Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
145results about "Sunshine duration recorders" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
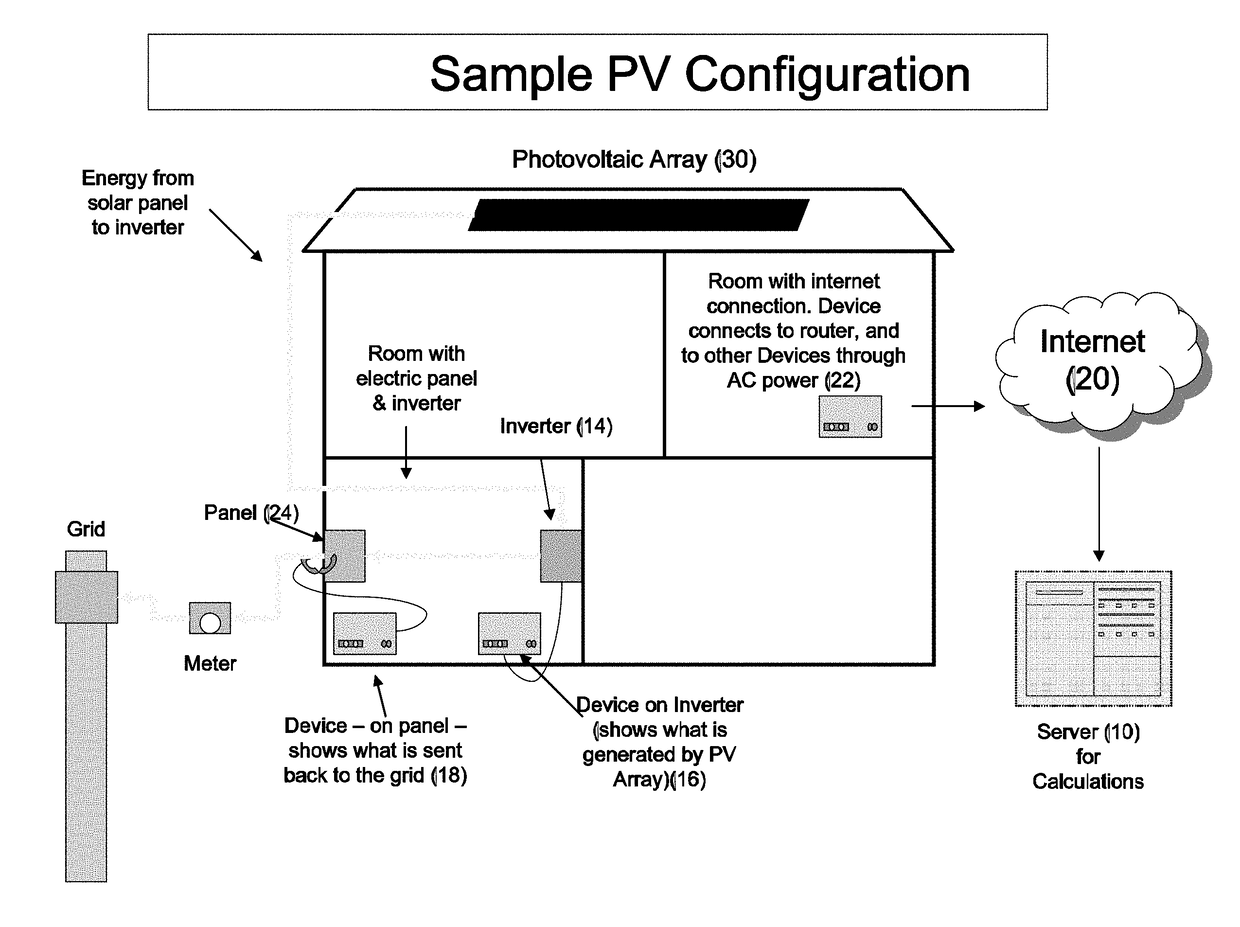
Assessment of solar energy potential on existing buildings in a region
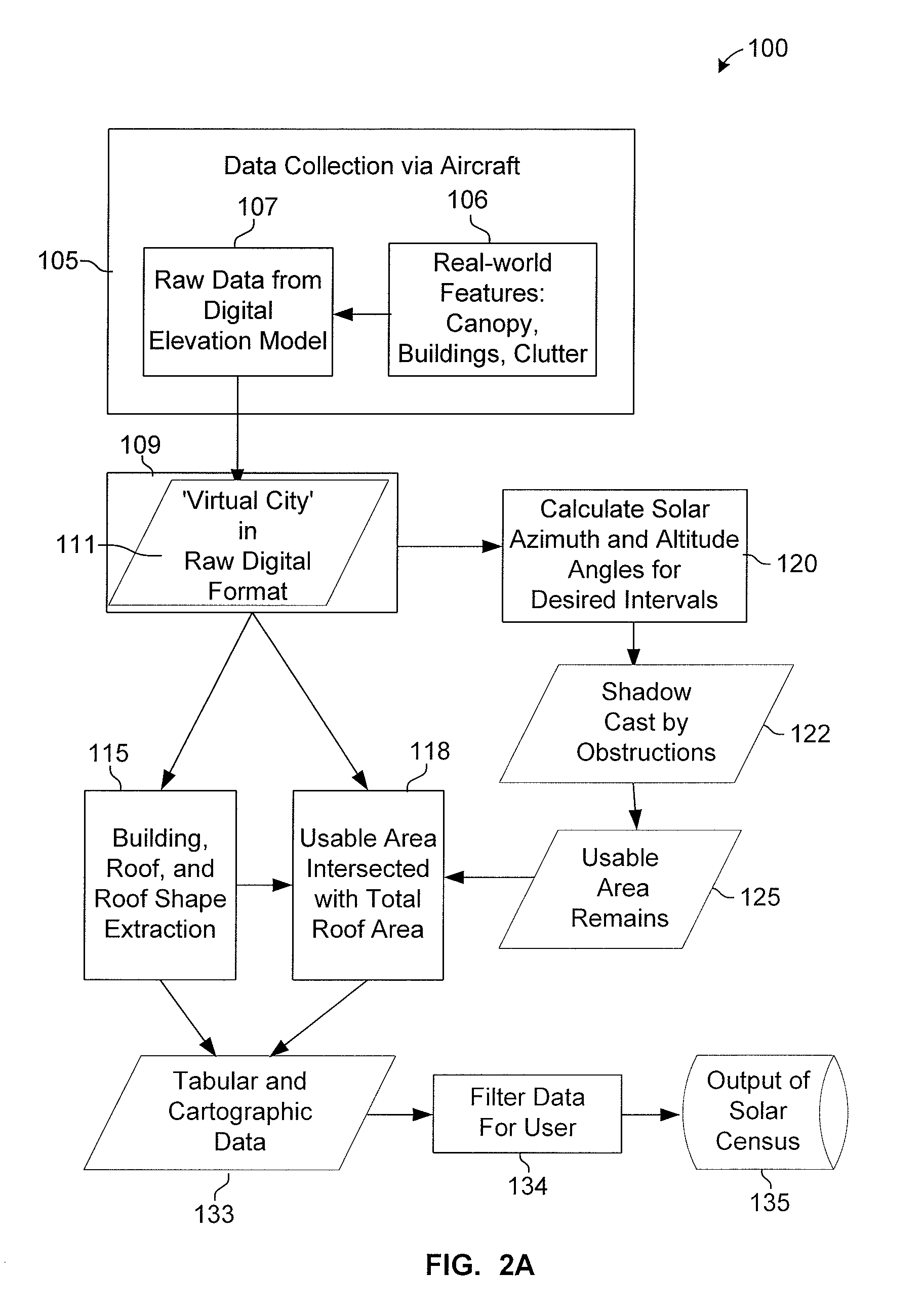
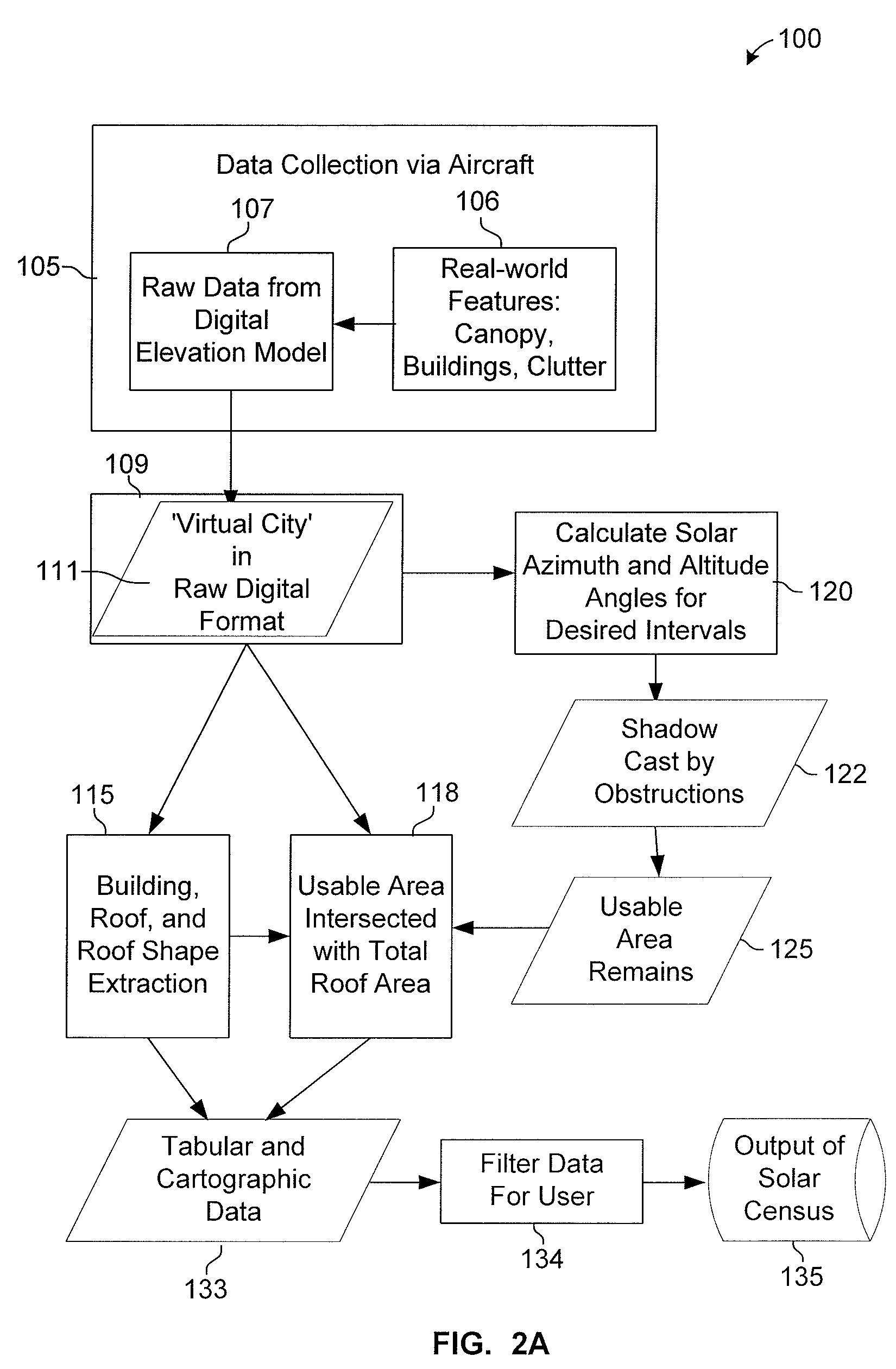
A method for assessing solar insolation potential upon existing building rooftops in a given region comprises: (a) computing Global Horizontal Insolation values based on topographical Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data for the region; computing a Sky Transmissivity parameter as it affects Global Horizontal Insolation based on available climate and cloud cover data for the region; (c) applying an Albedo parameter for ground reflectivity and scattering to determine Diffuse Insolation values; (d) applying a Shading Coefficient based on measuring shadow surface areas in relation to total area from aerial photographs of the region over defined times and periods; (e) determining Total Building Roof Area based on image analysis of aerial photographs of the region, and applying a typical roof slope factor; (f) estimating typical Roof Slope, Type, and Orientation (azimuth) selected from a defined set (vocabulary) of rooftop types based on a visual survey of the region; and (g) calculating Total Building Rooftop Insolation Potential for the given region based the values determined.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
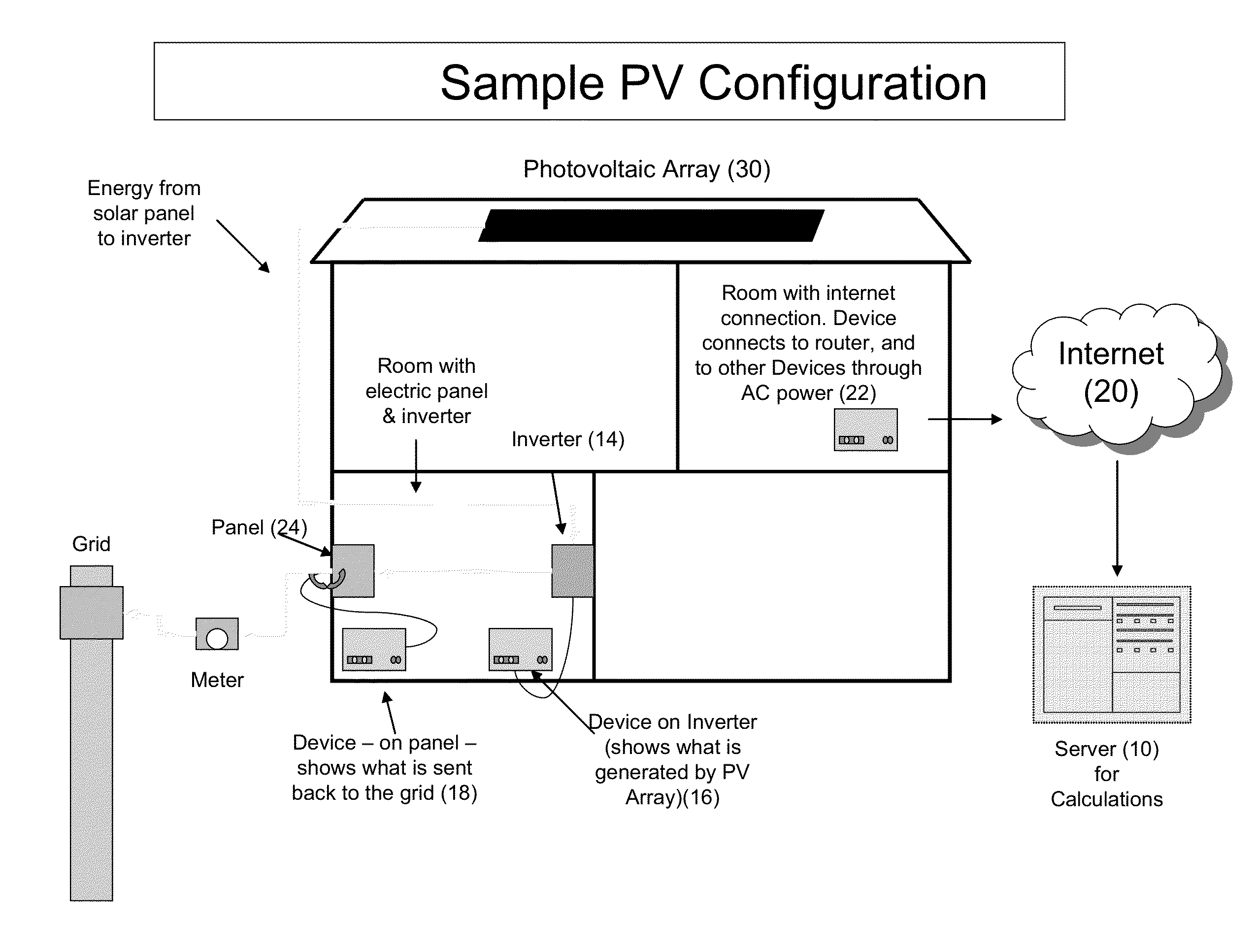
Weather and satellite model for estimating solar irradiance
ActiveUS20130166266A1Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkNatural satelliteThe Internet
Solar irradiance, the energy from the Sun's electromagnetic radiation, has a wide range of applications from meteorology to agronomy to solar power. Solar irradiance is primarily determined by a location's spatial relationship with the Sun and the atmospheric conditions that impact the transmission of the radiation. The spatial relationship between the Sun and a location on Earth is determined by established astronomical formulas. The impact of atmospheric conditions may be estimated via proxy using pixels from satellite imagery. While satellite-based irradiance estimation has proven effective, availability of the input data can be limited and the resolution is often incapable of capturing local weather phenomena. Brief qualitative descriptions of general atmospheric conditions are widely available from internet weather services at higher granularity than satellite imagery. This methodology provides logic for quantifying the impact of qualitative weather observations upon solar irradiance, and the integration of this methodology into solar irradiance estimation models.
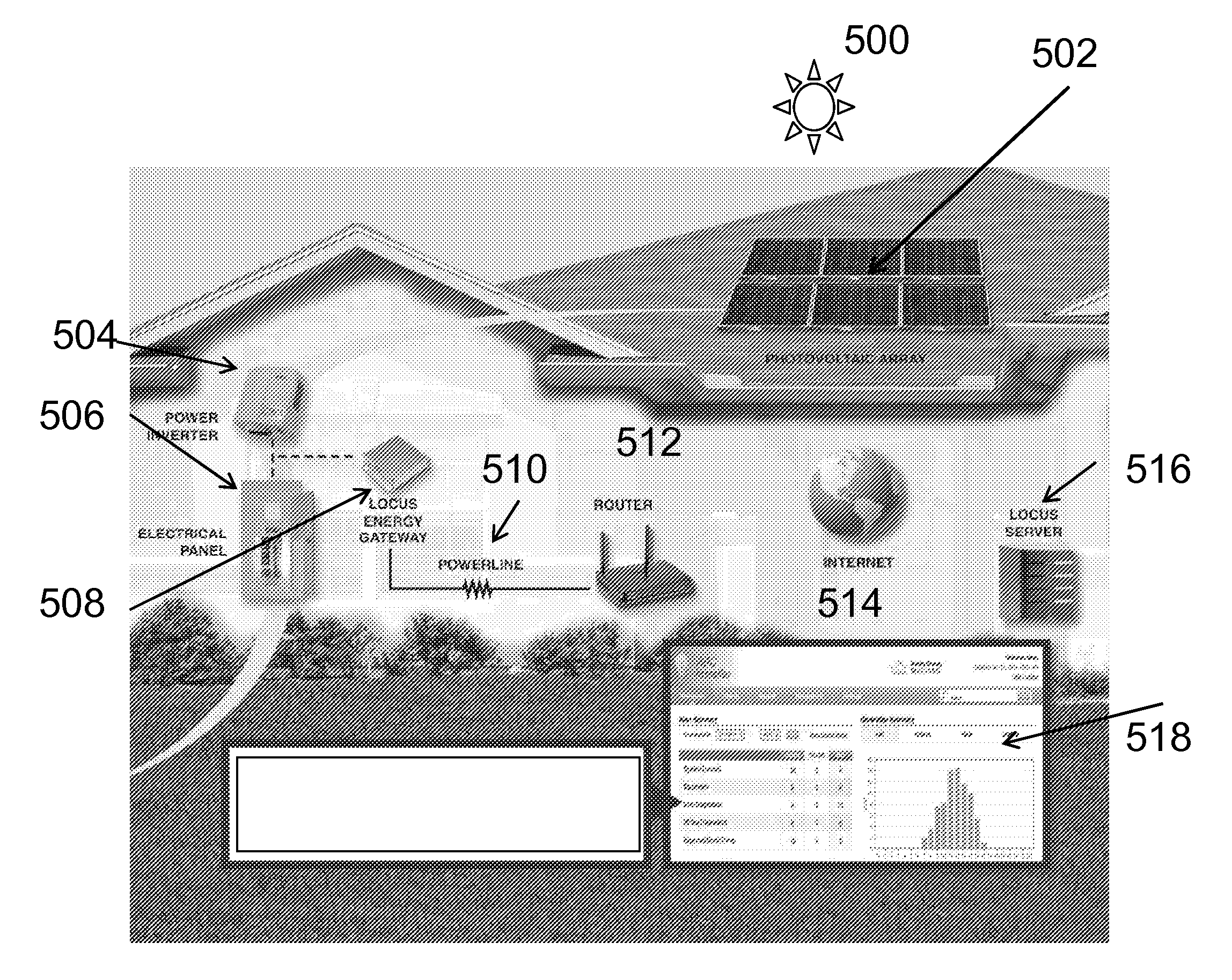
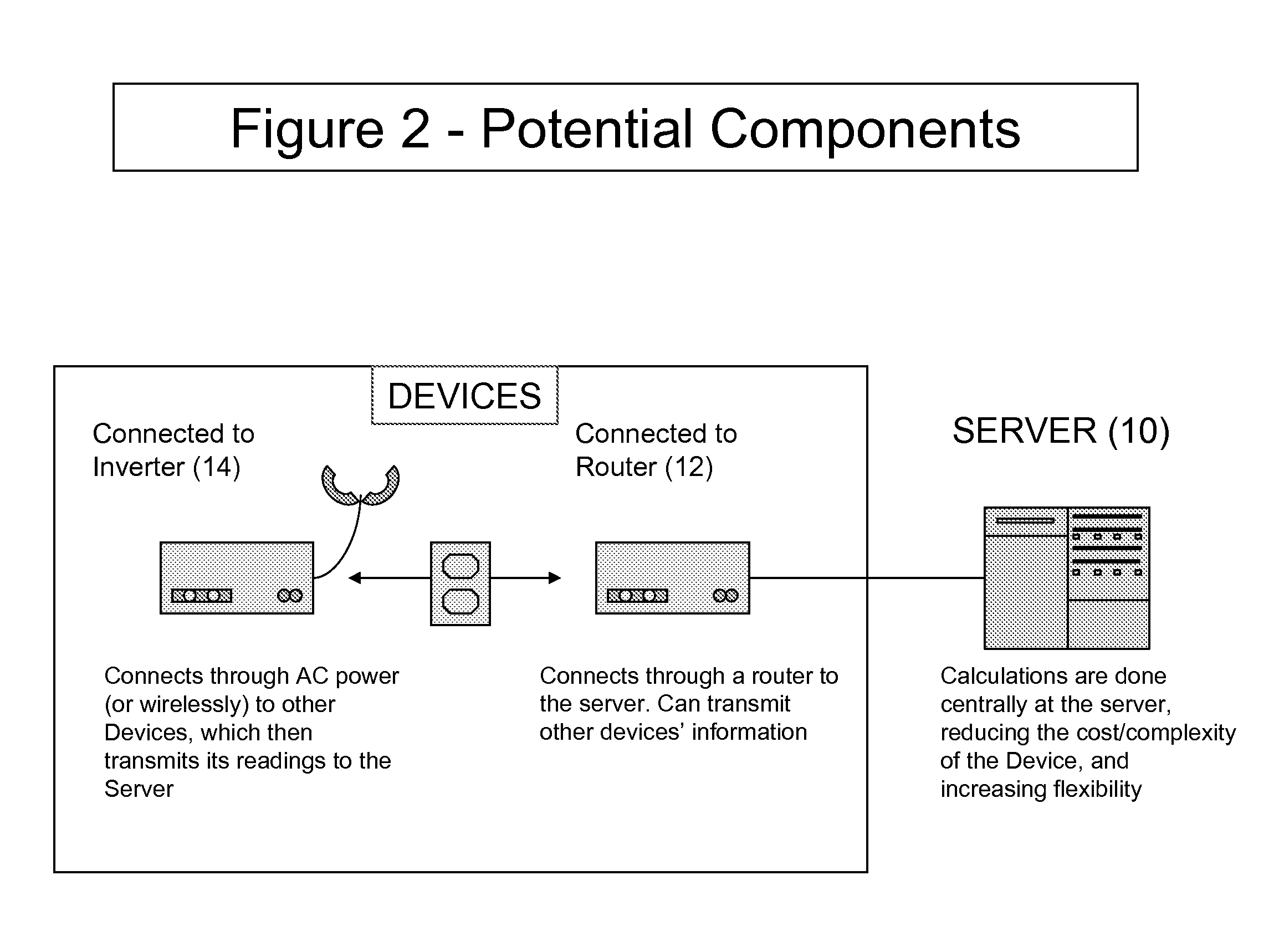
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
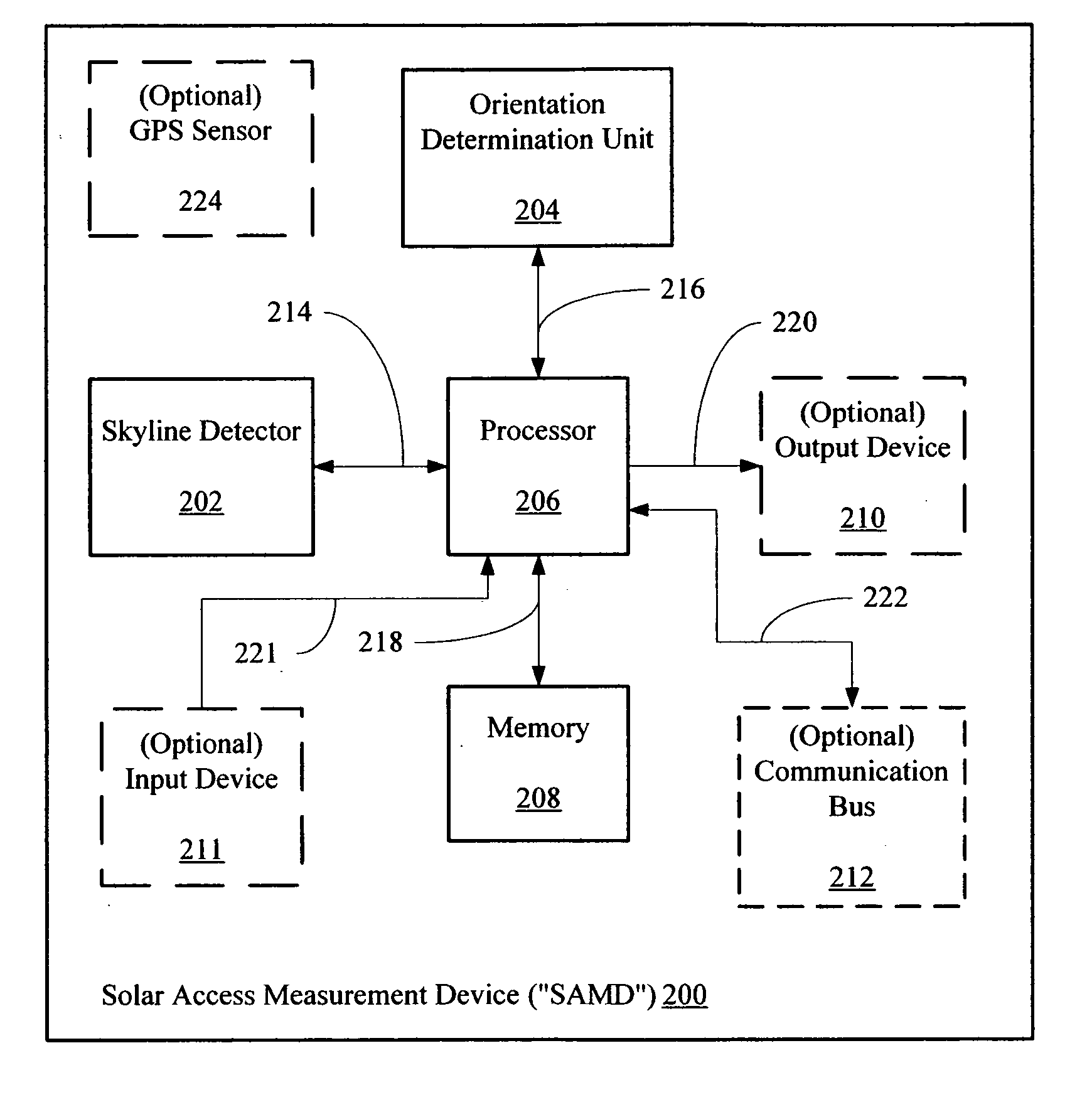
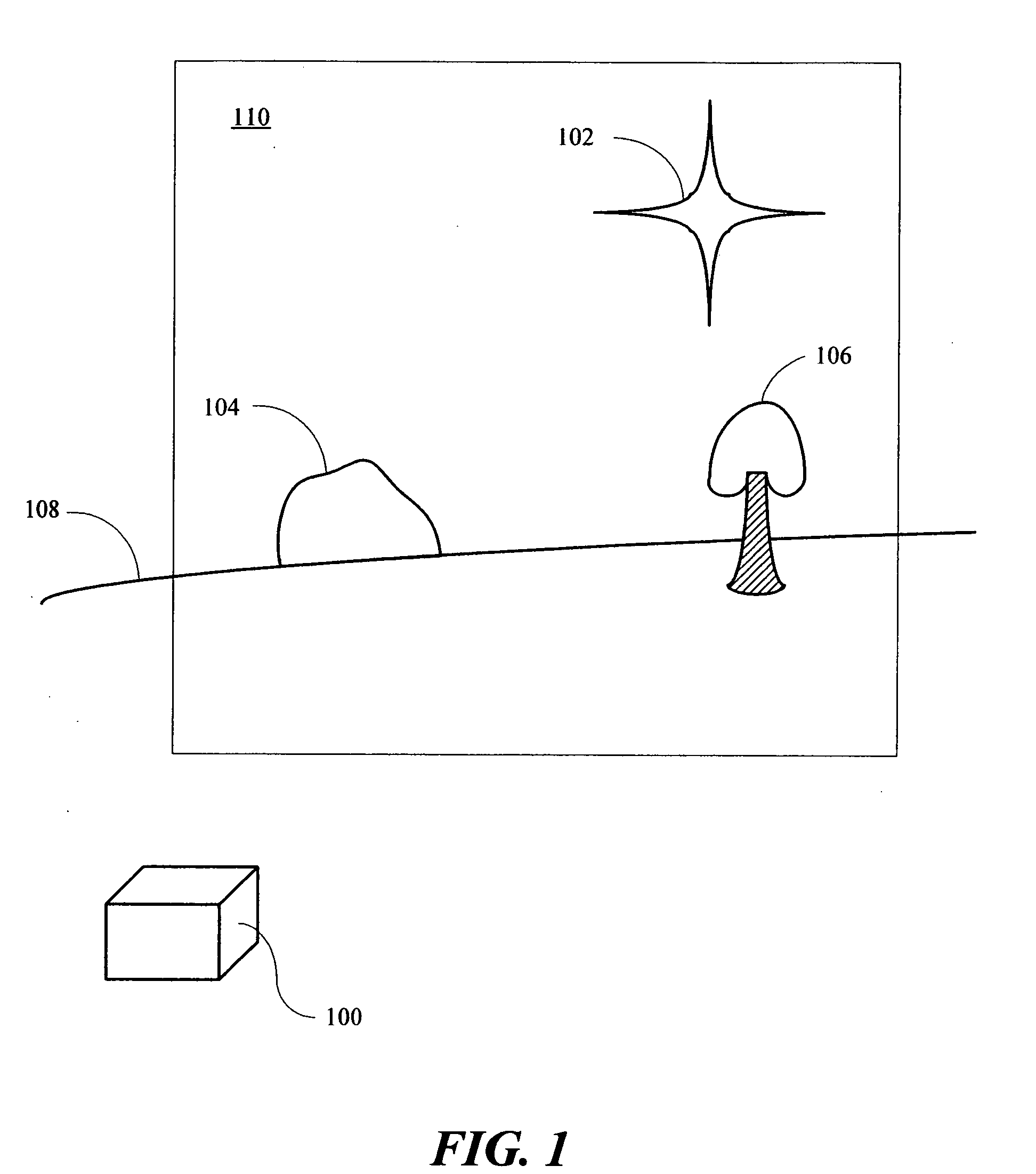
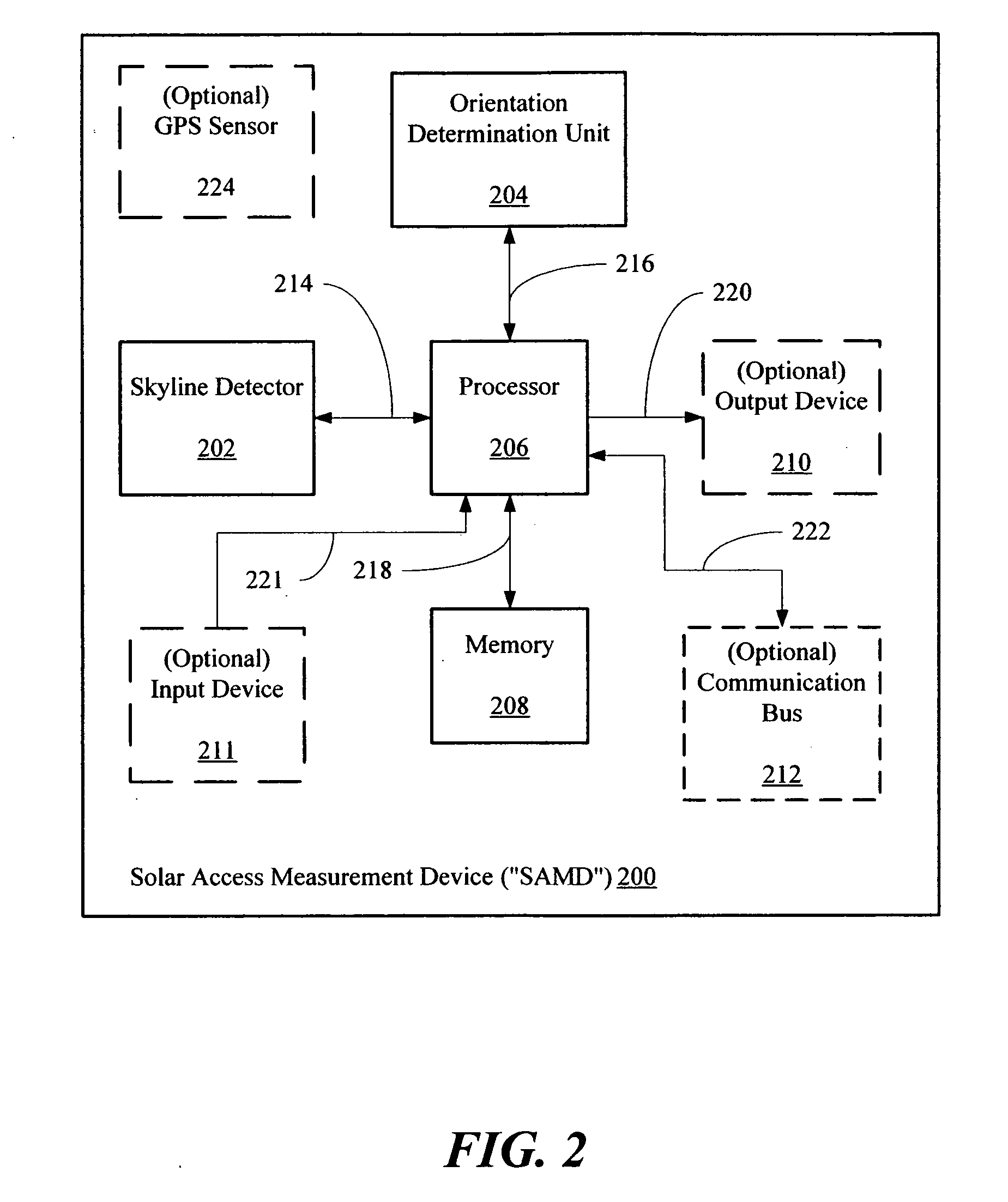
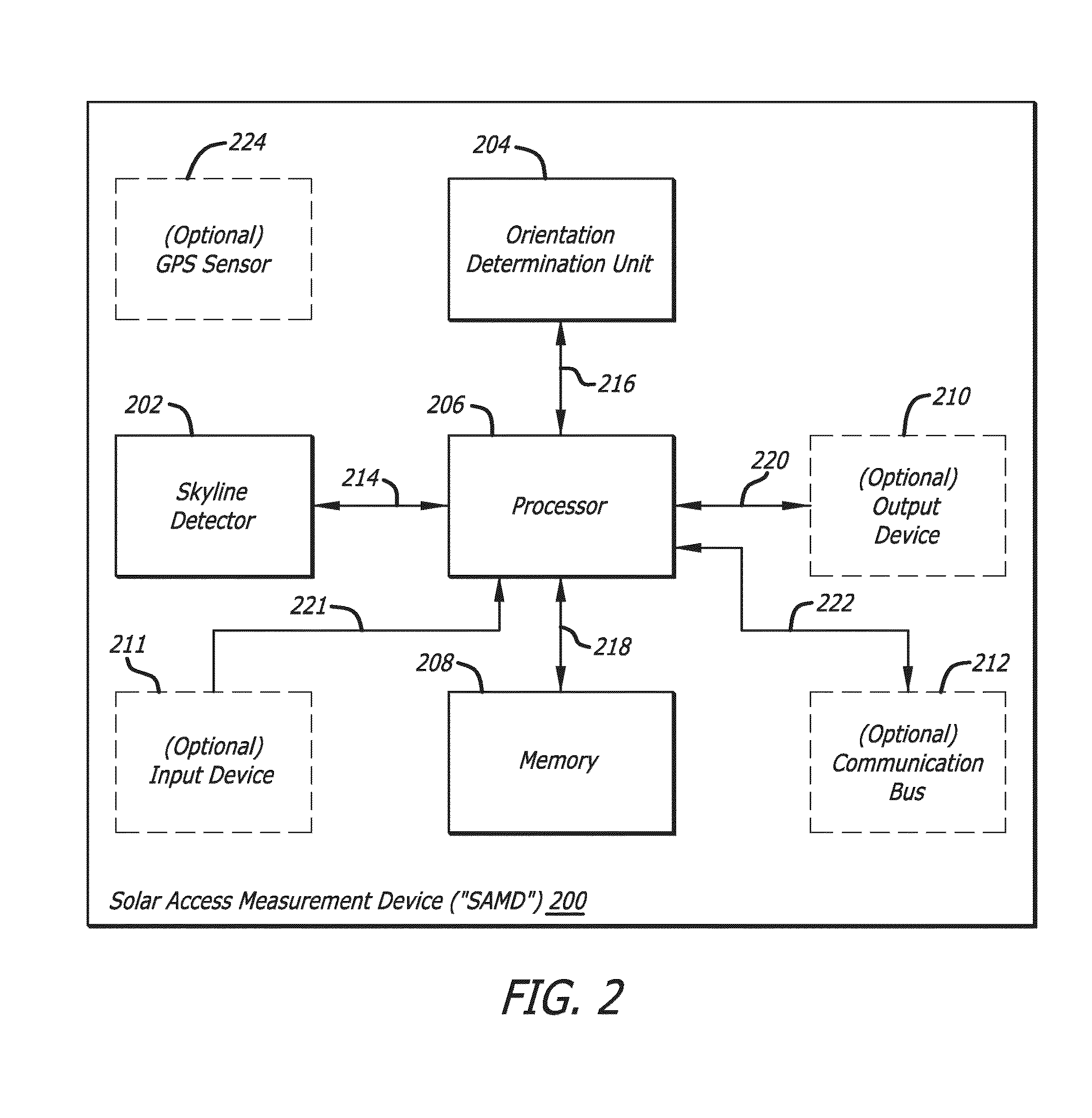
Solar access measurement device
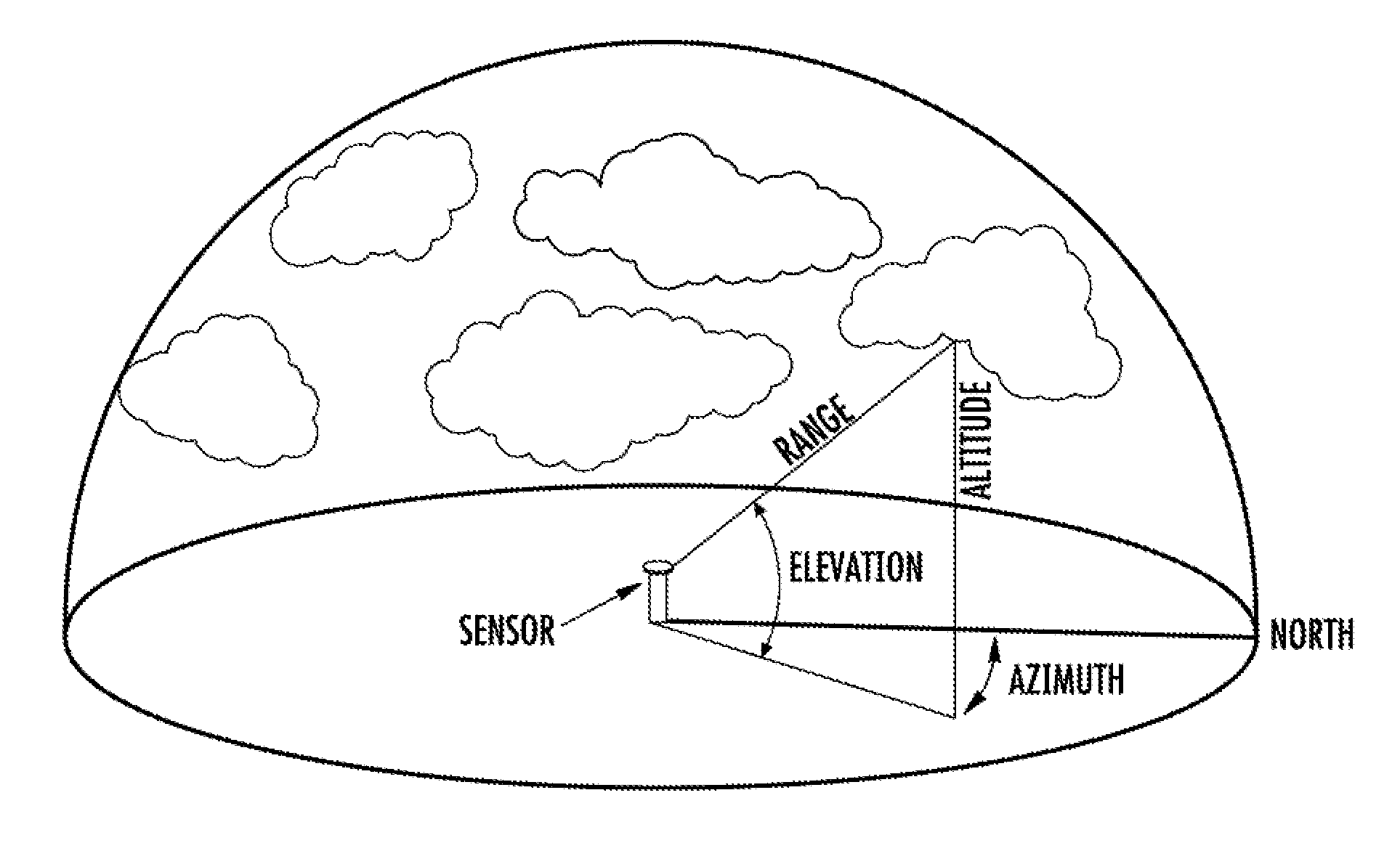
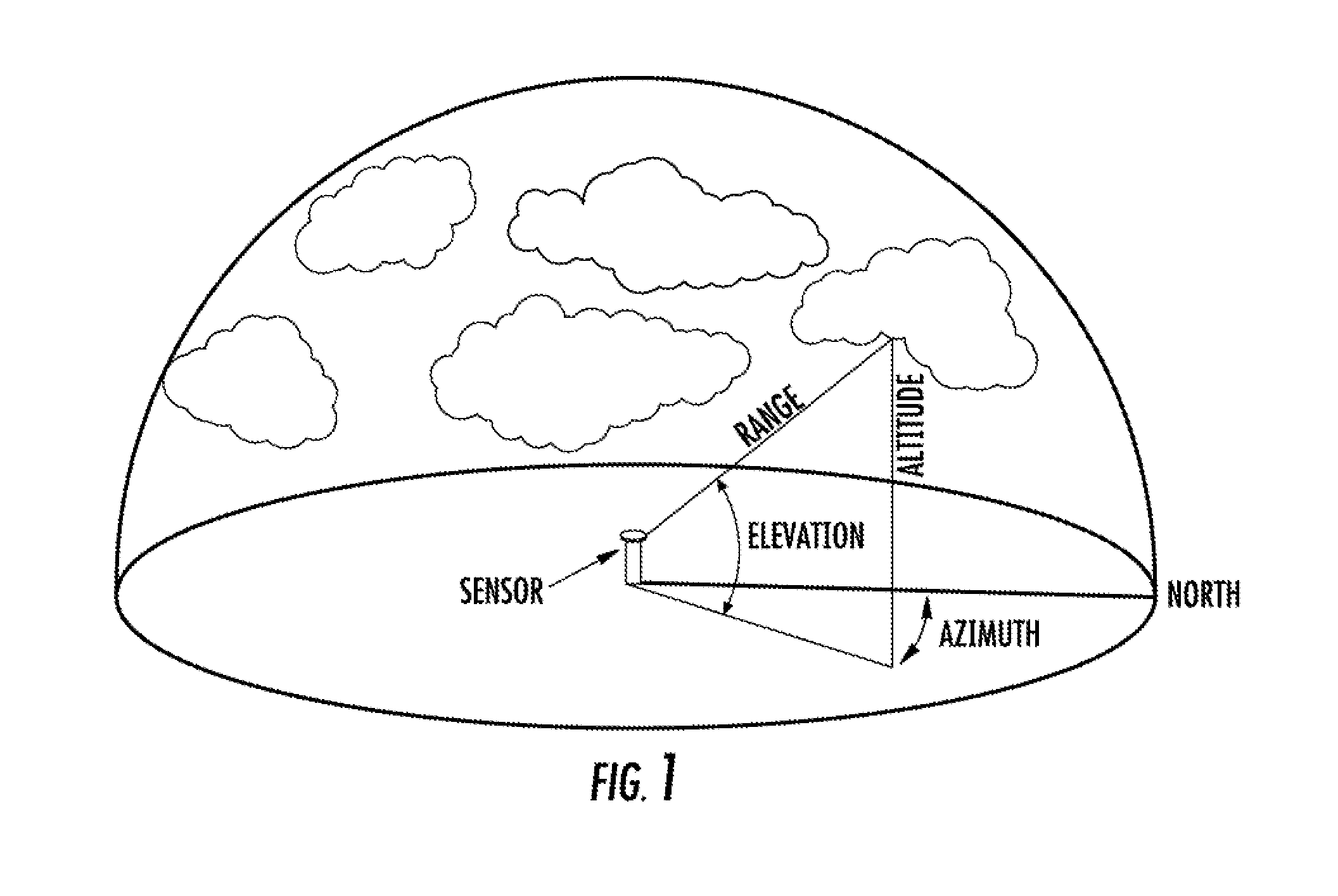
A Solar Access Measurement Device (“SAMD”) located at a predetermined position is disclosed. The SAMID may include a skyline detector enabled to detect a skyline of a horizon relative to the SAMD, an orientation determination unit enabled to determine the orientation of the skyline detector, and a processor in signal communication with the skyline detector and orientation determination unit.
Owner:SOLMETRIC
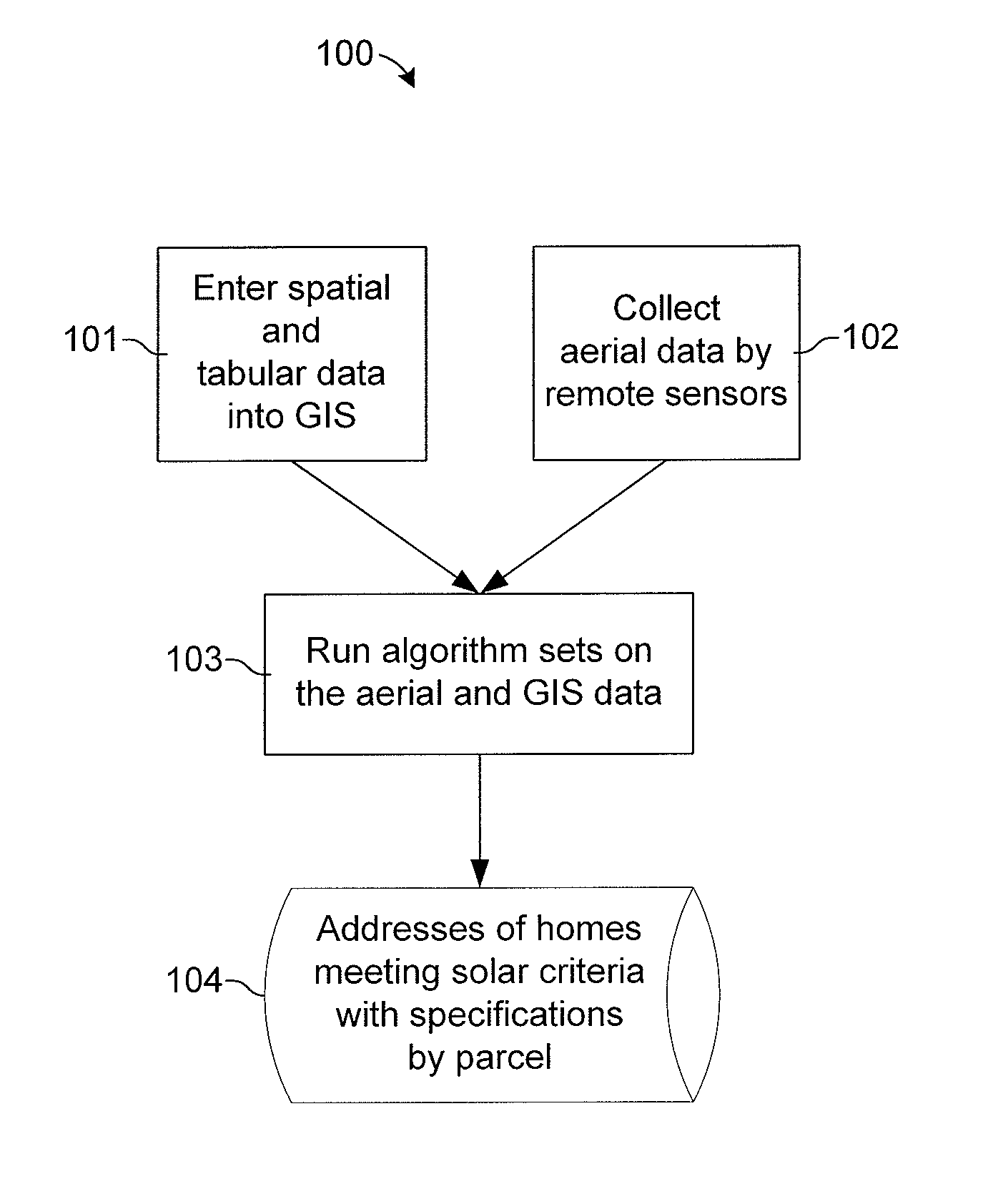
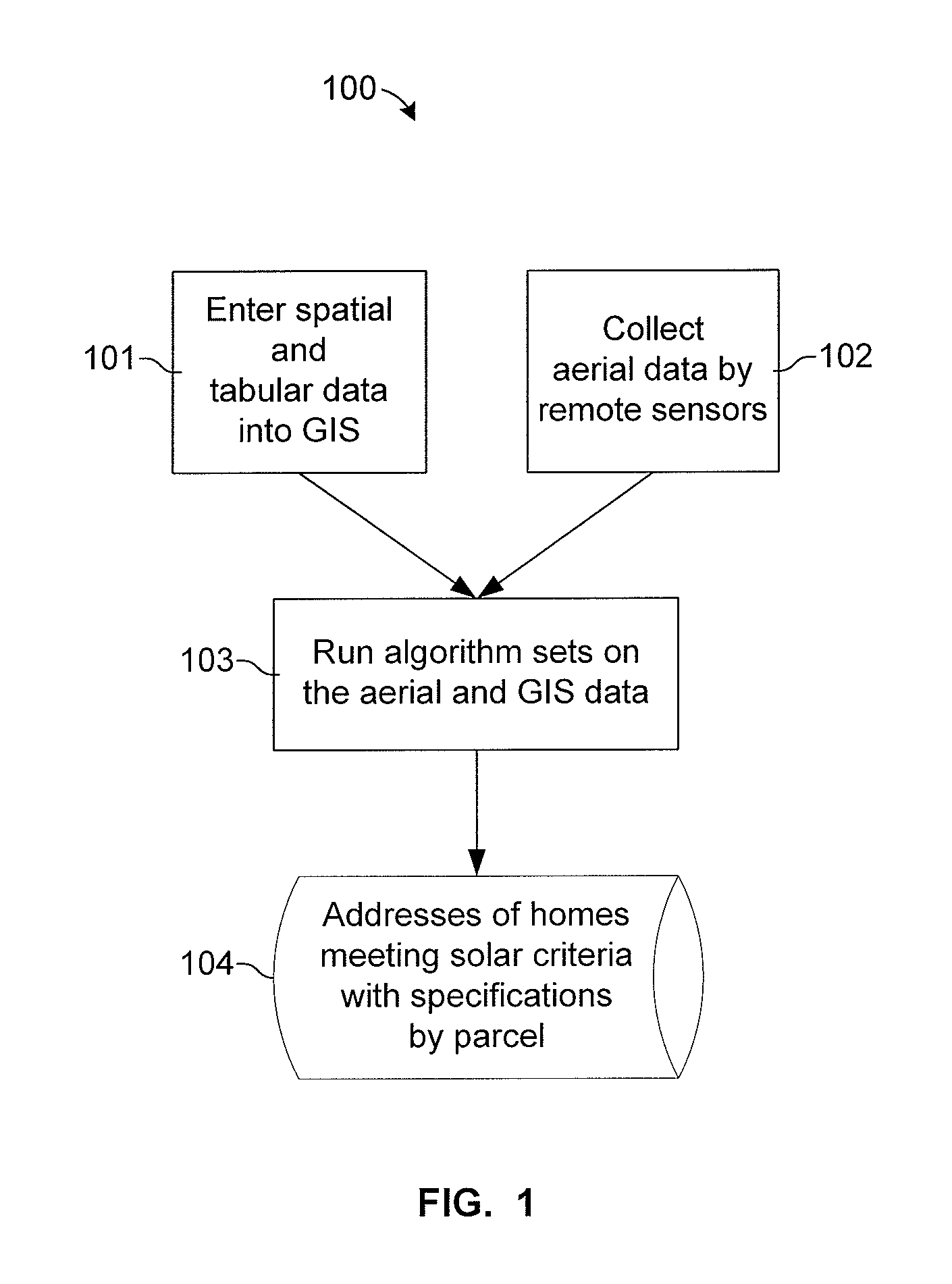
System And Method For Identifying The Solar Potential Of Rooftops
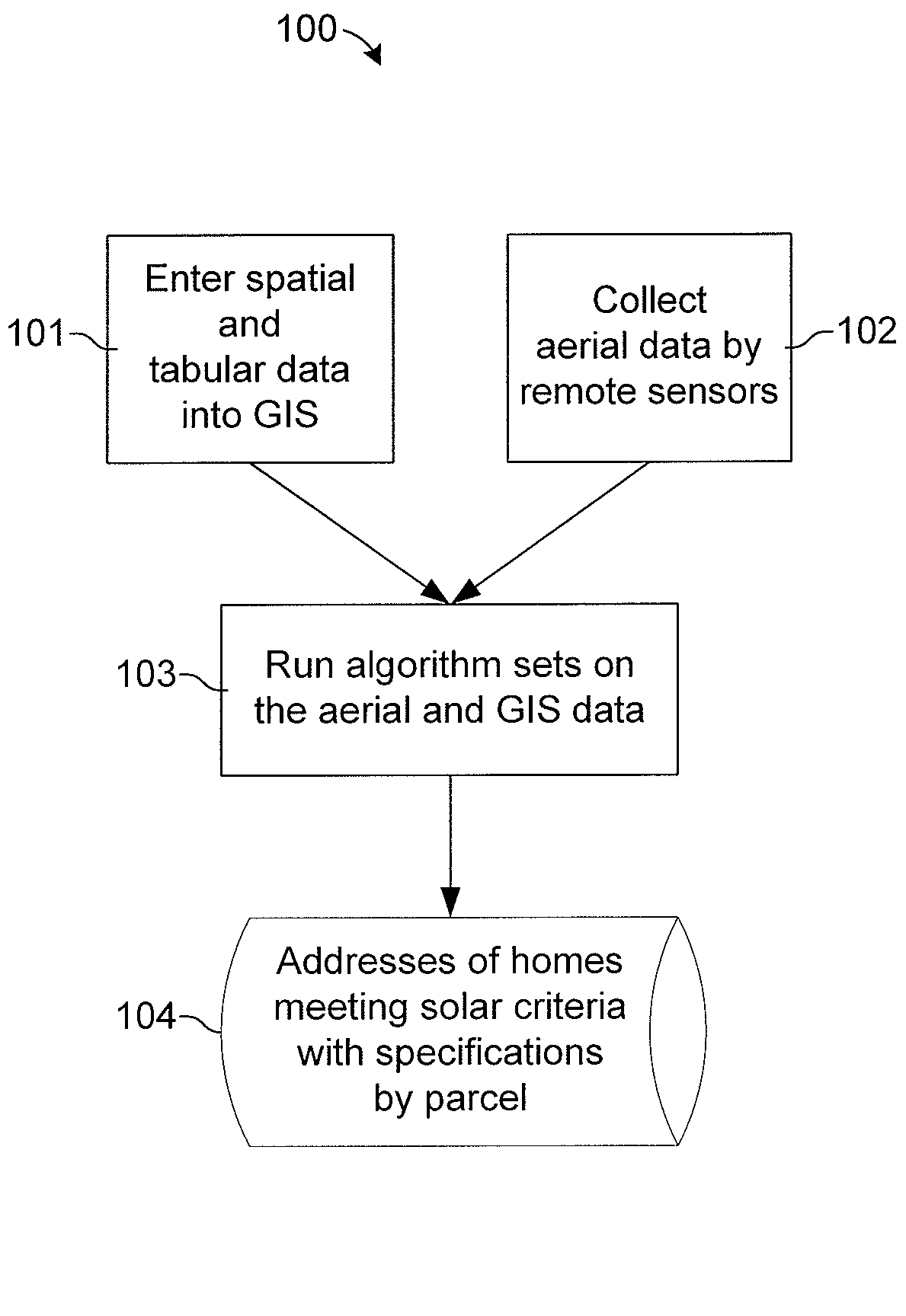
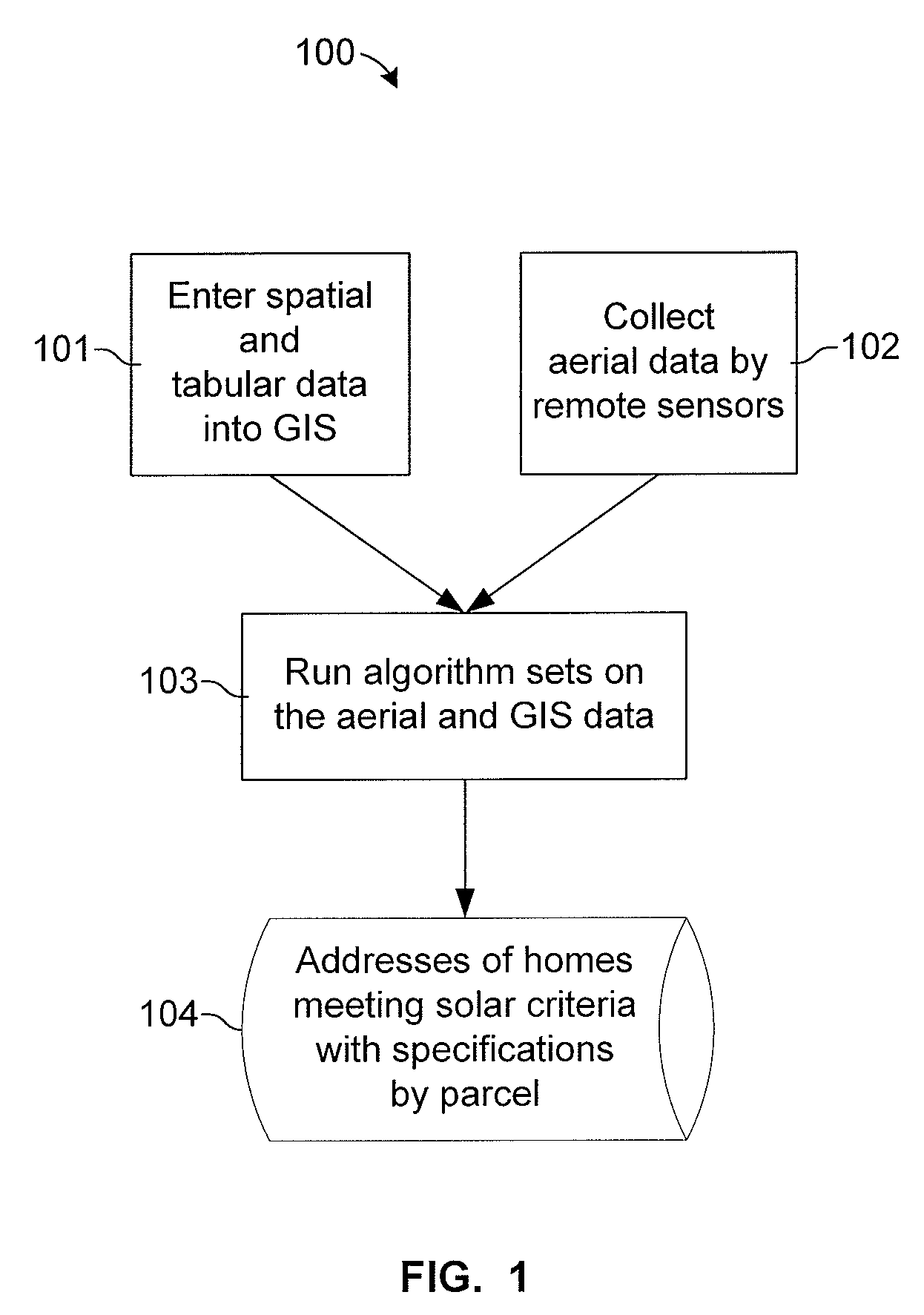
A system and method for identifying the solar potential of rooftops. In one embodiment, solar-potential criteria and three-dimensional spatial data and tabular data, for a selected area including parcels on which the rooftops are located, are entered into a geographic information system. Three-dimensional aerial data of the selected area, including the rooftops in the selected area, is collected. Solar azimuth and altitude angles are calculated for regular intervals to generate shadow simulation data representing shadows cast onto the rooftops by obstructions. The shadow simulation data is intersected with the XYZ coordinates of the rooftop shapes, as determined from the aerial data, to generate rooftop shade patterns for specific intervals over a specific period of time. The tabular data and the rooftop shade patterns are then used to determine addresses and per-parcel specifications of buildings having said rooftops meeting the solar-potential criteria.
Owner:PENDULUM IP LLC
Method for predicting and mitigating power fluctuations at a photovoltaic power plant due to cloud cover
ActiveUS20150134251A1Avoid sudden changesSunshine duration recordersMechanical power/torque controlIlluminanceCombined use
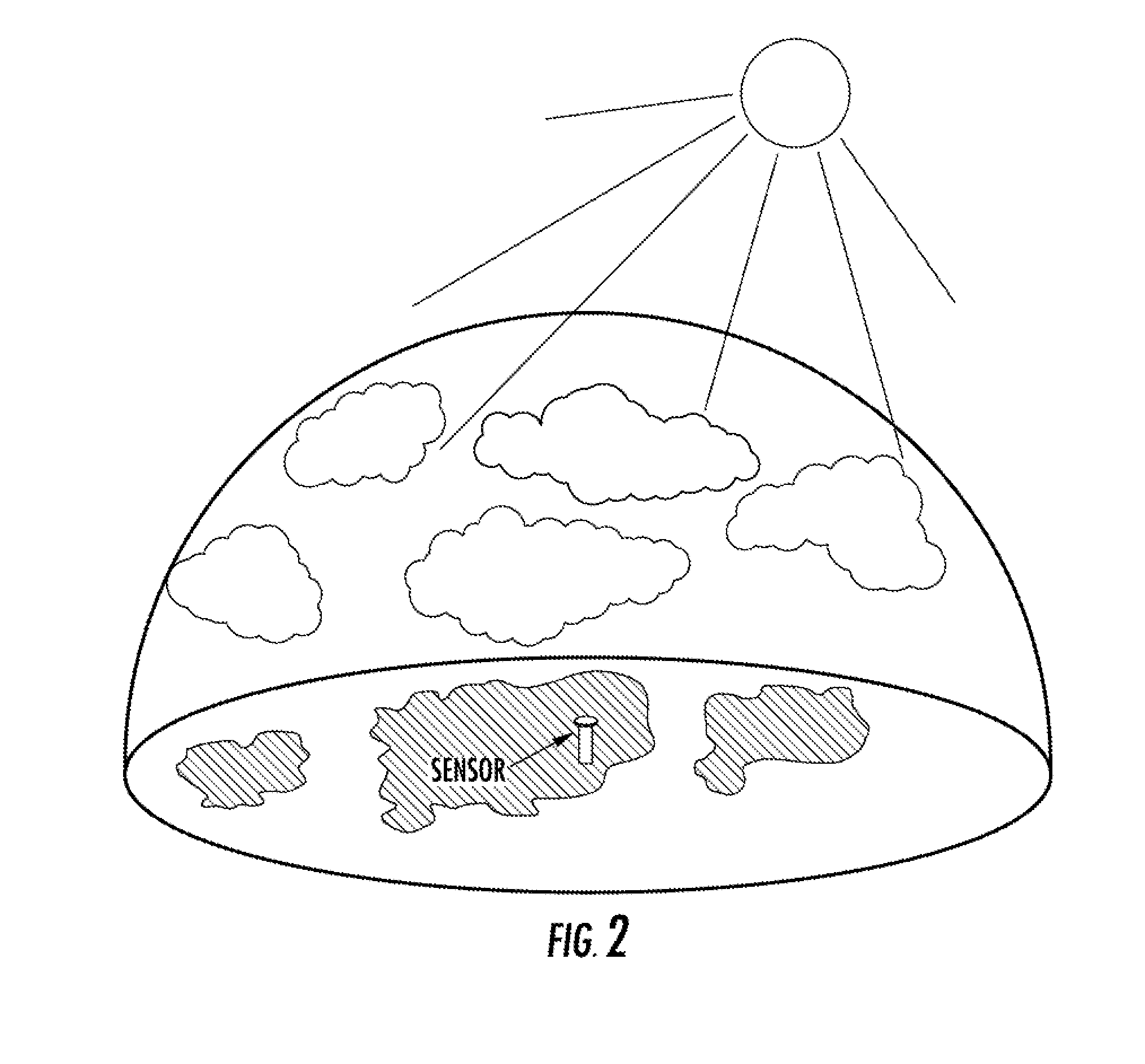
A method for forecasting reduction in sunlight intensity due to cloud cover at a photovoltaic power plant is described. The method comprises determining characteristics of one or more clouds from sensors surrounding the photovoltaic power plant. The cloud characteristics are used to create a 3D map of the clouds. The 3D map in combination with information on the angle of the sun is used to create a 3D projection on the surface of the earth, resulting in a 2D surface irradiance map. The 2D surface irradiance map may be taken in successive projections or used in combination with wind speed data to forecast fluctuation in irradiance at the photovoltaic power plant. The forecasted reductions in power may be used to enact measures at the plant such as reducing the power output of inverters to prevent sudden fluctuations in the power output of the photovoltaic plant feeding the utility.
Owner:TMEIC
System and method for identifying the solar potential of rooftops
A system and method for identifying the solar potential of rooftops. In one embodiment, solar-potential criteria and three-dimensional spatial data and tabular data, for a selected area including parcels on which the rooftops are located, are entered into a geographic information system. Three-dimensional aerial data of the selected area, including the rooftops in the selected area, is collected. Solar azimuth and altitude angles are calculated for regular intervals to generate shadow simulation data representing shadows cast onto the rooftops by obstructions. The shadow simulation data is intersected with the XYZ coordinates of the rooftop shapes, as determined from the aerial data, to generate rooftop shade patterns for specific intervals over a specific period of time. The tabular data and the rooftop shade patterns are then used to determine addresses and per-parcel specifications of buildings having said rooftops meeting the solar-potential criteria.
Owner:PENDULUM IP LLC
Solar access measurement
ActiveUS20170263049A1Sunshine duration recordersDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsSkyEngineering
A method of determining solar radiation exposure at a predetermined location is provided. The method may include generating a first two-dimensional (2D) matrix including a plurality of elements, wherein each element of the plurality of elements of the first 2D matrix includes an elevation / azimuth pair representing a light ray extending from the predetermined location to one or more positions in the sky. The method may further include generating a second 2D matrix including a plurality of elements, wherein each index of the second 2D matrix includes an associated elevation / azimuth pair of the first 2D matrix. Each element of the plurality of elements of the second 2D matrix represents an amount of solar radiation to impinge on the predetermined location from a direction of a respective elevation / azimuth pair.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
Streetlight monitoring and control
ActiveUS8290710B2Sunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkMicrocontrollerEngineering
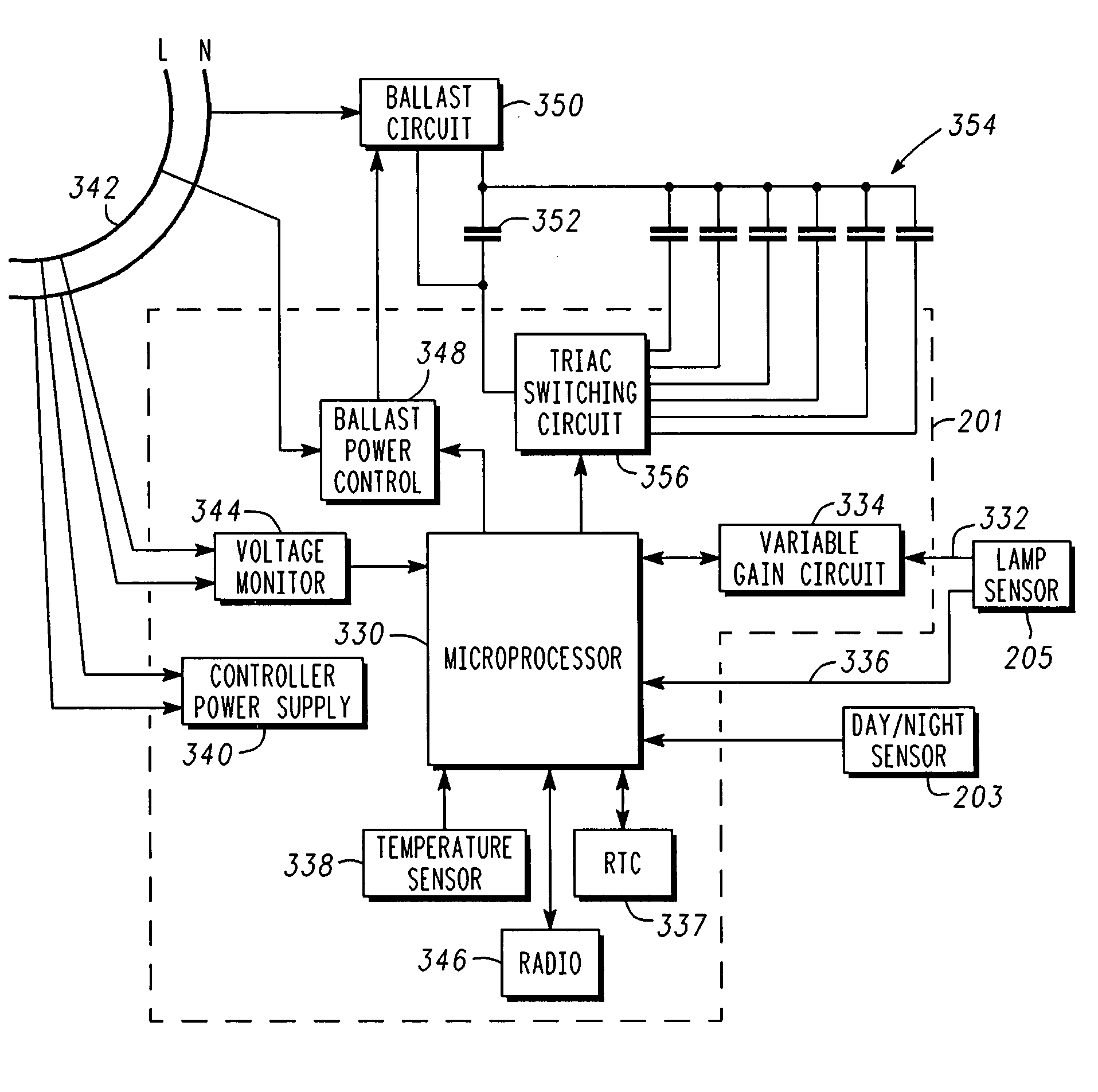
Methods and apparatus associated with monitoring and controlling streetlights include monitoring light levels and voltage levels at corresponding streetlights and controlling the streetlights to set or maintain a particular light output at the respective streetlights or providing power consumption estimates for respective streetlights (streetlight specific metering) based on the voltage levels and light levels. A streetlight controller for a streetlight includes a microcontroller; a first sensor to sense a light level from a lamp within the streetlight; a second sensor operative to sense a voltage level on a power supply for the streetlight; and a switching network coupled with the microcontroller and operative to adjust the light level of the lamp. Methods includes monitoring a light level and voltage level and adjusting a light level, estimating power consumption, or facilitating maintenance in accordance with the light level and voltage level. The methods may be performed all or in part at a streetlight, a local gateway or a central controller and database.
Owner:STREETLIGHT INTELLIGENCE INC +1
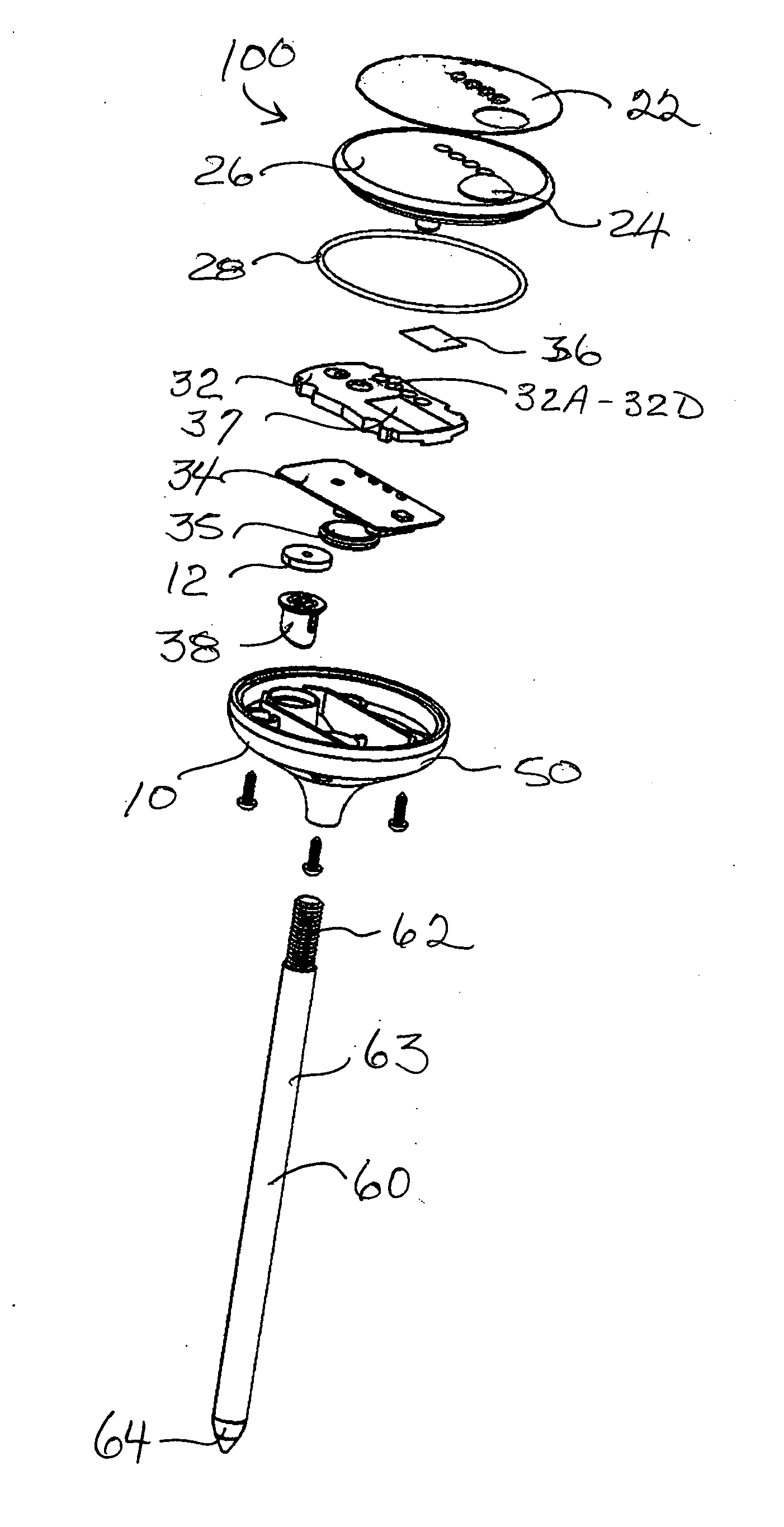
Methods and systems for solar shade analysis
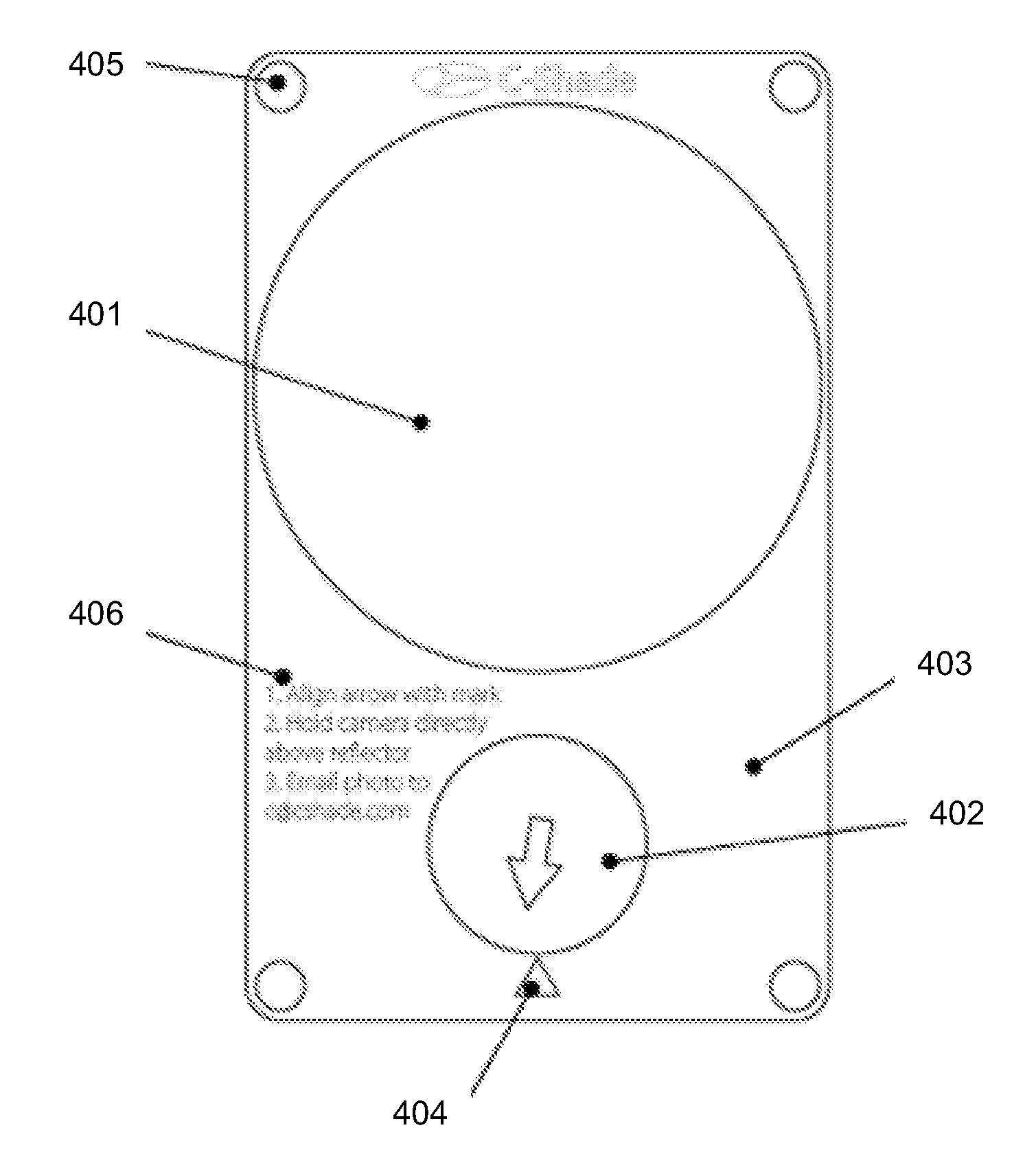
A device for performing solar shade analysis combines a spherical reflective dome and a ball compass mounted on a platform, with a compass alignment mark and four dots in the corners of the platform. A user may place the device on a surface of a roof, or in another location where solar shading analysis is required. A user, while standing above the device can take a photo of the device. The photographs can then be used in order to evaluate solar capacity and perform shade analysis for potential sites for solar photovoltaic systems. By using the device in conjunction with a mobile device having a camera, photographs may be taken and uploaded, to be analyzed and processed to determine a shading percentage. For example, the solar shade analysis system may calculate the percentage of time that the solar photovoltaic system might be shaded for each month of the year. These measurements and data, or similar measurements and data, may be valuable when applying for solar rebates or solar installation permits.
Owner:ARMAGEDDON ENERGY
Estimating solar irradiance components from plane of array irradiance and global horizontal irradiance
ActiveUS20120191351A1Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkDirect normal irradianceAtmospheric model
A computer implemented method of estimating at least one solar irradiance component, the method comprising: obtaining a sensor measurement from an instrument to provide a measured global horizontal irradiance (GHImeasured), wherein the measured global horizontal irradiance (GHImeasured) consists of at least an estimated diffuse horizontal irradiance (DHIestimated) and an estimated direct normal irradiance (DNIestimated); providing at least one modeled component, wherein at least one of the modeled components is a modeled global horizontal irradiance based on an atmospheric model (GHImodel); calculating an irradiance estimate modifier (IMOD) in a computing device according to the measured global horizontal irradiance (GHImeasured) and the modeled global horizontal irradiance (GHImodel); and providing at least one estimated solar irradiance component by a computing device according to the irradiance estimate modifier (IMOD) and at least one modeled component.
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
Multifunctional Sky Camera System for Total Sky Imaging and Spectral Radiance Measurement
InactiveUS20140320607A1Sunshine duration recordersImage enhancementSpatial light modulatorOptical flow
A multifunctional sky camera system and techniques for the use thereof for total sky imaging and spectral irradiance / radiance measurement are provided. In one aspect, a sky camera system is provided. The sky camera system includes an objective lens having a field of view of greater than about 170 degrees; a spatial light modulator at an image plane of the objective lens, wherein the spatial light modulator is configured to attenuate light from objects in images captured by the objective lens; a semiconductor image sensor; and one or more relay lens configured to project the images from the spatial light modulator to the semiconductor image sensor. Techniques for use of the one or more of the sky camera systems for optical flow based cloud tracking and three-dimensional cloud analysis are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Solar power monitoring and predicting of solar power output
InactiveUS20120166085A1Sunshine duration recordersSolar heating energyElectric power systemEngineering
A computer to improve prediction of solar output for a solar power system that includes a processor and a memory. The memory has software code which when executed causes the computer to receive power output data from the solar power system, calculate a statistical mean of the power output data, receive solar hour information from an almanac system and generate an almanac predicted power output for the solar power system for the specified time period. The computer receives weather information for the specified time period from a weather predicting source and calculates a weather prediction-to-solar almanac ratio based on a comparison of the solar hour information to the weather information. The computer generates a predicted power output for the specified time period by multiplying the almanac predicted power output for the solar power system by the weather prediction-to-solar almanac ratio and stores the predicted power output for the specified time period.
Owner:GEVORKIAN PETER
Method and system for solar power forecasting
InactiveUS20180275314A1Sunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkData packPower station
A method for generating a solar power output forecast for a solar power plant, comprising: using a processor, in a training mode, generating a trained artificial intelligence model using historical output data and historical input data including historical physical subsystem input data and historical physical subsystem forecasts for the solar power plant; in a runtime mode, for a predetermined forecast horizon, applying the trained artificial intelligence model to current input data including current physical subsystem input data and current physical subsystem forecasts for the solar power plant to produce the solar power output forecast; and, presenting the solar power output forecast on a display.
Owner:GREEN POWER LABS INC
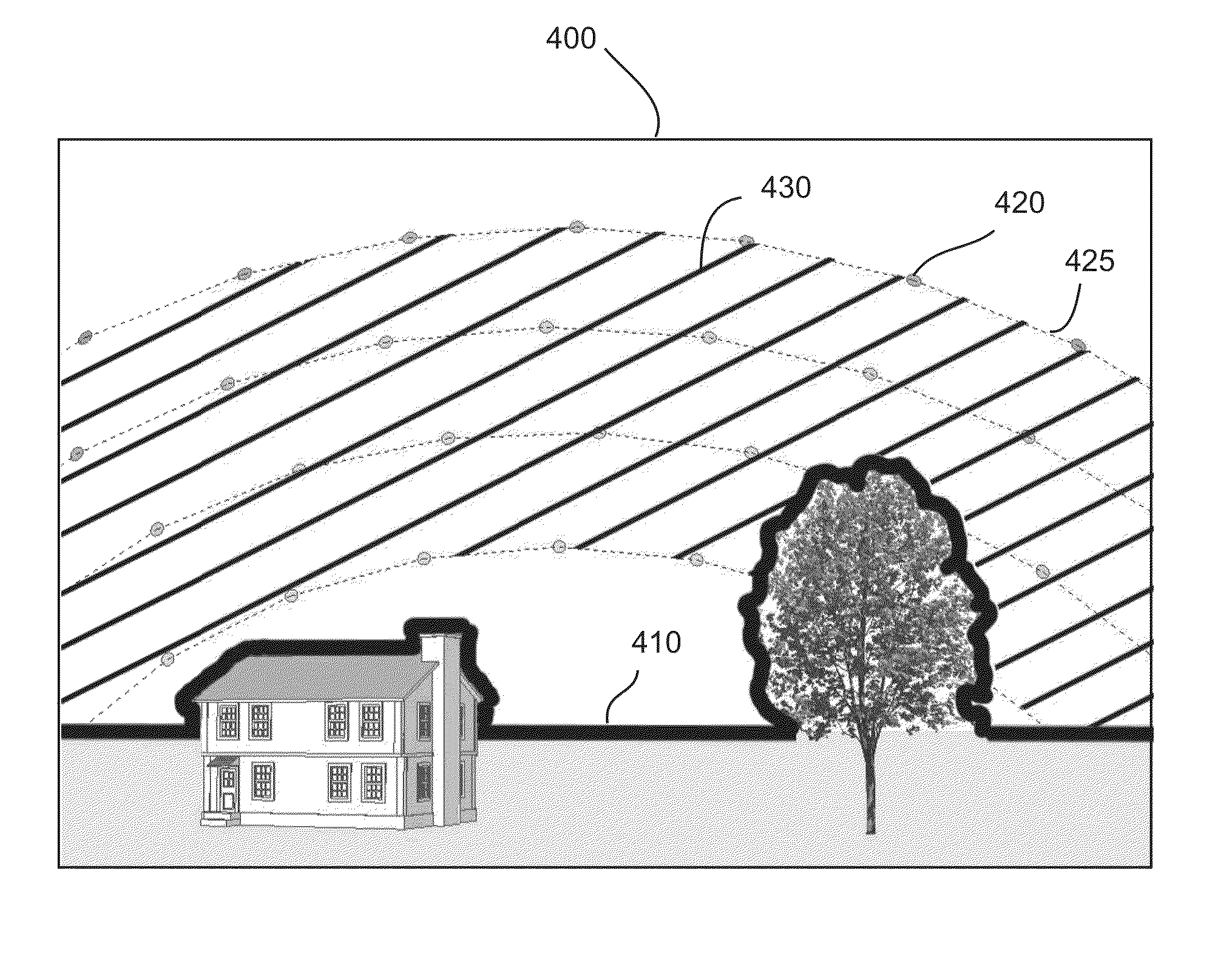
Solar site selection apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070214665A1Easy to adjustIncrease solar energy potentialSunshine duration recordersSolar heating energyEngineeringDigital image
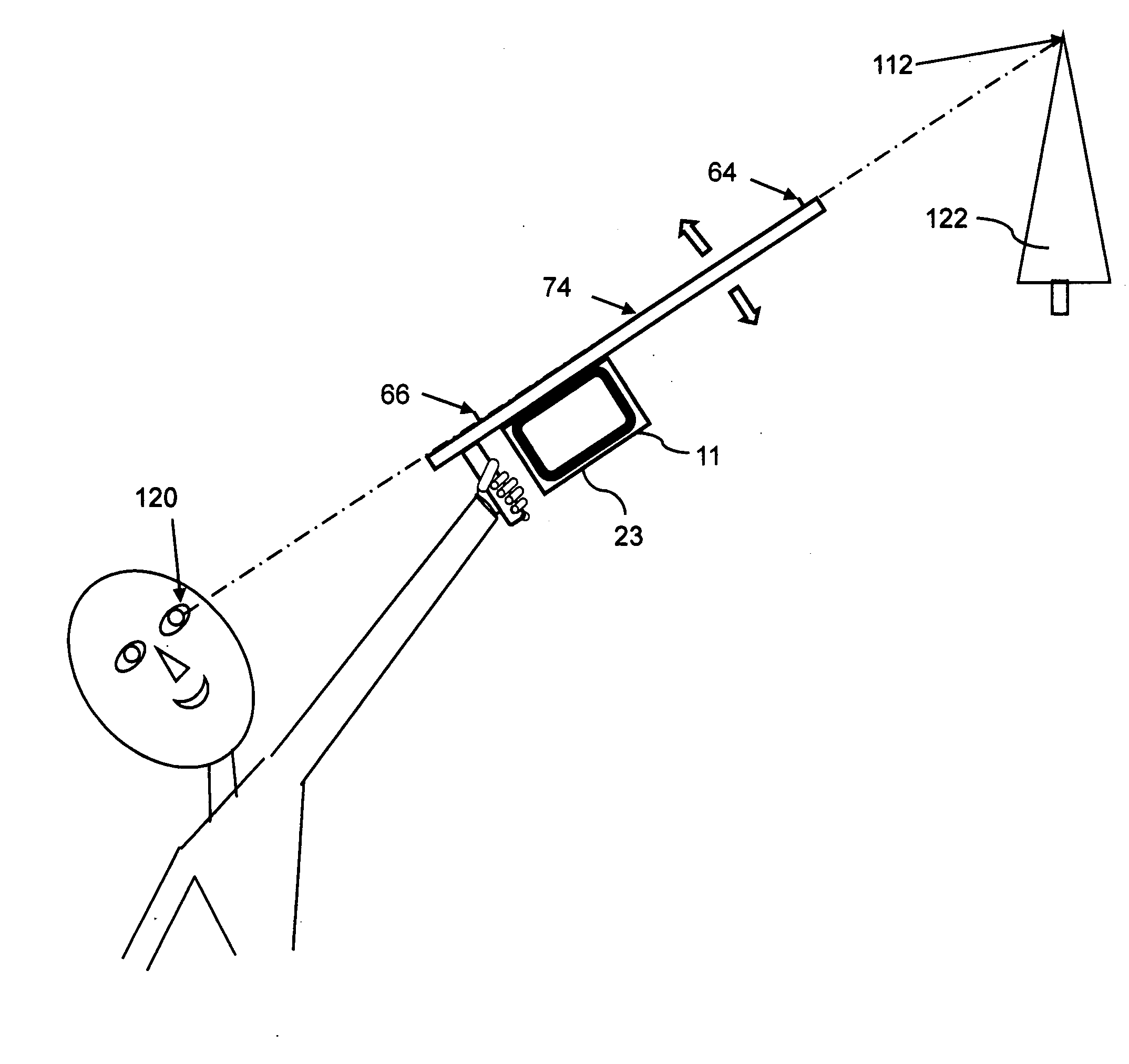
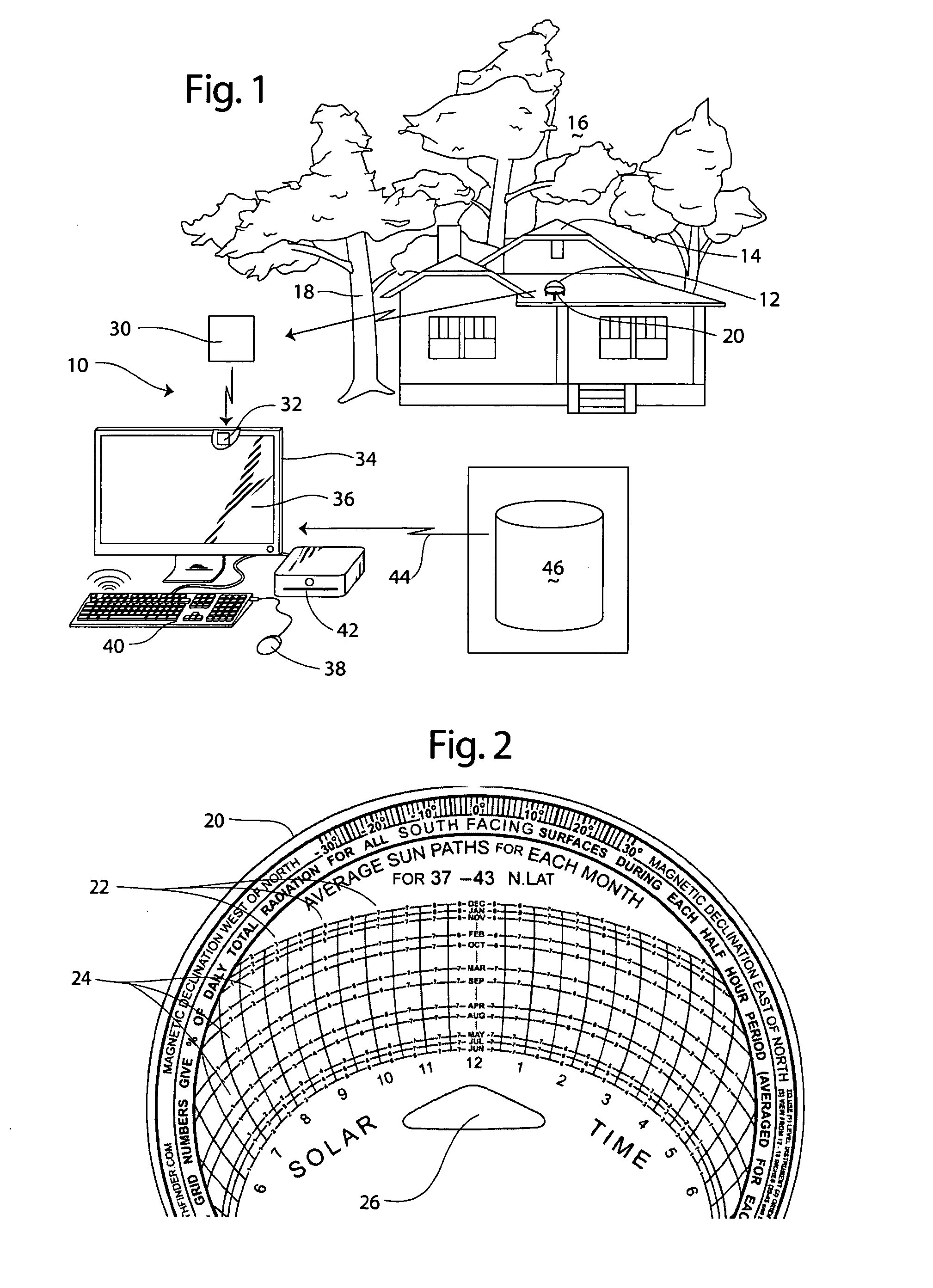
An apparatus receives a digital image of a sun trace chart having time gradient lines and a sun trace extent line for a site. A selector defines on a display points along the solar trace extent line to define a solar opportunity region. An adjuster adjusts the digital image based on the magnetic declination of the site. The solar exposure potential is determined based on the proportion of solar trace extent lines within solar opportunity region and potential solar exposure. Site adjustments to increase solar energy potential are facilitated. A method of evaluating a site for solar energy potential is disclosed. A solar exposure device for recording and analyzing a solar trace is disclosed.
Owner:COURTER ANTHONY
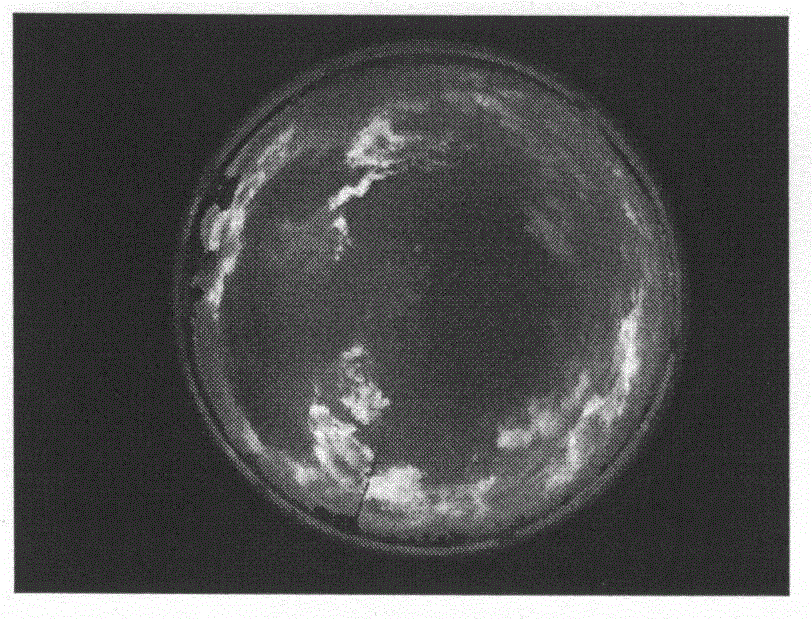
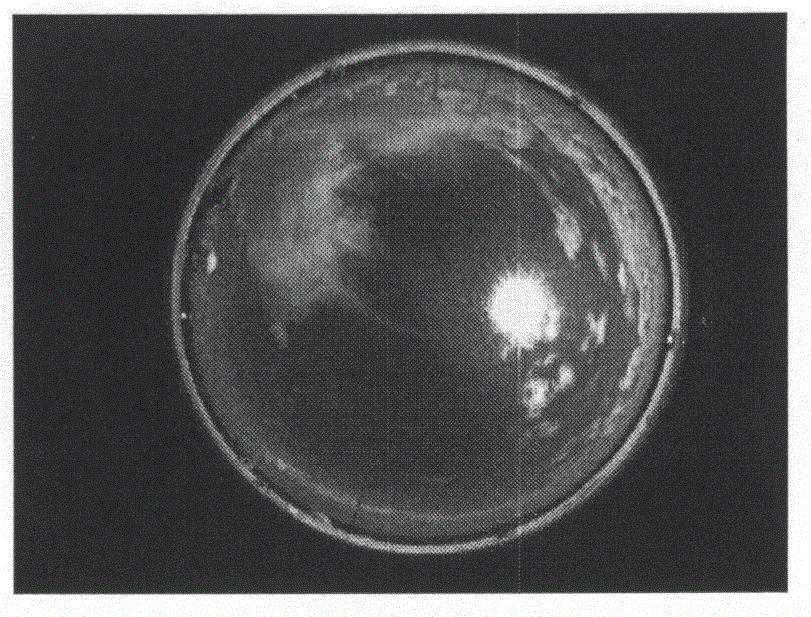
Shade analysis device
InactiveUS20100302363A1Quantity maximizationSunshine duration recordersSurveying instrumentsArray data structureSky
A shade analysis device includes an accelerometer providing samples that represent an elevation defined by a sighting reference, an electronic compass providing samples that represent an azimuth heading defined by the sighting reference, and a processor under the control of a program included in the shade analysis device, acquiring an array of the samples that represent an azimuth heading and an array of corresponding samples that represent the elevation, in response to tracing with the sighting reference, a skyline at an interface between an open sky and at least one solar obstruction over a range of azimuth headings.
Owner:SOLMETRIC
Solar site selection apparatus and method
InactiveUS7516557B2Easy to adjustIncrease solar energy potentialSunshine duration recordersAngle measurementEngineeringDigital image
An apparatus receives a digital image of a sun trace chart having time gradient lines and a sun trace extent line for a site. A selector defines on a display points along the solar trace extent line to define a solar opportunity region. An adjuster adjusts the digital image based on the magnetic declination of the site. The solar exposure potential is determined based on the proportion of solar trace extent lines within solar opportunity region and potential solar exposure. Site adjustments to increase solar energy potential are facilitated. A method of evaluating a site for solar energy potential is disclosed. A solar exposure device for recording and analyzing a solar trace is disclosed.
Owner:COURTER ANTHONY
Sunlight measuring device
InactiveUS20060038983A1Accurate measurementSunshine duration recordersColor/spectral properties measurementsMeasurement deviceVisual perception
A sunlight measuring device that quantifies the accumulation of light at a particular site. The sunlight measuring device is a battery-operated device mounted on a stake for easy insertion into the ground. The device is placed at the intended site for growing a plant. The light that falls on the sunlight measuring device over a period of time is accumulated and the light accumulation is represented by a visual signal that indicates one of four light conditions: full sun, partial sun, partial shade, full shade.
Owner:BAR DEV
Extrapolation system for solar access determination
InactiveUS20100061593A1Sunshine duration recordersGeometric image transformationReference imageSolar access
An extrapolation system includes acquiring a first orientation-referenced image at a first position, acquiring a second orientation-referenced image at a second position having a vertical offset from the first position, and processing the first orientation-referenced image and the second orientation-referenced image to provide an output parameter extrapolated to a third position that has an offset from the first position and the second position.
Owner:MACDONALD WILLARD S +1
Sun location prediction in image space with astronomical almanac-based calibration using ground based camera
A method for predicting location of the sun in an image space. The method includes providing a set of calibration images and offline intrinsic calibration of a camera and optical element. An extrinsic parameter calibration is then performed based on the calibration images and mapping between local three dimensional coordinates and real world three dimensional coordinates to provide an extrinsic projection matrix. The method also includes providing a real time image of the sky and determining sun location in spherical space based on the extrinsic projection matrix and a real time sun location in the world coordinate system for the real time image. A three dimensional vector is then mapped to provide a corrected two dimensional ideal point. Next, an inverse affine transformation is performed to provide a two dimensional real image point in image space.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
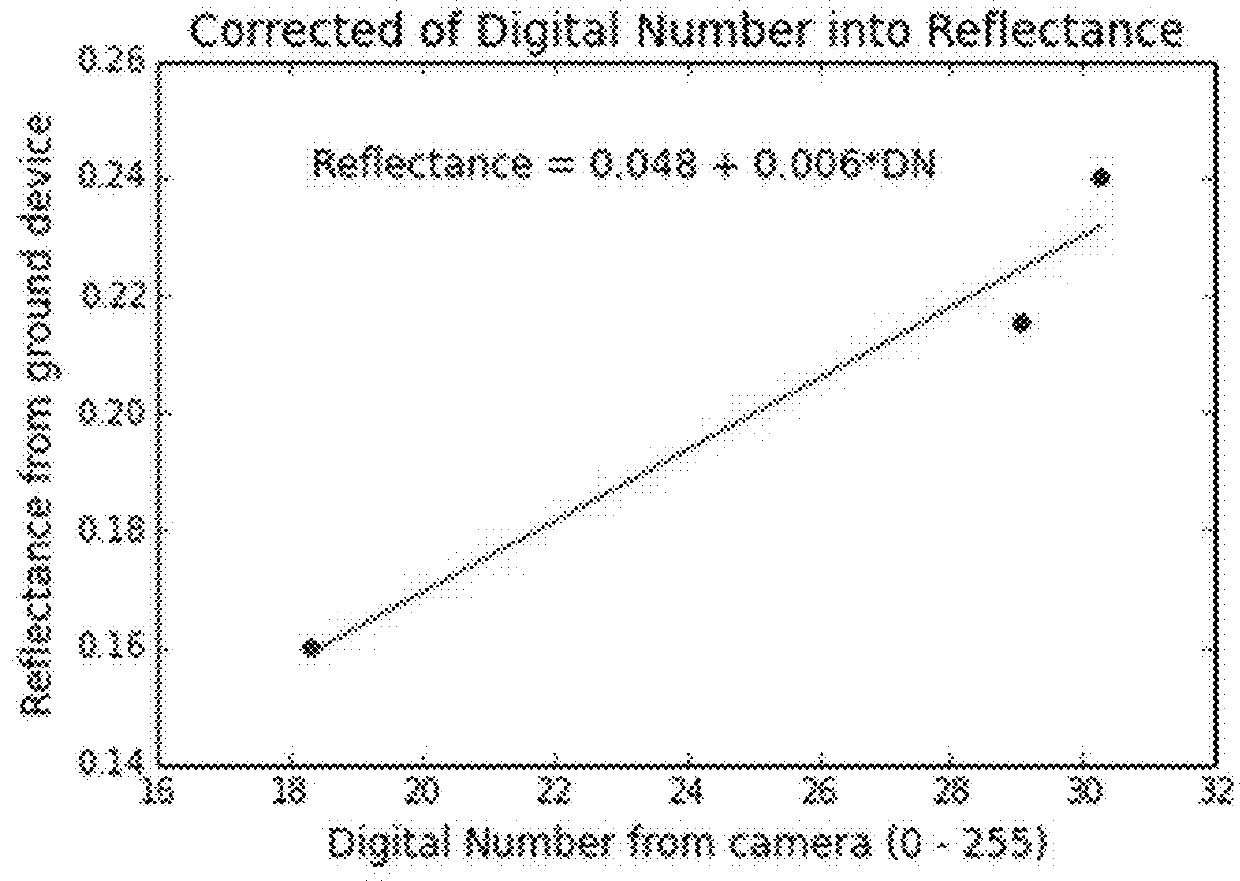
Apparatus for radiometric correction and orthorectification of aerial imagery
ActiveUS20180180768A1Increase harvest yieldThe location information is accurateSunshine duration recordersImage enhancementAviationAtmospheric sciences
The present inventors have developed a ground station that, when installed in a field, can collect upwelling and downwelling radiation, and GPS location coordinates, Data from remotely sensed imagery (RSI) can he used to monitor crop health. Use of the ground station can obviate the need for personnel to he deployed into the field during drone overflights for management of agriculture.
Owner:ARABLE LABS INC
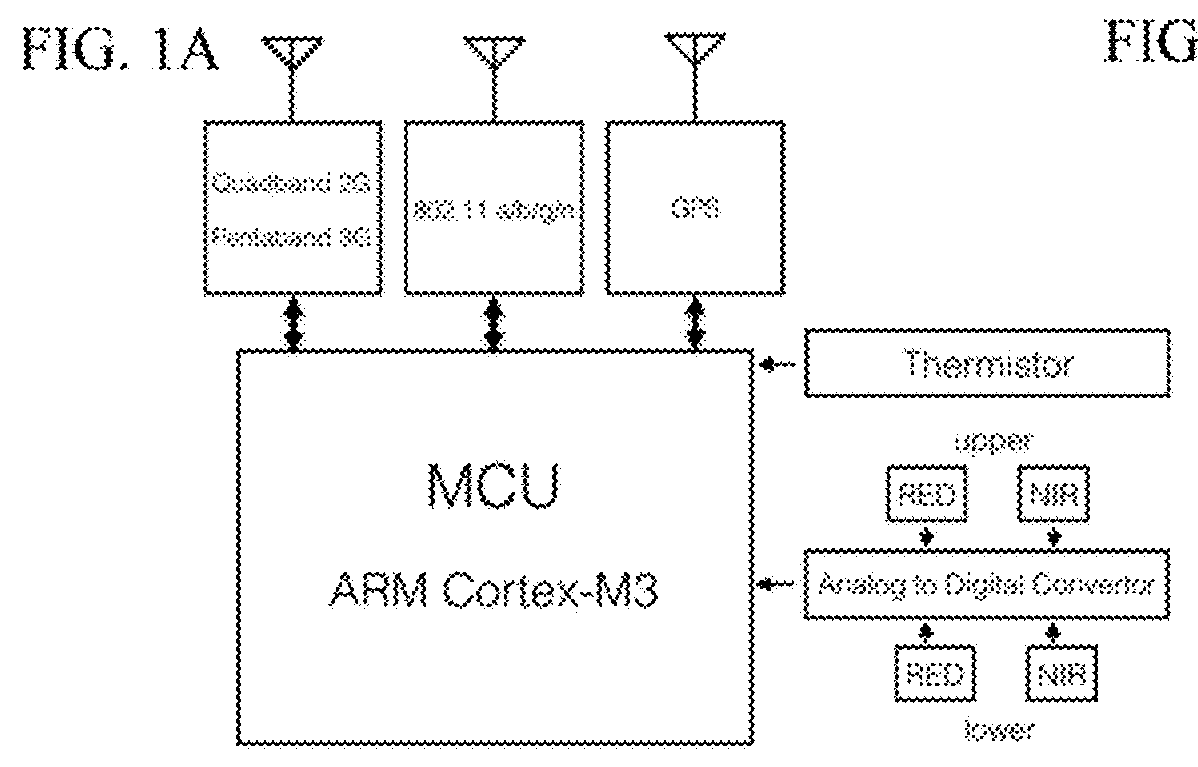
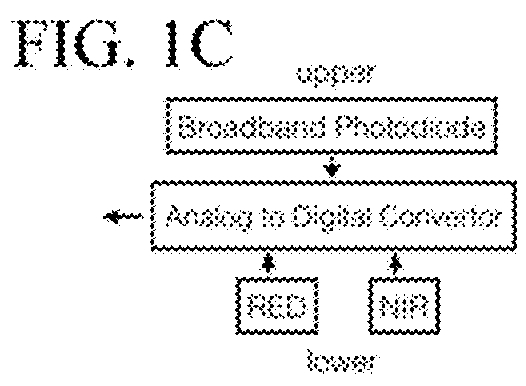
Electronic apparatus and ultraviolet avoidance information providing method thereof
ActiveUS20160300471A1Sunshine duration recordersPhotometry for measuring UV lightBiological bodyUltraviolet lights
An electronic apparatus and an ultraviolet avoidance information providing method are provided. The electronic apparatus includes a display; a biometric information acquisition module that acquires biometric information of a user; a location information acquisition module that acquires location information of a particular location; an ultraviolet intensity information acquisition module that acquires ultraviolet intensity information corresponding to the acquired location information; and a processor that controls the display to display ultraviolet avoidance information for avoiding ultraviolet light at the particular location based on the acquired biometric information and the acquired ultraviolet intensity information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Estimation of shading losses for photovoltaic systems from measured and modeled inputs
The present invention provides methods and systems to estimate energy losses due to shading in PV systems from data including the measured energy and power produced over the lifetime of the system, the system size and configuration data, the weather conditions (including irradiance, ambient & panel temperature, and wind conditions) over the lifetime of the system, and derived meteorological condition information (e.g., decomposed irradiance values at any time).
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
Weather and satellite model for estimating solar irradiance
ActiveUS20160026740A1Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkIlluminanceGranularity
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
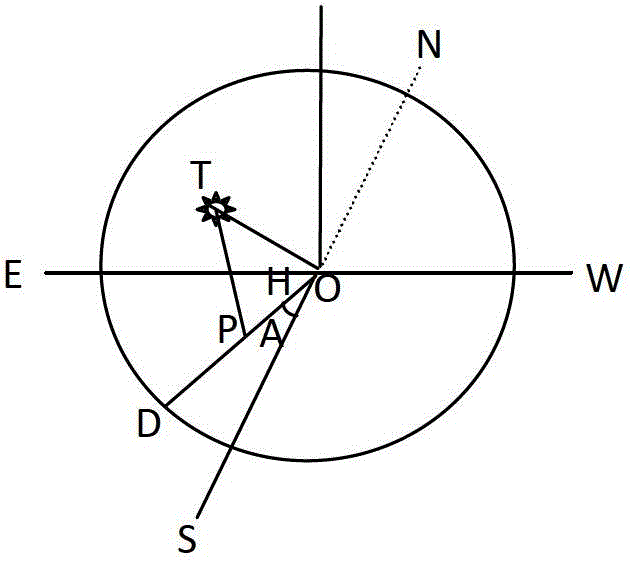
Methods for solar access measurement
ActiveUS20140176543A1Sunshine duration recordersPhotometry for measuring solar lightHorizonAzimuth direction
A method for determining solar access at a position includes: obtaining an image of a horizon that includes a skyline; determining the azimuth orientation and the inclination of the obtained image; and determining solar access based on the skyline within the obtained image, the measured azimuth orientation and inclination of the obtained image, and a position associated with the image of the horizon. Other features and embodiments relating to solar access measurement are disclosed.
Owner:SOLMETRIC
Sunshine duration measuring method based on sky visible-light images
ActiveCN102721988AReduce usageAvoid measurement errorsSunshine duration recordersImaging processingSky
The invention discloses a sunshine duration measuring method based on sky visible-light images. The sunshine duration measuring method includes acquiring a series of sky visible-light images by image acquisition equipment at preset intervals; searching high-brightness pixels in a preset area of each sky visible-light image and counting the quantity of the high-brightness pixels; judging whether sunshine is shot in each sky visible-light image or not; determining that the sunshine is shot in a certain sky visible-light image when the quantity of the high-brightness pixels of the sky visible-light image is larger than or equal to a high-brightness pixel quantity threshold, and determining that the sunshine is not shot in the certain sky visible-light image when the quantity of the high-brightness pixels of the sky visible-light image is smaller than the high-brightness pixel quantity threshold; and computing sunshine duration according to the time interval and the quantity of the sky visible-light images shot with the sunshine. The relevance among the sky visible-light images and the direct solar irradiation intensity is built by means of fitting analysis, and accordingly the novel method for detecting or measuring the direct solar irradiation intensity in an image processing and analyzing mode is provided. The method provides a novel selectable scheme for measuring the sunshine duration.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF METEOROLOGICAL SCI
Estimating solar irradiance components from plane of array irradiance and global horizontal irradiance
ActiveUS8972221B2Reduce model biasImprove accuracySunshine duration recordersGeneration forecast in ac networkIlluminanceDirect normal irradiance
Owner:LOCUS ENERGY
Sunlight measuring device
InactiveUS7271887B2Accurate measurementSunshine duration recordersColor/spectral properties measurementsMeasurement deviceGround level
A sunlight measuring device that quantifies the accumulation of light at a particular site. The sunlight measuring device is a battery-operated device mounted on a stake for easy insertion into the ground. The device is placed at the intended site for growing a plant. The light that falls on the sunlight measuring device over a period of time is accumulated and the light accumulation is represented by a visual signal that indicates one of four light conditions: full sun, partial sun, partial shade, full shade.
Owner:BAR DEV
Solar forecasting using machine learned cloudiness classification
ActiveUS20180039891A1Sunshine duration recordersWeather condition predictionState dependentClassification methods
Methods and systems for predicting irradiance include learning a classification model using unsupervised learning based on historical irradiance data. The classification model is updated using supervised learning based on an association between known cloudiness states and historical weather data. A cloudiness state is predicted based on forecasted weather data. An irradiance is predicted using a regression model associated with the cloudiness state.
Owner:IBM CORP
Estimating solar array power generation
Owner:IBM CORP
Solar power forecasting using mixture of probabilistic principal component analyzers
ActiveUS20170205537A1Sunshine duration recordersWeather condition predictionEngineeringSolar power forecasting
A method for solar forecasting includes receiving a plurality of solar energy data as a function of time of day at a first time, forecasting (620) from the solar energy data a mode, where the mode is a sunny day, a cloudy day, or an overcast day, and the forecast predicts the mode for a next solar energy datum, receiving (622) the next solar energy datum, updating a probability distribution function (pdf) of the next solar energy datum given the mode, updating a pdf of the mode for the next solar energy datum from the updated pdf of the new solar energy datum given the mode, forecasting (624, 626) a plurality of future unobserved solar energy data from the updated pdf of the mode, where the plurality of future unobserved solar energy data and the plurality of solar energy data have a Gaussian distribution for a given mode determined from training data.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Popular searches
Roof covering using slabs/sheets Roof covering using tiles/slates Solar heat simulation/prediction Solar heat devices Solar technique simulation Renewable energy source integration Load forecast in ac network Design optimisation/simulation Photovoltaic energy generation Special data processing applications
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com