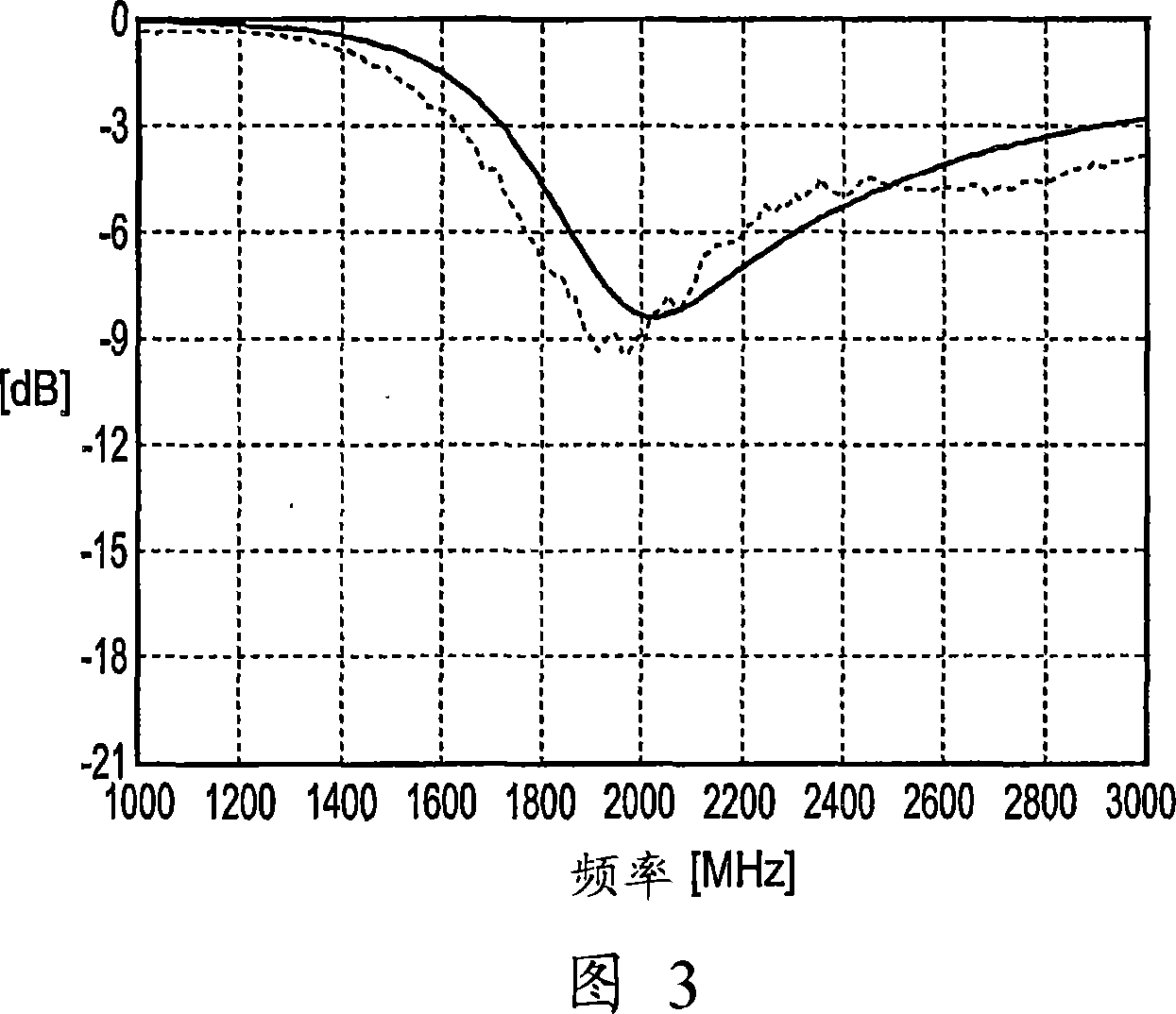
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Dielectric antennas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
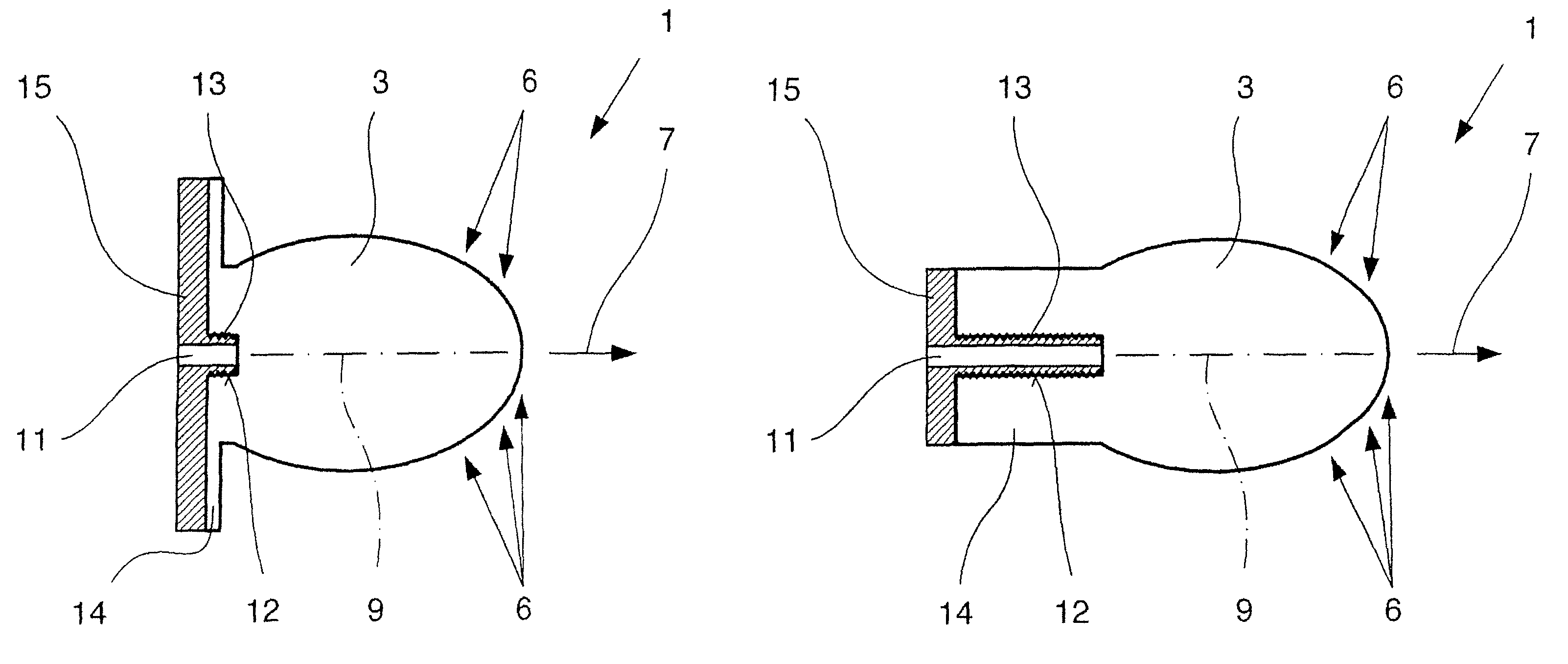
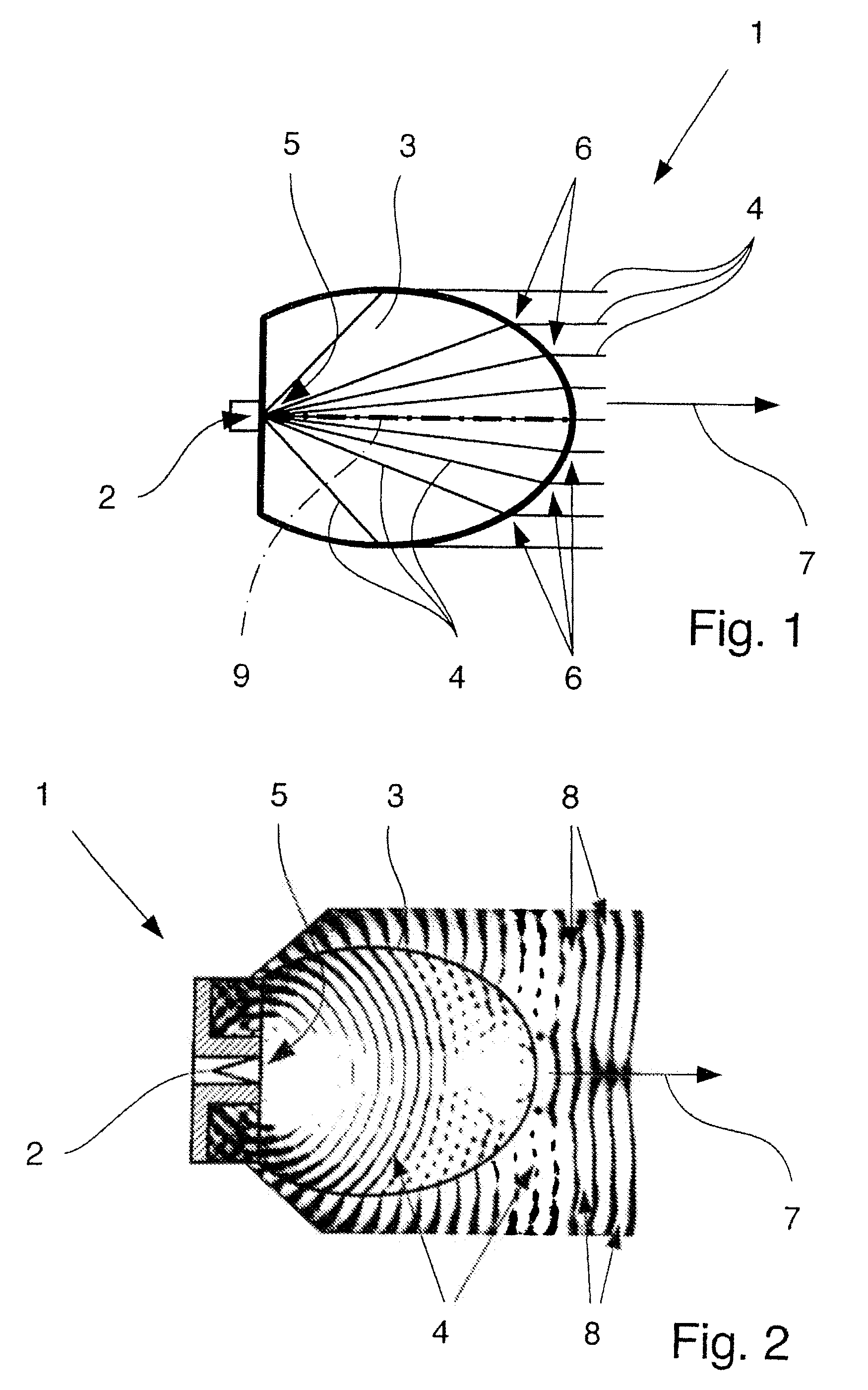
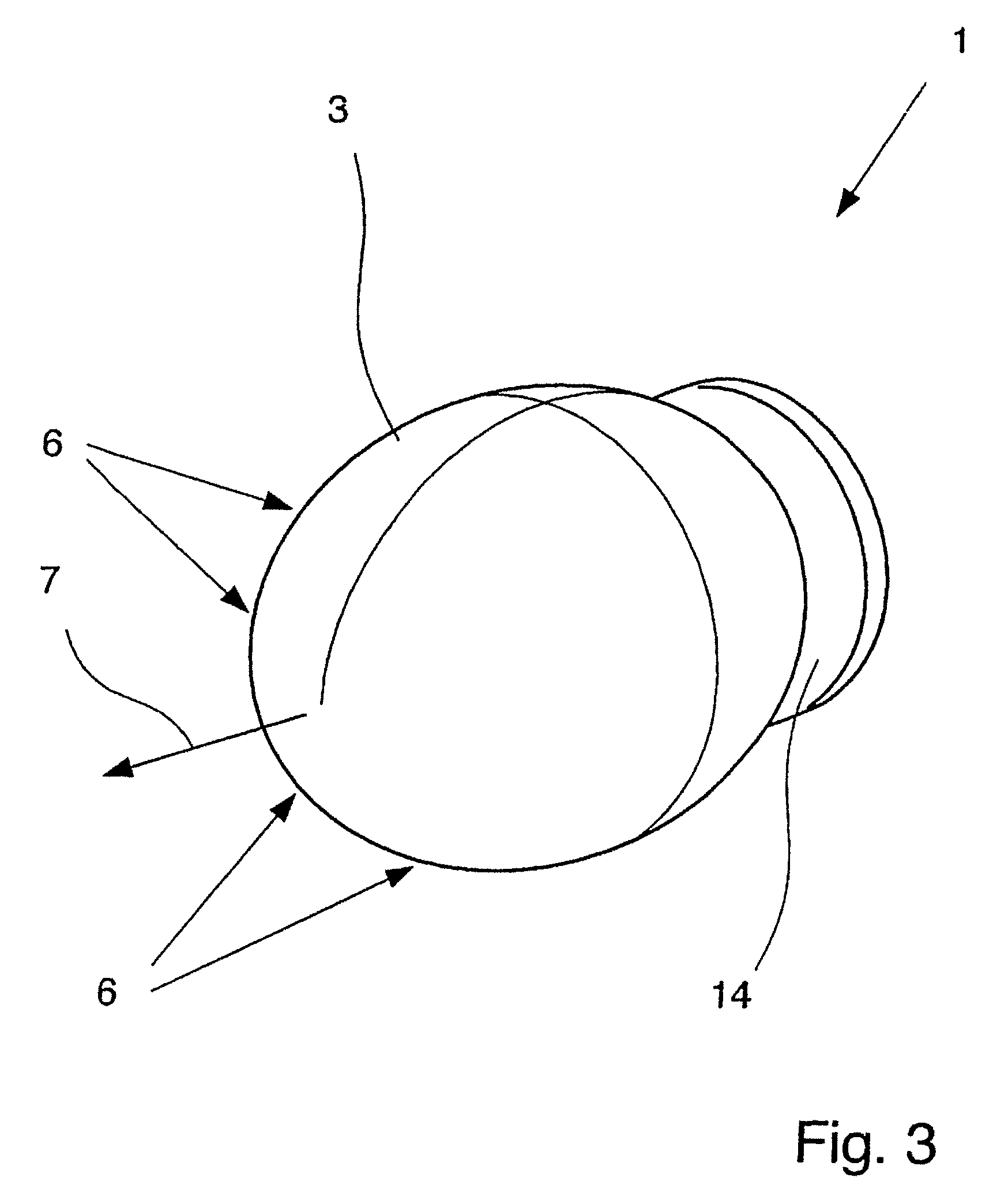
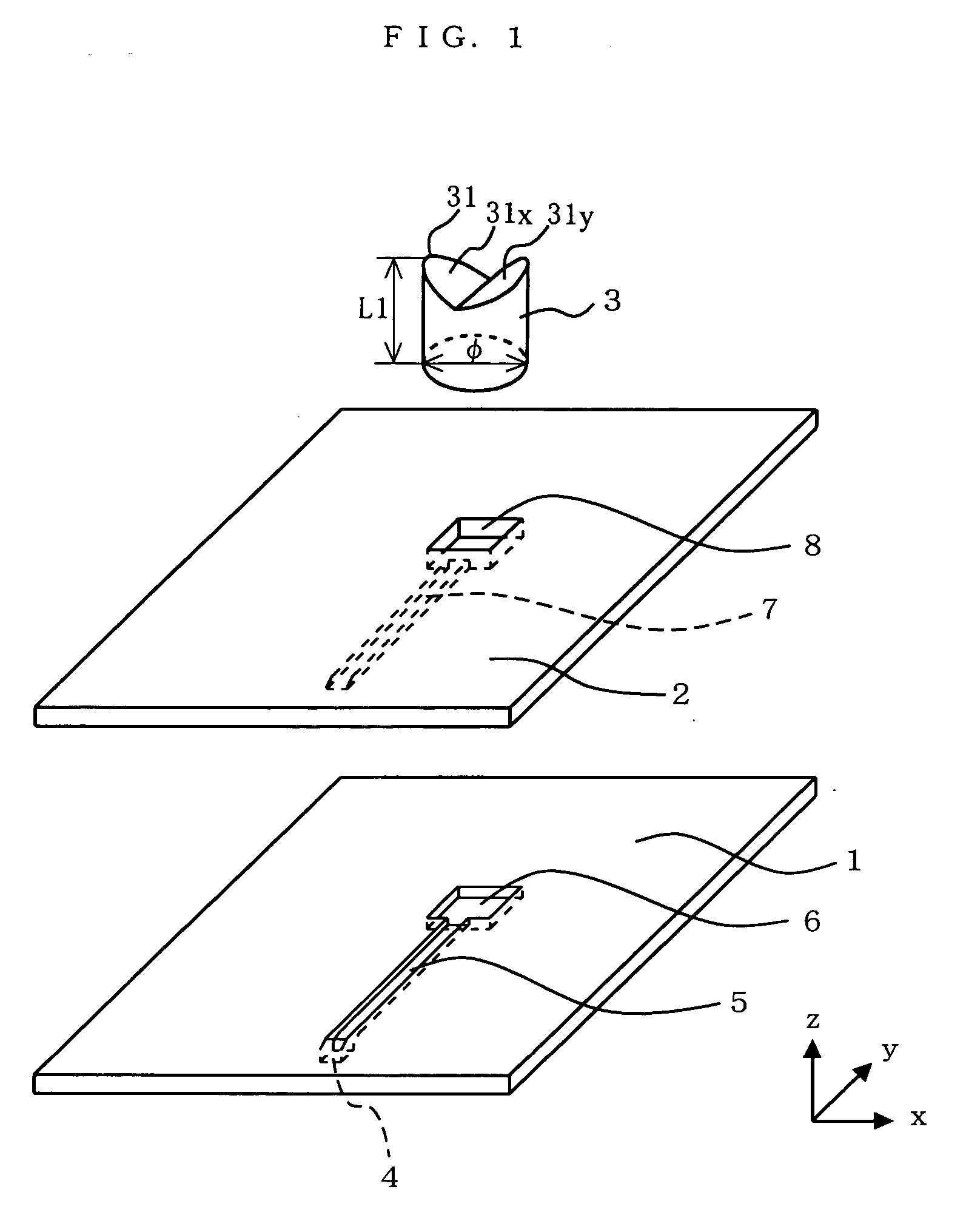
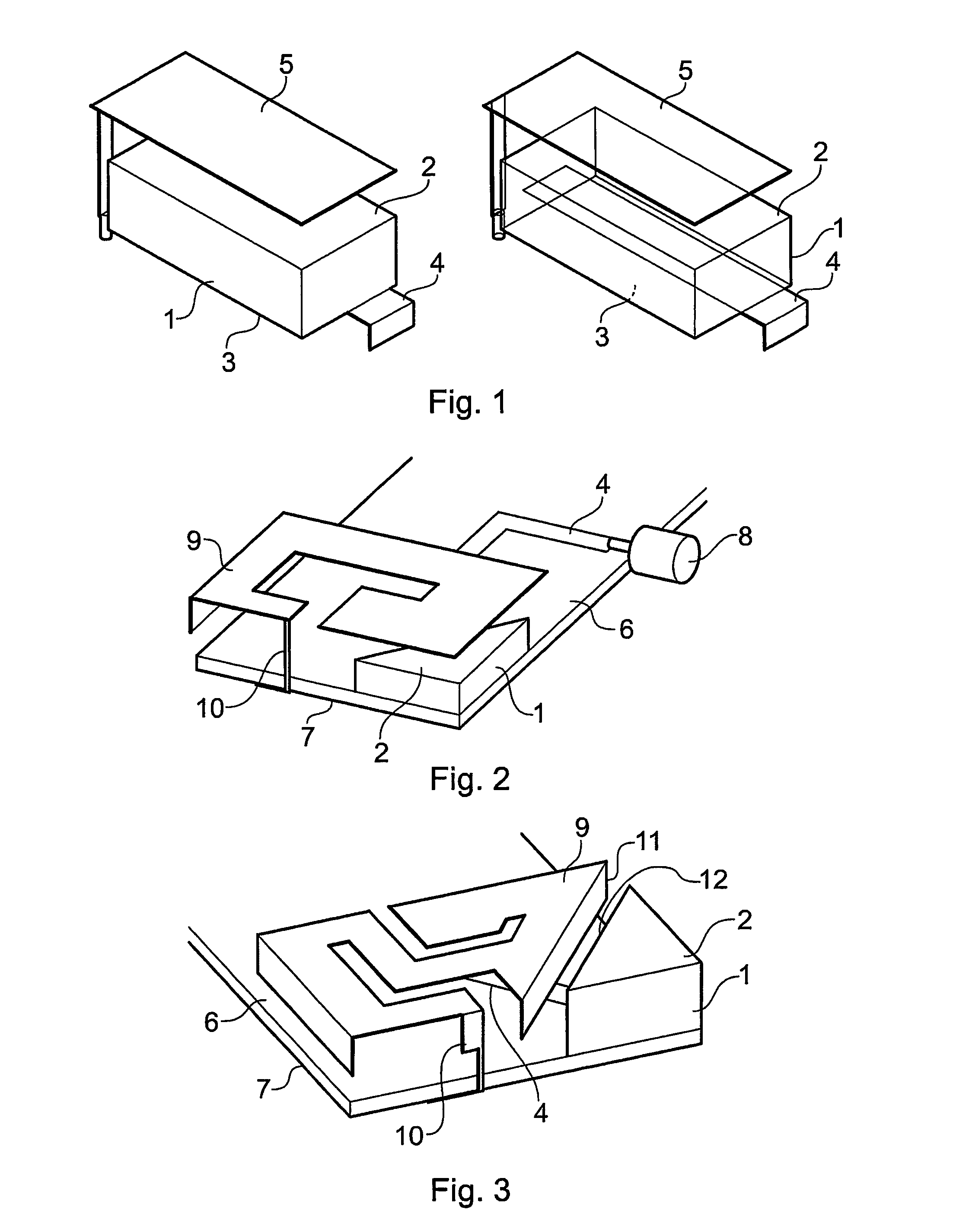
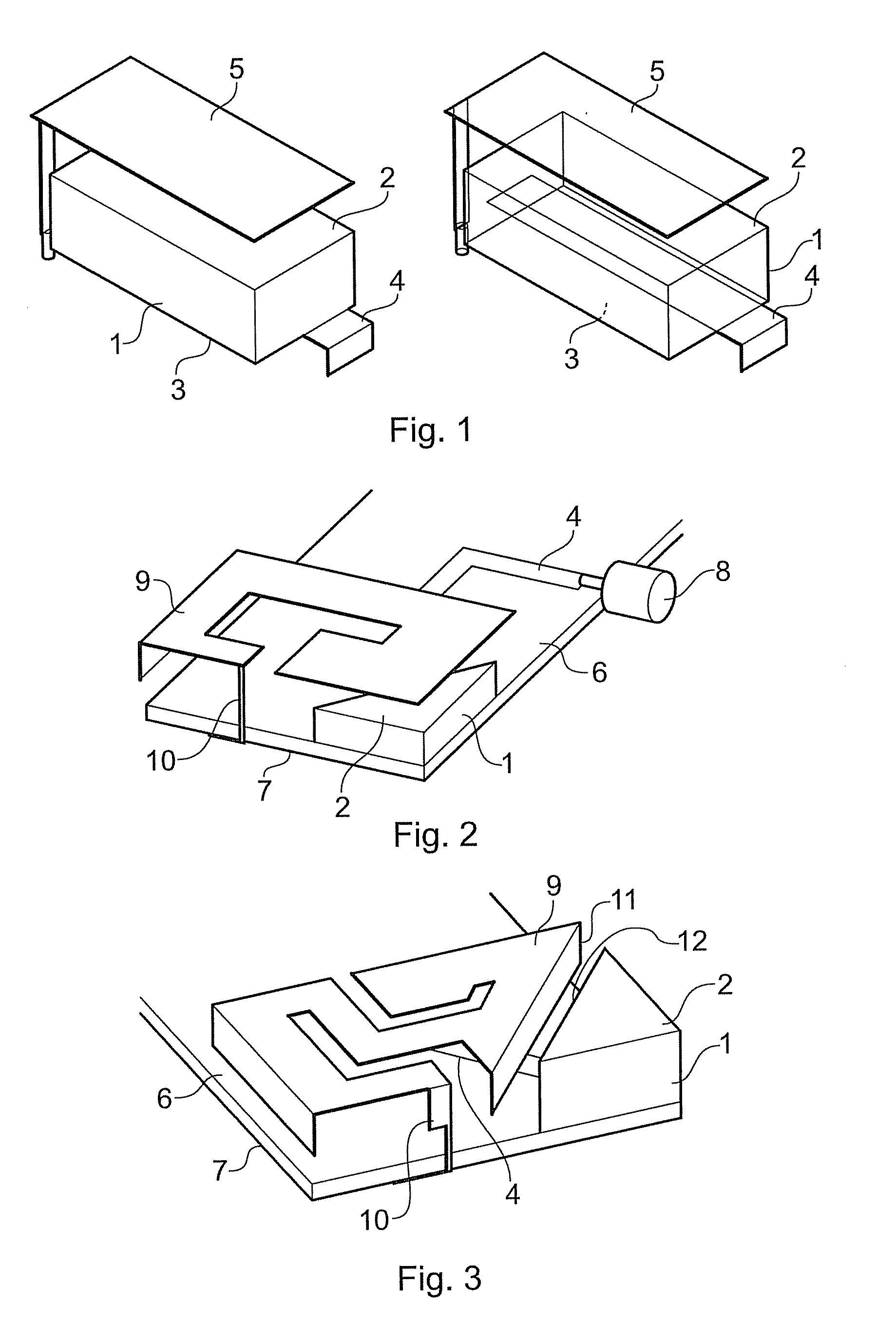
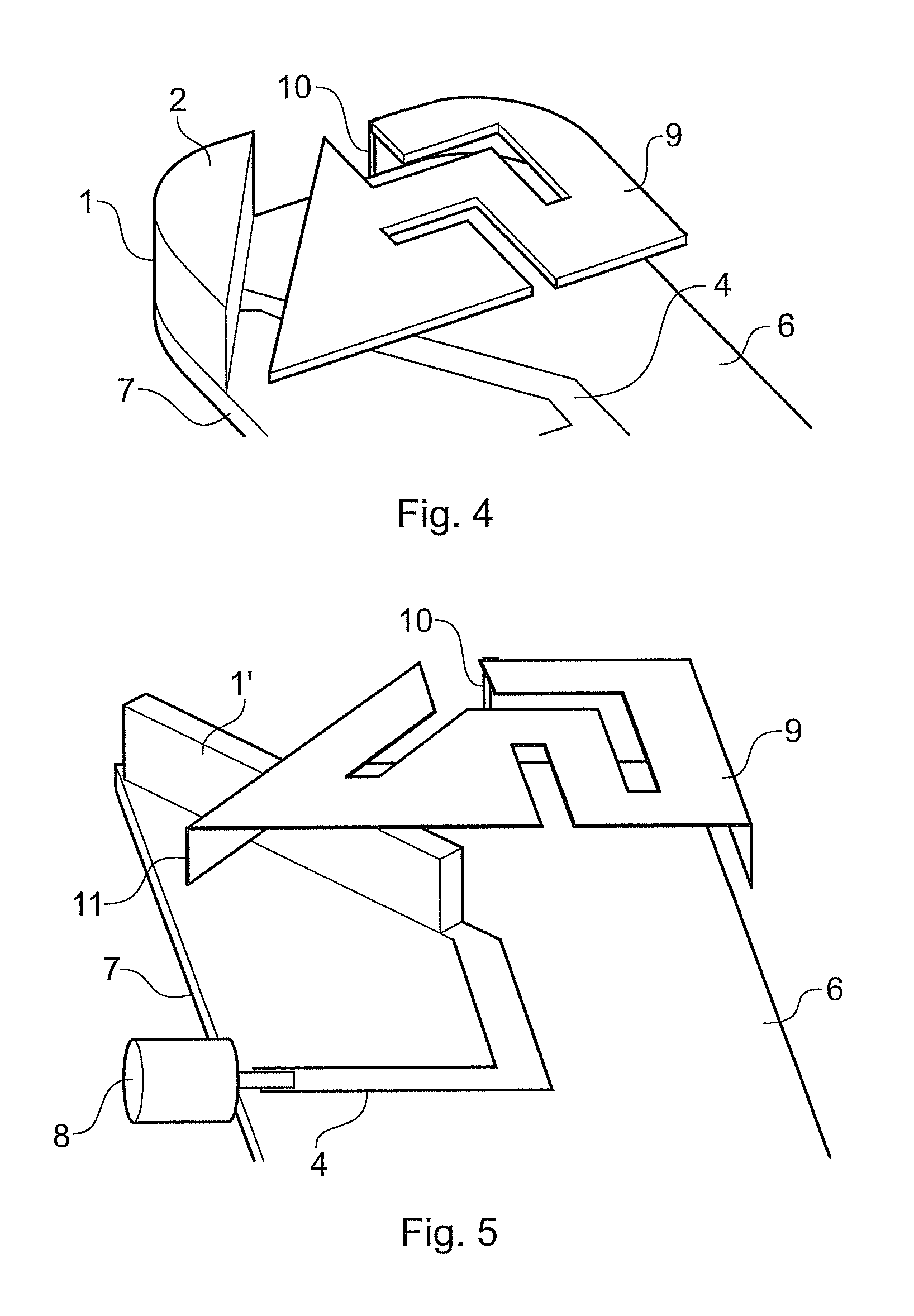
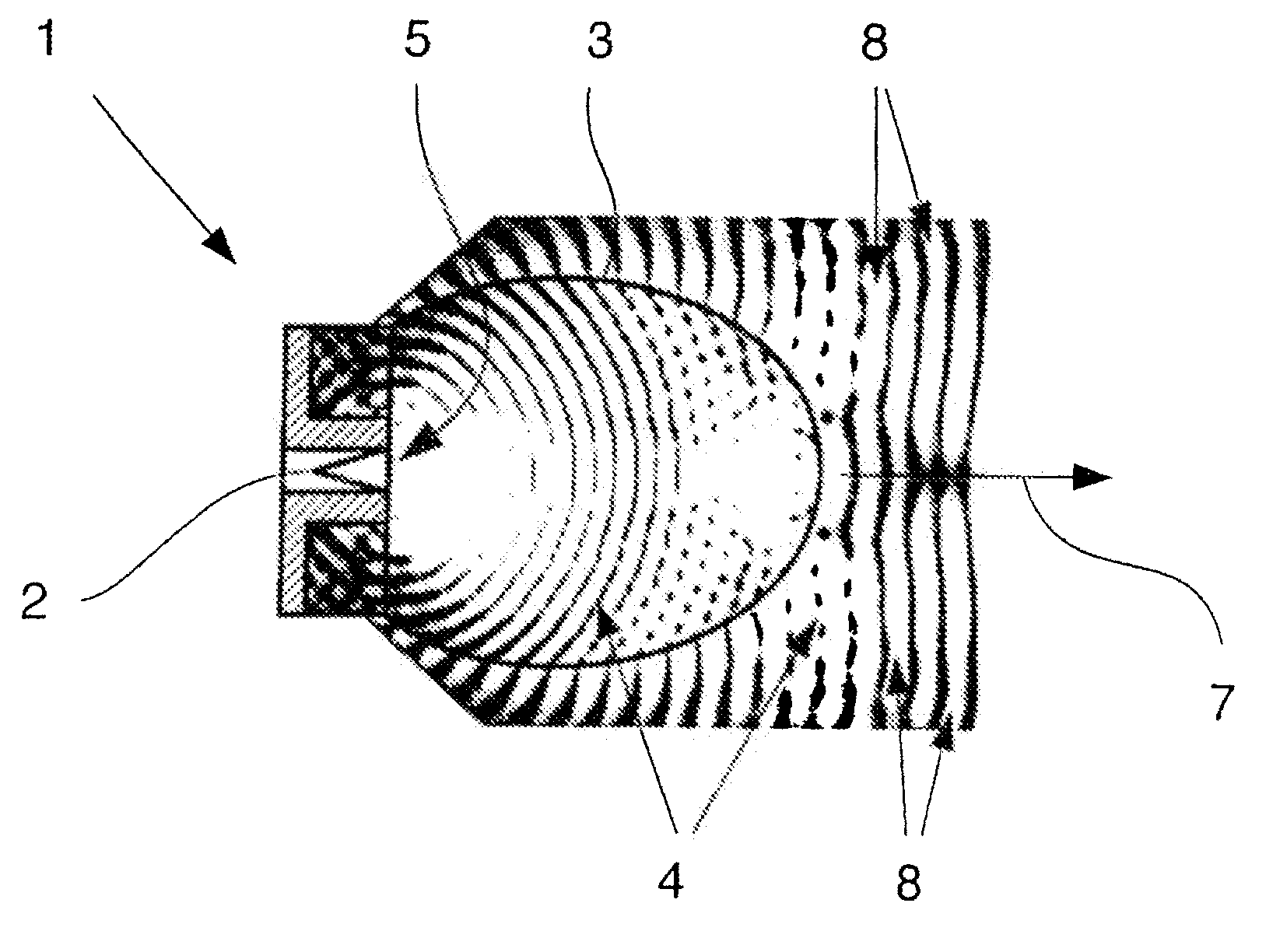
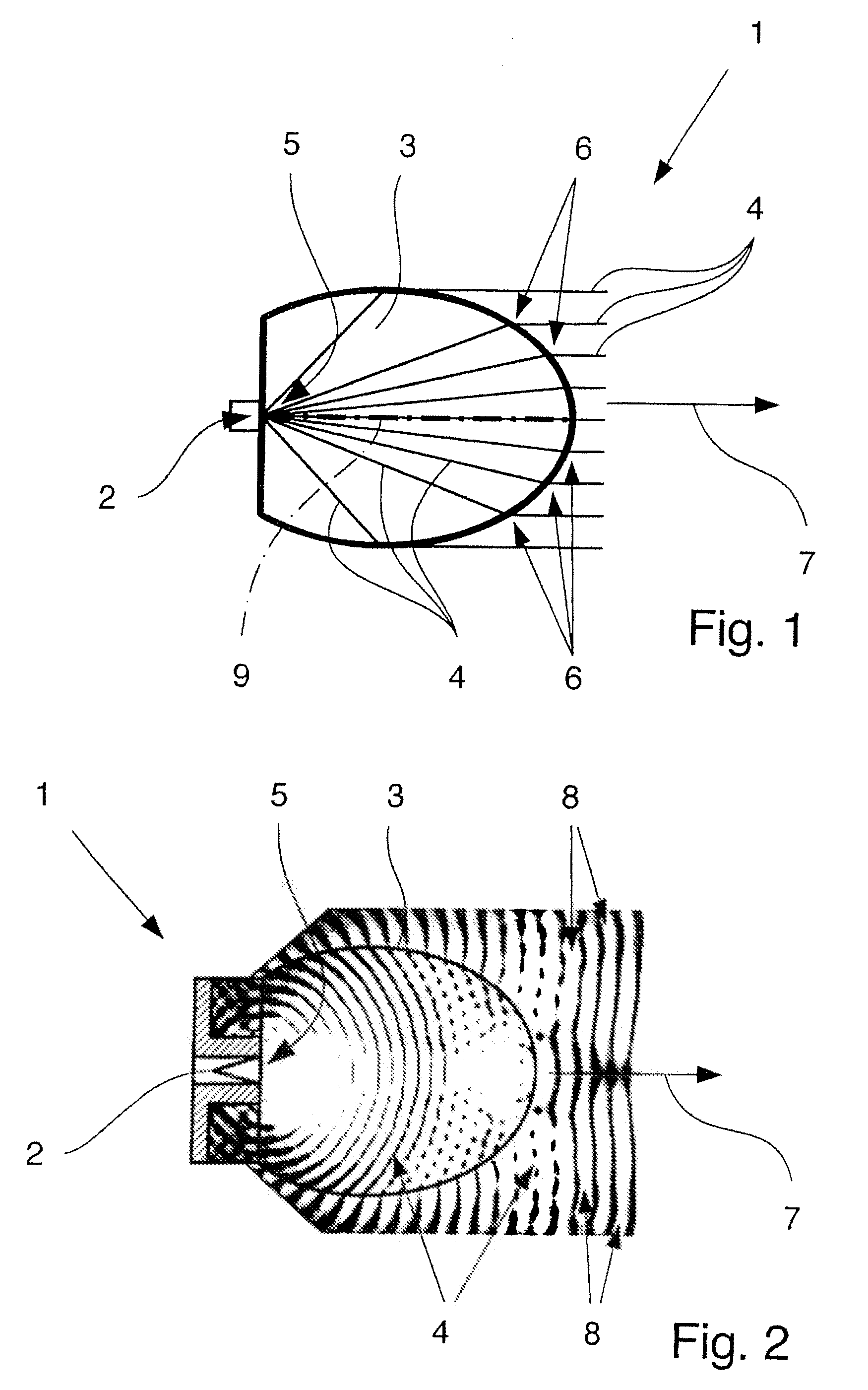
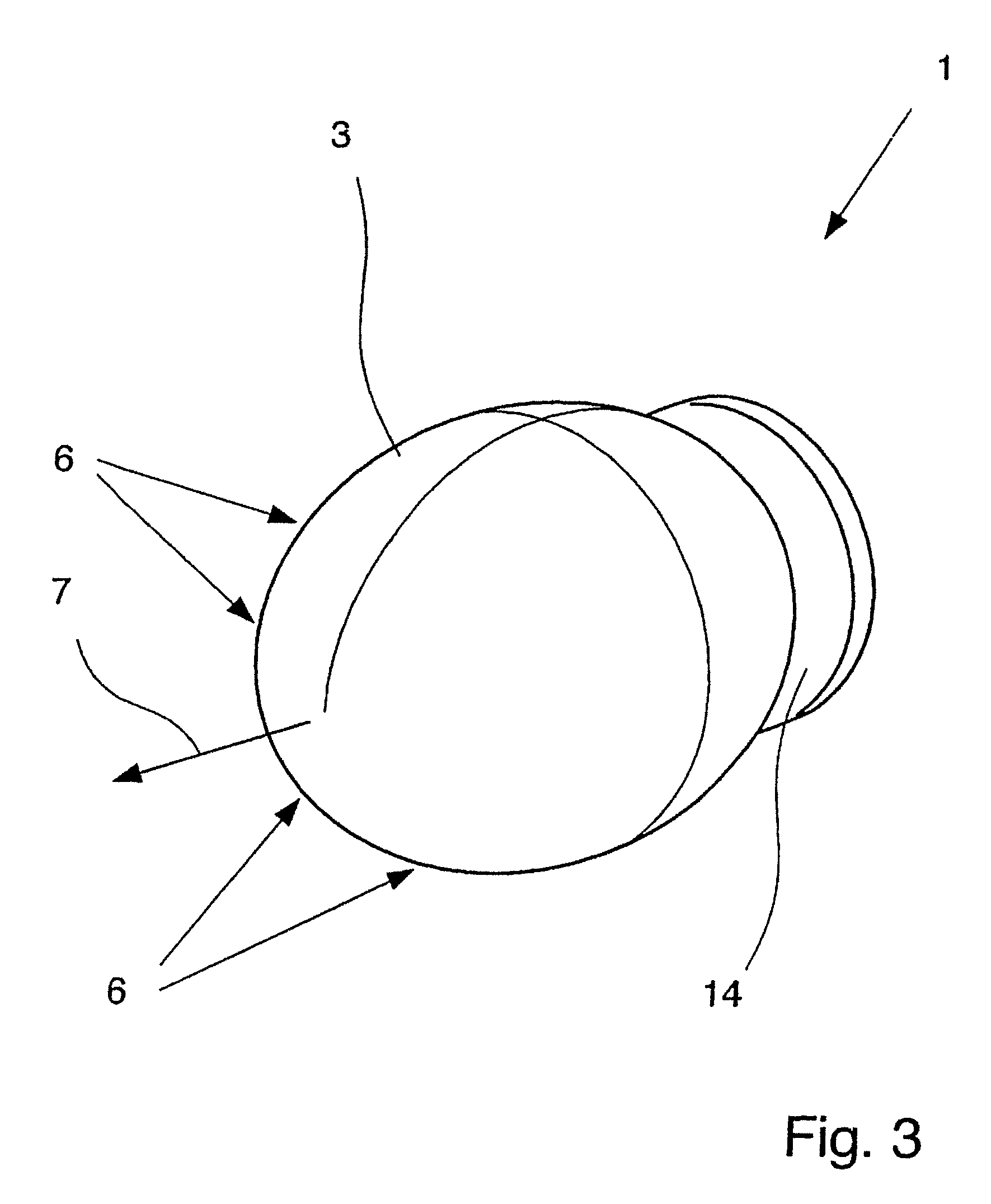
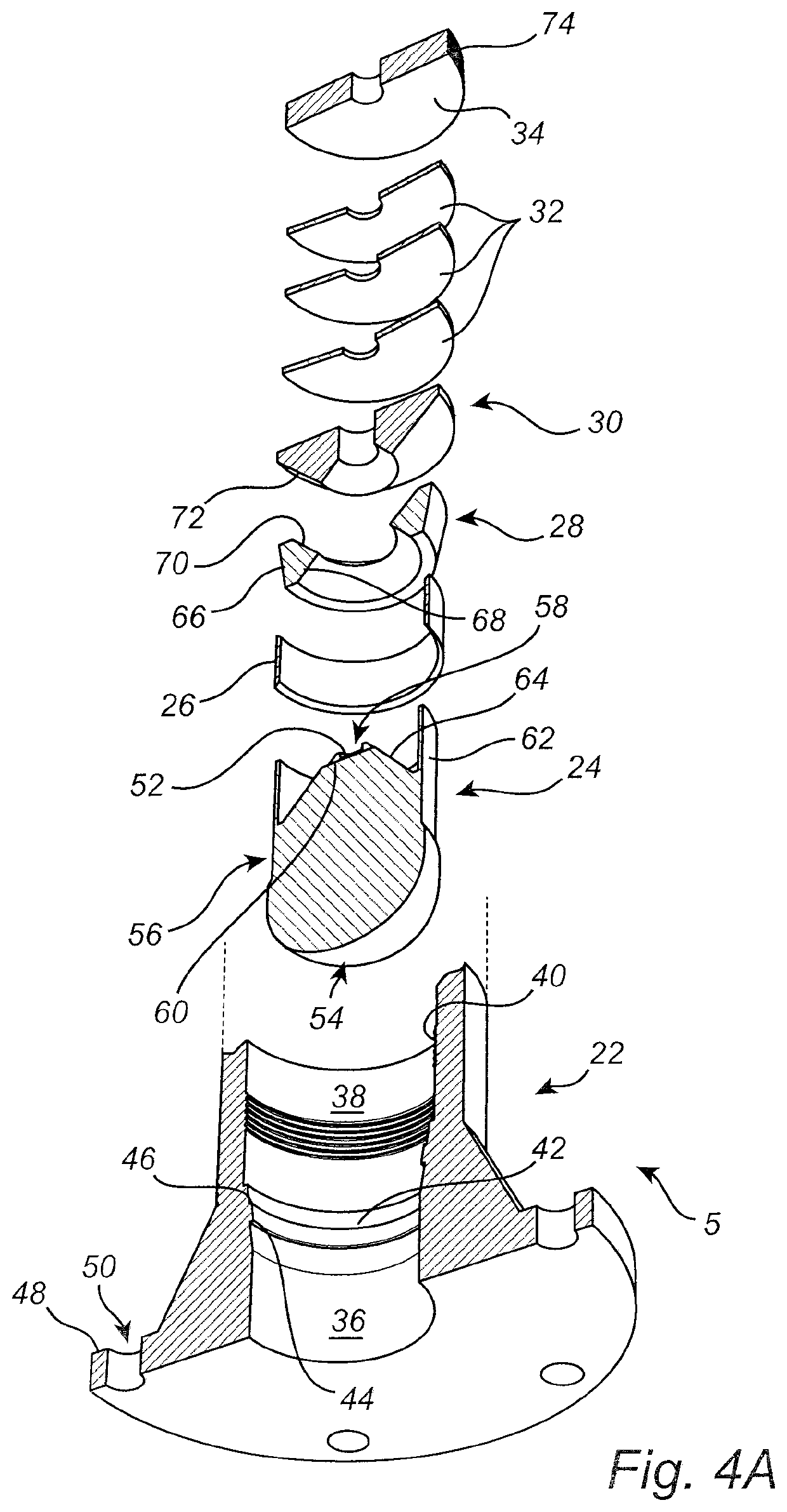
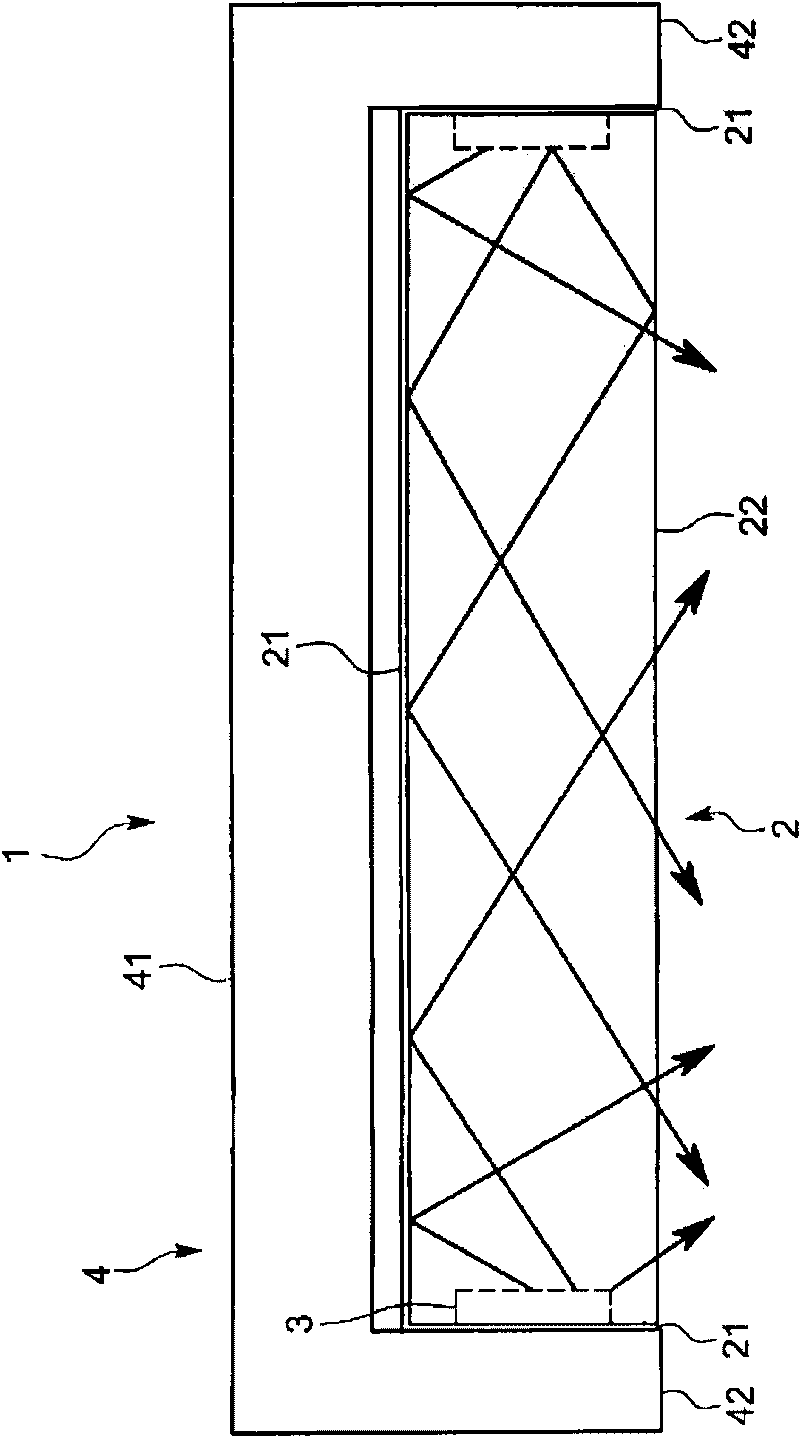
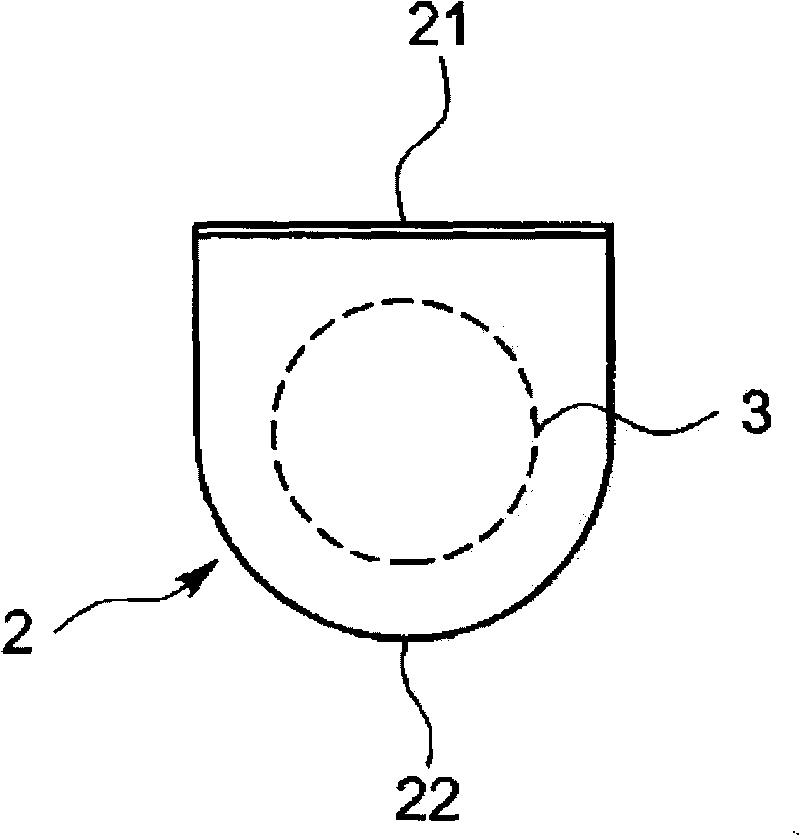
Dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element and with an ellipsoidal lens made of a dielectric material
ActiveUS8917215B2Avoid disadvantagesEasy to packWaveguide mouthsDielectric antennasElectromagnetic radiation
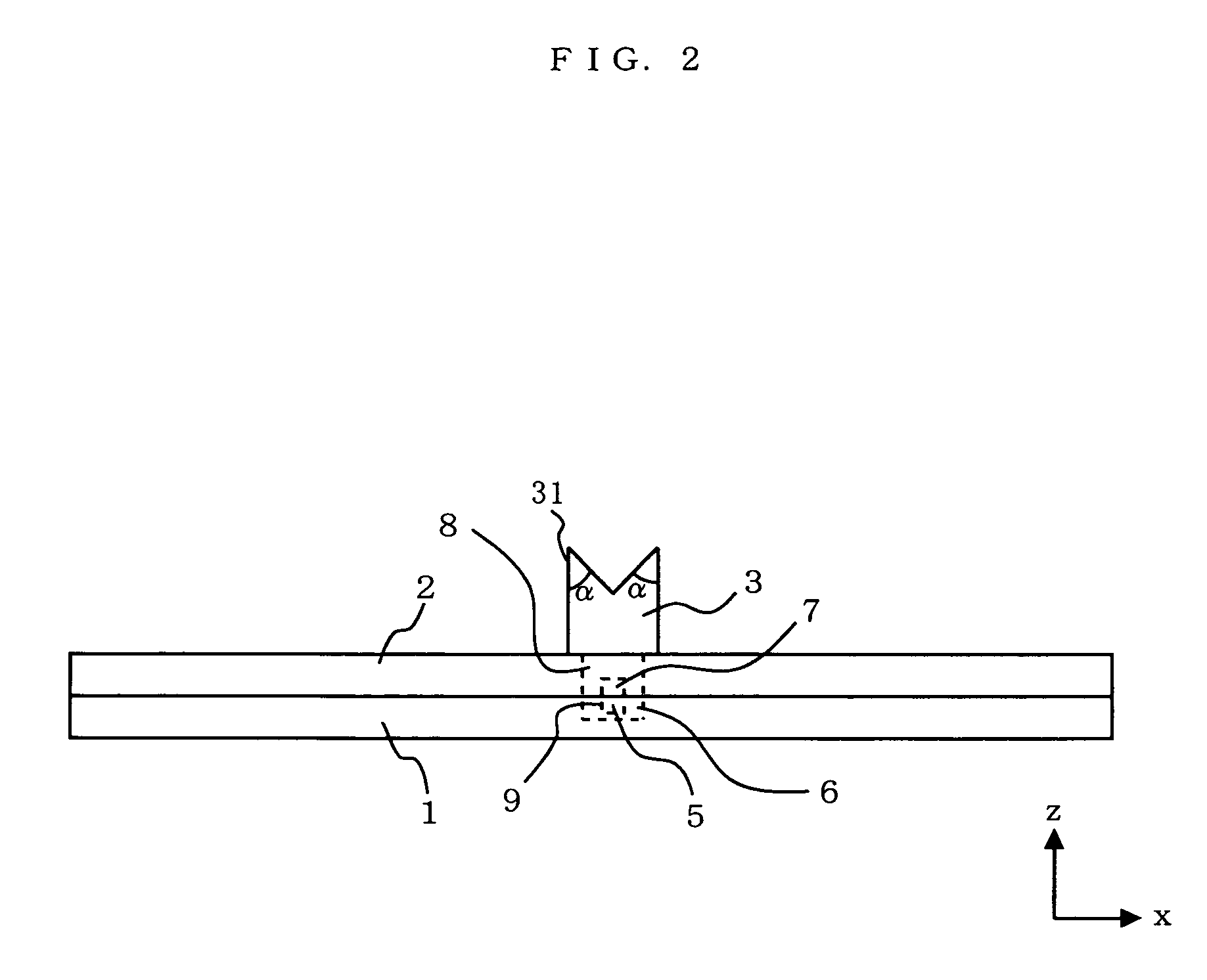
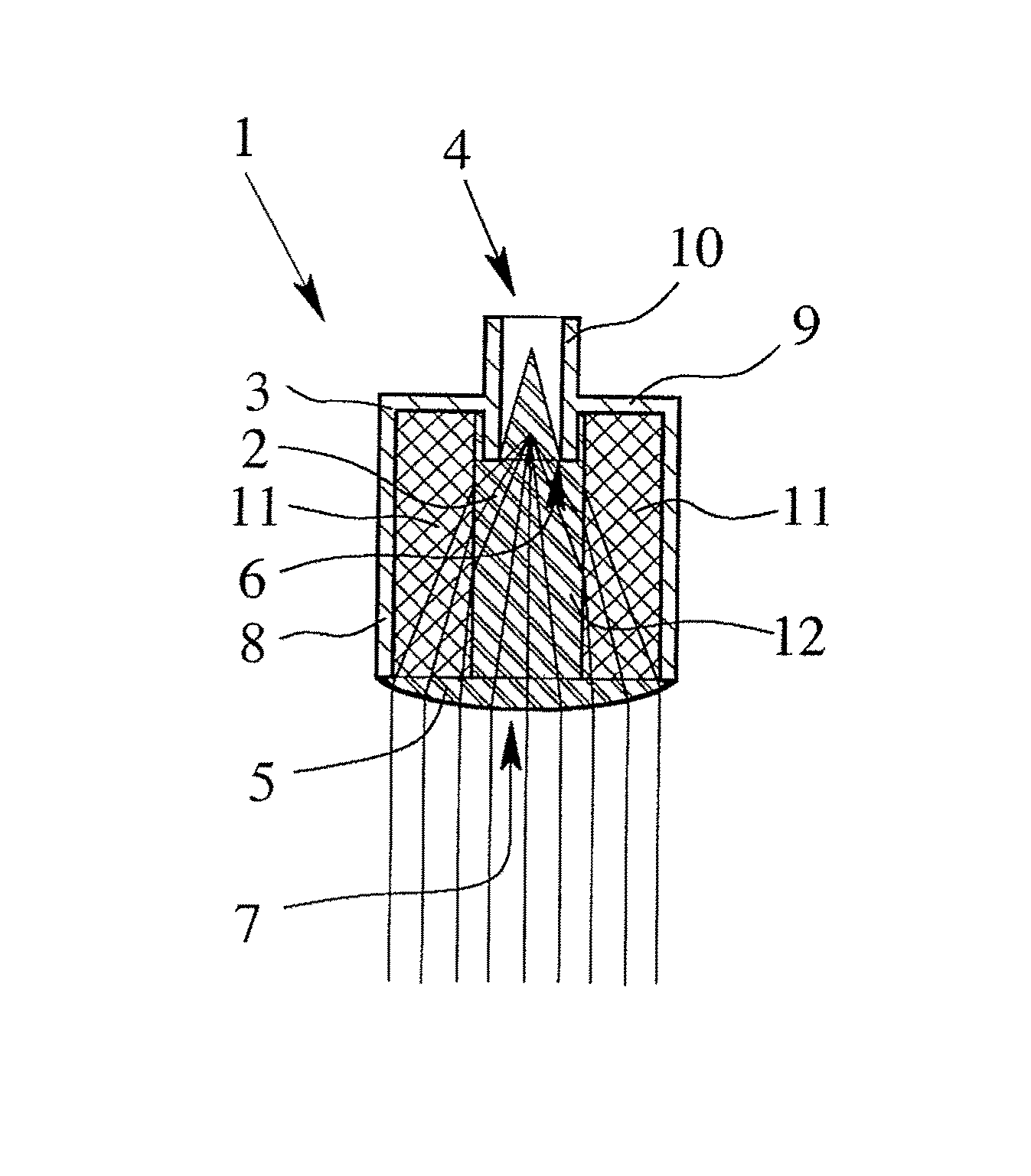
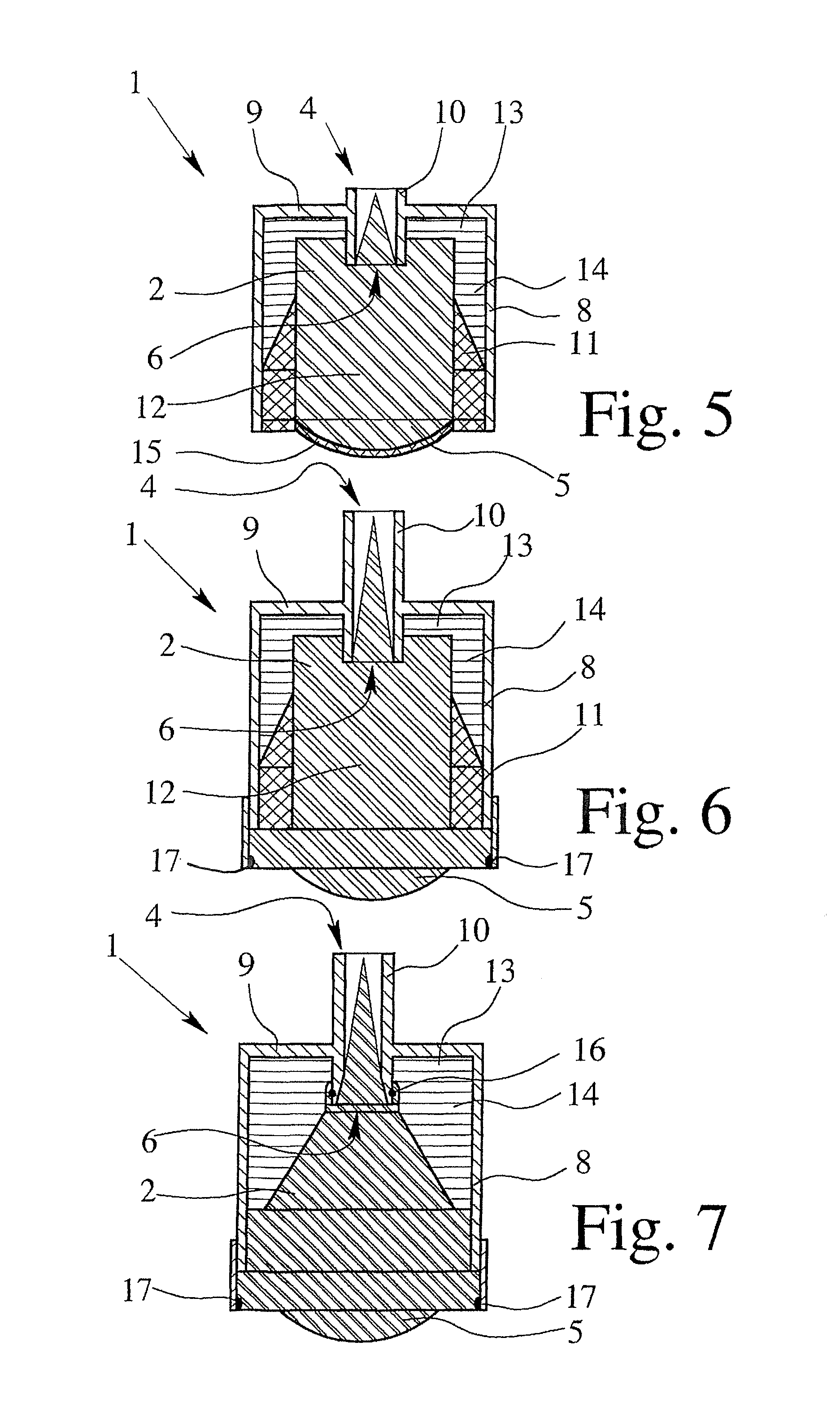
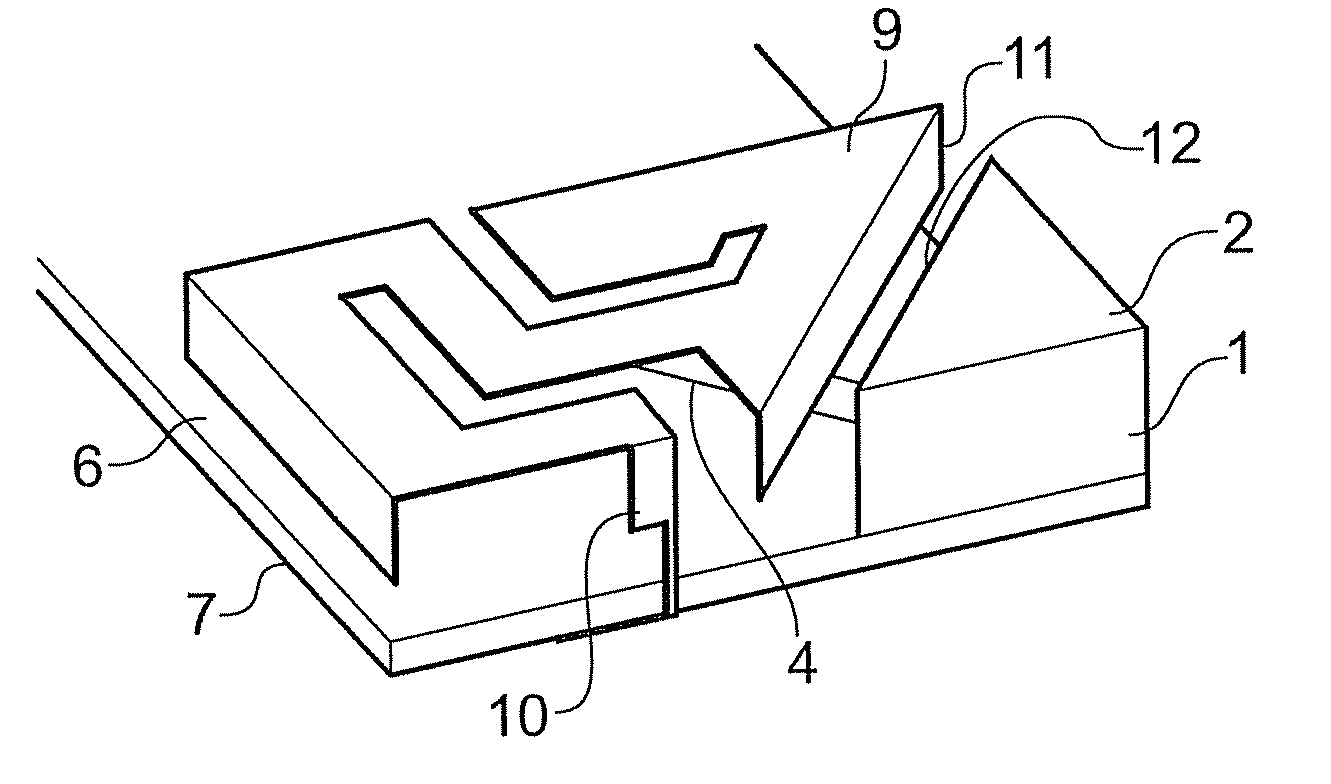
A dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element (2) and with a lens (3) made of a dielectric material, the feed element (2) emitting electromagnetic radiation (4) and the lens (3) being supplied with electromagnetic radiation (4) in the feed region (5), the lens (3) relaying the electromagnetic radiation (4) and radiating it with the transmission region (6). To configure these dielectric antennas such that the disadvantages of the dielectric antennas known from the prior art are at least partially avoided, first of all, the lens (3) is shaped essentially ellipsoidally at least in the transmission region (6) and the lens (3) is arranged relative to the feed element (2) such that the electromagnetic radiation (4) emitted by the lens (3) in the direction of maximum radiation (7) of the antenna has an essentially planar phase front.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Dielectric antenna and radio device using the same
ActiveUS20050057402A1High gainLarge primary beam widthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadio equipmentDielectric antennas
A dielectric antenna of the present invention includes a pillar-shaped dielectric section for radiating an electromagnetic wave being fed thereto. The dielectric section includes a depressed portion in an upper portion thereof. The vertical cross section of the depressed portion has such a shape that the height of the dielectric section gradually increases toward the side surface of the dielectric section. For example, the depressed portion is a notch having a V-shaped vertical cross section. Alternatively, the depressed portion includes a flat surface portion.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Dielectric antenna for high frequency wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS6995710B2Efficiently and preventing drop in efficiency of radiationImprove featuresSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrically long antennasDielectric antennasLine width
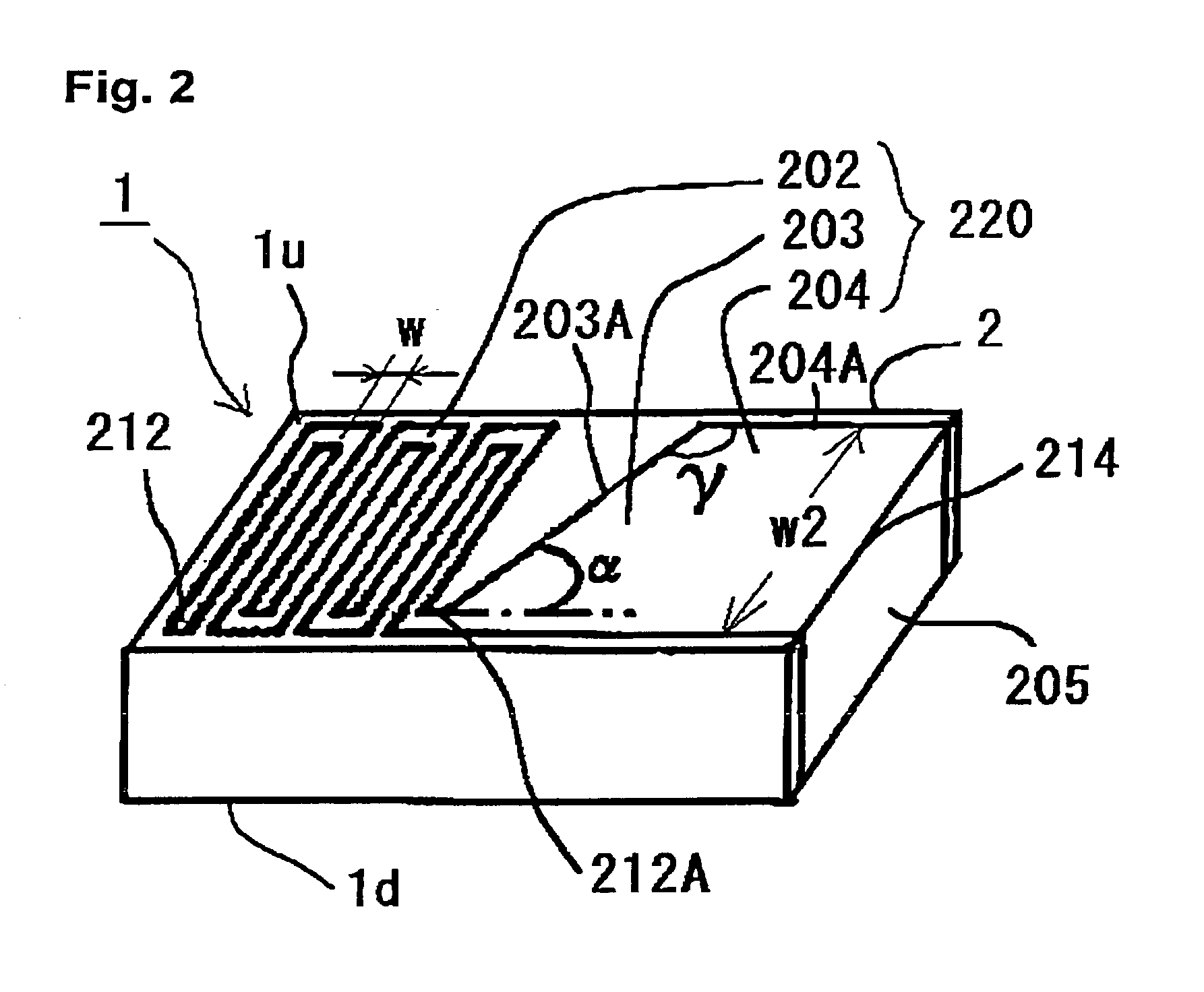
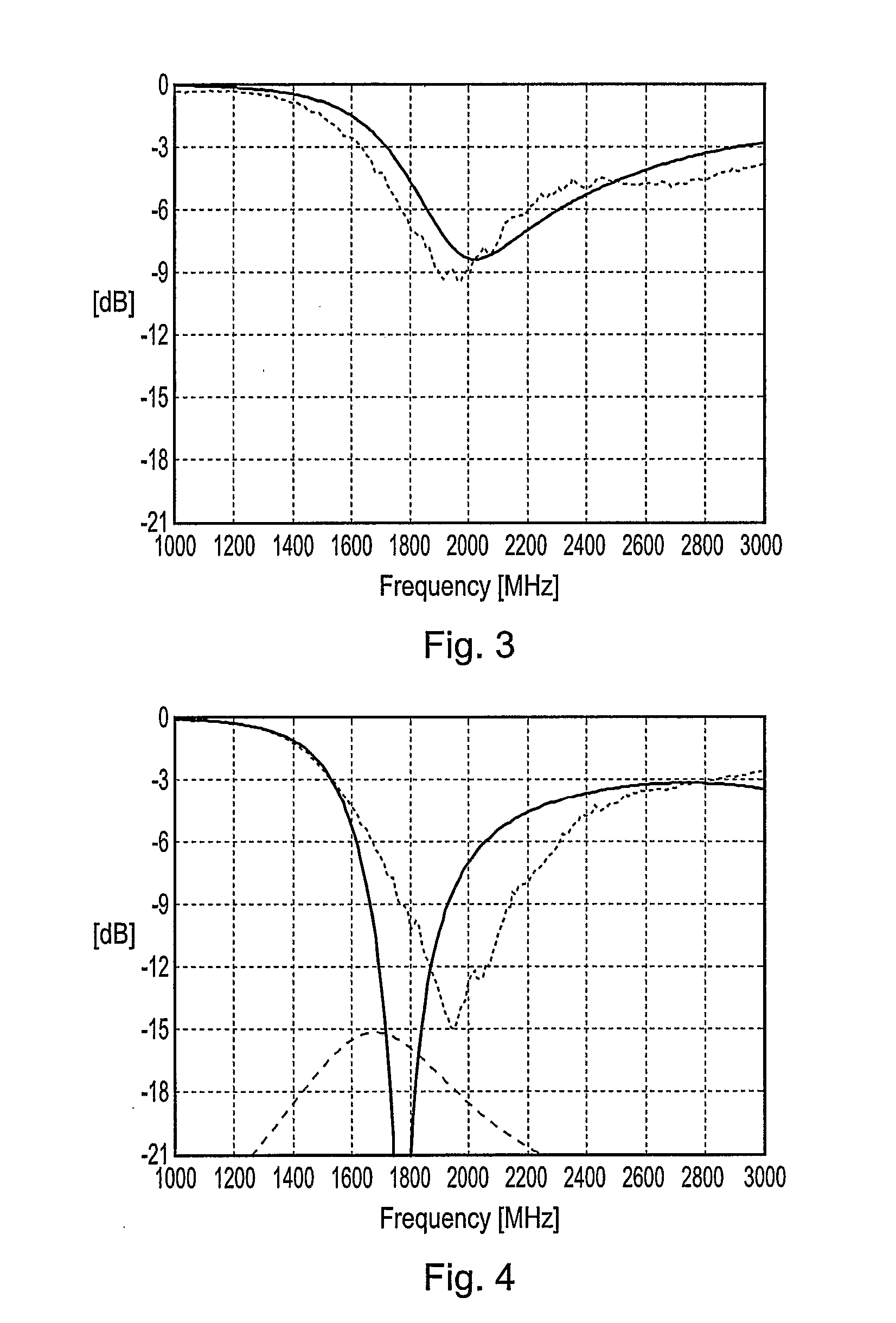
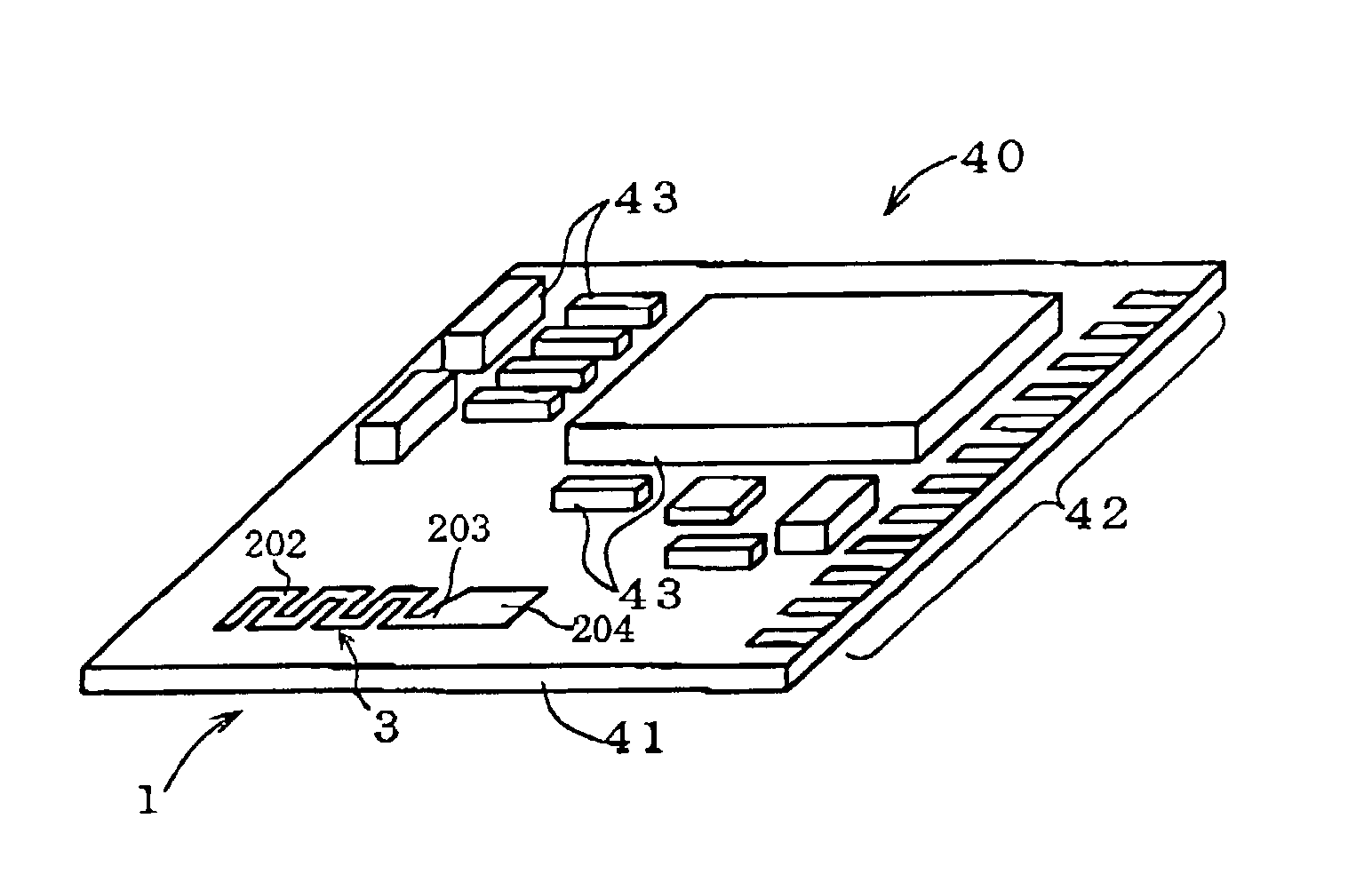
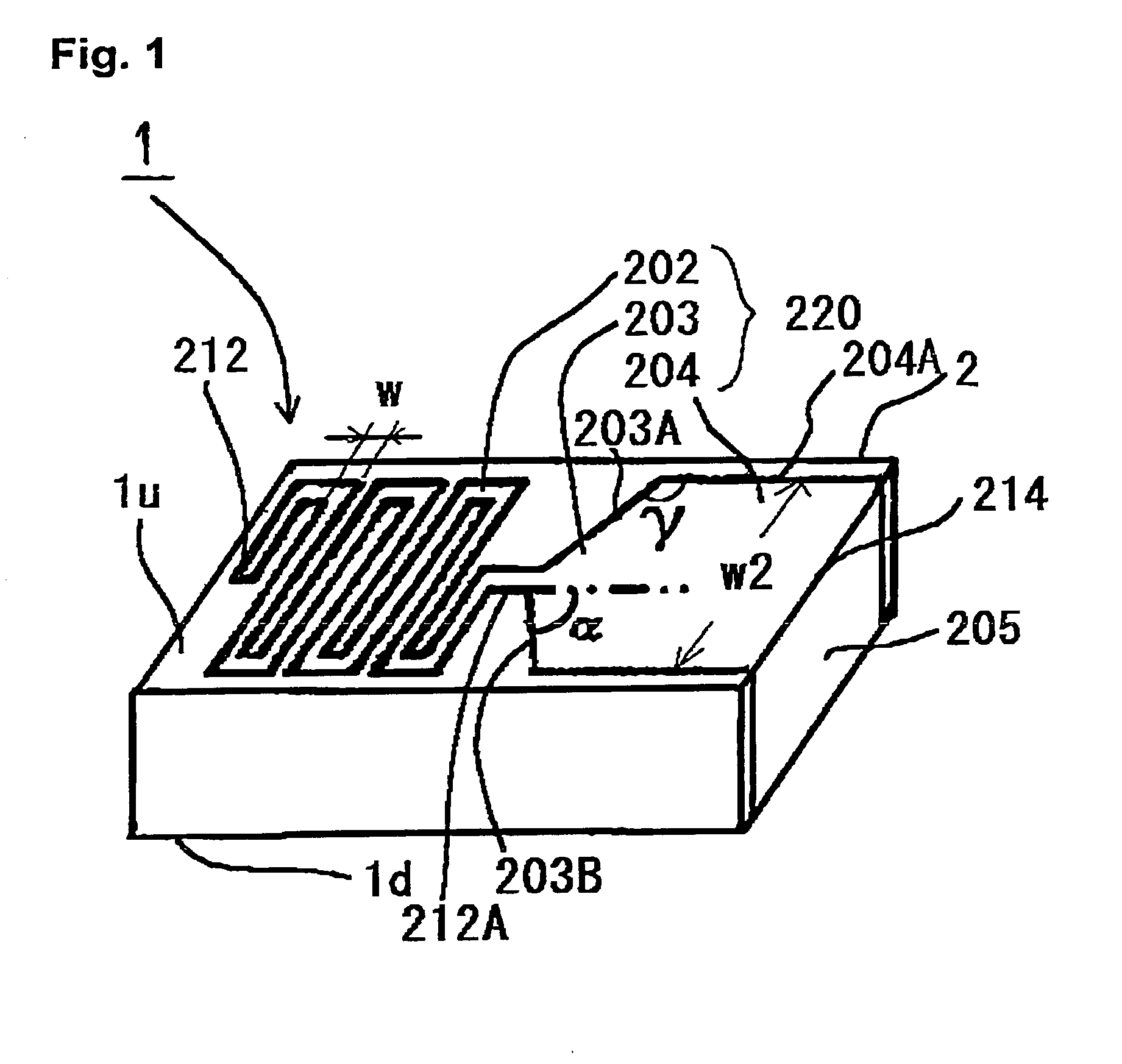
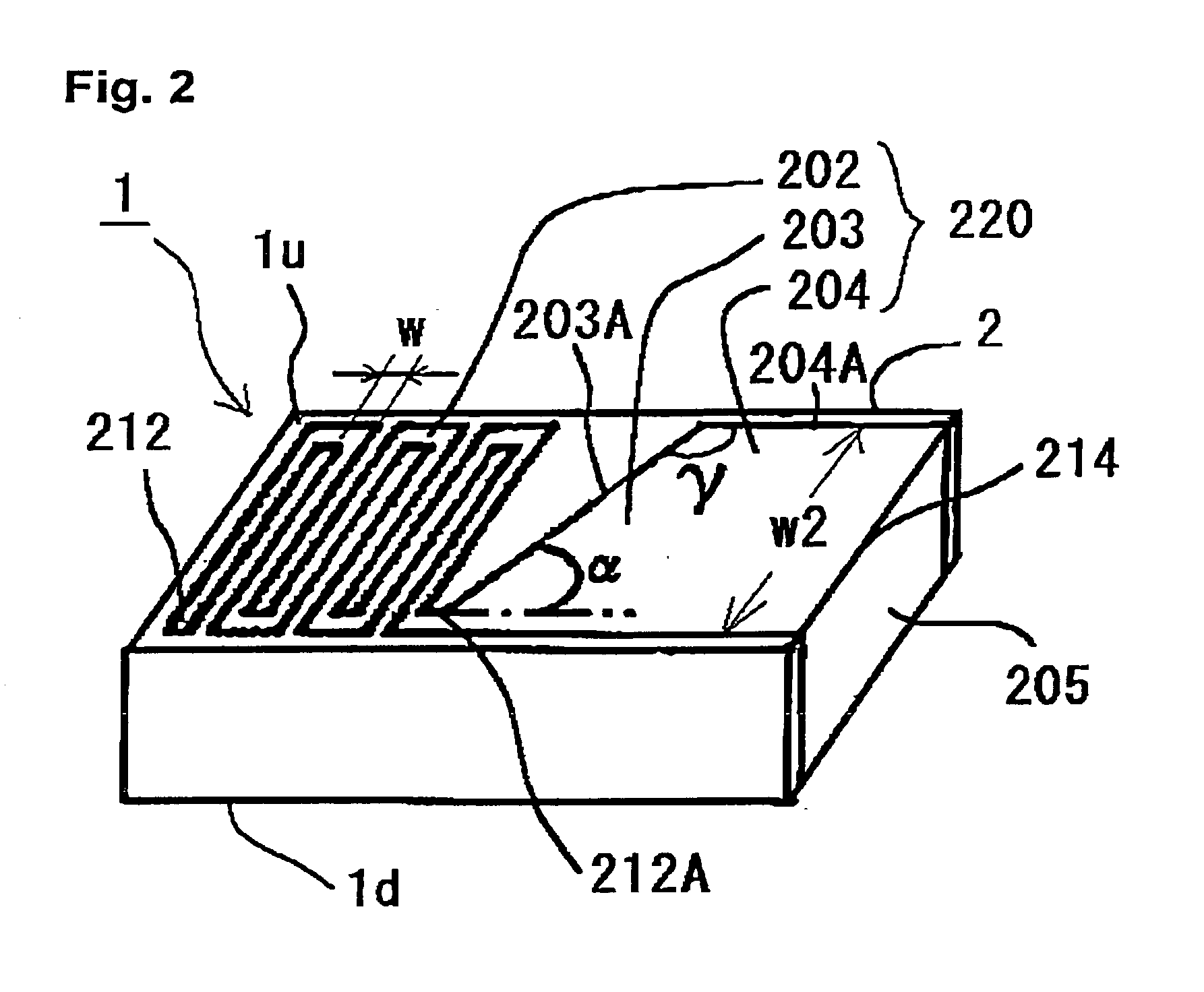
A dielectric antenna is provided for a high frequency wireless communication apparatus. The antenna includes a dielectric substrate and a conductive meander line layer formed on the dielectric substrate. A conductive feed line layer, having a greater line width than the width of the meander line layer, is also formed on the dielectric substrate. A conductive taper layer connects the conductive meander line layer to the conductive feed line layer. An edge of the conductive taper layer slants at an angle from an adjacent edge of the conductive feed line layer in a direction toward the conductive meander line layer.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Pure Dielectric Antennas and Related Devices
InactiveUS20070252778A1Improve radiation efficiencyImprove efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonanceDielectric antennas
There is disclosed an antenna device comprising an elongate dielectric radiating element having a longitudinal axis and a feeding mechanism for generating displacement currents in the dielectric radiating element. The radiating element is configured to support displacement current resonance modes parallel to the longitudinal axis but to inhibit displacement current resonance modes transverse to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Dielectric antenna for high frequency wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS20030092420A1Efficient matchingImprove featuresElectrically long antennasRadiating elements structural formsDielectric antennasLine width
A dielectric antenna is provided for a high frequency wireless communication apparatus. The antenna includes a dielectric substrate and a conductive meander line layer formed on the dielectric substrate. A conductive feed line layer, having a greater line width than the width of the meander line layer, is also formed on the dielectric substrate. A conductive taper layer connects the conductive meander line layer to the conductive feed line layer. An edge of the conductive taper layer slants at an angle from an adjacent edge of the conductive feed line layer in a direction toward the conductive meander line layer.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Hybrid antenna using parasitic excitation of conducting antennas by dielectric antennas
InactiveUS7545327B2High bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectric antennasIntegrated antenna
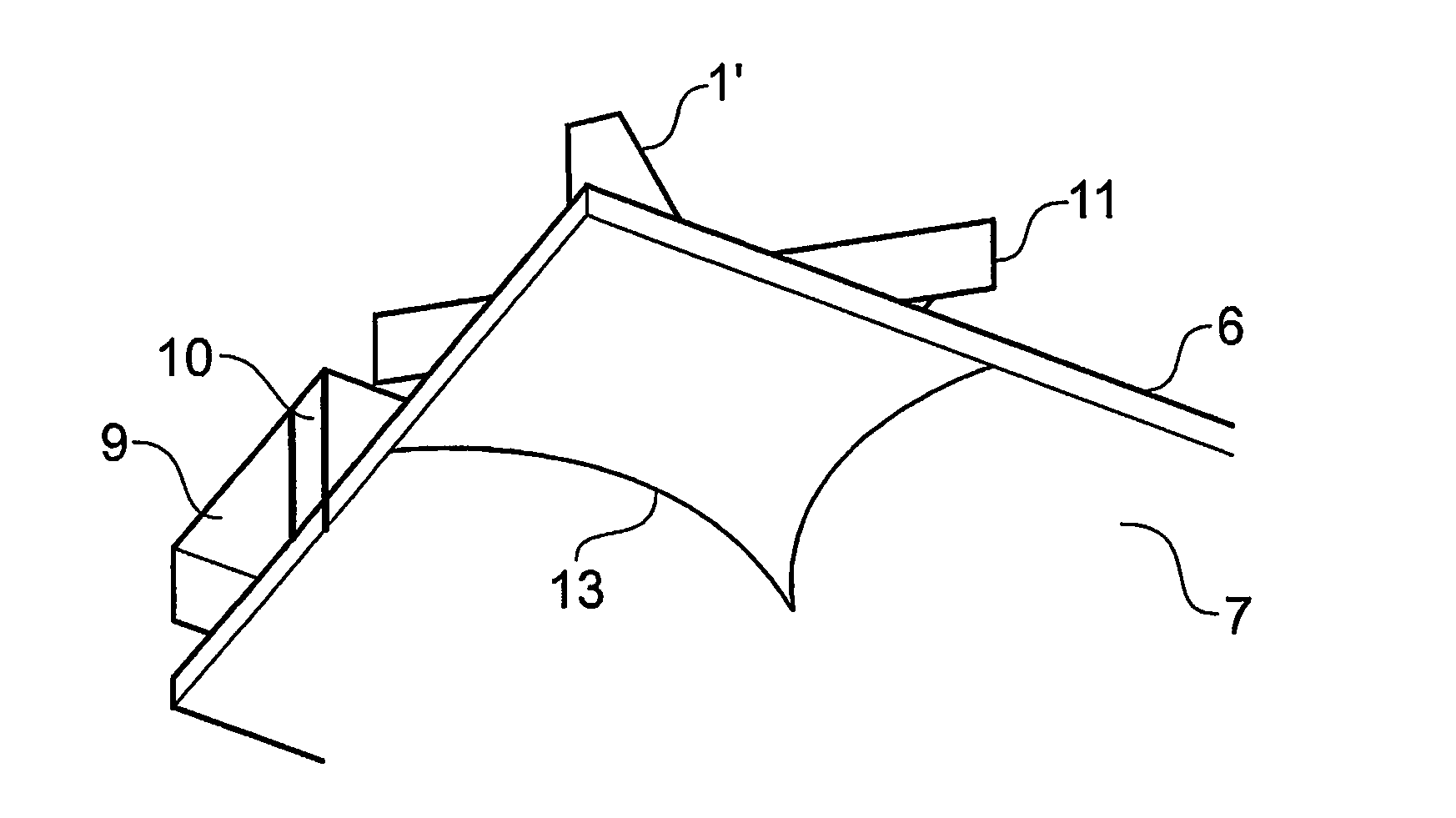
An integrated antenna device comprising a first, dielectric antenna component (1) and a second, electrically-conductive antenna component (9), wherein the first and second components are not electrically connected to each other but are mutually arranged such that the second component is parasitically driven by the first component when the first component is fed with a predetermined signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Dielectric antenna and radio device using the same
ActiveUS7161555B2High gainLarge primary beam widthIndividually energised antenna arraysResonant antennasRadio equipmentDielectric antennas
A dielectric antenna of the present invention includes a pillar-shaped dielectric section for radiating an electromagnetic wave being fed thereto. The dielectric section includes a depressed portion in an upper portion thereof. The vertical cross section of the depressed portion has such a shape that the height of the dielectric section gradually increases toward the side surface of the dielectric section. For example, the depressed portion is a notch having a V-shaped vertical cross section. Alternatively, the depressed portion includes a flat surface portion.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
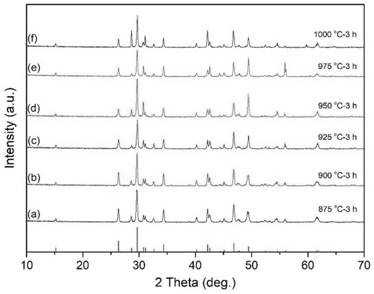
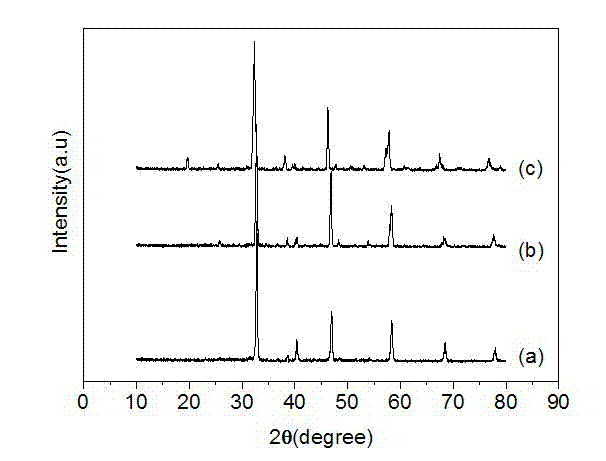
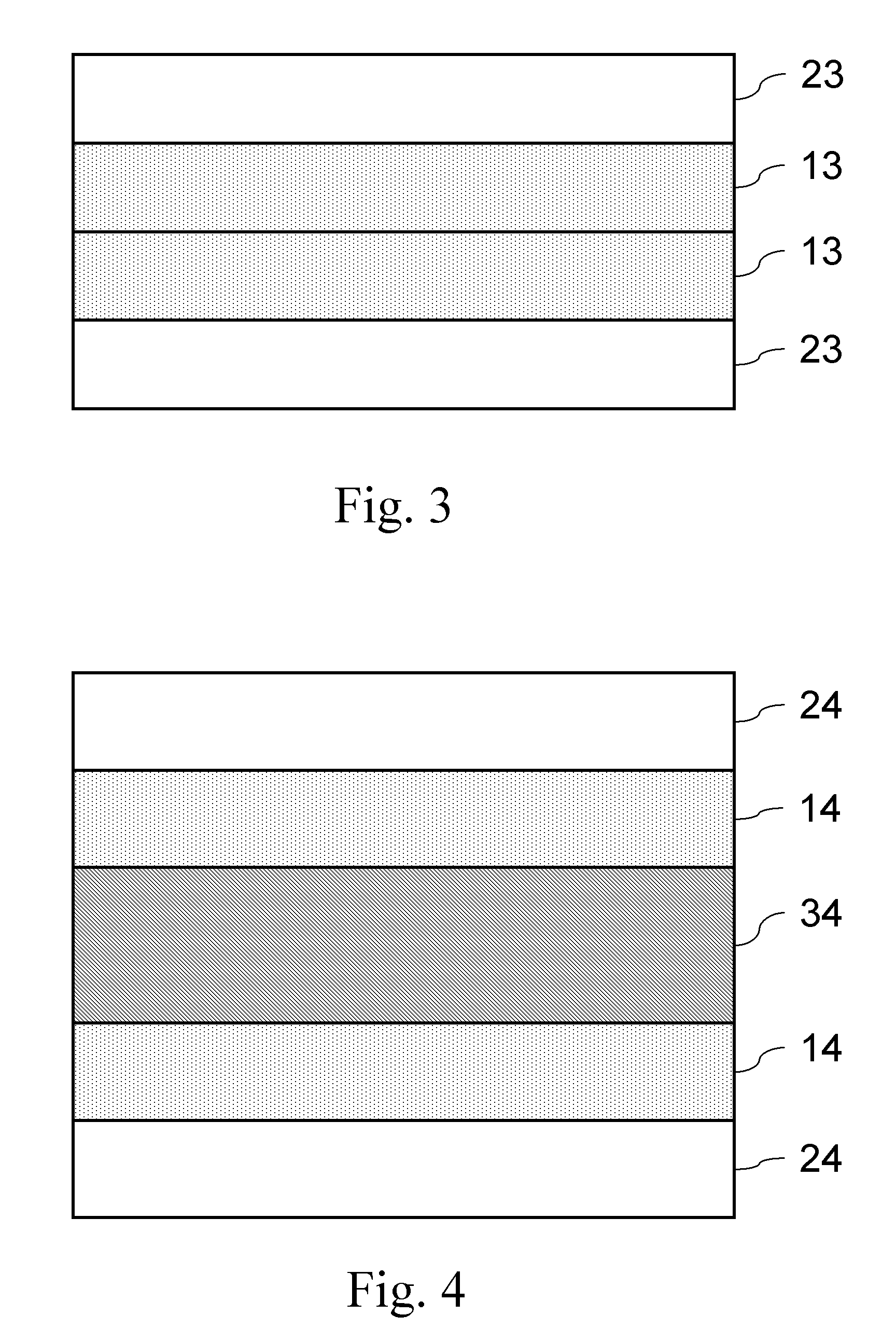
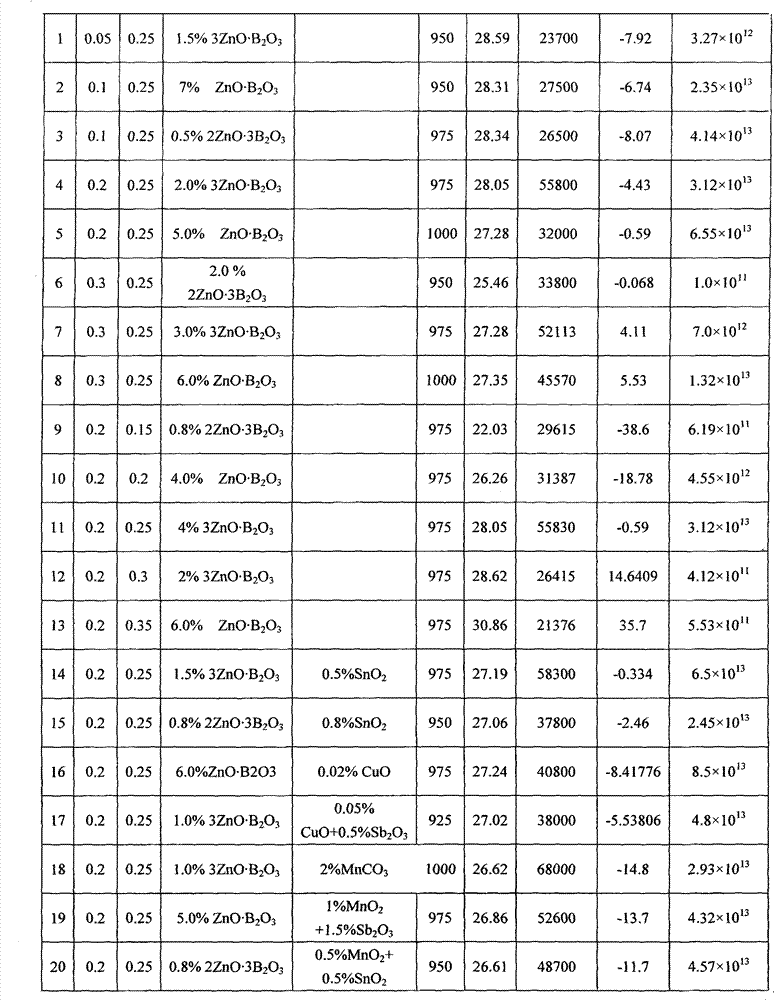
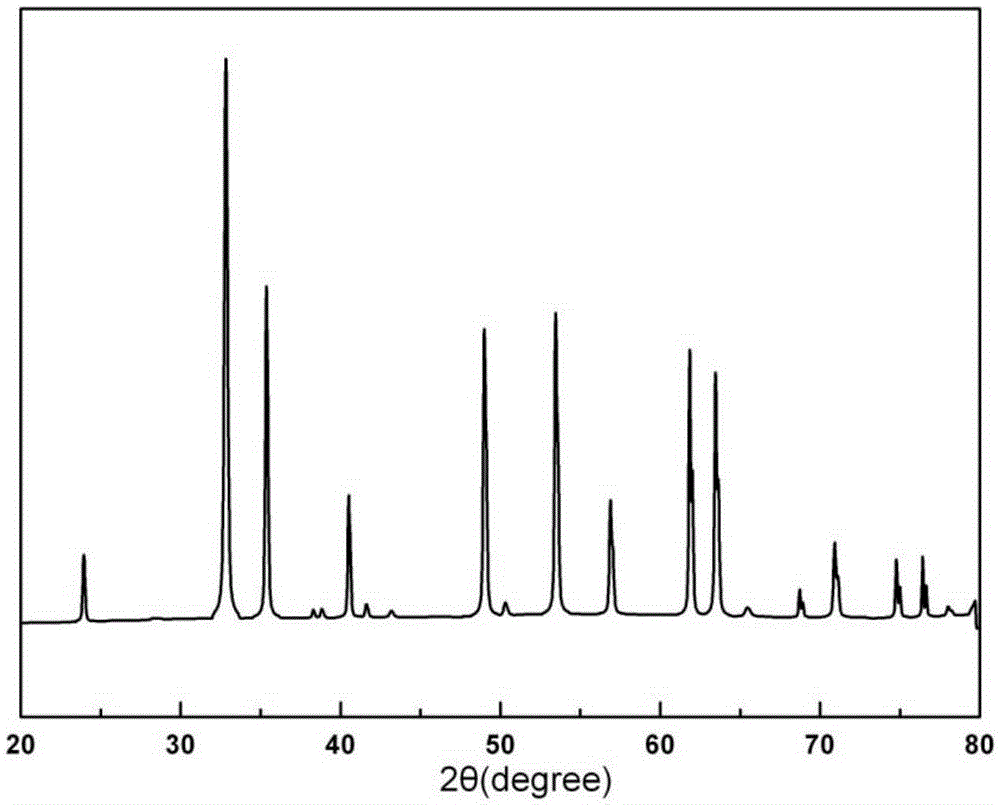
Low temperature sintered ZnO-MgO-TiO2 system microwave ceramic material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101475371ALow costExcellent electrical performanceCeramicsDielectric antennasCeramic capacitor
The invention discloses a low-temperature sintered ZnO-MgO-TiO2 system microwave ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The formula of raw materials of the ceramic material comprises the following compositions: 30 to 45 percent of zinc oxide, 2 to 14 percent of magnesium oxide, 50 to 60 percent of titania and an auxiliary sintering agent. The preparation method comprises: taking the zinc oxide, basic magnesium carbonate and the titania as raw materials, mixing the raw materials, adding a grinding aid for ball milling, drying, sieving and presintering, and obtaining clinker; and mixing the obtained clinker with the titania, the auxiliary sintering agent and an additive, performing drying, granulation and press forming after secondary ball milling, finally sintering the mixture for 2 to 8 hours at a temperature of between 900 DEG C and 1,000 DEG C, and obtaining the ceramic material. The ceramic material prepared by the method has the advantages of superior microwave dielectric property, low sintering temperature, low cost and the like, and is suitable for microwave devices such as multi-layer ceramic capacitors, filters, resonators and dielectric antennas.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
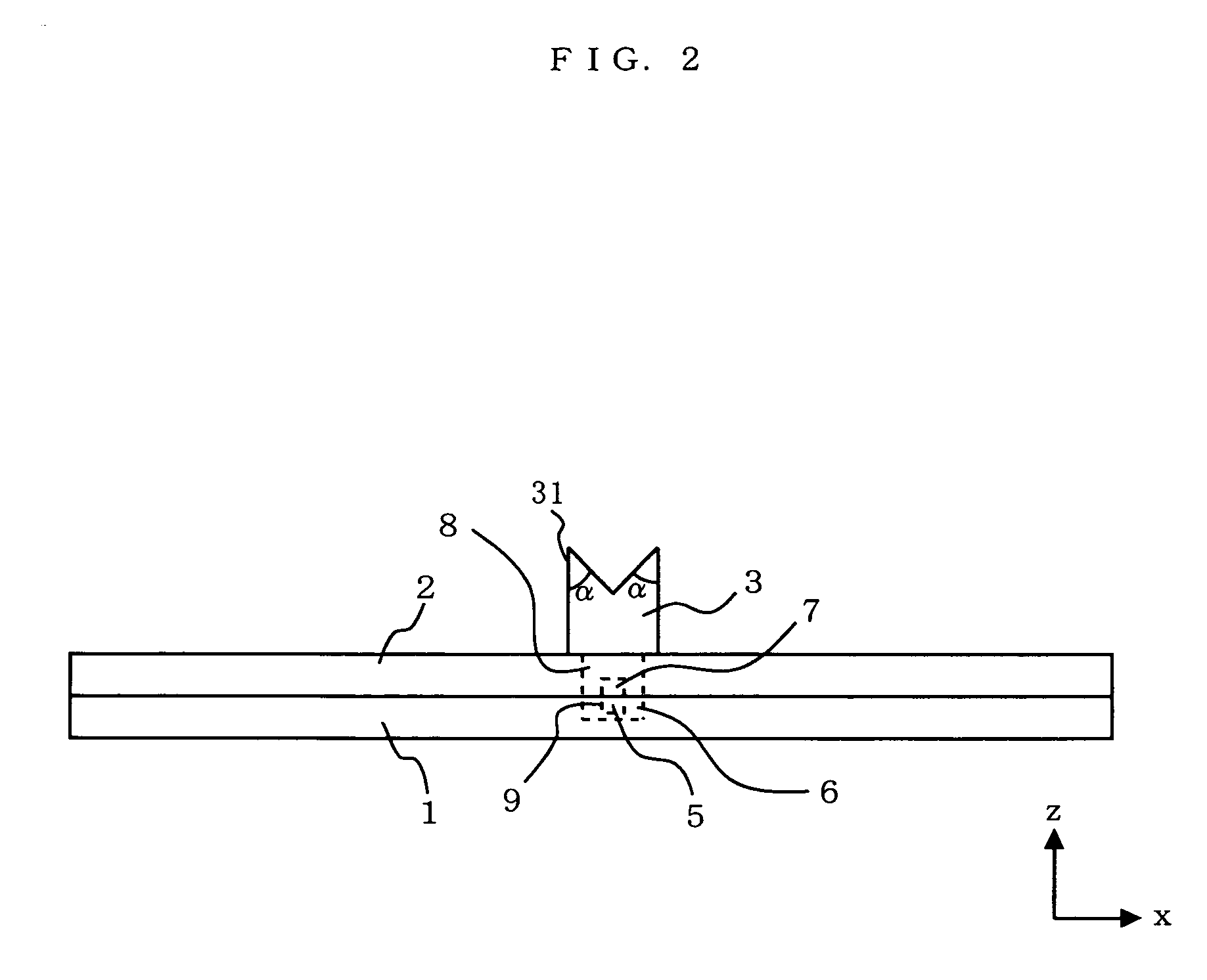
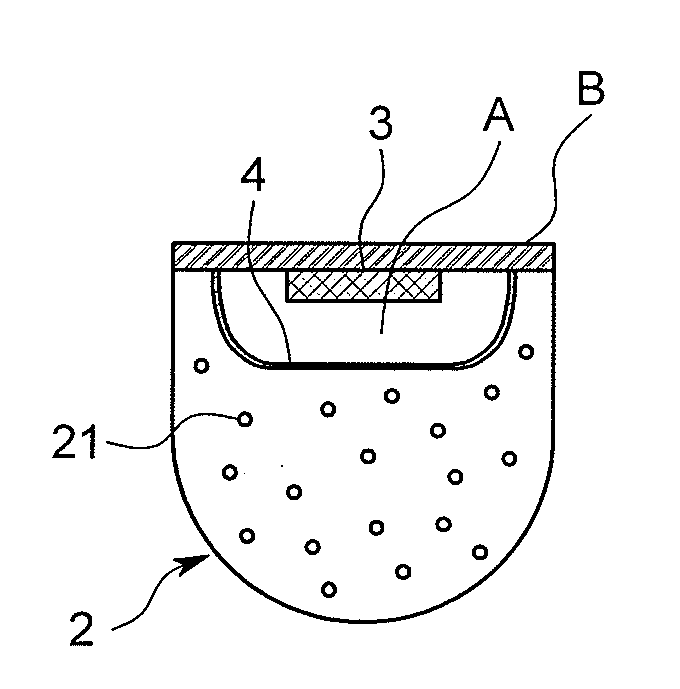
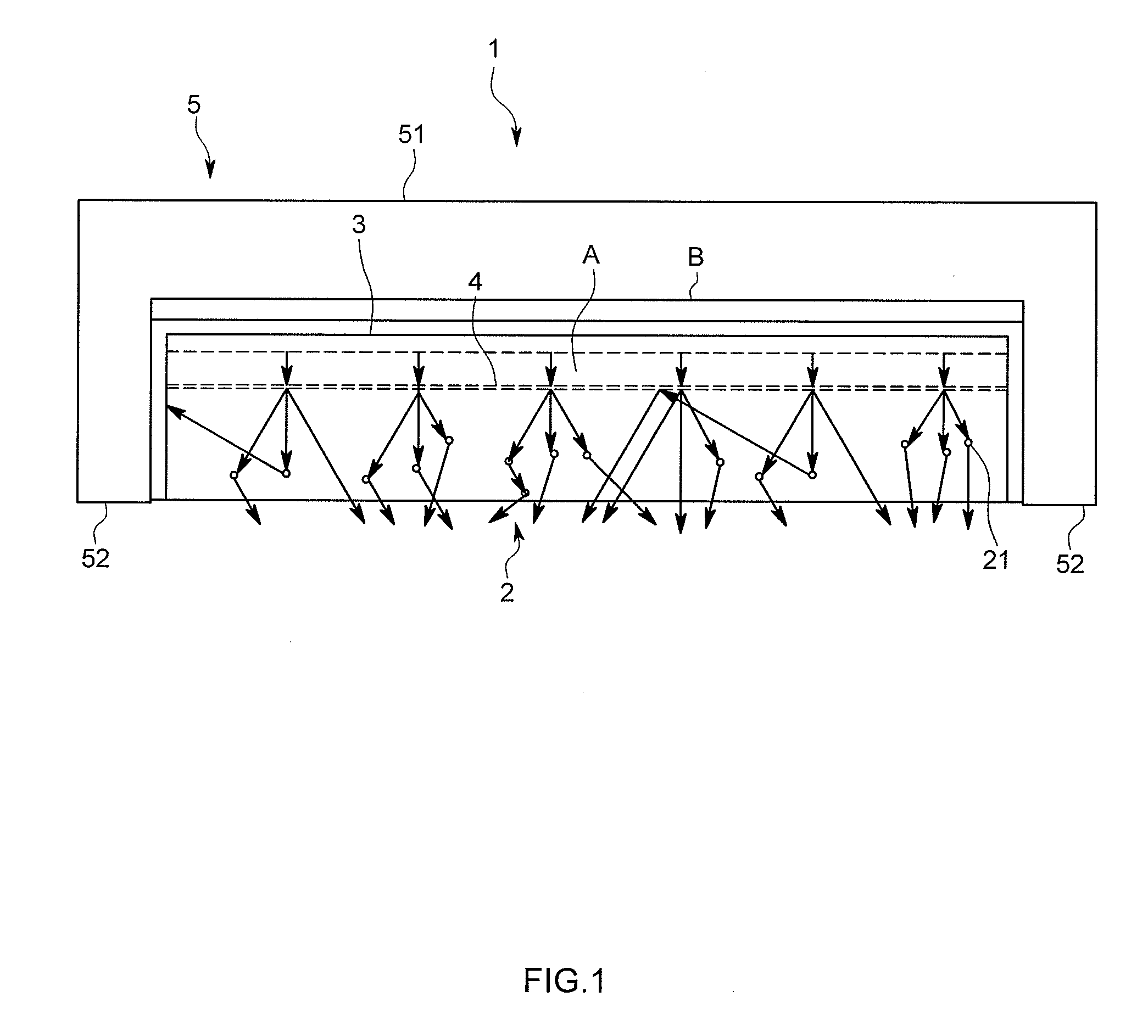
Dielectric antenna
InactiveUS8242965B2Less effortReduce correctionWaveguide hornsLevel indicatorsDielectric antennasElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Hybrid antenna using parasitic excitation of conducting antennas by dielectric antennas
InactiveUS20090213014A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectric antennasIntegrated antenna
An integrated antenna device comprising a first, dielectric antenna component and a second, electrically-conductive antenna component, wherein the first and second components are not electrically connected to each other but are mutually arranged such that the second component is parasitically driven by the first component when the first component is fed with a predetermined signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
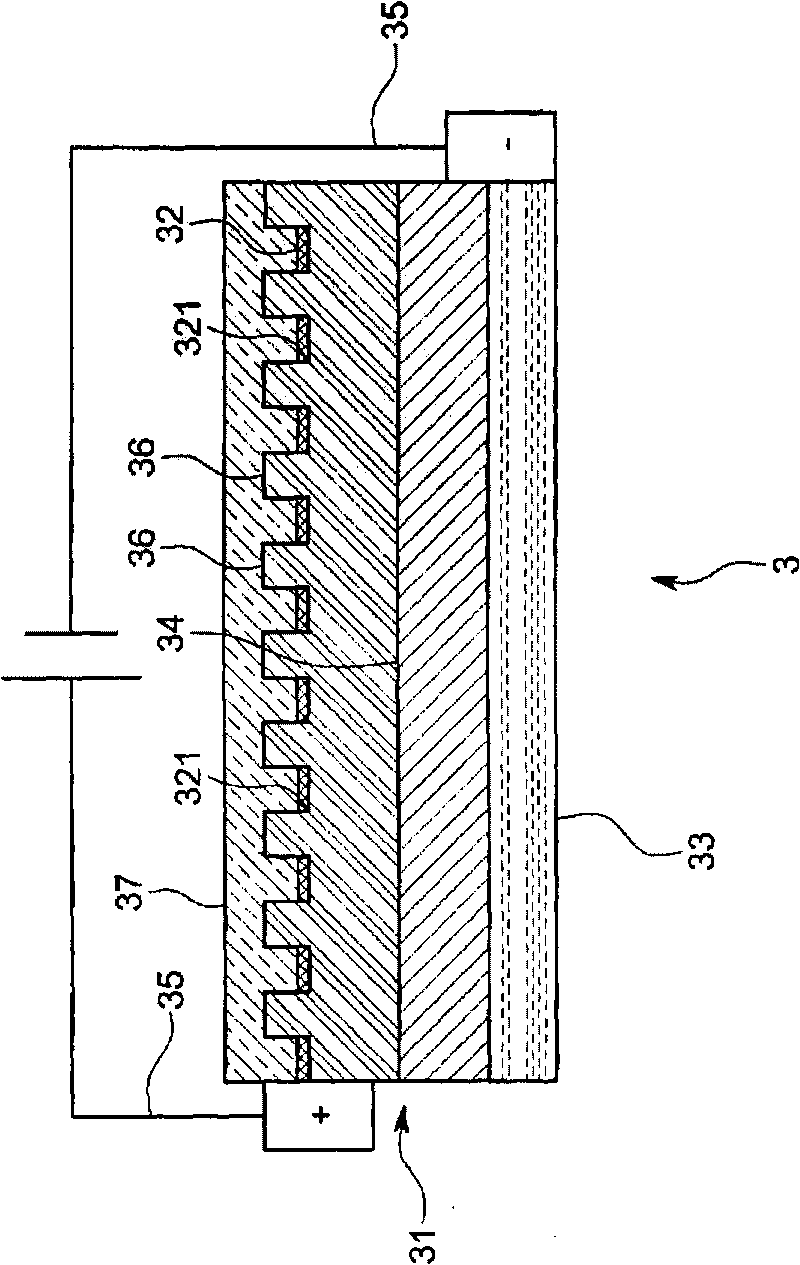
LED illumination device using diffraction member
InactiveUS20100181591A1Uniform lightLessen light diffusing degreeElongate light sourcesDiffusing elementsDielectric antennasP–n junction
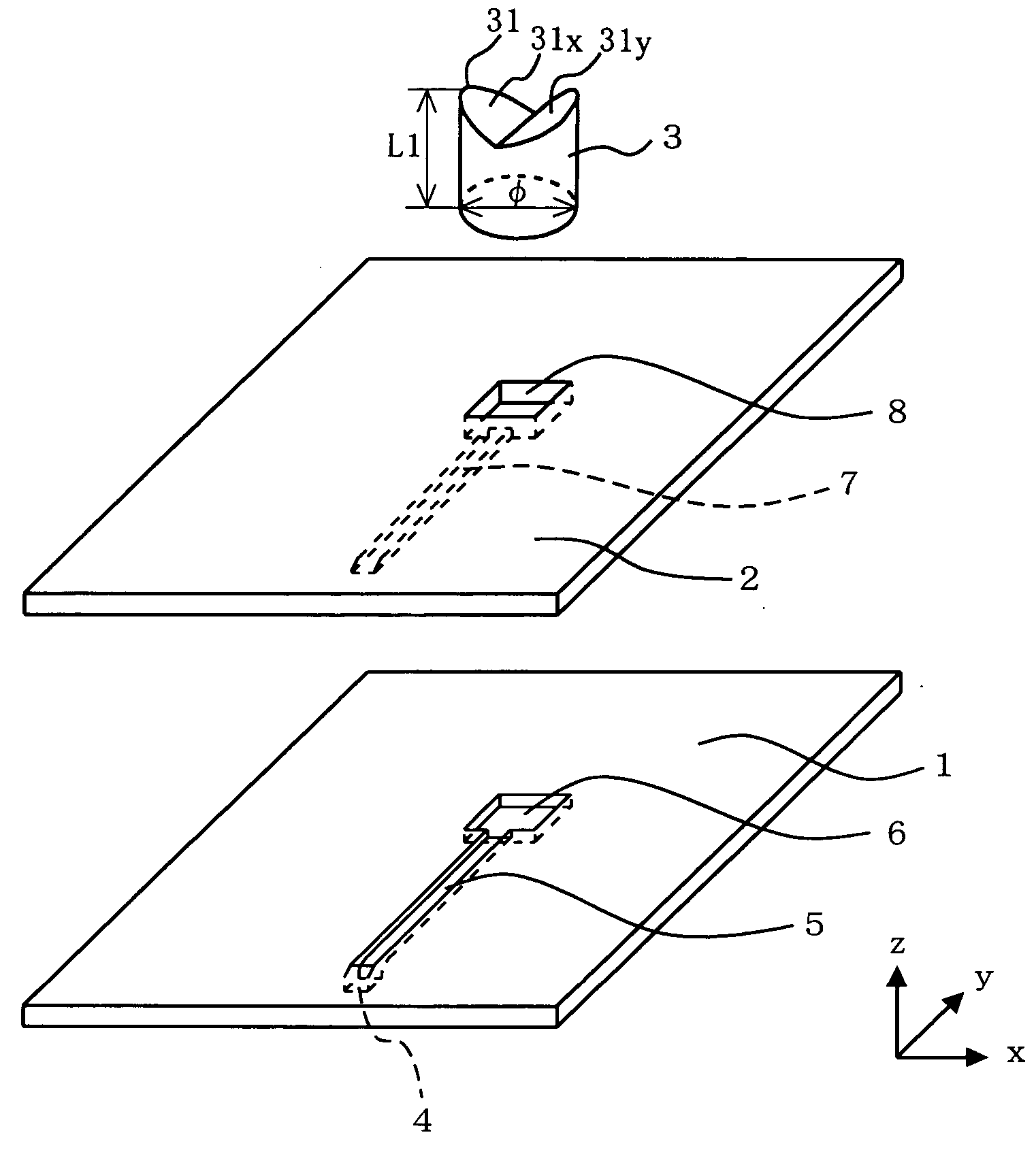
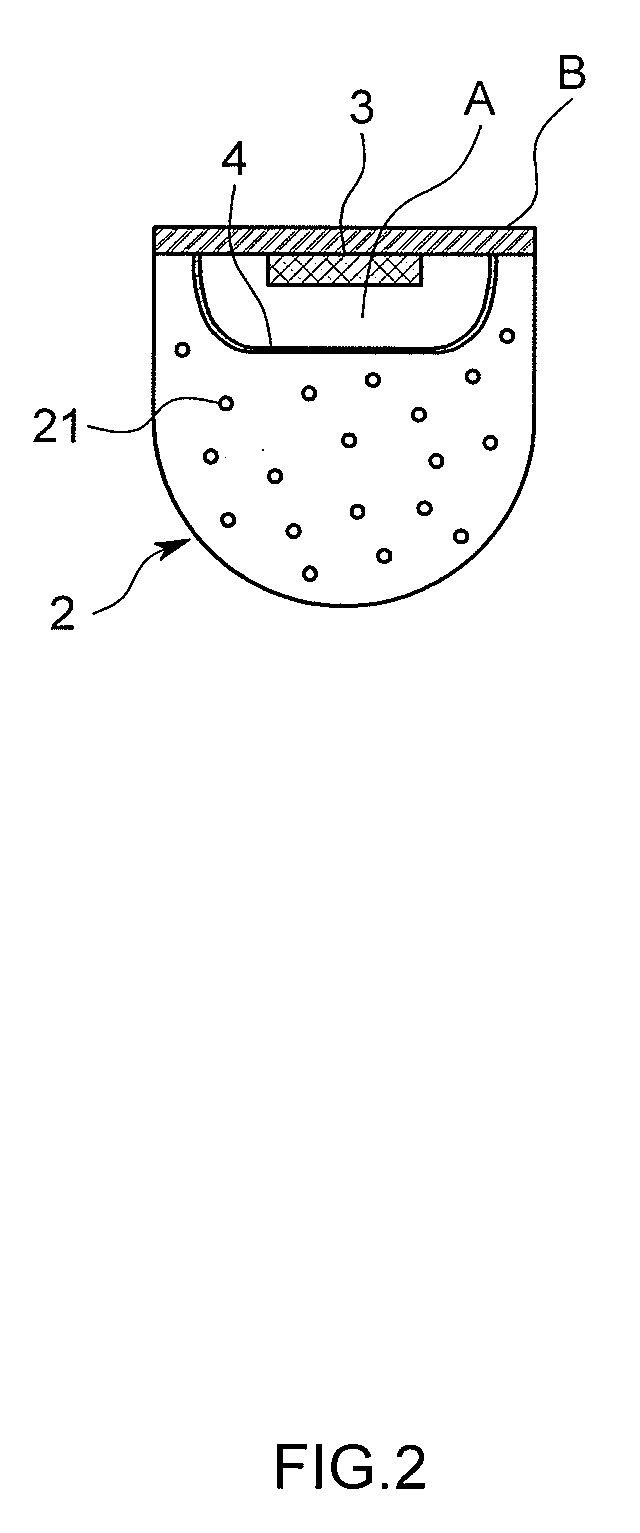
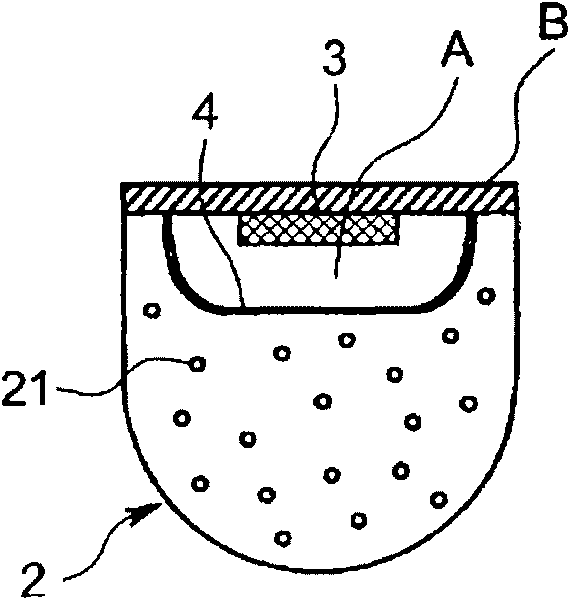
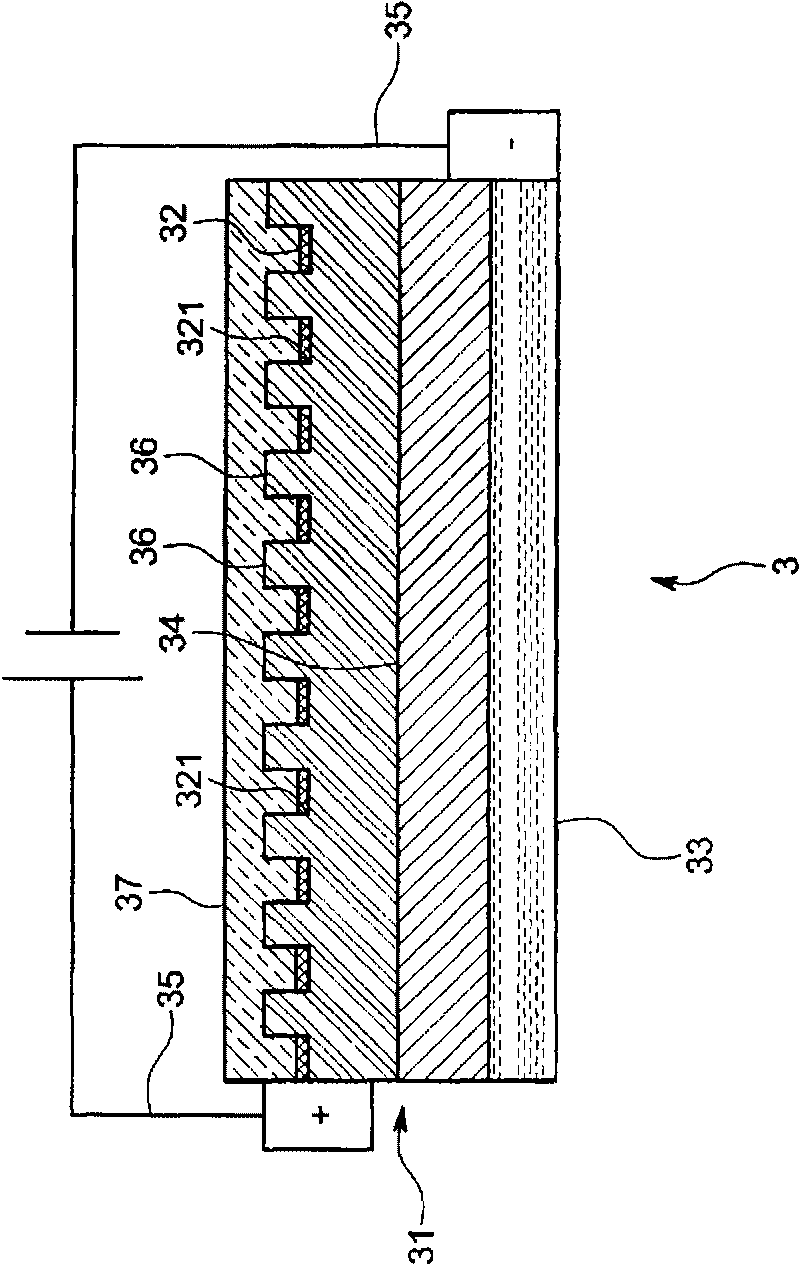
An object of this invention is to provide an LED illumination device that can substitute for a fluorescent light and obtain uniform light with high efficiency. The LED illumination device comprises an LED with a thin-plate-shaped semiconductor element body transmitting the light generated in a PN junction area in a thickness direction and emits it from the surface, a surface electrode that covers the surface of the semiconductor element body, and columnar dielectric antennas that penetrate the surface electrode in the thickness direction and that condense the light transmitted in a body of the semiconductor element and emit it outside, a diffraction member that is arranged on a luminous surface side of the LED and that diffracts and disperses the light emitted by the LED, and a diffusion member that is arranged outside the diffraction member and that diffuses the light dispersed by the diffraction member and emits it outside.
Owner:ABEL SYST
Led illumination device using diffraction member
InactiveCN101730819AReduce lossesReduced light diffusionElongate light sourcesDiffusing elementsDielectric antennasEngineering
An LED (3) is equipped with a thin-plate-shaped semiconductor element body (31) transmitting the light generated in a p-n junction region (34) in a thickness direction and emits it from the surface, a surface electrode (32) that is provided in such a manner as to cover the surface of the semiconductor element body (31), and a plurality of columnar dielectric antennas (36) penetrating through the surface electrode (32) in the thickness direction and condensing the light that is transmitted in the semiconductor element (31) body to emit it outside. There provided is an LED illuminator (1) provided with the LED (3), a diffraction member (4) that is arranged on the light emitting surface side of the LED (3) to diffract and disperse the light that is emitted by the LED (3), and a diffusion member (2) that is arranged outside the diffraction member (4) to diffuse the light that is dispersed by the diffraction member (4) and emits it outside. The LED illuminator (1) can substitute for a fluorescent light and can obtain uniform light with high efficiency.
Owner:ABEL SYST
Dielectric antenna
ActiveUS20100321262A1Easy to packSuitable for applicationWaveguide mouthsDielectric antennasElectromagnetic radiation
A dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element (2) and with a lens (3) made of a dielectric material, the feed element (2) emitting electromagnetic radiation (4) and the lens (3) being supplied with electromagnetic radiation (4) in the feed region (5), the lens (3) relaying the electromagnetic radiation (4) and radiating it with the transmission region (6). To configure these dielectric antennas such that the disadvantages of the dielectric antennas known from the prior art are at least partially avoided, first of all, the lens (3) is shaped essentially ellipsoidally at least in the transmission region (6) and the lens (3) is arranged relative to the feed element (2) such that the electromagnetic radiation (4) emitted by the lens (3) in the direction of maximum radiation (7) of the antenna has an essentially planar phase front.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
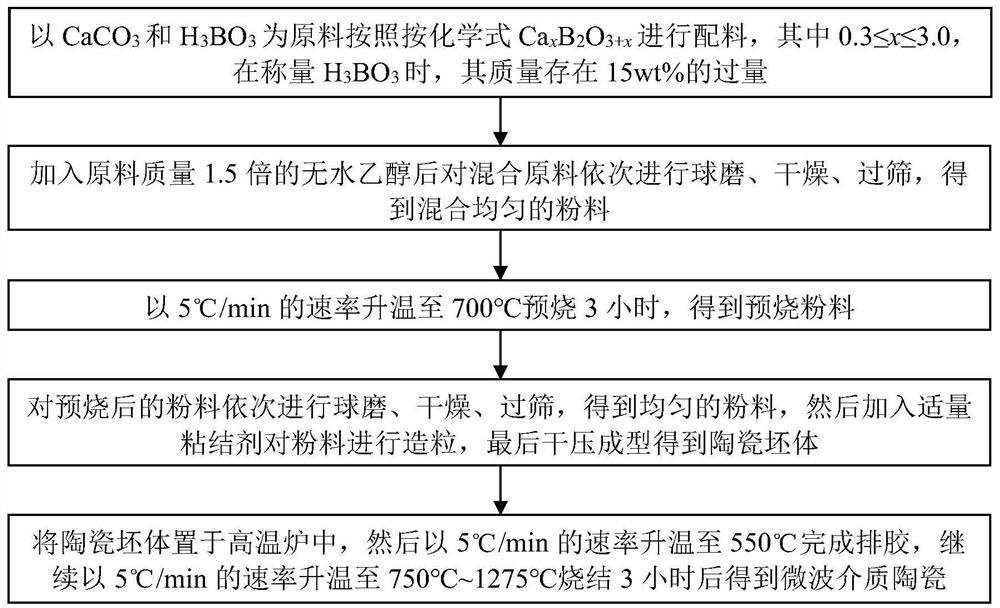
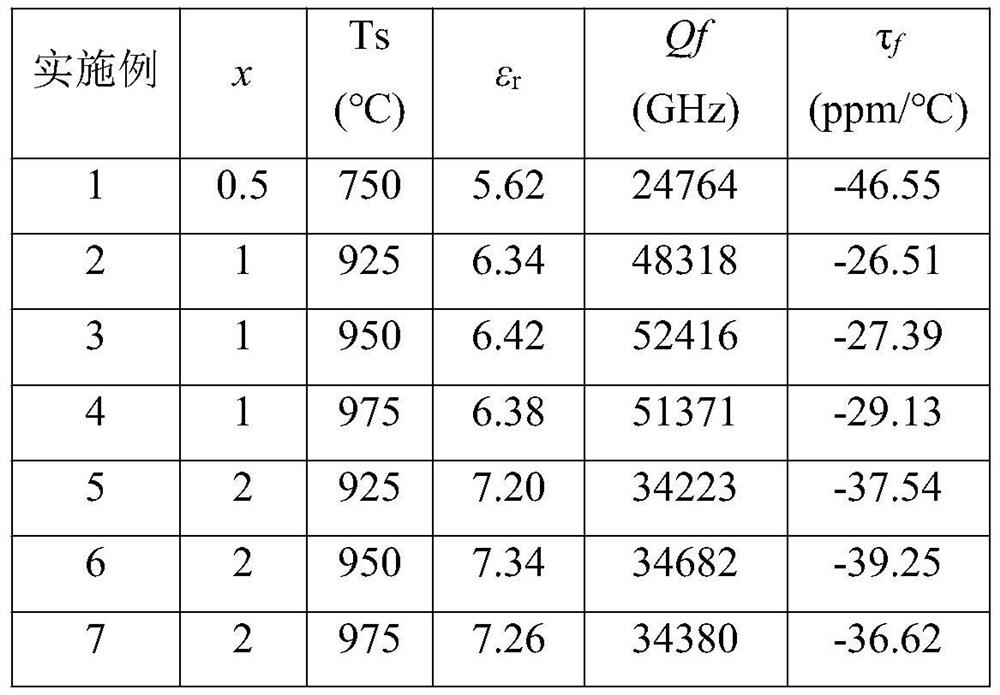
Borate-based low-dielectric microwave dielectric ceramic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113563052AIncrease transfer rateAlleviate signal delay problemResonatorsCircuit susbtrate materialsMicrowaveChemical composition
The invention discloses borate-based low-dielectric microwave dielectric ceramic and a preparation method thereof, the chemical composition of the microwave dielectric ceramic is Ca<x>B<2>O<3+x>, and x is more than or equal to 0.3 and less than or equal to 3.0. The dielectric constant of the microwave dielectric ceramic ranges from 5.62 to 10.12, the quality factor ranges from 13161 GHz to 52416 GHz, and the temperature coefficient of resonance frequency ranges from-20.42 ppm / DEG C to-54.65 ppm / DEG C. The microwave dielectric ceramic is obtained by heating to 700 DEG C at a speed of 5 DEG C / min, preserving heat for 3 hours to finish presintering synthesis, heating to 750-1275 DEG C at a speed of 5 DEG C / min, and preserving heat for 3 hours to finish sintering. The microwave dielectric ceramic prepared in the invention has the advantages of low dielectric constant, high quality factor and low sintering temperature, and is suitable for preparing LTCC substrates, dielectric resonators, filters, dielectric antennas and other microwave communication devices.
Owner:WENZHOU ADVANCED MFG TECH INST OF HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
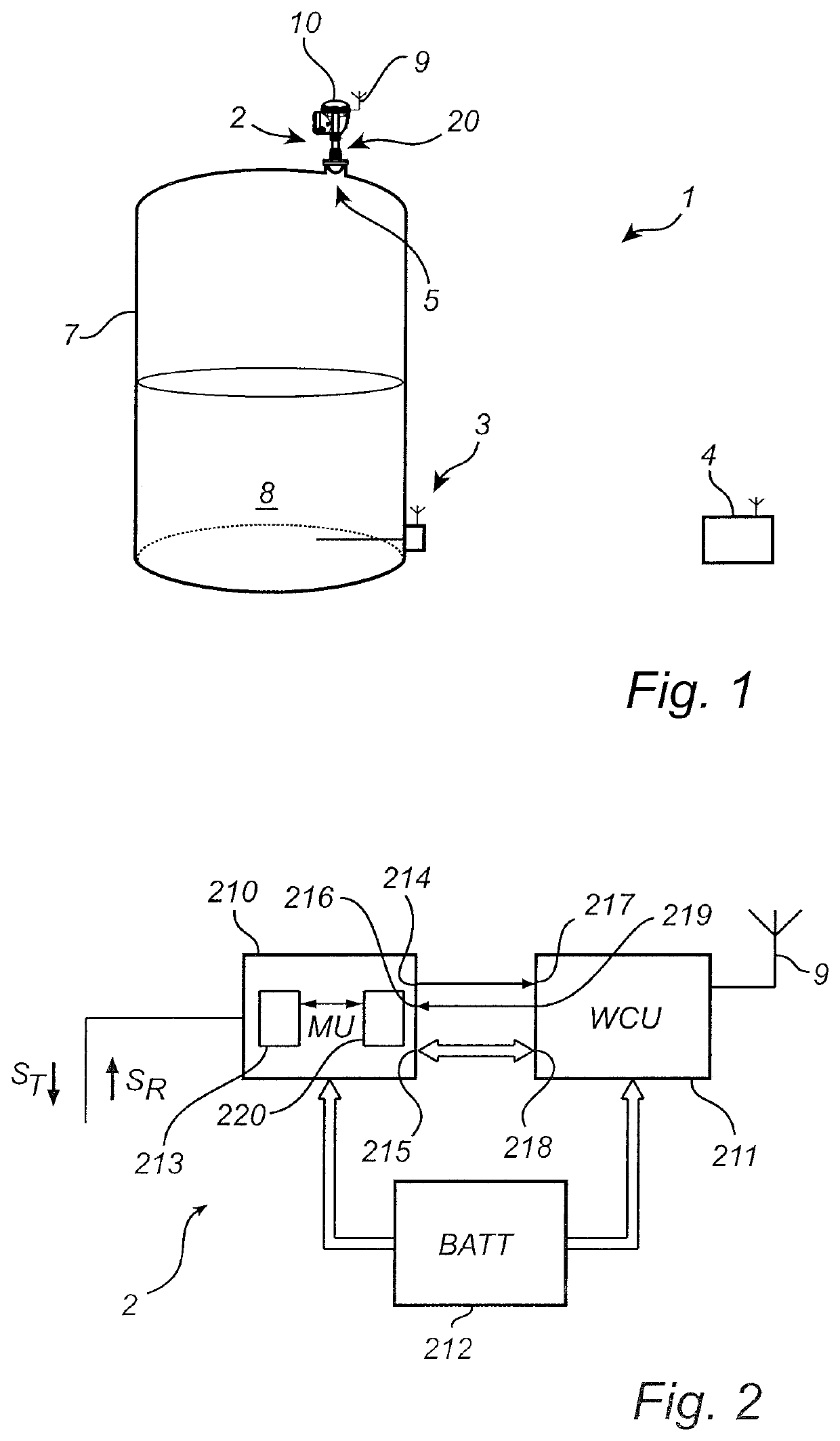
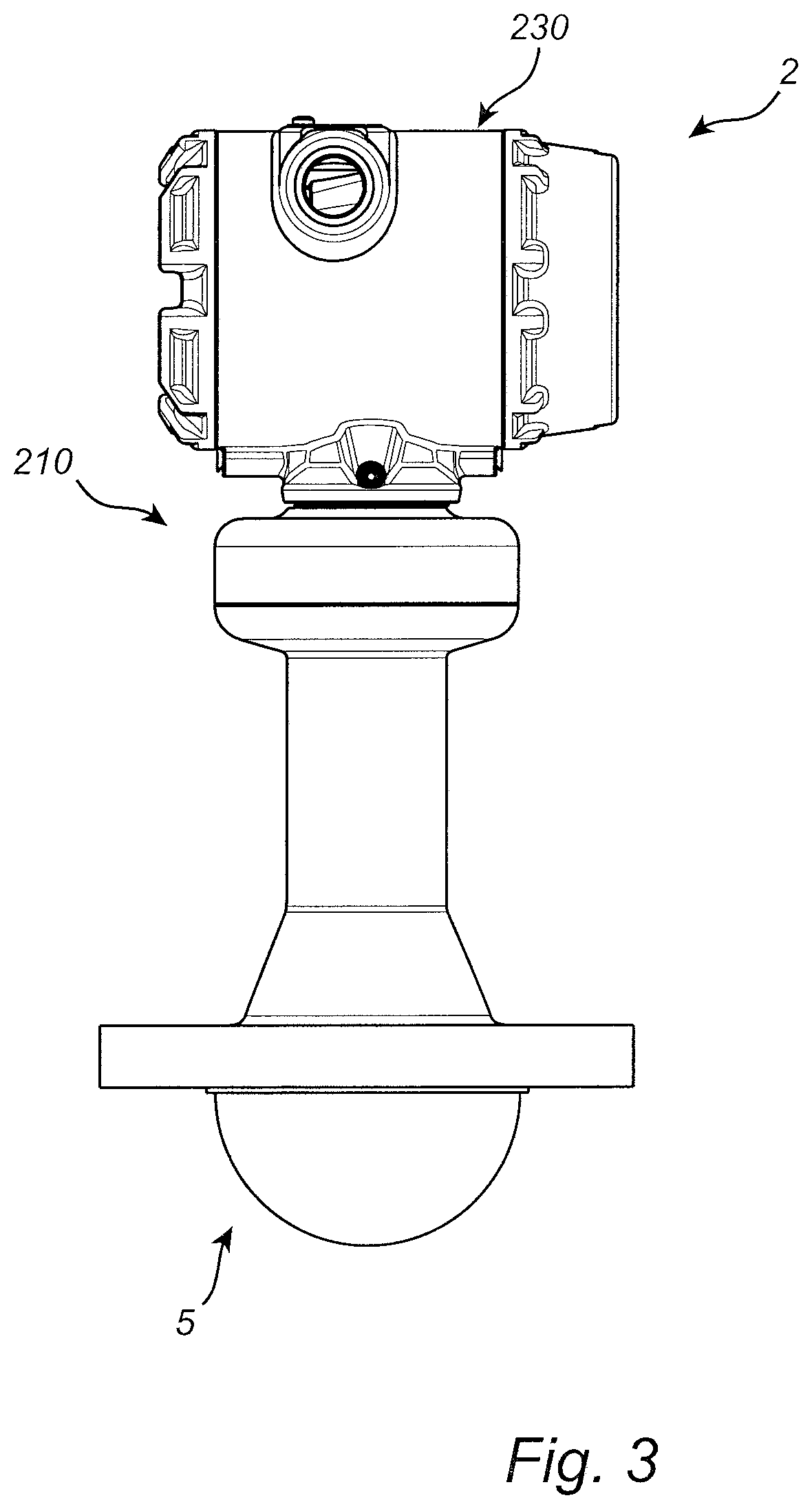
Radar level gauge system with dielectric antenna
ActiveUS11047725B2Avoid flowReduce generationAntenna supports/mountingsMachines/enginesTransceiverDielectric antennas
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
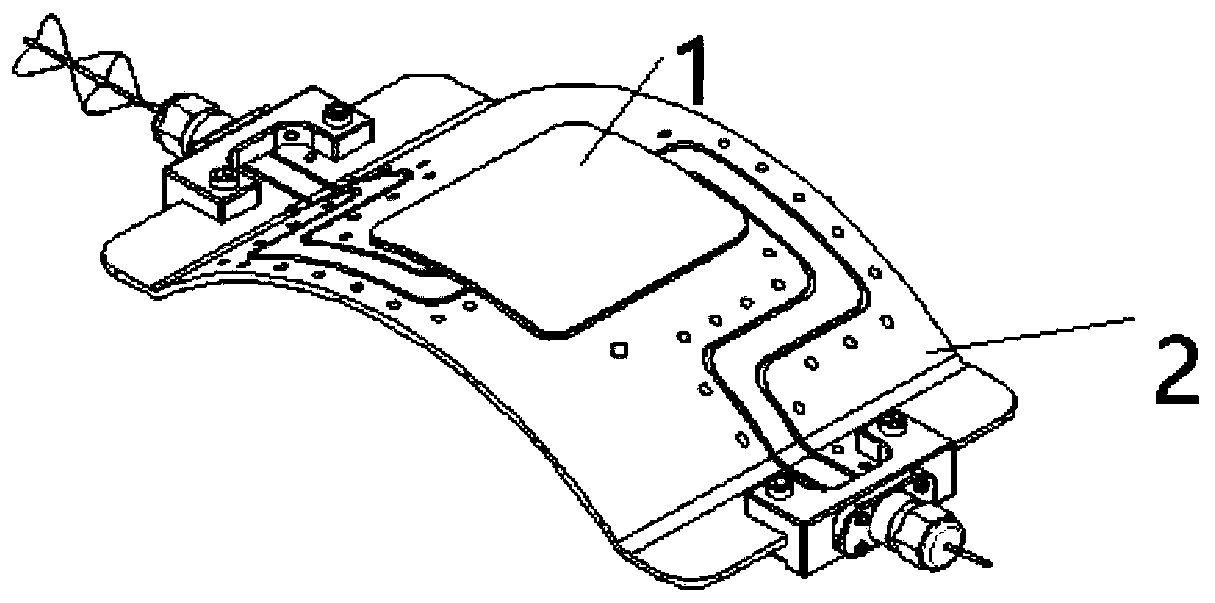
Flexible microwave device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110202880AAdjust working frequencyReduce lossSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingDielectric antennasThe Internet
The invention provides a flexible microwave device and a preparation method thereof. The device includes a flexible waveguide and flexible ferrite films; the flexible ferrite films are formed on the upper surface of the flexible waveguide. The surface of the flexible waveguide is provided with two parallel S-shaped channels, the flexible ferrite films are located in the middles of the S-shaped channels, and one end of each S-shaped channel is externally connected with an electromagnetic wave generator. The flexible microwave device is simple in structure, small in size, low in cost and good inperformance, can be used for preparing flexible microwave signal processing devices such as isolators, circulators, phase shifters, diplexers, filters, microwave dielectric antennas and ferrite switches, and has important application prospects in microwave communication, the Internet of Things, intelligent household appliances and other fields.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
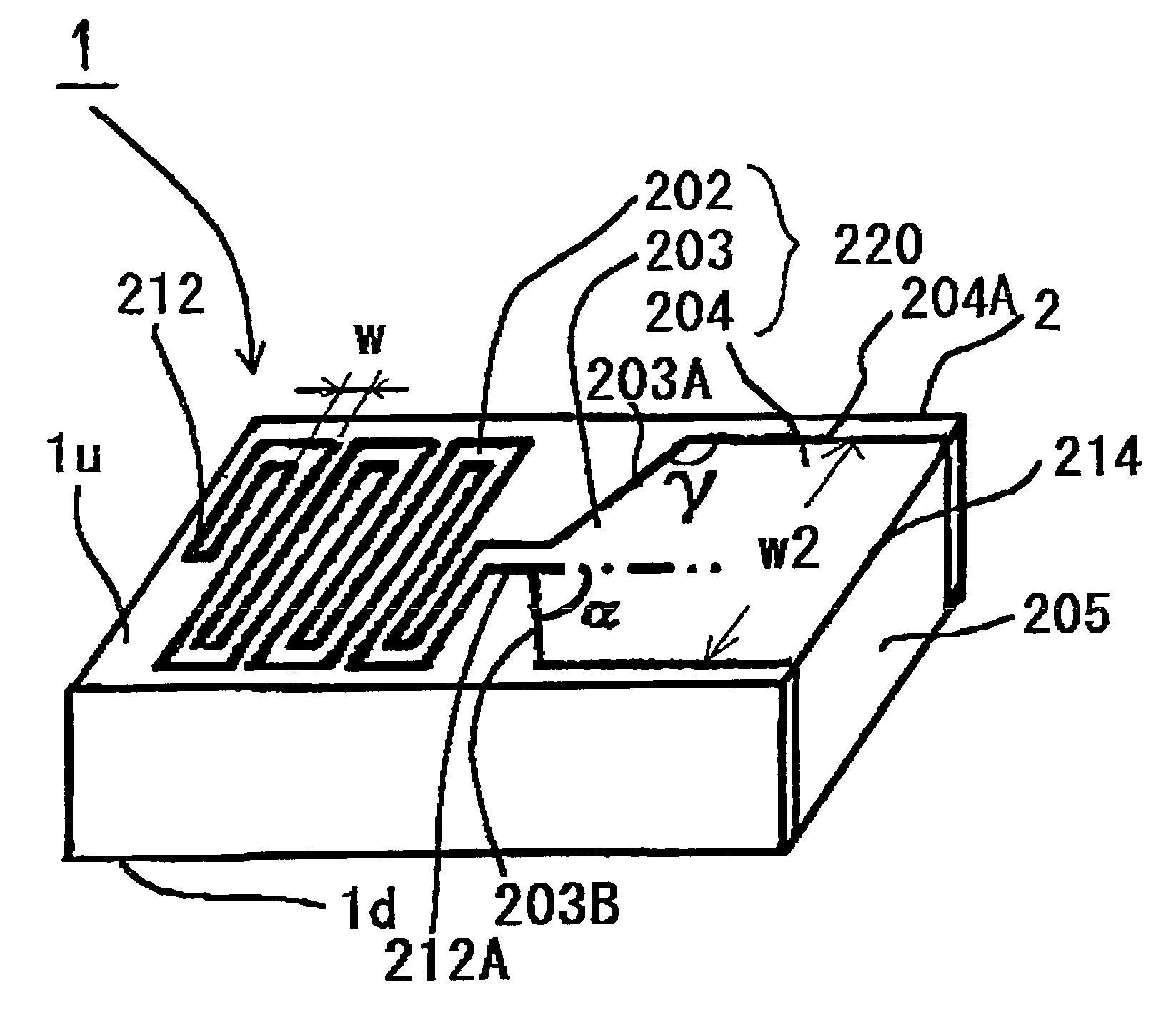
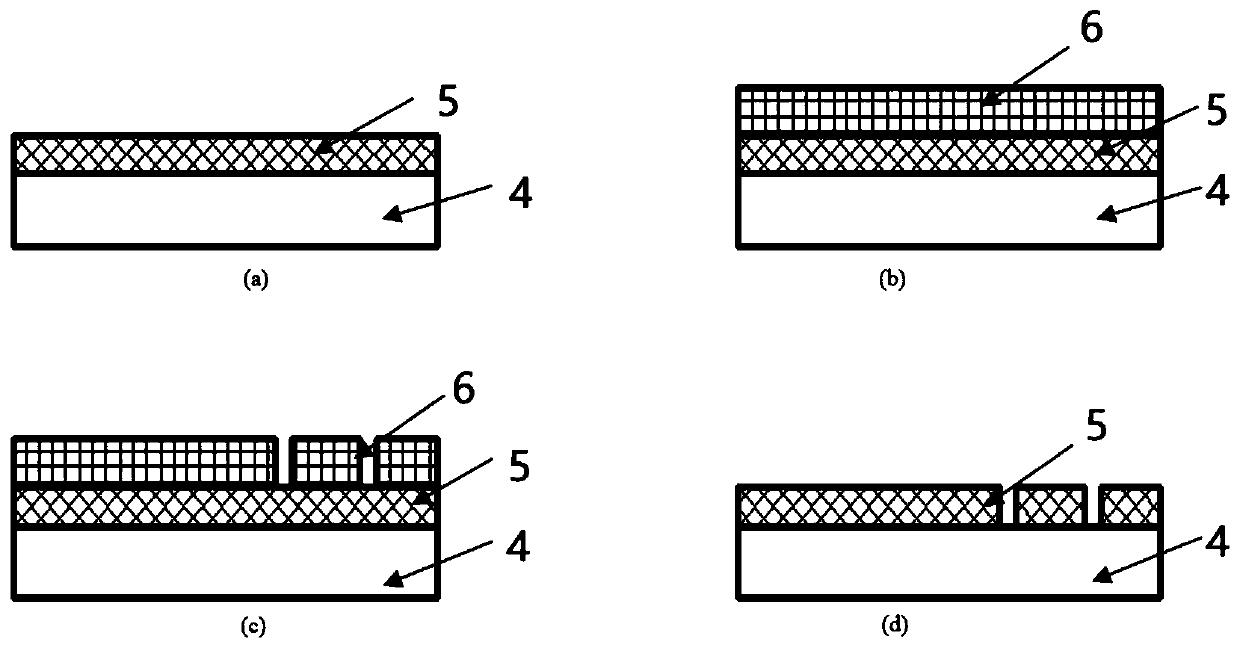
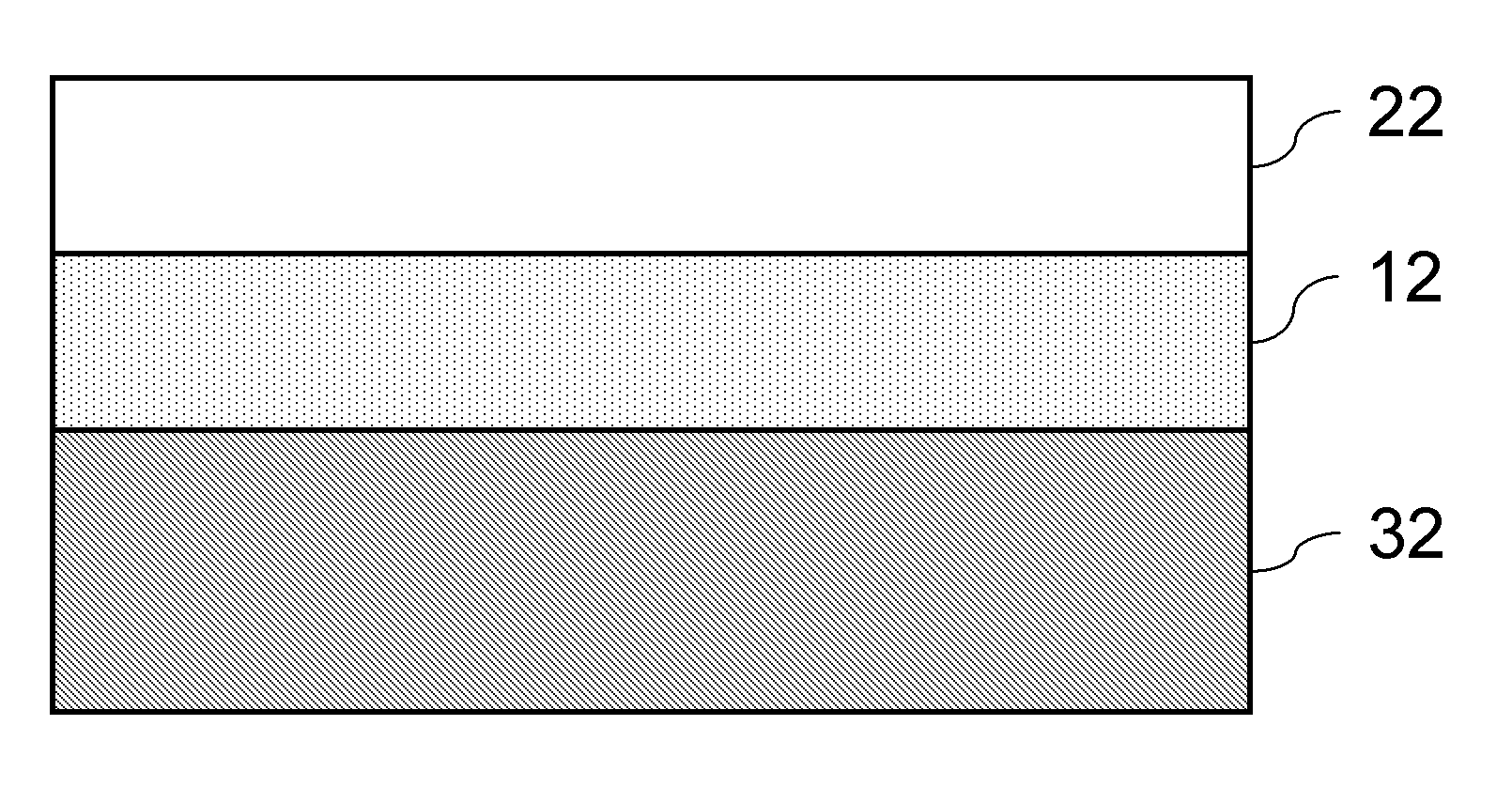
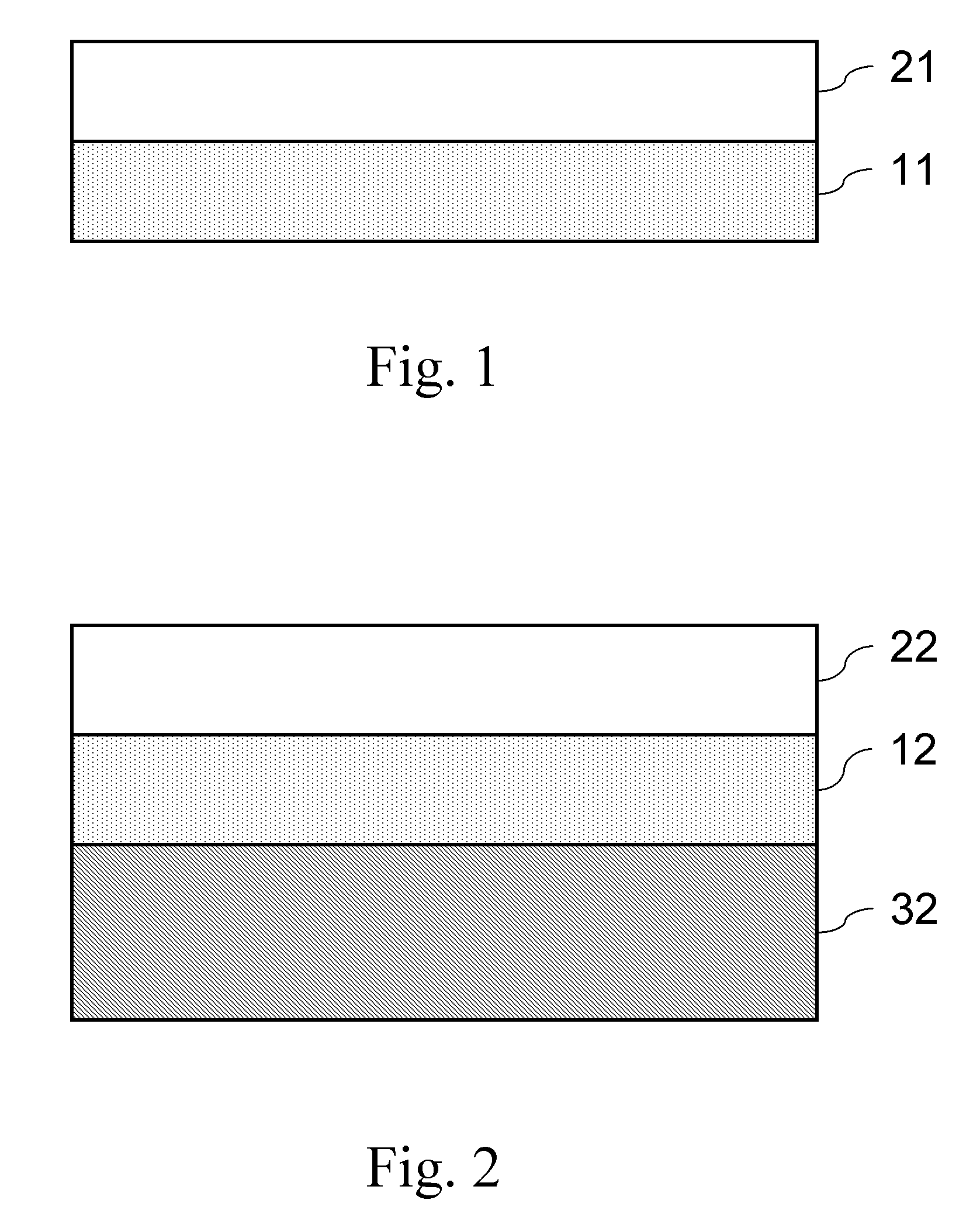
High dielectric antenna substrate and antenna thereof
ActiveUS20070152883A1Antenna area can be reducedReduce material costsSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric antennasAntenna substrate
A high dielectric antenna substrate and antenna thereof are provided. The substrate includes a first dielectric layer having a first dielectric constant, and a second dielectric layer having a second dielectric constant. The second dielectric layer is formed on one surface of the first dielectric layer. The second dielectric constant is lower than the first dielectric constant. Furthermore, a first metal layer and a second metal layer are optionally formed on the same surface or two surfaces of the first dielectric layer to compose a capacitor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Pure dielectric antennas and related devices
There is disclosed an antenna device comprising an elongate dielectric radiating element having a longitudinal axis and a feeding mechanism for generating displacement currents in the dielectric radiating element. The radiating element is configured to support displacement current resonance modes parallel to the longitudinal axis but to inhibit displacement current resonance modes transverse to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:ANTENOVA LTD
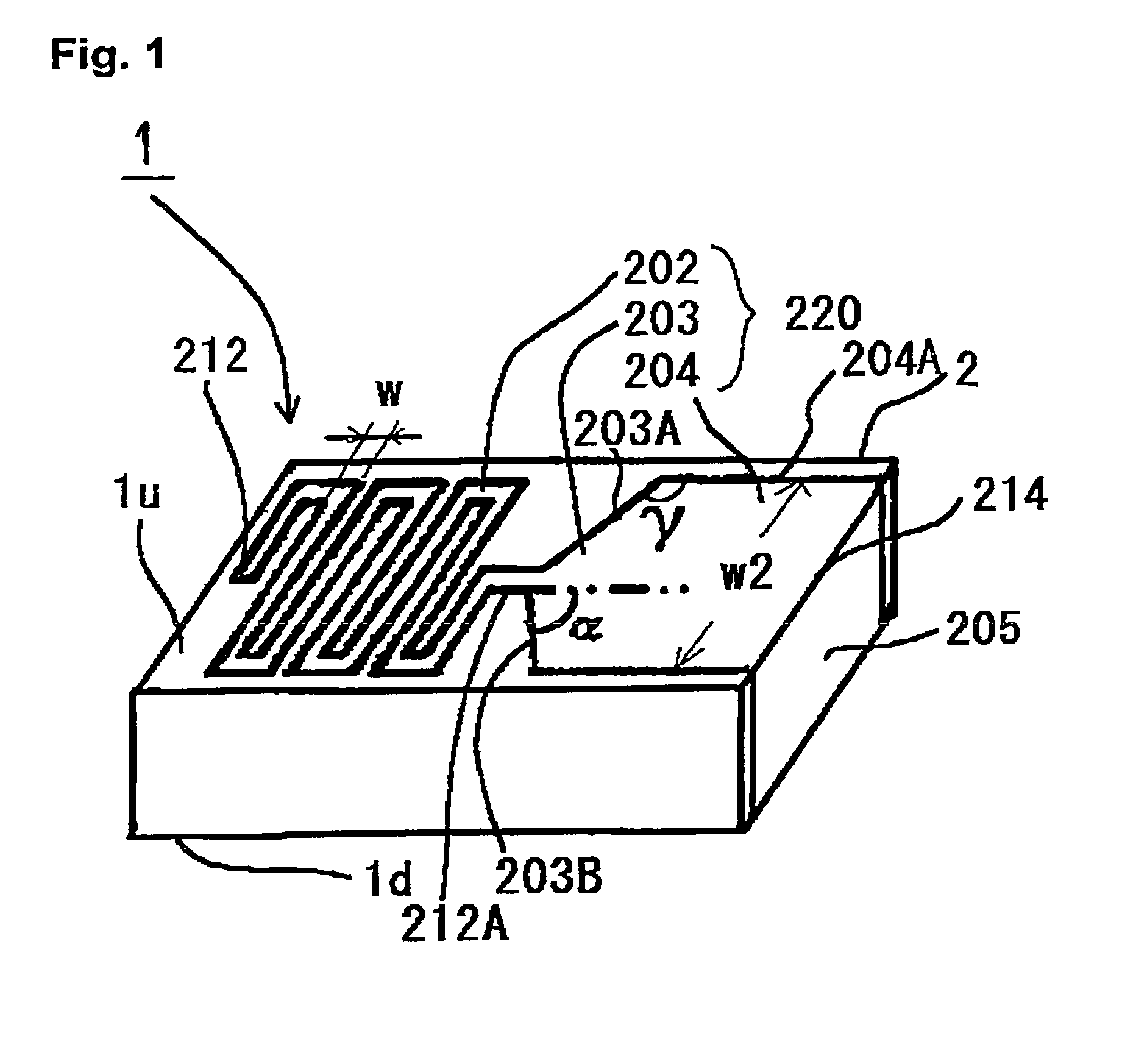
High dielectric antenna substrate and antenna thereof
ActiveUS7446711B2Reduce areaReduce material costsSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric antennasAntenna substrate
A high dielectric antenna substrate and antenna thereof are provided. The substrate includes a first dielectric layer having a first dielectric constant, and a second dielectric layer having a second dielectric constant. The second dielectric layer is formed on one surface of the first dielectric layer. The second dielectric constant is lower than the first dielectric constant. Furthermore, a first metal layer and a second metal layer are optionally formed on the same surface or two surfaces of the first dielectric layer to compose a capacitor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
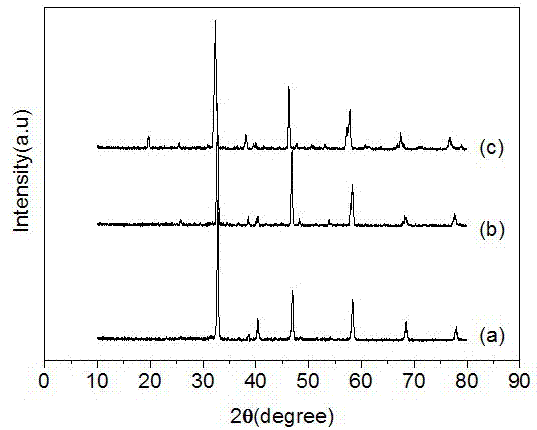
Microwave dielectric ceramic material with medium dielectric constant, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102358698AOvercome the disadvantage of large temperature coefficient of frequencyHas a dielectric constantAlcoholPolyvinyl alcohol
The present invention discloses a microwave dielectric ceramic material with a medium dielectric constant, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: mixing the following raw powders according to a chemical formula of Ca4La2Ti5-x(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3) xO17, wherein the raw powders comprise CaCO3, (MgCO3)4.Mg(OH)2.5H2O, TiO2, La2O3 and Nb2O5, the purities of the raw powders are more than 99%, x is more than or equal to 0, and less than or equal to 4; carrying out wet milling and mixing for 12-24 hours, wherein absolute alcohol is adopted as a solvent; drying, and then pre-burning for 4-6 hours at a temperature of 1300 DEG C under air atmosphere; adding an aqueous solution containing 3% of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) to the pre-burned powders, then mixing and drying; carrying out screening through a sieve with 100 meshes, and pelletizing; pressing into a cylindrical sample under pressure of 100 MPa; finally sintering for 4 hours at the temperature of 1480-1560 DEG C under air atmosphere to obtain the microwave dielectric ceramic material. According to the present invention, the prepared microwave dielectric ceramic has a high-frequency dielectric constant epsilonr of 34-72, high quality factor Q*f and small frequency temperature coefficient tauf, and can be widely used in dielectric resonators, filters, dielectric antennas and other microwave devices.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
High dielectric antenna substrate and antenna thereof
ActiveUS20090015488A1Antenna area can be reducedReduce material costsSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric antennasAntenna substrate
A high dielectric antenna substrate includes a first dielectric layer having a first dielectric constant, and a second dielectric layer having a second dielectric constant. The second dielectric layer is formed on one surface of the first dielectric layer. The second dielectric constant is lower than the first dielectric constant. Furthermore, a first metal layer and a second metal layer are optionally formed on the same surface or two surfaces of the first dielectric layer to compose a capacitor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Fluorescent-lamp-type led lighting device
InactiveCN101720404AHigh selectivityEnsure the amount of lightElongate light sourcesGlobesDielectric antennasEffect light
A fluorescent-lamp-type LED lighting device includes an LED (3) including a thin plate-like semiconductor element body (31) for transmitting light generated in a PN junction region (34) in the thickness direction for emitting from a surface, a surface electrode (32) provided to cover the surface of the element body (31) and a plurality of cylindrical dielectric antennas (36) for condensing the light which has passed through the surface electrode (32) in the thickness direction and transmitted through the inside of the element body (31) and emitting it outside, and a resin-made elongate exterior casing (2) having translucency. The LED (3) is provided at both ends of the exterior casing (2) or along its longitudinal direction. The lighting device is structured to shed the light emitted from the LED (3) outside through the exterior casing (2), has a large light quantity and can substitute for a highly efficient existing lighting device.
Owner:ABEL SYST
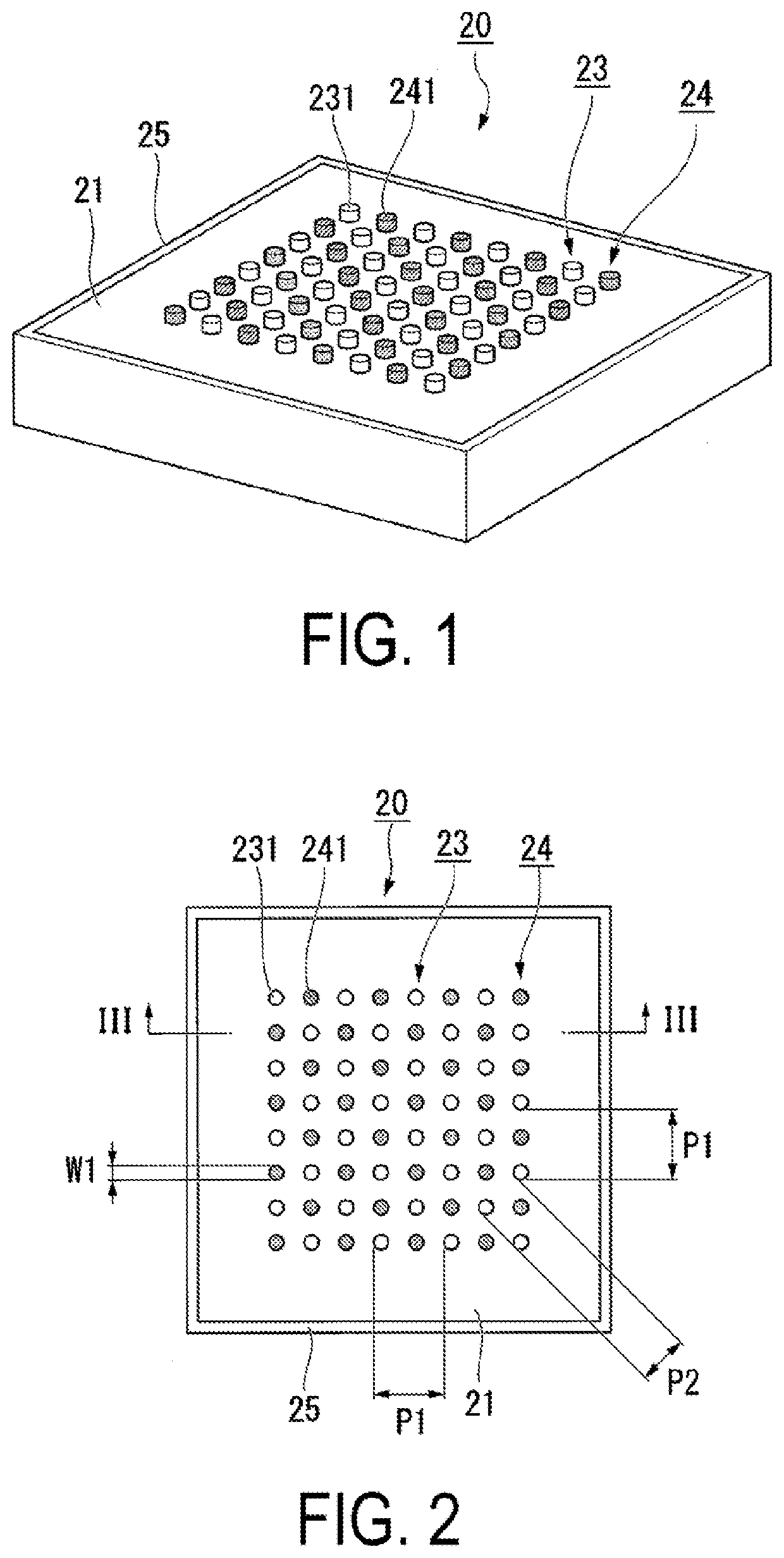
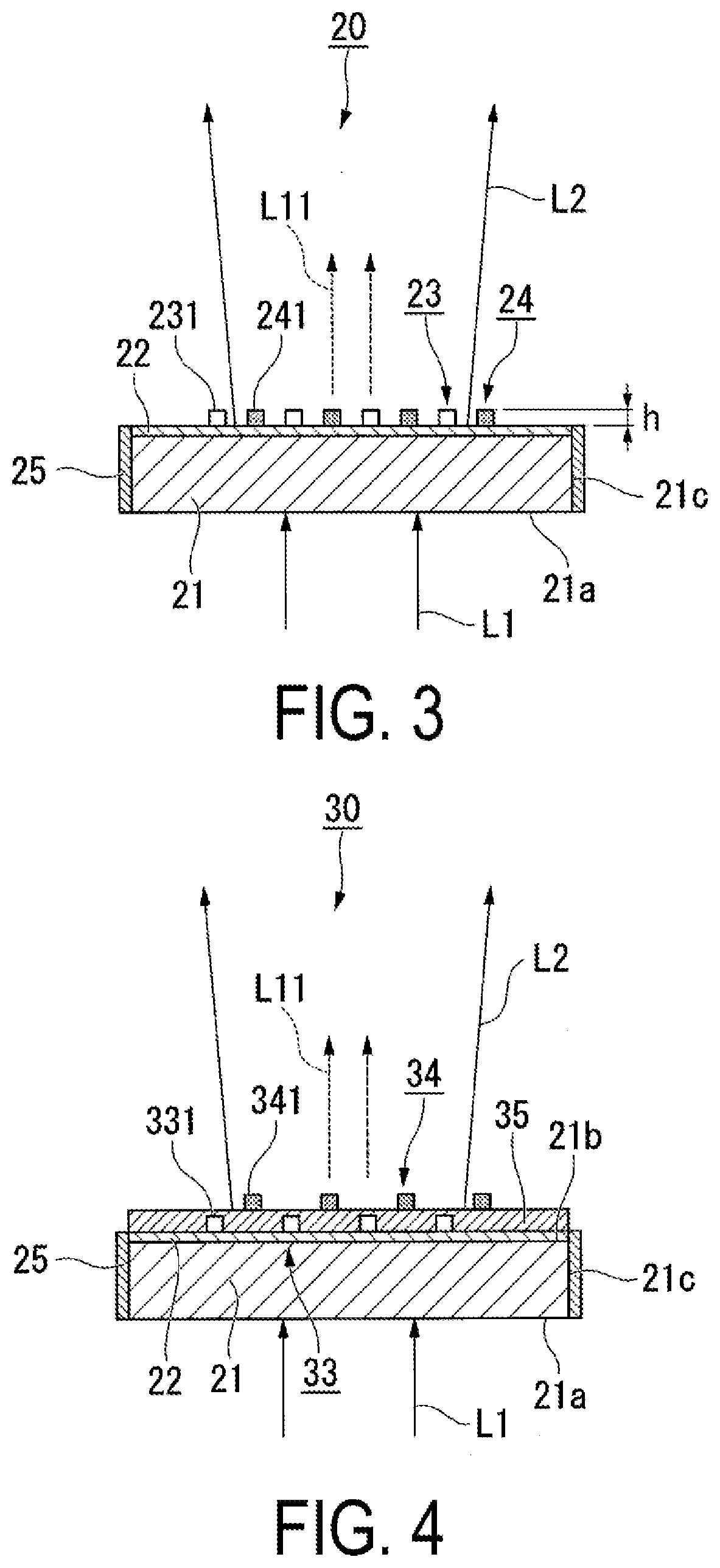
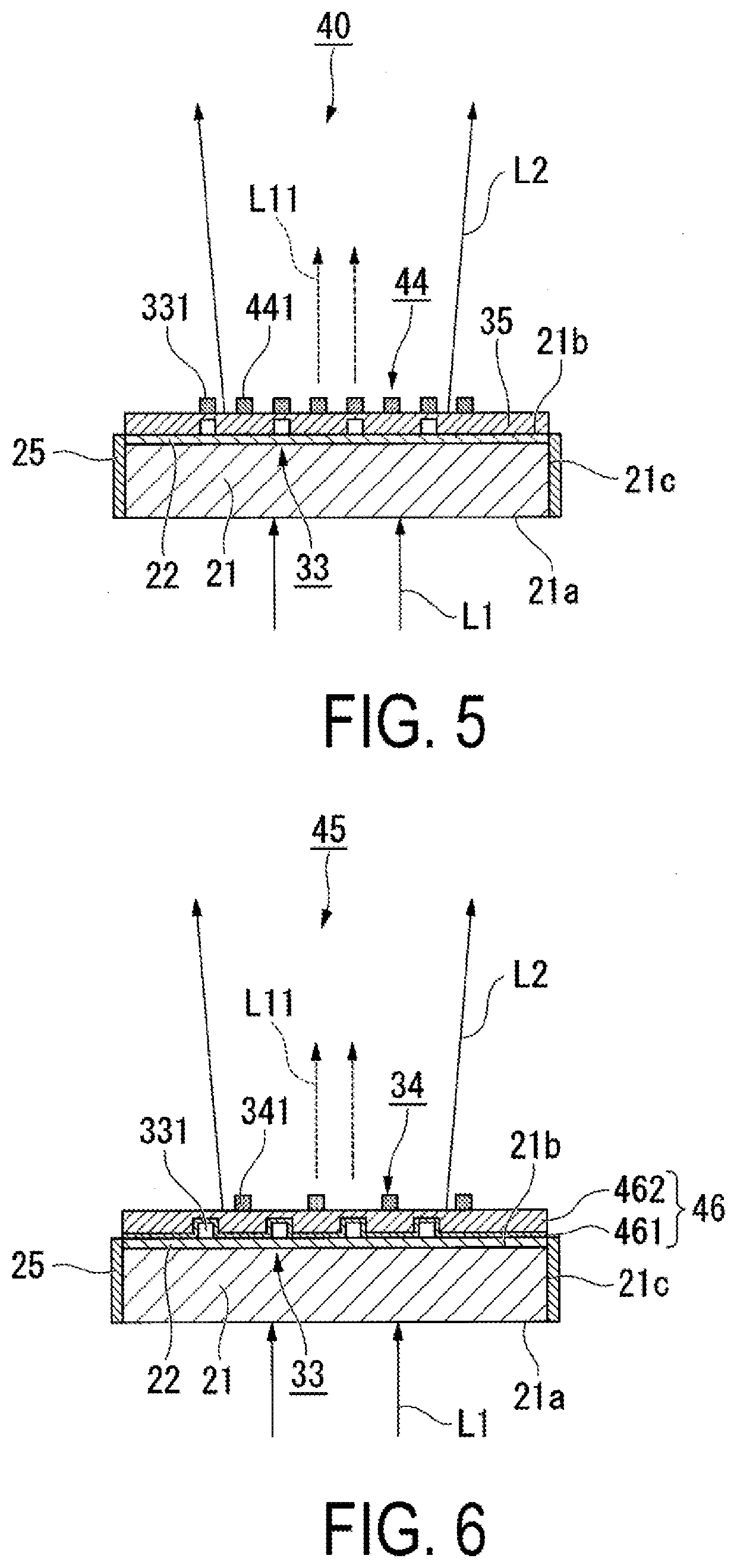
Wavelength converting element, light source device, and display device
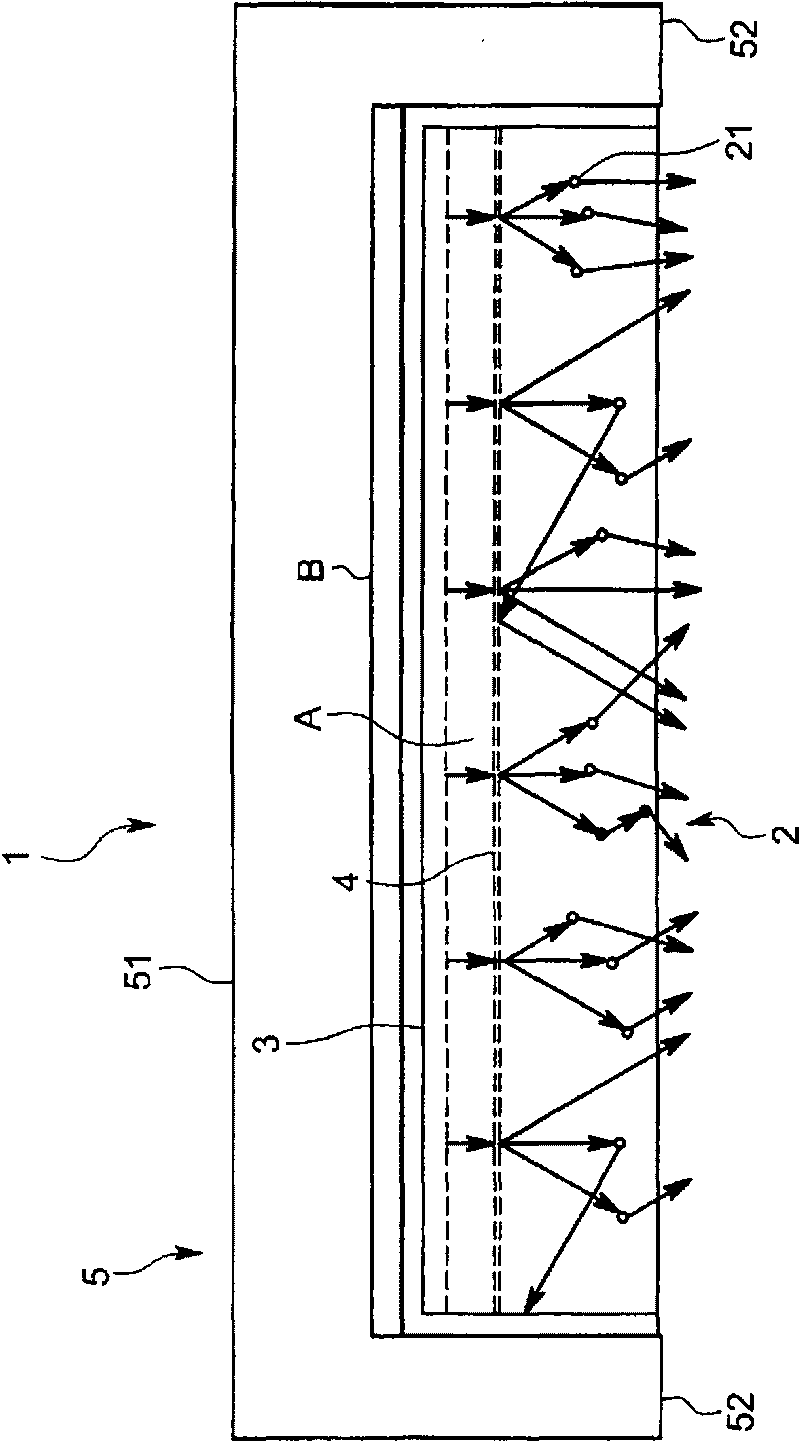
A wavelength converting element according to the present disclosure includes: a wavelength converting body including an incident surface and an exit surface and configured to perform wavelength conversion on a primary light in a first wavelength band, entered from the incident surface, thereby generating a secondary light in a second wavelength band, which differs from the first wavelength band, the wavelength converting body emitting the secondary light from the exit surface; a metallic antenna group provided in a close vicinity of the wavelength converting body and including a plurality of metallic antennas disposed so as to be spaced apart from each other at a distance of substantially an optical wavelength of the secondary light in the wavelength converting body; and a dielectric antenna group including a plurality of dielectric antennas and provided so as to face the exit surface of the wavelength converting body.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
High dielectric constant microwave dielectric material added with strontium oxide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106518063AAdjustable dielectric constantAdjustable temperatureRadiating elements structural formsMicrowaveDielectric antennas
Owner:ZHENGZHOU LIFUAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Low temperature sintered ZnO-MgO-TiO2 system microwave ceramic material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101475371BLow costImprove electrical performanceCeramicsDielectric antennasCeramic capacitor
The invention discloses a low-temperature sintered ZnO-MgO-TiO2 system microwave ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The formula of raw materials of the ceramic material comprises the following compositions: 30 to 45 percent of zinc oxide, 2 to 14 percent of magnesium oxide, 50 to 60 percent of titania and an auxiliary sintering agent. The preparation method comprises: taking the zinc oxide, basic magnesium carbonate and the titania as raw materials, mixing the raw materials, adding a grinding aid for ball milling, drying, sieving and presintering, and obtaining clinker; and mixing the obtained clinker with the titania, the auxiliary sintering agent and an additive, performing drying, granulation and press forming after secondary ball milling, finally sintering the mixture for 2 to 8 hours at a temperature of between 900 and 1,000 DEG C, and obtaining the ceramic material. The ceramic material prepared by the method has the advantages of superior microwave dielectric property, low sintering temperature, low cost and the like, and is suitable for microwave devices such as multi-layer ceramic capacitors, filters, resonators and dielectric antennas.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A zno-mgo-tio2 series ltcc material
The invention discloses a ZnO-MgO-TiO2 series LTCC material and a preparation method thereof. The material of the invention is composed of a ZnO-MgO-TiO2 series material and zinc borosilicate glass accounting for 0.25% to 5% by weight. ZnO- The composition of MgO-TiO2 series materials is (Zn1-xMgx)TiO3-yTiO2, in which 0.05≤x≤0.15, 0≤y≤0.3, zinc borosilicate glass composition by mole percentage is 40%~70%ZnO, 25%~45% B2O3, 5% to 15% SiO2. The LTCC material prepared by the present invention is well sintered at 850°C-900°C, the dielectric constant εr=20-27, Q×f=40000-70000GHz, the resonant frequency temperature coefficient τf=-80~+10ppm / °C, and can be widely used in Microwave devices such as resonators, filters, dielectric substrates, dielectric antennas, and dielectric waveguide circuits are especially suitable for high-frequency devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
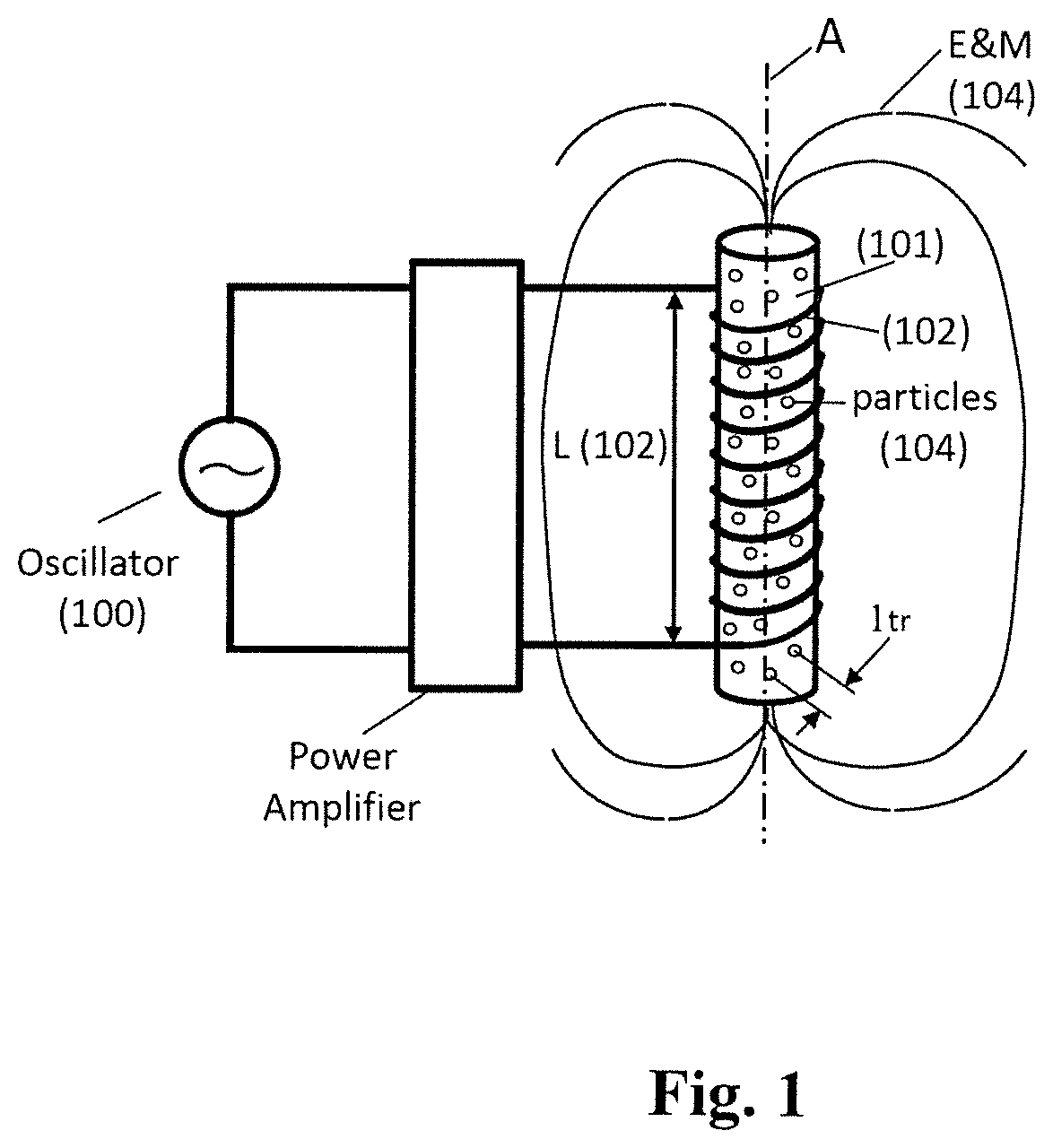
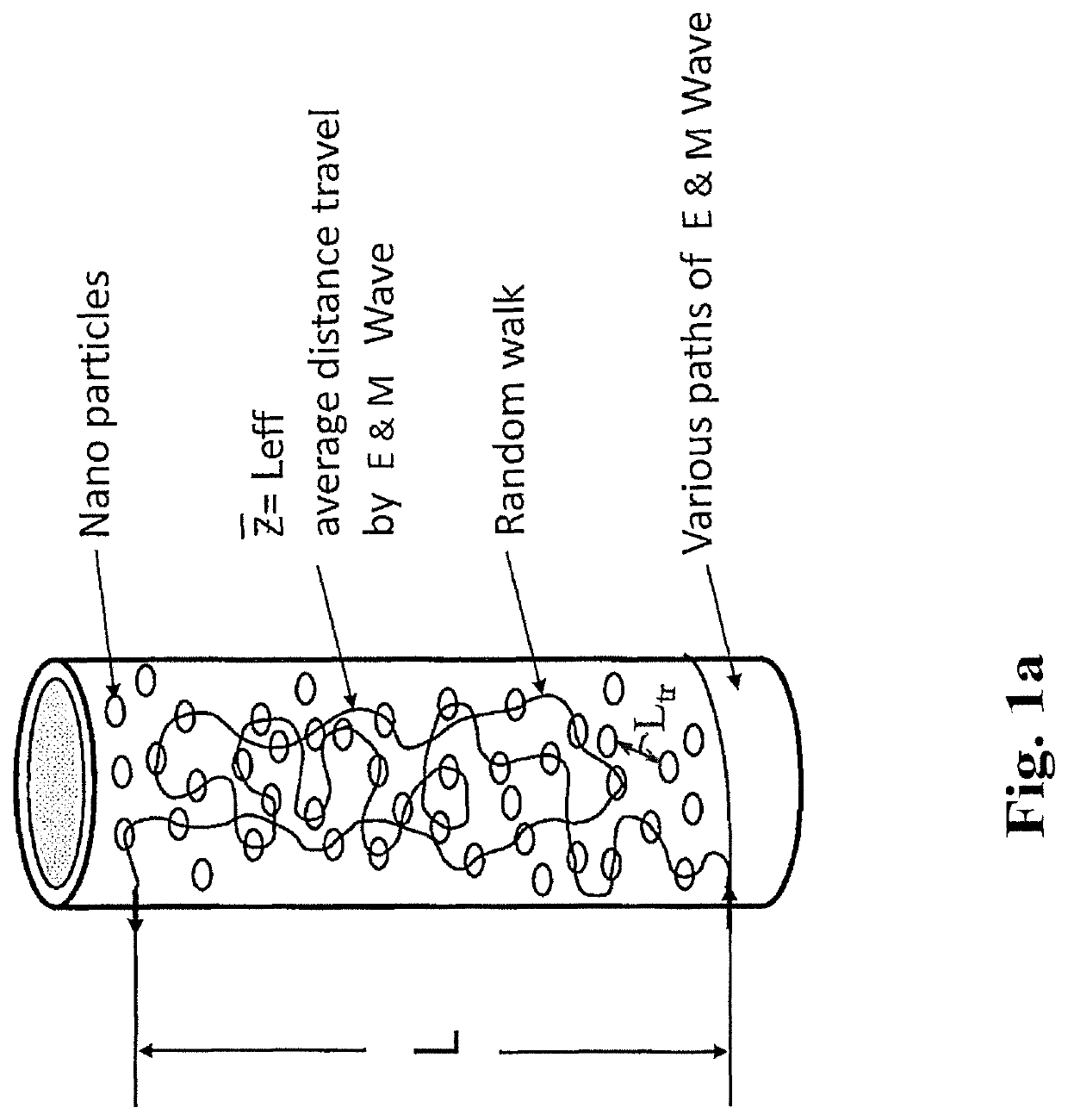
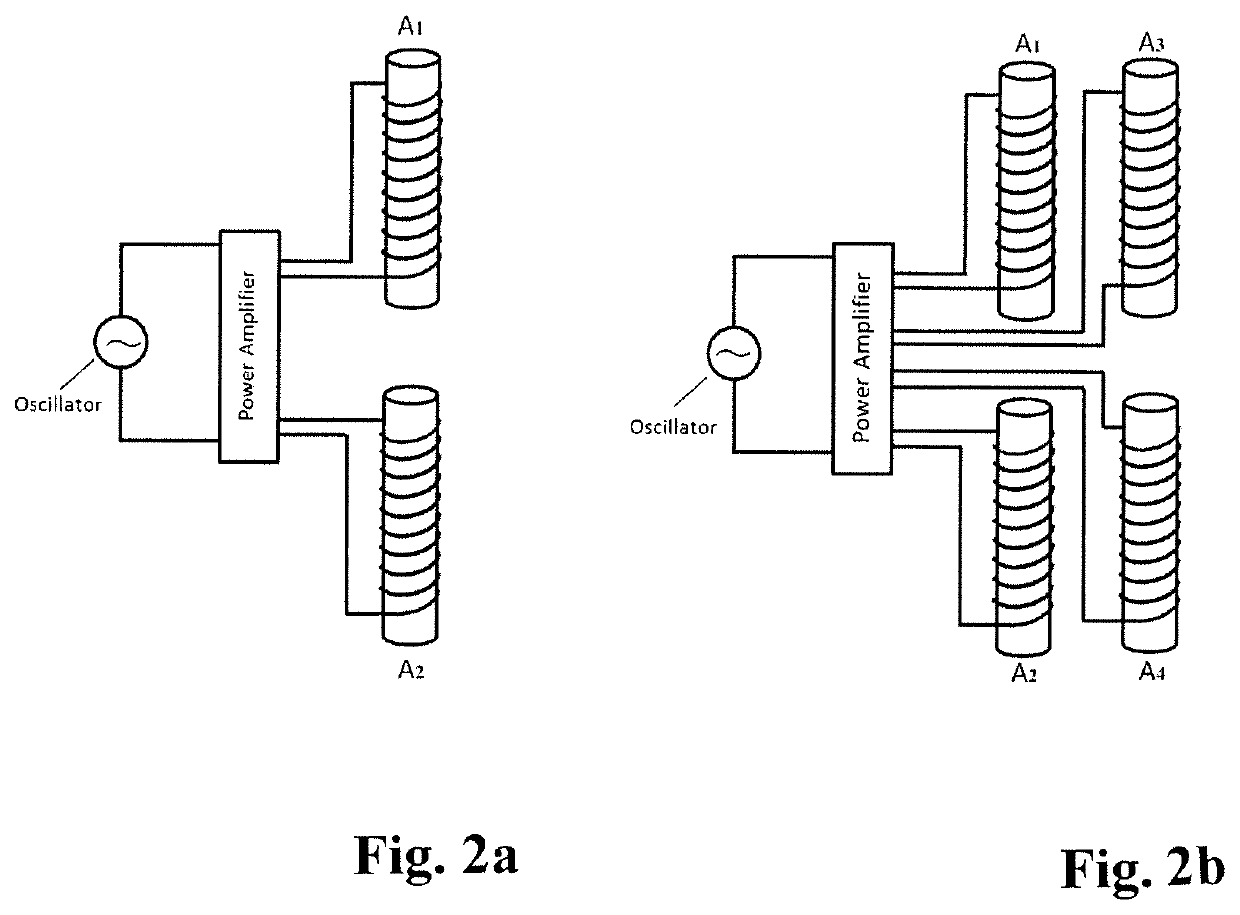
Random walk magnetic dielectric antenna to generate Brillouin and Sommerfeld precursors
ActiveUS10680334B2Loop antennas with ferromagnetic coreSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectric antennasEngineering
A Random Walk Antenna (RWA) generates VLF, ULF, RF, MHz and GHz waves by dispersion of a driving signal through a ferriomagnetic ferrite nano and micron composite in compact ultra-small antenna. When oscillator frequency spans several resonances of ferrite magnetic dielectric media consisting of resonances from optical phonons and magnon high frequency and lower frequency are produced from Sommerfeld Polaritons Precursor (SP) and Brillouin Polariton Precursors (BP), respectively. The ferrite nano and micron size particle in antenna resultant electromagnetic waves from RWA contain Sommerfeld and Brillouin polariton precursors. High and low-frequency waves propagate with an algebraic attenuation making them ideal for deep use in highly conductive or highly attenuating media such as in seawater, buildings, underground and or free space on the Earth. Warfighters can use the RAW ferrite nano and micron size antenna system.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT
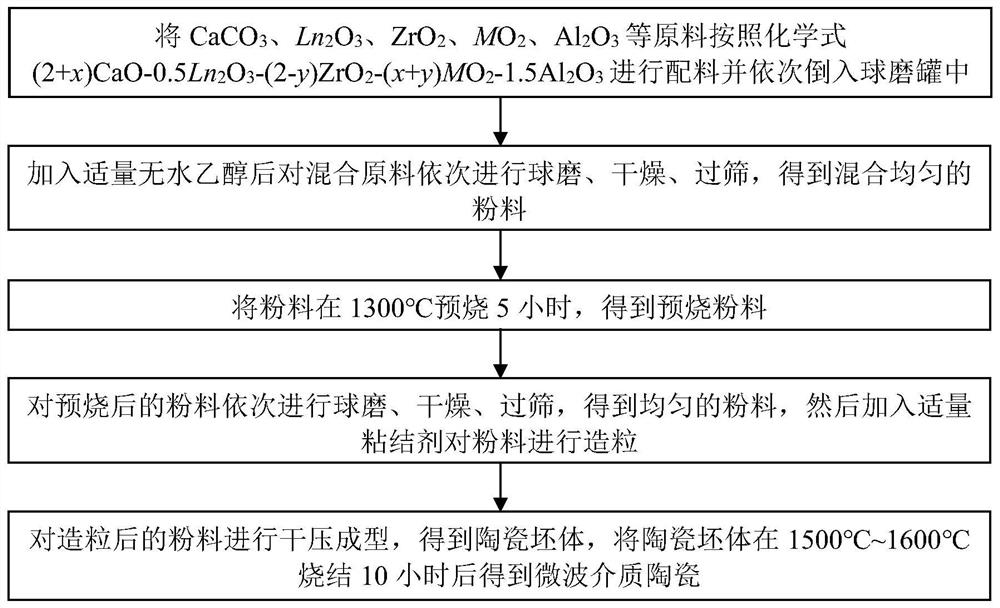
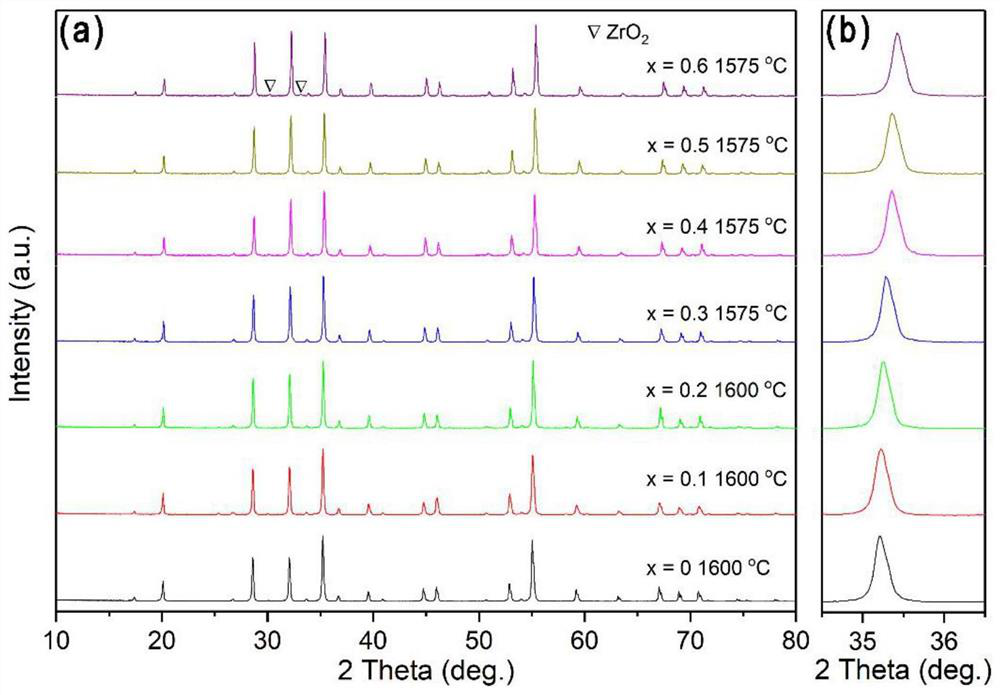
Aluminate-based low-dielectric microwave dielectric ceramic and preparation method thereof
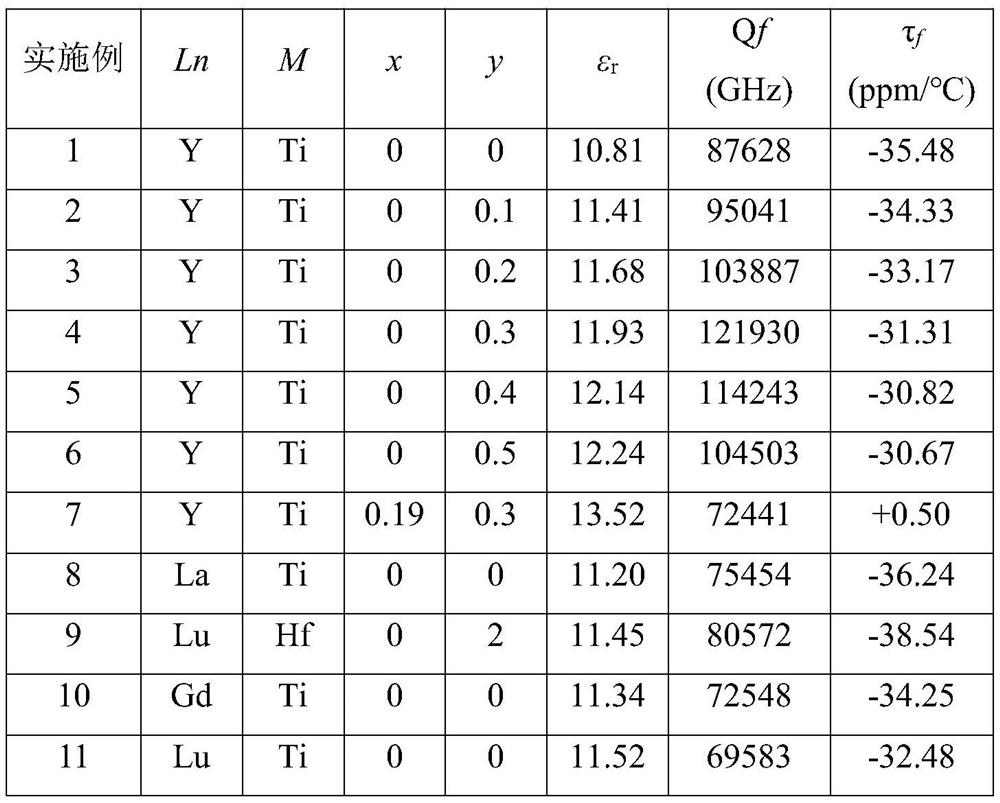
The invention discloses an aluminate-based low-dielectric microwave dielectric ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The main crystal phase of the microwave dielectric ceramic has a garnet type crystal structure, the specific chemical composition is (2+x)CaO-0.5Ln2O3-(2-y)ZrO2-(x+y)MO2-1.5Al2O3, Ln is Y, La, Lu, Gd or other lanthanide elements, M is Hf, Sn or Ti, x is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, and y is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 2.0. The dielectric constant of the microwave dielectric ceramic ranges from 10.81 to 13.52, the quality factor ranges from 72441 GHz to 121930 GHz, and the temperature coefficient of resonance frequency ranges from +0.50 ppm / DEG C to -35.48 ppm / DEG C. In the preparation process, the pre-sintering condition of the ceramic material is that the temperature is kept at 1300 DEG C for 5 hours, and the sintering condition is that the temperature is kept at 1500-1600 DEG C for 10 hours. The microwave dielectric ceramic prepared in the invention has the characteristics of low dielectric constant, high quality factor and adjustable resonant frequency temperature coefficient to near zero, and is suitable for preparing microwave communication devices such as dielectric substrates, dielectric resonators, dielectric antennas and the like.
Owner:WENZHOU ADVANCED MFG TECH INST OF HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Low dielectric constant and low temperature sintering microwave ceramic medium and its preparing process
ActiveCN100537473CMeet the design requirementsImprove conductivityDielectric antennasMaterials science
The invention discloses a low-dielectric constant low-temperature sintered microwave dielectric ceramic. The ceramic material is composed of [(Zn1-xMgx)O-ySiO2+awt%TiO2]+bwt%[zLi2O-(1-z)B2O3], wherein: 0≤x≤1, 0.5≤y≤1, 0≤a≤20, 0<b≤15, 0<z<1; the invention also discloses a preparation method of the porcelain material. The invention adopts Li2O-B2O3 composition, which can promote the sintering temperature of (Zn1-xMgx)O-ySiO2 ceramics from 1200°C to below 960°C; it has good microwave dielectric properties: the dielectric constant is 6-10, and the quality factor Qf> 12000GHz, frequency temperature coefficient can be adjusted according to needs. The material of the invention has low usage cost, stable process and good reproducibility, can be used in the design and production of multi-layer frequency devices such as multi-layer dielectric antennas, baluns, and various filters, and has great industrial value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Wavelength converting element, light source device, and display device
A wavelength converting element according to the present disclosure includes: a wavelength converting body including an incident surface and an exit surface and configured to perform wavelength conversion on a primary light in a first wavelength band, entered from the incident surface, thereby generating a secondary light in a second wavelength band, which differs from the first wavelength band, the wavelength converting body emitting the secondary light from the exit surface; a metallic antenna group provided in a close vicinity of the wavelength converting body and including a plurality of metallic antennas disposed so as to be spaced apart from each other at a distance of substantially an optical wavelength of the secondary light in the wavelength converting body; and a dielectric antenna group including a plurality of dielectric antennas and provided so as to face the exit surface of the wavelength converting body.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com