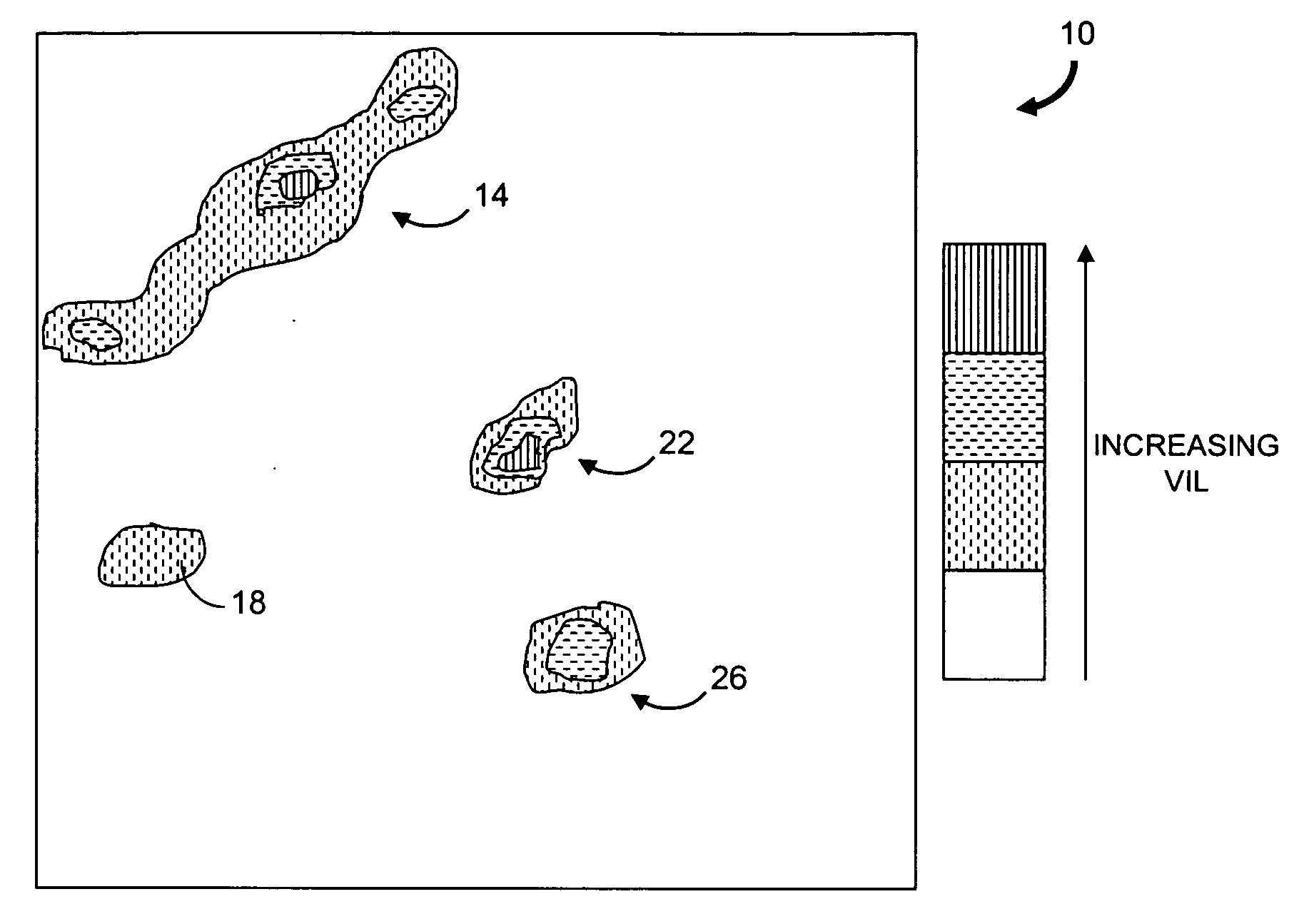
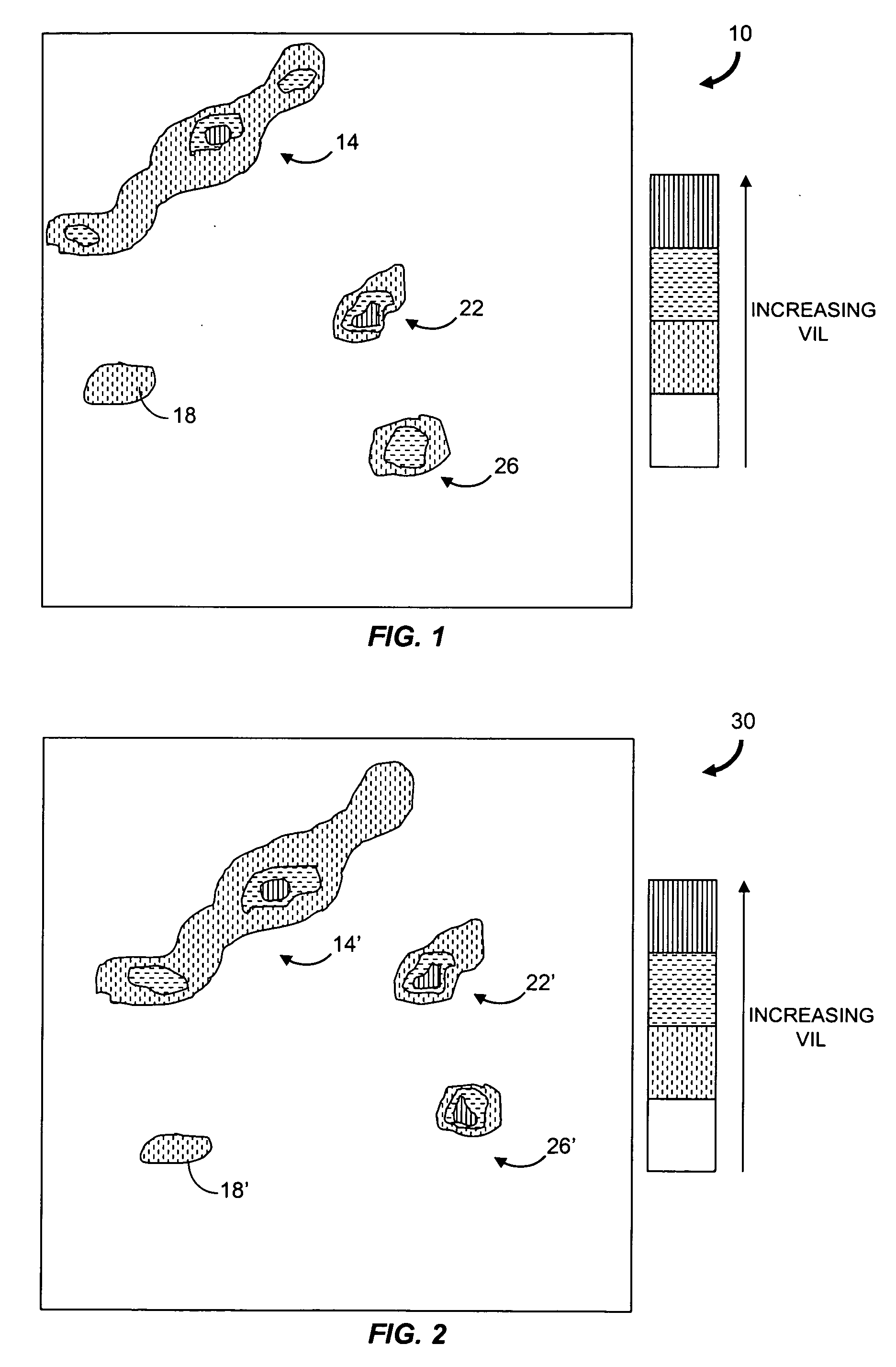
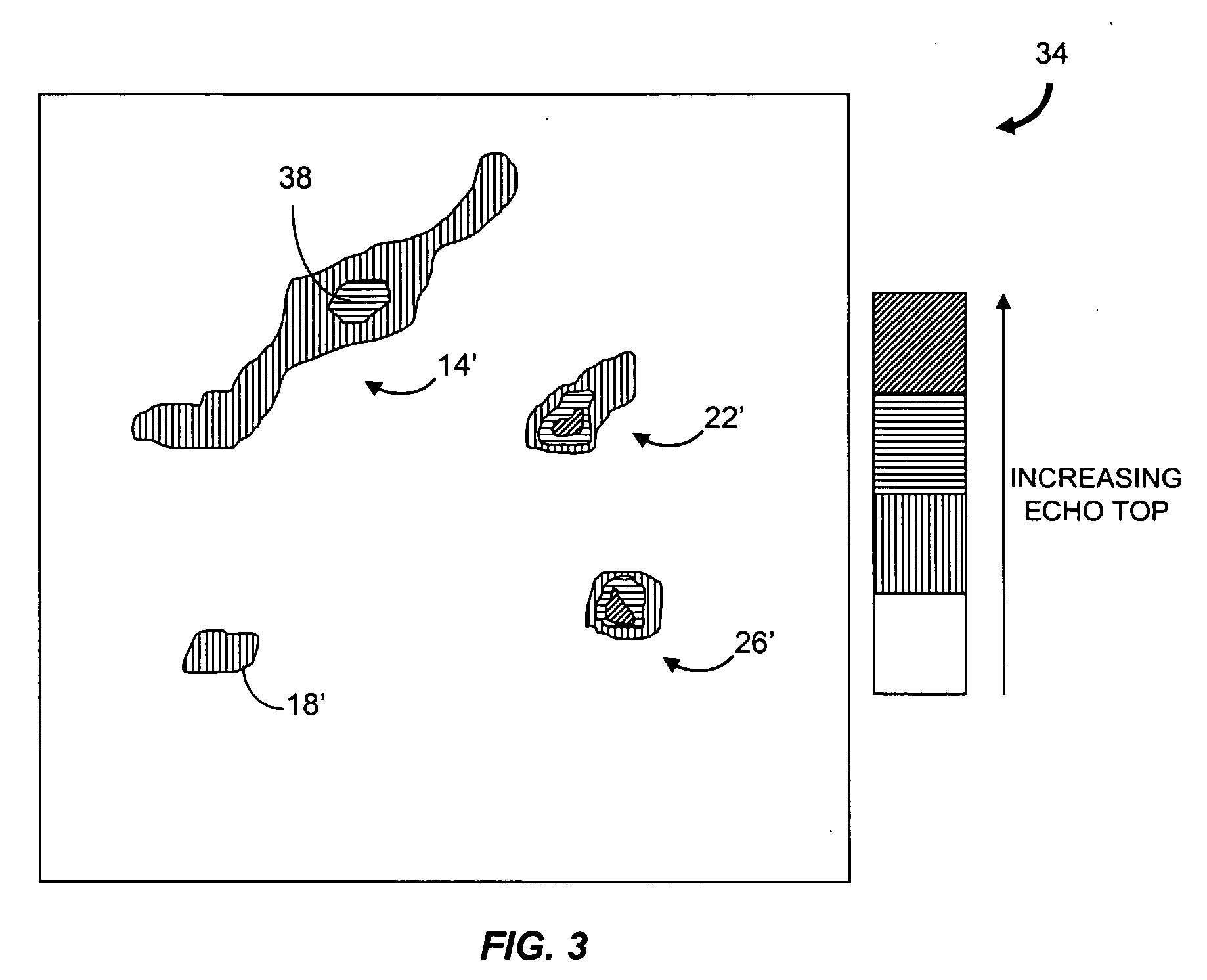
Weather radar echo tops forecast generation
ActiveUS20070005249A1Weather condition predictionCharacter and pattern recognitionWeather radarAtmospheric sciences
Described are a method and a system for generating a short-term forecast of echo tops as defined by weather radar measurements. The method includes receiving echo tops images for different times. An echo tops growth rate and an echo tops maximum value are determined for pixels in one of the images and used to generate echo tops prediction values for an echo tops prediction image. For pixels in regions of the image determined to be subject to convective initiation but where convective weather does not exist, an echo tops initiation height and the echo tops maximum value are determined and used with a predicted precipitation value to generate an echo tops prediction value for each pixel.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
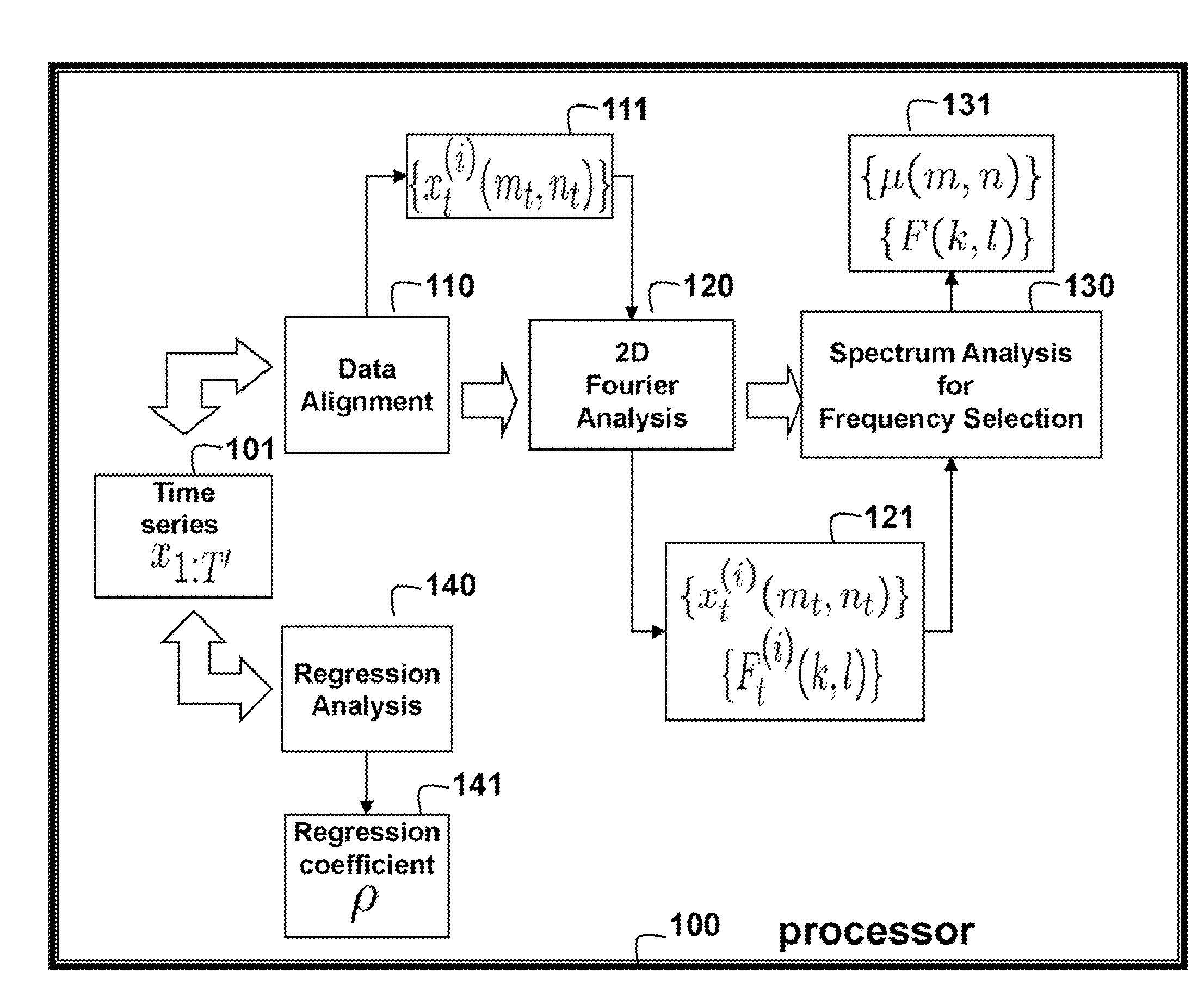
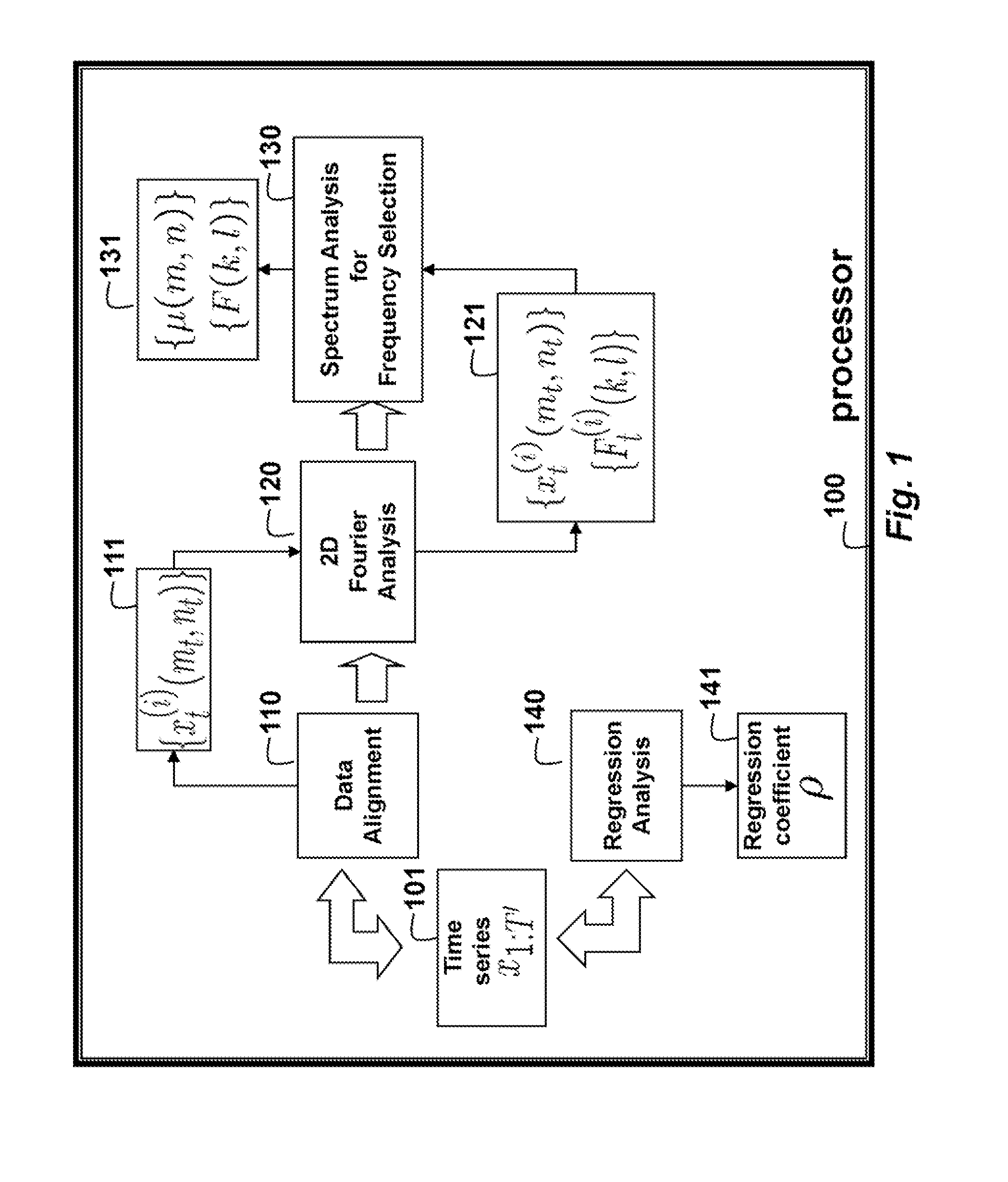
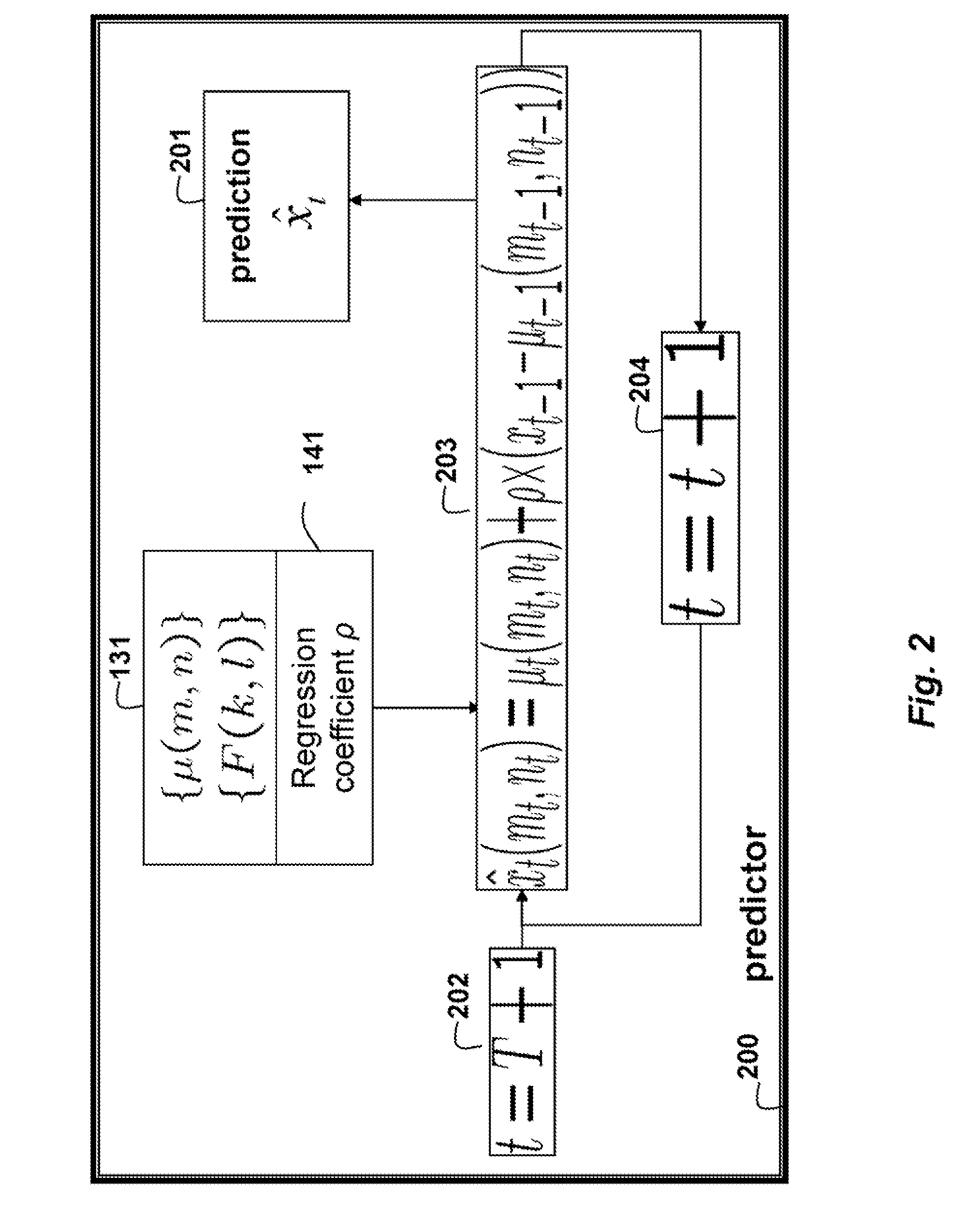
Method for Predicting Outputs of Photovoltaic Devices Based on Two-Dimensional Fourier Analysis and Seasonal Auto-Regression
InactiveUS20130262049A1Generation forecast in ac networkData processing applicationsRegression analysisPredictive methods
An output of a photovoltaic (PV) device is predicted by applying Fourier analysis to historical data to obtain frequencies and a mean of the frequencies in the data. Regression analysis is applied to the data to obtain a regression coefficient. Then, the prediction is a sum of the mean at the time step and a deviation from the mean at a previous time step, wherein the means are represented and approximated by selected frequencies, and the deviation for the previous time step is weighted by the regression coefficient.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Interactive advisory system
InactiveUS20080313037A1Easy to adaptAdvertisementsWeather condition predictionService provisionCommunicator device
A method for passing content to at least one communicator device. The user of a communicator device registers with at least one service provider for delivering a plurality of different types of content to be passed to the at least one communicator device. A user defined priority is assigned to the at least one type of content. The user-defined priority is stored on a computer readable medium. The different types of content are passed to the at least one communicator device based on the user defined priority.
Owner:LOCATOR IP
Method for predicting and mitigating power fluctuations at a photovoltaic power plant due to cloud cover
ActiveUS20150134251A1Avoid sudden changesSunshine duration recordersMechanical power/torque controlIlluminanceCombined use
A method for forecasting reduction in sunlight intensity due to cloud cover at a photovoltaic power plant is described. The method comprises determining characteristics of one or more clouds from sensors surrounding the photovoltaic power plant. The cloud characteristics are used to create a 3D map of the clouds. The 3D map in combination with information on the angle of the sun is used to create a 3D projection on the surface of the earth, resulting in a 2D surface irradiance map. The 2D surface irradiance map may be taken in successive projections or used in combination with wind speed data to forecast fluctuation in irradiance at the photovoltaic power plant. The forecasted reductions in power may be used to enact measures at the plant such as reducing the power output of inverters to prevent sudden fluctuations in the power output of the photovoltaic plant feeding the utility.
Owner:TMEIC
System for determining weather information and providing ambient parameter data
ActiveUS20050187714A1Easy to routeInstruments for road network navigationWeather condition predictionAtmospheric sciencesMarine navigation
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Method and system for predicting solar energy production
ActiveUS7580817B2Financial riskGeneration forecast in ac networkFinanceSolar powerLoad following power plant
A system, method and computer program product to assist in managing the physical plant mechanisms and market finances for a deregulated electricity grid or regulated utility grid, populated with solar electric generation capacity. This system provides tools to assist grid operators in the scheduling and dispatch of generation resources in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity, a week in advance, on an hourly basis. It also provides tools to assist companies engaged in generation, distribution and energy marketing, in the electrical power industry, to manage their contractual supply obligations in the day-ahead hourly wholesale market and the spot market, in an electrical grid populated with solar electric generation capacity. This process can also be used to predict solar loading of building structures, using forecast irradiance data as inputs to common building energy modeling programs, a week in advance, on an hourly basis.
Owner:NEO VIRTUS ENG
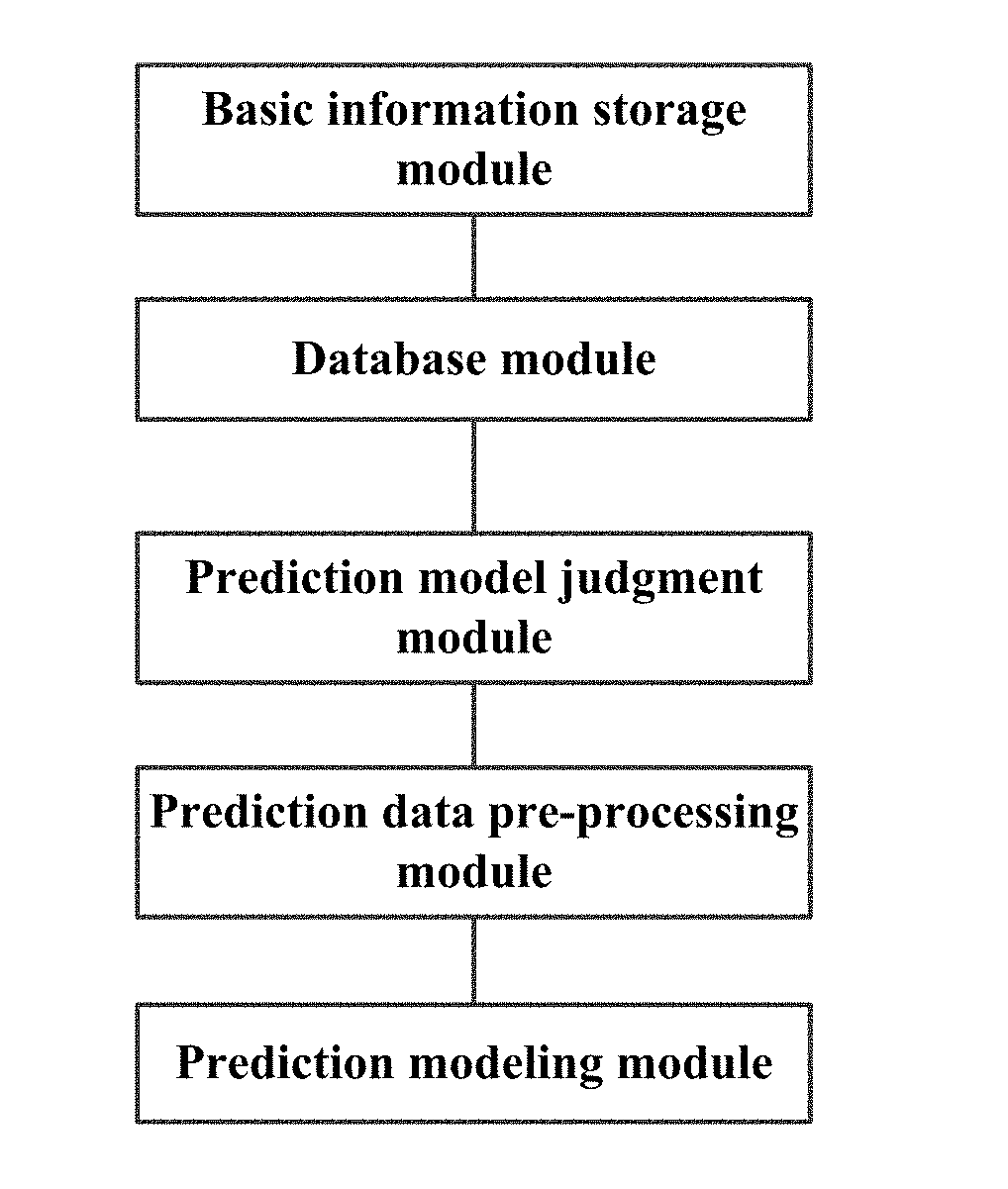
Whole-life-cycle power output classification prediction system for photovoltaic systems
InactiveUS20180046924A1Easy to operateFlexible extensibilityGeneration forecast in ac networkWeather condition predictionData pre-processingLife length
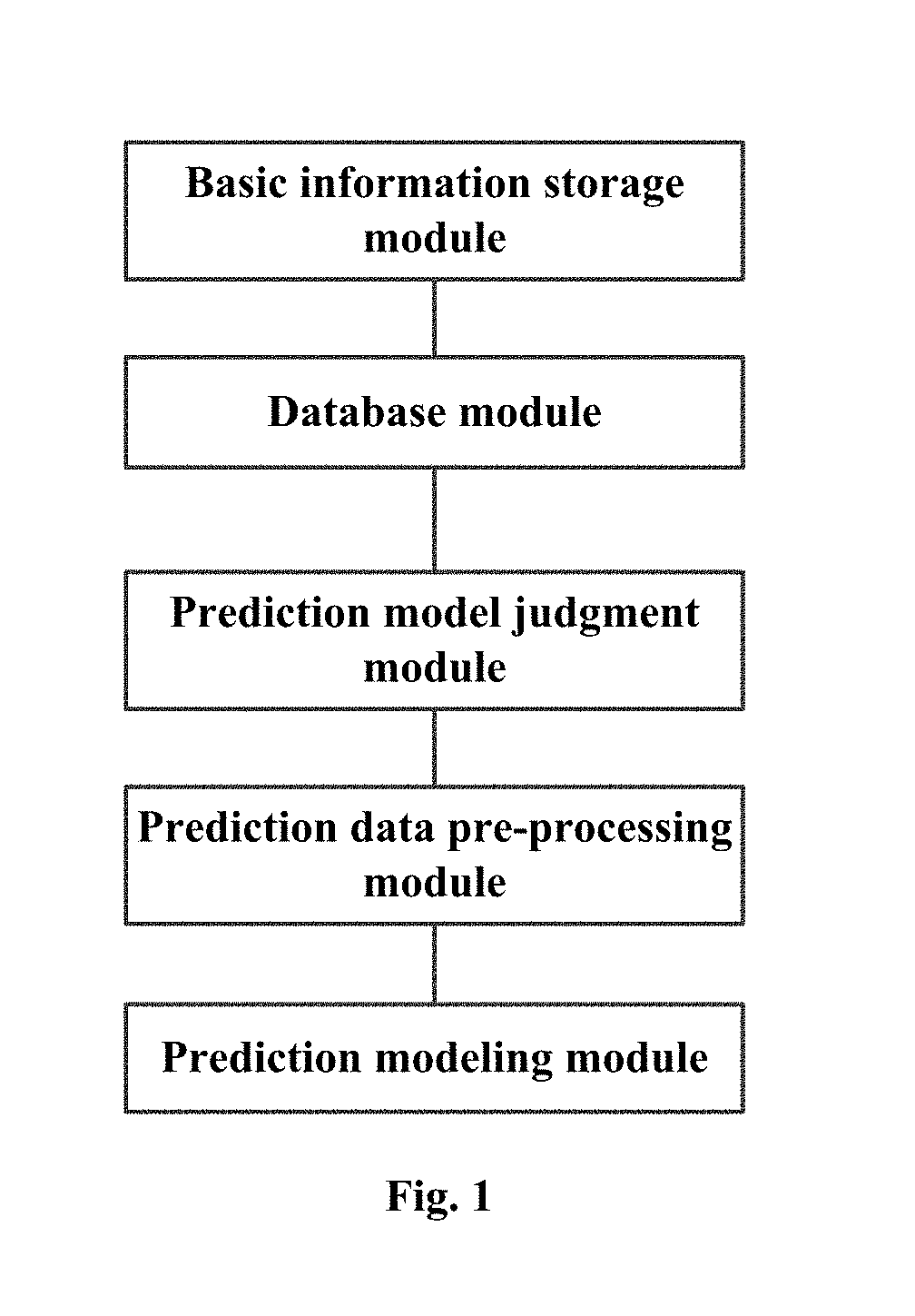
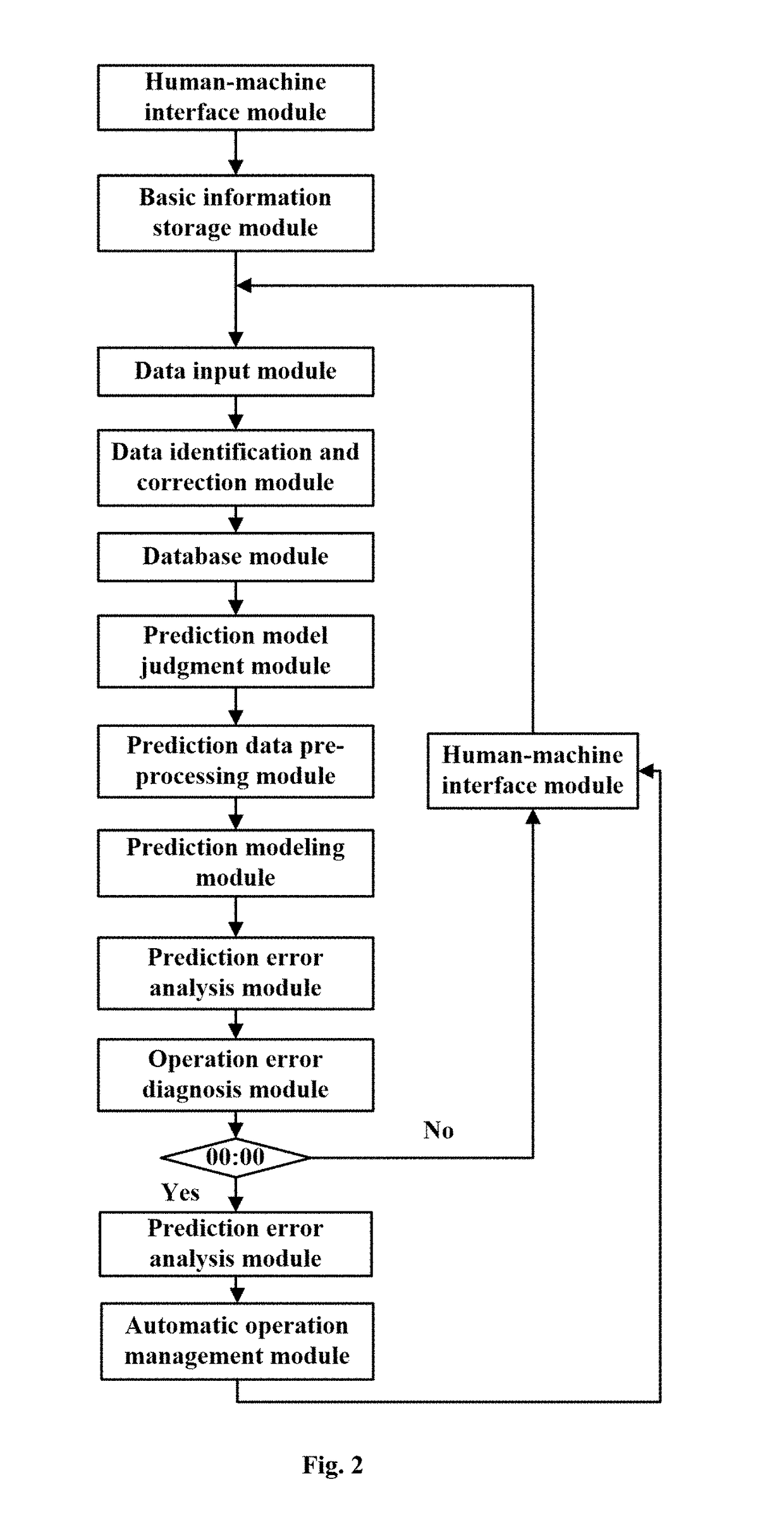
A whole-life-cycle power output classification prediction system for photovoltaic systems. The power output classification prediction system comprises a basic information storage module, a database module, a prediction model judgment module, a prediction data pre-processing module and a prediction modeling module. The system selects different prediction models to carry out training and predication according to acquired data types and operation time of the photovoltaic system, is a modularized and multi-type photovoltaic system output power prediction system, can be suitable for output power prediction requirements of a majority of photovoltaic systems at present, can carry out customization according to the scale of the photovoltaic system, user requirements, etc., can both meet economic requirements and reliability requirements, and has good adaptability and transportability. The prediction method can update automatically. The prediction system can carry out automatic operation management. And relatively high prediction precision and stability are achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com