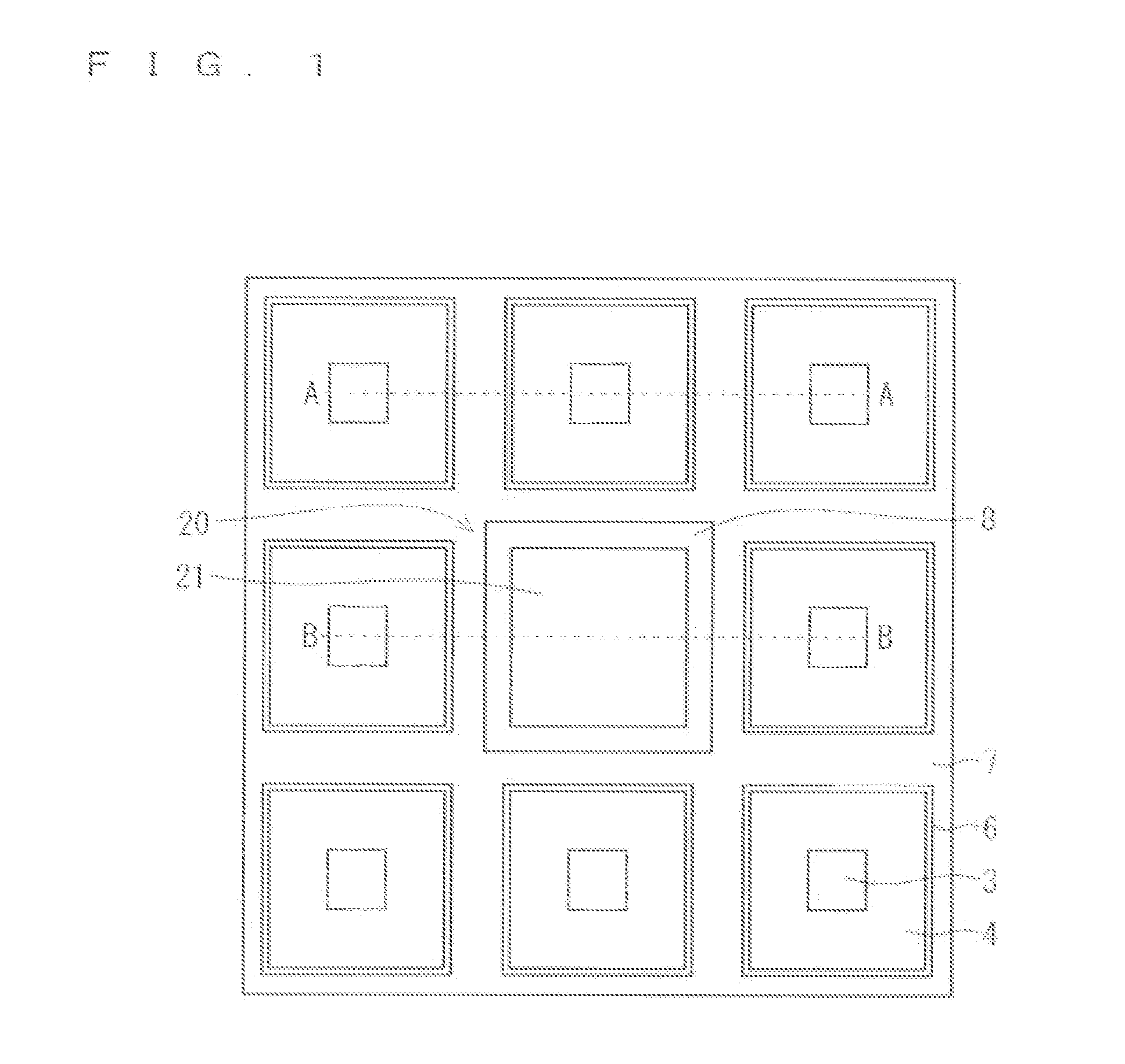
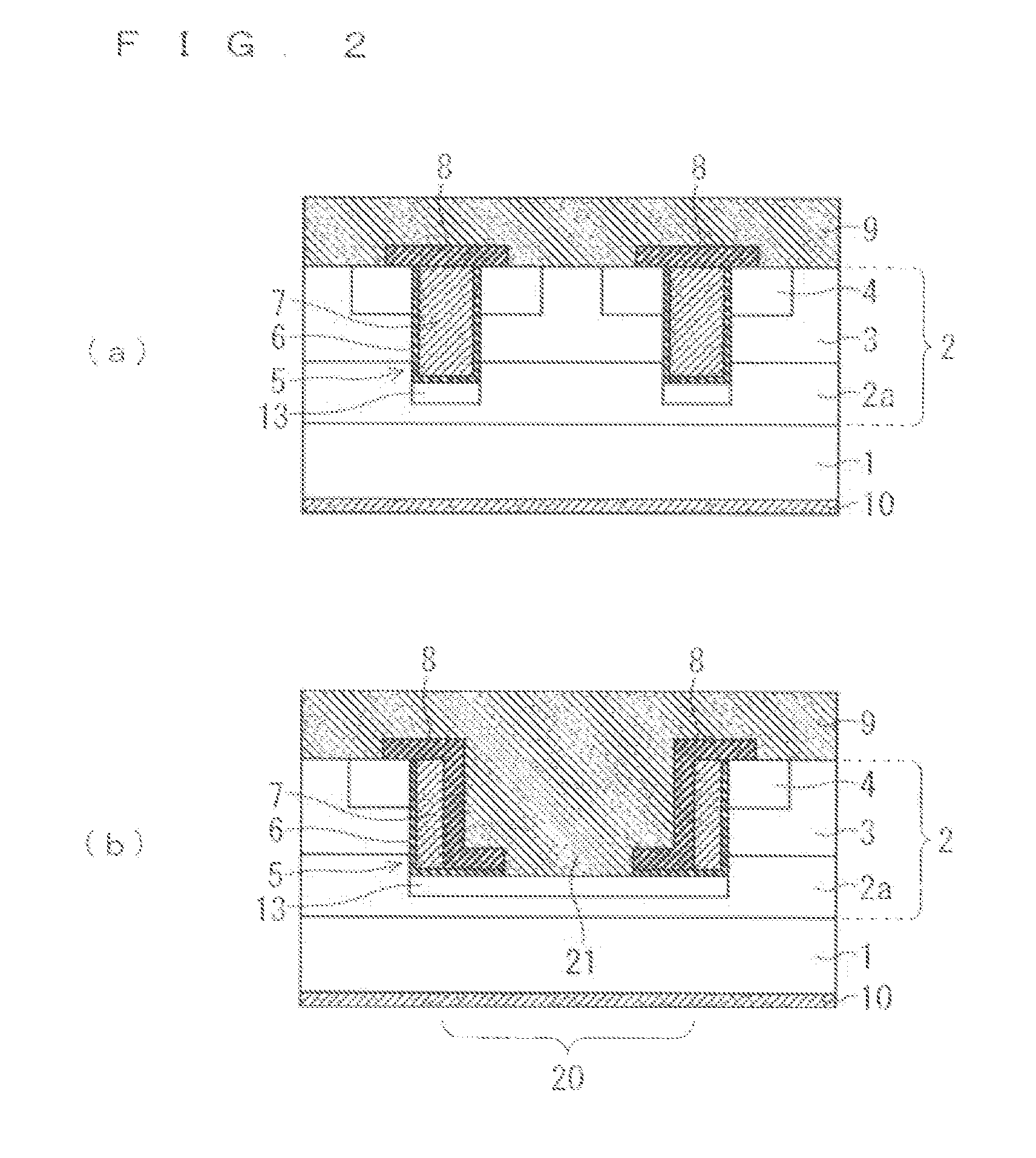
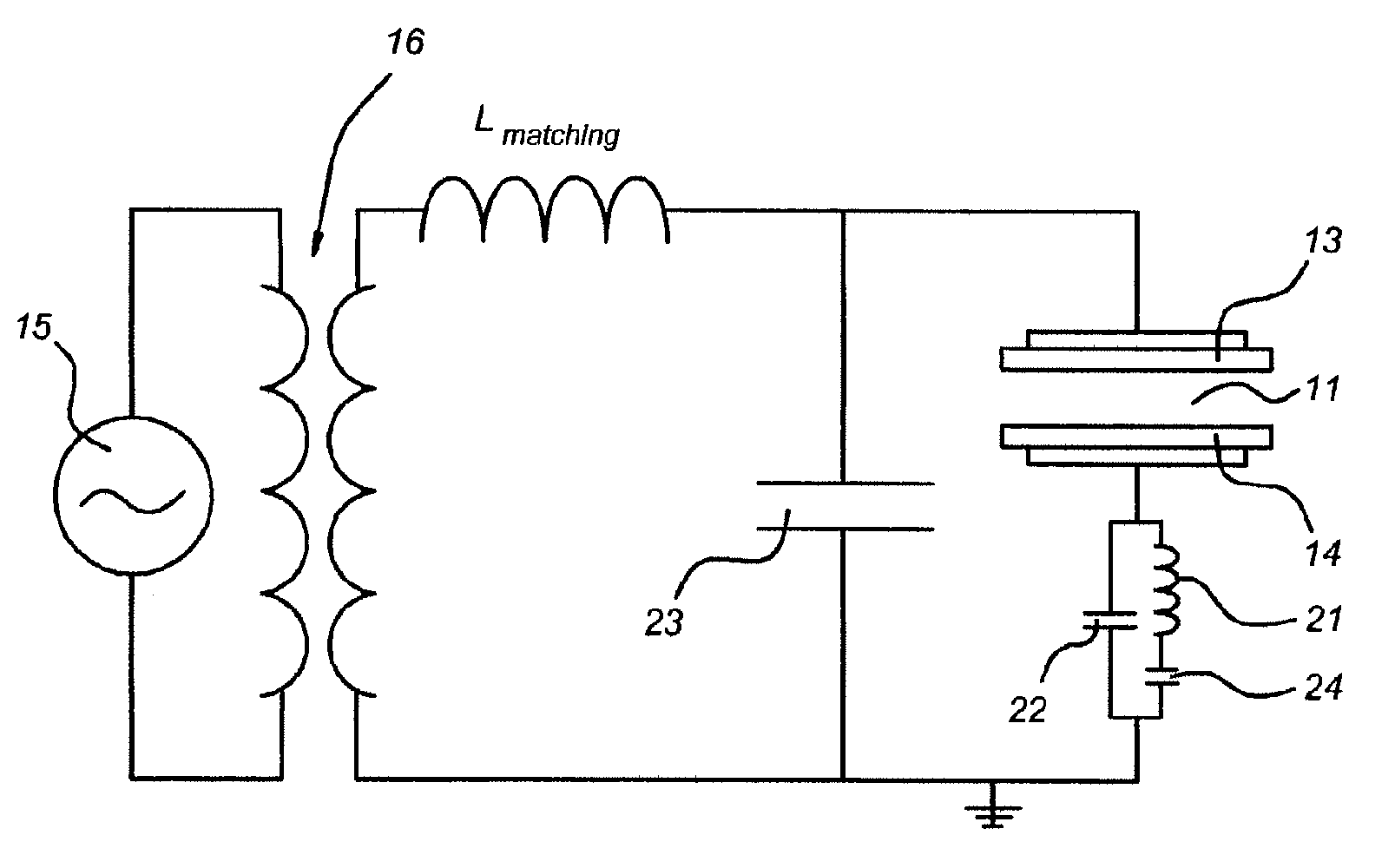
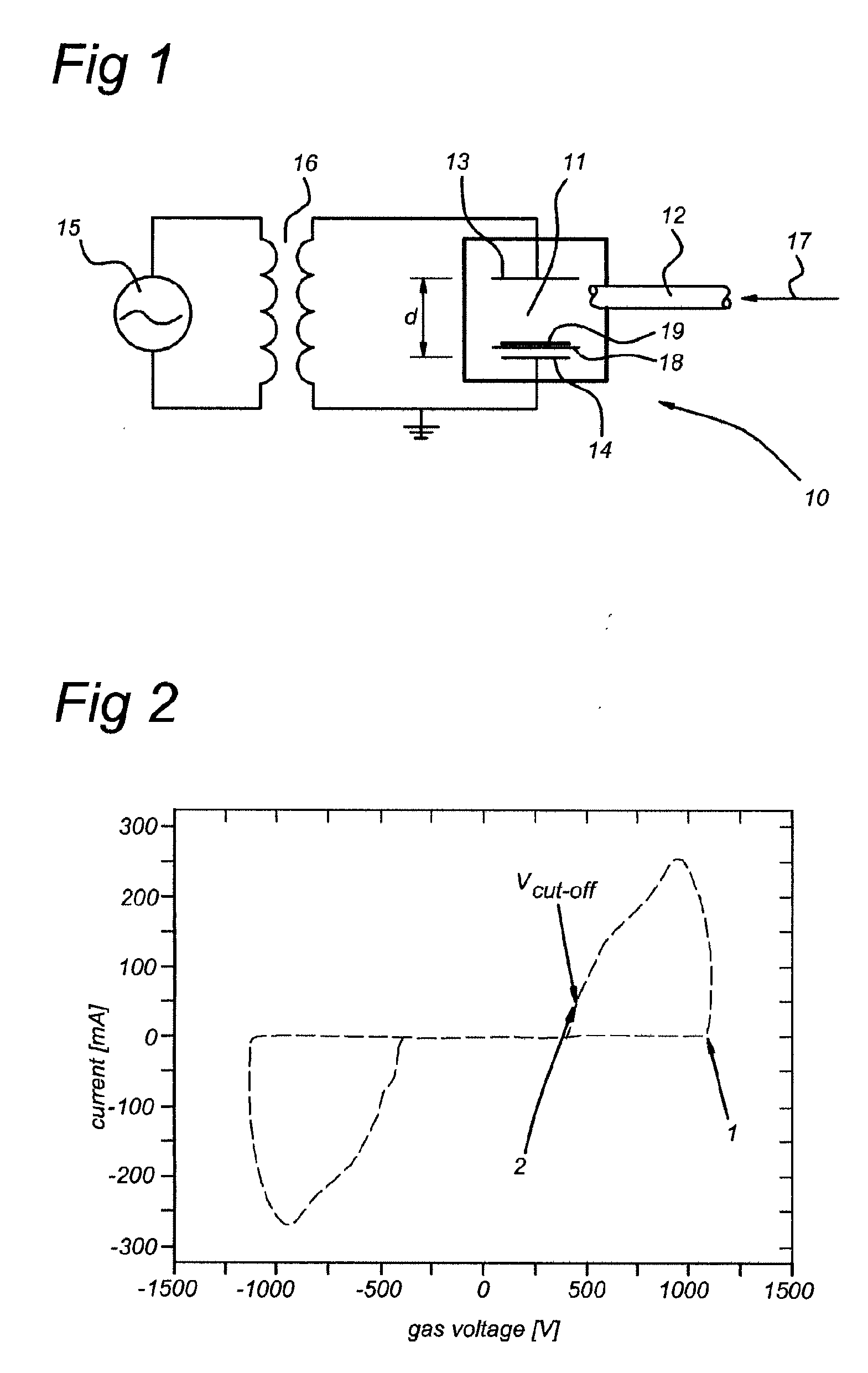
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
182 results about "Displacement current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electromagnetism, displacement current density is the quantity ∂D/∂t appearing in Maxwell's equations that is defined in terms of the rate of change of D, the electric displacement field. Displacement current density has the same units as electric current density, and it is a source of the magnetic field just as actual current is. However it is not an electric current of moving charges, but a time-varying electric field. In physical materials (as opposed to vacuum), there is also a contribution from the slight motion of charges bound in atoms, called dielectric polarization.
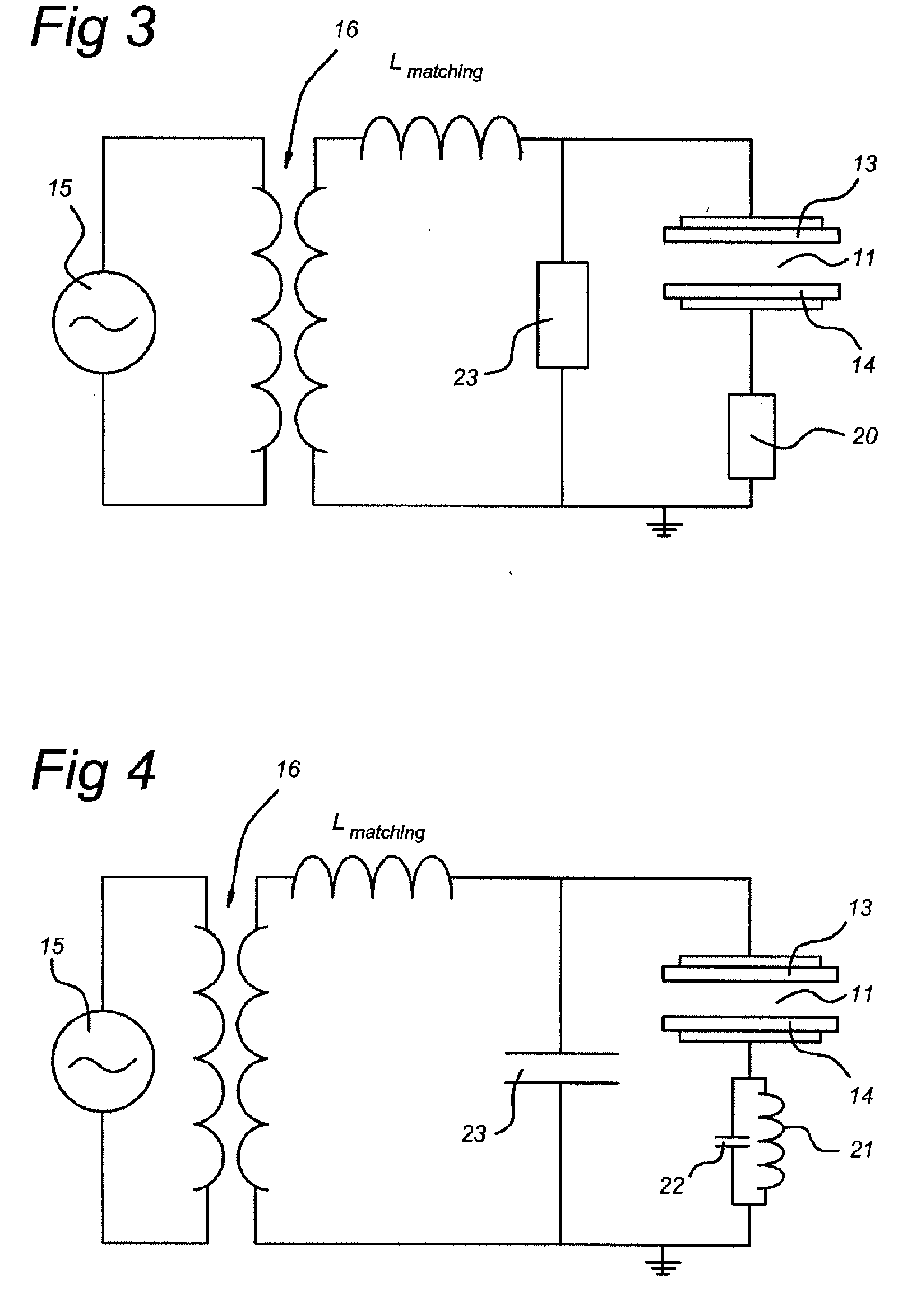
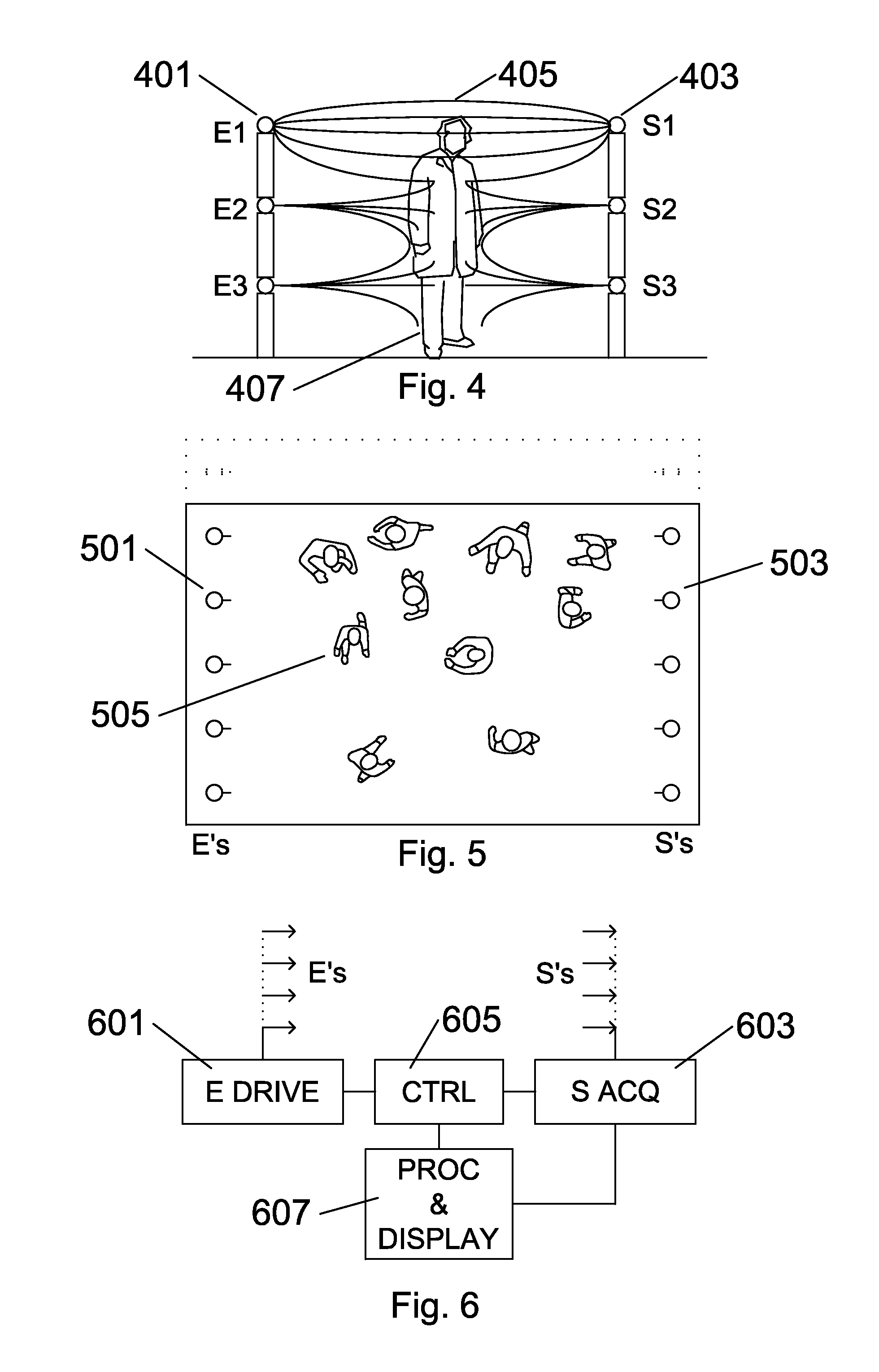
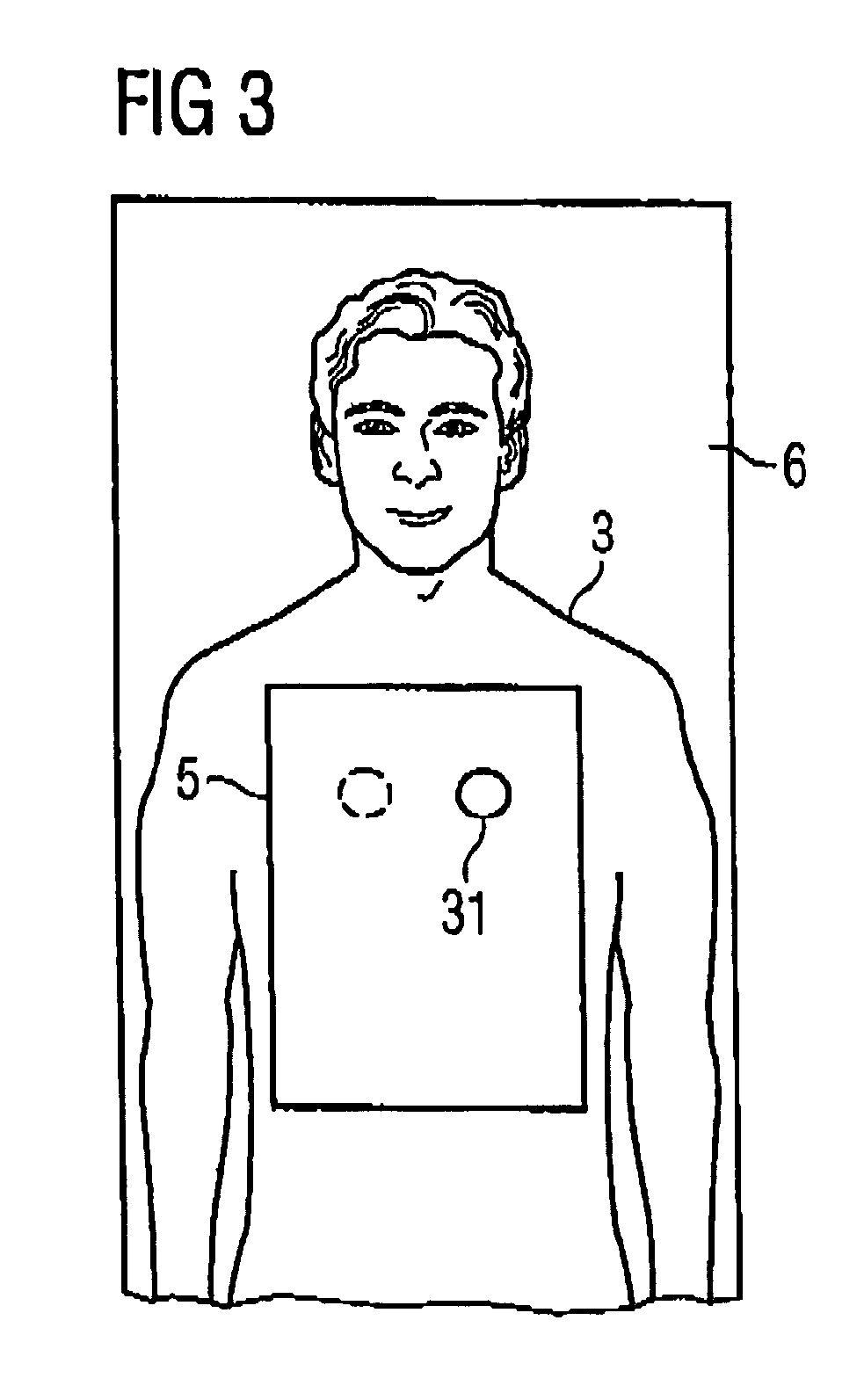
Apparatus and method for stimulation of biological tissue
ActiveUS20080046053A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyPermittivityDisplacement current
An apparatus for generating focused currents in biological tissue is provided. The apparatus comprises an electric source capable of generating an electric field across a region of tissue and means for altering the permittivity of the tissue relative to the electric field, whereby a displacement current is generated. The means for altering the permittivity may be a chemical source, optical source, mechanical source, thermal source, or electromagnetic source.
Owner:HIGHLAND INSTR INC
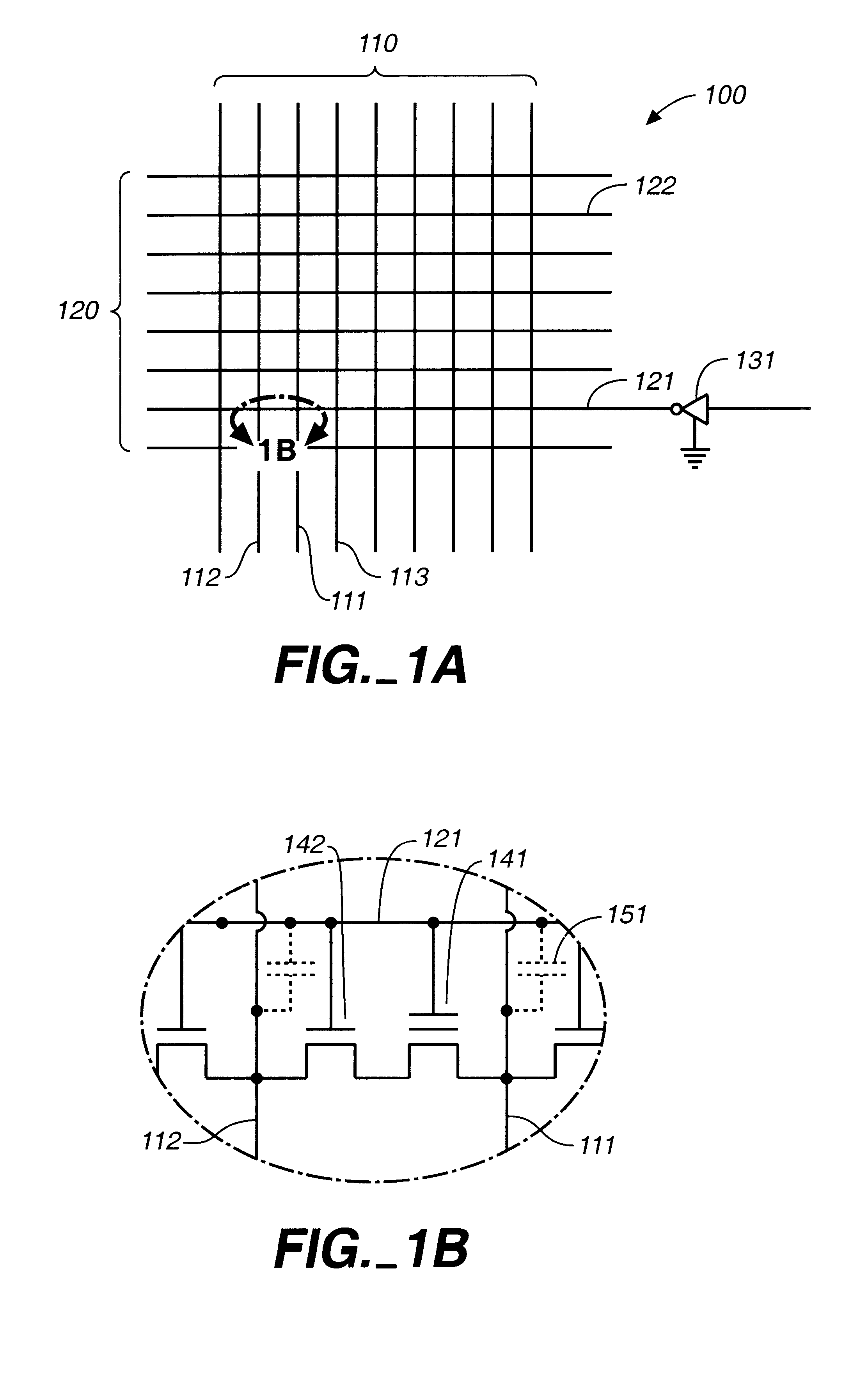
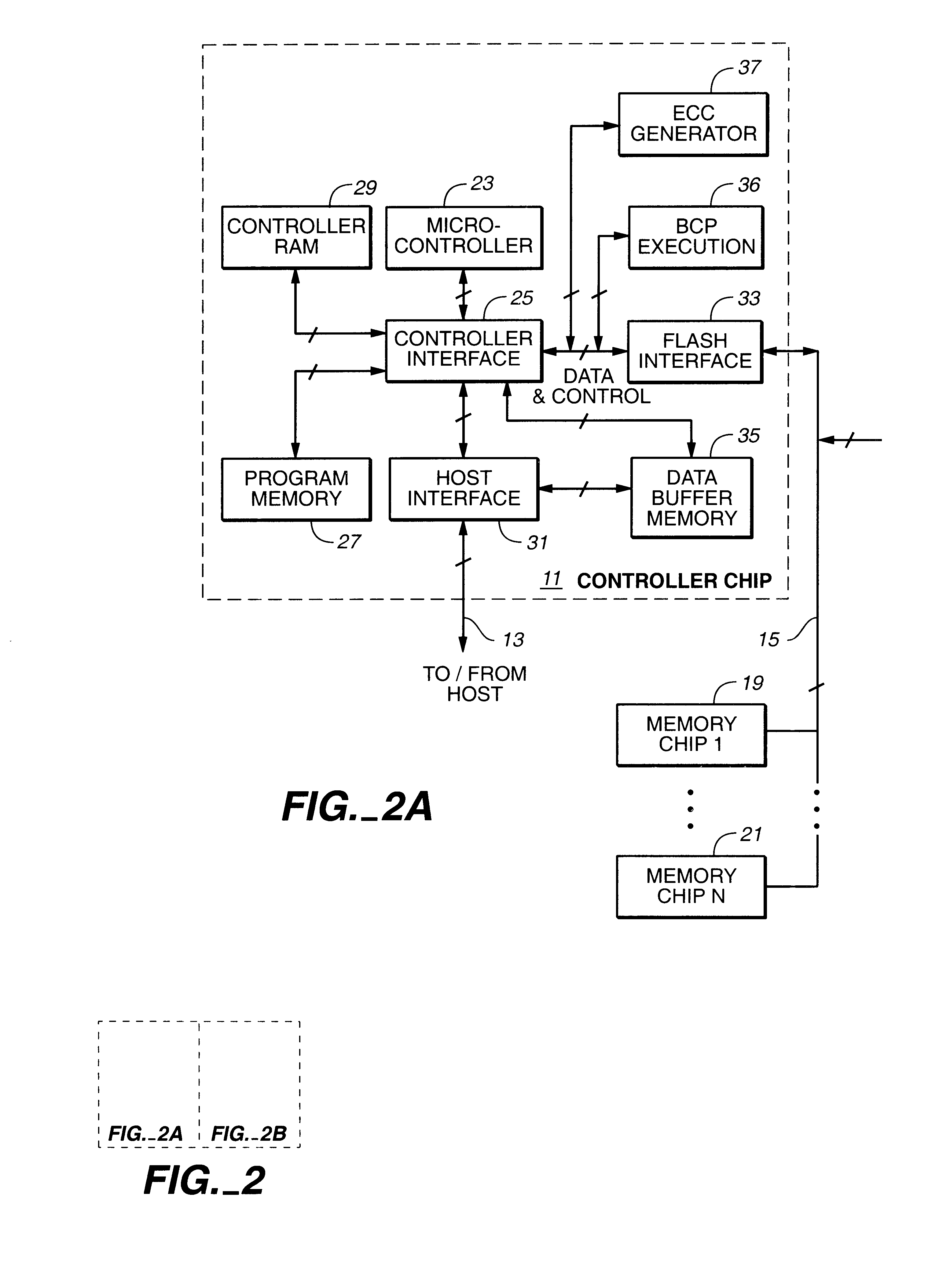
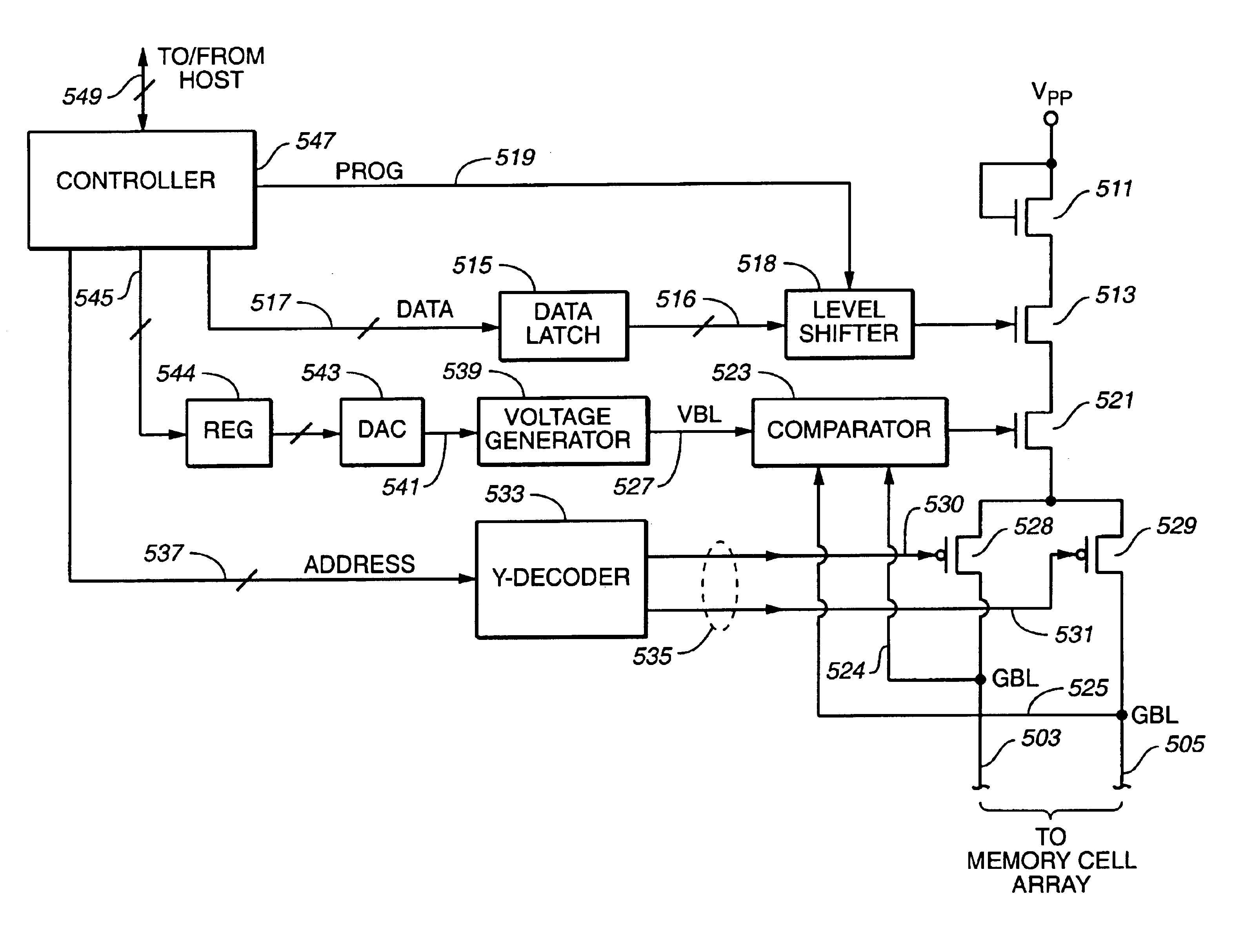
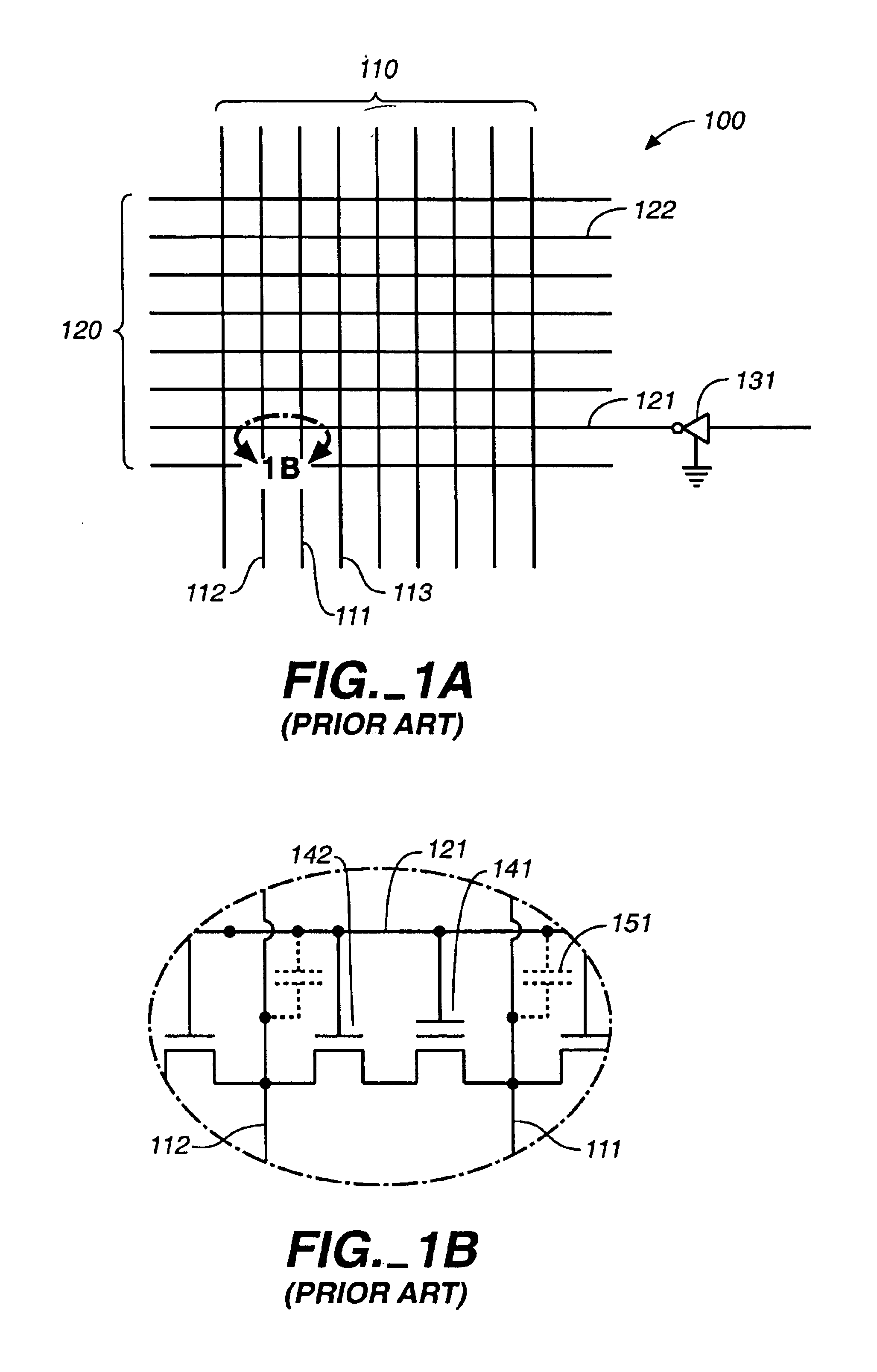
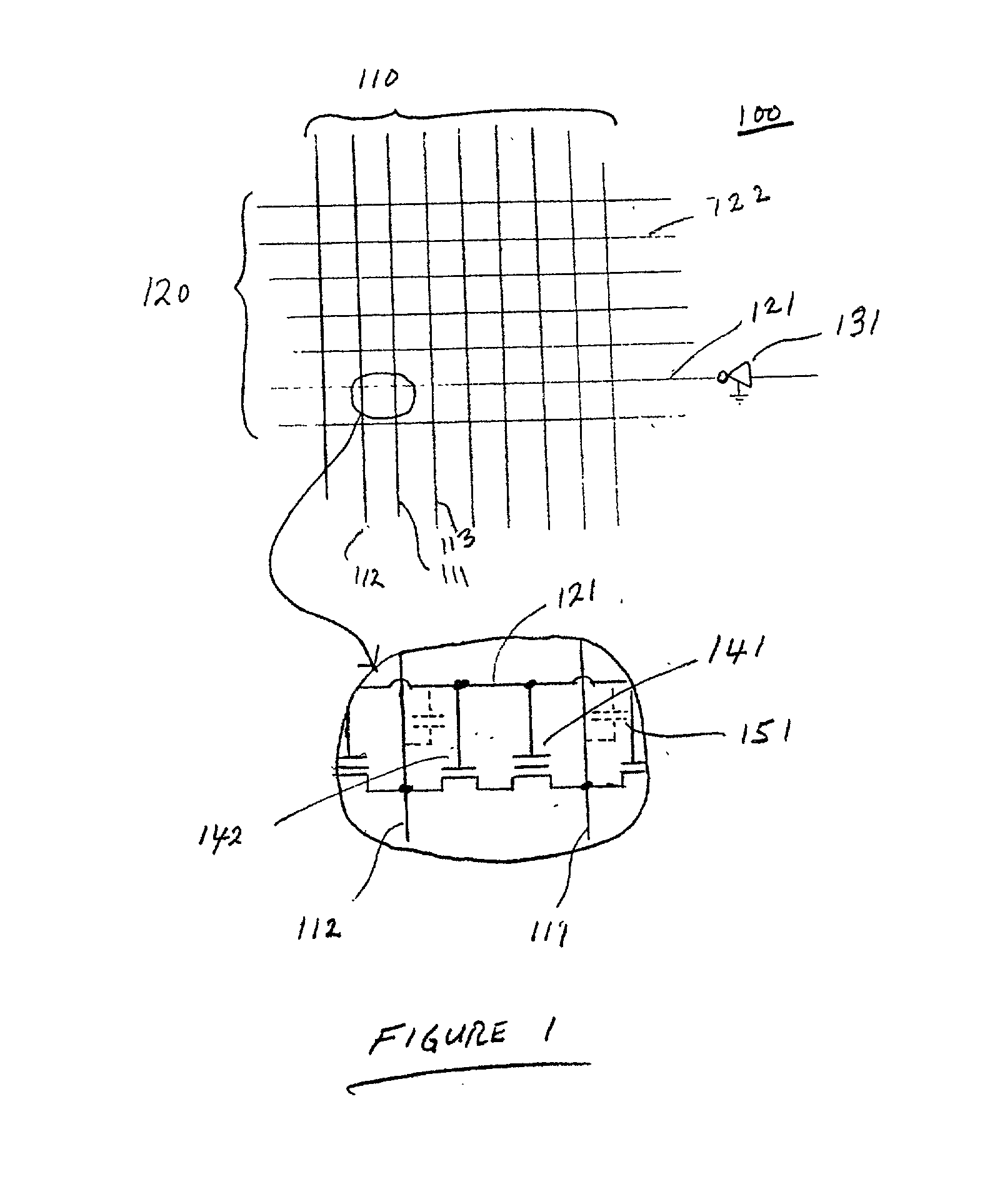
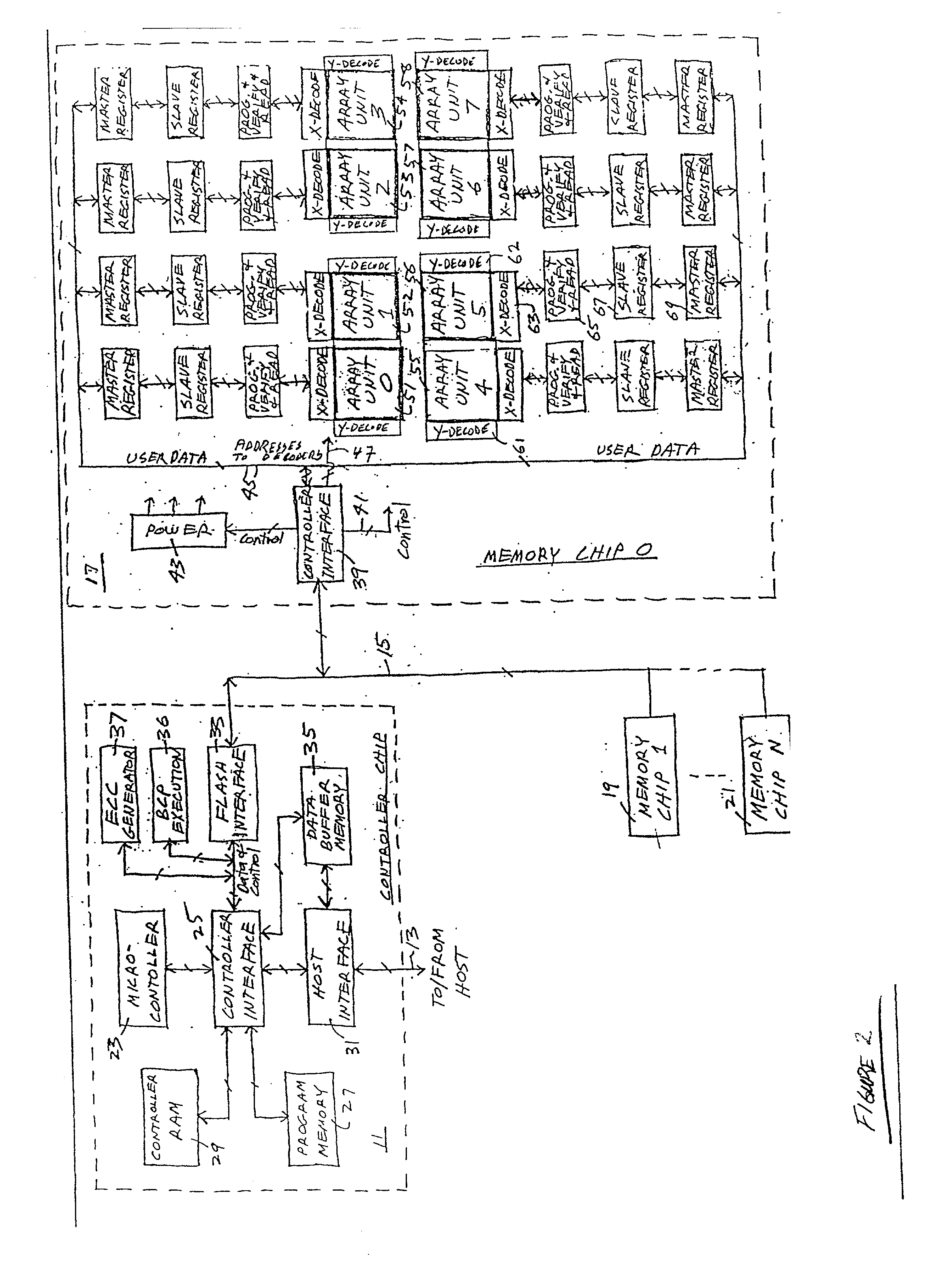
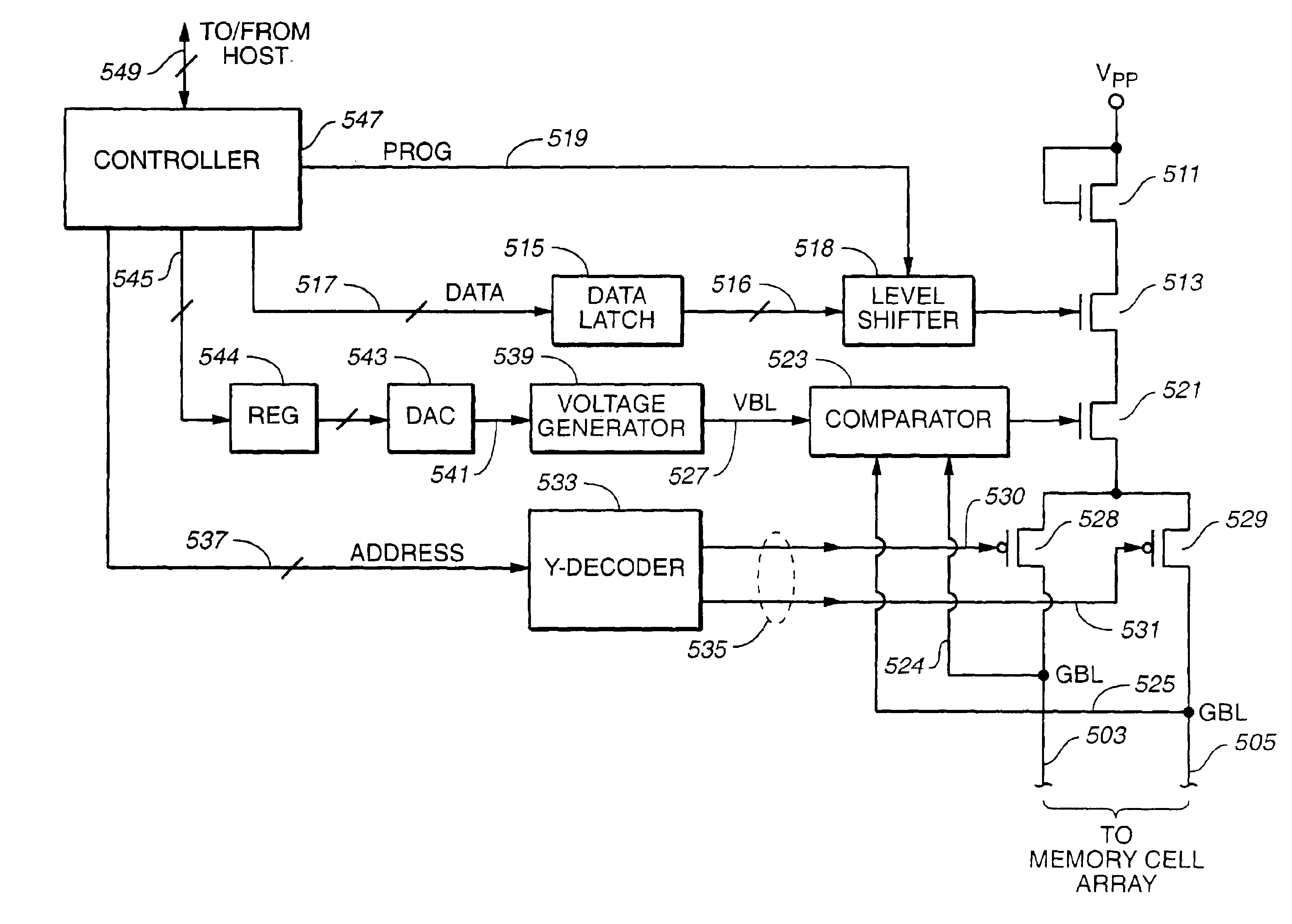
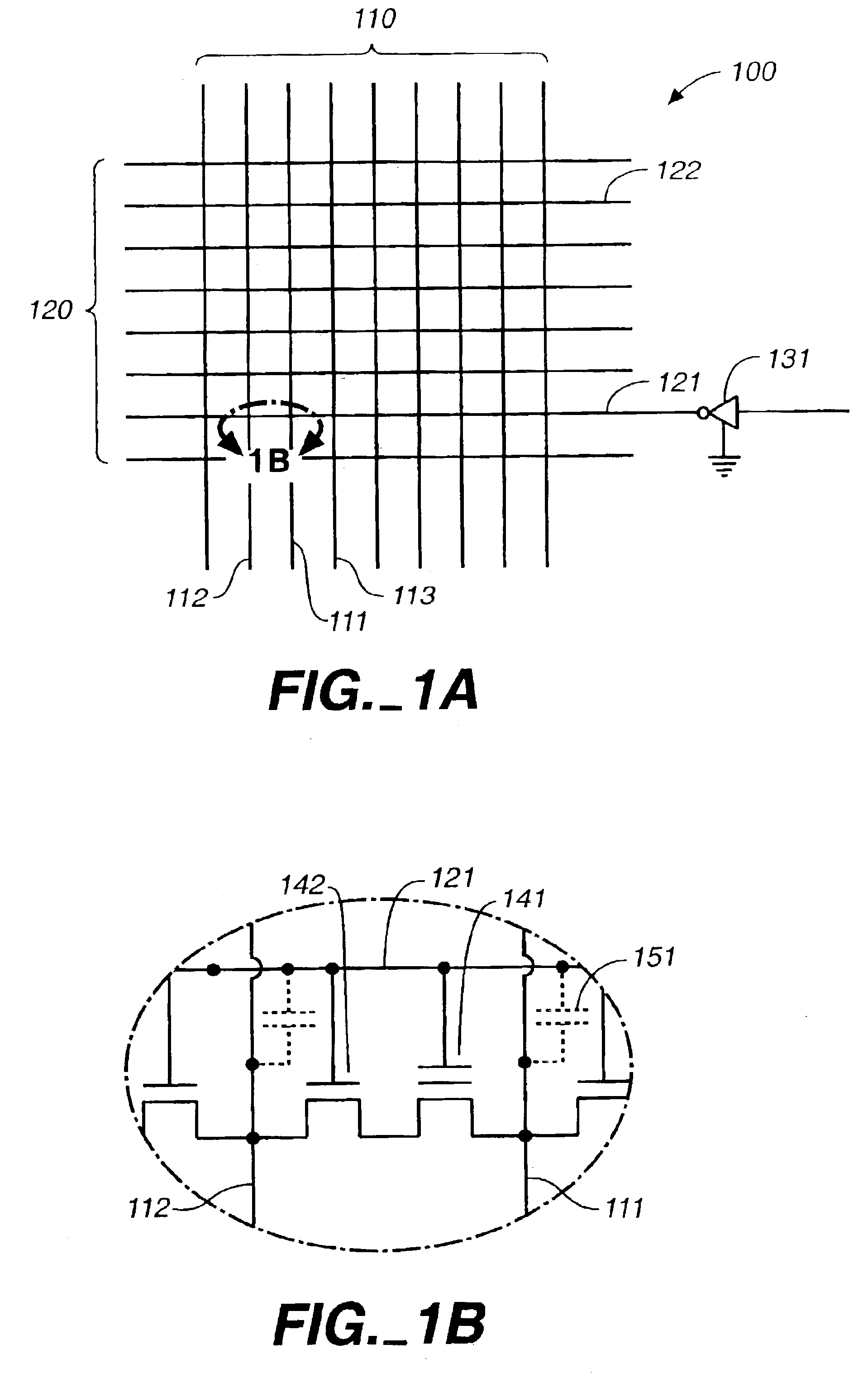
Method of reducing disturbs in non-volatile memory
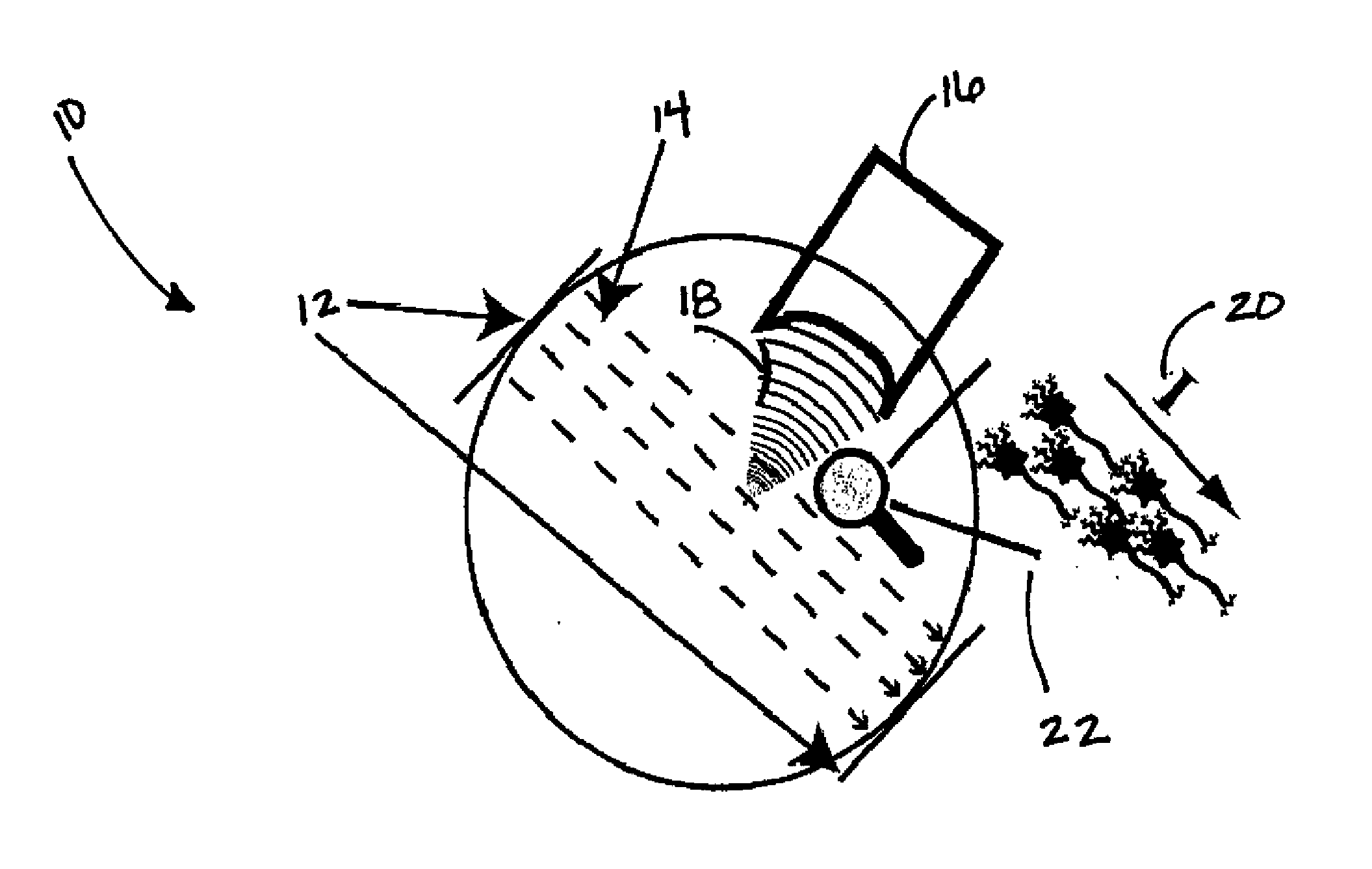
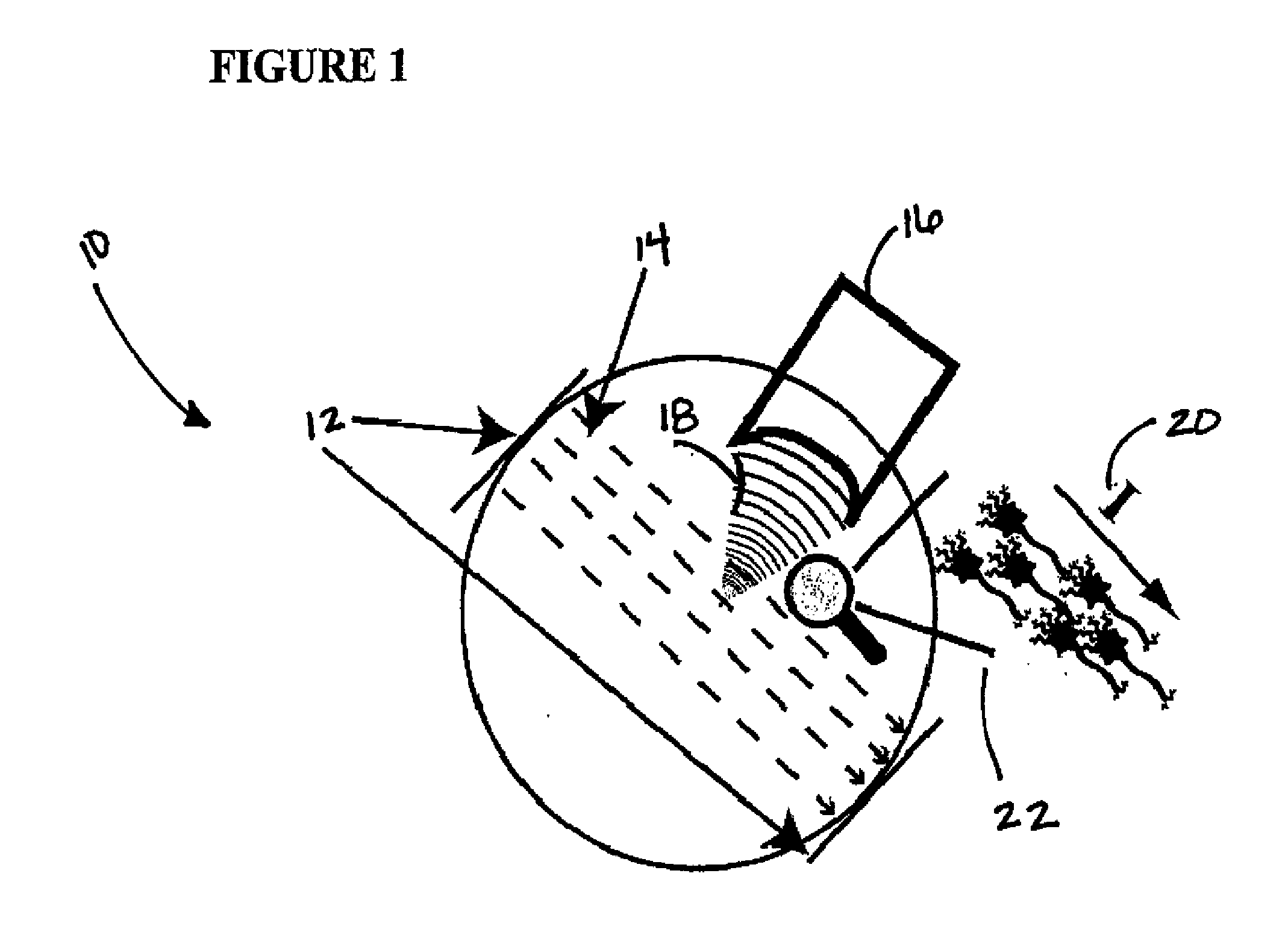
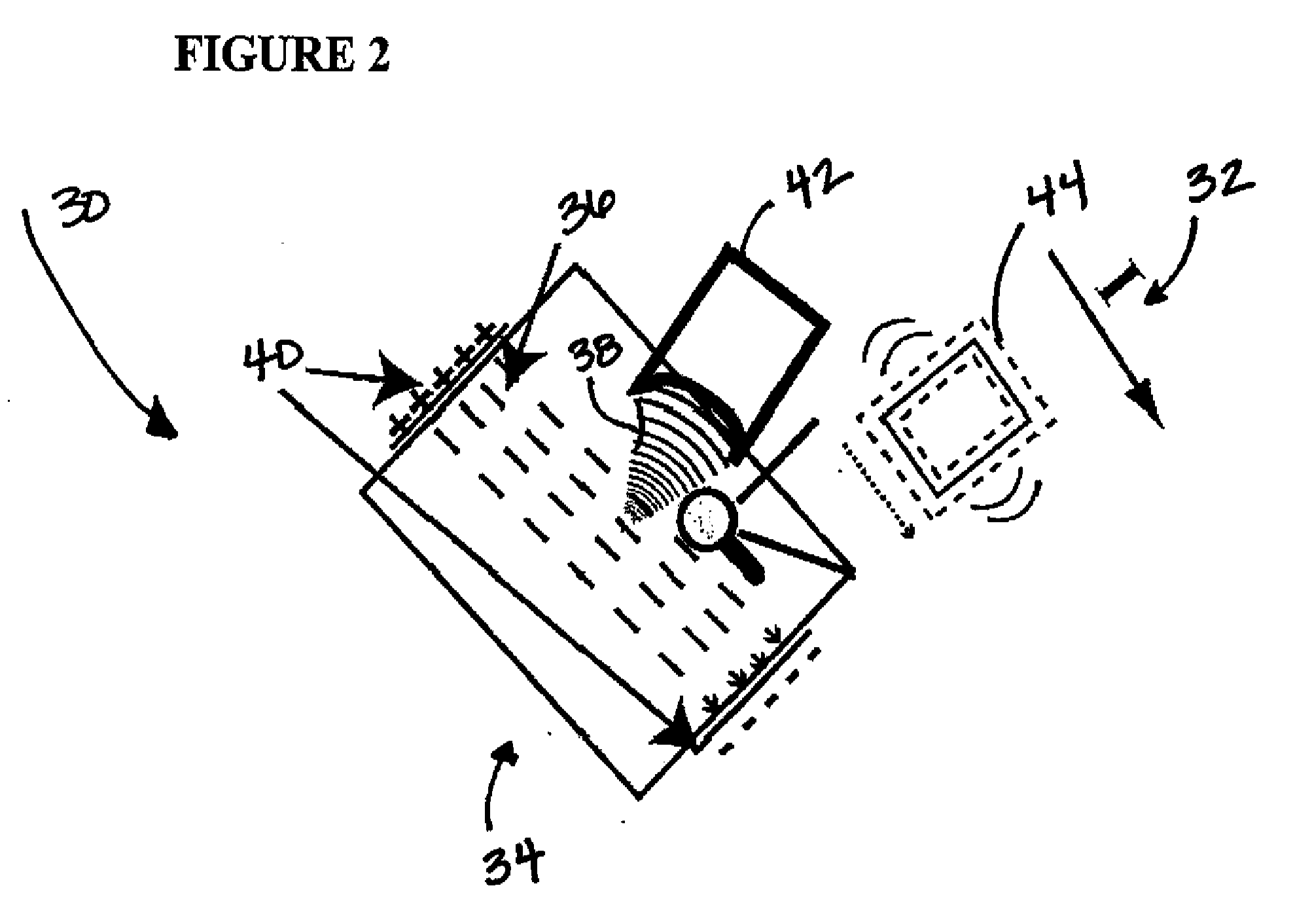
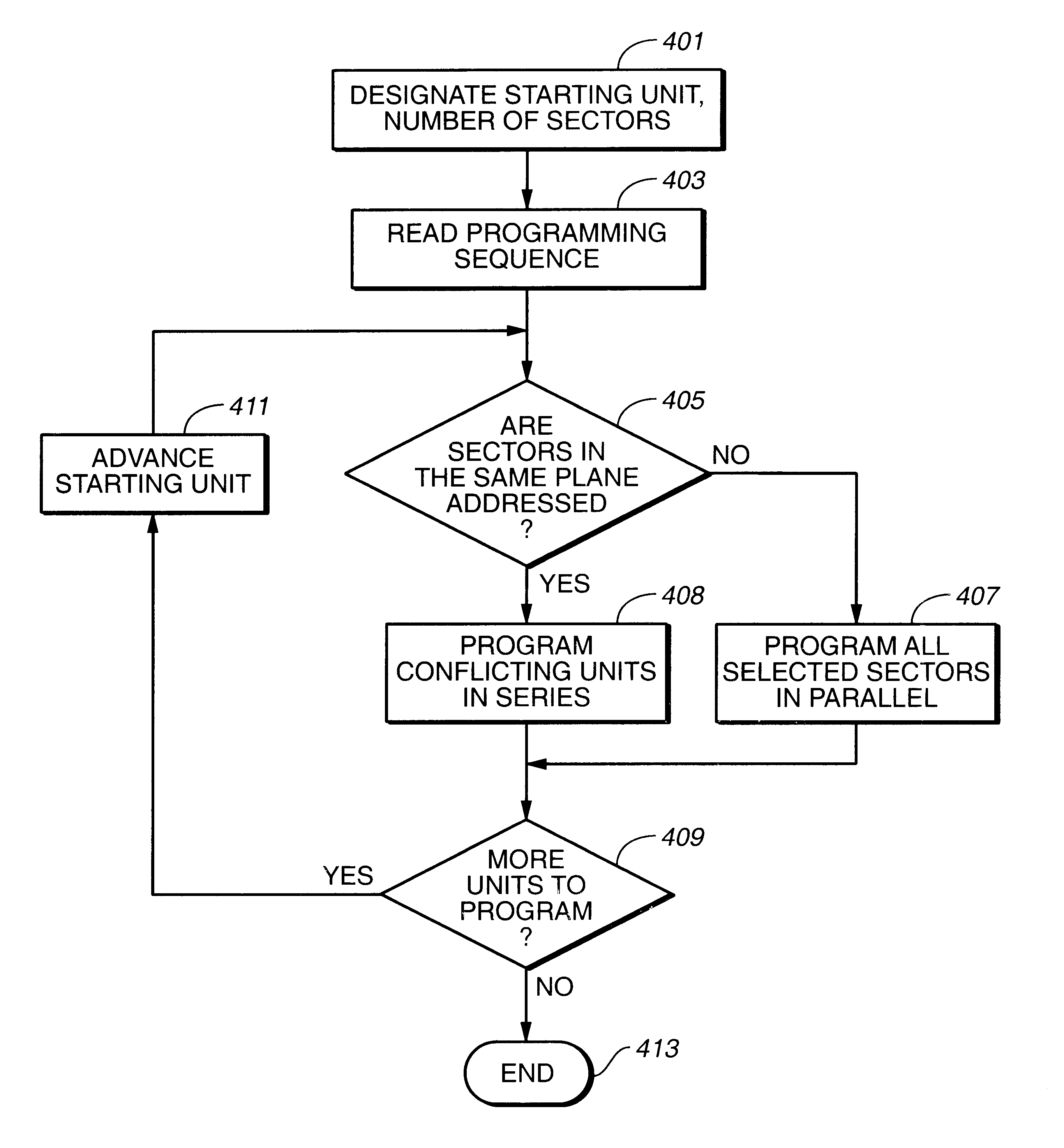
In a non-volatile memory, the displacement current generated in non-selected word lines that results when the voltage levels on an array's bit lines are changed can result in disturbs. Techniques for reducing these currents are presented. In a first aspect, the number of cells being simultaneously programmed on a word line is reduced. In a non-volatile memory where an array of memory cells is composed of a number of units, and the units are combined into planes that share common word lines, the simultaneous programming of units within the same plane is avoided. Multiple units may be programmed in parallel, but these are arranged to be in separate planes. This is done by selecting the number of units to be programmed in parallel and their order such that all the units programmed together are from distinct planes, by comparing the units to be programmed to see if any are from the same plane, or a combination of these. In a second, complementary aspect, the rate at which the voltage levels on the bit lines are changed is adjustable. By monitoring the frequency of disturbs, or based upon the device's application, the rate at which the bit line drivers change the bit line voltage is adjusted. This can be implemented by setting the rate externally, or by the controller based upon device performance and the amount of data error being generated.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Passenger detecting system and passenger detecting method
A passenger detecting system is disclosed, that comprises a seat, a plurality of electrodes disposed at predetermined intervals on at least the front surface of the seat, an oscillating circuit for generating a weak electric field between at least one particular electrode (referred to as a first type electrode) of the electrodes and the other electrodes (referred to as second type electrodes), a current / voltage converting circuit for detecting displacement currents that flow corresponding to the weak electric field and for converting the displacement currents into respective voltages, a controlling circuit for detecting a seating pattern of an passenger or the like on the seat corresponding to output signals of the current / voltage converting circuit, and an air bag device for inflating an air bag in case of a collision.
Owner:HONDA ELESYS CO LTD
Method of reducing disturbs in non-volatile memory
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
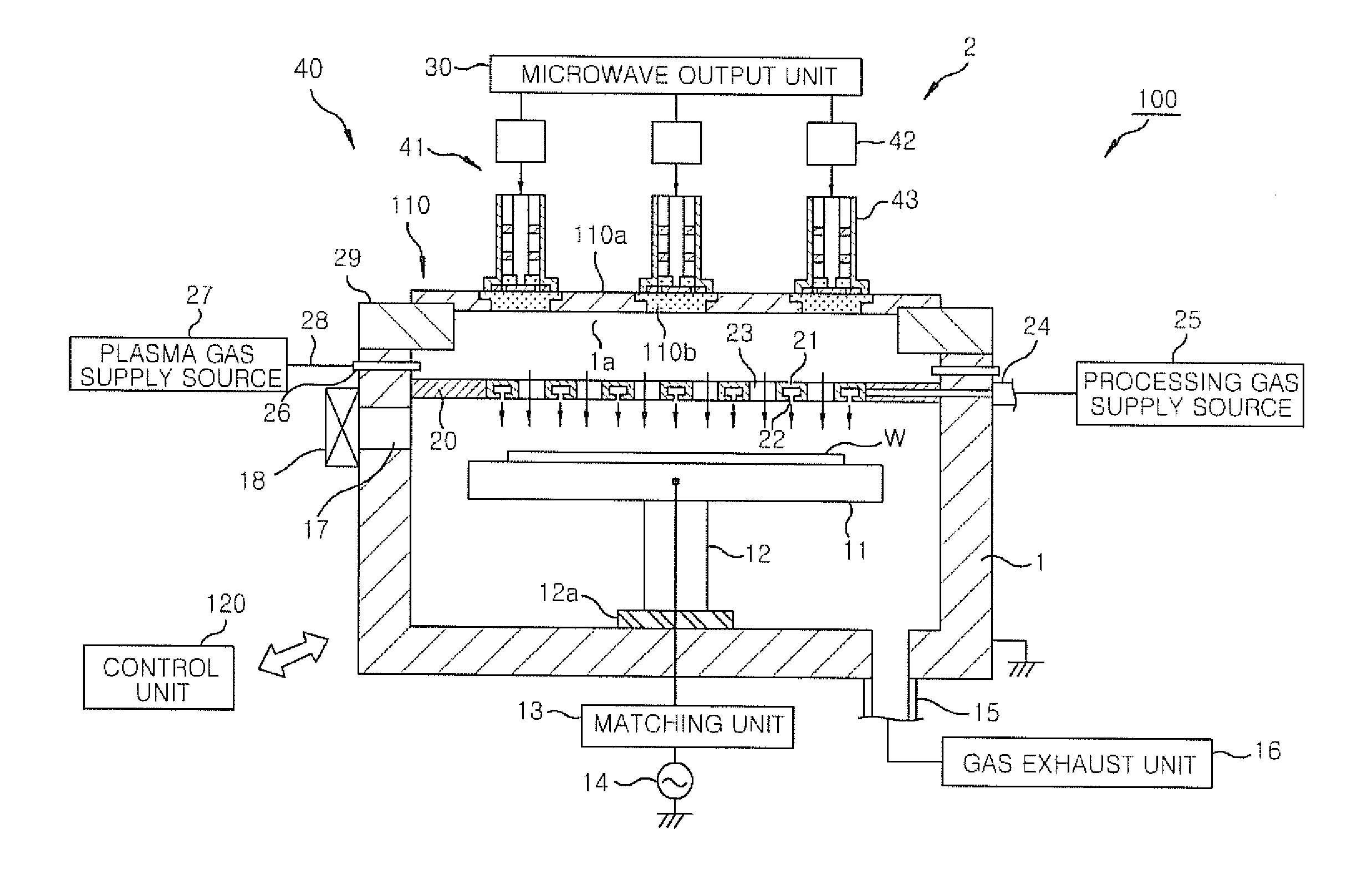
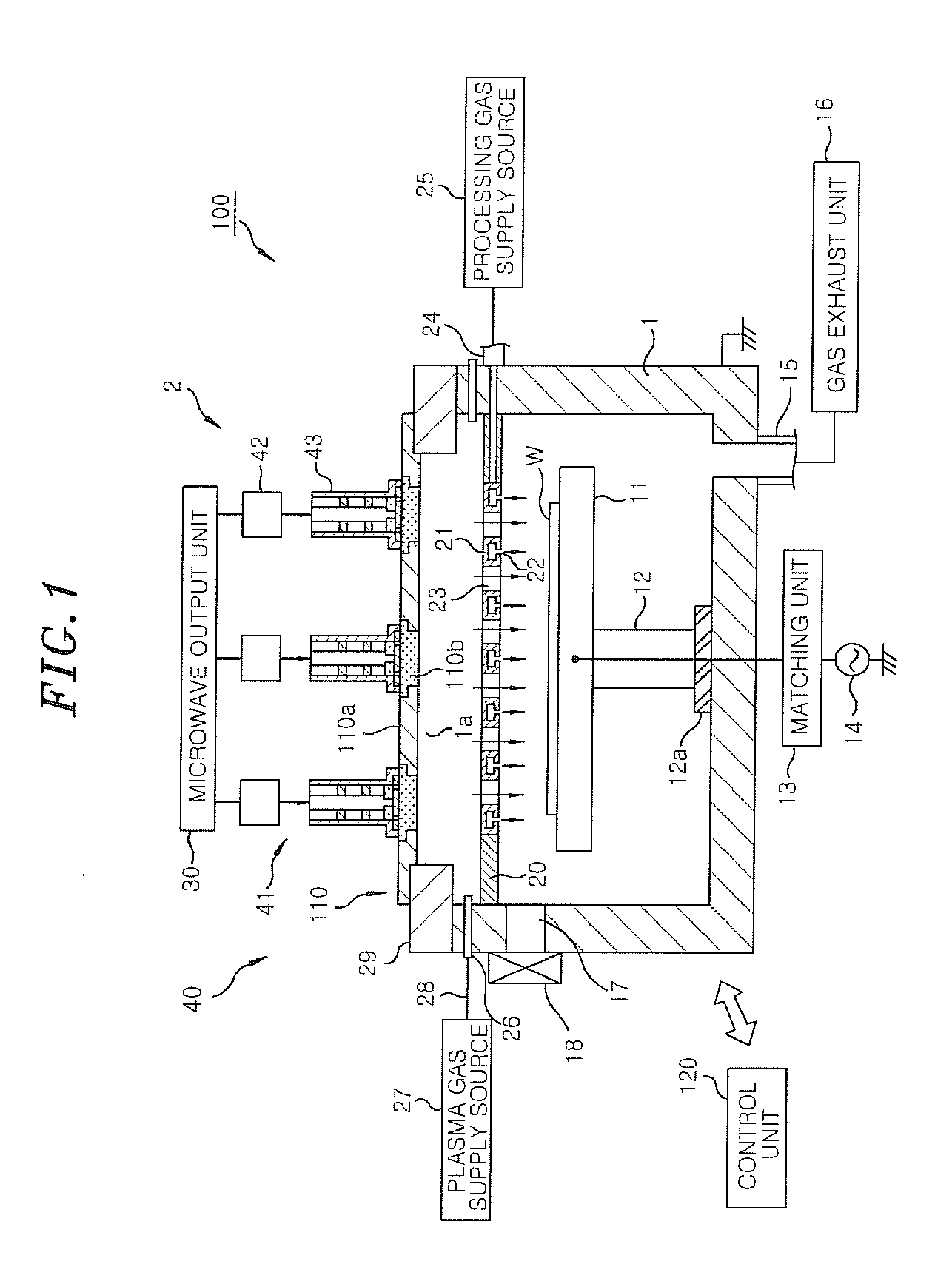
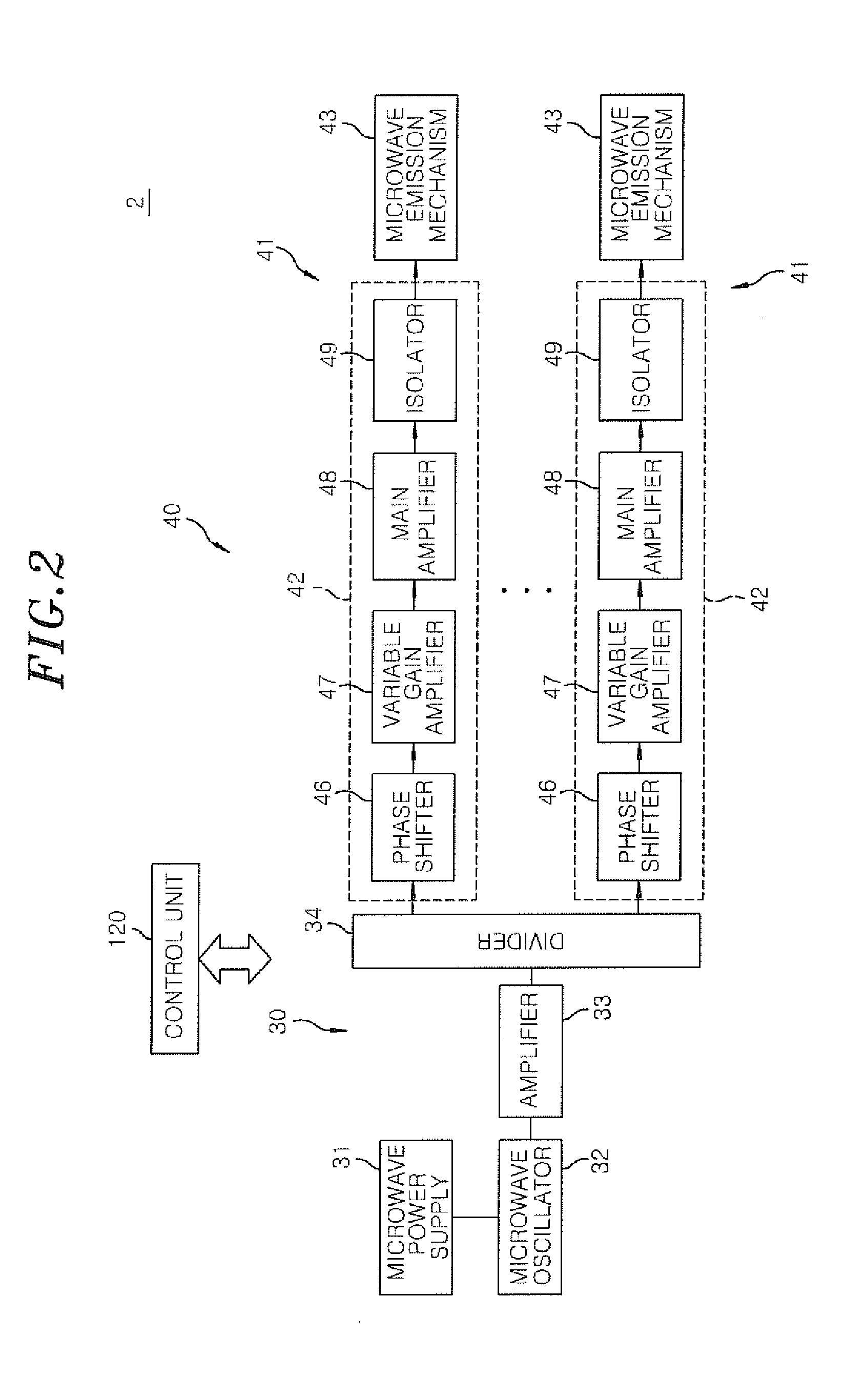
Microwave emission mechanism, microwave plasma source and surface wave plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS20140361684A1Increase probabilityIncrease ratingsElectric discharge tubesAntenna supports/mountingsDielectricElectricity
A microwave emission mechanism includes: a transmission path through which a microwave is transmitted; and an antenna section that emits into a chamber the microwave transmitted through the transmission path. The antenna section includes an antenna having a slot through which the microwave is emitted, a dielectric member through which the microwave emitted from the antenna is transmitted and a closed circuit in which a surface current and a displacement current flow. A surface wave is formed in a surface of the dielectric member. The closed circuit has at least: an inner wall of the slot; and the surface and an inner portion of the dielectric member. When a wavelength of the microwave is λ0, a length of the closed circuit is nλ0±δ, where n is a positive integer and δ is a fine-tuning component including 0.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method of reducing disturbs in non-volatile memory
In a non-volatile memory, the displacement current generated in non-selected word lines that results when the voltage levels on an array's bit lines are changed can result in disturbs. Techniques for reducing these currents are presented. In a first aspect, the number of cells being simultaneously programmed on a word line is reduced. In a non-volatile memory where an array of memory cells is composed of a number of units, and the units are combined into planes that share common word lines, the simultaneous programming of units within the same plane is avoided. Multiple units may be programmed in parallel, but these are arranged to be in separate planes. This is done by selecting the number of units to be programmed in parallel and their order such that all the units programmed together are from distinct planes, by comparing the units to be programmed to see if any are from the same plane, or a combination of these. In a second, complementary aspect, the rate at which the voltage levels on the bit lines are changed is adjustable. By monitoring the frequency of disturbs, or based upon the device's application, the rate at which the bit line drivers change the bit line voltage can be adjusted. This can be implemented by setting the rate externally, or by the controller based upon device performance and the amount of data error being generated.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
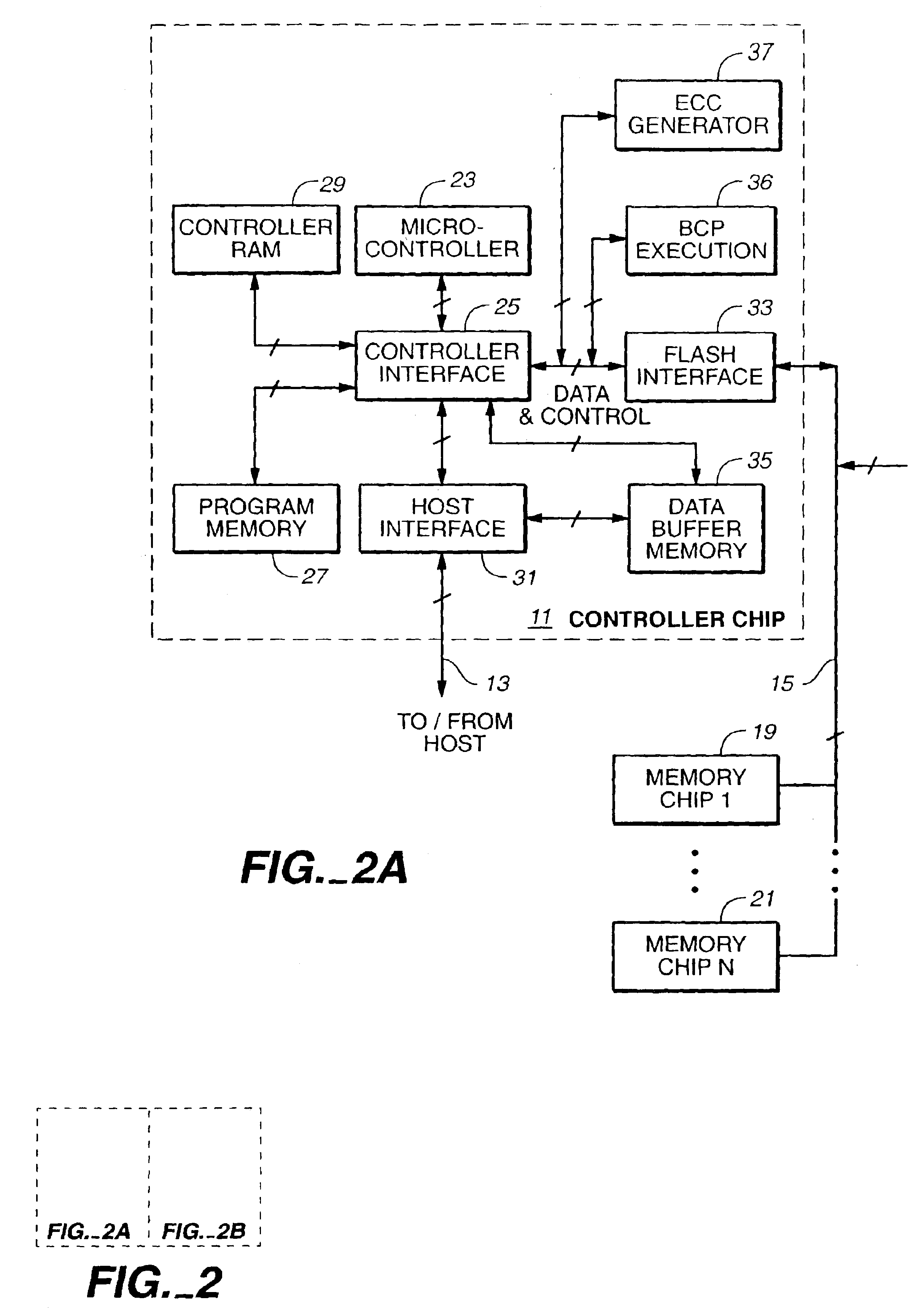
Method and apparatus for simulating physical fields
InactiveUS6665849B2Less storage spaceAvoid excessive intensityDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhysical fieldEngineering
In order to design on-chip interconnect structures in a flexible way, a CAD approach is advocated in three dimensions, describing high frequency effects such as current redistribution due to the skin-effect or eddy currents and the occurrence of slow-wave modes. The electromagnetic environment is described by a scalar electric potential and a magnetic vector potential. These potentials are not uniquely defined, and in order to obtain a consistent discretization scheme, a gauge-transformation field is introduced. The displacement current is taken into account to describe current redistribution and a small-signal analysis solution scheme is proposed based upon existing techniques for static fields in semiconductors. In addition methods and apparatus for refining the mesh used for numerical analysis is described.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS20090230304A1Low costSave spaceThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning tunneling microscopeScanning electron microscope
In a VP-SEM that uses gas multiplication induced within a low-vacuum sample chamber and uses a method of detecting a positive displacement current, a secondary electron detector for the VP-SEM that responds at high speed, which can acquire a TV-Scan rate image at a low cost while saving a space is provided. A secondary electron detector is formed by forming the electron supplying electrode and the detection electrode on the flexible thin film type substrate such as a polyimide film, etc., by an etching method. Thereby, the space can be saved while realizing low cost due to mass production. Further, the ion horizontally moving with respect to the surface of the secondary electron detector is detected and the ion moving in a vertical direction returned to the sample holder is not detected, making it possible to realize a high-speed response.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
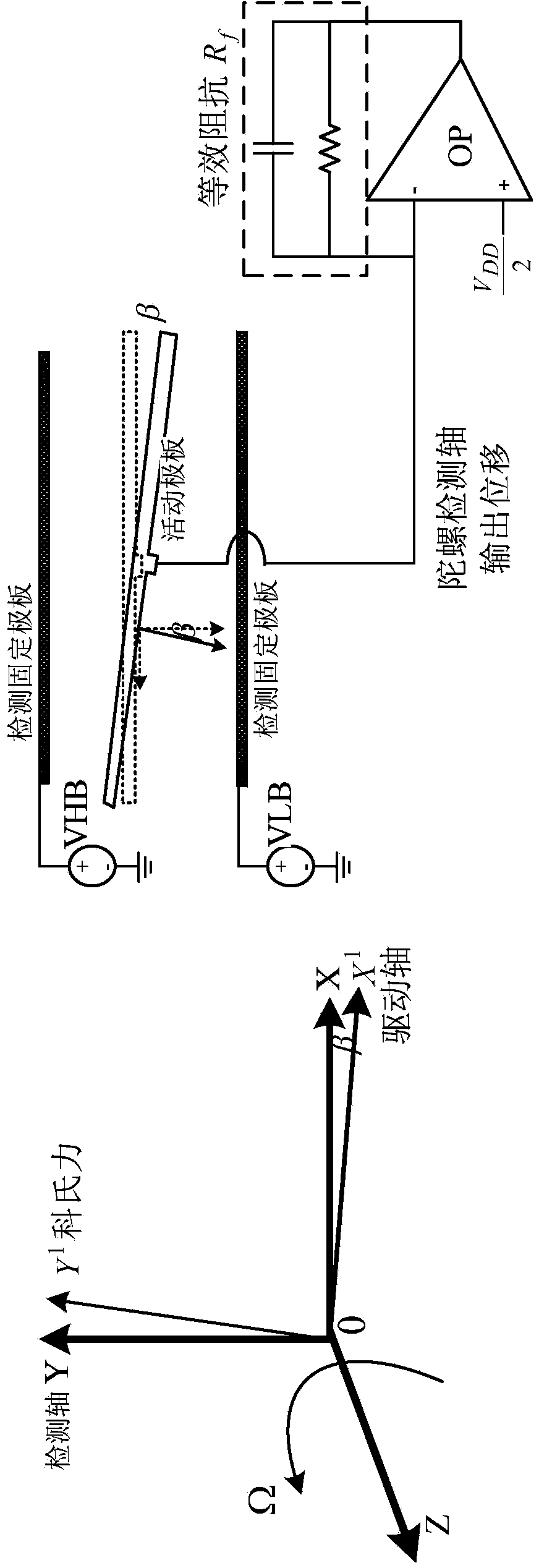
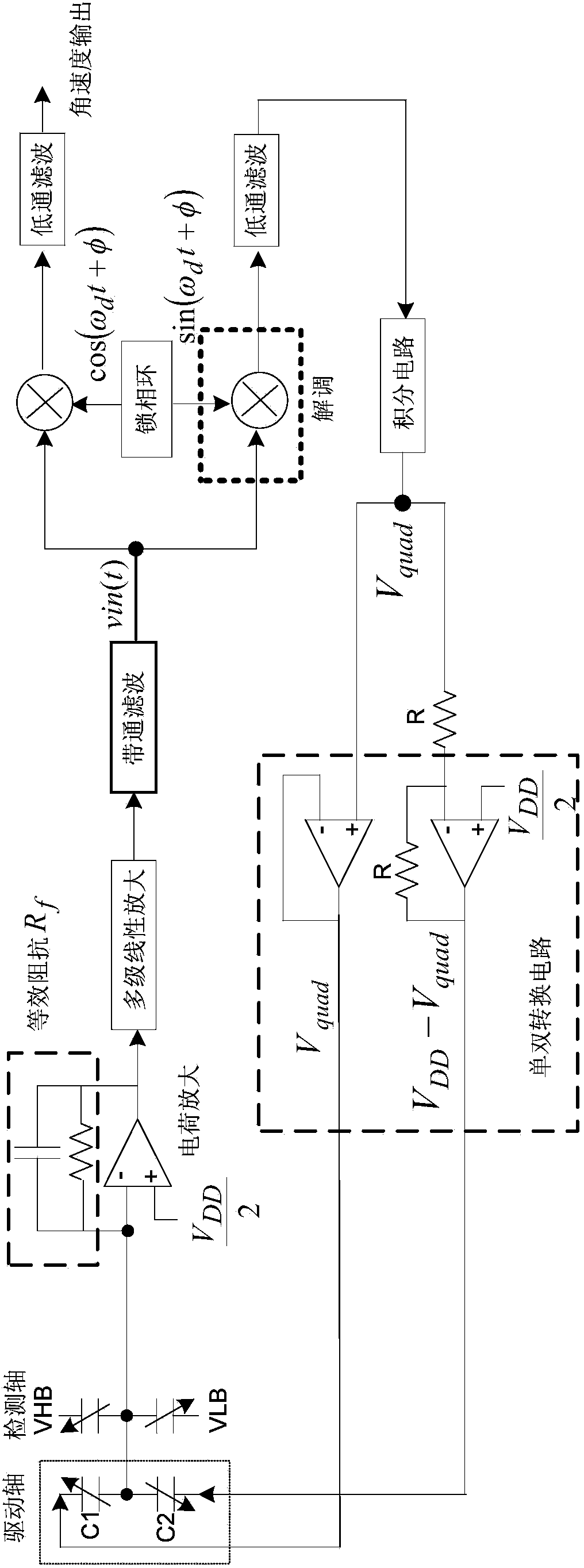
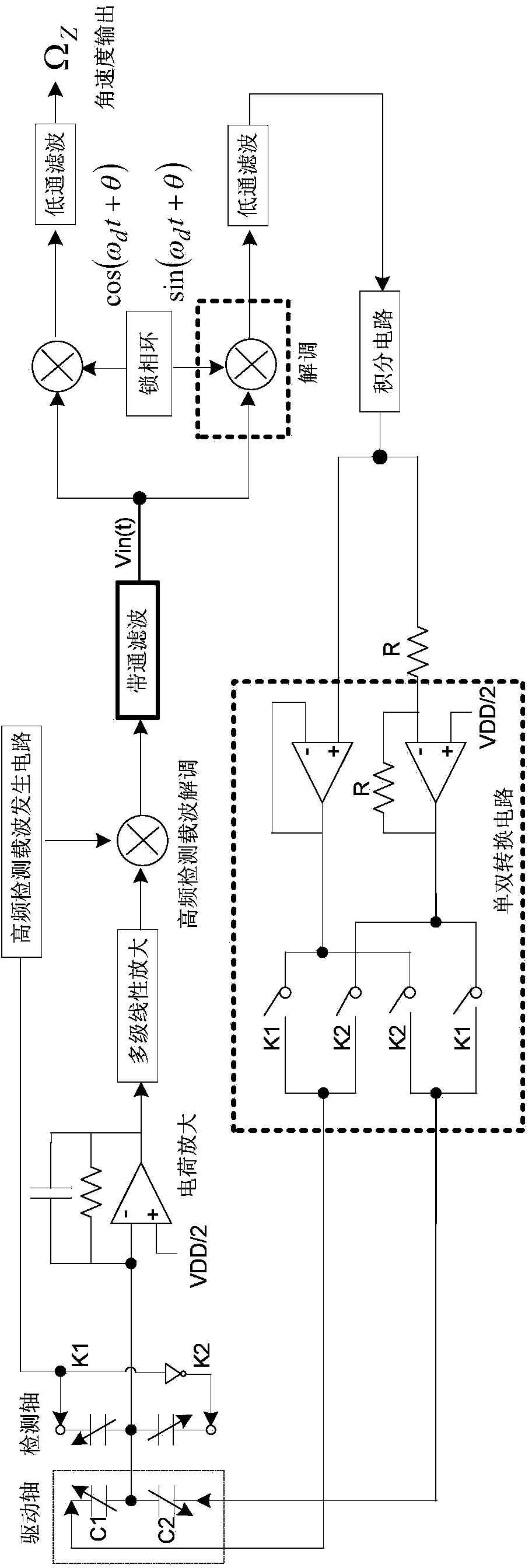
Quadrature error closed-loop compensating circuit for vibrating type silicon micromechanical gyroscope
ActiveCN103822623ARealize closed-loop compensationEliminates quadrature error voltageSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesVoltage amplitudeCapacitance
The invention discloses a quadrature error closed-loop compensating circuit for a vibrating type silicon micromechanical gyroscope. A gyroscope detection signal enters a synchronous demodulation circuit by diving into two parts after being amplified and filtered: one part of gyroscope detection signal is demodulated through reference signals generated by a phase-locked loop, and after low-pass filtering is performed, an angular velocity signal is obtained; the other part of the gyroscope detection signal is demodulated through the reference signals, which is subjected to phase displacement for 90 degrees, and generated by the phase-locked loop, after low-pass filtering is performed, the voltage amplitude of quadrature error signals in the detection signal is extracted out, and a feedback control voltage is obtained through an integrating circuit; the feedback control voltage passes through a single-double switching circuit and is modulated to the driving frequency through a driving detection capacitance so as to generate a feedback current to compensate quadrature displacement current in the detection shaft direction, and then quadrature error amount in the detection signal is eliminated and finally, the pure angular velocity is obtained. According to the invention, the quadrature error amount in an angular velocity detection loop is eliminated by using the feedback current to compensate the quadrature displacement current in the detection shaft direction of the micromechanical gyroscope, and high-precision closed-loop compensating for the quadrature error of the vibrating type silicon micromechanical gyroscope is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA INST OF OPTOELECTRONICS INTEGRATEDDEVICE
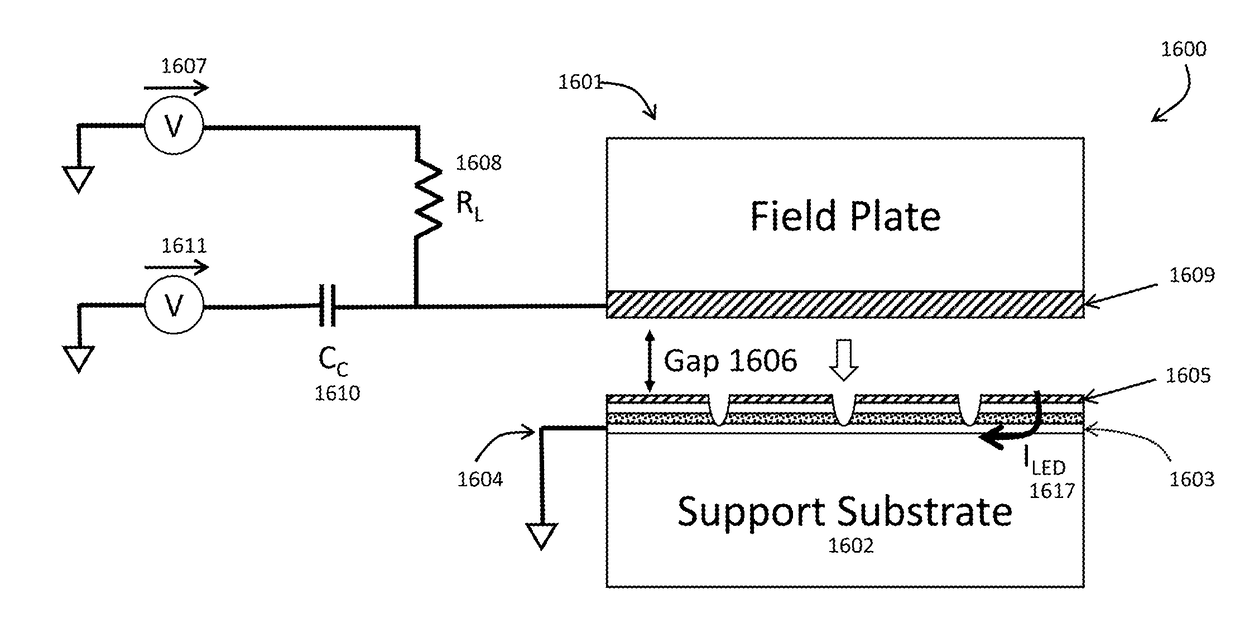
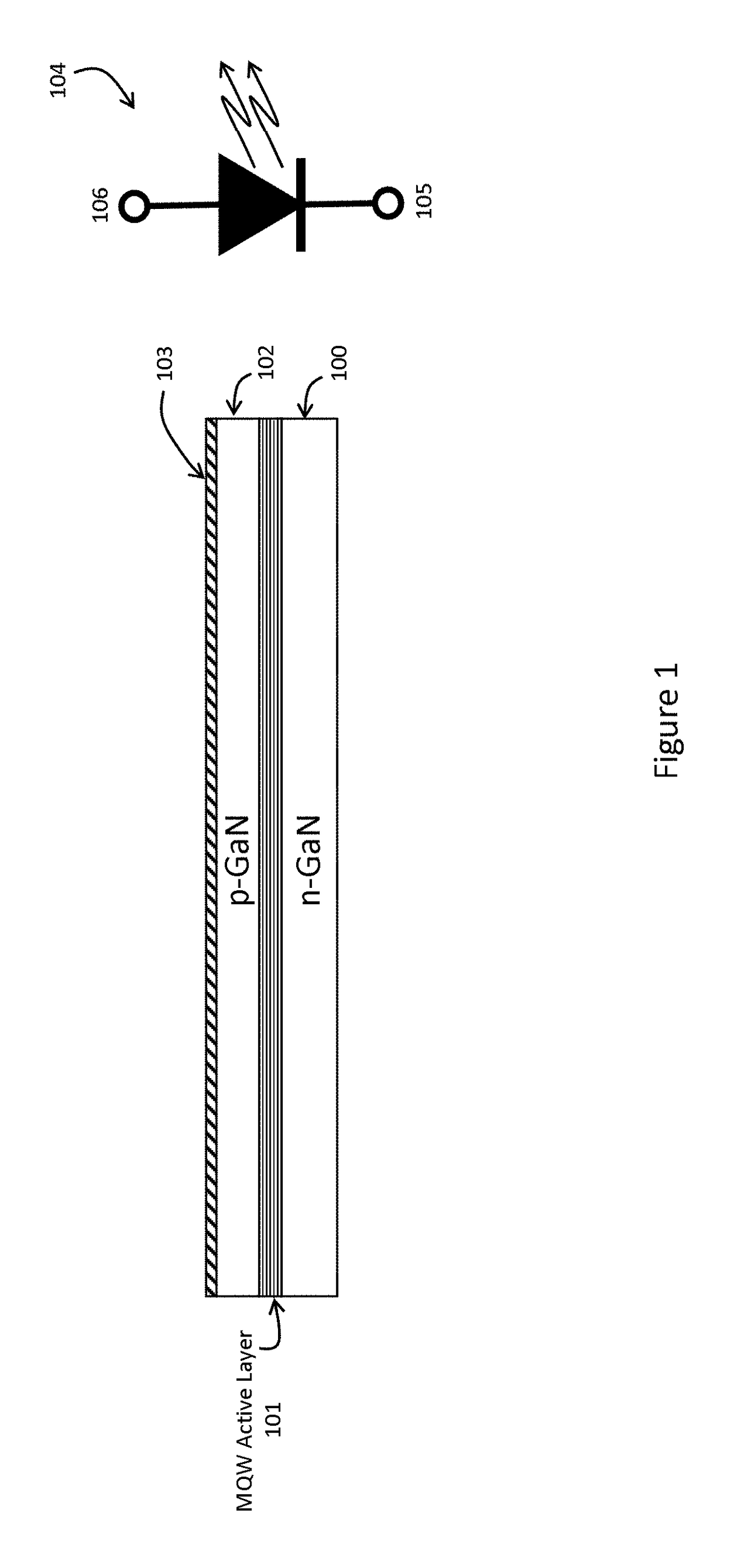
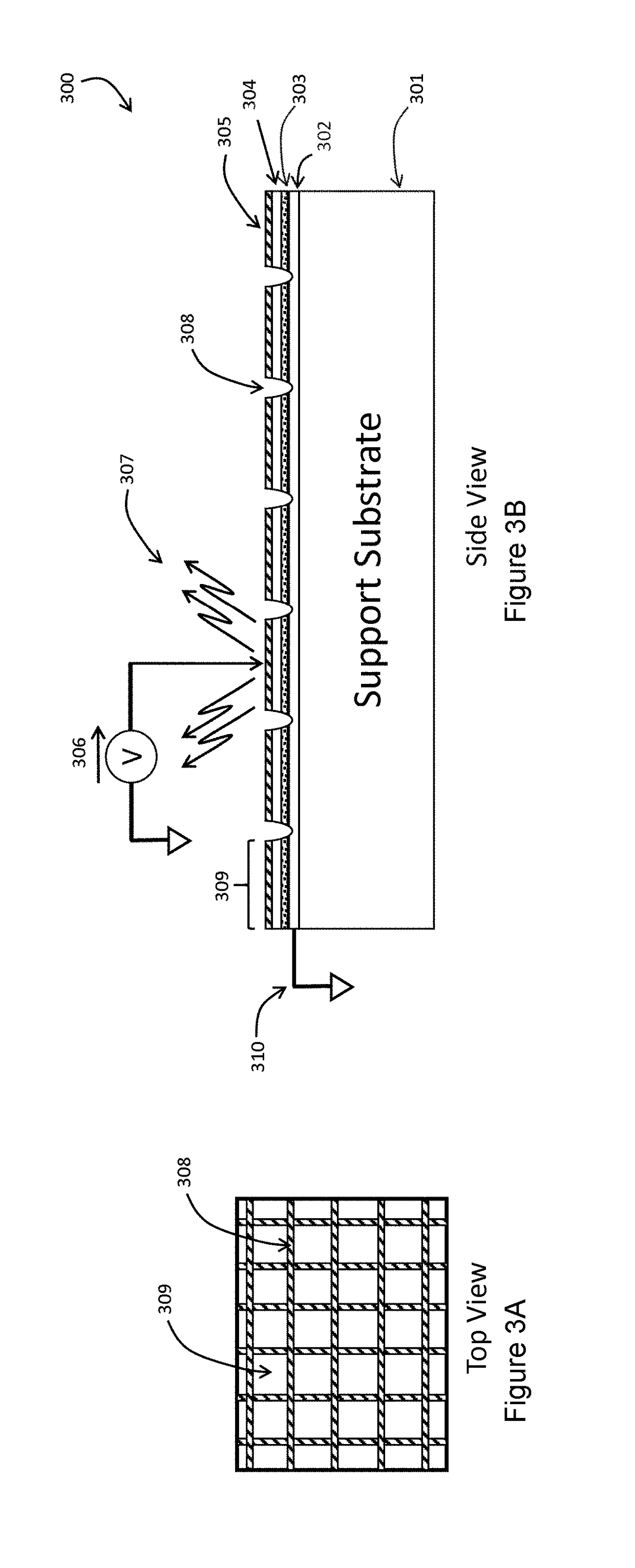
Light emitting diode (LED) test apparatus and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20180259570A1Charge coupling efficiencyEfficient Functional TestingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDiode testingElectricityQuantum efficiency
Embodiments relate to functional test methods useful for fabricating products containing Light Emitting Diode (LED) structures. In particular, LED arrays are functionally tested by injecting current via a displacement current coupling device using a field plate comprising of an electrode and insulator placed in close proximity to the LED array. A controlled voltage waveform is then applied to the field plate electrode to excite the LED devices in parallel for high-throughput. A camera records the individual light emission resulting from the electrical excitation to yield a function test of a plurality of LED devices. Changing the voltage conditions can excite the LEDs at differing current density levels to functionally measure external quantum efficiency and other important device functional parameters.
Owner:APPLE INC
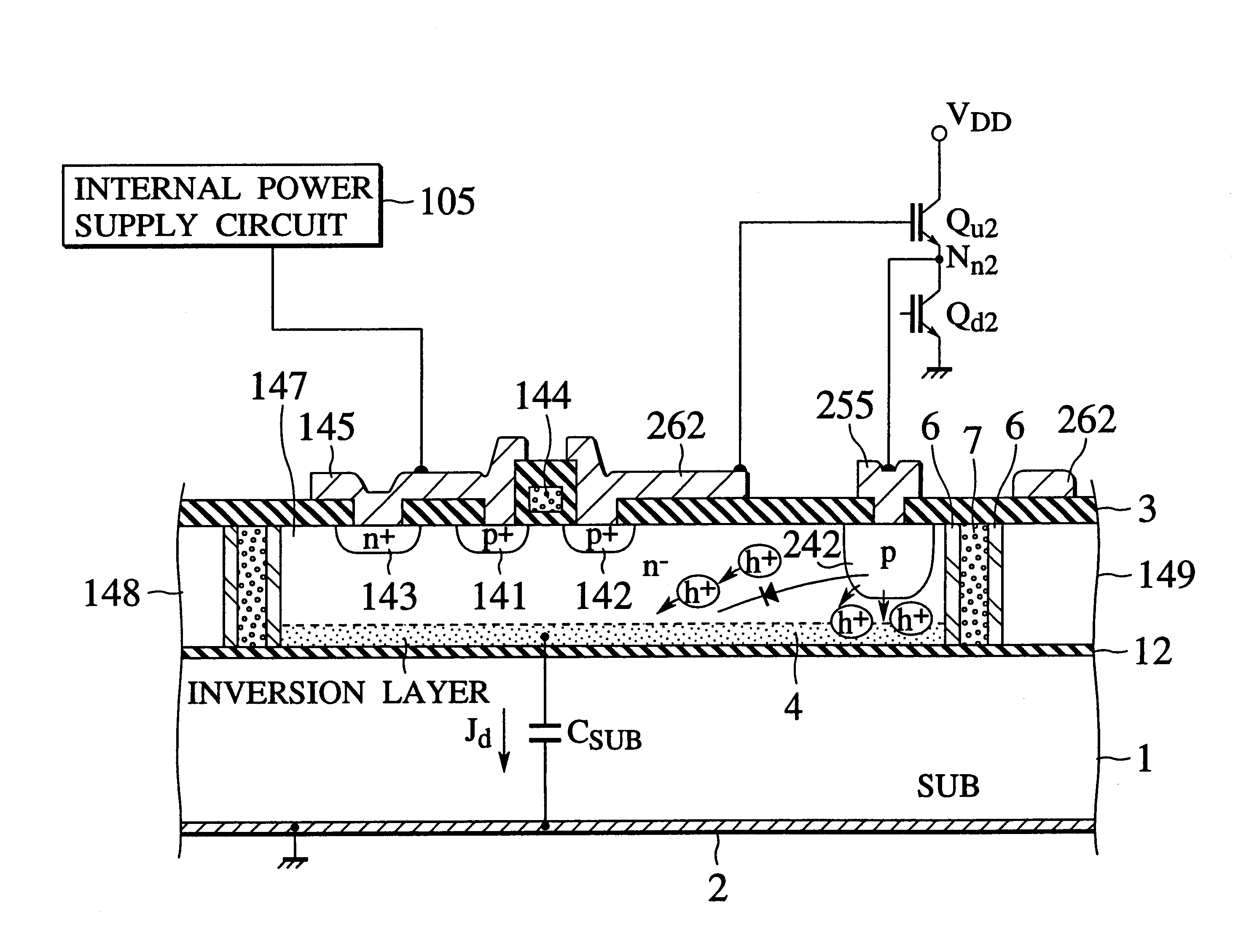
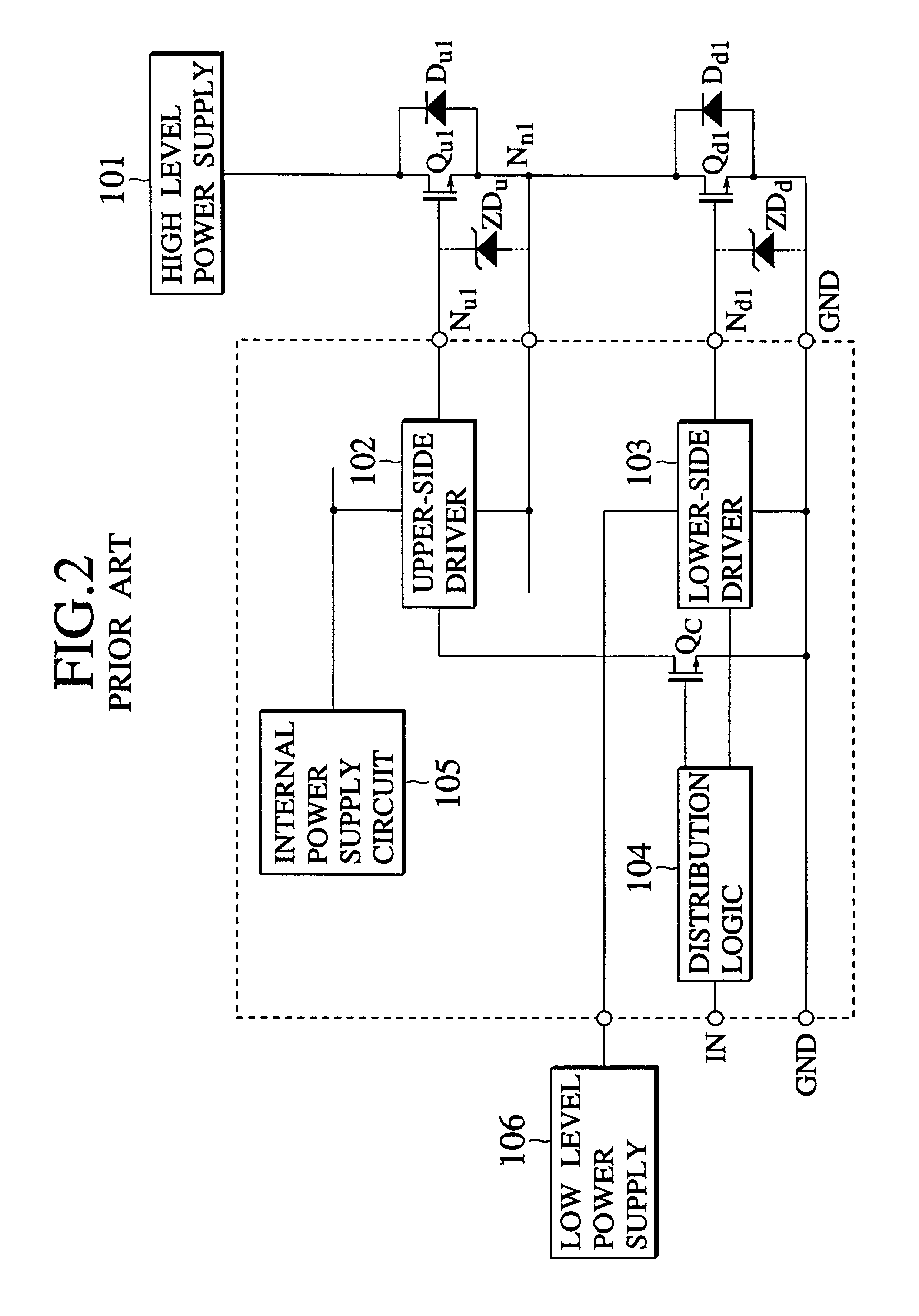
Dielectrically isolated IC driver having upper-side and lower-side arm drivers and power IC having the same
In an IC driver using SOI dielectric isolation structure having a lower and an upper arm side drivers, the upper arm side driver operates in a floating state, a carrier injector region is disposed in an semiconductor island where a switching device for the upper-side circuit is formed. The IC driver drives a set of an upper-side and a lower-side output power devices, a first main electrode of the upper-side output power device is connected to a high level power supply, a second main electrode of the upper-side output power device is connected to a first main electrode of the lower-side output power device, a second main electrode of the lower-side output power device is connected to ground potential (GND). The carrier injector region is formed deeper than a couple of main electrode regions of the switching device in the upper arm side driver. Moreover, this injector region is connected to an intermediate potential at connecting terminal of the upper-side and the lower-side output power devices. A current for compensating the displacement current Jd flowing in the parasitic condenser CSUB inherent to the SOI structure is supplied through the carrier injector from this intermediate potential terminal, to diminish the extra load of the internal power supply circuit for supplying the upper arm side driver with a predetermined voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and device for monitoring plasma discharges
InactiveUS20100231194A1Low costBroaden applicationElectric discharge tubesFrequency to phase shift conversionDisplacement currentAtomic physics
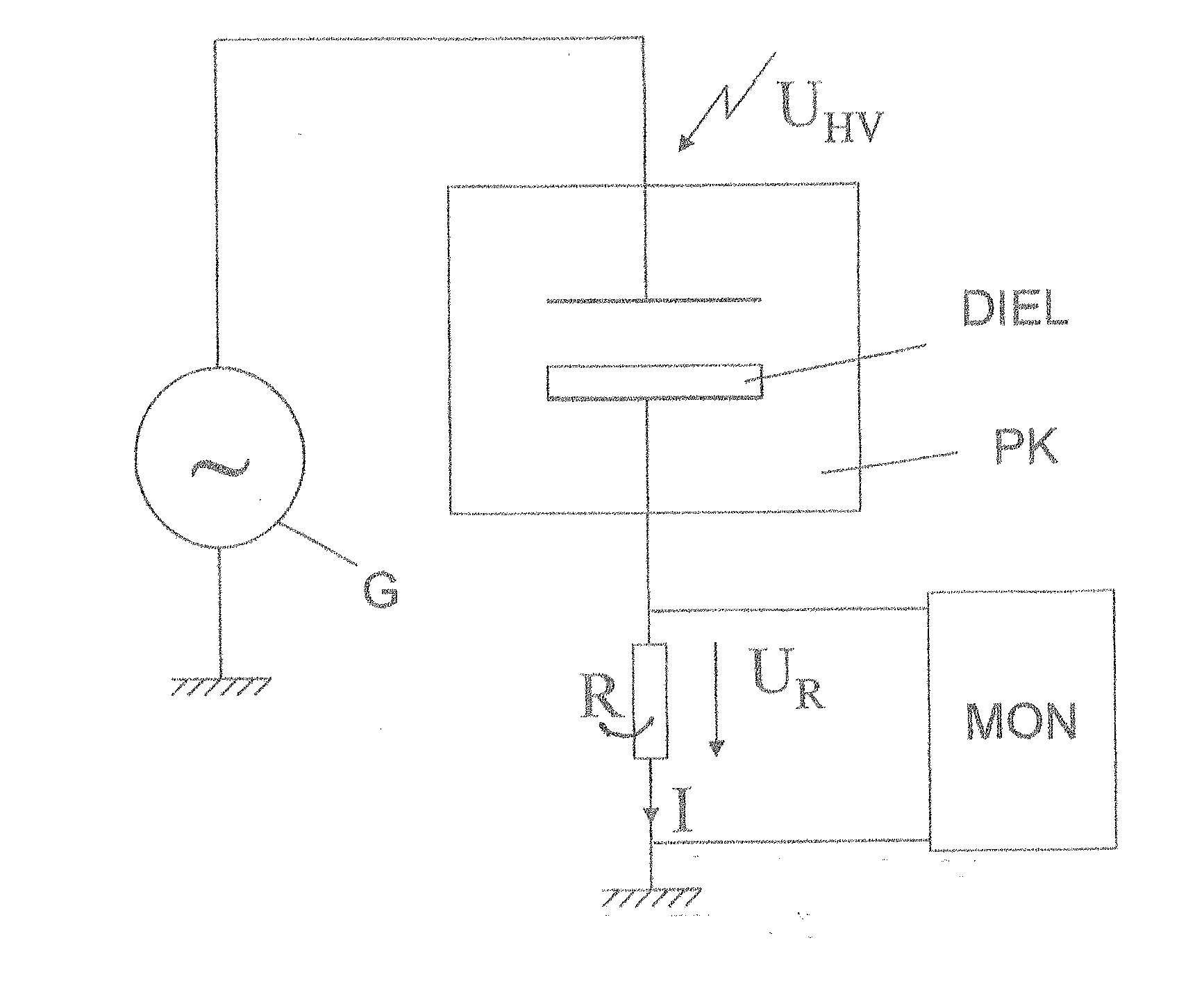
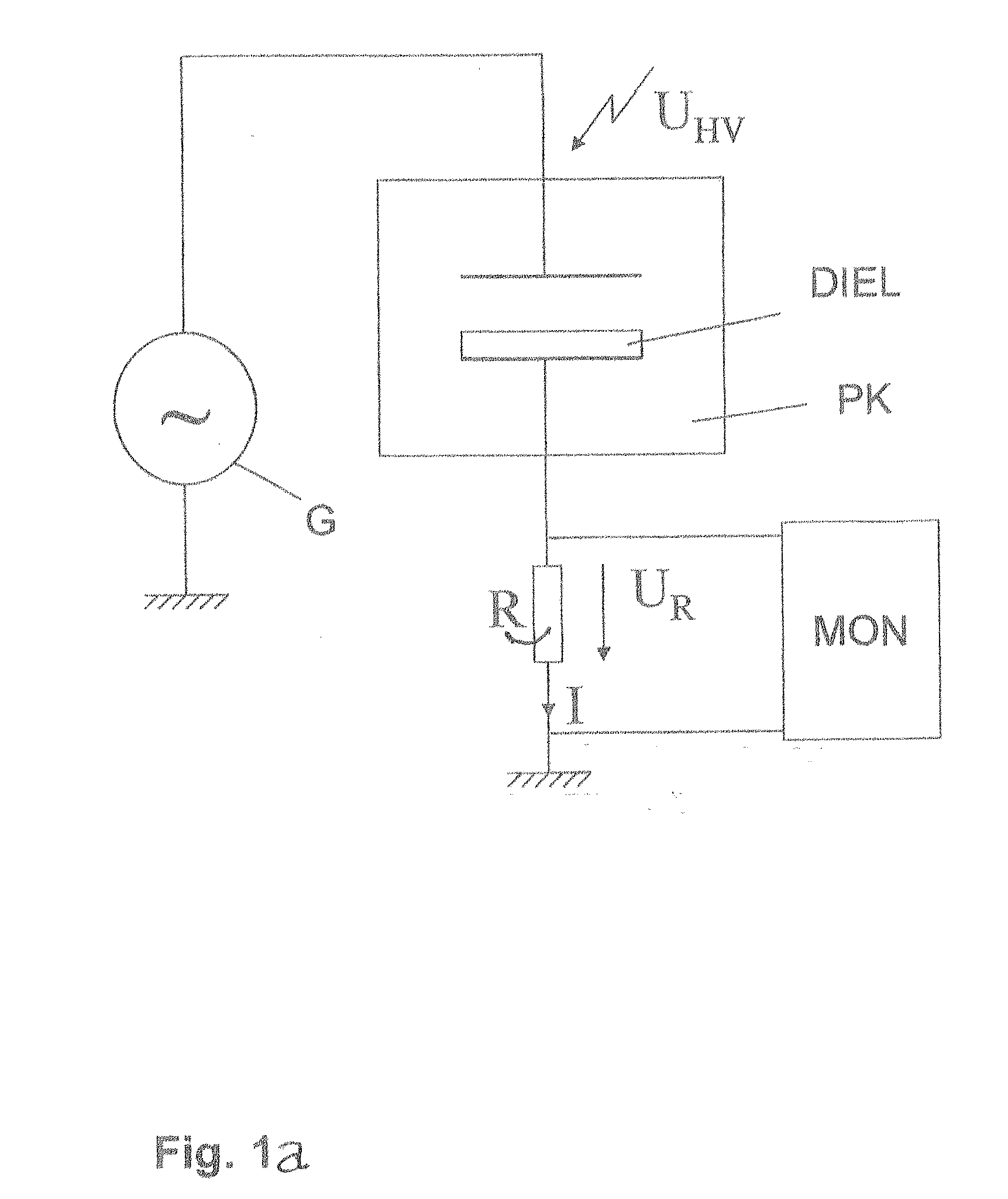
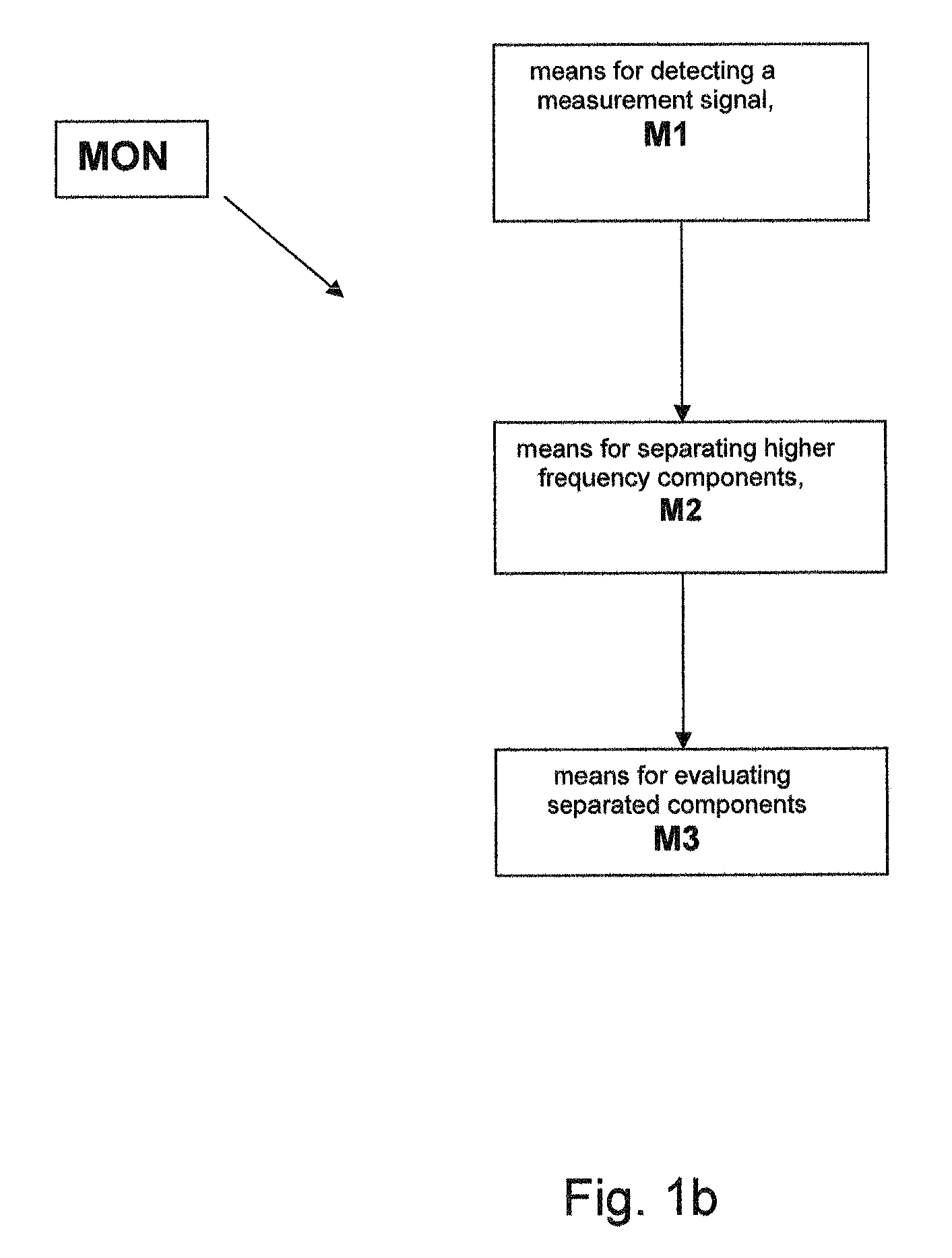
A method and a device (MON) for monitoring plasma-discharges during a surface treatment process are described. In this process electrodes within a gaseous medium are provided with an alternating voltage (UHV) for generating plasma. The monitoring device (MON) has a detector device (M1) for detecting a measurement signal (I) generated by the alternating voltage (UHV) within the gaseous medium, separating means (M2) for separating signal components above a preset frequency and evaluating means (M3) for evaluating the resulting separated signal components by comparing them with at least one preset reference. Preferably the generating of the plasma is achieved by dielectric barrier discharge and the electric current penetrating the medium, especially the dielectric displacement current, is measured as the measurement signal (I).
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20130285140A1Avoid contactResistance valueTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor devicePower flow
A trench-gate type semiconductor device that can prevent breakdown of a gate insulating film caused by a displacement current flowing into a protective diffusion layer at a portion of a trench underlying a gate electrode at a turn-off time and simultaneously improves a current density by narrowing a cell pitch. The semiconductor device includes a gate electrode embedded into a trench penetrating a base region. The gate electrode is disposed into a lattice shape in a planar view, and a protective diffusion layer is formed in a drift layer at the portion underlying thereof. At least one of blocks divided by the gate electrode is a protective contact region on which the trench is entirely formed. A protective contact for connecting the protective diffusion layer at a bottom portion of the trench and a source electrode is disposed on the protective contact region.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and Arrangement for Generating and Controlling a Discharge Plasma
InactiveUS20080317974A1Improve controllabilityLower ratioElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsVolumetric Mass DensityLocal current
Method and arrangement for controlling a discharge plasma in a discharge space (11) having at least two spaced electrodes (13, 14). A gas or gas mixture is introduced in the discharge space (11), and a power supply (15) for energizing the electrodes (13, 14) is provided for applying an AC plasma energizing voltage to the electrodes (13, 14). At least one current pulse is generated and causes a plasma current and a displacement current. Means for controlling the plasma are provided and arranged to apply a displacement current rate of change for controlling local current density variations associated with a plasma variety having a low ratio of dynamic to static resistance, such as filamentary discharges. By damping such fast variations using a pulse forming circuit (20), a uniform glow discharge plasma is obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM MFG EURO
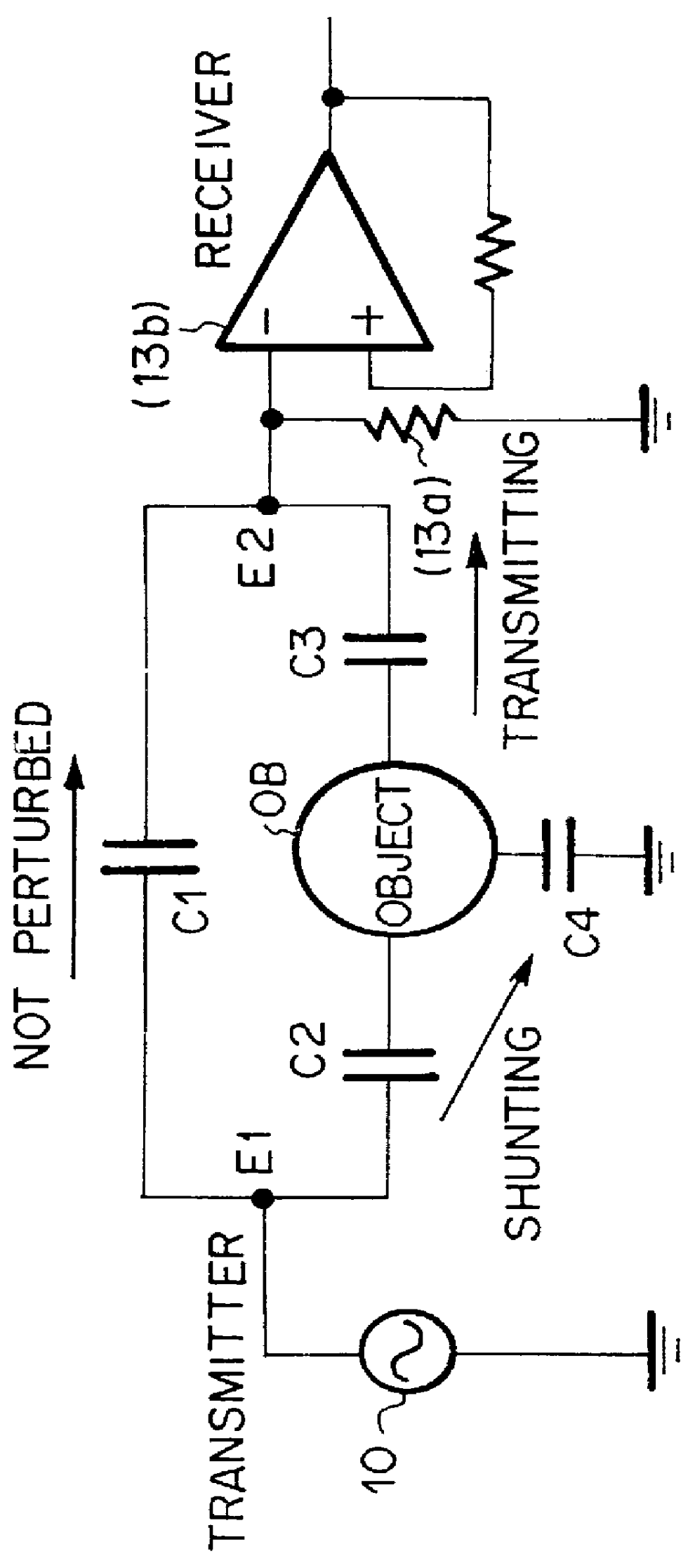
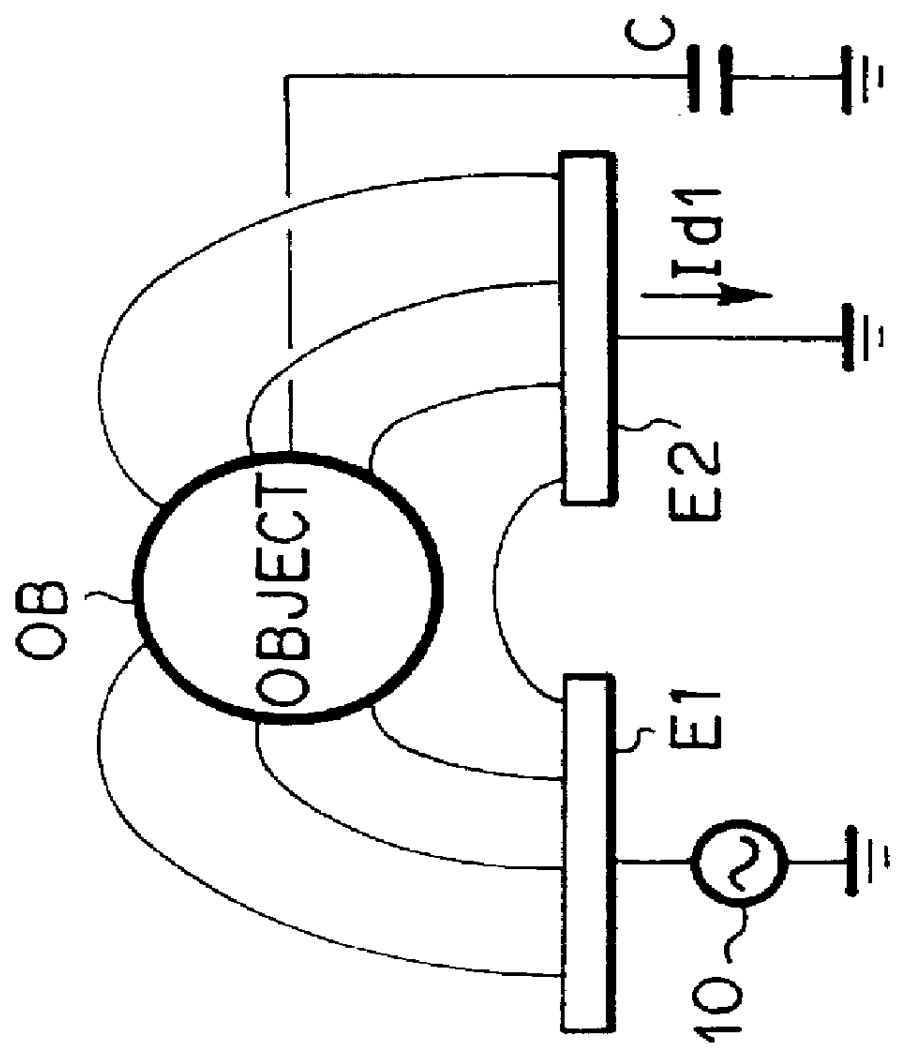
Systems and methods for detection of dielectric change in material and structure
ActiveUS7288945B2High sensitivityPrevent overloadResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingElectricityAudio power amplifier
Methods and systems are described for efficiently detecting an object. The system includes at least one electrode for measuring a displacement current. The at least one electrode is coupled to a floating ground configuration provided by an op-amp, where the inverting node of the op-amp is coupled to electrode and the non-inverting node is coupled to a signal generator. The system may include a single capacitance sensor for detecting an object. Systems may include a plurality of capacitance sensors in an array configuration for detecting an object.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Method and apparatus for simulating physical fields
InactiveUS20020042698A1Simple structureLess storage spaceDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhysical fieldEngineering
In order to design on-chip interconnect structures in a flexible way, a CAD approach is advocated in three dimensions, describing high frequency effects such as current redistribution due to the skin-effect or eddy currents and the occurrence of slow-wave modes. The electromagnetic environment is described by a scalar electric potential and a magnetic vector potential. These potentials are not uniquely defined, and in order to obtain a consistent discretization scheme, a gauge-transformation field is introduced. The displacement current is taken into account to describe current redistribution and a small-signal analysis solution scheme is proposed based upon existing techniques for static fields in semiconductors. In addition methods and apparatus for refining the mesh used for numerical analysis is described.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
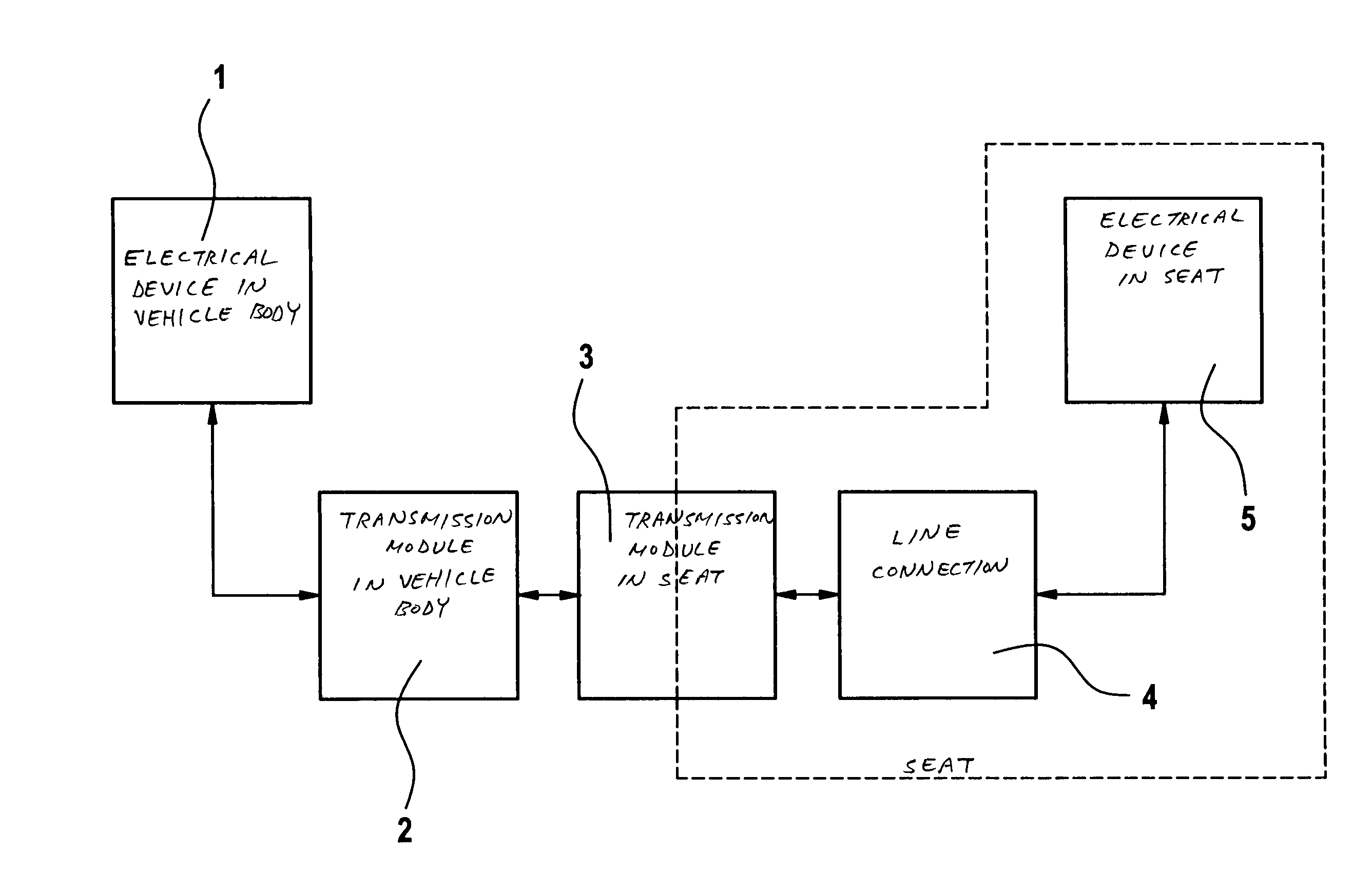
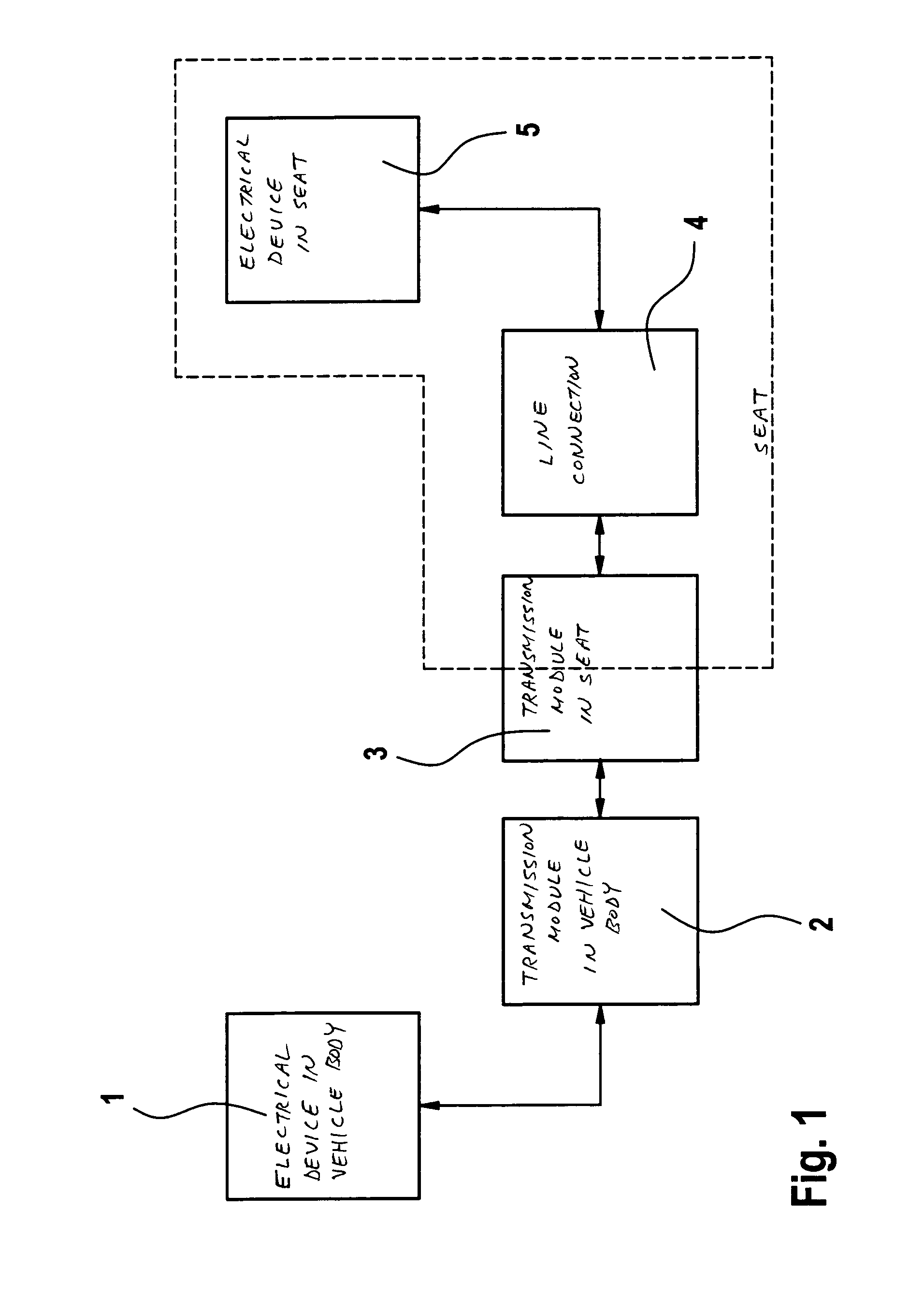
Device for transmitting signals and/or energy to a vehicle seat rail system
InactiveUS6960993B2Reliable energyReliable signalElectric signal transmission systemsNear-field transmissionWireless transmissionElectrical devices
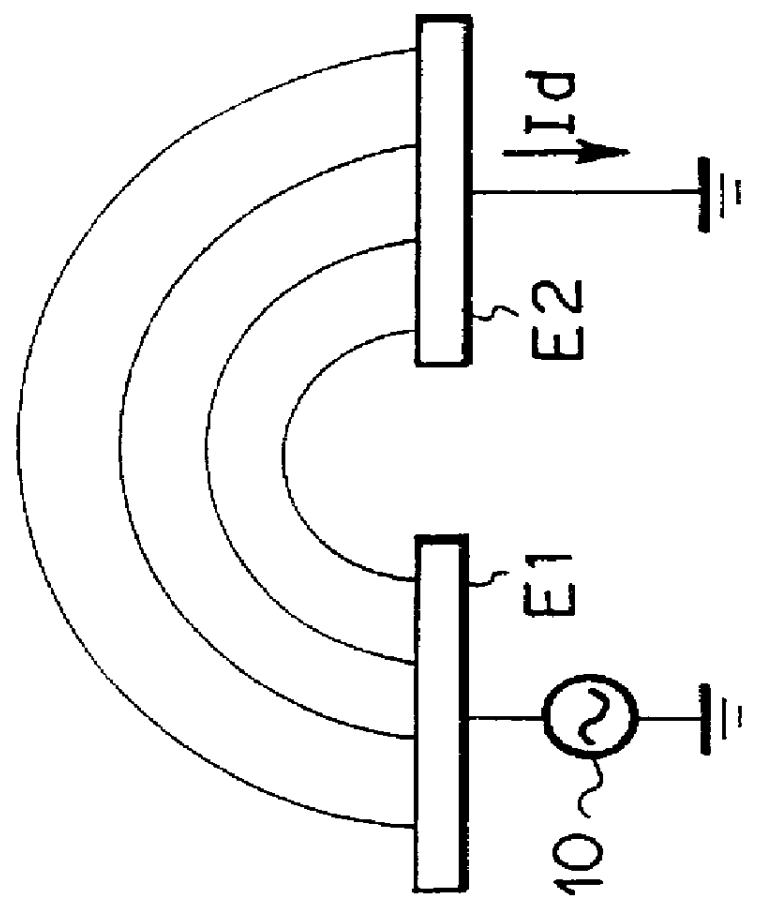
A device, using which signals and energy may be transmitted without contact between an electrical device on or in the vehicle body and an electrical device on or in a vehicle seat, reliable signal and energy transmission being ensured even in the event of frequent changes of the seating configuration, without the vehicle user having to take special precautions for this purpose. The two electrical devices are each assigned a transmission module. These transmission modules form a high-frequency wireless transmission path. The transmission module on or in the vehicle body is integrated into the rail system for the vehicle seat, while the transmission module on or in the seat may be coupled into the rail system in such a way that the signal and / or energy transmission occurs via the displacement current generated in the rail system.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Light emitting diode (LED) test apparatus and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20180174931A1Low costMass-production scale manufacturingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementStatic indicating devicesQuantumDisplacement current
Embodiments relate to functional test methods useful for fabricating products containing Light Emitting Diode (LED) structures. In particular, LED arrays are functionally tested by injecting current via a displacement current coupling device using a field plate comprising of an electrode and insulator placed in close proximity to the LED array. A controlled voltage waveform is then applied to the field plate electrode to excite the LED devices in parallel for high-throughput. A camera records the individual light emission resulting from the electrical excitation to yield a function test of a plurality of LED devices. Changing the voltage conditions can excite the LEDs at differing current density levels to functionally measure external quantum efficiency and other important device functional parameters.
Owner:APPLE INC
Pure Dielectric Antennas and Related Devices
InactiveUS20070252778A1Improve radiation efficiencyImprove efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonanceDielectric antennas
There is disclosed an antenna device comprising an elongate dielectric radiating element having a longitudinal axis and a feeding mechanism for generating displacement currents in the dielectric radiating element. The radiating element is configured to support displacement current resonance modes parallel to the longitudinal axis but to inhibit displacement current resonance modes transverse to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Electric Field Signature Detection Using Exciter-Sensor Arrays
An electric field signature detector for detecting and identifying objects that uses multiple electrostatic sensor nodes each having a passive sensing electrode whose free conduction electrons are displacement responsive to an externally applied or sensed electric field potential, and a transimpedance converter and amplifier exhibiting ultra-high input impedance for translating low level input displacement current from a sensing electrode into a useable output signal in response to a charge displacement signal induced on the passive sensing electrode by an external electric field. The electric field signature detector further includes an exciter for providing a reference electric field used in the retrieval and processing of an electric field signature representative of an object and class of object under investigation. The electric field signature detector having uses including military, security, anti-terrorist, and defense related.
Owner:RAMPART DETECTION SYST
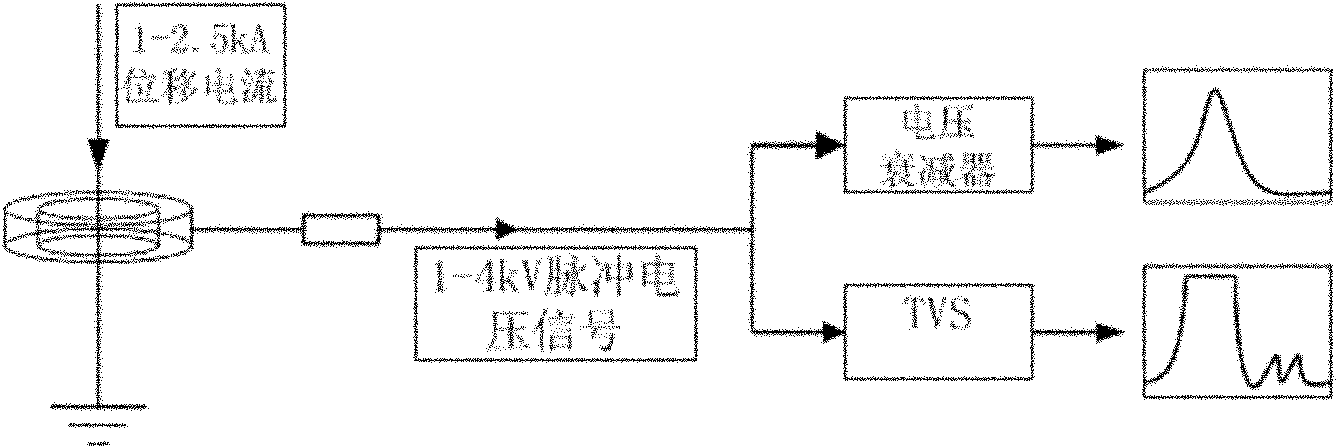
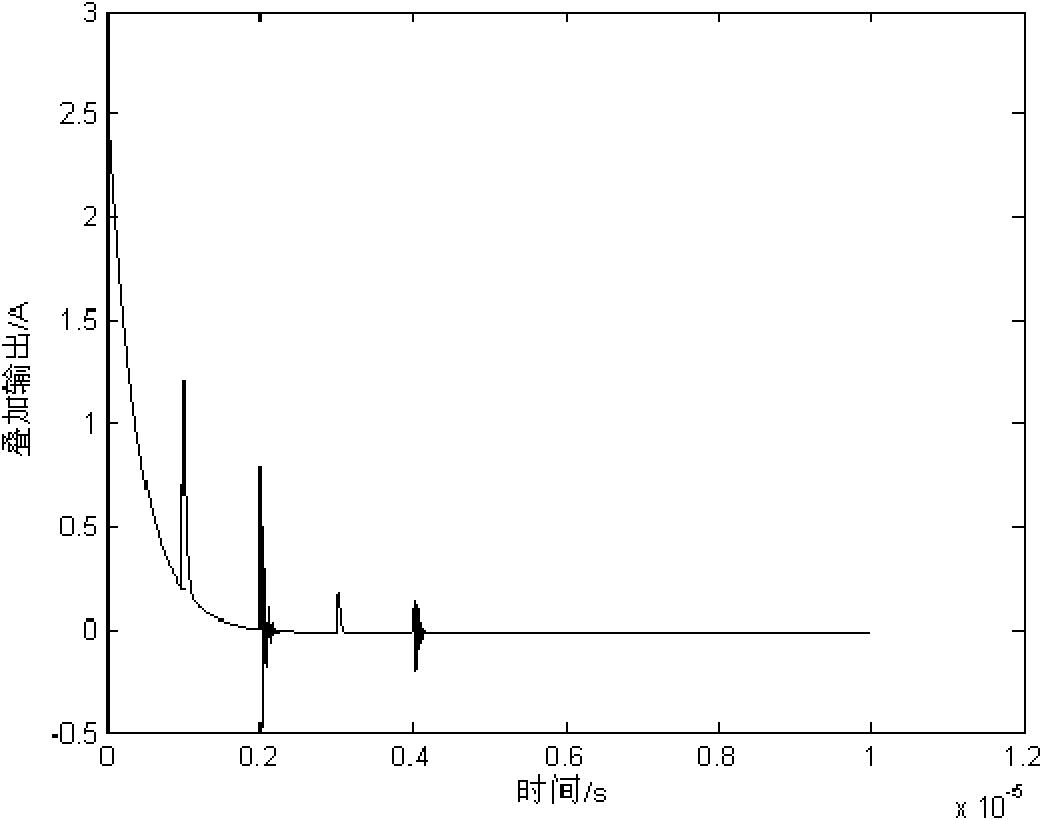
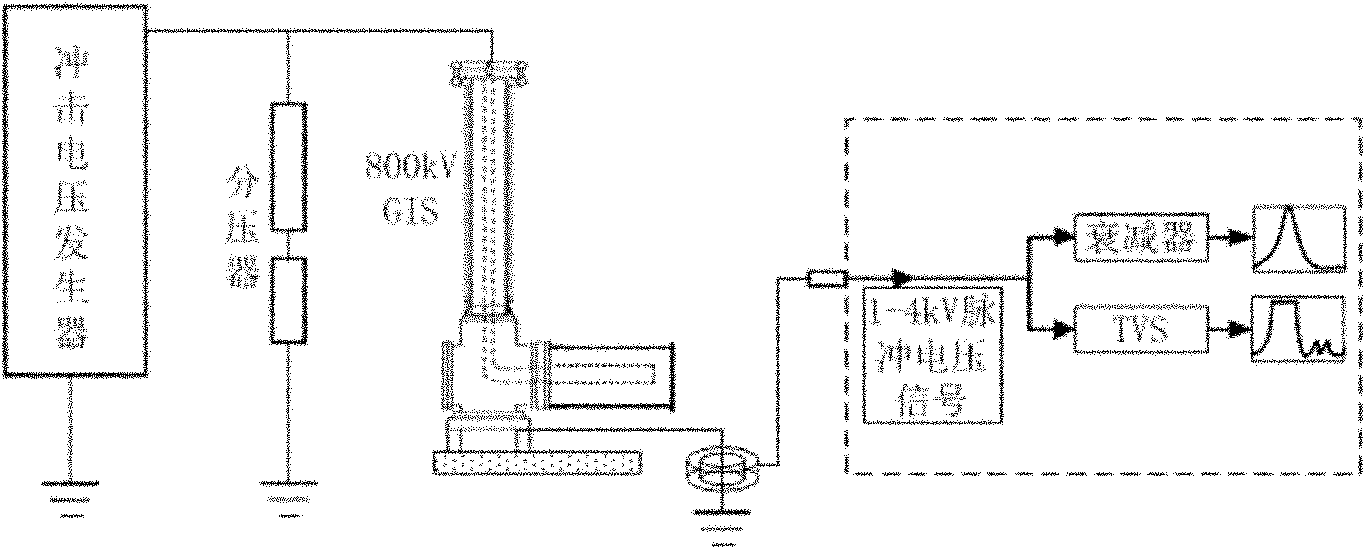
Partial discharge measurement device under impulse voltage on site and signal processing method thereof
The invention discloses a partial discharge measurement device under impulse voltage on site and a signal processing method thereof. The device comprises a current sensor, a tapping point, a voltage attenuator, a voltage transient suppression device and a back-end processing and displaying system, wherein the output end of the current sensor is connected to the input end of the tapping point through an integrating resistor and a coaxial-cable; one path of the output end of the tapping point is connected to the input end of the voltage attenuator, and the other path is connected to the input end of the voltage transient suppression device; and the output ends of the voltage attenuator and the voltage transient suppression device are respectively connected onto the backeend processing and displaying system. The partial discharge measurement device under impulse voltage on site detects a displacement current signal on a GIS (Geographic Information System) ground wire through a Rogowski coil, the on-site measurement for loop building is simple, and the measurement mode is easy to operate and ensures the security of personnel and equipment.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Local coil unit for a magnetic resonance apparatus
InactiveUS7002347B2Precise positioningReduce couplingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringB1 fieldMR - Magnetic resonance
A local coil unit for a magnetic resonance apparatus, which radiates a radio-frequency field into an examination subject, has a housing and at least a part of the housing is formed of an insulating dielectric material that passively compensates for an inhomogeneity in the high-frequency field in the subject. The material has a relative dielectric value εr of greater than 50, preferably greater than 100, and a dielectric loss factor tan δ of less than 2.5×10−2, preferably less than 1×10−3. In the dielectric material displacement currents are generated which create an additional magnetic field that compensates for the minima in the B1 field as a result of the eddy currents arising in the patient due to the radio-frequency radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Light emitting diode (LED) test apparatus and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20190004105A1Low costMass-production scale manufacturingDiode testingElectroluminescent light sourcesLight emissionDisplacement current
Owner:APPLE INC
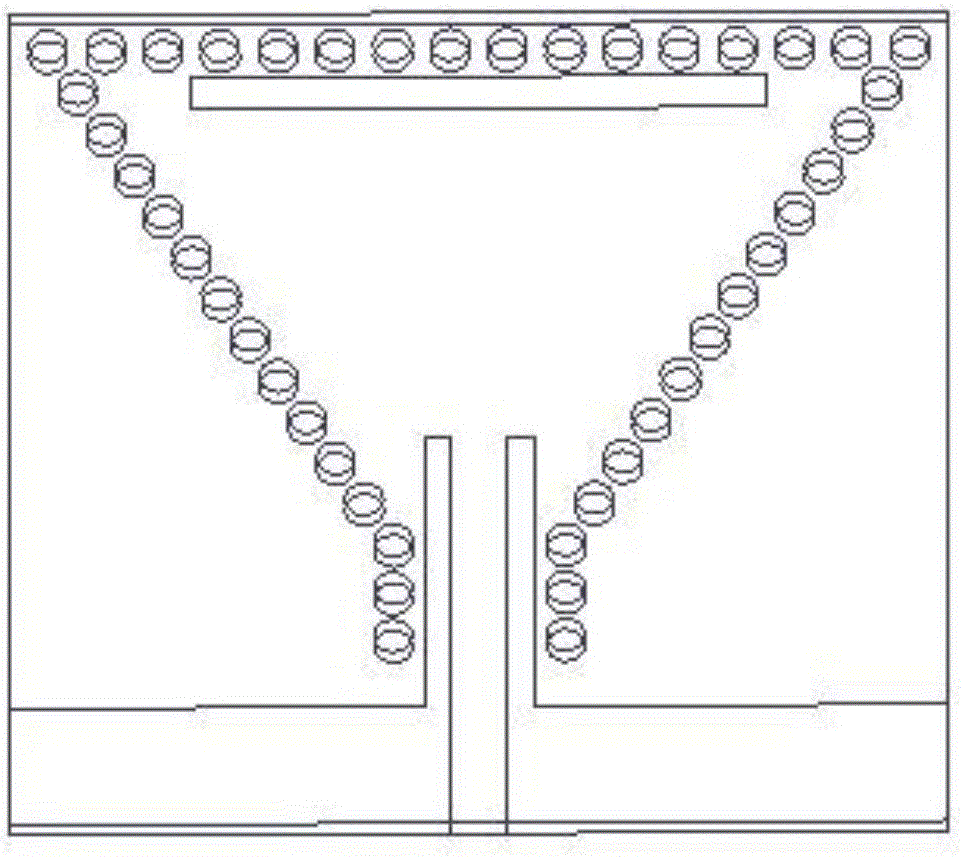
Triangle substrate-integrated waveguide resonator-based planar slot antenna
InactiveCN105958197AImprove radiation efficiencyEasy to integrateRadiating elements structural formsSlot antennasIsoetes triquetraDielectric plate
The invention discloses a planar slot antenna based on a triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity, which is fed by a coplanar waveguide on the lower surface of a dielectric plate by slotting in the edge region of the upper surface of an equilateral triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity. electricity, so that the antenna works in model. A rectangular slit is opened on the edge of the equilateral triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity, and made parallel to one side of the equilateral triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity, so that a displacement current will be generated on the slit, and electromagnetic waves will be radiated. The antenna retains the advantages of better radiation performance of the traditional cavity-backed slot antenna. At the same time, the entire antenna, including the radiation structure, feed structure and back cavity, is completely fabricated on a single-layer dielectric board, which greatly reduces the processing complexity and reduces the processing time. The cost also makes planar circuit integration easier.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
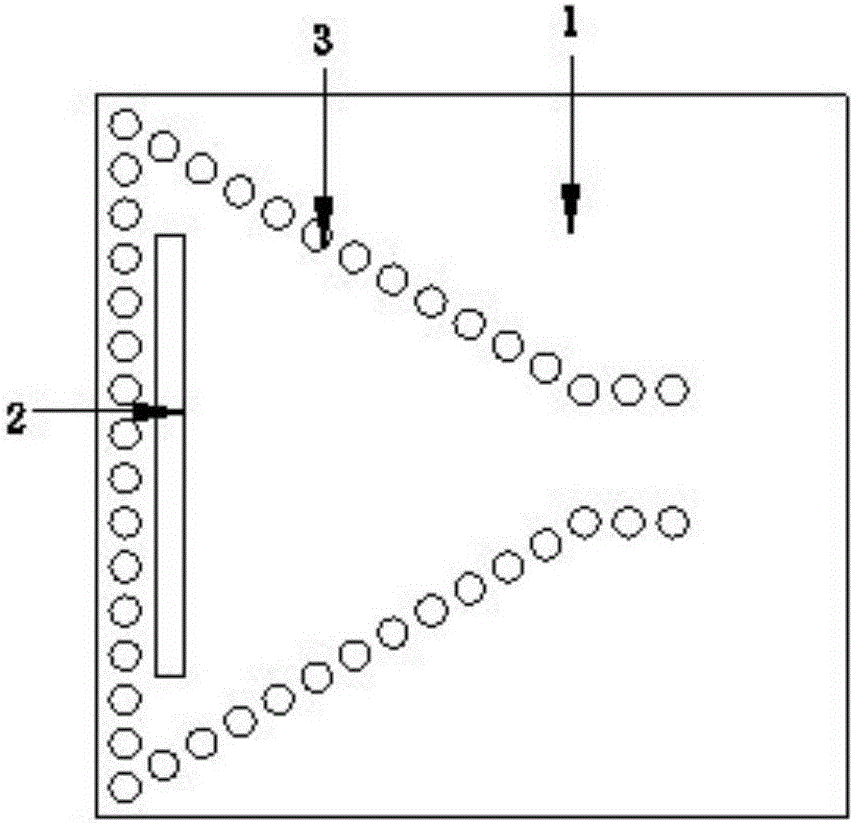
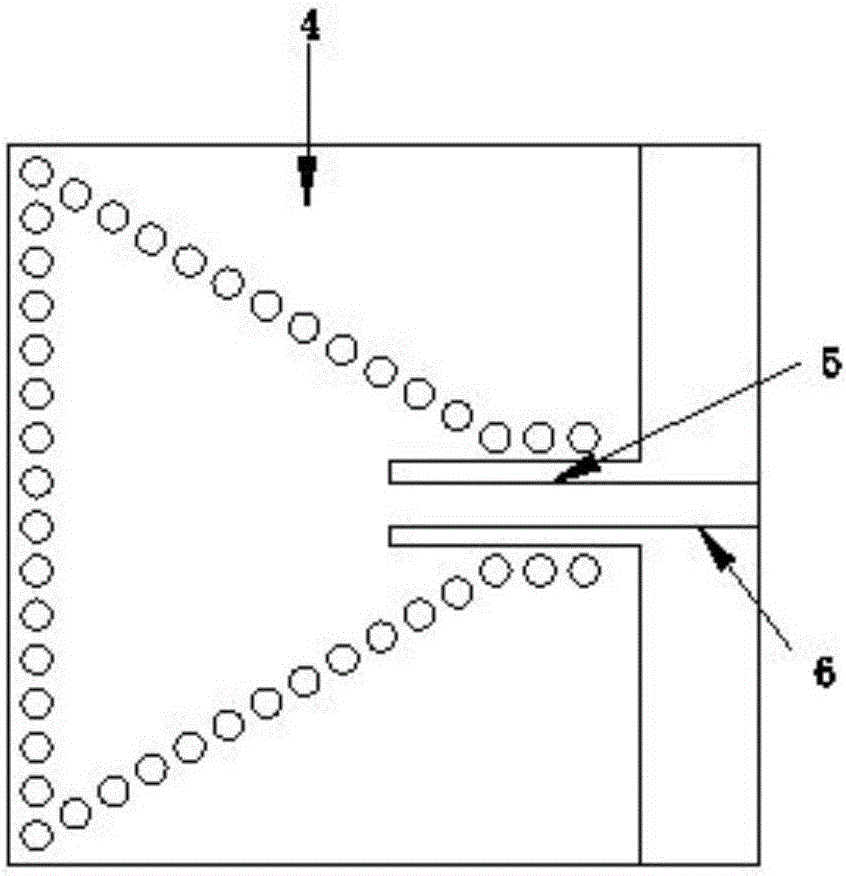
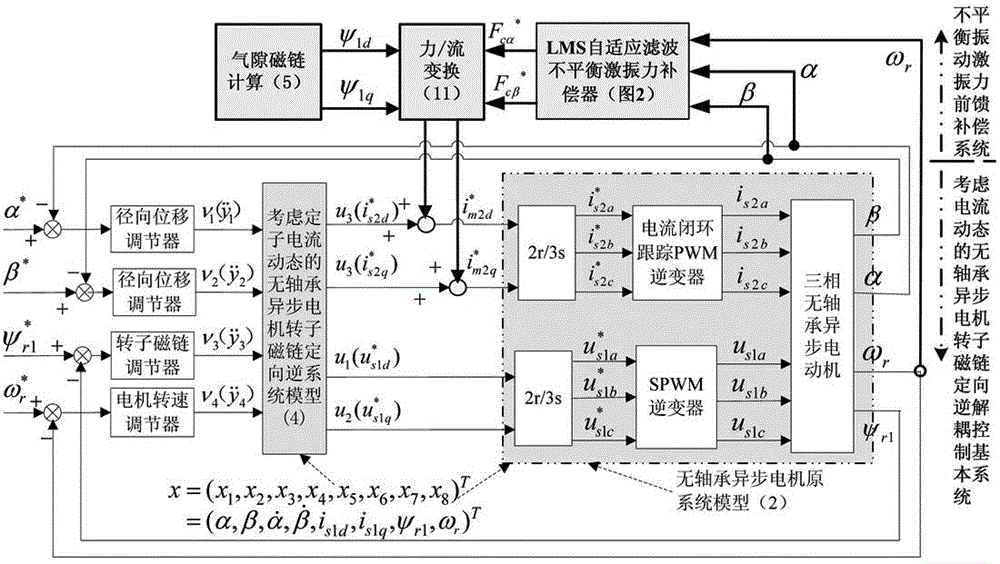
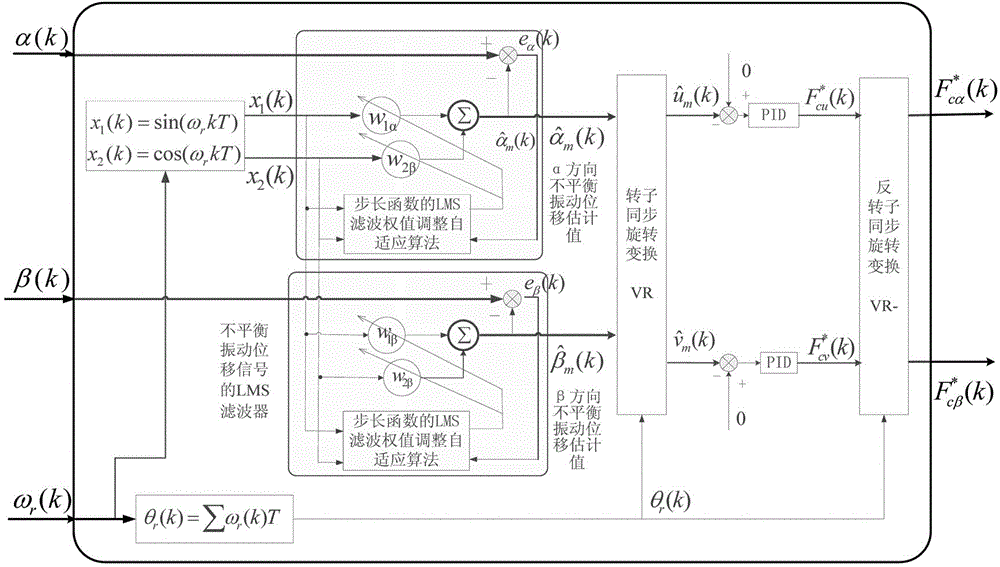
Unbalance vibration control system of bearingless asynchronous motor
InactiveCN104660136ARealize dynamic decouplingSimple structureElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVibration controlLoad torque
The invention provides an unbalance vibration control system of a bearingless asynchronous motor. The system consists of a directional inverse decoupling control system of a rotor flux linkage of the bearingless asynchronous motor and an unbalance exciting force feedforward compensation system, wherein the directional inverse decoupling control system of the rotor flux linkage of the bearingless asynchronous motor comprises an original system, an inverse system and four adjustors and realizes dynamic decoupling control of an electromagnetic torque, the rotor flux linkage and a random displacement component; the unbalance exciting force feedforward compensation system comprises an LMS self-adapted filter unbalance exciting force compensator and a force / flow conversion module and dynamically adjusts the unbalance displacement extraction speed and precision by using a simple step-length factor adjusting function; output of the feedforward compensation system and a steady random displacement current output by the inverse system are overlaid to form a magnetic suspension dynamic decoupling control system. The system provided by the invention cancels the links of online identification of a predictable load torque in the inverse system and a closed loop of a stator current of the original system, so that the influence of the unbalance exciting force can be effectively inhibited and the control precision and performance are improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Critical displacement forecasting and early warning method based on slope deformation failure mechanism
InactiveCN103712587ADetermine the deformation valueEarthquake measurementSeismologySlope monitoringProcess description
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
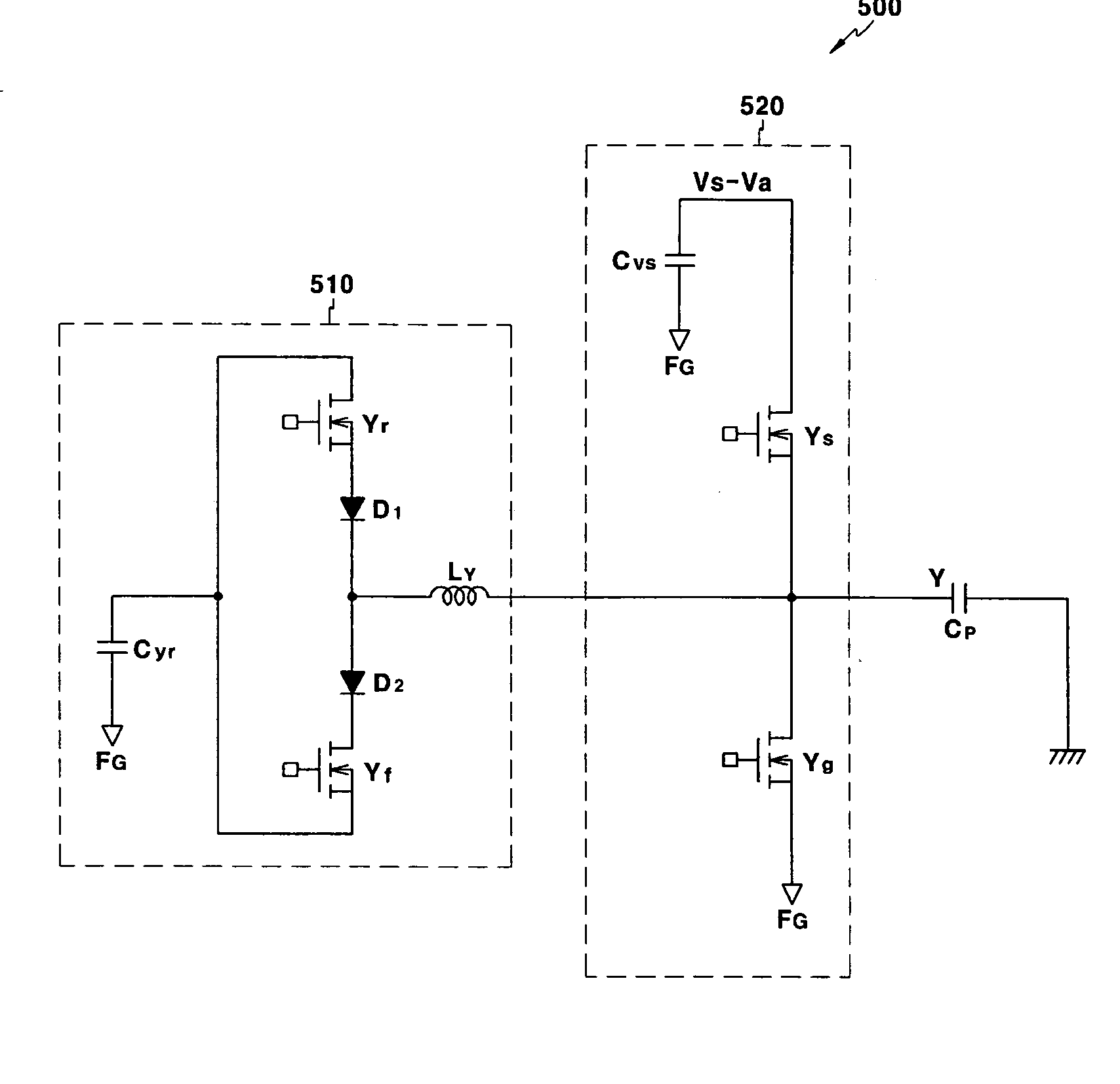
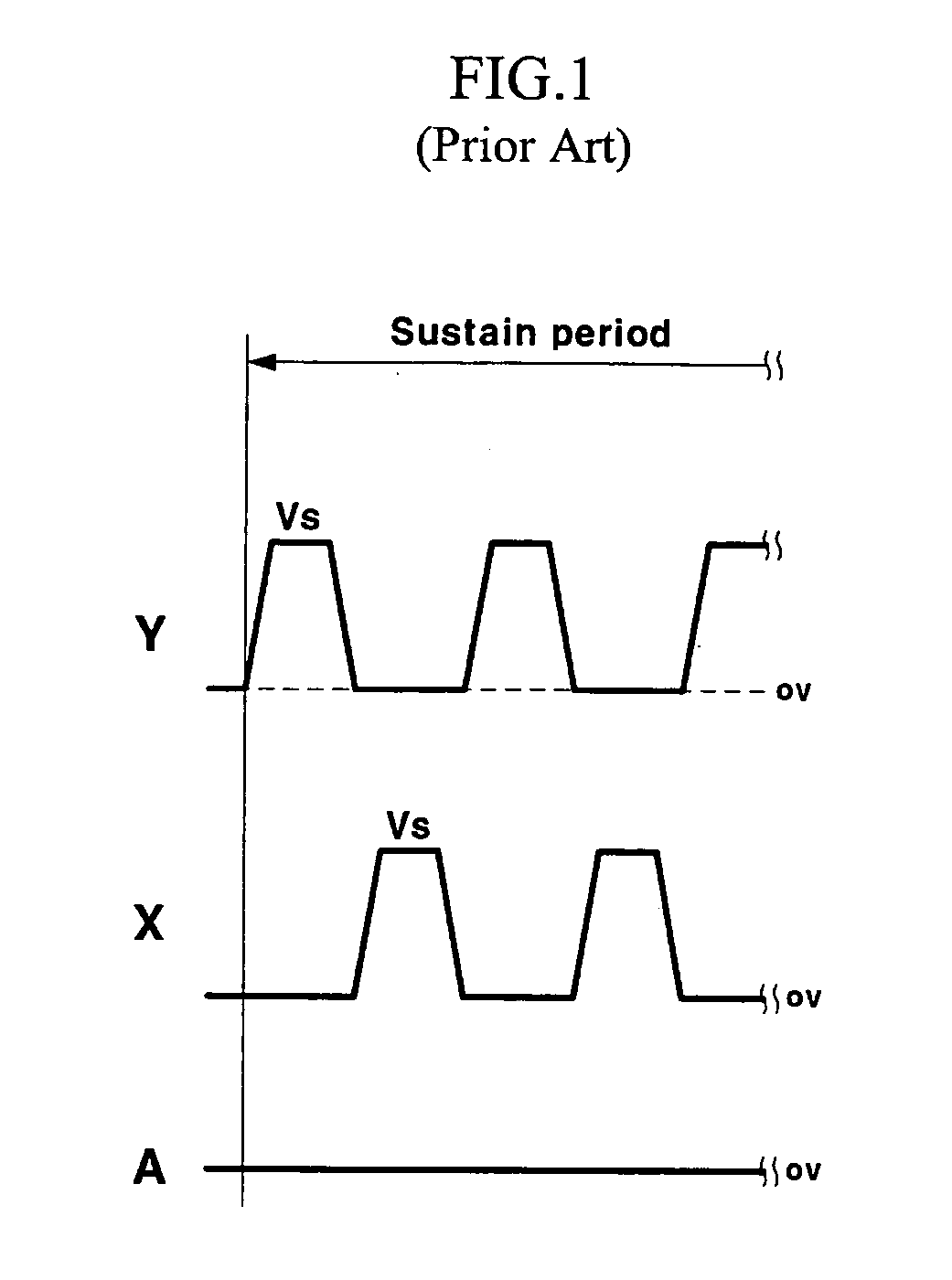
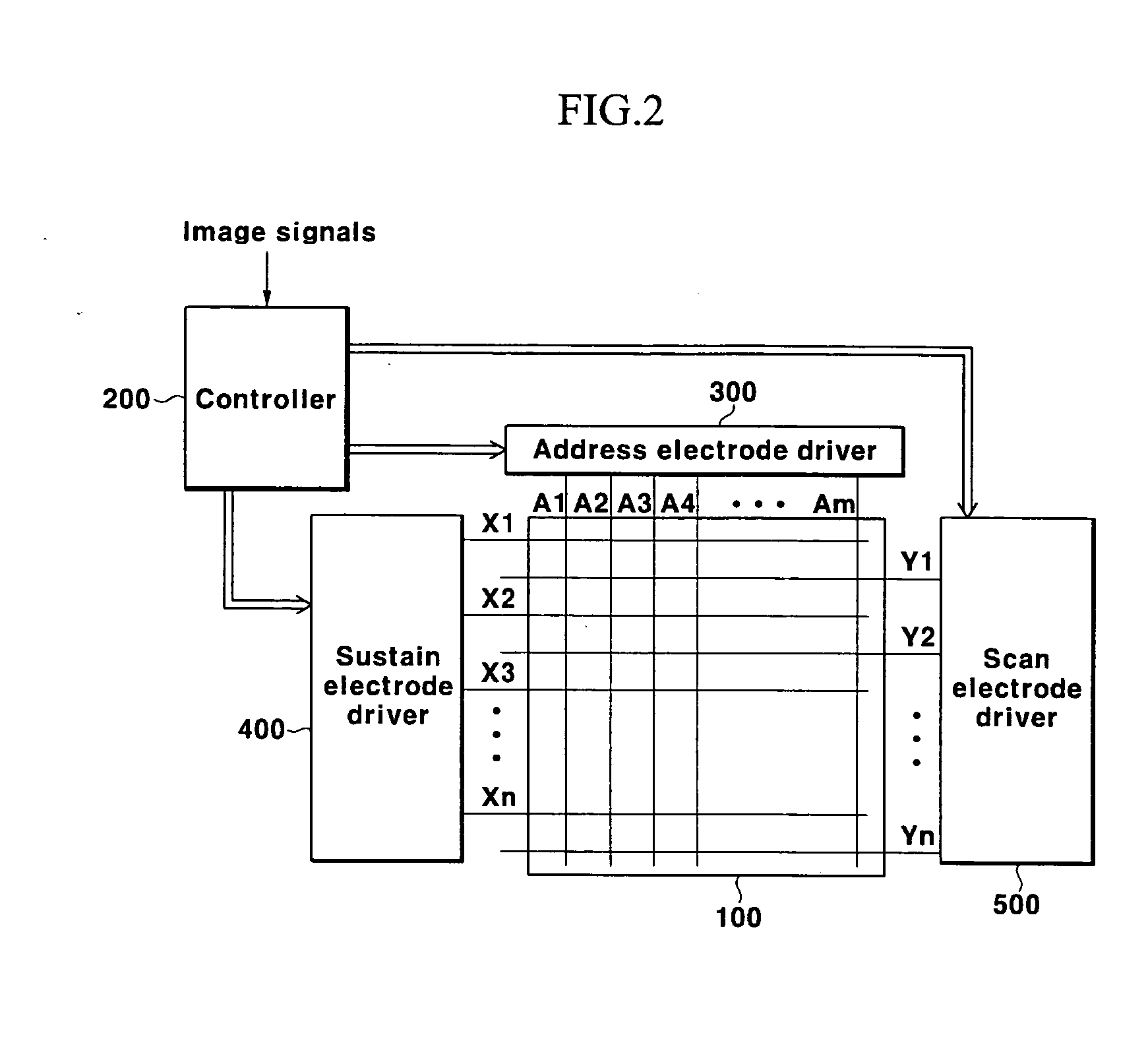
Plasma display device and driving method with reduced displacement current
InactiveUS20060103325A1Improve luminous efficiencyLight emission efficiencyStatic indicating devicesPulse voltageDisplacement current
A plasma display device and a driving method thereof. A scan electrode driver (or a sustain electrode driver) uses a power source for supplying the voltage Vs-Va to increase the initial voltage to the voltage Vs-Va and uses an address voltage output by an address electrode driver to increase the voltage Vs-Va to the voltage Vs to thus apply a sustain discharge pulse during a sustain period. Therefore, the voltage used by a driver for applying the sustain discharge pulse is reduced by using a voltage output by the address driver to apply the sustain pulse voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
ESD protection circuit
An embodiment of the present application discloses an ESD protection circuit, comprising a negative ESD protection module and a positive ESD protection module, wherein the negative ESD protection module comprises a first resistor, a charging capacitor, a first field effect transistor and a second field effect transistor, and the positive ESD protection module comprises a fourth field effect transistor. When a negative ESD event occurs, the gate of P-type GAN enhanced power supply will have a large transient voltage relative to the source, so that a displacement current from the source to the gate of the P-type GAN enhanced power supply is generated on the recharge capacitor, as that first field effect transistor is tur on, the first field effect transistor and the second field effect transistor form a path, thereby releasing negative ESD energy from the grid relative to the source. At that same time, when a negative steady-state voltage is apply to the gate electrode with respect to the source electrode, the first field effect transistor is in an off state, so that the negative voltage test at the steady-state state can be compatible.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method of reducing disturbs in non-volatile memory
InactiveUS6888752B2Reduce the number of cellsReduce in quantityRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineCommon word
In a non-volatile memory, the displacement current generated in non-selected word lines that results when the voltage levels on an array's bit lines are changed can result in disturbs. Techniques for reducing these currents are presented. In a first aspect, the number of cells being simultaneously programmed on a word line is reduced. In a non-volatile memory where an array of memory cells is composed of a number of units, and the units are combined into planes that share common word lines, the simultaneous programming of units within the same plane is avoided. Multiple units may be programmed in parallel, but these are arranged to be in separate planes. This is done by selecting the number of units to be programmed in parallel and their order such that all the units programmed together are from distinct planes, by comparing the units to be programmed to see if any are from the same plane, or a combination of these. In a second, complementary aspect, the rate at which the voltage levels on the bit lines are changed is adjustable. By monitoring the frequency of disturbs, or based upon the device's application, the rate at which the bit line drivers change the bit line voltage can be adjusted. This can be implemented by setting the rate externally, or by the controller based upon device performance and the amount of data error being generated.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Ferroelectric memory device and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20140233296A1Large capacityHigh capacity densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower flowEngineering
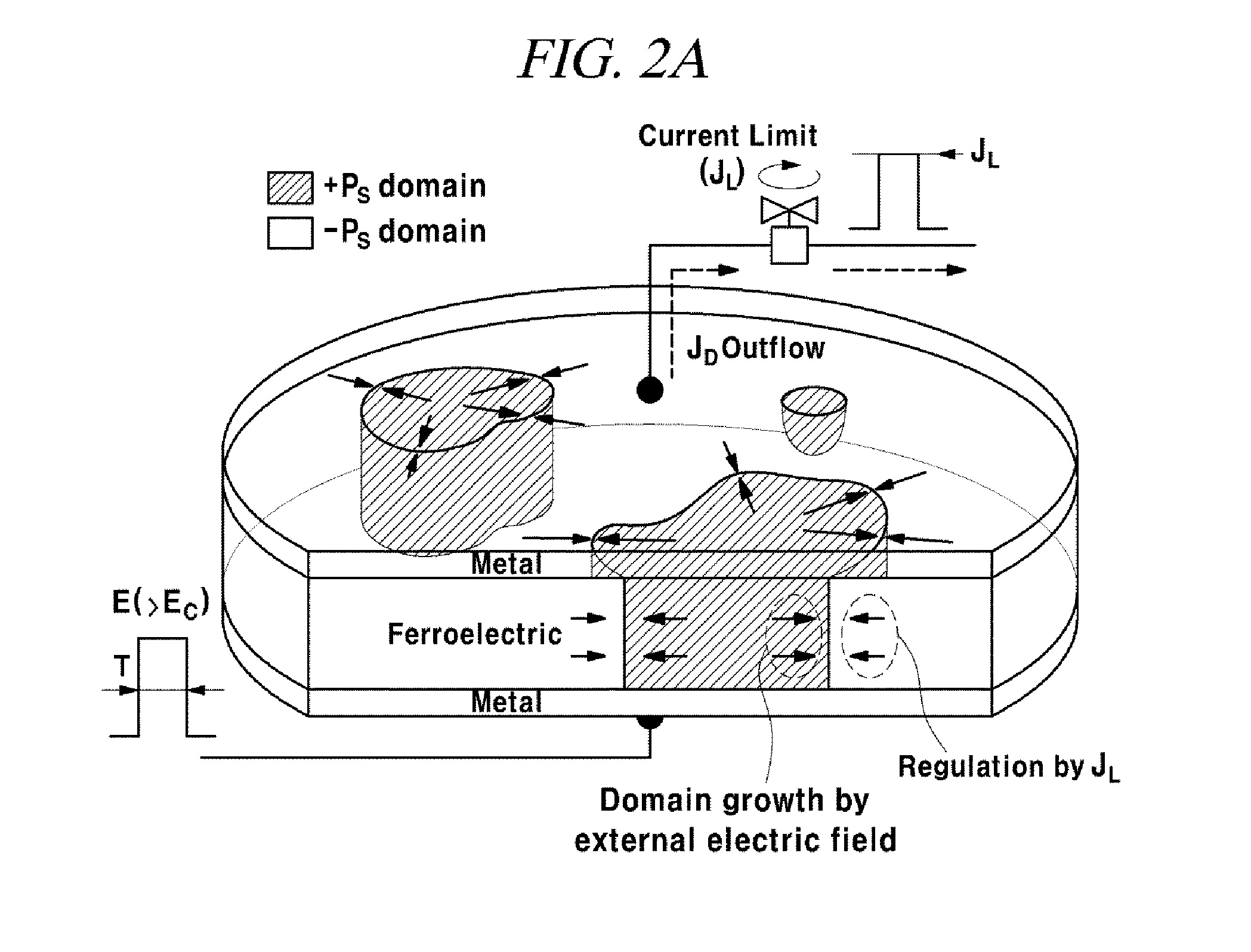
The present application relates to a ferroelectric memory device having a multilevel polarization (MLP) state generated due to adjustment of a displacement current and to a method for manufacturing the ferroelectric memory device.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com